
SVP
Broadcast
Microwave
HDT-02_H.264
HIGH DEFINITION DIGITAL
MULTIBAND - MULTIFUNCTION
TRANSMITTER
USER MANUAL V4.11
Accessories included in this manual:
PA-5
PA-10
AV-X03F
Antenna
GPS-02
Antenna
RTC-01
Remote Control

I
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction
This first chapter provides a general description of the High Definition HDT02_H.264 camera transmitter.
Chapter 2: Technical features
This second part offers transmitter physical and environmental
characteristics.
Chapter 3: Transmitter operation and Menus
This third part provides the user with all necessary information to control
and operate the equipment properly. It is detailed the function of each
button on the keyboard. It is also explained how the information is shown
on the display, transmitter menus, alarms, etc.
Chapter 4: GPS Application
In this chapter, the use of the GPS incorporated system and some of its
applications are shown.
Chapter 5: Web Server and SNMP
This chapter provides a detailed description of the Web Server tool. This
feature allows the control of the HDT-02_H.264 transmitter through a web
page.
Chapter 6: Remote Control
The use of the RTC-01 device provides a remote connection to the HDT02_H.264 transmitter.
Chapter 7: Equipment Installation
This seventh chapter indicates the available connections of the transmitter,
their characteristics and the installation of the transmitter.
Index A: PA-5 and PA-10 Power Amplifiers User’s Guide
Index B: AVF 203 Flexible Antenna User’s Guide
Index C: GPS User’s Guide
Index D: Modulation Standards

II
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Dear customer,
We would like to thank you for selecting this equipment and welcome you to
the SVP’s products user’s growing family.
We are sure that the addition of this equipment to your existing installation
will cause you nothing but satisfaction.
Please read these instructions carefully, and keep them at hand in case you
have to refer to them.

III
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
About this manual
This user’s guide provides indications and explanations about how to easily
set up the HDT-02 transmitter for the most common use cases.
This document is intended to help first time users:
- Find their way around the GUI.
- To understand the different possibilities of the HDT-02 transmitter.
- To configure the HDT-02 for their specific configurations.
Symbols
The symbols that appear in this manual are:
An information message which indicates explanations for the
proper operation of the equipment.
Advises users that failure to take, avoid or make a specific
action could result in damages of the device.
In the places where this symbol appears it means that by
pressing the Down button of the equipment the user can
access to the next screen.
This symbol means that pressing the OK button in the options
where this symbol appear, the user can access to the submenu
related to that option or can change the value of the
parameter.
<> These symbols mean that the parameter can be modified in the
same screen with the right and left keys.

IV
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Important Notes
1. The HDT-02_H.264 High Definition camera transmitter is completely
compatible with the DVB-T/T2/S2 Standards, included in the European
Standard ETSI EN300744 (DVB-T), ETSI EN300755 (DVB-T2), ETSI
EN302307 (DVB-S2) and ETSI EN300421 (DVB-S).
2. It is important that when the transmitter is switched on, the selected RF
output connection must have the suitable antenna or must be loaded.
3. The HDT-02 digital camera transmitter applies a MPEG-4 compression to
either HDMI, composite video or SDI input signals. An MPEG-1 layer 2
compression is applied to the corresponding 4 analogue audio channels,
the 2 stereo SDI embedded, the HDMI embedded and the AES digital
audio signals. The resulting multiplexed signal is transmitted using
COFDM modulation system.
4. The HDT-02_H.264 transmitter is available from 1 GHz to 6.4 GHz in
three ranges (1-2.8 GHz, 2.8-4 GHz and 4-6.4 GHz) for the DVB-T2 and
DVB-T RF stage and the L band for the DVB-S2 and DVB-S IF stage.
5. In 1080p Video Format, it can only be performed the Standard Delay,
not the Low Delay, Super Low Delay or Ultra Low Delay.
6. If the RF output is set to DVB-T2 and the bandwidth selected is 1.7 MHz
then, the device automatically disables the Audio2 and it sets the bitrate
of the Audio1 to 128 Kbps.
7. In case it is selected SDI input with 1080p format, the delay will be
automatically Standard.
8. Equipment’s maximum output power for the DVB-T2/T is 100mWatt
(selectable from -5 to +20 dBm) and for the DVB-S2 and DVB-S is from
-20 to + 5 dBm.
9. Special care should be taken with SDI cables, quality and length, these
are very important, especially when HD-SDI or 3G SDI signals are
transmitted.
10.If any audio or data channel are not used in a transmission, they should
be disabled, in order to assign that bitrate to the video and achieve a
higher quality transmitted video signal.
11.Only authorized personnel should open the product and any repair or
warranty will be invalidated if the seals are broken.

V
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Safe Operating Procedures
In this section there are shown safety requirements so as to ensure
awareness of potential hazard to the personnel operating and maintaining
the equipment.
FCC
This chapter has been done taking into account the OET bulletin 65, from
August 1997, recommended by the FCC (Federal Communications
Commission).
The HDT-02_H.264 transmitter designed to provide services for
broadcasting, will not create RF energy exceeding 1.0 mW/cm2, the FCC
limit for exposure. This is known as the Maximum Permissible Exposure
(MPE) limit. This transmitter follows this law (with the AVF flexible antenna
3 dBi) as long as the distance between the antenna and the person is at
least 4 cm. In case it is used the PA-5 (5 W power amplifier), the minimum
distance is 28.2 cm and if it is used the PA-10 (10 W power amplifier) the
minimum distance is 39.9cm. SVP Broadcast Microwave, in accordance with
the requirements set forth by the FCC, provides this information as a guide
to the user. Next there are shown the calculations made so as to obtain
those values:
S = MPE in mW/cm2 (milliwats per square centimeters)
So as to follow the law, S maximum must be 1.0 mW/cm
2
EIRP = P · G
Where:
EIRP: Equivalent isotropically radiated power
G (dBi): Antenna gain in dBi
P: Output power of the transmitter (W)
R: Distance from the antenna to the transmitter (cm)

VI
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
1. HDT-02 transmitter with AVF antenna (3 dBi)
G = 2
P
max
= 100 mW
EIRP = 200 mW
R
min
= 4 cm = 1.57 in
2. HDT-02 transmitter + PA-5 (5 W) with AVF antenna
G = 2
P
max
= 5000 mW
EIRP = 10000 mW
R
min
= 28.2 cm = 11.1 in
3. HDT-02 transmitter + PA-10 (10 W) with AVF antenna
G = 2
P
max
= 10000 mW
EIRP = 20000 mW
R
min
= 39.9 cm = 15.7 in

VII
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Declaration of RF Exposure Compliance for Exemption
from Routine Evaluation Limits
SAR Evaluation – AVF-203L antenna
As shown in the point number 2.5.1 from the RSS-102 Radio Standard
Specification, SAR evaluation is not required if the separation
distance between the user and the radiating element of the device
is more than 20 cm.
The equipment, which consists on the HDT-02 transmitter with the AVF203L antenna fixed to it fulfills with this requirement. As shown in the figure
below, the distance between the device’s radiating element (situated at the
top of the antenna) and the nearest part of the user’s body is further than
20 cm length. If the length from the radiating element to the bottom of the
antenna is 20 cm, then the distance between the nearest part of the user’s
body and the radiating element will be higher than 20 cm. As the
cameraman always uses the camera in the same way and the antenna is
fixed to the camera, the distance is always maintained.
Conclusion: This equipment is exempted from SAR evaluation.
VIII
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
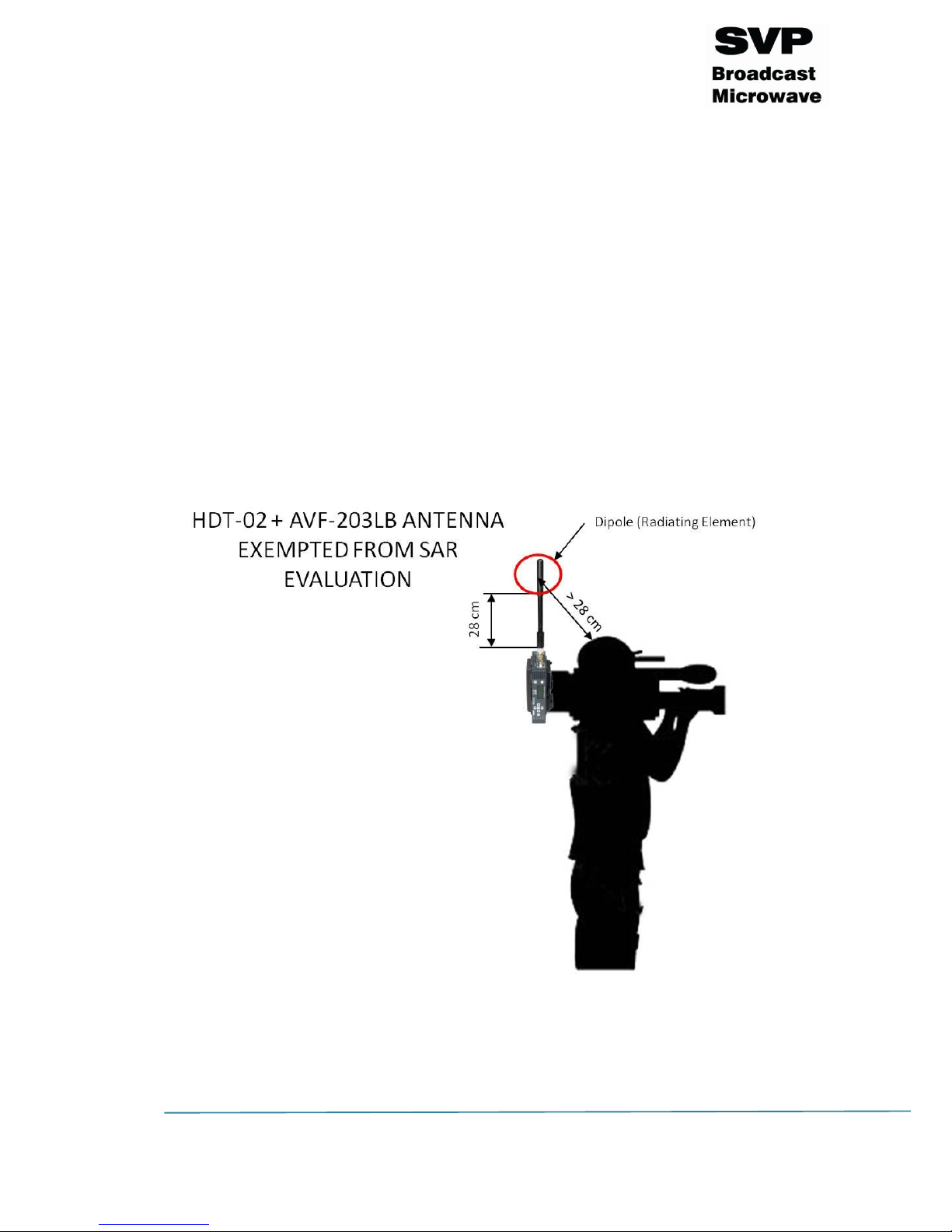
SAR Evaluation – AVF-203LB antenna
As shown in the point number 2.5.1 from the RSS-102 Radio Standard
Specification, SAR evaluation is not required if the separation
distance between the user and the radiating element of the device
is more than 20 cm.
The equipment, which consists on the HDT-02 transmitter with the AVF203LB antenna fixed to it fulfills with this requirement. As shown in the
figure below, the distance between the device’s radiating element (situated
at the top of the antenna) and the nearest part of the user’s body is further
than 20 cm length. If the length from the radiating element to the bottom
of the antenna is 28 cm, then the distance between the nearest part of the
user’s body and the radiating element will be higher than 28 cm and,
therefore, higher than 20 cm. As the cameraman always uses the camera in
the same way and the antenna is fixed to the camera, the distance is
always maintained.
Conclusion: This equipment is exempted from SAR evaluation.

IX
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
RF Exposure Evaluation
As shown in the point number 2.5.2 from the RSS-102 Radio Standard
Specification, RF exposure evaluation is required if the separation
distance between the user and the device’s radiating element is greater
than 20 cm, except when the device operates as follows:
- Below 1.5 GHz and the maximum e.i.r.p. of the device is equal
to or less than 2.5 W.
- At or above 1.5 GHz and the maximum e.i.r.p. is equal to or
less than 5 W.
Due to this equipment is going to operate above 1.5 GHz and the maximum
e.i.r.p. is 200 mW (with the AVF-203L or the AVF-203LB antenna), this
equipment is exempted from the RF exposure evaluation. When this
equipment is operating below 1.5 GHz, it is also exempted from the RF
exposure evaluation because the maximum e.i.r.p. (200mW) is lower than
2.5 W.
Conclusion: This equipment is exempted from the RF exposure
evaluation.

X
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
First Aid in Case of Electric Shock
DO NOT TOUCH THE VICTIM WITH YOUR BARE HANDS until the circuit is
broken. SWITCH OFF. If this is not possible, PROTECT YOURSELF with DRY
insulating material and pull the victim clear of the conductor.
If breathing has stopped, indicated by unconsciousness, lack of respiratory
movements and a ‘blue’ look to cheeks, lips, ears and nails, START
RESUSCITATION AT ONCE.
EMERGENCY RESUSCITATION – THE EXPIRED AIR METHOD
(Approved by the Royal Life Saving Society)
1. If possible, lie the victim on his back with his head slightly higher
than his feet. Clear the mouth and throat of any obvious obstruction.
2. Kneel on one side of the victim, level with his head. LIFT THE JAW
AND TILT THE HEAD BACK AS FAR AS POSSIBLE (Figs. 1a and 1b)
3. One of the following may happen:
a) Breathing may begin and consciousness return.
b) Breathing may begin but consciousness NOT
return. Turn the victim on his side and ensure
that the airway is kept clear.
c) Breathing may return but be NOISY which
means that the airway is not fully clear. Try to
clear the airway.
4. IF THERE NO SIGN OF BREATHING:
a) Check that the head is still tilted back.
b) Take a deep breath.
c) Pinch the victim’s nose and blow firmly into his
mouth (Fig. 2). As you do, the chest will RISE.
d) Turn your head away and take another breath,
watching for the chest to FALL (Fig. 3).
5. Start with four quick breaths and then continue with
one breath every five seconds (i.e. 12 times a
minute). This should be continued until the victim
revives or a doctor certifies death.
6. As consciousness returns the victim will start to
breathe on his own, and a ‘pink’ color replaces the
‘blue’ look: this is the time to stop resuscitation.
Continue to hold his chin up and so keep the airway
clear.
7. In the case of injuries to the mouth, it may be necessary to use
mouth-to-nose resuscitation. Seal the victim’s mouth with your cheek
and blow firmly into his nose, proceeding as above.

XI
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
8. In the case of severe facial injuries it may be necessary to do a
manual method of artificial respiration (Silvester-Brosch or Holger
Nielsen). Briefly, these methods apply compression to ribcage with
the victim lying on his back (S-B) or face down (H.N.) with associated
movement of his arms up and out. The cycle of movement should
take about five seconds, i.e. the normal breathing phase.
9. Whatever the method, it is ESSENTIAL to commence resuscitation
WITHOUT DELAY and to send for medical assistance immediately.
TREATMENT FOR BURNS
If the victim is also suffering from burns, then, without hindrance to
resuscitation, observe the following:
a) DO NOT ATTEMP TO REMOVE CLOTHING ADHERING TO THE BURN.
b) If possible alleviate the pain from the burnt part by immersing in
cold water.
c) If help as available or as soon as resuscitation is no longer required
the wound should be covered with a DRY clean dressing.
d) Oil or grease in any form should not be applied.
e) If severely burnt, get the victim to hospital immediately.

1
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Main Index
Chapter 1: Introduction ................................................................... 5
Chapter 2: Technical Features ....................................................... 10
Chapter 3: Transmitter Operation and Menus ................................ 14
3.1 Display .................................................................................. 14
3.1.1 Main Screen for the DVB-T2 ............................................... 17
3.1.2 Main Screen for the DVB-T ................................................. 19
3.1.3 Main Screen for the DVB-S2 ............................................... 21
3.1.4 Main Screen for the DVB-S ................................................. 23
3.2 Transmission Examples ........................................................... 25
3.3 LEDs ..................................................................................... 28
3.4 Front panel ............................................................................ 29
3.4.1 ON/OFF Button ................................................................. 29
3.4.2 OK Button ........................................................................ 30
3.4.3 Cross Button .................................................................... 30
3.4.4 Left and Right Button ........................................................ 31
3.4.5 Up and Down Button ......................................................... 31
3.4.6 RF Button ......................................................................... 32
3.5 Menus ................................................................................... 33
3.5.1 Menu Navigation ............................................................... 38
3.5.2 Menu Structure ................................................................. 39
3.5.2.1 Encoder Menu ............................................................. 40
3.5.2.1.1 SDI Input ............................................................... 41
3.5.2.1.2 HDMI Input ............................................................ 43
3.5.2.1.3 CVBS Input ............................................................ 45
3.5.2.1.4 ASI Input ............................................................... 47
3.5.2.1.5 Generator Input ...................................................... 48
3.5.2.1.6 Audio1 Embedded ................................................... 50
3.5.2.1.7 Audio1 Analogue ..................................................... 51
3.5.2.1.8 Audio1 AES-EBU ..................................................... 52
3.5.2.1.9 Audio1 Tone.Gen .................................................... 53
3.5.2.1.10 Audio2 Embedded ................................................. 54
3.5.2.1.11 Audio2 Analogue ................................................... 55
3.5.2.1.12 Audio2 AES-EBU ................................................... 56
3.5.2.1.13 Audio2 Tone.Gen ................................................... 57
3.5.2.1.14 Data .................................................................... 58
3.5.2.1.15 Encoder Output ..................................................... 60
3.5.2.1.16 TS Parameters ...................................................... 61
3.5.2.2 CA-BISS Menu ............................................................ 64
3.5.2.3 Mod&RF Menu ............................................................. 66
3.5.2.3.1 DVB-T2 .................................................................. 66
3.5.2.3.2 DVB-T2 Maximum Bitrates ....................................... 69
3.5.2.3.3 DVB-T ................................................................... 70

2
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.4 DVB-T Useful Bitrate ............................................... 72
3.5.2.3.5 DVB-S2 ................................................................. 74
3.5.2.3.6 Symbol Rate calculation ........................................... 78
3.5.2.3.7 DVB-S ................................................................... 79
3.5.2.4 Unit Menu ................................................................... 82
3.5.2.4.1 Profile .................................................................... 82
3.5.2.4.2 Alarms ................................................................... 83
3.5.2.4.3 Monitor .................................................................. 83
3.5.2.4.4 Ethernet ................................................................ 84
3.5.2.4.5 Firmware ............................................................... 85
3.5.2.4.6 Night Mode ............................................................ 89
3.5.2.4.7 Dist Units ............................................................... 89
3.5.2.4.8 Keyboard Beep ....................................................... 89
Chapter 4: GPS Application ............................................................ 90
4.1 Introduction ........................................................................... 90
4.2 Main Screen ........................................................................... 90
4.3 GPS Transmitter Screen .......................................................... 91
4.4 GPS HDR-106 Receiver Screen ................................................. 92
4.5 Application Example 1 – Constant Positioning ............................. 94
Chapter 5: Web Server ................................................................... 96
5.1 Introduction ........................................................................... 96
5.2 Web Page Overview ................................................................ 97
5.2.1 ENCODER ......................................................................... 98
5.2.1.1 Video ......................................................................... 98
5.2.1.2 Audio ......................................................................... 99
5.2.1.3 Data .......................................................................... 99
5.2.1.4 RS-232 .................................................................... 100
5.2.1.5 GPS ......................................................................... 100
5.2.1.6 TS Parameters .......................................................... 101
5.2.1.7 Output ..................................................................... 102
5.2.2 MOD_RF ........................................................................ 103
5.2.2.1 DVB-T ...................................................................... 104
5.2.2.2 DVB-T2 .................................................................... 105
5.2.2.3 DVB-S2 .................................................................... 107
5.2.2.4 DVB-S ...................................................................... 109
5.2.3 CA-BISS ........................................................................ 110
5.2.4 UNIT ............................................................................. 111
5.2.4.1 LEDs Status (reading parameters) ............................... 111
5.2.4.2 Alarms (reading parameter) ........................................ 112
5.2.4.3 Configuration ............................................................ 112
5.2.4.4 Monitor .................................................................... 112
5.3 Web Page Setup Notes .......................................................... 113
5.4 SNMP .................................................................................. 113
5.4.1 SNMP Commands ............................................................ 114
Chapter 6: Remote Control .......................................................... 115
6.1 Introduction ......................................................................... 115

3
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
6.2 Application Example .............................................................. 116
Chapter 7: Equipment Installation ............................................... 117
7.1 Introduction ......................................................................... 117
7.2 Connections ......................................................................... 117
7.2.1 Input connections ........................................................... 120
7.2.1.1 Power supply ............................................................ 120
7.2.1.2 CVBS/ SDI/ HDMI/ ASI Input ...................................... 121
7.2.1.3 Audio inputs ............................................................. 123
7.2.1.4 Data/GPS input ......................................................... 125
7.2.1.5 RTC connection ......................................................... 126
7.2.1.6 USB connection ......................................................... 127
7.2.1.7 Ethernet ................................................................... 127
7.2.2 Output Connections ......................................................... 128
7.2.2.1 RF output/Antenna .................................................... 128
7.2.2.2 ASI output ................................................................ 129
7.3 Mechanical Accessories .......................................................... 130
7.3.1 Transmitter Fastening ...................................................... 130
7.3.2 Battery Fastening ............................................................ 132
Index A - PA-5 and PA-10 Power Amplifiers ................................ 133
A.1 Introduction .............................................................................. 134
A.2 Technical Features ..................................................................... 135
A.2.1 Main Characteristics .............................................................. 135
A.2.2 Connections ......................................................................... 139
A.2.3 Thermal Protections .............................................................. 141
A.2.4 Before You Connect the Device ............................................... 142
A.2.5 Installation .......................................................................... 143
A.3 Power Amplifier Control ............................................................. 149
Index B – AVF X03 Flexible Antenna ............................................ 150
B.1 Description ................................................................................ 150
B.2 Technical Specifications .............................................................. 151
Index C – GPS Antenna ................................................................ 153
C.1 Description ................................................................................ 153
C.2 Technical Specifications .............................................................. 154
Index D – Modulation Standards .................................................. 156
D.1 DVB-T ...................................................................................... 156
D.1.1 How Does It Works ............................................................... 156
D.2 DVB-T2 .................................................................................... 157
D.2.1 How Does It Works ............................................................... 157
D.2.2 DVB-T2 New Features ........................................................... 157
D.2.3 DVB-T vs DVB-T2 ................................................................. 159

4
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
D.3 DVB-S ...................................................................................... 160
D.3.1 How Does It Works ............................................................... 160
D.4 DVB-S2 .................................................................................... 161
D.4.1 How Does It Works ............................................................... 161
D.4.2 Pilots in DVB-S2 ................................................................... 165
D.4.3 DVB-S vs DVB-S2 ................................................................. 166

5
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Chapter 1: Introduction
The HDT-02 is the new multifunction and multiband transmitter developed
by SVP Broadcast Microwave. The features of this equipment, achievable
only by SVP, make this transmitter the most advanced in the market up to
the date.
Its feature H.264 encodes for 3G, high definition (HD) and standard
definition (SD) signals with ultra-low latency. H.264 transmission is possible
using 40% lower bitrate than conventional MPEG-2 systems.
This new generation transmitter accepts analogue video, 3G/HD/SD-SDI
and HDMI video input signals. Analogue, SDI embedded, HDMI embedded
and AES audio inputs are available as standard. User data or GPS data can
be transmitted over the data channel.
The ASI output enables the user to use the transmitter as a standalone
encoder.
The HDT-02 transmitter performs DVB-T2 and DVB-T modulations with a
frequency band from 1 GHz to 6.4 GHz. DVB-T enables compatibility with
neatly all types of receivers. DVB-T2 modulation outperforms DVB-T
modulation and offers much higher data rate, which renders in a higher
signal quality or much more robust signal than DVB-T, achieving longer and
more difficult links.
This transmitter also performs DVB-S2 and DVB-S modulation. An L band IF
output is available, which enables the user to use the transmitter as a
satellite Encoder&Modulator unit.
This device has an exceptional RF performance with the highest bandwidth
available. In addition, it also includes up to three eligible frequency bands
for the DVB-T2/T (1 GHz to 2.8 GHz, 2.8 GHz to 4 GHz and 4 GHz to 6.4
GHz) and the L band for the DVB-S2 and DVB-S so as to transmit RF
signals.
Control, operation and monitoring of the HDT-02 transmitter are very
friendly. All the parameters of the transmitter can be configured in field.
Furthermore, 6 presets are configurable for quick equipment set up. A wide
range of accessories allow using this equipment in many different
applications.

6
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Features
Input video signals, composite video, 3G –SDI, HD-SDI, SD-SDI or HDMI
are MPEG-4 encoded, together with 4 analogue audios, 2 stereo AES/EBU
Channels, HDMI embedded or 4 digital audios embedded on the SDI signal.
The video formats can be 1080p (only in Standard Delay mode), 1080i,
720p, 576i or 480i. This transmitter also has a test pattern and test tone
generator available.
This device has a data channel available that allows transmitting user data
or GPS data as well as a Transport Stream ASI input so it can be used as a
repeater.
The encoder uses a H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 video compression that provides
output bitrates from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps and a MPEG-1 Layer II audio
compression which supplies different audio bit rates (128, 192, 256 or 384
Kbps).
Encoded signals can be encrypted using BISS-1 or BISS-E scrambling
system. Encrypted signal will only be received by the receivers that have a
valid descrambling key.
Transmitter system operation is very easy. It has a display and a keyboard
which make possible the configuration and monitorization of every
parameter of the equipment.
The equipment is fed with DC power supply from 7 to 36V. It can be
powered through DC power supply connector or through the battery mount.
Its excellent design, mechanical and electronic assembly make the HDT-02
a robust and reliable solution.
DVB-T2 features
It is available from 1 GHz to 6.4 GHz through three different output bands,
being maximum output power 100mWatt. High quality components have
been used to achieve the best output signal quality.
The HDT-02 digital camera transmitter uses COFDM (Coded Orthogonal
Frequency Division Multiplexing) modulation system (1K, 2K, 4K, 8K,
8K.ext) which provides a superior signal robustness and a higher link
performance. This technology provides operators with efficient means to
overcome the challenges of NLOS propagation and mobile channels
propagation.
OFDM spread spectrum modulation system distributes the data over a large
number of closely-spaced carriers, for example, 1705 carriers in 2K mode.
The data are divided into several parallel data streams, one for each carrier,
so, each carrier transports a lower data rate and the symbol duration is
longer. Each carrier is then modulated with a QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM or
256QAM scheme with a constellation rotation.

7
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
An OFDM modulated signal, since uses a low symbol rate modulation
scheme (i.e. where the symbols are relatively long compared to the channel
time characteristics) suffer less from intersymbol interference caused by
multipath propagation. As the duration of each symbol is long, it is feasible
to insert a guard interval between the OFDM symbols, thus eliminating the
intersymbol and co-channel interference. So, if one carrier’s information is
lost, it would only be lost a small part of the whole information.
Besides, in OFDM, the sub-carrier frequencies are chosen so that the subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, meaning that cross-talk, interference,
between the sub-channels is eliminated. The orthogonality allows high
spectral efficiency.
On the other hand, OFDM system is invariably used in conjunction with
channel coding (forward error correction). The error correction code used in
this equipment is Reed-Solomon coding, which is concatenated with LDPC,
and there is an additional interleaving between the two layers of coding.
Error correcting codes build redundancy into the transmitted data stream.
This redundancy allows bits that are in error or even missing to be corrected
in the receiver.
The European ETSI EN 300755 standard defines the following LDPC coding
rates: 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6. There is a compromise between the
coding rate (signal robustness) and the transmitted bit rate. If the coding
rate is higher the signal transmission is more robust (1/2 is the most
robust) but the bit rate that the system is capable to transmit is lower.
Used modulation scheme of each OFDM sub-carrier, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM
and 256 QAM is also connected with signal robustness and transmitted bit
rate. QPSK is the most robust and 256QAM is able to transport a higher bit
rate.
Besides the system can define 7 guard intervals: 1/4, 19/128, 1/8, 19/256,
1/16, 1/32 and 1/128. The guard interval is used to reduce intersymbol
interferences due to the multipath propagation.
In addition, it also provides several bandwidths: 1.7, 5, 6, 7 and 8 MHz in
case there are needed for different applications.
To summarize, with all of these characteristics, the maximum bit rate
achieved is 50.3 Mbps.

8
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
DVB-T features
The RF stage of the HDT-02 transmitter is the same as the DVB-T2 one. The
difference is found in the modulation part as is commented bellow.
The HDT-02 digital camera transmitter uses COFDM (Coded Orthogonal
Frequency Division Multiplexing) modulation system (2K mode).
The available modulations are QPSK, 16QAM or 64QAM where the most
robust is the QPSK one and the one with the bigger bit rate is the 64 QAM.
The European ETSI EN 300744 standard defines the following convolutional
coding rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8.
Used modulation scheme of each OFDM sub-carrier, QPSK, 16QAM and
64QAM, is also connected with signal robustness and transmitted bit rate.
QPSK is the most robust and 64QAM is able to transport a higher bit rate.
Besides the system can define 4 guard intervals: 1/4, 1/8, 1/16 and 1/32.
In conclusion, with all of these characteristics, the maximum bit rate
achieved is 31.67 Mbps.
DVB-S2 features
In case the HDT-02 transmitter is needed to be used as a satellite
transmitter, it features an IF stage in the L band with an output power level
from -20 to +5 dBm and a L band output that provides a 10 MHz reference
oscillator.
The HDT-02 digital camera transmitter uses single carrier or one modulation
from the next available: QPSK, 8PSK, 16APSK or 32 APSK where the most
robust is the QPSK one and the one with the bigger bit rate is the 32 APSK.
In addition, the European ETSI EN 302307 standard defines the following
LDPC coding rates: 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10.
In the modulation step it is also included a roll off factor (0.20, 0.25, 0.35)
which is used to reduce intersymbol interference where the value that most
reduces interference but with less bandwith is 0.20.
To sum up, with all of these characteristics, the maximum bit rate achieved
is 31 Msym/s.

9
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
DVB-S features
In case the HDT-02 transmitter is needed to be used as a satellite
transmitter, it features an IF stage in the L band with an output power level
from -20 to +5 dBm and a L band output that provides a 10 MHz reference
oscillator.
The HDT-02 digital camera transmitter uses QPSK modulation. In addition,
the European ETSI EN 300421 standard defines the following Reed Solomon
coding rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8.

10
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Chapter 2: Technical Features
RF Stage DVB-T2 and DVB-T
Frequency band: 1 to 6.4 GHz
Max. Output Power: 100 mW (selectable from -5 to +20 dBm)
IF Stage DVB-S2 and DVB-S
Frequency band: L band
Output Power Level: -20 to +5 dBm
10 MHz Ref. Oscillator: 0 dBm
Frequency Tolerance: ± 1.0 ppm
Frequency Stability: ± 0.30 ppm
Operating Temperature Range:-40 to +85ºC
Phase Noise: 10Hz_____-100 dBc/Hz
100Hz____-130 dBc/Hz
1KHz_____-147 dBc/Hz
10KHz____-156 dBc/Hz
100KHz___-160 dBc/Hz
1MHz_____-160 dBc/Hz
IF Stage (70 MHz) DVB-T2, DVB-T, DVB-S2 and DVB-S (Optional)
Output: 70 MHz
Video:
Inputs: 3G-SDI SMPTE-425M-A(299M)
HD-SDI SMPTE-292M(299M)
SD-SDI SMPTE-259M(272M)
HDMI (1.4a)
Composite video (PAL/NTSC)
Formats: 1080p (1920x1080) – 23.98/24/25/
29.97/30/50/59.94/60 Hz
1080i (1920x1080) – 50/59.94/60 Hz
720p (1280x720) – 23.98/24/25/29.97/
30/50/59.94/60 Hz
576i (720x576) – 50 Hz
480i (720x480) – 59.94 Hz
11
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Audio:
Input: SDI embedded / HDMI embedded
AES Digital / Analogue
Analogue: 2 Stereo / 4 Mono
Line,Micro Dynamic and Micro with Phantom
SDI embedded: 1 Group (4 audio channels)
AES/EBU: 2 Stereo channels
User Data
Data channel 1: User data or GPS
Data channel 2: Metadata in SDI (Optional)
Data rate: 1,200 to 57,600 bps
ASI
Input and Output: ASI Transport Stream (EN50083-9)
Remux: Built in ASI MUX (Optional)
Test Signals
Video: Bars with moving icon
Audio: 4 Audio tones
Encoder
Video compression: H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10
Profile: High 422, High, Main
Level: 3.0/3.1/3.2/4.0/4.1
Latency: Ultra Low delay: 33 ms
Audio compression: MPEG-1 Layer II
Audio bit rate: 128, 192, 256 or 384 Kbps
Output bit rate: 1 Mbps – 100 Mbps

12
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Encryption
BISS: BISS-1 and BISS-E
Modulation
DVB-T2: COFDM 1K,2K,4K, 8K,8K.ext
QPSK, 16 QAM, 64 QAM, 256 QAM
Constellation rotation
LDPC FEC: 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6
IG: 1/4, 19/128, 1/8, 19/256, 1/16, 1/32
1/128
Bandwidth: 1.7, 5, 6, 7, 8 MHz
Max. bit rate: 50.3 Mbps
DVB-T: COFDM 2K mode
QPSK, 16 QAM, 64 QAM
FEC: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
IG: 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32
Bandwidth: 5, 6, 7, 8 MHz
Max. bit rate: 31.67 Mbps
DVB-S2: QPSK, 8PSK, 16 APSK, 32 APSK
Constellation rotation
LDPC FEC: 1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4,
4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10
Max. Symbol Rate: 31 Msymb/s
Max. Bandwidth @ Rolloff: 0.35= 41.85 MHz
Max. Bitrate: 89.732 Mbps
DVB-S: QPSK
Constellation rotation
Reed Solomon FEC: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8
Baud Rate: 31 Msymb/s
Control & Monitorization
Control Interfaces: Front panel & display
Web browser interface
SNMP
RTC – 01 via cable
RTC – 01 via UHF (Optional)
Presets: 6 user defined presets
Monitoring: Encoding, modulation, frequency and
output power, alarms and warnings

13
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Power Supply
DC input: 8 to 36 V
And by batteries Anton-Bauer or V
Consumption: 16 Watt. (12V)
20 Watt. (28V)
Mechanical
Size: 124 x 45 x 193 mm
4.9x1.8x7.6 in
Weight: 1 Kg (without fastenings)
2.2 lb
Environmental
Aeronautical: RTCA / DO-160 compliant
Temperature range: -10 to 45 ºC
Height: 4500 m
Humidity: 95%
14
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Chapter 3: Transmitter Operation and Menus
This third chapter provides the user with all necessary information to
control, configure and operate the equipment properly.
3.1 Display
To turn the equipment on and off, press ON/OFF button. When the
equipment is turned on, the display will show the start-up message (model
and version of the equipment) for two seconds.
When a video, audio or data input has been selected, a character connected
to this input is displayed in the main screen.
Next, it is shown the main screen of the HDT-02_H.264 transmitter.
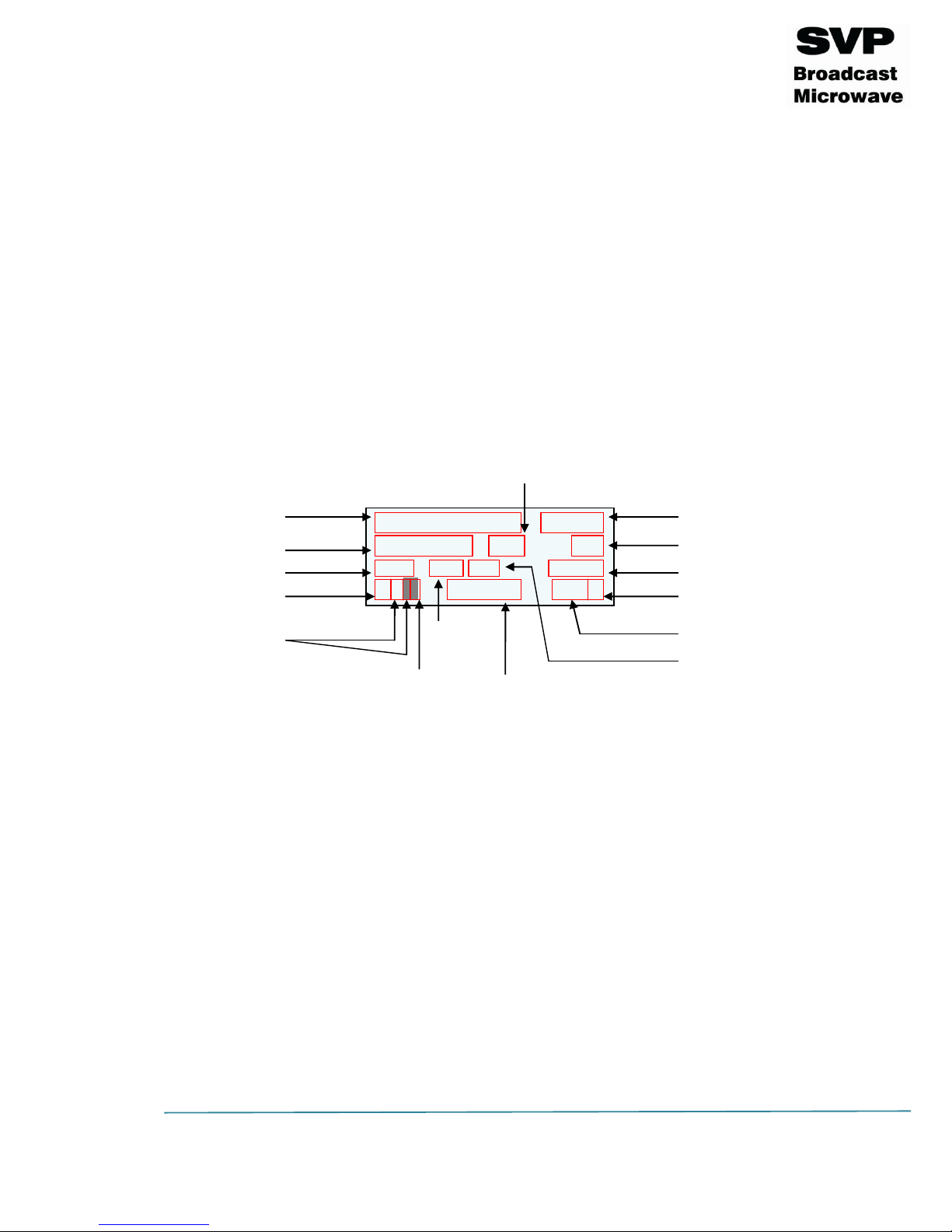
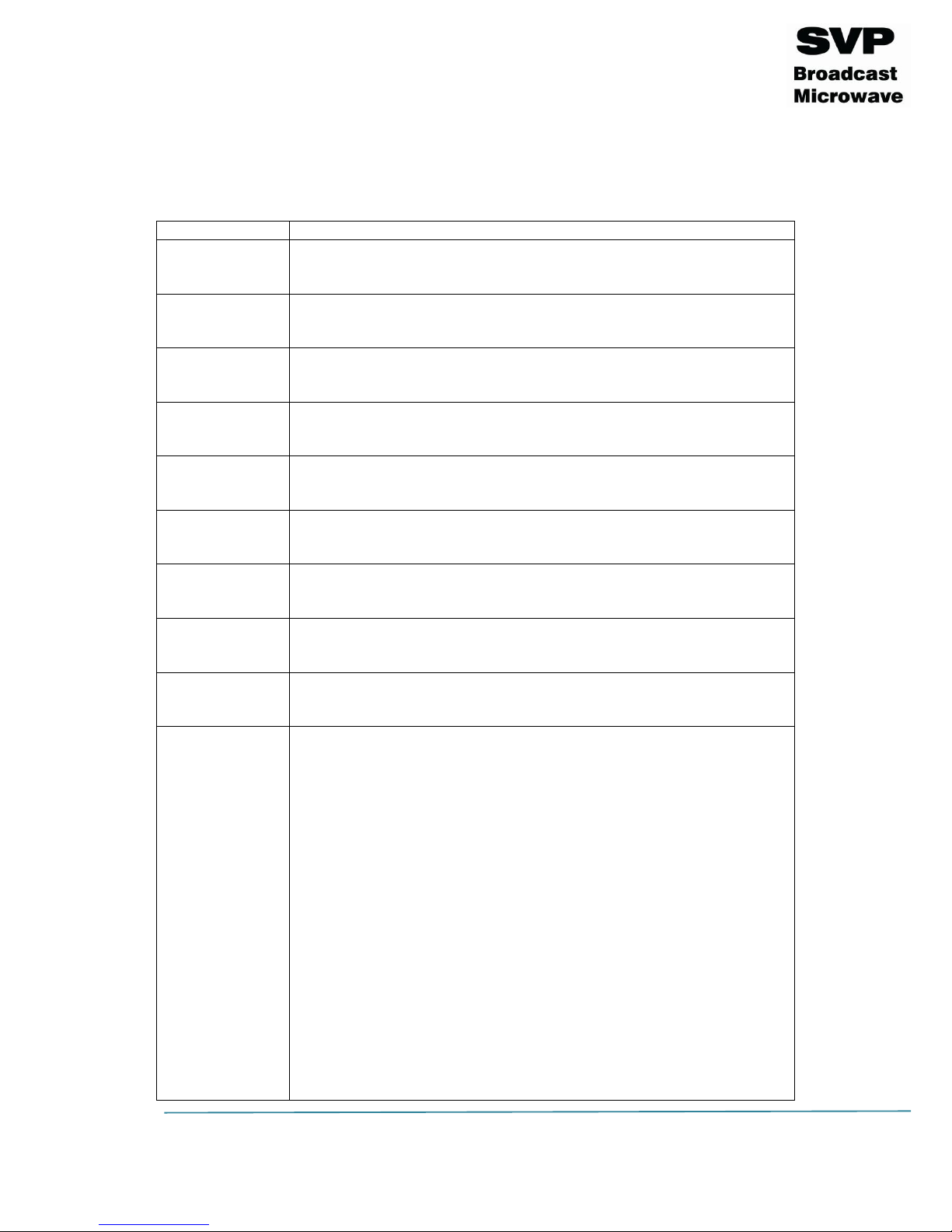
Figure 3.1 HDT-02 front panel/ Main screen explanation
F: 2350,00MHz DVBT2
P:+10dBm 8Ke B8
Q16 3/5 1/8 14.60
GAEX 576/50i 420S
Frequency
Output Power
Modulation Scheme
Video Input Selection
Audios Input Selection
FFT
Data Input Selection
FEC
Input Video Signal Format
Transmission Standard
Bandwidth
Bitrate
Latency
Guard Interval
Encoder Video Profile

15
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Once an option has been selected, the main screen appears where these
parameters are displayed:
Frequency (MHz).
Transmission Standard (DVB-T2, DVB-T, DVB-S2,DVB-S)
Output power (dBm): 3 options available:
- Variable power range from -5 to 20 dBm (DVB-T/T2) and from-20
to 5 dBm (DVB-S2/S).
- High power which means that the output power is 20 dBm.
- Low power which means that the output power is 14 dBm.
FFT number of points.
Bandwidth (MHz).
Modulation Scheme.
FEC.
Guard Interval.
Transmitted bitrate (Mbps).
Video Input selection:
- Possibilities: CVBS, HDMI, SDI, DVB-ASI Transport Stream or Generator.
- Behaviour of the corresponding character: If the character is static then
it means presence of that signal. If the character is blinking then it
means absence of that signal.
Audios status indication: If audio 1 or 2 is not darkened then it is
enabled. On the other hand, if audio 1 or 2 is darkened then it is
disabled.
Data status indication: If this field is not darkened then it means that
data is enabled. On the other hand, if this value is darkened it means
that data is disabled. Moreover, in case this field is static, its meaning is
presence of the data whereas if this field is blinking, it means absence of
the data.
Input video signal format.
Encoder Video Profile (4.2.0 or 4.2.2).
Latency (Standard delay, Low delay or Super Low Delay)
- Standard Delay (Lipsync < 10 ms)
- Low delay (Lipsync < 10 ms) 3 frame
- Super Low Delay (Lipsync < 10 ms) 2 frame
- Ultra Low Delay (Lipsync = 20ms) 1 frame
16
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Next there are shown the linkages between the input and the character
displayed in the principal screen:
Video
CVBS
C
HDMI
H
SDI S
ASI A
Test Pattern
G
Audio
Embedded
E
AES/EBU
U
Analogue
A
Test Tone
G
Data
RS232
D
GPS
G
Table 3.1 Linkages between the input and the character displayed
Next, it is shown the main screen for each output type (DVB-T2, DVB-T,
DVB-S2 and DVB-S):
17
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
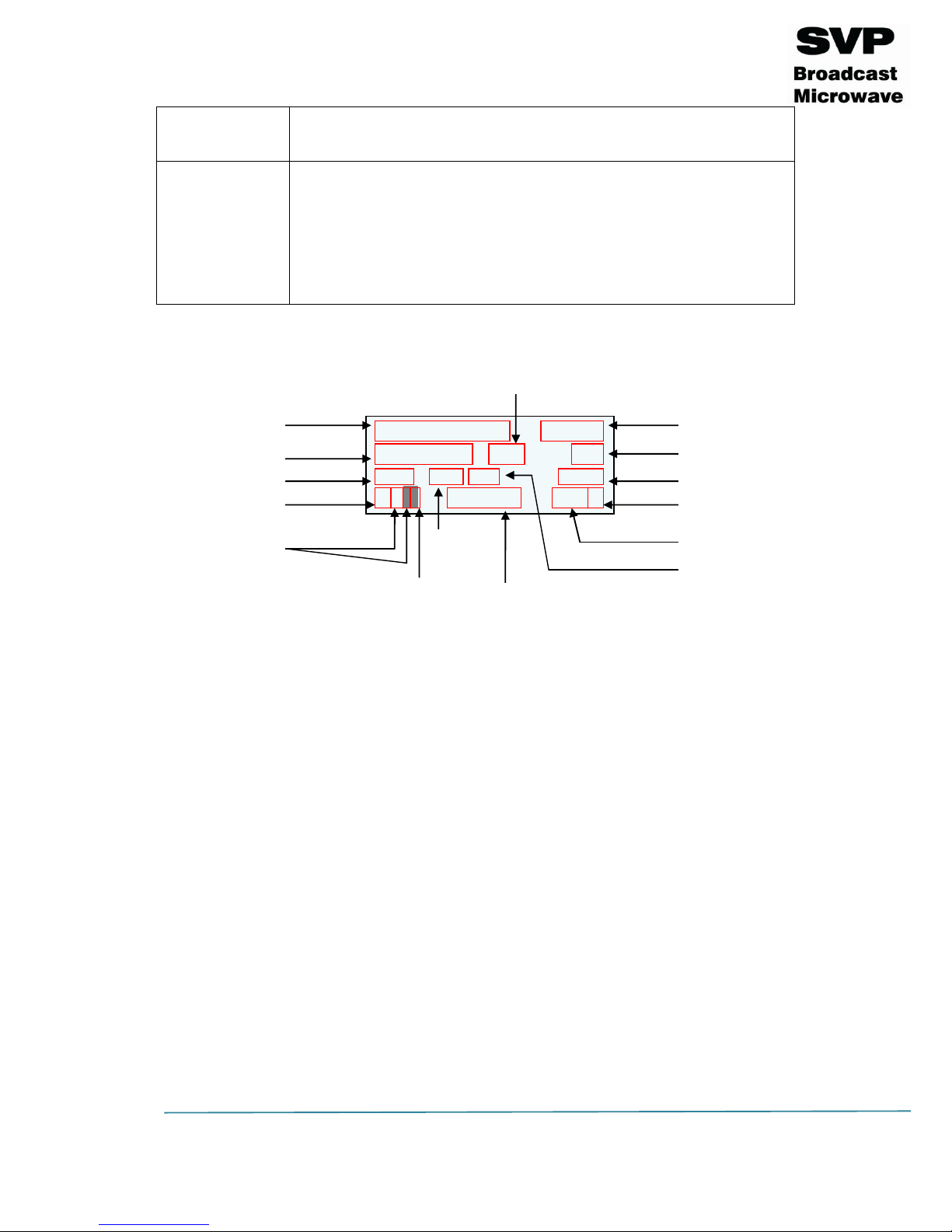
3.1.1 Main Screen for the DVB-T2
In the table below, it is explained the function of each parameter. These
values are numbered in the order they appear in the main screen.
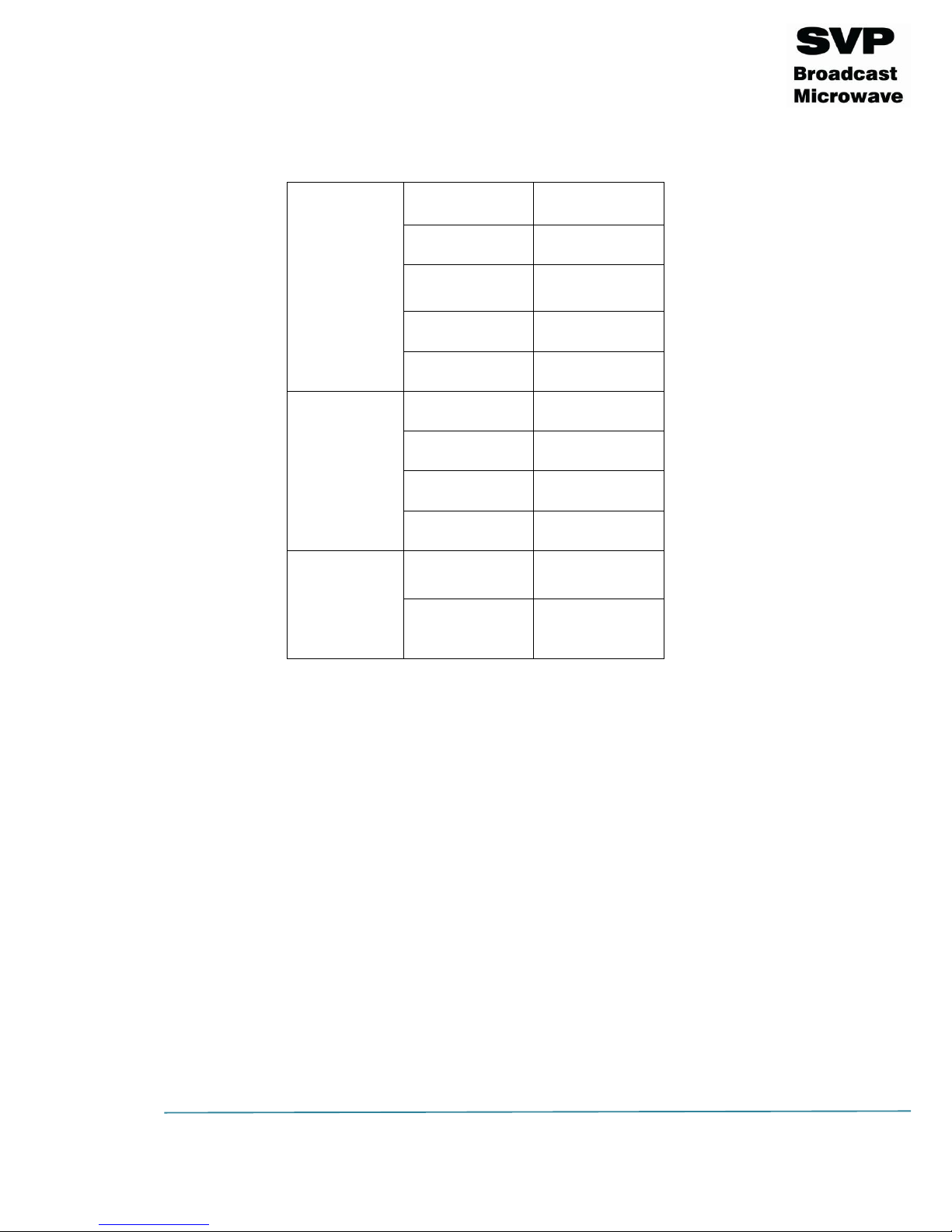
Parameter nº
Function
1
Transmission frequency (MHz)
2
Transmission standard (DVB-T2)
3
Output power (dBm)
4
FFT number of points (1K, 2K, 4K, 8K, 8k Ext)
5
Bandwidth (1.7, 5, 6, 7, 8 MHz)
6
Modulation (QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM)
7
LDPC FEC (1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10)
8
Interval Guard (1/4, 19/128, 1/8, 19/256, 1/16, 1/32, 1/128)
9
Transmitted bitrate (Mbps)
10
Character 1:
Video input selection (CVBS, HDMI, SDI, DVB-ASI Transport
Stream or Generator) and (static -> presence / blinking ->
absence)
Characters 2 (Audio 1) and 3 (Audio 2):
Audio inputs selection (Analog, Embedded or AES/EBU) and
(Audio 1 and 2 not darkened -> enabled / darkened ->
disabled)
Character 4:
Data input selection (None, GPS, RS232, RS485 or UDP) and
(not darkened -> enabled / darkened -> disabled) and (static
-> presence / blinking -> absence)
18
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
11
Video Format (1080p, 1080i, 720p, 576i, 480i)
12
Video options:
Profile (MPEG-4 4:2:0 or MPEG-4 4:2:2)
Delay (standard (S), low delay (L), super low delay (SL) or
ultra low delay (UL))
Table 3.2 Main screen for DVB-T2 standard
Figure 3.2 Main screen for DVB-T2 standard
F: 2350,00MHz DVBT2
P:+10dBm 8Ke B8
Q16 3/5 1/8 14.6
GAEX 576/50i 420S
Frequency
Output Power
Modulation Scheme
Video Input Selection
Audio Inputs Selection
Data Input Selection
FEC
Input Video Signal Format
Transmission Standard
Bandwidth
Bitrate
Latency
Guard Interval
Encoder Video Profile
FFT

19
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.1.2 Main Screen for the DVB-T
In the table below, it is explained the function of each parameter. These
values are numbered in the order they appear in the main screen.
Parameter nº
Function
1
Transmission frequency (MHz)
2
Transmission standard (DVB-T)
3
Output power (dBm)
4
FFT number of points (2K)
5
Bandwidth (5, 6, 7, 8 MHz)
6
Modulation (QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM)
7
LDPC FEC (1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8)
8
Interval Guard (1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32)
9
Transmitted bitrate (Mbps)
10
Character 1:
Video input selection (CVBS, HDMI, SDI, DVB-ASI Transport
Stream or Generator) and (static -> presence / blinking ->
absence)
Characters 2 (Audio 1) and 3 (Audio 2):
Audio inputs selection (Analog, Embedded or AES/EBU) and
(Audio 1 and 2 not darkened -> enabled / darkened ->
disabled)
Character 4:
Data input selection (None, GPS, RS232, RS485 or UDP) and
(not darkened -> enabled / darkened -> disabled) and (static
-> presence / blinking -> absence)

20
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
11
Video Format (1080p, 1080i, 720p, 576i, 480i)
12
Video options:
Profile (MPEG-4 4:2:0 or MPEG-4 4:2:2)
Delay (standard (S), low delay (L), super low delay (SL) or
ultra low delay (UL))
Table 3.3 Main screen for DVB-T standard
Figure 3.3 Main screen for DVB-T standard
F: 1250,00MHz DVBT
P: +5dBm 2K B8
QPSK 3/4 1/16 8.7
HAuG 1080/50p 422L
Frequency
Output Power
Modulation Scheme
Video Input Selection
Audio Input Selection
Data Input Selection
FEC
Input Video Signal Format
Transmission Standard
Bandwidth
Bitrate
Latency
Guard Interval
Encoder Video Profile
FFT

21
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.1.3 Main Screen for the DVB-S2
In the table below, it is explained the function of each parameter. These
values are numbered in the order they appear in the main screen.
Parameter nº
Function
1
Transmission frequency (MHz)
2
Transmission standard (DVB-S2)
3
Output power (dBm)
4
SR (Msymb)
5
Bandwidth
6
Modulation (QPSK, 8PSK, 16APSK, 32APSK)
7
LDPC FEC (1/4, 1/3, 2/5, 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6, 8/9, 9/10)
8
Transmitted bitrate (Mbps)
9
Character 1:
Video input selection (CVBS, HDMI, SDI, DVB-ASI Transport
Stream or Generator) and (static -> presence / blinking ->
absence)
Characters 2 (Audio 1) and 3 (Audio 2):
Audio inputs selection (Analog, Embedded or AES/EBU) and
(Audio 1 and 2 not darkened -> enabled / darkened ->
disabled)
Character 4:
Data input selection (None, GPS, RS232, RS485 or UDP) and
(not darkened -> enabled / darkened -> disabled) and (static
-> presence / blinking -> absence)
10
Video Format (1080p, 1080i, 720p, 576i, 480i)

22
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
11
Video options:
Profile (MPEG-4 4:2:0 or MPEG-4 4:2:2)
Delay (standard (S), low delay (L), super low delay (SL) or
ultra low delay (UL))
Table 3.4 Main screen for DVB-S2 standard
Figure 3.4 Main screen for DVB-S2 standard
F: 14000,000MHz DVBS2
P: +0.0 SR12.4000 B16
32APSK 8/9 53.300Mb
GEAD 576/50i 420S
Frequency
Output Power
Modulation Scheme
Video Input Selection
Audio Inputs Selection
Data Input Selection
Input Video Signal Format
Transmission Standard
Bandwidth
Bitrate
Latency
Encoder Video Profile
FEC
Symbol Rate

23
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.1.4 Main Screen for the DVB-S
In the table below, it is explained the function of each parameter. These
values are numbered in the order they appear in the main screen.
Parameter nº
Function
1
Transmission frequency (MHz)
2
Transmission standard (DVB-S)
3
Output power (dBm)
4
SR (Msymb)
5
Bandwidth
6
Modulation (QPSK)
7
LDPC FEC (1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8)
8
Transmitted bitrate (Mbps)
9
Character 1:
Video input selection (CVBS, HDMI, SDI, DVB-ASI Transport
Stream or Generator) and (static -> presence / blinking ->
absence)
Characters 2 (Audio 1) and 3 (Audio 2):
Audio inputs selection (Analog, Embedded or AES/EBU) and
(Audio 1 and 2 not darkened -> enabled / darkened ->
disabled)
Character 4:
Data input selection (None, GPS, RS232, RS485 or UDP) and
(not darkened -> enabled / darkened -> disabled) and (static
-> presence / blinking -> absence)
10
Video Format (1080p, 1080i, 720p, 576i, 480i)

24
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
11
Video options:
Profile (MPEG-4 4:2:0 or MPEG-4 4:2:2)
Delay (standard (S), low delay (L), super low delay (SL) or
ultra low delay (UL))
Table 3.5 Main screen for DVB-S2 standard
Figure 3.5 Main screen for DVB-S2 standard
F: 1360,500MHz DVBS
P: +3.0 SR08.000 B10
QPSK 7/8 12.901Mb
SEx 1080/50i 420UL
Frequency
Output Power
Modulation Scheme
Video Input Selection
Audio Inputs Selection
Data Input Selection
Input Video Signal Format
Transmission Standard
Bandwidth
Bitrate
Latency
Encoder Video Profile
FEC
Symbol Rate

25
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.2 Transmission Examples
Next, they are shown some setup examples and the image that appears in
the monitor screen.
Example 1 (DVB-T)
Setup:
Frequency: 1250 MHz
Transmission Standard: DVB-T
Output power: +5 dBm
FFT number of points: 2K
Bandwidth: 8 MHz
Modulation Scheme: QPSK
FEC: 3/4
Guard Interval: 1/16
Transmitted bitrate: 8.7 Mbps
Video input selection: HDMI
Audio inputs selection: Audio1 analogue (enabled), Audio2 AES/EBU
(disabled)
Data input selection: GPS
Input video signal format: no signal format
Encoder Video Profile: 4.2.2
Latency: Low Delay
Figure 3.6 HDT-02 Main screen. Example 1
The Audio2 status indication is darkened because it is not enabled. If it was
enabled, then this field would not be darkened.
When the data status field is enabled and blinkers, this means that there is
nothing connected to the data input. If it varies between a ‘G’ and a ‘g’ it
means that the GPS antenna is connected and it is trying to find three
localization satellites. If the ‘G’ does not vary, then it is connected to the
satellites.
F: 1250,00MHz DVBT
P: +5dBm 2K B8
QPSK 3/4 1/16 8.7
HAUG 1080/50p 422L
darkened
blinking

26
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Example 2 (DVB-S2)
Setup:
Frequency: 1500.00 MHz (L band)
Transmission Standard: DVB-S2
Output power: +0 dBm
Symbol rate: 12.4 Msymb/s
Bandwidth: 16 MHz
Modulation Scheme: 32APSK
FEC: 8/9
Transmitted BitRate: 53.3Mbps
Video input selection: SDI
Audio inputs selection: Audio1 embedded, Audio2 Analogue (both
enabled)
Data input selection: RS232
Input video signal format: 1080/50i
Padlock: BISS activated
Encoder Video Profile: 4.2.2
Latency: Standard
Figure 3.7 HDT-02 Main screen. Example 2
The input selection is not blinking because transmitter is receiving SDI (S)
video signal.
The Audio1 and 2 status indication is not darkened because both of them
are enabled. Letter ‘E’ corresponds to embedded and letter ‘A’ to analogue.
The data input has been selected to RS232 so letter ‘D’ appears in the data
gap.
Before the encoder profile a padlock appears when BISS encryption is
activated.
F: 1500,000MHz DVBS2
P: +0.0 SR12.400 B16
32APSK 8/9 53.300Mb
SEAD 1080/50i 422S
padlock

27
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Example 3 (DVB-S)
Setup:
Frequency: 1360.5 MHz (L band)
Transmission Standard: DVB-S
Output power: +3.0 dBm
Symbol rate: 8 Msymb/s
Bandwidth: 10 MHz
Modulation Scheme: QPSK
FEC: 7/8
Transmitted BitRate: 12.901Mbps
Video input selection: SDI
Audio inputs selection: Audio1 embedded, Audio2 None
Data input selection: UDP
Input video signal format: 1080/50i
Padlock: BISS activated
Encoder Video Profile: 4.2.0
Latency: Ultra Low Delay
Figure 3.8 HDT-02 Main screen. Example 3
F: 1360,500MHz DVBS
P: +3.0 SR08.000 B10
QPSK 7/8 12.901Mb
SEx 1080/50i 420UL

28
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.3 LEDs
The HDT-02 transmitter has 4 Leds on its front panel that show the
information detailed below.
The ON/OFF provides the following information:
If the Led is off the equipment is not being fed.
The Led flickers in red when there is power into the equipment but it is
turned off.
The Led lights up in green when the equipment is turned on.
The RF LED provides the following information:
If the Led is off the equipment does not transmit RF signal.
The Led lights up in green when the equipment transmits RF signal, RF
stage is active.
The ALARM LED provides the following information:
The LED lights up in red when any alarm occurs.
The different alarms that can appear in the transmitter are:
- Voltage High.
- Voltage Low.
- Temperature High.
- ASI Overflow:
This alarm means that the input bitrate is higher than the one that can
be modulated due to the parameters configured (constellation, FEC,
GI...).
The different warnings that can appear in the transmitter are:
- No Video Input.
- No GPS.
The STATUS LED provides the following information:
The LED lights up when a change in the configuration of the device is
being processed.
Figure 3.9 HDT-02 front panel LED indication
ON/OFF LED
ALARM LED
STATUS LED

29
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.4 Front panel
The HDT-02 camera transmitter is configured following a menus structure
on the display. The front panel has 8 buttons to enter and exit the
equipment’s control menus and submenus and to navigate through them.
Functions of each button are detailed in the following sections.
Figure 3.10 HDT-02 front panel
3.4.1 ON/OFF Button
To switch the equipment on and off, press this button. When the equipment
is turned on, the display will show the start-up message (model and version
of the equipment), and then it will display the main screen.
If the power fails while the equipment is operating, it will restart
automatically when the power returns, not being necessary to press the
on/off button again.
Figure 3.11 ON/OFF button
Display
Left
Button
Down
Button
Cross
Button
Leds
Right
Button
Up
Button
OK
Button
RF
Button
ON/OFF
Button

30
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.4.2 OK Button
This button is used to:
Enter submenus and parameters to be changed. So as to access to a
submenu, OK button must be pressed. Moreover, in the fields where the
enter symbol appears, by pressing the OK button the user can
change the values of the parameter selected. Besides, so as to save the
value introduced, the OK button must be pressed.
In case of being in the main screen, pressing the OK button allows the
user to access to the alarms screen where there are the different alarms
that are occurring. So as to return to the main screen, cross button must
be pressed.
Figure 3.12 OK button
3.4.3 Cross Button
This button is used to:
Enter from the equipment main screen to the setup menu and vice
versa.
Exit equipment submenus.
This button allows the user to access to the main screen from the alarms
screen.
Figure 3.13 Cross button
OK
X

31
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.4.4 Left and Right Button
These buttons are used to:
Once the parameter to change has been selected, they are used to move
the cursor towards the digit immediately on the left or right and to select
a parameter from different options.
Figure 3.14 Left and Right buttons
3.4.5 Up and Down Button
The up and down arrow buttons allow navigation in the main menu and
the rest of submenus. Using this buttons the submenu to be entered or
the parameter to be changed is selected. Once selected, to enter it OK
has to be pressed.
This buttons are also used to change, for example, the frequency and
PID parameter’s values. Pressing up and down arrows the value of those
parameters can be changed, increased or decreased respectively.
Figure 3.15 Up and Down buttons

32
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.4.6 RF Button
By pressing the RF button, RF output is enabled or disabled. The RF LED
indicates the status of the RF output. To enable or disable the RF output
just press RF button. It is important that before pressing this button, the
selected RF output must be conveniently loaded and there is no reflected
signal.
In case the device is switched off with the RF output enabled then, when it
is switched on again it is necessary to push again this button so as to
enable this feature.
However, if power supply fails when RF output is enabled then, once power
supply returns it is not necessary to push this button because RF output will
continue being enabled.
Figure 3.16 RF On/Off button
RF ON

33
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5 Menus
There is one menu in this transmitter that allows the operator to change
transmitter parameters and to configure them.
To enter the menu of this equipment cross button should be pressed.
In case it is wanted again to return to the principal screen from the menu,
cross button must be pressed. Furthermore, in case of being in the
submenus area, returning to the mainly screens is achieved by pressing the
cross button as much times as it is needed.
In the next page it is shown a scheme that specifies the different menu
options available.

34
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
continued
HDT-02_H.264 MENU STRUCTURE
Format
Encoder
Video
MAIN SCREEN
Frequency, standard, power, FFT, bandwidth,
modulation, FEC,GI, latency, output bitrate,
audio and video status, profile
SDI
HDMI
CVBS
ASI
GEN
Type
Format
Status
Format
Delay
Profile
Delay
Profile
Profile
Delay
Format
Bitrate
Profile
Delay
Analogue
Embedded
AES-EBU
Tone.Gen
None
Audio 1
Bitrate
Bitrate
Bitrate
Bitrate
Frequency
Level
continued
Format
DID
GOP
GOP
GOP
GOP

35
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
continued
continued
continued
continued
Audio 2
Data
Analogue
Embedded
AES-EBU
Tone.Gen
None
None
GPS
RS232
RS485
UDP
Bitrate
Type
Bitrate
Bitrate
Bitrate
Frequency
Level
BaudRate
Parity
Stop Bits
Encoder
DID

36
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
continued
continued
TS
Parameters
Output
Video PID
Bitrate
Audio1 PID
PMT PID
PCR PID
Data PID
Program Nº
Network
Name
Audio2 PID
TS id
Network id
Service Name
CA-BISS
Mode SW User
None
BISS-1
BISS-E
continued
Encoder

37
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
continued
Freq
Power
Modul
Mode
LDPC FEC
GI
Bandwidth
Roll Off
Freq
Modulator
Power
Const
Bandwidth
LDPC FEC
SR
10 MHz
Freq
Power
Modul
FEC
GI
Bandwidth
MOD&RF
Unit
DVB-T2
DVB-T
DVB-S2
Alarms
Monitor
Ethernet
Firmware
Night
Mode
Self Check
Temp
Voltage
Local IP
Subnet
Gateway
Spectrum
Spectrum
Pilots
DVB-S
Freq
Modulator
Power
Bandwidth
FEC
SR
10 MHz
Spectrum
Dist Units
Keyboard
Beep
Profile
Load
Save

38
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.1 Menu Navigation
This section contains a detailed description of each of the parameters that
can be configured in the HDT-02_H.264 camera transmitter via the MENU.
To enter the MENU, press the cross button in case of being in the principal
screen or in any submenu.
To select a parameter or a submenu use Up, Down arrows. Once selected
press OK button to access to a submenu or to edit a parameter. To exit a
submenu or a parameter press cross button.
Figure means that to have access to the right image that button
must be pushed.
Symbols <> mean that the parameter can be modified in the same screen
with the right and left keys.
Symbol means that pushing the OK button allows entering to the options
of the submenu.
Different types of parameters are available:
- Eligible: When the user can choose between predetermined
states. (They usually have the symbol <> near to them)
- Editable: When the user must enter a value in that option. (They
usually have the symbol near them). So as to save the
introduced value, the OK button must be pressed.
- Reading: When the value of that parameter is a monitored
parameter that can’t be changed.
To change any parameter, for example, the transmitted frequency, press
OK button in the wanted option and then with the Up, Down buttons choose
the value. Once the parameter is set, press OK so as to changes are done.
Next, they are shown the different menus and submenus with the options
and the different parameters. Also, in each figure, example parameters are
shown.

39
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2 Menu Structure
The following menu screen can be accessed by pressing the cross key from
the monitoring menu.
Figure 3.17 Menu
Encoder – All parameters relating to the video, audio and data inputs are
configured here. Besides, all video, audio, multiplexing and data encoding
parameters are accessed here.
CA-BISS – Encryption of signals can be configured in this option.
Mod&RF – DVB-T2/T/S2/S transmission parameters are set in this section.
Unit – Characteristics owned to the HDT-02 transmitter are accessed here.
HDT-02
Encoder Mod&RF
CA-BISS Unit

40
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1 Encoder Menu
By using the Up, Down arrow keys, select the Encoder option and press OK
key.
Figure 3.18 Encoder Menu
In the first field, the video input must be chosen with the Right and Left
arrows buttons. Once the video input has been selected, press the OK
button so as to configure the parameters relating to the video input
selected. There are five possibilities (SDI, HDMI, CVBS, ASI and GEN).
In the second field it can be chosen the sort of audio input through the
channel number 1 with the Right and Left arrows buttons. Once the audio 1
input has been selected, press the OK button so as to configure the
parameters relating to the audio 1 input selected. There are five possibilities
(Embedded, Analogue, AES-EBU, Tone.Gen and None).
In the third field it can be chosen the sort of audio input through the
channel number 2 with the Right and Left arrows buttons. Once the audio 2
input has been selected, press the OK button so as to configure the
parameters relating to the audio 2 input selected. There are five possibilities
(Embedded, Analogue, AES-EBU, Tone.Gen and None).
In the field number four the sort of data input can be selected. There are
five possibilities (None, GPS, RS232, RS485 and UDP).
In the field number five it can be selected the encoder output where,
pushing the OK button, the output bitrate can be configured.
The field number six consists on the configuration of the parameters of the
Transport Stream. In this option, the different program identifiers are
configured.
ENCODER
Video: ASI <>
Audio1: Tone.Gen <>
Audio2: AES-EBU <>
ENCODER
Data: GPS <>
Encoder Output
TS Parameters

41
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.1 SDI Input
Figure 3.19 SDI Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Format (SDI):
In this field, the format of the SDI input signal is displayed. (reading
parameter)
The available options are:
1080p (1920x1080) – 23.98/24/25/29.97/30/50/59.94/60 Hz
1080i (1920x1080) – 50/59.94/60 Hz
720p (1280x720) – 23.98/24/25/29.97/30/50/59.94/60 Hz
576i (720x576) – 50 Hz
480i (720x480) – 59.94 Hz
2
Delay:
In this field, the delay of the coding process is configured. So as to
select the desired delay, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Standard
Low Delay (3 frames of delay)
SuperLD (2 frames of delay)
Ultra Low Delay (1 frame of delay)
3
Profile:
In this field, the codification profile can be configured. So as to
select the wanted profile, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
4.2.2
4.2.0
ENCODER VIDEO SDI
Format: 1080/50i
Delay: SuperLD 2F <>
Profile: 4.2.0 <>
ENCODER
GOP: Auto 12 <>

42
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
4
GOP:
In this field, the group of figures parameter is displayed. It specifies
the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Auto
Manual (editable parameter)
Table 3.6 SDI Input menu options
In case HDMI video input is selected, it is necessary to specify the format
(1080p, 1080i, 720p). If any other video input (SDI, CVBS or ASI) is
selected, then the transmitter automatically captures its format and the
frame rate. If the video format is changed, the time detection of this new
format is less than 15 seconds.

43
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.2 HDMI Input
Figure 3.20 HDMI Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Format:
In this field, the format of the HDMI input signal must be
selected. So as to select a format first, press the OK button so as to
enter to the submenus where different formats available appear.
Then, choose the desired one with the UP, Down keys. (editable
parameter)
The available options are:
1080p (Only Standard Delay)
1080i
720p
2
Delay:
In this field, the delay of the coding process is configured. So as to
select the desired delay, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The options available are:
Standard
Low Delay (3 frames of delay)
SuperLD (2 frames of delay)
Ultra Low Delay (1 frame of delay)
3
Profile:
In this field, the codification profile can be configured. So as to
select the wanted profile, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (editable
parameter)
The options available are:
4.2.2
4.2.0
ENCODER VIDEO HDMI
Format: 1080p
Delay: Standard <>
Profile: 4.2.2 <>
ENCODER
GOP: Auto 12 <>

44
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
4
GOP:
In this field, the group of figures parameter is displayed. It specifies
the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Auto
Manual (editable parameter)
Table 3.7 HDMI Input menu options

45
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.3 CVBS Input
Figure 3.21 CVBS Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Format (CVBS):
In this field, the format of the CVBS input signal is
Displayed. (reading parameter)
The options available are:
480i
576i
2
Delay:
In this field, the delay of the coding process is configured. So as to
select the desired delay, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Standard
Low Delay (3 frames of delay)
SuperLD (2 frames of delay)
Ultra Low Delay (1 frame of delay)
3
Profile:
In this field, the codification profile can be configured. So as to
select the wanted profile, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
4.2.2
4.2.0
ENCODER VIDEO CVBS
Format: 480i
Delay: SuperLD 2F <>
Profile: 4.2.0 <>
ENCODER
GOP: Auto 12 <>

46
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
4
GOP:
In this field, the group of figures parameter is displayed. It specifies
the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Auto
Manual (editable parameter)
Table 3.8 CVBS Input menu options

47
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.4 ASI Input
Figure 3.22 ASI Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Status:
In this field it is indicated if there is any ASI signal in the ASI input.
In case there is an ASI signal, this field will display the word
present. If there is no ASI signal then, no present will be displayed.
(reading parameter)
The available options are:
Present
No Present
2
Bitrate:
Here is shown the bitrate of the ASI input signal. (reading
parameter)
3
Format:
In this field it is shown the format of the ASI input signal. (reading
parameter)
The available options are:
188 bytes
204 bytes
Table 3.9 ASI Input menu options
ASI INPUT
Status: Present
Bitrate: 18.0Mb
Format: 188

48
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.5 Generator Input
Figure 3.23 Generator Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Format:
In this field the format of the video signal generated is displayed.
The only option available is 576/50i. (reading parameter)
The available option is:
576/50i
2
Delay:
In this field, the delay of the coding process is configured. So as to
select the desired delay, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Standard
Low Delay (3 frames of delay)
SuperLD (2 frames of delay)
Ultra Low Delay (1 frame of delay)
3
Profile:
In this field, the codification profile can be configured. So as to
select the wanted profile, press Right, Left arrows buttons. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
4.2.2
4.2.0
ENCODER VIDEO GEN
Format: 576/50i
Delay: SuperLD 2F <>
Profile: 4.2.0 <>
ENCODER
GOP: Auto 12 <>

49
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
4
GOP:
In this field, the group of figures parameter is displayed. It specifies
the order in which intra- and inter-frames are arranged. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
Auto
Manual (editable parameter)
Table 3.10 Generator Input menu options

50
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.6 Audio1 Embedded
Figure 3.24 Audio Embedded Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 1. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The options available are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Group:
In this field the different numbers of input groups are displayed. In
case one group is not present then, a line appears. (reading
parameter)
DID:
In this field it can be selected the desired group. So as to select the
group, press Right, Left buttons. (eligible parameter)
The options available are:
G0
G1
G2
G3
Table 3.11 Audio Embedded Input menu options
If the video option selected is CVBS, ASI or Test Pattern generator then, the
option of audio embedded will be blinking because that configuration is not
possible.
ENCODER AUDIO1
Bitrate:256K <>
Gp: (1234) DID:G0 <>

51
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.7 Audio1 Analogue
Figure 3.25 Audio Analogue Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 1. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Type:
In this field, the sort of audio 1 signal introduced in the transmitter
is selected. So as to choose the type of audio1, press Right, Left
buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Line
Mic Dynamic
Mic Phantom
Table 3.12 Audio Analogue Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO1
Bitrate:256K <>
Type: Line <>

52
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.8 Audio1 AES-EBU
Figure 3.26 Audio AES-EBU Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 1. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
Table 3.13 Audio AES-EBU Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO1
Bitrate:384K <>

53
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.9 Audio1 Tone.Gen
Figure 3.27 Audio Generator Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 1. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Frequency (Hz):
In this field, the frequency of the generated tone is displayed.
(reading parameter)
3
Level (dBFs):
In this field it is displayed the level in dBF of the generated tone.
(reading parameter)
Table 3.14 Audio Generator Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO1
Bitrate:384K <>
Frequency: 1000Hz
Level: 18dBFs

54
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.10 Audio2 Embedded
Figure 3.28 Audio Embedded Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 2. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Group:
In this field the different numbers of input groups are displayed. In
case one group is not present then, a line appears. (reading
parameter)
DID:
In this field it can be selected the desired group. So as to select the
group, press Right, Left buttons. (eligible parameter)
The options available are:
G0
G1
G2
G3
Table 3.15 Audio Embedded Input menu options
If the video option selected is CVBS, ASI or Test Pattern Generator then,
the option of audio embedded will be blinking because that configuration is
not possible.
ENCODER AUDIO2
Bitrate:256K <>
Gp: (1234) DID:G0 <>

55
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.11 Audio2 Analogue
Figure 3.29 Audio Analogue Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 2. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Type:
In this field, the sort of audio 2 signal introduced in the transmitter
is selected. So as to choose the type of audio2, press Right, Left
buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Line
Mic Dynamic
Mic Phantom
Table 3.16 Audio Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO2
Bitrate:256K <>
Type: Line <>

56
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.12 Audio2 AES-EBU
Figure 3.30 Audio AES-EBU Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 2. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
Table 3.17 Audio AES-EBU Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO2
Bitrate:384K <>

57
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.13 Audio2 Tone.Gen
Figure 3.31 Audio Generator Input Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Bitrate:
In this option it can be selected the bitrate for the codification of the
audio signal 2. So as to select the desired bitrate, press Right, Left
arrows buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
128K
192K
256K
384K
2
Frequency (Hz):
In this field, the frequency of the generated tone is displayed.
(reading parameter)
3
Level (dBFs):
In this field it is displayed the level in dBF of the generated tone.
(reading parameter)
Table 3.18 Audio Generator Input menu options
ENCODER AUDIO2
Bitrate:384K <>
Frequency: 1000Hz
Level: 18dBFs

58
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.14 Data
So as to select the desired sort of data, press Right, Left buttons. (eligible
parameter)
Data option
Parameters
1
None:
This option is selected in case no data is sent to the transmitter.
2
GPS:
IF this option is selected and the GPS antenna is connected to the
GPS input of the transmitter then, by pressing the OK button, the
user can access to the different parameters sent by the GPS. Below,
it is explained the GPS screen and the meanings of the parameters
related to the GPS.
3
RS232:
If it is wanted to send data to the transmitter through a RS232
connection, this option must be selected. It is also needed to
configure the next parameters so as to achieve a successful
communication.
BaudRate:
Select the baudrate at which data user is received. (Baudrate
options are: 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600) (eligible
parameters)
Parity:
Select the same parity as the parity of the received data user
signal. (Parity options are None, Even, Odd) (eligible
parameters)
Stop Bit:
Select the same number of stop bits as the received data user
signal has. (Stop bit options are 1 or 2) (eligible parameter)
4
RS485:
If it is wanted to send data to the transmitter through a RS485
connection, this option must be selected.
5
UDP:
If it is wanted to send data to the transmitter through UDP, this
option must be selected.
Table 3.19 Data Parameters

59
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
GPS Screen
So as to access to the GPS screen first, go to the encoder option in the
menu. Then, go to the Data option and select GPS with the Right, Left keys.
Next, press the OK button so as to access to the GPS screen. Below, there
are shown the different parameters which appear in the GPS screen.
The format of the GPS coordinates used is decimal minutes as shown in the
next example:
N43º02.032’
W023º03.023’
Next there are shown the different fields meanings.
Figure 3.32 GPS transmitter screen
Latitude of the transmitter: Specifies the latitude position of the
transmitter.
Speed of the transmitter: Shows the speed of the transmitter in knot .
Direction of the transmitter: The direction of the transmitter is shown in
this field.
Longitude of the transmitter: Specifies the longitude position of the
transmitter.
Height of the transmitter: The height of the transmitter from ground is
specified in this value.
Satellite Level: The level of each satellite signal received is shown in this
field.
Date: Updated date is shown.
#--º--.---´ ---k ---º
#---º--.---´ -----mt
Satellite Level --/--/--
--:--:--
Level of the satellite signals
Time
Date
Height (meters)
Speed(knot)/
Direction(degrees)
Longitude of the
transmitter
Latitude of the
transmitter

60
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.15 Encoder Output
Figure 3.33 Encoder Output Menu
Line nº
Function
1
BitRate:
In this field, the output bitrate is shown. It case it is wanted to
select between an automatic bitrate or configure manually the
bitrate, press Right, Left buttons. If manual configuration is selected
then, press OK button so as to select the desired bitrate with the UP,
Down keys. Press the OK button so as to save the value introduced.
(eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Auto
Manual (editable parameter)
Table 3.20 Encoder Output menu options
In case the user selects the manual option, if the output bitrate is higher
than the one that is achievable with the selected configuration (modulation
scheme, FEC) then, in the main screen the line (third line) in which these
parameters (modulation scheme, FEC, bitrate) appear blinks.
ENCODER OUTPUT
BitRate: 10.0Mb <>

61
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.1.16 TS Parameters
Figure 3.34 Encoder TS Menu
ENCODER TS
Video PID: 273
Audio1 PID: 512
Audio2 PID: 513
ENCODER TS
Data PID: 2100
PMT PID: 291
PCR PID: 256
ENCODER TS
Program Nº: 1
TS id: 7
Network id: 7
ENCODER TS
Network Name
Service Name

62
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Line nº
Function
1
Video PID:
Here the video packet identifier must be entered. So as to change its
value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows
select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save the
value introduced. (editable parameter)
2
Audio1 PID:
Here the audio1 packet identifier must be entered. So as to change
its value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down
arrows select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save
the value introduced. (editable parameter)
3
Audio2 PID:
Here the audio2 packet identifier must be entered. So as to change
its value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down
arrows select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save
the value introduced. (editable parameter)
4
Data PID:
Here the data packet identifier must be entered. So as to change its
value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows
select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save the
value introduced. (editable parameter)
5
PMT PID:
Here the program map tables packet identifier must be entered. So
as to change its value first, press the OK button and then, with the
UP, Down arrows select the number wanted. Press the OK button so
as to save the value introduced. (editable parameter)
6
PCR PID:
Here the program clock reference packet identifier must be entered.
So as to change its value first, press the OK button and then, with
the UP, Down arrows select the number wanted. Press the OK
button so as to save the value introduced. (editable parameter)
7
Program Nº:
Here the program number must be entered. So as to change its
value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows
select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save the
value introduced. (editable parameter)

63
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
8
TS id:
Here the Transport Stream identifier must be entered. So as to
change its value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP,
Down arrows select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as
to save the value introduced. (editable parameter)
9
Network id:
Here the Network identifier must be entered. So as to change its
value first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows
select the number wanted. Press the OK button so as to save the
value introduced. (editable parameter)
10
Network Name:
Here the Network name must be entered. So as to change its value
first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows select
the letter wanted. With the Right, Left keys, the user can select the
character of the word. Press the OK button so as to save the value
introduced) (editable parameter)
11
Service Name:
Here the Service name must be entered. So as to change its value
first, press the OK button and then, with the UP, Down arrows select
the letter wanted. With the Right, Left keys, the user can select the
character of the word. Press the OK button so as to save the value
introduced. (editable parameter)
Table 3.21 Encoder TS menu options
64
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.2 CA-BISS Menu
By using the Up, Down arrow keys, select the CA-BISS option and press OK
key.
Figure 3.35 CA-BISS Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Mode:
So as to choose the desired encryption, press the Right, Left keys.
(eligible parameter)
The available options are:
None
BISS-1 (Uses an unencrypted key for the BISS key)
BISS-E (Uses an encrypted key)
2
SW:
In this field, the SW password must be introduced, which is valid for
BISS-1 and BISS-E encryption. (editable parameter)
3
User:
In this field, the User password must be introduced, which is valid
only for BISS-E encryption. (editable parameter)
Table 3.22 CA-BISS menu options
CONDITIONAL ACCESS
Mode: BISS-E <>
SW: ************
User: **********

65
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
So as to introduce the key in the BISS-1 option, follow these steps:
1. Choose BISS-1 option in the Mode field.
2. Go one field down (SW) and press OK button so as to be allowed to
introduce the key.
3. With Left and Right buttons select one field and with UP, Down
buttons choose one value from 0 to 9 or A to F.
4. Press OK button to set the key.
So as to introduce the key in the BISS-E option, follow these steps:
1. Choose BISS-E option in the Mode field.
2. Go one field down (SW) and press OK button so as to be allowed to
introduce the key.
3. With Left and Right buttons select one field and with UP, Down
buttons choose one value from 0 to 9 or A to F.
4. Press OK button to set the key.
5. Go another field down (User) and press OK button so as to be allowed
to introduce the User.
6. With Left, Right buttons select one field and with UP and Down
buttons choose one value from 0 to 9 or A to F.
7. Press OK button to set the User.
BISS encryption is activated in the modulator and in the ASI output.

66
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3 Mod&RF Menu
By using the Up, Down arrow keys, select the Mod&RF option and press OK
key.
Figure 3.36 Mod&RF Menu
3.5.2.3.1 DVB-T2
Figure 3.37 DVB-T2 & RF Menu
MODULATOR & RF
DVB-T2 DVB-S2
DVB-T DVB-S*
DVB-T2 & RF
Freq: 1.250,00MHz
Pwr: High <>
Modul: 256QAM <>
DVB-T2 & RF
LDPC Fec: 2/3 <>
GI: 1/8 (PP2) <>
Mode: 8K Ext <>
DVB-T2 & RF
Bandwidth: 8MHz <>

67
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Line nº
Function
1
Freq:
Select the frequency at which the signal is going to be transmitted.
So as to establish the frequency value first, press the OK button and
then, with the Up, Down arrows buttons select the wanted value. So
as to save the value introduced, press the OK button. (editable
parameter)
2
Power:
First, select with the Right, Left buttons the power option. High
power means an output power of 20 dBm, Low power an output
power of 10 dBm and Vble is selected when the user wants to select
the output power. So as to establish the output power value first,
press the OK button and then, with the Up, Down buttons select the
wanted value. So as to save the value introduced, press the OK
button. (editable parameter)
The available options are:
High (20 dBm)
Low (10 dBm)
Vble (from -5 to 20 dBm)
3
Modul:
Here the constellation of the modulation can be chosen. Use Right,
Left buttons so as to select the desired constellation. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
QPSK
16QAM
64QAM
256QAM
4
LDPC Fec:
Here the value of the Forward Error Correction can be chosen. Use
Right, Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
1/2
3/5
2/3
3/4
4/5
5/6

68
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
5
GI:
Here the Guard Interval value can be chosen. Use Right, Left
buttons so as to select the desired value. The value between
brackets means the scattered pilot pattern and is a monitoring
parameter. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
1/4
19/128
1/8
19/256
1/16
1/32
1/128
6
Mode:
Here the number of FFT points can be chosen. Use Right, Left
buttons so as to select the desired buttons. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
1K
2K
4K
8K
8K.ext
7
Bandwidth:
Here the bandwidth of the transmitted signal can be chosen. Use
Right, Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
1.7 MHz
5 MHz
6 MHz
7 MHz
8 MHz
Table 3.23 DVB-T2 & RF menu options

69
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.2 DVB-T2 Maximum Bitrates
These maximum values are reached under the following conditions: 8-MHz
channel, 8K mode,G.I.=1/128.
Modulation Scheme
Code Rate
Bit Rate (Mbps)
QPSK
1/2
7.0
3/5
8.4
2/3
9.4
3/4
10.5
4/5
11.3
5/6
11.7
16 QAM
1/2
14.5
3/5
17.5
2/3
19.4
3/4
21.8
4/5
23.3
5/6
24.3
64 QAM
1/2
21.5
3/5
25.9
2/3
28.8
3/4
32.4
4/5
34.6
5/6
36.0
256 QAM
1/2
29.0
3/5
34.9
2/3
38.8
3/4
43.7
4/5
46.6
5/6
48.6
Table 3.24 DVB-T2 Maximum Bitrates

70
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.3 DVB-T
Figure 3.38 DVB-T & RF Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Freq:
Select the frequency at which the signal is going to be transmitted.
So as to establish the frequency value first, press the OK button and
then, with the Up, Down arrows buttons select the wanted value. So
as to save the value introduced, press the OK button. (editable
parameter)
2
Power:
First, select with the Right, Left buttons the power option. High
power means an output power of 20 dBm, Low power an output
power of 10 dBm and Vble is selected when the user wants to select
the output power. So as to establish the output power value first,
press the OK button and then, with the Up, Down buttons select the
wanted value. So as to save the value introduced, press the OK
button. (editable parameter)
The available options are:
High (20 dBm)
Low (10 dBm)
Vble (from -5 to 20 dBm)
3
Modul:
Here the constellation of the modulation can be chosen. Use Right,
Left buttons so as to select the desired constellation. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
QPSK
16QAM
64QAM
DVB-T & RF
Freq: 1.040,50MHz
Pwr: Low <>
Modul: 64QAM <>
DVB-T & RF
Fec: 1/2 <>
GI: 1/16 <>
Bandwidth: 5MHz <>
DVB-T & RF
Spectrum: Normal <>

71
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
4
Fec:
Here the value of the Forward Error Correction can be chosen. Use
Right, Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available parameters are:
1/2
2/3
3/4
5/6
7/8
5
GI:
Here the Guard Interval value can be chosen. Use Right, Left
buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
1/4
1/8
1/16
1/32
6
Bandwidth:
Here the bandwidth of the transmitted signal can be chosen. Use
Right, Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
5 MHz
6 MHz
7 MHz
8 MHz
7
Spectrum:
Here the type of the spectrum is configured. Inverted spectrum is
just another method to help prevent signal theft. Use Right, Left
buttons so as to select the desired option. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Normal
Invert
Table 3.25 DVB-T & RF menu options

72
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.4 DVB-T Useful Bitrate
In this point, useful bitrates are given for the 4K mode in the following
tables and cover the 8 MHz, 7 MHz and 6 MHz channels.
In the following tables, the values in italics are approximate values for the
given channel bandwidth.
Table 3.26 Useful bitrate (Mbit/s) for non-hierarchical systems in 8 MHz
channels
Table 3.27 Useful bitrate (Mbit/s) for non-hierarchical systems in 7 MHz
channels

73
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Table 3.28 Useful bitrate (Mbit/s) for non-hierarchical systems in 6 MHz
channels
Table 3.29 Useful bitrate (Mbit/s) for non-hierarchical systems in 5 MHz
channels

74
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.5 DVB-S2
Figure 3.39 DVB-S2 & RF Menu
DVB-S2 & RF
Freq: 1.640,365MHz
Low Carrier <>
Power: +0.0dBm
DVB-S2 & RF
Modul: 32APSK <>
LDPC Fec: 9/10 <>
SR: 12.4MS/s BW:14
DVB-S2 & RF
Roll Off: 0,20 <>
Pilots: ON <>
Spectrum: Normal <>
DVB-S2 & RF
10MHz: On <>

75
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Line nº
Function
1
Freq:
Select the frequency at which the signal is going to be transmitted.
So as to establish the frequency value first, press the OK button and
then, with the Up and Down arrows buttons select the wanted value.
So as to save the value introduced, press the OK button. (editable
parameter)
2
Sort of output:
So as to select the sort of output, press Right and Left keys. Once
the option is selected, press the OK button so as to save it. (eligible
parameter)
The possibilities are:
Off (Turn off the RF output)
Low Carrier (the output signal is a continuous wave and the
output power is adjusted to 10 dB less than what is configured in
the power field)
Carrier (The RF output is carrier only (CW) without modulation.
So as specify the output power, select it in the power option)
Modulator (The RF output carrier with modulation. So as specify
the output power, select it in the field below)
3
Power:
In this field, the value of the output power can be selected. The
possible output power range is from -20 to 5 dBm. (editable
parameter)
4
Modul:
Here the constellation of the modulation can be chosen. Use Right
and Left buttons so as to select the desired constellation. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
QPSK
8PSK
16APSK
32APSK

76
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
5
LDPC Fec:
Here the value of the Forward Error Correction can be chosen. Use
Right and Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
1/4
1/3
2/5
1/2
3/5
2/3
3/4
4/5
5/6
8/9
9/10
6
Roll Off:
Here the value of Roff Off factor can be chosen. Use Right and Left
buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
0.20
0.25
0.35
7
Pilots:
In this field, selecting the ON option carrier pilots are transmitted. If
OFF option is selected, then no carrier pilots are transmitted. So as
to select an option, Right, Left keys must be pressed. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
ON
OFF
8
SR:
In this field, the value of the symbol rate can be introduced.
(editable parameter)
BW:
In this field it is displayed the value of the bandwidth of the
transmitted signal. (reading parameter)

77
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
9
Spectrum:
Here the type of the spectrum is configured. Inverted spectrum is
just another method to help prevent signal theft. Use Right and Left
buttons so as to select the desired option. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Normal
Invert
10
10 MHz:
This feature provides a reference signal of 10MHz to the satellite upconverter in case of being ON. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
ON
OFF
Table 3.30 DVB-S2 & RF menu options

78
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.6 Symbol Rate calculation
So as to calculate the symbol rate needed for a determined bandwidth, the
next equation must be implemented:
Where:
SR: Symbol Rate in Msymb/s
BW: Bandwidth in MHz
Next, it is shown a table as an example of the Symbol Rate values for a
determined Bandwidth of 28 MHz.
Bandwidth (MHz)
Roll-off
Symbol Rate
(Msymb/s)
28
0.20
23.33
28
0.25
22.4
28
0.35
20.74
Table 3.31 Symbol Rate calculation

79
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.3.7 DVB-S
Figure 3.40 DVB-S & RF Menu
DVB-S & RF
Freq: 1.360,500MHz
Modulator ON <>
Power: +0.0dBm
DVB-S & RF
FEC: 7/8 <>
SR: 12.4MS/s BW:14
Spectrum: Normal <>
DVB-S & RF
10MHz: On <>

80
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Line nº
Function
1
Freq:
Select the frequency at which the signal is going to be transmitted.
So as to establish the frequency value first, press the OK button and
then, with the Up and Down arrows buttons select the wanted value.
So as to save the value introduced, press the OK button. (editable
parameter)
2
Sort of output:
So as to select the sort of output, press Right and Left keys. Once
the option is selected, press the OK button so as to save it. (eligible
parameter)
The possibilities are:
Off (Turn off the RF output)
Low Carrier (the output signal is a continuous wave and the
output power is adjusted to 10 dB less than what is configured in
the power field)
Carrier (The RF output is carrier only (CW) without modulation.
So as specify the output power, select it in the power option)
Modulator (The RF output carrier with modulation. So as specify
the output power, select it in the field below)
3
Power:
In this field, the value of the output power can be selected. The
possible output power range is from -20 to 5 dBm. (editable
parameter)
4
Fec:
Here the value of the Forward Error Correction can be chosen. Use
Right and Left buttons so as to select the desired value. (eligible
parameter)
The available options are:
1/2
2/3
3/4
5/6
7/8
5
SR:
In this field, the value of the symbol rate can be introduced.
(editable parameter)

81
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
BW:
In this field it is displayed the value of the bandwidth of the
transmitted signal. (reading parameter)
6
Spectrum:
Here the type of the spectrum is configured. Inverted spectrum is
just another method to help prevent signal theft. Use Right and Left
buttons so as to select the desired option. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
Normal
Invert
7
10 MHz:
This feature provides a reference signal of 10MHz to the satellite upconverter in case of being ON. (eligible parameter)
The available options are:
ON
OFF
Table 3.32 DVB-S & RF menu options

82
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.4 Unit Menu
By using the Up, Down arrow keys, select the Unit option and press OK
key.
Figure 3.41 Unit Menu
3.5.2.4.1 Profile
Figure 3.42 Unit Menu
In this option, a new profile can be created or, otherwise, an existing profile
can be loaded. There are up to seven possible profiles that can be saved
and loaded in this device. So as to save the current configuration of the
device in a profile, go to the save option and select the desired number of
the profile with the Right, Left buttons and press the OK button so as to
save it. In order to load a desired profile, go to the load option, select the
desired profile to be loaded with the Right, Left buttons and press OK
button so as to load it.
UNIT
Profile
Alarms (02)
Monitor
UNIT
Ethernet
Night Mode: 0 <>
Dist Units: Km <>
UNIT
Keyboard Beep: On <>
Firmware
UNIT PROFILE
Load: 1 <>
Save: 3 <>

83
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.4.2 Alarms
In this option, different alarms which are present in the device are shown.
The alarm screen can be accessed by pressing the OK button from the main
screen as well. So as to return to the main screen from the alarm screen,
cross button must be pressed.
The different alarms that can appear in the transmitter are:
- Voltage High.
- Voltage Low.
- Temperature High.
- ASI Overflow: this alarm means that the input bitrate is higher than the
one that can be modulated due to the parameters configured
(constellation, FEC, GI...).
The different warnings that can appear in the transmitter are:
- No Video Input.
- No GPS.
3.5.2.4.3 Monitor
Figure 3.43 Unit Monitor Menu
Temperature:
In this field, the internal temperature of the device is displayed. With the
Right, Left keys, the user can select if the temperature is shown in ºC or
in ºF. Also, the value which is between square brackets means the speed
of the fans (values from 0 to 3) where 0 means that the fans are
stopped and value 3 is the maximum speed. (Reading parameter)
Voltage:
In this field, the voltage of the transmitter is shown. (Reading parameter)
UNIT MONITOR
Self Check: OK
Temp: +37,1ºC (0) >
Voltage: +11.6V

84
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.4.4 Ethernet
Figure 3.44 Encoder Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Local IP:
In this option it can be set the IP address of the device in case it is
wanted to control the device remotely. So as to change the IP
address first press OK button and then, with the Up and Down keys
select the desired number. So as to change from one character to
another, press Right and Left keys. Press the OK button so as to
save the value introduced. (editable parameter)
2
Subnet Mask:
Here it can be written the Subnet Mask address of the device. So as
to change the Subnet Mask address first press OK button and then,
with the Up and Down keys select the desired number. So as to
change from one character to another, press Right and Left keys.
Press the OK button so as to save the value introduced. (editable
parameter)
3
Gateway:
In this option, the address of the Gateway must be written. So as to
change the Gateway address first press OK button and then, with
the Up and Down keys select the desired number. So as to change
from one character to another, press Right and Left keys. Press the
OK button so as to save the value introduced. (editable parameter)
4
MAC ADDRESS (Reading parameter)
Table 3.33 Unit Ethernet menu options
UNIT ETHERNET
LOC 192.168.001.010
MSK 255.255.000.000
GAT 192.168.001.001
UNIT ETHERNET
00-00-5E-00-FA-CE

85
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3.5.2.4.5 Firmware
Figure 3.45 Encoder Menu
Line nº
Function
1
Check USB Memory:
This field is the one for updating the version of the device. So as to
update the equipment properly, follow the instructions below.
2
Restore Default:
In this option, the equipment is restored to the first factory version.
So as to restore the equipment to the initial set up, press the OK
button.
3
Rev:
In this field it is shown the number of the version installed in the
device. The characters which describe the number of the version are
the one inside the red box shown in the figure above. The rest of the
characters are important for the manufacturer but are not important
for the user.
Table 3.34 Unit Rev menu options
Check USB Memory
Restore Default
Rv:v5.0105041007-08
Number of the version of the device

86
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
Next, they are explained the necessary steps so as to make a successful
update.
1) The latest firmware is allocated in the webpage of SVP Broadcast
Microwave. So as to access to the firmware file, first enter to
www.svpbm.com in your web browser.
2) Click on the Support tab.
Figure 3.46 Updating firmware step 2

87
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
3) Click on Software.
Figure 3.47 Updating firmware step 3
4) Go to HDT-02_Firmware.
Figure 3.48 Updating firmware step 4

88
HDT-02_H.264 High Definition Digital Camera Transmitter
USER’S MANUAL V4.11
5) Select the firmware version to download the file.
Figure 3.49 Updating firmware step 5
6) Once the firmware file has been downloaded, save it in a USB device.
In the USB device, the only file that can be allocated inside it is the
firmware file of the device to be updated.
7) With the equipment completely power off (with no power
supply), insert the USB device in the USB connector, situated in the
rear panel.
Before introducing the USB device, remove the power supply of the
equipment.
8) Now, switch on the device.
9) Go to Unit menu. In case of being in the main screen, press cross
button so as to access to the menu. There, with the Up,Down
buttons, select the Unit option.
10) Select Firmware by pressing the OK button.
11) Select Check USB Memory with the OK button.
12) Now, automatically the device updates the firmware. The screens
which are shown below display the different steps that the device is
making while the updating process.
Don’t power off the device during the updating process.
 Loading...
Loading...