Page 1

C9Z390-CG/CGW
USER’S MANUAL
Revision 1.0
Page 2

!
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be accurate. The
vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document, makes
no commitment to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to notify any person
or organization of the updates. Please Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual,
please see our web site at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. ("Supermicro") reserves the right to make changes to the product described in this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software and documentation, is the property of Supermicro and/or its licensors, and is supplied only under a license. Any use or
reproduction of this product is not allowed, except as expressly permitted by the terms of said license.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR INABILITY
TO USE THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPERMICRO SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY
HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE
COSTS OF REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING, INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH
HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and customer shall be governed by the laws of Santa
Clara County in the State of California, USA. The State of California, County of Santa Clara shall be
the exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes. Super Micro's total liability for all claims
will not exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the authorized dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
California Best Management Practices Regulations for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning
applies only to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells. “Perchlorate Materialspecial handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate”
WARNING: This product can expose you to chemicals including
lead, known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth
defects or other reproductive harm. For more information, go
to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov.
Manual Revision: 1.0
Release Date: Oct 15, 2018
Unless you request and receive written permission from Super Micro Computer, Inc., you may not
copy any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies
referred to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark
holders.
Copyright © 2018 by Super Micro Computer, Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 3

Preface
Preface
This manual is written for system integrators, PC technicians and
knowledgeable PC users. It provides information for the installation and
use of the C9Z390-CG/CGW motherboard.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1 describes the features, specications and performance of
the motherboard, and provides detailed information on the Intel Z390
chipset.
Chapter 2 provides hardware installation instructions. Read this chapter when installing the processor, memory modules and other hardware
components into the system.
If you encounter any problems, see Chapter 3, which describes troubleshooting procedures for video, memory and system setup stored in the
CMOS.
Chapter 4 includes an introduction to the BIOS, and provides detailed
information on running the CMOS Setup utility.
Appendix A provides BIOS Error Beep Codes.
Appendix B lists software program installation instructions.
Appendix C contains UEFI BIOS Recovery instructions.
iii
Page 4

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Checklist
Congratulations on purchasing your computer motherboard from an acknowledged leader in the industry. Supermicro boards are designed with
the utmost attention to detail to provide you with the highest standards
in quality and performance.
Please check that the following items have all been included with your
motherboard. If anything listed here is damaged or missing, contact
your retailer.
The following items are included in the retail box:
• One (1) Supermicro Motherboard
• Four (4) SATA cables
• One (1) I/O shield
• One (1) Quick Reference Guide
• Two (2) Antenna (C9Z390-CGW only)
• One (1) Driver CD
Conventions Used in the Manual
Special attention should be given to the following symbols for proper
installation and to prevent damage done to the components or injury
to yourself:
Attention! Critical information to prevent damage to the components or injury to yourself.
Important: Important information given to ensure proper system installation or to relay safety precautions.
Note: Additional Information given to differentiate various models or provides information for correct system setup.
iv
Page 5

Standardized Warning Statements
Standardized Warning Statements
The following statements are industry-standard warnings, provided to
warn the user of situations which have the potential for bodily injury.
Should you have questions or experience difculty, contact Supermicro's
Technical Support department for assistance. Only certied technicians
should attempt to install or congure components.
Read this section in its entirety before installing or conguring compo-
nents in the Supermicro chassis.
Battery Handling
Warning!
There is a danger of explosion if the battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended
by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions
電池の取り扱い
電池交換が正しく行われなかった場合、破裂の危険性があります。 交換する電池はメー
カーが推奨する型、または同等のものを使用下さい。 使用済電池は製造元の指示に従
って処分して下さい。
警告
电池更换不当会有爆炸危险。请只使用同类电池或制造商推荐的功能相当的电池更
换原有电池。请按制造商的说明处理废旧电池。
警告
電池更換不當會有爆炸危險。請使用製造商建議之相同或功能相當的電池更換原有
電池。請按照製造商的說明指示處理廢棄舊電池。
Warnung
Bei Einsetzen einer falschen Batterie besteht Explosionsgefahr. Ersetzen
Sie die Batterie nur durch den gleichen oder vom Hersteller empfohlenen
Batterietyp. Entsorgen Sie die benutzten Batterien nach den Anweisungen
des Herstellers.
Attention
Danger d'explosion si la pile n'est pas remplacée correctement. Ne la
remplacer que par une pile de type semblable ou équivalent, recom-
mandée par le fabricant. Jeter les piles usagées conformément aux
instructions du fabricant.
v
Page 6

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
¡Advertencia!
Existe peligro de explosión si la batería se reemplaza de manera incorrecta. Reemplazar la batería exclusivamente con el mismo tipo o el
equivalente recomendado por el fabricante. Desechar las baterías gastadas según las instrucciones del fabricante.
!הרהזא
שי .הניקת אל ךרדב הפלחוהו הדימב הללוסה לש ץוציפ תנכס תמייק
ףילחהל
.תצלמומ ןרצי תרבחמ םאותה גוסב הללוסה תא
.ןרציה תוארוה יפל עצבל שי תושמושמה תוללוסה קוליס
경고!
배터리가 올바르게 교체되지 않으면 폭발의 위험이 있습니다. 기존 배터리와 동일
하거나 제조사에서 권장하는 동등한 종류의 배터리로만 교체해야 합니다. 제조사
의 안내에 따라 사용된 배터리를 처리하여 주십시오.
Waarschuwing
Er is ontplofngsgevaar indien de batterij verkeerd vervangen wordt. Vervang de batterij slechts met hetzelfde of een equivalent type die door de
fabrikant aanbevolen wordt. Gebruikte batterijen dienen overeenkomstig
fabrieksvoorschriften afgevoerd te worden.
Product Disposal
Warning!
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations.
vi
Page 7

Standardized Warning Statements
製品の廃棄
この製品を廃棄処分する場合、国の関係する全ての法律・条例に従い処理する必要が
ありま す。
警告
本产品的废弃处理应根据所有国家的法律和规章进行。
警告
本產品的廢棄處理應根據所有國家的法律和規章進行。
Warnung
Die Entsorgung dieses Produkts sollte gemäß allen Bestimmungen und
Gesetzen des Landes erfolgen.
¡Advertencia!
Al deshacerse por completo de este producto debe seguir todas las leyes
y reglamentos nacionales.
Attention
La mise au rebut ou le recyclage de ce produit sont généralement soumis
à des lois et/ou directives de respect de l'environnement. Renseignezvous auprès de l'organisme compétent.
רצומה קוליס
!הרהזא
.הנידמה יקוחו תויחנהל םאתהב תויהל בייח הז רצומ לש יפוס קוליס
경고!
이 제품은 해당 국가의 관련 법규 및 규정에 따라 폐기되어야 합니다.
Waarschuwing
De uiteindelijke verwijdering van dit product dient te geschieden in over-
eenstemming met alle nationale wetten en reglementen.
vii
Page 8

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email: marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Website: www.supermicro.com
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
's-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
Email: sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Website: www.supermicro.nl
Asia-Pacic
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
3F, No. 150, Jian 1st Rd.
Zhonghe Dist., New Taipei City 235
Taiwan (R.O.C)
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3992
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Website: www.supermicro.com.tw
viii
Page 9

Contacting Supermicro
Where to Find More Information
For your system to work properly, please follow the links below to
download all necessary drivers/utilities and the user's manual for your
motherboard.
Supermicro product manuals: http://www.supermicro.com/support/
manuals/
Product Drivers and utilities: https://www.supermicro.com/wftp/driver/
If you have any questions, please contact our support team at support@
supermicro.com.
ix
Page 10

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Table of Contents
Preface
Chapter 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Installation
2-1 Installation Components and Tools Needed ............................... 2-1
2-2 Static-Sensitive Devices .......................................................... 2-2
2-3 Processor and Heatsink Installation .......................................... 2-3
2-4 Installing DDR4 Memory ......................................................... 2-8
2-5 Motherboard Installation ....................................................... 2-11
2-6 M.2 Installation (optional) ..................................................... 2-13
2-7 Connectors/IO Ports ............................................................. 2-14
2-8 Connecting Cables ............................................................... 2-23
2-9 Jumper Settings .................................................................. 2-30
2-10 Onboard Indicators .............................................................. 2-33
2-11 Hard Drive Connections ........................................................ 2-35
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures ..................................................... 3-1
3-2 Technical Support Procedures .................................................. 3-3
3-3 Frequently Asked Questions .................................................... 3-4
3-4 Battery Removal and Installation ............................................. 3-5
3-5 Returning Motherboard for Service ........................................... 3-6
Chapter 4 BIOS
4-1 Introduction .......................................................................... 4-1
4-2 EZ Mode ............................................................................... 4-3
4-3 Overclocking ......................................................................... 4-5
4-4 CPU ................................................................................... 4-19
4-5 Memory .............................................................................. 4-25
4-6 Advanced ............................................................................ 4-27
4-7 H/W Monitor ....................................................................... 4-48
4-8 Save & Exit ......................................................................... 4-50
4-9 BIOS Update ....................................................................... 4-52
Appendix A BIOS Error Beep Codes
A-1 BIOS Error Beep Codes .......................................................... A-1
Appendix B Software Installation Instructions
B-1 Installing Drivers ................................................................... B-1
x
Page 11

Table of Contents
B-2 Conguring SuperDoctor® 5 ................................................... B-2
Appendix C UEFI BIOS Recovery Instructions
C-1 An Overview to the UEFI BIOS ................................................ C-1
C-2 How to Recover the UEFI BIOS Image ...................................... C-1
C-3 To Recover the Main BIOS Block Using a USB-Attached Device .... C-2
xi
Page 12

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Notes
Notes
xii
Page 13

Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
About this Motherboard
The C9Z390-CG/CGW motherboard supports a single 8th Generation
Intel® Core™ i9/i7/i5/i3 processor in an LGA1151 socket. With the
Intel Z390 chipset built in, the C9Z390-CG/CGW motherboard offers
substantial system performance and storage capability in a sleek pack-
age. Please refer to our website (http://www.supermicro.com/products/)
for processor and memory support updates.
1-2 Chipset Overview
Intel® Z390 Chipset Features
• Direct Media Interface (up 10Gb/s transfer, Full Duplex)
• Intel® Matrix Storage Technology and Rapid Storage Technology
• Intel® I/O Virtualization (VT-d) Support
• PCI Express 3.0 Interface (up to 8GT/s)
• SATA Controller (up to 6Gb/sec)
• Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI)
1-1
Page 14
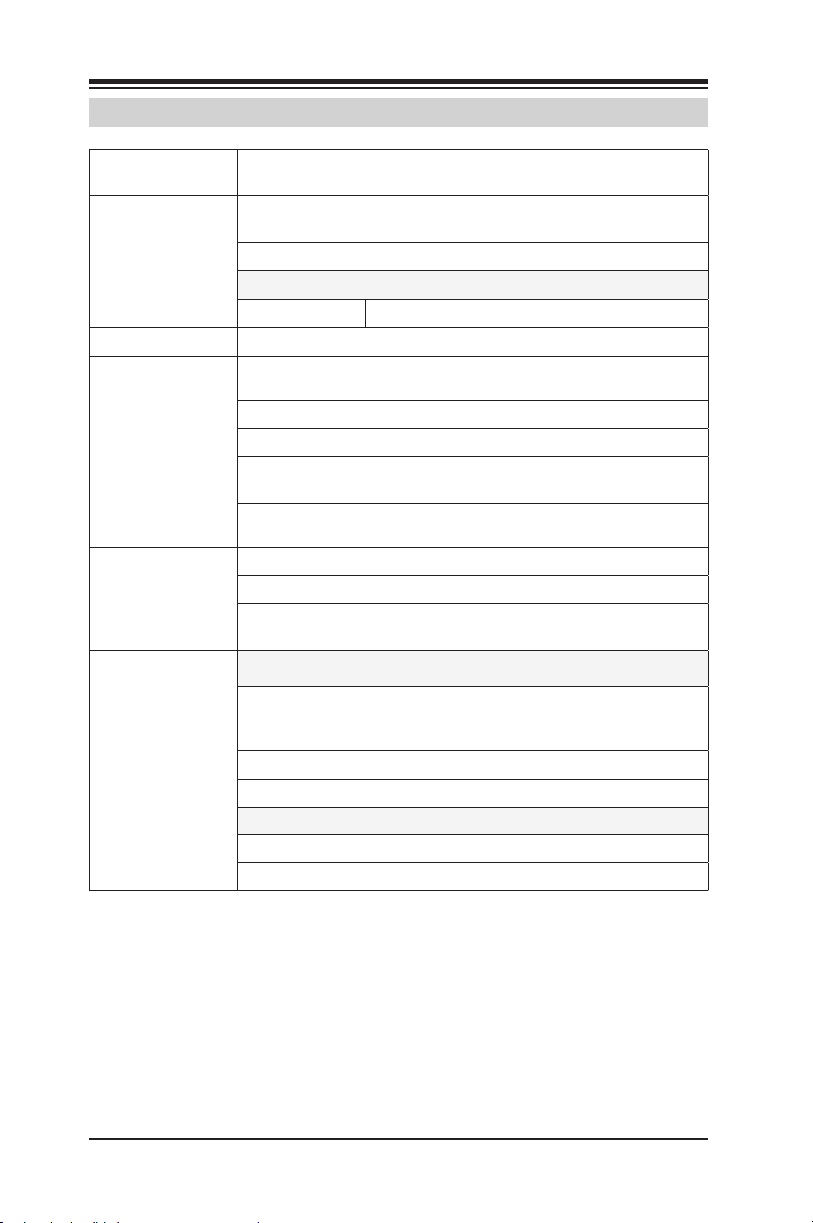
Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
1-3 Motherboard Features
CPU
Memory
Chipset
Expansion Slots
Network
Connections
Health
Monitoring
Single 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i9/i7/i5/i3 or 9000
series processor in an LGA1151 H4 type socket
Supports up to 64GB of unbuffered, non-ECC, DDR4
memory with speeds of up to 3733+ MHz (OC)
Dual-channel memory
DIMM sizes
UDIMM 4GB/8GB/16GB
Intel® Z390 chipset
Two (2) PCI-E x16 slots (16/NA, 8/8 or 8/4 in the
PCI-E x4 slot)
One (1) PCI-E 3.0 x4 slot
Three (3) PCI-E 3.0 x1 slots
Two (2) M-Key M.2 (2242/2280/22110 &
2260/2280/22110)
One (1) E-Key M.2 (C9Z390-CGW only; pre-installed
802.ac WiFi module)
Intel® I219v Network Controller
Aquantia AQC107 Network Controller (C9Z390-CGW only)
Two (2) RJ-45 ports with Link and Activity LEDs on the
I/O back panel (C9Z390-CGW only)
CPU Monitoring
Onboard monitors: +1.8V, +3.3V, +5V, +/- 12V, +3.3V
Stby, +5V Stby, VBAT, HT, Memory, PCH Temperature,
System Temperature, Memory Temperature
(6+2)-phase CPU switching voltage regulator
CPU Thermal Trip support
Fan Control
Five (5) 4-pin fan headers
Multi-speed fan control via onboard Super I/O
1-2
Page 15
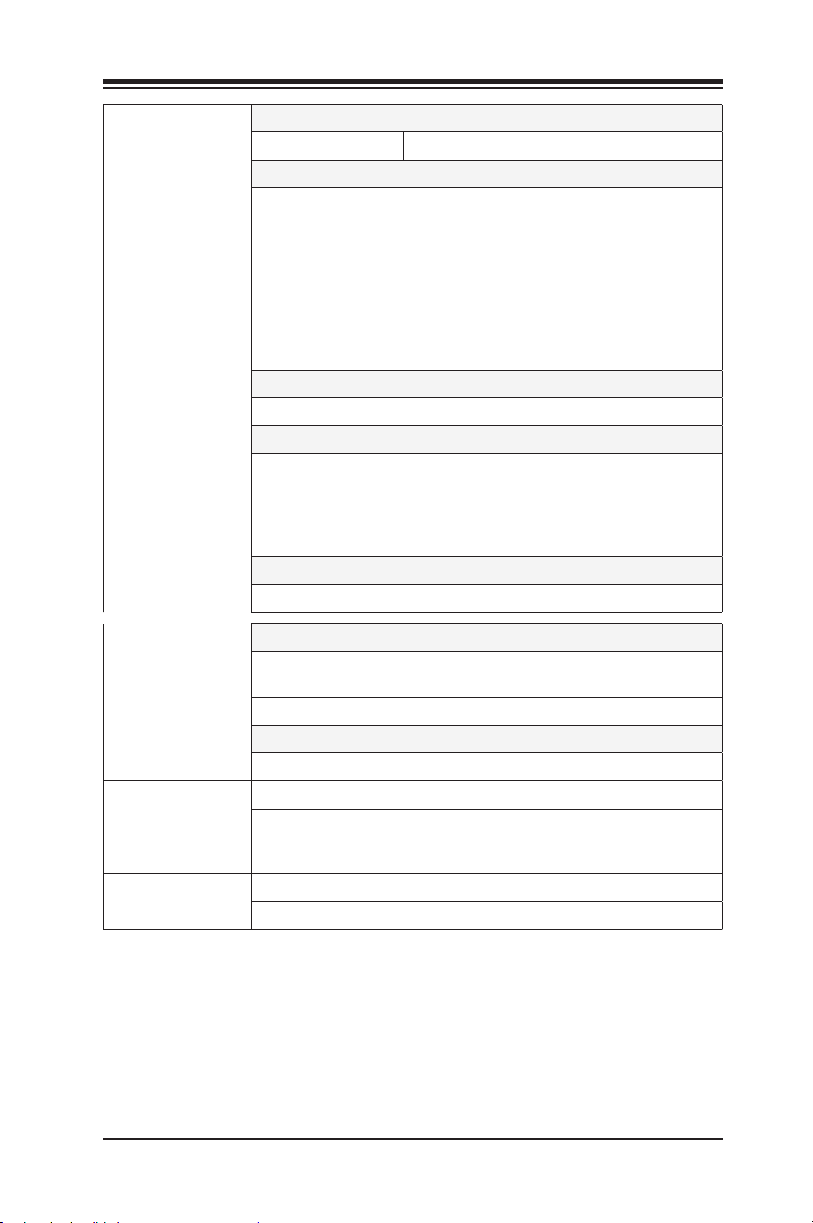
Chapter 1: Introduction
I/O Devices Hard Drive Connections
SATA 3.0 (6Gb/s) Six (6) SATA0~5 via Intel® Z390
USB Devices
C9Z390-CG/CGW
One (1) USB 3.1 Gen 2 Type-C port on the I/O back panel
Three (3) USB 3.1 Gen 2 Type-A ports on the I/O back
panel
One (1) front accessible USB 3.1 Gen 2 port
Two (2) USB 3.1 Gen 1 ports on the I/O back panel
Two (2) front accessible USB 3.1 Gen 1 ports via header
Two (2) front accessible USB 2.0 ports via header
Keyboard/Mouse
One PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse port on the I/O back panel
Other I/O Ports
Two (2) DisplayPort 1.2
One (1) HDMI 1.4b Port
One (1) Serial Port (COM) header
One (1) Trusted Platform Module header
Graphics
Integrated into Intel® Processor
Audio
One (1) High Denition Audio 7.1 channel connector
supported by Realtek ALC1220 on the back panel
One (1) Front Panel Audio Header
Super I/O
Nuvoton NCT6796D
BIOS
256Mb AMI BIOS® SPI Flash BIOS
SMBIOS 2.7, PCI F/W 3.0, ACPI 3.0, SPI dual/quad
speed support, Overclocking Support, Real Time Clock
wakeup
Power
Configuration
ACPI Power Management (S3/S4/S5)
Power-on mode for AC power recovery
1-3
Page 16
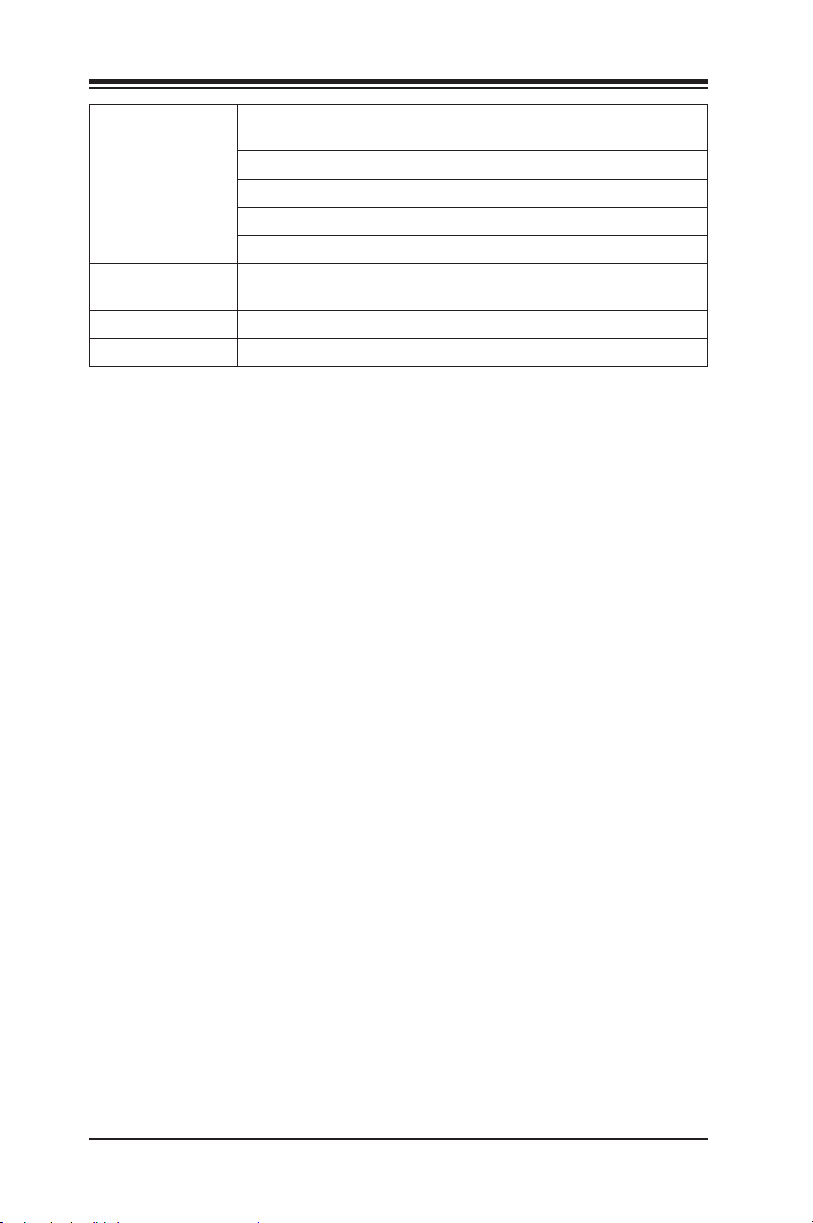
Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
System
Management
CD Utilities
LED Indicators
Dimensions
PECI (Platform Environment Conguration Interface)
2.0 support
System resource alert via SuperDoctor® 5
SuperDoctor® 5, NMI
Chassis Intrusion header and detection
Watch Dog Timer
BIOS ash upgrade utility
Drivers and software for Intel® Z390 chipset utilities
Power/suspend state
ATX form factor (12" x 9.6") (304.80 mm x 243.84 mm)
1-4
Page 17

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-4 Special Features
Recovery from AC Power Loss
Basic I/O System (BIOS) provides a setting for you to determine how
the system will respond when AC power is lost and then restored to
the system. You can choose for the system to remain powered off, (in
which case you must press the power switch to turn it back on), or for
it to automatically return to a power-on state. See the Advanced BIOS
Setup section to change this setting. The default setting is Last State.
1-5 PC Health Monitoring
This section describes the PC health monitoring features of the board.
All have an onboard System Hardware Monitoring chip that supports PC
health monitoring. An onboard voltage monitor will scan these onboard
voltages continuously: +1.8V, +3.3V, +5V, +/- 12V, +3.3V Stby, +5V
Stby, VBAT, HT, Memory Temperature, PCH Temperature, and System
Temperature. Once a voltage becomes unstable, a warning is given, or
an error message is sent to the screen. The user can adjust the voltage
thresholds to dene the sensitivity of the voltage monitor.
Fan Status Monitor with Firmware Control
PC health monitoring in the BIOS can check the RPM status of the cool-
ing fans. The onboard CPU and chassis fans are controlled by Thermal
Management via SIO.
Environmental Temperature Control
The thermal control sensor monitors the CPU temperature in real time
and will turn on the thermal control fan whenever the CPU temperature
exceeds a user-dened threshold. The overheat circuitry runs indepen-
dently from the CPU. Once the thermal sensor detects that the CPU
temperature is too high, it will automatically turn on the thermal fans to
prevent the CPU from overheating. The onboard chassis thermal circuitry
can monitor the overall system temperature and alert the user when the
chassis temperature is too high.
Note: To avoid possible system overheating, please be sure to
provide adequate airow to your system.
1-5
Page 18

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
System Resource Alert
This feature is available when the system is used with SuperDoctor®
5 in the Windows and Linux operating systems. SuperDoctor is used
to notify the user of certain system events. For example, you can also
congure SuperDoctor to provide you with warnings when the system
temperature, CPU temperatures, voltages and fan speeds go beyond
predened thresholds.
1-6 ACPI Features
ACPI stands for Advanced Conguration and Power Interface. The ACPI
specication denes a exible and abstract hardware interface that
provides a standard way to integrate power management features
throughout a PC system, including its hardware, operating system and
application software. This enables the system to automatically turn on
and off peripherals such as CD-ROMs, network cards, hard disk drives
and printers.
In addition to enabling operating system-directed power management,
ACPI also provides a generic system event mechanism for Plug and Play,
and an operating system-independent interface for conguration control.
ACPI leverages the Plug and Play BIOS data structures, while providing
a processor architecture-independent implementation that is compatible
with Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 2008 Operating Systems.
Slow Blinking LED for Suspend-State Indicator
When the CPU goes into a suspend state, the chassis power LED will
start to blink to indicate that the CPU is in suspend mode. When the user
presses any key, the CPU will wake up, and the LED will automatically
stop blinking and remain on.
1-6
Page 19

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-7 Power Supply
As with all computer products, a stable power source is necessary for
proper and reliable operation. It is even more important for processors
that have high CPU clock rates or overclocked processors.
This motherboard accommodates 24-pin ATX power supplies. Although
most power supplies generally meet the specications required by the
CPU, some are inadequate. In addition, the 12V 8-pin power connector
located at JPW2 is also required to ensure adequate power supply to the
system. Also your power supply must supply 1.5A for the Ethernet ports.
Attention! To prevent damage to the power supply or motherboard, please use a power supply that contains a 24-pin and a
8-pin power connector. Be sure to connect these connectors to
the 24-pin (JPW1) and the 8-pin (JPW2) power connectors on the
motherboard.
It is strongly recommended that you use a high quality power supply
that meets ATX power supply Specication 2.02 or above. It must also
be SSI compliant. (For more information, please refer to the website
at http://www.ssiforum.org/). Additionally, in areas where noisy power
transmission is present, you may choose to install a line lter to shield
the computer from noise. It is recommended that you also install a power
surge protector to help avoid problems caused by power surges.
1-8 Super I/O
The Super I/O supports one high-speed, 16550 compatible serial com-
munication port (UART). This UART includes a 16-byte send/receive FIFO,
a programmable baud rate generator, complete modem control capability
and a processor interrupt system. The UART provides legacy speed with
a baud rate of up to 115.2 Kbps as well as an advanced speed with baud
rates of 250 K, 500 K, or 1 Mb/s, which support higher speed modems.
The Super I/O provides functions that comply with ACPI (Advanced Con-
guration and Power Interface), which includes support of legacy and
ACPI power management through an SMI or SCI function pin. It also
features auto power management to reduce power consumption.
1-7
Page 20

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
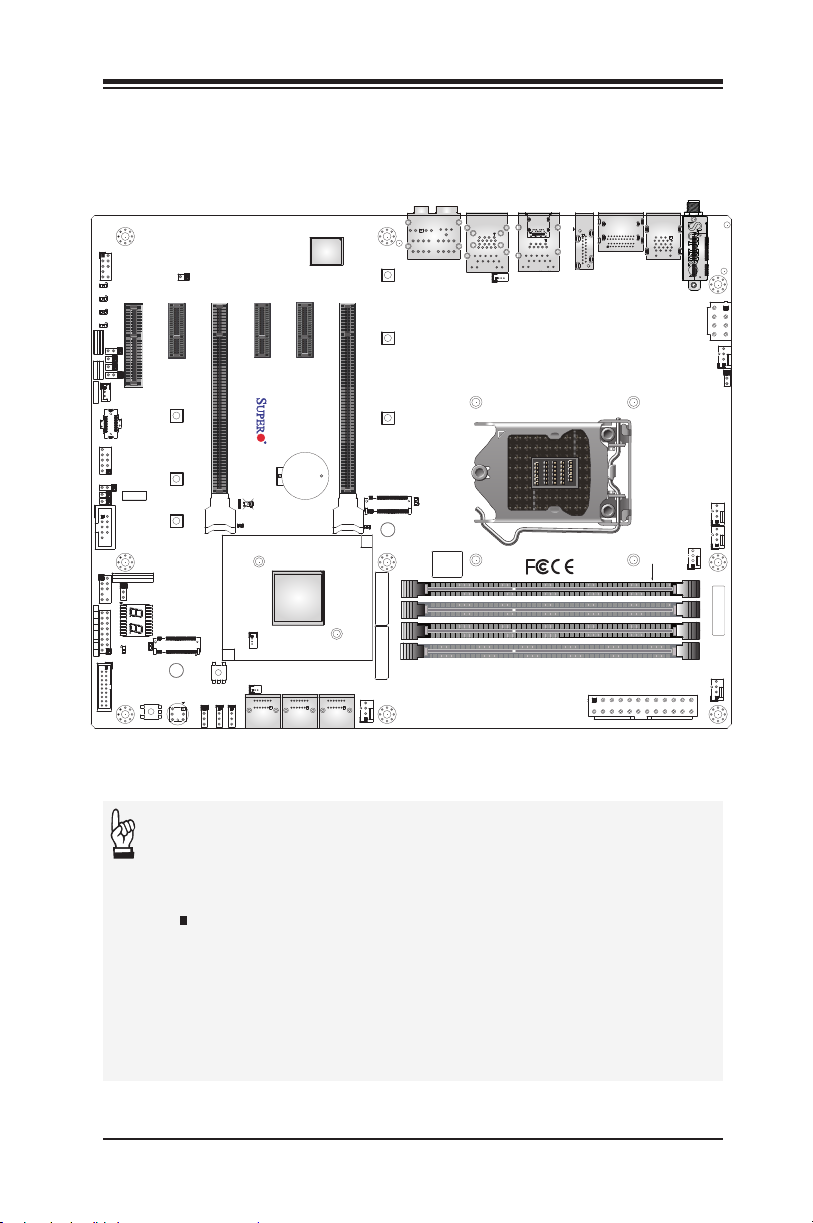
C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard Image
Note: All graphics shown in this manual were based upon the latest
PCB Revision available at the time of publishing of the manual. The
motherboard you've received may or may not look exactly the same
as the graphics shown in this manual.
1-8
Page 21
C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard Layout
Chapter 1: Introduction
AUDIO FP
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
RWP
DDH
1
2
OH/FF
X
RST
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
1-2:NORMAL
ON :ENABLE
JSTBY1:
JTPM1
LED
LED
NIC
NIC
PWR
J31
J9701/J9702
JI2C1/JI2C2
J37
COM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
LED4
C
LED1
A
JSPDIF_OUT
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
JRLED3
+12V G R B
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
D9017
SYS_FAN2
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
(3.0)
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
12V_PUMP_PWR1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
MH4
MAC CODE
SYS_FAN1
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
HDMI
JPW1
USB 2/3
Important Notes to the User
• See Chapter 2 for detailed information on jumpers, I/O ports and
JF1 front panel connections.
• " " indicates the location of "Pin 1".
• Jumpers not indicated are for testing only.
• When LED1 (Onboard Power LED Indicator) is on, system power
is on. Unplug the power cable before installing or removing any
components.
1-9
Page 22
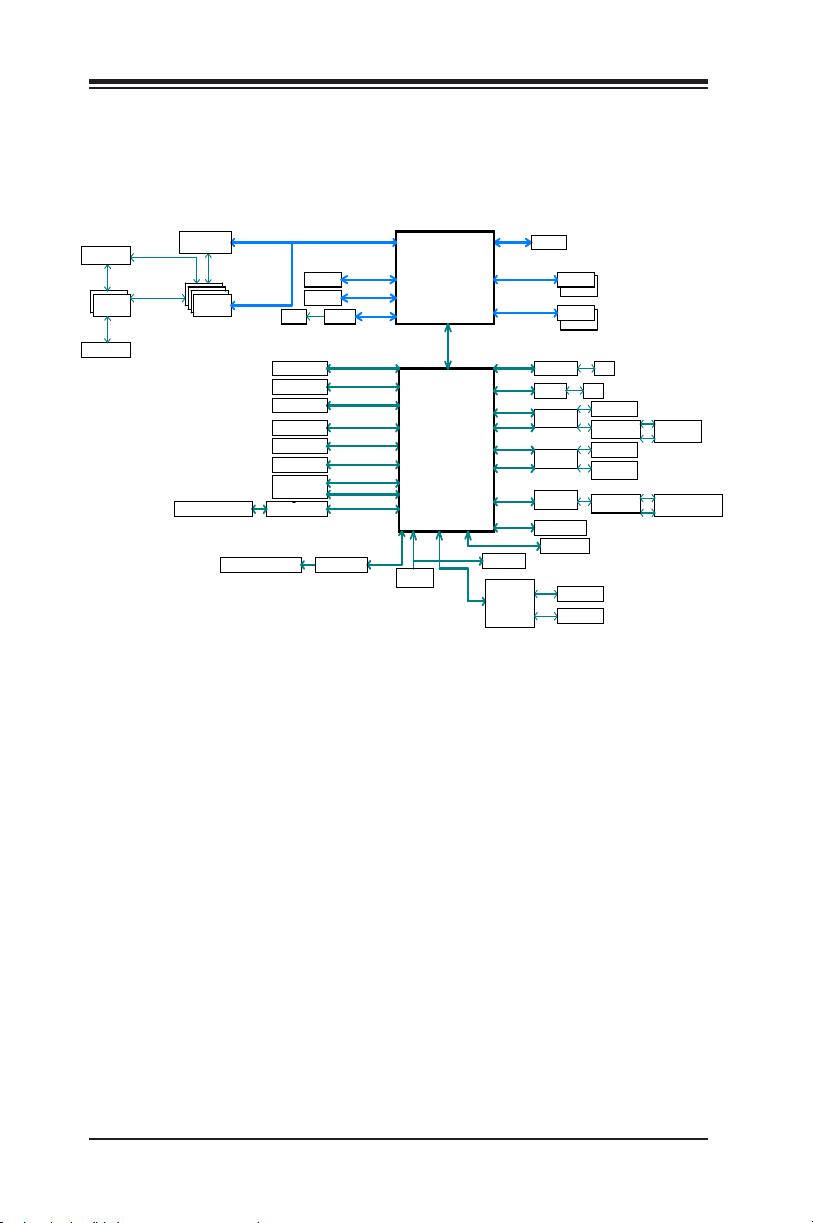
Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
2 X USB 2.0 Header
480Mbps
USB2.0
2667/2400MHz
INTEL LGA1151
SVID
IMVP8/9
DDR4 (CHA)
DIMMA0
DDR4 (CHB)
DIMMB0
2667/2400MHz
8GT/s
x4 DMI
RJ45
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1 GLAN1
I219V(1Gb)
PCH
Intel
CNL PCH-H
Z390
(Socket-H4)
AZALIA
Realtek ALC1220
Display Port 1.2
DDI2
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
PI3EQX1004
2 X M.2 SOCKET SSD
10Gb
USB3.1 Gen2
Rear Type-A X 1
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
PCIe x1 SLOT Rear
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x1
USB3.0
5Gbps
2 X USB 3.0 Rear
2 X USB 3.0 Header
5Gbps
USB3.0
6X SATA-III
SATA-III
6Gb/s
Audio Jack/ Audio Pin Header
PCIe
x1 SLOT Rear
PCIe x1 SLOT Rear
ASM1543 USB3.1
Rear Type-C X 1
PCIe3.0_x16
8.0GT/s
ASMedia Switch
ASM1480
ASMedia Switch
ASM1480
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x4
PCIe3.0_x4
PCIe x4(in x4) SLOT #2
8.0GT/s
8.0GT/s
or
PCIe x4(in x16) SLOT #4
or
PCIe x8(in x16) SLOT #6
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x8
PCIe x16 SLOT #6
PCIe x8(in x16) SLOT #4
PCIe3.0_x4
8.0GT/s
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x8
8.0GT/s
PCIe3.0_x8
8GT/s
PCIe3.0_x2 GLAN2
AQC107(10Gb)
PI3EQX1004
10Gb
USB3.1 Gen2
Rear Type-A X 1
Rear Type-A X 1
1 X M.2 Key E for
WiFi &
BT
CNVi I/F
480Mbps
USB2.0
RJ45
TPM2.0 Header
SPI
FLASH
SPI 256Mb
SPI
LPC
COM1 Header
NCT6796D
LPC I/O
PS2 KB/MS
PI3EQX1004
10Gb
USB3.1 Gen2
Front header Type-C X 1
ASM1543 USB3.1
Lane reverse
10Gb
USB3.1 Gen2
10Gb
USB3.1 Gen2
RENESAS R5F104AC
SMbus
On board RGB LED & Header
HDMI 1.4 ASM1442K
DDI3
Display Port 1.2
DDI1
C9Z390-CG/CGW Block Diagram
1-10
Page 23

C9Z390-CG/CGW Quick Reference
Chapter 1: Introduction
AUDIO FP
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
1-2:NORMAL
ON :ENABLE
JTPM1
J31
J9701/J9702
JI2C1/JI2C2
J37
COM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
LED4
C
LED1
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JD1
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
JRLED4
JRLED3
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
12V_PUMP_PWR1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
MH4
MAC CODE
SYS_FAN1
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
DP1/DP2
HDMI
JPW1
Jumper Description Default
CLEAR CMOS Clear CMOS Button Push Button Switch
J9701/J9702 Manufacturing Mode Pins 1-2: Normal
JI2C1/JI2C2 SMB to PCI-E Slots Open (Disable)
JPME2 Intel® Manufacturing Mode Pins 1-2 (Normal)
JWD1 Watch Dog Function Enable Pins 1-2 (Reset)
POWER BUTTON Onboard Power Button Push Button Switch
RESET BUTTON Onboard System Reset
Button
1-11
Push Button Switch
Page 24
Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Connector Description
12V_PUMP_PWR1 12V 4-pin power connector for CPU pump
of liquid cooling
Audio FP Front Panel Audio Header
B1 Onboard Battery
COM1 COM1 Header
CPU_FAN1/FAN2 CPU Fan Headers
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 x4 PCI-E 3.0 x4 Slot
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 x8
PCI Express x16 Slot (PCI-E 3.0 x8 link )
(IN x16)
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 x16 PCI Express x16 Slot (PCI-E 3.0 x16 link)
PCH SLOTS2/4/5 PCI-E 3.0 x1 Slots
DP1/DP2 DisplayPort 1.2 Ports
HDMI HDMI 1.4b Port
HD AUDIO High Denition Audio Ports
I-SATA0~5 SATA 3.0 Ports (6Gb/sec)
JD1 External Speaker Header
JF1 Front Control Panel Header
JL1 Chassis Intrusion Header
JPW1 24-pin ATX Main Power Connector
(Required)
JPW2 +12V 8-pin CPU power Connector
(Required)
JRLED1/2 JRLED1 connects to I/O cover's RGB board;
JRLED2 connects to PCH RGB board
JRLED3/4 External 12V RGB strips
JSD1 SATA DOM (Disk-On-Module) Power
Connector-
JSPDIF_Out Sony/Philips Digital Interface Audio Out-
put Header
JSTBY1 Standby Power Header
JTPM1 Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Header
JVR2 PWM SMB Programming (for debugging
only)
1-12
Page 25
Chapter 1: Introduction
Connector Description
KB/ MOUSE PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Port
LAN1 Gigabit RJ45 LAN Port
LAN2 10Gb RJ45 LAN Port
OC1 2-pin Header for Overclocking Support
PCI-E M.2 CONNECTORS
(E1, M1, M2)
PCI-E M.2 Connectors; small form factor
devices and other portable devices for
high speed NVMe SSDs, WiFi, and BT
SYS_FAN1/FAN2/FAN3 System Fan Headers
USB 0/1 Front Accessible USB 2.0 Header
USB2/3 USB 3.1 Gen 1 Back Panel Ports
USB4/5 USB 3.1 Gen 2 Back Panel Ports
USB6/7 USB 3.1 Gen 2 Back Panel Ports
USB8/9 Front Accessible USB 3.1 Gen 1 Header
USB10 Front Accessible USB 3.1 Gen 2 Header
LED Description Color/State
BOOT LED Bootable Device POST Status
CPU LED CPU POST Status
D9017/
D9019
LED Indication of PCI-E Link
Speed
Red: On
OFF: POST Complete
Yellow: On
OFF: POST Complete
Green: x16 Link
Yellow: x8/x4/x1 Link
DIMM LED DIMM POST Status
LED1
Power On
S3 (Suspend to RAM)
Blue: On
OFF: POST Complete
Green: Power On
Green Blinking: S3
LED4 Diagnostic LED Digital Readout
LED5 PCI-E M.2 Connector #1 LED
LED6 PCI-E M.2 Connector #2 LED
VGA LED Onboard VGA POST Status
Green: PCI-E Device Detected
Green: PCI-E Device Detected
Green: On
OFF: POST Complete
*Download the AMI status codes at https://ami.com/ami_downloads/
Aptio_V_Status_Codes.pdf
1-13
Page 26

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Notes
Notes
1-14
Page 27
Chapter 2: Installation
Chapter 2
Installation
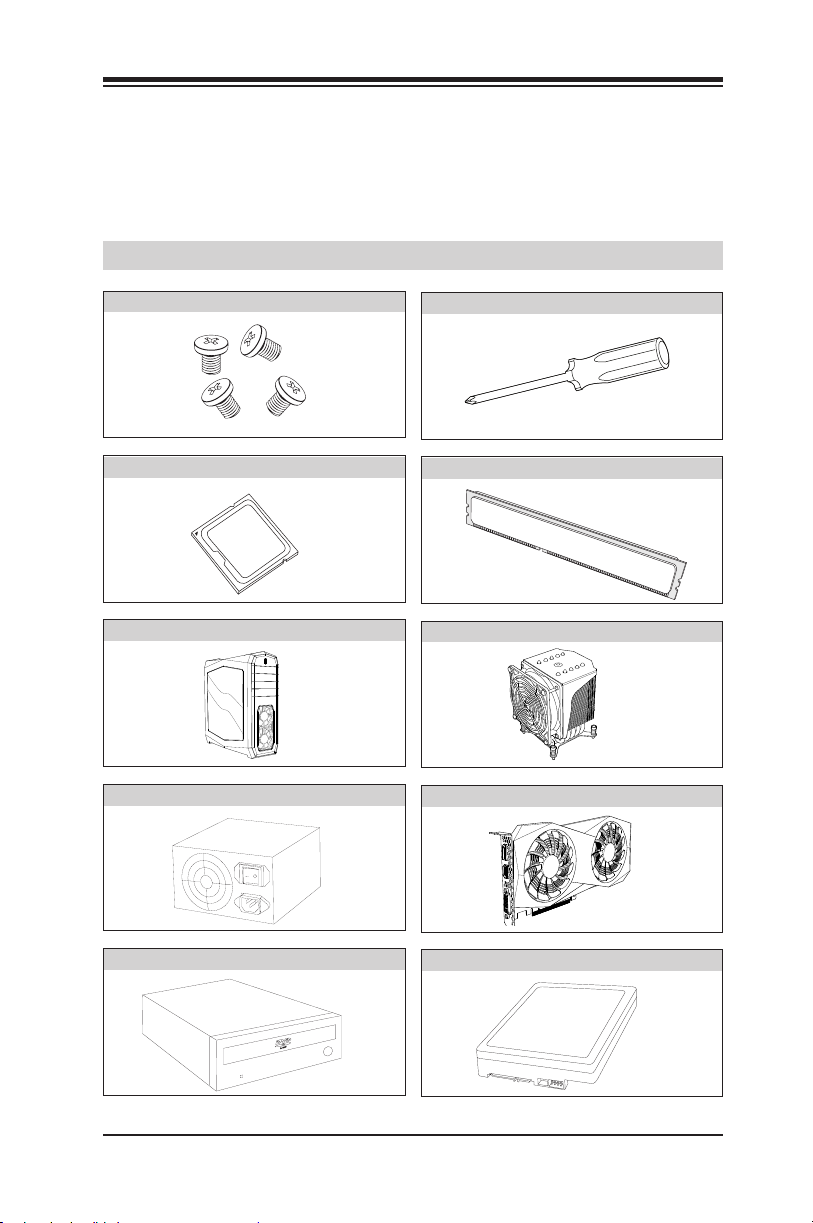
2-1 Installation Components and Tools Needed
Screws
Intel® LGA 1151 Processor
PC Chassis
Power Supply
Phillips-Head Screwdriver
DDR4 DIMMs
Heatsink with Fan
Video Card (Optional)
SATA/USB Optical Drive (Optional)
SATA Hard Disk Drive
2-1
Page 28

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
2-2 Static-Sensitive Devices
Electrostatic-Discharge (ESD) can damage electronic components. To
avoid damaging your system board, it is important to handle it very
carefully. The following measures are generally sufcient to protect your
equipment from ESD.
Precautions
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent static discharge.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the
antistatic bag.
• Handle the board by its edges only; do not touch its components,
peripheral chips, memory modules, or gold contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the motherboard and peripherals back into their antistatic bags
when not in use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure your computer chassis provides
excellent conductivity between the power supply, the case, the mounting fasteners, and the motherboard.
• Use only the correct type of onboard CMOS battery. Do not install the
onboard battery upside down to avoid possible explosion.
Unpacking
The motherboard is shipped in antistatic packaging to avoid static damage. When unpacking the board, make sure that the person handling it
is static protected.
2-2
Page 29
Chapter 2: Installation
2-3 Processor and Heatsink Installation
Attention! When handling the processor package, avoid placing
direct pressure on the label area of the fan.
Important:
• Always connect the power cord last, and always remove it before
adding, removing, or changing any hardware components. Make sure
that you install the processor into the CPU socket before you install
the CPU heatsink.
• If you buy a CPU separately, make sure that you use an Intel-certied
multi-directional heatsink only.
• Make sure to install the system board into the chassis before you
install the CPU heatsink.
• When receiving a server board without a processor pre-installed, make
sure that the plastic CPU socket cap is in place and none of the socket
pins are bent; otherwise, contact your retailer immediately.
• Refer to the Supermicro website for updates on CPU support.
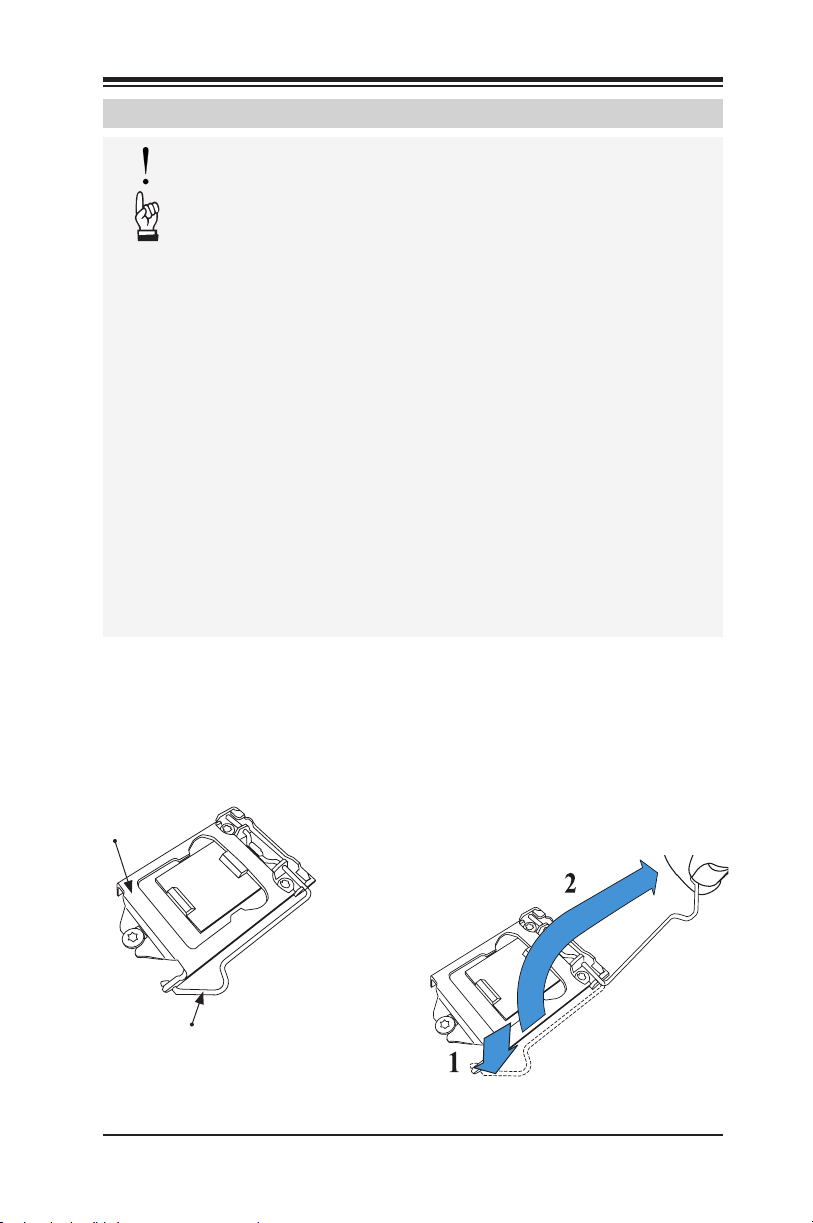
1. Press the load lever to release the load plate, which covers the CPU
Load Plate
Load Lever
Installing the Processor
socket, from its locking position.
2-3
Page 30
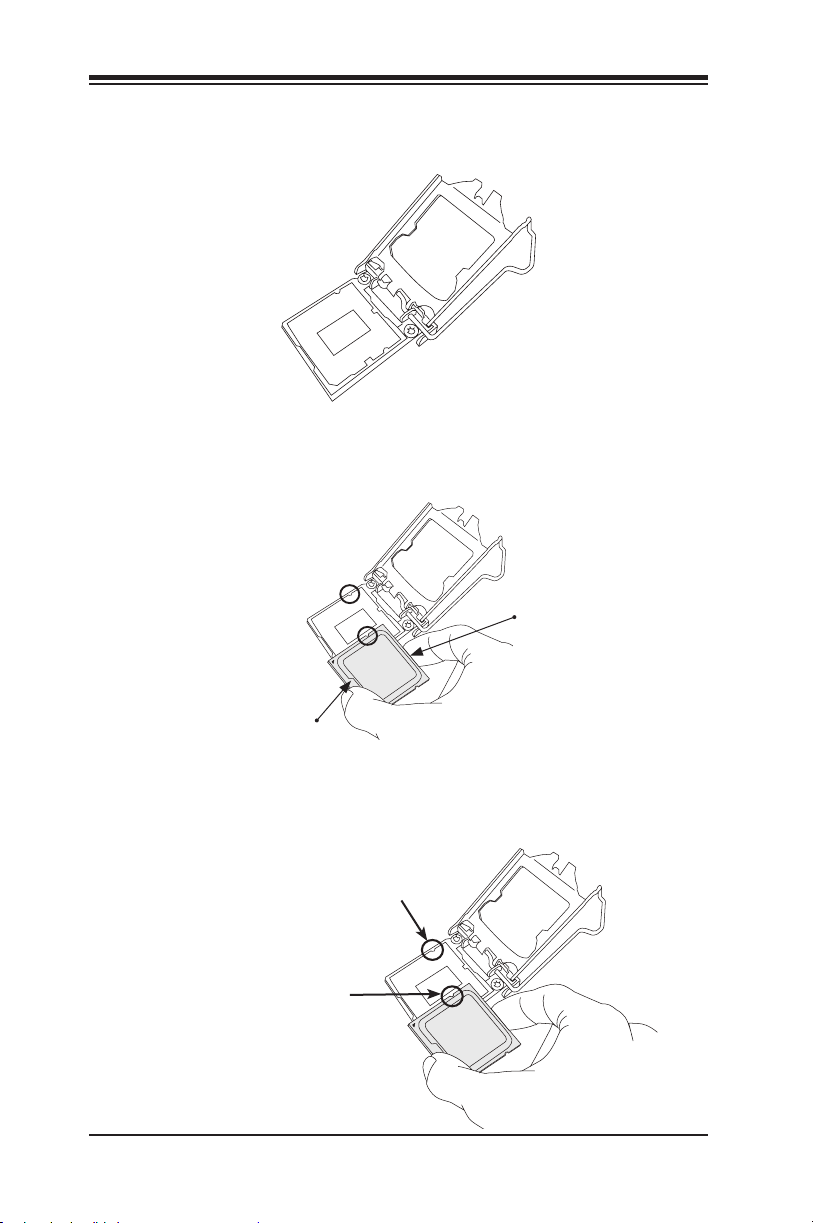
Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
2. Gently lift the load lever to open the load plate. Remove the plastic
cap.
3. Use your thumb and your index nger to hold the CPU at the North
center edge and the South center edge of the CPU.
North Center Edge
South Center Edge
4. Align the CPU key (the semi-circle cutouts) against the socket key.
Once it is aligned, carefully lower the CPU straight down into the
socket. Do not drop the CPU on the socket. Do not move the CPU
horizontally or vertically.
Socket Key
CPU Key
2-4
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installation
5. Do not rub the CPU against the surface or against any pins of the
socket to avoid damaging the CPU or the socket.
6. With the CPU inside the socket, inspect the four corners of the CPU
to make sure that the CPU is properly installed.
7. Close the load plate with the CPU inside the socket. Gently push
the load lever down to the lever locks.
CPU properly
installed
Load lever locked into
place
Note: You can only install the CPU inside the socket in one direction.
Make sure that it is properly inserted into the CPU socket before
closing the load plate. If it doesn't close properly, do not force it as
it may damage your CPU. Instead, open the load plate again and
double-check that the CPU is aligned properly.
2-5
Page 32

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Installing a CPU Heatsink
1. Apply the proper amount of thermal grease to the heatsink.
2. Place the heatsink on top of the CPU so that the four mount-
ing holes on the heatsink are aligned with those on the retention
mechanism. Tighten the screws in the following order:
Screw #4
Screw #3
Screw #2
3. Once the screws are tightened, plug the power cord into the
CPU_FAN1 connector.
Note: Screw #1 is not shown in the illustration.
Note: Graphic drawings included in this manual are for reference
only. They might look different from the components installed in
your system.
2-6
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installation
Removing a Heatsink
Warning: We do not recommend that the CPU or the heatsink be removed.
However, if you do need to remove the heatsink, please follow the instructions below to uninstall the heatsink to avoid damaging the CPU or other
components.
1. Unplug the power cord from the power supply.
2. Loosen the screws in the order below.
3. Gently wiggle the heatsink to loosen it. Do not use excessive force
when wiggling the heatsink.
Screw #4
Screw #3
Screw #2
4. Once the heatsink is loosened, remove it from the motherboard.
Note: Screw #1 is not shown in the illustration.
2-7
Page 34

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
SYS_FAN1
B
B
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
2-4 Installing DDR4 Memory
Note: Check the Supermicro website for recommended memory
modules.
Attention! Exercise extreme care when installing or removing
DIMM modules to prevent any possible damage.
DIMM Installation
1. Insert the desired number of
DIMMs into the memory slots,
starting with DIMMA2, then
DIMMB2, DIMMA1, and DIMMB1.
For the system to work properly,
please use the memory modules
of the same type and speed.
2. Push the release tab outwards
on the end of the DIMM slot to
unlock it.
3. Align the key of the DIMM module with the receptive point on the
memory slot.
4. Align one end of the DIMM module to the receptive point on the
stationary end of the slot, and the
other end of the DIMM to the locking end of the slot.
5. Press down on the stationary end of
the slot rst, then the locking end
until the module snaps into place.
6. Press the release tab to the lock
position to secure the DIMM module
into the slot.
AUDIO FP
J31
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
J9701
JSTBY1
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
J37
JWD1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
JL1
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
OC1
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
JF1
LED4
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
PCI-E M.2-M2
X
A
LED6
RST
C
LED1
PWR
ON
C
A
USB 8/9(3.0)
RESET
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
22110
MH15
REV:1.01
2280
+
MH14
B1
2260
MH13
D9019
JRLED2
CLEAR CMOS
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
JRLED3
I-SATA2I-SATA4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
POWER
JD1
BUTTON
+12V G R
V21+
G R
JD1
Release Tab
JUSBLAN2
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
HDMI
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
JPW1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
HD AUDIO
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
LED5
A
C
D9017
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
Notches
Press down on the
stationary end rst,
then the locking end.
PCI-E M.2-E1
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
12V_PUMP_PWR1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
Removing Memory Modules
Reverse the steps above to remove the
DIMM modules from the motherboard.
2-8
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installation
Memory Support
DIMMB2
DIMMB1
DIMMA2
DIMMA1
Towards the CPU
The C9Z390-CG/CGW suppor ts up to 64GB of Unbuffered (UDIMM)
non-ECC DDR4 memory with speeds of up to 3733+MHz (OC) in four
288-pin memory slots. Populating these DIMM modules with a pair of
memory modules of the same type and same size will result in interleaved memory, which will improve memory performance.
Note: Be sure to use memory modules of the same type and speed
on the motherboard. Mixing of memory modules of different types
is not allowed.
2-9
Page 36

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Memory Population Guidelines
When installing memory modules, the DIMM slots should be populated in
the following order: DIMMA2, DIMMB2, then DIMMA1, DIMMB1.
• Always use DDR4 DIMM modules of the same size, type, and speed.
• Mixed DIMM speeds can be installed. However, all DIMMs will run at the
speed of the slowest DIMM.
DIMMA2
DIMMA1
Towards the CPU
DIMMB2
DIMMB1
Recommended
Population
One DIMM
Two DIMM
Four DIMM
2-10
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installation
2-5 Motherboard Installation
All motherboards have standard mounting holes to t different types of
chassis. Make sure that the locations of all the mounting holes for both
motherboard and chassis match. Although a chassis may have both plastic and metal mounting fasteners, metal ones are highly recommended
because they ground the motherboard to the chassis. Make sure that the
metal standoffs click in or are screwed in tightly. Then use a screwdriver
to secure the motherboard onto the motherboard tray.
Tools Needed
Phillips Screwdriver (1)
Phillips Screws (9)
Standoffs (9)
Only if Needed
LED
LED LED
LED
5V STBY POWER
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
RWP
DDH
1
2
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
AUDIO FP
BOOT
AGV UPC
DIMM
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
LED
NIC
NIC
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
C
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JPME2
A
LED4
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB 6/7(3.1)
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
Location of Mounting Holes
Attention! 1) To avoid damaging the motherboard and its components, please do not use a force greater than 8 lb/inch on each mounting screw during motherboard installation. 2) Some components are
very close to the mounting holes. Please take precautionary measures
to avoid damaging these components when installing the motherboard
to the chassis.
1
SYS_FAN1
2-11
Page 38

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Installing the Motherboard
1. Install the I/O shield into the back of the chassis.
2. Locate the mounting holes on the motherboard. (See the previous
page.)
3. Locate the matching mounting holes on the chassis. Align the
mounting holes on the motherboard against the mounting holes on
the chassis.
4. Install standoffs in the chassis as needed.
5. Install the motherboard into the chassis carefully to avoid damaging
other motherboard components.
6. Using the Phillips screwdriver, insert a Phillips head #6 screw into a
mounting hole on the motherboard and its matching mounting hole
on the chassis.
7. Repeat Step 6 to insert remaining screws into all mounting holes.
8. Make sure that the motherboard is securely placed in the chassis.
Note: Images displayed are for illustration only. Your chassis
or components might look different from those shown in this
manual.
2-12
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installation
2-6 M.2 Installation (optional)
Two M.2 (M-key) connectors are supported by the C9Z390-CG/CGW. M.2
devices are used for solid state storage and internal expansion. Follow
the steps below in order to install an M.2 device.
1) Locate one of two standoffs.
Remove and set aside screw.
2) Plug M.2 device into M.2 connector and lower the semi-circle
notched end onto standoff.
3) Replace screw and tighten to
secure M.2 device into place. Do
not over-tighten so as to avoid
damaging the M.2 device.
2-13
Page 40

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
F
2-7 Connectors/IO Ports
The I/O ports are color coded in conformance with the industry standards.
See the gure below for the colors and locations of the various I/O ports.
I/O Back Panel
AUDIO FP
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
RWP
DDH
1
2
RST
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
J31
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
JSTBY1:
J37
COM1
JTPM1
LED
LED
NIC
NIC
OH/FF
X
PWR
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
C
LED1
A
JPME2
LED4
LED6
RESET
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
C
POWER
BUTTON
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
JD1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
JRLED3
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
MH7
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
USB 6/7(3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
HDMI
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
JPW1
A PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse G RJ45 1Gbit LAN M Center/LFE Out
B USB 3.1 Gen 1 Port 2 H USB 3.1 Gen 2 Port 4 (Type-A) N Surround Out
C USB 3.1 Gen 1 Port 3 I USB 3.1 Gen 2 Port 5 (Type-C) O SPDIF Out
D Display Port 1 J RJ45 10Gbit LAN P Line In
E Display Port 2 K USB 3.1 Gen 2 Port 6 Q Line Out
F HDMI L USB 3.1 Gen 2 Port 7 R Mic In
WIFI+BT
CPU_FAN2
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
1
SYS_FAN1
C9Z390-CG/CGW
P
A
G
D
B
E
C
H
I
2-14
M
J
K
L
Q
N
R
O
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installation
F
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
Four USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports (USB4/5/6/7; USB 4: Type-A, USB 5: Type-
C), and two USB 3.1 Gen 1 (USB 2/3) ports are on the I/O back panel.
In addition, one USB 2.0 header (USB0/1), one USB 3.1 Gen 1 header
(USB8/9), and one USB 3.1 Gen 2 Type-C header (USB 10) are located
on the motherboard to provide front chassis access using USB cables
(not included). Refer to the tables below for pin denitions.
USB (3.1 Gen 1) 2/3, USB (3.1 Gen 2) 4/5,
6/7 Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 +5V 5 +5V
2 USB_PN1 6 USB_PN0
3 USB_PP1 7 USB_PP0
4 Ground 8 Ground
Front Panel USB (2.0) Header 0/1 Pin
Definitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 +5V 2 +5V
3 USB_PN2 4 USB_PN3
5 USB_PP2 6 USB_PP3
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 Key 10 Ground
Front Panel USB (3.1 Gen 1) Header 8/9
Pin Definitions
Pin# Pin# Signal Name Description
1 19 VBUS Power
2 18 StdA_SSRX- SuperSpeed Receiver
3 17 StdA_SSRX+ Differential Pari
4 16 Ground Ground of PWR Return
5 15 StdA_SSTX- SuperSpeed Transmitter
6 14 StdA_SSTX+ Differential Pair
7 13 GND_DRAIN Ground for Signal
Return
8 12 D- USB 2.0 Differential Pair
9 11 D+
C9Z390-CG/CGW
AUDIO FP
J31
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
J9701
A
B
E
C
D
G
H
JSTBY1
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
J37
JWD1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
JL1
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
OC1
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
JF1
LED4
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
C
LED1
PWR
ON
A
USB 8/9(3.0)
A. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen1 Port2
B. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen1 Port3
C. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen2 Port4
D. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen2 Port5
E. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen2 Port6
F. Back panel USB 3.1 Gen2 Port7
G. USB 2.0 Header 0/1
H. USB 3.1 Gen1 Header 8/9
JUSBLAN2
DP1/DP2
HDMI
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
JPW1
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
A
LED6
C
RESET
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
22110
MH15
REV:1.01
2280
+
MH14
B1
2260
MH13
D9019
JRLED2
PCI-E M.2-M2
CLEAR CMOS
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
JRLED3
I-SATA2I-SATA4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
POWER
JD1
BUTTON
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G RB V21+
JD1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
LED5
A
C
D9017
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
12V_PUMP_PWR1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
SYS_FAN1
2-15
Page 42

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Front Panel USB (3.1 Gen 2 Type-C) Header 10
Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 VBUS 8 CC1 15 RX2+
2 TX1+ 9 SBU1 16 RX2-
3 TX1- 10 SBU2 17 GND
4 GND 11 VBUS 18 D-
5 RX1+ 12 TX2+ 19 D+
6 RX1- 13 TX2- 20 CC2
7 VBUS 14 GND
A. Front panel USB 3.1 Gen2 Port10
AUDIO FP
J31
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
JSTBY1:
COM1
JTPM1
LED
LED
NIC
NIC
PWR
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
LED4
C
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
22110
2280
2260
JSPDIF_OUT
MH15
MH14
MH13
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
CLEAR CMOS
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
A
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
RWP
DDH
1
2
OH/FF
X
RST
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
JRLED3
+12V G R B
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
MH7
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
MH4
MAC CODE
JVR2
1
SYS_FAN1
2-16
Page 43

Chapter 2: Installation
Ethernet Ports
There are two Ethernet ports (LAN1/2)
on the I/O back panel to provide network
connections. These ports accept RJ45
type cables.
Note: Please refer to the LED Indica-
tor Section for LAN LED information.
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 P2V5SB 10 SGND
2 TD0+ 11 Act LED
3 TD0- 12 P3V3SB
4 TD1+ 13 Link 100
5 TD1- 14 Link 1000
6 TD2+ 15 Ground
7 TD2- 16 Ground
8 TD3+ 17 Ground
9 TD3- 18 Ground
LAN Ports
Pin Definition
LED (Green,
+3V3SB)
LED (Yellow,
+3V3SB)
ATX PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Port
The ATX PS/2 keyboard and mouse port are located on the back panel
above USB Ports 2/3.
A. PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Port
B. LAN1
C. LAN2
C9Z390-CG/CGW
A
B
2-17
C
Page 44

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
F
HD AUDIO Ports
This motherboard features a 7.1+2 Channel High Denition Audio (HDA)
codec that provides 10 DAC channels. The HD Audio connections on the
I/O back panel simultaneously supports multiple-streaming 7.1 sound
playback with two channels of independent stereo output through the
front panel stereo out for front, rear, center and subwoofer speakers. Use
the Advanced software included in the CD-ROM with your motherboard
to enable this function.
DisplayPort
There are two DisplayPort ports on the I/O back panel. DisplayPort, developed by the VESA consortium, delivers digital display and fast refresh
rate. It can connect to virtually any display device using a DisplayPort
adapter for devices such as VGA, DVI, or HDMI.
HDMI
One HDMI (High Denition Multimedia Interface) port is located next to
the VGA port on the I/O back panel. This connector is used to display
both high denition video and digital sound through an HDMI-capable
display, using a single HDMI cable (not included).
A. DisplayPort 1
B. DisplayPort 2
C. HDMI
D. Center/LFE Out
E. Surround Out
F. S/PDIF Out
G. Line In
H. Line Out
I. Mic In
C9Z390-CG/CGW
G
D
A
C
E
B
2-18
H
I
Page 45

Chapter 2: Installation
JD1
JF1
JTPM1
JL1
OC1
JWD1
JPME2
JSTBY1
JI2C1
JI2C2
J9701
JSPDIF_OUT
JSD1
SYS_FAN2
B1
JPW1
SYS_FAN1
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
SYS_FAN3
JPW2
JVR2
MH7
J31
JD1
J37
1
BIOS LICENSE
C
A
DESIGNED IN USA
C9Z390-CGW
REV:1.01
+
BAR CODE
MAC CODE
G R B V21+
C
C
+12V G R B
A
A
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
LED6
LED1
JRLED3
JRLED4
USB 8/9(3.0)
NIC
1
NIC
OH/FF
RST
X
PWR
ON
LED
RWP
DDH
LED
I-SATA2I-SATA4
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
PCI-E M.2-M2
POWER
BUTTON
CLEAR CMOS
2
RESET
BUTTON
USB 0/1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
COM1
LED4
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2260
2280
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
MH14
MH13
USB 10(3.1)
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
AGV UPC
MH15
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
LED LED
LED
22110
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
AUDIO FP
BOOT
LED
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
PCI-E M.2-M1
2242
2280
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
HD AUDIO
22110
LED5
MH11
MH10
JRLED1
USB 6/7(3.1)
LAN1
MH12
LAN2
DIMMA2
DIMMB2
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
USB 2/3
KB/MOUSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
(3.0)
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
JUSBLAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
DIMM
J9702
PCI-E M.2-E1
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
D9019
D9017
WIFI+BT
MAC CODE
12V_PUMP_PWR1
Front Control Panel
JF1 contains header pins for various buttons and indicators that are
normally located on a control panel at the front of the chassis. These
connectors are designed specically for use with Supermicro chassis. See
the gure below for the descriptions of the front control panel buttons
and LED indicators. Refer to the following section for descriptions and
pin denitions.
POWER LED (-)
HDD LED (-)
NIC1 LED (-)
NIC2 LED (-)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (-)
JF1 Header Pins
1516
POWER LED (+)
HDD LED (+)
NIC1 LED (+)
NIC2 LED (+)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (+)
X
Ground
Ground
2
X
Reset
PWR
1
2-19
Reset Button
Power Button
Page 46

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Front Control Panel Pin Definitions
Power LED
The Power LED connection is located on
pins 15 and 16 of JF1. Refer to the table
on the right for pin denitions.
HDD LED
The HDD LED connection is located on
pins 13 and 14 of JF1. Attach a cable
here to indicate the status of HDDrelated activities, including IDE and SATA
activities. Refer to the table on the right
for pin denitions.
NIC1/NIC2 Activty LED
The NIC (Network Interface Controller)
LED connection for LAN port 1 is located
on pins 11 and 12, and for LAN port 2 is
located on pins 9 and 10. Attach NIC LED
cables here to display network activities.
Refer to the table on the right for pin
denitions.
Power LED
Pin Definitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
15 PWR LED (+)
16 PWR LED (-)
HDD LED
Pin Definitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
13 HDD LED (+)
14 HDD LED (-)
LAN LED
Pin Definitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
9 NIC2 LED (-)
10 NIC2 LED (+)
11 NIC1 LED (-)
12 NIC1 LED (+)
POWER LED (-)
A
HDD LED (-)
B
C
NIC1 LED (-)
NIC2 LED (-)
D
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (-)
X
Ground
Ground
1516
POWER LED (+)
HDD LED (+)
NIC1 LED (+)
NIC2 LED (+)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (+)
X
Reset
Reset Button
PWR
Power Button
1
2
2-20
B. HDD LED
C. NIC1 LED
D. NIC2 LED
A. PWR LED
Page 47

Chapter 2: Installation
Overheat (OH)/Fan Fail
Connect an LED cable to OH/Fan Fail
connections on pins 7 and 8 of JF1 to
provide warnings for chassis overheat/
fan failure. Refer to the table on the right
for pin denitions.
OH/Fan Fail LED
Pin Definitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
8 OH/Fan Fail LED
OH/Fan Fail Indicator
Status
State Denition
Off Normal
On Overheat
Flashing Fan Fail
POWER LED (-)
HDD LED (-)
NIC1 LED (-)
NIC2 LED (-)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (-)
Ground
Ground
1516
POWER LED (+)
HDD LED (+)
NIC1 LED (+)
NIC2 LED (+)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (+)
Reset
PWR
X
Reset Button
Power Button
2-21
X
A
A. Overheat/Fan Fail
Page 48

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Power Button
The Power Button connection is located
on pins 1 and 2 of JF1. Momentarily
contacting both pins will power on/off
the system. This button can also be con-
gured to function as a suspend button
(with a setting in the BIOS - see Chapter
4). To turn off the power in the suspend
mode, press the button for at least four
seconds. Refer to the table on the right
for pin denitions.
Reset Button
The Reset Button connection is located
on pins 3 and 4 of JF1. Attach it to a
hardware reset switch on the computer
case to reset the system. Refer to the
table on the right for pin denitions.
Power Button
Pin Definitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
1 Signal
2 Ground
Reset Button
Pin Denitions (JF1)
Pin# Denition
3 Reset
4 Ground
POWER LED (-)
HDD LED (-)
NIC1 LED (-)
NIC2 LED (-)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (-)
Ground
Ground
1516
POWER LED (+)
HDD LED (+)
NIC1 LED (+)
NIC2 LED (+)
Overheat/
Fan Fail LED (+)
X
2
X
Reset
Reset Button
PWR
Power Button
1
2-22
B
A
A. Power Button
B. Reset Button
Page 49

Chapter 2: Installation
SYS_FAN1
2-8 Connecting Cables
This section provides brief descriptions and pin-out denitions for onboard headers and connectors. Be sure to use the correct cable for each
header or connector.
ATX Main PWR and CPU PWR
Connectors
The 24-pin main power connector
(JPW1) provides power to the motherboard. The 8-pin CPU PWR connector
(JPW2) is also required for the processor. These power connectors meet the
SSI EPS 12V specication. Refer to the
table on the right for pin denitions.
12V 8-pin Power Connector
Pin Definitions
Pins Denition
1-4 Ground
5-8 +12V
(Required)
LED
LED LED
LED
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
USB 8/9(3.0)
AUDIO FP
BOOT
AGV UPC
DIMM
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
COM1
JTPM1
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
C
LED1
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
LED4
LED6
RESET
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
22110
MH15
2280
MH14
2260
MH13
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
C
CLEAR CMOS
POWER
JD1
BUTTON
JD1
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
JRLED4
JRLED3
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
HD AUDIO
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
LED5
A
C
D9017
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
ATX Power 24-pin Connector
Pin Definitions (JPW1)
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
13 +3.3V 1 +3.3V
14 -12V 2 +3.3V
15 Ground 3 Ground
16 PS_ON 4 +5V
17 Ground 5 Ground
18 Ground 6 +5V
19 Ground 7 Ground
20 Res (NC) 8 PWR_OK
21 +5V 9 5VSB
22 +5V 10 +12V
23 +5V 11 +12V
24 Ground 12 +3.3V
A. 24-Pin ATX Main PWR
B. 8-Pin PWR
JUSBLAN2
LAN2
JRLED1
USB4/5 (3.1)
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
A
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
JPW2
B
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
2-23
Page 50

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
F
Fan Headers
The motherboard has five 4-pin fan
headers (CPU_FAN1/2, SYS_FAN1/2/3).
Although pins 1-3 of the system fan
headers are backward compatible with
the traditional 3-pin fans, we recommend
the use of 4-pin fans to take advantage
Fan Header
Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition
1 Ground (Black)
2 2.5A/+12V
(Red)
3 Tachometer
4 PWM_Control
of the fan speed control. This allows the
fan speeds to be automatically adjusted
based on the motherboard temperature.
Refer to the table on the right for pin
denitions.
Pump Power Header
The C9Z390-CG/CGW has one +12V header for optional CPU liquid cooling systems. When using a liquid cooling system, attach the pump power
cable to the PUMP_PWR1 header.
A. CPU_FAN1
B. CPU_FAN2
C. SYS_FAN1
D. SYS_FAN2
E. SYS_FAN3
F. 12V_PUMP_PWR1
LED
LED LED
LED
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
USB 8/9(3.0)
AUDIO FP
J31
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
1-2:NORMAL
ON :ENABLE
JTPM1
J9701/J9702
JI2C1/JI2C2
J37
COM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
C
LED1
A
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
22110
MH15
2280
MH14
2260
MH13
LED4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
CLEAR CMOS
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
DIMM
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
+12V G R B
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MH7
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
D
USB4/5 (3.1)
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
E
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
B
CPU_FAN1
MH4
A
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
SYS_FAN1
C
2-24
Page 51

Chapter 2: Installation
SYS_FAN1
Speaker
On the JD1 header, pins 3 and 4 are
used for a buzzer. If you wish to use an
external speaker, close pins 1-4 with a
cable. Refer to the table on the right for
Speaker Connector
Pin Definitions
Pin Setting Denition
Pins 3-4 Buzzer
Pins 1-4 External Speaker
pin denitions.
RGB LED Headers
The JRLED1/2/3/4 headers are used to enable software control for connected RBG LED lighting devices.
Chassis Intrusion
A Chassis Intrusion header is located at
JL1 on the motherboard. Attach the appropriate cable from the chassis to inform
you of a chassis intrusion when the chassis
Chassis Intrusion
Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition
1 Intrusion Input
2 Ground
is opened.
A. Speaker Header
B. JRLED1
C. JRLED2
D. JRLED3/4
E. Chassis Intrusion
AUDIO FP
J31
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
J9701/J9702
JI2C1/JI2C2
COM1
JTPM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
C
LED1
A
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
22110
MH15
2280
MH14
2260
MH13
LED4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
CLEAR CMOS
POWER
RESET
JD1
BUTTON
BUTTON
DIMM
LED
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
E
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
A
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
JRLED4
JRLED3
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
D
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
C
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MH7
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
MH11
B
MH10
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
USB4/5 (3.1)
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
2-25
Page 52

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
SYS_FAN1
Serial Header
There is one serial (COM) header on
the motherboard. Refer to the table on
the right for pin denitions.
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 DCD 6 DSR
2 RXD 7 RTS
Serial/COM Port
Pin Definitions
3 TXD 8 CTS
4 DTR 9 RI
5 Ground 10 N/A
OC1 Header
Attach an external switch to the OC1 header to enable overclocking set-
tings as pre-dened in the BIOS.
Power SMB (I2C) Header
Power System Management Bus headers at JI2C1/JI2C2 monitor the power
supply, fan, and systems temperatures. Refer to the table on the right
for pin denitions.
Power SMB
Pin Denitions
Pin# Denition
1 Clock
2 Data
3 Power Fail
4 Ground
5 +3.3V
A. COM1
AUDIO FP
J31
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
COM1
JTPM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
C
LED1
A
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
22110
MH15
2280
MH14
2260
MH13
A
JPME2
LED4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
CLEAR CMOS
POWER
RESET
JD1
BUTTON
BUTTON
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
C
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
B
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
JRLED4
JRLED3
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
22110
MH11
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MH7
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
MH10
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
USB4/5 (3.1)
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
B. Overclocking
Setting Header
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
C. JI2C1/2
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
2-26
Page 53

Chapter 2: Installation
SYS_FAN1
DOM PWR Connector
The Disk-On-Module (DOM) power connector, located at JSD1, provides 5V
power to a solid state DOM storage
device connected to one of the SATA
ports. Refer to the table on the right for
DOM PWR
Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition
1 5V
2 Ground
3 Ground
pin denitions.
Battery Connector
B1 is a two-pin connector for an external CMOS battery. Refer to Chapter
3 for battery installation instructions. This connector is also used to clear
the CMOS. To clear the CMOS, remove the battery, short pins 1 and 2
and then install the battery.
SPDIF_Out Headers
The Sony/Philips Digital Interface (JSPDIF_Out) header is used for digital
audio. Place a cap on the header for audio support. You will also need
to have a cable to use the connection.
A. DOM PWR
B. Battery Connector
C. SPDIF_Out
C
AUDIO FP
J31
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
J9701/J9702
JI2C1/JI2C2
J37
COM1
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
C
LED1
A
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
22110
MH15
2280
MH14
2260
MH13
LED4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
CLEAR CMOS
POWER
RESET
JD1
BUTTON
BUTTON
JD1
DIMM
LED
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
JRLED4
JRLED3
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
B
I-SATA2I-SATA4
A
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MH7
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
USB4/5 (3.1)
DP1/DP2
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
2-27
Page 54

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
M.2 Connectors
M.2 is formerly known as Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF). The three
M.2 connectors are designed for internal mounting devices and provide
M-Key 2242/2280/22110 (M.2-M1) and 2260/2280/22110 (M.2-M2) for
native PCI-E SSD support, and E-Key (M.2-E1) dedicated support for
WiFi + BT devices with the ultimate performance capability in a PCI
Express 3.0 interface.
Standby Power Header
The Standby Power header is located at
JSTBY1 on the motherboard. Refer to
the table on the right for pin denitions.
AUDIO FP
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
LED4
C
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
22110
2280
2260
JSPDIF_OUT
MH15
MH14
MH13
B
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
D
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
+12V G R B
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
HD AUDIO
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
A
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
Pin# Denition
1 +5V Standby
2 Ground
3 Wake-up
A. PCI-E M.2-M1
B. PCI-E M.2-M2
C. PCI-E M.2-E1
D. Standby Power
JUSBLAN2
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
USB 6/7(3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
Standby Power
Pin Definitions
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
HDMI
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
JPW1
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
C
1
SYS_FAN1
2-28
Page 55

Chapter 2: Installation
Front Panel Audio Header
A 10-pin Audio header at AUDIO FP is
supported on the motherboard. This
header allows you to connect the motherboard to a front panel audio control
panel, if needed. Connect an audio cable
to the audio header to use this feature
(not supplied). Refer to the table on the
right for pin denitions for the header.
TPM Header/Port 80
A Trusted Platform Module/Port 80 header is located at JTPM1 to provide TPM
support and Port 80 connection. Use this
header to enhance system performance
and data security. Refer to the table on
the right for pin denitions.
A. AUDIO FP
B. TPM Header
10-in Audio
Pin Definitions
Pin# Signal
1 Microphone_Left
2 Audio_Ground
3 Microphone_Right
4 Audio_Detect
5 Line_2_Right
6 Ground
7 Jack_Detect
8 Key
9 Line_2_Left
10 Ground
TPM/Port 80 Header
Pin Definitions
Pin# Denition Pin# Denition
1 LCLK 2 GND
3 LFRAME# 4 <(KEY)>
5 LRESET# 6 +5V (X)
7 LAD 3 8 LAD 2
9 +3.3V 10 LAD1
11 LAD0 12 GND
13 SMB_CLK4 14 SMB_DAT4
15 +3V_DUAL 16 SERIRQ
17 GND 18 CLKRUN# (X)
19 LPCPD# 20 LDRQ# (X)
AUDIO FP
J31
A
B
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
J9701
JSTBY1
22110
USB 10(3.1)
MH15
USB 0/1
J37
2280
MH14
JWD1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
JL1
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
OC1
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
2260
MH13
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
JF1
LED4
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
PCI-E M.2-M2
X
A
LED6
RST
C
LED1
PWR
ON
C
A
CLEAR CMOS
USB 8/9(3.0)
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
+12V G R B
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MH7
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
(3.0)
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
PCI-E M.2-E1
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
MH4
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
SYS_FAN1
2-29
Page 56

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
2-9 Jumper Settings
Explanation of Jumpers
To modify the operation of the motherboard, jumpers can be used to
choose between optional settings. Jumpers create shorts between two
pins to change the function of the connector. Pin 1 is identied with a
square solder pad on the printed circuit board.
Note: On two-pin jumpers, Closed means the jumper is on, and Open
means the jumper is off the pins.
2-30
Page 57

Chapter 2: Installation
SYS_FAN1
CLEAR CMOS
CLEAR CMOS is used to clear the saved system setup conguration stored
in the CMOS chip. Pressing this button will erase all user settings and
revert everything to their factory defaults.
Watch Dog Timer Enable/Disable
Watch Dog (JWD1) is a system monitor
that can reboot the system when a software application hangs. Close pins 1 and
2 to reset the system if an application
hangs. Close pins 2 and 3 to generate a
non-maskable interrupt signal for the application that hangs. Refer to the table on
the right for jumper settings.
AUDIO FP
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
LED4
C
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
A
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
B
JL1
OC1
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
+12V G R B
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
HD AUDIO
MH12
22110
2280
2242
MH7
USB 6/7(3.1)
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
BIOS LICENSE
Jumper Settings
Pin# Denition
1-2 Reset (default)
2-3 NMI
Open Disabled
A. CLEAR CMOS
B. Watch Dog Timer
JUSBLAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
HDMI
LAN1
JPW1
LAN2
JRLED1
Watch Dog
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
1
2-31
Page 58

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Manufacturing Mode
Close pins 2 and 3 of jumper JPME2
to bypass SPI flash security and force
the system to operate in Manufacturing
Mode, allowing the user to flash the system rmware from a host server for system setting modications. Refer to the
table on the right for jumper settings.
Manufacturing Mode
Jumper Settings
Pin# Denition
1-2 Normal (Default)
2-3 Manufacturing
Mode
A. Manufacturing Mode
LED
LED LED
LED
5V STBY POWER
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
DDH
2
USB 8/9(3.0)
AUDIO FP
BOOT
AGV UPC
DIMM
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
JSTBY1:
USB 10(3.1)
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
NIC
1
NIC
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
LED4
C
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
A
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
22110
2280
2242
MH7
MH12
MH11
MH10
A
2-32
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
USB 6/7(3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
LED5
C
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
1
SYS_FAN1
Page 59

2-10 Onboard Indicators
SYS_FAN1
Chapter 2: Installation
LAN LEDs
One LAN port is on the I/O back panel.
This Ethernet LAN port has two LEDs
(Light Emitting Diode). The yellow LED
indicates activity, while the Link LED
may be green, amber, or off to indicate
the speed of the connections. Refer to
the tables on the right for more information.
LAN
Link LED
Activity LED
Onboard Power LED
An Onboard Power LED is located at
LED1. When this LED is on, the AC power
cable is connected. Make sure to disconnect the power cable before removing or
installing a component.
GLAN Activity Indicator
LED Settings
Color Status Denition
Yellow Flashing Active
10GLAN Link Indicator
LED Settings
LED Color Denition
Off No Connection/10 Mbps
Amber 5Gbps/1Gbps/100 Mbps
Green 10 Gbps
GLAN Link Indicator
LED Settings
LED Color Denition
Off No Connection/10 Mbps
Amber 100 Mbps
Green 1 Gbps
Onboard PWR LED Indicator
LED Status
Status Denition
Off System Off
Solid
Green
System on, or
System off and PWR
Cable Connected
A
AUDIO FP
J31
JSPDIF_OUT
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
J9701
JSTBY1
22110
USB 10(3.1)
MH15
USB 0/1
J37
2280
MH14
JWD1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
JL1
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
OC1
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
2260
MH13
COM1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
JF1
LED4
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
PCI-E M.2-M2
X
A
LED6
RST
C
LED1
PWR
ON
C
A
B
USB 8/9(3.0)
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
G R B V21+
JD1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
+12V G R B
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
+
B1
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
22110
2280
2242
PCI-E M.2-M1
D9017
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
SYS_FAN2
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
MH12
USB 6/7(3.1)
MH11
MH10
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
HDMI
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
JPW1
PCI-E M.2-E1
DP1/DP2
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
WIFI+BT
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
JPW2
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
1
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
12V_PUMP_PWR1
MH4
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
MAC CODE
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
2-33
A. LAN LEDs
B. Onboard Power
LED
Page 60

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
BIOS
LICENSE
MAC CODE
IPMI CODE
BAR CODE
+
PCIE M.2 CONNECTOR 2
PCIE M.2 CONNECTOR 1
SPEAKER:1-4
BUZZER:3-4
JD1
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
CPU SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
1-2 ENABLE
2-3 DISABLE
JPAC1:AUDIO
J*
LED1
JPAC1
JPG1
JBT1
JSTBY1
MH12
MH14
LED6903
LED6904
B2
PCH
Status Display
LED4 is made up of two alphanumeric displays that will display
a status or POST code, when
the motherboard is powered on.
Please download the following
AMI publication for a complete
list of POST codes:
https://ami.com/ami_downloads/Aptio_V_Status_Codes.pdf
AUDIO FP
J31
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
DIMM
LED
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:DEBUG MODE
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
JSTBY1:
J9701
JSTBY1
22110
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
J37
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JTPM1
JF1
LED
RWP
LED
DDH
NIC
1
NIC
2
OH/FF
X
RST
PWR
ON
COM1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
JPME2
LED4
C
LED1
A
2280
2260
A
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JWD1
OC1
JL1
USB 8/9(3.0)
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
A. Status LED
JUSBLAN2
HD AUDIO
LAN2
USB 6/7(3.1)
JRLED1
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
DP1/DP2
HDMI
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
1
SYS_FAN1
2-34
Page 61

2-11 Hard Drive Connections
F
Chapter 2: Installation
SATA Connections (I-SATA0~ISATA5)
Six Serial ATA (SATA) 3.0 connectors
(I-SATA 0~5) are supported by the
Intel Z390 chip. Refer to the table on the
right for pin denitions.
AUDIO FP
BOOT
LED
LED LED
AGV UPC
DIMM
LED
2-3:DEBUG MODE
OFF:DISABLE
5V STBY POWER
USB 10(3.1)
USB 0/1
JWD1
JL1
OC1
JTPM1:TPM/PORT80
JF1
RWP
DDH
1
2
RST
ON
USB 8/9(3.0)
J9701/J9702
1-2:NORMAL
JI2C1/JI2C2
ON :ENABLE
JSTBY1:
COM1
JTPM1
LED
LED
NIC
NIC
OH/FF
X
PWR
J31
J9702
JI2C2
JI2C1
J9701
JSTBY1
J37
JPME2:
1-2:NORMAL
2-3:ME MANUFACTURING MODE
C
LED1
JWD1:WATCH DOG
1-2:RST
2-3:NMI
JL1:CHASSISINTRUSION
JPME2
LED4
A
CPU SLOT1 PCI-E 3.0 X4
22110
2280
2260
PCI-E M.2-M2
A
LED6
C
POWER
RESET
BUTTON
BUTTON
JSPDIF_OUT
PCH SLOT2 PCI-E 3.0 X1
MH15
MH14
MH13
CLEAR CMOS
JRLED3
JD1
JD1:SPEAKER:1-4
+12V G R B
G R B V21+
JD1
PCH SLOT4 PCI-E 3.0 X1
C9Z390-CGW
CPU SLOT3 PCI-E 3.0 X8 (IN X16)
DESIGNED IN USA
REV:1.01
+
B1
D9019
JRLED2
JSD1:SATA DOM PWR
JSD1
JRLED4
I-SATA5 I-SATA3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
PCH SLOT5 PCI-E 3.0 X1
I-SATA2I-SATA4
CPU SLOT6 PCI-E 3.0 X16
I-SATA0
I-SATA1
D9017
SYS_FAN2
PCI-E M.2-M1
MAC CODE
BAR CODE
HD AUDIO
MH12
22110
MH11
2280
MH10
2242
LED5
A
C
MH7
BIOS LICENSE
A CDE
B
USB 6/7(3.1)
SATA 2.0/3.0 Connectors
Pin Definitions
Pin# Signal
1 Ground
2 SATA_TXP
3 SATA_TXN
4 Ground
5 SATA_RXN
6 SATA_RXP
7 Ground
A. I-SATA4
B. I-SATA5
C. I-SATA2
D I-SATA3
E. I-SATA0
F. I-SATA1
JUSBLAN2
LAN2
USB4/5 (3.1)
LAN1
JRLED1
DP1/DP2
HDMI
JPW1
KB/MOUSE
(3.0)
USB 2/3
(For C9Z390-CGW only)
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
WIFI+BT
12V_PUMP_PWR1
JPW2
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
DIMMA1
DIMMA2
DIMMB1
DIMMB2
PCI-E M.2-E1
SYS_FAN3
JVR2
MH4
MAC CODE
1
SYS_FAN1
2-35
Page 62

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Notes
Notes
2-36
Page 63

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
Chapter 3
Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures to troubleshoot your system. If you have
followed all of the procedures below and still need assistance, refer to the
‘Technical Support Procedures’ and/or ‘Returning Merchandise for Service’
section(s) in this chapter. Always disconnect the AC power cord before
adding, changing or installing any hardware components.
Before Power On
1. Make sure that the Standby PWR LED is not on. (Note: If it is on,
the onboard power is on. Be sure to unplug the power cable before
installing or removing the components.)
2. Make sure that there are no short circuits between the motherboard
and chassis.
3. Disconnect all ribbon/wire cables from the motherboard, including
those for the keyboard and mouse. Also, be sure to remove all addon cards.
4. Install a CPU and heatsink (be sure that it is fully seated) and then
connect the chassis speaker and the power LED to the motherboard. Check all jumper settings as well.
No Power
1. Make sure that there are no short circuits between the motherboard
and chassis.
2. Make sure that all jumpers are set to their default positions.
3. Check if the 115V/230V switch on the power supply is properly set.
4. Turn the power switch on and off to test the system.
3-1
Page 64

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
5. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to make sure
that it still supplies ~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new
one.
No Video
1. If the power is on, but you have no video--in this case, you will
need to remove all the add-on cards and cables rst.
2. Use the speaker to determine if any beep codes exist. (Refer to Appendix A for details on beep codes.)
3. Remove all memory modules and turn on the system. (If the
alarm is on, check the specications of memory modules, reset the
memory or try a different one.)
Memory Errors
1. Make sure that the DIMM modules are properly installed and fully
seated in the slots.
2. You should be using unbuffered Non-ECC DDR4 (up to 3733+MHz
if overclocked) memory recommended by the manufacturer. Also,
it is recommended that you use the memory modules of the same
type and speed for all DIMMs in the system. Do not use memory
modules of different sizes, different speeds and different types on
the same motherboard.
3. Check for bad DIMM modules or slots by swapping modules between slots to see if you can locate the faulty ones.
4. Check the switch of 115V/230V power supply.
When the System is Losing the Setup Configuration
1. Please be sure to use a high quality power supply. A poor quality
power supply may cause the system to lose CMOS setup information. Refer to Section 1-7 for details on recommended power supplies.
2. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to verify that
it still supplies ~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new one.
3-2
Page 65

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3. If the above steps do not x the Setup Conguration problem,
contact your vendor for repairs.
3-2 Technical Support Procedures
Before contacting Technical Support, please make sure that you have
followed all the steps listed below. Also, note that as a motherboard
manufacturer, Supermicro does not sell directly to end users, so it is
best to rst check with your distributor or reseller for troubleshooting
services. They should know of any possible problem(s) with the specic
system conguration that was sold to you.
1. Please go through the ‘Troubleshooting Procedures’ and 'Frequently
Asked Question' (FAQ) sections in this chapter or see the FAQs on
our website (http://www.supermicro.com/support/faqs/) before
contacting Technical Support.
2. BIOS upgrades can be downloaded from our website at (http://
www.supermicro.com/support/bios/).
Note: Not all BIOS can be ashed. Some cannot be ashed; it
depends on the boot block code of the BIOS.
3. If you've followed the instructions above to troubleshoot your
system, and still cannot resolve the problem, then contact Supermicro's technical support and provide them with the following information:
• Motherboard model and PCB revision number
• BIOS release date/version (this can be seen on the initial display when
your system rst boots up)
• System conguration
• An example of a Technical Support form is on our website at (http://
www.supermicro.com/support/contact.cfm)
4. Distributors: For immediate assistance, please have your account
number ready when placing a call to our technical support depart-
ment. We can be reached by e-mail at support@supermicro.com,
by phone at: (408) 503-8000, option 2, or by fax at (408)503-
8019.
3-3
Page 66

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
3-3 Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What type of memory does my motherboard support?
Answer: The C9Z390-CG/CGW supports up to 64GB of unbuffered Non-
ECC DDR4. See Section 2-4 for details on installing memory.
Question: How do I update my BIOS?
Answer: We do NOT recommend that you upgrade your BIOS if you are
not experiencing any problems with your system. Updated BIOS les are
located on our website at http://www.supermicro.com/support/bios/.
Please check our BIOS warning message and the information on how
to update your BIOS on our website. Select your motherboard model
and download the BIOS ROM le to your computer. Also, check the current BIOS revision to make sure that it is newer than your BIOS before
downloading. You may choose the zip le or the .exe le. If you choose
the zipped BIOS le, please unzip the BIOS le onto a bootable device
or a USB pen/thumb drive. To ash the BIOS, run the batch le named
"ami.bat" with the new BIOS ROM le from your bootable device or USB
pen/thumb drive. Use the following format:
F:\> ami.bat BIOS-ROM-lename.xxx <Enter>
Note: Always use the le named “ami.bat” to update the
BIOS, and inser t a space between "ami.bat" and the lename.
The BIOS-ROM-lename will bear the motherboard name (i.e.,
C9Z390) and build version as the extension. For example,
"C9Z390.115". When completed, your system will automatically
reboot.
If you choose the .exe le, please run the .exe le under Windows to create the BIOS ash oppy disk. Insert the oppy disk
into the system you wish to ash the BIOS. Then, boot the system to the oppy disk. The BIOS utility will automatically ash
the BIOS without any prompts. Please note that this process
may take a few minutes to complete. Do not be concerned if
the screen is paused for a few minutes.
When the BIOS ashing screen is completed, the system will
reboot and will show “Press F1 or F2”. At this point, you will
need to load the BIOS defaults. Press <F1> to go to the BIOS
setup screen, and press <F9> to load the default settings. Next,
press <F10> to save and exit. The system will then reboot.
Attention! Do not shut down or reset the system while updating
the BIOS to prevent possible system boot failure!
3-4
Page 67

Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
Question: I think my BIOS is corrupted. How can I recover my BIOS?
Answer: Please see Appendix C - BIOS Recovery for detailed instructions.
3-4 Battery Removal and Installation
Battery Removal
To remove the onboard battery, follow the steps below:
1. Power off your system and unplug your power cable.
2. Locate the onboard battery as shown below.
3. Using a tool such as a pen or a small screwdriver, push the battery
lock outwards to unlock it. Once unlocked, the battery will pop out
from the holder.
4. Remove the battery.
Proper Battery Disposal
Battery
Lock
Attention! Please handle used batteries carefully. Do not damage
the battery in any way; a damaged battery may release hazardous
materials into the environment. Do not discard a used battery in the
garbage or a public landll. Please comply with the regulations set
up by your local hazardous waste management agency to dispose of
your used battery properly.
Battery
3-5
Page 68

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Battery Installation
1. To install an onboard battery, follow the steps 1 and 2 above and
continue below:
2. Identify the battery's polarity. The positive (+) side should be facing up.
3. Insert the battery into the battery holder and push it down until
you hear a click to ensure that the battery is securely locked.
Attention! When replacing a battery, be sure to only replace it with
the same type.
1
This side up
2
Press down until
you hear a click.
3-5 Returning Motherboard for Service
A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is
required before any warranty service will be rendered. You can obtain
service by calling your vendor for a Returned Merchandise Authorization
(RMA) number. For faster service, you may also obtain RMA authorizations online (http://www.supermicro.com/RmaForm/). When you return
the motherboard to the manufacturer, the RMA number should be
prominently displayed on the outside of the shipping carton, and mailed
prepaid or hand-carried. Shipping and handling charges will be applied
for all orders that must be mailed when service is complete.
This warranty only covers normal consumer use and does not cover
damages incurred in shipping or from failure due to the alteration,
misuse, abuse or improper maintenance of products.
During the warranty period, contact your distributor rst for any product problems.
3-6
Page 69

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
Chapter 4
BIOS
4-1 Introduction
This chapter describes the AMI BIOS Setup Utility for the C9Z390-CG/CGW.
The ROM BIOS is stored in a Flash EEPROM and can be easily updated.
This chapter describes the basic navigation of the AMI BIOS Setup Utility setup screens.
Note: For AMI BIOS Recovery, please refer to the UEFI BIOS Recovery Instructions in Appendix C.
How To Change the Configuration Data
The conguration data that determines the system parameters may be
changed by entering the AMI BIOS GUI Setup utility. This Setup util-
ity can be accessed by pressing <Del> at the appropriate time during
system boot.
Note: For the purposes of this manual, options that are printed in
Bold are default settings.
Each BIOS menu option is described in this manual. The Advanced Mode
BIOS Setup screen has two main areas. The top area is the main Navigation, and the bottom area is the Information Section. Icons that do not
respond when the mouse pointer is hovering on top are not congurable.
4-1
Page 70

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
The AMI BIOS GUI Setup Utility uses a mouse pointer navigation system
similar to standard graphical user interfaces. Hover and click an icon to
select a section, or click a down arrow to select from an options list.
You may press the <F1> on any screen under the Setup Section to see
a list of Hot Keys that are available. Press <F12> to print the screen.
The keyboard's Escape key <ESC> cancels the current screen and will
return you back to the previous screen.
Changing Between EZ Mode and Advanced Mode
To change between EZ Mode and Advanced Mode, hit F7 on the keyboard.
When in EZ Mode, select feature options and an overview of hardware
status are displayed (see Section 4-2). When in Advanced Mode, all following conguration menus and their contents become available.
4-2
Page 71

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
4-2 EZ Mode
While in EZ Mode, the following information will be displayed:
BIOS Version - The current BIOS version
CPU Information - The model, speed, and voltage of installed CPU
Memory Frequency - The frequency of installed memory
System Temp - Displays CPU and PCH temperatures
CPU Prole - Allows changing of the CPU prole by clicking the left
or right arrows
DRAM Status - Status of all DIMM slots
SATA Info - Displays which SATA ports are connected to storage
devices
Boot Priority - Allows changing of the boot order, or click a device to
boot selected device
Note: Using this will reboot the computer.
X.M.P. - Allows changing the X.M.P. prole
4-3
Page 72

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Intel Rapid Storage Technology - Allows for enabling Intel Rapid
Storage Technology
Fan Prole - Displays current fan speeds
4-4
Page 73

4-3 Overclocking
CPU Overclocking
Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
CPU Prole
This feature allows for preset CPU overclocking proles to be selected.
The options are Stable, Default, and Performance.
Advanced CPU OC Setting
This feature controls the CPU overclocking settings. The options are
Manual, 4.3GHz, 4.4GHz, 4.5GHz, 4.6GHz, 4.7GHz, 4.8GHz, 4.9GHz,
5.0GHz, 5.1GHz, 5.2GHz, 5.3GHz, 5.4GHz, and 5.5GHz.
1-Core ~ 8-Core Ratio Limit Override
Enter a value for the each invidual CPU core.
Active Processor Cores
Use this feature to select the number of active processor cores. The
default option is All. These options depend on how many cores are supported by the CPU.
BCLK Clock Frequency(1/100 MHz)
Enter a value for the BCLK frequency. The default is 10000.
4-5
Page 74

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
FCLK Frequency for Early Power On
Select the FCLK frequency for early power on. The options are Normal
(800MHz), 1GHz, 400MHz, and Auto.
BCLK Aware Adaptive Voltage
This feature enables BCLK Aware Adaptive Voltage, which helps avoid high
voltage overrides by forcing pcode to be aware of the BCLK frequency
when making calculations. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Core Max OC Ratio
This feature controls the general maximum overclocking ratio for the CPU
cores and Ring. The default is 0.
AVX Ratio Offset
Enter a value for AVX Ratio Offset. The default is 0.
TjMax Offset
Enter a value to change the Tj-Max value to. The default is 0.
Power Limit 1 Override
This feature enables Power Limit 1 override. If set to Disabled, the BIOS
will program a default power limit and power limit time window. If set
to Enabled, the following feature become available. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Power Limit 1
Enter a value for Power Limit 1. The default is 95000.
Power Limit 2 Override
This feature enables Power Limit 2 override. If set to Disabled, the BIOS
will program a default power limit and power limit time window. The op-
tions are Disabled and Enabled.
Power Limit 2
Enter a value for Power Limit 2. The default is 113750.
TVB Ratio Clipping
This feature enables CPU core frequency reduction for processors that
implement Intel Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB). For overclocking, this
feature must be Disabled.
4-6
Page 75

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
TVB Voltage Optimizations
This feature enables thermal base voltage optimizations for processors
that implement Intel Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB). The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
CPU feature
Hyper-Threading
This feature enables hyper-threading, which is a software method
to control logical processor threads. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Boot Performance Mode
This feature controls the performance state that the BIOS will set
initially. The options are Max Non-Turbo Performance and Turbo
Performance.
Intel(R) SpeedStep(tm)
Intel® SpeedStep Technology allows the system to automatically adjust processor voltage and core frequency in an effort to reduce power
consumption and heat dissipation. Please refer to Intel’s website
for detailed information. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Race To Halt (RTH)
This feature enables Race To Halt, which dynamically increases CPU
frequency in order to enter package C-State faster. This will reduce
overall power consumption. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Intel(R) Speed Shift Technology
This feature enables Intel® Speed Shift, which allows the operating
system to hand control of CPU frequency and voltage to the processor.
This increases P-state change speed and improves power efciency.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
C states
C-state architecture, a processor power management platform developed by Intel, can further reduce power consumption from the basic C1
(Halt State) state that blocks clock cycles to the CPU. Select Enabled
for CPU C-State support. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Thermal Monitor
4-7
Page 76

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
This feature enables the CPU thermal monitor. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Ring
Ring Max OC Ratio
Enter a value for the maximum overclock ratio for CPU Ring. The
default is 0.
Ring Down Bin
This feature enables Ring Down Bin. If set to Enabled, the maximum ring ratio will not be observed. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Min Ring Ratio Limit
Enter a value for the minimum ratio limit for CPU Ring. The default
is 0.
Max Ring Ratio Limit
Enter a value for the maximum ratio limit for CPU Ring. The default
is 0.
CPU VR Settings
VR Power Delivery Design
This feature is intended for motherboard validation purposes. The
species the CFL-S board design for VR settings override values.
The default is Auto.
PSYS Slope
Enter a value for the PSYS Slope. The range is 0-200. The default
is 0.
PSYS Offset
Enter a value for the PSYS Offset. The range is 0-255. The default
is 0.
PSYS PMax Power
4-8
Page 77

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
Enter a value for the PSYS PMax Power. The range is 0-8192. The
default is 0.
Acoustic Noise Settings
Acoustic Noise Mitigation
This feature enables Acoustic Noise Mitigation, which mitigates
acoustic noise on certain CPUs when they are in deep C-states.
If set to Enabled, the following features may be congured:
Pre-Wake Time
Ramp Up Time
Ramp Down Time
Enter a value for the desired feature. The range is 0-255. The
default is 0.
Disable Fast PKG C State Ramp for IA Domain
Disable Fast PKG C State Ramp for GT Domain
Disable Fast PKG C State Ramp for SA Domain
Disable Fast PKG C State Ramp for VccIn Domain
This feature disables fast package C-state ramping in a specic
domain. If set to FALSE, the selected domain will continue to
fast ramp. If set to TRUE, the selected domain will disable fast
ramping. The options are TRUE and FALSE.
Slow Slew Rate for IA Domain
Slow Slew Rate for GT Domain
Slow Slew Rate for SA Domain
Slow Slew Rate for VccIn Domain
This feature controls the slow slew rate for a specic domain.
The options are Fast/2, Fast/4, Fast/8, and Fast/16.
Core/IA VR Settings
VR Cong Enable
This feature enables VR Cong. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
AC Loadline
Enter a value for AC Loadline.
4-9
Page 78

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
DC Loadline
Enter a value for DC Loadline.
PS Current Threshold1
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold1. The range is 0-512.
The default is 80.
PS Current Threshold2
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold2. The range is 0-512.
The default is 20.
PS Current Threshold3
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold3. The range is 0-512.
The default is 4.
PS3 Enable
This feature enables PS3. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
PS4 Enable
This feature enables PS4. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
IMON Slope
Enter a value for IMON Slope. The range is 0-200. The default
is 0.
IMON Offset
Enter a value for IMON Offset. The range is 0-63999. The default is 0.
IMON Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a
negative (-). The options are “+” and “-”.
VR Current Limit
Enter a value for the voltage regulator current limit, with each
whole number equating to 1/4A (i.e. 400 = 100A). Enter 0 for
Auto.
4-10
Page 79

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
VR Voltage Limit
Enter a value (in mV) for the voltage regulator voltage limit. The
range is 0-7999. Enter 0 for Auto.
TDC Enable
This feature enables TDC. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
TDC Current Limit
Enter a value for the TDC Current Limit, with each whole number
equating to 1/8A (i.e. 1000 = 125A). The range is 0-32767. The
default is 800.
TDC Time Window
This feature controls the TDC Time Window. The options are 1
ms, 2 ms, 3 ms, 4 ms, 5 ms, 6 ms, 7 ms, 8 ms, and 10 ms.
TDC Lock
This feature enables TDC Lock. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
GT VR Settings
VR Cong Enable
This feature enables VR Cong. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
AC Loadline
Enter a value for AC Loadline.
DC Loadline
Enter a value for DC Loadline.
PS Current Threshold1
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold1. The range is 0-512.
The default is 80.
PS Current Threshold2
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold2. The range is 0-512.
The default is 20.
4-11
Page 80

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
PS Current Threshold3
Enter a value for PS Current Threshold3. The range is 0-512.
The default is 4.
PS3 Enable
This feature enables PS3. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
PS4 Enable
This feature enables PS4. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
IMON Slope
Enter a value for IMON Slope. The range is 0-200. The default
is 0.
IMON Offset
Enter a value for IMON Offset. The range is 0-63999. The default is 0.
IMON Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a
negative (-). The options are “+” and “-”.
VR Current Limit
Enter a value for the voltage regulator current limit, with each
whole number equating to 1/4A (i.e. 400 = 100A). Enter 0 for
Auto.
VR Voltage Limit
Enter a value (in mV) for the voltage regulator voltage limit. The
range is 0-7999. Enter 0 for Auto.
TDC Enable
This feature enables TDC. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
TDC Current Limit
Enter a value for the TDC Current Limit, with each whole number
equating to 1/8A (i.e. 1000 = 125A). The range is 0-32767. The
default is 240.
4-12
Page 81

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
TDC Time Window
This feature controls the TDC Time Window. The options are 1
ms, 2 ms, 3 ms, 4 ms, 5 ms, 6 ms, 7 ms, 8 ms, and 10 ms.
TDC Lock
This feature enables TDC Lock. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
Intersil VR Command
This feature enables Intersil VR Command to x VR C-state issues.
The options are Disabled, Send for IA/GT rails, and Send for IA/
GT/SA rails.
Memory OverClocking
This section displays the following memory prole information for Default,
Custom, XMP1, and XMP2 proles:
tCK [MHz]
tCL
tRCD/tRP
tRAS
tCWL
tFAW
tREFI
tRFC
tRRD
tRTP
tWR
tWTR
NMode
VDD [mV]
Realtime Memory Timing
This feature enables realtime memory timing changes to be made after
MRC_DONE. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Memory prole
This feature controls the memory prole. The options are Default pro-
le, Custom prole, and XMP prole 1.
*When the Memory prole feature (above) is set to "Custom prole", the
following memory timing congurations become available.
4-13
Page 82

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Memory Reference Clock
This feature controls the memory reference clock, in MHz. The options
are 133 and 100.
Memory Ratio
This feature controls the memory ratio. The memory frequency is equal
to the memory ratio times the reference clock.
Memory Voltage
Enter a value for the memory voltage override. The default is 1200.
QCLK Odd Ratio
If set to Enabled, this feature adds the Memory Reference Clock amount
to the QCLK frequency. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Note: When the Memory prole feature (above) is set to "Custom
prole" the following memory timings may be manually changed.
The defaults are listed below.
tCL
tRCD/tRP
tRAS
tCWL
tFAW
tREFI
tRFC
tRRD
tRTP
tWR
tWTR
NMode
tRRD_sg
tRRD_dg
tRDRD_sg
tRDRD_dg
tRDRD_dr
tRDRD_dd
tRDWR_sg
tRDWR_dg
tRDWR_dr
tRDWR_dd
tWRRD_sg
tWRRD_dg
tWRRD_dr
tWRRD_dd
tWRWR_sg
4-14
Page 83

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
tWRWR_dg
tWRWR_dr
tWRWR_dd
tCKE
ODT RTT WR(CHA)
This feature controls ODT RTT WR(CHA). The options are Auto, 0, 80,
120, 240, and 255.
ODT RTT PARK(CHA)
This feature controls ODT RTT PARK(CHA). The options are Auto, 0, 34,
40, 48, 60, 80, 120, and 240.
ODT RTT NOM(CHA)
This feature controls ODT RTT NOM(CHA). The options are Auto, 0, 34,
40, 48, 60, 80, 120, and 240.
ODT RTT WR(CHB)
This feature controls ODT RTT WR(CHB). The options are Auto, 0, 80,
120, 240, and 255.
ODT RTT PARK(CHB)
This feature controls ODT RTT PARK(CHB). The options are Auto, 0, 34,
40, 48, 60, 80, 120, and 240.
ODT RTT NOM(CHB)
This feature controls ODT RTT NOM(CHB). The options are Auto, 0, 34,
40, 48, 60, 80, 120, and 240.
RcompTarget[RdOdt]
RcompTarget[WrDS]
RcompTarget[WrDSCmd]
RcompTarget[WrDSCtl]
RcompTarget[WrDSClk]
SCompDq StageDelayPS
SCompCmd StageDelayPS
SCompCtl StageDelayPS
SCompClk StageDelayPS
RTLatency_CH0_DIMM0
RTLatency_CH1_DIMM0
IOLatency_CH0_DIMM0
IOLatency_CH1_DIMM0
DllBwEn[0]
4-15
Page 84

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
DllBwEn[1]
DllBwEn[2]
DllBwEn[3]
Graphics OverClocking
GT OverClocking Frequency
Enter a value for the overclocked RP0 frequency (in multiples of 50 MHz)
in the GT domain. The default is 0.
GT Voltage Mode
This feature controls the voltage mode in the GT domain. The options
are Adaptive and Override.
GT Voltage Override
When "GT Voltage Mode" is set to Override, enter a value for the GT
Voltage Override.
GT Extra Turbo Voltage
Enter a value for the extra turbo voltage (in mV) that will be applied
while GT is operating in turbo mode. The default is 0.
GT Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the offset voltage (in mV) that will be applied to the
GT domain. The default is 0.
Offset Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a negative
(-). The options are “+” and “-”.
GT OverClocking Frequency
Enter a value for the overclocked RP0 frequency (in multiples of 50 MHz)
in the GT Unslice domain. The default is 0.
GT Voltage Mode
This feature controls the voltage mode in the GT Unslice domain. The
options are Adaptive and Override.
GT Voltage Override
When "GT Voltage Mode" is set to Override, enter a value for the GT
Voltage Override.
4-16
Page 85

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
GT Extra Turbo Voltage
Enter a value for the extra turbo voltage (in mV) that will be applied
while GT is operating in turbo mode. The default is 0.
GTU Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the offset voltage (in mV) that will be applied to the
GT domain. The default is 0.
Offset Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a negative
(-). The options are “+” and “-”.
Voltage Configuration
System Agent Voltage (mV)
Enter a value for the System Agent voltage (in mV). The default is 1050.
Core Voltage Mode
This feature controls the core voltage mode. The options are Adaptive
and Override.
SVID
When "Core Voltage Mode" is set to Override, this feature enables SVID.
The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Core Voltage Override
When "Core Voltage Mode" is set to Override, enter a value for the Core
Voltage Override. The default is 0.
Core Extra Turbo Voltage
Enter a value for the extra turbo voltage (in mV) that will be applied
while IA Core is operating in turbo mode. The default is 0.
Core Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the offset voltage (in mV) that will be applied to the
IA Core domain. The default is 0.
Offset Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a negative
(-). The options are “+” and “-”.
4-17
Page 86

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
PCH Voltage
Enter a value for the PCH voltage override. The default is 1010.
CPU_IO Voltage
Enter a value for the CPU IO voltage override. The default is 936.
Load Line Calibration
This feature congures Load Line Calibration. The options are Disabled,
Auto, Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, and Level 4.
Uncore
Uncore Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the offset voltage (in mV) that will be applied to the
Uncore domain. The default is 0.
Offset Prex
Use this feature to set the prex value as a positive (+) or a negative
(-). The options are “+” and “-”.
Voltage PLL Trim Controls
Core PLL Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the Core PLL voltage offset, with each whole number
equating to 17.5 mV. The range is 0-63. The default is 0.
GT PLL Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the GT PLL voltage offset, with each whole number
equating to 17.5 mV. The range is 0-63. The default is 0.
Ring PLL Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the Ring PLL voltage offset, with each whole number
equating to 17.5 mV. The range is 0-63. The default is 0.
System Agent PLL Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the System Agent PLL voltage offset, with each whole
number equating to 17.5 mV. The range is 0-63. The default is 0.
Memory Controller PLL Voltage Offset
Enter a value for the Memory Controller PLL voltage offset, with each
whole number equating to 17.5 mV. The range is 0-63. The default is 0.
4-18
Page 87

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
4-4 CPU
The following information is displayed in this section:
• Type - the brand, model name, model number of the CPU, and rated
clock speed
• Speed - the detected CPU speed
• ID - the unique CPU ID
• Stepping - the processor stepping
• Number of Processors - the number of cores detected
• Microcode Revision - the CPU's microcode patch version
• GT Information - the processor's GT Information
• IGFX VBIOS Version - the Integrated Graphics VBIOS version
• IGFX GOP Version - the Integrated Graphics GOP version
• Memory RC Version - the memory RC version
4-19
Page 88

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
CPU Conguration
The following CPU information will be displayed:
• Type - the brand, model name, model number of the CPU, and
rated clock speed
• ID - the unique CPU ID
• Speed - the detected CPU speed
• L1 Data Cache - displays if Level 1 cache is supported
• L1 Instruction Cache - displays if Level 1 instruction cache is
supported
• L2 Cache - displays if Level 2 cache is supported
• L3 Cache - displays if Level 3 cache is supported
• VMX - displays if VMX is supported
• SMX/TXT - displays if SMX/TXT is supported
C6DRAM
This feature enables moving DRAM contents to PRM memory when the
CPU is in a C6 state. The options are Disabled or Enabled.
SW Guard Extension (SGX)
Select Enabled to activate the Software Guard Extensions (SGX). The
options are Disabled, Enabled, and Software Controlled.
Select Owner EPOCH Input Type
There are three Owner EPOCH modes (Each EPOCH is 64 bit). The
options are No Change in Owner EPOCHs, Change to New Random
Owner EPOCH, and Manual User Dened Owner EPOCHs.
*If set to Manual User Dened, the following two features become
available for conguration. For back-up purposes, write down the
original values before modifying them.
Software Guard Extensions Epoch 0
Software Guard Extensions Epoch 1
4-20
Page 89

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
Hardware Prefetcher
(Available when supported by the CPU)
If set to Enabled, the hardware prefetcher will prefetch streams of data
and instructions from the main memory to the L2 cache to improve
CPU performance. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
(Available when supported by the CPU)
Select Enabled for the CPU to prefetch both cache lines for 128 bytes
as comprised. Select Disabled for the CPU to prefetch both cache lines
for 64 bytes. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Intel (VMX) Virtualization Technology
(Available when supported by the CPU)
Select Enabled to use the Intel Virtualization Technology to allow
one platform to run multiple operating systems and applications in
independent partitions, creating multiple "virtual" systems in one
physical computer. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Note: If there is any change to this setting, you will need to
power off and reboot the system for the change to take effect.
Please refer to Intel’s website for detailed information.
Active Processor Cores
Use this feature to select the number of active processor cores. The
options are All, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. These options depend on how many
cores are supported by the CPU.
Hyper-Threading (when supported by the CPU)
Select Enabled to support Intel Hyper-threading Technology to enhance
CPU performance. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
BIST
Select Enabled to activate the Built-In Self Test (BIST) on reset. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
AES
This feature enables Intel CPU Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Instructions support to enhance data integrity. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
4-21
Page 90

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Machine Check
Select Enable to activate Machine Check. The options are Disabled
and Enabled.
MonitorMWait
This feature enables the Monitor/Mwait instructions. The Monitor in-
structions monitor a region of memory for writes, and MWait instructions instruct the CPU to stop until the monitored region begins to
write. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
TXT support (when supported by the CPU)
Intel TXT (Trusted Execution Technology) helps protect against
software-based attacks and ensures protection, condentiality and
integrity of data stored or created on the system. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Reset AUX Content (when supported by the CPU)
Use this feature to reset the TPM Auxiliary content. The options are
Yes and No.
FCLK Frequency for Early Power On
Select the FCLK frequency for early power on. The options are Normal
(800MHz), 1GHz, and 400MHz.
Power & Performance
CPU - Power Management Control
Boot Performance Mode
This feature enables the selection of the default CPU performance
during system boot. The options are Max Non-Turbo Perfor-
mance, Max Battery, and Turbo Performance.
Intel(R) SpeedStep(tm)
Intel SpeedStep Technology allows the system to automatically
adjust processor voltage and core frequency in an effort to reduce
power consumption and heat dissipation. Please refer to Intel’s
website for detailed information. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
4-22
Page 91

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
C States
C-State architecture, a processor power management platform
developed by Intel, can further reduce power consumption from
the basic C1 (Halt State) state that blocks clock cycles to the CPU.
Select Enabled for CPU C-State support. The options are Disabled
or Enabled. If this feature is set to Enabled, the following features
will be displayed:
Enhanced C-states
(Available when "C States" is set to Enabled)
This feature enables Enhanced C1 Power State to boost system
performance. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
C-State Auto Demotion
When this feature is enabled, the CPU will conditionally demote C
State based on un-cored auto-demote information. The options are
Disabled, C1, C3, and C1 and C3.
C-State Un-demotion
When this feature is enabled, the CPU will conditionally undemote
from demoted C3 or C1. The options are Disabled, C1, C3, and C1
and C3.
Package C-State Demotion
This feature enables the Package C-State demotion. The options
are Disabled and Enabled.
Package C-State Un-Demotion
When this feature is enabled, the CPU will conditionally undemote
from demoted Package C-State Un-Demotion. The options are Dis-
abled and Enabled.
CState Pre-Wake
Use this feature to enable the C-State pre wake. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
4-23
Page 92

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
IO MWAIT Redirection
When enabled, this feature will map and send the IO read instructions to the IO registers. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Package C State Limit
Select Auto for the AMI BIOS to automatically set the limit on the
C-State package register. The options are C0/C1, C2, C3, C6, C7,
C7s, C8, C9, C10, Cpu Default, and Auto.
Package C State Workaround
This feature enables a workaround for Package C State 6/7. The
options are Disabled and Enabled.
GT - Power Management
RC6(Render Standby)
Use this feature enable Render Standby support. The options are
Disabled and Enabled.
Maximum GT frequency
This feature denes the Maximum GT Frequency. Choose between
100MHz (RPN) and 1200MHz (RP0). Any value beyond this range
will be clipped to its min/max supported by the CPU. The options
are Default Max Frequency and 100MHz~1200MHz (in increments
of 50MHz).
Disable Turbo GT frequency
This feature disables Turbo GT frequency. If set to Enabled, Turbo
GT frequency becomes disabled. If set to Disabled, GT frequency
limiters will be removed.
4-24
Page 93

4-5 Memory
The following information is displayed:
• Memory RC Version
Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
• Memory Frequency
• Memory Timings (tCL-tRCD-tRP-tRAS)
• DIMM#A1 ~ DIMM#B2 information
Maximum Memory Frequency
This feature selects the type/speed of the memory installed. The options
are 1333, 1600, 1867, 2133, 2400, and 2667. All values are in MHz.
Default speed is auto detected.
Memory Scrambler
This feature enables memory scrambler support for memory error correction. The settings are Disabled and Enabled.
Force ColdReset
Use this feature when ColdBoot is required during MRC execution. The
settings are Disabled and Enabled.
4-25
Page 94

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Force Single Rank
When enabled, only Rank0 will be used in each DIMM. The settings are
Disabled and Enabled.
Memory Remap
PCI memory resources will overlap with the total physical memory if 4GB
of memory (or above) is installed on the motherboard. When this occurs,
Enable this function to reallocate the overlapped physical memory to a
location above the total physical memory to resolve the memory overlap-
ping situation. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
MRC Fast Boot
This feature enables or disables fast path through MRC. The settings are
Disabled and Enabled.
4-26
Page 95

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
4-6 Advanced
Setup Mode
This feature sets the default mode to start in after entering BIOS. The
options are EZ Mode and Advanced Mode.
Boot Feature
Fast Boot
This feature enables the system to boot with a minimal set of required
devices to launch. This has no effect on BBS boot options. The options
are Disabled and Enabled.
Quiet Boot
Use this feature to select the screen display between the POST messages
and the OEM logo upon bootup. Uncheck the box to display the POST
messages. Check the box to display the OEM logo instead of the normal
POST messages. The default is Checked.
Bootup Num-Lock
Use this feature to set the Power-on state for the <Numlock> key. The
options are Off and On.
4-27
Page 96

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Wait for "F1" If Error
Use this feature to force the system to wait until the "F1" key is pressed
if an error occurs. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Re-try Boot
If this feature is enabled, the BIOS will automatically reboot the system
from a specied boot device after its initial boot failure. The options are
Disabled, Legacy Boot, and EFI Boot.
Watch Dog Function
If enabled, the Watch Dog Timer will allow the system to reset or generate NMI based on jumper settings when it is expired for more than
5 minutes. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
AC Loss Policy Depend on
Use this feature to set the power state after a power outage. Select
Stay Off for the system power to remain off after a power loss. Select Power On for the system power to be turned on after a power
loss. Select Last State to allow the system to resume its last power
state before a power loss. The options are Stay Off, Power On,
and Last State.
Power Button Function
This feature controls how the system shuts down when the power button is pressed. Select 4 Seconds Override for the user to power off the
system after pressing and holding the power button for four seconds or
longer. Select Instant Off to instantly power off the system as soon as
the user presses the power button. The options are Instant Off and 4
Seconds Override.
DeepSx Power Policies
Use this feature to congure the Advanced Conguration and Power
Interface (ACPI) settings for the system. Enable S5 to power off the
whole system except the power supply unit (PSU) and keep the power
button “alive” so that the user can “wake up” the system by using a USB
keyboard or mouse. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
Install Window 7 USB Support
Enable this feature to use the USB keyboard and mouse during the Windows 7 installation since the native XHCI driver support is unavailable.
Use a SATA optical drive as a USB drive. USB CD/DVD drives are not
supported. Disable this feature after the XHCI driver has been installed
in Windows. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
4-28
Page 97

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
RGB Led Control
This feature enables RGB LED controls. The options are Disabled and
Enabled.
NCT6792D Super IO Configuration
SuperIO Chip NCT6792D
Serial Port 1 Conguration
Serial Port
This feature will Enable or Disable Serial Port 1 (COM1). Click to check
the box to enable Serial Port 1. The default is Enabled.
Device Settings
This feature displays the current IRQ setting for Serial Port 1 (COM1).
Change Settings
This feature congures the IRQ setting for Serial Port 1 (COM1).
The options for Serial Port 1 are Auto, IO=3F8h; IRQ=4, IO=3F8h;
IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10,
11, 12, IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, and IO=2E8h;
IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12.
Serial Port Console Redirection
COM 1
Console Redirection
Select Enabled to enable COM Port 1 Console Redirection, which will allow
a client machine to be connected to a host machine at a remote site for
networking. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following features will become
available for conguration:
4-29
Page 98

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Console Redirection Settings
Terminal Type
This feature allows the user to select the target terminal emulation
type for Console Redirection. Select VT100 to use the ASCII Character
set. Select VT100+ to add color and function key support. Select ANSI
to use the Extended ASCII Character Set. Select VT-UTF8 to use UTF8
encoding to map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The op-
tions are ANSI, VT100, VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
Bits per second
Use this feature to set the transmission speed for a serial port used
in Console Redirection. Make sure that the same speed is used in the
host computer and the client computer. A lower transmission speed
may be required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600, 19200,
38400, 57600, and 115200 (bits per second).
Data Bits
Use this feature to set the data transmission size for Console Redirection. The options are 7 (Bits) and 8 (Bits).
Parity
A parity bit can be sent along with regular data bits to detect data
transmission errors. Select Even if the parity bit is set to 0, and the
number of 1's in data bits is even. Select Odd if the parity bit is set
to 0, and the number of 1's in data bits is odd. Select None if you
do not want to send a parity bit with your data bits in transmission.
Select Mark to add a mark as a parity bit to be sent along with the
data bits. Select Space to add a Space as a parity bit to be sent with
your data bits. The options are None, Even, Odd, Mark, and Space.
Stop Bits
A stop bit indicates the end of a serial data packet. Select 1 Stop Bit
for standard serial data communication. Select 2 Stop Bits if slower
devices are used. The options are 1 and 2.
Flow Control
Use this feature to set the ow control for Console Redirection to prevent data loss caused by buffer overow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop
sending data when the receiving buffer is full. Send a "Start" signal
to start sending data when the receiving buffer is empty. The options
are None and Hardware RTS/CTS.
4-30
Page 99

Chapter 4: AMI BIOS
VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
Select Enabled to enable VT-UTF8 Combination Key support for ANSI/
VT100 terminals. The options are Disabled (unchecked) and Enabled
(checked).
Recorder Mode
Select Enabled to capture the data displayed on a terminal and send
it as text messages to a remote server. The options are Disabled
(unchecked) and Enabled (checked).
Resolution 100x31
Select Enabled for extended-terminal resolution support. The options
are Disabled (unchecked) and Enabled (checked).
Legacy OS Redirection Resolution
Use this feature to select the number of rows and columns used in
Console Redirection for legacy OS support. The options are 80x24
and 80x25.
Putty KeyPad
This feature selects Function Keys and KeyPad settings for Putty, which
is a terminal emulator designed for the Windows OS. The options are
VT100, LINUX, XTERMR6, SCO, ESCN, and VT400.
Redirection After BIOS POST
Use this feature to enable or disable legacy Console Redirection after
BIOS POST. When the option-Bootloader is selected, legacy Console
Redirection is disabled before booting the OS. When the option Always
Enable is selected, legacy Console Redirection remains enabled upon
OS bootup. The options are Always Enable and Bootloader.
Serial Port for Out-of-Band Management/Windows Emergency
Management Services (EMS)
The submenu allows the user to congure Console Redirection settings
to support Out-of-Band Serial Port management.
Console Redirection
Select Enabled to use a COM port selected by the user for EMS Console
Redirection. The options are Disabled and Enabled.
*If the item above is set to Enabled, the following features will become
available for user conguration:
4-31
Page 100

Supermicro C9Z390-CG/CGW Motherboard User’s Manual
Console Redirection Settings
Out-of-Band Mgmt Port
The feature selects a serial port in a client server to be used by the
Windows Emergency Management Services (EMS) to communicate
with a remote host server. The options are dependent on the avail-
able COM ports.
Terminal Type
Use this feature to select the target terminal emulation type for Console Redirection. Select VT100 to use the ASCII character set. Select
VT100+ to add color and function key support. Select ANSI to use the
extended ASCII character set. Select VT-UTF8 to use UTF8 encoding
to map Unicode characters into one or more bytes. The options are
ANSI, VT100, VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
Bits per second
This feature sets the transmission speed for a serial port used in Console Redirection. Make sure that the same speed is used in both host
computer and the client computer. A lower transmission speed may
be required for long and busy lines. The options are 9600, 19200,
57600, and 115200 (bits per second).
Flow Control
Use this feature to set the ow control for Console Redirection to prevent data loss caused by buffer overow. Send a "Stop" signal to stop
data sending when the receiving buffer is full. Send a "Start" signal
to start data sending when the receiving buffer is empty. The options
are None, Hardware RTS/CTS, and Software Xon/Xoff.
The setting for each these features is displayed:
Data Bits, Parity, Stop Bits
System Agent (SA) Configuration
The following information is displayed:
• SA PCIe Code Version
• VT-d Capability
4-32
 Loading...
Loading...