Page 1
Sun™SNMP Management Agent
Addendum for the
Netra™440 Server
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
www.sun.com
Part No. 817-6832-10
April 2004, Revision A
Submit comments about this document at: http://www.sun.com/hwdocs/feedback
Page 2

Copyright 2004Sun Microsystems,Inc., 4150 NetworkCircle, SantaClara, California95054, U.S.A. Allrights reserved.
Sun Microsystems,Inc. hasintellectual propertyrights relating to technology thatis described in this document.In particular, and without
limitation, theseintellectual propertyrights may includeone ormore ofthe U.S. patentslisted athttp://www.sun.com/patentsand one or
more additionalpatents orpending patent applicationsin theU.S. and inother countries.
This documentand the product to whichit pertainsare distributedunder licenses restricting theiruse, copying, distribution, and
decompilation. Nopart of the product orof thisdocument may bereproduced in any formby any means without priorwritten authorization of
Sun andits licensors, if any.
Third-party software, including font technology,is copyrighted and licensed fromSun suppliers.
Parts ofthe productmay be derivedfrom BerkeleyBSD systems,licensed from the University ofCalifornia. UNIX is a registered trademark in
the U.S.and in other countries, exclusivelylicensed throughX/Open Company, Ltd.
Sun, Sun Microsystems,the Sunlogo, AnswerBook2, docs.sun.com,Sun Fire,OpenBoot, Netra,and Solaris are trademarksor registered
trademarks ofSun Microsystems,Inc. in theU.S. andin other countries.
All SPARC trademarks are used underlicense andare trademarksor registeredtrademarks of SPARC International,Inc. in theU.S. andin other
countries. Productsbearing SPARC trademarks are based uponan architecturedeveloped by SunMicrosystems, Inc.
The OPENLOOK and Sun™ Graphical UserInterface was developed by SunMicrosystems, Inc.for its users and licensees. Sun acknowledges
the pioneeringefforts ofXerox inresearching anddeveloping the conceptof visualor graphical userinterfaces forthe computer industry. Sun
holds anon-exclusive license from Xeroxto the Xerox GraphicalUser Interface, which license alsocovers Sun’s licensees who implementOPEN
LOOK GUIsand otherwise comply with Sun’swritten license agreements.
U.S. GovernmentRights—Commercial use.Government users are subject tothe Sun Microsystems, Inc.standard licenseagreement and
applicable provisionsof theFAR and its supplements.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING ANYIMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT,
ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Copyright 2004Sun Microsystems,Inc., 4150 NetworkCircle, SantaClara, Californie95054, Etats-Unis. Tous droitsréservés.
Sun Microsystems,Inc. ales droits de propriété intellectuels relatants àla technologiequi est décritdans cedocument. En particulier, et sans la
limitation, cesdroits depropriété intellectuels peuvent inclure un ou plusdes brevetsaméricains énumérés àhttp://www.sun.com/patentset
un oules brevetsplus supplémentaires ou les applicationsde breveten attente dans les Etats-Uniset dans les autres pays.
Ce produitou documentest protégépar un copyrightet distribuéavec des licencesqui enrestreignent l’utilisation,la copie, ladistribution, etla
décompilation. Aucunepartie de ce produit oudocument nepeut êtrereproduite sousaucune forme, parquelque moyenque ce soit,sans
l’autorisation préalableet écrite de Sun etde ses bailleurs de licence,s’il y ena.
Le logicieldétenu par des tiers, etqui comprendla technologie relative aux policesde caractères, est protégé parun copyrightet licencié pardes
fournisseurs deSun.
Des partiesde ce produit pourront être dérivées des systèmes BerkeleyBSD licenciés par l’Université deCalifornie. UNIX est une marque
déposée auxEtats-Unis et dans d’autres payset licenciéeexclusivement par X/OpenCompany, Ltd.
Sun, SunMicrosystems, lelogo Sun, AnswerBook2,docs.sun.com, SunFire, OpenBoot,Netra, et Solarissont desmarques de fabrique ou des
marques déposéesde SunMicrosystems, Inc.aux Etats-Unis etdans d’autrespays.
Toutes lesmarques SPARC sont utiliséessous licenceet sont desmarques defabrique oudes marques déposées de SPARC International, Inc.
aux Etats-Uniset dans d’autres pays. Lesproduits portantles marquesSPARCsont basés sur une architecture développée parSun
Microsystems, Inc.
L’interfaced’utilisation graphiqueOPEN LOOK etSun™ aété développée parSun Microsystems,Inc. pourses utilisateurs etlicenciés. Sun
reconnaît lesefforts depionniers de Xerox pour la recherche et le développementdu concept des interfaces d’utilisationvisuelle ougraphique
pour l’industriede l’informatique. Sun détient unelicense non exclusive de Xeroxsur l’interfaced’utilisation graphique Xerox, cette licence
couvrant égalementles licenciées de Sun quimettent en place l’interface d’utilisation graphique OPEN LOOK etqui enoutre se conforment
aux licencesécrites de Sun.
LA DOCUMENTATION EST FOURNIE "EN L’ÉTAT" ET TOUTES AUTRES CONDITIONS, DECLARATIONS ET GARANTIES EXPRESSES
OU TACITES SONT FORMELLEMENTEXCLUES, DANSLA MESURE AUTORISEE PAR LA LOIAPPLICABLE, Y COMPRIS NOTAMMENT
TOUTE GARANTIE IMPLICITE RELATIVE A LA QUALITE MARCHANDE, A L’APTITUDE A UNE UTILISATION PARTICULIERE OU A
L’ABSENCE DE CONTREFAÇON.
Page 3

Contents
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 1
Sun SNMP Management Agent 2
Netra 440 Server SNMP Containment Model 2
Component and Indicator Identification 10
Fans and Fan Trays 14
Fan Failures 14
Detecting Fan Status 17
Power Supplies 17
Power Supply Failures 18
Detecting Power Supply Status 21
Dry Contact Alarm Relays and LED Indicators 21
Alarm State Changes 22
i
Page 4

ii Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 5

Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server
This document describes how the Netra™ 440 server fans, power supplies, and LED
indicators are represented in the Sun™ Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) Agent for Sun Fire™ and Netra Systems. This document contains the
following sections:
■ “Sun SNMP Management Agent” on page 2
■ “Netra 440 Server SNMP Containment Model” on page 2
■ “Component and Indicator Identification” on page 10
■ “Fans and Fan Trays” on page 14
■ “Power Supplies” on page 17
■ “Dry Contact Alarm Relays and LED Indicators” on page 21
Note – For instructions on installing and using the Sun SNMP Management Agent,
refer to the Sun SNMP Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra Systems (817-2559-xx)
manual. See “Sun SNMP Management Agent” on page 2 for more information.
1
Page 6

Sun SNMP Management Agent
The Sun SNMP Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra Systems provides the
management of supported systems using the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP). Using the Sun SNMP Management Agent, you can monitor inventory,
configuration, and service indicators, as well as environmental and fault reports.
You can download the Sun SNMP Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra
Systems software and documentation at the following web site:
http://www.sun.com/servers/entry/sun_management.html
For instructions on installing and configuring the software, refer to the Sun SNMP
Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra Systems (817-2559-xx). The SNMP
management agent manual contains a detailed overview of the agent software,
including an introduction to the SNMP environment and a description of how the
agent models hardware platforms using the Sun Platform SNMP model (SunPSM).
The manual also describes how the SNMP interface presents managed objects and
their relationships using the ENTITY-MIB and SUN-PLATFORM-MIB management
information bases (MIB).
This document supplements the Sun SNMP Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra
Systems manual by documenting how the agent represents the Netra 440 server fans,
power supplies, and certain LED indicators. This document provides Netra 440
server-specific information only. For complete descriptions of the SNMP agent
terminology, management models, and trap properties, refer to the Sun SNMP
Management Agent for Sun Fire and Netra Systems manual.
For additional information about the Netra 440 server, refer to the server’s
documentation at the following web site:
http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/docs/Servers/Netra_Servers/Netra_440/
Netra 440 Server SNMP Containment Model
TABLE 1 presents an example of how the Sun SNMP agent models the Netra 440
server component hierarchy. Because this component hierarchy may vary depending
on your server and the SNMP agent software version, query the SNMP agent to
identify your server’s hierarchy. To locate these server components, see the figures in
“Component and Indicator Identification” on page 10.
2 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 7
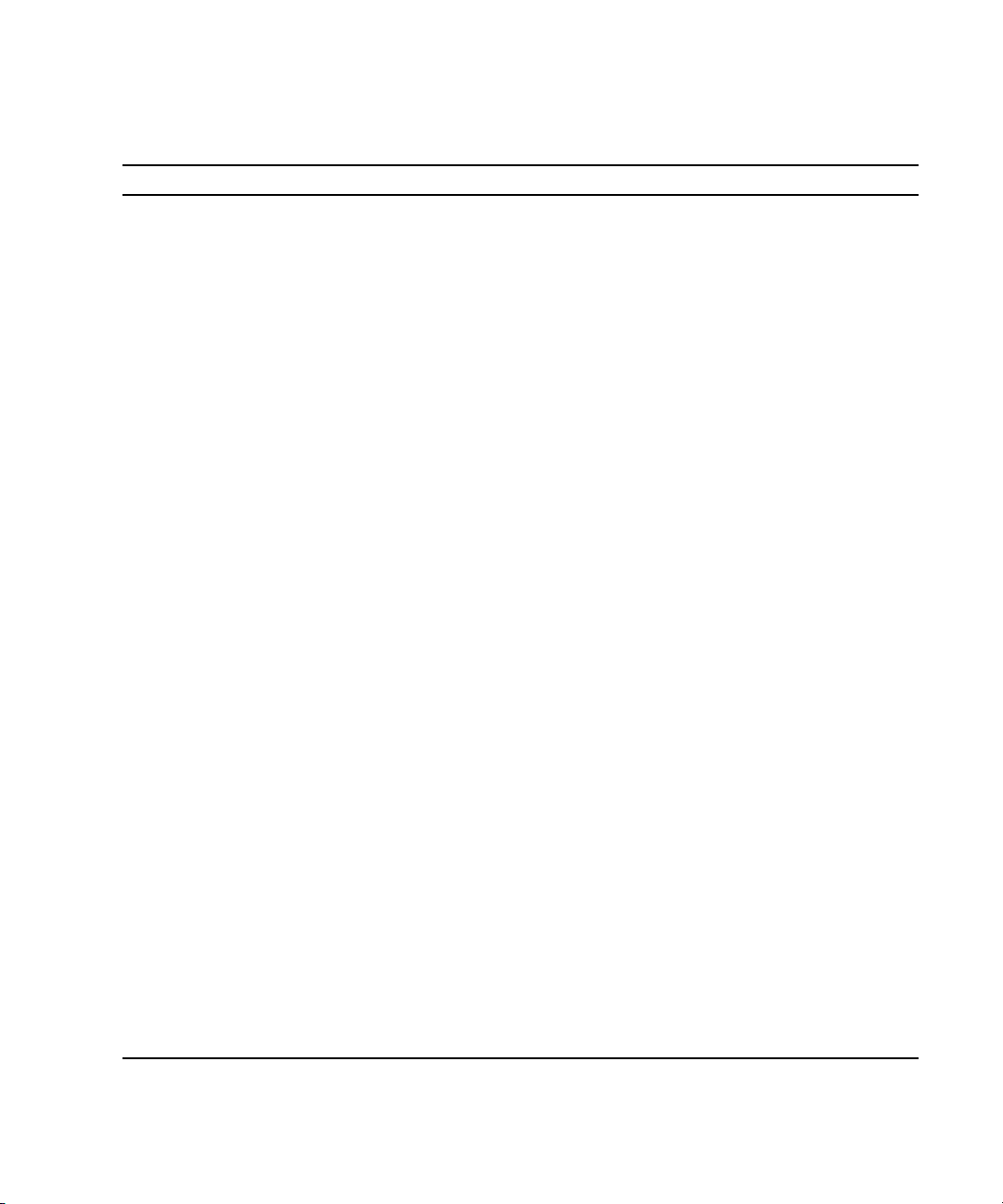
TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy)
Model Description For Location, See:
Netra 440 Chassis
➥ Alarm Board
Critical Alarm Relay
Major Alarm Relay
Minor Alarm Relay
User Alarm Relay
➥ System Board
OpenBoot PROM
➥ Battery
Battery Voltage Monitor
➥ CPU/Memory Slot 0 (far left - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 2
➥ CPU/Memory Module 0 FIGURE 4 – item 2
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 0 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 5
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 1
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 2
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 1 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 6
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 3
➥ Processor 0 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 2
FIGURE 5 – item 4
➥ CPU 0 (far left - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 2
CPU 0 Core Temperature Monitor
CPU 0 Power OK Fault Sensor
CPU 0 Ambient Temperature Sensor
➥ CPU/Memory Slot 1 (2nd from left - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 3
➥ CPU/Memory Module 1 FIGURE 4 – item 3
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 3
Page 8

TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
Model Description For Location, See:
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 0 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 5
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 1
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 2
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 1 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 6
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 3
➥ Processor 1 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 3
FIGURE 5 – item 4
➥ CPU 1 (2nd from left - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 3
CPU 1 Core Temperature Monitor
CPU 1 Power OK Fault Sensor
CPU 1 Ambient Temperature Sensor
➥ CPU/Memory Slot 2 (2nd from right - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 4
➥ CPU/Memory Module 2 FIGURE 4 – item 4
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 0 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 5
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 1
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 2
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 1 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 6
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 3
➥ Processor 2 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 4
FIGURE 5 – item 4
➥ CPU 2 (2nd from right - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 4
CPU 2 Core Temperature Monitor
CPU 2 Power OK Fault Sensor
4 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 9

TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
Model Description For Location, See:
CPU 2 Ambient Temperature Sensor
➥ CPU/Memory Slot 3 (far right - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 5
➥ CPU/Memory Module 3 FIGURE 4 – item 5
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 0 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 5
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 1
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 0 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 2
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 1 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 6
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 0 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 3
➥ Processor 3 Memory Bank 1 DIMM 1 FIGURE 4 – item 5
FIGURE 5 – item 4
➥ CPU 3 (far right - viewed from front) FIGURE 4 – item 5
CPU 3 Core Temperature Monitor
CPU 3 Power OK Fault Sensor
CPU 3 Ambient Temperature Sensor
PCI Slot 0 (33Mhz 5V) (far left - viewed from front)
PCI Slot 1 (33Mhz 5V) (2nd from left - viewed from front)
*
PCI Slot 2 (33/66Mhz 3.3V) (3rd from left - viewed from front)
PCI Slot 3 (33Mhz 5V) (3rd from right - viewed from front)
*
PCI Slot 4 (33/66Mhz 3.3V) (2nd from right - viewed from front)
PCI Slot 5 (33/66Mhz 3.3V) (far right - viewed from front)
➥ System Controller Slot
➥ System Controller
FIGURE 3 – item 11
FIGURE 3 – item 10
*
FIGURE 3 – item 9
FIGURE 3 – item 8
*
FIGURE 3 – item 7
FIGURE 3 – item 6
Motherboard Ambient Temperature Sensor
+1.5V Rail Monitor
+3.3V Rail Monitor
Standby Monitor
+5V Rail Monitor
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 5
Page 10

TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
Model Description For Location, See:
+12V Rail Monitor
-12V Rail Monitor
Ethernet 0 1.2V Analog Rail Monitor
Ethernet 0 1.2V Digital Rail Monitor
Ethernet 1 1.2V Analog Rail Monitor
Ethernet 1 1.2V Digital Rail Monitor
SCSI Controller 1.8V Rail Monitor
Tomatillo/Cassini 2.5V Rail Monitor
Motherboard Power OK Fault Sensor
Internal SCSI Termination Power Rail Fault Sensor
External SCSI Termination Power Rail Fault Sensor
SCSI Disk Backplane
➥ Chassis Indicator Panel
➥ System Active Indicator (front) FIGURE 1 – item 3
System Locator (front)
System Service-Required Indicator (front)
Asynchronous Serial Port
SCSI Port
Alarm Port
USB 0 Port (top left - viewed from rear)
USB 1 Port (bottom left - viewed from rear)
USB 2 Port (top right - viewed from rear)
USB 3 Port (bottom right - viewed from rear)
Management Network Port
Management Serial Port
➥ Fan Tray 0 FIGURE 2 – item 2
➥ Fan 0 FIGURE 2 – item 2
➥ Fan 0 Active Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 6
Fan 0 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 4 – item 6
FIGURE 1 – item 1
FIGURE 1 – item 2
FIGURE 3 – item 24
FIGURE 3 – item 17
FIGURE 3 – item 25
FIGURE 3 – item 22
FIGURE 3 – item 22
FIGURE 3 – item 21
FIGURE 3 – item 21
FIGURE 3 – item 4
FIGURE 3 – item 5
FIGURE 2 – item 5
Fan 0 Tachometer
6 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 11

TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
Model Description For Location, See:
➥ Fan Tray 1 FIGURE 2 – item 14
➥ Fan 1 FIGURE 2 – item 14
➥ Fan 1 Active Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 9
Fan 1 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 2 – item 8
Fan 1 Tachometer
➥ Fan Tray 2 FIGURE 2 – item 16
➥ Fan 2 FIGURE 2 – item 16
➥ Fan 2 Active Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 12
Fan 2 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 2 – item 11
Fan 2 Tachometer
➥ Fan Tray 3 FIGURE 4 – item 1
Fan 3
System Control Keyswitch
System Active Indicator (rear)
System Locator (rear)
System Service-Required Indicator (rear)
Critical Alarm Indicator (front)
Major Alarm Indicator (front)
Minor Alarm Indicator (front)
User Alarm Indicator (front)
➥ Hard Disk Drive 0 Bay (left - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 1
➥ HDD0 Okay To Remove Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 4
HDD0 Service Required Indicator
†
FIGURE 4 – item 1
FIGURE 1 – item 5
FIGURE 3 – item 3
FIGURE 3 – item 1
FIGURE 3 – item 2
FIGURE 1 – item 8
FIGURE 1 – item 9
FIGURE 1 – item 10
FIGURE 1 – item 11
Hard Disk Drive 0 (left - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 1
➥ Hard Disk Drive 1 Bay (2nd from left - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 3
➥ HDD1 Okay To Remove Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 7
HDD1 Service Required Indicator
†
Hard Disk Drive 1 (2nd from left - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 3
➥ Hard Disk Drive 2 Bay (2nd from right - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 15
➥ HDD2 Okay To Remove Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 10
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 7
Page 12

TABLE 1 Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
Model Description For Location, See:
HDD2 Service Required Indicator
†
Hard Disk Drive 2 (2nd from right - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 15
➥ Hard Disk Drive 3 Bay (right - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 17
➥ HDD3 Okay To Remove Indicator FIGURE 2 – item 13
HDD3 Service Required Indicator
†
Hard Disk Drive 3 (right1 - viewed from front) FIGURE 2 – item 17
➥ Power Supply 0 Bay (right - viewed from rear) FIGURE 3 – item 15
➥ Power Supply 0 FIGURE 3 – item 15
➥ PS 0 Okay-To-Remove Indicator FIGURE 3 – item 15 and item 14
PS 0 Active Indicator
PS 0 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 3 – item 15 and item 12
FIGURE 3 – item 15 and item 13
PS 0 Over-Current Fault Monitor
PS 0 Fan Under-Speed Fault Monitor
PS 0 Over-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 0 Under-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 0 Power Inlet Presence Monitor
PS 0 Over-Temperature Fault Monitor
➥ Power Supply 1 Bay (2nd from right - viewed from rear) FIGURE 3 – item 16
➥ Power Supply 1 FIGURE 3 – item 16
➥ PS 1 Okay-To-Remove Indicator FIGURE 3 – item 16 and item 14
PS 1 Active Indicator
PS 1 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 3 – item 16 and item 12
FIGURE 3 – item 16 and item 13
PS 1 Over-Current Fault Monitor
PS 1 Fan Under-Speed Fault Monitor
PS 1 Over-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 1 Under-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 1 Power Inlet Presence Monitor
PS 1 Over-Temperature Fault Monitor
➥ Power Supply 2 Bay (2nd from left - viewed from rear) FIGURE 3 – item 20
➥ Power Supply 2 FIGURE 3 – item 20
8 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 13

TABLE 1
Model Description For Location, See:
Netra 440 Server Containment Model (Hierarchy) (Continued)
➥ PS 2 Okay-To-Remove Indicator FIGURE 3 – item 20 and item 14
PS 2 Active Indicator
PS 2 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 3 – item 20 and item 12
FIGURE 3 – item 20 and item 13
PS 2 Over-Current Fault Monitor
PS 2 Fan Under-Speed Fault Monitor
PS 2 Over-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 2 Under-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 2 Power Inlet Presence Monitor
PS 2 Over-Temperature Fault Monitor
➥ Power Supply 3 Bay (left - viewed from rear) FIGURE 3 – item 23
➥ Power Supply 3 FIGURE 3 – item 23
➥ PS 3 Okay-To-Remove Indicator FIGURE 3 – item 23 and item 14
PS 3 Active Indicator
PS 3 Service-Required Indicator
FIGURE 3 – item 23 and item 12
FIGURE 3 – item 23 and item 13
PS 3 Over-Current Fault Monitor
PS 3 Fan Under-Speed Fault Monitor
PS 3 Over-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 3 Under-Voltage Fault Monitor
PS 3 Power Inlet Presence Monitor
PS 3 Over-Temperature Fault Monitor
➥ System Configuration Card Reader FIGURE 1 – item 4
➥ System Configuration Card FIGURE 1 – item 4
➥ DVD Drive Bay FIGURE 1 – item 6
➥ DVD Drive FIGURE 1 – item 6
➥ Power Distribution Module Bay FIGURE 1 – item 7
➥ Power Distribution Module FIGURE 1 – item 7
Ethernet Port 0 (left - viewed from rear)
Ethernet Port 1 (right - viewed from rear)
* The SNMP model mayshow frequency valuesfor slots 1- 4 that are differentfrom those shownin this table;if that isthe case, ignore
the frequency values shown inthe SNMP model, and use the frequencyvalues shown in this table and theregular Netra 440 server
labels and documents instead. Refer to the Netra 440 Server Release Notes for more information.
† While the service-required indicator is represented in the containment model, it is not supported.
FIGURE 3 – item 19
FIGURE 3 – item 18
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 9
Page 14

Component and Indicator Identification
The following figures show the location of the Netra 440 server components. TABLE 1
lists of how the agent models these components in an SNMP hierarchy.
1
23
4
8
9
10
11
7
FIGURE 1 Front Panel Indicators and Components
Indicators:
1. System locator
2. System service-required
3. System active
5
6
SCC
4. System configuration card reader
5. System control keyswitch
6. DVD drive bay/DVD drive
7. Power distribution module bay
8. Critical alarm
9. Major alarm
10. Minor alarm
11. User alarm
10 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 15

9
8
7
6
5
10
11
12
13
4
3
2
1
SCC
Components and indicators:
1. Hard disk drive (HDD) 0
2. Fan tray 0
3. HDD 1
4. HDD0 okay to remove
5. Fan tray 0 service required
6. Fan tray 0 active
7. HDD1 okay to remove
8. Fan tray 1 service required
9. Fan tray 1 active
FIGURE 2 Hard Disk Drive and Fan Tray Components and Indicators
14
15
16
17
10. HDD2 okay to remove
11. Fan tray 2 service required
12. Fan tray 2 active
13. HDD3 okay to remove
14. Fan tray 1
15. HDD 2
16. Fan tray 2
17. HDD 3
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 11
Page 16

25
1
23
4
6
5
7
8
910
11
12
13
14
24
23
22
21
20
Components and indicators:
1. System locator
2. System service-required
3. System active
4. Network management port
5. Serial management port
6. PCI card slot 5
7. PCI card slot 4
8. PCI card slot 3
9. PCI card slot 2
10. PCI card slot 1
11. PCI card slot 0
12. Power supply (PS) active
13. PS service-required
14. PS okay-to-remove
FIGURE 3 Rear Panel Components and Indicators
1819
17
15. PS 0
16. PS 1
17. SCSI port
18. NET 1 ethernet port
19. NET 0 ethernet port
20. PS 2
21. USB 2 and 3 ports
22. USB 0 and 1 ports
23. PS 3
24. Serial port
25. Alarm port
1516
12 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 17

1
FIGURE 4 Internal Components
2
3
4
Internal components:
1. Fan Tray 3/Fan 3
2. CPU/memory module 0
5
3. CPU/memory module 1
4. CPU/memory module 2
5. CPU/memory module 3
6. SCSI disk backplane
6
Memory banks and DIMMs
1. Memory bank 0 DIMM 0
2. Memory bank 0 DIMM 1
3. Memory bank 1 DIMM 0
4. Memory bank 1 DIMM 1
5. Memory bank 0
4123
6. Memory bank 1
5
FIGURE 5 Memory Banks and DIMMs
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 13
6
Page 18

Fans and Fan Trays
The Netra 440 server fans in the fan trays are identified in the ENTITYMIB::entPhysicalTable by the entPhysicalDescr of Fan number, where number is a
number in the range from 0 to 3. The fans are represented in the following tables that
extend the entPhysicalTable:
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatEquipmentTable
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatFanTable
Note – The fans in fan trays 0-2 have certain sensors that give status and failure
information, whereas the fan in fan tray 3 does not; therefore, the information in the
remainder of this section will apply only to the fans in fan trays 0-2, not the fan in
fan tray 3. Also, if the fan in fan tray 3 fails, the Netra 440 server automatically shuts
down and no SNMP traps are generated.
The fans in fan trays 0-2 contain a tachometer used to indicate the current speed of
the fan expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM). The tachometers are identified
by their entPhysicalDescr of Fan number Tachometer, where number is a number in
the range from 0 to 2 corresponding to the fan tray being monitored. The fan
tachometers are represented in the following tables that extend the entPhysicalTable:
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatEquipmentTable
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatSensorTable
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatNumericSensorTable
Fan Failures
If the speed of a fan falls below the threshold indicated by its tachometer's
sunPlatNumericSensorLowerThresholdNonCritical value, the fan is considered to
have failed and the following will occur:
■ The sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState value for the fan will change from
enabled(2) to disabled(1) and a sunPlatStateChange trap will be generated
with the form shown in
■ A sunPlatEnvironmentalAlarm trap with a sunPlatNotificationPerceivedSeverity
value of warning(5) will be generated for the fan with the form shown in
TABLE 3.
■ The sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus value for the fan will change from
cleared(7) to warning(5) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap will be
generated with the form shown in
14 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
TABLE 2.
TABLE 4.
Page 19

■ The sunPlatAlarmState values for the status LEDs will change and
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger traps will be generated with the form shown in
TABLE 5.
If the fan recovers from the failure, the following changes will occur:
■ The sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState value for the fan will change from
disabled(1) to enabled(2) and a sunPlatStateChange trap will be generated
with the form shown in
■ A sunPlatEnvironmentalAlarm trap with a sunPlatNotificationPerceivedSeverity
TABLE 2.
value of cleared(6) will be generated for the fan with the form shown in
TABLE 3.
■ The sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus value for the fan will change from
warning(5) to cleared(7) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap will be
generated with the form shown in
■ The sunPlatAlarmState values for the status LEDs will change and
TABLE 4.
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger traps will be generated with the form shown in
TABLE 5.
TABLE 2 sunPlatStateChange Trap for a Fan Failure or Recovery
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.fan instance
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState.fan instance
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger disabled(1) or enabled(2)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger disabled(1) or enabled(2)
* fan instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the fan.
*
*
TABLE 3 sunPlatEnvironmentalAlarm Trap for a Fan Failure or Recovery
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.fan instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationAdditionalInfo 0.0 (null)
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 15
Page 20

TABLE 3 sunPlatEnvironmentalAlarm Trap for a Fan Failure or Recovery (Continued)
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationAdditionalText entPhysicalName of the fan tachometer: Tachometer
threshold crossed
sunPlatNotificationPerceivedSeverity warning(5) or cleared(6)
sunPlatNotificationProbableCause coolingFanFailure(107)
sunPlatNotificationSpecificProblem coolingFanFailure
sunPlatNotificationRepairAction
* fan instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the fan.
TABLE 4
Variable Value
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Change in the sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus of a Fan
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.fan instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus.fan instance
*
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger warning(5) or cleared(7)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger warning(5) or cleared(7)
* fan instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the fan.
TABLE 5 sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Change in the sunPlatAlarmState of an LED
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.LED instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatAlarmState.LED instance
*
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger off(2) or steady(3)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger off(2) or steady(3)
* LED instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the LED.
16 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 21
Detecting Fan Status
You can detect fan status using the following mechanisms:
■ Polling sunPlatNumericSensorCurrent and
sunPlatNumericSensorLowerThresholdNonCritical for the fan's tachometer and
comparing their values.
■ Polling the sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState of the fan.
■ Receiving a sunPlatStateChange trap corresponding to the change of the
sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState of the fan.
■ Receiving a sunPlatEnvironmentalAlarm trap with a
sunPlatNotificationProbableCause of coolingFanFailure(107).
Power Supplies
The power supplies are identified in the ENTITY-MIB::entPhysicalTable by the
entPhysicalDescr of Power Supply number where number is 0, 1 2 or 3. The power
supplies are represented in the SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatEquipmentTable.
Each power supply contains the following sensors:
■ Power Inlet Presence Monitor
■ Fan Under-Speed Fault Monitor
■ Over-Voltage Fault Monitor
■ Under-Voltage Fault Monitor
■ Over-Temperature Fault Monitor
■ Over-Current Fault Monitor
These sensors are represented in the following tables:
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatEquipmentTable
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatSensorTable
■ SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatBinarySensorTable
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 17
Page 22

Power Supply Failures
If any of the power supply sensors detect a fault the following changes will occur:
■ The sunPlatBinarySensorCurrent value for the sensor that detected the fault will
change from true(1) to false(2) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap
will be generated with the form shown in
■ The sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState for the power supply will change from
enabled(2) to disabled(1) and a sunPlatStateChange trap will be generated
with the form shown in
■ A sunPlatEquipmentAlarm trap for the power supply will be generated with the
form shown in
■ The sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus value for the power supply will change from
TABLE 8.
TABLE 7.
cleared(7) to major(2) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap will be
generated with the form shown in
■ The sunPlatAlarmState values for the status LEDs will change and
TABLE 9.
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger traps will be generated with the form shown in
TABLE 10.
Recovery from the power supply fault will result in the following changes:
■ The sunPlatBinarySensorCurrent value for the sensor that detected the fault will
change from false(2) to true(1) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap
will be generated with the form shown in
■ The sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState for the power supply will change from
disabled(1) to enabled(2) and a sunPlatStateChange trap will be generated
with the form shown in
■ A sunPlatEquipmentAlarm trap with a sunPlatNotificationPerceivedSeverity
TABLE 7.
value of cleared(6) will be generated for the power supply with the form
shown in
■ The sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus value for the power supply will change from
TABLE 8.
major(2) to cleared(7) and a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap will be
generated with the form shown in
■ The sunPlatAlarmState values for the status LEDs will change and
TABLE 9.
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger traps will be generated with the form shown in
TABLE 10.
TABLE 6.
TABLE 6.
18 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 23

TABLE 6 sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Power Supply Sensor
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.ps sensor instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatBinarySensorCurrent.ps sensor instance
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger true(1) or false(2)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger true(1) or false(2)
* ps sensor instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the power supply sensor.
TABLE 7 sunPlatStateChange Trap for a Power Supply Fault or Recovery
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.ps instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState.ps instance
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger disabled(1) or enabled(2)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger disabled(1) or enabled(2)
* ps instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the power supply.
*
*
TABLE 8 sunPlatEquipmentAlarm Trap for a Power Supply Fault or Recovery
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.ps instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationAdditionalInfo 0.0 (null)
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 19
Page 24

TABLE 8 sunPlatEquipmentAlarm Trap for a Power Supply Fault or Recovery (Continued)
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationAdditionalText entPhysicalName of the sensor: Voltage threshold crossed
sunPlatNotificationPerceivedSeverity major(3) or cleared(6)
sunPlatNotificationProbableCause powerProblem(58)
sunPlatNotificationSpecificProblem powerProblem
sunPlatNotificationRepairAction
* ps instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the power supply.
TABLE 9 sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Change in the sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus of a Power
Supply
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.ps instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatEquipmentAlarmStatus.ps instance
*
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger major(2) or cleared(7)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger major(2) or cleared(7)
* ps instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the power supply.
TABLE 10 sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Change in the sunPlatAlarmState of an LED
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.LED instance
*
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatAlarmState.LED instance
*
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger off(2) or steady(3)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger off(2) or steady(3)
* LED instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the LED.
20 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
Page 25

Detecting Power Supply Status
You can use the following mechanisms to detect power supply status:
■ Poll the value of sunPlatBinarySensorCurrent for each of the power supply
sensors.
■ Poll the value of sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState for the power supply.
■ Receiving a sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger trap corresponding to a change in the
sunPlatBinarySensorCurrent value for one of the power supply sensors.
■ Receiving a sunPlatStateChange trap corresponding to a change in the
sunPlatEquipmentOperationalState for the power supply.
■ Receiving a sunPlatEquipmentAlarm trap with a
sunPlatNotificationProbableCause value of powerProblem(58).
Dry Contact Alarm Relays and LED Indicators
The Netra 440 server has four dry contact alarm relays and four corresponding LED
indicators. The alarm relays are identified in the ENTITY-MIB::entPhysicalTable by
the following entPhysicalDescr values:
■ Critical Alarm Relay
■ Major Alarm Relay
■ Minor Alarm Relay
■ User Alarm Relay
The alarm LED indicators are identified in the ENTITY-MIB::entPhysicalTable by the
following entPhysicalDescr values:
■ Critical Alarm Indicator (front)
■ Major Alarm Indicator (front)
■ Minor Alarm Indicator (front)
■ User Alarm Indicator (front)
The alarm relays and the alarm LED indicators are represented in the
SUN-PLATFORM-MIB::sunPlatAlarmTable which extends the
ENTITY-MIB::entPhysicalTable.
Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server 21
Page 26

Alarm State Changes
The alarm relay state cannot be changed using SNMP set commands. However, the
alarm relay state can be changed using the Sun Advanced Lights Out Manager
(ALOM) setalarm command. For more information about ALOM commands, refer
to the Sun Advanced Lights Out Manager Software User's Guide for the Netra 440 Server
(817-5481-xx).
The alarm relay states can also be changed using the alarm relay output application
programming interface (API). For information about this API, refer to the Netra 440
Server System Administration Guide (817-3884-xx).
If one of the alarm relays changes its state, the sunPlatAlarmState values associated
with the relay and its corresponding indicator change state, and
sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger traps will be generated in the format shown in
TABLE 11.
TABLE 11 sunPlatAttributeChangeInteger Trap for a Change in the sunPlatAlarmState of an Alarm Relay
or an Alarm Relay Indicator
Variable Value
sunPlatNotificationEventId unique numeric identifier
sunPlatNotificationTime date time
sunPlatNotificationObject entPhysicalDescr.instance
sunPlatNotificationCorrelatedNotifications
sunPlatNotificationChangedOID sunPlatAlarmState.instance
sunPlatNotificationOldInteger off(2) or steady(3)
sunPlatNotificationNewInteger off(2) or steady(3)
* instance indicates the row in the entPhysicalTable associated with the alarm relay or the alarm indicator.
*
*
22 Sun SNMP Management Agent Addendum for the Netra 440 Server • April 2004
 Loading...
Loading...