Page 1

Sun Enterprise 10000
Capacity on Demand 1.0
Administrator Guide
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
901 San Antonio Road
Palo Alto, CA 94303-4900 USA
650 960-1300 Fax 650 969-9131
Part No.: 806-2190-10
Revision A, October 1999
Send comments about this document to: docfeedback@sun.com
Page 2

Copyright 1999 Sun Microsystems,Inc.,901SanAntonioRoad,PaloAlto,California94303-4900U.S.A.Allrightsreserved.
This productordocumentisprotectedbycopyrightanddistributedunderlicensesrestrictingitsuse,copying,distribution,anddecompilation.
No part of this productordocumentmaybereproducedinanyformbyanymeanswithoutpriorwrittenauthorizationofSunanditslicensors,
if any. Third-partysoftware,includingfonttechnology,iscopyrightedandlicensedfromSunsuppliers.
Parts of the productmaybederivedfromBerkeleyBSDsystems,licensedfromtheUniversityofCalifornia.UNIXisaregisteredtrademarkin
theU.S.andothercountries,exclusivelylicensedthroughX/OpenCompany, Ltd.ForNetscapeCommunicator™,thefollowingnoticeapplies:
(c) Copyright 1995 Netscape Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Sun, Sun Microsystems,theSunlogo,AnswerBook2,docs.sun.com,SunEnterprise,andSolarisaretrademarks,registeredtrademarks,or
service marks of Sun Microsystems,Inc.intheU.S.andothercountries.AllSPARC trademarks areusedunderlicenseandaretrademarksor
registeredtrademarksofSPARCInternational,Inc.intheU.S.and other countries. Products bearing SPARCtrademarksarebaseduponan
architecturedevelopedbySunMicrosystems,Inc.
The OPEN LOOK and Sun™ Graphical User Interface was developed by Sun Microsystems,Inc.foritsusersandlicensees.Sunacknowledges
the pioneering effortsofXeroxinresearchinganddevelopingtheconceptofvisualorgraphicaluserinterfacesforthecomputerindustry.Sun
holds a non-exclusive license fromXeroxtotheXeroxGraphicalUserInterface,whichlicensealsocoversSun’slicenseeswhoimplementOPEN
LOOK GUIs and otherwise comply with Sun’s written license agreements.
RESTRICTEDRIGHTS:Use, duplication, or disclosurebytheU.S.GovernmentissubjecttorestrictionsofFAR 52.227-14(g)(2)(6/87) and FAR
52.227-19(6/87), or DFAR252.227-7015(b)(6/95)andDFAR227.7202-3(a).
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONSANDWARRANTIES,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,FITNESSFORAPARTICULARPURPOSEORNON-INFRINGEMENT,
ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TOTHEEXTENTTHAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLYINVALID.
Copyright 1999 Sun Microsystems,Inc.,901SanAntonioRoad,PaloAlto,Californie94303-4900U.S.A.Tous droitsréservés.
Ce produitoudocumentestprotégéparun copyright et distribué avec des licences qui en restreignentl’utilisation,lacopie,ladistribution,etla
décompilation. Aucune partie de ce produitoudocumentnepeutêtrereproduitesousaucuneforme,parquelquemoyenquecesoit,sans
l’autorisation préalable et écrite de Sun et de ses bailleurs de licence, s’il y en a. Le logiciel détenu par des tiers, et qui comprendlatechnologie
relativeauxpolicesdecaractères,estprotégéparuncopyrightetlicenciépardesfournisseursdeSun.
Des parties de ce produitpourrontêtredérivéesdessystèmes Berkeley BSD licenciés par l’Université de Californie. UNIX est une marque
déposée aux Etats-Unis et dans d’autrespaysetlicenciéeexclusivementparX/OpenCompany, Ltd. La notice suivante est applicable à
Netscape
Sun, Sun Microsystems,lelogoSun,AnswerBook2,docs.sun.com,SunEnterprise,etSolarissontdesmarquesdefabriqueoudesmarques
déposées, ou marquesdeservice,deSunMicrosystems,Inc.auxEtats-Unisetdansd’autrespays.TouteslesmarquesSPARCsontutiliséessous
licence et sont des marquesdefabriqueoudesmarques déposées de SPARCInternational,Inc.auxEtats-Uniset dans d’autres pays. Les
produitsportantlesmarquesSPARCsontbaséssurunearchitecturedéveloppéeparSunMicrosystems,Inc.
L’interfaced’utilisationgraphiqueOPENLOOKetSun™aétédéveloppéeparSunMicrosystems,Inc.poursesutilisateursetlicenciés.Sun
reconnaîtleseffortsdepionniersdeXeroxpourlarechercheetledéveloppementduconceptdesinterfacesd’utilisationvisuelleougraphique
pour l’industrie de l’informatique. Sun détient une licence non exclusive de Xeroxsurl’interfaced’utilisationgraphiqueXerox,cettelicence
couvrant également les licenciés de Sun qui mettent en place l’interface d’utilisation graphique OPEN LOOK et qui en outreseconformentaux
licences écrites de Sun.
CETTE PUBLICATIONESTFOURNIE"ENL’ETAT"ETAUCUNEGARANTIE,EXPRESSEOUIMPLICITE,N’ESTACCORDEE,YCOMPRIS
DES GARANTIES CONCERNANT LA VALEUR MARCHANDE, L’APTITUDEDELAPUBLICATIONAREPONDREAUNEUTILISATION
PARTICULIERE,OULEFAIT QU’ELLE NE SOIT PASCONTREFAISANTEDEPRODUITDETIERS.CEDENIDEGARANTIENE
S’APPLIQUERAIT PAS, DANS LA MESURE OU IL SERAIT TENU JURIDIQUEMENT NUL ET NON AVENU.
Communicator™:(c)Copyright1995NetscapeCommunicationsCorporation.Allrightsreserved.
Please
Recycle
Page 3

Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP Attributions:
This software is copyrighted by the Regents of the University of California, Sun Microsystems, Inc., and other
parties. The following terms apply to all files associated with the software unless explicitly disclaimed in individual
files.
The authors hereby grant permission to use, copy, modify, distribute, and license this software and its documentation
for any purpose, provided that existing copyright notices are retained in all copies and that this notice is included
verbatim in any distributions. No written agreement, license, or royalty fee is required for any of the authorized uses.
Modifications to this software may be copyrighted by their authors and need not follow the licensing terms described
here, provided that the new terms are clearly indicated on the first page of each file where they apply.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR DISTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE TO ANY PARTY FOR DIRECT,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF
THIS SOFTWARE, ITS DOCUMENTATION, OR ANY DERIVATIVES THEREOF, EVEN IF THE AUTHORS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
THE AUTHORS AND DISTRIBUTORS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIM ANY WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT
NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS, AND THE
AUTHORS AND DISTRIBUTORS HAVE NO OBLIGATION TO PROVIDE MAINTENANCE, SUPPORT,
UPDATES, ENHANCEMENTS, OR MODIFICATIONS.
RESTRICTED RIGHTS: Use, duplication or disclosure by the government is subject to the restrictions as set forth
in subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software Clause as DFARS 252.227-7013
and FAR 52.227-19.
This is scotty, a simple tcl interpreter with some special commands to get information about TCP/IP networks.
Copyright (c) 1993, 1994, 1995, J. Schoenwaelder, TU Braunschweig, Germany, Institute for Operating Systems and
Computer Networks. Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its documentation for any
purpose and without fee is hereby granted, provided that this copyright notice appears in all copies. The University
of Braunschweig makes no representations about the suitability of this software for any purpose. It is provided “as
is" without express or implied warranty.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Preface vii
Before You Read This Book vii
Using UNIX Commands viii
Typographic Conventions viii
Shell Prompts ix
Related Documentation ix
Accessing Sun Documentation Online x
Sun Welcomes Your Comments x
Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 1
Software Requirements 2
Using a Spare SSP with Capacity on Demand 2
Switching From the Main SSP to the Spare SSP 2
Configuring Capacity on Demand Resources 3
License Keys 4
Tiered Licenses 4
Obtaining a License Key 4
▼ To Obtain the Primary Host ID for Your Sun Enterprise 10000 System 5
License Certificate 5
v
Page 6

Installing the License Key 5
▼ To Install License Keys for Processors on an Existing Board 6
▼ To Install License Keys for Processors On a Board that Is Not in a Domain or
On a New Board 7
Blacklisting Processors 8
Capacity on Demand Daemon 9
License Violation Actions 9
Platform Log License Violation Message Examples 10
Email License Violation Message Example 11
/etc/motd License Violation Message Example 11
Broadcast License Violation Message Example 11
License Violation Messages 12
Capacity on Demand Secure Logging 13
Using Multiple Domains 13
▼ To Shut Down One Domain and Bring Up Another 14
Upgrading the SSP Software or Solaris Operating Environment 14
▼ To Upgrade the Solaris Operating Environment 15
▼ To Upgrade the SSP Software 15
vi Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 7

Preface
This document describes how to obtain and install processor license keys for your
Sun Enterprise™ 10000 Capacity on Demand system, and the use of other Capacity
on Demand 1.0 features.
Before You Read This Book
This manual is intended for the Sun Enterprise 10000 system administrator who is
familiar with SSP administration. Refer to the Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.1.1 User
Guide and Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.1.1 Reference Manual. SSP 3.1.1 is the first
release of SSP software that supports Capacity on Demand 1.0. The Sun Enterprise
10000 system administrator must also have a working knowledge of UNIX®
systems, particularly those based on the Solaris™ operating environment. If you do
not have such knowledge, you must first read the Solaris User and System
Administrator AnswerBook2™ collections provided with this system, and consider
UNIX system administration training.
vii
Page 8

Using UNIX Commands
This document does not contain information on basic UNIX commands and
procedures such as shutting down the system, booting the system, and configuring
devices.
See one or more of the following for this information:
■ AnswerBook online documentation for the Solaris software environment,
particularly those dealing with Solaris system administration
■ Other software documentation that you received with your system
Typographic Conventions
TABLEP-1 Typographic Conventions
Typeface or
Symbol Meaning Examples
AaBbCc123 The names of commands, files,
and directories; on-screen
computer output.
AaBbCc123 What you type, when contrasted
with on-screen computer output.
AaBbCc123 Book titles, new words or terms,
words to be emphasized
Command-line variable; replace
with a real name or value
viii Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Edit your .login file.
ls -a to list all files.
Use
% You have mail.
% su
Password:
Read Chapter 6 in the User’s Guide.
These are called class options.
You must be superuser to do this.
To delete a file, type
rm filename
Page 9
Shell Prompts
TABLEP-2 Shell Prompts
Shell Prompt
C shell machine_name%
C shell superuser machine_name#
Bourne shell and Korn shell $
Bourne shell and Korn shell superuser #
Related Documentation
TABLEP-3 Related Documentation
Application Title Part Number
Installation Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0
Installation Guide and Release Notes
Reference (man pages) Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0
Reference Manual
Other Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.1.1 User Guide 805-7519-10
Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.1.1 Reference Manual 805-7520-10
Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic Reconfiguration
User’s Guide
Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic Reconfiguration
Reference Manual
Sun Enterprise Server Alternate Pathing User ’s
Guide
Sun Enterprise Server Alternate Pathing Reference
Manual
806-2283-10
806-2191-10
805-7985-10
805-7986-10
805-5985-10
805-5986-10
Preface ix
Page 10

Accessing Sun Documentation Online
The docs.sun.comSMweb site enables you to access Sun technical documentation
on the Web. You can browse the docs.sun.com archive or search for a specific book
title or subject at:
http://docs.sun.com
Sun Welcomes Your Comments
We are interested in improving our documentation and welcome your comments
and suggestions. You can email your comments to us at:
docfeedback@sun.com
Please include the part number (806-2190-10) of your document in the subject line of
your email.
x Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 11

Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0
Capacity on Demand provides processor licensing for the Sun Enterprise 10000
server. A Sun Enterprise 10000 system with Capacity on Demand 1.0 is shipped
with:
■ The Capacity on Demand 1.0 software installed on the SSP
■ A minimum configuration of five system boards containing four processors each
■ A minimum of eight processor licenses (more can be ordered at the time the order
is placed)
You can also convert an existing Sun Enterprise 10000 system to be a Capacity on
Demand system. Contact your sales representative for more information.
The Capacity on Demand software consists of:
■ Capacity on Demand daemon, codd(1M), which performs license validation
checks on startup and at regular intervals
■ codlit(1M), a utility for installing license keys
■ codcheck(1M), a utility for validating the secure log (for the use of Sun service
personnel only)
■ codsendlog(1M), a utility used to send the secure log file to Sun (for the use of
Sun service personnel only)
You can obtain license keys for the remaining processors as needed. You can also
add system boards and licenses for processors on the new boards as needed (up to a
maximum of 16 boards and 64 processors).
1
Page 12

Software Requirements
Capacity on Demand 1.0 requires:
■ SSP 3.1.1 or 3.2 software (SSP 3.1.1 is the first release of SSP software that
supports Capacity on Demand 1.0)
■ Solaris 2.6 or Solaris 7 operating environment
Using a Spare SSP with Capacity on Demand
If you are using a spare SSP on your Capacity on Demand system, the main SSP and
the spare SSP must be running the same version of the Solaris operating
environment, the SSP software, and the Capacity on Demand software.
You must also install the Capacity on Demand license keys on both the main and
spare SSP (or copy the license file from the main SSP to the spare) and copy the
cod_resource file (in the /var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private directory) and
blacklist(4) file from the main SSP to the spare SSP. You can copy these files by
backing up the main SSP with ssp_backup(1M) and then restoring the backup file
on the spare SSP with ssp_restore(1M); ssp_backup(1M) saves the SSP
environment, including the files required for Capacity on Demand.
If you add new license keys to the license file, or change the cod_resource file or
blacklist(4) file on the main SSP, be sure to back up the main SSP and restore the
backup file on the spare SSP or copy the changed files to the spare SSP.
Switching From the Main SSP to the Spare SSP
The procedure for switching from the main SSP to the spare SSP is documented in
the Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.1.1 User Guide. In addition to performing the steps
described in that manual, you must backup the main SSP before switching to the
spare and restore the backup on the spare SSP, or copy the following files to the
spare SSP:
■ License file (/var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private/SUNWcod.lic)
■ cod_resource file
(/var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private/cod_resource)
2 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 13

■ Secure log file and the copies of the log file that are saved monthly
(/var/opt/SUNWssp/adm/cod.log and
/var/opt/SUNWssp/adm/cod.log.*)
■ blacklist(4) file (/var/opt/SUNWssp/etc/platform_name/blacklist)
Configuring Capacity on Demand Resources
The cod_resource file, located in the /var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private
directory, contains Capacity on Demand resource information. The resources in the
cod_resource file have the following format:
resource_name:resource_value
where
resource_name is the name of the resource. Resource names are case sensitive and can
only occur once in the cod_resource file.
resource_value is the value for the resource.
The LicenseNotifyList resource lists user names to which email violation
notifications are sent. The value of LicenseNotifyList is a list of email addresses
separated by spaces. In the default cod_resource file, LicenseNotifyList
contains the ssp user. The SunAddr resource specifies the email address at Sun to
which the secure log file is automatically sent each month. You can modify the email
address specified by SunAddr so that it is compatible with your email system.
You can modify the resources in the cod_resource file by editing the file with a
text editor. The default cod_resource file contains the following:
LicenseNotifyList:ssp
SunAddr:COD_lic@sun.com
3
Page 14

License Keys
You must have a license (or Right to Use (RTU)) for each processor you are using in
your Capacity on Demand system. A Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand
system is shipped with one or more license certificates containing the license key, or
keys, for all the licenses (RTUs) you ordered for the system. The license keys are also
provided as an attachment in an email message from Sun. Your initial license keys
were installed in the Capacity on Demand license file by Sun personnel.
Note – The license certificate shipped with your Capacity on Demand system lists
the serial numbers and the license keys that were installed on the system. If you
need to recreate the Capacity on Demand license file because of a disk crash or other
problem and you do not have a backup file of the SSP environment that includes the
license file (see ssp_backup(1M)), you will need the email attachment containing
the license keys. You can also create a text file containing the license keys by typing
in the license keys listed at the bottom of the license certificate.
If you want to use one or more processors for which you do not have a license, you
must contact your sales representative to obtain a license key or keys. See
“Obtaining a License Key” below. When you purchase and install new license keys
(see “Installing the License Key” on page 5), a line is added to the license file for
each additional license key.
Tiered Licenses
Capacity on Demand systems have a tiered licensing scheme. You must purchase all
of the licenses in the lower tier before you can purchase and install licenses in the
next tier.
Obtaining a License Key
To obtain license keys for processors on your Capacity on Demand system, contact
your sales representative. You will need the host ID for the primary domain on the
Sun Enterprise 10000 system.
4 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 15

▼ To Obtain the Primary Host ID for Your Sun
Enterprise 10000 System
1. Log in as user ssp and type:
ssp% cd /var/opt/SUNWssp/.ssp_private/eeprom_save
2. Type:
ssp% sys_id -x -f eeprom.image.domain_name
a65f04
where domain_name is the name of the primary domain on your Sun Enterprise 10000
system. The primary host ID displayed by sys_id(1M) is a hexadecimal number
that begins with a65. If you do not know which domain is the primary domain, you
need to examine each eeprom.image file until you find the one that has a host ID
that begins with a65.
When you give this host ID to your sales representative, add the prefix 80 to the
hexadecimal host ID shown by sys_id(1M) to create an eight-digit host ID. In the
example output for sys_id(1M) shown above, the six-digit host ID is a65f04; the
eight-digit host ID to give to the sales representative in this case is 80a65f04.
License Certificate
After you order license keys, you will receive one or more license certificates that
contain the license key, or keys, for the RTU licenses you ordered. You will also
receive an email message with an attachment, or attachments, that contains the
license key, or keys. Save the each attachment; you will use these files to install the
license keys. See “Installing the License Key” below.
When obtaining license keys for multiple processors, you can request one license key
with RTUs for multiple processors.
Installing the License Key
After you have received the email with an attachment containing license keys and
have saved the attachment, or attachments, to one or more license key files, you
must copy the license key files to the SSP and install the license keys to be able to
use the additional processors.
5
Page 16
The following is an example of a license key:
SERVER E10k 80a65352 1726
DAEMON sunwlicd /etc/opt/licenses/sunwlicd
INCREMENT StarfireProc1_1_0 sunwlicd 1.000 01-jan-0 20 \
6B5AD001B156D5D9DA39 "0" 80a65352
▼ To Install License Keys for Processors on an Existing
Board
Use this procedure to install one or more license keys for processors that are on
boards that are currently in a domain.
1. Log in to the SSP as user ssp and type:
ssp% codlit filenames
codlit: x license key(s) installed from file, filename
where filenames is a list of one or more filenames (separated by spaces) that contain
license keys. codlit prints a line for each file specified on the command line that
indicates how many license keys were installed from that file.
2. Edit the blacklist(4) file.
Remove the processor you want to use from the blacklist(4) file.
You can edit the blacklist(4) file with a text editor or by using Hostview. See
“Blacklisting Processors” on page 8.
3. Activate the processor or processors.
You can activate processors by performing a DR Detach on the appropriate board,
then performing a DR Attach of that board (refer to the Sun Enterprise 10000 Dynamic
Reconfiguration User’s Guide). If the domain configuration does not support DR,
reboot the domain.
4. Backup the main SSP by using ssp_backup(1M).
If you have a spare SSP, restore the backup file on the spare SSP with
ssp_restore(1M). ssp_backup(1M) saves the SSP environment, including files
needed for Capacity on Demand such as the license file and secure log file. You must
maintain the same SSP environment on the main and spare SSP. This backup file can
also be used to restore the SSP environment, including the license file and license
keys, in the event of a disk failure.
6 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 17

▼ To Install License Keys for Processors On a Board
that Is Not in a Domain or On a New Board
1. Log in to the SSP as user ssp and type:
ssp% codlit filenames
codlit: x license key(s) installed from file, filename
where filenames is a list of one or more filenames (separated by spaces) that contain
license keys. codlit prints a line for each file specified on the command line that
indicates how many license keys were installed from that file.
2. If you are installing license keys for processors on a new board, install the board
and power it on.
3. Edit the blacklist(4) file as required.
■ If you are adding a processor that is on a new system board, add the processors
for which you do not have licenses to the blacklist(4) file.
■ If you are adding a processor that is on a system board you already had, remove
the processor from the blacklist(4) file.
You can edit the blacklist(4) file with a text editor or by using Hostview. See
“Blacklisting Processors” on page 8.
4. Add the board to a domain or create a new domain containing the board.
■ If you want to add the board to an existing domain and the domain configuration
supports DR, attach the board to the domain by performing a DR Attach.
■ If you want to add the board to an existing domain, but the domain configuration
does not support DR, follow these steps:
a. Halt the domain.
b. Perform a domain_remove(1M) on the domain to which you are adding the
board, then perform a domain_create(1M) on the same domain.
c. Bring up the domain.
■ If you want to create a new domain, use domain_create(1M), then bring up the
domain.
5. Backup the main SSP by using ssp_backup(1M).
If you have a spare SSP, restore the backup file on the spare SSP with
ssp_restore(1M). ssp_backup(1M) saves the SSP environment, including files
needed for Capacity on Demand such as the license file and secure log file. You must
7
Page 18
maintain the same SSP environment on the main and spare SSP. This backup file can
also be used to restore the SSP environment, including the license file and license
keys, in the event of a disk failure.
Blacklisting Processors
The processors in your Capacity on Demand system for which you do not have
license keys must be added to the blacklist(4) file. System resources that are
listed in this file are not booted (see blacklist(4)). If you do not add these
processors to the blacklist(4) file, codd(1M) will generate license violation
messages.
To blacklist a component, you can edit the blacklist(4) file with a text editor, or
with Hostview. When a domain runs POST, hpost(1M) reads the blacklist(4) file
and automatically excludes the components specified in that file. Thus, changes that
you make to the blacklist(4) file do not take effect until the domain is rebooted or
a DR operation is performed.
When you add processors to the blacklist(4) file, you may want to distribute the
licensed processors over the boards in the system to optimize performance. Add the
number 3 processors on each board to the blacklist(4) file, then the number 2
processors, and so on, until the correct number of processors have been added to the
file. If you are blacklisting two processors on a board, blacklist the number 3
processor and the number 1 processor.
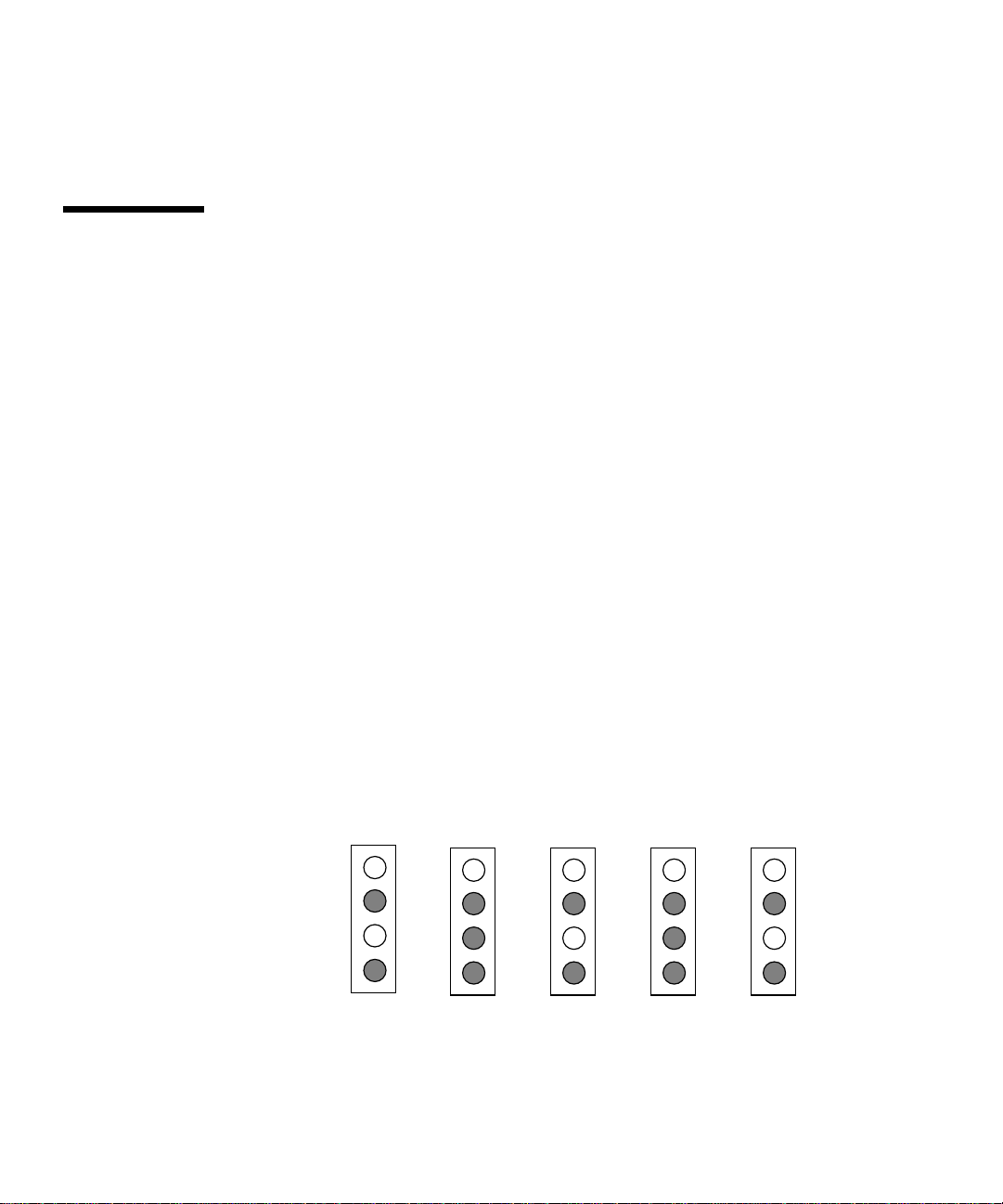
For example, if you have the minimum configuration of 5 boards and 8 licensed
processors, add processors 1 and 3 on boards 0, 2, and 4 to the blacklist(4) file,
then add processors 1, 2, and 3 on boards 1 and 3. This example is shown in
FIGURE 1; the shaded processors are added to the blacklist(4) file.
Processor 0
Processor 1
Processor 2
Processor 3
Board 0 Board 1 Board 2 Board 3 Board 4
FIGURE 1 Blacklisting Processors Example
8 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 19

Capacity on Demand Daemon
The Capacity on Demand resource monitoring daemon, codd(1M), is started by the
SSP startup scripts. When it is started, codd(1M) logs a message to the platform
message file and to the secure log.
The Capacity on Demand daemon performs the following license validation checks
when it is started:
■ Verifies that the license file exists
■ Verifies that the license file has not been modified
■ Verifies that all licenses listed in the license file are valid for this host
■ Verifies that the number of processors in use does not exceed the number of
licenses
If any of these validation checks fail, license violation actions are taken, as described
in “License Violation Actions” below.
After codd(1M) starts, it runs until the SSP is shutdown and does the following at
regular intervals:
■ Performs the license validation checks listed above
■ Writes a heartbeat message to the secure log (see “Capacity on Demand Secure
Logging” on page 13).
License violation checks are also performed when you bring up a domain or perform
a Dynamic Reconfiguration operation.
License Violation Actions
If the Capacity on Demand daemon detects a license violation, it generates a
warning message and sends it to:
■ Platform messages file on the SSP ($SSPLOGGER/messages)
■ The system log file on the SSP (/var/adm/messages)
■ Secure Capacity on Demand log file ($SSPLOGGER/cod.log)
■ ssp user as an email message, and to any other users listed in the
LicenseNotifyList resource in the cod_resource file (see “Configuring
Capacity on Demand Resources” on page 3 or cod_resource(4).)
■ All users logged on to the SSP (sent by using wall(1M))
■ /etc/motd file on the SSP (You can remove license violation messages from
/etc/motd by editing the file with a text editor.)
9
Page 20

Note – Be sure to read, and delete, the email sent to user ssp. Email messages
regarding license violations can accumulate.
The Capacity on Demand daemon will continue to generate warning messages at
regular intervals until the number of processors in use is the same as, or less than,
the number of processor licenses.
Platform Log License Violation Message Examples
The following types of messages are written to the SSP platform message log by
codd(1M):
■ Capacity on Demand daemon startup, indicating the process ID of the daemon
and the primary host ID. For example:
Aug 16 11:52:36 xf4-ssp syslog: codd [allxf4]: WARNING:
codd.c,1505: SSP codd started, pid 29701; platform hostid a65ff7
■ License violations. For example:
1005: Aug 16 11:52:41 xf4-ssp syslog: codd [allxf4]: ERR: codd.c,
461: STARFIRE COD LICENSE_VIOLATION: 8 of 33 processors in use, 0
licensed
■ Internal errors. For example:
Aug 17 19:04:59 xf4-ssp syslog: codd [allxf4]: ERR: snmpmgr.c,
2331: read trap_fd 4 failed; returned -1; errno Bad file number
10 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 21

Email License Violation Message Example
When email regarding a license violation is sent to the ssp user, the email message
subject line specifies the primary domain host ID. The body of the email message
contains a description of the license violation detected. For example:
Date: Sat, 17 Jul 1999 22:27:20 -0700 (PDT)
From: SSP User <ssp@xf8-ssp.West.Sun.COM>
Subject: COD License Problem for host: 80a65123
Mime-Version: 1.0
To: undisclosed-recipients:;
1005: STARFIRE COD LICENSE_VIOLATION: 64 of 64 processors in use,
21 licensed
/etc/motd License Violation Message Example
The Capacity on Demand daemon adds license violation messages to the end of the
SSP message of the day file (/etc/motd). For example:
1001: Thu Aug 19 14:43:10 1999 STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION:
Modified key encountered: Line void: INCREMENT StarfireProc1_1_0
sunwlicd 1.000 01-jan-0 21 9BDAB0F1A675DF98CB3F 0 HOSTID=80a65f04
Broadcast License Violation Message Example
When the Capacity on Demand daemon detects a license violation, it sends a
message by using wall(1M) to all users who are logged in to the SSP. For example:
1001: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Modified key encountered:
Line void: INCREMENT StarfireProc1_1_0 sunwlicd 1.000 01-jan-0 21
9BDAB0F1A675DF98CB3F 0 HOSTID=80a65f04
11
Page 22

License Violation Messages
The following table lists the license violations that can occur and the corresponding
warning messages generated. Note that the content of the messages can vary slightly
depending upon the delivery mechanism, as shown in the previous examples.
TABLE1 Command Line Prompt Conventions
Violation Warning Message
Corrupted license key in
license file.
Invalid host ID in license
key in license file.
Number of processors in
use exceeds number of
licenses.
License has expired. 1006: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: StarfireProc
Duplicate entries in
license file.
License file contains
invalid tiered license key.
1001: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Modified license
key encountered: line void: text_of_void_line
1002: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid hostid [x - expected hostid y]: Line void: text_of_void_line
1003: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid INCREMENT line in license file - hostid must be
specified: Line void: text_of_void_line
1004: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid hostid representation: Line void: text_of_void_line
1005: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: x of y processors
in use; z licensed.
license key has expired: Line void: text_of_void_line
1007: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Duplicate entry
in license file is void: text_of_duplicate_line
1008: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid tier information [class out of range | tier out of range
|requirements out of range]: Line void: text_of_void_line
1009: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Invalid tier class
encountered: Line void: text_of_void_line
1010: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Invalid license
file: x tier n RTUs not counted - insufficient lower tier RTUs
1022: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid tier field.
1023: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid tier requirements field.
12 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 23

TABLE1 Command Line Prompt Conventions (Continued)
Violation Warning Message
Other validity checks
fail.
1011: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: License key
structure invalid: Line void: text_of_void_line
1012: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid license key: Line void: text_of_void_line
1013: STARFIRE COD LICENSE VIOLATION: Encountered
invalid feature in license file: Line void: text_of_void_line
Capacity on Demand Secure Logging
Capacity on Demand secure logging provides a log file (cod.log in the
/var/opt/SUNWssp/adm directory) and logging mechanism for license violation
messages; you cannot modify the secure log file. Messages are written to the secure
log in the following situations:
■ When codd(1M) is started
■ When a license violation is detected
■ At regular intervals (codd(1M) heartbeat message)
■ When codd(1M) validation checks that are performed at regular intervals fail
(license violation message)
Capacity on Demand 1.0 also provides a script that is run by cron(1M) once a
month that sends an email message to Sun containing the secure log, saves the
current secure log to a new file, then clears the old log. Secure log files are kept for
12 months before being overwritten. The address to which the email message is sent
is specified by the SunAddr resource in the cod_resource(4) file; you can modify
the email address specified by SunAddr so that it is compatible with your email
system.
Capacity on Demand 1.0 also provides codcheck(1M), a utility used by Sun
personnel to validate the secure log.
Using Multiple Domains
If your Capacity on Demand system has multiple domains and the total number of
processors used by all the domains is greater than the number of licensed
processors, you cannot have all of the domains running at the same time.
13
Page 24

For example, if your system has two domains, each of which uses eight processors
and you have license keys for eight processors, only one domain can be running at a
time. The total number of processors in use by the running domains must not exceed
the number of licensed processors.
If you need to shut down one domain and bring up another domain that uses some,
or all, of the same system boards, you must power off the system boards in the
domain you shut down that are not in the domain you are bringing up.
▼ To Shut Down One Domain and Bring Up Another
1. Log in to the domain as superuser.
2. Run shutdown(1M) on the domain to be shut down.
3. Power off all the system boards in the domain you shut down in Step 2 that are
not in the domain you want to bring up.
4. Power on the system boards in the domain you want to bring up that do not
already have power.
5. Log in to the SSP as user ssp and type:
ssp% domain_switch domain_name
where domain_name is the name of the domain you want to bring up.
6. Bring up the domain by using the bringup(1M) command.
Upgrading the SSP Software or Solaris Operating Environment
Before you upgrade the SSP software or the Solaris operating environment, back up
the SSP environment using ssp_backup(1M). The backup file created by
ssp_backup(1M) will include the following files that are used by Capacity on
Demand:
■ License file ($SSPVAR/.ssp_private/SUNWcod.lic)
■ cod_resource file ($SSPVAR/.ssp_private/cod_resource)
14 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
Page 25

■ Secure log file and the copies of the log file that are saved monthly
(/var/opt/SUNWssp/adm/cod.log and
/var/opt/SUNWssp/adm/cod.log.*)
■ blacklist(4) file
▼ To Upgrade the Solaris Operating Environment
1. Upgrade the Solaris operating environment.
Refer to the Solaris 7 Installation Collection—Solaris Advanced Installation Guide.
2. Re-install the same version of the SSP software as described in the Sun Enterprise
10000 SSP 3.1.1 Installation Guide and Release Notes or Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.2
Installation Guide and Release Notes.
If you install SSP 3.1.1, you must also install patch 108135-01.
3. Restore the SSP environment by typing:
ssp# ./ssp_restore backup_directory/ssp_backup.cpio
where backup_directory is the directory in which the ssp_backup.cpio file you
created with ssp_backup(1M) resides.
4. Re-install the Capacity on Demand 1.0 software as described in the Sun Enterprise
10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Installation Guide and Release Notes.
▼ To Upgrade the SSP Software
1. Remove the Capacity on Demand 1.0 software package (SUNWcod). See
pkgrm(1M).
2. Upgrade the SSP software as described in the Sun Enterprise 10000 SSP 3.2
Installation Guide and Release Notes.
3. Re-install the Capacity on Demand 1.0 software as described in the Sun Enterprise
10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Installation Guide and Release Notes.
15
Page 26

16 Sun Enterprise 10000 Capacity on Demand 1.0 Administrator Guide • October 1999
 Loading...
Loading...