Supermicro PDSML-LN1+, PDSML-LN2+, PDSML-E+, Supero PDSML-LN1+, Supero PDSML-LN2+ User Manual
...
PDSML-LN1+
PDSML-LN2+
PDSML-E+
USER’S MANUAL
Revision 1.1b
Manual Revision: Rev. 1.1b
Release Date: June 9, 2009
Unless you request and receive written permission from SUPER MICRO COMPUTER, INC., you
may not copy any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and companies
referred to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or mark
holders.
Copyright © 2009 by Super Micro Computer, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America
The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be accurate.
The vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this document,
makes no commitment to update or to keep current the information in this manual, or to notify any
person or organization of the updates. Please Note: For the most up-to-date version of this
manual, please see our web site at www.supermicro.com.
Super Micro Computer, Inc. ("Supermicro") reserves the right to make changes to the product
described in this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software, if any,
and documentation may not, in whole or in part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated or
reduced to any medium or machine without prior written consent.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPER MICRO COMPUTER, INC. BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, SPECULATIVE OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF
THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, SUPER MICRO COMPUTER, INC.
SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED
WITH THE PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING,
INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and customer shall be governed by the laws of Santa
Clara County in the State of California, USA. The State of California, County of Santa Clara shall
be the exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes. Super Micro's total liability for all
claims will not exceed the price paid for the hardware product.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference with radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference, in which case you will be required to correct the interference at your
own expense.
California Best rnia Best Management Practices Regulations for Perchlorate Materials: This Perchlorate warning applies only to products containing CR (Manganese Dioxide) Lithium coin cells.
“Perchlorate Material-special handling may apply. See www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate”
WARNING: Handling of lead solder materials used in this
product may expose you to lead, a chemical known to the
State of California to cause birth defects and other reproductive harm.

Preface
About This Manual
This man u al i s wr i tten for syste m in t egra tors , PC t echn ician s an d
knowledgeable PC users. It provides information for the installation and use of the
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ motherboard. It supports single
Intel® Xeon® 3200/3000, Core™ 2 Duo Series, Pentium® D (Dual-Core), Pentium
4, and Celeron® D LGA (Land Grid Array) 775 Processors at system bus speeds of
1066/800/533 MHz. The processor is housed in a Flip-Chip Land Grid Array (FC-
LGA4) package that interfaces with the motherboard via an LGA775 socket. The
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ also supports Intel Hyper-Threading (HT)
technology, EM64T technology, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology (EIST) and
Matrix Storage Technology. Please refer to the motherboard specications pages
on our web site (http://www.supermicro.com/products/motherboard/) for updates or
visit Intel's web site for processor support. This product is intended to be installed
and serviced by a professional technician.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1 describes features, specications and detailed information about the
motherboard and the chipset.
Chapter 2 provides hardware installation instructions. Read this chapter when
installing the processor, memory modules and other hardware components into
the system.
Chapter 3 describes troubleshooting procedures for the video, the memory and the
system setup stored in CMOS if you encounter problems.
Chapter 4 includes an introduction to BIOS and provides detailed information on
running the CMOS Setup utility.
Appendix A and Appendix B list BIOS POST Error Codes and Messages. Ap-
pendix C provides Software Installation Instructions.
Conventions Used in the Manual
Special attention should be given to the following symbols for proper installation
of the components and to prevent damage done to the components or injury to
yourself:
Danger/Caution: Instructions to be strictly followed to prevent catastrophic
system failure or to avoid bodily injury.
Warning: Important information given to ensure proper system installation or
to prevent damage to the components.
Note: Additional Information given to differentiate various models or to ensure
correct system setup.
Preface
iii

PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
Table of Contents
Preface
About This Manual ...................................................................................................... iii
Manual Organization .................................................................................................... iii
Conventions Used in the Manual .................................................................................. iii
Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 Overview ......................................................................................................... 1-1
Checklist ..................................................................................................... 1-1
Contacting Supermicro ............................................................................... 1-2
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ Image ....................... 1-3
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ Layout ....................... 1-4
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ Quick Reference ........ 1-5
Motherboard Features ................................................................................ 1-6
Intel 3000/3010 Chipset: System Block Diagram .................................... 1-8
1-2 Chipset Overview ........................................................................................... 1-9
1-3 Special Features ........................................................................................... 1-10
1-4 PC Health Monitoring ................................................................................... 1-10
1-5 ACPI Features ............................................................................................... 1-11
1-6 Power Supply .................................................................................................. 1-12
1-7 Super I/O ........................................................................................................ 1-13
1-8 Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) .......................................... 1-13
Chapter 2: Installation
2-1 Electro-Static Sensitive Devices ..................................................................... 2-1
2-2 Processor and Heatsink Installation ............................................................... 2-2
2-3 Mounting the Motherboard in the Chassis ..................................................... 2-5
2-4 Installing DDR 2 Memory .............................................................................. 2-6
2-5 Control Panel Connectors/IO Ports ................................................................. 2-8
A. Back Panel Connectors/IO Ports ................................................................. 2-8
B. Front Control Panel ...................................................................................... 2-8
C. Front Control Panel Pin Denitions ............................................................. 2-9
NMI Button ............................................................................................... 2-9
Power LED ............................................................................................... 2-9
HDD LED ................................................................................................. 2-10
NIC1/NIC2 LED Indicators ..................................................................... 2-10
Overheat/Fan Fail LED ............................................................................2-11
Power Fail LED .........................................................................................2-11
iv

v
Reset Button ............................................................................................ 2-12
Power Button ........................................................................................... 2-12
2-6 Connecting Cables ....................................................................................... 2-13
ATX Power Connector .......................................................................... 2-13
Processor Power Connector ................................................................. 2-13
Serial Ports ............................................................................................... 2-14
Chassis Intrusion ...................................................................................... 2-14
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ...................................................................... 2-15
GLAN (Ethernet Ports) ............................................................................. 2-15
ATX PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Ports ..................................................... 2-16
Speaker Connector ................................................................................ 2-16
Fan Headers .......................................................................................... 2-17
Wake-On-Ring .......................................................................................... 2-18
Wake-On-LAN .......................................................................................... 2-18
VGA Connector ........................................................................................ 2-19
Power LED ............................................................................................... 2-19
Power Fault .............................................................................................. 2-20
Power SMB Connector ............................................................................. 2-20
Power Alarm Reset .................................................................................. 2-21
2-7 Jumper Settings ............................................................................................ 2-22
Explanation of Jumpers ......................................................................... 2-22
GLAN Enable/Disable ............................................................................ 2-22
CMOS Clear ........................................................................................... 2-23
VGA Enable .............................................................................................. 2-23
Power Force On Enable ........................................................................... 2-24
I
2
C Bus to PCI/PCI-E Slots ...................................................................... 2-24
2-8 Onboard Indicators ....................................................................................... 2-25
GLAN LEDs .............................................................................................. 2-25
2-9 Floppy, Hard Disk Drive, and IPMI 2.0 Connections .................................... 2-26
Floppy Connector .................................................................................... 2-26
IDE Connectors ........................................................................................ 2-27
IPMI 2.0 Slot ............................................................................................. 2-27
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures ........................................................................... 3-1
Before Power On ....................................................................................... 3-1
No Power ................................................................................................... 3-1
No Video .................................................................................................. 3-1
Table of Contents

Memory Errors ........................................................................................... 3-2
Losing the System’s Setup Conguration ................................................ 3-2
3-2 Technical Support Procedures ........................................................................ 3-2
3-3 Frequently Asked Questions ........................................................................... 3-3
3-4 Returning Merchandise for Service ................................................................. 3-4
Chapter 4: BIOS
4-1 Introduction ....................................................................................................... 4-1
4-2 Running Setup ................................................................................................. 4-2
4-3 Main BIOS Setup ............................................................................................. 4-3
4-4 Advanced Setup ............................................................................................... 4-7
4-5 Security Setup ............................................................................................... 4-18
4-6 Boot Setup ...................................................................................................... 4-19
4-7 Exit .................................................................................................................. 4-20
Appendices:
Appendix A: BIOS POST Error Messages ................................................................A-1
Appendix B: BIOS POST Codes ................................................................................ B-1
Appendix C: Installing Software Drivers and the Operating System .........................C-1
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
vi
Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1
Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
Checklist
Congratulations on purchasing your computer motherboard from an acknowledged
leader in the industry. Supermicro motherboards are designed with the utmost
attention to detail to provide you with the highest standards in quality and perfor-
mance.
Please check that the following items have all been included with your motherboard.
If anything listed here is damaged or missing, contact your retailer.
All the items below are included in the retail box only
One (1) Supermicro Mainboard
One (1) IDE cable (CBL-0036L-02)
One (1) oppy drive ribbon cable (CBL-0022L)*
Four (4) SATA cables (CBL-0044L)*
One (1) IO Shield (CSE-PT07L)*
One (1) IO Shield (CSE-PT2)**
One (1) Supermicro CD containing drivers and utilities
One (1) User's/BIOS Manual
*For the PDSML-LN2+ and PDSML-E+ only
**For the PDSML-LN1+ only

1-2
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
Contacting Super Micro
Headquarters
Address: Super Micro Computer, Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email: marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Web Site: www.supermicro.com
Europe
Address: Super Micro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
's-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
Email: sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Asia-Pacic
Address: Super Micro, Taiwan
4F, No. 232-1 Liancheng Road
Chung-Ho 235, Taipei Hsien, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3991
Web Site: www.supermicro.com.tw
Technical Support:
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Tel: 886-2-8228-1366, ext.132 or 139
Chapter 1: Introduction
1-3
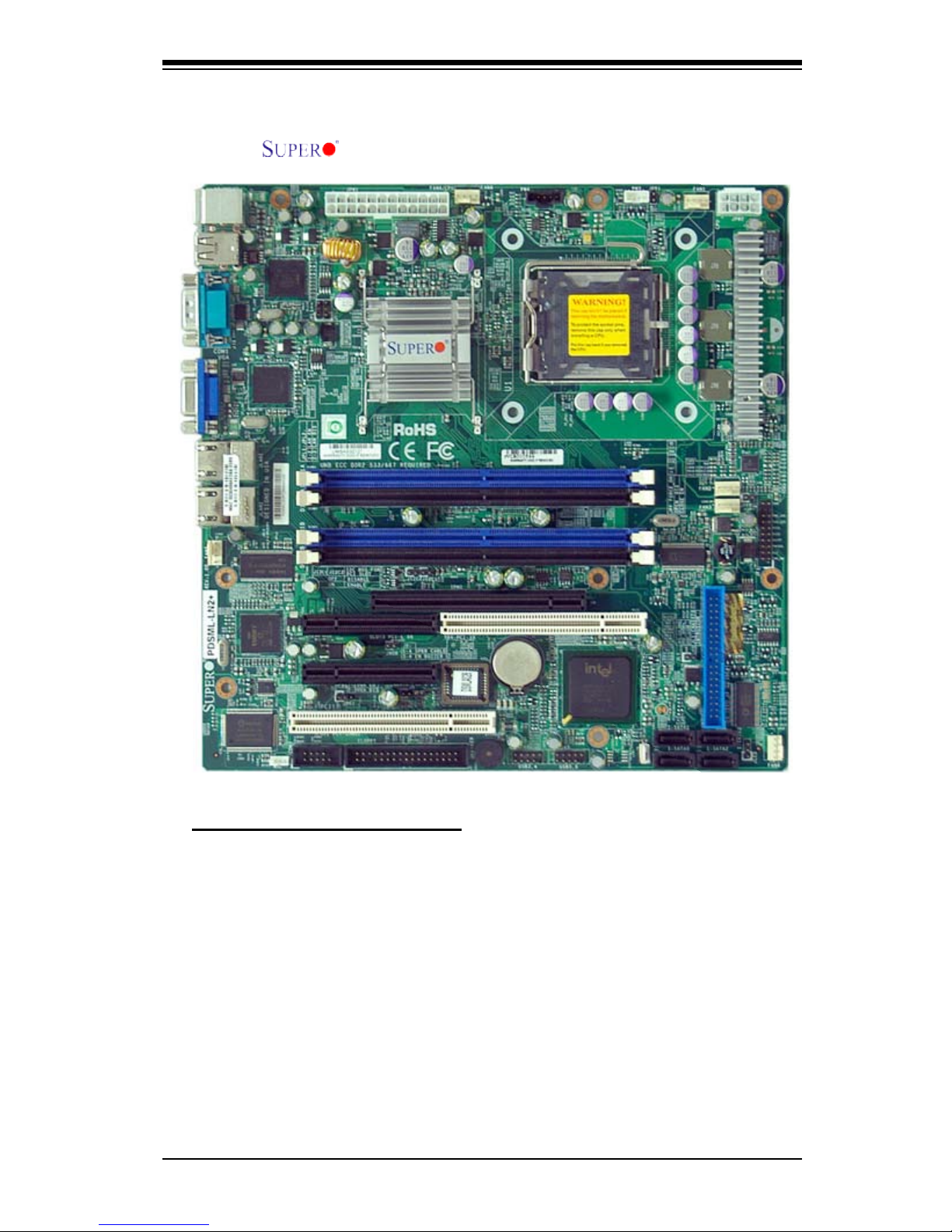
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ Image
An Important Note to the User
• All images and layouts shown in this manual were based upon the latest PCB
Revision available at the time of publishing of this manual. The motherboard
you've received may or may not look exactly the same as the graphics shown
in this manual.
• Please see Note 5 on Page 1-4.
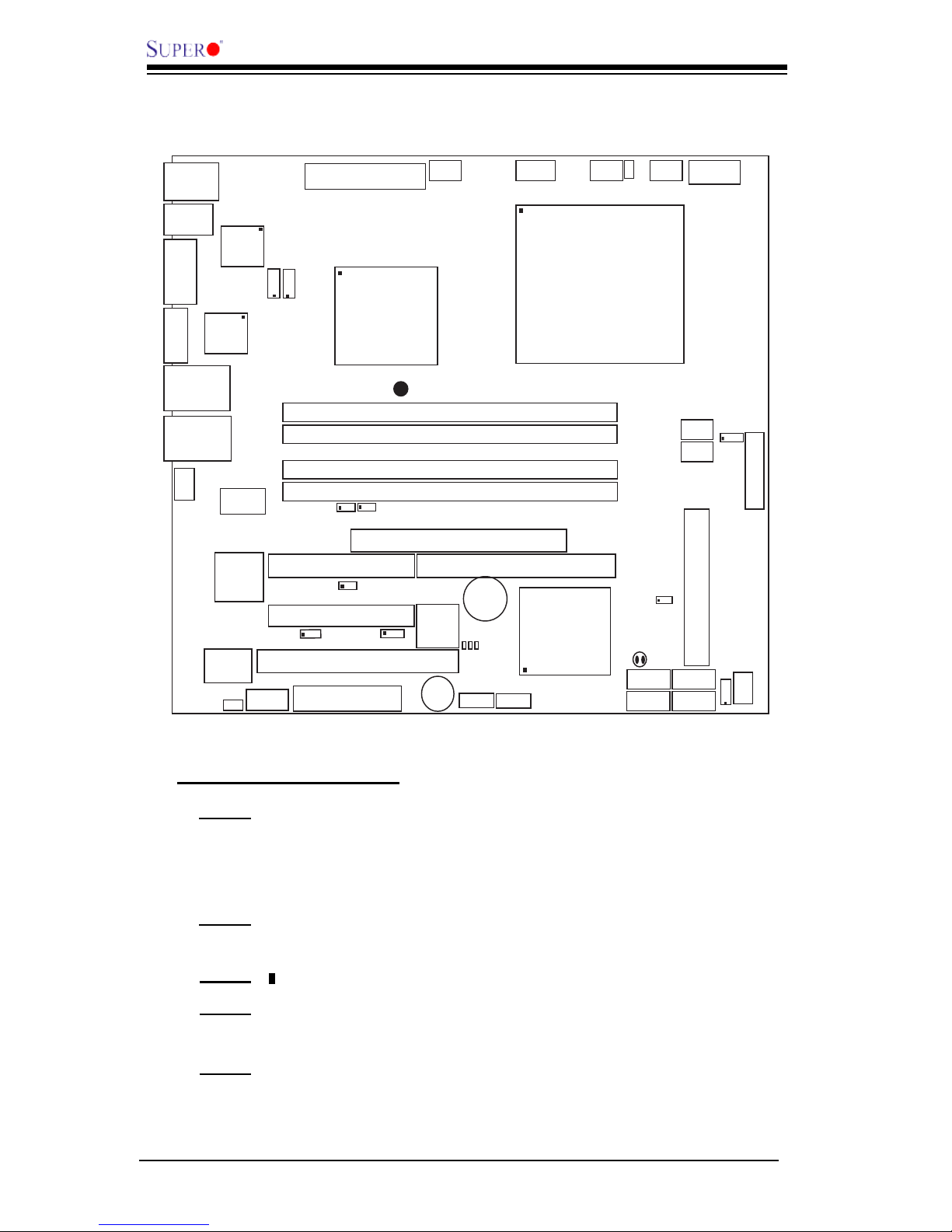
1-4
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
Important Notes to the User
• Note 1 All images and graphics shown in this manual were based upon the
latest PCB Revision available at the time of publishing of this manual. The
motherboard you've received may or may not look exactly the same as the
graphics shown in this manual.
• Note 2 See Chapter 2 for detailed information on jumpers, I/O ports and JF1
front panel connections.
•Note 3 " " indicates the location of Pin 1.
•Note 4 When the LE1 LED is on, onboard power is on. Maker sure to unplug
the AC power cord before installing or removing components.
•Note 5 IPMI and LAN2 are available on the PDSML-LN2+ and PDSML-E+
only. To use IPMI, install the optional AOC-SIM1U/SIM1U+ or AOC-SIMLC
IPMI card on the IPMI slot (J19). Please refer to page 1-13 for more informa-
tion.
Motherboard Layout
(not drawn to scale)
S
UPER PDSML-LN1+/LN2+/E+
®
LGA 775 CPU
KB/MS
JLAN1
Intel
3000
North Bridge
4naF
24-Pin ATX PWR
ICH7R
South Bridge
J 2 8
8-pin PWR
Battery
J 9
USB 1/2
J15
VGA
JG1
JLAN2
COM2
Floppy
DIMM 2B
PCI-E x8
BIOS
JPW1
J27
3J
IDE
JP F
DIMM 1B
DIMM 2A
DIMM 1A
DIMM 1
DIMM 2
DIMM 3
DIMM 4
Fan1
JPW2
J 8
Fan5
LAN
CTRL2
JPL 2
JPL 1
WOL
JWOR
rezzuB
J45
JL1
JI
2
C1
JBT1
J46
SATA1
JPG1
Fan3
FP CTRL
JF1
Fan2
USB3/4
LAN
CTRL1
SPKR
JI2C2
IPMI
J19
Slot6
SBX: PCI-33 MHz
VGA
CTRL
PCI2
J10
PCI-E x4
Slot5
PCI1
Slot4
PCI-33 MHz
LE 3
COM1
J 3 1
VGA
Memory
LE 4
LE 1
JS1
JS2
JS3
JS4
JLED
Fan6
CPU
Fan
JPR1
PW3
PWRFault
PW4
PWR SMB
(*LN2+)
(*LN2+)
USB5/6
SATA0
SATA2
SATA3
PDSML-E+ Only
3010
OR
Intel
S I/O

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-5
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ Quick Reference
Jumpers Description Default Setting
JBT1 CMOS Clear See Section 2-7
JI2C1/JI2C2 I2C Bus to PCI Slots 1/2 Open (Disabled)
JPF Power Force-On Open (Disabled)
JPG1 VGA Enable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JPL1/JPL2 (Note) Giga-bit LAN 1/2 Enable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
Connectors Description
24-PIn ATX (JPW1) ATX 24-pin Power Connector
8-Pin PWR (JPW2) 12V 8-pin PWR Connector
Alarm Reset (JPR1) Redundant Power Alarm Reset
Chassis Intrusion (JL1) Chassis Intrusion Header
COM1 (J31), COM2 COM Port 1 & COM 2 Header
DIMM#1A,#2A,#1B,#2B Memory (DIMM) Slots (DIMM 1-DIMM 4)
Fans 1-6 System Fan Headers (Fans 1-5), Fan6: CPU Fan
FP Control (JF1) Front Panel Control Header
Floppy Connector (J27) Floppy Disk Connector
IDE (J3) IDE#1 Slot
IPMI (Note) IPMI 2.0 Slot
KB/MS (J28) PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Connectors
LAN1-LAN2 (JLAN1/2)(Note) Ethernet RJ45 (Gigabit LAN) Port1/Port2 Connections
Power Fault (PW3) Power Fault Header
Power LED (JLED) PWR LED Header
Power SMB (I2C) (PW4) Power SMB (System Management Bus) Connector
SATA 0-3 Intel SATA Ports (#1-#4)
Slot 4 PCI 32-bit 33MHz slot
Slot 5 PCI-Express x4 slot
Slot 6 + SBX PCI-Express x8 slot + SBX: PCI 32-bit 33MHz slot
Speaker (J9) Speaker Connector (Pins 3-4:Internal,Pins 1-4:External)
USB1/2 (J15) Back Panel Universal Serial Bus Ports 1,2
USB3/4 (J46),USB5/6 (J45) Front Panel Accessible USB Ports 3,4,5,6
VGA (JG1) VGA Connector
WOL (WOL) Wake On LAN header
WOR (JWOR) Wake On Ring header
LED Indicator Description (*(Refer to Addendum A)
LE 1 Onboard PWR warning LED Indicator
LE3/LE4 BIOS POST Code Indicators
Note: JPL2, IPMI and LAN2 are available on the PDSML-LN2+ and PDSML-E+only.
Please refer to Note 5 on the previous page.

1-6
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
Motherboard Features
Processor
• Single Intel Xeon 3200/3000/Core 2 Duo Series//Pentium D dual-core/Pentium
4/Celeron D processors at system bus speeds of 1066/800/533 MHz.
• Hyper-Threading (HT), EM64T, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep (EIST) supported
The EM64T Feature is supported when:
• 64-bit OS (Windows XP Professional x64 Ed, Server 2003x64 Ed.) and
• 64-bit drivers for all MB components, devices and add-on cards are installed
on the motherboard.
Hyper-Threading (HT) Technology is supported when:
• A CPU that supports Hyper-Threading Technology is used,
• An OS that supports HT is installed onboard, including Windows XP/2003
Server and Linux 2.4x. (Under Linux, use the HT compiler to compile the code.
For other operating systems, be sure to disable the HT feature in the BIOS.)
• HT features are enabled in the BIOS (under the "Advanced" Setting) before
a supported OS is installed. (Note: visit www.Intel.com for CPU support and
driver updates.)
Memory
• Four DIMM slots support dual Channel DDR2 667/533 MHz up to 8 GB of Unbuf-
fered ECC/Non-ECC SDRAM.
Chipset
• Intel 3000 (PDSML-LN1+ and PDSML-LN2+)
• Intel 3010 (PDSML-E+)
• Intel ICH7R
Expansion Slots
• Two (2) PCI 32-Bit/33 MHz slots (Slot 4 & SBX)
• Two (2) PCI-Express slots: x4 (Slot 5) & x8 (Slot 6)
BIOS
• 8Mb Firmware Hub, Phoenix® BIOS
• DMI 2.3, PCI 2.2, ACPI 1.0, Plug and Play (PnP), SMBIOS 2.3, Hardware BIOS
Virus Protection
PC Health Monitoring
• Onboard voltage monitors for CPU core, Memory, +1.5V, +1.8V, +3.3V, +5V, +5V
Standby, +12V, −12V, Vbatt and VTT.
• Status monitor for fan speed & System Overheat/Fan Fail LED/Control
• Pulse Width Modulation Fan Control & Low noise fan speed control
• SuperDoctor III, NMI
• System Resource alert via SuperDoctor III

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-7
ACPI Features
• Slow blinking LED for suspend state indicator
• BIOS support for USB keyboard/Mouse
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on
Onboard I/O
• One ATA/100 EIDE Channel
• Intel ICH7R SATA Controller, 4 connectors for 4 devices with support of RAID
0, 1, 5 and 10 (Note)
• One oppy port interface (up to 2.88 MB)
• One Fast UART 16550 compatible serial port
• Two Intel single-port 82573 V/L PCI-E Gigabit Ethernet Controllers with two
GLAN ports (82573L for LN1) (See Note on the following page)
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard ports
• Up to 6 USB (Universal Serial Bus) 2.0 ports
• VGA Connector
• One IPMI 2.0 Slot (Note)
• Super I/O (Winbond® 83627 HG) with hardware monitoring
• XGI® Volari® Graphics with16MB DDR memory
Temperature
• Monitoring CPU, chassis environment
• CPU Thermal Trip support
• Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2) (available if supported by the CPU)
Other
• Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
• Wake-on-Ring (WOR)
• Onboard Standby PWR warning LED Indicator ("LE 1")
CD Utilities
• Drivers and software for Intel 3000 chipset utilities
Dimensions
• 9.6" (W) x 9.6" (L) (243.84 mmx 243.84 mm)
Note: IPMI and LAN2 options are available on the PDSML-LN2+ and PDSML-E+
only.
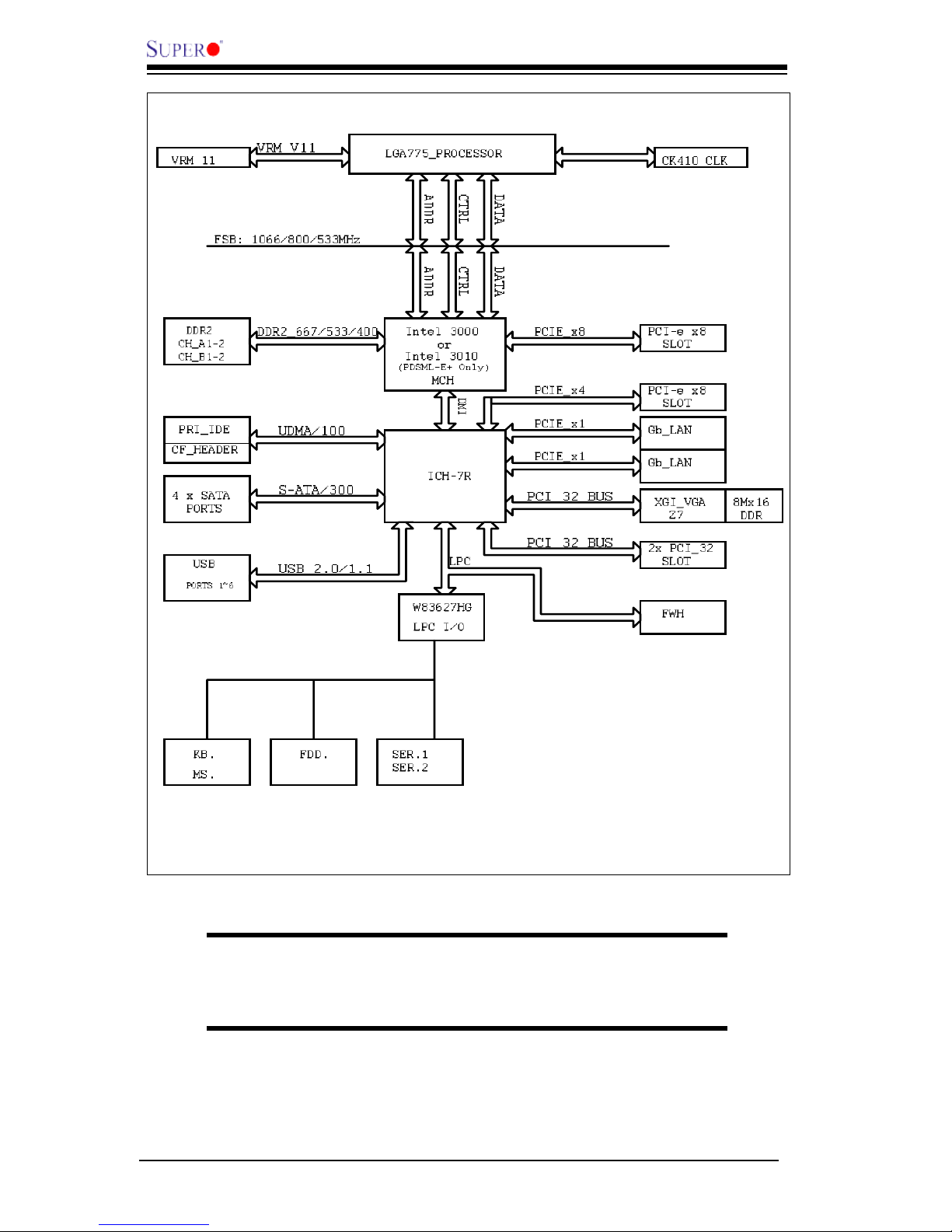
1-8
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
The Intel 3000/3010 Chipset:
System Block Diagram
Note: This is a general block diagram and may not exactly represent
the features on your motherboard. See the following pages for the
actual specications of the motherboard.

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-9
1-2 Chipset Overview
The Intel 3000/3010 chipset is comprised of two primary components: the Memory
Controller Hub (MCH) and the I/O Controller Hub (ICH7R). With the capabilities
provided by the Intel 3000/3010 chipset, the PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+
provides the performance and feature-set required for cost-effective UP servers.
Memory Controller Hub (MCH)
The function of the MCH is to manage the data ow between four interfaces: the
processor interface (FSB), the System Memory Interface (DRAM Controller), the
Direct Media Interface (DMI) and the PCI Express Interface.
Using a scalable FSB Vcc_CPU, the MCH supports FSB speed up to 1066 MT/s
(266 MHz). Hyper-Threading Technology (HT) and FSB Dynamic Bus Inversion
(DBI) are among the Host Interface features supported. It integrates a system
memory DDR2 controller with two 64-bit interfaces and supports one or two chan-
nels of DDR2 SDRAM.
The I/O Controller (ICH7R) provides the data buffering and interface arbitration re-
quired for the system to operate efciently. It also provides the bandwidth needed
for the system to maintain its peak performance. The Direct Media Interface (DMI)
provides the chip-to-chip connection between the MCH and the ICH7R.
The ICH7R supports up to four Serial ATA ports, six USB 2.0 ports and two IDE
devices. In addition, the ICH7R offers the Intel Matrix Storage Technology which
provides various RAID options for data protection and rapid data access. It also
supports the next generation of client management through the use of PROActive
technology in conjunction with Intel's next generation Gigabit Ethernet controller.
Intel ICH7 (ICH7R) System Features
The I/O Controller Hub provides the I/O subsystem with access to the rest of the
system. Functions and capabilities include:
*Advanced Conguration and Power Interface, Version 2.0 (ACPI)
*Intel I/O External Design Specication (EDS)
* The Intel 3000 or Intel 3010 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) External Design
Specication (EDS)
*Intel I/O Controller Hub 7 (ICH7R) Thermal Design Guideline

1-10
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
1-3 Special Features
Recovery from AC Power Loss
BIOS provides a setting for you to determine how the system will respond when AC
power is lost and then restored to the system. You can choose for the system to
remain powered off (in which case you must hit the power switch to turn it back on)
or for it to automatically return to a power- on state. See the Power Lost Control
setting in the Advanced BIOS Setup section to change this setting. The default
setting is Last State.
1-4 PC Health Monitoring
This section describes the PC health monitoring features of the PDSML-LN1+/LN2+.
The motherboard has an onboard System Hardware Monitor chip that supports PC
health monitoring.
Onboard Voltage Monitors for the CPU Cores, memory, +1.5V, +1.8V,
+3.3V, +5V, +12V, -12V, +5V Standby, VTT and Vbat
An onboard voltage monitor will scan these voltages continuously. Once a voltage
becomes unstable, a warning is given or an error message is sent to the screen. The
user can adjust the voltage thresholds to dene the sensitivity of the voltage monitor.
Fan Status Monitor with Firmware Control
The PC health monitor can check the RPM status of the cooling fans. The onboard
CPU and chassis fans are controlled by Thermal Management via BIOS (under
Hardware Monitoring in the Advanced Setting).
Environmental Temperature Control
The thermal control sensor monitors the CPU temperature in real time and will turn
on the thermal control fan whenever the CPU temperature exceeds a user-dened
threshold. The overheat circuitry runs independently from the CPU. Once it de-
tects that the CPU temperature is too high, it will automatically turn on the thermal
fan control to prevent any possible CPU overheat. The onboard chassis thermal
circuitry can monitor the overall system temperature and alert the user when the
chassis temperature is too high.
CPU Fan Auto-Off in Sleep Mode
The CPU fan activates when the power is turned on. It continues to operate when
the system enters Standby mode. When in sleep mode, the CPU will not run at
full power, thereby generating less heat.

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-11
CPU Overheat LED and Control
This feature is available when the user enables the CPU overheat warning function
in the BIOS. This allows the user to dene an overheat temperature. When this
temperature exceeds the predened temperature threshold, both overheat fan and
the warning LED will be activated.
System Resource Alert
This feature is available when used with Supero Doctor III in the Windows OS
environment or used with Supero Doctor II in Linux. Supero Doctor is used to
notify the user of certain system events. For example, if the system is running
low on virtual memory and there is insufcient hard drive space for saving the
data, you can be alerted of the potential problem. You can also congure Supero
Doctor to provide you with warnings when the system temperature goes beyond
a pre-dened range.
1-5 ACPI Features
ACPI stands for Advanced Conguration and Power Interface. The ACPI speci-
cation denes a exible and abstract hardware interface that provides a standard
way to integrate power management features throughout a PC system, including its
hardware, operating system and application software. This enables the system to
automatically turn on and off peripherals such as CD-ROMs, network cards, hard
disk drives and printers. This also includes consumer devices connected to the PC
such as VCRs, TVs, telephones and stereos.
In addition to enabling operating system-directed power management, ACPI
provides a generic system event mechanism for Plug and Play and an operating
system-independent interface for conguration control. ACPI leverages the Plug
and Play BIOS data structures while providing a processor architecture-independent
implementation that is compatible with Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows
2003 Server.
Slow Blinking LED for Suspend-State Indicator
When the CPU goes into a suspend state, the chassis power LED will start blinking
to indicate that the CPU is in suspend mode. When the user presses any key, the
CPU will wake-up and the LED will automatically stop blinking and remain on.
Main Switch Override Mechanism
When an ATX power supply is used, the power button can function as a system
suspend button to make the system enter a SoftOff state. The monitor will be
suspended and the hard drive will spin down. Pressing the power button again will
cause the whole system to wake-up. During the SoftOff state, the ATX power

1-12
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
supply provides power to keep the required circuitry in the system alive. In case
the system malfunctions and you want to turn off the power, just press and hold
the power button for 4 seconds. This option can be set in the Power section of
the BIOS Setup routine.
External Modem Ring-On
Wake-up events can be triggered by a device such as the external modem ringing
when the system is in the Standby or Off state. Note that external modem ring-on
can only be used with an ATX 2.01 (or above) compliant power supply.
Wake-On-LAN
Wake-On-LAN is dened as the ability of a management application to remotely
power up a computer that is powered off. Remote PC setup, up-dates and asset
tracking can occur after hours and on weekends so that daily LAN trafc is kept to
a minimum and users are not interrupted. The motherboard has a 3-pin header
(WOL) to connect to the 3-pin header on a Network Interface Card (NIC) that has
WOL capability. In addition, an onboard LAN controller can also support WOL
without any connection to the WOL header. The 3-pin WOL header is to be used
with a LAN add-on card only.
Note: Wake-On-LAN requires an ATX 2.01 (or above) compliant power supply.
1-6 Power Supply
As with all computer products, a stable power source is necessary for proper and
reliable operation. It is even more important for processors that have high CPU
clock rates.
The PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ can only accommodate a 24-pin ATX
power supply. Although most power supplies generally meet the specications
required by the motherboard, some are inadequate. You should use one that will
supply at least 400W of power. In addition, the 12V 8-pin power connector is also
required for adequate power supply to the system. Also your power supply must
supply 1.5A of current for the Ethernet ports.
It is strongly recommended that you use a high quality power supply that meets ATX
power supply Specication 2.01 or above. It must also be SSI compliant (info at
http://www.ssiforum.org/). Additionally, in areas where noisy power transmission is
present, you may choose to install a line lter to shield the computer from noise. It
is recommended that you also install a power surge protector to help avoid problems
caused by power surges.

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-13
1-7 Super I/O
The disk drive adapter functions of the Super I/O chip include a oppy disk drive
controller that is compatible with industry standard 82077/765, a data separator,
write pre-compensation circuitry, decode logic, data rate selection, a clock genera-
tor, drive interface control logic and interrupt and DMA logic. The wide range of
functions integrated onto the Super I/O greatly reduces the number of components
required for interfacing with oppy disk drives. The Super I/O supports 360 K, 720
K, 1.2 M, 1.44 M or 2.88 M disk drives and data transfer rates of 250 Kb/s, 500 Kb/s
or 1 Mb/s. It also provides two high-speed, 16550 compatible serial communication
ports (UARTs). Each UART includes a 16-byte send/receive FIFO, a programmable
baud rate generator, complete modem control capability and a processor interrupt
system. Both UARTs provide legacy speed with baud rate of up to 115.2 Kbps
as well as an advanced speed with baud rates of 250 K, 500 K, or 1 Mb/s, which
support higher speed modems.
The Super I/O supports one PC-compatible printer port (SPP), Bi-directional Printer
Port (BPP) , Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) or Extended Capabilities Port (ECP).
The Super I/O provides functions that comply with ACPI (Advanced Conguration
and Power Interface), which includes support of legacy and ACPI power manage-
ment through an SMI or SCI function pin. It also features auto power management
to reduce power consumption.
1-8 Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI)
IPMI is a management interface that enables a user or administrator to remotely
access, monitor, diagnose and manage servers and networks. To use the IPMI
2.0 slot on this motherboard, use Supermicro’s AOC-SIM1U, AOC-SIM1U+ or the
AOC-SIMLC Intelligent Management module, and the IPMIView software utility that
is included in the package.
With the Raritan® KIRATM 100 Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) built-in,
the AOC-SIM1U/SIM1U+ and the AOC-SIMLC supports the 2D/VGA-compatible
Graphics Core with the PCI interface, Virtual Media, and Keyboard/Video/Mouse
(KVM) Redirection modules.
The KIRA 100 BMC interfaces with the host system via a PCI interface to com-
municate with the graphics core. It supports USB 2.0 and 1.1 for remote keyboard/
mouse/virtual media emulation. It also provides LPC interface to control Super IO
functions. The KIRA 100 is connected to the network via an external Ethernet PHY
module to provide network interfacing and management.

1-14
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User’s Manual
For more information on IPMI conguration, please refer to the AOC-SIM1U/SIM1U+
and AOC-SIMLC User’s Guide posted on our website at http://www.supermicro.com/
products/accessories/addon/SIM.cfm.

Chapter 2: Installation
2-1
Chapter 2
Installation
2-1 Electro-Static Sensitive Devices
Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) can damage electronic com ponents. To
prevent damage to your system board, it is important to handle it very
carefully. The following measures are generally sufcient to protect your
equipment from ESD.
Precautions
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent electro-static build up.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the anti-static
bag to discharge any electro-static build up.
• Handle the board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral
chips, memory modules or gold contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the motherboard and peripherals back into their anti-static bags when not in
use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure your computer chassis provides excellent
conductivity between the power supply, the case, the mounting fasteners and
the motherboard.
• Use only the correct type of onboard CMOS battery. Do not install the onboard
battery upside down to avoid possible explosion.
Unpacking
The motherboard is shipped in anti-static packaging to avoid ESD damage. When
unpacking the board, make sure the person handling it is ESD protected.
!
Note: Be sure to mount the motherboard into the chassis before you install the CPU
onto the motherboard. All motherboards have standard mounting holes to t different
types of chassis. Make sure that the locations of all the mounting holes for both
motherboard and chassis match and the metal standoffs click in or are screwed in
tightly. Use a screwdriver to secure the motherboard.
Caution: 1. Please do not use a force greater than 8 lb/inch on each mounting
screw during motherboard installation. 2. Some components are very close to the
mounting holes. Please take precautionary measures to prevent damage to these
components when installing the motherboard to the chassis.

2-2
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User's Manual
Installation of the LGA775 Processor
1. Press the socket clip to release
the load plate, which covers the CPU
socket, from its locking position.
Socket Clip
2. Gently lift the socket clip to open the
load plate.
Load Plate
Load Plate
When handling the processor package, avoid placing
direct pressure on the label area of the fan.
Notes: 1. Always connect the power cord last and always remove it before adding,
removing or changing any components. Make sure that you install the processor
into the CPU socket before you install the CPU heatsink.
2. Intel's boxed processor package contains the CPU fan and heatsink assembly. If
you buy a CPU separately, make sure that you use an Intel-certied multi-directional
heatsink and fan.
3. The LGA 775 heatsink and fan comes with a push-pin design and no tool is
needed for installation.
4. When purchasing an LGA 775 CPU or when receiving a motherboard with an LGA
775 CPU pre-installed, make sure that the CPU plastic cap is in place and none of
the CPU pins are bent; otherwise, contact the retailer immediately.
5. Refer to the MB Features Section for more details on CPU support.
!
2-2 Processor, Heatsink and Fan Installation
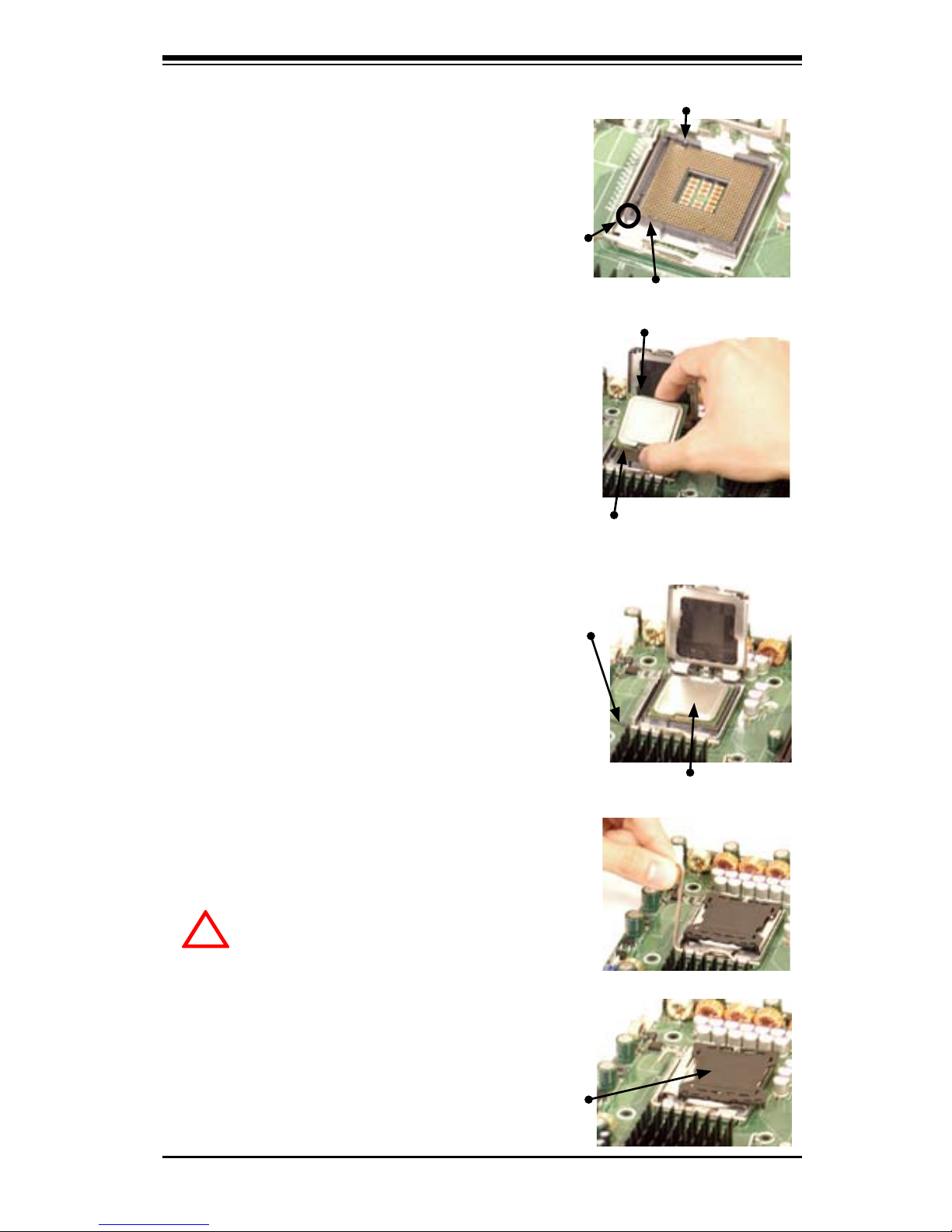
Chapter 2: Installation
2-3
Pin 1
South Key
North Key
South Center Edge
North Center Edge
Socket clip
CPU in the CPU socket
Plastic cap is released
from the load plate if
CPU properly installed.
3. Locate Pin 1 on the CPU socket. Note:
Pin 1 is the corner marked with a triangle.
Please note that the North Key and the
South Key are located vertically in the
CPU housing.
4. Position the motherboard in such a way
that Pin 1 of the CPU socket is located at
the left bottom of the CPU housing.
5. Use your thumb and your index nger to
hold the CPU at the North Center Edge and
the South Center Edge of the CPU.
6. Align Pin 1 of the CPU with Pin 1 of the
socket. Once aligned, carefully lower the
CPU straight down to the socket. (**Do not
drop the CPU on the socket. Do not move
the CPU horizontally or vertically. Do not
rub the CPU against the surface or against
any pins of the socket to avoid damage to
the CPU or the socket.)
7. With the CPU inside the socket, inspect
the four corners of the CPU to make sure
that the CPU is properly installed.
8. Use your thumb to gently push the
socket clip down to the clip lock.
9. If the CPU is properly installed into the
socket, the plastic cap will be automatically
released from the load plate when the Clip
is pushed in the clip lock. Remove the
plastic cap from the motherboard.
Warning: Please keep the plastic
cap. The motherboard and the CPU
must be shipped with the plastic cap
properly installed to protect the CPU pins.
Shipment without the CPU plastic cap
properly installed will void the warranty.
!
2-4
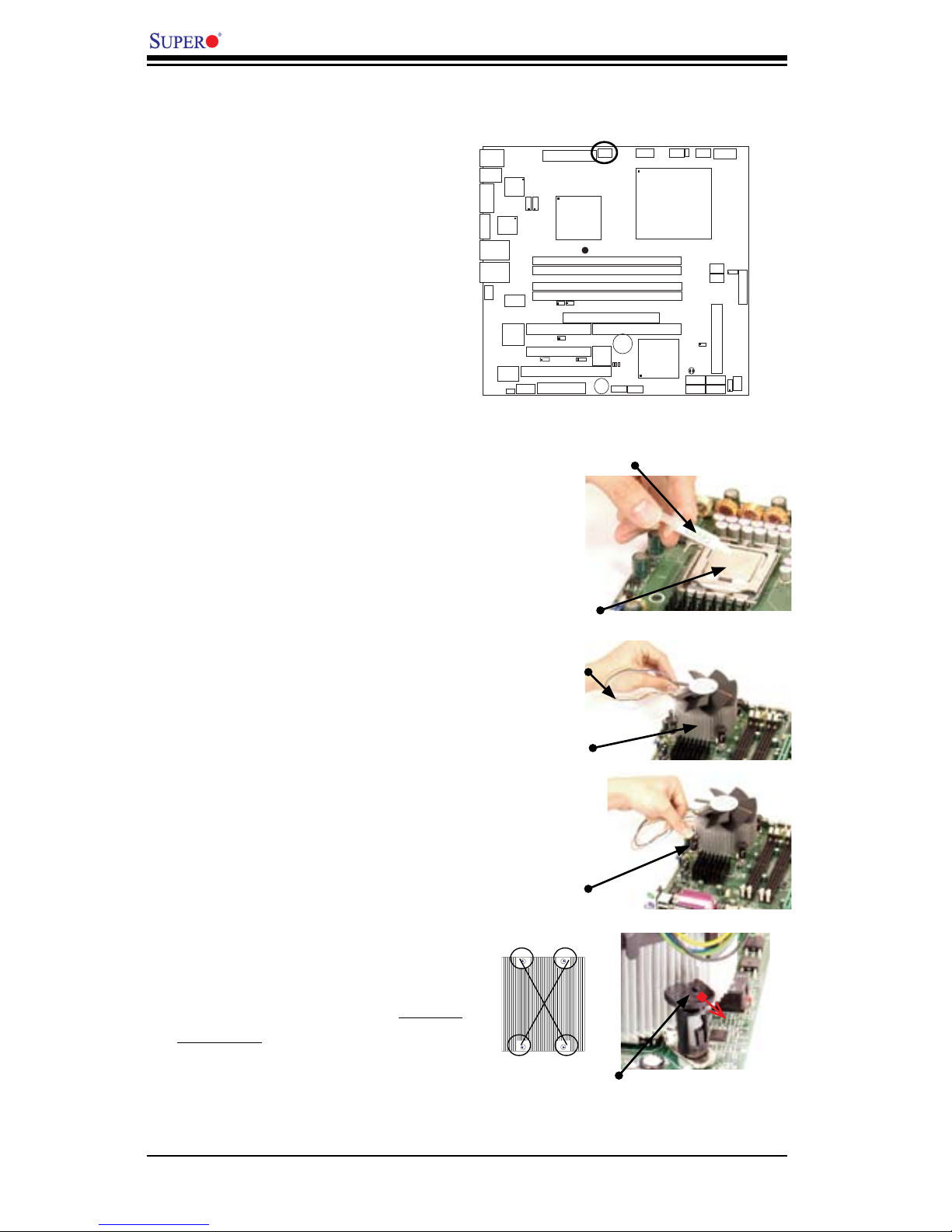
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User's Manual
Fan Wires
Thermal Grease
CPU
Heatsink
Fastener
Heatsink Fins
1. Locate the CPU Fan on the mother-
board. (Refer to the layout on the right
for the CPU Fan location.)
2. Position the heatsink so that the
heatsink fan wires are closest to the
CPU fan and are not interfered with
other components.
3. Inspect the CPU Fan wires to make
sure that the wires are routed through
the bottom of the heatsink.
4. Remove the thin layer of the protec-
tive lm from the copper core of the
heatsink.
Warning: CPU may overheat if the
protective lm is not removed from the
heatsink.
5. Apply the proper amount of thermal
grease on the CPU. Note: if your heat-
sink came with a thermal pad, please
ignore this step.
6. If necessary, rearrange the wires
to make sure that the wires are not
pinched between the heatsink and the
CPU. Also make sure to keep clear-
ance between the fan wires and the
ns of the heatsink.
7. Align the four heatsink fasten-
ers with the mounting holes on the
motherboard. Gently push the pairs of
diagonal fasteners (#1 & #2, and #3 &
#4) into the mounting holes until you
hear a click. Note: Make sure to orient
each fastener so that the narrow end
of the groove points outward.
Installation of the Heatsink
#2
#3
#4
#1
Narrow end of the groove
points outward
S
UPER PDSML -LN1+/LN 2+/E+
®

Chapter 2: Installation
2-5
2-3 Mounting the Motherboard in the Chassis
All motherboards have standard mounting holes to t different types of chassis.
Make sure the locations of all the mounting holes for both the motherboard and
the chassis match. Make sure the metal standoffs click in or are screwed in tightly.
Then use a screwdriver to secure the motherboard onto the motherboard tray.
Note: Some components are very close to the mounting holes. Please take all
necessary precautionary measures to prevent damage done to these components
when installing the motherboard into the chassis. Please do not use a force greater
than 8 lb/inch on each mounting screw during installation to prevent damage to the
motherboard.
8. Repeat Step 6 to insert all four heatsink
fasteners into the mounting holes.
9. Once all four fasteners are securely
inserted into the mounting holes and the
heatsink is properly installed on the moth-
erboard, connect the heatsink fan wires to
the CPU Fan connector.
1. Unplug the power cord from the power
supply.
2. Disconnect the heatsink fan wires from
the CPU fan header.
3. Use your nger tips to gently press on the
fastener cap and turn it counterclockwise
to make a 1/4 (900) turn, and then pull the
fastener upward to loosen it.
4. Repeat Step 3 to loosen all fasteners from
the mounting holes.
5. With all fasteners loosened, remove the
heatsink from the CPU.
Heatsink Removal

2-6
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User's Manual
2-4 Installing DDR2 Memory
Memory Module Installation
Exercise extreme care when installing or removing memory mod-
ules to prevent any possible damage.
1. Insert each DDR2 memory module vertically into its slot. Pay attention to the
notch along the bottom of the module to prevent inserting the module incor-
rectly. (See support information below.)
2. Gently press down on the memory module until it snaps into place.
Support
The PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ supports up to 8GB of dual chan-
nel, ECC/Non-ECC, unbuffered DDR2 667/533 MHz SDRAM. Both interleaved
and non-interleaved memory are supported, so you may populate any number
of DIMM slots. Populating DIMM#1A,DIMM#1B, and/or DIMM#2A, DIMM#2B
with memory modules of the same size and of the same type will result in dual
channel, two-way interleaved memory which is faster than the single channel,
non-interleaved memory. Note that when ECC memory is used, it may take
25-40 seconds for the VGA to display.
Notes:
1. Due to chipset limitation, 8GB Memory can only be supported by the following
operating systems:
32-Bit: Windows 2000 Advanced Server, Windows Server 2003 Enterprise
Edition; 64-Bit: Windows Server 2003 Standard x64 Edition, Windows XP
Professional x64 Edition, Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition.
2. DIMM sizes of 256MB, 512MB, 1GB and 2GB are supported (240-pin, 1.8V
only).
3. Due to memory allocation to system devices, memory remaining available for
operational use will be reduced when 4 GB of RAM is used. The reduction in
memory availability is disproportional. Refer to the Memory Availability Table
on the following page for details.
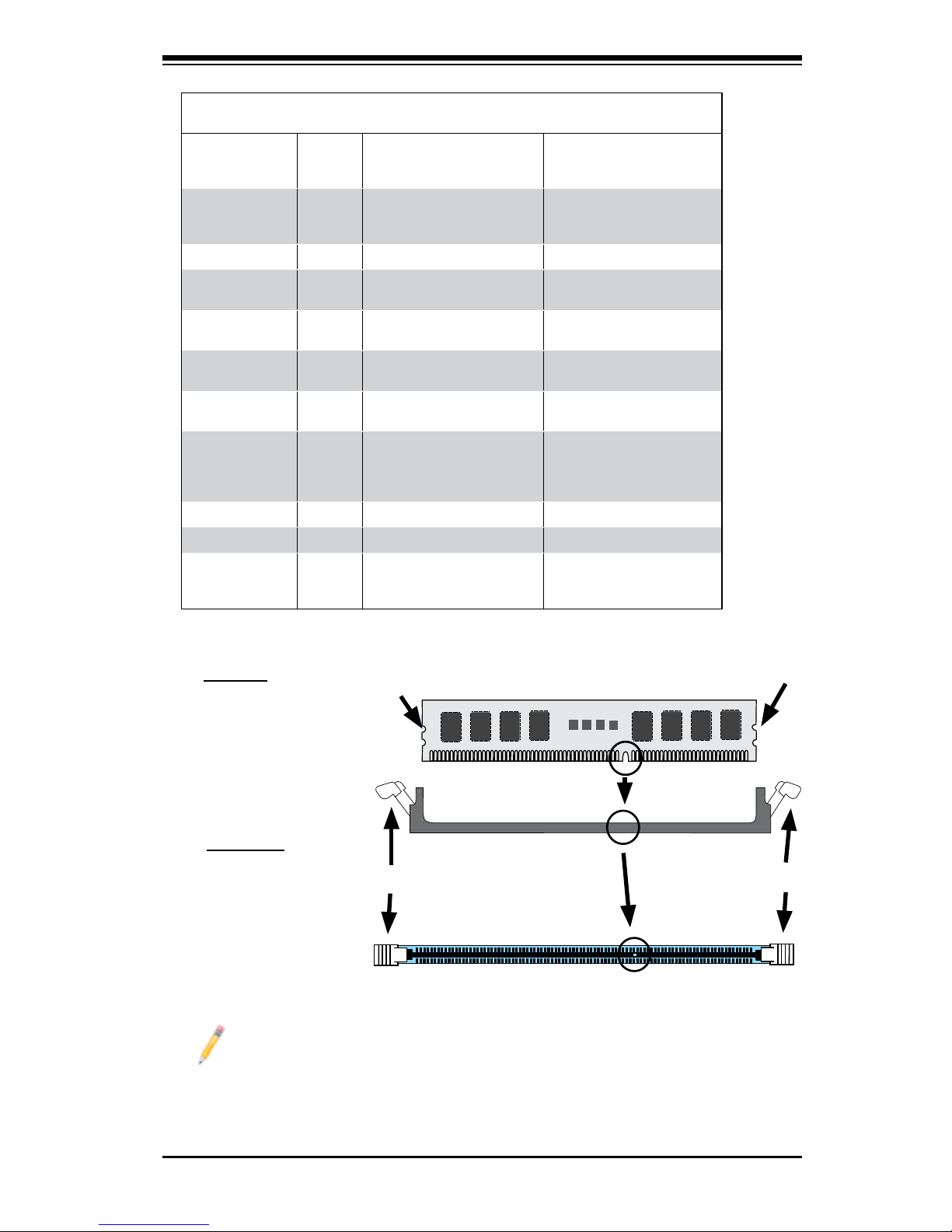
Chapter 2: Installation
2-7
To Install:
Insert module vertically and press down
until it snaps into
place. Pay attention
to the notch.
Installing a DIMM Module into a Slot
To Remove:
Use your thumbs to
gently push each
release tab outward
to release the DIMM
from the slot.
Possible System Memory Allocation & Availability
System Device Size Physical Memory
Remaining (-Available)
(3 GB Total System Memory)
Physical Memory
Remaining (-Available)
(4 GB Total System Memory)
Firmware Hub
ash memory
(System BIOS)
1 MB 3.00 3.99
Local APIC 4 KB 3.00 3.99
Area Reserved
for the chipset
2 MB 3.00 3.99
I/O APIC (4
Kbytes)
4 KB 3.00 3.99
PCI Enumeration
Area 1
256 MB 3.00 3.76
PCI Express (256
MB)
256 MB 3.00 3.51
PCI Enumeration
Area 2 (if needed)
-Aligned on 256MB boundary-
512 MB 3.00 3.01
VGA Memory 16 MB 2.85 2.85
TSEG 1 MB 2.84 2.84
Memory available
to BIOS, OS,
applications
2.84 2.84
Microsoft implemented a design change in Windows XP with Service Pack
2 (SP2) and Windows Vista. This change improves driver compatibility,
but however reduces the available memory compared to what is physically
insalled. For more information, please read the following article at Microsoft's
Knowledge Base website at: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/888137.
Note To Microsoft Windows Users
Release Tab
Release Tab
Note: Notch should align
wit h the receptive key
point on the slot.
Notch
Notch
Front View

2-8
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User's Manual
S
UPER PDSML- LN1+/LN 2+/E+
®
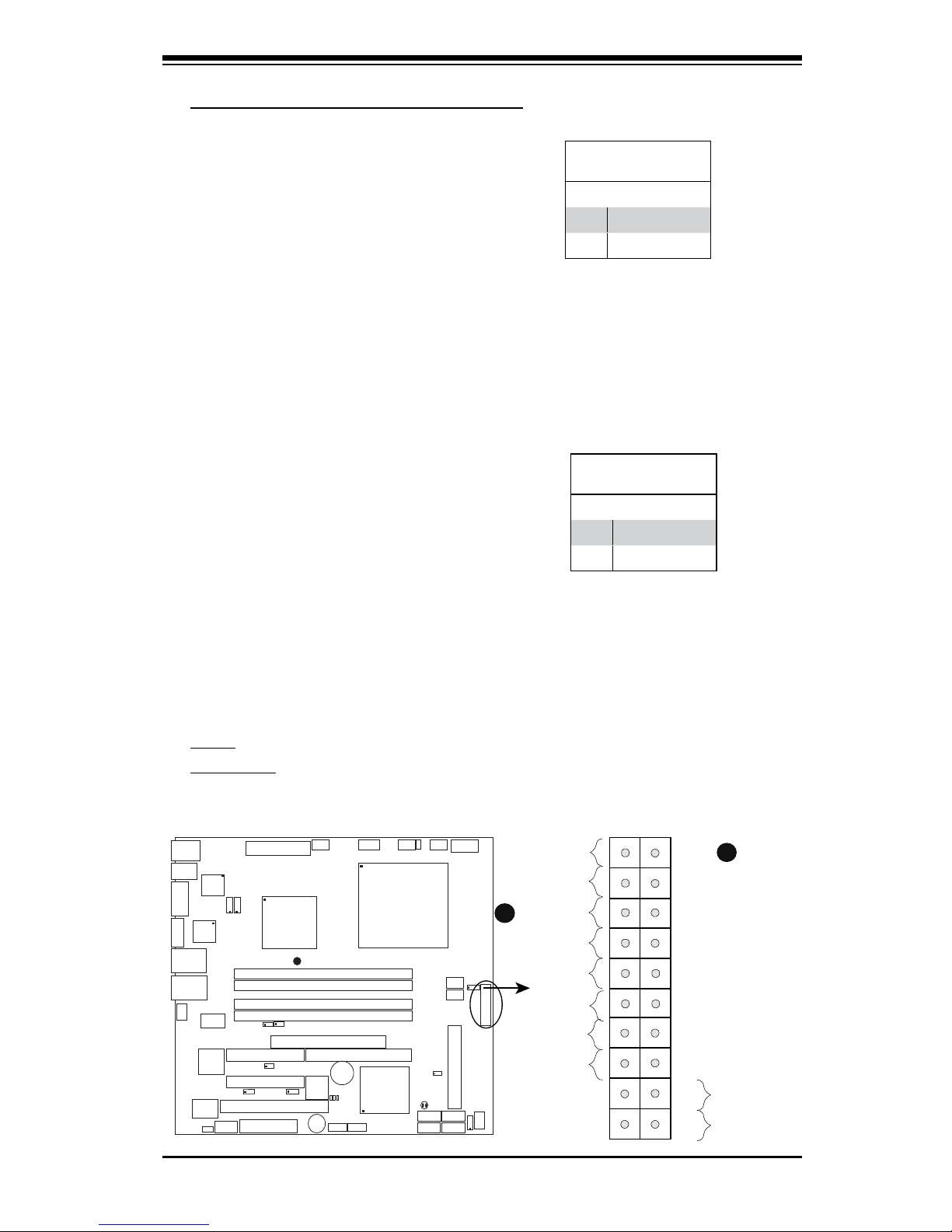
B. Front Control Panel
JF1 contains header pins for various buttons and indicators that are normally located
on a control panel at the front of the chassis. These connectors are designed
specically for use with Supermicro server chassis. Refer to the following section
for descriptions and pin denitions.
JF1 Header Pins
Power Button
OH/Fan Fail LED
1
NIC1 LED
Reset Button
2
HDD LED
Power LED
Reset
PWR
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Ground
Ground
1920
Vcc
X
Ground
NMI
X
Vcc
PWR Fail LED
NIC2 LED
S
UPER P DSML -LN1 +/LN 2+/E+
®
2-5 Control Panel Connectors/IO Ports
The I/O ports are color coded in conformance with the PC 99 specication. See
below for the colors and locations of the various I/O ports.
A. Back Panel Connectors/IO Ports
BackPanelI/OPortLocationsandDenitions
Back Panel Connectors
1. Keyboard (Purple) 5. COM Port 1 (Turquoise)
2. PS/2 Mouse (Green) 6. VGA Port (Blue)
3. Back Panel USB Port 1 7. Gigabit LAN 1
4. Back Panel USB Port 2. 8. Gigabit LAN 2 (*For PDSML-LN2+ and
PDSML-E+ only.)
(*See Section 2-6 for details.)
1234567
8
Chapter 2: Installation
2-9
S
UPER PDSML- LN1+/LN2+/E+
®
LGA 775 CPU
KB/MS
JLAN1
Intel
3000/3010
North Bridge
4naF
24-Pin ATX PWR
ICH7R
South Bridge
8-pin PWR
Batt ery
USB 1/2
VGA
JLAN2
COM2
Flo ppy
DIMM 2B
PCI-E x8
BI OS
IDE
JPF
DIMM 1B
DIMM 2A
DIMM 1A
Fan1
J8
Fan5
LAN
CTRL2
JPL2
JPL1
WOL
JWOR
rezzuB
JL 1
JI
2
C1
JBT1
SA TA 1
JPG1
Fan3
FP CTRL
JF1
Fan2
USB3 /4
LAN
CTRL1
SPK R
JI2C2
IPMI
Slot6
SBX: PCI-33 MHz
VGA
CT R L
J1 0
PCI-E x4
Slot5
PCI1
Slot4
PCI-33 MHz
LE 3
COM1
VGA
Memo ry
LE 4
LE 1
JLED
Fan6
CPU
Fan
JPR1
PWR FaultPWR SMB
(* LN2 +)
(* LN2 +)
USB5 /6
SA TA 0 S AT A2
SA TA 3
S I /O
Power Button
OH/Fan Fail LED
1
NIC1 LED
Reset Button
2
HDD LED
Power LED
Reset
PWR
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Ground
Ground
1920
Vcc
X
Ground
NMI
X
Vcc
PWR Fail LED
NIC2 LED
Power LED
The Power LED connection is located
on pins 15 and 16 of JF1. Refer to
the table on the right for pin deni-
tions. For 3-pin power LED applica-
tions, please see Power LED on page
2-19.
NMI Button
The non-maskable interrupt button
header is located on pins 19 and 20
of JF1. Refer to the table on the right
for pin denitions.
NMI Button
PinDenitions(JF1)
Pin# Denition
19 Control
20 Ground
Power LED
PinDenitions(JF1)
Pin# Denition
15 +5V
16 Ground
C.FrontControlPanelPinDenitions
A. NMI
B. PWR LED
A
B
2-10
PDSML-LN1+/PDSML-LN2+/PDSML-E+ User's Manual
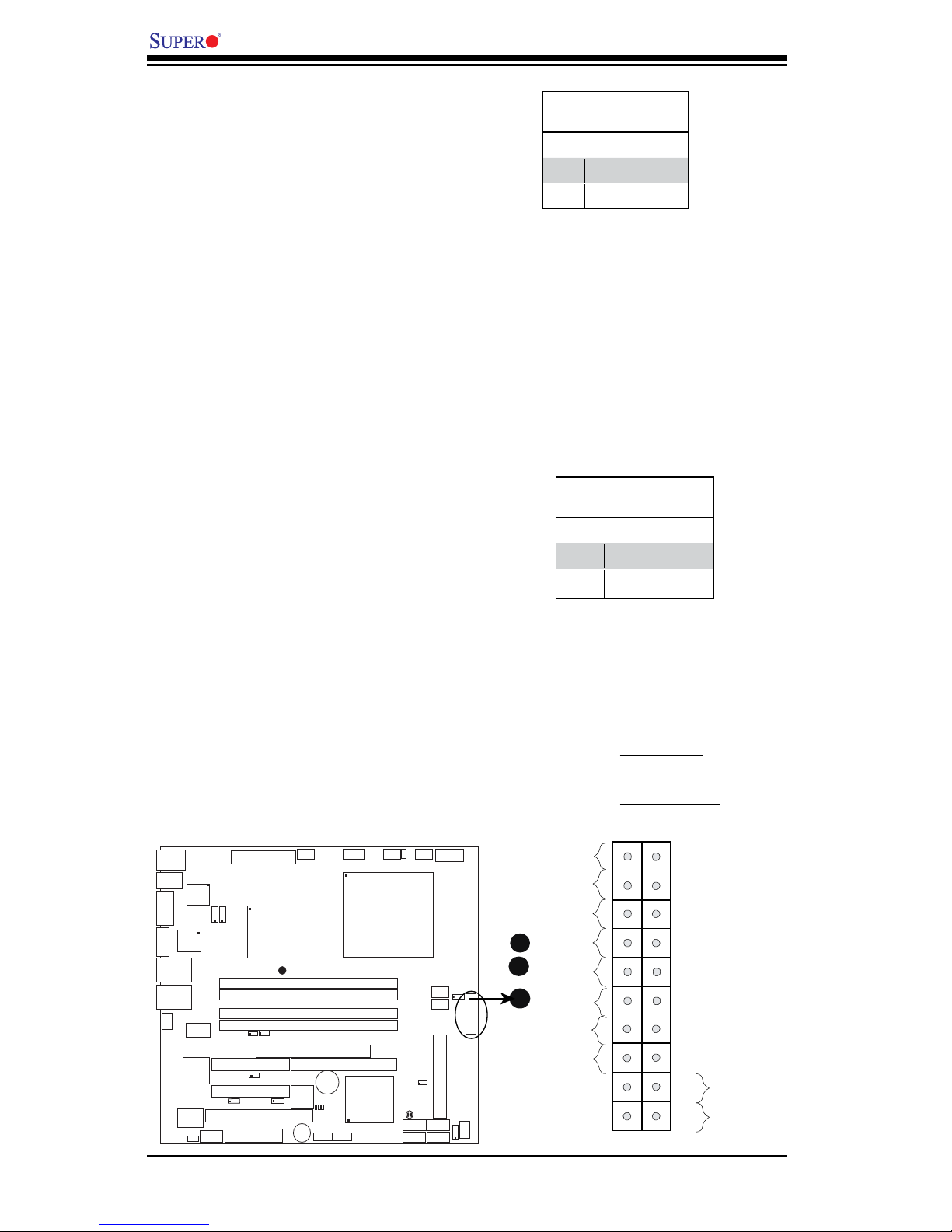
NIC1/NIC2 LED Indicators
The NIC (Network Interface Control-
ler) LED connection for GLAN port1
is located on pins 11 and 12 of JF1,
for GLAN port2 is on Pins 9 and 10
of JF1. Attach the NIC LED cables to
display network activity. Refer to the
table on the right for pin denitions.
HDD LED
The HDD LED connection is located
on pins 13 and 14 of JF1. Attach the
hard drive LED cable here to display
disk activity (for any hard drives on the
system, including Serial ATA and IDE
if available). See the table on the right
for pin denitions.
HDD LED
PinDenitions(JF1)
Pin# Denition
13 +5V
14 HD Active
GLAN1/2 LED
PinDenitions(JF1)
Pin# Denition
9/11 Vcc
10/12 Ground
A
B
C
A. HDD LED
B. GLAN1 LED
C. GLAN2 LED
Power Button
OH/Fan Fail LED
1
NIC1 LED
Reset Button
2
HDD LED
Power LED
Reset
PWR
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Ground
Ground
1920
Vcc
X
Ground
NMI
X
Vcc
PWR Fail LED
NIC2 LED
S
UPER PDSML- LN1+/LN2+/E+
®
LGA 775 CPU
KB/MS
JLAN1
Intel
3000/3010
North Bridge
4naF
24-Pin ATX PWR
ICH7R
South Bridge
8-pin PWR
Batt ery
USB 1/2
VGA
JLAN2
COM2
Flo ppy
DIMM 2B
PCI-E x8
BI OS
IDE
JPF
DIMM 1B
DIMM 2A
DIMM 1A
Fan1
J8
Fan5
LAN
CTRL2
JPL2
JPL1
WOL
JWOR
rezzuB
JL 1
JI
2
C1
JBT1
SA TA 1
JPG1
Fan3
FP CTRL
JF1
Fan2
USB3 /4
LAN
CTRL1
SPK R
JI2C2
IPMI
Slot6
SBX: PCI-33 MHz
VGA
CT R L
J1 0
PCI-E x4
Slot5
PCI1
Slot4
PCI-33 MHz
LE 3
COM1
VGA
Memo ry
LE 4
LE 1
JLED
Fan6
CPU
Fan
JPR1
PWR FaultPWR SMB
(* LN2 +)
(* LN2 +)
USB5 /6
SA TA 0 S AT A2
SA TA 3
S I /O
 Loading...
Loading...