Page 1
Sun Java™ System
Content Delivery Server 5.0
Administration Guide
2005Q4
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
www.sun.com
Part No.: 819-3209-10
2005Q4
Submit comments about this document at: http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/form/comments
Page 2

Copyright ©2005 SunMicrosystems, Inc., 4150Network Circle, SantaClara, California 95054, U.S.A. Allrights reserved.
Sun Microsystems,Inc. has intellectual property rights relatingto technology embodied in theproduct that isdescribed inthis document. In
particular,and without limitation, these intellectualproperty rights mayinclude oneor more ofthe U.S. patents listed at
http://www.sun.com/patents and one or more additional patents or pendingpatent applicationsin the U.S.and inother countries.
U.S. GovernmentRights -Commercial software. Government users are subject to the SunMicrosystems, Inc. standardlicense agreement and
applicable provisionsof the FAR and its supplements.
This distributionmay includematerials developed by third parties.
Sun, SunMicrosystems, the Sun logo, Java,and J2ME aretrademarks or registeredtrademarks of SunMicrosystems, Inc. in the U.S.and other
countries.
UNIX isa registered trademarkin the U.S. and othercountries, exclusively licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd.
Netscape andNetscape Navigatoris a trademark or registered trademarkof Netscape Communications Corporation inthe United States and
other countries.
Products covered by and informationcontained in this service manualare controlled byU.S. Export Controllaws and may be subjectto the
export orimport lawsin other countries. Nuclear, missile, chemical biologicalweapons or nuclear maritime enduses orend users, whether
direct orindirect, are strictly prohibited.Export orreexportto countriessubject to U.S. embargo or to entities identifiedon U.S. export exclusion
lists, including,but notlimited to, the denied personsand specially designated nationals listsis strictly prohibited.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESSFOR APARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT,
ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Copyright ©2005 SunMicrosystems, Inc., 4150Network Circle, SantaClara, California 95054, Etats-Unis. Tous droits réservés.
Sun Microsystems,Inc. détient les droits de propriétéintellectuels relatifs àla technologieincorporée dans leproduit qui est décrit dansce
document. Enparticulier, et ce sanslimitation, ces droitsde propriété intellectuellepeuvent inclure unou plusdes brevets américainslistés à
l’adresse http://www.sun.com/patents et unou lesbrevets supplémentaires ou les applications debrevet en attenteaux Etats- Unis et
dans lesautres pays.
Cette distributionpeut comprendre descomposants développés par des tierces parties.
Sun, SunMicrosystems, le logo Sun, Java,et J2ME sont des marques de fabrique oudes marques déposéesde SunMicrosystems,Inc. auxEtatsUnis etdans d'autres pays.
UNIX estune marque déposée aux Etats-Uniset dans d’autrespays et licenciée exlusivement parX/Open Company, Ltd.
Netscape etNetscape Navigatorest une marquede Netscape Communications Corporation auxEtats-Unis et dans d'autres pays.
Les produitsqui font l'objet de cemanuel d'entretien etles informations qu'il contient sontregis par lalegislation americaineen matiere de
controle desexportations et peuvent etre soumis au droit d'autres paysdans ledomaine des exportationset importations.Les utilisations
finales, ouutilisateurs finaux,pour des armes nucleaires, des missiles, des armesbiologiques et chimiques ou dunucleaire maritime,
directement ouindirectement, sont strictementinterdites. Les exportationsou reexportations versdes payssous embargo desEtats-Unis, ou
vers desentites figurantsur les listes d'exclusion d'exportationamericaines, y compris, mais demaniere non exclusive,la liste de personnes qui
font objetd'un ordre dene pas participer, d'une facon directe ouindirecte,aux exportationsdes produits oudes services qui sont regi par la
legislation americaineen matiere de controle des exportations et laliste de ressortissantsspecifiquement designes, sont rigoureusement
interdites.
LA DOCUMENTATION ESTFOURNIE "EN L'ETAT" ET TOUTES AUTRES CONDITIONS, DECLARATIONSET GARANTIES EXPRESSES
OU TACITES SONT FORMELLEMENT EXCLUES, DANSLA MESURE AUTORISEEPAR LA LOI APPLICABLE, YCOMPRIS NOTAMMENT
TOUTE GARANTIEIMPLICITE RELATIVEA LAQUALITE MARCHANDE, AL'APTITUDE AUNE UTILISATIONPARTICULIERE OU A
L'ABSENCE DECONTREFACON.
Page 3

Contents
Preface xv
1. Introduction 1
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server 1
Catalog Manager 3
Catalog Manager Processes 4
Automated Content Validation 5
Content Management 5
Device Management 6
Account Management 6
Plan Management 6
Fulfillment Manager 7
Vending Manager 7
Vending Manager Processes 9
Content Management 9
Plan Management 9
Account Management 9
Reporting 10
Administration Consoles 10
Browser Requirements 10
iii
Page 4

Accessing the Administration Consoles 11
▼ Logging in to the Catalog Manager 11
▼ Logging in to the Vending Manager 12
2. Catalog Manager 13
Managing Content 13
Managing Content Categories 14
▼ Viewing Categories 14
▼ Adding a Category 16
▼ Editing a Category 17
▼ Deleting a Category 18
Managing Content Types 19
Content Submissions 19
Content Protection 20
Inapplicable Content 21
Using CDS DRM Agents and CDS OMA
Forward Lock 21
Using OMA DRM 1.0 23
OMA DRM 1.0 and Non-Compliant Devices 24
MIME Types for OMA DRM 1.0 24
Associating Content Types with DRMs 25
Enabling and Disabling a DRM 26
Pricing Content 26
Pricing Options 29
Changing the Pricing of Content 29
Disassociating Content From Pricing Options 30
▼ Viewing Supported Content Types and MIME Types 31
▼ Viewing Properties for a Supported MIME Type 32
▼ Adding a Content Type 32
iv Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 5

▼ Editing a Content Type 34
▼ Creating a Pricing Option 35
▼ Editing a Pricing Option 37
▼ Deleting a Content Type 39
▼ Disabling a Pricing Option 39
▼ Registering a MIME Type 40
▼ Editing a MIME Type 41
▼ Deleting a MIME Type 43
Managing Submitted Content 44
▼ Viewing Submitted Content 44
▼ Viewing Submitted Editions 47
▼ Removing an Edition 48
▼ Searching for Content 49
▼ Changing the Status of Content 50
▼ Changing the Status of Editions 52
▼ Editing Content 52
Managing Published Content 55
▼ Viewing Published Content 56
▼ Removing Content 57
▼ Viewing Published Editions 57
▼ Copying or Moving Categories of Content 58
▼ Copying or Moving Content Items 62
Setting Custom Prices for Published Content 66
Managing Devices 68
Managing Device Libraries 69
▼ Viewing Device Libraries 70
▼ Viewing Properties for a Specific Device Library 70
▼ Adding a Device Library 71
Contents v
Page 6

▼ Editing a Device Library 73
▼ Deleting a Device Library 74
Managing Content Descriptor Templates 74
▼ Viewing Content Descriptor Templates 76
▼ Adding a Content Descriptor Template 77
▼ Editing a Content Descriptor Template 78
Managing Device Definitions 78
Viewing Devices 78
▼ Adding a Device 80
▼ Specifying Device Capabilities 83
▼ Activating New or Quarantined Devices 85
▼ Mapping MIME Types to a Device 86
▼ Setting a Compatible Device 88
▼ Adding Supported Devices to Existing Content 89
▼ Editing a Device 89
▼ Setting the Default Device 90
▼ Deleting a Device 91
▼ Importing Devices 91
▼ Exporting Devices 92
Managing Server Locales 92
▼ Adding a New Locale 92
▼ Changing a Locale 94
Deleting a Locale 94
Managing Accounts 94
▼ Viewing Accounts 95
Managing Vending Manager Accounts 97
▼ Viewing Vending Manager Accounts 97
▼ Adding a Vending Manager Account 97
vi Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 7

▼ Editing a Vending Manager Account 99
▼ Deleting a Vending Manager Account 100
Managing Developer Accounts 101
▼ Viewing Developer Accounts 101
▼ Adding a Developer Account 101
▼ Editing a Developer Account 103
▼ Deleting a Developer Account 104
Managing Catalog Manager Administrator Accounts 104
▼ Viewing Catalog Manager Administrator Accounts 104
▼ Adding a Catalog Manager Administrator Account 105
▼ Editing a Catalog Manager Administrator Account 106
▼ Deleting a Catalog Manager Administrator Account 106
Managing Plans 107
Managing Vending Plans 107
▼ Viewing Vending Plans 107
▼ Adding a Vending Plan 108
▼ Editing a Vending Plan 110
▼ Viewing Vending Plan Members 111
▼ Adding a Member to a Vending Plan 111
▼ Removing a Member from a Vending Plan 112
▼ Setting the Default Vending Plan 112
▼ Deleting a Vending Plan 113
Managing Developer Plans 114
▼ Viewing Profiles 114
▼ Adding a Profile 115
▼ Editing a Profile 117
▼ Deleting a Profile 118
▼ Viewing Developer Plans 119
Contents vii
Page 8

▼ Adding a Developer Plan 119
▼ Editing a Developer Plan 120
▼ Viewing Developer Licensees 121
▼ Adding a Developer Licensee to a Developer Plan 122
▼ Removing a Developer Licensee from a Developer Plan 123
▼ Setting the Default Developer Plan 123
▼ Deleting a Developer Plan 124
Getting Background Job Status 125
▼ Getting Job Status 126
Examining Job Details 127
Clearing a Failed Job 128
3. Vending Manager 129
Administrator Tasks 130
Managing Categories 130
▼ Adding a Category 130
▼ Editing a Category 132
▼ Deleting a Category 133
Managing Catalog Content 134
▼ Viewing Published Content 134
▼ Searching for Published Content 137
▼ Viewing the Properties of Published Content 137
▼ Viewing Editions of Published Content 139
Setting Stocking Options 141
▼ Stocking Content Manually 142
▼ Stocking Multiple Content Items 144
Viewing Stocking Jobs 149
Clearing the Stocking Jobs list 150
▼ Stopping a Stocking Job 150
viii Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 9

Checking the Status of a Stocking Job 151
▼ Updating the Catalog for Stocked Content 152
Pricing for Content for a Locale 153
▼ Setting Local Pricing 153
Price Update Notification 155
▼ Changing the Price of Individual Content Items 156
Managing Stocked Content 156
Viewing Stocked Content 156
▼ Searching for Stocked Content 156
▼ Changing the Status of Stocked Content 157
▼ Unstocking Content 158
▼ Editing Stocked Content 159
▼ Editing External Content IDs 161
Updating Stocked Content 162
▼ Copying or Moving Categories of Content 163
▼ Copying or Moving Content Items 167
▼ Customizing Prices for Stocked Content 170
Managing Bundles 173
Bundle Pricing 174
▼ Creating a Bundle 175
▼ Viewing Bundle Information 179
▼ Deleting a Bundle 181
▼ Editing External Content IDs 181
▼ Changing the Status of a Bundle 182
▼ Editing a Bundle 183
▼ Managing Testing Content 183
▼ Stocking Testing Content 184
Creating Customized Marketing Campaigns 184
Contents ix
Page 10

▼ Creating a Campaign 185
▼ Specifying a Campaign Type 185
▼ Specifying Campaign Options and Target Audience 186
▼ Specifying a Campaign Message 187
▼ Specifying Content for the Campaign 188
▼ Specifying Campaign Pricing Characteristics 189
▼ Specifying Campaign Scheduling 190
▼ Viewing Campaign Details 191
▼ Editing a Campaign 193
▼ Testing a Campaign 193
Working with Subscriber Segments 194
▼ Displaying Subscriber Segments 195
▼ Creating a Subscriber Segment 195
▼ Editing a Subscriber Segment 197
Working with Campaign Templates 197
▼ Displaying Available Campaign Templates 197
▼ Creating a Campaign Template 197
▼ Editing a Campaign Template 201
Managing Vending Manager Administrator Accounts 201
▼ Viewing Vending Manager Administrator Accounts 201
▼ Adding a Vending Manager Administrator Account 202
▼ Editing a Vending Manager Administrator Account 204
▼ Deleting a Vending Manager Administrator Account 205
Customer Care Agent Tasks 205
▼ Viewing Stocked Content 206
▼ Setting the Display of Stocked Content for Subscribers 207
▼ Viewing the Properties of Stocked Content 208
▼ Viewing Editions of Stocked Content 209
x Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 11

Managing Subscriber Accounts 209
▼ Viewing Subscriber Accounts 210
▼ Adding a Subscriber Account 210
▼ Editing a Subscriber Account 212
▼ Viewing a Subscriber’s Download History 213
▼ Managing Subscriber Licenses 213
▼ Extending Trial Usage 214
▼ Issuing a Refund 215
▼ Deleting a Subscriber Account 215
Managing Subscriber Plans 216
▼ Viewing Subscriber Plans 216
▼ Adding a Subscriber Plan 217
▼ Editing a Subscriber Plan 218
▼ Viewing Subscriber Plan Members 219
▼ Adding Members to a Subscriber Plan 220
▼ Removing Members from a Subscriber Plan 221
▼ Setting a Default Plan for New Subscribers 221
▼ Deleting a Subscriber Plan 222
▼ Editing Your Administrator Account 223
▼ Viewing Reports 223
Sending MMS Messages 225
▼ Choosing MMS as the Content Delivery System 225
Displaying MMS Messages 225
▼ Creating an MMS Message 226
▼ Editing an MMS Message 228
▼ Testing an MMS Message 229
Testing a New MMS Message 229
▼ Testing an Existing MMS Message 230
Contents xi
Page 12

▼ Deleting an MMS Message 230
▼ Using the MMS Test Log 231
A. Device Capabilities 233
Descriptions of the Capabilities 233
System Capabilities 233
Mandatory Capabilities 234
Content Delivery Server-Specific Capabilities 234
Browser Capabilities 235
User Interface and Software Capabilities 235
Specifying a Capability Value 236
List 237
Integer 237
Boolean 237
Device Specifications 237
Nokia 6310i 238
User-Defined Devices 239
B. Content Pricing 241
Pricing Scenarios 243
Glossary 247
Index 255
xii Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 13

Tables
TABLE 2-1 DRM Types 20
TABLE 2-2 CDS DRM Agents 21
TABLE 2-3 OMA DRM 1.0 Formats 23
TABLE 2-4 Required MIME Types for OMA DRM 1.0 24
TABLE 2-5 DRM Options and Associated DRM Types and Content Types 25
TABLE 2-6 Content Delivery Server Pricing Models 27
TABLE 2-7 DRM Options and Pricing Models 28
TABLE 2-8 Content Status Types 44
TABLE 2-9 Content Status Types 50
TABLE 2-10 Content Delivery Server Pricing Models 54
TABLE 2-11 Content Attributes for Content Descriptor Templates 75
TABLE 2-12 Account Types 95
TABLE 2-13 Search and Display Operations 96
TABLE 2-14 Plan Types 107
TABLE 2-15 Background Job Indicators 125
TABLE 3-1 Content Status Symbols 136
TABLE 3-2 Properties Available for Notification Templates 198
TABLE A-1 Mandatory Capabilities 234
TABLE A-2 Content Delivery Server-Specific Capabilities 234
TABLE A-3 User Interface and Software Capabilities 235
xiii
Page 14

TABLE A-4 Nokia 6310i Device Specifications 238
TABLE A-5 Device Specifications for a User-Defined Device 1 239
TABLE A-6 Device Specifications for a User-Defined Device 2 239
TABLE B-1 Associated DRMs, Content Types, and Pricing Models 241
TABLE B-2 Initial Pricing Set for Items 1 and 2 244
TABLE B-3 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 1 244
TABLE B-4 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 2 244
TABLE B-5 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 3 245
TABLE B-6 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 4 245
TABLE B-7 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 5 245
TABLE B-8 Resulting Pricing for Items 1 and 2 in Scenario 6 246
xiv Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 15
Preface
This guide provides an overview of the Sun Java™ System Content Delivery Server.
It describes how to administer the Catalog Manager and Vending Manager
components. It describes the device capabilities and the content pricing models
supported by the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server.
Before You Read This Document
This guide is written for system administrators who are responsible for
administering the Catalog Manager or Vending Manager. It assumes some
knowledge of networking, database, and web technologies.
Note – Sun is not responsible for the availability of third-party web sites mentioned
in this document, and does not endorse and is not responsible or liable for any
content, advertising, products, or other materials available through such sites.
How This Document Is Organized
This guide is divided into the following chapters:
■ Chapter 1 introduces the Content Delivery Server and describes the content life
cycle as it relates to the Catalog Manager and Vending Manager. It describes the
automatic content validation process that the Content Delivery Server performs
on submitted content. It also describes how to log in to the Catalog Manager and
Vending Manager administration consoles.
xv
Page 16

■ Chapter 2 describes how to administer the Catalog Manager. It provides
instructions on how to review, categorize, and publish content. It describes how
to define the mobile devices supported and their capabilities. It also describes
how to manage access for developers and Vending Managers.
■ Chapter 3 describes how to administer the Vending Manager. It describes how to
stock content, manage Administrator and Subscriber Accounts, and run system
reports.
■ Appendix A describes the capability matching process and defines the device
capabilities currently supported by the Content Delivery Server.
■ Appendix B provides a description of the digital rights management types
supported in the Content Delivery Server and provides a set of business scenarios
involving content pricing and availability in the Catalog and Vending Managers.
■ The Glossary defines the terms used in the context of this guide.
Typographic Conventions
The following tables define the typographical conventions and terms used
throughout this guide:
a
Typeface
AaBbCc123 The names of commands, files,
AaBbCc123
AaBbCc123 Book titles, new words or terms,
a The settings on your browser might differ from these settings.
xvi Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Meaning Examples
Edit your .login file.
and directories; on-screen
computer output
What you type, when
contrasted with on-screen
computer output
words to be emphasized
Command-line variable; replace
with a real name or value
Use ls -a to list all files.
% You have mail.
% su
Password:
Read Chapter 6 in the User’s Guide.
These are called class options.
Yo u must be super user to do this.
To delete a file, type rm filename.
Page 17

Related Documentation
The Sun Java System Content Delivery Server manuals are available as Portable
Document Format (PDF) and Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) files. These files
are available in the Documentation subdirectory of the directory where the
Content Delivery Server is installed as well as online at http://docs.sun.com.
The following table summarizes the books included in the Content Delivery Server
documentation set.
Book Title Description Part Number
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Branding and Localization Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Capacity Planning Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Content Developer Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Customization Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Error Messages
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Installation Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Integration Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
Migration Guide
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
System Management Guide
Describes how to customize the Subscriber Portal
and Developer Portal components of the Content
Delivery Server for the look and feel of your
enterprise. This guide also describes how to localize
the Content Delivery Server interfaces.
Provides guidelines for determining what hardware
and software is needed to efficiently run the Content
Delivery Server.
Describes how to submit content to the Content
Delivery Server.
Describes the Content Delivery Server APIs that can
be used to create customized adapters for use in
integrating Content Delivery Server with the existing
infrastructure.
Describes error messages that are generated by the
Content Delivery Server and suggests actions to take
to resolve problems reported.
Provides information about installing and
configuring the Content Delivery Server.
Describes adapters for integrating the Content
Delivery Server with existing systems such as billing,
user data, WAP gateway, and push delivery. It also
describes the framework for creating device-specific
versions of the Subscriber Portal.
Describes how to migrate from a previous version of
the Content Delivery Server to the current version.
Provides information on running and maintaining
the Content Delivery Server.
819-3210-10
819-3211-10
819-3212-10
819-3213-10
819-3214-10
819-3215-10
819-3216-10
819-3217-10
819-3218-10
Preface xvii
Page 18

Accessing Sun Documentation Online
The Sun Product Documentation web site enables you to access Content Delivery
Server documentation on the web at http://docs.sun.com.
Sun Welcomes Your Comments
Sun is interested in improving its documentation and welcomes your comments and
suggestions.
To share your comments, go to http://docs.sun.com and click Send Comments.
In the online form, provide the document title and part number.
xviii Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 19

CHAPTER
1
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the Sun Java™ System Content Delivery
Server. It describes the content lifecycle and provides an overview of the Catalog
Manager, Fulfillment Manager, and Vending Manager components. It describes the
automatic content validation process that takes place when content is submitted to
the Content Delivery Server.
This chapter also describes how to log in to the Catalog Manager and Vending
Manager administration components.
Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
The Sun Java System Content Delivery Server is a high-performance software
solution that lets operators manage the complexity of delivering virtually any type
of wireless content over-the-air (OTA) to their subscribers. The Content Delivery
Server separates content aggregation, presentation, and delivery into two distinct
managers, the Catalog Manager and the Vending Manager. With these managers,
operators can centrally manage content, customize multiple subscriber interfaces,
and provide fast downloads.
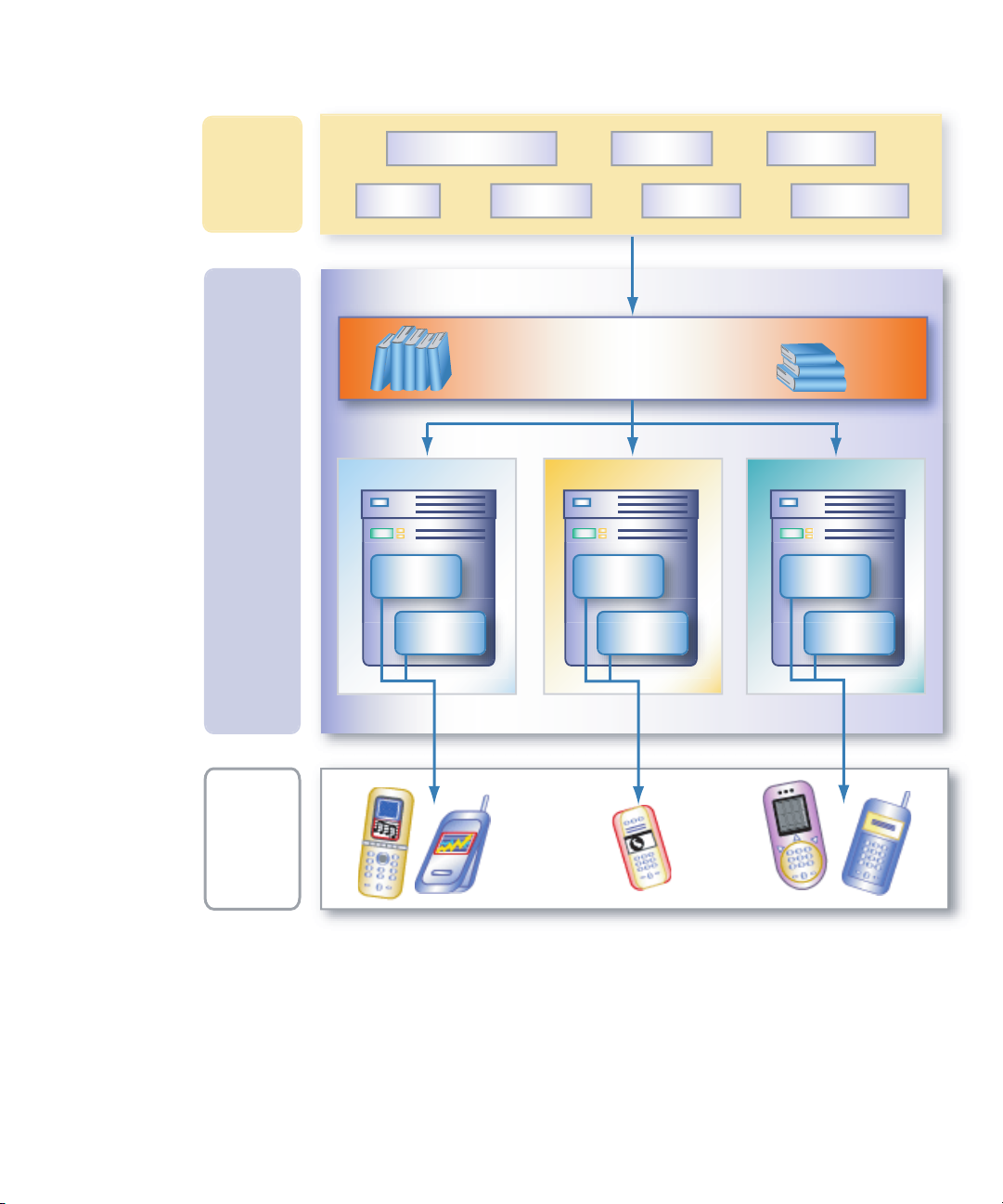
The following figure provides a high-level overview of the Content Delivery Server.
1
Page 20
Content
Providers
Java Applications Ringtones Wallpapers
GamesMusic Videos Extensible...
Operator
Subscriber
Java System Content Delivery Server
Catalog Manager
Vending Manager
Subscriber
Portal
Fulfillment
Manager
Vending Manager
Subscriber
Portal
Fulfillment
Manager
Vending Manager
Subscriber
Portal
Fulfillment
Manager
1. The content provider creates an application and submits it to the Catalog
Manager using the web-based Developer Portal.
2. The Catalog Manager validates the content.
2 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 21

3. The Catalog Manager administrator publishes the content, making it available to
the Vending Manager.
4. The Vending Manager administrator selects content published from the Catalog
Manager and stocks the content, making it available to subscribers.
Catalog Manager
The Catalog Manager is the content aggregator or warehouse. It manages all the
content coming from the developer community. After the content is authorized, the
Catalog Manager makes the content available to the Vending Managers. The
Vending Managers then sell the content to their unique subscriber community.
The Catalog Manager supports any type of content. The Catalog Manager
administrators define the type of content that they want to accept for their
enterprise.
The Catalog Manager administrator manages these functions:
■ Submitted and published content
■ Supported mobile devices
■ Content provider access and pricing
■ Vending Manager access and content
■ Administrator access
The following figure provides a high-level overview of the role of the Catalog
Manager in the lifecycle of an application. It also illustrates the Catalog Manager
processes.
Chapter 1 Introduction 3
Page 22
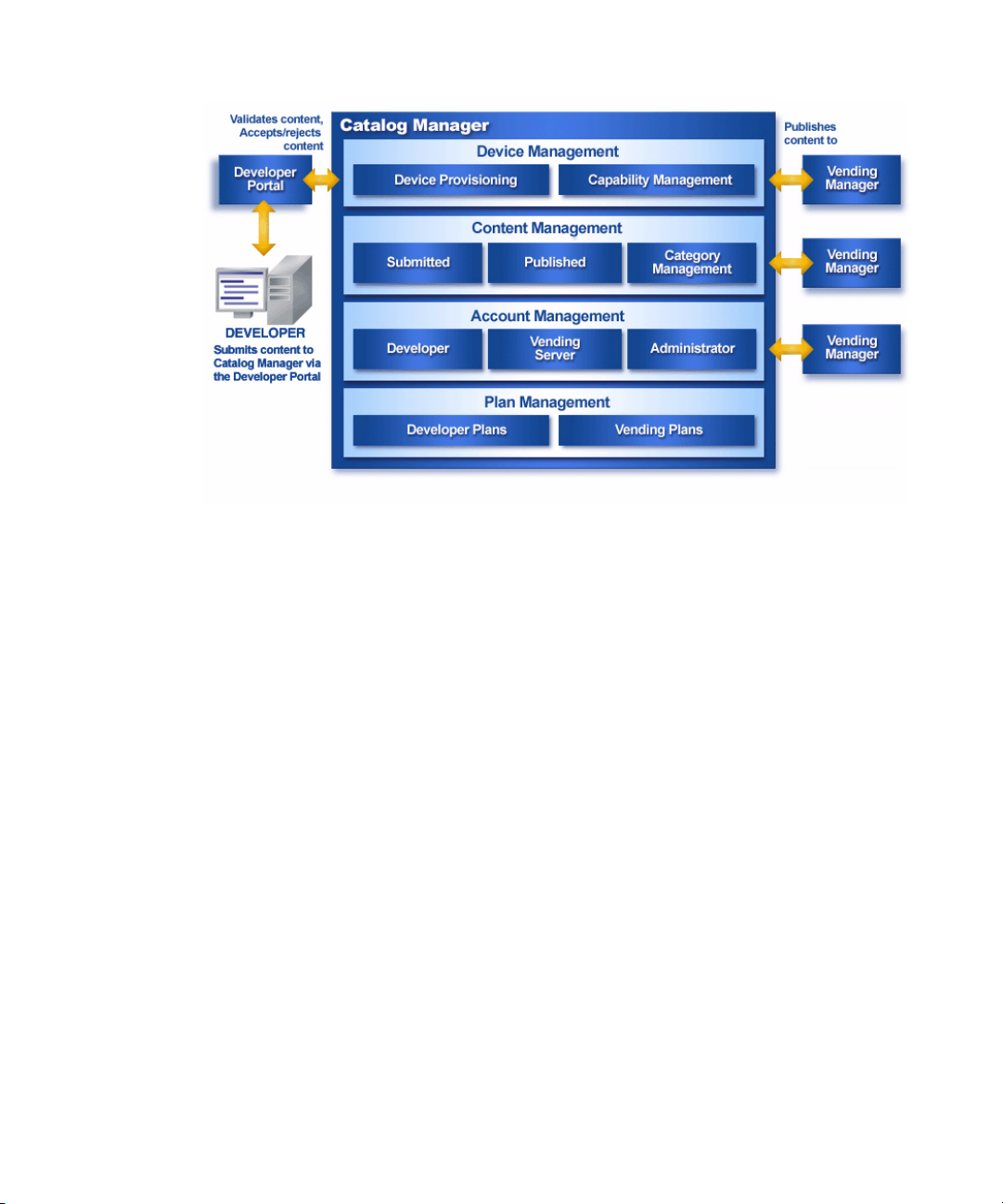
1. Developers submit content to the Catalog Manager. The Catalog Manager runs an
automated validation process on the content to ensure there is no malicious
content and that the content matches the supported devices.
2. The content goes to the Submitted Content section of the Catalog Manager for
review by the administrator. The administrator reviews the content and, if
required, edits the content and modifies the pricing and category assignments.
The administrator can accept or reject the content.
3. The Catalog Manager publishes the content, which makes it available to the
Vending Manager.
Catalog Manager Processes
As shown in the previous figure, the Catalog Manager manages content submitted
by developers and controls which Vending Managers access which content. The
Catalog Manager is responsible for the following functions:
■ Automated Content Validation
■ Content Management
■ Device Management
■ Account Management
■ Plan Management
4 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 23

Automated Content Validation
The Sun Java System Content Delivery Server performs an automated validation of
content. If an application fails at any stage of validation, it is not submitted to the
Catalog Manager.
Note – The default implementation of content validation performs automated
validation on MIDlets only. You can customize the validation process to validate
other types of content.
Content validation includes the following tasks:
■ API Filtering. The API Filter checks that the APIs used in the MIDlet application
are allowed. Developer Plans define the set of APIs allowed. When a developer
submits content, the API Filter checks the APIs used by the submitted application.
If any API is not allowed by the Developer Plans associated with the developer,
the content fails.
■ Instrumentation. The instrumentation process inserts code into the MIDlet
application to interpret the pricing model assigned. For example, the inserted
code interprets whether the application is priced per download, on first
download only, by subscription, or any combination of these.
The instrumented code maintains licensing information on the device and
periodically communicates with the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server to
verify that the subscriber is authorized to run the application. If a license has
expired, the subscriber is given the opportunity to renew the license.
■ Customized Steps. You can customize the validation process to meet the needs of
your organization. You can disable selected processes or add processes as needed.
For example, you might want to add a step to obfuscate an application.
Obfuscation makes the code difficult to understand when it is decompiled and
can reduce the size of the Java Archive (JAR) file.
Content Management
Once content passes the automated validation process, it goes to the submitted
content section for review by the Catalog Manager administrator. This section
describes the content and categories managed by the Catalog Manager:
Chapter 1 Introduction 5
Page 24

■ Submitted Content. The administrator reviews submitted content and, if
required, edits the content and modifies the pricing and category assignments.
The administrator can accept or reject the content.
■ Published Content. After accepting the content, the administrator publishes the
content to make it available to the Vending Manager.
■ Categories. Content categories are central to content management. They are
logical containers or buckets that hold the content managed by the Sun Java
System Content Delivery Server. The Catalog Manager uses content categories to
control Vending Manager access.
See “Managing Content” on page 13 for more information.
Device Management
The Catalog Manager defines the devices and the device capabilities supported by
the Content Delivery Server. As a Catalog Manager administrator, you can add new
devices, delete devices no longer supported, and edit the characteristics and
capabilities of any device model. “Managing Devices” on page 68 describes how to
manage the devices supported for your network.
Account Management
Accounts define access to the Catalog Manager. The Catalog Manager has three
types of accounts:
■ Vending Manager. A Vending Manager Account is for a specifically-branded
Vending Manager that stocks content from the Catalog Manager. It is associated
with one or more Vending Plans.
■ Developer. Developer Accounts are for corporations or individuals that submit
content to the Catalog Manager. Developer Accounts are associated with one or
more Developer Plans.
■ Administrator. Administrator Accounts are for individuals who administer the
Catalog Manager.
See “Managing Accounts” on page 94 for more information.
Plan Management
The Catalog Manager uses the following plans to control content submission for
developers and content access for Vending Managers:
6 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 25

■ Vending Plans. Vending Plans define the categories that a Vending Manager can
access. Vending Plans can contain a nested hierarchy of other Vending Plans. Each
Vending Manager Account is associated with one or more Vending Plans.
■ Developer Plans. Developer Plans define the set of APIs that developers can use
in applications that they submit. Profiles define the classes in a specific library
that developers can use. A Developer Plan contains one or more Profiles.
See “Managing Plans” on page 107 for more information.
Fulfillment Manager
The Fulfillment Manager controls and delivers content to subscribers through a
high-performance and cost-effective download architecture. The following figure
provides a high-level overview of the Fulfillment Manager processes.
No administration tasks are associated with the Fulfillment Manager.
Vending Manager
The Vending Manager handles selling and pricing content. Vending Managers are
generally configured to serve separate enterprises. A single Catalog Manager can
serve multiple Vending Managers.
The Vending Manager manages content published by the Catalog Manager. Content
stocked on the Vending Manager is available for subscribers to download.The
Vending Manager also controls subscriber access and purchase pricing, and provides
daily statistical reports on the Content Delivery Server.
Chapter 1 Introduction 7
Page 26
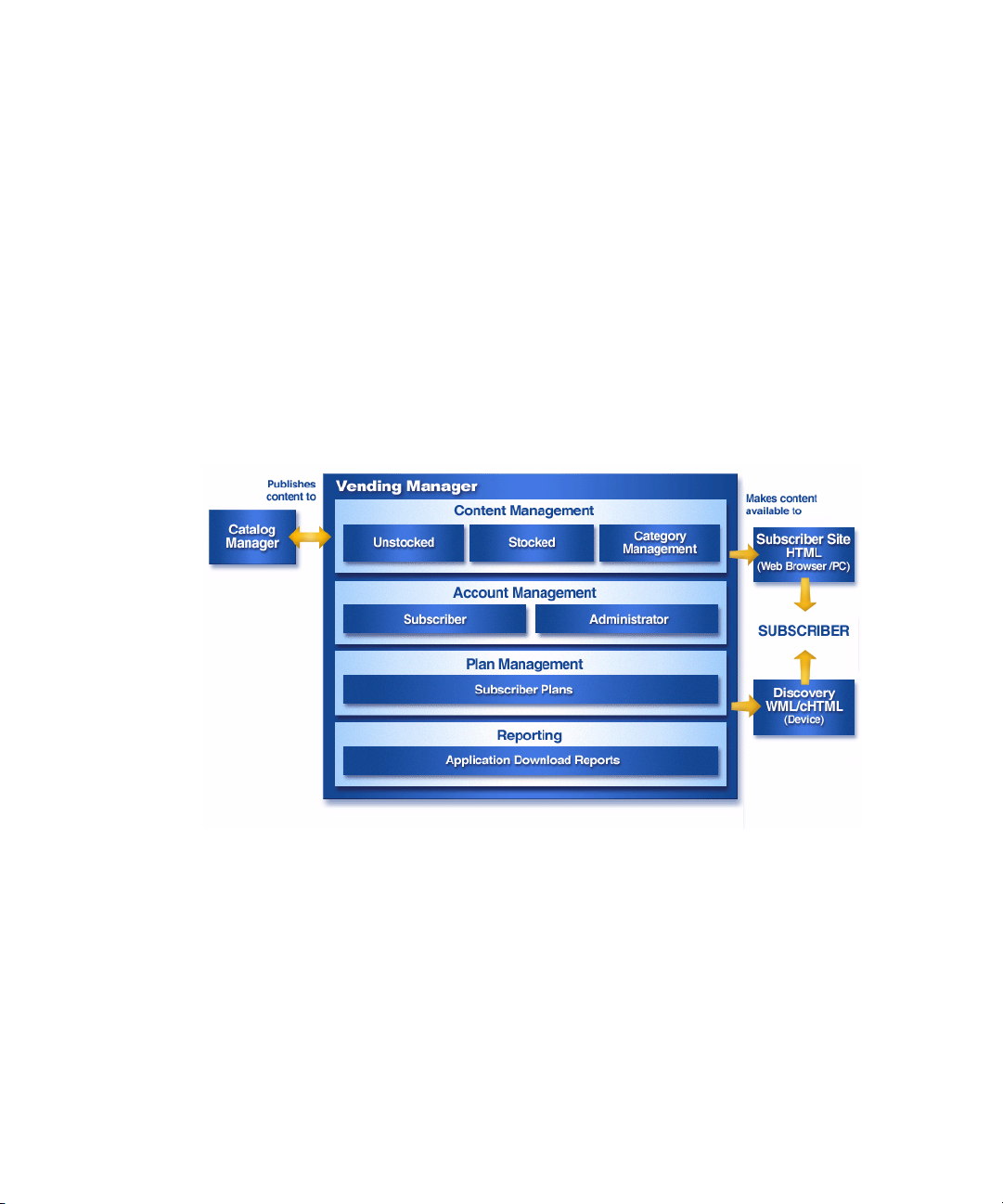
The Vending Manager administrator manages the following functions:
■ Stocked content
■ Subscriber access and subscriber licenses
■ Purchase pricing and trial periods
■ Administrator access
■ Statistical reports
In addition to the Vending Manager administrator, the Content Delivery Server can
have Vending Manager Customer Care Agents. Customer Care Agents have limited
administrator privileges. A Customer Care Agent manages the following functions:
■ Subscriber access and subscriber licenses
■ Statistical reports
The following figure provides a high-level overview of the role of the Vending
Manager in the lifecycle of an application. It also illustrates the Vending Manager
processes.
1. The Catalog Manager publishes content and makes it available to the Vending
Manager.
2. The Vending Manager administrator accesses the content published by the
Catalog Manager. The administrator can change the subscriber pricing of the
content, assign it to a new category, and change the properties of the content.
3. The Vending Manager administrator stocks the content and makes it available to
the subscriber. The administrator uses Subscriber Plans to define the content
categories that subscribers can access.
8 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 27

Vending Manager Processes
The previous figure illustrates the Vending Manager processes. The Vending
Manager is responsible for the following practices:
■ Content Management
■ Plan Management
■ Account Management
■ Reporting
Content Management
The Catalog Manager publishes content to the Vending Manager. The Vending
Manager is responsible for stocking this content to make it available to the
subscriber. The Vending Manager administrator can change the subscriber pricing of
the content, allow trial usage, and assign the content to a new category. The
administrator can also change the category assignments and add new categories to
control subscriber access to content. See “Managing Catalog Content” on page 134
for more information.
Plan Management
The Vending Manager uses Subscriber Plans to control subscriber access to content.
Each Subscriber Account is assigned to one or more Subscriber Plans. Subscriber
Plans determine what content a subscriber can access and download.
A Subscriber Plan is mapped to selected categories in the Vending Manager. The
content in the selected categories is made available to plan members. If content is in
a category that is not supported by the Subscriber Plan, the subscriber cannot access
it for download. See “Managing Subscriber Plans” on page 216 for more
information.
Account Management
Accounts define access to the Vending Manager. The Vending Manager is
responsible for two types of accounts:
■ Subscriber. Subscriber Accounts are for individuals who subscribe to a service
plan that provides them with the download service. Each Subscriber Account is
associated with one or more Subscriber Plans. See “Managing Subscriber
Accounts” on page 209 for more information.
■ Administrator. Administrator Accounts are for individuals who administer the
Vending Manager. There are two administrator roles: Administrator for
administrators with full privileges for administering the Vending Manager, and
Chapter 1 Introduction 9
Page 28

Customer Care Agent for administrators with privileges for viewing content and
managing subscribers. Administrator Accounts can be disabled when you do not
want an individual accessing the Vending Manager. See “Managing Vending
Manager Administrator Accounts” on page 201 for more information.
Reporting
The Vending Manager provides daily statistical reports that enable you to view and
track application download information and usage statistics downloads. See
“Viewing Reports” on page 223 for more information.
Administration Consoles
Administer the Catalog Manager using the Catalog Manager administration console.
You administer the Vending Manager using the Vending Manager administration
console. These consoles are accessed through a web browser.
Developers can submit content to the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server
using the Developer Portal. Subscribers can download content from the Sun Java
System Content Delivery Server using the Subscriber Portal from either a PC or a
mobile device.
Note – The Developer Portal and Subscriber Portal are outside the scope of this
guide. See the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Content Developer Guide for
information on submitting content through the Developer Portal.
Browser Requirements
The administration consoles can be run with:
■ Internet Explorer 6.0
■ Netscape Navigator
■ Firefox 1.0
Note – Cookies must be enabled in the browser to use the administration consoles.
10 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
TM
7.0
Page 29

Accessing the Administration Consoles
To access the Catalog Manager and Vending Manager administration consoles for
the first time, use the default login ID and password that were created when you
installed the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server. The default values for the
Login ID and Password are admin and admin.
Change the password after you initially log in (note that the password is case
sensitive). After you log in to the Catalog Manager and Vending Manager, you can
add additional accounts as needed. See “Adding a Catalog Manager Administrator
Account” on page 105 and “Adding a Vending Manager Administrator Account” on
page 202 for more information.
▼ Logging in to the Catalog Manager
To log in to the Catalog Manager, follow these steps:
1. Start the Catalog Manager.
For information on starting the Catalog Manager, see the Sun Java System Content
Delivery Server Installation Guide.
2. From a browser window, enter the following address:
http://
The Catalog Manager Log In page is displayed.
localhost
/admin/main
Chapter 1 Introduction 11
Page 30
3. Enter your administrator name and password.
4. Click Log In.
▼ Logging in to the Vending Manager
1. Start the Vending Manager. For information on starting the Vending Manager, see
the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Installation Guide.
2. From a browser window, enter http://localhost/vsadmin/main.
The Vending Manager Log In page is displayed.
3. Enter your administrator name and password.
4. Click Log In.
12 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 31

CHAPTER
2
Catalog Manager
This chapter describes how to administer the Catalog Manager. Following are some
of the responsibilities of the Catalog Manager administrator:
■ Managing Content
■ Accepting or rejecting content submitted by developers
■ Creating and managing categories
■ Creating and managing MIME types
■ Publishing content
■ Managing Devices
■ Adding new devices supported by your network
■ Deleting devices no longer supported
■ Adding, editing, and removing characteristics and capabilities of devices
■ Creating and managing device libraries
■ Creating and managing descriptor templates
■ Managing Accounts
■ Creating and managing Vending Manager Accounts
■ Creating and managing Developer Accounts
■ Creating and managing Catalog Manager Administrator Accounts
■ Managing Plans
■ Creating and managing Vending Plans
■ Creating and managing and Developer Plans and Profiles
Managing Content
The Content section of the Catalog Manager displays content submitted by
developers and published. The Categories section enables you to create custom
catalogs of content. The MIME Types section enables you to define the types of
content that you want the Content Delivery Server to manage.
13
Page 32

The following content management tasks are described in this section:
■ Managing Content Categories
■ Managing Content Types
■ Managing Submitted Content
■ Managing Published Content
When an operation is performed (editing, deleting, adding, and so on), the Content
Deliver Server puts a background job notification in the main menu bar. You can
click on the notice to see details of jobs that were or are running in the current
session. See
“Getting Job Status” on page 126 for more information.
Managing Content Categories
Content categories are central to content management. They are logical containers
that hold the content that has been submitted to the Content Delivery Server. Your
first task as an administrator is to create appropriate categories for your enterprise.
As an administrator, you use content categories to control Vending Manager access
to content.
A default set of categories is provided with the Catalog Manager. You can edit or
delete these categories. You can also add categories and subcategories.
▼ Viewing Categories
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
The Content Database Management page is displayed.
2. Click the Categories tab.
The Categories page displays a list of the main categories defined.
14 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 33

3. Click a category to view its subcategories.
The Categories page displays a list of the subcategories for the selected category. The
menu bar at the top of the page displays the hierarchy level of the selected category.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 15
Page 34

To return to the list of main categories, click Home in the category navigation bar. To
display any level of your current category hierarchy, click the category name in the
category navigation bar.
4. Click the arrow keys to move a category up or down the list to change the display
order.
▼ Adding a Category
1. From the Categories page, navigate to the level to which you want to add the
category.
For example, if you want to add a game subcategory to the Entertainment category,
click Entertainment.
2. Click Add New Category.
The Edit Category page is displayed.
16 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 35

3. Enter a name and short description of the category.
The name must be unique within the category. You cannot have two categories of the
same name under the same level of hierarchy.
4. Click Add Category.
The Add New Category confirmation page is displayed.
Note – You can set the maximum number of category levels that can be added in a
session in the CommonConsole.properties file in the
$CDS_HOME/deployment/deployment_name/conf/ directory. The default number
of levels of categories is set to 10. That is, top-level and sublevel categories can be
created but sub-sublevel categories cannot. If you modify the property, you must
restart the server to enact the change.
▼ Editing a Category
1. From the Categories page, navigate to the category you want to edit.
2. Click the Edit Category button .
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 17
Page 36

The Edit Category page is displayed.
3. Modify the name or short description as needed, and click OK.
The category is updated in the database.
▼ Deleting a Category
1. From the Categories page, navigate to the category you want to delete.
You can only delete categories that do not contain content. You must either move or
delete content in an undesired category before you can delete that category.
2. When the category is displayed, click the Delete Category button .
If the category contains content, the delete icon is not present.
3. Click OK.
The category and all its subcategories are deleted and removed from all plans and
content that they are associated with.
4. Click OK to close the confirmation page.
18 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 37

Managing Content Types
The default content types supported by the Content Delivery Server are MIDlets,
ring tones, and images. You can define additional content types as needed. Each
content type must be associated with one or more MIME types.
MIME types specify the format of the content and enable information to be
exchanged between applications. The Content Delivery Server provides support for
a default set of common MIME types, each of which is associated with one of the
default content types. You can modify or delete these MIME types, register
additional MIME types, or associate the MIME type to a different content type as
needed.
In addition, each content type needs to be associated with digital rights management
(DRM). The following section discusses the DRM options supported in the Content
Delivery Server and their association with content types.
Content Submissions
The Catalog Manager administrator configures the Content Delivery Server to setup
either separate or single content type submission. By default, the Content Delivery
Server is configured for separate content type submissions. The two setups are
described as follows:
■ Separate content types - Each format of a content item is submitted individually.
Submitting content on a per format basis has the following benefits:
■ Individual formats of content can be submitted and managed individually
■ Defining the metadata and the pricing of content per format (for example, a
higher resolution image can be priced higher while a lower resolution image
can be priced lower)
■ Providing subscribers with the ability to choose from among compatible
content formats
For example, a content provider submits a screen saver image, Sunset, of content
type image and makes a separate submission of Sunset that has that content type
sms_picture. Each format of Sunset has its own metadata and price.
■ Single content types - Content is submitted under one content type. Once the
initial content is submitted, edition can be submitted for each format of the
content. Editions have the same pricing option and preview file, if any, as the
original content. Submitting content on a per content type basis has the following
benefits:
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 19
Page 38

■ Defining the metadata and price for all content formats is done once
■ Publishing and stocking for all content formats is done once
■ Choosing and delivering compatible content formats to subscribers is
automatically done for them
For example, a content provider has a ring tone, Melody, to submit. The content is
submitted with the ringtone content type. After the content is submitted, the
content provider then submits an edition of Melody that has a monophonic
format. The monophonic version of Melody is automatically assigned the
metadata and price of the initial submission.
Content Protection
Previously the Content Delivery Server offered digital rights protection of content
with Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Digital Rights Management (CDS
DRM) agents. The current version of the Content Delivery Server offers additional
DRM agents that can be applied to content, as described in
TABLE 2-1 DRM Types
DRM Type Description
CDS DRM Agents Content is protected using the CDS DRM Agents available in this
release of the Content Delivery Server. CDS DRM can only be used
for MIDlets.
CDS OMA DRM
Forward Lock
Open Mobile
Alliance (OMA)
DRM 1.0
Content is protected using the OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock format
only.
Content is protected per the guidelines defined by OMA DRM 1.0.
OMA DRM 1.0 offers three types of protection formats: Forward
Lock, Combined Delivery, and Separate Delivery.
TABLE 2-1.
The system administrator determines which DRM types are available in the Content
Delivery Server at deployment time. The system administrator can choose one or
more of the following DRM options:
■ None (no DRM protection)
■ CDS DRM
■ CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock
■ OMA DRM 1.0
To use OMA DRM 1.0 in the Content Delivery Server, you must have an OMA
DRM 1.0 provider. See the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Installation
Guide for details.
20 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 39

Inapplicable Content
Short Messaging Service (SMS) content types (monophonic ringtone, operator
logo, group logo, and sms picture) are supported in the Content Delivery
Server. Due to the delivery format for SMS content, DRM protection cannot be
applied. The No DRM option is associated by default for all SMS content types.
Remotely hosted copyrighted content also cannot have DRM associated with it.
Attempts to submit remotely hosted content items that have content types that are
associated with one of the DRM options (other than No DRM) fail.
See “Pricing Content” on page 26 for information on the pricing models that can be
used for these types of content.
Using CDS DRM Agents and CDS OMA Forward Lock
The Content Delivery Server provides you with CDS DRM Agents and CDS OMA
DRM 1.0 Forward Lock. CDS DRM Agents can only be used for MIDlet content
types while CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock can be used for any supported
content type in the Content Delivery Server. CDS DRM has several agents that verify
a subscriber’s license.
TABLE 2-2 CDS DRM Agents
TABLE 2-2 describes the CDS DRM Agents.
Title Description
Disconnected Time
Sensitive
Disconnected Use
Sensitive
Disconnected Use
and Time Sensitive
Supports the download-based (free always, first download only, and
every download) pricing model and the time-based (recurring
subscription and per period) pricing model.
Supports the download-based (free always, first download only, and
every download) pricing model, the usage-based (trial and per use)
pricing model and the time-based (per period) pricing model.
Supports all pricing models.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 21
Page 40

TABLE 2-2 CDS DRM Agents (Continued)
Title Description
Small Connected
Use and Time
Sensitive
Midsize Connected
Use and Time
Sensitive
Standard
Connected Use and
Time Sensitive
Supports all pricing models.
Note: To prevent runtime errors, do not use this DRM agent with
applications that perform the following actions:
• Show an alert before calling the startApp method.
• List their Record Stores.
• Modify or remove the Content Delivery Server Record Store.
Supports all pricing models.
Note: To prevent runtime errors, do not use this DRM agent with
applications that perform the following actions:
• Show an alert before calling the startApp method.
• Modify or remove the Content Delivery Server Record Store.
Supports all pricing models.
When no DRM agent is selected, only the download-based (free always, first download
only, and every download) pricing model is supported. No code is added.
Each agent handles license validation differently. For further details of these types,
see the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Installation Guide.
CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock is simply the OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock
format (no Combined or Separate Delivery) only and can be used with any content
type. It provides basic copy protection with the content and it does not allow content
to be forwarded to another device.
The default setting of Enabled is used for CDS DRM Agents and CDS OMA DRM 1.0
Forward Lock and when no DRM is selected. You can disable one or more of these
options or enable OMA DRM 1.0 with the cdsi db command, see the Sun Java
System Content Delivery Server Installation Guide for information on this command.
22 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 41

Using OMA DRM 1.0
OMA DRM 1.0 offers three different formats for applying protection, as described in
TABLE 2-3.
TABLE 2-3 OMA DRM 1.0 Formats
DRM Type Description
Forward Lock Content is delivered with basic copy protection. Content cannot be
forwarded to another device.
Combined Delivery Content is delivered together with basic copy protection and
additional usage rights are included. Content cannot be forwarded
to another device.
Separate Delivery Encrypted content is delivered separately from the digital rights.
Content can be forwarded to another device.
For a thorough discussion of OMA DRM 1.0, go to
http://www.openmobilealliance.org/. The default setting for OMA DRM 1.0
in the Content Delivery Server is Disabled. You can enable this DRM after
deployment (see
If OMA DRM 1.0 is selected as an available DRM type, the system administrator can
set a preference for the type of rights delivery format, as follows:
■ Only combined delivery is used
■ Only separate deliver is used
■ Separate delivery is used whenever possible, otherwise, combined delivery is
used
“Enabling and Disabling a DRM” on page 26 for more information).
The last preference option provides flexibility in providing digital rights protection
with content. Work with your system administrator to determine what rights
delivery preference to use, if desired. The preference is set in the configuration
properties file for the Content Delivery Server.
Content with Forward Lock or Combined Delivery is available to compliant devices
that support Combined Delivery. Compliant devices that do not support Separate
Delivery cannot receive content that has Separate Delivery unless the delivery
preferences are set to allow compliant devices to receive content using Separate
Delivery by using Combined Delivery.
The possible associations of DRM types to content types are listed in Appendix B.
See “Adding a Content Type” on page 32 for information on how to assign DRM
types to content types.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 23
Page 42

OMA DRM 1.0 and Non-Compliant Devices
For devices that are not compliant with OMA DRM 1.0, the Catalog Manager
administrator can configure the Content Delivery Server with one of the following
options to deliver content with a free always, first download only, or every
download pricing model:
■ Deliver all content to non-compliant devices as unprotected original content (that
is, content as received from the content provider). The free always, first download
only, and every download pricing models are available to content under this
option.
■ Deliver only free content as unprotected original content to non-compliant
devices. Only the free always pricing model is available to content under this
option.
■ Make the content unavailable to non-compliant devices.
For a discussion of pricing models, see “Pricing Content” on page 26.
MIME Types for OMA DRM 1.0
To support the OMA DRM 1.0 formats, a device must support the MIME types listed
in
TABLE 2-4.
TABLE 2-4 Required MIME Types for OMA DRM 1.0
OMA DRM 1.0 Format Required MIME Type Support
Forward Lock application/vnd.oma.drm.message
Combined Delivery application/vnd.oma.drm.message
Separate Delivery application/vnd.oma.drm.rights+xml
These MIME types are used to determine the OMA DRM 1.0 format supported on a
device. Support for these MIME types must be added to device profiles for devices
capable of receiving OMA DRM 1.0 protected content.
24 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
application/vnd.oma.drm.rights+xml
application/vnd.oma.drm.rights+wbxml
application/vnd.oma.drm.content
Page 43

Associating Content Types with DRMs
When assigning a DRM type to a content type, be aware that CDS DRM can only be
used with MIDlets. Be aware also that SMS content types and remotely hosted
copyrighted content cannot be assigned a DRM. Other than these restrictions, the
choice of no DRM, CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock, and OMA DRM 1.0 can be
used with any content type.
This release of the Content Delivery Server contains the default associations of DRM
types to content types shown in
TABLE 2-5 DRM Options and Associated DRM Types and Content Types
DRM Type Content Type
None (no DRM protection) group logo
CDS DRM midlet Enabled
CDS OMA DRM 1.0
Forward Lock
OMA DRM 1.0:
Forward Lock
Combined Delivery
Separate Delivery
a Although no content type is associated with CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock by default, you can as-
sign it to the content type of your choice through the Catalog Manager.
TABLE 2-5.
Default Setting for DRM
Type
Enabled
iappli
image
midlet
monophonic ringtone
operator logo
ringtone
sms picture
video
a
none
none Disabled
Enabled
You can assign a DRM through the MIME types page in the Catalog Manager.
During deployment only one DRM can be associated with a particular content type.
That means that even though None, CDS OMA DRM 1.0 Forward Lock, and OMA
DRM 1.0 are all enabled, only one of them can be associated with the picture
content type. The Content Delivery Server provides six CDS DRM Agents. Only one
agent can be used per deployment. See
Appendix B for a list of DRMs and content
type associations. See TABLE 2-2 for agent descriptions.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 25
Page 44

You can assign the DRM options to the associated content types given in TABLE 2-5
but you are not restricted to those combinations, for instance, you can apply None to
all content types if you wish. For steps on how to assign a DRM, see
Content Type” on page 32.
You can change the DRM option for a content type after deployment if needed. See
“Enabling and Disabling a DRM” on page 26 for more information.
“Adding a
Enabling and Disabling a DRM
You can change the DRM selection for a content type after the Content Delivery
Server is running by switching DRMs. You can also enable or disable DRMs after
deployment. For example, if None is assigned to content type, image, and you later
choose to use OMA DRM 1.0, you can enable that DRM during runtime and assign
that DRM to the image content type.
If you decide you no longer want to support the CDS DRM Agent, you can disable
that agent during runtime and assign another option, such as None to MIDlets
content. Use caution when disabling a DRM. Make sure that the DRM you are
disabling is not currently associated with a content type. Follow this sequence:
1. Change the DRM assigned to the content type.
2. Disable the old DRM.
Even though the DRM is disabled, content protected under that DRM can still exist
in the Content Delivery Server. Content submitted after a new DRM is assigned is
protected under the new DRM. Another factor affected by changing the DRM is the
pricing model associated with the content type. Changing DRMs can change which
pricing models are available. The following section discusses pricing content in more
detail.
Pricing Content
The Catalog Manager administrator must associate one or more pricing models for
each content type. A pricing model is the condition of purchase (per download, per
periods of uses, and per number of uses) associated with content. The pricing
models supported in the Content Delivery Server are defined in
26 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
TABLE 2-10.
Page 45

TABLE 2-6 Content Delivery Server Pricing Models
Pricing Model Definition
Free always No charge for downloading content. Content can be downloaded
any number of times for however long content is available.
Trial No charge for content on initial download. Subscriber must
purchase content for subsequent downloads.
First download only Subscriber is charged for initial download of content. Subscriber
is not charged for subsequent downloads.
Every download
Per use Subscriber can download content once after purchase and is
Per period Subscriber can download content once after purchase and is
Per subscription Subscriber can download content an unlimited number of times
Per interval Subscriber can download content an unlimited number of times
a A grace period can be applied for this pricing model by the Vending Manager administrator.
a
Subscriber is charged for each download of content.
charged for N uses.
charged for running content for the specified length of time, for
example, 3 days, 2 weeks, or 1 month.
Charge for N days, weeks, months, or years.
during the subscription period and is automatically charged for
the next period of use when the current period expires.
Charge recurring fee daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly.
during the interval and is charged for running content from the
specified start date to the specified end date.
Charge for use starting mm/dd/yyyy through mm/dd/yyyy.
The former usage pricing model of X downloads in Y days is no longer available by
default. That pricing model is now used, optionally, as a grace period. A grace
period, if configured at deployment, can be attributed to the Every Download
pricing model (see
TABLE 2-10). Upon purchase, a grace period allows additional
numbers of downloads or extends the download period. The system administrator
can set the properties pricing.model.recurringDownload.numberOfDays and
pricing.model.recurringDownload.numberOfTimes to enable a grace period.
See the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Installation Guide for information on
setting a grace period.
Each DRM supports some set of the pricing models available in the Content Delivery
Server. The pricing models that you can assign to a content type are dependent on
the DRM that is associated with the content type.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 27
Page 46

The Content Delivery Server supports the combinations of DRM options and pricing
models as shown in
TABLE 2-7 DRM Options and Pricing Models
DRM Type Pricing Model
None (no DRM protection) Free always
CDS DRM Agents Free always
CDS OMA DRM 1.0
Forward Lock
OMA DRM 1.0
Forward Lock, Combined, or
Separate Delivery
TABLE 2-7.
First download only
Every download
Trial
First download only
Every download
Per use
Per period
Per subscription
Free always
First download only
Every download
Free always
First download only
Every download
Per use
Per period
Per interval
You determine whether to enable all the available pricing models for a content type
or just a subset. For instance, if you associate a CDS DRM Agent with MIDlets, you
can elect to enable all the available pricing models possible with that DRM or a
subset, such as first download only, per use, and per period.
You make the DRM selections and the pricing model selections for a content type on
the MIME Types page in the Catalog Manager. All the pricing models supported by
the Content Delivery Server are listed. Non applicable pricing models are not
selectable. Therefore, if you selected None for the image content type, you cannot
select the Per Use pricing model because it is not available without DRM protection.
Previously, a content item, such as a MIDlet, could have a combination of pricing
models such as charge on first download only and charge per subscription. Such
combinations are not possible with the use of digital rights management. To simplify
management of content, all content items can have only one pricing model. For
preexisting content items that have a pricing model combination, the first download
only and recurring download models are no longer applicable.
28 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 47

Pricing Options
At the same time that you select a pricing model, you have the option of creating
pricing options for it. Having predefined pricing options gives you more control
over the pricing of content and can make managing content easier. You can set up
predefined pricing options for content providers to choose from instead of having
them decide content pricing and usage terms.
Another benefit to creating predefined pricing options is that it enables you to apply
the same purchase criteria to all contents with the same content type. For instance,
all image content types can have the pricing option of $0.50 for every download. By
changing the purchase price of a pricing option, you change the purchase price for
all content using that pricing option at once. You always have the ability to edit a
pricing option or create custom prices for specific content items as needed.
A pricing option consists of a unique ID for the pricing option, an option name, and
the purchase characteristics of the content. The pricing option consists of the
following elements:
■ External options ID - A unique designation used by the billing system to identify
this pricing option.
■ Pricing option name - A name that identifies a specific pricing option.
■ Purchase price - A monetary value, which can be 0.
■ Specific pricing model - The condition for purchase. Only one model can be
applied.
A pricing option looks like this, for example:
1222 Ringtones-Jazz $.99 1st Download Only.
Pricing options cannot be deleted, you can only enable or disable them once they are
created. Regardless of whether a pricing option is enabled or disabled, you can still
edit the option through the Catalog Manager.
As the Catalog Manager administrator, you determine whether content providers are
required to use the pricing options you enable for the content type or create a
custom price based on the available pricing model. An option on the MIME types
page allows you to restrict the content type to the pricing options you enabled.
Content providers submitting content of that type must use the assigned pricing
option.
Changing the Pricing of Content
You can change the pricing of content in the following ways:
■ Edit the content type
■ Edit the properties of a submitted, published, or unpublished content item
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 29
Page 48

■ Edit the pricing option
■ Create a customized price for a published content item
Changing the pricing of content is dependent on several factors, such as the content
item status, the DRM assigned, and whether the content item is copyrighted.
For a copyrighted content item, the pricing options you can choose from are
dependent on the item’s content type preferences alone because copyrighted content
cannot have a DRM associated with it.
For a submitted content item that has a status of new, pending, or denied and is not
copyrighted, the pricing options you can choose from are dictated by the DRM
associated with the item’s content type.
For a content item with a status of published or testing, the pricing options you can
choose from depend on the following factors:
■ The content item’s current pricing option
■ The currently allowed pricing models for the item’s content type
■ The DRM used by the content item
For example, suppose SpruceDraw, a content item of type midlet is published. At
the time it is published, midlet has no DRM assigned and the pricing model of first
download only. Therefore, SpruceDraw has no DRM assigned to it and uses the first
download only pricing option. If no change occurs to the content type, the Edit
Content page for SpruceDraw allows you to choose either first download only or
every download.
Later, the content type preferences are edited so that midlet now uses OMA DRM
1.0 and the pricing models are changed to first download only and per interval.
Because SpruceDraw is already published, its DRM option does not change, it is still
None. While the available pricing models for midlet are now first download only,
every download, and per interval, the per interval model is not available to content
without DRM protection. So the Edit Content page for SpruceDraw does not list per
interval in the Catalog Price list. When editing SpruceDraw, you can choose from
first download only or every download.
If a content item uses OMA DRM 1.0 and one of the trials, per use, per period, or per
interval pricing models, the pricing model cannot be changed because the content
item would require reprotection, that is, a reapplication of the DRM. You can change
the purchase price of the item, but not whether it has or does not have trial usage or
its pricing model.
Disassociating Content From Pricing Options
Sometimes you or a Vending Manager administrator might want to change the
purchase price of a specific item of content. By doing so, you disassociate a content
item from its pricing option. For example, suppose an item of content named Roses
30 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 49

has the content type picture and a pricing option of $0.75 for first download only.
You determine that Roses is priced at $.50 for first download only. When you edit
the content and change its price, Roses becomes disassociated from other content of
type picture with that pricing option. If the purchase price for picture content
changes later, Roses is unaffected by the change because it is no longer associated
with its original pricing option. Roses is considered to have a custom price. Any
future changes to the purchase price for Roses must be made explicitly to that
content item.
▼ Viewing Supported Content Types and MIME Types
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed. This page shows the content types that are
defined and the MIME types that are currently associated with each content type.
The following information is displayed for each MIME type:
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 31
Page 50

■ Content Type - The type of content that the MIME type is associated with.
■ MIME Type - The string that identifies the MIME type.
■ File Extensions - The file extensions that are associated with the MIME type.
▼ Viewing Properties for a Supported MIME Type
1. Click the string in the MIME Type column on the MIME Types page.
The properties page for the MIME type is displayed.
In addition to providing the Content type, MIME type, and File Extensions, the
Properties page also provides a brief description of the MIME type.
2. Click OK to close the properties page.
▼ Adding a Content Type
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
3. Click New Content Type.
The New Content Type definition page is displayed.
32 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 51

4. Enter the following information:
■ Content Type - Enter the name of the content type that you are adding.
■ Description - Enter a brief description of the content type.
■ Preview - Choose whether content type of this type can have a preview available
for subscribers.
If you disable the Preview feature, the Preview field is not displayed in the
Content Properties page.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 33
Page 52

5. Select a DRM.
Administrators must know which DRMs are applicable for specific content types.
See
Appendix B for a table of DRMs and associated pricing models. If an
inapplicable DRM is assigned, submission of content with that DRM fails.
For instance, if you erroneously assign CDS DRM Agent to the image content type
and a content provider attempts to submit a content item of type image, the content
provider receives an error message that the submission failed.
See “Content Protection” on page 20 for a discussion of DRMs.
6. Select the pricing models you want available for the content type.
All the pricing models appropriate for the selected DRM are available for selection.
See Appendix B for a table of DRMs and associated pricing models to be sure you
are selecting an appropriate pricing model for the DRM selected.
7. Click Done when finished.
8. Click OK to close the confirmation page.
▼ Editing a Content Type
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed.
3. Click the content type that you want to edit.
The Content Type Preferences page is displayed.
Make the necessary changes to the content type and description:
■ Content Type - The name of the content type that you are adding.
■ Description - A brief description of the content type.
■ Preview - The preview options for this content type.
■ DRM Preference - The DRM associated with this content type. Changing the
DRM changes the pricing models that can be applied to content.
Only newly published content items have the new DRM and any new pricing
options. Existing content items still have the previously assigned DRM and
pricing option and are still available to subscribers.
■ Pricing Models - The pricing models available for this content type.
If you unselect a pricing model, existing content retains their pricing options. For
unpublished content items that used that pricing model, you must choose another
pricing model when editing that content item.
34 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 53

■ Pricing Options - This section addresses two items:
■ Required Pricing Options - Enables or disables content providers to set their
own pricing options for content. This option is only available when a pricing
option is defined for the content type.
Clicking the option restricts content providers to selecting the predefined
pricing options you have enabled.
If you do not check Require Pricing, content providers can create custom
pricing for the content being submitted. Note that content submitted with
custom pricing must be manually edited.
■ Available Pricing Options - Enables or disables predefined pricing options for
this content type. You can also go to the Edit Pricing page from this section to
edit existing pricing options. Predefined pricing options are listed in the
Available Pricing Options section, which is only displayed when at least one
pricing option is defined for the content type. You can enable or disable one or
more options by checking or clearing the check box next to each Options ID.
If the list of pricing options requires no change or no pricing options exist yet,
you can go directly to Step 4.
To create predefined pricing options, see “Creating a Pricing Option” on
page 35 for instructions. For a discussion of pricing options and why you
would want to create them, see “Pricing Options” on page 29.
4. Click Done when finished.
All changes to the content type are saved.
▼ Creating a Pricing Option
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
3. Click a content type.
4. Click New Option.
The New Pricing Option page is displayed.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 35
Page 54

The fields displayed are relevant to the selected pricing models on the previous
page. If no existing pricing options exist yet for the content type, the Available
Pricing Options section is not displayed.
5. Enter a unique Option ID.
The Option ID identifies this specific pricing option for this content type.
6. Enter a unique Pricing Option Name.
The Option Name is an identifier that external systems can use to identify the
pricing option for this content type.
36 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 55

7. Select free usage or non-free usage or enter the number of free trials.
The fields shown are dependent on the pricing models you made available for this
content type when creating or editing the content type.
TABLE 2-6 lists and defines the
supported pricing models.
8. Select the Charge option you want to apply to the content type.
Unless the pricing model is Always Free, enter a monetary value and enter values
for other fields in the option as required.
9. Click Save to add the new option to the list of available pricing options.
You can continue to add more options. Click Save after each option to add it to the
pricing options list. Click Reset to clear all the fields on the page.
Clicking OK before clicking Save cancels the pricing option creation and clears the
fields in the page. You are returned to the Content Type Preferences page.
Clicking Cancel terminates the operation and cancels any saved pricing options
10. Click OK.
You are returned to the Content Type Preferences page.
11. Click Done to complete the operation.
Clicking Cancel terminates the operation being performed on this page and returns
you to the MIME Types page.
▼ Editing a Pricing Option
You can edit attributes of an existing pricing option other than the pricing model. All
content items that use that pricing option are changed immediately both in the
Catalog and Vending Managers and on subscriber devices.
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
3. Click a content type.
The Content Type Preferences page is displayed.
4. In the Available Pricing Options section, click Edit for the option you want to
change.
The Content Type - Edit Pricing page is displayed.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 37
Page 56

5. Change the following fields as needed:
■ Option ID - Unique identifier for this option. Values can consists of numbers,
characters, or a combination of both.
■ Option Name - Name of option. Values can consists of numbers, characters, or a
combination of both.
■ Purchase Price - Monetary value.
6. Click Save to save your changes.
The Content Type Preferences page is displayed. Changes to the pricing option are
immediate and content using that pricing option are updated in the Catalog
Manager. If auto-updating of prices is selected in the Vending Manager, any change
to the purchase price to both the pricing option itself and to content using the
pricing option is automatically updated in the Vending Manager. Otherwise, the
Vending Manager administrator must manually update the purchase price of the
pricing option and the affected content.
38 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 57

7. Click Done.
8. Click OK to close the Confirmation page.
To create a custom price for an individual item of content, see “Editing Content” on
page 52. To create a custom price for multiple content items at once, see “Setting
Custom Prices for Published Content” on page 66.
▼ Deleting a Content Type
Deleting a content type removes that content type and its associated pricing options
from the current deployment of the Content Delivery Server. Use caution when
using this command because it cannot be undone.
Content types with associated MIME types cannot be deleted unless the associated
MIME types are deleted first (see
supported content types that cannot be deleted at all are midlet and iappli.
Content types with existing pricing options cannot be deleted.
To delete a content type before a MIME type is associated, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed.
3. Click the content type that you want to delete.
The Content Types Preferences page is displayed.
“Deleting a MIME Type” on page 43). The only
4. Click Delete Content Type.
You are prompted to confirm the deletion.
5. Click OK.
A page is displayed indicating that the content type is deleted.
6. Click OK to close the Confirmation page.
▼ Disabling a Pricing Option
Pricing options cannot be deleted, but you can disable a content type’s pricing
option. When an option is disabled, content providers do not see that pricing option
in the list of predefined pricing options when submitting content of that content
type. Existing content in the catalog that use that pricing option are not affected.
Subscribers can see the existing content and can purchase the content with the
original price. You can enable the pricing option at a later time if desired.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 39
Page 58

1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed.
3. Click the content type with the pricing option you want to disable.
The Content Type Preferences page is displayed.
4. In the Available Pricing Options section, clear the check box under the Enabled
column for the pricing option you want to disable.
You can clear more than one option at a time. If you clear all the available pricing
options, the Require Pricing Options feature is unchecked. Content providers are
forced to create custom prices for content being submitted.
An alternative to disabling a pricing option is to make it unavailable by editing the
content type and clearing one or more of the checked pricing models. Once the
pricing model is made unavailable, content providers do not see any predefined
pricing options that use that model when submitting content.
5. Click Done.
6. Click OK to close the Confirmation page.
▼ Registering a MIME Type
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
3. Click New MIME Type.
The MIME Type definition page is displayed.
40 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 59

4. Enter the following information:
■ Content Type - Select from the list the type of content with which the MIME type
is associated.
■ MIME Type - Enter the string that identifies the MIME type, for example,
image/jpeg.
■ Description - Enter a brief description of the MIME type.
■ File Extensions - Enter the file extensions associated with the MIME type. Each
extension must be preceded by a period (.). To specify more than one extension,
separate each entry with a comma (,), for example,
.jpg, .jpeg.
5. Click Save to save the MIME type.
A Confirmation page is displayed.
6. Click OK.
The list of MIME types is displayed.
▼ Editing a MIME Type
When associated with MIDlets, the following MIME types are required by the
Content Delivery Server and cannot be edited or deleted:
■ application/java-archive
■ text/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptor
When associated with iAppli applications, the following MIME types are required
by the Content Delivery Server and cannot be edited or deleted:
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 41
Page 60

■ application/java-archive
■ application/x-jam
When associated with other content types, the MIME types previously listed are
treated as any other MIME type.
To edit a MIME type, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed.
3. Click the MIME type that you want to edit.
The properties page for the MIME type is displayed.
4. Click Edit.
The MIME Types Definition page is displayed. An asterisk (*) beside a field indicates
that it is a required field.
5. Make the necessary changes.
6. Click Save.
A Confirmation page is displayed.
42 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 61

7. Click OK.
The MIME Type Properties page is displayed.
8. Click OK to close the confirmation message.
▼ Deleting a MIME Type
You cannot delete a MIME type if content with that MIME type is submitted or if a
device references it. You cannot delete the following MIME types under the
conditions listed:
■ When associated with MIDlets, the following MIME types are required by the
Content Delivery Server and cannot be edited or deleted:
■ application/java-archive
■ text/vnd.sun.j2me.app-descriptor
■ When associated with iAppli applications, the following MIME types are required
by the Content Delivery Server and cannot be edited or deleted:
■ application/java-archive
■ application/x-jam
When associated with other content types, the MIME types previously listed are
treated as any other MIME type.
To delete a MIME type, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the MIME Types tab.
The MIME Types page is displayed.
3. Click the MIME type that you want to delete.
The MIME Types properties are displayed.
4. Click Delete.
You are prompted to confirm the deletion.
5. Click OK.
A page is displayed indicating that the MIME type is deleted.
6. Click OK.
The list of MIME types is displayed.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 43
Page 62

Managing Submitted Content
Developers submit content in packages that consist of their created content and XML
files with support and description information. Developers submit content through
the Developer portal. When content is submitted to the Catalog Manager, the
Catalog Manager runs an automated validation process on the content to ensure
there is no malicious content and the content matches the Catalog Manager’s
supported devices.
The Submitted Content page displays all content submitted to the Catalog Manager.
This is the default page displayed when you first log in to the Catalog Manager.
Use the Submitted Content page to review content before you publish it to your
Vending Managers. The page provides the total number of submitted contents.
These items can consist of content undergoing review as well content whose status
has changed from Published to Pending, Testing, or Denied. The total number of
items in a particular state are displayed to the left of each state.
Submitted content can have one of the statuses described in TABLE 2-8.
TABLE 2-8 Content Status Types
State Definition
New Content that has successfully passed the Catalog Manager’s
automatic validation process, but requires your review and
approval before it is published.
Pending Content that requires further review before being published.
Testing Content currently undergoing or requiring testing prior to being
published.
Unpublished Content that was published but is currently unavailable to the
Vending Manager and subscribers.
Denied Content that is rejected, but is not deleted from the database yet.
Note – Testing content is available to Vending Managers for distribution to certain
subscribers. Testing content is available only to subscribers with testing roles
(assigned by the Vending Manager) and published content is available to regular
subscribers.
▼ Viewing Submitted Content
The Submitted Content page displays the total number of submitted content, so you
know what the manager’s workload is and what to expect. You can view a list of all
content in any state.
44 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 63

To view submitted content by state, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
The Content Database Management page is displayed for submitted content.
2. Click the title of the state that you want to view.
For example, click New to view all new content.
The Browse and Search Results page shows all submitted content for the selected
state.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 45
Page 64

The following information is displayed for each item:
■ Title - The name of the content.
■ Developer - The name of the developer who submitted the content.
■ Categories - The categories in which the content is defined.
■ Catalog Price - The price specified by the Catalog Manager administrator. By
default, this price is the same as the cost until you change it.
If the content was submitted for free, the Catalog Price and Cost shows Charge
Free always.
■ Recommended Price - The price specified by the content provider.
■ Short Description - A short description of the content.
■ Type - The type of content. Select the type from the list of supported types.
3. Click Review Process on the navigation bar or click Content in the main menu bar
to display the list of submitted content.
To view all submitted content, use the search feature. Leave the search field blank
and select All Categories and Any Status. When searching for content, you can enter
a part of a content title or the full title in the Search text field. A list of all content
containing an exact match of the search entry is displayed.
To view the properties for an item, click the title of the item. The View Application
Properties page is displayed. If icons, documentation, or screen shots were
submitted with the content, you can click the View button for the item to see what
was submitted. If the item is a ring tone and a preview was submitted, you can click
the Listen button to hear the preview.
46 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 65

▼ Viewing Submitted Editions
The Editions Database Management page displays the total number of submitted
editions, and, of that total, how many editions are in a New, Pending, or Denied
state.
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
The Content Database Management page is displayed for submitted content.
2. Click Edition Updates.
The Editions Database Management page is displayed.
3. Click the status that you want to view.
For example, click New Editions to view all new editions. The Browse and Search
Results page shows all submitted editions for the selected status.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 47
Page 66

The following information is displayed for each edition:
■ Title - The name of the parent item with which the edition is associated.
■ Edition Name - The name of the edition.
■ Edition Description - A short description of the edition.
■ Version - The version of the edition.
■ Type - The type of content. Select the type from the list of supported types.
■ Developer - The name of the content provider who submitted the edition.
To view the properties for a specific edition, click the title of the desired edition.
The properties for the edition are displayed in the View Content Edition page.
Clicking OK displays the View Content Properties page for the original content.
Click Back on the View Content Properties page to return to the list of editions.
For content that is defined to have one or more supporting devices, you might need
to add additional supporting devices as they become available. To add devices to
existing content, see
“Adding Supported Devices to Existing Content” on page 89.
To return to the main page for Submitted Content, click Review Process in the
navigation bar.
▼ Removing an Edition
You can remove an edition by making it unavailable for use by subscribers by
specifying that no devices are matched to the edition.
To make an edition unavailable to subscribers, follow these steps:
48 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 67

1. From the Submitted Content page, select the status of the edition you want to
disable.
2. Click the title of the content.
3. Go to the Editions section of the View Content Properties for the selected content.
4. Click on the instrumented version of the edition.
5. Click Select on the Supported Devices field of the View Content Edition page.
6. Select the option, Force no devices to be selected for this edition (disable edition).
7. Click OK.
No devices are associated with the selected edition. The edition does not appear in
the subscriber’s content list but does appear in the list of submitted content. The
View Content Edition page for the edition shows no devices listed in the Capable
Device Models and Matched Devices fields.
▼ Searching for Content
To find a specific item of content, follow these steps:
1. From the Submitted Content (or the Published Content) tabbed page, enter either
the content name or a part of a content title or the full title in the Search text field.
You can refine your search by selecting the category and status that you want to
search from the drop-down lists. From the Published Content tabbed page, search in
categories for content.
Searching in Submitted Content shows matches for all submitted content, including
content that is published. Searching in Published Content shows matches only for
published content.
Note that you can only search for content and not editions.
2. Click Submit.
A list of all content containing an exact match of the search entry is displayed.
To show all submitted content, leave the search field blank and select All Categories
and Any Status. You can click on a highlighted column title to alphabetically sort the
content for that information type.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 49
Page 68

▼ Changing the Status of Content
You can change that status of submitted content to one of the types described in
TABLE 2-9.
TABLE 2-9 Content Status Types
Status Definition
Published Content available for use by subscribers.
Pending Content requiring further review before being made available.
Denied Content rejected.
Deleted Content removed.
Testing Content available for use by testing subscribers.
When a content’s status is changed, a notification of the change in status is sent to
the content provider. For more information on notifications sent to the provider, see
the Sun Java System Content Delivery Server Content Developer Guide.
To change the status of content, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
The Content Database Management page is displayed for submitted content.
2. Select Full Submissions.
3. Click the title of the status that contains the content with which you want to work.
For example, click New to work with new content.
4. Select the items that you want to change.
To select all the items in the list, select Select All from the Select on Page drop-down
list.
5. From the Change Status To drop-down list, select the status that you want to
assign to the item.
You can select either Published, Pending, Denied, Deleted, or Testing.
50 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 69

6. Click GO.
The Confirm: Change Status page is displayed. You can enter a message to the
developer to provide an explanation of the status of the content.
7. Click OK in the Change Status page to confirm the status change.
The status of the content is updated. If there are content items remaining in the
selection list, clicking OK displays the Browse and Search Result with the list of
content items. Repeat Steps 4 through 6 until you have changed the status of all the
remaining content items.
When a status change is made to the last content items, the Browse and Search
Result page displays a confirmation message.
8. Click Done in the Browse and Search Result page to close the confirmation
message.
If the vending server is busy at the time you change the content status, instead of a
confirmation page, you are notified that the server is busy and the Vending Manager
did not receive the change yet.
If an error occurs when communicating with the Vending Manager, an error message
appears instead of the confirmation page.
You can also change the status of content from the Edit Application Properties page.
See
“Editing Content” on page 52.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 51
Page 70

▼ Changing the Status of Editions
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
The Content Database Management page is displayed for submitted content.
2. Select Edition Updates.
The Editions Database Management page is displayed.
3. Click the title of the status that contains the edition with which you want to work.
For example, click New Editions to work with new editions.
4. Select the editions that you want to change.
To select all the editions in the list, select Select All from the Select on Page dropdown list.
5. From the Change Status To drop-down list, select the status you want to assign to
the edition.
You can select either Published, Pending, Denied, Deleted, or Testing.
6. Click GO.
A confirmation page is displayed. You can enter a message to the developer to
provide an explanation of the edition status.
7. Click OK to confirm the status change.
▼ Editing Content
You can use the Edit Content page to change one or more properties of a content
item. For instance, you can change which categories contain the content item. You
can also use this page to change the pricing option for submitted content on an
individual basis if the pricing option currently set for the content is not desired
1. Locate the content on one of the status lists or perform a content search to locate
the content.
2. Click the title of the content that you want to edit.
The View Content Properties page is displayed. This information is taken from the
content originally submitted by the developer. All editable fields are displayed with
a white background. You can also view and edit the content developer’s profile by
clicking View Profile next to the developer’s name. See
Account” on page 103 for more information.
If icons, documentation, or screen shots were submitted with the content, you can
view the items by clicking on the View button for the item. If the item is a ring tone
and a preview was submitted, you can click the Listen button to hear the preview.
52 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
“Editing a Developer
Page 71

3. Click Edit from the View Content Properties page.
The Edit Content page is displayed. An asterisk (*) beside a field indicates that it is a
required field.
This page allows you to edit the following fields:
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 53
Page 72

■ General Information - Contains content status and any additional messages
displayed to the content provider.
■ Pricing - Shows the price specified by the content provider.
The pricing options designated by the content provider are displayed just above
the Catalog Price section. You can change the purchase price in the Catalog Price
section.
TABLE 2-10 Content Delivery Server Pricing Models
Pricing Model Definition
Free always No charge for downloading content. Content can be downloaded
Trial No charge for content on initial download. Subscriber must
First download only Subscriber is charged for initial download of content. Subscriber
Every download
Per use Subscriber can download content once after purchase and is
Per period Subscriber can download content once after purchase and is
Per subscription Subscriber can download content an unlimited number of times
Per interval Subscriber can download content an unlimited number of times
a A grace period can be applied to this pricing model by the Vending Manager administrator.
TABLE 2-10 describes the pricing options.
any number of times for however long content is available.
purchase content for subsequent downloads.
is not charged for subsequent downloads.
a
Subscriber is charged for each download of content.
charged for N uses.
charged for running content for the specified length of time, for
example, 3 days, 2 weeks, or 1 month:
Charge for N days, weeks, months, or years.
during the subscription period and is automatically charged for
the next period of use when the current period expires:
Charge recurring fee daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly.
during the interval and is charged for running content from the
specified start date to the specified end date.
Charge for use starting mm/dd/yyyy through mm/dd/yyyy.
■ Catalog Price - Shows the price charged to subscribers. You can change the price
in one of the following ways:
■ Select one of the available pricing options.
Once the content is published, the only attribute that can be changed later
without disassociating the content from its pricing option is the purchase price.
See “Changing the Pricing of Content” on page 29 for more information.
54 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 73

■ Create a custom price for this content item.
Be aware that by creating a custom price, you are disassociating this item for
its pricing option. If you need to reapply a pricing option to the content later,
you can do so, however, you must select a pricing model that is compatible
with the pricing model used with the custom price.
For example, if the custom price used a download pricing model (for instance
$0.99 for every download), the pricing option you reapply must also use a
download pricing model (first download only, every download, or free
always).
■ Catalog Description - Provides the following information about the content:
■ Product name
■ Version
■ Short content description (maximum of 40 characters)
■ Long content description (maximum of 256 characters)
■ Device icon (GIF image 40 x 40 pixels)
■ Small icon (GIF image 40 x 40 pixels)
■ Large icon (GIF image 80 x 80 pixels)
■ Primary Screen Shot (JPEG images 200 pixels wide by 190 pixels high)
■ Secondary Screen shots (JPEG images 200 pixels wide by 190 pixels high)
■ User Guide (PDF file only)
■ Preview (must be of a format supported in the Content Delivery Server)
If other descriptive fields are present for the content, edit those fields as necessary.
■ Category Description - Assigns categories to the content.
4. Edit the content as needed, then click OK.
The View Content Properties page displays the updated content.
To set the pricing characteristics for multiple content items at once, see “Setting
Custom Prices for Published Content” on page 66.
Managing Published Content
The Published Content section displays all content that is published to the Vending
Managers. The administration tasks associated with Published Content are the same
as those associated with managing Submitted Content. This section describes
viewing published content and published editions. See
Content” on page 44 for information on searching for, changing the status of, and
editing content.
“Managing Submitted
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 55
Page 74

Note – If you change a content’s status from Published to another state, the content
is removed from the Published Content list and is not included in the list of
published categories.
▼ Viewing Published Content
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
The Published Content page displays a list of the main categories defined. A number
beside each category indicates the number of published content packages.
3. If a category has subcategories, click the category name to expand the category.
For categories without subcategories, click the name to display the list of content in
that category.
56 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 75

To view the properties for an item, click the title of the item. The View Content
Properties page is displayed. If icons, documentation, or screen shots were
submitted with the content, click the View button for the item to see what was
submitted. If the item is a ring tone and a preview was submitted, you can click the
Listen button to hear the preview.
▼ Removing Content
You can either make content temporarily unavailable or remove content from the
catalog by changing its status.
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
3. Navigate to the content you want to unpublish.
4. Select one or more content items.
5. Select Unpublished or Deleted from the Change Status To drop-down list.
■ Unpublished - Keeps the content item in the Catalog Manager database but
makes it unavailable to the Vending Manager and the subscriber. You can
republish the content item when desired. You can keep the pricing option the
same when you republish or change the pricing option of unpublished content if
desired, in effect, making it new content and then you can republish it.
Note that for unpublished content using OMA DRM 1.0, you can change the
purchase price but not the pricing model. You can change the pricing option of
content with any other DRM type, including No DRM.
■ Deleted - Removes the content item. The content item must be resubmitted by the
content provider to make it available to subscribers again. You delete a content
item when you no longer want to offer that content.
You might want to provide an explanation for removing the content item in the
message field.
6. Click OK.
▼ Viewing Published Editions
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 57
Page 76

3. Navigate to the item that you want to work with.
You can use the search feature or view the list of content for the category that
contains the item.
You can sort the display of the content items by clicking on a highlighted column
title on the Browse and Search Result page.
4. Click the title of the item.
The View Content Properties page is displayed. The list of editions available are
shown in the Editions section at the end of the page.
5. Click the name of the edition that you want to view.
The edition properties are displayed in the View Content Edition page. Click OK to
return to the View Content Properties page of the original content. Click an
instrumented edition version and you can select supported devices for it. See
“Adding Supported Devices to Existing Content” on page 89 for details.
Removing a Published Edition
You can make a published edition unavailable to subscribers by disabling the
edition, that is, by specifying that no devices are matched to the edition. To disable
an edition, click on the instrumented edition you want to disable in the Editions
section of the View Content Properties page and follow steps 5-7 in
Edition” on page 48.
“Removing an
▼ Copying or Moving Categories of Content
You can move or copy whole categories of content at a single time in the Catalog
Manager saving you considerable time and effort. By copying or moving one or
more categories, you are copying or moving all the content items within those
categories.
Note – When scheduling a copy or move operation, be aware that if large numbers
of categories and content are being copied or moved, the operation can take some
time to complete.
You can also selectively move or copy individual items of content, see “Copying or
Moving Content Items” on page 62 for more information.
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
58 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 77

3. Click Copy/Move Content.
The Copy/Move Content page is displayed. The default selection is
Category/Categories.
Category and content item names change from gray to black as the categories and
content items are loaded. Wait until all items are loaded before making a selection.
4. Select the categories you want to copy or move.
Under the source column on the left, select one or more categories to copy or move.
If you select a higher level category, all of its subcategories, including their content
items, are also copied or moved. You cannot select individual items of content. Also,
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 59
Page 78

you cannot copy or move a parent category into one of its child categories. You must
click the check box to select an item in the tree. See
“Copying or Moving Content
Items” on page 62 for more information.
Note that an X indicates a selected category. A dot (.) indicates that at least one
category has been selected in the column. A higher level category with a dot
indicates that at least one of its subcategories is selected.
5. Select one or more destination categories.
Under the destination column on the right, select one or more higher level
categories. The destination category you select cannot be a terminal category. A
terminal category is the lowest level category and contains only content items. You
must click the check box to select an item in the tree.
60 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 79

6. Click Copy or Move.
The Copy and Move buttons only become active when at least one selection is made
in both the source and destination trees. If one category tree does not have a
selection, for instance, if you clear all selections in a tree, the buttons are inactive.
7. Confirm or cancel the operation.
If copied, categories and their associated content are duplicated under each
destination category. If moved, categories and their content are removed from the
original location and placed in the destination category. If more than one destination
category is selected, categories and content are duplicated under each destination
category.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 61
Page 80

The preceding figure shows the results of moving the Mobile Mail, Investment, and
Accounting categories to the Business and Professional category. All content items in
Mobile Mail, Investment, and Accounting were also moved.
If you copy or move a category to another category and decide you no longer want
that category in its new location, you can take one of the following actions:
■ If the category is empty, that is, it contains no content items or subcategories, you
can delete the category from its new location. See
page 18 for more information.
■ If the category is not empty, you must remove its subcategories and content items
by moving or copying them to another location before you can delete the
category.
62 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
“Deleting a Category” on
Page 81

▼ Copying or Moving Content Items
By selecting Individual items on the Copy/Move Content page, you can select
specific content items to copy or move to other categories.
Note – When scheduling a copy or move operation, be aware that if large numbers
of categories and content are being copied or moved, the operation can take some
time to complete.
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Content on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
3. Click Copy/Move Content.
The Copy/Move Content page is displayed.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 63
Page 82

Category and content item names change from gray to black as the categories and
content items are loaded. Wait until all items are loaded before making a selection.
4. Click Individual Items.
5. Select the content items in one or more categories that you want to copy or move.
Under the source column on the left, you can select one or more content items to
copy or move but you cannot select categories. You can expand a category to see its
content items. You must click the check box to select an item in the tree. See
“Copying or Moving Categories of Content” on page 58 for more information.
Note that an X indicates a selected content item. A dot (.) indicates that at least one
content item has been selected in the column. A category with a dot indicates that at
least one of its content items is selected.
64 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 83

6. Select one or more destination categories.
Under the source column on the right, the destination categories you select must be
terminal categories. A terminal category is the lowest level category and contains
only content items. You must click the check box to select an item in the tree.
7. Click Copy or Move.
The Copy and Move buttons only become active when at least one selection is made
in both the source and destination trees. If one category tree does not have a
selection, for instance, if you clear all selections in a tree, the buttons are inactive.
8. Confirm or cancel the operation.
If copied, content is duplicated under each destination category. If moved, content is
removed from the original location and placed in the destination category. If more
than one destination category is selected, content is duplicated under each category.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 65
Page 84

The preceding figure shows the results of copying the content items, N_Ringer and
Splash Screen to the Personal Productivity category. The content items are still
available in the Mobile Mail category.
If you copy a content item to a category and decide that you do not want the item in
that category, you can edit the content to change the category assignment. See
“Editing Content” on page 52 for information.
Setting Custom Prices for Published Content
Another way for you to manage content pricing is to set the price for multiple
content items at once. You can change the purchase price for content in one ore more
categories. Note that while you can change the purchase price, you cannot change
the pricing model.
66 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 85

For instance, if you select the Featured and Entertainment categories, you can
change the purchase price for all the content in those categories or specific content
items in those categories. You set a specific purchase price, apply a percentage
increase or decrease, or increase or decrease the price by a set amount.
Note – Setting custom prices has no Undo operation. Before making the change,
carefully review all settings to ensure that the correct changes will be applied only to
the intended contents. Changing the purchase price in this way, disassociates all
affected content items from their pricing options and they are considered to have
custom pricing.
Pricing for content published as Free cannot be changed using the Customize Prices
feature.
Creating Custom Prices for Content per Category
1. Click Content from the Catalog Manager’s main menu.
2. Click the Published Content tab.
3. Click Customize Prices.
The Customize Prices page is displayed. An asterisk (*) beside a field indicates that
it is a required field.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 67
Page 86

4. Select the category or subcategories of content or specific contents.
To change the purchase price of all the contents of a category, simply click the
category itself.
To change the purchase price of specific content items in a category, navigate
through the category to select individual content items.
68 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 87

5. Change the purchase price in one of the following ways:
■ Enter a new purchase price.
■ Increase or decrease the purchase amount by N per cent.
■ Increase or decrease the purchase price by a dollar amount.
The price is applied to all selected content regardless of their pricing models. For
example, if SpruceDraw is $5.00 per monthly subscription and Launch Screen is
$0.50 per download, increasing the purchase price by 10% results in SpruceDraw
being offered at $5.50 per monthly subscriptions and Launch Screen at $0.55 per
download.
6. Click Customize Price.
7. Click OK in the confirmation dialog box to establish the change.
This procedure has no Undo operation. Carefully check that your pricing changes
will affect only the desired contents before you click OK. Otherwise, you must
manually reset the pricing for erroneously affected content.
Managing Devices
The Catalog Manager manages the devices supported by the Content Delivery
Server. A device in the Catalog Manager refers to a specific mobile device model.
Device capabilities are the criteria that the Catalog Manager uses to define which
devices can download specific content. When a developer submits content to the
Content Delivery Server, device capabilities are matched to the content submitted.
Note – When capability matching is run for all content for a device and one or more
items of content fail verification, the process completes but the Background Jobs list
shows a failed job. You cannot retry this job. The failed content items must be
corrected. Another capability matching process then starts for those items. You can
check the Background Job Detail page for the failed job to see which content failed
verification. See “Getting Job Status” on page 126 for information on background
jobs.
Device capabilities include the following:
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 69
Page 88

■ System capabilities - Capabilities primarily used by the Content Delivery Server.
They define capabilities that a device must have to perform Content Delivery
Server functionality. For instance, system capabilities define whether a device
supports Short Message Service (SMS) or Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
Push.
■ Mandatory capabilities - Capabilities that must be defined for a device to accept
MIDlet applications.
■ Content Delivery Server-specific capabilities - Non-industry standard
capabilities that are specific to the server’s functionality. For example, the
Supported Libraries capability enables you to set the libraries that the device
supports. Libraries define the API sets that are supported. The Supported
Libraries capability enables the Content Delivery Server to match an application
to a device that supports the libraries used by the MIDlet.
■ User interface and software capabilities - Capabilities that specify the
characteristics of the device. The Content Delivery Server uses these capabilities
to refine the capability matching process.
To determine which devices can access the submitted content, the Content Delivery
Server performs a capability match comparing the capabilities of the devices defined
in the Catalog Manager with the capabilities required by the content submitted by
the developer. Only subscribers with devices capabilities that match the capabilities
required by the content can access the content.
Define the devices that you want to support before you make the Content Delivery
Server available to developers and subscribers.
The following device management tasks are described in this section:
■ Managing Device Libraries
■ Managing Content Descriptor Templates
■ Managing Device Definitions
■ Managing Server Locales
When an operation is performed (editing, deleting, adding, and so on), the Content
Deliver Server puts a background job notification in the main menu bar. You can
click on the notice to see details of jobs that were or are running in this session. See
“Getting Job Status” on page 126 for more information.
Managing Device Libraries
Device libraries identify the APIs that are supported by a device. Libraries are also
used in Developer Profiles to define the set of APIs that developers can use in the
applications that they submit. See
information on plans and profiles.
70 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
“Managing Developer Plans” on page 114 for
Page 89

Device libraries are based on the Java class library. When you define a device library
to the Content Delivery Server, you submit the JAR or ZIP file that contains the APIs
that you want to support.
▼ Viewing Device Libraries
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Libraries tab.
The Device Libraries page is displayed, showing the submitted libraries.
The following information is displayed for each library:
■ Library Name - The name of the library.
■ Description - A brief description of the library and its contents.
■ Last Modified Date - The last date that changes were made to the library.
▼ Viewing Properties for a Specific Device Library
To view the properties for a specific device library, follow these steps:
1. Click the library name.
The properties page shows the name, description, date last modified, and the APIs
allowed for devices and profiles that include the library.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 71
Page 90

2. When you are done viewing the properties, click OK to close the properties page.
▼ Adding a Device Library
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Libraries tab.
The list of libraries is displayed.
3. Click New Library.
The Library Definition page is displayed.
72 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 91

4. Enter the following information:
■ Name - A name for the new library.
■ Description - A brief description of the library and its contents.
■ Select JAR File - The path of the class library that you want to submit or click
Browse to locate file. The library file can be either a JAR file or a ZIP file.
5. Click Next.
The second page of the library definition process is displayed.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 73
Page 92

6. Select the items in the tree that you want to include in the library.
Clear any items that you do not want to include.
To select individual methods, expand the package by clicking the plus sign (+) next
to the check box for the package.
7. Click OK to save the new library.
A confirmation page is displayed.
8. Click OK to return to the list of libraries.
▼ Editing a Device Library
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Libraries tab.
The Device Libraries page is displayed.
3. Click the name of the library that you want to edit.
The Library Definition page is displayed.
4. Click Edit.
74 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 93

5. Make the necessary changes.
You can edit only the name and description of a library that is in use. A library is in
use if it is assigned to a device or a Developer Profile.
6. Click OK.
A confirmation page is displayed.
7. Click OK to display the library properties.
▼ Deleting a Device Library
You cannot delete a library that is in use. A library is in use if it has been assigned to
a device or a Developer Profile.
To delete a device library, follow these steps:
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Libraries tab.
The Device Libraries page is displayed.
3. Click the name of the library that you want to delete.
The Library Definition page is displayed.
4. Click Delete.
You are prompted to confirm the deletion of the library.
5. Click OK.
The library is deleted.
6. Click OK to display the list of libraries.
Managing Content Descriptor Templates
Content descriptor templates are used to describe content other than MIDlets (such
as ring tones, pictures, and Symbian applications) similar to the way Java
Application Descriptor (JAD) files are used to describe MIDlets. The templates are
also used to describe the download mechanism used by a device.
Content descriptor templates are required for two step downloading of content to a
device. You specify one step or two step downloading when you assign capabilities
to a device. See
information.
“Specifying Device Capabilities” on page 83 for additional
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 75
Page 94

The Content Delivery Server provides descriptor templates for Content Object
Descriptor (COD) and General Content Descriptor (GCD). You can define other
templates as needed.
TABLE 2-11 shows the Content Delivery Server content attributes that you can use to
customize the template for your needs.
TABLE 2-11 Content Attributes for Content Descriptor Templates
1
Attribute
Name The name of the content.
Version The version of the content.
Size The size of the content.
Vendor The name of the content developer who submitted the content.
ShortDescription A brief description of the content.
Description A detailed description of the content.
DownloadURL The URL from which the content can be downloaded.
BillingURL The URL contacted to verify licenses.
ConfirmURL The URL to which download confirmation or error messages are
ID The ID assigned to the content.
BinaryExtension The extension of the file that contains the content.
BinaryMimeType The MIME type associated with the content.
ContentType The type of content submitted.
ModifiedDate The date the content was last changed.
1
All property names must be preceded by /ContentItem/. For example, /ContentItem/Name.
Definition
NOTE: This attribute is required.
NOTE: This attribute is required.
sent.
NOTE: This attribute is required.
The following code shows a sample content descriptor template.
CODE EXAMPLE 2-1 Sample Content Descriptor Template
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
version="1.0">
<xsl:output method="text" indent="yes"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
Content-Type: <xsl:value-of select=
"/ContentItem/BinaryMimeType"/>
76 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 95

CODE EXAMPLE 2-1 Sample Content Descriptor Template (Continued)
Content-Name: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/Name"/>
Content-Version: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/Version"/>
Content-Vendor: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/Vendor"/>
Content-URL: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/DownloadURL"/>
Content-Size: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/Size"/>
Confirm-URL: <xsl:value-of select="/ContentItem/ConfirmURL"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
▼ Viewing Content Descriptor Templates
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Templates tab.
The Content Descriptor Templates page is displayed, showing the currently defined
templates.
The following information is displayed for each template:
■ Template Name - The name of the template.
■ MIME Type - The MIME type associated with the template.
■ Extension - The extension of the files that use the template. The extension must be
preceded by a period (.). For example,
name of the template. For example,
.cod. This extension is also used as the
cod.xsl.
To view the properties for a specific template, click the template name. The
properties page shows the name, MIME type, extension, and XSL description of the
template.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 77
Page 96

▼ Adding a Content Descriptor Template
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Templates tab to display the list of templates.
3. Click New Template.
The Content Descriptor Template Definition page is displayed.
4. Enter the following information:
■ Template Name - A name for the new library.
■ MIME Type - The string to define the MIME type.
■ Extension - The extension that is associated with the MIME type.
■ Descriptor file - The content descriptor template using XSL. You can enter the
statements directly in the edit field or paste an existing template and make
modifications to it. See
use in the template. Information about XSL is available from the Internet. Click on
one of the default templates to see an example.
5. Click Save to save the new template.
A confirmation page is displayed.
6. Click OK to display the list of templates.
78 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
TABLE 2-11 for information on the attributes that you can
Page 97

▼ Editing a Content Descriptor Template
1. From the Catalog Manager administration console, click Devices on the main
menu bar.
2. Click the Templates tab.
The list of templates is displayed.
3. Click the name of the template that you want to edit.
The template properties are displayed.
4. Click Edit.
5. Make the necessary changes to the template properties.
The fields are the same as those described in “Adding a Content Descriptor
Template” on page 77.
6. Click Save.
A confirmation page is displayed.
7. Click OK to display the template properties.
Managing Device Definitions
Device definitions identify the devices supported by the Content Delivery Server
and describe the capabilities of the device. You can add devices as needed and
remove devices that are not being used.
Viewing Devices
To view the devices defined for your enterprise, click Devices from the main menu
bar. The Device Management page lists the models in the order in which they were
created in the system.
Periodically, the Content Delivery Server might detect that a new device exists. The
new device is added to the list of devices but has a status of new or quarantined.
Auto-detection and provisioning of detected devices is only possible if the property,
autoCreate.newDevice, is set to true in the Subscriber Portal properties file.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 79
Page 98

The following information is displayed for each device.
■ Model Name - The name of the device model.
■ Model Number - The model number of the device.
■ Manufacturer - The name of the company that manufactured the device.
■ User-agent - The unique identifier for the device. The user-agent is a regular
expression that contains information about the device, such as hardware, browser,
and model information. Specifying the user-agent enables the Content Delivery
Server to identify the device without having to ask the subscriber to specify the
device details.
■ Description - A short description of the device.
■ Status - The status of the device, as follows:
■ Active - A device whose capabilities are known and is available for use by
subscribers. Developers can submit content to active devices.
■ New - An auto-provisioned device whose capabilities are not completely
known but is available for subscribers to use. Developers can submit content
for new devices. An example of unknown capabilities might be that at the time
the device was detected, only an incomplete list of its supported libraries was
available. Determine the device’s capabilities before changing its status.
You can change the status of a device from New to Active by clicking the
Activate button on the selected new device’s Device View page.
80 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
Page 99

■ Quarantined - An auto-provisioned device whose capabilities are not
completely known and is unavailable to subscribers. Developers cannot submit
content to quarantined devices. Determine the device’s capabilities before
changing its status.
Change the status of a device from Quarantined to Active by clicking the
Activate button on the selected quarantined device’s Device View page.
▼ Adding a Device
Use the New Device command to add a device to the Content Delivery Server
database. An XML file of the device definitions is created for you. If you have an
existing device, you can import it directly into the Content Delivery Server, see
“Importing Devices” on page 91.
1. On the Device Management page, click New Device.
The Device Management page is displayed. An asterisk (*) beside a field indicates
the field is required.
Chapter 2 Catalog Manager 81
Page 100

2. Specify the following fields:
■ Name - The name of the device.
■ Description - A description of the device.
■ Manufacturer - The name of the manufacturer.
■ Manufacturer Number - The number of the manufacturer.
■ User-agent - The unique identifier for the device. The user-agent is a regular
expression that contains information about the device, such as hardware, browser,
and model information. Specifying the user-agent enables the Content Delivery
Server to identify the device without having to ask the subscriber to specify the
device details.
The regular expression you enter must match the entire user-agent expression
given by the device. You can specify wildcards in the string as .* but be careful
where you place it. For example, if the user-agent from a device is
SAMSUNG-SGH-E700-OLYMPIC2004/1.0 UP.Browser/6.1.0.6 (GUI)
MMP/1.0 (Browser WAP Proxy/1.0), the user-agent regular expression
82 Administrator Guide • 2005Q4
 Loading...
Loading...