Syba SY-ENC35028, SY-ENC25042 User Manual

SY-ENC35028
3.5” 2-BAY RAID Storage Enclosure
User Manual
1 Introduction
1.1 Features
-Supports JBOD, RAID0,RAID1,Normal mode
-Enhanced data protection and high -performance storage
-Automatic disk rebuild (Under SAFE Mode)
-Supports USB3.0 high speed to reach 5.0Gbps
-Supports Plug-play and Hot-plug
-Supports mode select via jumper setting
1.2 Specifications
Inner Interface: SATA
Outer Interface:USB3.0
Date Transfer rate: Support USB 3.0 super-speed (5Gbps),
Complies with USB 2.0 high speed (480Mbps),USB 1.1 Full speed (12Mbps)
Suitability: 2 x 3.5” SATA I/II/III HDD

Supports Plug-play and Hot-plug
Power Supply: AC 100~240V, 50~60Hz ; DC 12V, 2.5A
Material: Aluminum
Cooling Fan: One 25x25mm Cooling Fan
OS Compatibility: Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8, Linux and MAC OS 10.4 or
above
Dimension:220 x 120 x 68 mm (L x W xH)
1.3 System Requirements
PC Requirements
· Minimum Intel Processor Pentium II/50MHz, 64MB RAM
· Windows 2000 / XP / VISTA/7/8
· Active USB port
MAC Requirements
· Minimum Apple G processor, 64MB RAM
· Mac OS 10.4 and above
· Active USB port
Supported Hard Drives
· One or two 3.5” SATA I/II/III hard drives
· capacity up to 4TB or more
· Hard drives of identical capacities are recommended
· Supports large volumes in excess of 2TB
Note: In order for the computer to access volumes larger than 2TB. Both the
hardware and OS need to have the capacity to support large volumes(e.g.:
Windows 7/Vista or Mac OS 10.4 and above).
1.4 Package Contents
· 2-bay raid storage enclosure
· Power supply

· USB cable
· Manual
2 RAID Function
What is RAID?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a set of technology
standards for teaming disk drives to improve fault tolerance and performance
Why RAID?
Increased data protection. If in an unfortunate event where a drive fails,
the same data is preserved on the mirrored drive.
Intelligent array controllers can apply different types of RAID for different
hard disk drives.
Increased overall network system data capacity.
Increased I/O read/write efficiency.
Changing the RAID Mode:
The RAID mode should be set before installing the drives and then first
formatting the drives.
1. Make sure the power is off.
2. Set the RAID switch and select your preferred RAID mode. There are 2
mode switches on the inner panel of the product. 4 alternate arrays can be
created through these 2 switches. View the diagram below to see the
different configuration settings for the RAID switches:
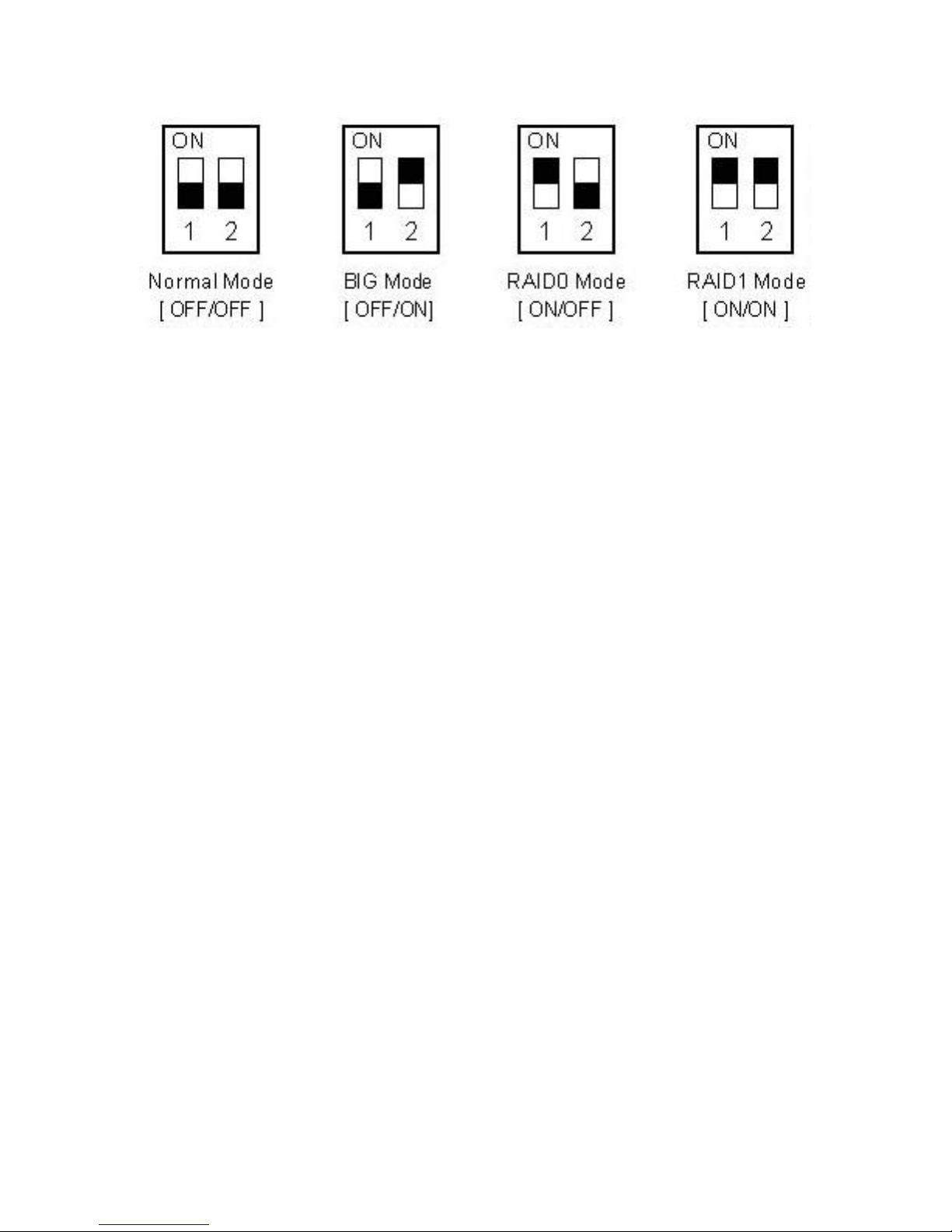
3. Install the hard drives and turn on the power.
4. Format the drives.
5. Done
Note: Changing the RAID mode will require you to re-format the drivers. Make
sure to backup all existing data first!
※ Normal Mode (Non-Raid):
Normal mode is the default setting of HDD enclosure, and will not use any
RAID mode. In Normal mode, both of the two hard disks inside the enclosure
are in an independent operation state, and also will be identified as two
separate drives in the system explorer. Users can choose any hard drive for
storing files. If one hard drive is damaged, the other hard drives data will not be
affected.
※ JBOD Mode (Spanning):
In JBOD mode two hard drives will be merged into one. Performance and
literacy speed will be the same as a single hard drive. The total capacity of the
portable hard drive is equal to the sum of the two hard drives combined. When
writing data to the JBOD array, the system will write date to the first disk. When
the storage space of the first disk is full the data will start be stored on the
second disk. If the data in the first disk is damaged, then all data in the array
 Loading...
Loading...