Page 1

SUN SEEBEYOND
eWAY™ ADAPTER FOR VSAM
USER’S GUIDE
Release 5.1.3
Page 2

Copyright © 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc., 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, California 95054, U.S.A. All rights reserved. Sun
Microsystems, Inc. has intellectual property rights relating to technology embodied in the product that is described in this
document. In particular, and without limitation, these intellectual property rights may include one or more of the U.S. patents
listed at http://www.sun.com/patents and one or more additional patents or pending patent applications in the U.S. and in
other countries. U.S. Government Rights - Commercial software. Government users are subject to the Sun Microsystems, Inc.
standard license agreement and applicable provisions of the FAR and its supplements. Use is subject to license terms. This
distribution may include materials developed by third parties. Sun, Sun Microsystems, the Sun logo, Java, Sun Java Composite
Application Platform Suite, SeeBeyond, eGate, eInsight, eVision, eTL, eXchange, eView, eIndex, eBAM, eWay, and JMS are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. All SPARC trademarks are used
under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries.
Products bearing SPARC trademarks are based upon architecture developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc. UNIX is a registered
trademark in the U.S. and other countries, exclusively licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd. This product is covered and
controlled by U.S. Export Control laws and may be subject to the export or import laws in other countries. Nuclear, missile,
chemical biological weapons or nuclear maritime end uses or end users, whether direct or indirect, are strictly prohibited.
Export or reexport to countries subject to U.S. embargo or to entities identified on U.S. export exclusion lists, including, but
not limited to, the denied persons and specially designated nationals lists is strictly prohibited.
Copyright © 2007 Sun Microsystems, Inc., 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, California 95054, Etats-Unis. Tous droits réservés.
Sun Microsystems, Inc. détient les droits de propriété intellectuels relatifs à la technologie incorporée dans le produit qui est
décrit dans ce document. En particulier, et ce sans limitation, ces droits de propriété intellectuels peuvent inclure un ou plus
des brevets américains listés à l'adresse http://www.sun.com/patents et un ou les brevets supplémentaires ou les
applications de brevet en attente aux Etats - Unis et dans les autres pays. L'utilisation est soumise aux termes de la Licence.
Cette distribution peut comprendre des composants développés par des tierces parties. Sun, Sun Microsystems, le logo Sun,
Java, Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite, Sun, SeeBeyond, eGate, eInsight, eVision, eTL, eXchange, eView, eIndex,
eBAM et eWay sont des marques de fabrique ou des marques déposées de Sun Microsystems, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans
d'autres pays. Toutes les marques SPARC sont utilisées sous licence et sont des marques de fabrique ou des marques déposées
de SPARC International, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans d'autres pays. Les produits portant les marques SPARC sont basés sur une
architecture développée par Sun Microsystems, Inc. UNIX est une marque déposée aux Etats-Unis et dans d'autres pays et
licenciée exclusivement par X/Open Company, Ltd. Ce produit est couvert à la législation américaine en matière de contrôle
des exportations et peut être soumis à la règlementation en vigueur dans d'autres pays dans le domaine des exportations et
importations. Les utilisations, ou utilisateurs finaux, pour des armes nucléaires, des missiles, des armes biologiques et
chimiques ou du nucléaire maritime, directement ou indirectement, sont strictement interdites. Les exportations ou
réexportations vers les pays sous embargo américain, ou vers des entités figurant sur les listes d'exclusion d'exportation
américaines, y compris, mais de manière non exhaustive, la liste de personnes qui font objet d'un ordre de ne pas participer,
d'une façon directe ou indirecte, aux exportations des produits ou des services qui sont régis par la législation américaine en
matière de contrôle des exportations et la liste de ressortissants spécifiquement désignés, sont rigoureusement interdites.
Part Number: 820-0978
Version 20070424231148
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 2 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Chapter 1
Introducing the VSAM eWay 7
About VSAM 7
About the VSAM eWay 8
eWay Operation 8
What’s New in This Release 8
About This Document 9
VSAM eWay Javadoc 9
Scope 10
Intended Audience 10
Text Conventions 10
Related Documents 10
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site 11
Documentation Feedback 11
Chapter 2
Installing the VSAM eWay 12
Installing the VSAM eWay 12
Installing the VSAM eWay on an eGate supported system 13
Adding the eWay to an Existing Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation
13
Copying JAR files to the eDesigner Library 14
Installing Third-Party Products 14
After Installation 14
Extracting the Sample Projects and Javadocs 14
ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures 15
Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins 16
Viewing Alert Codes 17
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 3 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 3
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay 20
Creating and Configuring a VSAM eWay 20
Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties 20
Transaction Support Levels Between Different Versions 22
Configuring the eWay Environment Properties 23
eWay Connectivity Map Properties 24
Connectivity Map (Outbound) CP eWay Properties 25
Connectivity Map Outbound non-Transactional eWay Properties 25
eWay Environment Properties 26
Inbound VSAM eWay Properties 26
(Outbound) VSAM CP eWay Properties 26
JDBC Connector Settings 27
Connection Retry Settings 29
Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay Properties 30
JDBC Connector Settings 30
Connection Retry Settings 32
Chapter 4
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard 34
About the Database OTD Wizard 34
Creating a New VSAM OTD 34
Select Wizard Type 35
Connect To Database 35
Select Database Objects 36
Select Tables/Views/Aliases 37
Add Prepared Statement 41
Specify the OTD Name 44
Review Selections 45
Resulting OTD 46
Steps to Edit an Existing VSAM OTD 47
Chapter 5
Using VSAM OTDs 49
Overview 49
Using Tables 49
Using the select Method 50
Select Operations 51
Insert Operations 51
Update Operations 51
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 4 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 5

Contents
Delete Operations 51
Using Views 52
Using Prepared Statements 52
Chapter 6
Using VSAM Operations 53
VSAM eWay Database Operations (BPEL) 53
Activity Input and Output 53
VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD) 55
The Table 55
The Query (Select) Operation 56
The Insert Operation 57
The Update Operation 58
The Delete Operation 58
Prepared Statement 59
Batch Operations 59
Chapter 7
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects 61
About the VSAM eWay Sample Projects 61
Operations Used in the VSAM Sample Projects 62
Assigning Operations in JCD 63
Assigning Operations in BPEL 63
About the eInsight Engine and eGate Components 63
Running the Sample Projects 64
Running the SQL Script 64
Importing a Sample Project 65
Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project 65
Creating a Project 66
Creating the OTDs 66
Creating the Business Process 67
Creating the Business Process Flow 67
Configuring the bpInsert Modeling Elements 68
Configuring the bpUpdate Modeling Elements 72
Configuring the bpDelete Modeling Elements 74
Configuring the bpTableSelect Modeling Elements 76
Configuring the bpPsSelect Modeling Elements 79
Creating the Connectivity Map 83
Populating the Connectivity Map 83
Binding the eWay Components 84
Creating an Environment 85
Configuring the eWays 86
Configuring the eWay Properties 87
Configuring the Environment Explorer Properties 88
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 5 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 6

Contents
Configuring the Integration Server 89
Creating the Deployment Profile 89
Creating and Starting the Domain 90
Building and Deploying the Project 91
Running the Sample Project 91
Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project 92
Creating a Project 92
Creating the OTDs 92
Creating a Connectivity Map 94
Populating the Connectivity Map 94
Creating the Collaboration Definitions (Java) 95
jcdDelete Collaboration 96
jcdInsert Collaboration 96
jcdPsSelect Collaboration 97
jcdTableSelect Collaboration 97
jcdUpdate Collaboration 98
Create the Collaboration Business Rules 98
Creating the jcdDelete Business Rules 98
Creating the jcdInsert Business Rules 99
Creating the jcdPsSelect Business Rules 100
Creating the jcdTableSelect Business Rules 102
Creating the jcdUpdate Business Rules 104
Binding the eWay Components 105
Creating an Environment 106
Configuring the eWays 107
Configuring the eWay Properties 108
Configuring the Environment Explorer Properties 109
Configuring the Integration Server 110
Creating the Deployment Profile 110
Creating and Starting the Domain 111
Building and Deploying the Project 112
Running the Sample 112
Index 114
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 6 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 7

Introducing the VSAM eWay
Welcome to the Sun SeeBeyond eWay™ Adapter for VSAM User’s Guide. This document
includes information about installing, configuring, and using the Sun Java Composite
Application Platform Suite VSAM eWay™ Adapter, referred to as the VSAM eWay
throughout this guide.
This chapter provides a brief overview of operations, components, general features,
and system requirements of the VSAM eWay.
What’s in This Chapter
About VSAM on page 7
About the VSAM eWay on page 8
What’s New in This Release on page 8
About This Document on page 9
Related Documents on page 10
Chapter 1
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site on page 11
Documentation Feedback on page 11
1.1 About VSAM
Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) is one of several access methods that defines
the technique by which data is stored and retrieved. It is a GET/PUT interface used to
transfer data from a direct-access storage device (DASD) to an application program.
VSAM does not support data stored on tape.
VSAM stores data as a collection of data sets. IBM uses a collection of three data-set
organizations—sequential, indexed, and direct-access, together with the access
methods and utilities used on mainframe operating systems.
VSAM data sets must be cataloged in an integrated catalog facility (ICF) structure.
Records are arranged by an index key or by relative-byte addressing. VSAM uses direct
or sequential processing of fixed and variable-length records stored on a DASD.
VSAM also provides the following features:
Allows you to organize and access data (record management).
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 7 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 8
Chapter 1 Section 1.2
Introducing the VSAM eWay About the VSAM eWay
Maintains information about this data, which is stored or referenced in a catalog
(catalog management).
Supports Entry-sequenced Data Set (ESDS) and Key-sequenced Data Set (KSDS)
files.
The VSAM eWay allows you to utilize and extend all of these features. For more
information on VSAM, see IBM’s Web site.
1.2 About the VSAM eWay
The VSAM eWay enables eGate™ Integrator to exchange data with external IBM VSAM
mainframe file systems. This eWay is similar to other database eWays, such as IAM,
ADABAS, and IDMS. The eWay uses its own properties settings and eGate components
to enable VSAM data integration.
1.2.1 eWay Operation
This eWay enables eGate to communicate with VSAM files on a mainframe host system
via TCP/IP. The eWay utilizes an IBM WebSphere Information Integrator Classic
Federatione component that allows you to view and access VSAM in the same way as
any standard relational database system.
For details on operating and using eGate and its user interface, the Enterprise Designer,
see the Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator User’s Guide.
1.3 What’s New in This Release
The Sun SeeBeyond eWay Adapter for VSAM includes the following changes and new
features:
New for Version 5.1.3
This is a maintenance release. No new features.
New for Version 5.1.2
This is a maintenance release. No new features.
New for Version 5.1.1
This is a maintenance release. No new features.
New for Version 5.1.0
Version Control: An enhanced version control system allows you to effectively
manage changes to the eWay components.
Multiple Drag-and-Drop Component Mapping from the Deployment Editor: The
Deployment Editor now allows you to select multiple components from the
Editor’s component pane, and drop them into your Environment component.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 8 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 9
Chapter 1 Section 1.4
Introducing the VSAM eWay About This Document
Support for Runtime LDAP Configuration: eWay configuration properties now
support LDAP key values.
Connection Retry Support: Allows you to specify the number of attempts to
reconnect, and the interval between retry attempts, in the event of a connection
failure.
Relaunchable OTD Support: An OTD can be rebuilt and saved (under the same
name) then relaunched back to the same Java Collaboration or BPEL. This allows
you to change the metadata in an OTD without having to completely recreate the
business logic from scratch.
Editable OTD Support: An existing OTD can be edited and saved using the OTD
Wizard. This allows you to make minor changes to an OTD without having to
completely recreate the OTD from scratch. The OTD is then rebuilt, saved, and then
relaunched back to the same Java Collaboration or BPEL.
Connectivity Map Generator: Generates and links your Project’s Connectivity Map
components using a Collaboration or Business Process.
Many of these features are documented further in the Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator
User’s Guide or the Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator System Administration Guide.
1.4 About This Document
This document includes the following chapters:
Chapter 1 “Introducing the VSAM eWay”: Provides an overview description of
the product as well as high-level information about this document.
Chapter 2 “Installing the VSAM eWay”: Describes the system requirements and
provides instructions for installing the VSAM eWay.
Chapter 3 “Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay”: Provides instructions for
configuring the eWay to communicate with your legacy systems.
Chapter 4 “Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard”: Provides information for
creating Object Type Definitions to be used with the VSAM eWay.
Chapter 5 “Using VSAM OTDs”: Describes operations you can perform using
VSAM Object Type Definitions (OTDs) in eGate.
Chapter 6 “Using VSAM Operations”: Provides instructions on using VSAM
database eWay operations in BPEL and JCD.
Chapter 7 “Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects”: Provides
instructions for installing and running the sample Projects.
VSAM eWay Javadoc
A VSAM eWay Javadoc is also provided that documents the Java methods available
with the VSAM eWay. The Javadoc is uploaded with the eWay’s documentation file
(VSAMeWayDocs.sar) and downloaded from the Documentation tab of the Sun Java
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 9 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 10
Chapter 1 Section 1.5
Introducing the VSAM eWay Related Documents
Composite Application Platform Suite Installer. To access the full Javadoc, extract the
Javadoc to an easily accessible folder, and double-click the index.html file.
1.4.1 Scope
This user’s guide provides a description of the VSAM eWay Adapter. It includes
directions for installing the eWay, configuring the eWay properties, and implementing
the eWay’s sample Projects. This document is also intended as a reference guide, listing
available properties, functions, and considerations. For a reference of available VSAM
eWay Java methods, see the associated Javadoc.
1.4.2 Intended Audience
This guide is intended for experienced computer users who have the responsibility of
helping to set up and maintain a fully functioning Java Composite Application
Platform Suite system. This person must also understand any operating systems on
which the Java Composite Application Platform Suite will be installed (Windows and
UNIX), and must be thoroughly familiar with Windows-style GUI operations.
1.4.3 Text Conventions
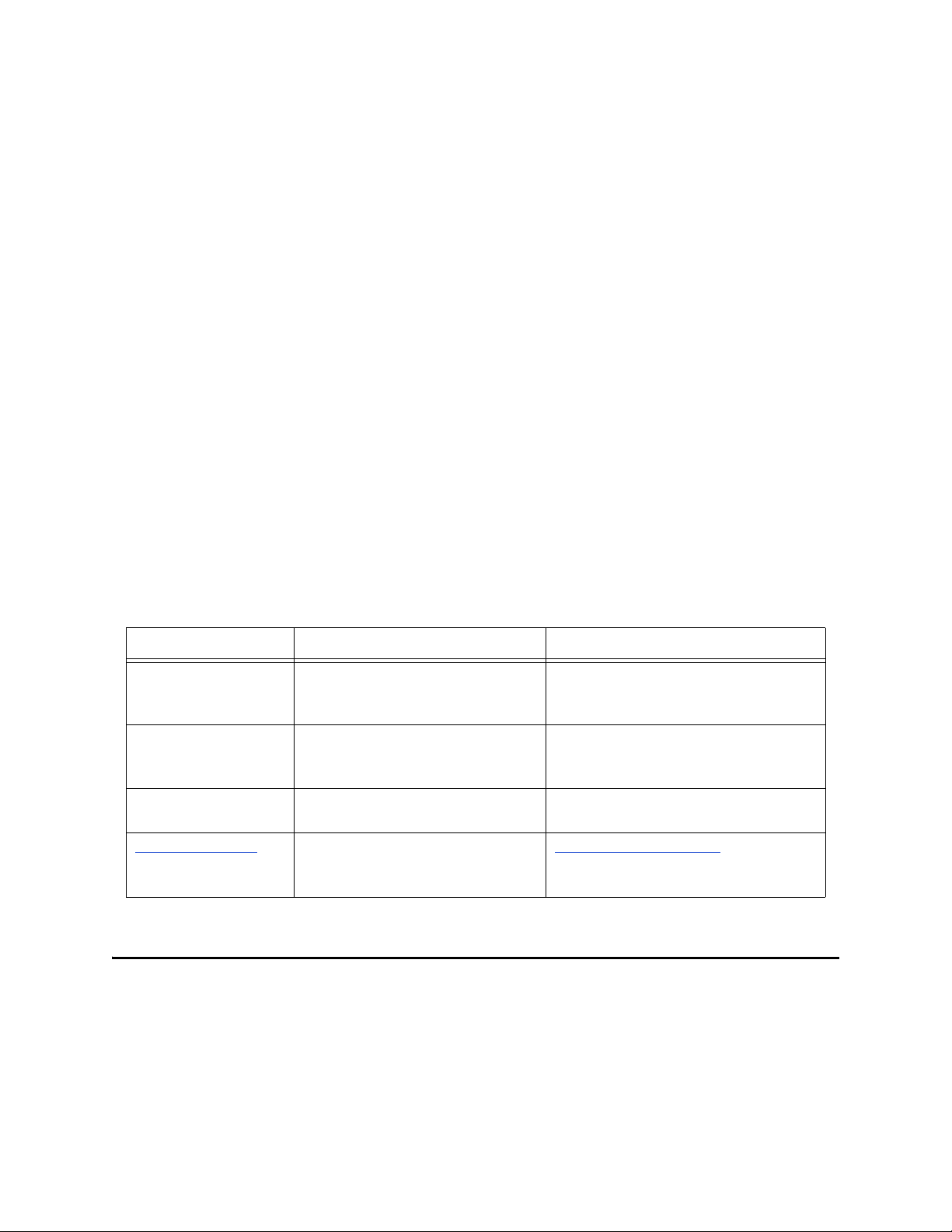
The following conventions are observed throughout this document.
Table 1 Text Conventions
Text Convention Used For Examples
Bold Names of buttons, files, icons,
parameters, variables, methods,
menus, and objects
Monospaced Command line arguments, code
samples; variables are shown in
bold italic
Blue bold
Blue underlined
1.5 Related Documents
Hypertext links within
document
Hypertext links for Web
addresses (URLs) or email
addresses
Click OK.
On the File menu, click Exit.
Select the eGate.sar file.
java -jar filename.jar
See
Text Conventions on page 10
http://www.sun.com
The following Sun documents provide additional information about the Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite product:
Sun SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator User’s Guide
Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation Guide
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 10 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 11

Chapter 1 Section 1.6
Introducing the VSAM eWay Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site
1.6 Sun Microsystems, Inc. Web Site
The Sun Microsystems web site is your best source for up-to-the-minute product news
and technical support information. The site’s URL is:
http://www.sun.com
1.7 Documentation Feedback
We appreciate your feedback. Please send any comments or suggestions regarding this
document to:
CAPS_docsfeedback@sun.com
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 11 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 12

Installing the VSAM eWay
This chapter explains how to install the VSAM eWay.
What’s in This Chapter
Installing the VSAM eWay on page 12
ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures on page 15
Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins on page 16
2.1 Installing the VSAM eWay
The Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer, referred to throughout this
guide as the Suite Installer, is a web-based application that is used to select and upload
core products, composite applications, and add-on files (eWays) during the installation
process. The following section describes how to install the components required for this
eWay.
Chapter 2
Refer to the readme for the latest information on:
Supported Operating Systems
System Requirements
External System Requirements
The VSAM eWay Readme is uploaded with the eWay’s documentation file
(VSAMeWayDocs.sar) and can be accessed from the Documentation tab of the Sun
Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer. Refer to the VSAM eWay Readme
for the latest requirements before installing the VSAM eWay.
Note: When the Repository is running on a UNIX operating system, the eWays are loaded
from the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer running on a
Windows platform connected to the Repository server using Internet Explorer.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 12 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 2 Section 2.1
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing the VSAM eWay
2.1.1 Installing the VSAM eWay on an eGate supported system
Follow the directions for installing the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite
in the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation Guide. After you have
installed Core Products, do the following:
1 From the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer’s Select Sun
Java Composite Application Suite Products to Install table (Administration tab),
click the Click to install additional products link.
2 Expand the eWay option.
3 Select the products for your Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite and
include the following:
File eWay (the File eWay is used by most sample Projects)
VSAMeWay
To upload the VSAM eWay User’s Guide, Help file, Javadoc, Readme, and sample
Projects, expand the Documentation option and select VSAMeWayDocs.
4 Once you have selected all of your products, click Next in the top-right or bottom-
right corner of the Select Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite
Products to Install box.
5 From the Selecting Files to Install box, locate and select your first product’s SAR
file. ONce you have selected the SAR file, click Next. Your next selected product
appears. Follow this procedure for each of your selected products. The Installation
Status window appears and installation begins after the last SAR file has been
selected.
6 Once your product’s installation is finished, continue installing the Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite as instructed in the Sun Java Composite
Application Platform Suite Installation Guide.
Adding the eWay to an Existing Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation
If you are adding the eWay to an existing Sun Java Composite Application Platform
Suite installation, do the following:
1 Complete steps 1 through 4 above.
2 Once your product’s installation is complete, open the Enterprise Designer and
select Update Center from the Tools menu. The Update Center Wizard appears.
3 For Step 1 of the wizard, simply click Next.
4 For Step 2 of the wizard, click the Add All button to move all installable files to the
Include in Install field, then click Next.
5 For Step 3 of the wizard, wait for the modules to download, then click Next.
6 The wizard’s Step 4 window displays the installed modules. Review the installed
modules and click Finish.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 13 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 14

Chapter 2 Section 2.1
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing the VSAM eWay
7 When prompted, restart the IDE (Integrated Development Environment) to
complete the installation.
Copying JAR files to the eDesigner Library
The VSAM eWay SAR file no longer includes the WebSphere Information Integrator
Classic Federation JDBC Driver for VSAM databases. You are required to copy the
product’s JDBC JAR file (cacjdbc30.jar) to the following location prior to running a
VSAM project:
<JavaCAPS51>\edesigner\lib\ext
where <JavaCAPS51> is the directory where the Sun Java Composite Application
Platform Suite is installed.
Note: If eDesigner is running, it must be restarted to pickup the new JAR file.
Installing Third-Party Products
In order to run the VSAM eWay you must also install the IBM WebSphere Information
Integrator Classic Federation. The product is no longer shipped with the VSAM eWay.
For complete details on how to install the Classic Federation, see the IBM WebSphere
Information Integrator Installation Guide for Classic Federation and Classic Event.
Important: When you install the Classic Federation, be sure to configure the properties for
VSAM. See the appropriate Federation documentation for details.
After Installation
Once you install the eWay, it must then be incorporated into a Project before it can
perform its intended functions. See the eGate Integrator User’s Guide for more
information on incorporating the eWay into an eGate Project.
2.1.2 Extracting the Sample Projects and Javadocs
The VSAM eWay includes sample Projects and Javadocs. The sample Projects are
designed to provide you with a basic understanding of how certain database
operations are performed using the eWay, while Javadocs provide a list of classes and
methods exposed in the eWay.
Steps to extract the Javadoc include:
1 Click the Documentation tab of the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite
Installer, then click the Add-ons tab.
2 Click the VSAM eWay Adapter link. Documentation for the VSAM eWay appears
in the right pane.
3 Click the icon next to Javadoc and extract the ZIP file.
4 Open the index.html file to view the Javadoc.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 14 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 15

Chapter 2 Section 2.2
Installing the VSAM eWay ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures
Steps to extract the Sample Projects include:
1 Click the Documentation tab of the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite
Installer, then click the Add-ons tab.
2 Click the VSAM eWay Adapter link. Documentation for the VSAM eWay appears
in the right pane.
3 Click the icon next to Sample Projects and extract the ZIP file. Note that the
VSAM_eWay_Sample.zip file contains two additional ZIP files for each sample
Project.
Refer to “Importing a Sample Project” on page 65 for instructions on importing the
sample Project into your repository via the Enterprise Designer.
2.2 ICAN 5.0 Project Migration Procedures
This section describes how to transfer your current ICAN 5.0.x Projects to the Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite 5.1.3. To migrate your ICAN 5.0.x Projects to the
Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite 5.1.3, do the following:
Export the Project
1 Before you export your Projects, save your current ICAN 5.0.x Projects to your
Repository.
2 From the Project Explorer, right-click your Project and select Export from the
shortcut menu. The Export Manager appears.
3 Select the Project that you want to export in the left pane of the Export Manager and
move it to the Selected Projects field by clicking the Add to Select Items (arrow)
button, or click All to include all of your Projects.
4 In the same manner, select the Environment that you want to export in the left pane
of the Export Manager and move it to the Selected Environments field by clicking
the Add to Select Items (arrow) button, or click All to include all of your
Environments.
5 Browse to select a destination for your Project ZIP file and enter a name for your
Project in the ZIP file field.
6 Click Export to create the Project ZIP file in the selected destination.
Install Java CAPS 5.1.3
1 Install Java CAPS 5.1.3, including all eWays, libraries, and other components used
by your ICAN 5.0 Projects.
2 Start the Java CAPS 5.1.3 Enterprise Designer.
Import the Project
1 From the Java CAPS 5.1.3 Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer tree, right-click the
Repository and select Import Project from the shortcut menu. The Import Manager
appears.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 15 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 16

Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
2 Browse to and select your exported Project file.
3 Click Import. A warning message, “Missing APIs from Target Repository,” may
appear at this time. This occurs because various product APIs were installed on the
ICAN 5.0 Repository when the Project was created, that are not installed on the Java
CAPS 5.1.3 Repository. These APIs may or may not apply to your Projects. You can
ignore this message if you have already installed all of the components that
correspond to your Projects. Click Continue to resume the Project import.
4 Close the Import Manager after the Project is successfully imported.
Deploy the Project
1 A new Deployment Profile must be created for each of your imported Projects.
When a Project is exported, the Project’s components are automatically “checked in”
to Version Control to write-protected each component. These protected components
appear in the Explorer tree with a red padlock in the bottom-left corner of each icon.
Before you can deploy the imported Project, the Project’s components must first be
“checked out” of Version Control from both the Project Explorer and the
Environment Explorer. To “check out” all of the Project’s components, do the
following:
A From the Project Explorer, right-click the Project and select Version Control >
Check Out from the shortcut menu. The Version Control - Check Out dialog box
appears.
B Select Recurse Project to specify all components, and click OK.
C Select the Environment Explorer tab, and from the Environment Explorer, right-
click the Project’s Environment and select Version Control > Check Out from
the shortcut menu.
D Select Recurse Environment to specify all components, and click OK.
2 If your imported Project includes File eWays, these must be reconfigured in your
Environment prior to deploying the Project.
To reconfigure your File eWays, do the following:
A From the Environment Explorer tree, right-click the File External System, and
select Properties from the shortcut menu. The Properties Editor appears.
B Set the inbound and outbound directory values, and click OK. The File External
System can now accommodate both inbound and outbound eWays.
3 Deploy your Projects.
Note: Only projects developed on ICAN 5.0.2 and later can be imported and migrated
successfully into the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite.
2.3 Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
The Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Manager is a Web-based interface you use to monitor
and manage your Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite applications. The
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 16 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 17

Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
Enterprise Manager requires an eWay specific “plug-in” for each eWay you install.
These plug-ins enable the Enterprise Manager to target specific alert codes for each
eWay type, as well as start and stop the inbound eWays.
The Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installation Guide describes how to
install Enterprise Manager. The Sun SeeBeyond eGate Integrator System Administration
Guide describes how to monitor servers, Services, logs, and alerts using the Enterprise
Manager and the command-line client.
The eWay Enterprise Manager Plug-ins are available from the List of Components to
Download under the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer’s
Downloads tab.
There are two ways to add eWay Enterprise Manager plug-ins:
From the Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Manager
From the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer
To add plug-ins from the Enterprise Manager
1 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click configuration.
2 Click the Web Applications Manager tab, go to the Auto-Install from Repository
sub-tab, and connect to your Repository.
3 Select the application plug-ins you require, and click Install. The application plug-
ins are installed and deployed.
To add plug-ins from the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer
1 From the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer’s Downloads
tab, select the Plug-Ins you require and save them to a temporary directory.
2 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click configuration.
3 Click the Web Applications Manager tab and go to the Manage Applications sub-
tab.
4 Browse for and select the WAR file for the application plug-in that you
downloaded, and click Deploy. The plug-ins is installed and deployed.
2.3.1 Viewing Alert Codes
You can view and delete alerts using the Enterprise Manager. An alert is triggered
when a specified condition occurs in a Project component. The purpose of the alert is to
warn the administrator or user that a condition has occurred.
To View the eWay Alert Codes
1 Add the eWay Enterprise Manager plug-in for this eWay.
2 From the Enterprise Manager’s Explorer toolbar, click configuration.
3 Click the Web Applications Manager tab and go to the Manage Alert Codes sub-
tab. Your installed eWay alert codes display under the Results section. If your eWay
alert codes are not displayed under Results, do the following:
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 17 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 18
Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
A From the Install New Alert Codes section, browse to and select the eWay alert
properties file for the application plug-in that you added. The alert properties
files are located in the alertcodes folder of your Sun Java Composite Application
Platform Suite installation directory.
B Click Deploy. The available alert codes for your application are displayed under
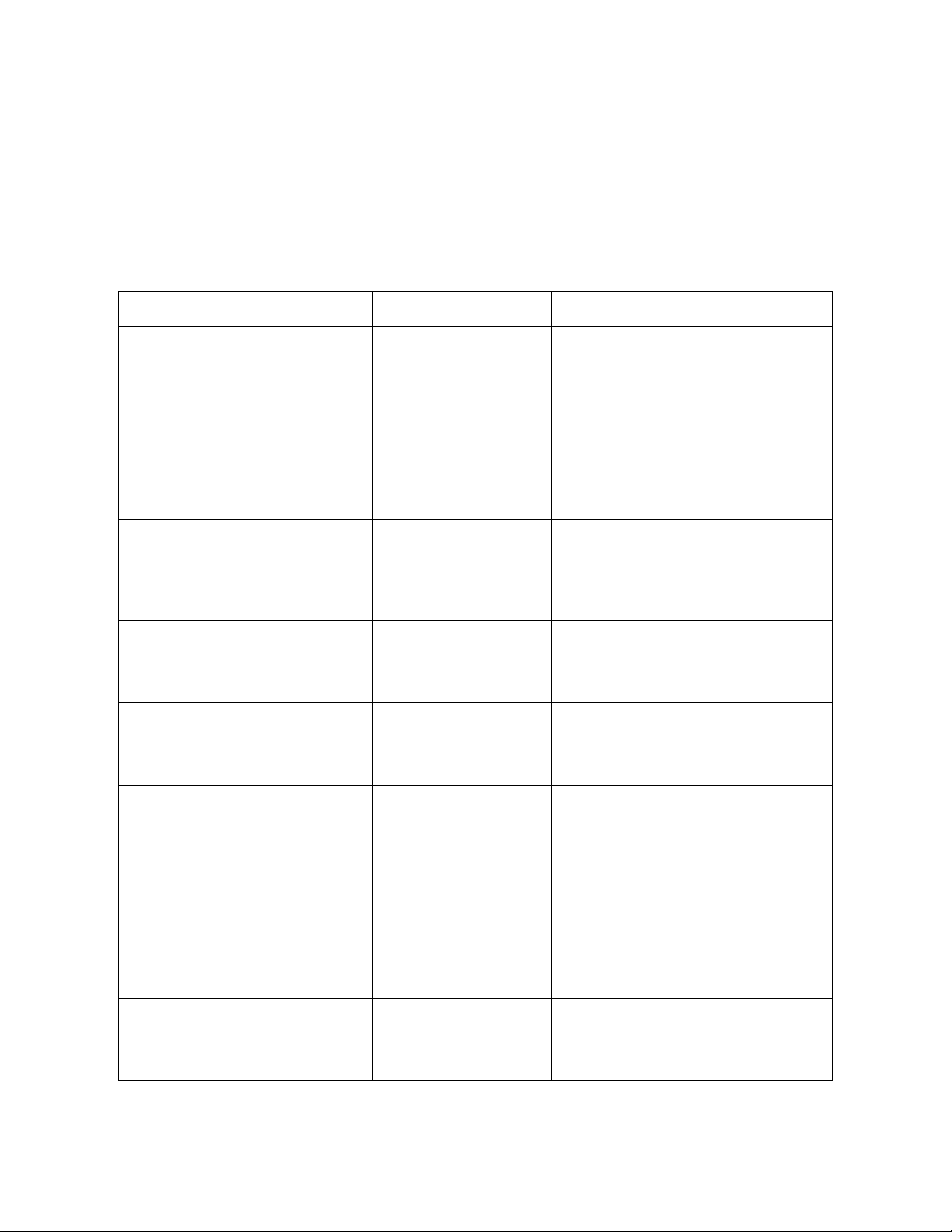
Results. A listing of the eWay’s available alert codes is displayed in Table 2.
Table 2 Alert Codes for the VSAM eWay
Alert Code\Description Description Details User Actions
DBCOMMON-CONNECTFAILED000001=Failed to connect
to database {0} on host {1}.
Reason: The Pooled connection
could not be allocated: [{2}]
DBCOMMON-CONNECTFAILED000002=Operation failed
because of a database
connection error. Reason: [{0}]
DBCOMMON-CONNECTFAILED000005=Connection
handle not usable. Reason:[{0}]
DBCOMMON-XARESOURCEFAILED000001=Unable to get
XAResource for the database.
Reason: [{0}]
Occurs during the
initial database
connection
establishment.
Occurs while
retrieving a
connection from the
database or the
connection pool.
The connection in the
pool is stale and is not
usable.
Could not obtain
XAResource for the
connection.
Database is down; start your
database.
External configuration
information is invalid. You may
need to verify the following:
Server name
Database name
User
Password
Port
Verify that the database has not
terminated with unexpected
errors.
Probably a database restart
occurred causing the connection
to be stale, retry the operation
after the database is up.
Check if the database supports XA
and has been configured for
Distributed Transaction Support.
DBCOMMON-XACONNECTFAILED000001=Failed to connect
to database {0} on host {1}. The
XA connection could not be
allocated: Reason [{2}]
DBCOMMON-XASTARTFAILED000001=Unable to
perform XAStart for the
connection. Reason: [{0}]
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 18 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Occurs during the
initial database
connection
establishment.
A connection error
has occurred which
caused XASTART to
fail.
Check if the database is
configured for XA and if the
database is running.
External configuration
information is invalid. You may
need to verify the following:
Server name
Database name
User
Password
Port
Check if the database is running,
and there are no network issues.
Page 19
Chapter 2 Section 2.3
Installing the VSAM eWay Installing Enterprise Manager eWay Plug-Ins
Alert Code\Description Description Details User Actions
DBCOMMON-XAENDFAILED000001=XAEnd failed.
Reason: [{0}]
DBCOMMON-CANNOT-GETISOLATION-LEVEL=Unable to
get isolationLevel for the
transaction. Reason: [{0}]
For information on Managing and Monitoring alert codes and logs, as well as how to
view the alert generated by the project component during runtime, see the Sun
SeeBeyond eGate™ Integrator System Administration Guide.
Error occurred during
commit on XA
connection.
Could not read
transaction isolation
information of the
connection.
Look for the detailed error
mentioned in the alert for the
appropriate action.
Transaction isolation is one of the
following constants:
Connection.TRANSACTION_RE
AD_UNCOMMITTED
Connection.TRANSACTION_RE
AD_COMMITTED
Connection.TRANSACTION_RE
PEATABLE_READ
Connection.TRANSACTION_SE
RIALIZABLE
Connection.TRANSACTION_N
ONE
Note: Confirm with the
vendor that the getIsolation()
method of the connection is
implemented correctly.
Note: An alert code is a warning that an error has occurred. It is not a diagnostic. The user
actions noted above are just some possible corrective measures you may take. Refer
to the log files for more information. For information on Managing and Monitoring
alert codes and logs, see the Sun SeeBeyond eGate Integrator System
Administration Guide.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 19 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 20

Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay
This chapter explains how to set the properties of the VSAM eWay.
What’s in This Chapter
Creating and Configuring a VSAM eWay on page 20
Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties on page 20
Configuring the eWay Environment Properties on page 23
eWay Connectivity Map Properties on page 24
eWay Environment Properties on page 26
3.1 Creating and Configuring a VSAM eWay
All eWays contain a unique set of default configuration parameters. After the eWays are
established and a VSAM External System is created in the Project’s Environment, the
eWay parameters are modified for your specific system. The VSAM eWay configuration
parameters are modified from two locations:
Chapter 3
Connectivity Map: These parameters most commonly apply to a specific
component eWay, and may vary from other eWays (of the same type) in the Project.
Environment Explorer : These parameters are commonly global, applying to all
eWays (of the same type) in the Project. The saved properties are shared by all
eWays in the VSAM External System window.
Collaboration or Business Process: VSAM eWay properties may also be set from
your Collaboration or Business Process, in which case the settings will override the
corresponding properties in the eWay’s Connectivity Map configuration. Any
properties that are not overridden retain their configured default settings.
3.2 Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties
When you connect an External Application to a Collaboration, Enterprise Designer
automatically assigns the appropriate eWay to the link. Each eWay is supplied with a
list of eWay connections (transaction support levels) from which to choose.
Transaction support levels provided by the VSAM eWay include:
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 20 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 21
Chapter 3 Section 3.2
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties
VSAM CP eWay
Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay
To configure the eWay properties:
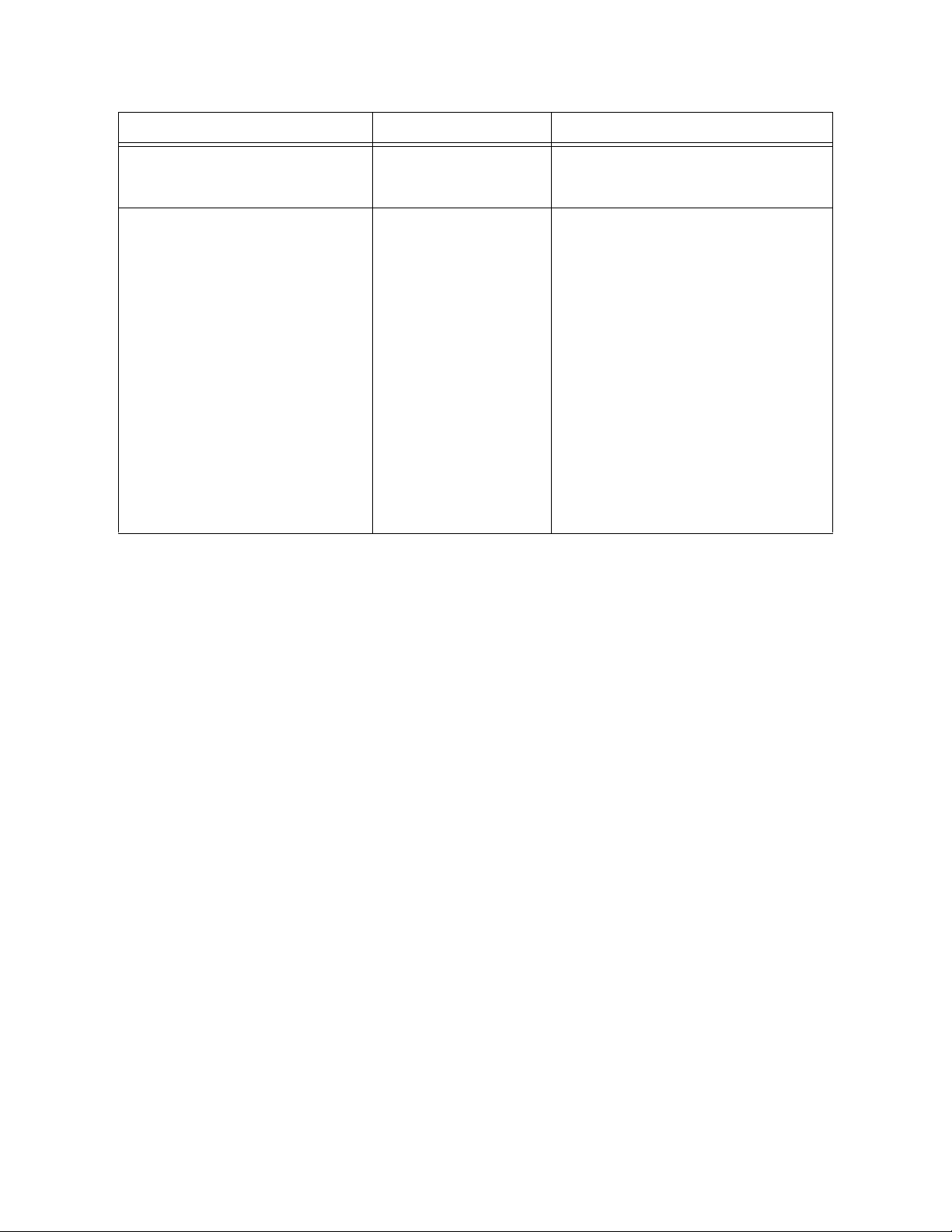
1 On the Enterprise Designer’s Connectivity Map, double-click the VSAM eWay icon.
The eWay Connections window appears.
Figure 1 Connectivity Map with Components
VSAM eWay
2 Select a parameter from the list and click OK.
Figure 2 Template window
The choices to make are as follows:
VSAM CP eWay: Also referred to as LocalTransaction, this support level is
opposite to NoTransaction, and this means that the transaction, when The
Properties window opens, displaying the default properties for the eWay.
Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay: Also referred to as NoTransaction,
this support level indicates that the Collaboration does not support transactions.
This means that when a transaction aborts, there is no ability to roll back any
changes to the previous update.
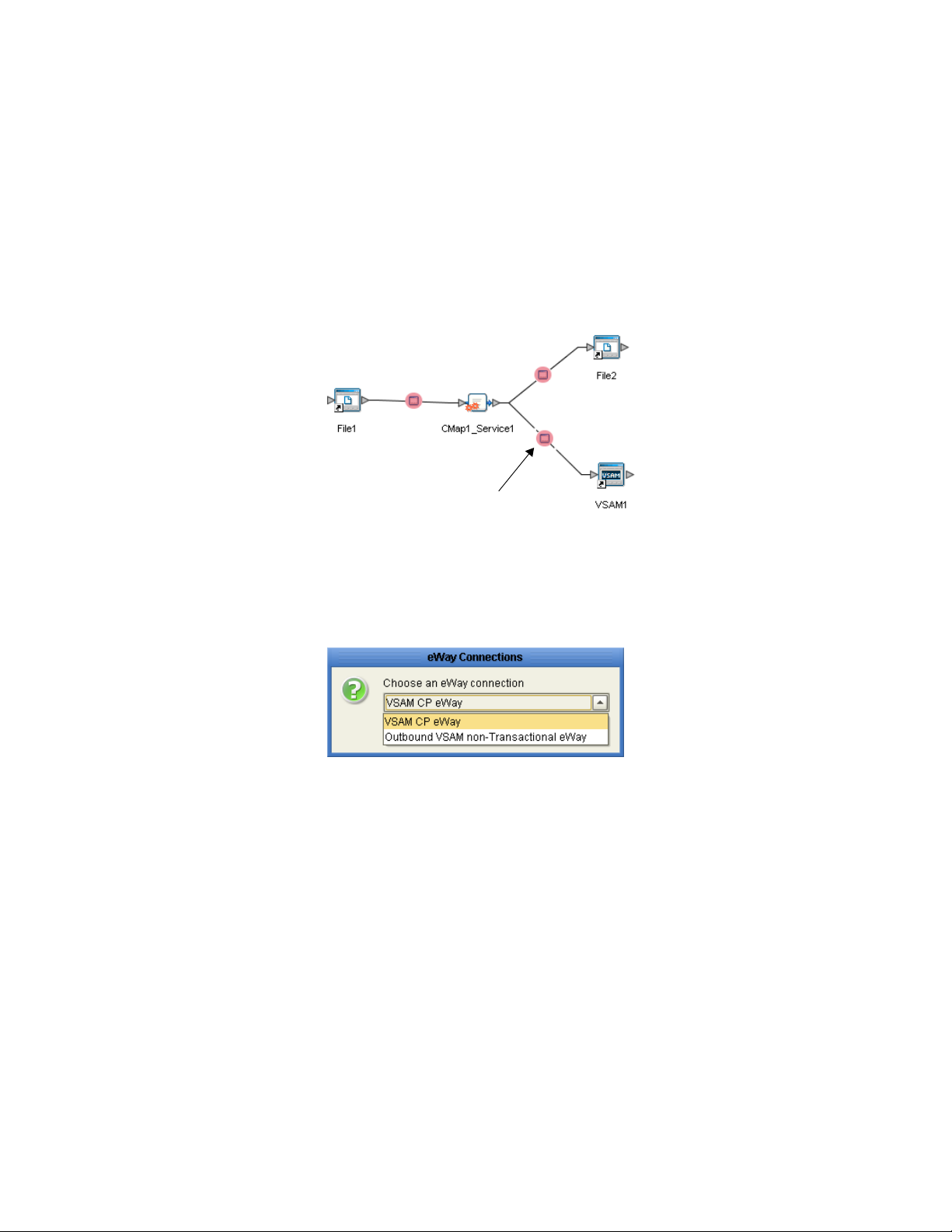
3 The Properties window opens, displaying the default properties for the eWay.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 21 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 22
Chapter 3 Section 3.2
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay Configuring the eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Figure 3 Outbound eWay Properties
3.2.1 Transaction Support Levels Between Different Versions
The types of transaction support levels used in Java CAPS 5.1.0 may be different
from the support levels used in Java CAPS 5.1.3. Projects that are imported from a
Java CAPS 5.1.0 version can potentially display different results, depending on
whether the 5.1.0 Java Collaboration Definition (JCD) included multiple (insert/
update/delete) operations. This only affects non-XA transactions. Example:
In 5.1.0, five new records are to be inserted into a table. If the last record fails to
insert (such as when a duplicate key exists), all previous records will have been
inserted. This is the behavior of NoTransaction support.
In 5.1.3, five new records are to be inserted into a table. If one of the records fails to
insert (such as when a duplicate key exists), the other four records will not be
inserted. This is the behavior of the LocalTransaction.
In order to achieve the same result as in 5.1.0 versions, you can choose the method
below:
A In the Connectivity Map, delete the link to the database external application,
then reconnect the link and select NoTransaction.
B Fill in the NoTransaction property for the database external system under the
Environment.
C Rebuild the Project.
If you want 5.1.3 behavior for a LocalTransaction, then set your eWay connection to
be Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay (NoTransaction).
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 22 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 3 Section 3.3
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay Configuring the eWay Environment Properties
3.3 Configuring the eWay Environment Properties
The eWay Environment Configuration properties contain parameters that define how
the eWay connects to and interacts with other eGate components within the
Environment. When you create a new VSAM External System, you may configure the
type of External System required.
Available External System properties include:
Inbound VSAM eWay
(Outbound) VSAM CP eWay
Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay
To Configure the Environment Properties:
1 In Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment Explorer tab.
2 Expand the Environment created for the VSAM Project and locate the VSAM
External System.
Note: For more information on creating an Environment, see the “Sun SeeBeyond eGate
Integrator Tutorial”.
3 Right-click the External System created for the VSAM Project and select Properties
from the list box. The Environment Configuration Properties window appears.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 23 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 24
Chapter 3 Section 3.4
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Connectivity Map Properties
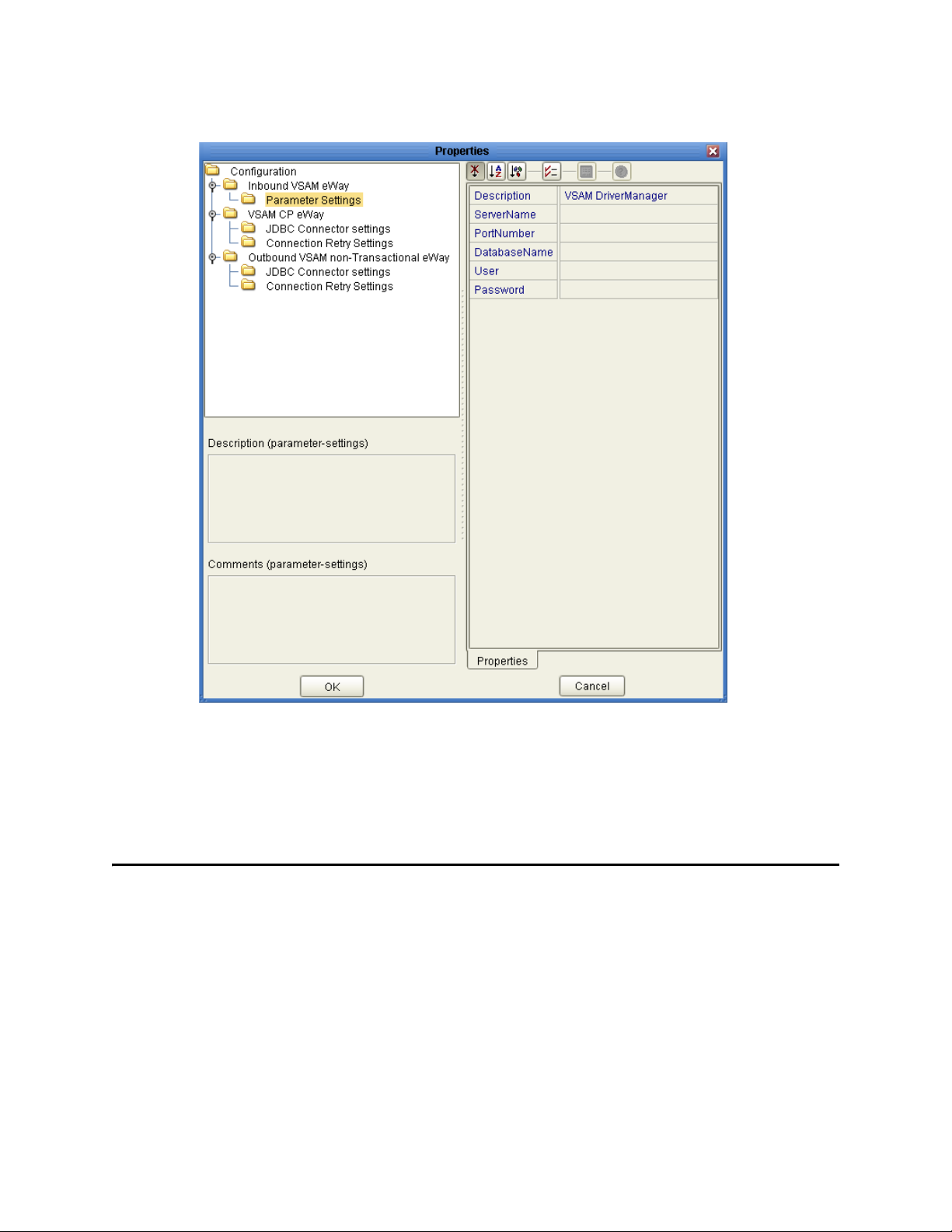
Figure 4 VSAM eWay Environment Configuration
4 Click on any folder to display the default configuration properties for that section.
5 Click on any property field to make it editable.
After modifying the configuration properties, click OK to save the changes.
3.4 eWay Connectivity Map Properties
The eWay Connectivity Map consists of the following properties categories.
Outbound eWay
Connectivity Map (Outbound) CP eWay Properties on page 25
Outbound non-Transactional eWay
Connectivity Map Outbound non-Transactional eWay Properties on page 25
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 24 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 25
Chapter 3 Section 3.4
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Connectivity Map Properties
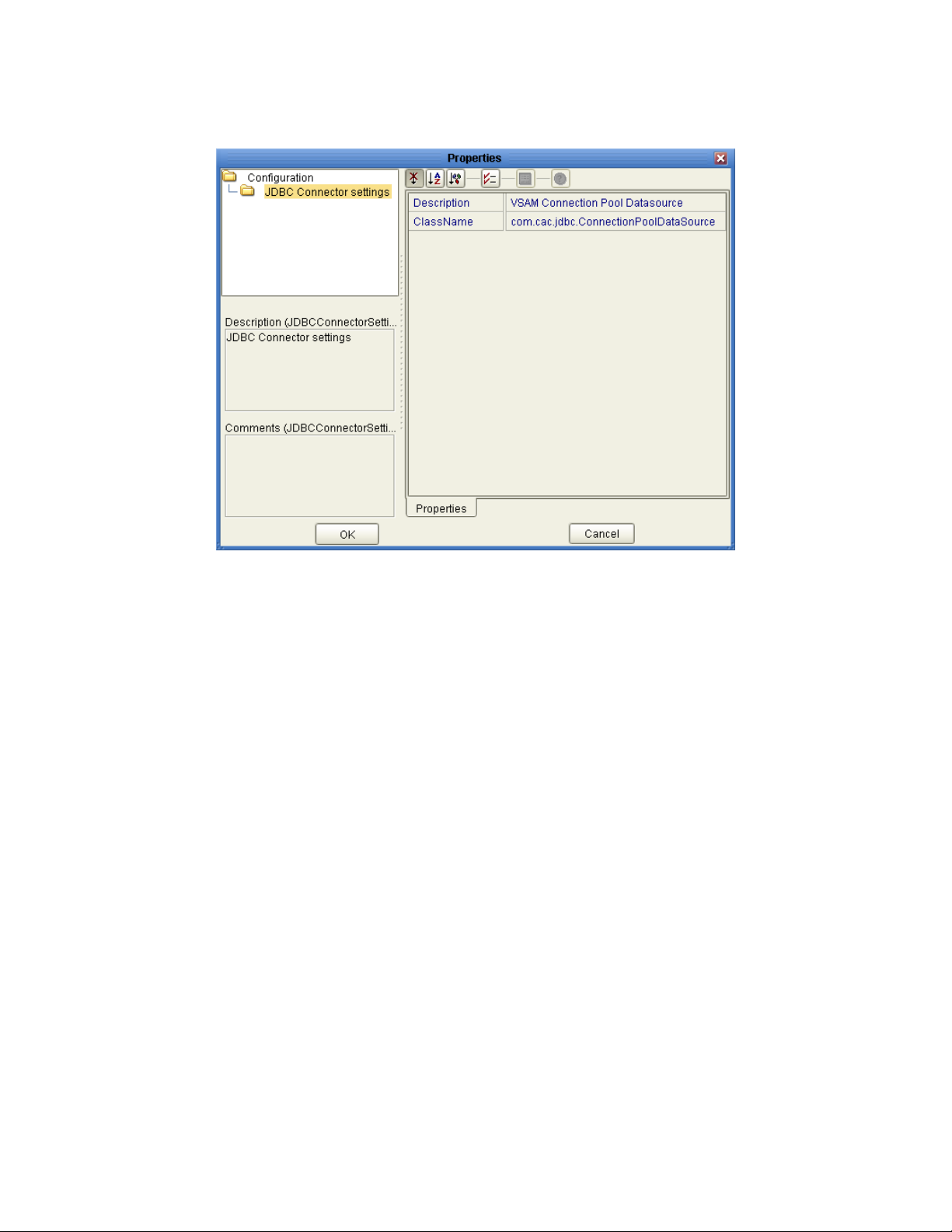
3.4.1 Connectivity Map (Outbound) CP eWay Properties
The Outbound eWay Properties include outbound parameters used by the external
database.
Table 3 Outbound eWay—JDBC Connector Settings
Name Description Required Value
Description VSAM Connection Pool Datasource. A valid string.
ClassName Displays the Java class in the JDBC driver
that is used to implement the
ConnectionPoolDataSource interface.
3.4.2 Connectivity Map Outbound non-Transactional eWay
A valid class name.
The default is:
com.cac.jdbc.ConnectionPoo
lDataSource
Note: Do not change
this value.
Properties
You can create VSAM databases with or without logging enabled. If logging is disabled,
then Non-Transactional mode must be used. Because data logs are not retained during
Non-Transactional execution of SQL calls, data recovery is not possible during
accidental or unscheduled shut-down of the database server.
Disabled logging also prevents transactions—enclosed in BEGIN-Tran and END-Tran
statements—from occurring. This means that Non-Transactional mode cannot be used
in XA (two-phase commit) transactions.
The Outbound non-Transactional eWay Properties listed in Table 4 include inbound
parameters used by the external database.
Table 4 Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay Connectivity Map Properties
Name Description Required Value
Description Enter a description for the database. A valid string. The default is
VSAM non-Transactional
Connection Pool Datasource.
ClassName Specifies the Java class in the JDBC driver
that is used to implement the nonTransactional ConnectionPoolDataSource
interface.
A valid class name. The
default is
com.cac.jdbc.ConnectionPool
DataSource
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 25 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 26
Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
3.5 eWay Environment Properties
eWay External System properties must be configured from within the Environment.
Until you have successfully configured all eWays for your Java CAPS project, your
project cannot be properly executed or deployed. The following list identifies the
VSAM eWay properties. There are two Environment Configuration categories that the
VSAM eWay implements.
Property Categories Configured in the Logical Host Environment
Inbound VSAM eWay Properties on page 26
(Outbound) VSAM CP eWay Properties on page 26
Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay Properties on page 30
3.5.1 Inbound VSAM eWay Properties
Before deploying your eWay, you will need to set the Environment properties. The
Inbound VSAM eWay includes the following configuration section:
Parameter Settings
Details for the Inbound VSAM eWay Parameter Settings are listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Inbound VSAM eWay—Parameter Settings
Name Description Required Value
Description The description of the database. A valid string.
ServerName This setting specifies the host name of the
external database server.
PortNumber Specifies the I/O port number on which
the server is listening for connection
requests.
DatabaseName Specifies the name of the database
instance. This parameter is configured in
conjuction with the Data Catalogue name
you created in WebSphere Classic
Federation’s Data Mapper.
User Specifies the user name the eWay uses to
connect to the database.
Password Specifies the password used to access the
database.
Any valid string.
A valid port number.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
3.5.2 (Outbound) VSAM CP eWay Properties
The (Outbound) VSAM CP eWay includes the following configuration sections:
JDBC Connector Settings
Connection Retry Settings
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 26 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 27
Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
JDBC Connector Settings
Details for the VSAM CP eWay JDBC Connector Settings used by the external database
are detailed in Table 6.
Table 6 VSAM CP eWay—JDBC Connector Settings
Name Description Required Value
Description The description of the database. A valid string. The configured default
is VSAM Connection Pool Datasource.
ServerName This setting specifies the host name
of the external database server.
PortNumber Specifies the I/O port number on
which the server is listening for
connection requests.
Any valid string.
A valid port number.
DatabaseName Specifies the name of the database
instance.
User Specifies the user name the eWay
uses to connect to the database.
Password Specifies the password used to
access the database.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 27 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 28
Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 6 VSAM CP eWay—JDBC Connector Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
DriverProperties The Connection Pool DataSource
implementation may need to execute
additional methods to assure a
successful run. The additional
methods will need to be identified in
the Driver Properties. You must
ensure that the driver is installed on
both the Logical Host machine and
the Enterprise Designer machine.
The delimiter set by the user. For more
information, see the Delimiter
property below.
Valid delimiters are:
“<method-name-1>#<param-
1>#<param-2>#.........<param-
n>##<method-name-2>#<param-
1>#<param-2>#........<param-
n>##......##”.
For example: to execute the method
setSpyAttributes, give the method a
String for the URL
“setSpyAttribute#<url>##”.
Note: The setSpyAttributes (for
Data Direct drivers) that are
contained in the following
examples (between the last set
of double octothorps [##]
within each example), are used
for debugging purposes and
need not be used on every
occasion.
Delimiter This is the delimiter character to be
used in the DriverProperties prompt.
Optional—if you are using Spy Log:
“setURL#jdbc:Seebeyond:VSAM://
<server>:4100;DatabaseName=<datab
ase>##setSpyAttributes#log=(file)c:/
temp/spy.log;logTName=yes##”
The default is #. See the
DriverProperties property above for
more information on how the default
value is used.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 28 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 29
Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 6 VSAM CP eWay—JDBC Connector Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
MinPoolSize Specifies the minimum number of
physical connections the pool
should keep available at all times. 0
(zero) indicates that there should be
no physical connections in the pool
and the new connections should be
created as needed.
If the pool size is too small, you may
experience a longer connection time
due to the existing number of
physical connections.
A connection that stays in the pool
allows transactions to use it via a
logical connection (which is faster).
MaxPoolSize Specifies the maximum number of
physical connections the pool
should keep available at all times. 0
(zero) indicates that there is no
maximum.
If the pool size is too big, you may
end up with too many connections
with the database. The pool size
depends on the transaction volume
and response time.
A valid numeric value. The default is 0.
A valid numeric value. The default is
10.
MaxIdleTime Specifies the maximum number of
seconds that a physical connection
may remain unused before it is
closed. 0 (zero) indicates that there is
no limit.
A valid numeric value. The default is 0.
Connection Retry Settings
Details for the VSAM CP eWay Connection Retry Settings used by the external database
are detailed in Table 7.
Table 7 VSAM CP eWay—Connection Retry Settings
Name Description Required Value
ConnectionRetries Specifies the number of retries to
establish a connection upon failure
to acquire one.
A valid numeric value. The
default is 0.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 29 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 30
Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 7 VSAM CP eWay—Connection Retry Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
ConnectionRetryInterval Specifies the milliseconds of pause
before each attempt to reaccess the
database. This setting is used in
conjunction with the 'Connection
Retries' setting.
For example: In the event that the
eWay cannot connect to the
Database, the eWay will try to
reconnect to the database 10 times
in 5 seconds apart when the
Connection Retries is 10 and the
Connection Retry Interval is 5000.
3.5.3 Outbound VSAM non-Transactional eWay Properties
A valid numeric value. The
default is 1000.
The (Outbound) VSAM non-Transactional eWay includes the following configuration
sections:
JDBC Connector Settings
Connection Retry Settings
JDBC Connector Settings
Details for the VSAM non-Transactional eWay JDBC Connector Settings used by the
external database are detailed in Table 8.
Table 8 VSAM non-Transactional eWay—JDBC Connector Settings
Name Description Required Value
Description The description of the database. A valid string. The configured default
is VSAM non-Transactional
Connection Pool Datasource.
ServerName This setting specifies the host name
of the external database server.
PortNumber Specifies the I/O port number on
which the server is listening for
connection requests.
DatabaseName Specifies the name of the database
instance.
User Specifies the user name the eWay
uses to connect to the database.
Password Specifies the password used to
access the database.
Any valid string.
A valid port number.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
Any valid string.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 30 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 31

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 8 VSAM non-Transactional eWay—JDBC Connector Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
DriverProperties The Connection Pool DataSource
implementation may need to execute
additional methods to assure a
successful run. The additional
methods will need to be identified in
the Driver Properties. You must
ensure that the driver is installed on
both the Logical Host machine and
the Enterprise Designer machine.
The delimiter set by the user. For more
information, see the Delimiter
property below.
Valid delimiters are:
“<method-name-1>#<param-
1>#<param-2>#.........<param-
n>##<method-name-2>#<param-
1>#<param-2>#........<param-
n>##......##”.
For example: to execute the method
setSpyAttributes, give the method a
String for the URL
“setSpyAttribute#<url>##”.
Note: The setSpyAttributes (for
Data Direct drivers) that are
contained in the following
examples (between the last set
of double octothorps [##]
within each example), are used
for debugging purposes and
need not be used on every
occasion.
Delimiter This is the delimiter character to be
used in the DriverProperties prompt.
Optional—if you are using Spy Log:
“setURL#jdbc:Seebeyond:VSAM://
<server>:4100;DatabaseName=<datab
ase>##setSpyAttributes#log=(file)c:/
temp/spy.log;logTName=yes##”
The default is #. See the
DriverProperties property above for
more information on how the default
value is used.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 31 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 32

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 8 VSAM non-Transactional eWay—JDBC Connector Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
MinPoolSize Specifies the minimum number of
physical connections the pool
should keep available at all times. 0
(zero) indicates that there should be
no physical connections in the pool
and the new connections should be
created as needed.
If the pool size is too small, you may
experience a longer connection time
due to the existing number of
physical connections.
A connection that stays in the pool
allows transactions to use it via a
logical connection (which is faster).
MaxPoolSize Specifies the maximum number of
physical connections the pool
should keep available at all times. 0
(zero) indicates that there is no
maximum.
If the pool size is too big, you may
end up with too many connections
with the database. The pool size
depends on the transaction volume
and response time.
A valid numeric value. The default is 0.
A valid numeric value. The default is
10.
MaxIdleTime Specifies the maximum number of
seconds that a physical connection
may remain unused before it is
closed. 0 (zero) indicates that there is
no limit.
A valid numeric value. The default is 0.
Connection Retry Settings
Details for the VSAM non-Transactional eWay Connection Retry Settings used by the
external database are detailed in Table 9.
Table 9 VSAM non-Transactional eWay—Connection Retry Settings
Name Description Required Value
ConnectionRetries Specifies the number of retries to
establish a connection upon failure
to acquire one.
A valid numeric value. The
default is 0.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 32 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 33

Chapter 3 Section 3.5
Setting Properties of the VSAM eWay eWay Environment Properties
Table 9 VSAM non-Transactional eWay—Connection Retry Settings (Continued)
Name Description Required Value
ConnectionRetryInterval Specifies the milliseconds of pause
before each attempt to reaccess the
database. This setting is used in
conjunction with the 'Connection
Retries' setting.
For example: In the event that the
eWay cannot connect to the
Database, the eWay will try to
reconnect to the database 10 times
in 5 seconds apart when the
Connection Retries is 10 and the
Connection Retry Interval is 5000.
A valid numeric value. The
default is 1000.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 33 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 34

Chapter 4
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard
This chapter describes how to use the VSAM eWay Database wizard to build Object
Type Definitions (OTDs).
What’s in This Chapter
About the Database OTD Wizard on page 34
Creating a New VSAM OTD on page 34
Resulting OTD on page 46
Steps to Edit an Existing VSAM OTD on page 47
4.1 About the Database OTD Wizard
The Database OTD Wizard generates OTDs by connecting to external data sources and
creating corresponding Object Type Definitions. The OTD Wizard can create OTDs
based on any combination of Tables, Stored Procedures, or Prepared Statements.
Field nodes are added to the OTD based on the Tables in the external data source. Java
method and parameter nodes are added to provide the appropriate JDBC functionality.
For more information about the Java methods, refer to your JDBC developer’s
reference.
The OTD Wizard allows the addition and removal of columns/nodes in an OTD.
Nodes with the same name and type as existing nodes are allowed by the Wizard, but
should not be created, and will result in generic code generation errors upon activation
of the OTD.
Note: Database OTDs are not messagable. For more information on messagable OTDs, see
the eGate Integrator User’s Guide.
4.2 Creating a New VSAM OTD
The following steps are required to create a new OTD for the VSAM adapter.
Select Wizard Type on page 35
Connect To Database on page 35
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 34 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Select Database Objects on page 36
Select Tables/Views/Aliases on page 37
Add Prepared Statement on page 41
Specify the OTD Name on page 44
Review Selections on page 45
4.2.1 Select Wizard Type
Select the type of wizard required to build an OTD in the New Object Type Definition
Wizard.
Steps Required to Select the VSAM Database OTD Wizard Include:
1 On the Project Explorer tree, right click the Project and select New > Object Type
Definition from the shortcut menu. The Select Wizard Type page appears,
displaying the available OTD wizards.
2 From the New Object Type Definition Wizard window, select the VSAM Database
and click Next. See Figure 5.
Figure 5 OTD Wizard Selection
4.2.2 Connect To Database
Enter the VSAM database connection information in the Connection Information frame.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 35 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 36

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Required Database Connection Fields include:
Host name – the database service host name.
Port ID – the database service connection port ID/number.
Database name – the name of the VSAM database.
User name – a valid VSAM database username.
Password – a password for the user name noted above.
Figure 6 Database Connection Information
4.2.3 Select Database Objects
Select the type of VSAM database objects you want included in the OTD.
Steps Required to Select Database Objects Include:
1 When selecting Database Objects, you can select any combination of Ta b l es , Views,
or Prepared Statements you would like to include in the OTD file. Click Next to
continue. See Figure 7.
Note: Views are read-only and are for informational purposes only.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 36 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 7 Select Database Objects
4.2.4 Select Tables/Views/Aliases
Select the types of tables or views required in the OTD.
Note: Aliases are not supported in the current release of the VSAM eWay.
Steps Required to Select Table and Views Include:
1 In the Select Tables/Views/Aliases window, click Add. See Figure 8.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 37 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 38

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 8 Select Tables/Views/Aliases
2 In the Add Tables window, select if your selection criteria will include table data,
view only data, both, and/or system tables.
3 From the Table/View Name drop down list, select the location of your database
table and click Search. See Figure 9.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 38 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 39

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 9 Database Wizard - All Schemes
4 Select the table of choice and click OK.
The table selected is added to the Selected Tables/Views/Aliases section. See Figure 10.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 39 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 40

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 10 Selected Tables/Views/Aliases window with a table selected
5 In the Selected Tables/Views/Aliases section, review the table(s) you have selected.
To make changes to the selected Table or View, click Change. If you do not wish to
make any additional changes, click Next to continue.
6 In the Ta b le /Vi ew C olu mns window, you can select or deselect your table columns.
You can also change the data type for each table by highlighting the data type and
selecting a different one from the drop down list. If you would like to change any of
the tables columns, click Change. See Figure 11.
The data type is usually listed as Other when the driver cannot detect the data type.
In these situations we recommend changing the data type to one that is more
appropriate for the type of column data.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 40 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 11 Table/View Columns
7 Click Advanced to change the data type, percision/length, or scale. Once you have
finished your table choices, click OK. In general, you will not need to make any
changes. See Figure 12.
Figure 12 Table/View Columns — Advanced
4.2.5 Add Prepared Statement
Add a Prepared Statement object to your OTD.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 41 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 42

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Steps Required to Add Prepared Statements Include:
Note: When using a Prepared Statement, the ‘ResultsAvailable()’ method will always
return true. Although this method is available, you should not use it with a ‘while’
loop. Doing so would result in an infinite loop at runtime and will stop all of the
system’s CPU. If it is used, it should only be used with the ‘if’ statement.
1 On the Add Prepared Statements window, click Add.
Figure 13 Prepared Statement
2 Enter the name of a Prepared Statement or create a SQL statement by clicking in the
SQL Statement window. If you are not logging into the VSAM database with the
default user name, you must enter the Table schema name in the SQL Prepared
Statement. When finished creating the statement, click Save As giving the
statement a name.
This name will appear as a node in the OTD. Click OK. See Figure 14.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 42 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 43

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 14 Prepared SQL Statement
3 On the Add Prepared Statement window, the name you assigned to the Prepared
Statement appears. To edit the parameters, click Edit Parameters. You can change
the datatype by clicking in the Type field and selecting a different type from the list.
4 Click Add if you want to add additional parameters to the Statement or highlight a
row and click Remove to remove it. Click OK. Figure 15.
Figure 15 Edit the Prepared Statement Parameters
.
5 To edit Resultset Columns, click Edit Resultset Columns. The ResultSet Columns
window appears. See Figure 16.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 43 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 44

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 16 ResultSet Columns
6 Click Add to add a new ResultSet column. Both the Name and Type are editable.
7 Click OK to return to the Add Prepared Statements window.
4.2.6 Specify the OTD Name
Specify the name that your OTD will display in the Enterprise Designer Project
Explorer.
Steps Required to Specify the OTD Name:
1 Enter a name for the OTD. The OTD contains the selected tables and the package
name of the generated classes. See Figure 17.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 44 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 4 Section 4.2
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Creating a New VSAM OTD
Figure 17 Naming an OTD
2 Click Next.
4.2.7 Review Selections
Review the selections made for the new OTD.
Steps Required to Review Your OTD Selections:
1 View the summary of the OTD. If you find you have made a mistake, click Back and
correct the information.
2 If you are satisfied with the OTD information, click Finish to begin generating the
OTD. See Figure 18.
The resulting OTD appears on the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 45 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 46

Chapter 4 Section 4.3
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Resulting OTD
Figure 18 Database Wizard - Summary
4.3 Resulting OTD
The resulting VSAM OTD appears on the Enterprise Designer’s canvas, in the
OTD Editor window. See Figure 19.
In the example, a node in the OTD has been expanded, allowing you to view some
of its structure.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 46 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Steps to Edit an Existing VSAM OTD
Figure 19 OTD Editor in Enterprise Designer
4.4 Steps to Edit an Existing VSAM OTD
You can edit any database OTD you create directly from the Enterprise Designer Project
Explorer.
Steps to Edit the OTD from the Enterprise Designer Include:
1 Unlock the OTD. To do this, right-click the OTD in the Project Explorer and select
Ver s i on C o n tr o l > Check Out from the menu.
The Version Control - Check Out window appears.
2 Select the OTD you want to check out, then click Check Out.
3 From the Project Explorer, right-click the OTD again and select Edit from the menu.
The VSAMDatabase Connection Information wizard appears.
4 Enter the connection information as described in “Connect To Database” on
page 35, and click Next.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 47 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 48

Chapter 4 Section 4.4
Using the VSAM eWay Database Wizard Steps to Edit an Existing VSAM OTD
5 Step through each of the wizard steps and click Finish to save your changes.
Note: You must verify during project activation or at runtime that no errors are generated
after editing an OTD. Errors could occur if you delete a database object such as a
table or column that is included in a Collaboration.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 48 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 49

Using VSAM OTDs
This chapter describes operations you can perform using VSAM Object Type
Definitions (OTDs) in eGate.
What’s in This Chapter
Overview on page 49
Using Tables on page 49
Using Views on page 52
Using Prepared Statements on page 52
5.1 Overview
This section explains the types of VSAM OTDs used with the eWay within the
Collaboration Editor (Java), including the OTD’s methods.
Chapter 5
You can use VSAM OTD methods with:
Tab le s ( ta bl e O TD )
Views (view OTD)
Prepared statements (prepared statement OTD)
Views are read-only and for informational purposes only. Use the OTD wizard (see
Chapter 4) to create the VSAM Database OTDs.
User-defined OTD
You can use the OTD wizard to create an eGate User-defined OTD. See the eGate
Integrator User’s Guide for a complete explanation of how to create a User-defined OTD.
5.2 Using Tables
A table OTD represents a database table. It consists of fields and methods. Fields
correspond to the columns of a table, while methods are the operations that you can
apply to the OTD. This setup allows you to perform select, update, insert, and delete
SQL operations in a table.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 49 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 50

Chapter 5 Section 5.2
Using VSAM OTDs Using Tables
5.2.1 Using the select Method
The select method returns result sets according to a group of predefined defaults.
However, you can change these defaults, if desired. In using the select method, you can
specify the following types of result sets:
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY
TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE
TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE
You can also specify the following result sets with a type of concurrency:
CONCUR_READ_ONLY
CONCUR_UPDATABLE
To perform an update, insert or delete operation, the type of the result set returned by
the select method must be CONCUR_UPDATABLE.
Instead of specifying the type of result set and concurrency in the select method, you
can also use the following methods:
setConcurrencytoUpdatable
setConcurrentlytoReadOnly
setScrollTypetoForwardOnly
setScrollTypetoScrollSensitive
setScrollTypetoInsensitive
Note: Because of driver limitations, before you can do any modifications (insert, update, or
delete) to a table, the table must be under CICS control on the mainframe.
To call a method in the Collaboration Editor (Java)
1 Open the eGate Enterprise Designer’s Collaboration Editor (Java) for the desired
Collaboration Definition.
2 In the editor, navigate to the Business Rules Designer.
3 Right-click on the desired node (right or left pane) where you want to call the
method.
A pop-up Method selection menu appears, showing the methods available for the
node.
4 Select the desired method.
A Method box appears in the center pane of the Business Rules Designer. This box
represents the chosen method.
Note: Using the commit method is optional for all update operations because the
Collaboration automatically commits the current transaction when it is done.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 50 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 5 Section 5.2
Using VSAM OTDs Using Tables
5.2.2 Select Operations
To perform a select operation on a table
1 From the Collaboration Editor (Java), call the select method with the where clause
specified, if necessary.
The text from the Te x t node instructs the Business Process exactly which data needs
to be selected. For example, the content of the input text could be EMPID>100.
2 Loop through the result set using the next method.
3 For each loop, process the return record.
5.2.3 Insert Operations
To perform an insert operation on a table
1 From the Collaboration Editor (Java), call the insert method.
2 Set the fields of the table OTD where you want to do the insertion and insert the
row using a Literal.
If you want to update multiple columns, you can repeat the Copy rule, as desired.
3 Activate the insertion by calling the insertRow method.
For multiple insert operations, you can use a while rule.
5.2.4 Update Operations
To perform an update operation on a table
1 From the Collaboration Editor (Java), call the update method with the where clause
specified, if necessary.
In this case, a Literal is used instead of the text node. Either way of specifying the
where clause is acceptable.
2 Call the next method.
3 Update the row by calling updateRow.
To update more than one column, you can repeat the Copy rule, as desired.
5.2.5 Delete Operations
To perform a delete operation on a table
From the Collaboration Editor (Java), call the delete method with the where clause
specified, if necessary.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 51 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 52

Chapter 5 Section 5.3
Using VSAM OTDs Using Views
5.3 Using Views
Views are used to look at data from selected columns within selected tables. View OTDs
are read-only.
For select operations, see “Select Operations” on page 51.
5.4 Using Prepared Statements
You can perform table operations with prepared statements with the same method
nodes you use for the regular table operations, that is, select, update, insert, and delete
SQL operations.
Prepared statements allow you to create any valid SQL statements that comply with
ANSI standards. Using this feature, you can execute select statements such as joins and
union, insert, update and delete operations. You can also include database operations
such as to_date, to manipulate input or output values. Parameter markers are also
supported.
Any prepared statement you create shows up in the Collaboration Editor (Java) on the
OTD where it was created, as a node with the name you assigned to it. You can
implement the statement by dragging its node onto the method box for the action (the
desired select, update, insert, or delete operation) in which you want the statement to
be used.
Note: When using a Prepared Statement, the ResultsAvailable() method will always
return true. Although this method is available, you should not use it with a ‘while’
loop. Doing so would result in an infinite loop at runtime and will stop all of the
system’s CPU. If it is used, it should only be used with the ‘if’ statement.
To use a prepared statement in a Collaboration (Java)
1 Using the Enterprise Designer and VSAM OTD wizard, create an OTD that contains
a prepared statement. See “Add Prepared Statement” on page 41 for details.
2 Create the desired Collaboration Definition (Java) using this OTD.
The Collaboration Editor (Java) displays the OTD with a Prepared Statement node.
In the OTD structure, you can see both the input parameter and the result set
represented as nodes.
3 You can assign a Literal value or the input from another OTD to the parameter.
4 To run the prepared statement, select the executeQuery method from the Prepared
Statement node.
5 To view the result set after the query is finished, create a while rule. For the
condition, create a next method from the result set node ($Statement1Results in the
example). You can continue creating your business logic by adding more Business
Rules, if desired.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 52 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 53

Using VSAM Operations
The database operations used in the VSAM eWay are used to access the VSAM
database. Database operations are either accessed through Activities in BPEL, or
through methods called from a JCD Collaboration.
What’s in This Chapter
VSAM eWay Database Operations (BPEL) on page 53
VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD) on page 55
6.1 VSAM eWay Database Operations (BPEL)
The VSAM eWay uses a number operations to query the VSAM database. Within a
BPEL business process, the VSAM eWay uses BPEL Activities to perform basic
outbound database operations, including:
Chapter 6
Insert
Update
Delete
SelectOne
SelectMultiple
SelectAll
In addition to these outbound operations, the VSAM eWay also employs the inbound
Activity ReceiveOne within a Prepared Statement OTD.
6.1.1 Activity Input and Output
The Sun SeeBeyond Enterprise Designer – Business Rules Designer includes Input and
Output columns to map and transform data between Activities displayed on the
Business Process Canvas.
Figure 20 displays the business rules between the FileClient.write and
otdVSAM.CICSEMPDelete Activities. In this example, the whereClause appears on
the Input side.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 53 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 54

Chapter 6 Section 6.1
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (BPEL)
Figure 20 Input and Output Between Activities
The following table lists the expected Input and Output of each database operation
Activity.
Table 10 VSAM Operations
eInsight Operation Activity Input Activity Output
SelectAll where() clause (optional) Returns all rows that fit the
condition of the where()
clause.
SelectMultiple number of rows
where() clause (optional)
Returns the number of rows
specified that fit the condition
of the where() clause, and the
number of rows to be
returned.
For example: If the number of
rows that meet the condition
are 5 and the number of
available rows are 10, then
only 5 rows will be returned.
Alternately, if the number of
rows that meet the condition
are 20, but if the number of
available rows are 10, then
only 10 rows are returned.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 54 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 55

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
Table 10 VSAM Operations (Continued)
eInsight Operation Activity Input Activity Output
SelectOne where() clause (optional) Returns the first row that fits
the condition of the where()
clause.
Insert definition of new item to be
inserted
Update where() clause Returns status.
Delete where() clause Returns status.
6.2 VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
Returns status.
The same database operations are also used in the JCD, but appear as methods to call
from the Collaboration.
Tables and Views are manipulated through OTDs. Methods to call include:
insert()
insertRow()
update(String sWhere)
updateRow()
delete(String sWhere)
deleteRow()
select(String where)
Note: Refer to the Javadoc for a full description of methods included in the VSAM eWay.
6.2.1 The Table
A table OTD represents a database table. It consists of fields and methods. Fields
correspond to the columns of a table while methods are the operations that you can
apply to the OTD. This allows you to perform query, update, insert, and delete SQL
operations in a table. The ability to update via a resultset is called “Updatable
Resultset”, which is a feature supported by this eWay.
By default, the Table OTD has UpdatableConcurrency and ScrollTypeForwardOnly.
Normally you do not have to change the default setting.
The type of result returned by the select() method can be specified using:
SetConcurrencytoUpdatable
SetConcurrencytoReadOnly
SetScrollTypetoForwardOnly
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 55 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 56

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
SetScrollTypetoScrollSensitive
SetScrollTypetoInsensitive
The Query (Select) Operation
To perform a query operation on a table:
1 Execute the select() method with the “where” clause specified if necessary.
2 Loop through the ResultSet using the next() method.
3 Process the return record within a while() loop.
For example:
package prjVSAM_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdTableSelect
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive(
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
otdVSAM.OtdVSAMOTD otdVSAM_1, dtd.otdOutputDTD_1935483687.Emp
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1, com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication
FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Selecting record(s) from CICSEMP table
via table select .." );
FileClient_1.write();
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().select( input.getText() );
while (otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().next()) {
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setENAME(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getENAME() );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setPHONE( typeConverter.intToString(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getPHONE(), "#", false, "" ) );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setMAILID(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getMAILID() );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setSALARY(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getSALARY().toString() );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setJOBID( typeConverter.doubleToString(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getJOBID(), "#.000000;-#.000000", false, "" )
);
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setEMPID( typeConverter.intToString(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getEMPID(), "#", false, "" ) );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setDEPTID( typeConverter.shortToString(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getDEPTID(), "#", false, "" ) );
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.setDEPARTMENT(
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().getDEPARTMENT() );
FileClient_1.setText( otdOutputDTD_Emp_1.marshalToString()
);
FileClient_1.write();
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Done table select." );
FileClient_1.write();
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 56 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 57

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
}
}
The Insert Operation
To perform an insert operation on a table:
1 Execute the insert() method. Assign a field.
2 Insert the row by calling insertRow()
This example inserts an employee record:
package prjVSAM_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdInsert
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive(
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
dtd.otdInputDTD_622919076.Emp otdInputDTD_Emp_1, otdVSAM.OtdVSAMOTD
otdVSAM_1, com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication
FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Inserting records into CICSEMP table
.." );
FileClient_1.write();
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.unmarshalFromString( input.getText() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().insert();
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < otdInputDTD_Emp_1.countX_sequence_A();
i1 += 1) {
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setENAME(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getENAME() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setPHONE(
typeConverter.stringToInt( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getPHONE(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setMAILID(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getMAILID() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setSALARY( new
java.math.BigDecimal( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getSALARY() ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setJOBID(
typeConverter.stringToDouble( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getJOBID(), "#.000000;-#.000000", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setEMPID(
typeConverter.stringToInt( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getEMPID(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setDEPTID(
typeConverter.stringToShort( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getDEPTID(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setDEPARTMENT(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getDEPARTMENT() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().insertRow();
}
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 57 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 58

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
FileClient_1.setText( "Done Insert." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
The Update Operation
To perform an update operation on a table:
1 Execute the update() method.
2 Using a while loop together with next(), move to the row that you want to update.
3 Assign updating value(s) to the fields of the table OTD
4 Update the row by calling updateRow().
package prjVSAM_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdUpdate
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive(
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
otdVSAM.OtdVSAMOTD otdVSAM_1, dtd.otdOutputDTD_1935483687.Emp
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1, com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication
FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Update the Department .. " );
FileClient_1.write();
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().update( input.getText() );
while (otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().next()) {
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setDEPARTMENT( "QAQAQA" );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().updateRow();
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Done Update." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
The Delete Operation
To perform a delete operation on a table:
1 Execute the delete() method.
In this example DELETE an employee.
package prjVSAM_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdDelete
{
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 58 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 59

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive(
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
otdVSAM.OtdVSAMOTD otdVSAM_1, dtd.otdOutputDTD_1935483687.Emp
otdOutputDTD_Emp_1, com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication
FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Delete record .." );
FileClient_1.write();
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().delete( input.getText() );
FileClient_1.setText( "Done delete." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
6.2.2
Prepared Statement
A Prepared Statement OTD represents a SQL statement that has been compiled. Fields
in the OTD correspond to the input values that users need to provide.
Prepared statements can be used to perform insert, update, delete and query
operations. A prepared statement uses a question mark (?) as a place holder for input.
For example:
insert into EMP_TAB(Age, Name, Dept No) value(?, ?, ?)
To execute a prepared statement, set the input parameters and call executeUpdate() and
specify the input values if any.
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(23);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(‘Peter Pan’);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(6);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().executeUpdate();
Batch Operations
6.2.3
To achieve better performance, consider using a bulk insert if you have to insert many
records. This is the “Add Batch” capability. The only modification required is to include
the addBatch() method for each SQL operation and then the executeBatch() call to
submit the batch to the database server. Batch operations apply only to Prepared
Statements.
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(23);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(‘Peter Pan’);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(6);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().addBatch();
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(45);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(‘Harrison
Ford’);
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(7);
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 59 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 60

Chapter 6 Section 6.2
Using VSAM Operations VSAM eWay Database Operations (JCD)
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().addBatch();
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().executeBatch();
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 60 Sun Microsytems, Inc.
Page 61

Chapter 7
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects
This chapter provides an introduction to the VSAM eWay components, and
information on how these components are created and implemented in a Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite Project. Sample Projects are designed to provide
an overview of the basic functionality of the VSAM eWay by identifying how
information is passed between eGate and supported external databases.
It is assumed that you understand the basics of creating a Project using the Enterprise
Designer. For more information on creating an eGate Project, see the eGate Tutorial and
the eGate Integrator User’s Guide.
What’s in This Chapter
About the VSAM eWay Sample Projects on page 61
Running the Sample Projects on page 64
Running the SQL Script on page 64
Importing a Sample Project on page 65
Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project on page 65
Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project on page 92
7.1 About the VSAM eWay Sample Projects
The VSAM eWay VSAM_eWay_Sample.zip file contains two sample Projects that
provide basic instruction on using VSAM operations in the Java Collaboration
Definition (JCD), or the Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) Projects.
prjVSAM_JCD: demonstrates how to select, insert, update, and delete data from a
VSAM database using JCDs.
prjVSAM_BPEL: demonstrates how to select, insert, update, and delete data from
a VSAM database using a BPEL business process.
Both the prjVSAM_JCD and prjVSAM_BPEL sample Projects demonstrate how to:
Select employee records from the database using a prepared statement.
Select employee records from the CICSEMP table.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 61 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 62

Chapter 7 Section 7.1
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects About the VSAM eWay Sample Projects
Insert employee records data into the CICSEMP table.
Update an employee record in the CICSEMP table.
Delete an employee record from the CICSEMP table.
In addition to sample Projects, the VSAM510_SAMPLE_projects.zip file also includes
six sample input trigger files and ten sample output files (five per sample).
Sample input files include:
TriggerDelete.in.~in
TriggerInsert.in.~in (for JCE projects only)
TriggerBpInsert.in.~in (for BPEL projects only)
TriggerPsSelect.in.~in
TriggerTableSelect.in.~in
TriggerUpdate.in.~in
Sample output JCD files include:
JCD_Delete_output0.dat
JCD_Insert_output0.dat
JCD_PsSelect_output0.dat
JCD_TableSelect_output0.dat
JCD_Update_output0.dat
Sample output BPEL files include:
BPEL_Delete_output0.dat
BPEL_Insert_output0.dat
BPEL_PsSelect_output0.dat
BPEL_TableSelect_output0.dat
BPEL_Update_output0.dat
7.1.1 Operations Used in the VSAM Sample Projects
The following database operations are used in both BPEL and JCD sample Projects:
Insert
Update
Delete
Select (BPEL “SelectAll” Activity)
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 62 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 63

Chapter 7 Section 7.1
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects About the VSAM eWay Sample Projects
Assigning Operations in JCD
Database operations are listed as methods in the JCD. Perform the following steps to
access these methods:
1 Create a Collaboration that contains a database OTD created from the VSAM
database.
2 Right-click the OTD listed in your Collaboration and then select Select Method to
Call from the shortcut menu.
3 Browse to and select a method to call.
Assigning Operations in BPEL
You can associate an eInsight Business Process Activity with the eWay, both during the
system design phase and during run time. To make this association:
1 Select the desired receive or write operation under the eWay in the Enterprise
Explorer.
2 Drag the operation onto the eInsight Business Process canvas.
The operation automatically changes to an Activity with an icon identifying the
component that is the basis for the Activity.
At run time, the eInsight engine invokes each step in the order that you defined in the
Business Process. Using the engine’s Web Services interface, the Activity in turn
invokes the eWay. You can open a file specified in the eWay and view its contents before
and after the Business Process is executed.
Note: Inbound database eWays are only supported within BPEL Collaborations.
7.1.2 About the eInsight Engine and eGate Components
You can deploy an eGate component as an Activity in an eInsight Business Process.
Once you have associated the desired component with an Activity, the eInsight engine
can invoke it using a Web Services interface.
Examples of eGate components that can interface with eInsight in this way are:
Object Type Definitions (OTDs)
An eWay
Collaborations
Using the eGate Enterprise Designer and eInsight, you can add an Activity to a
Business Process, then associate that Activity with an eGate component, for example,
an eWay. When eInsight run the Business Process, it automatically invokes that
component via its Web Services interface.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 63 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 64

Chapter 7 Section 7.2
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Running the Sample Projects
7.2 Running the Sample Projects
The following steps are required to run the sample projects that are contained in the
VSAMeWayDocs.sar file.
1 Run the SQL script.
This creates the tables and records required by the sample Project.
2 Import the sample Projects.
3 Build, deploy, and run the sample Projects.
You must do the following before you can run an imported sample Project:
Create an Environment
Configure the eWays
Create a Deployment Profile
Create and start a domain
Deploy the Project
4 Check the output.
7.3 Running the SQL Script
The data used for both the JCD and BPEL sample Projects are contained within a table
called CICSEMP. You create this table by using the SQL statement
VSAM_sample_script.sql, that is included in the sample Project. Note that you must
use a database tool to run the script.
Following is the SQL statement designed for the sample Projects.
drop table CICSEMP
go
create table CICSEMP (
ENAME CHAR(20),
PHONE INTEGER(4),
MAILID CHAR(6),
SALARY DECIMAL(7,2),
JOBID FLOAT(4),
EMPID INTEGER(4),
DEPTID SMALLINT(2),
DEPARTMENT CHAR(15))
go
The sample Projects provided with the VSAM eWay use input files to pass predefined
data or conditions into the Collaboration or BPEL business process, which then
transforms the database contents, and delivers the result set.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 64 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 65

Chapter 7 Section 7.4
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Importing a Sample Project
7.4 Importing a Sample Project
Sample eWay Projects are included as part of the installation CD-ROM package. To
import a sample eWay Project to the Enterprise Designer do the following:
1 Extract the samples from the Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite
Installer to a local file.
Sample files are uploaded with the eWay’s documentation SAR file, and then
downloaded from the Installer’s Documentation tab. The
VSAM_eWay_Sample.zip file contains the various sample Project ZIP files.
Note: Make sure you save all unsaved work before importing a Project.
2 From the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer pane, right-click the Repository
and select Import Project from the shortcut menu. The Import Manager appears.
3 Browse to the directory that contains the sample Project ZIP file. Select the sample
file and click Import.
4 Click Close after successfully importing the sample Project.
7.5 Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample
Project
The following provides step-by-step instructions for manually creating the
prjVSAM_BPEL sample Project.
Steps required to create the sample project include:
Creating a Project on page 65
Creating the OTDs on page 66
Creating the Business Process on page 67
Creating the Connectivity Map on page 83
Creating an Environment on page 85
Configuring the eWays on page 86
Creating the Deployment Profile on page 89
Creating and Starting the Domain on page 90
Building and Deploying the Project on page 91
Running the Sample Project on page 91
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 65 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 66

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
7.5.1 Creating a Project
The first step is to create a new Project in the Enterprise Designer.
1 Start the Enterprise Designer.
2 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the Repository and select New Project. A
new Project (Project1) appears on the Project Explorer tree.
3 Right-click Project1 and select rename from the shortcut menu. Rename the Project
(for this sample, prjVSAM_BPEL).
7.5.2 Creating the OTDs
The sample Project requires three OTDs to interact with the VSAM eWay. These OTDs
include:
VSAM Database OTD
Inbound DTD OTD
Outbound DTD OTD
Steps required to create a VSAM Database OTD include:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
The New Object Type Definition Wizard window appears.
2 Select the VSAM Database OTD Wizard from the list of OTD Wizards and click
Next.
3 Enter the connection information for the VSAM database. Connection fields
include:
Host name:
Port ID:
Database Name:
User name:
Password:
4 Click Next, and select the types of database object you want to include in the
sample Project. For this example, select the following:
Tables/Views/Aliases
Prepared Statements
5 Click Add to select tables from the VSAM database. The Add Tables window
appears.
6 Search for or type in the name of the database. In this example we use the
CICSEMP table. Click Select when the database appears in the Results selection
frame. Click OK to close the Add Tables window
7 Click Next the Add Prepared Statements Wizard appears.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 66 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 67

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
8 Click Add, the Add Prepared Statement window appears. Enter the following:
Prepared Statement Name: Select_ps
SQL Statement:
select * from CICSEMP where EMPID > ? order by EMPID
Note: In our example, the SQL statement includes the ? placeholder for input. This
placeholder represents the value for the Where Clause.
9 Click the OK button to close the Prepared Statement window, and then click Next
on the Prepared Statements Wizard window.
10 Enter an OTD name. In this example, we use otdVSAM.
11 Click Next and review your settings, then click Finish to create the OTD.
Steps required to create inbound and outbound DTD OTDs:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
The New Object Type Definition Wizard window appears.
2 Select DTD from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Browse to and then select a DTD file. For our example, select one of the following
DTD files from the sample Project, and then click Next.
otdInputDTD.dtd
otdOutputDTD.dtd
4 The file you select appears in the Select Document Elements window. Click Next.
5 Click Finish to complete the DTD based OTD. Repeat this process again to create
the second DTD file.
7.5.3 Creating the Business Process
Steps required to create the Business Process include:
Creating the business process flow
Configuring the modeling elements
Creating the Business Process Flow
The business process flow contains all the BPEL elements that make up a business
process.
Steps to create a business process flow include:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Business Process from the shortcut menu. The eInsight Business
Process Designer appears and BusinessProcess1 is added to the Project Explorer
tree. Rename BusinessProcess1 to bpInsert.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 67 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 68

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
2 Create four additional business processes and rename them as follows:
bpUpdate
bpDelete
bpPsSelect
bpTableSelect
3 Add the following activities to the Business Process Designer canvas.
Table 11 Business Process Activities
Business Process Activity
bpInsert FileClient.Receive
FileClient.Write
otdVSAM.CICSEMPInsert (inside a Scope)
otdInputDTD_Emp.unmarshal
FileClient.Write
bpUpdate FileClient.receive
FileClient.write
otdVSAM.CICSEMPUpdate
FileClient.write
bpDelete FileClient.receive
FileClient.write
otdVSAM.CICSEMPDelete
FileClient.write
bpPsSelect FileClient.receive
FileClient.write
otdVSAM.Select_psPSSelectAll
Decision
FileClient.write (inside a Scope renamed “No records”)
otdInputDTD_DBemployees.marshal (inside a Scope renamed
“Records found”)
FileClient.write (inside a Scope renamed “Records found”)
FileClient.write
bpTableSelect FileClient.receive
FileClient.write
otdVSAM.CICSEMPSelectAll
otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal
FileClient.write
FileClient.write
Configuring the bpInsert Modeling Elements
Business Rules, created between the Business Process Activities, allow you to configure
the relationships between the input and output Attributes of the Activities using the
Business Process Designer’s Business Rule Designer.
Once you have connected the modeling elements together, begin adding the business
processes necessary to facilitate the Insert operation. See Figure 21 for an illustration of
how all the modeling elements appear when connected.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 68 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 69

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Note: Review the eInsight Business Process Manager User’s Guide for a more detailed
description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to a modeling
elements in a business process.
Figure 21 bpInsert Business Process
Steps required to configure the bpInsert business process:
1 Configure the business rule between FileClient.receive and FileClient.write
Activities, as seen in Figure 22.
Figure 22 bpInsert Business Rule # 1
2 Configure the business rule between the FileClient.write Activity and
otdInputDTD_Emp.unmarshal Activity, as seen in Figure 23.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 69 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 70

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 23 bpInsert Business Rule # 2
3 Configure the business rule between otdInputDTD_Emp.unmarshal Activity and
the Insert (Scope element), as seen in Figure 24.
Figure 24 bpInsert Business Rule # 3
4 Configure the business rule in the While statement that connects to the
otdVSAM.CICSEMPInsert Activity, as seen in Figure 25.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 70 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 71

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 25 bpInsert Business Rule # 4
5 Configure the business rule in the While statement that connects from the
otdVSAM.CICSEMPInsert Activity, as seen in Figure 26.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 71 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 72

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 26 bpInsert Business Rule # 5
6 Configure the business rule from the Insert (Scope element) to the FileClient.write
Activity, as seen in Figure 27.
Figure 27 bpInsert Business Rule # 6
Configuring the bpUpdate Modeling Elements
The bpUpdate business process describes how to update a record in the VSAM
database using the Business Process Designer.
Once you have connected the modeling elements together, begin adding the business
processes necessary to facilitate the Update operation. Figure 28 illustrates how all the
modeling elements appear when connected.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 72 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 73

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Note: The where clause in the business rule reads the trigger value as a placeholder for
input. This permits you to modify the query to select a specific record. Also note that
all records are selected from the database when the TriggerUpdate.in file is empty.
Note: Review the eInsight Business Process Manager User’s Guide for a more detailed
description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to a modeling
elements in a business process.
Figure 28 bpUpdate Business Process
Steps required to configure the bpUpdate business process:
1 Configure the business rule between FileClient.receive and FileCleint.write
Activities, as seen in Figure 29.
Figure 29 bpUpdate Business Rule # 1
2 Configure the business rule between the FileClient.write Activity and
otdVSAM.CICSEMPUpdate Activity, as seen in Figure 30.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 73 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 74

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 30 bpUpdate Business Rule # 2
3 Configure the business rule between the otdVSAM.CICSEMPUpdate Activity and
the FileClient.write Activity, as seen in Figure 31.
Figure 31 bpUpdate Business Rule # 3
Configuring the bpDelete Modeling Elements
The bpDelete business process describes how to delete a record in the VSAM database
using the Business Process Designer.
Once you have connected the modeling elements together, begin adding the business
processes necessary to facilitate the Delete operation. See Figure 32 for an illustration of
how all the modeling elements appear when connected.
Note: The where clause in the business rule reads the trigger value as a placeholder for
input. This permits you to modify the query to select a specific record. Also note that
all records are selected from the database when the TriggerDelete.in file is empty.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 74 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 75

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Note: Review the eInsight Business Process Manager User’s Guide for a more detailed
description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to a modeling
elements in a business process.
Figure 32 bpDelete Business Process
Steps required to configure the bpDelete business process:
1 Configure the business rule between FileClient.receive and FileCleint.write
Activities, as seen in Figure 33.
Figure 33 bpDelete Business Rule # 1
2 Configure the business rule between the FileClient.write Activity and
otdVSAM.CICSEMPDelete Activity, as seen in Figure 34.
Figure 34 bpDelete Business Rule # 2
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 75 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 76

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
3 Configure the business rule between the otdVSAM.CICSEMPDelete Activity and
the FileClient.write Activity, as seen in Figure 35.
Figure 35 bpDelete Business Rule # 3
Configuring the bpTableSelect Modeling Elements
The bpTableSelect business process is describes how to select all records the VSAM
database using the Business Process Designer.
Once you have connected the modeling elements together, begin adding the business
processes necessary to facilitate the SelectAll operation. See Figure 36 for an illustration
of how all the modeling elements appear when connected.
Note: The where clause in the business rule reads the trigger value as a placeholder for
input. This permits you to modify the query to select a specific record. Also note that
all records are selected from the database when the TriggerTableSelect.in file is
empty.
Note: Review the eInsight Business Process Manager User’s Guide for a more detailed
description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to a modeling
elements in a business process.
Figure 36 bpTableSelect Business Process
Steps required to configure the bpTableSelect business process:
1 Configure the business rule between FileClient.receive and FileClient.write
Activities, as seen in Figure 37.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 76 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 77

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 37 bpTableSelect Business Rule # 1
2 Configure the business rule between the FileClient.write Activity and
otdVSAM.CICSEMPSelectAll Activity as seen in Figure 38.
Figure 38 bpTableSelect Business Rule # 2
3 Configure the business rule between the otdVSAM.CICSEMPSelectAll Activity
and the otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal Activity as seen in Figure 39.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 77 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 78

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 39 bpSelectTable Business Rule # 3
4 Configure the business rule between the otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal Activity and
the FileClient.write Activity as seen in Figure 40.
Figure 40 bpTableSelect Business Rule # 4
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 78 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 79

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
5 Configure the business rule between the FileClient.write Activity and the
FileClient.write Activity as seen in Figure 41.
Figure 41 bpTableSelect Business Rule # 5
Configuring the bpPsSelect Modeling Elements
The bpPsSelect business process describes how to use a Prepared Statement query to
select all records in the VSAM database via the Business Process Designer.
Once you have connected the modeling elements together, begin adding the business
processes necessary to facilitate the SelectAll operation. See Figure 42 for an illustration
of how all the modeling elements appear when connected.
Note: Review the eInsight Business Process Manager User’s Guide for a more detailed
description of the steps required to connect and add business rules to a modeling
elements in a business process.
Figure 42 bpPsSelect Business Process
Steps required to configure the bpPsSelect business process:
1 Configure the business rule between FileClient.receive and FileCleint.write
Activities as seen in Figure 43.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 79 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 80

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 43 bpPsSelect Business Rule # 1
2 Configure the business rule between FileClient.write Activity and
otdVSAM.Select_psPSSelectAll Activity as seen in Figure 44.
Figure 44 bpPsSelect Business Rule # 2
3 Configure Case 1 of the Decision branching activity. This requires adding business
rules between the otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal and the FileClient.write Activities
within the Scope element.
Figure 45 Activities within Case 1 Scope
4 Configure the business rule between the start of the Scope element in Case 1 and
the otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal Activity, as seen in Figure 46.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 80 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 81

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 46 Case 1 Scope Business Rule # 3
5 Configure the business rule between otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal Activity and
FileClient.write Activity in the Scope element, as seen in Figure 47.
Figure 47 Case 1 Scope Business Rule # 4
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 81 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 82

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
6 Configure Case 2 of the Decision branching activity. This requires adding business
rules between the otdInputDTD_Emp.marshal and the FileClient.write Activities
within the Scope element.
Figure 48 Activities within Case 2 Scope
7 Configure the business rule between the start of the Scope element in Case 2 and
the FileClient.Write Activity, as seen in Figure 49.
Figure 49 Case 2 Scope Business Rule # 5
8 Configure the business rule between the Decision.end Element and the
FileClient.write Activity, as seen in Figure 50.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 82 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 83

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 50 bpSelectTable Business Rule # 6
7.5.4 Creating the Connectivity Map
The Connectivity Map provides a canvas for assembling and configuring a Project’s
components.
Steps required to create the Connectivity Map:
1 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the new prjVSAM_BPEL Project and
select New > Connectivity Map from the shortcut menu.
2 The New Connectivity Map appears, and a node for the Connectivity Map is added
under the Project on the Project Explorer tree labeled CMap1.
Create four additional Connectivity Maps—CMap2, CMap3. CMap4, and
CMap5—and rename them as follows:
cmDelete
cmInsert
cmPsSelect
cmTableSelect
cmUpdate
The icons in the toolbar represent the available components used to populate the
Connectivity Map canvas.
Populating the Connectivity Map
Add the Project components to the Connectivity Map by dragging the icons from the
toolbar to the canvas.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 83 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 84

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Each Connectivity Map in the prjVSAM_BPEL sample Project requires the following
components:
File External Application (2)
VSAM External Application
Business Process
Any eWay added to the Connectivity Map is associated with an External System. To
establish a connection to VSAM, first select VSAM as an External System to use in your
Connectivity Map.
To Select a VSAM External System
1 Click the External Application icon on the Connectivity Map toolbar.
2 Select the external systems necessary to create your Project (for this sample, VSAM
and File). Icons representing the selected external systems are added to the
Connectivity Map toolbar.
3 Rename the following components and then save changes to the Repository:
File1 to FileClientIN
File2 to FileClientOUT
VSAM1 to eaVSAMOUT
To Select a VSAM Business Process
1 Drag a business process from the Enterprise Explorer Project Explorer onto the
corresponding Connectivity Map. For example, drag the bpDelete business process
onto the cmDelete Connectivity Map.
2 Save your changes to the Repository
Binding the eWay Components
The final step in creating a Connectivity Map is binding the eWay components together.
Steps required to bind eWay components together:
1 Open one of the Connectivity Maps and double-click a Business Process, for
example the bpDelete Business Process in the cmDelete Connectivity Map. The
bpDelete Binding dialog box appears.
2 From the bpDelete Binding dialog box, map FileSender (under Implemented
Services) to the FileClientIN (File) External Application. To do this, click on
FileSender in the bpDelete Binding dialog box, and drag the cursor to the
FileClientIN External Application in the Connectivity Map. A link is now visible
between FileClientIN and bpDelete.
3 From the bpDelete Binding dialog box, map VSAM_otdVSAM (under Invoked
Services) to the eaVSAMOUT External Application.
4 From the bpDelete Binding dialog box, map FileReceiver to the FileClientOUT
External Application, as seen in Figure 51.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 84 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 85

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 51 Connectivity Map - Associating (Binding) the Project’s Components
5 Minimize the bpDelete Binding dialog box by clicking the chevrons in the upper-
right corner.
6 Save your current changes to the Repository, and then repeat this process for each of
the other Connectivity Maps.
7.5.5 Creating an Environment
Environments include the external systems, Logical Hosts, Integration Servers and
message servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these
components. Environments are created using the Enterprise Designer’s Environment
Editor.
Steps required to create an Environment:
1 From the Enterprise Designer’s Enterprise Explorer, click the Environment
Explorer tab.
2 Right-click the Repository and select New Environment. A new Environment is
added to the Environment Explorer tree.
3 Rename the new Environment to envVSAMProj.
4 Right-click envVSAMProj and select New > VSAM External System. Name the
External System esVSAM. Click OK. esVSAM is added to the Environment Editor.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 85 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 86

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
5 Right-click envVSAMProj and select New > File External System. Name the
External System esFileClient. Click OK. esFileClient is added to the Environment
Editor.
6 Right-click envVSAMProj and select New > Logical Host. The LogicalHost1 box is
added to the Environment, and LogicalHost1 is added to the Environment Editor
tree.
7 Right-click LogicalHost1 and select New > Sun SeeBeyond Integration Server. A
new Integration Server (IntegrationSvr1) is added to the Environment Explorer tree
under LogicalHost1 (see Figure 52).
Figure 52 Environment Editor - envVSAMProj
8 Save your current changes to the Repository.
7.5.6 Configuring the eWays
eWays facilitate communication and movement of data between the external
applications and the eGate system. Each Connectivity Map in the The prjVSAM_BPEL
sample Project use three eWays that are represented as a nodes between the External
Applications and the Business Process, as seen in Figure 53.
You must configure eWay properties in both the Connectivity Map and the
Environment Explorer.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 86 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 87

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 53 eWays in the cmDelete Connectivity Map
FileClientOUT eWay
FileClientIN eWay
eaVSAMOUT eWay
Configuring the eWay Properties
Steps required to configure the eWay properties:
1 Double-click the FileClientIN eWay on each of the Connectivity Maps and modify
the properties for your system, as seen in Table 12. Click OK to close the Properties
Editor.
Table 12 FileClientIN eWay Property Settings
Connectivity Map Property Name Required Values
cmDelete Input file name TriggerDelete.in
cmInsert Input file name TriggerBpInsert.in
cmPsSelect Input file name TriggerPsSelect.in
cmTableSelect Input file name TriggerTableSelect.in
cmUpdate Input file name TriggerUpdate.in
2 Double-click the FileClientOUT eWay on each of the Connectivity Maps and
modify the properties for your system, as seen in Table 13. Click OK to close the
Properties Editor.
Table 13 FileClientOUT eWay Property Settings
Connectivity Map Property Name Required Values
cmDelete Output file name BPEL_Delete_output%d.dat
cmInsert Output file name BPEL_Insert_output%d.dat
cmPsSelect Output file name BPEL_PsSelect_output%d.dat
cmTableSelect Output file name BPEL_TableSelect_output%d.d
at
cmUpdate Output file name BPEL_Update_output%d.dat
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 87 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 88

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Configuring the Environment Explorer Properties
Steps required to configure the Environment Explorer properties:
1 From the Environment Explorer tree, right-click the VSAM External System
(esVSAM in this sample), and select Properties. The Properties Editor opens to the
VSAM eWay Environment configuration.
2 Modify the VSAM eWay Environment configuration properties for your system (see
Inbound VSAM eWay Properties on page 26 and (Outbound) VSAM CP eWay
Properties on page 26), and click OK.
3 From the Environment Explorer tree, right-click the File External System
(esFileClient in this sample), and select Properties. The Properties Editor opens to
the File eWay Environment configuration.
4 Modify the File eWay Environment configuration properties for your system, as
seen in Table 14, and click OK.
Table 14 File eWay Environment Properties
Section Property Name Required Values
Configuration > Inbound
File eWay > Parameter
Settings
Configuration >
Outbound File eWay >
Parameter Settings
Directory Enter the directory that
contains the input files
(trigger files included in the
sample Project).
Trigger files include:
TriggerBpInsert.in.~in
TriggerDelete.in.~in
TriggerPsSelect.in.~in
TriggerTableSelect.in.~in
TriggerUpdate.in.~in
Directory Enter the directory where
output files are written. In this
sample Project, the output
files include:
BPEL_Delete_output0.dat
BPEL_Insert_output0.dat
BPEL_PsSelect_output0.dat
BPEL_TableSelect_output0.
dat
BPEL_Update_output0.dat
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 88 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 89

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Configuring the Integration Server
You must set your SeeBeyond Integration Server Password property before deploying
your Project.
1 From the Environment Explorer, right-click IntegrationSvr1 under your Logical
Host, and select Properties from the shortcut menu. The Integration Server
Properties Editor appears.
2 Click the Password property field under Sun SeeBeyond Integration Server
Configuration. An ellipsis appears in the property field.
3 Click the ellipsis. The Password Settings dialog box appears.
4 Enter STC as the Specific Value and as the Confirm Password, and click OK.
5 Click OK to accept the new property and close the Properties Editor.
For more information on deploying a Project see the Sun SeeBeyond Java™ Composite
Application Platform Suite Deployment Guide.
7.5.7 Creating the Deployment Profile
A Deployment Profile is used to assign services and message destinations to the
Integration Server and message server. Deployment profiles are created using the
Deployment Editor.
Steps required to create the Deployment Profile:
1 From the Enterprise Explorer’s Project Explorer, right-click the prjVSAM_BPEL
Project and select New > Deployment Profile.
2 Enter a name for the Deployment Profile (for this sample dpVSAM_BPEL). Select
envVSAMProj as the Environment and click OK.
3 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Automap icon. The Project’s
components are automatically mapped to their system windows, as seen in Figure
54.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 89 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 90

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
Figure 54 Deployment Profile
7.5.8 Creating and Starting the Domain
To build and deploy your Project, you must first create a domain. A domain is an
instance of a Logical Host. After the domain is created, the Project is built and then
deployed.
Note: You are only required to create a domain once when you install the Sun Java
Composite Application Platform Suite
Steps required to create and start the domain:
1 Navigate to your <JavaCAPS51>\logicalhost directory (where <JavaCAPS51> is
the location of your Sun Java Composite Application Platform Suite installation).
2 Double-click the domainmgr.bat file. The Domain Manager appears.
3 If you have already created a domain, select your domain in the Domain Manager
and click the Start an Existing Domain button. Once your domain is started, a
green check mark indicates that the domain is running.
4 If there are no existing domains, a dialog box indicates that you can create a domain
now. Click Yes . The Create Domain dialog box appears.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 90 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 91

Chapter 7 Section 7.5
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_BPEL Sample Project
5 Make any necessary changes to the Create Domain dialog box and click Create. The
new domain is added to the Domain Manager. Select the domain and click the Start
an Existing Domain button. Once your domain is started, a green check mark
indicates that the domain is running.
Note: For more information about creating and managing domains see the eGate
Integrator System Administration Guide.
7.5.9 Building and Deploying the Project
The Build process compiles and validates the Project’s Java files and creates the Project
EAR file.
Build the Project
1 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Build icon.
2 If there are any validation errors, a Validation Errors pane will appear at the bottom
of the Deployment Editor and displays information regarding the errors. Make any
necessary corrections and click Build again.
3 After the Build has succeeded you are ready to deploy your Project.
Deploy the Project
1 From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Deploy icon. Click Yes when the
Deploy prompt appears.
2 A message appears when the project is successfully deployed. You can now test
your sample.
7.5.10 Running the Sample Project
Additional steps are required to run the deployed sample Project.
Steps required to run the sample Project:
1 Rename one of the trigger files included in the sample Project from
<filename>.in.~in to <filename>.in to run the corresponding operation.
The File eWay polls the directory every five seconds for the input file name (as
defined in the Inbound File eWay Properties window). The Business Process then
transforms the data, and the File eWay sends the output to an Output file name (as
defined in the outbound File eWay Properties window).
The Where Clause defined in the business rule recognizes the trigger as a
placeholder for input, allowing a set condition, such as EMPID = 100, to determine
the type of output data.
You can modify the following input files to view different output.
TriggerTableSelect.in
TriggerDelete.in
TriggerUpdate.in
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 91 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 92

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
Having no content in these files causes the operation to read all records.
2 Verify the output data by viewing the sample output files. See “About the VSAM
eWay Sample Projects” on page 61 for more details on the types of output files
used in this sample Project. The output files may change depending on the number
of times you execute the sample Project, the input file, and also the content of your
database table.
7.6 Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample
Project
The following provides step-by-step instructions for manually creating the
prjVSAM_JCD sample Project.
Steps required to create the sample project include:
Creating a Project on page 92
Creating the OTDs on page 92
Creating a Connectivity Map on page 94
Creating the Collaboration Definitions (Java) on page 95
Create the Collaboration Business Rules on page 98
Binding the eWay Components on page 105
Creating an Environment on page 106
Configuring the eWays on page 107
Creating the Deployment Profile on page 110
Creating and Starting the Domain on page 111
Building and Deploying the Project on page 112
Running the Sample on page 112
7.6.1 Creating a Project
The first step is to create a new Project in the Enterprise Designer.
1 Start the Enterprise Designer.
2 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the Repository and select New Project. A
new Project (Project1) appears on the Project Explorer tree.
3 Click twice on Project1 and rename the Project (for this sample, prjVSAM_JCD).
7.6.2 Creating the OTDs
The sample Project requires three OTDs to interact with the VSAM eWay. These OTDs
include:
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 92 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 93

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
VSAM Database OTD
Inbound DTD OTD
Outbound DTD OTD
Steps required to create a VSAM Database OTD:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
The New Object Type Definition Wizard window appears.
2 Select the VSAM Database OTD Wizard from the list of OTD Wizards and click
Next.
3 Enter the connection information for the VSAM database. Connection fields
include:
Host name:
Port ID:
Database Name:
User name:
Password:
4 Click Next, and select the types of database object you want to include in the
sample Project. For our example, select the following:
Tables/Views/Aliases
Prepared Statements
5 Click Add to select tables from the VSAM database. The Add Tables window
appears.
6 Search for or Type in the name of the database. In this example we use the
CICSEMP table. Click Select when the database appears in the Results selection
frame. Click OK to close the Add Tables window
7 Click Next the Add Prepared Statements Wizard appears.
8 Click Add, the Add Prepared Statement window appears. Enter the following:
Prepared Statement Name: Select_ps
SQL Statement:
select * from CICSEMP where EMPID > ? order by EMPID
Note: In this example, the SQL statement includes the ? placeholder for input. This
placeholder represents the Where Clause.
9 Click the OK button to close the Prepared Statement window, and then click Next
on the Prepared Statements Wizard window.
10 Enter an OTD name. In this example, use otdVSAM.
11 Click Next and review your settings, then click Finish to create the OTD.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 93 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 94

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
Steps required to create inbound and outbound DTD OTDs include:
1 Right-click your new Project in the Enterprise Designer’s Project Explorer, and
select New > Object Type Definition.
The New Object Type Definition Wizard window appears.
2 Select DTD from the list of OTD Wizards and click Next.
3 Browse to and then select a DTD file. For this example, select one of the following
DTD files from the sample Project, and then click Next.
otdInputDTD.dtd
otdOutputDTD.dtd
4 The file you select appears in the Select Document Elements window. Click Next.
5 Click Finish to complete the DTD based OTD. Repeat this process again to create
the second DTD file.
7.6.3 Creating a Connectivity Map
The Connectivity Map provides a canvas for assembling and configuring a Project’s
components.
Steps required to create a new Connectivity Map:
1 From the Project Explorer tree, right-click the new prjVSAM_JCD Project and select
New > Connectivity Map from the shortcut menu.
2 The New Connectivity Map appears and a node for the Connectivity Map is added
under the Project, on the Project Explorer tree labeled CMap1.
Create four additional Connectivity Maps—CMap2, CMap3. CMap4, and
CMap5— and rename them as follows:
cmDelete
cmInsert
cmPsSelect
cmTableSelect
cmUpdate
The icons in the toolbar represent the available components used to populate the
Connectivity Map canvas.
Populating the Connectivity Map
Add the Project components to the Connectivity Map by dragging the icons from the
toolbar to the canvas.
Each Connectivity Map in the prjVSAM_JCD sample Project requires the following
components:
File External Application (2)
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 94 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 95

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
VSAM External Application
Service
Any eWay added to the Connectivity Map is associated with an External System. To
establish a connection to VSAM, first select VSAM as an External System to use in your
Connectivity Map.
Steps required to select a VSAM External System:
1 Click the External Application icon on the Connectivity Map toolbar.
2 Select the external systems necessary to create your Project (for this sample, VSAM
and File). Icons representing the selected external systems are added to the
Connectivity Map toolbar.
3 Rename the following components and then save changes to the Repository:
File1 to FileClientIN
File2 to FileClientOUT
VSAM1 to eaVSAMOUT
4 Rename each Connectivity Map Service to match the intended operation, as for
example:
jcdDelete
jcdInsert
jcdPsSelect
jcdTableSelect
jcdUpdate
7.6.4 Creating the Collaboration Definitions (Java)
The next step is to create Collaborations using the Collaboration Definition Wizard
(Java). Since the sample Project includes five database operations, you must create five
separate Collaboration Definitions (Java), or JCDs. Once you create the Collaboration
Definitions, you can write the Business Rules of the Collaborations using the
Collaboration Editor.
JCDs required for the prjVSAM_JCD sample include:
jcdDelete
jcdInsert
jcdPsSelect
jcdTableSelect
jcdUpdate
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 95 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 96

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
jcdDelete Collaboration
Steps required to create the jcdDelete Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdDelete) and click Next.
3 For Step 2 of the wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window,
double-click Sun SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient > receive. The File Name
field now displays receive. Click Next.
4 For Step 3 of the wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click
prjVSAM_JCD > otdALL > otdVSAM. The otdVSAM OTD is added to the
Selected OTDs field.
5 Click the Up One Level button twice to return to the Repository. Double-click Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient. The Selected OTDs field now lists the
FileClient OTD.
6 Click Finish. The Collaboration Editor with the new jcdDelete Collaboration
appears in the right pane of the Enterprise Designer.
jcdInsert Collaboration
Steps required to create the jcdInsert Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdInsert) and click Next.
3 For Step 2 of the wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window,
double-click Sun SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient > receive. The File Name
field now displays receive. Click Next.
4 For Step 3 of the wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click
prjVSAM_JCD > otdALL > otdVSAM. The otdVSAM OTD is added to the
Selected OTDs field.
5 In the same window, double-click otdInputDTD_CICSEMP. The
otdInputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is added to the Selected OTDs field.
Note: The otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is created from the otdInputDTD.dtd that is
included in the Sample Project.
6 Click the Up One Level button twice to return to the Repository. Double-click Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient. The Selected OTDs field now lists the
FileClient OTD.
7 Click Finish. The Collaboration Editor with the new jcdInsert Collaboration
appears in the right pane of the Enterprise Designer.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 96 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 97

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
jcdPsSelect Collaboration
Steps required to create the jcdPsSelect Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdPsSelect) and click Next.
3 For Step 2 of the wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window,
double-click Sun SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient > receive. The File Name
field now displays receive. Click Next.
4 For Step 3 of the wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click
prjVSAM_JCD > otdALL > otdVSAM. The otdVSAM OTD is added to the
Selected OTDs field.
5 In the same window, double-click otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP. The
otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is added to the Selected OTDs field.
Note that the otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is created from the
otdOutputDTD.dtd that is included in the Sample Project.
6 Click the Up One Level button twice to return to the Repository. Double-click Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient. The Selected OTDs field now lists the
FileClient OTD.
7 Click Finish. The Collaboration Editor with the new jcdPsSelect Collaboration
appears in the right pane of the Enterprise Designer.
jcdTableSelect Collaboration
Steps required to create the jcdTableSelect Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdTableSelect) and click
Next.
3 For Step 2 or the wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window,
double-click Sun SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient > receive. The File Name
field now displays receive. Click Next.
4 For Step 3 of the wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click
prjVSAM_JCD > otdALL > otdVSAM. The otdVSAM OTD is added to the
Selected OTDs field.
5 In the same window, double-click otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP. The
otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is added to the Selected OTDs field.
Note: The otdOutputDTD_CICSEMP OTD is created from the otdOutputDTD.dtd that
is included in the Sample Project.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 97 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 98

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
6 Click the Up One Level button twice to return to the Repository. Double-click Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient. The Selected OTDs field now lists the
FileClient OTD.
7 Click Finish. The Collaboration Editor with the new jcdTableSelect Collaboration
appears in the right pane of the Enterprise Designer.
jcdUpdate Collaboration
Steps required to create the jcdUpdate Collaboration:
1 From the Project Explorer, right-click the sample Project and select New >
Collaboration Definition (Java) from the shortcut menu. The Collaboration
Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
2 Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this sample jcdUpdate) and click Next.
3 For Step 2 of the wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window,
double-click Sun SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient > receive. The File Name
field now displays receive. Click Next.
4 For Step 3 of the wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click
prjVSAM_JCD > otdALL > otdVSAM. The otdVSAM OTD is added to the
Selected OTDs field.
5 Click the Up One Level button twice to return to the Repository. Double-click Sun
SeeBeyond > eWays > File > FileClient. The Selected OTDs field now lists the
FileClient OTD.
6 Click Finish. The Collaboration Editor with the new jcdUpdate Collaboration
appears in the right pane of the Enterprise Designer.
7.6.5 Create the Collaboration Business Rules
The next step in the sample is to create the Business Rules of the Collaboration using
the Collaboration Editor.
Creating the jcdDelete Business Rules
The jcdDelete Collaboration implements the Input Web Service Operation to read the
TriggerDelete.in file and then delete a record under a specific criteria. The
Collaboration also writes a message to JCD_Delete_output0.dat to confirm a deleted
record.
Note: The where clause in the business rule reads the trigger value as a placeholder for
input. This permits you to modify the query to select a specific record. Also note that
all records are deleted from the database when the TriggerDelete.in file is empty.
The jcdDelete Collaboration contains the Business Rules displayed in Figure 55.
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 98 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 99

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
Figure 55 jcdDelete Business Rules
Creating the jcdInsert Business Rules
The jcdInsert Collaboration implements the Input Web Service Operation to read the
TriggerInsert.in. file. It then unmarshals data from the input data into the
otdInputDTD_CICSEMP OTD, calls the otdVSAM OTD, and inserts records into the
database via a For Loop. The Collaboration also writes a message to
JCD_Insert_output0.dat to confirm an inserted record.
The jcdInsert Collaboration contains the Business Rules displayed in Figure 56.
Figure 56 jcdInsert Business Rules
Sample code from the jcdInsert Includes:
package prjVSAM_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdInsert
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 99 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Page 100

Chapter 7 Section 7.6
Implementing the VSAM eWay Sample Projects Building and Deploying the prjVSAM_JCD Sample Project
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage
input, dtd.otdInputDTD_622919076.Emp otdInputDTD_Emp_1,
otdVSAM.OtdVSAMOTD otdVSAM_1,
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
\\ Writes out a message stating records are being inserted.
FileClient_1.setText( "Inserting records into CICSEMP table .."
);
FileClient_1.write();
\\ Unmarshals data from the input XML data into the
otdInputDTD_DBEmployees OTD.
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.unmarshalFromString( input.getText() );
\\ Calls the otdVSAM OTD, and inserts multiple records into the
database via a For Loop. The first insert() method opens the table
result set for insert operations, while the insertRow() method
inserts records into the table result set.
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < otdInputDTD_Emp_1.countX_sequence_A();
i1 += 1) {
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setENAME(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getENAME() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setPHONE(
typeConverter.stringToInt( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getPHONE(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setMAILID(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getMAILID() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setSALARY( new
java.math.BigDecimal( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getSALARY() ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setJOBID(
typeConverter.stringToDouble( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getJOBID(), "#.000000;-#.000000", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setEMPID(
typeConverter.stringToInt( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getEMPID(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setDEPTID(
typeConverter.stringToShort( otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1
).getDEPTID(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().setDEPARTMENT(
otdInputDTD_Emp_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getDEPARTMENT() );
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().insertRow();
\\ Writes a message to confirm an inserted records.
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Done Insert." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
otdVSAM_1.getCICSEMP().insert();
Creating the jcdPsSelect Business Rules
The jcdPsSelect Collaboration implements the Input Web Service Operation to read the
TriggerPsSelect.in file. It then copies the database resultset (as noted in the prepared
VSAM eWay Adapter User’s Guide 100 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...