Page 1

24-Port 10/100M
Ethernet Rack-Mount Switch
With Fiber Support
User Guide
#482824DXFSZ1
Page 2

2
FCC Statement
This equipment can generate, use and radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause interference to radio communications.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against
radio interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be
required to take whatever measures are necessary to correct the interference.
WARNING! Any changes or modifications to this product not expressly approved by the
manufacturer could void any assurances of safety or performance and could result in violation
of Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
CE Declaration of conformity
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Trademarks
All company, brand, and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Page 3

3
Contents
1:Introduction
………………………………………
4
1.1 Feature & Benefit
…………………………
4
1.2 Technical Specification
……………………
6
1.3 Package Contents
…………………………
7
1.4 Glossary
……………………………………
7
2: Hardware Installation
…………………………
10
2.1 Overview……………………………………
10
2.2 Hardware Connection
………………………
12
3: Using Configuration Menu
……………………
14
3.1 Software Installation
………………………
14
3.2 Using RRCP
………………………………
14
3.3 Status
…………………………………
15
3.3.1 Overview…………………………………
16
3.3.2 Port Status………………………………
17
3.3.3 MIB Counter……………………………
18
3.4 Configuration
………………………………
20
3.4.1 Port Configuration………………………
20
3.4.2 Cobal Configuration………………………
23
3.4.3 Qos Configuration………………………
24
3.4.4 VLAN Configuration……………………
26
3.4.5 VLAN Control……………………………
28
3.4.6 Device Features…………………………
30
3.5 Security
……………………………………
31
3.6 Diagnostic
…………………………………
32
3.6.1 Fault Information…………………………
32
3.6.2 Device Reset……………………………
33
3.6.3 Script……………………………………
34
3.7 System Menu
………………………………
35
3.7.1 Save and Load Configuration……………
35
3.7.2 Option……………………………………
36
3.7.3 Help………………………………………
37
Page 4

4
1. Introduction
The 24-Port 100/10M N-Way Rack-Mount Smart Switch is the latest design in its N-Way
Switches series for easy installation and high-performance in an environment where traffic on the
network and the number of users increase continuously. Provide 24-Port 100/10M Ethernet Switch
support Auto MDI/MDI-X. Small businesses and corporate branch offices can take full advantage
of 100Mbps Fast Ethernet performance and preserve existing desktop investment with no changes
required to PCs, NICs, cabling,drivers, or PC configurations.
1.1 Feature and Benefit
Feature
1. Provide 24-Port 100/10M Ethernet Switch to support Auto MDI/MDI-X
2. Provide one fiber slide-in port for expansion the workgroup distance to 2,000 meters
3. Provide back-pressure in half-duplex and flow control in full-duplex
4. Store-and-forward switching scheme capability supports rate adaptation and ensures data
integrity
5. N-way Auto-negotiation on each RJ-45 port. This allows for auto-sensing of speed
(100/10Mbps) and auto-detecting mode (full-duplex or half-duplex) thereby providing
you with automatic and flexible solutions in your network connections
6. Auto-polarity detection for correction of incorrect polarity on the received twisted-pair
7. Data fowarding rate 148,800 pps per port at 100% of wire-speed
8. Data filtering rate eliminates all error packets, runts, etc. at 148,800pps per port at 100% of wire
speed
9. Conform to IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T, IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX /FX, and IEEE 802.3x
flow control for full-duplex standards
10. Provide non-blocking twenty-four ports full-wire speed access
11. Support one fiber slide-in port for expansion with the 24th port
12. Full/half-duplex mode operation on all ports
13. Auto-negotiation capability
14. Source address learning and aging function
15. Provide 8K MAC address and 2.5Mbits SSRAM buffer
16. LEDs to indicate Power, link/activity, full-duplex/collision, and 100 status
17. Support up to 32 VLAN groups for port pased VLAN.
Page 5

5
Benefit
Fiber Slide-in Slot
The Switch has fiber. With fiber the workgroup distance could beextended to 2,000 meters and
solve the distance limit.
Full/Half-Duplex and Easy Expansion
The Switch supports both full/half-duplex on all ports which are able to provide 200Mbps of
bandwidth to the connected devices using auto-negotiation. The Switches also expandable by
cascading two or more switches together or connecting any RJ-45 (MDI-X) port on the Switch to
any device such as a workstation or a server.
Store-and-Forward Scheme
The Switch uses store-and forward switching to ensure all error packets will be filtered and
maintain maximum data integrity, even under heavy loading.
Upgrade
Designed for plug-and-play, the Switch is fully compatible with existing Ethernet networks, thus
saving your current network properties. The 24-Port 100/10M N-Way Rack-Mount Smart Switch
offers a solution in accelerating Ethernet workgroup’s bandwidth.
Remote Control Protocol
Remote Control Protocol is a simple control protocol and window based proposed to enhance
the functionalities of configuration and management. This easily-using program provides completed
smart function for small medium business. Such as VLAN、Trunk、Class of Service、Bandwidth
Control …etc. With these functions, the network bandwidth will be utilized more efficiently and
management will be more convenient.
Page 6
6
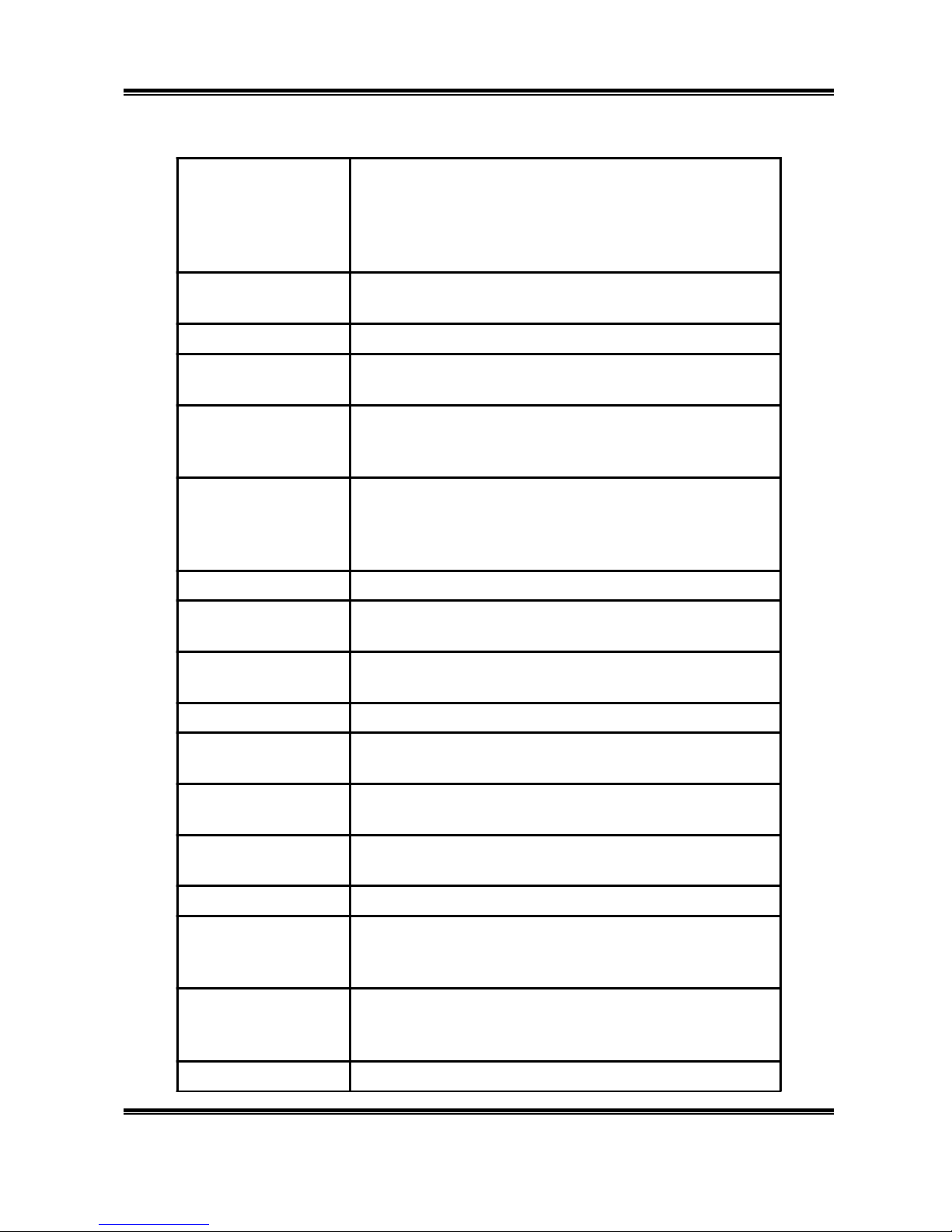
1.2 Technical Specification
Standards: IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100 BASE-TX/FX Fast Ethernet
ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3 N-way auto-negotiation
IEEE 802.3 MAC layer frame size:64-1536 Bytes
IEEE 802.3x flow control for Full-Duplex
Protocol: CSMA/CD
Topology: Star
Transm ission
Method: Store-and-Forward
Transfer Rate:
Ethernet:
Fast Ethern et:
10M (half-duplex);20M (full-duplex)
100M (half-duplex);200M (full-duplex)
Media:
10BASE-T:
100BASE-TX:
100BASE-FX:
UTP Cat.3,4,5 (Max. cable length 100m);
UTP Cat.5 (Max. cable length 100m);
Multi-mode Fiber cable (Max. cable length 2000m)
No. of Ports: 24 100/10Mbps RJ-45 ports
Media Interface
Exchange: 24 RJ-45 ports support Auto MDI/MDIX
Port Module
Option: Side-in slots for 100M fiber module
RAM Buffer: Total 2.5Mb its per device
Filterin g Adress
Table: 8K
Packet Filtering
/Forwarding Rate:
148800/14800pps
Wire speed per port (for 100Mbps & 10Mbps)
Power: Internal Universal Power,
Input:90-264V(47-63Hz);Output:3.3V/7A
Consumption: 10 watts maximum
Temperature:
Operating:
Storage:
0
0
C ~ 45 0C
0
0
C
~ 60
0
C
Humidity:
Operating:
Storage:
10% ~ 90%
5% ~ 95%
Conformance: FCC Class A, CE Mark Class A
Page 7

7
1.3 Package Contents
1.One 24-Port 100/10M N-Way Rack-Mount Smart Switch
2.One Power Cord
3.Two Mounting Brackets
4.One CD-ROM including User Manual
Note: If any item is damaged or missing, please contact your supplier.
1.4 Glossary
10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3 specification for 10 Mbps Ethernet over two pairs of Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable.
100BASE-TX
IEEE 802.3u specification for 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet over two pairs of Category 5 UTP cable.
Ethernet
A network communication system developed and standardized by DEC, Intel, and Xerox, using
baseband transmission, CSMA/CD access, logical bus topology, and coaxial cable. The successor
IEEE 802.3 standard provides for integration into the OSI model and extends the physical layer and
media with repeaters and implementations that operate on fiber, thin coax and twisted-pair
cable.
Fast Ethernet
A 100 Mbps network communication system based on Ethernet and the CSMA/CD access method.
Media Access Control (MAC)
A portion of the networking protocol that governs access to the transmission medium, facilitating
the exchange of data between network nodes.
Auto-negotiation
Signalling method allowing each node to select its optimum operational mode (e.g., 10 Mbps or
100 Mbps and half or full duplex) based on the capabilities of the node to which it is connected.
Bandwidth
The difference between the highest and lowest frequencies available for network signals. Also
synonymous with wire speed, the actual speed of the data transmission along the cable.
Page 8

8
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect is the communication method employed by
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet.
Full Duplex
Transmission method that allows switch and network card to transmit and receive concurrently,
effectively doubling the bandwidth of that link.
Port Trunk
Defines a network link aggregation and trunking method which specifies how to create a
single high-speed logical link that combines several lower-speed physical links.
Virtual LAN (VLAN)
A Virtual LAN is a collection of network nodes that share the same collision domain regardless
of their physical location or connection point in the network. A VLAN serves as a logical
workgroup with no physical barriers, and allows users to share information and resources as though
located on the same LAN.
IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN Tagging—Defines Ethernet frame tags which carry VLAN information. It allows
switches to assign endstations to different virtual LANs, and defines a standard way for VLANs to
communicate across switched networks.
IEEE 802.1p
An IEEE standard for providing quality of service (QoS) in Ethernet networks. The standard
uses packet tags that define up to eight traffic classes and allows switches to transmit packets based
on the tagged priority value.
Port Mirroring
A method whereby data on a target port is mirrored to a monitor port for troubleshooting with a
logic analyzer or RMON probe. This allows data on the target port to be studied unobstructively.
Bandwidth Control
This function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic transmitted
or received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge of a network to
limit traffic into or out of the network. Traffic that falls within the rate limit is transmitted, while
packets that exceed the acceptable amount of traffic are dropped.
Page 9

9
IGMP Snooping
Listening to IGMP Query and IGMP Report packets transferred between IP Multicast Routers
and IP Multicast host groups to identify IP Multicast group members.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
A protocol through which hosts can register with their local router for multicast services. If there
is more than one multicast router on a given subnetwork, one of the routers is made the “querier”
and assumes responsibility for keeping track of group membership.
Page 10

10
2. Hardware Installation
This chapter describes the front panel, LED indicators, and rear panel on the Switch.
2.1 Overview
5
678
9
10
11
12
13 14
15
16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 (24)
24*10/100Mbps RJ-45 Ports - Uses these twenty-four ports to connect to another Switches or Hubs.
Each portuses auto-negotiation for automatic speed and mode selection.
Fiber Module Slot - Extends the workgroup distance up to 2,000 meters.(Option)
90~264VAC
47~63Hz
Front Panel
Rear Panel
Page 11

11
The LED indicators are all located on the front panel which include one Power per device, one
Link/Act., one FDX/Col, and one 100 indicator per port.
LED Color Status Description
Power Green On Lights to indicate the switch is power on.
Link/Act Green On Lights to indicate a functional network link through
the corresponding port with an attached device.
Flashing Blinks to indicate that the router is actively sending or
receiving data over that port.
FDX/COL Green On Lights to indicate that the connected port is under
Full-Duplex mode.
Off Off to indicate that the connected port is under
Half-Duplex mode.
Flashing Blinks to indicate that the connected port is under
collision status.
100 Green On Lights for any port to indicate that the port is
operating at 100 Mbps.
Off Off to indicate that the port is operating at 10 Mbps
while the network is still operating.
LED Indicators
Page 12

12
2.2 Hardware Connection
The power receptacle is located on the rear panel of the switch. The standard power receptacle is
for the AC power cord.
The Switch contains 24 10BASE-T /
100BASE-TX RJ-45 ports. All of these ports
support automatic MDI/MDI-X operation, so you can use straight-through cables for all network
connections to PCs or servers, or to other switches or hubs. Each of these ports also support
auto-negotiation, so the optimum transmission mode (half or full duplex), and data rate (10 or 100
Mbps) can be selected automatically.
See the following section to get more details about connection of RJ-45 ports.
Connecting to PC or Server
You can connect any RJ-45 station port
on the Switch to a PC via twisted-pair cable
with RJ-45 plugs at both ends. Use Category
3, 4 or 5 cable for standard 10Mbps
Ethernet connections, or Category 5 cable
for 100Mbps Fast Ethernet connections.
Make sure you have installed a
10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX network
interface card for connecting a PC to the
Switch’s RJ-45 (MDI-X) station ports. If
LEDs don’t light afterpowering on the Switch, check if the LAN card, the cable and connectors are
properly attached to the PC and the Switch. When a attached PC is powered on or reset:
1. The Link/Act LED will light
2. The FDX/Col LED depends on the installed LAN card’s capabilities for the PC and the Switch
connection.
3. The 100M LED will light for 100Mbps connection, otherwise it will be unlighted.
Power
RJ-45 Ports
12
5678
9101112131415161718192021222324
91011121721222324
MAC
Phone
Jack
LED
Page 13

13
Connecting to Switch or Hub
You can also connect any RJ-45 station port on the Switch to the Uplink port of a Hub or any
port of another switch via straight cable with RJ-45 plugs at both ends.
When a attached 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Hub is powered on or reset:
(10BASE-T Hub)
The Link/Act LED will light
The FDX/Col LED will be unlighted
The 100 LED will be unlighted
(100BASE-TX Hub)
The Link/Act LED will light
The FDX/Col LED will be unlighted
The 100 will light
When a Switch or other devices is switched on:
The Link/Act LED will light
The FDX/Col LED depends on the attached Switch or other devices’ capabilities.
The 100 LED will light for 100Mbps connection, otherwise it will be unlighted.
591011121721222324
J5Cabe
Page 14

14
3. Using Configuration Menu
The Remote Control Protocol (RRCP) is a simple control protocol proposed to enhance the
functionalities of this Layer 2 switches by software. The RRCP Management Application, is a
Window-based software package that implements RRCP functions at the management host side.
The RRCP Management Application gives network administrators the ability to configure and
monitor switches like intelligent switches.
Before you getting started, make sure that you meet the following requirements.
1. A computer with an Ethernet network card installed and CD-ROM Drive
2. This CD-ROM with RRCP program
3. Your Windows CD, if your computer is running Windows 98,XP,2000,NT4.0,Service Pack 6
or ME
4. UTP network cable with RJ-45 connector
3.1 Software Installation
WinPcap 3.0 Installation
1. Insert the attached CD-ROM with this switch into PC’s CD-ROM drive.
2 .Select the “WinPcap 3.0” and click “Install”. Then follow the install wizard to finish
installation.
RRCP Installation
1.On the main screen, select “RRCP” and click “Install”. Then follow the install wizard to finish
installation.
2.After installation, there will be a “RRCP Icon” on the desktop.
3.2 Using RRCP
1. Double click the RRCP’s icon or select the “RMT” in the start program menu.
2. Select the Network adapter which is connecting to switch. Then click “OK”.
Page 15

15
3.3 Status
After entering RRCP program, the following screen will be shown up. The Management
Application shows one switch’s information at one time. You can select a switch using the pull
down menu – “Select Switch Mac” which displayed switches discovered in the network.
Page 16

16
3.3.1 Overview
Discover Device Information
List all switches founded in the network. You can named the switches by double-click the item
in the list box.
Network topology link vector
Show the link status of the switches.
Update button
You can click it to get the latest information of the connected switches on the network.
Switch database button
The switch database screen displays “switch’s name”, “MAC Address”, Authentication Key
“.
Page 17

17
3.3.2 Port Status
Select the “Port Status” sheet. You can check each port’s link status and configration
information in this sheet. Click “Refresh” to get the latest information.
Page 18

18
3.3.3 MIB Counter
Select the “MIB Counter” sheet. You can view the MIB counter about the RX, TX and
Diagnostic Counter. Click the Diagnostic Counter column header, there are three objects you can
select, such as Drop count, CRC error count and Collision count.
Byte Count button
Showing the each port’s amounts of bytes are sent and received.
Packet Count button
Showing the each port’s amounts of packets are sent and received.
Bandwidth Utilization button
Display the each port’s traffic utilization. It will show the TX, RX and Diagnostic Counter to
utilization mode.
Polling
Start button – Click “Start” to start counter.
Stop button – Click “Stop” to stop counter.
Page 19

19
Clear Counter button – Click “Clear Counter” to clear all MIB counters, it will reset the
counters to zero.
Polling Interval – You can set the time period to count by click “Polling Interval”. The
Maximum Time setting is “1410065407” seconds and minimum is “6” seconds.
Page 20

20
3.4 Configuration
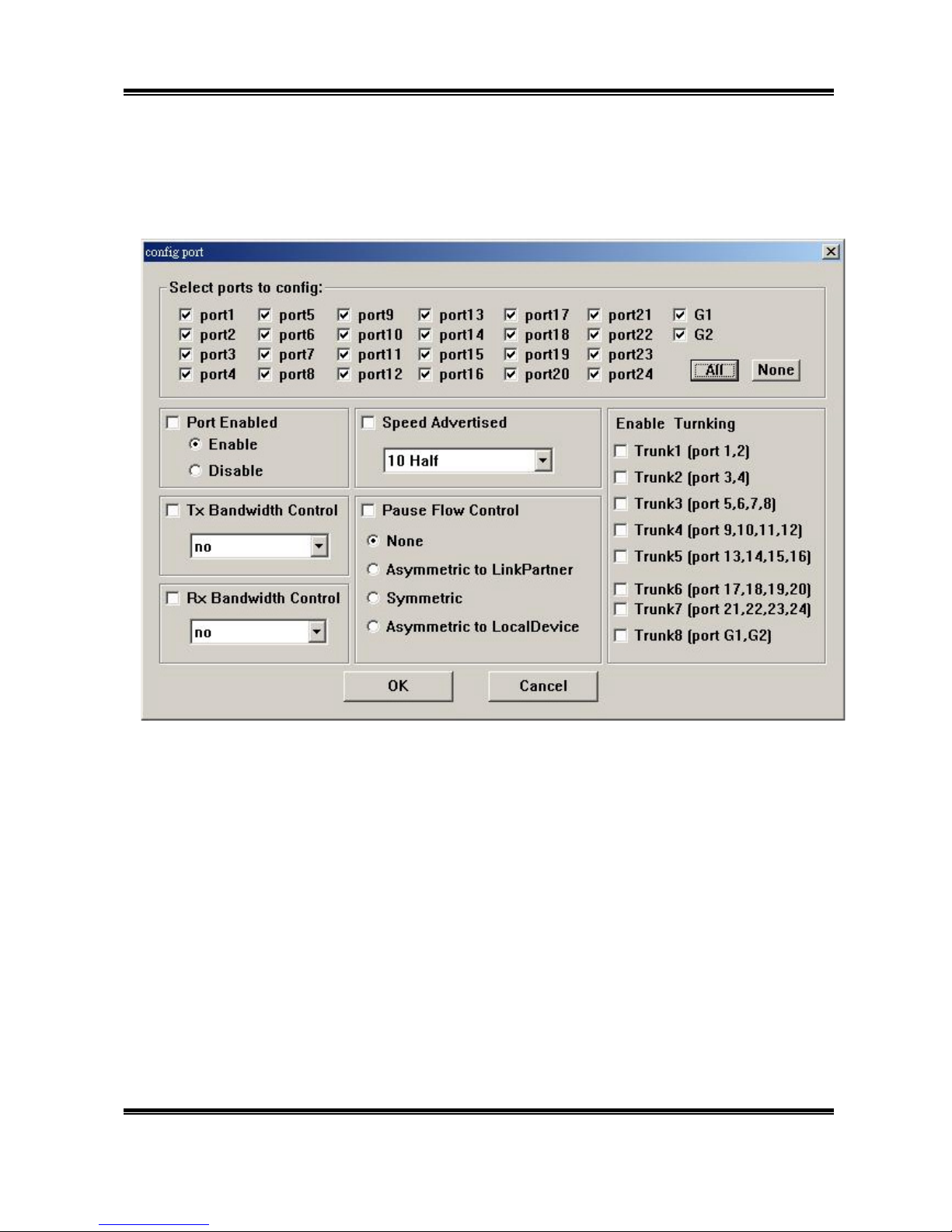
3.4.1 Port Configuration
On the “Port Configuration” sheet, you can check each port’s configuration information
including port enable/disable, Tx/Rx bandwidth setting, full/half-duplex, flow control, trunk
setting.
Note: There will not have port G1 and G2 if you use 24-Port 10/100M Ethernet Rack-Mount
Switch With Fiber Support
Click “Config” button to change the settings.
Select ports to config
Mark the port number which you want to configure. You can click “All” to mark all ports or
click “None” to unmark.
Port Enable
Mark “enable” to set the port is enabled to connect, otherwise not. The default setting is enable.
Page 21

21
Tx Bandwidth control
Use pull down menu to select the transmission bandwidth you’d like to give. There are 8
options to choose – no, 128Kbps, 256Kbps, 512Kbps, 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 4Mbps, 8Mbps. The
default setting is no.
Rx bandwidth control
Use pull down menu to select the receiving bandwidth you’d like to give. There are 8 options to
choose – no, 128Kbps, 256Kbps, 512Kbps, 1Mbps, 2Mbps, 4Mbps, 8Mbps. The default
setting is no.
Speed Advertise
Use pull down menu to select the speed type. There are 4 options to choose – 10Mbps and
Half-duplex, 10Mbps and Full-duplex, 100Mbps and Half-duplex, 100Mbps and Full-duplex.
Note: The default setting is Auto-Negotiation. That means the switch will auto select its
Optimum operational mode based on the capabilities of the node to which it is connected.
Pause Flow Control
None – Mark this column to enable flow control.
Asymmetric to Link Partner – Mark this item to force the flow control stop of the node to
which it is connected.
Symmetric – Mark this item to make the flow control start if the node to which it is connected
enable flow control function.
Asymmetric to Local Device – Mark this item to make the flow control start if the node to
which it is connected enable flow control function.
Page 22
22
Enable Trunking
Mark the items which you want to set port trunks.
Note: There will not have port G1 and G2 if you use 24-Port 10/100M Ethernet Rack-Mount
Switch With Fiber Support
Page 23

23
3.4.2 Clobal Configuration
Global Configuration is used to configure the global port control registers. Press the Refresh
button to read the status of the registers. Press the Update button to set the registers as shown in this
frame.
Half-duplex back pressure flow control
Mark Enable/Disable to enable/disable this function.
Broadcast Storm filtering control
Mark Enable/Disable to enable/disable this function.
Page 24

24
3.4.3 QoS Configuration
Qos Configuration is used to configure the Qos control registers. Press the Refresh button to
read the status of the registers. Press the Update button to set the registers.
There are three options in QoS Configuration and two options in priority queue. You can
enable/disable these functions via marking the columns.
TOS/Diff Serv. priority
When you enable this function, the switch can recognize TCP/IP Differentiated Services
Codepoint (DSCP) priority information from the DS-field defined in RFC2474. The DS field
byte for IPv4 is the Type-of-Service (TOS) octet, and for IPv6, it is the Traffic-Class octet. The
recommended DiffServ Codepoints is defined in RFC2597 to classify the traffic into different
service classes. This switch can extract the codepoint value of the DS-field from IPv4 and IPv6
packets, and identify the priority of the incoming IP packet as following definitions:
High priority: whose DS-field = (EF,expected forwarding:) 101110
(AF, Assured Forwarding:) 001010; 010010; 011010; 10001
0
Page 25

25
(Network Control:) 11x000
Low priority: whose DS-field = others values.
802.1p priority
When 802.1p tag priority is applied, the switch can recognize the 802.1Q VLAN tag frames and
extract the 3-bit User_Priority information from the VLAN tag. The default setting of the
threshold of User_Priority is 3. Therefore, VLAN tagged frames with User_Priority value = 4~7
will be treated as high priority frames, and treat other User_Priority values = 0~3 as low priority
frames.
Adapted Flow Control Ability
The switch can automatically turn off 802.3x flow control and Back pressure flow control for
1~2 seconds whenever the port receives a high priority frames. The flow control is re-enabled
when no priority frames are received for 1~2 seconds.
Priority Weighted Ratio
This switch supports 2 level priority queues. The queue service rate is based on the packet based
Weighted Round Robin algorithm. The packet based service weight ratio of high-priority and
low-priority queuing can be set as 4:1, 8:1, 16:1 or "Always high priority first". The default
setting is 16:1.
Force Set High Priority Port
When Port based priority is applied, any packet received from the a high priority port will be
treated as a high priority frame.
Page 26

26
3.4.4 VLAN Configuration
This sheet allows you to set the VLANs. This switch supports Port-based and Tag-based
VLANs. Press the Refresh button to read the status of the registers. Press the Add VLAN/Edit
VLAN/Delete VLAN button and select one VLAN in the list box or double-click the VLAN you
want to configure, it will pop up a dialog like following to set the VLAN registers.
Page 27

27
TAG Control button
Press this button you will see a dialog like following. To configure a port, please double-click
the port you want to configure. There are three types of VLAN Tag Control for you to choose:
1.Remove the VLAN tag from all tagged frame.
2.Insert priority tag into the untagged high-priority frame. (Set priority field = 7, VID field =
0 for high priority frame.)
3.Insert priority tag into the all untagged frame. (Set priority field = 7, VID field = 0 for
high priority frame; Set priority field = 0, VID field = 0 for low priority frame.)
4.Don't touch. (Not modify the packet)
Note: The function could be enabled even the VLAN function is not enabled.
Page 28

28
Save VLAN button
When finishing VLAN settings, don’t forget to click “Save VLAN” button to save the
configuration.
3.4.5 VLAN Control
This sheet is to set VLAN Control Registers. Press the Refresh button to read the VLAN control
registers. Press the Update button to set the registers, and it will set all VLAN control registers to
the selection.
VLAN Function
Mark Enable/Disable to enable/disable VLAN function.
Unicast Packet Inter-VLAN Leaky
A received unicast frame will be forward to the destination port when its destination port is in
the different VLAN as the source port, if this function is enabled. Or the frame will be discarded,
when the destination port and source port belong to a different VLAN.
Page 29

29
ARP broadcast Packet Inter-VLAN
The packets with ARP frame will broadcast to all switch ports, if enable this function.
IP Multicast Packet Inter-VLAN
This function is to enable IP multicast packet to be flood to all the multicast address group
member set and the VLAN member set domain limitation will be ignored.
802.1Q VLAN Tag aware
This function is to enable/disable 802.1Q VLAN Tag aware.
Ingress Rule for acceptable frame types control
This function is to admit all frames or to admit only VLAN-tagged frames.
Ingress Rule for Ingress Filtering control
This function is to enable filtering the frame received from a port which is not included in the
classified VLAN group member.
Page 30

30
3.4.6 Device Features
Setting IGMP Snooping Control register and IP Multicast Router Port Discovery register.
Router port report will show the IP multicast Router port list. Press the Refresh button to read the
register. Press the Update button to set the registers, and it will set the register to the selection.
Page 31

31
3.5 Security
This page displays the authentication key of the switch, and the RRCP Management Security
Mask Configuration. The authentication key is readable. You can press the Refresh button to read
the register, and press the Update button to set the registers, and it will set the register to your
selection.
Page 32

32
3.6 Diagnostic
3.6.1 Fault Information
This page shows some information likes Trunk Port Fault, Network Loop Fault Test.
Note: There will be no GigaPHY 1/2 information if you use 24-Port 10/100M Ethernet
Rack-Mount Switch With Fiber Support
Page 33

33
3.6.2 Device Reset
Click “Restart Switch” to reset the system to the initial state. The MAC table and VLAN table
data will be kept. All the current user configured values of internal registers will be kept. The
EEPROM download will NOT be done again. But the system will restart the process of Auto
Negotiation.
Note: The hardware will not be reset. If you want to reset hardware, unplug the power line and
wit for at least 5 seconds then replug.
Page 34

34
3.6.3 Script
This page is for system manufacture using only.
Page 35

35
3.7 System Menu
3.7.1 Save and Load Configuration
You can save or load the configuration to a file.
To save a file
In the Browser, click System | Save Configuration.
To load a file
In the Browser, click System | Load Configuration. And in the Open File dialog box, select a
“.rrcp” file and click Load. In the Setting Active Switch dialog box, select a switch you want to
set, and click OK.
To save to hardware
In the Browser, click System | Save to Hardware.
Page 36

36
3.7.2 Option
Hello Polling
Select Option | Hello Polling to set the time interval.
Counter Polling
Select Option | Counter Polling to set the time interval.
Authentication Key
System will automatically generate the authentication key. The authentication key can not be
changed manually.
Auto Detect and Reload
Choose the system will load the configuration automatically or not.
Page 37

37
3.7.3 Help
About RRCP
You can check the RRCP software’s version here.
 Loading...
Loading...