Page 1

SUN SEEBEYOND
eWAY™ ADAPTER FOR SAP BAPI
USER’S GUIDE
Release 5.1.3
Page 2

Copyright © 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc., 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, California 95054, U.S.A. All rights reserved. Sun
Microsystems, Inc. has intellectual property rights relating to technology embodied in the product that is described in this
document. In particular, and without limitation, these intellectual property rights may include one or more of the U.S. patents
listed at http://www.sun.com/patents and one or more additional patents or pending patent applications in the U.S. and in
other countries. U.S. Government Rights - Commercial software. Government users are subject to the Sun Microsystems, Inc.
standard license agreement and applicable provisions of the FAR and its supplements. Use is subject to license terms. This
distribution may include materials developed by third parties. Sun, Sun Microsystems, the Sun logo, Java, Sun Java Composite
Application Platform Suite, SeeBeyond, eGate, eInsight, eVision, eTL, eXchange, eView, eIndex, eBAM, eWay, and JMS are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. All SPARC trademarks are used
under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
Products bearing SPARC trademarks are based upon architecture developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc. UNIX is a registered
trademark in the U.S. and other countries, exclusively licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd. This product is covered and
controlled by U.S. Export Control laws and may be subject to the export or import laws in other countries. Nuclear, missile,
chemical biological weapons or nuclear maritime end uses or end users, whether direct or indirect, are strictly prohibited.
Export or reexport to countries subject to U.S. embargo or to entities identified on U.S. export exclusion lists, including, but
not limited to, the denied persons and specially designated nationals lists is strictly prohibited.
Copyright © 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc., 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, California 95054, Etats-Unis. Tous droits réservés.
Sun Microsystems, Inc. détient les droits de propriété intellectuels relatifs à la technologie incorporée dans le produit qui est
décrit dans ce document. En particulier, et ce sans limitation, ces droits de propriété intellectuels peuvent inclure un ou plus
des brevets américains listés à l'adresse http://www.sun.com/patents et un ou les brevets supplémentaires ou les
applications de brevet en attente aux Etats - Unis et dans les autres pays. L'utilisation est soumise aux termes de la Licence.
Cette distribution peut comprendre des composants développés par des tierces parties. Sun, Sun Microsystems, le logo Sun,
Java, Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite, Sun, SeeBeyond, eGate, eInsight, eVision, eTL, eXchange, eView, eIndex,
eBAM et eWay sont des marques de fabrique ou des marques déposées de Sun Microsystems, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans
d'autres pays. Toutes les marques SPARC sont utilisées sous licence et sont des marques de fabrique ou des marques déposées
de SPARC International, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans d'autres pays. Les produits portant les marques SPARC sont basés sur une
architecture développée par Sun Microsystems, Inc. UNIX est une marque déposée aux Etats-Unis et dans d'autres pays et
licenciée exclusivement par X/Open Company, Ltd. Ce produit est couvert à la législation américaine en matière de contrôle
des exportations et peut être soumis à la règlementation en vigueur dans d'autres pays dans le domaine des exportations et
importations. Les utilisations, ou utilisateurs finaux, pour des armes nucléaires, des missiles, des armes biologiques et
chimiques ou du nucléaire maritime, directement ou indirectement, sont strictement interdites. Les exportations ou
réexportations vers les pays sous embargo américain, ou vers des entités figurant sur les listes d'exclusion d'exportation
américaines, y compris, mais de manière non exhaustive, la liste de personnes qui font objet d'un ordre de ne pas participer,
d'une façon directe ou indirecte, aux exportations des produits ou des services qui sont régis par la législation américaine en
matière de contrôle des exportations et la liste de ressortissants spécifiquement désignés, sont rigoureusement interdites.
Part Number: 820-0973
Version 20070425133748
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 2 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 3
Contents
Contents
Chapter 1
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay 7
About SAP 7
About the SAP BAPI eWay 7
Invoking BAPI/RFC Methods 8
The SAP BAPI eWay Data Flows 9
Outbound Data Flow: Java CAPS to SAP R/3 9
Inbound Data Flow: SAP R/3 to Java CAPS 9
What’s New in This Release 11
What’s In This Document 12
Scope 13
Intended Audience 13
Text Conventions 13
Related Documents 14
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site 14
Documentation Feedback 14
Chapter 2
Installing the eWay 15
Installing the SAP BAPI eWay 15
Installing the SAP BAPI eWay on an eGate supported system 15
Adding the eWay to an Existing Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation 16
After Installation 17
Extracting the Sample Projects and Javadocs 17
ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures 17
Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins 19
Viewing Alert Codes 20
Deploying an EAR File 22
WebLogic Application Servers 22
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 3 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties 23
Creating and Configuring a SAP BAPI eWay 23
Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties 23
eWay Connectivity Map Properties 25
Configuring the Inbound eWay Properties 25
Server Connection Settings 25
Configuring the Outbound eWay Properties 27
Client Connection Settings 27
Configuring the eWay Environment Properties 30
eWay External Properties 31
Inbound SAP BAPI eWay 32
Server Connection Settings 32
MDB Settings 34
Outbound SAP BAPI eWay 35
Client Connection Settings 35
Connection Retry Settings 37
Connection Pool Settings 37
Chapter 4
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs 39
SAP BAPI Encoding 39
Date and Time Stamp Requirements 40
SAP JCo Installation 40
Procedures (Windows 32) 40
Procedures (UNIX) 41
Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs 41
BAPI and RFC OTDs 45
Chapter 5
Configuring SAP R/3 48
Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay 48
Configuration Needed in SAP R/3 to Send and Receive IDocs 53
Configuring the Distribution Model 54
Naming the Logical System 54
Specifying the Distribution Model 57
Configuring Communications 60
Defining the Communications Port 60
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 4 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 5

Contents
Creating a Partner Profile 62
Configuring a Partner Profile 64
Security Issues 67
Chapter 6
Reviewing the Sample Projects 69
About the Sample Projects 69
prjBapiOutbound.zip 70
prjIDocInbound.zip 70
SAP Version Support 70
Steps Required to Run the Sample Project 70
Importing a Sample Project 71
Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project 71
Create a Project 72
Create the OTDs 72
Create the Java Collaboration Definitions 73
Create the Collaboration Business Rules 74
Create the Business Process 80
Create a Connectivity Map 84
Populate the Connectivity Map 84
Bind the eWay Components 85
Create an Environment 86
Configure the eWays 87
Configure the eWay Properties in the Connectivity Map 88
Configure the File eWay External Environment Properties 89
Configure the SAP BAPI eWay External Environment Properties 89
Create the Deployment Profile 90
Create and Start the Domain 91
Build and Deploy the Project 92
Run the Sample Project 92
Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project 92
Create a Project 93
Create the OTDs 93
Create the Java Collaboration Definitions 95
Creating the Collaboration Business Rules 96
Creating the Collaboration Business Rules 98
Create the Business Process 100
Configuring the bpIDocInbound Business Rule Components 102
Create a Connectivity Map 106
Populate the Connectivity Map 107
Bind the eWay Components 108
Create an Environment 109
Configure the eWays 110
Configure the eWay Properties in the Connectivity Map 111
Configure the File eWay External Environment Properties 112
Configure the SAP BAPI eWay External Environment Properties 112
Create the Deployment Profile 113
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 5 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 6

Contents
Create and Start the Domain 114
Build and Deploy the Project 115
Run the Sample 115
Additional Sample Project Scenarios 116
About Sending IDocs to SAP R/3 Using tRFCs 116
The RFC OTD used to send/receive IDOCs 116
Client Mode - sending IDOCs to SAP R/3 via IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCRONOUS 117
Appendix A
SAP Data Type Conversion Table 121
Index 122
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 6 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 7

Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay
The Sun SeeBeyond eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI, also noted throughout this book as
the SAP BAPI eWay, provides Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite (Java
CAPS) Projects with the ability to exchange data with SAP R/3 software. This chapter
provides an overview of the SAP BAPI eWay.
What’s In This Chapter
About SAP on page 7
About the SAP BAPI eWay on page 7
What’s New in This Release on page 11
What’s In This Document on page 12
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site on page 14
Documentation Feedback on page 14
Chapter 1
1.1 About SAP
SAP creates software for the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) business sector. The
company main product is SAP R/3 which uses a three-tier application architecture—
database, application server, and client—to facilitate real-time data processing.
1.2 About the SAP BAPI eWay
The SAP BAPI eWay enables Java CAPS Projects to exchange data with SAP R/3
software using Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPIs), RFCs, and
IDocs.
The SAP BAPI eWay uses the SAP Java Connector (SAP JCo) to allow Java applications
to access BAPIs and RFCs.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 7 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 8
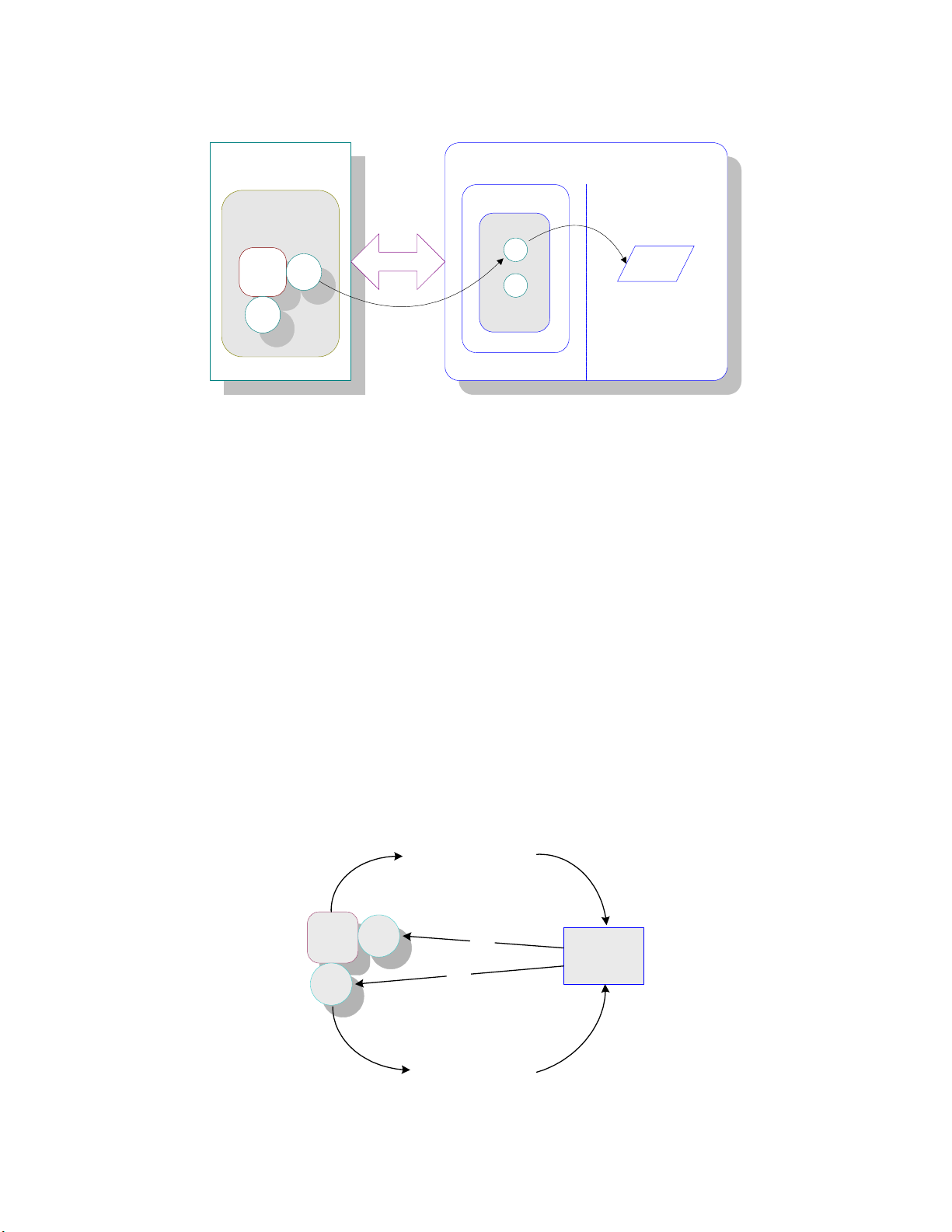
Chapter 1 Section 1.2
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay About the SAP BAPI eWay
Figure 1 BAPI eWay
SAP R/3
Business Object
Repository
Cost
Center
BAPI
B
BAPI
A
SAP JCo
The functionality of the SAP BAPI eWay simplifies the process of determining the
requisite IMPORT, EXPORT, CHANGING, and TABLE parameters—collecting all
the necessary data using the correct type and format, calling the Remote Function
Module (RFM) that represents the BAPI, and then extracting and parsing data from the
EXPORT and/or TABLE parameters.
1.2.1 Invoking BAPI/RFC Methods
Before it can be invoked, a BAPI or RFM requires the following parameters:
BAPI eWay
A
B
BAPI
Repository
eGate Integrator
RFC
Function
OTD
A
IMPORT parameters: data provided to the BAPI
EXPORT parameters: data returned by the BAPI
CHANGING parameters: data provided to and/or returned by the BAPI/RFC
TABLE parameters - data provided to and/or returned by the BAPI/RFC
The detailed metadata for these parameters such as descriptions of their value types
and mandatory or optional nature, can be found under SAP transaction SE37.
Figure 2 Meta Data Extraction
IMPORT parameters
EXPORT parameters
TABLE parameters
CHANGING parameters
Cost
Center
BAPI
BAPI
IMPORT parameters
EXPORT parameters
TABLE parameters
CHANGING parameters
R
F
C
SAP R/3
C
F
R
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 8 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 9
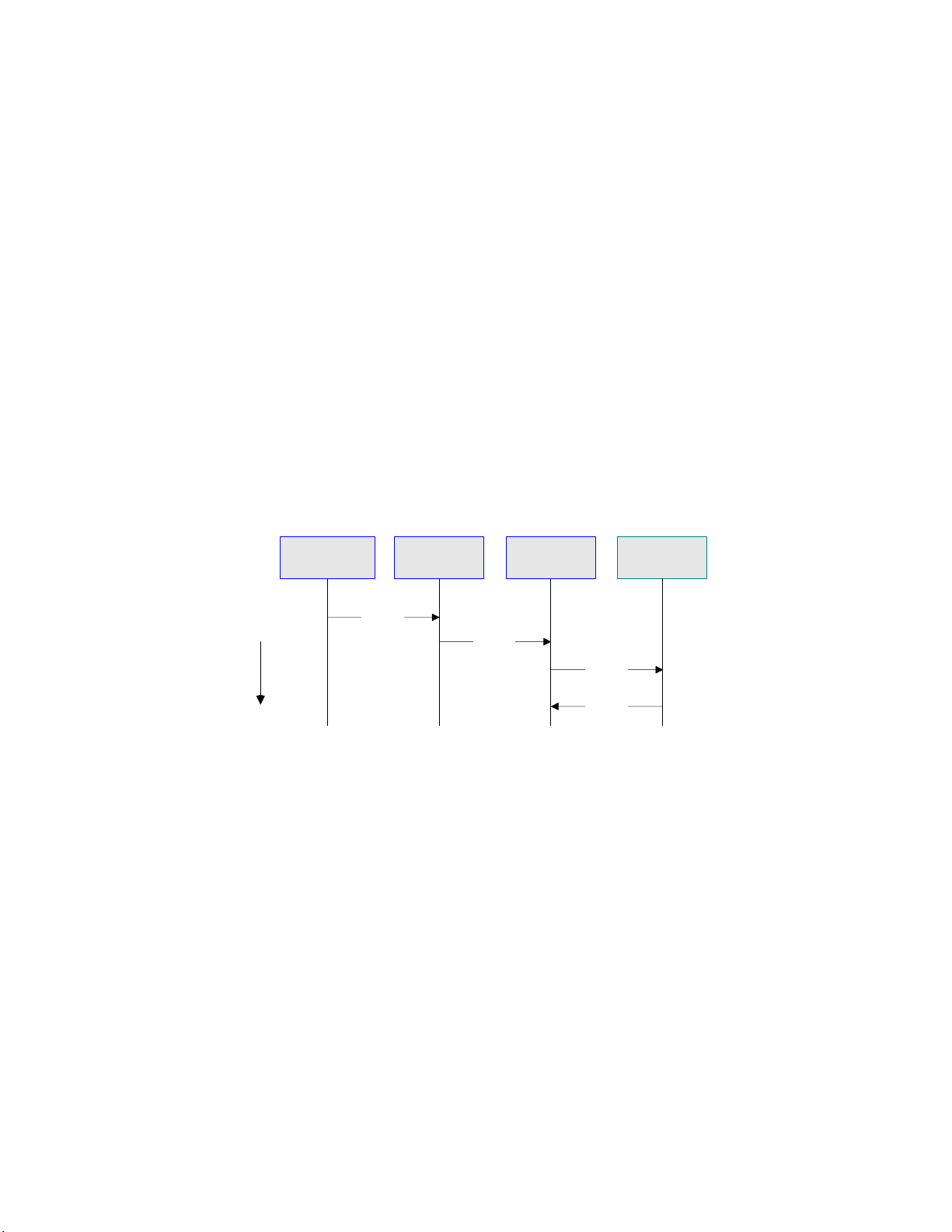
Chapter 1 Section 1.2
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay About the SAP BAPI eWay
The meta data for a BAPI/RFC in SAP R/3 is extracted by the BAPI wizard, which uses
it to build the BAPI/RFC OTD. This OTD is used in Java Collaborations and eInsight
Business Processes to invoke or receive the BAPI/RFC call.
1.2.2 The SAP BAPI eWay Data Flows
When the SAP BAPI eWay communicates with the SAP R/3 software, it uses the RFC
protocol. The list below shows the RFC types of communication used:
Outbound (Java CAPS to SAP R/3): non-transactional (regular) RFC and
transactional RFC (tRFC)
Inbound (SAP R/3 to Java CAPS): non-transactional and transactional RFC (tRFC)
Outbound Data Flow: Java CAPS to SAP R/3
Outbound communications occur when the eWay receives data from Java CAPS and
sends it to SAP R/3 by calling a specific BAPI or RFM. The figure below shows a nontransactional outbound process.
Figure 3 Outbound Data Flow: Java CAPS to SAP R/3
Business Process
Time
Collaboration
execute()
BAPI
OTD
BAPI
eWay
execute()
Call RFM
Call RFM
Return
SAP R/3
System
The figure above shows the following steps for the outbound data flow:
1 The Collaboration or Business Process populates the appropriate BAPI or RFC
Import, Changing, and Table parameter nodes on the BAPI/RFC OTD with data
from an inbound OTD.
2 The eWay logs onto the SAP R/3 application using preconfigured properties.
3 The eWay calls the BAPI OTD's execute() method. Any work performed is
immediately committed by SAP R/3 through autocommit.
4 The SAP R/3 applications returns successfully.
Inbound Data Flow: SAP R/3 to Java CAPS
For the inbound data flow, the SAP BAPI eWay can receive data from SAP R/3 via RFC
or tRFC. The sections below describe each protocol.
To enable the SAP BAPI eWay to receive data from SAP R/3, configure the
Environment properties with an RFC destination created within SAP R/3. For
information, refer to “Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay” on page 48.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 9 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 10
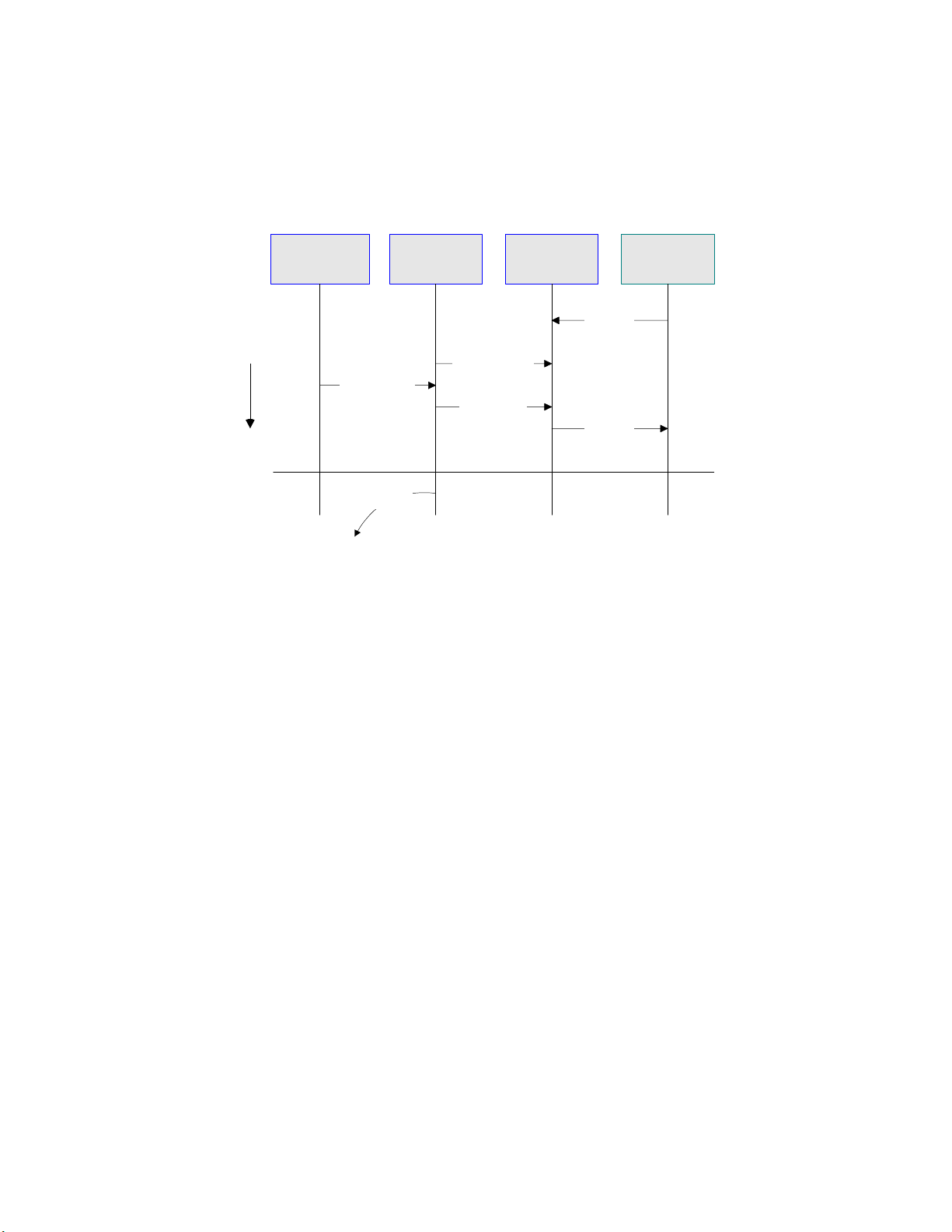
Chapter 1 Section 1.2
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay About the SAP BAPI eWay
Inbound Data Flow via RFC
The sequence diagram uses a sample CostCenter OTD to describe the RFC inbound
sequence.
Figure 4 Inbound Data Flow via RFC
Business Process SAP R/3
Time
Populate OTD
exception
BAPI
CostCenter
OTD
GetListReceive
GetListReply
BAPI eWay
(JCo server)
System
Call RFM
Call RFM
Return
The figure above shows the following steps for the inbound data flow via RFC:
1 The Business Process is activated when an RFM call is received from SAP R/3.
2 Finding that data from an RFM is available, the Business Process accesses all
pertinent data nodes and sends the gathered information to other Java CAPS
components.
3 The eWay returns the results of the RFM execution back to SAP.
Inbound Data Flow via tRFC
Communication via tRFC is the similar to RFC, except that it adds transactional
verification steps prior to committing or rolling back. tRFC is preferred over RFC
because of the additional reliability. By using unique TIDs associated with a BAPI/
RFM call, SAP R/3 processes the data once, and only once. The figure below shows
inbound data flow via tRFC.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 10 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 11
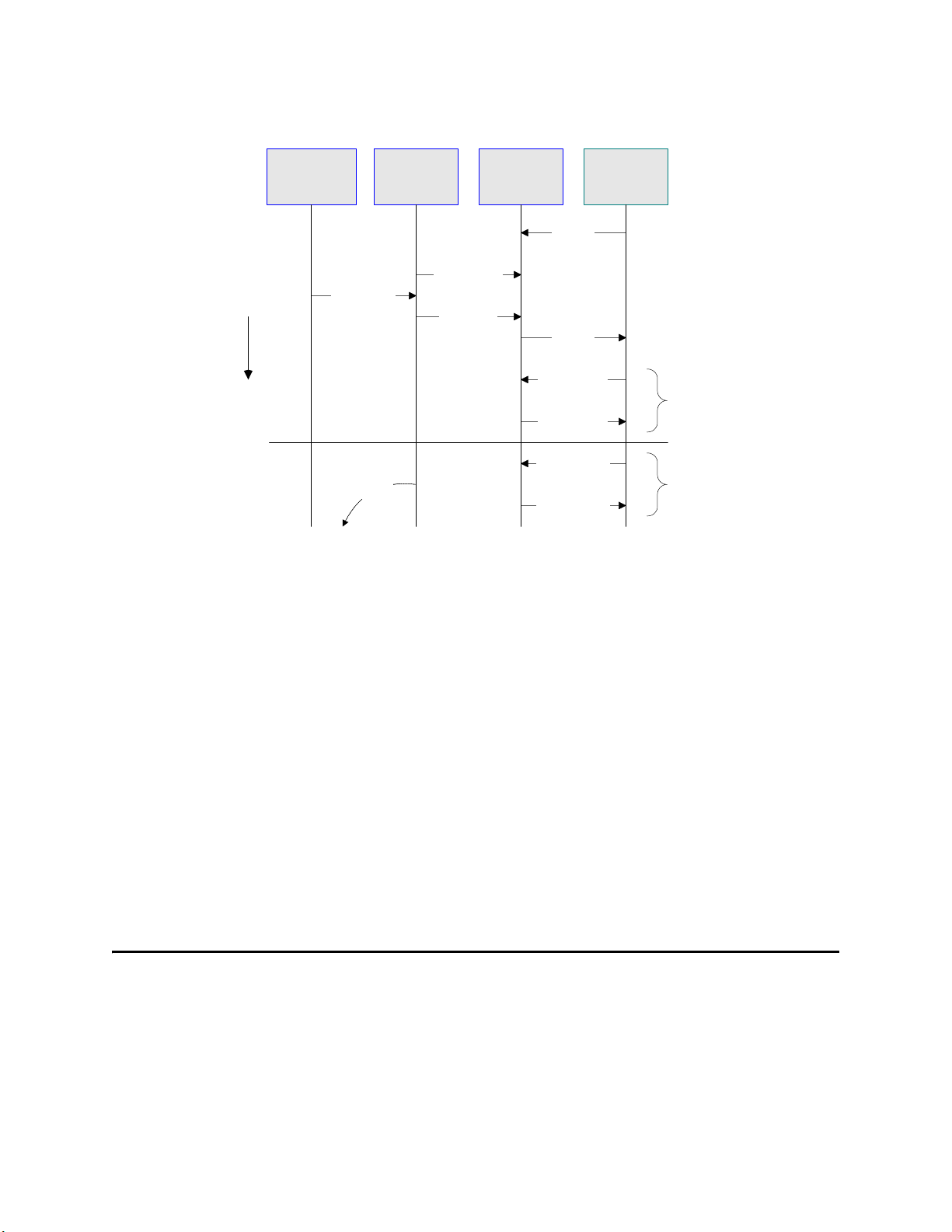
Chapter 1 Section 1.3
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay What’s New in This Release
Figure 5 Inbound Data Flow via tRFC
Time
Business
Process
Populate OTD
exception
BAPI
CostCenter
OTD
GetListReceive
BAPI
eWay
(JCo server)
Call RFM
GetListReply
Call RFM
onCommitTID()
onCommitTID()
onRollbackTID()
onRollbackTID()
SAP R/3
System
Return
Commit
Sequence
Return
OR
Rollback
Sequence
Return
The figure above shows the following steps for the inbound data flow via tRFC:
1 The Business Process is activated when an RFM call is received from SAP R/3.
2 Finding that data from an RFM is available, the Business Process accesses all
pertinent data nodes and sends the gathered information to other Java CAPS
components.
3 The eWay returns the results of the RFM execution back to SAP R/3.
4 If the RFM call returned successfully without exceptions, SAP R/3 informs the
eWay that the data can be committed by calling onCommitTID().
5 The eWay updates the TID in the file database as being Committed, commits the
data, and sends an onCommitTID() return to SAP R/3.
6 If the RFM call did not return successfully for any reason, SAP R/3 informs the
eWay that the data must be rolled back by calling onRollbackTID().
7 The eWay sends an onRollbackTID() return to SAP R/3, confirming that the TID
was not committed.
1.3 What’s New in This Release
The SAP BAPI eWay includes the following new features:
What’s New in Version 5.1.3
Added support: Supports automatic deployment of EAR files to WebLogic
Application Server (version 9.1).
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 11 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 12

Chapter 1 Section 1.4
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay What’s In This Document
What’s New in Version 5.1.2
Support for SAP ECC 6.0 (Unicode only)
What’s New in Version 5.1.1
Supports automatic deployment of EAR files to WebLogic Application Server
(version 9.1).
What’s New in Version 5.1
Version Control: An enhanced version control system allows you to effectively
manage changes to the eWay components.
Manual Connection Management: Establishing a connection can now be performed
manually (using OTD methods from the Java Collaboration) for outbound Projects
only.
Multiple Drag-and-Drop Component Mapping from the Deployment Editor: The
Deployment Editor now allows you to select multiple components from the Editor’s
component pane, and drop them into your Environment component.
Support to obtain configuration from LDAP at Runtime: eWay configuration
properties now support LDAP key values.
MDB Pool Size Support: Provides greater flow control (throttling) by specifying the
maximum and minimum MDB pool size.
Connection Retry Support: Allows you to specify the number of attempts to
reconnect, and the interval between retry attempts, in the event of a connection
failure.
Relaunchable OTD Support: An OTD can be rebuilt and saved (under the same
name) then relaunched back to the same Java Collaboration or Business Process.
This allows you to rebuild the OTD with changed metadata without having to
completely recreate the business logic from scratch.
Connectivity Map Generator: Generates and links your Project’s Connectivity Map
components using a Collaboration or Business Process.
Additional methods to commit rollback BAPI/RFC in the Java Collaboration
Definition (JCD).
All BAPI OTDs can now be used to communicate with both Unicode and non-
Unicode SAP R/3 systems.
Support for BAPI/RFC with table types, changing parameters, and nested
structures.
Date fields are now represented as Java data type strings in the JCD.
1.4 What’s In This Document
This document includes the following chapters:
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 12 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 13
Chapter 1 Section 1.4
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay What’s In This Document
Chapter 1 “Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay”: Provides an overview description of
the product as well as high-level information about this document.
Chapter 2 “Installing the eWay”: Describes the system requirements and provides
instructions for installing the SAP BAPI eWay.
Chapter 3 “Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties”: Describes how to configure the
SAP BAPI eWay properties to enable data exchange between the SAP R/3 software
and a Java CAPS project.
Chapter 4 “Creating SAP BAPI OTDs”: Provides instructions for creating Object
Type Definitions to be used with the SAP BAPI eWay
Chapter 5 “Configuring SAP R/3”: Describes the configuration settings and
parameters of SAP R/3 in order to communicate with the SAP BAPI eWay.
Chapter 6 “Reviewing the Sample Projects”: Provides instructions for installing,
creating, and running the sample Projects.
Appendix A “SAP Data Type Conversion Table”: Provides a table that shows the
mapping between SAP data types to the SAP JCo and their corresponding Java data
types.
1.4.1 Scope
This document describes the process of installing, configuring, and running the SAP
(BAPI) eWay.
This document does not cover the Java methods exposed by this eWay. For information
on the Java methods, download and view the SAP (BAPI) eWay Javadoc files from the
Sun Java Composite Application Suite Installer.
1.4.2 Intended Audience
This guide is intended for experienced computer users who have the responsibility of
helping to set up and maintain a fully functioning Java Composite Application
Platform Suite. This person must also understand any operating systems on which the
Java Composite Application Platform Suite will be installed (Windows and UNIX), and
must be thoroughly familiar with Windows-style GUI operations. Familiarity with SAP
R/3 is recommended.
1.4.3 Text Conventions
The following conventions are observed throughout this document.
Table 1 Text Conventions
Text Convention Used For Examples
Bold Names of buttons, files, icons,
parameters, variables, methods,
menus, and objects
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 13 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Click OK.
On the File menu, click Exit.
Select the eGate.sar file.
Page 14
Chapter 1 Section 1.5
Introducing the SAP BAPI eWay Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site
Table 1 Text Conventions (Continued)
Text Convention Used For Examples
Monospaced Command line arguments, code
samples; variables are shown in
bold italic
Blue bold
Blue underlined
1.4.4 Related Documents
Hypertext links within
document
Hypertext links for Web
addresses (URLs) or email
addresses
The following Sun documents provide additional information about the Sun Java CAPS
product:
Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator User’s Guide
Composite Application Platform Suite Installation Guide
1.5 Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site
The Sun Microsystems web site is your best source for up-to-the-minute product news
and technical support information. The site’s URL is:
java -jar filename.jar
See
Text Conventions on page 13
http://www.sun.com
http://www.sun.com
1.6 Documentation Feedback
We appreciate your feedback. Please send any comments or suggestions regarding this
document to:
CAPS_docsfeedback@sun.com
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 14 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 15

Installing the eWay
This chapter describes the requirements and procedures for installing the SAP BAPI
eWay. Procedures for implementing sample projects, are described in Reviewing the
Sample Projects on page 69.
What’s In This Chapter
“Installing the SAP BAPI eWay” on page 15
“ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures” on page 17
“Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins” on page 19
“Deploying an EAR File” on page 22
2.1 Installing the SAP BAPI eWay
Chapter 2
The Java CAPS Installer, a web-based application, is used to select and upload eWays
and add-on files during the installation process. The following section describes how to
install the components required for this eWay.
Refer to the readme for the latest information on:
Supported Operating Systems
External System Requirements
Java Composite Application Platform Suite Requirements
Known Issues
Note: When the Repository is running on a UNIX operating system, the eWays are loaded
from the Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer, running on a
Windows platform connected to the Repository server using Internet Explorer.
2.1.1 Installing the SAP BAPI eWay on an eGate supported system
Follow the directions for installing Java CAPS in the Composite Application Platform Suite
Installation Guide.
After you have installed eGate or eInsight, do the following:
1 From the Suite Installer, click the Administration tab, and then click the link to
install additional products.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 15 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 16

Chapter 2 Section 2.1
Installing the eWay Installing the SAP BAPI eWay
2 Select the following products from the eWay category:
FileeWay (the File eWay is used by most sample Projects)
SAPALEeWay (the SAP ALE eWay is used by the SAP BAPI eWay sample
Project)
SAPBAPIeWay
Select the following in the Documentation category to upload the User’s Guide,
Help file, Javadoc, Readme, and sample Projects for the Sun SeeBeyond eWay
Adapter for SAP BAPI:
SAPBAPIeWayDocs
3 Once you have selected all of your products, click Next in the top-right or bottom-
right corner of the Select Java Composite Application Platform Suite Products to
Install box.
4 From the Selecting Files to Install box, locate and select your first product’s SAR
file. Once you have selected the SAR file, click Next. Your next selected product
appears. Follow this procedure for each of your selected products. The Installation
Status window appears and installation begins after the last SAR file has been
selected.
5 Once your product’s installation is finished, continue installing the Java Composite
Application Platform Suite as instructed in the Composite Application Platform Suite
Installation Guide.
2.1.2 Adding the eWay to an Existing Sun Java Composite
Application Platform Suite Installation
It is possible to add the eWay to an existing Java CAPS installation.
Steps required to add an eWay to an Existing Java CAPS installation include:
1 Complete steps 1 through 4 in Installing the SAP BAPI eWay on an eGate
supported system on page 15.
2 Once your product’s installation is finished, open the Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise
Designer and select Update Center from the Tools menu. The Update Center
Wizard appears.
3 For Step 1 of the wizard, simply click Next.
4 For Step 2 of the wizard, click the Add All button to move all installable files to the
Include in Install field, then click Next.
5 For Step 3 of the wizard, wait for the modules to download, then click Next.
6 The wizard’s Step 4 window displays the installed modules. Review the installed
modules and click Finish.
7 When prompted, restart the IDE (Integrated Development Environment) to
complete the installation.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 16 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 17

Chapter 2 Section 2.2
Installing the eWay ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures
After Installation
You must incorporate the installed eWay components into a Project before using the
intended functions. See the Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator User’s Guide for more
information on incorporating the eWay into an eGate Project.
2.1.3 Extracting the Sample Projects and Javadocs
The SAP (BAPI) eWay includes sample Projects and Javadocs. The sample Projects are
designed to provide you with a basic understanding of how certain operations are
performed using the eWay, while Javadocs provide a list of classes and methods
exposed in the eWay.
Steps to extract the Javadoc include:
1 Click the Documentation tab of the Suite Installer, then click the Add-ons tab.
2 Click the Sun SeeBeyond eWay SAP BAPI Adapter link. Documentation for the SAP
BAPI eWay appears in the right pane.
3 Click the icon next to Javadoc and extract the ZIP file. Note that two separate
Javadocs are contained within, including:
Flight.zip
RFC_IDOC_ASYNCHRONOUS.zip
4 Extract each ZIP and then open the index.html within each extracted file to view
the Javadoc.
Steps to extract the Sample Projects include:
1 Click the Documentation tab of the Suite Installer, then click the Add-ons tab.
2 Click the Sun SeeBeyond eWay SAP BAPI Adapter link. Documentation for the SAP
BAPI eWay appears in the right pane.
3 Click the icon next to Sample Projects and extract the ZIP file. Note that the SAP
BAPI_eWay_Sample.zip file contains two additional ZIP files for each sample
Project.
Refer to Importing a Sample Project on page 64 for instructions on importing the
sample Project into your repository via the Enterprise Designer.
2.2 ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures
This section describes how to transfer your current ICAN 5.0.x Projects to the Java
CAPS, version 5.1.3.
To migrate your ICAN 5.0.x Projects, do the following:
Export the Project
1 Before you export your Projects, save your current ICAN 5.0.x Projects to your
Repository.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 17 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 18

Chapter 2 Section 2.2
Installing the eWay ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures
2 From the Project Explorer, right-click your Project and select Export from the
shortcut menu. The Export Manager appears.
3 Select the Project that you want to export in the left pane of the Export Manager and
move it to the Selected Projects field by clicking the Add to Select Items (arrow)
button, or click All to include all of your Projects.
4 In the same manner, select the Environment that you want to export in the left pane
of the Export Manager and move it to the Selected Environments field by clicking
the Add to Select Items (arrow) button, or click All to include all of your
Environments.
5 Browse to select a destination for your Project ZIP file and enter a name for your
Project in the ZIP file field.
6 Click Export to create the Project ZIP file in the selected destination.
Install Java CAPS 5.1.3
1 Install the Java CAPS 5.1.3, including all eWays, libraries, and other components
used by your ICAN 5.0.x Projects.
2 Start the Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Designer.
Import the Project
1 From the Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer tree, right-click the
Repository and select Import Project from the shortcut menu. The Import Manager
appears.
2 Browse to and select your exported Project file.
3 Click Import. A warning message, “Missing APIs from Target Repository,” may
appear at this time. This occurs because various product APIs were installed on the
ICAN 5.0.x Repository when the Project was created, that are not installed on the
Java CAPS 5.1.3 Repository. These APIs may or may not apply to your Projects. You
can ignore this message if you have already installed all of the components that
correspond to your Projects. Click Continue to resume the Project import.
4 Close the Import Manager after the Project is successfully imported.
Deploy the Project
1 A new Deployment Profile must be created for each of your imported Projects.
When a Project is exported, the Project’s components are automatically “checked in”
to Version Control to write-protected each component. These protected
components appear in the Explorer tree with a red padlock in the bottom-left corner
of each icon. Before you can deploy the imported Project, the Project’s components
must first be “checked out” of Version Control from both the Project Explorer and the
Environment Explorer. To “check out” all of the Project’s components, do the
following:
A From the Project Explorer, right-click the Project and select Version Control >
Check Out from the shortcut menu. The Version Control - Check Out dialog box
appears.
B Select Recurse Project to specify all components, and click OK.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 18 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
C Select the Environment Explorer tab, and from the Environment Explorer, right-
click the Project’s Environment and select Version Control > Check Out from
the shortcut menu.
D Select Recurse Environment to specify all components, and click OK.
2 If your imported Project includes File eWays, these must be reconfigured in your
Environment prior to deploying the Project.
To reconfigure your File eWays, do the following:
A From the Environment Explorer tree, right-click the File External System, and
select Properties from the shortcut menu. The Properties Editor appears.
B Set the inbound and outbound directory values, and click OK. The File External
System can now accommodate both inbound and outbound eWays.
3 Deploy your Projects.
Note: Only projects developed on ICAN 5.0.2 and above using SAP BAPI 5.0.3 can be
imported and migrated successfully into the Java Composite Application Platform
Suite.
Note: Java collaborations that use date fields on the 5.0.3 BAPI/RFC OTD must be
corrected appropriately after importing into Java CAPS 5.1.3, since these fields in
5.1.3 are now represented as Java data type strings. In 5.0.x these date fields were
represented as data type java.util.Date.
2.3 Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
The Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Manager, also referred to as Enterprise Manager
throughout the document, is a Web-based interface that allows you to monitor and
manage your Java CAPS applications. The Enterprise Manager requires an eWay
specific “plug-in” for each different eWay you install. These plug-ins enable the
Enterprise Manager to target specific alert codes for each eWay type.
The Composite Application Platform Suite Installation Guide describes how to install
Enterprise Manager. The Sun SeeBeyond eGate Integrator System Administration Guide
describes how to monitor servers, Services, logs, and alerts using the Enterprise
Manager and the command-line client.
The eWay Enterprise Manager plug-ins are available from the List of Components to
Download under the Suite Installer’s DOWNLOADS tab. The plug-in required for
SAP BAPI is listed as the SAP BAPI eWay Enterprise Manager Plug-in.
The following steps are required to install eWay plug-ins into the Enterprise Manager:
1 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click the Configuration icon.
2 Click the Web Applications Manager tab, go to the Auto-Install from Repository
sub-tab, and connect to your Repository.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 19 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 20
Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
3 Select the application plug-ins you require, and click Install. The application plug-
ins are installed and deployed.
Alternately, you can install eWay plug-ins using the following steps:
1 From the Suite Installer’s Download tab, select the Plug-Ins you require and save
them to a temporary directory.
2 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click the Configuration icon.
3 Click the Web Applications Manager tab and go to the Manage Applications sub-
tab.
4 Browse for and select the WAR file for the application plug-in that you
downloaded, and click Deploy. The plug-in is installed and deployed.
Viewing Alert Codes
You can view and delete alerts using the Enterprise Manager. An alert is triggered
when a specified condition occurs in a Project component. The purpose of the alert is to
warn the administrator or user that a condition has occurred.
To View the eWay Alert Codes
1 Add the eWay Enterprise Manager plug-in for this eWay.
2 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click the Configuration icon.
3 Click the Web Applications Manager tab and go to the Manage Alert Codes sub-
tab. Your installed eWay alert codes display under the Results section.
For information on Managing and Monitoring alert codes and logs, as well as how to
view the alert generated by the project component during runtime, see the Sun
SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator System Administration Guide.
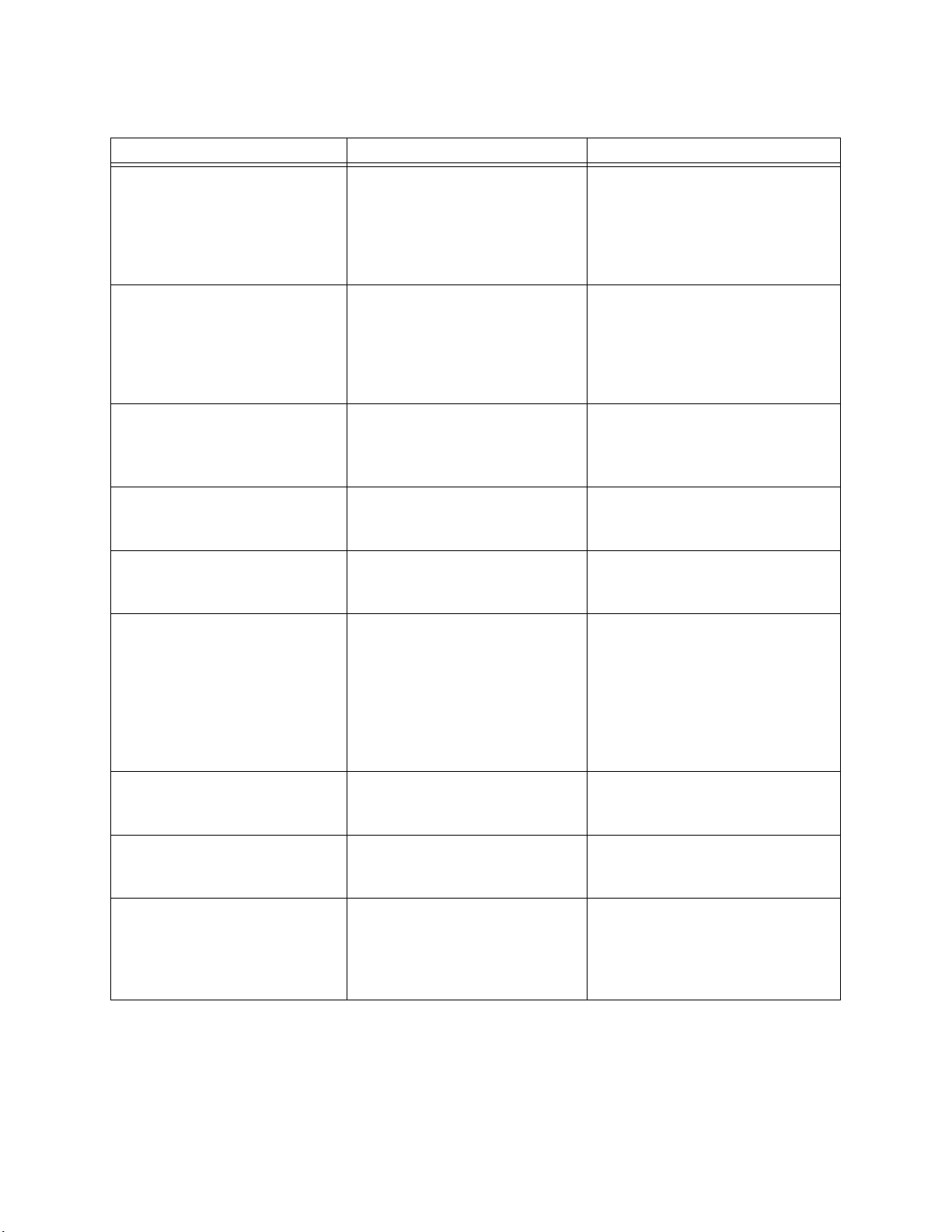
Table 2 SAP BAPI Alert Codes
Table 3
Alert Code\Description Description Details User Actions
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-CLIENTFAILED000001=
Alert to indicate that the SAP
JCO client initialization has
failed.
The eWay is unable to connect
to SAP as a client. Make sure that
the eWay is able to reach the SAP
system. Also check your SAP
BAPI External System values for
the Outbound SAP BAPI eWay.
In addition, check the SAP trace
logs.
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-CLIENTSUCCEEDED000002=
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 20 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Alert to indicate that the SAP
JCO client initialization has
succeeded.
None
Page 21
Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
Table 3
Alert Code\Description Description Details User Actions
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-CLIENTUP000003=
Alert to indicate that the SAP
JCO client is alive and valid.
If you are running in manual
mode, and this is an unexpected
state, check your collaboration
and verify all connect() calls;
otherwise, this Alert is only
informational.
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-CLIENTDOWN000004=
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-CLIENTRETRY000005=
SAPBAPI-TIDFILENOTAVAIL000006=
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-SERVERSTARTED000007=
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-SERVERSTARTED-ERROR000008=
Alert to indicate that the SAP
JCO client is disconnected.
Alert to indicate that the SAP
BAPI eWay is unable to
connect to SAP R/3 and is in
retry mode.
Alert to indicate that the TID
File is inaccessible.
Alert to indicate that SAP JCO
Server is registered with SAP R/
3 and started.
Alert to indicate that SAP JCO
Server could not be registered
with SAP R/3 and is not started.
If you are running in manual
mode, and this is an unexpected
state, check your collaboration
and verify all disconnect() calls;
otherwise, this Alert is only
informational.
None
Check that the directory for the
TID file exists and has write
permission for the user.
None
The eWay is unable to register
with SAP as a server. Make sure
that the eWay is able to reach the
SAP system. Also check your SAP
BAPI External System values for
the Inbound SAP BAPI eWay. In
addition, check the SAP trace
logs.
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-SERVERSTOPPED000009=
SAPBAPI-CONNECT-SERVERSTOPPED-ERROR000010=
SAPBAPI-RFCNOTPROCESSEDERROR000011=
Alert to indicate that SAP JCO
Server was successfully
shutdown.
Alert to indicate that SAP JCO
Server could not be properly
shutdown.
Alert to indicate that an
incoming RFC Function was
not processed due to a failure
in the Collaboration or
Business Process.
None
Check your domain server.log
and the SAP trace logs for further
information.
Check your domain server.log
for further information.
Note: An alert code is a warning that an error has occurred. It is not a diagnostic. The user
actions noted above are just some possible corrective measures you may take. Refer
to the log files for more information. For information on Managing and Monitoring
alert codes and logs, see the Sun SeeBeyond eGate Integrator System
Administration Guide.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 21 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 22

Chapter 2 Section 2.4
Installing the eWay Deploying an EAR File
2.4 Deploying an EAR File
The Sun Java CAPS Enterprise Designer can be configured to automatically deploy an
EAR file to the Sun Java System Application Server. To configure the Enterprise
Designer for deployment, follow the directions for deploying applications to the Sun
Java System Application Server, provided in the Sun SeeBeyond eGate Integrator System
Administration Guide. Because automatic deployment is not supported directly from
Enterprise Designer for the Weblogic Application Server, additional instructions are
provided below.
2.4.1 WebLogic Application Servers
1 Build the EAR file, which is generated in the Enterprise Designer.
2 Use your WebLogic Admin console to deploy the EAR file.
Refer to your application server’s documentation for requirements regarding working
directories.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 22 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 23
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties
This chapter describes how to set the SAP BAPI eWay properties to enable data
exchange between the SAP R/3 software and a Java CAPS project.
What’s In This Chapter
Creating and Configuring a SAP BAPI eWay on page 23
Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties on page 23
eWay Connectivity Map Properties on page 25
Configuring the eWay Environment Properties on page 30
eWay External Properties on page 31
3.1 Creating and Configuring a SAP BAPI eWay
Chapter 3
All eWays contain a unique set of default parameters which you must configure from
the following locations:
From the Connectivity Map—which contains the parameters specific to the SAP
BAPI eWay, and may vary from other SAP BAPI eWays in the Project.
From the Environment Explorer tree—which contains global SAP connectivity
parameters that commonly apply to all SAP BAPI eWays (SAP BAPI external
systems having the same connectivity configuration) in the Project. Saved
parameters are shared by all eWays in the SAP BAPI External System Properties
window.
For additional information on creating the Connectivity Map components in a sample
Project, see Create a Connectivity Map on page 84. For information on creating the
Environment Explorer components, see Create an Environment on page 86.
Note: You must set configuration parameters for the SAP BAPI eWay in both locations.
3.2 Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties
When you connect an External Application to a Collaboration, Enterprise Designer
automatically assigns the appropriate eWay to the link. Each eWay is supplied with a
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 23 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 24
Chapter 3 Section 3.2
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties
template containing default configuration properties that are accessible on the
Connectivity Map.
To configure the eWay properties:
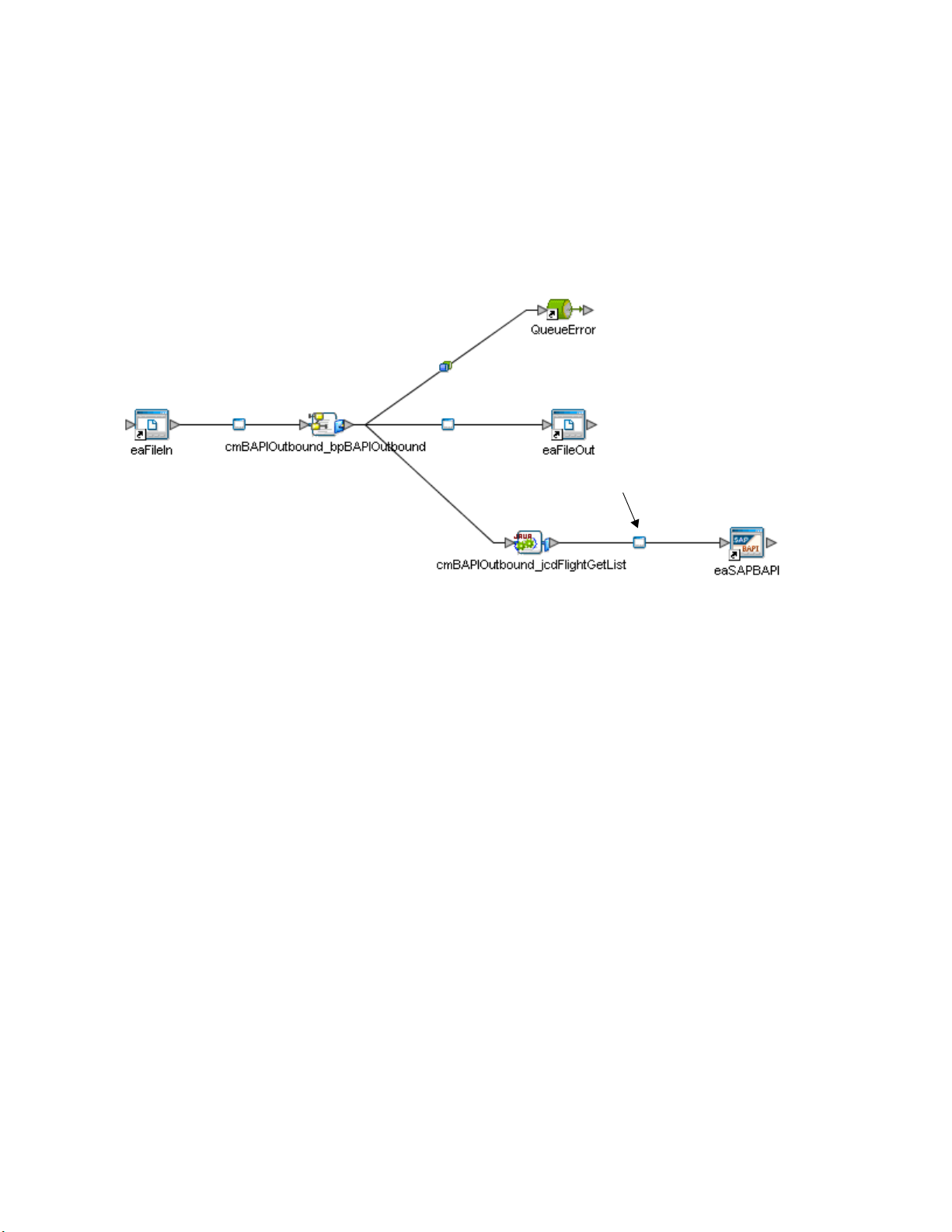
1 On the Enterprise Designer’s Connectivity Map, double-click the SAP BAPI eWay
icon.
Figure 6 Connectivity Map with Components
SAP BAPI eWay
2 The Configuration properties window opens, displaying the default properties for
the eWay. The properties default to the correct eWay direction. In this case, it opens
properties for the outbound eWay.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 24 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 25
Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Figure 7 Outbound eWay Properties
3.3 eWay Connectivity Map Properties
The eWay Connectivity Map consists of the following properties categories.
Inbound eWay Configuration Sections Include:
Server Connection Settings
Outbound eWay Configuration Settings Include:
Client Connection Settings
3.3.1 Configuring the Inbound eWay Properties
The Inbound eWay Properties include parameters required to receive data from SAP
R/3 into Java CAPS. The following server connection settings are configured in the
Inbound eWay Properties window.
Server Connection Settings
The following Server Connection Settings are used by the external database:
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 25 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 26
Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Table 4 Inbound eWay—Server Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Enable RFC Trace You enable RFC tracing with the Enable
RFC Trace property. The trace file
contains RFC API calls, and data sent to
and received from the SAP R/3 host.
The trace file is rfcnumber.trc, for
example, rfc00310_0156.trc.
RFC Trace Level Trace level specifies the complexity of
the information in the trace file. 0
provides minimal trace logging and 5
provides the maximum trace logging of
diagnostic information in the trace file.
Yes or No.
The default mode is No; the RFC
tracing is disabled.
Setting the Enable RFC Trace
parameter to Yes creates both the
JCo and RFC Trace logs. Both are
created in the same location under:
logicalhost\is\domains\<doma
in name>\config
The JCoTrace log provides Java
Runtime, version, and path
information. It also provides a
manifest.
If Enable RFC Trace is set to No, then
no trace file is generated.
Integer value from 0 (min) to 5 (max)
The default number is 0.
The Enable RFC Trace level only
affects the JCo trace level. It has no
effect on the RFC trace level.
Number of RFC
Servers to create
Specify the number of RFC servers to
create. The created RFC servers
facilitate parallel processing when
Integer value from 1 to 10.
The default number is 1.
receiving multiple requests from SAP
R/3.
Transaction Mode Specifies the transaction mode. The
transaction mode specifies whether
tRFC is enforced. With tRFC,
A transaction mode of Non-
Transactional or Transactional
RFC(tRFC)
transactions have unique TIDs and are
processed only once by this eWay.
The default mode is Non-
Transactional.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 26 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 27
Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Table 4 Inbound eWay—Server Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Transaction ID
Verification
Database
3.3.2 Configuring the Outbound eWay Properties
Specifies the location of the
Transaction ID Verification database.
Specify the name of the file-based
database which persists the TIDs.
Provide the path to the database file
that records the disposition of all
transactions outgoing from this eWay.
The database records whether
transactions are:
C (committed)
U (unprocessed or rolled-back)
R (reserved or pending)
A valid path to the database file.
For example, the default location is:
C:\JavaCAPS51\data\SapTRFC.TIDdb
The Outbound eWay Properties include parameters required to communicate from
Java CAPS to SAP/R3. The following server connection settings are configured in the
Outbound eWay Properties window.
Client Connection Settings
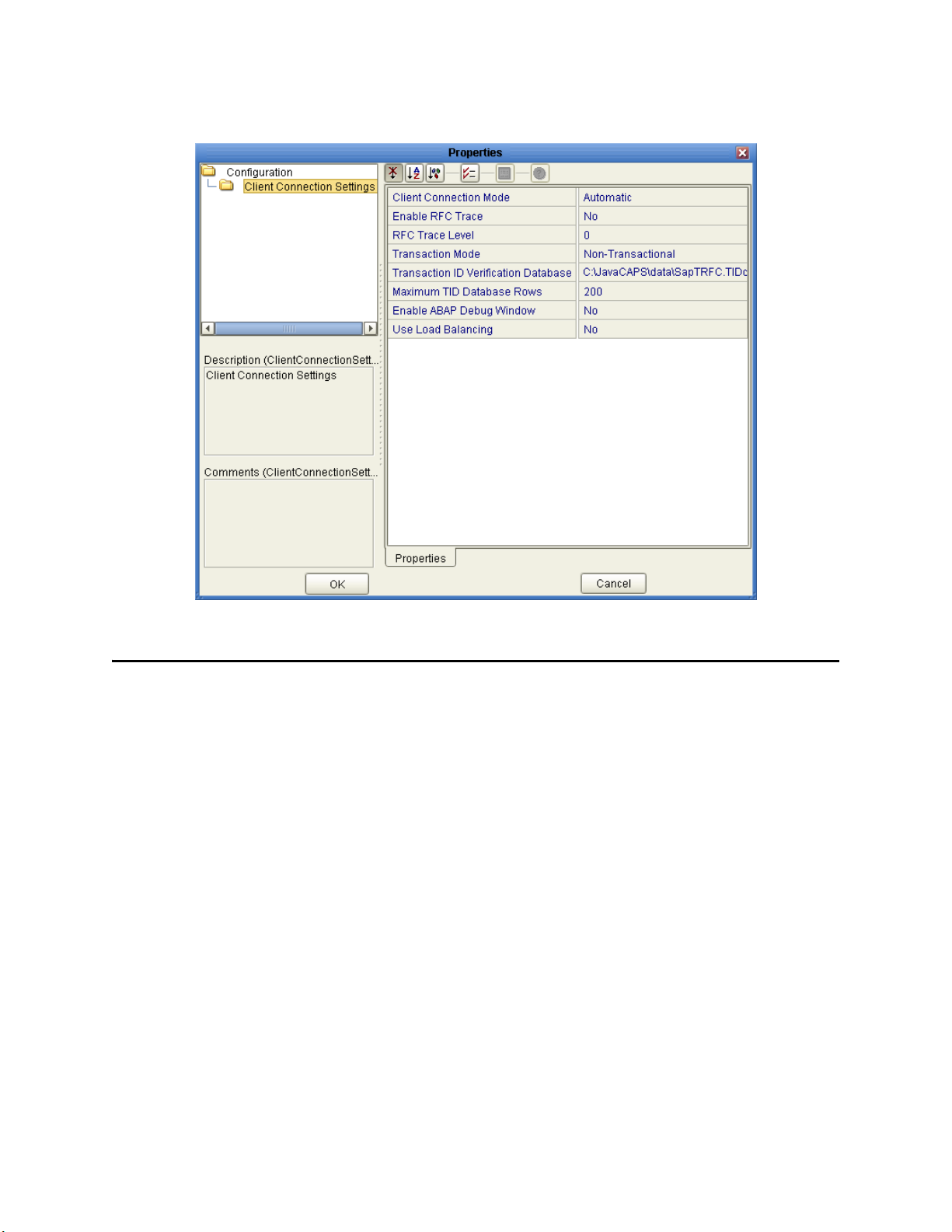
The following Client Connection Settings are used by the outbound eWay:
Name Description Required Value
Client Connection
Mode
Table 5 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Determines the type of client connection
to use when logging onto SAP R/3.
Automatic or Manual.
The default mode is
Automatic.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 27 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 28
Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Table 5 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Enable RFC Trace You enable RFC tracing with the Enable
RFC Trace property. The trace file is
rfcnumber.trc, for example,
rfc00310_0156.trc.
RFC Trace Level Trace level specifies the complexity of the
information in the trace file. 0 provides
minimal trace logging and 5 provides the
maximum trace logging of diagnostic
information in the trace file.
Yes or No.
The default mode is No; the
RFC tracing is disabled.
Setting the Enable RFC Trace
parameter to Yes creates both
the JCo and RFC Trace logs.
Both are created in the same
location under:
logicalhost\is\domains\
<domain name>\config
The JCoTrace log provides
Java Runtime, version, and
path information. It also
provides a manifest.
If Enable RFC Trace is set to
No, then no trace file is
generated.
Integer value from 0 to 5.
The default number is 0.
The Enable RFC Trace level
only affects the JCo trace
level. It has no effect on the
RFC trace level.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 28 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 29
Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Table 5 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Transaction Mode Specifies the transaction mode.
Non-Transactional
Actions performed by BAPI call are
committed immediately and
automatically by SAP R/3 (auto commit). In
this mode, use the execute() method in
the OTD.
Transactional RFC (tRFC)
eWay communicates with SAP R/3 using
unique transaction IDs (TID) to avoid
message repeats. Use the
executeAsynchronous(eid) method in the
OTD in this mode.
VIA COMMIT/ROLLBACK BAPI
Performs a single phase commit, where
actions performed by BAPI calls are
committed or rolled back by calling
BAPI_TRANSACTION_COMMIT or
BAPI_TRANSACTION_ROLLBACK. In this
mode you must use the commit and
rollback methods on the BAPI/RFC OTD.
A transaction mode of Non-
Transactional or Transactional
RFC(tRFC), via VIA COMMIT/
ROLLBACK BAPI.
The default mode is NONTRANSACTIONAL.
Transaction ID
Verification
Database
Specifies the location of the Transaction
ID Verification database.
Specify the name of the file-based
database which persists the TIDs. Provide
the path to the database file that records
the disposition of all transactions
outgoing from this eWay. The database
records whether transactions are:
C (committed)
U (unprocessed or rolled-back)
R (reserved or pending)
A valid path to the database
file.
For example, the default
location could be:
C:\JavaCAPS\data\SapTRFC.TI
Ddb
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 29 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 30
Chapter 3 Section 3.4
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties Configuring the eWay Environment Properties
Table 5 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Maximum TID
Database Rows
Enable ABAP Debug
Window
Use Load Balancing Enables load balancing for outbound
Specifies the maximum amount of rows
for the Transaction ID (TID) database for
outbound eWays.
Set this property only if tRFC is used. This
property specifies the maximum number
of rows in the outbound TID database
that are kept before the oldest rows are
purged and their corresponding TIDs
confirmed on SAP R/3. Confirmation
allows SAP R/3 to remove those TIDs from
its TID tracking database and reduce
resource consumption.
Enables the ABAP debugging window.
Enabling the Enable ABAP Debug
Window property opens the ABAP
debugging window on the Logical Host.
The window shows the debug
information for the RFC-enabled ABAP
application that is called by SAP R/3.
This property only works if the SAPGUI
software is installed on the Logical Host.
eWays.
This property allows you to take
advantage of the workload balancing
provided by SAP R/3. SAP R/3 provides
workload balancing to automatically
route requests to the SAP application
server within a group of servers that has
the best response time determined at that
moment by an SAP message server.
If you disable load balancing, use the
System number property as described in
“System Number” on page 34.
At least 1 row.
The default is 200 rows.
Yes or No.
The default mode is No; the
ABAP Debug window is
disabled.
Yes or No.
The default mode is No; load
balancing is disabled by
default.
3.4 Configuring the eWay Environment Properties
The eWay Environment Configuration properties contain parameters that define how
the eWay connects to and interacts with SAP R/3 within the Environment. When you
create a new SAP BAPI External System, you may configure the type of External
System required.
To Configure the Environment Properties:
1 In Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment Explorer tab.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 30 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 31

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
2 Expand the Environment created for the SAP BAPI Project and locate the SAP BAPI
External System.
Note: For more information on creating an Environment, see the “Sun SeeBeyond
eGate™ Integrator Tutorial”.
3 Right-click the External System created for the SAP BAPI Project and select
Properties from the list box. The Environment Configuration Properties window
appears.
Figure 8 SAP BAPI eWay Environment Configuration
4 Click on any folder to display the default configuration properties for that section.
5 Click on any property field to make it editable.
After modifying the configuration properties, click OK to save the changes.
3.5 eWay External Properties
The eWay External System consists of the following properties categories.
Inbound SAP BAPI eWay on page 32
Outbound SAP BAPI eWay on page 35
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 31 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 32

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Inbound eWay Configuration Sections Include:
Server Connection Settings
MDB Settings
Outbound eWay Configuration Settings Include:
Client Connection Settings
Connection Retry Settings
Connection Pool Settings
3.5.1 Inbound SAP BAPI eWay
The inbound eWay Environment properties include server connection parameters that
are required to implement the project, and are configured in the inbound eWay
Environment Properties window.
The Inbound SAP BAPI eWay includes the following configuration section:
Server Connection Settings
MDB Settings
Server Connection Settings
The following are the Server Connection Settings:
Table 6 Inbound SAP BAPI eWay—Server Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Gateway Hostname Specifies the gateway hostname of the
SAP R/3 application server.
An alphanumeric string. Do
not omit leading zeros.
There is no default setting.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 32 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 33

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Table 6 Inbound SAP BAPI eWay—Server Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Router String
(optional)
Specifies the router string needed to
access the SAP R/3 Application Server.
This property is optional; use it only to
gain access to an SAP system that is
behind a firewall.
The string is composed of the
hostnames or IP addresses of all the
SAP routers that are in between this
logical host and the SAP gateway host.
For example, if there are two routers,
saprouter1, and saprouter2, in order,
from the Logical Host to the SAP R/3, as
follows:
saprouter1: 204.79.199.5
saprouter2:
207.105.30.146
The router string in this case is as
follows:
/H/204.79.199.5/H/
207.105.30.146/H/
A valid router string.
There is no default setting.
Do not omit the “/H/” tokens to begin,
separate, and end the routers.
Gateway Service Specifies the gateway service of
SAP R/3
The gateway service of the SAP R/3
system sends transactions.
Program ID Specifies the Program ID used to
register the SAP JCo server of the eWay
with SAP R/3.
Application Server
Hostname
Specifies the host name of the SAP R/3
application server.
The SAP recommended value
is the string sapgw
concatenated with the SAP
system number. For example,
if the system number is 00, the
gateway service is sapgw00.
There is no default setting.
Program ID is shown in the
SAPGUI transaction SM59.
This entry must match the
SAPGUI exactly; this entry is
case sensitive.
There is no default setting.
Any valid Hostname.
There is no default setting.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 33 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 34

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Table 6 Inbound SAP BAPI eWay—Server Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
System Number Specifies the system number of the
SAP R/3 application server.
Use this property when you are not
using SAP load balancing. For
information, refer to
Balancing” on page 30
Client Number Specifies the SAP client number used
to access the R/3 system.
User Specifies the user ID used to log on to
the SAP R/3 system.
Password Specifies the password for the logon
user.
Language Specifies the logon language used for
SAP R/3 access by the eWay.
“Use Load
.
Any numeric value.
There is no default setting.
An alphanumeric string. Do
not omit leading zeros.
There is no default setting.
Any alphanumeric value.
There is no default setting.
An alphanumeric string.
There is no default setting.
A base language is required.
Languages include:
EN – English
DE – German
JA – Japanese
KO – Korean
System ID Specifies the system ID of the SAP R/3
instance.
Character Set Sets the character encoding of the
connecting SAP R/3 system.
MDB Settings
The following MDB Settings are used:
Table 7 Inbound SAP BAPI eWay—MDB Settings
Name Description Required Value
Max Pool Size Specifies the maximum number of
physical connections the pool should
keep available at all times. 0 (zero)
indicates that there is no maximum.
The default is EN, English.
Any valid SAP System ID.
There is no default setting.
Unicode or Non-unicode.
The default value is Non-
unicode.
Any numeric value.
The default is 1000.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 34 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
3.5.2 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay
The outbound eWay Environment properties include client connection parameters that
are required to implement the project using the eWay in outbound mode
communication. These parameters are configured in the outbound eWay Environment
Properties window.
The Outbound SAP BAPI eWay includes the following configuration sections:
Client Connection Settings
Connection Retry Settings
Connection Pool Settings
Client Connection Settings
The following Client Connection Settings are used:
Table 8 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay— Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Application
Server
Hostname
System Number Specifies the system number of the
Client Number Specifies the SAP client number used
User Specifies the user ID used to log on
Password Specifies the password for the logon
Language Specifies the logon language used
Specifies the host name of the SAP R/
3 application server.
SAP R/3 application server.
Use this property when you are not
using SAP load balancing. For
information, refer to
Balancing” on page 30
to access the R/3 system.
to the SAP R/3 system.
user.
for SAP R/3 access by the eWay.
“Use Load
.
Any valid Hostname.
There is no default setting.
Any numeric value.
There is no default setting.
An alphanumeric string. Do not omit
leading zeros.
There is no default setting.
Any alphanumeric value.
There is no default setting.
An alphanumeric string.
There is no default setting.
There are no required values.
EN – English
DE – German
JA – Japanese
KO – Korean
The default is EN, English.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 35 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 36

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Table 8 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay— Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
System ID Specifies the System ID of the
SAP R/3 instance.
Gateway
Hostname
(optional)
Specifies an Gateway host name for
the Application Server. This
parameter is optional and should be
configured when NOT using SAP
Load Balancing.
Do not specify any optional Router
String here, as the value is
prepended to the Gateway
Hostname.
Gateway Service
(optional)
Specifies an Gateway Service for the
Application Server. This parameter is
optional and should be configured
when NOT using SAP Load
Balancing.
Message Server
Hostname
Specifies the host name of the R/3
Message Server IF using Load
Balancing. NOTE: Do not specify any
optional Router String here, as the
value will be prepended.
Application
Server Group
Specifies the name of the group of
SAP Application Servers that will be
sharing the workload. This parameter
should be configured ONLY when
using SAP Load Balancing.
Any valid SAP System ID.
There is no default setting.
An alphanumeric string. Do not omit
leading zeros.
There is no default setting.
The SAP recommended value is the
string sapgw concatenated with the
SAP system number. For example, if
the system number is 00, the gateway
service is sapgw00.
There is no default setting.
There is no default value.
There are no required values.
There is no default setting.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 36 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Table 8 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay— Client Connection Settings
Name Description Required Value
Router String
(optional)
Specifies the router string needed to
access the SAP R/3 Application
Server.
This property is optional; use it only
to gain access to an SAP system that
is behind a firewall.
The string is composed of the
hostnames or IP addresses of all the
SAP routers that are in between this
logical host and the SAP gateway
host. For example, if there are two
routers, saprouter1, and saprouter2,
in order, from the Logical Host to the
SAP R/3, as follows:
saprouter1:
204.79.199.5 saprouter2:
207.105.30.146
The router string in this case is as
follows:
/H/204.79.199.5/H/
207.105.30.146/H/
A valid router string.
There is no default setting.
Do not omit the “/H/” tokens to
begin, separate, and end the routers.
Connection Retry Settings
The following Connection Retry Settings are used:
Table 9 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay—Connection Retry Settings
Name Description Required Value
Connection Retries Number of retries to establish a
connection upon failure to acquire
one.
Connection Retry Interval Milliseconds of pause before each
reattempt to access the SAP system.
Used in conjunction with the
'Connection Retry Count' setting.
Connection Pool Settings
The following Connection Pool Settings are used by the external database:
The default is 0.
The default is 1000.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 37 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 38

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting SAP BAPI eWay Properties eWay External Properties
Table 10 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay—Connection Pool Settings
Name Description Required Value
Steady pool size The minimum number of physical
connections the pool should keep
available at all times. 0 (zero)
indicates that there should be no
physical connections in the pool and
that new connections should be
created as needed.
Maximum pool size The maximum number of physical
connections the pool should
contain. 0 (zero) indicates that there
is no maximum.
Max Idle Timeout in
Seconds
A timer thread periodically removes
unused connections. This parameter
defines the interval at which this
thread runs. This thread removes
unused connections after the
specified idle time expires. It allows
the user to specify the amount of
time a connection can remain idle in
the pool. When this is set to greater
than 0, the container removes or
destroys any connections that are
idle for the specified duration. A
value of 0 specifies that idle
connections can remain in the pool
indefinitely.
The default number of
connections is 2.
The default number of
connections is 10.
The default is 300.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 38 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 39

Creating SAP BAPI OTDs
The SAP BAPI wizard is used to create BAPI and RFC OTDs. You use these OTDs in
Java Collaborations and eInsight business processes to create the needed business rules
to communicate with SAP R/13.
What’s In This Chapter
SAP BAPI Encoding on page 39
Date and Time Stamp Requirements on page 40
SAP JCo Installation on page 40
Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs on page 41
BAPI and RFC OTDs on page 45
4.1 SAP BAPI Encoding
Chapter 4
SAP BAPI/RFC OTDs are encoding independent of the SAP R/3 system. This means
that OTDs created on a Unicode SAP R/3 instance can seamlessly interact with nonUnicode SAP R/3 instances, and vice versa.
In addition, the marshal and unmarshal encoding methods on the
IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS OTD only apply to the data, and not to the SAP
R/3 instance. The default for all processed byte data is UTF-8, regardless of connection
type (Unicode or non-Unicode).
When attempting to unmarshal data flows using an encoding other than UTF-8, such as
UTF-16, then you must also call the setUnmarshalEncoding method to specify this
encoding. This enables the eWay to properly unmarshal the byte array.
You also need to set the correct Character Set in the Environment parameters for an
inbound eWay when receiving data from SAP R/3. This way, the eWay knows whether
it is receiving Unicode or non-Unicode data from the SAP R/3 instance. The
setMarshalEncoding method is only for marshaling the OTD data into a byte array and
is not related to the SAP R/3 system character set.
Like the outbound data flows mentioned above, attempting to marshal data flows
using an encoding other than UTF-8, such as UTF-16, requires setting the
setMarshalEncoding method to match this encoding. This enables the data received
from SAP R/3 to be correctly converted to a byte array of the desired encoding.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 39 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 40

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs Date and Time Stamp Requirements
4.2 Date and Time Stamp Requirements
Date and time stamp fields in the OTD are now typed as java.lang.String fields. This
means that the OTD expects values assigned to date fields as YYYYMMDD, where
February 14, 2006 becomes 20060214.
The data format time fields is HHMMSS, where 11:59:59 PM becomes 235959, or
12:00:00 AM becomes 000000.
4.3 SAP JCo Installation
The SAP Java Connector file, sapjco.jar, is a middleware component that enables the
development of SAP-compatible components and applications in Java. This component
is required by the SAP BAPI OTD Wizard to create BAPI and RFC OTDs during design
time, and to support inbound and outbound SAP server communication during
runtime.
Since we are installing the SAP Java Connector as standalone component, certain
installation files are required. Download the installation files from SAPNet at
service.sap.com/connectors. Once logged in, this link redirects you to SAP Service
Marketplace. Click the following links to access the SAP Java Connector (SAP JCo) tools
and services page:
SAP NetWeaver > SAP NetWeaver in Detail > Application Platform >
Connectivity > Connectors > SAP Java Connector > Tools & Services
The following section details the basic guidelines for installation.
4.3.1 Procedures (Windows 32)
The following instructions apply for Windows 32 operating systems.
1 Create a directory, for example C:\SAPJCo, and extract the JCo ZIP file into this
directory.
2 Copy the files librfc32.dll and sapjcorfc.dll from your SAP JCo main directory to
C:\WINNT\SYSTEM32, as long as the version that is already there is not a more
recent version than the one that is delivered with the SAP JCo.
3 Copy the file sapjco.jar from your SAP JCo main directory to
<JavaCAPS51>\edesigner\lib\ext, where <JavaCAPS51> is the Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite install directory.
4 The sapjco.jar file is also required during runtime. For this, add the JAR file to
<JavaCAPS51>\logicalhost\is\lib.
5 Download the following DLL files. These are available, free of charge, from various
sources on the Internet:
msvcp71.dll
msvcr71.dll
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 40 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs
You must manually add these files to the following location:
c:\WINNT\system32
Note: Restart both Enterprise Designer and the domain after installing the JAR file.
4.3.2 Procedures (UNIX)
The instructions for the installation of SAP JCo on other operating systems are included
in the corresponding download files. On UNIX operating systems, add the OS specific
shared lib files to the library path. Check the SAP BAPI eWay readme to confirm the
supported operating systems.
Note: The SAP Java Connector file, JCo version 2.1.6 is not backwards compatible with
previous versions, such as 2.1.3. Confirm backwards compatibility issues with SAP
before attempting to switch between different JCo versions on different machines.
Note: SAP BAPI eWays can run on a 64-bit JVM, but only after the correct 64-bit JCo
files (version 2.1.3 or later) have been applied.
Note: The SAP R/3 application must be configured to communicate with the SAP BAPI
eWay as described in Configuring SAP R/3 in the SAP BAPI eWay Intelligent
Adapter User’s Guide.
Note: We recommend only using the directory path when setting your library path, not
the directory path and file name.
Note: JCo 2.1.6 does not support mixed case, users may need to convert passwords to
upper case for all design time and runtime SAP connection configurations.
Note: You need to copy the JCo JAR file to the \compile\lib\ext folder before
deploying and running command line code generation. You also need to copy the
JCo JAR file to the c:\Sun\ApplicationServer\lib folder before
deploying and running via the Sun Java™ System Application Server Enterprise
Edition 8.1.
Note: You also need to copy the JCo JAR file to the
c:\bea\weblogic91\samples\domains\wl_server\lib folder before
deploying and running via the WebLogic Application Server, version 9.1.
4.4 Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs
You create BAPI and RFC OTDs with the SAP BAPI wizard in the Enterprise Designer.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 41 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 42

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs
To create BAPI OTDs
1 In the Explorer tab of the Enterprise Designer, right click the Project, click New, and
click Object Type Definition. The New Object Type Definition Wizard dialog box
appears.
2 Click SAP BAPI and click Next. The Select SAP Object page appears.
Figure 9 BAPI Wizard—SAP Object Selection
3 To convert a BAPI object to OTD, select the BAPI option.
To convert an RFC object to OTD, select the RFC option.
4 Click Next. The System Parameters page appears.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 42 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 43

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs
Figure 10 BAPI Wizard—System Parameters
5 Enter the information for the SAP R/3 system for the SAP eWay to connect to:
For this option Enter
System ID System ID of the SAP R/3 system.
Application server Host name of the SAP R/3 system.
System number System number of the SAP R/3 system.
SAP Routing String Router string of hostnames/IP addresses
of all SAP routers between the Logical
Host and the SAP gateway host (optional).
Language Language used for SAP R/3 access.
RFC Trace NO to disable RFC tracing (default); YES
to enable RFC tracing, which creates the
trace files in: \edesigner\bin
6 Click Next. The Login Parameters page appears.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 43 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 44

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs Creating BAPI and RFC OTDs
Figure 11 BAPI Wizard—Login Parameters
7 Enter the information to log into the SAP system:
For this option Enter
Client Number Client number of the SAP R/3 system.
User name User name.
Password Login password.
8 Click Next. The Select BAPI/RFC page appears, showing the application
components
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 44 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 4 Section 4.5
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs BAPI and RFC OTDs
Figure 12 BAPI Wizard—Select BAPI/RFC
In the BAPI tree, you can navigate to a particular SAP application component and
select a BAPI object.
9 Expand the SAP application component folder, click a BAPI, and click Finish. The
OTD Editor window appears, displaying the OTD.
For information about the BAPI and RFC OTDs, refer to the section below.
You can now built the Collaborations or Business Processes as described in Building
and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project on page 71 and Building and
Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project on page 92. The section below
describes the BAPI methods (operations) that are available for you to use in the Java
Collaborations or Business Process.
4.5 BAPI and RFC OTDs
When an OTD is built for an SAP R/3 business object such as:
Application Components
J Controlling J CostCenter.
This creates an OTD which has methods corresponding to all BAPIs in the Cost Center
Business Object of SAP R/3.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 45 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 46

Chapter 4 Section 4.5
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs BAPI and RFC OTDs
Figure 13 CostCenter OTD
The figure above shows the CostCenter OTD. The OTD has nodes for each of the BAPIs
in the CostCenter business object. The OTD also has WSDL operations such as
GetListExecute and GetListReceive. These WSDL operations are used when the OTD is
used in a Business Process. The execute methods are used for client mode operations.
The receive methods are used for server mode operations.
If required, you can also use the Relaunch option of the OTD to relaunch the
CostCenter OTD wizard, see Figure 14, and rebuild the BAPI OTD for the same BAPI/
RFC.
Please note that selecting a BAPI/RFC other than the original one used to build the
OTD will corrupt your OTD and its associated Collaborations and Business Processes.
On Relaunch, the OTD is rebuilt again with the changed meta data, and any Java
Collaborations and Business Processes using this BAPI OTD are synchronized with the
new changes.
If your Java Collaborations or Business Processes are using OTD nodes that are now
absent in the relaunched BAPI/RFC OTD, you will be prompted to correct the business
rules by validation errors.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 46 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 4 Section 4.5
Creating SAP BAPI OTDs BAPI and RFC OTDs
Figure 14 CostCenter OTD — Relaunch
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 47 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 48

Configuring SAP R/3
For the SAP BAPI eWay to interact successfully with SAP R/3, you must configure the
SAP R/3 application as described in this chapter.
The SAP R/3 screen captures in this chapter correspond to SAPGUI version 6.2, and
SAP R/3 version 4.7. They are included to illustrate the general nature of the
procedures, and contain only example values. Refer to the documentation supplied
with your SAP R/3 system to determine the exact procedures.
What’s In This Chapter
Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay on page 48
Security Issues on page 67
5.1 Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay
Chapter 5
For the SAP BAPI eWay to receive communications from SAP R/3, you must set the
eWay up as an RFC destination in SAP R/3 as described below.
To create the RFC destination for the eWay
1 In the SAP R/3 window, click the forward arrow to display the navigation box if
necessary.
2 Type SM59 into the text field and press ENTER.
Figure 15 Navigating to the SM59 Transaction
This displays the RFC Destination Maintenance window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 48 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 49

Chapter 5 Section 5.1
Configuring SAP R/3 Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay
Figure 16 RFC Destination Maintenance Window
3 Click TCP/IP connections and Create to display the RFC Destination entry
window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 49 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 50

Chapter 5 Section 5.1
Configuring SAP R/3 Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay
Figure 17 RFC Destination Entry Window
4 Type in the name of the RFC Destination (use a Logical System name refer to
Naming the Logical System on page 54), an accompanying Description, and enter
<T> for the Connection Type (TCP/IP).
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 50 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 5 Section 5.1
Configuring SAP R/3 Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay
Figure 18 RFC Destination
5 Click Save to display the RFC Destination window corresponding to your entry.
6 Select the Registered as Server Program option.
7 Enter the Program ID and click Save.
This program ID must be exactly the same as that specified in the eWay Program ID
property. This value is case sensitive. For information, refer to “Program ID” on
page 33.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 51 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 52

Chapter 5 Section 5.1
Configuring SAP R/3 Creating the RFC Destination for the eWay
Figure 19 RFC Destination Window
8 Click Test Connection, which tests the connection for logon speed and message
transfer speed. When the inbound Project is deployed and running, the results are
displayed in a table; otherwise, return code 3 is displayed.
Figure 20 Connection Test Results
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 52 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 53

Chapter 5 Section 5.2
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuration Needed in SAP R/3 to Send and Receive IDocs
5.2 Configuration Needed in SAP R/3 to Send and Receive
IDocs
For the SAP BAPI eWay to interact successfully with the SAP R/3 system, you must
configure the SAP R/3 system as described in this chapter.
The SAP R/3 screen captures in this chapter correspond to SAPGUI version 6.2, and
SAP R/3 version 4.0. They are included to illustrate the general nature of the
procedures, and contain only example values. Refer to the documentation supplied
with your SAP R/3 system to determine the exact procedures.
Figure 21 Distribution Model Hierarchy
Distribution
Model View
Client
Logical System
Name (eWay)
IDoc Name
Following this high-level setup, you need to define Communications parameters in
SAP R/3 to specify the correct routing of IDocs (either inbound to or outbound from
SAP R/3). The hierarchy of this Communication system is shown in Figure 22. The
individual steps involved in the configuration are:
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 53 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 54

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
Figure 22 Communications Hierarchy
RFC Destination
Communications
Port
Partner Profile
The RFC Destination defines the entity to which Remote Function Calls (RFCs) can be
made; it is the same as the Logical System in the Distribution Model. The
Communications Port defines a channel for communication of IDocs. The Partner
Profile acts as an identifier for the eGate system, and provides a communications
gateway by incorporating elements of the ALE interface.
5.3 Configuring the Distribution Model
You need to complete the following in SAP R/3 to run a tRFC BAPI inbound.
Naming the Logical System on page 54
Specifying the Distribution Model on page 57
5.3.1 Naming the Logical System
Transaction: SALE
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 54 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 55

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
Figure 23 SAP R/3 System Window
1 In the SAP R/3 System home window, type SALE into the command field and click
Enter to display the Distribution (ALE) Structure window.
Figure 24 Distribution (ALE) Structure Display Window
2 Expand the tree to display IDoc Interface / Application Link Enabling (ALE) > Basic
Settings > Logical Systems > Define Logical System.
3 Click the Activity button to select Define Logical System. This displays the Logical
Systems Overview window.
4 Click the New entries button to display the New Entries window.
5 Enter the logical name for your SAP eWay using capital letters and a brief
descriptive name.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 55 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 56

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
Figure 25 New Entries Window
6 Click Save. The Change Request Entry window appears.
Figure 26 Change Request Entry Window (1)
7 Click the Create request button, to display the Create Request window.
8 Enter a short description (e.g., eWay Test) and click Save. The Change Request
entry window appears.
9 Click Enter to add the new data into the system. You are now returned to the
Logical Systems Overview window, and the new Logical System appears in the
list.
10 Click Save and select the Back button repeatedly until the SAP R/3 System window
appears.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 56 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 57

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
5.3.2 Specifying the Distribution Model
Cautionary Notes
Two notes of caution are appropriate at this point:
1 We recommend that you should use the Z prefix when defining a name. This prefix
is reserved for external use, and does not conflict with any SAP naming
conventions.
Following these rules should prevent any interference with standard SAP functionality
or conflicts with standard SAP terminology.
Transaction: SALE
Figure 27 SAP R/3 System Window
1 In the SAP R/3 System home window, type SALE into the command field and click
Enter to display the Distribution (ALE) Structure window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 57 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 58

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
Figure 28 Distribution Structure Window
1 Click the Activity button next to Maintain Distribution Model and Distribute
Views to display the Maintain Distribution Model window.
Figure 29 Maintain Distribution Model Window
2 Select the Menu path Edit > Model View > Create to display the Create Model
View dialog box.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 58 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 59

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring the Distribution Model
Figure 30 Create Model View Dialog Box
3 Enter the logical name you want for the new Distribution Model View, along with a
brief descriptive name or message (for your own use).
4 Click Continue (Enter), which returns you to the previous window. Your new
Model View now appears in the tree, as shown in Figure 31.
Figure 31 Maintain Distribution Model Tree
5 Highlight the new entry and select Add Message Type. This displays the Add
Message Type dialog box.
Figure 32 Add Message Type Dialog Box
6 Type the desired values for the four parameters into the text boxes, or select them
from the drop-down menus. For example, CREMAS is the message type used for
Creditor Master Data.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 59 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 60

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
7 Select Continue (Enter), which returns you to the previous window. The values you
select now appear in the Distribution Model tree, as shown in Figure 33.
Figure 33 Maintain Distribution Model Tree
8 Save your entry, click Back and then Cancel to return to the Distribution Structure
window.
5.4 Configuring Communications
This section describes the necessary communication configuration.
Defining the Communications Port on page 60
Creating a Partner Profile on page 62
Configuring a Partner Profile on page 64
5.4.1 Defining the Communications Port
This section describes how to set up the communication port for Transactional RFC.
Transaction: WE21
The Communications Port defines the type of connection with the Partner (see Creating
a Partner Profile on page 62). In this step you specify the outbound file name, directory
path, and any associated function modules.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 60 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 61

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 34 SAP R/3 System Window
1 In the SAP R/3 System home window, type WE21 into the command field and click
Continue (Enter) to display the WF-EDI Port Definition window.
Figure 35 WF-EDI Port Definition Tree
2 Expand the tree under Transactional RFC to display the currently-defined Ports.
3 Select the desired Port from the list, or select Change to display the Port Definition
for Asynchronous RFC Overview window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 61 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 62

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 36 Port Details Window
4 Type in a Version (specifies IDoc record type), Logical destination, and Description,
matching the entries made previously.
5 Select Enter, which displays the Change Request Query dialog window. [Note that
you must have CTS (Correction and Transport System) turned on for this screen to
be displayed.]
6 Select Create Request, which displays the Create Request dialog window.
7 Enter a Short description and Save.
8 Select Back repeatedly to return to the SAP R/3 System window.
5.4.2 Creating a Partner Profile
Transaction: WE20
Here you create the Partner for the Logical System you created earlier. Note that the LS
Partner Type is used for all ALE distribution scenarios.
Figure 37 SAP R/3 System Window
1 In the SAP R/3 System home window, type WE20 into the command field and then
click Continue (Enter) to display the Partner Profile: Initial Screen window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 62 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 63
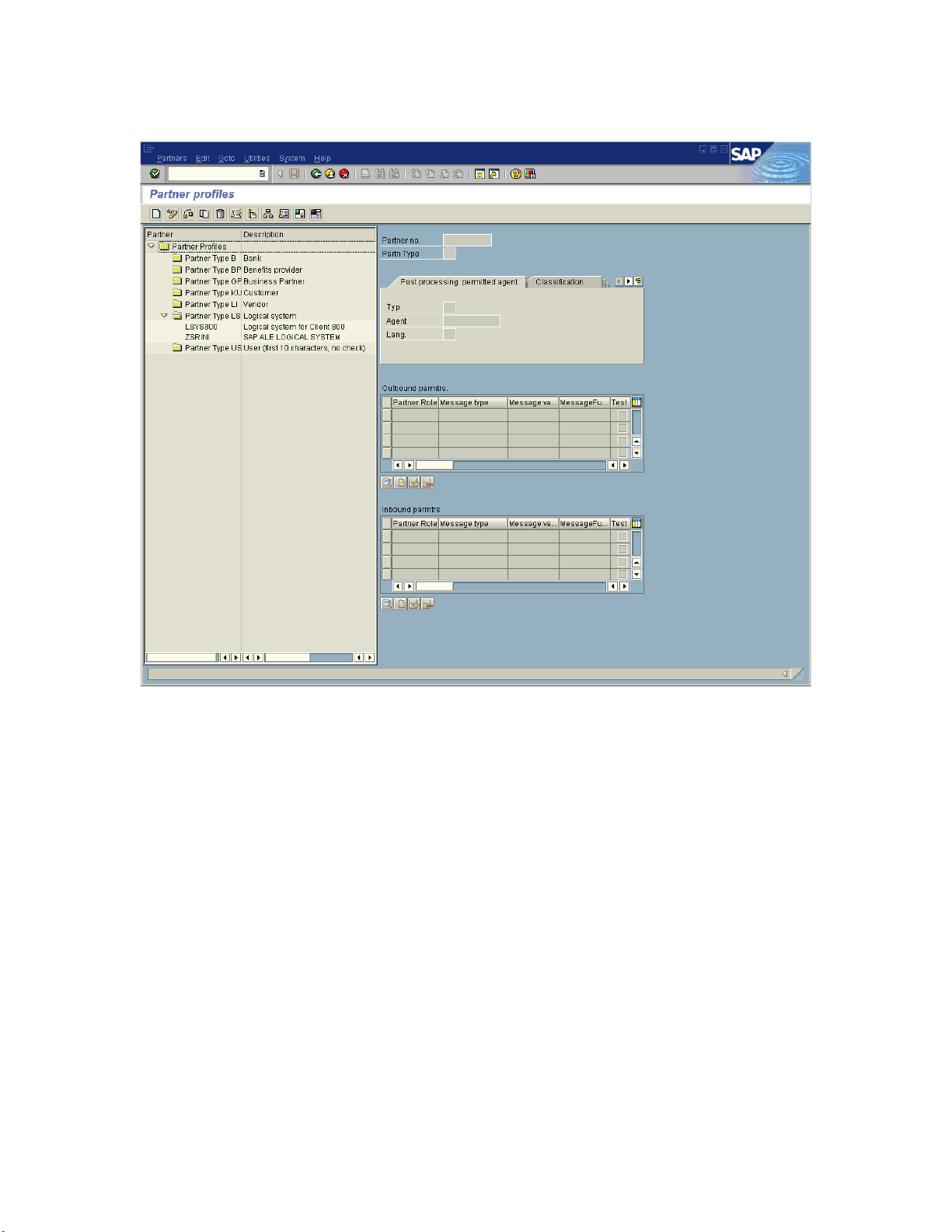
Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 38 Partner Profile: Initial Screen Window
2 Type the name of the logical system created previously into the Partner number
field, select LS for the Partner type, and select Create. This creates the Partner, and
displays the Create Partner Profile <Partner Number> window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 63 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 64

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 39 Create Partner Profile Window
3 Under the Classification tab, select ALE for the Partner class and A (Active) for the
Partner status, then Save. You now have created the Partner, and need to continue
to the next section to configure the Partner Profile.
5.4.3 Configuring a Partner Profile
Transaction: WE20
In this section, you configure the Inbound or Outbound Parameters in the Partner
Profile.
1 In the Partner Profile: Initial Screen window, select the desired Partner Number,
for example ZSRINI.
2 Select the Inbound parameters.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 64 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 65

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 40 New Entries: Details of Created Entries Window
3 Select CREMAS as a Message type and CRE1 as a Process code from the drop-down
menus, then click Save. The entries now appear in the list in the EDI Partner
Profile: Inbound Parameters Overview window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 65 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 66

Chapter 5 Section 5.4
Configuring SAP R/3 Configuring Communications
Figure 41 EDI Partner Profile: Inbound Parameters Overview Window
4 Follow the same procedure for Outbound parameters, as seen in Figure 42.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 66 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 67

Chapter 5 Section 5.5
Configuring SAP R/3 Security Issues
Figure 42 EDI Partner Profile: Outbound Parameters
5 After making your entries, Save and then Back to get to the main SAP R/3 System
window.
5.5 Security Issues
SAP R/3 uses authorization objects to allow access to various levels of operation. A
minimum set of authorization objects required for the SAP BAPI eWay to operate is
described below. Use this only as a reference for setting up your own profiles.
These settings are located under Cross-Application Authorization Objects. Refer to the
SAP R/3 documentation for additional information.
Function Group Access
Under Auth. check for RFC access, select:
ARFC
EDIN
ERFC
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 67 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 68

Chapter 5 Section 5.5
Configuring SAP R/3 Security Issues
RFC1
SCCR
SYST
ZDG1
Permission for Processing BAPI Type
Under BAPI/EDI > Distributing master data and BAPI/EDI, select:
Receiving BAPIs via RFC
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 68 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 69

Reviewing the Sample Projects
This chapter provides an introduction to the SAP BAPI eWay components, and
information on how these components are created and implemented in a Java CAPS
Project.
It is assumed that the reader understands the basics of creating a Project using the Sun
SeeBeyond Enterprise Designer. For more information on creating an eGate Project, see
the “Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Tutorial” and the “Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator User’s
Guide”.
What’s In This Chapter
About the Sample Projects on page 69
Steps Required to Run the Sample Project on page 70
Importing a Sample Project on page 71
Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project on page 71
Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project on page 92
Chapter 6
6.1 About the Sample Projects
Two sample Projects are included with the SAP BAPI eWay. These sample Projects
enable you to see how Java CAPS can work with SAP R/3 applications. The SAP BAPI
eWay sample Projects are provided in the zip file: SAP_BAPI_eWay_Sample.zip
This file contains two sample Project zip files to import:
prjBAPIOutbound.zip
prjIDocInbound.zip
You can use these to further your understanding of the product, or expand upon to
build more complicated Projects. Each sample Project uses a combination of eGate and
eInsight components. You must install these components into Java CAPS prior to
running the samples.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 69 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 70

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Reviewing the Sample Projects SAP Version Support
6.1.1 prjBapiOutbound.zip
The prjBapiOutbound.zip file contains the prjBAPIOutbound sample project, which
demonstrates how to access flight ID and type by passing the airline code via an
outbound BAPI.
In addition to the sample Project, the SAP_BAPI_eWay_Sample.zip file also contains
the following files generated by running the prjBAPIOutbound sample Project:
inputBAPIFlightGetList.txt—an input text file that contains the airline carrier code
“BA”.
outputFlight1.dat—a sample output file received after running the sample Project.
6.1.2 prjIDocInbound.zip
The prjIDocInbound.zip file contains the prjIDocInbound sample project, which
demonstrates how to use an inbound RFC to receive IDocs.
In addition to the sample Project, the SAP_BAPI_eWay_Sample.zip file also contains
the following files generated by running the prjIDocInbound sample Project:
CREMASoutput1.dat—a sample output file containing CREMAS message type
data.
MATMASoutput1.dat—a sample output file containing MATMAS message type
data.
6.2 SAP Version Support
The sample Projects described within support SAP version 4.6x, 4.7, ECC 5.0 and ECC
6.0.
6.3 Steps Required to Run the Sample Project
The following steps are required to run the sample projects contained in the
SAPBAPIeWayDocs.sar file.
1 Import the sample Project.
2 Configure, build, deploy, and run the sample Projects.
You must do the following before you can run an imported sample Project:
Create an Environment
Configure the eWays
Create a Deployment Profile
Create and start a domain
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 70 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 71

Chapter 6 Section 6.4
Reviewing the Sample Projects Importing a Sample Project
Deploy the Project
3 Check the output.
6.4 Importing a Sample Project
Sample eWay Projects are included as part of the installation package. To import a
sample eWay Project to the Enterprise Designer do the following:
1 Extract the samples from the Enterprise Manager to a local file.
Sample files are uploaded with the eWay’s documentation SAR file, and then
downloaded from the Enterprise Manager’s Documentation tab. The
SAP_BAPI_eWay_Sample.zip file contains the sample Project ZIP files.
Note: Save all work before importing a sample Project.
2 From the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer pane, right-click the Repository
and select Import Project from the shortcut menu. The Import Manager appears.
3 Browse to the directory that contains the sample Project ZIP file. Select a sample
Project file and click Import.
4 Click Close after successfully importing the sample Project.
6.5 Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample
Project
The following sections provide instructions on how to manually create the sample
Project, which was based on SAP R/3 6.0 ECC.
This sample demonstrates how to use the GetList BAPI of the Flight business object. It
has a Java Collaboration Definition (JCD) which executes the BAPI to retrieve flight
information. Input data to this JCD is passed from a File eWay running in a Business
Process. Output data of the JCD is given to a File eWay to write out the results of the
executed BAPI. The Business Process has an exception handler to catch any exception
raised by the JCD, which it writes to an error queue.
Steps required to create the sample Project include:
Create a Project on page 72
Create the OTDs on page 72
Create the Java Collaboration Definitions on page 73
Create the Business Process on page 80
Create a Connectivity Map on page 84
Bind the eWay Components on page 85
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 71 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 72

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Create an Environment on page 86
Configure the eWays on page 87
Create the Deployment Profile on page 90
Create and Start the Domain on page 91
Run the Sample Project on page 92
6.5.1 Create a Project
The first step is to create a new Project in the Enterprise Designer.
1 Start the Enterprise Designer.
2 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the Repository and select New Project. A
new Project (Project1) appears on the Project Explorer tree.
3 Rename the Project prjBAPIOutbound.
6.5.2 Create the OTDs
The sample Project requires two OTDs to interact with the SAP BAPI eWay. These
OTDs include:
Flight—OTD that is used to check availability, check details, and return results of
flight lists.
CustBAPI—Custom defined OTD that is used to receive and send data to the
triggering Business Process.
Additional information on creating OTDs is found at Creating SAP BAPI OTDs on
page 39.
Steps required to create the Flight OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
The New Object Type Definition Wizard window appears.
2 Select SAP BAPI from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Enter the system parameters for the SAP R/3 system and click Next.
4 Enter the SAP R/3 system login parameters and click Next.
5 Select the following business object from the available list of objects:
Application_Components > Basis_Components >
ABAP_Workbench_Java_IDE_and_Infrastructure > Flight
6 Click Finish to create the OTD.
Steps required to create the CustBAPI OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
2 Select User Defined OTD from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 72 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 73

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
3 Enter a new name for the OTD. For this example, use CustBAPI.
4 Click Finish to create the CustBAPI OTD.
5 Open the new CustBAPI OTD and add a new field under the CustBAPI element
and rename it test1.
6.5.3 Create the Java Collaboration Definitions
The next step is to create the Java Collaboration Definitions using the Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java). Once you create a Collaboration Definition, you can write
the Business Rules using the Collaboration Editor.
Steps required to create the jcdFlightGetList Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Name your Collaboration jcdFlightGetList.
3 Under Web Service Type, select New: Create a new Web Service operation, and
then click Next.
4 Enter the operation name flightInput and click Next.
5 Select prjBAPIOutbound > CustBAPI, and then click Next.
6 Select prjBAPIOutbound > Flight, then click Add. The Flight OTD appears in a list
of selected OTDs.
7 Click Finish, the jcdFlightGetList Collaboration is created.
Figure 43 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 73 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 74

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Create the Collaboration Business Rules
The following steps demonstrate how to create the business rules for the
jcdFlightGetList Collaboration.
1 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon and then connect the test1
field under Input, to the AIRLINE field under Flight_1 > GetList > ImportParams.
Figure 44 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
2 Click the Math icon from the Business Rules Designer toolbar and select Literal
number from the drop-down list. Give the number a value of 3 and connect this to
MAX_ROWS under jcdFlightGetList > Flight_1 > GetList > ImportParams.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 74 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 75

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 45 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
3 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon. Next, right-click GetList
(located under Flight_1), and choose Select method to call... from the list of
available options. Select the execute() method from the list of available methods.
The execute() method now appears in the Business Rules Designer window.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 75 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 76

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 46 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
4 Select a new rule from the Business Rules toolbar. Next, select String > Concat from
the Business Rules Designer toolbar. A Concat appears on the canvas.
5 Select String > Literal String from the Business Rules toolbar, then enter OUTPUT
type: = in the String box and connect this to the String of the Concat. Next, drag
TYPE, located under jcdFlightGetList > GetList > Return to str (String) in the
concat.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 76 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 77

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 47 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
6 Using the same procedures documented in the previous step, make the following
field connections to the concat in the Business Rules Designer window:
ID to str (Sting) with Literal String “ID =”
Number to str (Sting) with Literal String “NUM =”
Message to str (Sting) with Literal String “MESSAGE =”
The result should appear as seen in Figure 48.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 77 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 78

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 48 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
7 Connect the result (String) in the concat to the test1 field, located under
jcdFlightGetList > output.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 78 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 79

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 49 jcdFlightGetList Collaboration
8 The resulting collaboration should display the following code:
package prjBAPIOutbound;
public class jcdFlightGetList
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void flightInput( ud1.CustBAPI_1621432015.CustBAPI input,
ud1.CustBAPI_1621432015.CustBAPI output, flight.Flight Flight_1 )
throws Throwable
{
Flight_1.getGetList().getImportParams().setAIRLINE( input.getTest1() );
Flight_1.getGetList().getImportParams().setMAX_ROWS( 3 );
Flight_1.getGetList().execute();
if (Flight_1.getGetList().hasRETURN()) {
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < Flight_1.getGetList().countRETURN(); i1 += 1) {
output.setTest1( "OUTPUT : Type = ".concat( Flight_1.getGetList().getRETURN( i1
).getTYPE() + " ID = " + Flight_1.getGetList().getRETURN( i1 ).getID() + " NUM = " +
Flight_1.getGetList().getRETURN( i1 ).getNUMBER() + " MESSAGE = " +
Flight_1.getGetList().getRETURN( i1 ).getMESSAGE() ) );
}
}
}
}
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 79 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 80

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
6.5.4 Create the Business Process
The next step in the sample is to create the bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business
Process in which the business rules are defined.
Steps to create a business process include:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Business Process from the shortcut menu. The eInsight Business
Process Designer appears and BusinessProcess1 is added to the Project Explorer
tree. Rename BusinessProcess1 to bpBAPIOutbound.
2 Drag a FileClient.receive and a FileClient.write Activity, located under Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient, to the Business Process canvas.
Figure 50 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process
3 From the Business Process toolbar, drag a Scope to the canvas. Once on your
canvas, double-click the icon to expand the scope.
Figure 51 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process
4 Drag a flightInput activity from the Project Explorer to the scope in the Business
Process canvas, and then connect the canvas elements together as seen in Figure 51.
Figure 52 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process
5 Create a business rule between the start of the Scope and
jcdFlightGetList.flightInput. Next, connect the text field under
FileClient.receive.Output to the Test1 field located under
jcdFlightGetList.flightInput.Input > CustBapi.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 80 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 81

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 53 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process — business rule
6 Create a business rule between jcdFlightGetList.flightInput and the end of the
Scope. Next, connect the Test1 field under jcdFlightGetList.flightInput.Output >
CustBapi to the text field located under FileClient.write.Input.
Figure 54 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process — business rule
7 From the Business Process toolbar, drag a Catch Named Exception (from the
Intermediate Events drop-down list) to the Fault Handler canvas icon (the icon on
the bottom of the Scope). An un-configured Exception Handler appears on the
canvas.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 81 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 82

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 55 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process
8 Double-click to open the Exception handler box.
9 From the Business Process toolbar, drag a Business Rule activity to the Exception
Handler canvas. Also drag a JMS.send activity from the Project Explorer, located
under Sun SeeBeyond > eGate > JMS to the Exception Handler canvas.
10 Double-click the Business Rule activity, and then in the Business Rules Designer
connect the Message field, located under jcdFlightGetList.flightInput.Fault to the
TextMessage field, located under JMS.Send.Input > JMS > MessageProperties.
Figure 56 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process — business rule
11 Connect the activities in the Exception Handler together, as seen in Figure 57.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 82 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 83
Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 57 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process
12 Click on the Exception Handler box and then from the Business Process toolbar,
click the Show Property Sheet icon, then configure the following for the Exception
Handler.
Exception Name --> ns4:JavaException
Output --> jcdFlightGetList.flightInput.Fault
Figure 58 bpBAPIOutbound eInsight Business Process — Exception Handler
Note: Review the Sun SeeBeyond eInsight™ Business Process Manager User’s Guide for
a more detailed description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to
a modeling elements in a business process.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 83 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 84

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
6.5.5 Create a Connectivity Map
The Connectivity Map provides a canvas for assembling and configuring a Project’s
components.
Steps required to create a new Connectivity Map:
1 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the new prjBAPIOutbound Project and
select New > Connectivity Map from the shortcut menu.
2 The New Connectivity Map appears and a node for the Connectivity Map is added
under the Project, on the Project Explorer tree labeled CMap1. Rename this project
to be cmBapiOutbound.
Populate the Connectivity Map
You add the Project components to the Connectivity Map by dragging the icons from
the Connectivity Map toolbar to the canvas.
The cmBAPIOutbound Connectivity Map in the prjBAPIOutbound Project requires
the following components:
File External Application (x2)
SAP BAPI External Application
jcdFlightGetList – Java Collaboration
bpBAPIOutbound – eInsight Business Process
JMS Queue
Any eWay added to the Connectivity Map is associated with an External Application.
To establish a connection to SAP BAPI, first select SAP BAPI as an External Application
to use in your Connectivity Map.
Steps required to select a SAP BAPI External System:
1 Click the External Application icon on the Connectivity Map toolbar.
2 Select the external systems necessary to create your Project (for this sample, SAP
BAPI and File). Icons representing the selected external systems are added to the
Connectivity Map toolbar.
3 Rename the following components and then save changes to the Repository:
File1 to eaFileIn
File2 to eaFileOut
Queue1 to QueueError
SAP BAPI1 to eaSAPBAPI
The Connectivity Map components should appear as they do in Figure 59.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 84 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 85

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 59 Connectivity Map Components
6.5.6 Bind the eWay Components
The final step in creating a Connectivity Map is binding the eWay components
together.
Steps required to bind eWay components together:
1 Double-click the cmBAPIOutbound Connectivity Map in the Project Explorer tree.
The Connectivity Map appears in the Enterprise Designers canvas.
2 Double-click both the cmBAPIOutbound_bpBAPIOutbound Business Process and
the cmBAPIOutbound_jcdFlightGetList Collaboration to display their Binding
dialog boxes.
Map the following Services:
jcdFlightGetList under Invoked Services of
cmBAPIOutbound_bpBAPIOutbound to CustBAPI under Implemented
Services of cmBAPIOutbound_jcdFlightGetList.
FileSender under Implemented Services of
cmBAPIOutbound_bpBAPIOutbound to eaFileIn.
JMSDestination under Invoked Services of
cmBAPIOutbound_bpBAPIOutbound to QueueError.
FileReceiver under Invoked Services of cmBAPIOutbound_bpBAPIOutbound
to eaFileOut.
Flight_1 under Invoked Services of cmBAPIOutbound_jcdFlightGetList to
eaSAPBAPI.
The connected components are seen in Figure 60.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 85 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 86

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 60 Connectivity Map - Binding the Components
3 Minimize the Binding dialog boxes by clicking the chevrons in the upper-right
corners.
4 Save your current changes to the Repository.
6.5.7 Create an Environment
Environments include the external systems, Logical Hosts, Integration Servers and
Message Servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these
components. Environments are created using the Enterprise Designer’s Environment
Editor.
Steps required to create an Environment:
1 From the Enterprise Designer’s Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment
Explorer tab.
2 Right-click the Repository and select New Environment. A new Environment is
added to the Environment Explorer tree.
3 Rename the new Environment to envBAPIOutbound.
4 Right-click envBAPIOutbound and select New SAP BAPI External System. Name
the External System esBAPIExt. Click OK. esBAPIExt is added to the Environment
Editor.
5 Right-click envBAPIOutbound and select New File External System. Name the
External System esFileExt. Click OK. esFileExt is added to the Environment Editor.
6 Right-click envBAPIOutbound and select New Logical Host. The LogicalHost1
box is added to the Environment Editor tree. Rename the Logical Host
lhBAPIOutbound.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 86 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 87

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
7 Right-click lhBAPIOutbound and select New Integration Server. A new
Integration Server (IntegrationSvr1) is added to the Environment Explorer tree
under lhBAPIOutbound. Rename the Integration Server isBAPIOutbound.
8 Right-click lhBAPIOutbound and select Sun SeeBeyond JMS IQ Manager. A new
SBJMSIQMgr1 gets added to the Environment Explorer tree under
lhBAPIOutbound.
A screen shot of the Environment components is seen in Figure 61.
Figure 61 Environment Editor - envBAPIOutbound
9 Save your current changes to the Repository.
6.5.8 Configure the eWays
eWays facilitate communication and movement of data between the external
applications and the eGate system. The Connectivity Map in the sample Project uses
three eWays, represented as nodes between the External Applications and the Business
Process, as seen in Figure 62.
You must configure eWay properties in both the Connectivity Map and the
Environment Explorer.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 87 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 88

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 62 eWays in the cmDelete Connectivity Map
Inbound File eWay
Outbound File eWay
Outbound SAP BAPI eWay
Configure the eWay Properties in the Connectivity Map
The prjBAPIOutbound sample Project requires outbound eWay properties.
Steps required to configure the Inbound File eWay properties:
1 Double-click the eaFileIn eWay and modify the following property for your
system:
Parameter Settings > Input File Name: input*.txt
2 Click OK to save your changes and close the window.
Steps required to configure the Outbound File eWay properties:
1 Double-click the eaFileOut eWay and modify the following property for your
system:
Parameter Settings > Output File Name: outputFlight%d.dat
2 Click OK to save your changes and close the window.
Steps required to configure the Outbound SAP BAPI eWay properties:
1 Double-click the eaSAPBAP eWay and modify the following properties for your
system under Client Connection Settings:
Table 11 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Name Required Value
Client Connection Mode Automatic.
Enable RFC Trace No
RFC Trace Level 0
Transaction Mode NON-TRANSACTIONAL.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 88 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 89

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Table 11 Outbound eWay—Client Connection Settings
Name Required Value
Transaction ID Verification
Database
Maximum TID Database
Rows
Enable ABAP Debug Window No
Use Load Balancing No
C:\JavaCAPS\data\SapTRFC.TIDdb
200
2 Click OK to save your changes and close the window.
Note: For additional information on these properties, see Configuring the Outbound
eWay Properties on page 27.
Configure the File eWay External Environment Properties
The prjBAPIOutbound sample Project requires outbound File eWay Environment
properties.
Steps required to configure the outbound SAP BAPI eWay Environment properties:
1 Expand the envBAPIOutbound Environment in the Environment Explorer.
2 Right-click esFileExt and select Properties. The Properties window appears.
3 Click Outbound File eWay > Parameter Settings and modify the following
properties:
Directory: C:/temp
Configure the SAP BAPI eWay External Environment Properties
The prjBAPIOutbound sample Project requires outbound eWay Environment
properties.
Steps required to configure the outbound SAP BAPI eWay Environment properties:
1 Expand the envBAPIOutbound Environment in the Environment Explorer.
2 Right-click esBAPIExt and select Properties. The Properties window appears.
3 Click Client Configuration Settings under Outbound SAP BAPI eWay and
modify the following properties:
Table 12 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay— Client Connection Settings
Name Required Value
Application Server Hostname Any valid Hostname.
There is no default setting.
System Number Any numeric value.
There is no default setting.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 89 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 90

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Table 12 Outbound SAP BAPI eWay— Client Connection Settings
Name Required Value
Client Number An alphanumeric string. Do not
omit leading zeros.
There is no default setting.
User Any alphanumeric value.
There is no default setting.
Password An alphanumeric string.
There is no default setting.
Language There are no required values.
EN – English
DE – German
JA – Japanese
KO – Korean
The default is EN, English.
System ID Any valid Hostname.
There is no default setting.
Note: For additional information on these properties, see Outbound SAP BAPI eWay
on page 35.
6.5.9 Create the Deployment Profile
A Deployment Profile is used to assign services and message destinations to both the
Integration Server and the Message Server. Deployment profiles are created using the
Deployment Editor.
Steps required to create the Deployment Profile:
1 From the Enterprise Explorer’s Project Explorer, right-click the prjBAPIOutbound
Project and select New > Deployment Profile.
2 Enter a name for the Deployment Profile (for this sample dpSAPBAPI). Select
envBAPIOutbound as the Environment and click OK.
3 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Automap icon. The Project’s
components are automatically mapped to their system windows, as seen in Figure
63.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 90 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 91

Chapter 6 Section 6.5
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjBAPIOutbound Sample Project
Figure 63 Deployment Profile
6.5.10 Create and Start the Domain
To build and deploy your Project, you must first create a domain. A domain is an
instance of a Logical Host. After the domain is created, the Project is built and then
deployed.
Note: You are only required to create a domain once when you install the Java Composite
Application Platform Suite.
Steps required to create and start the domain:
1 Navigate to your <JavaCAPS51>\logicalhost directory (where <JavaCAPS51> is
the location of your Java Composite Application Suite installation.
2 Double-click the domainmgr.bat file. The Domain Manager appears.
3 If you have already created a domain, select your domain in the Domain Manager
and click the Start an Existing Domain button. Once your domain is started, a
green check mark indicates that the domain is running.
4 If there are no existing domains, a dialog box indicates that you can create a domain
now. Click Yes. The Create Domain dialog box appears.
5 Make any necessary changes to the Create Domain dialog box and click Create. The
new domain is added to the Domain Manager. Select the domain and click the Start
an Existing Domain button. Once your domain is started, a green check mark
indicates that the domain is running.
For more information about creating and managing domains see the eGate Integrator
System Administration Guide.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 91 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 92

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
6.5.11 Build and Deploy the Project
The Build process compiles and validates the Project’s Java files and creates the Project
EAR file.
Build the Project
1 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Build icon.
2 If there are any validation errors, a Validation Errors pane will appear at the
bottom of the Deployment Editor and displays information regarding the errors.
Make any necessary corrections, save and then click Build again.
3 After the Build has succeeded you are ready to deploy your Project.
Deploy the Project
1 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Deploy icon. Click Yes when the
Deploy prompt appears.
2 A message appears when the project is successfully deployed. You can now test
your sample.
3 You can also deploy applications using Enterprise Manager. For more information,
see the Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator System Administration Guide.
6.5.12 Run the Sample Project
Additional steps are required to run the deployed sample Project.
Steps required to run the sample Project:
1 Use the inputBAPIFlightGetList.txt trigger file included in the sample Project to
execute the SAP BAPI function module.
The File eWay polls the directory for the input file name (as defined in the Inbound
File eWay Properties window). The Business process then uses a Java Collaboration
to acquire a list of flight information from the designated carrier. The resulting
information is then saved to an output file outputFlight%d.dat.
2 Verify the output data by viewing the sample output files.
6.6 Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample
Project
The following sections provide instruction on how to manually create the sample
Project.You must have SAP ALE installed to run this sample Project.
This sample Project shows how to use the IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS RFC
OTD to receive IDocs from SAP R/3 in a generic manner. It then checks for the message
type of the received IDoc and then unmarshals it to the appropriate OTD. The IDoc
data is then passed onto the respective JCDs for further processing.
Steps required to create the sample project include:
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 92 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 93

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
Create a Project on page 93
Create the OTDs on page 93
Create the Java Collaboration Definitions on page 95
Create the Business Process on page 100
Create a Connectivity Map on page 106
Bind the eWay Components on page 108
Create an Environment on page 109
Configure the eWays on page 110
Create the Deployment Profile on page 113
Create and Start the Domain on page 114
Build and Deploy the Project on page 115
Run the Sample on page 115
6.6.1 Create a Project
The first step is to create a new Project in the Enterprise Designer.
1 Start the Enterprise Designer.
2 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the Repository and select New Project. A
new Project (Project1) appears on the Project Explorer tree.
3 Click twice on Project1 and rename the Project (for this sample, prjIDocInbound).
6.6.2 Create the OTDs
The sample Project requires three OTDs to interact with the SAP BAPI eWay. These
OTDs include:
RFC_IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS—The RFC OTD that is used to
receive or send IDocs to SAP R/3.
IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A—An IDoc OTD that is used to manipulate / manage
CREAMAS IDoc data.
IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C—An IDoc OTD that is used to manipulate / manage
MATMAS IDoc data.
Additional information on creating OTDs is found at Creating SAP BAPI OTDs on
page 39.
Steps required to create the IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
2 Select SAP BAPI from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Select the RFC radio button for the type of object you want to convert, and click
Next.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 93 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 94

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
4 Specify the SAP R/3 login parameters for your system, and click Next.
5 select IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS from the list of RFCs to retrieve, and
then click Finish.
6 The IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS OTD is added to the Enterprise
Explorer.
Steps required to create the IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
2 Select SAP IDoc from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Select the From SAP Directly radio button and click Next.
4 Enter the system parameters for the SAP R/3 system and click Next.
5 Enter the SAP R/3 system login parameters and click Next.
6 Select the following IDoc parameters for the SAP Metadata:
System Release: 4.6C
IDoc Type: CREAMAS03
Click the List IDocs button to display the IDoc Type List window. Scroll down to
select the CREAMAS03 IDoc type (Vendor master data distribution)
7 Click Next to review your selections. To close this wizard and create the OTD, click
Finish.
Steps required to create the IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
2 Select SAP IDoc from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Select the From SAP Directly radio button and click Next.
4 Enter the system parameters for the SAP R/3 system and click Next.
5 Enter the SAP R/3 system login parameters and click Next.
6 Select the following IDoc parameters for the SAP Metadata:
System Release: 4.6C
IDoc Type: MATMAS04
Click the List IDocs button to display the IDoc Type List window. Scroll down to
select the MATMAS04 IDoc type (Material Master).
7 Click Next to review your selections. To close this wizard and create the OTD, click
Finish.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 94 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 95

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
6.6.3 Create the Java Collaboration Definitions
The next step is to create the Java Collaboration Definitions or JCDs using the
Collaboration Definition Wizard (Java). Once you create the Collaboration Definition,
you can write the Business Rules using the Collaboration Editor.
The prjIDocInbound sample Project requires two JCDs:
jcdProcessCREMAS—used to handle vendor information (Vendor master data
distribution)
jcdProcessMATMAS—used to handle materials (Material Master)
Steps required to create the jcdProcessCREMAS Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdProcessCREMAS).
3 Under Web Service Type, select New: Create a new Web Service operation, and
then click Next.
4 Enter a new Operation name. In this example enter inputCREMAS.
5 Select the input message by selecting prjIDocInbound >
IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A, then click Next.
6 Select the output message by selecting prjIDocInbound >
IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A, then click Next.
7 Select the OTDs used in this Collaboration by selecting Sun SeeBeyond > eWays >
File > FileClient.
8 Click Finish, the jcdProcessCREMAS Collaboration is created.
Figure 64 jcdProcessCREMAS
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 95 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 96

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
Creating the Collaboration Business Rules
The following steps demonstrate how the business rules for the jcdProcessCREMAS
Collaboration.
1 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon. Next, right-click input
(located under jcdProcessCREMAS), and choose Select method to call... from the list
of available options. Select the marshal() method from the list of available methods.
the marshal method appears in the Business Rules Designer window.
2 Connect result(byte[]) to byteArray under jcdProcessCREMAS > FileClient_1.
Figure 65 jcdProcessCREMAS Business Rule
3 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon. Next, right-click FileClient_1
(located under jcdProcessCREMAS), and choose Select method to call... from the list
of available options. Select the writeBytes() method.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 96 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 97

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
Figure 66 jcdProcessCREMAS Business Rule
4 The resulting Collaboration displays the following code:
package prjIDocInbound;
public class jcdProcessCREMAS
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void inputCREMAS( com.stc.sapale.iDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A.IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A input,
com.stc.sapale.iDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A.IDOC_CREMAS03_4X_46A output,
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setByteArray( input.marshal() );
FileClient_1.writeBytes();
}
}
Steps required to create the jcdProcessMATMAS Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdProcessMATMAS).
3 Under Web Service Type, select New: Create a new Web Service operation, and
then click Next.
4 Enter a new Operation name. In this example enter inputMATMAS.
5 Select the input message by selecting prjIDocInbound >
IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C, then click Next.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 97 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 98

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
6 Select the output message by selecting prjIDocInbound >
IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C, then click Next.
7 Select the OTDs used in this Collaboration by selecting Sun SeeBeyond > eWays >
File > FileClient.
8 Click Finish, the jcdProcessMATMAS Collaboration is created.
Figure 67 jcdProcessMATMAS
Creating the Collaboration Business Rules
The following steps demonstrate how the business rules for the jcdProcessMATMAS
Collaboration.
1 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon. Next, right-click input
(located under jcdProcessMATMAS), and choose Select method to call... from the
list of available options. Select the marshal() method from the list of available
methods. the marshal method appears in the Business Rules Designer window.
2 Connect result(byte[]) to byteArray under jcdProcessMATMAS > FileClient_1.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 98 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 99

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
Figure 68 jcdProcessMATMAS Business Rule
3 From the Business Rules toolbar, select the Rule icon. Next, right-click FileClient_1
(located under jcdProcessMATMAS), and choose Select method to call... from the
list of available options. Select the writeBytes() method.
Figure 69 jcdProcessMATMAS Business Rule
4 The resulting Collaboration displays the following code:
package prjIDocInbound;
public class jcdProcessMATMAS
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 99 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 100

Chapter 6 Section 6.6
Reviewing the Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjIDocInbound Sample Project
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void inputMATMAS( com.stc.sapale.iDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C.IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C input,
com.stc.sapale.iDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C.IDOC_MATMAS04_4X_46C output,
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setByteArray( input.marshal() );
FileClient_1.writeBytes();
}
}
6.6.4 Create the Business Process
The next step in the sample is to create the bpIDocInbound eInsight Business Process
in which the business rules are defined.
Steps required to create the Business Process include:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Business Process from the shortcut menu. The eInsight Business
Process Designer appears and BusinessProcess1 is added to the Project Explorer
tree. Rename BusinessProcess1 to bpIDocInbound.
2 Drag a IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUSReceive operation, located under
the RFC_IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS OTD to the Business Process
canvas. The following two Activities are created:
RFC_IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS.IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRON
OUSReceive.Receive
RFC_IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRONOUS.IDOC_INBOUND_ASYNCHRON
OUSReceive.Reply
Figure 70 bpIDocInbound Business Rule
3 From the Business Process toolbar, click the Branching Activities icon and drag a
Decision from the drop-down list.
eWay™ Adapter for SAP BAPI User’s Guide 100 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...