Page 1

AMI Hydrogen QED
Version 6.22 and higher
A-96.250.791 / 040219
Operator’
s Manual
Page 2

© 2017, SWAN ANALYTISCHE INSTRUMENTE AG, Switzerland, all rights reserved
subject to change without notice.
Customer Support
SWAN and its representatives maintain a fully trained staff of technical specialists
around the world. For any technical question, contact your nearest
SWAN representative, or the manufacturer:
SWAN ANALYTISCHE INSTRUMENTE AG
Studbachstrasse 13
8340 Hinwil
Switzerland
Internet: www.swan.ch
E-mail: support@swan.ch
Document Status
Title:
AMI Hydrogen QED Operator’s Manual
ID:
A-96.250.791
Revision Issue
00 April 2014 First Edition
01 July 2017 New mainboard V2.5, firmware V6.20
Page 3

AMI Hydrogen QED
A-96.250.791 / 040219 1
Table of Contents
1. Safety Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1. Warning Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2. General Safety Regulations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2. Product Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1. Description of the System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2. Technical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3. Instrument Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3. Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.1. Installation Check List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.2. Mounting of Instrument Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.3. Connecting Sample Inlet and Outlet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.3.1 Swagelok Fitting Stainless Steel at Sample Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.3.2 Sample Outlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.4. Electrical Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.5. Connection Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.6. Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.7. Relay Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7.1 Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7.2 Alarm Relay. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.7.3 Relay Contacts 1 and 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.8. Signal Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.8.1 Signal output 1 and 2 (current outputs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.9. Interface Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.9.1 Signal Output 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.9.2 Profibus, Modbus Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.9.3 HART Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.9.4 USB Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4. Instrument Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.1. Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5. Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.1. Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.2. Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.3. Software Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.4. Changing Parameters and Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Page 4

2 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
6. Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.1. Maintenance Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.2. Stop of Operation for Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.3. Maintenance of the Hydrogen Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.3.1 Hydrogen Sensor Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.3.2 Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.3.3 Faraday Verification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.3.4 Replace Hydrogen Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.4 Maintenance of the Faraday Electrode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.5. Quality Assurance of the Instrument. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.5.1 Activate SWAN Quality assurance procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.5.2 Pre-test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
6.5.3 Connect the sample lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
6.5.4 Carry out comparison measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
6.5.5 Completion of the measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
6.6. Longer Stop of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7. Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.1. Error List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.2. Replacing Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8. Program Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.1. Messages (Main Menu 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.2. Diagnostics (Main Menu 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.3. Maintenance (Main Menu 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
8.4. Operation (Main Menu 4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
8.5. Installation (Main Menu 5). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
9. Program List and Explanations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
1 Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
2 Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
5 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
10. Default Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
11. Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
12. Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Page 5

AMI Hydrogen QED
Safety Instructions
A-96.250.791 / 040219 3
AMI Hydrogen QED Operator’s Manual
This document describes the main steps for instrument setup, operation and maintenance.
1. Safety Instructions
General The instructions included in this section explain the potential risks
associated with instrument operation and provide important safety
practices designed to minimize these risks.
If you carefully follow the information contained in this section, you
can protect yourself from hazards and create a safer work environment.
More safety instructions are given throughout this manual, at the
respective locations where observation is most important.
Strictly follow all safety instructions in this publication.
Tar get
audience
Operator: Qualified person who uses the equipment
for its intended purpose.
Instrument operation requires thorough knowledge of applications,
instrument functions and software program as well as all applicable
safety rules and regulations.
OM Location The AMI Operator’s Manual shall be kept in proximity of the instru-
ment.
Qualification,
Training
To be qualified for instrument installation and operation, you must:
read and understand the instructions in this manual as well as
the Material Safety Data Sheets.
know the relevant safety rules and regulations.
Page 6
4 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Safety Instructions
1.1. Warning Notices
The symbols used for safety-related notices have the following significance:
DANGER
Your life or physical wellbeing are in serious danger if such
warnings are ignored.
Follow the prevention instructions carefully.
WARNING
Severe injuries or damage to the equipment can occur if such
warnings are ignored.
Follow the prevention instructions carefully.
CAUTION
Damage to the equipment, minor injury, malfunctions or incorrect process can be the consequence if such warnings are ignored.
Follow the prevention instructions carefully.
Mandatory
Signs
The importance of the mandatory signs in this manual.
Safety goggles
Safety gloves
Page 7
AMI Hydrogen QED
Safety Instructions
A-96.250.791 / 040219 5
Warning Signs The importance of the warning signs in this manual.
1.2. General Safety Regulations
Legal
Requirements
The user is responsible for proper system operation.
All precautions must be followed to ensure safe operation
of the instrument.
Spare Parts
and
Disposables
Use only official SWAN spare parts and disposables. If other parts
are used during the normal warranty period, the manufacturer’s
warranty is voided.
Electrical shock hazard
Corrosive
Harmful to health
Flammable
Warning general
Attention general
Page 8

6 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Safety Instructions
Modifications Modifications and instrument upgrades shall only be carried out by
an authorized Service Technician. SWAN will not accept responsibility for any claim resulting from unauthorized modification or alteration.
WARNING
Risk of Electrical Shock
If proper operation is no longer possible, the instrument must be
disconnected from all power lines, and measures must be taken
to prevent inadvertent operation.
To prevent from electrical shock, always make sure that the
ground wire is connected.
Service shall be performed by authorized personnel only.
Whenever electronic service is required, disconnect instru-
ment power and power of devices connected to.
–relay 1,
–relay 2,
– alarm relay
WARNING
For safe instrument installation and operation you must read
and understand the instructions in this manual.
WARNING
Only SWAN trained and authorized personnel shall perform the
tasks described in this document.
Page 9

AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
A-96.250.791 / 040219 7
2. Product Description
This chapter contains technical data, requirements and performance data.
2.1. Description of the System
Application
Range
The AMI Hydrogen QED is a monitor for continuous measurement
of dissolved hydrogen in water.
Signal
Outputs
Two signal outputs programmable for measured values (freely scalable, linear or bilinear) or as continuous control output (control parameters programmable).
Current loop: 0/4 –20 mA
Maximal burden: 510 Ω
Third signal output available as an option. The third signal output
can be operated as a current source or as a current sink (selectable
via switch).
Relay Two potential-free contacts programmable as limit switches for
measuring values, controllers or timer for system cleaning with automatic hold function. Both contacts can be used as normally open
or normally closed.
Maximum load: 1 A/250 VAC
Alarm Relay One potential free contact.
Alternatively:
Open during normal operation, closed on error and loss of
power.
Closed during normal operation, open on error and loss of
power.
Summary alarm indication for programmable alarm values and instrument faults.
Input For potential-free contact to freeze the measuring value or to inter-
rupt control in automated installations (hold function or remote-off)
Safety
Features
No data loss after power failure. All data is saved in non-volatile
memory. Over voltage protection of in- and outputs. Galvanic separation of measuring inputs and signal outputs.
Page 10

8 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
Communica-
tion Interface
(optional)
USB Interface for logger download
Third signal output (can be used in parallel to the USB interface)
RS485 with Fieldbus protocol Modbus or Profibus DP
HART interface
Faraday
Verification
The Faraday verification is used to check the sensor periodically.
The intervals can be freely programmed in the menu operation.
Measuring
principle
Hydrogen is measured by an amperometric method. A small voltage, called polarization voltage, is applied between two electrodes.
If a hydrogen molecule hits the positively charged platinum electrode (anode) it will be oxidized. This means that two electrons are
removed under the influence of the positive voltage and the catalytic properties of the platinum. This leaves two (charged) protons and
two electrons behind.
(1) H2 ––> 2 H
+
+ 2 e
-
The two electrons are transported by the polarization voltage
source to the negatively charged silver-silver chloride electrode
(cathode), causing the following reaction:
(2) AgCl + 2 e
-
––> Ag + 2 Cl
-
Finally the two kinds of ions produced will combine into a small
amount of hydrochloric acid:
(3) 2 H+ + 2 Cl
-
––> 2 HCl
If the hydrogen concentration in the sample increases, more hydrogen molecules will hit the platinum anode within a given time.
Therefore, more electrons will be transported within a given time,
which corresponds to an increased electrical current. This current
can be measured by the electronics. It is directly proportional to the
concentration of hydrogen in the sample. Formula (2) indicates that
in the course of the hydrogen measurement the silver chloride is reduced to elemental silver. If all silver chloride has been converted to
silver the hydrogen sensor has to be refurbished in the factory.
However, there is enough silver chloride provided to keep the sensor operational during two years under normal conditions.
The actual SWAN hydrogen-sensor design is based on the wellknown Clark principle. Clark-type hydrogen sensors have been
successfully in use for many years.
Page 11
AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
A-96.250.791 / 040219 9
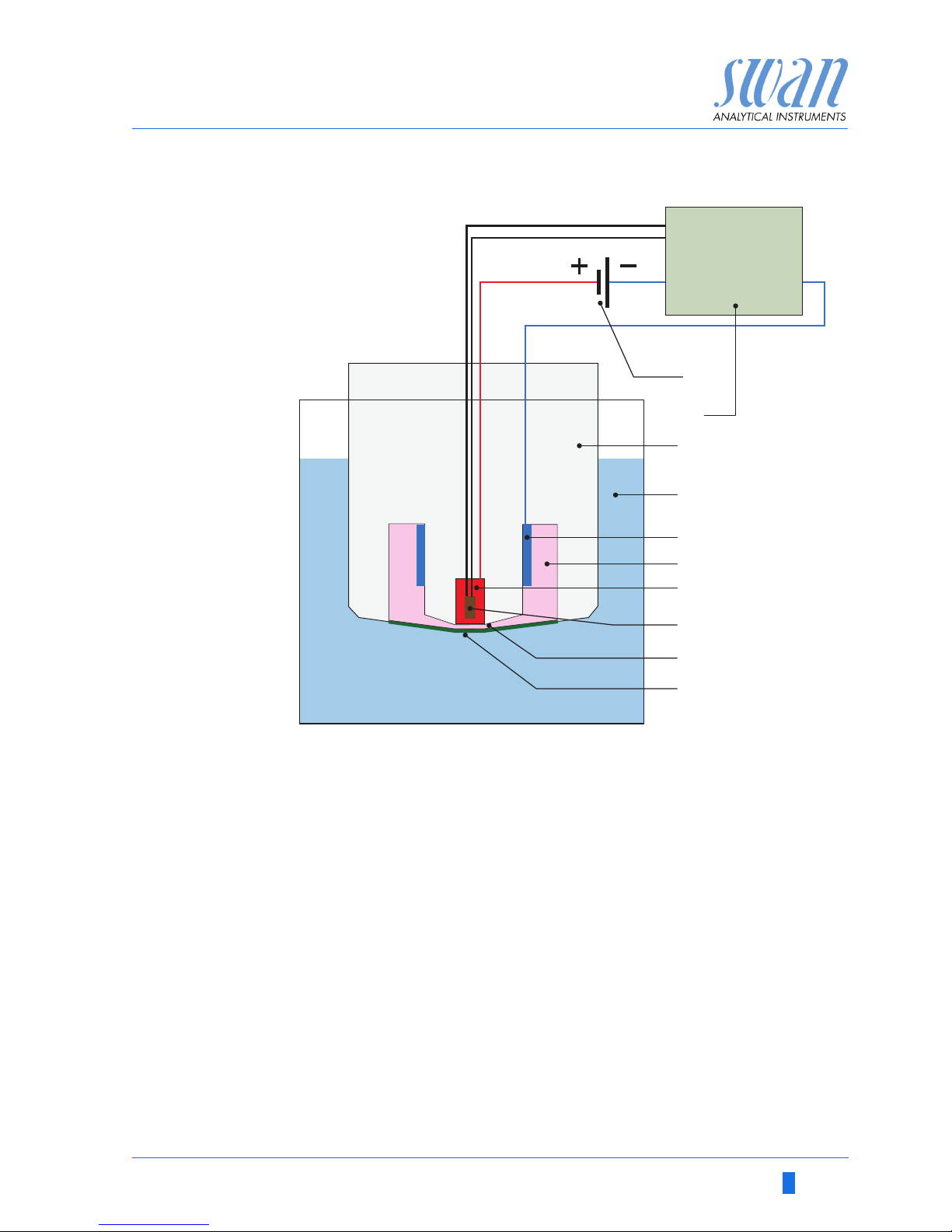
Hydrogen
sensor
schematic
view
A
B
C
D
E
F
Polarization voltage source
Display
Sensor body
Sample
Cathode
Electrolyte
G
H
I
J
Anode
Temperature sensor
Thin layer of electrolyte
Hydrogen permeable
membrane
25.6 °C
1.24 ppb
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
I
Page 12
10 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
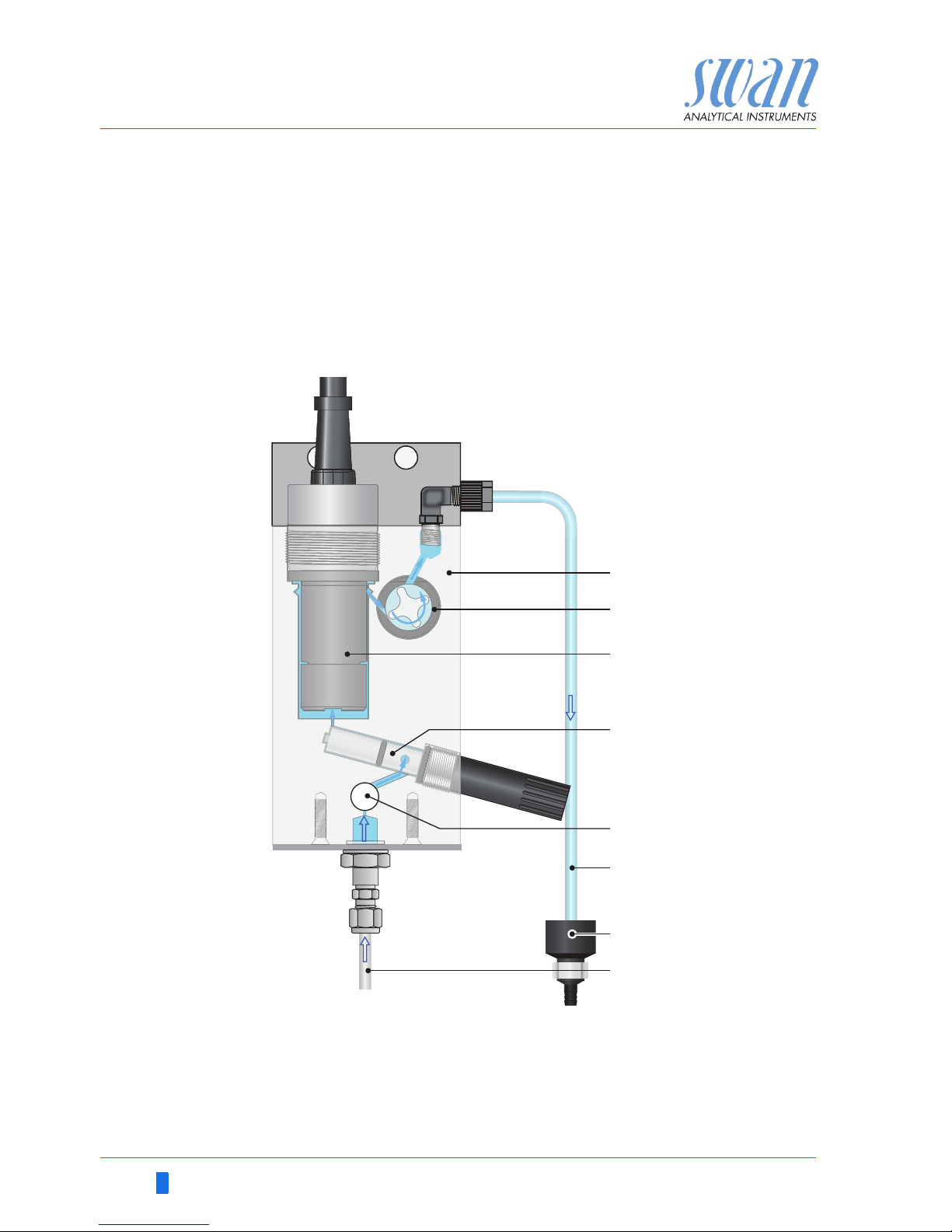
Fluidics Swansensor Hydrogen combined with QV-flow PMMA OTG flow
cell [A].
The sample flows via sample inlet [H] through the flow regulating
valve [E], where the flow rate can be adjusted. Then the sample
flows through the Faraday electrode [D] into the measuring cell
were the hydrogen concentration of the sample is measured.
The sample leaves the measuring cell via flow sensor [B] through
the sample outlet [F] and flows into the drain funnel [G].
A
B
C
D
Flow cell
Flow sensor
Swansensor hydrogen
Faraday electrode
E
F
G
H
Flow regulating valve
Sample outlet
Drain funnel
Sample inlet
A
B
C
D
F
E
G
H
Page 13

AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
A-96.250.791 / 040219 11
2.2. Technical Data
Power Supply Voltage:
Power consumption:
100–240 VAC (± 10%)
50/60 Hz (± 5%)
or 24 VDC (± 10%)
max. 30 VA
Electronics Aluminium with a protection degree of IP 66 / NEMA 4X
housing Ambient temperature:
Limit range of operation:
Storage and transport:
Humidity:
Display:
-10 to +50 °C
-25 to +65 °C
-30 to +85 °C
10–90% rel., non condensing
backlit LCD, 75 x 45 mm
Sample
requirements
Flow rate:
Temperature:
Inlet pressure:
Outlet pressure:
6 to 20 l/ h
up to 45 °C
0.2 to 1 bar
pressure free
Flow cell and
connection
Flow cell made of acrylic glass with built-in flow adjustment valve
and digital sample flow meter
Sample inlet:
Sample outlet:
1/4” Swagelok tube adapter
flexible tube 8x 6 mm
Measuring
range
Range
0.01–9.99 ppb
10.0–99.9
100–800 ppb
0–50% saturation
Resolution
0.01 ppb
0.1 ppb
1 ppb
0.1% Saturation
Accuracy
Reprodu-
cibility
±5% of measured value or ± 0.5 ppb
±1% of measured value or ± 0.5 ppb
Page 14
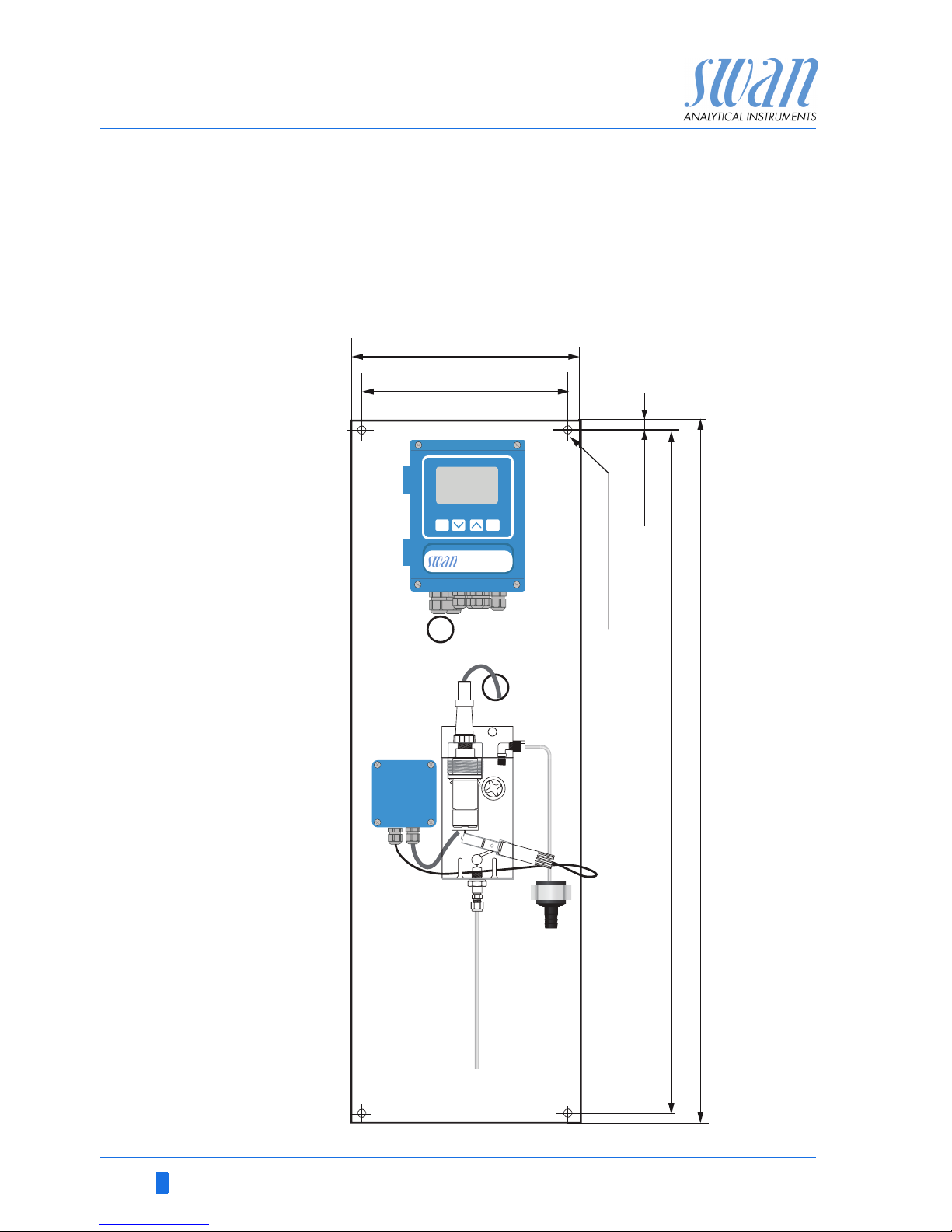
12 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
Dimensions Panel:
Mounting hole distance
Screws:
Weight:
280x850x150 mm
254x 824
8 mm
12.0 kg
Exit Enter
AMI Hydrogen
850 mm / 33½”
13 mm / ½”
4 x dia. 10 mm /
3
/
8
”
254 mm/ 10”
280 mm/ 11”
824 mm / 32
7
/
16
”
Page 15

AMI Hydrogen QED
Product Description
A-96.250.791 / 040219 13
2.3. Instrument Overview
A
B
C
D
E
F
Panel
AMI Transmitter
Sample outlet
Flow cell
Flow sensor
Hydrogen sensor
G
H
I
J
K
Faraday control
Faraday electrode
Flow regulating valve
Drain funnel
Sample inlet
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
Page 16

14 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3. Installation
3.1. Installation Check List
3.2. Mounting of Instrument Panel
The first part of this chapter describes the preparing and placing of
the system for use.
The instrument must only be installed by trained personnel.
Mount the instrument in vertical position.
For ease of operation mount it so that the display is at eye
level.
For the installation a kit containing the following installation
material is available:
– 4 Screws 8x 60 mm
– 4 Dowels
– 4 Washers 8.4/ 24 mm
Mounting re-
quirements
The instrument is only intended for indoor installation.
For dimensions see Dimensions, p. 12
Check
Instrument’s specification must conform to the National
Electrical Code, all state and local codes, and all plant codes
and standards for electrical equipment.
Installation
Connect the sample and waste line.
Electrical Wiring
Do not switch on the Instrument until all electrical connections
are made.
Connect all external devices like limit switches, current loops
and pumps.
Connect power cord, see Electrical Connections, p. 17.
Power-up
Open the flow regulating valve.
Switch on power
Adjust the sample flow to 6–20 l/ h.
Instrument
Setup
Program all parameters for external devices (interface,
recorders, etc.).
Program all parameters for instrument operation (limits,
alarms).
Run-in period
Let the instrument run continuously for 1 h.
Page 17
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 15
3.3. Connecting Sample Inlet and Outlet
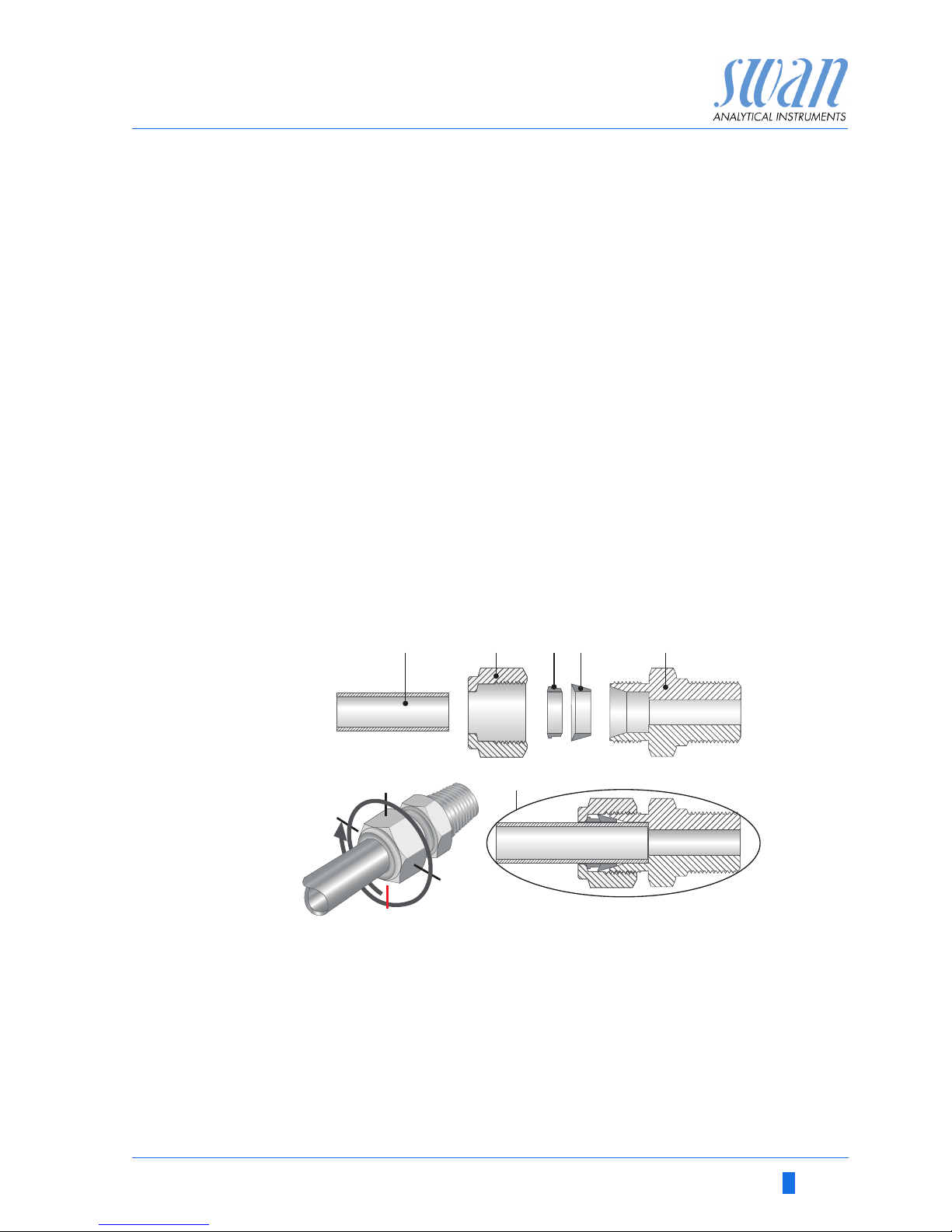
3.3.1 Swagelok Fitting Stainless Steel at Sample Inlet
Preparation Cut the tube to length and deburr it. The tube must be straight and
free from blemishes for approximately 1,5 x tube diameter from the
end.
Lubrication with lubricating oil, MoS2, Teflon etc. is recommended
for the assembly and reassembly of bigger sized unions (thread,
compression cone).
Installation 1 Insert the compression ferrule [C] and the compression
cone [D] into the union nut [B].
2 Screw on the union nut onto the body, do not tighten it.
3 Push the stainless steel pipe through the union nut as far as it
reaches the stop of the body.
4 Mark the union nut at 6 o’clock position.
5 While holding the fitting body steady, tighten the nut union 1¼
rotation using an open ended spanner.
A
B
C
Stainless steel tube
Union nut
Compression ferrule
D
E
F
Compression cone
Body
Tightened connection
12
3
9
6
ABCDE
F
Page 18

16 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3.3.2 Sample Outlet
1/2” tube at waste funnel.
Connect the 1/2” tube [C] to the hose nozzle [B] and place it into a
pressure free drain.
A
B
C
Waste funnel
Hose nozzle
1/2” tube
A
B
C
Page 19
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 17
3.4. Electrical Connections
WARNING
Risk of electrical shock.
Do not perform any work on electrical components if the transmitter is switched on. Failure to follow safety instructions could
result in serious injury or death.
Always turn off power before manipulating electric parts.
Grounding requirements: Only operate the instrument from
an power outlet which has a ground connection.
Make sure the power specification of the instrument corre-
sponds to the power on site.
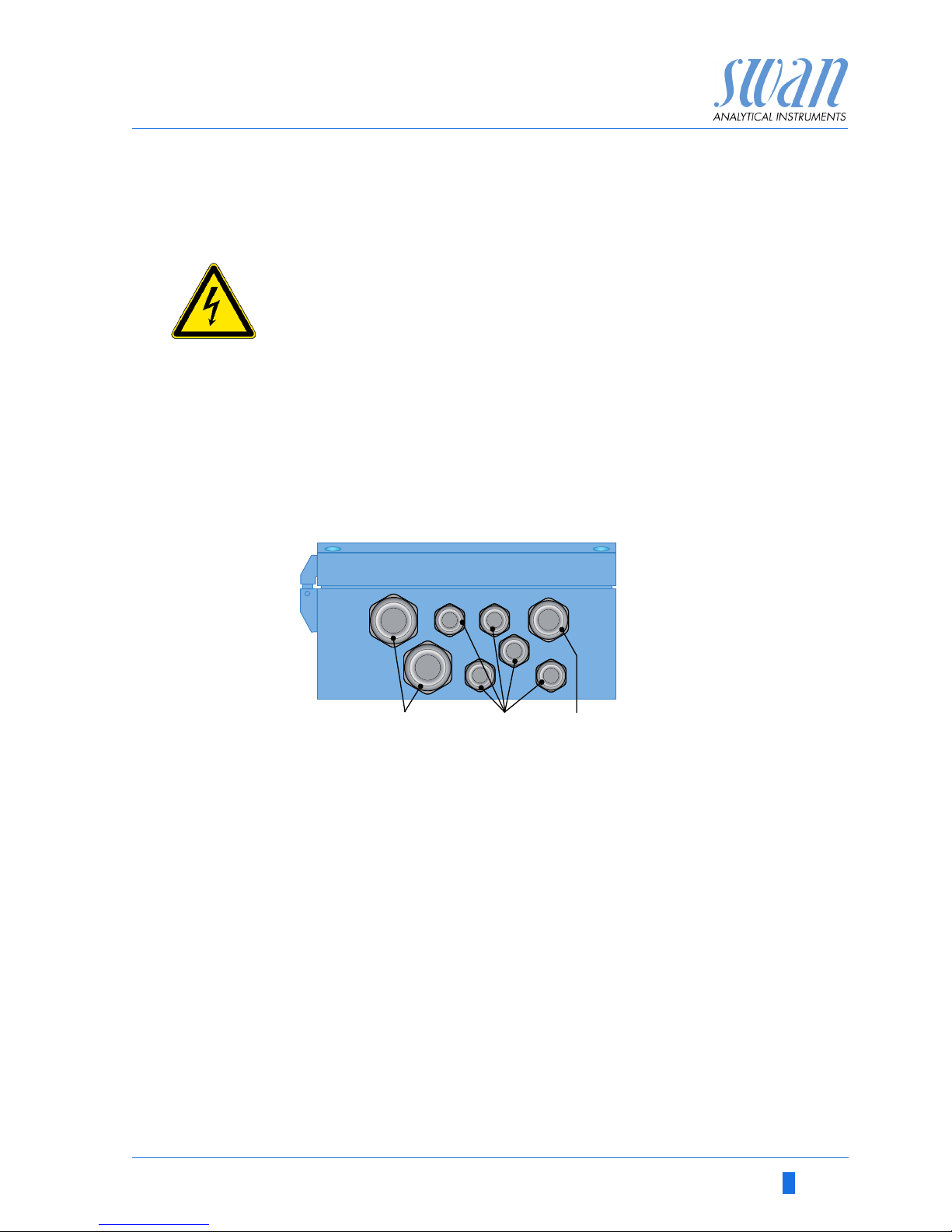
Cable
thicknesses
In order to comply with IP66, use the following cable thicknesses
NOTICE: Protect unused cable glands
Wire For power and relays: Use max. 1.5 mm
2
/ AWG 14 stranded
wire with end sleeves.
For signal outputs and input: Use 0.25 mm
2
/ AWG 23
stranded wire with end sleeves.
A
B
C
PG 11 cable gland: cable Ø
outer
5–10 mm
PG 7 cable gland: cable Ø
outer
3–6.5 mm
PG 9 cable gland: cable Ø
outer
4–8 mm
ABC
Page 20
18 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
WARNING
External Voltage.
External supplied devices connected to relay 1 or 2 or to the
alarm relay can cause electrical shocks
Make sure that the devices connected to the following con-
tacts are disconnected from the power before resuming installation.
–relay 1
–relay 2
– alarm relay
WARNING
To prevent from electrical shock, do not connect the instrument
to the power unless the ground wire (PE) is connected.
Do not connect unless specifically instructed to do so.
WARNING
The mains of the AMI Transmitter must be secured by a main
switch and appropriate fuse or circuit breaker.
Page 21

AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 19
3.5. Connection Diagram
CAUTION
Use only the terminals shown in this diagram, and only for the
mentioned purpose. Use of any other terminals will cause short
circuits with possible corresponding consequences to material
and personnel.
Page 22
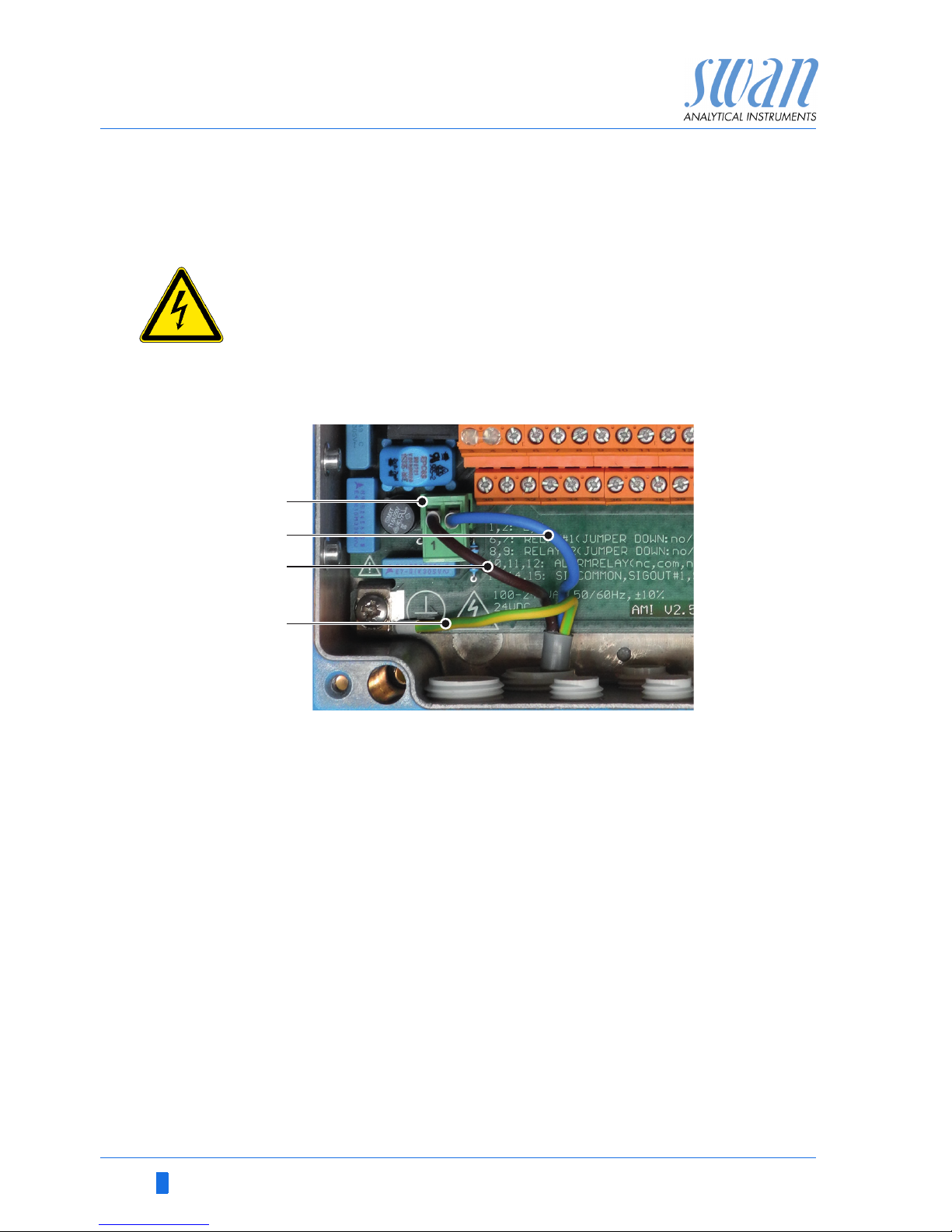
20 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3.6. Power Supply
WARNING
Electrical shock hazard
Installation and maintenance of electrical parts must be performed by professionals.
Always turn off power before manipulating electric parts.
NOTICE: The protective earth wire (ground) has to be
connected to the grounding terminal.
Installation
requirements
The installation must meet the following requirements.
Mains fuse 1.6 AT
Mains cable to comply with standards IEC 60227 or IEC
60245; flammable rating FV1
Mains equipped with an external switch or circuit-breaker
– near the instrument
– easily accessible to the operator
– marked as interrupter for AMI Hydrogen QED
A
B
C
D
Power supply connector
Neutral conductor, Terminal 2
Phase conductor, Terminal 1
Protective earth PE
A
B
C
D
Page 23
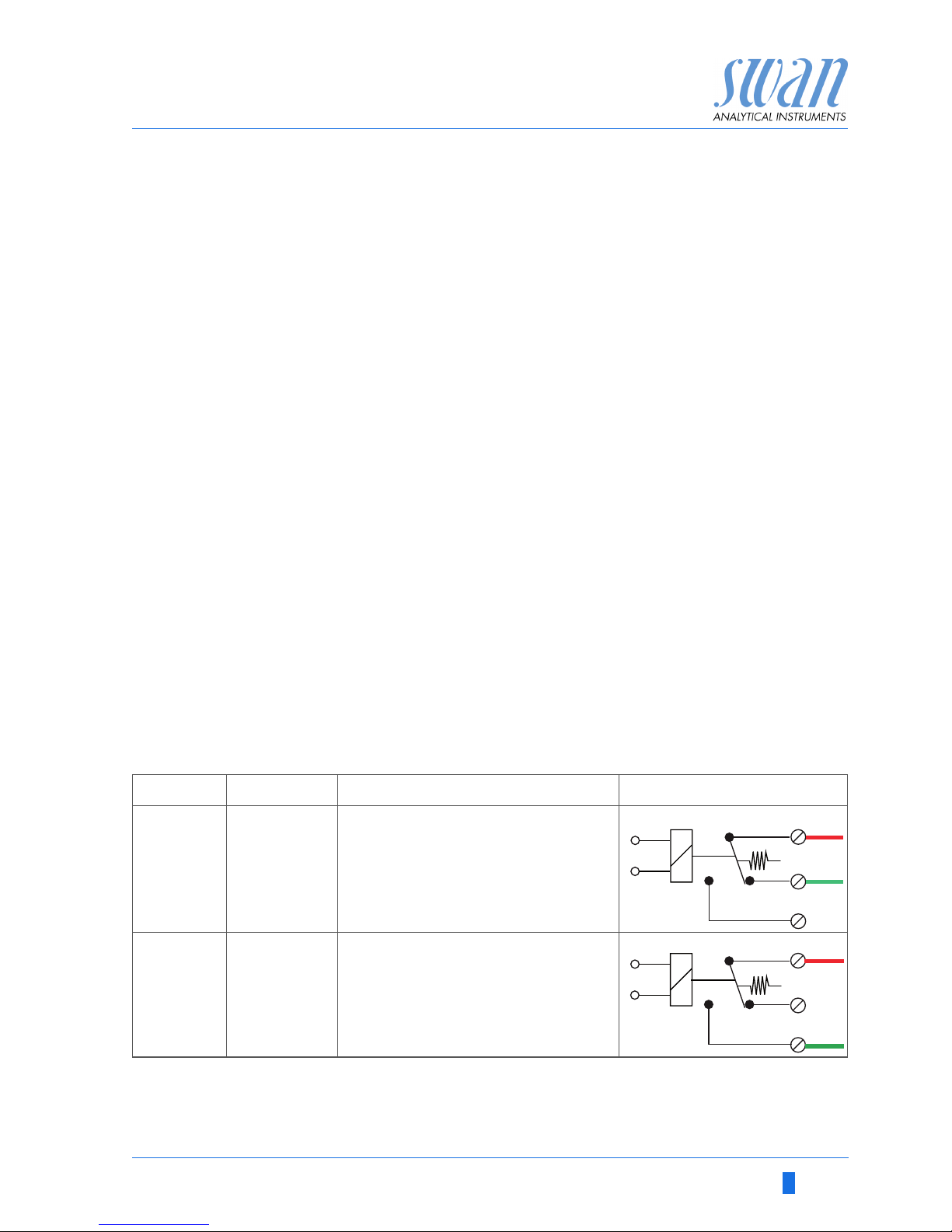
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 21
3.7. Relay Contacts
Programming of the relay contacts see 5.3 Relay Contacts, p. 65.
3.7.1 Input
NOTICE: Use only potential-free (dry) contacts.
The total resistance (sum of cable resistance and resistance of
the relay contact) must be less than 50 Ω.
Terminals 16/42
If signal output is set to hold, measurement is interrupted if input is
active.
For programming see menu 5.3.4, p. 71.
3.7.2 Alarm Relay
NOTICE: Max. load1 A T / 250 VAC
Alarm output for system errors.
Error codes see Troubleshooting, p. 46
Programming see menu 5.3.1, p. 65
NOTICE: With certain alarms and certain settings of the AMI
transmitter the alarm relay does not switch. The error, however,
is shown on the display.
1) usual use
Terminals Description Relay connection
NC
1)
Normally
Closed
10/11 Active (opened) during normal
operation.
Inactive (closed) on error and
loss of power.
NO
Normally
Open
12/11 Active (closed) during normal
operation.
Inactive (opened) on error and
loss of power.
10
12
11
0V
1)
10
12
11
0V
Page 24
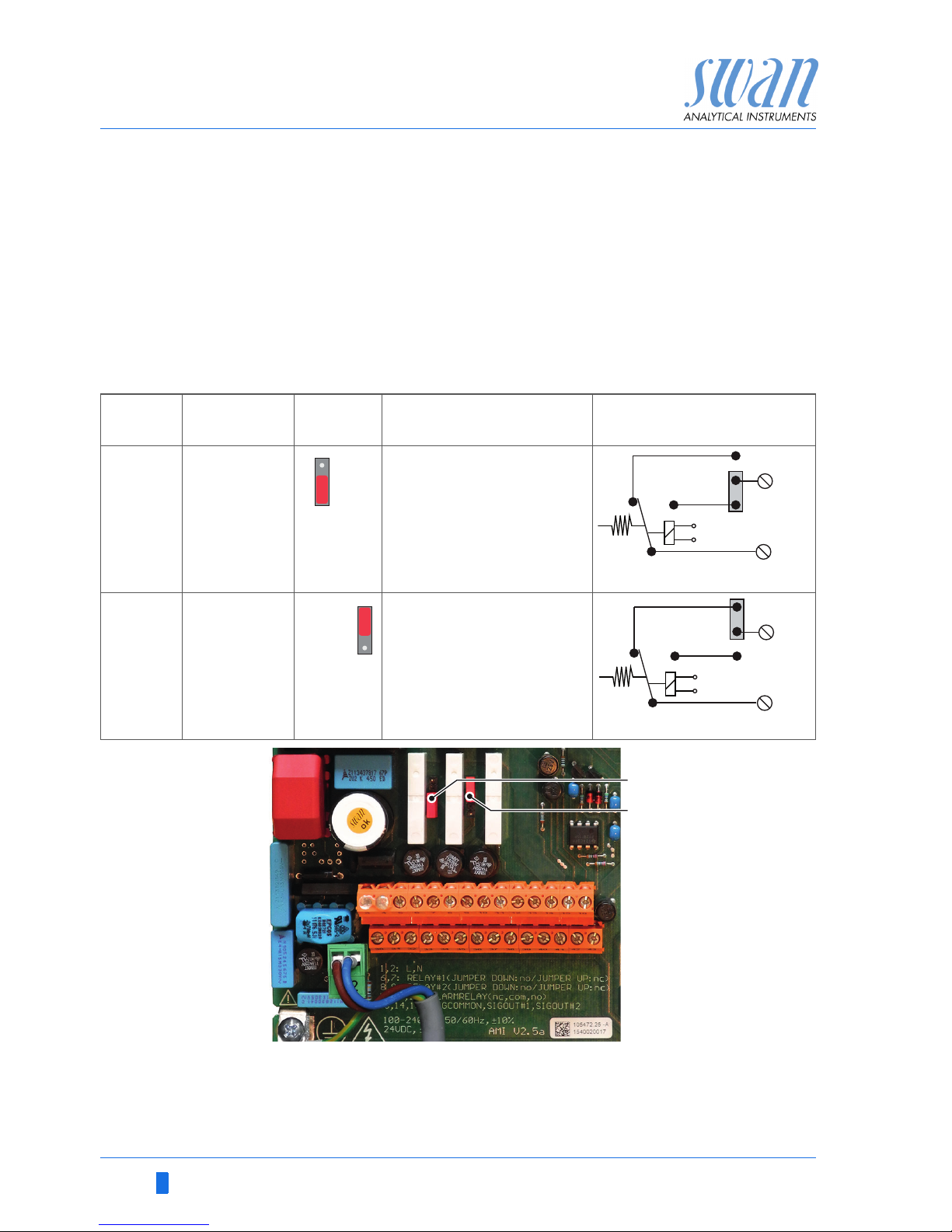
22 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3.7.3 Relay Contacts 1 and 2
NOTICE: Rated load 1 AT / 250 VAC
Relay 1 and 2 can be configured as normally open or as normally
closed. Standard for both relays is normally open. To configure a
Relay as normally closed, set the jumper in the upper position.
NOTICE: Some error codes and the instrument status may
influence the status of the relays described below.
For programming see Menu Installation 5.3.2 and 5.3. 3, p. 67
Relay
config. Terminals
Jumper
pos. Description Relay configuration
Normally
Open
6/7: Relay 1
8/9: Relay 2
Inactive (opened) during
normal operation and
loss of power.
Active (closed) when a
programmed function is
executed.
Normally
Closed
6/7: Relay 1
8/9: Relay 2
Inactive (closed) during
normal operation and
loss of power.
Active (opened) when a
programmed function is
executed.
6
0V
7
6
0V
7
ABJumper set as normally open (standard setting)
Jumper set as normally closed
A
B
Page 25

AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 23
CAUTION
Risk of damage of the relays in the AMI transmitter due to
heavy inductive load.
Heavy inductive or directly controlled loads (solenoid valves,
dosing pumps) may destroy the relay contacts.
To switch inductive loads > 0.1 A use an AMI relay box avail-
able as an option or suitable external power relays.
Inductive load Small inductive loads (max 0.1 A) as for example the coil of a pow-
er relay can be switched directly. To avoid noise voltage in the
AMI transmitter it is mandatory to connect a snubber circuit in parallel to the load.
Resistive load Resistive loads (max. 1 A) and control signals for PLC, impulse
pumps and so on can be connected without further measures
Actuators Actuators, like motor valves, are using both relays: One relay con-
tact is used for opening, the other for closing the valve, i.e. with the
2 relay contacts available, only one motor valve can be controlled.
Motors with loads bigger than 0.1 A must be controlled via external
power relays or an AMI relay box.
A
B
C
D
E
AC or DC power supply
AMI Transmitter
AMI Relay box
Snubber
Power relay coil
A
BC
DE
A
B
C
AMI transmitter
PLC or controlled pulse pump
Logic
AB
C
A
B
C
AC or DC power supply
AMI transmitter
Actuator
M
A
BC
Page 26

24 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3.8. Signal Outputs
3.8.1 Signal output 1 and 2 (current outputs)
NOTICE: Max. burden 510 Ω.
If signals are sent to two different receivers, use signal isolator
(loop isolator).
Signal output 1: Terminals 14 (+) and 13 (-)
Signal output 2: Terminals 15 (+) and 13 (-)
Programming see menu 5.2 Signal Outputs, p. 61
3.9. Interface Options
The slot for interfaces can be used to expand the functionality of
the AMI instrument with either:
Third signal output
a Profibus or Modbus connection
a HART connection
an USB interface
A
B
C
D
AMI transmitter
Slot for interfaces
Frontend PCB
Screw terminals
A
B
C
D
Page 27

AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 25
3.9.1 Signal Output 3
Terminals 38 (+) and 37 (-).
Requires the additional board for the third signal output 0/4– 20 mA.
The third signal output can be operated as a current source or as a
current sink (switchable via switch [A]). For detailed information see
the corresponding installation instruction.
NOTICE: Max. burden 510 Ω.
Third signal output 0/4 - 20 mA PCB
3.9.2 Profibus, Modbus Interface
Terminal 37 PB, Terminal 38 PA
To connect several instruments by means of a network or to config-
ure a PROFIBUS DP connection, consult the PROFIBUS manual.
Use appropriate network cable.
NOTICE: The switch must be ON, if only one instrument is
installed, or on the last instrument in the bus.
Profibus, Modbus Interface PCB (RS 485)
A Operating mode selector switch
A
A On - OFF switch
ON
OFF
A
Page 28

26 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Installation
3.9.3 HART Interface
Terminals 38 (+) and 37 (-).
The HART interface PCB allows for communication via the HART
protocol. For detailed information, consult the HART manual.
HART Interface PCB
3.9.4 USB Interface
The USB Interface is used to store logger data and for firmware upload. For detailed information see the corresponding installation instruction.
The optional third signal output 0/4 – 20 mA PCB [B] can be
plugged onto the USB interface and used in parallel.
USB Interface
A USB interface PCB
B Third signal output 0/4 - 20 mA PCB
A
B
Page 29

AMI Hydrogen QED
Instrument Setup
A-96.250.791 / 040219 27
4. Instrument Setup
Establish
sample flow
1 Open the flow regulating valve [A].
2 Switch on the instrument.
3 The following start-up sequence lasts 8 min, during this time the
instrument is on hold.
4 Adjust the sample flow to 6– 20 l/h. The actual flow is shown on
the transmitter display.
A
HOLD
25.1 °C
0.0 l/h
15:20:18
07:18
R1
R2
Start-up
Sequence
Page 30

28 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Instrument Setup
4.1. Programming
Sensor
parameters
Check the sensor parameters in menu <Installation>\
<Sensors>\<Sensor parameters>.
The sensor characteristics are printed on the label of each sensor.
The following parameters are required:
I
s
(saturation current)
p (air pressure)
External
devices
Program all parameters for external devices (interface, recorders,
etc.)
Limits, alarms Program all parameters for instrument operation (limits, alarms).
See Program List and Explanations, p. 55.
SwanSensor Hydrogen
A-87.260.001 Is: 3.025 µA
xxxxxxx p: 953 hPa
Page 31

AMI Hydrogen QED
Operation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 29
5. Operation
5.1. Keys
Program
Access, Exit
Sensor
Maintenance
An automatic sensor regeneration is carried out at configurable intervals and takes 2 minutes. During this time the signal outputs are
set to hold.
A to exit a menu or command (rejecting any changes)
to move back to the previous menu level
B to move DOWN in a menu list and to decrease digits
C to move UP in a menu list and to increase digits
D to open a selected sub-menu
to accept an entry
Exit Enter
BCDA
25.4°C
RUN
9 l/h
14:10:45
R1
1.05 ppb
R2
1
Installation
Operation
Diagnostics
Messages
Maintenance
Main Menu
Enter
Exit
Sensor
Maintenance
HOLD
25.1 °C
0.0 l/h
15:20:18
01:45
R1
R2
Page 32

30 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Operation
5.2. Display
Relay status, symbols
A RUN normal operation
HOLD input closed or cal delay: Instrument on hold (shows
status of signal outputs).
OFF input closed: control/limit is interrupted (shows status
of signal outputs).
B ERROR Error
Fatal Error
C Keys locked, transmitter control via Profibus
D Time
E Process values
F Sample temperature
G Sample flow in l/ h
H Relay status
upper/lower limit not yet reached
upper/lower limit reached
control upw./downw. no action
control upw./downw. active, dark bar indicates control intensity
motor valve closed
motor valve: open, dark bar indicates approx. position
timer
timer: timing active (hand rotating)
RUN
23 °C
23 l/h
15:20:18
R1
R2
ppm
1.05
AB CD
F
E
G
H
Page 33

AMI Hydrogen QED
Operation
A-96.250.791 / 040219 31
5.3. Software Structure
Menu Messages 1
Reveals pending errors as well as an event history
(time and state of events that have occurred at an
earlier point of time).
It contains user relevant data.
Menu Diagnostics 2
Provides user relevant instrument and sample data.
Menu Maintenance 3
For instrument calibration, relay and signal output
simulation, and to set the instrument time.
It is used by the service personnel.
Menu Operation 4
User relevant parameters that might need to be
modified during daily routine. Normally password
protected and used by the process-operator.
Subset of menu 5 - Installation, but process-related.
Menu Installation 5
For initial instrument set up by SWAN authorized
person, to set all instrument parameters. Can be
protected by means of password.
1
Messages
Operation
Maintenance
Diagnostics
Main Menu
Installation
1.1
Pending Errors
Messages
Maintenance List
Message List
2.1
Interface
I/O State
Sample
Identification
Sensors
Diagnostics
3.1
Calibration
Maintenance
Set Time 23.09.06 16:30:00
Simulation
Service
4.1
Logger
Relay Contacts
Sensors
Operation
5.1
Interface
Miscellaneous
Relay Contacts
Sensors
Signal Outputs
Installation
Page 34

32 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Operation
5.4. Changing Parameters and Values
Changing
parameters
The following example shows how to change the logger interval:
Changing
values
1 Select the parameter you want to
change.
2 Press [Enter].
3 Press [ ] or [ ] key to
highlight the required parameter.
4 Press [Enter] to confirm the selec-
tion or [Exit] to keep the previous
parameter).
The selected parameter is
highlighted (but not saved yet).
5 Press [Exit].
Yes is highlighted.
6 Press [Enter] to save the new pa-
rameter.
The system reboots, the new
parameter is set.
5.1.2
Sensors
Sensor type FOME
Temperature NT5K
Standards
Disinf. Free chlorine
4.4.1
Logger
Log interval 30 min
Clear logger no
4.1.3
Logger
Clear logger no
Log interval 30min
1 Hour
Interval.
5 min
30 min
10 min
4.1.3
Logger
Log interval 10 min
Clear logger no
4.1.3
Logger
Log interval
Clear logger no
No
Save ?
Yes
1 Select the value you want to
change.
2 Press [Enter].
3 Set required value with [ ] or
[] key.
4 Press [Enter] to confirm the new
value.
5 Press [Exit].
Yes is highlighted.
6 Press [Enter] to save the new val-
ue.
5.3.1.1.1
Alarm High 10.00 ppb
Alarm Hydrogen
Alarm Low 2.00 ppb
Hysteresis 0.10 ppb
Delay 5 Sec
5.3.1.1.1
Alarm Hydrogen
Alarm Low 2.00 ppb
Hysteresis 0.10 ppb
Delay 5 Sec
Alarm High 8.00 ppb
Page 35

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 33
6. Maintenance
6.1. Maintenance Table
6.2. Stop of Operation for Maintenance
1 Shut off power of the instrument.
2 Stop sample flow by closing the flow regulating valve.
If required
Perform a calibration.
Two years or if
required
Send the sensor to Swan for revision.
After installation of the revised sensor, program saturation
current and air pressure (5.1.3.1, p. 60 and 5.1.3.2, p. 60)
as indicated on the sensor label.
To avoid a longer interruption of the measuring operation, a
second hydrogen sensor can be purchased. The two sensors
can then be used alternately. If two sensors are available, the
following procedure is recommended:
Send the replacement sensor to Swan for revision shortly
before replacement.
After installing the revised sensor, store the unused sensor
in its original packaging in a cold, dry and dark place.
Page 36

34 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.3. Maintenance of the Hydrogen Sensor
6.3.1 Hydrogen Sensor Handling
Never attempt to open the hydrogen sensor.
Always store the sensor in water or in the wet flow cell.
Always keep the sensor connected to the AMI transmitter.
Always keep the sensor polarized. Without polarization the
sensor suffers a loss of sensitivity.
The AMI Hydrogen QED has a buffered polarization source
which will keep the hydrogen sensor polarized for some days,
even if the AMI Hydrogen QED is switched off.
However, it is a good idea to keep the AMI running all the
time. The AMI Hydrogen QED should be connected to the
power supply and switched on even if it is not in use.
During calibration, do not expose the sensor to 100 % hydro-
gen for more than 6 minutes. Otherwise the extremely dry gas
might dry out the capillary layer of electrolyte between platinum anode and plastic membrane, which makes the sensor
response unstable.
The hydrogen molecule is very small and migrates into al-
most any material including electrolyte, plastics and even
metals and will remain there for some time. After a calibration
it may take a few hours until the residual current of the sensor
has dropped enough to measure very low levels of hydrogen
again.
The hydrogen sensor usually shows a small positive offset,
which means there is a small positive value in air (without hydrogen, normally below one ppb). This value can be set to
zero: <Installation > Sensors > Miscellaneous > Offset. Use
with care!
6.3.2 Calibration
The hydrogen sensor of the AMI Hydrogen QED is calibrated with
pure hydrogen. To perform a calibration proceed as follows:
NOTICE: Do not expose the sensor to 100% hydrogen for more
than 6 minutes.
1 Stop the sample flow at the main tap.
2 Navigate to menu <Maintenance> / <Calibration>.
Page 37

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 35
3 Press [Enter] to start the calibration and follow the dialog on the
display.
If the calibration fails again, the hydrogen sensor has to replaced
by a new one.
4 Unscrew and remove the thread-
ed sleeve [A].
5 Remove the hydrogen sensor [B]
from the flow cell.
6 Dry the sensor membrane and the
flow cell with a soft paper tissue.
7 Flush the flow cell with hydrogen.
8 Stop hydrogen flow and dry the
flow cell.
9 Re-insert the hydrogen sensor into
the flow cell.
Make sure that the sensor
membrane is dry.
10 Start the hydrogen flow.
11 Press [Enter] to start the calibra-
tion measurement.
The saturation should reach 100%,
the saturation current should be about
2.0 A to 4.5 A. If the measuring values are not stable during the measuring period, the calibration will be
discarded.
If this is the case, check and if necessary correct your measurement arrangement and try again.
If the calibration was successful press
[Enter] to save.
3.1.5
Calibration
Close regulating valve
to turn off sample flow.
<Enter> to continue
3.1.5
Calibration
Take sensor out of
flow cell and dry
membrane and sensor
<Enter> to continue
3.1.5
Calibration
Connect flow cell to a
source of hydrogen and
Dry flow cell inside.
flush with hydrogen.
<Enter> to continue
3.1.5
Calibration
Remount sensor and let
hydrogen stream through
value is accepted.
flow cell gently until
<Enter> to continue
3.1.1
Calibration
Saturation xx.x%
Sat. Current x.xx
A
Progress
3.1.1
Calibration
Saturation xx.x %
Sat. Current x.xx
A
<Enter> to save
Page 38

36 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.3.3 Faraday Verification
The Faraday verification works only for hydrogen concentrations
below 40–50 ppb. If automatic Faraday verification is enabled, a
periodic check of the system is performed. A manual verification
can be started for test purposes.
Automatic
verification
Per default the instrument performs an automatic Faraday verification every 3 hours. To change the settings for automatic verification
navigate to menu <Operation>/<Faraday Parameter>, see menu
4.1.3, p. 58 for details.
Possible settings are:
off
interval
daily
weekly
Manual
verification
To start a manual verification:
1 Navigate to menu 3.2.2 <Maintenance>/<Service>/<Faraday
Verification>.
Results are saved in the Verification history menu 2.2.1.5
If the Faraday efficiency is below 50%, message E018 is displayed
and the Faraday electrode needs to be cleaned, see Maintenance
of the Faraday Electrode, p. 38.
2 Press [Enter] to start the Faraday
Verification.
The verification then starts
immediately.
3 Press [Enter] to confirm the Fara-
day Verification.
3.3
Progress
Faraday Verification
<Enter> to stop
Current Value 1.62 ppb
Faraday Conc.
12.85 ppb
3.3
Progress
Faraday Verification
Done
Efficiency 91.5 %
Faraday Conc. 12.85 ppb
Page 39

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 37
6.3.4 Replace Hydrogen Sensor
To replace the hydrogen sensor proceed as follows:
Remove the
old sensor
1 Switch off the AMI Hydrogen QED.
2 Close the flow regulating valve [D].
3 Unscrew and remove the threaded sleeve [A] from the flow cell.
4 Remove the hydrogen sensor [C] from the flow cell.
5 Unscrew and remove the sensor connector [B] from the hydro-
gen sensor.
Install the new
sensor
1 Screw the connector onto the hydrogen sensor and tighten it.
2 Put the hydrogen sensor into the flow cell.
3 Screw the threaded sleeve into the thread of the flow cell to fix
the hydrogen sensor.
4 Open the flow regulating valve and adjust the sample flow to
6–20 l/h.
5 Switch on the AMI Inspector Hydrogen.
6 Let the new sensor run in for at least 1h.
A
B
C
D
Threaded sleeve
Sensor connector
Hydrogen sensor
Flow regulating valve
A
B
C
D
Page 40

38 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.4 Maintenance of the Faraday Electrode
1 Switch off the instrument and close the flow regulating valve.
2 Open the Faraday control unit.
3 Disconnect and remove the cable from the Faraday control unit.
4 Unscrew and remove the fixing sleeve (A).
5 Remove the Faraday electrode from the flow cell, do not pull on
the cable.
6 Remove the washer (C) and the o-ring [D] from the electrode
body (B).
7 Unscrew the electrode tip containing the hollow electrode (G).
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Fixing sleeve
Electrode body
Washer
O-ring
Inner electrode
O-ring
Hollow electrode
A
C
D
E
F
G
B
Page 41

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 39
8 Clean the inner electrode (E) with a tissue and the hollow elec-
trode with a pipe cleaner.
The electrode surfaces should be shining metallic after
cleaning. If necessary, use a polishing detergent or a small
amount of toothpaste.
9 Rinse all parts well with water.
10 Replace the O-ring and the washer if necessary.
11 Screw the hollow electrode finger-tight onto the electrode body.
12 Insert the faraday electrode into flow cell.
13 Tighten fixing sleeve firmly.
14 Feed the electrode cable through the cable gland of the faraday
control unit.
15 Connect the electrode cable to terminal 5 (green) and terminal 6
(white).
16 Switch the instrument on.
17 Open the flow regulating valve and adjust the sample flow be-
tween 6 and 20 l/ h.
Page 42

40 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.5. Quality Assurance of the Instrument
Every SWAN on-line instrument is equipped with integrated, autonomous quality assurance functions to survey the plausibility of each
measurement.
For the AMI Hydrogen QED these are:
continuous monitoring of sample flow
continuous monitoring of the temperature inside the transmit-
ter case
periodic accuracy test with ultra high precision resistors
Further a manual, menu driven inspection procedure can be carried
out using a certified reference instrument. The AMI Inspector is
connected to the same sample point and provides the reference
value. After enabling the quality assurance procedure by defining
the quality assurance level, the instrument reminds the user periodically to run the procedure and results are stored in a history for review.
Quality
assurance
level
Central feature of the quality assurance function is the assignment
of the monitored process to a Quality assurance level.
There are three predefined levels plus a user level. Hereby the inspection interval, the deviation limits of temperature and measuring
result between the inspection equipment and the monitoring instrument are defined.
Level 1: Trend; Measurement used as an additional informa-
tion to follow the process indicating trends.
Level 2: Standard; Monitoring of several parameters of a pro-
cess (e.g. hydrogen, saturation). In case of instrument failure,
other parameters can be used for process monitoring.
Level 3: Crucial; Monitoring of critical processes, value is
used for control of another part or subsystem (valve, dosing
unit, etc.).
Additional level:
Quality level 4: User; User defined inspection interval, maxi-
mal deviation of temperature and measuring result.
Page 43

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 41
Procedure The standard workflow contains following procedures:
1 Activate SWAN Quality assurance procedure
2 Pre-test
3 Connect instruments
4 Carry out comparison measurement
5 Completion of the measurement
NOTICE: The procedure should only be carried out through
qualified personnel.
6.5.1 Activate SWAN Quality assurance procedure
Enable quality assurance procedure at each instrument to be verified by selecting the quality level in menu 5.1.4.
The corresponding submenus are then activated.
NOTICE: The activation is necessary the first time only.
Quality Level
max. deviation
temperature [°C]
a)
max. deviation
result [%]
min. inspection
interval
0: Off
Off Off
Off
1: Trend
0.5 °C 10%
annual
2: Standard
0.4 °C 5%
quarterly
3: Crucial
0.3 °C 5%
monthly
4: User
0–2 °C 0–20%
annual, quarterly,
monthly
a) sample temperature must have 25°C +/- 5°C.
Page 44

42 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.5.2 Pre-test
Reference instrument: AMI Inspector Hydrogen:
– Check certificate; reference instrument certificate not older
than one year.
– Check battery; Battery of the AMI Inspector Hydrogen
should be completely charged. Remaining operating time
on display minimum 20 hours.
– Sensor is in working condition.
On-line instrument: Monitor AMI Hydrogen:
– Good order and condition; Flow cell free of particles,
Sensor surface free of deposits.
– Check message list; Review the message list in menu 1.3
and check for frequently occurring alarms (as for example
flow alarms). If alarms occur frequently remove cause
before starting the procedure.
6.5.3 Connect the sample lines
See corresponding chapter in the manual of the process monitor
which shall be checked with a reference instrument.
The choice of sampling depends strongly on local conditions on
site. Possible sampling:
via sample point,
via T-fitting or
via piggyback/ downstream
NOTICE:
• avoid ingress of air, use screwed fitting,
• sample as near as possible to the process monitor,
• wait approx. 10 minutes, whilst measurement is running, until
measurement value and temperature are stabilized.
Example As an example following picture shows the connection of the refer-
ence instrument via T-fitting to the process monitor.
Page 45

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 43
1 Stop sample flow to the monitor AMI Hydrogen QED by closing
the appropriate valve, e.g. back pressure regulator, sample
preparation or flow regulating valve at flow cell.
2 Connect sample line of the monitor AMI Hydrogen QED [A] with
the sample inlet of the reference instrument AMI Inspector Hydrogen [B]. Use the supplied tube.
3 Connect sample outlet of the reference instrument AMI Inspec-
tor Hydrogen to the sample outlet funnel of the monitor.
4 Switch on the AMI Inspector Hydrogen. Open the flow regulat-
ing valve and regulate the sample flow to 10 l/h. The actual flow
is shown on the transmitter.
A
B
C
D
Monitor AMI Hydrogen QED
AMI Inspector Hydrogen
Reference flow cell
On-line flow cell
E
F
G
Sample outlet
Sample inlet
T-fitting
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Page 46

44 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
6.5.4 Carry out comparison measurement
The comparison measurement is menu driven. Start by selecting
Quality Assurance in menu 3.5 of the monitor AMI Hydrogen QED.
1 Navigate to menu Maintenance / Quality Assurance.
2 Press [Enter].
3 Follow the dialog on the Display.
4 Carry out pre test preparations
Connect instruments.
Regulate sample flow to 10 l/h using the appropriate valve.
5 Wait 10 minutes whilst measure-
ment is running.
Press [Enter] to continue.
6 Read the hydrogen value of the
reference instrument and enter under “Inspector.” by using the
[ ] or [ ] keys.
7 Press [Enter] to confirm.
8 Read temperature value of the ref-
erence instrument and enter under “Inspector Temp.” by using the
[ ] or [ ] keys.
9 Press [Enter] to confirm.
10 Press [Enter] to continue.
The results are saved in QA-
History regardless if successful
or not
3.5.5
Quality Assurance
- Carry out preparations
- Install Inspector
- Sample flow to 10 l/h
<Enter> to continue
3.5.5
Quality Assurance
Value H2 0.05 ppb
Value Temp. 25.00 C
Wait 10 Minutes
<Enter> to continue
3.5.3
Quality Assurance
Value H2 0.05 ppb
Value Temp. 25.00 C
<Enter> to continue
Inspector H2 0.06 ppb
Inspector Temp. 25.0 C
3.5.4
Quality Assurance
Value H2 0.05 ppb
Value Temp. 25.00 C
<Enter> to continue
Inspector 0.06 ppm
Inspector Temp. 25.0 C
3.5.5
Quality Assurance
Max. Dev. H2 0.5 %
Max. Dev. Temp. 0.4 °C
QA-Check succesful
Dev. H2 0.1 %
Dev. Temp. 0.4 °C
Page 47

AMI Hydrogen QED
Maintenance
A-96.250.791 / 040219 45
6.5.5 Completion of the measurement
1 Stop the sample flow to the AMI Hydrogen QED by closing the
appropriate valve, e.g. back pressure regulator, sample preparation or flow regulating valve at flow cell again.
2 Close flow regulating valve of the AMI Inspector.
3 Disconnect the AMI Inspector by removing the tubes.
4 Start sample flow again.
5 Adjust the sample flow to 6–20 l/h. The actual flow is shown on
the transmitter display.
6 Shut down the AMI Inspector Hydrogen.
If the AMI Inspector will not be used for a longer period of time, proceed according to section Longer Stop of Operation in the manual
of the AMI Inspector.
6.6. Longer Stop of Operation
1 Stop sample flow.
2 Do not shut off power of the instrument.
NOTICE: The hydrogen sensor is polarized and a loss of
polarization will result in loss of sensitivity. If the AMI Hydrogen
QED is switched off, the polarization buffer will be discharged
within a few days.
3 Leave the sensor in the wet flow cell.
Page 48

46 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Troubleshooting
7. Troubleshooting
7.1. Error List
Error
Non-fatal Error. Indicates an alarm if a programmed value is exceeded. Such errors are marked E0xx (bold and black).
Fatal error (blinking symbol)
Control of dosing devices is interrupted.
The indicated measured values are possibly incorrect.
Fatal errors are divided in the following two categories:
Errors which disappear if correct measuring conditions are re-
covered (i.e. Sample Flow low).
Such errors are marked E0xx (bold and orange)
Errors which indicate a hardware failure of the instrument.
Such errors are marked E0xx (bold and red)
Error or fatal error
Error not yet acknowledged.
Check Pending Errors 1.1.5 * and
take corrective action.
Press [ENTER].
Navigate to menu Messages.
Press [ENTER].
Navigate to menu Pending Errors.
Press [ENTER].
Press [ENTER] to acknowledge the
Pending Errors. The error is reset and
saved in the Message List.
* Menu numbers see
Program Overview, p. 50
25.4°C
HOLD
8 l/h
14:10:45
R1
7.04 ppm
R2
1
Installation
Operation
Diagnostics
Messages
Maintenance
Main Menu
1.1
Message List
Pending Errors
Maintenance List
Messages
1.1.5
Pending Errors
Error Code E002
Alarm low
<Enter> to Acknowledge
Page 49

AMI Hydrogen QED
Troubleshooting
A-96.250.791 / 040219 47
Error Description Corrective action
E001 Hydrogen Alarm high
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.1.1, p. 65
E002 Hydrogen Alarm low
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.1.25, p. 65
E003 Saturation Alarm high
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.4, p. 66
E004 Saturation Alarm low
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.4, p. 66
E007 Sample Temp. high
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.3.1, p. 66
E008 Sample Temp. low
– check process
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.3.25, p. 66
E009 Sample Flow high
– check sample flow
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.2.2, p. 66
E010 Sample Flow low
– establish sample flow
– clean instrument
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.2.35, p. 66
E011 Temp. shorted
– check wiring of sensor
– check sensor
E012 Temp. disconnected
– check wiring of sensor
– check sensor
Page 50

48 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Troubleshooting
E013 Case Temp. high
– check case/environment temperature
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.5.1, p. 67
E014 Case Temp. low
– check case/environment temperature
– check programmed value,
see 5.3.1.5.2, p. 67
E017 Control Timeout
– check control device or programming in
Installation, Relay contact, Relay 1/2
see 5.3.2 and 5.3.3, p. 67
E018 Faraday Efficiency
– clean Faraday electrode, see
Maintenance of the Faraday Electrode,
p. 38
E019 Quality Assurance
– perform QA Procedure using a
reference instrument, e.g. AMI Inspector
E024 Input active
– see If Fault Yes is programmed in Menu
see 5.3.4, p. 71
E026 IC LM75
– call service
E028 Signal output open
– check wiring on signal outputs 1 and 2
E030 EEProm Frontend
– call service
E031 Calibration Recout
– call service
E032 Wrong Frontend
– call service
E033 Power-on
– none, normal status
E034 Power-down
– none, normal status
Error Description Corrective action
Page 51

AMI Hydrogen QED
Troubleshooting
A-96.250.791 / 040219 49
7.2. Replacing Fuses
WARNING
External Voltage.
External supplied devices connected to relay 1 or 2 or to the
alarm relay can cause electrical shocks.
Make sure that the devices connected to the following con-
tacts are disconnected from the power before resuming installation.
– relay 1
– relay 2
– alarm relay
When a fuse has blown, find out the cause and fix it before
replacing it with a new one.
Use tweezers or needle-nosed pliers to remove the defective fuse.
Use original fuses provided by SWAN only.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
1.6 AT/250V Instrument power supply
1.0 AT/250V Relay 1
1.0 AT/250V Relay 2
1.0 AT/250V Alarm relay
1.0 AF/125V Signal output 2
1.0 AF/125V Signal output 1
1.0 AF/125V Signal output 3
A
B
CDEF G
Page 52

50 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program Overview
8. Program Overview
For explanations about each parameter of the menus see Program
List and Explanations, p. 55.
Menu 1 Messages informs about pending errors and mainte-
nance tasks and shows the error history. Password protection
possible. No settings can be modified.
Menu 2 Diagnostics is always accessible for everybody. No
password protection. No settings can be modified.
Menu 3 Maintenance is for service: Calibration, simulation of
outputs and set time/date. Please protect with password.
Menu 4 Operation is for the user, allowing to set limits, alarm
values, etc. The presetting is done in the menu Installation
(only for the System engineer). Please protect with password.
Menu 5 Installation: Defining assignment of all inputs and
outputs, measuring parameters, interface, passwords, etc.
Menu for the system engineer. Password strongly recommended.
8.1. Messages (Main Menu 1)
8.2. Diagnostics (Main Menu 2)
Pending Errors Pending Errors 1.1.5* * Menu numbers
1.1*
Maintenance List Maintenance List 1.2.5*
1.2*
Message List Number 1.3.1*
1.3* Date, Time
Identification Desig. AMI Hydrogen * Menu numbers
2.1* Version 6.22-08 /18
Factory Test Instrument 2.1.3.1*
2.1.3* Motherboard
Front End
Operating Time Years / Days / Hours / Minutes / Seconds 2.1.4.1*
2.1.4*
Page 53

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program Overview
A-96.250.791 / 040219 51
8.3. Maintenance (Main Menu 3)
Sensors Sensor Current Value
2.2* 2.2.1* (Raw value tc)
(Raw value)
Saturation
Cal. History Number 2.2.1.5.1*
2.2.1.5* Date, Time
Sat. Current
Air pressure
Miscellaneous Case Temp. 2.2.2.1*
2.2.2* Air pressure
QA History QA History 2.2.3.1*
2.2.3*
Sample Sample ID 2.3.1*
2.3* Temperature °C
Nt5K Ohm
I/O State Alarm Relay 2.4.1*
2.4* Relay 1/2 2.4.2*
Input
Signal Output 1/2
Interface Protocol 2.5.1*
2.5* USB Stick
Calibration Calibration 3.1.5 * Menu numbers
3.1*
Sevice Electrolyte Last filling
3.2* 3.2.1* Remaining amount
Remaining time
New Filling 3.2.1.5*
Faraday Verification Progress
3.2.2
Simulation Alarm Relay 3.2.1*
3.3* Relay 1 3.2.2*
Relay 2 3.2.3*
Signal Output 1 3.2.4*
Signal Output 2 3.2.5*
Page 54

52 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program Overview
8.4. Operation (Main Menu 4)
Set Time (Date), (Time)
3.4*
Quality Assurance Quality Assurance 3.5.5*
3.5*
Sensors Filter Time Const. 4.1.1*
4.1* Hold after Cal. 4.1.2*
Faraday Parameter Mode
4.1.3 Interval
Delay
Signal outputs
Output/ Control
Relay Contacts Alarm Relay Alarm Hydrogene Alarm High 4.2.1.1.1*
4.2* 4.2.1* 4.2.1.1* Alarm Low 4.2.1.1.25*
Hysteresis 4.2.1.1.35*
Delay 4.2.1.1.45*
Alarm Saturation Alarm High 4.2.1.2.1*
4.2.1.2* Alarm Low 4.2.1.2.25*
Hysteresis 4.2.1.2.35*
Delay 4.2.1.2.45*
Relay 1/ 2 Setpoint 4.2.x.100*
4.2.2* - 4.2.3* Hysteresis 4.2.x.200*
Delay 4.2.x.30*
Input Active 4.2.4.1*
4.2.4* Signal Outputs 4.2.4.2*
Output / Control 4.2.4.3*
Fault 4.2.4.4*
Delay 4.2.4.5*
Logger Log Interval 4.3.1*
4.3* Clear Logger 4.3.2* * Menu numbers
Eject USB Stick 4.3.3*
Page 55

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program Overview
A-96.250.791 / 040219 53
8.5. Installation (Main Menu 5)
Sensors Miscellaneous Flow 5.1.1.1* * Menu numbers
5.1* 5.1.1* Offset 5.1.1.2*
Maintenance Int. 5.1.1.3*
Quality Assurance Level 5.1.2.1*
5.1.2*
Sensor parameters Sat. current 5.1.3.1*
5.1.3* Air pressure 5.1.3.2*
Signal Outputs Signal Output 1 /2 Parameter 5.2.1.1 - 5.2.2.1*
5.2* 5.2.1* - 5.2.2* Current Loop 5.2.1.2 - 5.2.2.2*
Function 5.2.1.3 - 5.2.2.3*
Scaling Range Low 5.2.x.40.10/11*
5.2.x.40 Range High 5.2.x.40.20/21*
Relay Contacts Alarm Relay Alarm Hydrogen Alarm High 5.3.1.1.1*
5.3* 5.3.1* 5.3.1.1* Alarm Low 5.3.1.1.25
Hysteresis 5.3.1.1.35
Delay 5.3.1.1.45
Sample Flow Flow Alarm 5.3.1.2.1
5.3.1.2* Alarm High 5.3.1.2.2*
Alarm Low 5.3.1.2.35*
Sample Temp. Alarm High 5.3.1.3.1*
5.3.1.3* Alarm Low 5.3.1.3.25*
Alarm Saturation Alarm High 5.3.1.4.1*
5.3.1.4* Alarm Low 5.3.1.4.25
Hysteresis 5.3.1.4.35
Delay 5.3.1.4.45
Case Temp. Case Temp. high 5.3.1.5.1*
5.3.1.5* Case Temp. low 5.3.1.5.2*
Relay 1/2 Function 5.3.2.1– 5.3.3.1*
5.3.2* - 5.3.3* Parameter 5.3.2.20–5.3.3.20*
Setpoint 5.3.2.300– 5.3.3.301*
Hysteresis 5.3.2.400– 5.3.3.401*
Delay 5.3.2.50–5.3.3.50*
Input Active 5.3.4.1*
5.3.4* Signal Outputs 5.3.4.2*
Output/Control 5.3.4.3*
Page 56

54 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program Overview
Fault 5.3.4.4*
Delay 5.3.4.5*
Miscellaneous Language 5.4.1*
5.4* Set defaults 5.4.2*
Load Firmware 5.4.3*
Password Messages 5.4.4.1*
5.4.4* Maintenance 5.4.4.2*
Operation 5.4.4.3*
Installation 5.4.4.4*
Sample ID 5.4.5*
Line break detection 5.4.6*
Interface Protocol USB Stick
5.5* 5.5.1* * Menu numbers
Page 57

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 55
9. Program List and Explanations
1 Messages
1.1 Pending Errors
1.1.5 Provides the list of active errors with their status (active, acknowledged). If an active error is acknowledged, the alarm relay is active
again. Cleared errors are moved to the Message list.
1.2 Maintenance List
1.2.5 Provides the list of necessary maintenance. Cleared maintenance
messages are moved to the Message list.
1.3 Message List
1.3.1 Shows the error history: Error code, date / time of issue and status
(active, acknowledged, cleared). 65 errors are memorized. Then
the oldest error is cleared to save the newest error (circular buffer)..
2 Diagnostics
In diagnostics mode, the values can only be viewed, not modified.
2.1 Identification
Desig.: Designation of the instrument.
Version: Firmware of instrument (e.g. 6.22-08/18)
2.1.3 Factory Test: Test date of the Instrument and Motherboard.
2.1.4 Operating Time: Shows the operating time in Years, Days, Hours,
Minutes and Seconds.
2.2 Sensors
2.2.1 Sensor
Current value: Shows the actual measuring value in ppb.
Raw value tc: Shows the actual temperature compensated mea-
suring value in mA.
Raw value: Shows the actual uncompensated measuring value
in mA.
Saturation Shows the actual saturation in %
Page 58

56 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
2.2.1.5 Cal. History
Review the diagnostic values of the last calibration of the hydrogen
sensor. Max. 64 data records are memorized.
Number
Date, Time
Sat. Current
Air pressure
2.2.2 Miscellaneous:
2.2.2.1 Case Temp: Shows the actual temperature in °C inside the
transmitter.
Air pressure: Shows the actual air pressure in hPa
2.2.3 QA History
Review QA values (Number, Date, Time, Deviation Hydrogen, Deviation Temperature, Status of QA check) of the last quality assurance procedures.
2.3 Sample
2.3.301 Sample ID: Shows the assigned sample identification. This
identification is defined by the user to identify the location of the
sample.
Temperature: Shows temperature in °C.
(Nt5K): Shows raw value of the temperature in Ω.
Sample Flow: Shows the sample flow in l/ h
(Raw value) Shows the sample flow in Hz
2.4 I/O State
Shows actual status of all in- and outputs.
2.4.1
2.5 Interface
2.5.1 Only available if optional interface is installed.
Shows the programmed communication settings.
Alarm Relay: Active or inactive
Relay 1 and 2: Active or inactive
Input: Open or closed
Signal Output 1 and 2: Actual current in mA
Signal Output 3: Actual current in mA (if option is installed)
Page 59

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 57
3 Maintenance
3.1 Calibration
3.1.1 Start a calibration and follow the instructions on the screen. Displayed values are saturation in % and the saturation current in mA.
The indication bar shows the progress. Detailed explanation see
Calibration, p. 34.
3.2 Service
3.2.1 Electrolyte
Not applicable.
3.2.2 Faraday Verification
Start a manual faraday verification. Displayed values are current
value in ppb and the faraday concentration in %.
Current value: Measuring value in ppb
Faraday conc.: Hydrogen concentration in % after activating the
faraday verification.
Progress: The progress bar shows the progress of the faraday
verification.
3.3 Simulation
In this menu the following relays and signal outputs can be tested:
Alarm relay
Relay 1and 2
Signal output 1and 2
Signal output 3 (if option is installed)
Select a relay or signal output with the [ ] or [ ] keys,
press the [Enter]> key to confirm. Then change the value with the
[ ] or [ ] keys. After confirming the setting with the [Enter]
key, the value is simulated by the relay/signal output.
At the absence of any key activities, the instrument will switch back
to normal mode after 20 min. If you quit the menu, all simulated
values will be reset.
Alarm Relay: Active or inactive
Relay 1 and 2: Active or inactive
Input: Open or closed
Signal Output 1 and 2: Current in mA
Signal Output 3: Current in mA (if option is installed)
Page 60

58 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
3.4 Set Time
Adjust date and time.
3.5 Quality Assurance
Performs a Quality Assurance according to your settings. Follow
the commands on the screen. Detailed explanation see Quality
Assurance of the Instrument, p. 40.
4 Operation
4.1 Sensors
4.1.1 Filter Time Constant: Used to damp noisy signals. The higher the
filter time constant, the slower the system reacts to changes of the
measured value.
Range: 5– 300 s
4.1.2 Hold after Cal: Delay permitting the instrument to stabilize again
after calibration. During calibration plus hold-time, the signal
outputs are frozen (held on last valid value), alarm values, limits are
not active.
Range: 0– 6‘000 s
4.1.3 Faraday Parameter
4.1.3.1 Mode: Can be set to Interval, daily, weekly or off. If Mode is set to
“Off”, no further settings are available. The Faraday Verification has
to be started manually.
4.1.3.20 Interval: The interval can be set between 1 h and 12 h
4.1.3.21 Start Time: Start time appears if Mode is set to daily, how to set the
start time see 5.3.2.341, p. 70.
4.1.3.22 Calendar: Calendar appears if Mode is set to weekly, how to set
the Calendar see 5.3.2.342, p. 70.
4.1.3.3 Delay: during Faraday Verification plus the delay time the signal
and control outputs are held in the operating mode programmed
below.
Range: 0– 6’000 s
Page 61

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 59
4.1.3.4 Signal Outputs: Select operating mode of the signal output:
4.1.3.5 Output/Control: Select operating mode of the controller output:
4.2 Relay Contacts
See Relay Contacts, p. 21
4.3 Logger
The instrument is equipped with an internal logger. The logger data
can be copied to a PC with an USB stick if option USB interface is
installed.
The logger can save approx. 1500 data records. The Records
consists of: Date, time, alarms, measuring values, raw values, case
temperature, flow.
4.3.1 Log Interval: Select a convenient log interval. Consult the table
below to estimate the max logging time. When the logging buffer is
full, the oldest data record is erased to make room for the newest
one (circular buffer).
Range: 1 Second to 1 hour
4.3.2 Clear Logger: If confirmed with yes, the complete logger data is
deleted. A new data series is started.
Cont.: Signal outputs continue to issue the measured value.
Hold: Signal outputs hold the last valid measured value.
Measurement is interrupted. Errors, except fatal errors,
are not issued.
Off: Signal outputs are switched off (set to 0 or 4 mA).
Errors, except fatal errors, are not issued.
Cont.: Controller continues normally.
Hold: Controller continues based on the last valid value.
Off: Controller is switched off.
Interval 1 s 5 s 1 min 5 min 10 min 30 min 1 h
Time 25 min 2 h 25 h 5 d 10 d 31 d 62 d
Page 62

60 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
5 Installation
5.1 Sensors
5.1.1 Miscellaneous
5.1.1.1 Flow: If a flow cell without flow measurement (e.g. B-Flow) is used,
choose none. With flow measurement select Q-Flow
5.1.1.2 Offset: Manual, small correction of the offset. Range 0– 3 ppb.
5.1.1.3 Maintenance Int.: Select the interval of the automatic sensor
regeneration:
Off
3 hours
6 hours
12 hours
5.1.2 Quality Assurance
5.1.2.1 Level: Choose the quality level according to your requirements:
Level 0: Off
Quality assurance procedure switched off. Any additional QA
menus are hidden.
Level 1: Trend
Level 2: Standard
Level 3: Crucial
Level 4: User
Edit user-specific limits in menu 5.1.2.2
5.1.3 Sensor parameters
5.1.3.1 Saturation current: Enter the saturation current printed on the
sensor label.
Range: 2.000 –4.500 µA
5.1.3.2 Air pressure: Enter the air pressure printed on the sensor label.
Range: 900– 1100 hPa
Page 63

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 61
5.2 Signal Outputs
NOTICE: The navigation in the menu <Signal Output 1> and
<Signal Output 2> is equal. For reason of simplicity only the
menu numbers of Signal Output 1 are used in the following.
5.2.1 and 5.2.2 Signal Output 1 and 2: Assign process value, the current loop
range and a function to each signal output.
5.2.1.1 Parameter: Assign one of the process values to the signal output.
Available values:
Hydrogen
Temperature
Sample Flow (if a flow sensor is selected)
Saturation
5.2.1.2 Current Loop: Select the current range of the signal output.
Make sure the connected device works with the same current
range.
Available ranges: 0–20 mA or 4–20 mA
5.2.1.3 Function: Define if the signal output is used to transmit a process
value or to drive a control unit. Available functions are:
Linear, bilinear or logarithmic for process values.
See As process values, p. 61
Control upwards or control downwards for controllers.
See As control output, p. 63
As process
values
The process value can be represented in 3 ways: linear, bilinear or
logarithmic. See graphs below.
ABlinear
bilinear
X Measured value
20
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
10 12
(0 - 20 [mA])
0 / 4
(4 - 20 [mA])
[mA]
X
AB
Page 64

62 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
5.2.1.40 Scaling: Enter beginning and end point (Range low & high) of the
linear or logarithmic scale. In addition, the midpoint for the bilinear
scale.
Parameter: Hydrogen.
Range low: 0.00 ppb – 20.00 ppm
Range high: 0.00 ppb –20.00 ppm
Parameter: Temperature
Range low: -30 to +130 °C
Range high: -30 to +130 °C
Parameter: Sample flow
Range low: 0–50 l/h
Range high: 0– 50 l/h
Parameter: Saturation
Range low: 0–200%
Range high: 0– 200%
X Measured value (logarithmic)
20
1
01234
10 100 1’000 10’000
10 12
(0 - 20 [mA])
0 / 4
426
(4 - 20 [mA])
[mA]
X
Page 65

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 63
As control
output
Signal outputs can be used for driving control units. We distinguish
different kinds of controls:
P-controller: The controller action is proportional to the devia-
tion from the setpoint. The controller is characterized by the
P-Band. In the steady-state, the setpoint will never be
reached. The deviation is called steady-state error.
Parameters: setpoint, P-Band.
PI-controller: The combination of a P-controller with an
I-controller will minimize the steady-state error. If the reset
time is set to zero, the I-controller is switched off.
Parameters: setpoint, P-Band, reset time.
PD-controller: The combination of a P-controller with a
D-controller will minimize the response time to a fast change
of the process value. If the derivative time is set to zero, the
D-controller is switched off.
Parameters: setpoint, P-Band, derivative time.
PID-controller: The combination of a P-, an I - and a D-con-
troller allows a proper control of the process.
Parameters: setpoint, P-Band, reset time, derivative time.
Ziegler-Nichols method for the optimization of a PID controller:
Parameters: Setpoint, P-Band, Reset time, Derivative time
The point of intersection of the tangent with the respective axis will
result in the parameters a and L.
Consult the manual of the control unit for connecting and
programming details. Choose control upwards or downwards.
A
B
X
Response to maximum control output
Tangent on the inflection point
Time
Xp
Tn
Tv
= 1.2/a
= 2L
= L/2
X
Y
B
A
L
a
Page 66

64 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
Setpoint: User defined precess value for the selected parameter.
P-Band: Range below (upwards control) or above (downwards
control) the set-point, within which the dosing intensity is reduced
from 100% to 0% to reach the set-point without overshooting.
5.2.1.43 Control Parameters: if Parameter = Hydrogen
5.2.1.43.10 Setopint:
Range: 0.00 ppb –20.00 ppm
5.2.1.43.20 P-Band:
Range: 0.00 ppb –20.00 ppm
5.2.1.43 Control Parameters: if Parameter = Temperature
5.2.1.43.11 Setopint:
Range: -30 to +130 °C
5.2.1.43.21 P-Band:
Range: 0 to +100 °C
5.2.1.43 Control Parameters: if Parameter = Sample flow
5.2.1.43.12 Setopint:
Range: 0– 50 l/h
5.2.1.43.22 P-Band:
Range: 0– 50 l/h
5.2.1.43 Control Parameters: if Parameter = Saturation
5.2.1.43.13 Setopint:
Range: 0– 200%
5.2.1.43.23 P-Band:
Range: 0– 200%
5.2.1.43.3 Reset time: The reset time is the time till the step response of a
single I-controller will reach the same value as it will be suddenly
reached by a P-controller.
Range: 0– 9’000 s
5.2.1.43.4 Derivative time: The derivative time is the time till the ramp
response of a single P-controller will reach the same value as it will
be suddenly reached by a D-controller.
Range: 0– 9’000 s
5.2.1.43.5 Control timeout: If a controller action (dosing intensity) is constantly
over 90% during a defined period of time and the process value
does not come closer to the setpoint, the dosing process will be
stopped for safety reasons.
Range: 0– 720 min
Page 67

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 65
5.3 Relay Contacts
5.3.1 Alarm Relay: The alarm relay is used as cumulative error indicator.
Under normal operating conditions the contact is active.
The contact is inactive at:
Power loss
Detection of system faults like defective sensors or electronic
parts
High case temperature
Process values out of programmed ranges
Program alarm levels for the following parameters:
Meas. Value
Temperature
Sample Flow (if a flow sensor is selected)
Case Temperature high
Case Temperature low
5.3.1.1 Alarm Hydrogen
5.3.1.1.1 Alarm High: If the measured value rises above the alarm high
value, the alarm relay is activated and E001, is displayed in the
message list.
Range: 0.00 ppb – 20.00 ppm
5.3.1.1.25 Alarm Low: If the measured value falls below the alarm low value,
the alarm relay is activated and E002 is displayed in the message
list.
Range: 0.00 ppb – 20.00 ppm
5.3.1.1.35 Hysteresis: Within the hyst. range, the relay does not switch. This
prevents damage of relays contacts when the measured value
fluctuates around the alarm value.
Range. 0.00 ppb – 20.00 ppm
5.3.1.1.45 Delay: Duration, the activation of the alarm relay is retarded after
the measuring value has risen above/fallen below the programmed
alarm.
Range: 0– 28‘800 s
Page 68

66 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
5.3.1.2 Sample Flow: Define at which sample flow a flow alarm should be
issued.
5.3.1.2.1 Flow Alarm: Program if the alarm relay should be activated if there
is a flow alarm. Choose between yes or no. The flow alarm will
always be indicated in the display, pending error list, saved in the
message list and the logger.
Available values: Yes or no
NOTICE: Sufficient flow is essential for a correct measurement.
We recommend to program yes.
5.3.1.2.2 Alarm High: If the measuring values rises above the programmed
value E009 will be issued.
Range: 12– 20 l/h
5.3.1.2.35 Alarm Low: If the measuring values falls below the programmed
value E010 will be issued.
Range: 5– 20 l/h
5.3.1.3 Sample Temp.: Define at which sample temperature an alarm
should be issued.
5.3.1.3.1 Alarm High: If the measured value rises above the alarm high
value, the alarm relay is activated and E007 is issued.
Range: 30– 100 °C
5.3.1.3.25 Alarm Low: If the measured value rises above the alarm high value,
the alarm relay is activated and E008 is issued.
Range: -10 to +20 °C
5.3.1.4 Alarm Saturation
5.3.1.4.1 Alarm High: If the measured value rises above the alarm high
value, the alarm relay is activated and E001, is displayed in the
message list.
Range: 0.00 –200%
5.3.1.4.25 Alarm Low: If the measured value falls below the alarm low value,
the alarm relay is activated and E002 is displayed in the message
list.
Range: 0.00 –200%
5.3.1.4.35 Hysteresis: Within the hyst. range, the relay does not switch. This
prevents damage of relays contacts when the measured value
fluctuates around the alarm value.
Range. 0.00 –200%
5.3.1.4.45 Delay: Duration, the activation of the alarm relay is retarded after
the measuring value has risen above/fallen below the programmed
alarm.
Range: 0– 28‘800 s
Page 69

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 67
5.3.1.5 Case Temp.
5.3.1.5.1 Case Temp. high: Set the alarm high value for temperature of
electronics housing. If the value rises above the programmed value
E013 is issued.
Range: 30– 75 °C
5.3.1.5.2 Case Temp. low: Set the alarm low value for temperature of
electronics housing. If the value falls below the programmed value
E014 is issued.
Range: -10 to +20 °C
5.3.2 and 5.3.3 Relay 1 and 2: The function of relay contacts 1 or 2 are defined by
the user
NOTICE: The navigation in the menu <Relay 1> and <Relay 2>
is equal. For reason of simplicity only the menu numbers of
Relay 1 are used in the following.
1 First select the functions as:
- Limit upper/ lower
- Control upwards/ downwards
- Timer
- Fieldbus
2 Then enter the necessary data depending on the selected func-
tion. The same values may also be entered in menu 4.2 Relay
Contacts, p. 59
When the relays are used as upper or lower limit switches, program
the following:
5.3.2.20 Parameter: choose one of the following process values
Hydrogen
Temperature
Sample Flow
Saturation
5.3.2.300 Setpoint: If the measured value rises above respectively falls below
the set-point, the relay is activated.
Parameter Hydrogen: Range: 0.00 ppb –20.00 ppm
Parameter Temperature: Range: -30 to + 130 °C
Parameter Sample flow: Range: 0–50 l /h
Parameter Saturation: Range: 0 –200 %
5.3.2.1 Function = Limit upper/ lower:
Page 70

68 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
5.3.2.400 Hysteresis: within the hysteresis range, the relay does not switch.
This prevents damage of relay contacts when the measured value
fluctuates around the alarm value.
Parameter Hydrogen; Range: 0.00 ppb –20.00 ppm
Parameter Temperature; Range: 0–100 °C
Parameter Sample flow; Range: 0– 50 l/h
Parameter Saturation; Range: 0– 200 %
5.3.2.50 Delay: Duration, the activation of the alarm relay is retarded after
the measuring value has risen above/fallen below the programmed
alarm.
Range. 0– 600 s
The relays may be used to drive control units such as solenoid
valves, membrane dosing pumps or motor valves. When driving a
motor valve both relays are needed, relay 1 to open and relay 2 to
close the valve.
5.3.2.22 Parameter: choose one of the following process values
Hydrogen
Temperature
Sample Flow
Saturation
5.3.2.32 Settings
Choose the respective actuator:
Time proportional
Frequency
Motor valve
Examples of metering devices that are driven time proportional are
solenoid valves, peristaltic pumps.
Dosing is controlled by the operating time.
5.3.2.32.20 Cycle time: duration of one control cycle (on/off change).
Range: 0– 600 s
5.3.2.32.30 Response time: Minimal time the metering device needs to react.
Range: 0– 240 s
5.3.2.32.4 Control Parameters:
Range for each Parameter same as 5.2.1.43, p. 64.
5.3.2.1 Function = Control upwards/downwards::
Actuator = Time proportional
Page 71

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 69
Examples of metering devices that are pulse frequency driven are
the classic membrane pumps with a potential free triggering input.
Dosing is controlled by the repetition speed of dosing shots.
5.3.2.32.21 Pulse frequency: Max. pulses per minute the device is able to re-
spond to. Range: 20–300/min
5.3.2.32.31 Control Parameters:
Range for each Parameter same as 5.2.1.43, p. 64
Dosing is controlled by the position of a motor driven mixing valve.
5.3.2.32.22 Run time: Time needed to open a completely closed valve
Range: 5– 300 s.
5.3.2.32.32 Neutral zone: Minimal response time in % of the runtime. If the re-
quested dosing output is smaller than the response time, no
change will take place.
Range: 1– 20 %
5.3.2.32.4 Control Parameters:
Range for each Parameter same as 5.2.1.43, p. 64
The relay will be active repetitively depending on the programmed
time scheme.
5.3.2.24 Mode: Operating mode (interval, daily, weekly)
5.3.2.340 Interval: The interval can be programmed within a range
of 1–1440 min
5.3.2.44 Run Time: Enter the time the relay stays active.
Range: 5– 32400 s
5.3.2.54 Delay: during run time plus the delay time the signal and control
outputs are held in the operating mode programmed below.
Range: 0– 6’000 s
Actuator = Frequency
Actuator = Motor valve
5.3.2.1 Function = Timer
5.3.2.24
Interval
Page 72

70 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
The relay contact can be activated daily, at any time of a day.
5.3.2.341 Start time: to set the start time proceed as follows:
1 Press [Enter], to set the hours.
2 Set the hour with the [ ] or [ ] keys.
3 Press [Enter], to set the minutes.
4 Set the minutes with the [ ] or [ ] keys.
5 Press [Enter], to set the seconds.
6 Set the seconds with the [ ] or [ ] keys.
Range: 00:00:00– 23:59:59
5.3.2.44 Run Time: see Interval
5.3.2.54 Delay: see Interval
5.3.2.6 Signal Outputs: see Interval
5.3.2.7 Output/Control: see Interval
The relay contact can be activated at one or several days, of a
week. The daily starting time is valid for all days.
5.3.2.342 Calendar:
5.3.2.342.1 Start time: The programmed start time is valid for each of the pro-
grammed days. To set the start time see 5.3.2.341, p. 70.
Range: 00:00:00– 23:59:59
5.3.2.342.2 Monday: Possible settings, on or off
to
5.3.2.342.8 Sunday: Possible settings, on or off
5.3.2.44 Run Time: see Interval
5.3.2.54 Delay: see Interval
5.3.2.6 Signal Outputs: see Interval
5.3.2.7 Output/Control: see Interval
The relay will be switched via the Profibus input. No further parameters are needed.
5.3.2.24
daily
5.3.2.24
weekly
5.3.2.1 Function = Fieldbus
Page 73

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 71
5.3.2.6 Signal Outputs: Select operating mode of the signal output:
5.3.2.7 Output/Control: Select operating mode of the controller output:
5.3.4 Input: The functions of the relays and signal outputs can be
defined depending on the position of the input contact, i.e. no
function, closed or open.
5.3.4.1 Active: Define when the input should be active:
5.3.4.2 Signal Outputs: Select the operation mode of the signal outputs
when the relay is active:
5.3.4.3 Output/Control: (relay or signal output):
Cont.: Signal outputs continue to issue the measured value.
Hold: Signal outputs hold the last valid measured value.
Measurement is interrupted. Errors, except fatal errors,
are not issued.
Off: Signal outputs are switched off (set to 0 or 4 mA).
Errors, except fatal errors, are not issued.
Cont.: Controller continues normally.
Hold: Controller continues based on the last valid value.
Off: Controller is switched off.
No: Input is never active.
When closed Input is active if the input relay is closed
When open: Input is active if the input relay is open
Cont.: Signal outputs continue to issue the measured
value.
Hold: Signal outputs issue the last valid measured value.
Measurement is interrupted. Errors, except fatal
errors, are not issued.
Off: Set to 0 or 4 mA respectively. Errors, except fatal
errors, are not issued.
Cont.: Controller continues normally.
Hold: Controller continues on the last valid value.
Off: Controller is switched off.
Page 74

72 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
5.3.4.4 Fault:
5.3.4.5 Delay: Time which the instrument waits, after the input is
deactivated, before returning to normal operation.
Range: 0– 6‘000 Sec
5.4 Miscellaneous
5.4.1 Language: Set the desired language.
Available settings: German /English/ French/ Spanish
5.4.2 Set defaults: Reset the instrument to factory default values in three
different ways:
Calibration: Sets calibration values back to default. All other
values are kept in memory.
In parts: Communication parameters are kept in memory. All
other values are set back to default values.
Completely: Sets back all values including communication
parameters.
5.4.3 Load Firmware: Firmware updates should be done by instructed
service personnel only.
5.4.4 Password: Select a password different from 0000 to prevent
unauthorized access to the menus “Messages”, “Maintenance”,
“Operation” and “Installation”.
Each menu may be protected by a different password.
If you forgot the passwords, contact the closest SWAN
representative.
5.4.5 Sample ID: Identify the process value with any meaning full text,
such as KKS number.
5.4.6 Line Break Detection: Define if message E028 should be issued in
case of a line break on signal output 1 or 2.
Choose between <Yes> or <No>.
No: No message is issued in pending error list and the
alarm relay does not close when input is active.
Message E024 is stored in the message list.
Yes: Message E024 is issued and stored in the mes-
sage list. The Alarm relay closes when input is
active.
Page 75

AMI Hydrogen QED
Program List and Explanations
A-96.250.791 / 040219 73
5.5 Interface
Select one of the following communication protocols. Depending on
your selection, different parameters must be defined.
5.5.1
Protocol: Profibus
5.5.20
Device address:
Range: 0–126
5.5.30
ID-Nr.:
Range: Analyzer; Manufacturer; Multivariable
5.5.40
Local operation:
Range: Enabled, Disabled
5.5.1
Protocol: Modbus RTU
5.5.21
Device address:
Range: 0–126
5.5.31
Baud Rate:
Range: 1200–115
200 Baud
5.5.41
Parity:
Range: none, even, odd
5.5.1
Protocol: USB-Stick:
Only visible if an USB interface is installed. No further settings are
possible.
5.5.1
Protocol: HART
Device address:
Range: 0–63
Page 76

74 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Default Values
10. Default Values
Operation:
Sensors: Filter Time Const.:......................................................................10 s
Hold after Cal.:......................................................................... 300 s
Faraday Parameter:
Mode: ................................................................................Interval
Interval:.....................................................................................4 h
Delay ...................................................................................... 60 s
Signal Outputs........................................................................hold
Output/Control ....................................................................... hold
Alarm Relay ...................................................................... same as in Installation
Relay 1/ 2 ...................................................................... same as in Installation
Input ...................................................................... same as in Installation
Logger: Logger Interval:..................................................................... 30 min
Clear Logger: ................................................................................no
Installation:
Sensors Miscellaneous; Flow: ............................................................... None
Miscellaneous; Offset:...........................................................0.0 ppb
Maintenance Interval ...................................................................3 h
Quality Assurance; Level: ........................................................0: Off
Sensor parameters; Saturation current.............................. 3.500 µA
Sensor parameters; Air pressure ...................................... 1013 hPa
Signal Output 1 Parameter: ........................................................................ Hydrogen
Current loop: .....................................................................4 –20 mA
Function: ..................................................................................linear
Scaling: Range low: ............................................................0.00 ppb
Scaling: Range high:........................................................10.00 ppm
Signal Output 2 Parameter: ....................................................................Temperature
Current loop: .....................................................................4 –20 mA
Function: ..................................................................................linear
Scaling: Range low: ................................................................0.0 °C
Scaling: Range high:.............................................................50.0 °C
Alarm Relay: Alarm Hydrogen; Alarm high:...........................................10.00 ppm
Alarm Hydrogen; Alarm low: ...............................................0.00 ppb
Alarm Hydrogen; Hysteresis: ...............................................100 ppb
Alarm Hydrogen; Delay:...............................................................5 s
If Flow = Q-Flow
Sample Flow, Flow Alarm: .......................................................... yes
Sample Flow, Alarm high: .......................................
............. 14.0 l/ h
Page 77

AMI Hydrogen QED
Default Values
A-96.250.791 / 040219 75
Sample Flow, Alarm low: ........................................................6.0 l/h
Sample Temp., Alarm High:..................................................... 50 °C
Sample Temp., Alarm Low:........................................................ 0 °C
Alarm Saturation; Alarm high..................................................120 %
Alarm Saturation; Alarm low ....................................................0.0 %
Alarm Saturation; Hysteresis......................................................2 %
Alarm Saturation; Delay............................................................... 5 s
Case temp. high: .....................................................................65 °C
Case temp. low:......................................................................... 0 °C
Relay 1 Function: .......................................................................... limit upper
Parameter:........................................................................ Hydrogen
Setpoint: ..........................................................................10.00 ppm
Hysteresis:........................................................................... 100 ppb
Delay: ........................................................................................ 30 s
Relay 2 Function: .......................................................................... limit upper
Parameter:....................................................................Temperature
Setpoint: ..................................................................................50 °C
Hysteresis:.................................................................................1 °C
Delay: ........................................................................................ 30 s
If Function = Control upw. or dnw:
Parameter:.................................................................... Meas. Value
Settings: Actuator: ..........................................................Frequency
Settings: Pulse Frequency: ..............................................120/min
Settings: Control Parameters: Setpoint: ....................... 10.00 ppm
Settings: Control Parameters: P-band: ............................100 ppb
Settings: Control Parameters: Reset time: ............................... 0 s
Settings: Control Parameters: Derivative Time: ....................... 0 s
Settings: Control Parameters: Control Timeout:................... 0 min
Settings: Act. Time prop.: Cycle time: ................................... 60 s
Settings: Act. Time prop.: Response time: ............................ 10 s
Settings: Act. Motor valve: Run time: .................................... 60 s
Settings: Act. Motor valve: Neutral zone: ................................5%
If Function = Timer:
Mode:.................................................................................... Interval
Interval: ................................................................................ 1 min
Mode: ........................................................................................daily
Start time:........................................................................ 00.00.00
Mode:..................................................................................... weekly
Calendar; Start time: ....................................................... 00.00.00
Calendar; Monday to Sunday:.................................................. Off
Run time: ................................................................................... 10 s
Delay: .......................................................................................... 5 s
Page 78

76 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Default Values
Signal output:............................................................................. cont
Output/Control: ..........................................................................cont
Input: Active ............................................................................when closed
Signal Outputs ........................................................................... hold
Output/Control ..............................................................................off
Fault..............................................................................................no
Delay.......................................................................................... 10 s
Miscellaneous Language:.............................................................................English
Set default:....................................................................................no
Load firmware: ..............................................................................no
Password: ........................................................... for all modes 0000
Sample ID: ....................................................................... - - - - - - - -
Line break detection .....................................................................no
Interface Protocol:....................................................... depending on interface
Page 79

A-96.250.791 / 040219 77
AMI Hydrogen QED
Index
11. Index
A
Actuators . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Alarm Relay
. . . . . 7, 21, 65
Application
. . . . . . . . . . . 7
Application Range . . . . . . . 7
C
Cable thicknesses . . . . . . 17
Calendar
. . . . . . . . . . . 70
Changing values
. . . . . . . 32
D
Default Values . . . . . . . . 74
E
Electrical wiring . . . . . . . 14
Establish Sample Flow . . . 27
F
Fluidics . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
H
HART . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
I
Inductive load . . . . . . . . 23
Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7, 21
Instrument Setup . . . . 14, 44
Interface
HART
. . . . . . . . . . 26
Modbus . . . . . . . . . 25
Profibus
. . . . . . . . . 25
USB . . . . . . . . . . . 26
L
Longer Stop of Operation. . 45
M
Measuring Range . . . . . . 11
Modbus
. . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Mounting requirements
. . . 14
P
P-Band . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Power Supply . . . 11, 20–21
Profibus
. . . . . . . . . . . . 26
R
Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Relay Contacts 1 and 2. . . 22
Resistive load . . . . . . . . 23
S
Sample Flow . . . . . . . . . 66
Sample requirements
. . . . 11
Signal Outputs . . . . . . . 7, 24
Software . . . . . . . . . . . 31
T
Terminals . 19, 21–22, 24–25
U
USB Interface . . . . . . . . 26
W
Wire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Page 80

78 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
Notes
12. Notes
Page 81

AMI Hydrogen QED
Notes
A-96.250.791 / 040219 79
Page 82

80 A-96.250.791 / 040219
AMI Hydrogen QED
SWAN
is represented worldwide by subsidiary companies
and distributors.
cooperates with independent representatives
all over the world.
SWAN Products
Analytical Instruments for:
High Purity Water
Feedwater, Steam and Condensate
Potable Water
Pool and Sanitary Water
Cooling Water
Waste Water and Effluents
Made in Switzerland
 Loading...
Loading...