Page 1

SUPER
SUPER P6DLS
SUPER P6DLE
SUPER P6SLS
SUPER P6SLA
®
USER’S MANUAL
Revision 1.2
Page 2
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be
accurate. The vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be
contained in this document, makes no commitment to update or to keep current the
information in this manual, or to notify any person or organization of the updates.
SUPERMICRO COMPUTER reserves the right to make changes to the product described in
this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software, if any, and
documentation may not, in whole or in part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated
or reduced to any medium or machine without prior written consent.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO COMPUTER BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, THE VENDOR SHALL NOT HAVE
LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE
PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF THE REPAIRING, REPLACING, OR
RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Unless you request and receive written permission from SUPERMICRO COMPUTER, you
may not copy any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and
companies referred to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 1997 by SUPERMICRO COMPUTER INC.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Page 3

Preface
About This Manual
This manual is written for system houses, PC technicians and
knowledgeable PC end users. It provides information for the installation and use of SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA
motherboard. SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA supports
Pentium II 300/266/233 MHz.
The Pentium II processor with the Dual Independent Bus Architecture is housed in a new package technology called the Single Edge
Contact (S.E.C.) cartridge. This new cartridge package and its associated "Slot 1" infrastructure will provide the headroom for future
high-performance processors.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1, Introduction, describes the features, specifications and
performance of the SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA system
board, provides detailed information about the chipset, and offers
warranty information.
Refer to Chapter 2, Installation, for instructions on how to install the
Pentium II processor, the retention mechanism, and the heat sink
support. This chapter provides you with the instructions for handling static-sensitive devices. Read this chapter when you want to
install or remove DIMM memory modules and to mount the system
board in the chassis. Also refer to this chapter to connect the floppy
and hard disk drives, IDE interfaces, parallel port, serial ports, as
well as the cables for the power supply, reset cable, Keylock/Power
LED, speaker and keyboard.
iii
Page 4

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
If you encounter any problem, please see Chapter 3, Troubleshooting, which describes troubleshooting procedures for video, memory, and the setup configuration stored in memory. Instructions are
also included on contacting a technical assistance support representative and returning merchandise for service and the BBS# for
BIOS upgrades.
iv
Page 5
Preface
Table of Contents
Preface
About This Manual ......................................................................................... iii
Manual Organization...................................................................................... iii
Quick Reference ........................................................................................... viii
Chapter 1:
1-1 Overview............................................................................................... 1-1
SUPER P6DLS ............................................................................. 1-2
SUPER P6DLE ............................................................................. 1-3
SUPER P6SLA .............................................................................. 1-4
SUPER P6DLS Motherboard Layout ........................................ 1-5
SUPER P6DLE Motherboard Layout ........................................ 1-6
SUPER P6SLS Motherboard Layout ........................................ 1-7
SUPER P6SLA Motherboard Layout ........................................ 1-8
SUPER P6DLS Features ............................................................ 1-9
SUPER P6DLE Features .......................................................... 1-11
SUPER P6SLS Features .......................................................... 1-13
SUPER P6SLA Features .......................................................... 1-15
1-2 PC Health Monitoring ...................................................................... 1-17
1-3 ACPI/PC 98 Features ...................................................................... 1-20
1-4 Chipset Overview.............................................................................. 1-22
1-5 Wake-on-LAN .................................................................................... 1-22
1-6 Power Supply .................................................................................... 1-22
1-7 National Semiconductor Super I/O................................................ 1-23
1-8 AIC 7880 SCSI Controller................................................................ 1-23
1-9 Warranty, Technical Support, and Service .................................. 1-24
Parts.............................................................................................. 1-24
BIOS .............................................................................................. 1-24
v
Page 6

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Labor............................................................................................. 1-24
Returns......................................................................................... 1-24
Chapter 2: Installation
2-1 Pentium II Processor Installation ................................................... 2-1
OEM Pentium II and Heat Sink Support.................................. 2-5
Removing the Pentium II Processor........................................ 2-6
2-2 Static-Sensitive Devices ................................................................... 2-6
Precautions ................................................................................... 2-7
Unpacking...................................................................................... 2-7
2-3 Changing the CPU Speed ............................................................... 2-8
Turbo Function.............................................................................. 2-8
2-4 Mounting the Motherboard in the Chassis ................................... 2-9
2-5 Connecting Cables ............................................................................ 2-9
Power Supply Connectors.......................................................... 2-9
PW_ON Connector ...................................................................... 2-10
Infra-Red Connector ...................................................................2-10
Reset Connector ........................................................................ 2-11
Keylock/Power LED Cable Connector ................................... 2-11
Hard Drive LED .......................................................................... 2-12
Speaker Connector .................................................................... 2-12
SCSI LED ..................................................................................... 2-13
Power On/Off State .................................................................... 2-13
ATX PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Ports ................................... 2-14
Universal Serial Bus .................................................................. 2-14
ATX Serial Ports ......................................................................... 2-15
SMI................................................................................................. 2-15
CMOS Clear................................................................................. 2-16
External Battery ........................................................................... 2-16
Wake-on-LAN .............................................................................. 2-17
Fan Connectors.......................................................................... 2-17
vi
Page 7
Table of Contents
2-6 Installing/Removing the DIMM Modules ...................................... 2-18
DIMM Module Installation.......................................................... 2-18
Removing DIMM Modules ......................................................... 2-19
2-7 Connecting Parallel, FDD and HDD ............................................ 2-20
Parallel Port Connector ............................................................ 2-21
Floppy Connector ....................................................................... 2-22
IDE Interfaces ............................................................................. 2-23
SCSI Connectors......................................................................... 2-24
AGP Port ....................................................................................... 2-26
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures ........................................................... 3-1
No Video ........................................................................................ 3-1
Troubleshooting Flowchart ........................................................ 3-2
Memory Error ................................................................................. 3-3
Losing the System’s Setup Configuration.............................. 3-3
3-2 Technical Support Procedures........................................................ 3-4
3-3 Returning Merchandise for Service................................................ 3-4
vii
Page 8

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Quick Reference
Jumpers Function Page
JB1, JB2, JB3, JB4 CPU Speed Selection 2-8
JC1, JC2, JC3 External Bus Speed 2-8
JBT1 CMOS Clear 2-16
JP19 SMI 2-15
JP20 Power On/Off State 2-13
JC4, JL2, JP17 Manufacturer Default 1-4
Connectors Function Page
J17 USB 2-14
J18 USB 2-14
J19 Printer Port 2-21
J20 COM 1 2-15
J21 COM 2 2-15
J32 ATX Power 2-9
J34 PS/2 KB and Mouse 2-14
JA1 UW SCSI 2-25
JA2 Ultra SCSI 2-24
JBT2 External Battery 2-16
JF1 IDE LED 2-12
Keylock 2-11
Speaker 2-12
JF2 IR Connector 2-10
PW_ON 2-10
Reset 2-11
JL1 Chassis Intrusion 1-14
JPA3 SCSI LED 2-13
JT1 CPU 1 Fan 2-17
JT2 CPU 2 Fan 2-17
JT3 Thermal/Overheat Fan 2-17
WOL Wake-on-LAN 2-17
viii
Page 9

Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE supports dual Pentium II 300/266/233 MHz
or higher processors. SUPER P6SLS/P6SLA supports single
Pentium II. They are based on Intel’s 440 LX chipset which enables
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP), Wake-on-LAN, SDRAM, concurrent PCI and Ultra DMA 33 MB/s burst data transfer rate.
All motherboards are ATX size and have 4 PCI slots, 3 ISA slots and
an AGP connector. SUPER P6DLS, P6DLE and P6SLS accommodate a total of 1 GB EDO or 512 MB SDRAM memory with 4 168-pin
DIMM sockets. SUPER P6SLA accommodates a total of 768 MB
EDO or 384 MB SDRAM memory with 3 168-pin DIMM sockets.
AGP reduces contention with the CPU and I/O devices by broadening the bandwidth of graphics to memory. It delivers a maximum of
532 MB/s 2x transfer mode which is quadruple the PCI speed!
Wake on LAN allows remote network management and configuration of the PC, even in off-hours when the PC is turned off. This
reduces the complexity of managing the network.
Other features that maximize customer satisfaction and simplicity in
managing the computer are PC 98-ready and support for Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI). With PC Health Monitoring, you can protect your system from problems before they even
occur.
Included I/O on all motherboards are 2 EIDE ports, a floppy port, an
ECP/EPP parallel port, PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard, 2 serial
ports, an infrared port and 2 USB ports. SUPER P6DLS and P6SLS
provide an on-board Adaptec 2940UW Ultra Wide SCSI controller
with fast data transfer rate of up to 40 MB/s.
1-1
Page 10

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
SUPER P6DLS
Figure 1-1. SUPER P6DLS Motherboard Picture
1-2
Page 11
Chapter 1: Introduction
SUPER P6DLE
Figure 1-2. SUPER P6DLE Motherboard Picture
1-3
Page 12

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
SUPER P6SLA
Figure 1-3. SUPER P6SLA Motherboard Picture
1-4
Page 13
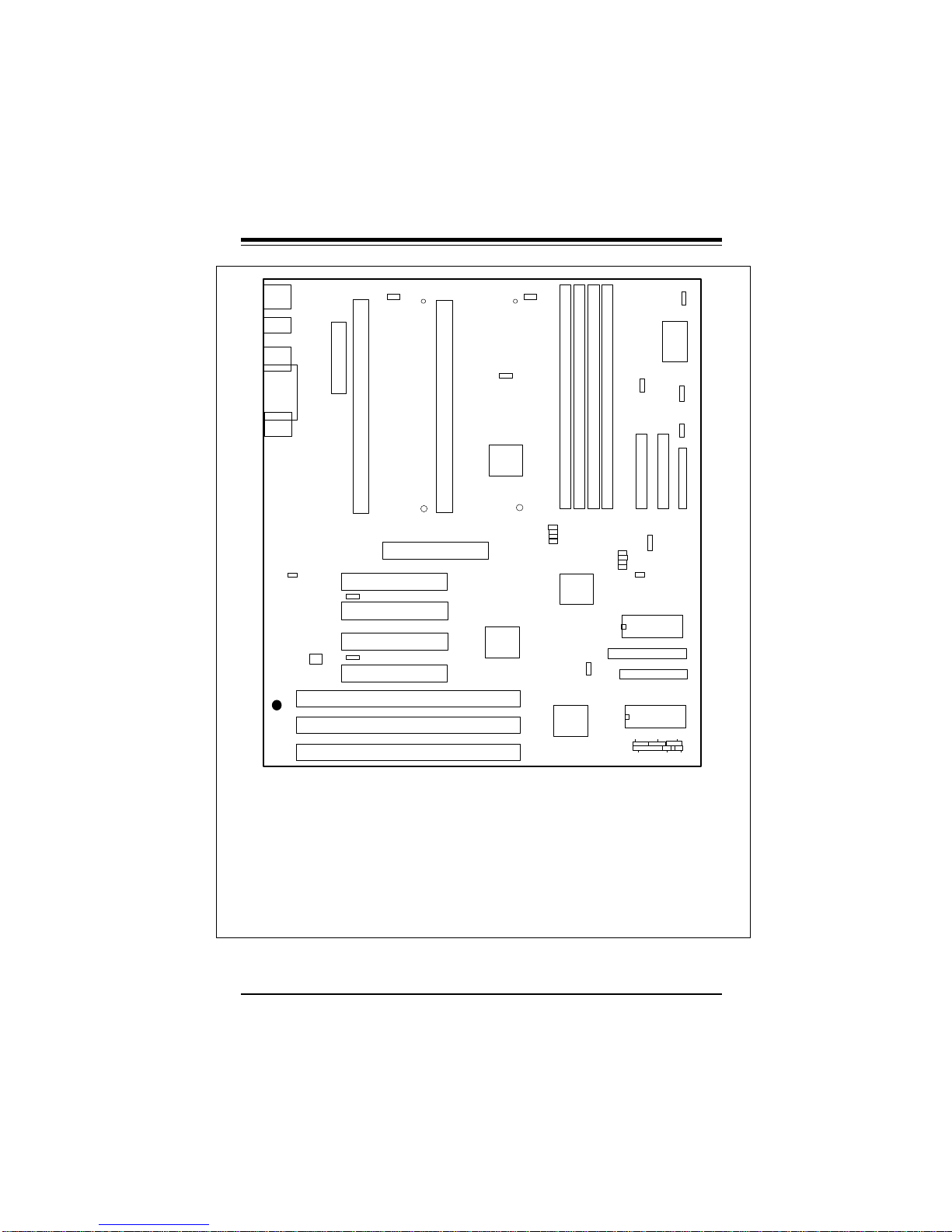
Chapter 1: Introduction
JL1
Chassis
Intrusion
®
J34
PS/2 KB
PS/2 MOUSE
J17, J18
USB
J21
COM2
J19
PRINTER
J20
COM1
U34
JJ14
J14
J13
J32
ATX POWER
1 JP19
1
JT1
J1
1
CPU 1
FAN
JL2
S UPER P6DLS
——–—— Manufacturer Settings ————
JC4: OFF
JL1: OFF (normal)
ON (intrusion)
JL2: OFF
JP17: 2-3
JP19: 1-2 APIC SMI (default)
2-3 PIIX4 SMI
JP20: 1-2 PIIX4 CTL
2-3 Save PD State (default)
JBT1: 1-2 (default)
2-3 CMOS Clear
To clear the CMOS completely,
disconnect the power source.
WOL: Wake-on-LAN
——–———————–———–——–——–—
AGP
J12
J11
J10
J2
J8
J9
JT2
1
CPU 2
FAN
JP17
1
Bank0
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
U9
JC1
JC2
JC3
JC4
JB1
JB2
JB3
UA7
JB4
U14
WOL
1
U27
IDE LED/KEYLOCK/SPEAKER
JF1
JF2
IR CON
—————Pentium II CPU Speed–————
MHz JB1 JB2 JB3 JB4
200 ON OFF ON ON
233 OFF OFF ON ON
266 ON ON OFF ON
300 OFF ON OFF ON
333 ON OFF OFF ON
366 OFF OFF OFF ON
400 ON ON ON OFF
——–—–————————————————
—————Bus Speed–————
MHz JC1 JC2 JC3
50 ON ON ON
60 ON OFF OFF
66 OFF OFF OFF
75 OFF ON OFF
——–—–——————————
Thermal
Control Fan
BATTERY
JBT1
1
CMOS
Clear
J15 J16
1 1
IDE 1
IDE 2
JPA3
1
JA4
Termination
UA5
JA2
ULTRA SCSI
JA1
UW SCSI
U29
BIOS
PW_ON
BT2
Ext Battery
SCSI
LED
SCSI
JT3
-
+
JBT2
1
JP20
1
J22
1
FLOPPY
RESET
1
1
Figure 1-4. SUPER P6DLS Motherboard Layout
1-5
Page 14
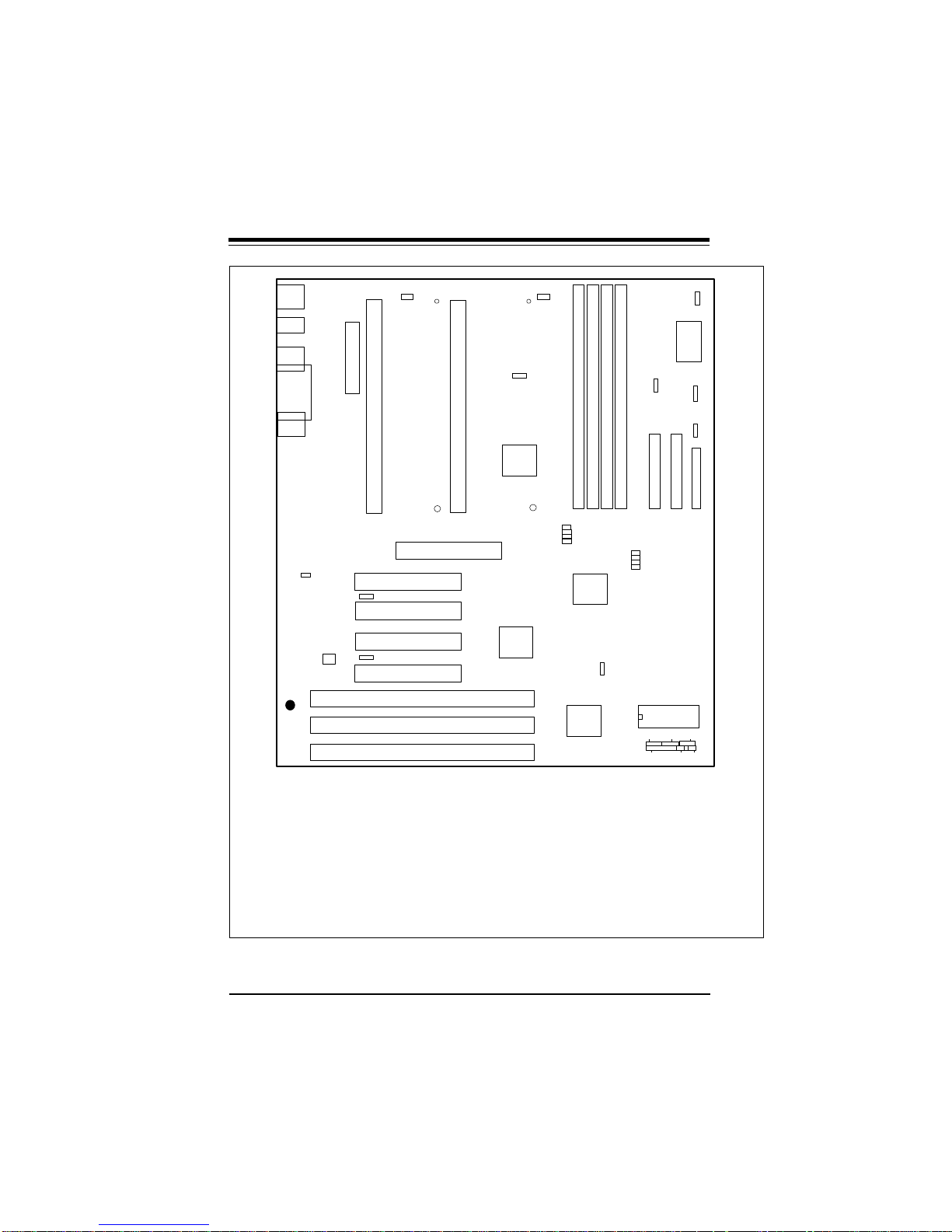
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
JL1
Chassis
Intrusion
®
J34
PS/2 KB
PS/2 MOUSE
J17, J18
USB
J21
COM2
J19
PRINTER
J20
COM1
U34
JJ14
J14
J13
J32
ATX POWER
1 JP19
1
JT1
J1
1
CPU 1
FAN
JL2
S UPER P6DLE
——–—— Manufacturer Settings ————
JC4: OFF
JL1: OFF (normal)
ON (intrusion)
JL2: OFF
JP17: 2-3
JP19: 1-2 APIC SMI (default)
2-3 PIIX4 SMI
JP20: 1-2 PIIX4 CTL
2-3 Save PD State (default)
JBT1: 1-2 (default)
2-3 CMOS Clear
To clear the CMOS completely,
disconnect the power source.
WOL: Wake-on-LAN
——–———————–———–——–——–—
AGP
J12
J11
J10
J2
J8
J9
JT2
1
CPU 2
FAN
JP17
1
Bank0
Bank3
Bank2
Bank1
U9
JC1
JC2
JC3
JC4
JB1
JB2
JB3
UA7
JB4
U14
WOL
1
U27
IDE LED/KEYLOCK/SPEAKER
JF1
JF2
IR CON
—————Pentium II CPU Speed–————
MHz JB1 JB2 JB3 JB4
200 ON OFF ON ON
233 OFF OFF ON ON
266 ON ON OFF ON
300 OFF ON OFF ON
333 ON OFF OFF ON
366 OFF OFF OFF ON
400 ON ON ON OFF
——–—–————————————————
—————Bus Speed–————
MHz JC1 JC2 JC3
50 ON ON ON
60 ON OFF OFF
66 OFF OFF OFF
75 OFF ON OFF
——–—–——————————
Control Fan
BATTERY
JBT1
1
CMOS
Clear
J15 J16
1 1
IDE 1
U29
Thermal
IDE 2
BIOS
PW_ON
JT3
-
BT2
+
JBT2
1
Ext Battery
JP20
1
J22
1
FLOPPY
RESET
Figure 1-5. SUPER P6DLE Motherboard Layout
1-6
Page 15

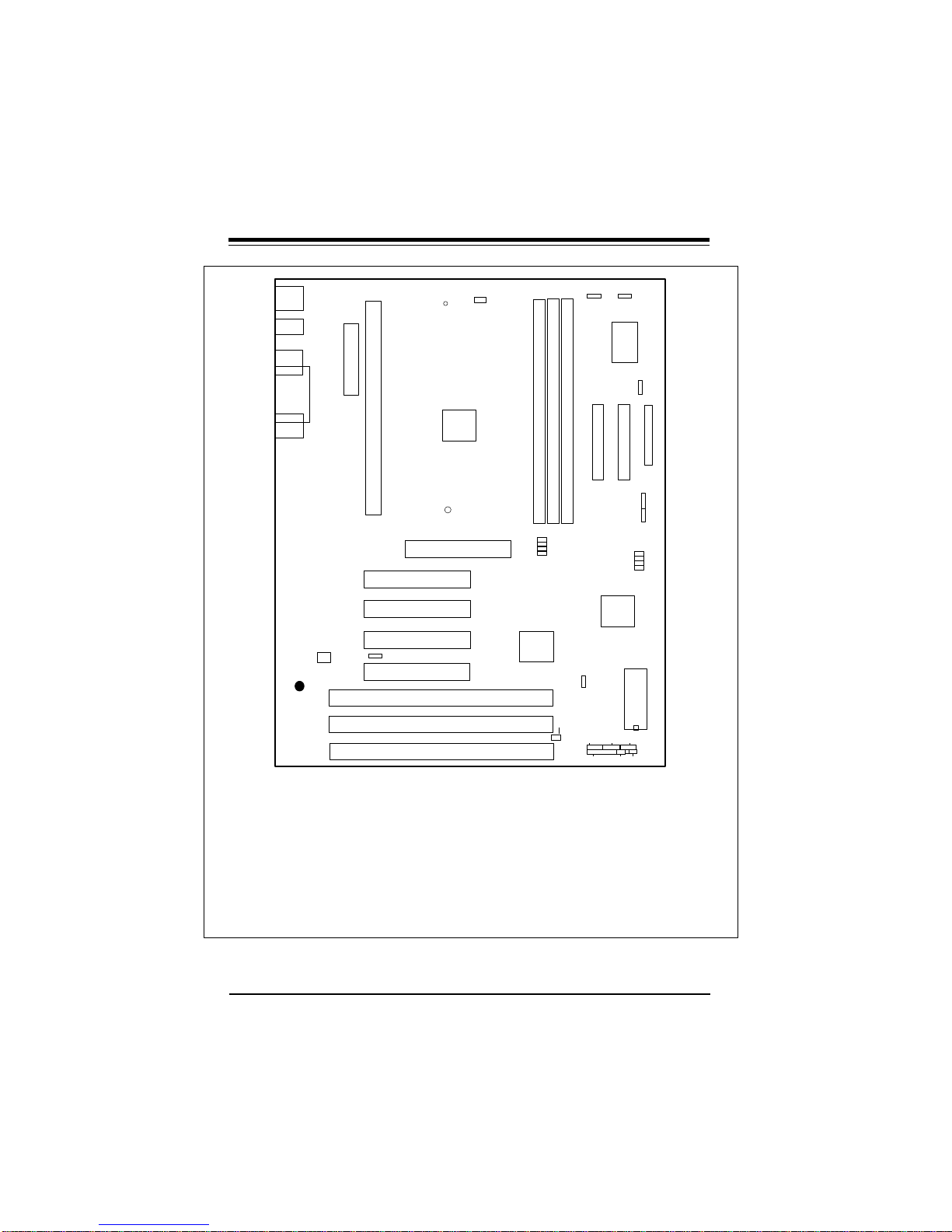
Chapter 1: Introduction
JL1
Chassis
Intrusion
®
J34
PS/2 KB
PS/2 MOUSE
J17, J18
USB
J21
COM2
J19
PRINTER
J20
COM1
U34
JJ14
J14
J13
J32
ATX POWER
1 JP19
1
JT1
J1
1
CPU 1
FAN
JL2
S UPER P6SLS
——–—— Manufacturer Settings ————
JC4: OFF
JL1: OFF (normal)
ON (intrusion)
JL2: OFF
JP17: 2-3
JP19: 1-2 APIC SMI (default)
2-3 PIIX4 SMI
JP20: 1-2 PIIX4 CTL
2-3 Save PD State (default)
JBT1: 1-2 (default)
2-3 CMOS Clear
To clear the CMOS completely,
disconnect the power source.
WOL: Wake-on-LAN
——–———————–———–——–——–—
AGP
J12
J11
J10
J9
J2
JT2
J2 is for
termination
J8
1
CPU 2
FAN
JP17
1
Bank3
U9
JC1
JC2
JC3
JC4
UA7
U14
U27
—————Pentium II CPU Speed–————
MHz JB1 JB2 JB3 JB4
200 ON OFF ON ON
233 OFF OFF ON ON
266 ON ON OFF ON
300 OFF ON OFF ON
333 ON OFF OFF ON
366 OFF OFF OFF ON
400 ON ON ON OFF
——–—–————————————————
—————Bus Speed–————
MHz JC1 JC2 JC3
50 ON ON ON
60 ON OFF OFF
66 OFF OFF OFF
75 OFF ON OFF
——–—–——————————
Bank2
WOL
Bank1
1
JB1
JB2
JB3
JB4
Bank0
JT3
Thermal
Control Fan
-
BT2
BATTERY
+
JBT1
1
JBT2
1
CMOS
Clear
Ext Battery
JP20
J15 J16
1
1 1
J22
1
FLOPPY
IDE 1
IDE 2
JPA3
SCSI
LED
1
SCSI
JA4
Termination
UA5
JA2
ULTRA SCSI
JA1
UW SCSI
U29
BIOS
IDE LED/KEYLOCK/SPEAKER
JF1
JF2
PW_ON
IR CON
RESET
1
1
Figure 1-6. SUPER P6SLS Motherboard Layout
1-7
Page 16
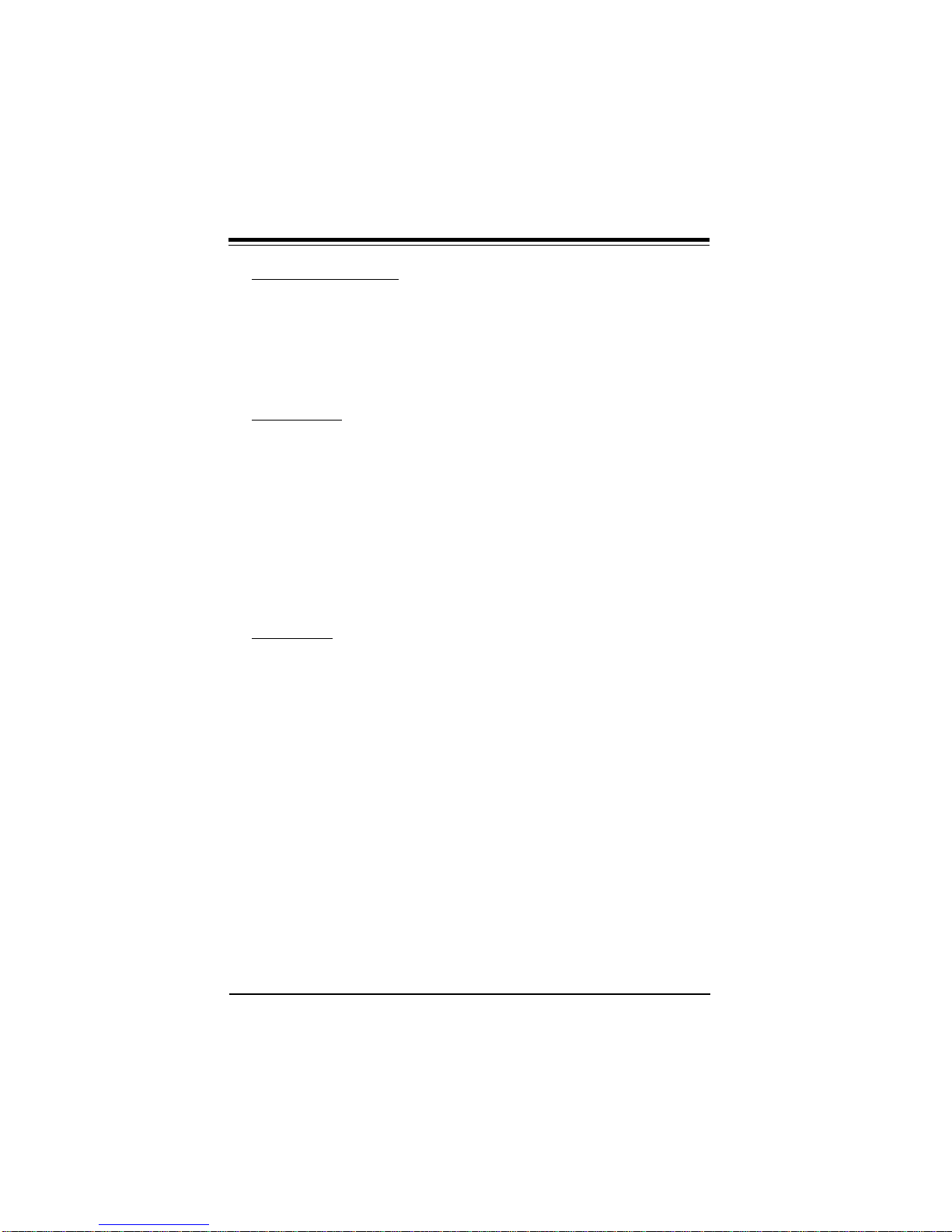
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
J34
PS/2 KB
PS/2 MOUSE
J17, J18
USB
J21
COM2
J19
PRINTER
J20
COM1
J1
J32
ATX POWER
JT1
1
CPU
FAN
U9
Bank2
Bank1
Bank0
JT2
BATTERY
J15 J16
1
JT3
Overheat
Fan
-
BT2
+
JP20
1
J22
1
1
U34
®
S UPER P6SLA
——–—— Manufacturer Settings ————
JC4: OFF
JL1: OFF (normal)
ON (intrusion)
JL2: OFF
JP20: 1-2 PIIX4 CTL
2-3 Save PD State (default)
JBT1: 1-2 (default)
2-3 CMOS Clear
To clear the CMOS completely,
disconnect the power source.
WOL: Wake-on-LAN
JT1: CPU1 fan
JT2: CPU2 fan
JT3: Overheat fan
——–———————–———–——–——–—
JJ14
J14
J13
1
JL2
J8
JC1
U14
JC2
JC3
JC4
JL1
WOL
Chassis Intrusion
IDE LED/KEYLOCK/SPEAKER
JF1
JF2
AGP
J12
J11
J10
J9
—————Pentium II CPU Speed–————
MHz JB1 JB2 JB3 JB4
200 ON OFF ON ON
233 OFF OFF ON ON
266 ON ON OFF ON
300 OFF ON OFF ON
333 ON OFF OFF ON
366 OFF OFF OFF ON
400 ON ON ON OFF
——–—–————————————————
—————Bus Speed–————
MHz JC1 JC2 JC3
50 ON ON ON
60 ON OFF OFF
66 OFF OFF OFF
75 OFF ON OFF
——–—–——————————
IR CON
IDE 1
CMOS Clear
1
FLOPPY
IDE 2
Ext Battery
1
1
JB1
JB2
JB3
JB4
U27
U29
BIOS
PW_ON RESET
JBT2
JBT1
Figure 1-7. SUPER P6SLA Motherboard Layout
1-8
Page 17

Chapter 1: Introduction
SUPER P6DLS Features
The following list covers the general features of SUPER P6DLS:
CPU
• Dual Pentium II processor 233/266/300 MHz or higher
Memory
• 1 GB EDO or 512 MB SDRAM
• Error Checking and Correction and Parity Checking support
Chipset
• Intel 440LX
Expansion Slots
• 4 PCI slots
• 3 ISA slots
• 1 AGP slot
BIOS
• AMI® Flash BIOS with boot block support
• DMI 2.0, Plug and Play (PnP)
PC Health Monitoring (LM78)
• Seven on-board voltage monitors for 2 CPU cores, +3.3V, ±5V,
and ±12V
• Three fans status monitors with firmware/software control on/off
• CPU/chassis temperature monitor and control
• CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
• CPU overheat control and alarm
• Chassis intrusion detection
• System resource alert
• Hardware BIOS virus protection
• Switching voltage regulator for the CPU core
• SUPERMICRO SUPER Doctor and Intel LANDesk® Client
Manager (LDCM) support
1-9
Page 18
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
ACPI/PC 98 Features
• Microsoft OnNow
• Slow blinking LED for sleep-state indicator
• BIOS support for USB keyboard
• Real time clock wake-up alarm
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on if system is in SoftOff state
On-Board I/O
• 68-pin 16-bit Ultra-Wide SCSI connector and
50-pin 8-bit Ultra SCSI connector
• 2 EIDE Bus Master interfaces support Ultra DMA/33 and Mode 4
• 1 floppy interface
• 2 Fast UART 16550 serial ports
• EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and ECP (Extended Capabilities
Port) parallel port
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard
• Infrared port
• 2 USB ports
Dimensions
• ATX (12" x 10.85")
1-10
Page 19

Chapter 1: Introduction
SUPER P6DLE Features
The following list covers the general features of SUPER P6DLE:
CPU
• Dual Pentium II processor 233/266/300 MHz or higher
Memory
• 1 GB EDO or 512 MB SDRAM
• Error Checking and Correction and Parity Checking support
Chipset
• Intel 440LX
Expansion Slots
• 4 PCI slots
• 3 ISA slots
• 1 AGP slot
BIOS
• AMI® Flash BIOS with boot block support
• DMI 2.0, Plug and Play (PnP)
PC Health Monitoring (LM78)
• Seven on-board voltage monitors for 2 CPU cores, +3.3V, ±5V,
and ±12V
• Three fans status monitors with firmware/software control on/off
• CPU/chassis temperature monitor and control
• CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
• CPU overheat control and alarm
• Chassis intrusion detection
• System resource alert
• Hardware BIOS virus protection
• Switching voltage regulator for the CPU core
• SUPERMICRO SUPER Doctor and Intel LANDesk® Client
Manager (LDCM) support
1-11
Page 20
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
ACPI/PC 98 Features
• Microsoft OnNow
• Slow blinking LED for sleep-state indicator
• BIOS support for USB keyboard
• Real time clock wake-up alarm
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on if system is in SoftOff state
On-Board I/O
• 2 EIDE Bus Master interfaces support Ultra DMA/33 and Mode 4
• 1 floppy interface
• 2 Fast UART 16550 serial ports
• EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and ECP (Extended Capabilities
Port) parallel port
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard
• Infrared port
• 2 USB ports
Dimensions
• ATX (12" x 10.85")
1-12
Page 21

Chapter 1: Introduction
SUPER P6SLS Features
The following list covers the general features of SUPER P6SLS:
CPU
• Single Pentium II processor 233/266/300 MHz or higher
Memory
• 1 GB EDO or 512 MB SDRAM
• Error Checking and Correction and Parity Checking support
Chipset
• Intel 440LX
Expansion Slots
• 4 PCI slots
• 3 ISA slots
• 1 AGP slot
BIOS
• AMI® Flash BIOS with boot block support
• DMI 2.0, Plug and Play (PnP)
PC Health Monitoring (LM78)
• Seven on-board voltage monitors for the CPU core, CPU I/O,
+3.3V, ±5V, and ±12V
• Three fans status monitors with firmware/software control on/off
• CPU/chassis temperature monitor and control
• CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
• CPU overheat control and alarm
• Chassis intrusion detection
• System resource alert
• Hardware BIOS virus protection
• Switching voltage regulator for the CPU core
• SUPERMICRO SUPER Doctor and Intel LANDesk® Client
Manager (LDCM) support
1-13
Page 22

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
ACPI/PC 98 Features
• Microsoft OnNow
• Slow blinking LED for sleep-state indicator
• BIOS support for USB keyboard
• Real time clock wake-up alarm
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on if system is in SoftOff state
On-Board I/O
• 68-pin 16-bit Ultra-Wide SCSI connector and
50-pin 8-bit Ultra SCSI connector
• 2 EIDE Bus Master interfaces support Ultra DMA/33 and Mode 4
• 1 floppy interface
• 2 Fast UART 16550 serial ports
• EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and ECP (Extended Capabilities
Port) parallel port
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard
• Infrared port
• 2 USB ports
Dimensions
• ATX (12" x 10.85")
1-14
Page 23

Chapter 1: Introduction
SUPER P6SLA Features
The following list covers the general features of SUPER P6SLA:
CPU
• Single Pentium II processor 233/266/300 MHz or higher
Memory
• 768 MB EDO or 384 MB SDRAM
• Error Checking and Correction and Parity Checking support
Chipset
• Intel 440LX
Expansion Slots
• 4 PCI slots
• 3 ISA slots
• 1 AGP slot
BIOS
• AMI® Flash BIOS with boot block support
• DMI 2.0, Plug and Play (PnP)
PC Health Monitoring (LM78)
• Seven on-board voltage monitors for the CPU core, CPU I/O,
+3.3V, ±5V, and ±12V
• Three fans status monitors with firmware/software control on/off
• CPU/chassis temperature monitor and control
• CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
• CPU overheat control and alarm
• Chassis intrusion detection
• System resource alert
• Hardware BIOS virus protection
• Switching voltage regulator for the CPU core
• SUPERMICRO SUPER Doctor and Intel LANDesk® Client
Manager (LDCM) support
1-15
Page 24

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
ACPI/PC 98 Features
• Microsoft OnNow
• Slow blinking LED for sleep-state indicator
• BIOS support for USB keyboard
• Real time clock wake-up alarm
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on if system is in SoftOff state
On-Board I/O
• 2 EIDE Bus Master interfaces support Ultra DMA/33 and Mode 4
• 1 floppy interface
• 2 Fast UART 16550 serial ports
• EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and ECP (Extended Capabilities
Port) parallel port
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard
• Infrared port
• 2 USB ports
Dimensions
• ATX (12" x 8.2")
1-16
Page 25

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-2 PC Health Monitoring
This section describes the PC health monitoring features of SUPER
P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA. They have an on-board LM78 System Hardware Monitor chip which can support PC health monitoring.
Seven On-Board Voltage Monitors for the CPU Core/s,
CPU I/O, +3.3V, ±±5V, and ±±12V
The on-board voltage monitor will scan the seven monitored voltages every second. Once a voltage becomes unstable, it will report
a warning or an error message on the screen. Users can adjust
the threshold of the monitored voltage to determine the sensitivity of
the voltage monitor.
Three-Fan Status Monitors with Firmware/Software
Control On/Off
The PC health monitor can check the RPM status of the cooling
fans. The on-board 3-pin CPU fan is controlled by the ACPI BIOS
and the ACPI enabled operating system. The thermal fans are controlled by the overheat detection logic.
CPU/Chassis Temperature Control
The thermal control sensor will monitor the real-time CPU temperature. It will turn on the back-up fan whenever the CPU temperature
goes over the user-defined threshold. The overheat circuitry runs
independently from the CPU. It can still monitor the overheat condition even if the CPU is in sleep mode. Once it detects that the CPU
temperature is too high, it will automatically turn on the back-up fan
to prevent any overheat damage to the CPU. The on-board chassis
thermal circuitry can monitor the overall system temperature and
alert users when the chassis temperature is too high.
1-17
Page 26

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
CPU Fan Auto-Off in Sleep Mode
The CPU fan will turn on when the power is on. It can be turned off
when the CPU is in sleep mode. When the CPU is in sleep mode,
it means that it will not run at full power, thereby generating less
heat. For power saving purposes, the user can have the option to
shut down the CPU fan.
CPU Overheat Alarm and Control
This feature is available when used with SUPERMICRO's SUPER
Doctor Utility. The program will generate a beep sound via the
speaker when it detects CPU overheat condition. This overheat
condition can be configured by the user. The program can also give
an indication on the screen when the CPU overheats.
Chassis Intrusion Detection
The chassis intrusion circuitry can detect unauthorized intrusion to
the system. The chassis intrusion connector is located on JL1.
Attach a micro-switch to JL1. When the micro-switch is close, it
means that the chassis has been opened. The circuitry will then
alert the user with a warning message when the system is turned
on. The circuitry uses the on-board battery to power up. Even if the
whole system is powered off, the detection can still work properly.
System Resource Alert
This feature is available when used with Intel LANDesk Client Manager. The user can be notified of certain system events. For example, if the system is running low on virtual memory, the hard
drive space is not enough to save the data, you are then alerted of
the potential problems.
1-18
Page 27

Chapter 1: Introduction
Hardware BIOS Virus Protection
The system BIOS is protected by hardware so that no virus can
infect the BIOS area. The user can only change the BIOS content
through the flash utility provided by SUPERMICRO. This feature can
prevent viruses from infecting the BIOS area and from losing your
valuable data.
Switching Voltage Regulator for the CPU Core
The switching voltage regulator for the CPU core can support up to
20A current, with auto-sensing voltage ID ranging from 2.1V to 3.5V.
This will allow the regulator to run cooler and make the system
more stable.
Intel LANDesk® Client Manager (LDCM) Support
As the computer industry grows, PC systems have become more
complex and harder to manage. Historically, only experts have
been able to fully understand and control these complex systems.
Today's users want manageable systems that interact automatically
with the user. Client Manager enables both administrators and clients to:
• Review system inventory
• View DMI-compliant component information
• Back-up and restore system configuration files
• Troubleshoot
• Receive notification for system events
• Transfer files to and from client workstations
• Remotely reboot client workstations
1-19
Page 28

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
1-3 ACPI/PC 98 Features
ACPI stands for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface. The
ACPI specification defines a flexible and abstract hardware interface that provides a standard way to integrate power management
features throughout a PC system, including hardware, operating
system and application software. This enables the system to automatically turn on and off peripherals such as CD-ROMs, network
cards, hard disk drives, and printers. This also includes consumer
devices connected to the PC such as VCRs, TVs, phones, and stereos.
In addition to enabling operating system-directed power management, ACPI provides a generic system event mechanism for Plug
and Play and an operating system-independent interface for configuration control. ACPI leverages the Plug and Play BIOS data
structures while providing a processor architecture-independent
implementation that is compatible with both Windows 95 and Windows NT.
Microsoft OnNow
The OnNow design initiative is a comprehensive, system-wide approach to system and device power control. OnNow is a term for a
PC that is always on but appears off and responds immediately to
user or other requests.
Slow Blinking LED for Sleep-state Indicator
When the CPU goes into a sleep state, the power LED will start
blinking to indicate that the CPU is in sleep mode. When the user
presses any key, the CPU will wake-up and the LED will automatically stop blinking and remain on.
1-20
Page 29

Chapter 1: Introduction
BIOS Support for USB Keyboard
If the USB keyboard is the only keyboard in the system, the USB
keyboard will work like a normal keyboard during system boot-up.
Real Time Clock Wake-up Alarm (ATX power only)
The PC is perceived to be off when not in use, but is still capable of
responding to wake-up events due to a scheduled date and time of
the month. The user can set up a timer to wake-up or shutdown the
system at some predetermined time.
Main Switch Override Mechanism
When an ATX power supply is used, the power button can function
as a system suspend button. When the user press on the power
button, the system will enter a SoftOff state. The monitor will be
suspended, and the hard drive will spin down. Pressing the power
button again will cause the whole system to wake-up. During the
SoftOff state, the ATX power supply provides power to keep the required circuitry on the system alive. In case the system malfunctions and you want to turn off the power, just press down on the
power button for 4 seconds. The power will turn off and no power is
provided to the motherboard.
External Modem Ring-on if System is in SoftOff State
Wake-up events can be triggered by a device such as the external
modem ringing when the system is in SoftOff state.
1-21
Page 30

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
1-4 Chipset Overview
The 440LX chipset is developed by Intel as the ultimate Pentium II
processor platform targeted for emerging 3D graphics and multimedia applications. Along with System-to-PCI bridge integrated
with optimized DRAM controller and data path, the chipset introduces the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) interface. AGP is a high
performance, component level interconnect targeted at 3D applications and is based on a set of performance enhancements to PCI.
The I/O subsystem portion of the 440LX platform is based on the
PIIX4, a highly integrated version of Intel's PCI-to-ISA bridge family.
The 440LX PCI/AGP Controller (PAC) system bus interface supports
up to two Pentium II processors. It provides an optimized 72-bit
DRAM interface (64-bit data plus ECC). This interface supports
3.3V DRAM technologies. The PAC provides the interface to a PCI
bus operating at 33 MHz. This interface implementation is compliant with the PCI Rev 2.1 Specification. The AGP interface is based
on the AGP Specification Rev 1.0. It can support up to 133 MHz
(532 MB/s) data transfer rates.
1-5 Wake-On-LAN (WOL)
Wake on LAN is defined as the ability of a management application
to remotely power up a computer which is powered off. Remote PC
setup, updates, and asset tracking can occur after hours and on
weekends so daily LAN traffic is kept to a minimum and users are
not interrupted.
The motherboards have a 3-pin header (WOL) used to connect to
the 3-pin header on the Network Interface Card (NIC) which has
WOL capability.
1-6 Power Supply
As with all computer products, a stable power source is necessary
for proper and reliable operation. It is even more important for high
1-22
Page 31

Chapter 1: Introduction
CPU clock rates like 300, 266, 233 MHz Pentium II processors.
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA accommodates ATX power
supplies. Although most power supplies generally meet the specifications required by the CPU, some power supplies are not adequate.
It is highly recommended that you use a high quality power supply.
Additionally, in areas where noisy power transmission is present,
you may choose to install a line filter to separate noise from the
computer. You can also install a power surge protector to help
avoid problems caused by power surges.
1-7 National Semiconductor Super I/O Controller
The National Semiconductor 87307 Super I/O Controller incorporates an IDE control logic, two full function serial ports, an IEEE
1284 parallel port, industry standard floppy disk controller with 16
byte FIFO, Real Time Clock and an 8042 compatible keyboard controller all in one chip.
The IDE interfaces provide up to Mode 4 support. The two serial
ports are software compatible with the Fast UART 16550. The parallel port is EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) and ECP (Extended Capabilities Port) compatible, including level 2 support. It includes a
protection circuit against damage caused when the printer is powered up. EPP mode provides for greater throughput than Compatible or Extended modes by supporting faster transfer rates and a
mechanism that allows the host to address peripheral device registers directly. Faster transfers are achieved by automatically generating the address and data strobes. EPP is compatible with both
Compatible and Extended mode parallel-port devices.
1-8 AIC 7880 SCSI Controller
SUPER P6DLS/P6SLS has an on-board SCSI controller which is
100% compatible with an Adaptec 2940UW. Connectors include a
68-pin 16-bit SCSI connector (JA1) and a 50-pin 8-bit internal SCSI
1-23
Page 32

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
connector (JA2). You can connect up to 15 devices (seven 8-bit
internal and eight 16-bit internal or external SCSI devices, or 15
Wide internal and external SCSI devices).
When Fast SCSI devices are connected, the total length of all
cables (internal and external) must not exceed 3 meters (9.8 ft) to
ensure reliable operation. If no Fast SCSI devices are connected,
the total length of all cables must not exceed 6 meters (19.7 ft).
1-9 Warranty, Technical Support, and Service
The manufacturer will repair or exchange any unit or parts free of
charge due to manufacturing defects for one year (12 months) from
the original invoice date of purchase.
Parts
Defective parts will be exchanged or repaired within one year (12
months) from the manufacturer’s original invoice purchase date.
BIOS
The manufacturer will exchange the BIOS (shipping and handling
excluded) due to existing incompatibility issues within one year
from the manufacturer’s original invoice purchase date.
Labor
Mail-in or carry-in service is available for one year (12 months) from
the manufacturer’s original invoice purchase date.
Returns
If you must return products for any reason, refer to Chapter 3 in this
manual, “Returning Merchandise for Service.”
1-24
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installation
Chapter 2
Installation
2-1 Pentium II Processor Installation
1. Check the Intel boxed processor kit for the following items: the
processor with the fan heatsink attached, two black plastic pegs,
two black plastic supports, and one power cable.
2. Install the retention mechanism attach mount under the
motherboard. Do this before mounting the motherboard into the
chassis. Do not screw too tight. Mount the two black plastic pegs
onto the motherboard (Figure 2.1). These pegs will be used to
attach the fan heatsink supports. Notice that one hole and the base
of one peg are larger than the other hole and peg base. Push each
peg into its hole firmly until you hear it "click" into place.
Figure 2-1. Mounting the Pegs
Retention
Mechanism
Large peg and hole
2-1
Page 34

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
3. Slide a black plastic support onto each end of the fan heatsink,
making sure that the hole and clip are on the outside edge of the
support. If the supports are reversed, the holes will not line up with
the pegs on the motherboard. Slide each support toward the center
of the processor until the support is seated in the outside groove in
the fan housing.
Figure 2-2. Support for Fan Heatsink
Top of processor
Groove in fan housing
Hole and clip on outside edge
2-2
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installation
4. Slid the clip (A) on each support toward the processor, exposing
the hole that will fit over the peg on the motherboard. Push the
latches (B) on the processor toward the center of the processor
until they click into place.
5. Hold the processor so that the fan shroud is facing toward the
pegs on the motherboard. Slide the processor (C) into the retention mechanism and slide the supports onto the pegs. Ensure that
the pegs on the motherboard slide into the holes in the heatsink
support and that the alignment notch in the SEC cartridge fits over
the plug in Slot 1. Push the processor down firmly, with even pressure on both sides of the top, until it is seated.
Figure 2-3. Retention Mechanism
B
C
A
Do not screw too tight!
2-3
Page 36

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
6. Slide the clips on the supports (A) forward until they click into
place to hold the pegs securely. Apply slight pressure on the peg
and push the peg toward the clip while pushing the clip forward.
Push the latches on the processor (B) outward until they click into
place in the retention mechanism. The latches must be secured for
proper electrical connection of the processor.
7. Attach the small end of the power cable (C) to the three-pin con-
nector on the processor, then attach the large end to the three-pin
connector on the motherboard.
Figure 2-4. Attaching the Power Cable
B
C
A
2-4
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installation
OEM Pentium II and Heat Sink Support
The heat sink support shown on Figure 2-5 consists of a top bar, a
base bar, four posts on the top bar and two posts on the base bar.
The two posts on the base snaps into the motherboard. Install the
two pins into the base bar. Insert the Pentium II with the heat sink
on it into Slot 1. Install the top support bar. The four top posts
should be close to Slot 1. The bottommost row of fins in the heat
sink should fit between the top support bar and the bottom support
bar as shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-5. Heat Sink Support
Figure 2-6. Pentium II Heat Sink
2-5
Heat Sink
Page 38

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Removing the Pentium II Processor
To remove the Pentium II processor from the motherboard, follow
these steps (the reverse of the installation process).
1. Disconnect the fan power cable from the motherboard. It is rec-
ommended to leave the cable connected to the processor.
2. Slide the clips on the supports backward to release the pegs in
the motherboard. Push the latches on the processor toward the
center of the processor until they click into place.
3. Lift one end of the processor until it is freed from Slot 1. Lift the
other end of the processor until it is freed from Slot 1. Lift the entire
processor (with the fan heatsink supports attached) until it is free
from the retention mechanism.
4. Remove the heatsink support pegs from the motherboard and
discard them. With one hand, squeeze together the two halves of
the peg on the bottom side of the motherboard. With the other
hand, pull the peg out of the hole in the motherboard. Do not reuse
the pegs.
When handling the Pentium II processor, avoid
placing direct pressure on the label area of the fan.
When removing the Pentium II processor, avoid pressing
down on the motherboard or components. Instead,
press down on the plastic connectors.
2-2 Static-Sensitive Devices
Static-sensitive electric discharge can damage electronic components. To prevent damage to your system board, it is important
to handle it very carefully. The following measures are generally
sufficient to protect your equipment from static discharge.
2-6
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installation
Precautions
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed for static discharge.
• Touch a grounded metal object before you remove the board
from the anti-static bag.
• Handle the board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral chips, memory modules, or gold contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the system board and peripherals back into their anti-static
bags when not in use.
• Be sure your computer system’s chassis allows excellent
conductive contacts between its power supply, case, mounting
fasteners, and the system board for grounding purposes.
Unpacking
The system board is shipped in anti-static packaging to avoid static
damage. When unpacking the board, be sure the person handling
the board is static-protected.
2-7
Page 40

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
2-3 Changing the CPU Speed
To change the CPU speed for a Pentium II processor, change the
jumpers shown below on Table 2-1. Refer to Table 2-2 for the
external bus speed jumper settings. The default bus speed is 66
MHz.
Table 2-1. Pentium II Speed Selection
MHz JB1 JB2 JB3 JB4
200 ON OFF ON ON
233 OFF OFF ON ON
266 ON ON OFF ON
300 OFF ON OFF ON
333 ON OFF OFF ON
366 OFF OFF OFF ON
400 ON ON ON OFF
Table 2-2. External Bus Speed Selection
MHz JC1 JC2 JC3
50 ON ON ON
60 ON OFF OFF
66 OFF OFF OFF
75 OFF ON OFF
Turbo Function
There are no jumpers for turbo switch and turbo LED. By default, all
the motherboards are in turbo mode.
2-8
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installation
2-4 Mounting the Motherboard in the Chassis
All the motherboards have standard mounting holes to fit different
types of chassis. Chassis may come with a variety of mounting
fasteners, made of metal or plastic. Although a chassis may have
both metal and plastic fasteners, metal fasteners are the most
highly recommended because they ground the system board to the
chassis. Therefore, use as many metal fasteners as possible for
better grounding.
2-5 Connecting Cables
Power Supply Connector
After you have securely mounted the motherboard to the chassis,
you are ready to connect the cables. Attach power supply cables to
J32 for an ATX power supply. See Table 2-3 for pin definitions of an
ATX power supply.
Table 2-3. ATX Power Supply Connector Pin Definitions
Connector Pin Pin
Number Number Function Number Function
J32 1 3.3V 11 3.3V
2 3.3V 12 -12V
3 COM 13 COM
4 5V 14 PS-ON
5 COM 15 COM
6 5V 16 COM
7 COM 17 COM
8 PW-OK 18 -5V
9 5VSB 19 5V
10 12V 20 5V
2-9
Page 42

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
PW_ON Connector
The PW_ON connector is located on pins 9 and 10 of JF2. Momentary contacting both pins will power on/off the system. To turn off
the power, hold down the power button for at least 4 seconds. See
Table 2-4 for pin definitions.
Table 2-4. PW_ON Connector Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Definition
9 PW_ON
10 Ground
Infrared Connector
The infrared connector is located on pins 1-8 of JF2. See Table 25 for pin definitions.
Table 2-5. Infrared Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Definition
1 +5V
2 Key
3 IRRX
4 Ground
5 IRTX
6 IRSEL0
7 IRSEL1
8 IRSEL2
2-10
Page 43

Chapter 2: Installation
Reset Connector
The reset connector is located on pins 12 and 13 of JF2. This
connector attaches to the hardware Reset switch on the computer
case. See Table 2-6 for pin definitions.
Table 2-6. Reset Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Definition
12 Reset
13 Ground
Keylock/Power LED Connector
The keylock/power LED connector is located on pins 5 to 9 of JF1.
See Table 2-7 for pin definitions. Pins 5 and 7 are for the power
LED. Pins 8 and 9 are for the keylock.
Table 2-7. Keylock/Power LED Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function Definition
5 + Red wire, LED power
6 Key No connection
7 GND Black wire
8 Keyboard inhibit
9 GND Black wire
2-11
Page 44

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Hard Drive LED
The hard drive LED is located on pins 1 to 4 of JF1. Attach the hard
drive LED cable onto pins 1 and 2. See Table 2-8 for pin definitions.
Table 2-8. Hard Drive LED Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Definition
1 +5V
2 Key
3 HD Active
4 +5V
Speaker Connector
The speaker connector is located on pins 10 to 13 of JF1. See
Table 2-9 for pin definitions.
Table 2-9. Speaker Connector Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function Definition
10 + Red wire, speaker data
11 Key No connection
12 VCC Speaker data
13 GND Black wire
2-12
Page 45

Chapter 2: Installation
SCSI LED
The SCSI LED JPA3 has four pins. See Table 2-10 for pin definitions.
Table 2-10. SCSI LED Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function
1 +5V
2 Control
3 Control
4 +5V
Power On/Off State
Refer to Table 2-11 on how to set JP20. Save Power Down (PD)
State is the default and is used when you want the system to be in
power off state the first time you apply power to the system or when
the system comes back from AC power failure. PIIX4 control is
used if you want the system to be in power on state the first time
you apply power to the system or when the system comes back
from AC power failure.
Table 2-11. JP20 Pin Definitions
Connector Jumper
Number Position Function
JP20 1-2 PIIX4 Ctrl
2-3 Save PD State
2-13
Page 46

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
ATX PS/2 Keyboard and PS/2 Mouse Ports
The ATX PS/2 keyboard and the PS/2 mouse are located on J34.
See Table 2-12 for pin definitions.
Table 2-12. PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function
1 Data
2 NC
3 Ground
4 VCC
5 Clock
6 NC
Universal Serial Bus
The Universal Serial Bus is located on J17 and J18. See Table 213 for pin definitions.
Table 2-13. USB Pin Definitions
Pin J17 Pin J18
Number Function Number Function
1 +5V 1 +5V
2 P0- 2 P0 3 P0+ 3 P0+
4 GND 4 GND
5 N/A 5 Key
2-14
Page 47

Chapter 2: Installation
ATX Serial Ports
ATX serial port COM1 is located on J20 and serial port COM2 is
located on J21. See Table 2-14 for pin definitions.
Table 2-14. Serial Ports Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 DCD 6 CTS
2 DSR 7 DTR
3 Serial In 8 RI
4 RTS 9 GND
5 Serial Out 10 NC
SMI
Refer to Table 2-15 for instructions on how to use JP19 for SUPER
P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS. This jumper should normally be set to 1-2
APIC SMI.
Table 2-15. SMI Pin Definitions
Connector Jumper
Number Position Function
JP19 1-2 APIC SMI
2-3 PIIX4 SMI
2-15
Page 48

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
CMOS Clear
Refer to Table 2-16 for instructions on how to clear the CMOS. For
ATX power supply, you need to completely shut down the system,
then use JBT1 to clear the CMOS. Do not use the PW_ON connec-
tor to clear the CMOS.
Table 2-16. CMOS Clear Pin Definitions
Connector Jumper
Number Position Function
JBT1 1-2 Normal
2-3 CMOS Clear
External Battery
Connect an external battery to JBT2. Refer to Table 2-17 for pin
definitions.
Table 2-17. External Battery Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function
1 +3 V
2 NC
3 NC
4 Ground
2-16
Page 49

Chapter 2: Installation
Wake-on-LAN
The Wake-on-LAN connector is located on WOL. Refer to Table 218 for pin definitions.
Table 2-18. Wake-on-LAN Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function
1 +5V Standby
2 Ground
3 Wake up
Fan Connectors*
The thermal/overheat fan is located on JT3. The CPU fans are
located on JT1 and JT2. Refer to Table 2-19 for pin definitions.
Table 2-19. Fan Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Function
1 Ground
2 +12 V
3 Tachometer
* Caution: These connectors are DC direct.
2-17
Page 50

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
2-6 Installing/Removing the DIMM Modules
SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS can accommodate a maximum of 1
GB EDO or 512 MB SDRAM, using standard 168-pin 3.3V unbuffered DIMM memory modules. SUPER P6SLA can accommodate a
maximum of 768 MB EDO or 384 MB SDRAM.
There are three types of EDO and SDRAM DIMM modules: x4, x8
and x16. If you are using the x4 type, you can populate the DIMM
slots with either 4 single-sided memory modules or 2 double-sided
memory modules. For memory configurations of 512 MB EDO
DIMMs or higher, it is recommended to use the x8 or x16 type of
memory. It is not recommended to mix EDO DIMM modules with
SDRAM DIMM modules.
There are no jumpers needed to configure the on-board memory.
Memory timing requires 70ns or faster for EDO memory. Refer to
Figure 2-7 and the instructions below for installing or removing
DIMM modules.
CAUTION
Exercise extreme care when installing or removing the
DIMM modules to prevent any possible damages.
DIMM Module Installation
1. Insert DIMM modules in Bank 0 through Bank 3 as required
for the desired system memory.
2. Insert each DIMM module vertically into its socket. Pay
attention to the two notches to prevent inserting the DIMM at a
wrong position. The component side of the DIMM module
must face the CPU socket. The latter statement is applicable
for DIMMs with components on one side only.
3. Gently press the DIMM module until it snaps upright into place
in the socket.
2-18
Page 51

Chapter 2: Installation
To Remove:
Use your thumb to gently push the edge of
the socket and release the module. Do this
on both sides for each module.
To Install:
Insert
vertically,
press down
until it snap
into place.
Pay attention
to the two
notches.
DIMM
Figure 2-7. Installing/Removing a DIMM Memory Module
Removing DIMM Modules
1. Remove DIMM modules in any order.
2. Gently push the edge of the sockets to the side to release the
module. Remove one side of the DIMM module first, and then
the other side, to prevent breaking the socket.
2-19
Page 52

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
2-7 Connecting Parallel, Floppy and Hard Disk
Drives
Use the following information to connect the floppy and hard disk
drive cables.
• The floppy disk drive cable has seven twisted wires.
• A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1.
• A single floppy disk drive ribbon cable has 34 wires and two
connectors to provide for two floppy disk drives. The connector
with twisted wires always connects to drive A, and the connector
that does not have the twisted wires always connects to drive B.
• An IDE hard disk drive requires a data ribbon cable with 40 wires,
and a SCSI hard disk drive requires a SCSI ribbon cable with 50
wires. A wide SCSI hard disk drive requires a SCSI ribbon cable
with 68 wires.
• A single IDE hard disk drive cable has two connectors to provide
for two drives. To select an IDE disk drive as C, you would normally set the drive select jumper on the drive to DS1. To select
an IDE disk drive as D, you would normally set the drive select
jumper on the drive to DS2. Consult the documentation that
came with your disk drive for details on actual jumper locations
and settings.
• A single SCSI ribbon cable typically has three connectors to provide for two hard disk drives and the SCSI adapter. (Note: most
SCSI hard drives are single-ended SCSI devices.) The SCSI ID
is determined by jumpers or a switch on the SCSI device. The
last internal (and external) SCSI device cabled to the SCSI
adapter must be terminated.
• Some drives require a special controller card. Read your disk
drive manual for details.
2-20
Page 53

Chapter 2: Installation
Parallel Port Connector
The parallel port is located on J19. See Table 2-20 for pin definitions.
Table 2-20. Parallel Port Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 Strobe- 2 Auto Feed 3 Data Bit 0 4 Error 5 Data Bit 1 6 Init 7 Data Bit 2 8 SLCT IN 9 Data Bit 3 10 GND
11 Data Bit 4 12 GND
13 Data Bit 5 14 GND
15 Data Bit 6 16 GND
17 Data Bit 7 18 GND
19 ACJ- 20 GND
21 BUSY 22 GND
23 PE 24 GND
25 SLCT 26 NC
2-21
Page 54

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Floppy Connector
The floppy connector is located on J22. See Table 2-21 for pin
definitions.
Table 2-21. Floppy Connector Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 GND 2 FDHDIN
3 GND 4 Reserved
5 Key 6 FDEDIN
7 GND 8 Index9 GND 10 Motor Enable
11 GND 12 Drive Select B13 GND 14 Drive Select A15 GND 16 Motor Enable
17 GND 18 DIR19 GND 20 STEP21 GND 22 Write Data23 GND 24 Write Gate25 GND 26 Track 0027 GND 28 Write Protect29 GND 30 Read Data31 GND 32 Side 1 Select33 GND 34 Diskette
2-22
Page 55

Chapter 2: Installation
IDE Interfaces
There are no jumpers to configure the on-board IDE interfaces J15
and J16. Refer to Table 2-22 for the pin definitions.
Table 2-22. IDE Connector Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 Reset IDE 2 GND
3 Host Data 7 4 Host Data 8
5 Host Data 6 6 Host Data 9
7 Host Data 5 8 Host Data 10
9 Host Data 4 10 Host Data 11
11 Host Data 3 12 Host Data 12
13 Host Data 2 14 Host Data 13
15 Host Data 1 16 Host Data 14
17 Host Data 0 18 Host Data 15
19 GND 20 Key
21 DRQ3 22 GND
23 I/O Write- 24 GND
25 I/O Read- 26 GND
27 IOCHRDY 28 BALE
29 DACK3- 30 GND
31 IRQ14 32 IOCS1633 Addr 1 34 GND
35 Addr 0 36 Addr 2
37 Chip Select 0 38 Chip Select 139 Activity 40 GND
2-23
Page 56

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
SCSI Connectors (P6DLS and P6SLS only)
There are no jumpers to configure the on-board SCSI interfaces
JA1 and JA2. Refer to Table 2-23 for the pin definitions for JA2.
Refer to Table 2-24 for the pin definitions for JA1.
Table 2-23. 50-pin SCSI Connector Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 GND 26 -DB (0)
2 GND 27 -DB (1)
3 GND 28 -DB (2)
4 GND 29 -DB (3)
5 GND 30 -DB (4)
6 GND 31 -DB (5)
7 GND 32 -DB (6)
8 GND 33 -DB (7)
9 GND 34 -DB (P)
10 GND 35 GND
11 GND 36 GND
12 Reserved 37 Reserved
13 Open 38 Termpwr
14 Reserved 39 Reserved
15 GND 40 GND
16 GND 41 -ATN
17 GND 42 GND
18 GND 43 -BSY
19 GND 44 -ACK
20 GND 45 -RST
21 GND 46 -MSG
22 GND 47 -SEL
23 GND 48 -C/D
24 GND 49 -REQ
25 GND 50 -I/O
2-24
Page 57

Chapter 2: Installation
Table 2-24. 68-pin SCSI Connector Pin Definitions
Pin Pin
Number Function Number Function
1 GND 35 GND
2 GND 36 -DB (8)
3 GND 37 -DB (9)
4 GND 38 -DB (10)
5 GND 39 -DB (11)
6 GND 40 -DB (12)
7 GND 41 -DB (13)
8 GND 42 -DB (14)
9 GND 43 -DB (15)
10 GND 44 -DB (P1)
11 GND 45 -ACKB
12 GND 46 GND
13 GND 47 -REQB
14 GND 48 -DB (16)
15 GND 49 -DB (17)
16 GND 50 -DB (18)
17 Termpwrb 51 Termpwrb
18 Termpwrb 52 Termpwrb
19 GND 53 -DB (19)
20 GND 54 -DB (20)
21 GND 55 -DB (21)
22 GND 56 -DB (22)
23 GND 57 -DB (23)
24 GND 58 -DB (P2)
25 GND 59 -DB (24)
26 GND 60 -DB (25)
27 GND 61 -DB (26)
28 GND 62 -DB (27)
29 GND 63 -DB (28)
30 GND 64 -DB (29)
31 GND 65 -DB (30)
32 GND 66 -DB (31)
33 GND 67 -DB (P3)
34 GND 68 GND
2-25
Page 58

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
AGP Port
There are no jumpers to configure the AGP port J8. Refer to Table
2-25 for the pin definitions.
Table 2-25. AGP Port Pin Definitions
Pin# B A
1 Spare 12V
2 5.0V Spare
3 5.0V Reserved *
4 USB+ USB5 GND GND
6 INTB# INTA#
7 CLK RST#
8 REQ# GNT#
9 VCC3.3 VCC3.3
10 ST0 ST1
11 ST2 Reserved
12 RBF# PIPE#
13 GND GND
14 Spare Spare
15 SBA0 SBA1
16 VCC3.3 VCC3.3
17 SBA2 SBA3
18 SB_STB Reserved
19 GND GND
20 SBA4 SBA5
21 SBA6 SBA7
22 KEY KEY
23 KEY KEY
24 KEY KEY
25 KEY KEY
26 AD31 AD30
27 AD29 AD28
28 VCC3.3 VCC3.3
29 AD27 AD26
2-26
Page 59

Chapter 2: Installation
30 AD25 AD24
31 GND GND
32 AD_STB1 Reserved
33 AD23 C/BE3#
34 Vddq3.3 Vddq3.3
35 AD21 AD22
36 AD19 AD20
37 GND GND
38 AD17 AD18
39 C/BE2# AD16
40 Vddq3.3 Vddq3.3
41 IRDY# FRAME#
42
43 GND GND
44
45 VCC3.3 VCC3.3
46 DEVSEL# TRDY#
47 Vddq3.3 STOP#
48 PERR# Spare
49 GND GND
50 SERR# PAR
51 C/BE1# AD15
52 Vddq3.3 Vddq3.3
53 AD14 AD13
54 AD12 AD11
55 GND GND
56 AD10 AD9
57 AD8 C/BE0#
58 Vddq3.3 Vddq3.3
59 AD_STB0 Reserved
60 AD7 AD6
61 GND GND
62 AD5 AD4
63 AD3 AD2
64 Vddq3.3 Vddq3.3
65 AD1 AD0
66 SMB0 SMB1
2-27
Page 60

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
2-28
Page 61

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
Chapter 3
Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures to troubleshoot your system. If you
have followed all of the procedures below and still need assistance,
refer to the ‘Technical Support Procedures’ and/or ‘Returning
Merchandise for Service’ section(s) in this chapter.
No Video
Use the following steps for troubleshooting your system configuration.
1. If you have no video, remove all the add-on cards and cables.
2. Check for shorted connections, especially under the
motherboard.
3. Check the jumpers settings, clock speed, and voltage settings.
4. Use the speaker to determine if any beep codes exist. Refer to
Appendix C of the AMI BIOS Reference Manual for details about
beep codes.
3-1
Page 62

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
Install only the CPU, memory, and speaker
Power
On
N
Power
LED on?
Y
8 beeps
Y
Motherboard
N
Good
Power
Supply OK?
Y
N
Replace
Power
Supply
Speaker
Beeps?
Check memory,
BIOS
and CPU
Speaker
Beeps?
Replace
Motherboard
Y
N
Figure 3-1. Troubleshooting Flowchart
3-2
Page 63

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
NOTE
If you are a system integrator, VAR or OEM, a POST
diagnostics card is recommended for port 80h codes.
Refer to Appendix D.
Memory Error
If you encounter memory error, follow the procedures below.
1. Check to determine if DIMM modules are improperly installed.
2. Make sure that different types of DIMMs have not been installed in different banks (e.g., a mixture of 2MB x 36 and 1
MB x 36 DIMMs in Banks 0).
3. Determine if different speeds of DIMMs have been installed in
the same or different banks, and the BIOS setup is configured
for the fastest speed of RAM used. It is recommended to use
the same RAM speed for DIMMs in different banks.
4. Check for bad DIMM modules or chips.
Losing the System’s Setup Configuration
1. Ensure that you are using a high quality power supply. A poor
quality power supply may cause the system to lose CMOS
setup. Refer to Chapter 1 of this manual for details.
2. If the above step does not fix the Setup Configuration problem, contact your vendor for repair.
3-3
Page 64

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
3-2 Technical Support Procedures
1. Go through the ‘Troubleshooting Procedures’ section in this
chapter of the manual before calling Technical Support.
2. BIOS upgrades can be downloaded from the SUPER BBS#
(408) 895-2022, 24 hours a day, using 1200-14400 baud, 8
data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity. BIOS upgrades can also be
downloaded from our web site at http://www.supermicro.com.
Note: Not all BIOS can be flashed depending on the modifications on the boot block code.
3. If you still cannot get the problem resolved, have the following
information ready before you call for technical support:
• BIOS release date/version
• System board serial number
• Product model name
• Invoice number and date
• System configuration
3-3 Returning Merchandise for Service
A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is
required before any warranty service will be rendered. You can
obtain service by calling your vendor for a Returned Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) number. When returning to the manufacturer,
the RMA number should be prominently displayed on the outside of
the shipping carton, and mailed prepaid or hand-carried. Shipping
and handling charges will be applied for all orders that must be
mailed when service is complete.
This warranty only covers normal consumer use and does not cover
damages incurred in shipping or from failure due to the alternation,
misuse, abuse, or improper maintenance of products.
During the warranty period, contact your distributor first for any
product problems.
3-4
Page 65

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3-5
Page 66

SUPER P6DLS/P6DLE/P6SLS/P6SLA User’s Manual
3-6
 Loading...
Loading...