Page 1

Sun Java System Application
Server Enterprise Edition 8.1
2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
4150 Network Circle
Santa Clara, CA 95054
U.S.A.
Part No: 819–2553
Page 2

Copyright 2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, CA 95054 U.S.A. All rights reserved.
This product or document is protected by copyright and distributed under licenses restricting its use, copying, distribution, and decompilation. No
part of this product or document may be reproduced in any form by any means without prior written authorization of Sun and its licensors, if any.
Third-party software, including font technology, is copyrighted and licensed from Sun suppliers.
Parts of the product may be derived from Berkeley BSD systems, licensed from the University of California. UNIX is a registered trademark in the U.S.
and other countries, exclusively licensed through X/Open Company, Ltd.
Sun, Sun Microsystems, the Sun logo, docs.sun.com, AnswerBook, AnswerBook2, and Solaris are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of
SPARC International, Inc. in the U.S. and other countries. Products bearing SPARC trademarks are based upon an architecture developed by Sun
Microsystems, Inc.
The OPEN LOOK and Sun™ Graphical User Interface was developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc. for its users and licensees. Sun acknowledges the
pioneering efforts of Xerox in researching and developing the concept of visual or graphical user interfaces for the computer industry. Sun holds a
non-exclusive license from Xerox to the Xerox Graphical User Interface, which license also covers Sun’s licensees who implement OPEN LOOK GUIs
and otherwise comply with Sun’s written license agreements.
U.S. Government Rights – Commercial software. Government users are subject to the Sun Microsystems, Inc. standard license agreement and
applicable provisions of the FAR and its supplements.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE
DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Copyright 2005 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 4150 Network Circle, Santa Clara, CA 95054 U.S.A. Tous droits réservés.
Ce produit ou document est protégé par un copyright et distribué avec des licences qui en restreignent l’utilisation, la copie, la distribution, et la
décompilation. Aucune partie de ce produit ou document ne peut être reproduite sous aucune forme, par quelque moyen que ce soit, sans
l’autorisation préalable et écrite de Sun et de ses bailleurs de licence, s’il y en a. Le logiciel détenu par des tiers, et qui comprend la technologie relative
aux polices de caractères, est protégé par un copyright et licencié par des fournisseurs de Sun.
Des parties de ce produit pourront être dérivées du système Berkeley BSD licenciés par l’Université de Californie. UNIX est une marque déposée aux
Etats-Unis et dans d’autres pays et licenciée exclusivement par X/Open Company, Ltd.
Sun, Sun Microsystems, le logo Sun, docs.sun.com, AnswerBook, AnswerBook2, et Solaris sont des marques de fabrique ou des marques déposées, de
Sun Microsystems, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans d’autres pays. Toutes les marques SPARC sont utilisées sous licence et sont des marques de fabrique ou
des marques déposées de SPARC International, Inc. aux Etats-Unis et dans d’autres pays. Les produits portant les marques SPARC sont basés sur une
architecture développée par Sun Microsystems, Inc.
L’interface d’utilisation graphique OPEN LOOK et Sun™ a été développée par Sun Microsystems, Inc. pour ses utilisateurs et licenciés. Sun reconnaît
les efforts de pionniers de Xerox pour la recherche et le développement du concept des interfaces d’utilisation visuelle ou graphique pour l’industrie
de l’informatique. Sun détient une licence non exclusive de Xerox sur l’interface d’utilisation graphique Xerox, cette licence couvrant également les
licenciés de Sun qui mettent en place l’interface d’utilisation graphique OPEN LOOK et qui en outre se conforment aux licences écrites de Sun.
CETTE PUBLICATION EST FOURNIE “EN L’ETAT” ET AUCUNE GARANTIE, EXPRESSE OU IMPLICITE, N’EST ACCORDEE, Y COMPRIS DES
GARANTIES CONCERNANT LA VALEUR MARCHANDE, L’APTITUDE DE LA PUBLICATION A REPONDRE A UNE UTILISATION
PARTICULIERE, OU LE FAIT QU’ELLE NE SOIT PAS CONTREFAISANTE DE PRODUIT DE TIERS. CE DENI DE GARANTIE NE
S’APPLIQUERAIT PAS, DANS LA MESURE OU IL SERAIT TENU JURIDIQUEMENT NUL ET NON AVENU.
050727@12762
Page 3

Contents
1 Quick Start 5
Variable Names and Default Paths 5
About Application Server Administration 6
Starting the Server 7
Starting the Domain Administration Server 7
▼ To Start the Domain on Solaris and Linux 7
▼ To Start the Domain on Windows 8
Logging in to the Admin Console 9
▼ To Log In to the Admin Console 9
Examining the Log File 11
▼ To View the Domain Administration Server Log File 11
Creating a Cluster 12
▼ To Start the Node Agent 12
▼ To Create a Cluster 12
Deploying an Application 15
▼ To Deploy the Sample Application 15
▼ To Start the Cluster 16
▼ To Verify the Application Deployment 16
Setting up Load Balancing 17
Installing Web Server Software 18
▼ To Install the Web Server Using the Java Enterprise System Installer 18
▼ To Install the Web Server for Stand-Alone Application Server
Installations 18
Installing the Load Balancer Plug-in 19
▼ To Install the Load Balancer Plug-in 19
Creating a Load Balancer Configuration 19
▼ To Create an HTTP Load Balancer Configuration 20
3
Page 4

Starting Load Balancing 20
Verifying Load Balancing 20
▼ To Verify Load Balancing 21
Cleaning Up 22
▼ To Uninstall Completely 22
▼ To Remove the Sample Cluster Only 23
Where to Go Next 24
2 Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 25
About High Availability Clusters and HADB 26
HADB Preinstallation Steps 26
▼ To Configure Your System for HADB 27
Installing HADB 28
▼ To Install HADB 28
Starting HADB 28
▼ To Start HADB in a Java Enterprise System Installation on Solaris or
Linux 29
▼ To Start HADB in a Java Enterprise System Installation on Windows 29
▼ To Start HADB in a Stand-Alone Installation on Solaris or Linux 29
▼ To Start HADB in a Stand-Alone Installation on Windows 30
Configuring a Cluster and Application for High Availability 30
▼ To Configure a Cluster and Application for High Availability 30
Restarting the Cluster 31
▼ To Restart the Cluster 31
Verifying HTTP Session Failover 32
▼ To Verify HTTP Session Failover 32
Cleaning Up 33
▼ To Uninstall Completely 34
▼ To Remove the Sample Cluster 35
Where to Go Next 37
4 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 5

CHAPTER 1
Quick Start
Welcome to the Quick Start Guide. This guide is for developers, system
administrators, and Application Server administrators who are interested in learning
about the capabilities of the Sun Java System Application Server 8.1 2005Q2 software.
This guide describes basic and advanced steps for using Application Server. The steps
are presented in the order that you should complete them. The basic steps, which
usually require less than 45 minutes to complete, are in these sections:
■
“Starting the Server” on page 7
■
“Creating a Cluster” on page 12
■
“Deploying an Application” on page 15
The advanced steps, which usually require about 45 minutes to complete, are in these
sections:
■
The steps for setting up load balancing, in “Setting up Load Balancing” on page
17
■
The steps for setting up high availability and failover, in Chapter 2
The final sections of this guide include instructions for cleaning up and information on
sources of information to use after completing this Quick Start Guide.
Variable Names and Default Paths
The following table describes what the variable names and default paths are for the
directories used in this guide. Variable names are in the first column, and default paths
are in the second column.
5
Page 6
Variable Name Description and Path
install-dir By default, the Application Server installation directory is located
here:
■
Solaris Java Enterprise System installations:
/opt/SUNWappserver/appserver
■
Linux Java Enterprise System installations:
/opt/sun/appserver/
■
Windows Java Enterprise System installations:
SystemDrive:\Sun\ApplicationServer
■
Solaris and Linux stand-alone Application Server installations,
non-root user: user_home_directory/SUNWappserver
■
Solaris and Linux stand-alone Application Server installations,
root user: /opt/SUNWappserver
■
Windows stand-alone installations:
SystemDrive:\Sun\AppServer
domain_root_dir By default, the directory containing all domains is located here:
domain_dir By default, domain directories are located here: domain_root_dir
■
Solaris Java Enterprise System installations:
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/domains/
■
Linux Java Enterprise System installations:
/var/opt/sun/appserver/domains/
■
All other installations: install-dir/domains/
/domain_dir
About Application Server Administration
To enable administrators to manage server instances and clusters running on multiple
hosts, Application Server provides these tools:
■
The Admin Console, a browser-based graphical user interface (GUI)
■
The asadmin utility, a command-line tool
■
Programmatic Java™ Management Extensions (JMX™) APIs
These tools connect to a server called the Domain Administration Server, a specially
designated Application Server instance that intermediates in all administrative tasks.
The Domain Administration Server (DAS) provides a single secure interface for
validating and executing administrative commands regardless of which interface is
used.
6 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 7

A domain is a collection of configuration data, deployed applications, and machines
with a designated administrator. The domain definition describes and can control the
operation of several applications, stand-alone application server instances, and
clusters, potentially spread over multiple machines. When the DAS is installed, a
default domain called domain1 is always installed. You work with the default domain
in this guide.
To complete most of the steps presented in this guide, you will use the Admin
Console.
Starting the Server
This topic, the first of three basic topics, provides the following sections
■
“Starting the Domain Administration Server” on page 7
■
“Logging in to the Admin Console” on page 9
■
“Examining the Log File” on page 11
Starting the Domain Administration Server
To start the Domain Administration Server, start the default domain, domain 1, using
the following procedures.
Note – Because this guide instructs you to set an environment variable
AS_ADMIN_USER for administrative user name, it does not instruct you to supply a
user name argument when the asadmin command is used. Without the environment
variable, you supply this argument when you type the command. The general syntax
is:
asadmin command_verb --user username command_arguments
For example, if your user name is admin, the syntax for asadmin start-domain is:
asadmin start-domain --user admin domain1
▼ To Start the Domain on Solaris and Linux
Steps
1. Add the install-dir/bin/ directory to the PATH environment variable.
2. Set the AS_ADMIN_USER environment variable so that you do not need to type it
for every command.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 7
Page 8

Set the value of AS_ADMIN_USER to the admin user you specified when you
installed the Application Server. For example, setenv AS_ADMIN_USER admin
3. Start the server by entering this command from the install-dir:
asadmin start-domain domain1
When you are prompted for the admin password and the master password, enter
the passwords that you provided during installation.
4. A message appears telling you that the Domain Administration Server is
starting:
Starting Domain domain1, please wait. Log redirected to
domain_dir/domain1/logs/server.log...
5. When the startup process has completed, an additional message appears:
Domain domain1 started
▼ To Start the Domain on Windows
Steps
1. From the Explorer window or desktop, right click My Computer.
2. Choose Properties to display the System Properties dialog.
3. Click the Advanced tab.
4. Click Environment Variables.
5. In the User variables section:
■
If a PATH variable exists, verify that install-dir\bin exists in the path:
install-dir\bin;other_entries.
■
If a PATH variable is not present, click New. In Variable Name, type PATH.In
Variable Value, type the path to the server’s bin directory: install-dir\bin.
Click OK to commit the change.
6. Add a new environment variable AS_ADMIN_USER and set it to the
Administrative User Name that you assigned during installation.
7. Click OK to commit the change and close the remaining open windows.
8. Start the Application Server
■
For Java Enterprise System installations, from the Start menu, choose
Programs ⇒ Sun Microsystems ⇒ Application Server⇒ Start Admin Server.
■
For stand-alone installations, from the Start menu, choose Programs ⇒ Sun
Microsystems ⇒ Application Server EE ⇒ Start Admin Server.
8 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 9

9. When a command prompt window opens to prompt you for the admin password
and the master password, enter the passwords that you provided during
installation.
A window appears with a message telling that you the server is starting:
Starting Domain domain1, please wait.
Log redirected to domain_dir\domain1\logs\server.log...
When the startup process has completed, you see an additional message:
Domain domain1 started.
Press any key to continue ...
10. Press a key to close the message window.
Logging in to the Admin Console
The Admin Console is a browser interface that simplifies a variety of administration
and configuration tasks. It is commonly used to:
■
Deploy and undeploy applications
■
Enable, disable, and manage applications
■
Configure resources and other server settings
■
Configure clusters and node agents
■
Manage server instances and clusters
■
Select and view log files
For further information about using the Admin Console, consult the online help or the
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Administration Guide.
▼ To Log In to the Admin Console
Steps
1. Type this URL in your browser:
https:// localhost:4849/asadmin
Because the Admin Console is a secure web application, you must use https
instead of http.
Replace the localhost variable with the name of the system that the Domain Admin
Server is running on.
4849 is the Admin Console’s default port number. If you changed the port number
during the installation, use that number instead.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 9
Page 10
Note – If a popup window appears with a message such as Website Certified
by an Unknown Authority, click OK.
This message appears because your browser does not recognize the self-signed
certificate that the Domain Administration Server uses to service the Admin
Console over the secure transmission protocol.
2. When the log in window appears, enter the admin user name and password.
3. Click Log In.
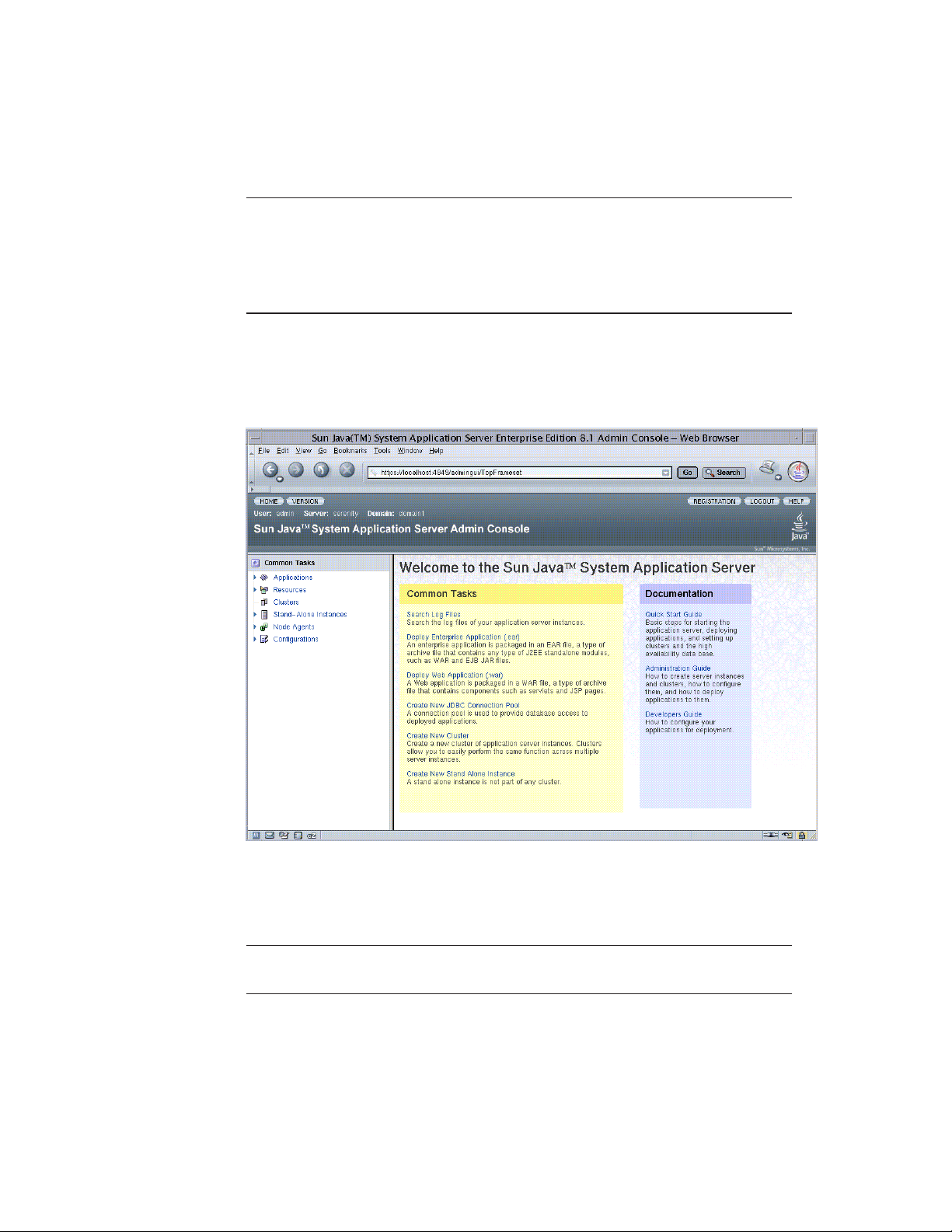
When the Admin Console appears, it looks like this:
In the left pane, select what you want to manage from the tree provided. In the
right pane, various administrative tasks are listed under the “Common Tasks”
heading.
Tip – Click the Registration tab to register your software if you have not already
done so.
10 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 11
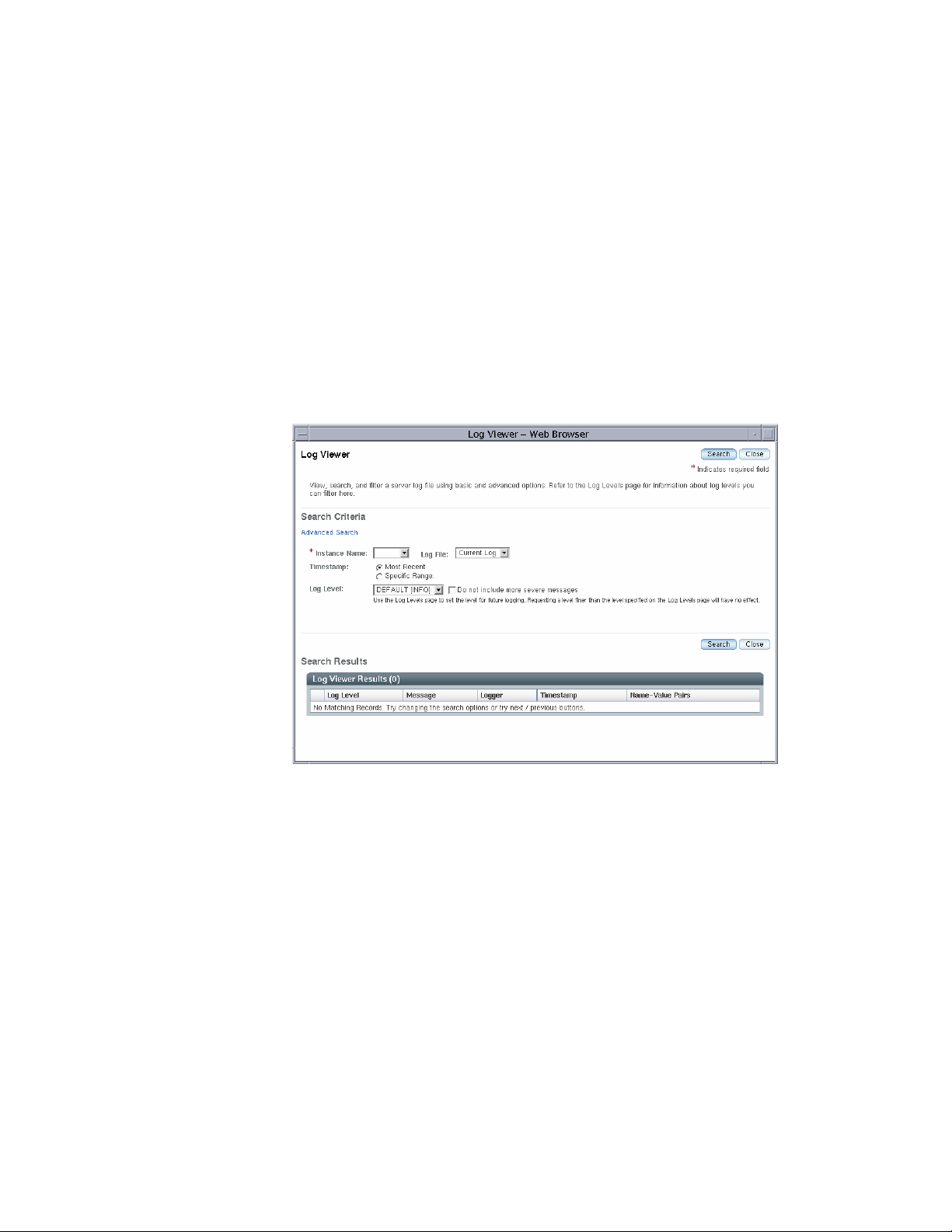
Examining the Log File
Application Server instances and the Domain Administration Server produce
annotated logs on the file system. By default, all errors, warnings or useful informative
messages are logged.
▼ To View the Domain Administration Server Log File
Steps
1. From the Common Tasks list in the right pane, click Search Log Files to launch a
new browser window for Log Viewer.
2. In the Log Viewer window, select “server” from the Instance Name drop–down
list and click Search.
The Domain Administration Server’s recent log file entries are displayed.
3. Scan the messages and look for any WARNING or SEVERE messages indicating
that problems were encountered during server start-up.
You can close Log Viewer at any time. After you create clusters and deploy
applications, examine log files if any of the operations failed. Use Log Viewer to
view the log files of any running Application Server instance in the domain.
For more information about the log file, see Chapter 16, “Configuring Logging,” in
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Administration
Guide.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 11
Page 12

Next Steps
▼ To Start the Node Agent
In this section you started the Domain Administration Server and confirmed that it is
running. You also logged in to the Admin Console and used the Log Viewer. You can
stop the Quick Start trail here if you do not wish to continue, or you can go on to the
next section.
Creating a Cluster
This section, the second of three basic topics, explains how to create a cluster that
contains two Application Server instances. For simplicity, the cluster runs completely
within one machine. This topic includes the following tasks:
■
“To Start the Node Agent” on page 12
■
“To Create a Cluster” on page 12
A node agent is a lightweight process running on each machine that participates in an
Application Server administrative domain. The node agent is responsible for starting
and stopping server instances on the host. It also collaborates with the Domain
Administration Server to create new Application Server instances.
One node agent is needed on a machine, for each Application Server administrative
domain that the machine belongs to. If you chose the Node Agent Component during
installation, a default node agent called hostname was created.
Steps
1. In a terminal window, type this command:
asadmin start-node-agent hostname
Replace the variable hostname with the name of the host where the Application
Server is running.
2. When you are prompted, provide the master password.
The node agent starts and connects with the Domain Administration Server.
Note – If the Domain Administration Server is not running, the node agent might
fail to start.
▼ To Create a Cluster
A cluster is a group of server instances (typically on multiple hosts) that share the same
configurations, resources, and applications. A cluster facilitates load balancing across
server instances and high availability through failover. You can create clusters
12 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 13

spanning multiple machines and manage them with the help of the node agent
process on each machine. In this guide, for simplicity, our sample cluster will be on
one host, the same one where the Domain Administration Server is running.
Before You
Begin
Steps
You must have already started the node agent process on each machine, as described
in previous section. When you specify instances during cluster creation, you must
associate the instance with a running node agent for the machine on which you want
the instance to run. If the node agent is not running, the instance will not start. Node
agent and instance names must be unique across clusters that are created in a domain.
1. Log in to the Administration Console at https:// localhost:4849 if you have
not already done so.
Replace the localhost variable with the name of the system that the Domain
Administration Server is running on.
4849 is the Admin Console’s default port number. If you changed the port number
during the installation, use that number instead.
2. On the right pane, under Common Tasks, click Create New Cluster to display
the Create Cluster input page.
3. Type FirstCluster as the name of the new cluster.
4. From the drop-down list of available configuration templates, select the
default-config configuration and choose Make a copy of the selected
Configuration.
5. Click the Add button twice, to create two entries to specify two instances for the
cluster.
6. Type i1 and i2 as instance names. The node agent name is automatically
populated with the name of the local machine.
You see a screen like this:
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 13
Page 14

7. Click OK. The create process can take a few minutes.
Note – This exercise requires automatically assigned port numbers for HTTP,
HTTPS, IIOP and IIOPS. You can change them later, if desired.
When the create process is completed, the Cluster Created Successfully page
appears, and FirstCluster appears in the tree in the left pane. A copy of the
configuration template default-config was made for this cluster, and the name
FirstCluster-config was assigned to it.
8. In the left pane, expand Clusters and click FirstCluster to display the General
Information page for clusters.
9. Click the Instances tab to display i1 and i2, the instances that you created.
a. Click i1 to examine this instance.
b. From the tabs above the General Information heading of the right pane, click
Properties and see the value for HTTP_LISTENER_PORT.
c. Repeat these steps for i2.
14 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 15

Note – By default, the HTTP ports are 38081 for i1 and 38080 for i2. If these ports
were busy on your machine when you created these clusters, or if you had
already assigned these ports to other instances and clusters, different port
numbers were assigned.
Next Steps
▼ To Deploy the Sample Application
In this section you have created a simple cluster on a single machine. You can also
create clusters spanning multiple machines using the same basic steps (as long as you
have the software installed and a node agent running on each machine).
You can stop the Quick Start trail here if you do not wish to continue, or you can go on
to the next section.
Deploying an Application
This section, the third of three basic topics, presents the following steps:
■
“To Deploy the Sample Application” on page 15
■
“To Start the Cluster” on page 16
■
“To Verify the Application Deployment” on page 16
This guide uses the clusterjsp sample application to demonstrate web path load
balancing capabilities. This task shows you how to deploy that application.
Steps
1. Click the Home button to go to the Common Tasks page, if you are not there
already.
2. On the right pane, under Common Tasks, click Deploy Enterprise Application.
3. In the File to Upload text box, click Browse, and navigate to
install-dir/samples/ee-samples/highavailability/apps/clusterjsp/
clusterjsp.ear.
4. Click Next to display the Deploy Enterprise Application page.
5. Scroll down to the Targets section of the page.
6. Select FirstCluster from the Available list, and click Add to move it to the
Selected list.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 15
Page 16

7. Click OK.
The clusterjsp application is now deployed to FirstCluster.
▼ To Start the Cluster
Steps
1. In the tree on the left pane, click the FirstCluster node under Clusters.
2. In the right pane, click the General tab if it is not already active.
3. Click the Start Instances button to start the cluster.
4. Verify that it has started by checking that the Status field, which indicates what
instances are running.
▼ To Verify the Application Deployment
This procedure verifies that the application was deployed properly and is accessible
on each instance in the cluster.
Steps
16 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
1. Type the following URL in your browser:
Page 17

http://localhost:port/clusterjsp
Replace the localhost variable with the name of the system that the Domain Admin
Server is running on.
Replace the port variable with the value of HTTP-LISTENER-PORT for i1. This
example uses http://localhost:38081/clusterjsp.
2. Add some session attribute data.
3. Examine the Session and Host information displayed. For example:
■
Executed From Server: localhost
■
Server Port Number: 38081
■
Executed Server IP Address: 198.19.255.255
■
Session Created: Day Mon 05 14:55:34 PDT 2005
4. Add some session data and click the Add to Session button.
5. Repeat this procedure for instance i2 by typing this URL in your browser:
http://localhost :38080/clusterjsp
In this section you deployed an application to a cluster and tested that the
application is available on all instances in the cluster.
Congratulations! You have completed the basic steps in this Quick Start Guide. You
can stop the Quick Start trail here if you do not wish to proceed to the advanced
steps.
Setting up Load Balancing
A load balancer is typically deployed in front of a cluster. It:
■
Allows an application or service to be scaled horizontally across multiple physical
(or logical) hosts yet still presents the user with a single URL
■
Insulates the user from host failures or server crashes, when it is used with session
replication
■
Enhances security by hiding the internal network from the user
Application Server includes load balancing plug-ins for popular web servers like
Apache, Microsoft Windows IIS, and Sun Java™ System Web Server.
This section provides instructions on how to download and set up the Web Server
software to act as a load balancer to the cluster of Application Servers. To complete
this section, you must have sufficient memory to run a Web Server on your system in
addition to the Domain Administration Server and the two Application Server
instances you have created so far in this guide. A system with 512 Mbytes to 1024
Mbytes of memory is recommended to complete this section.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 17
Page 18

This topic presents the following steps:
■
“Installing Web Server Software” on page 18
■
“Installing the Load Balancer Plug-in” on page 19
■
“Creating a Load Balancer Configuration” on page 19
■
“Starting Load Balancing” on page 20
■
“Verifying Load Balancing” on page 20
Installing Web Server Software
If you already have Web Server software installed, and if you can identify a Web
Server instance to serve as the load balancer, note the location of this instance in the
file system and skip to “Installing the Load Balancer Plug-in” on page 19.
▼ To Install the Web Server Using the Java Enterprise System
Installer
If you are using Sun Java Enterprise System software, the Web Server is selected for
installation automatically when you choose to install the Load Balancer Plug-in.
However, you can also install Web Server software using these steps:
Steps
1. Launch the Java Enterprise System installer.
2. Select the Sun Java System Web Server component in the Component Selection
page.
3. Choose “Configure Now” to be prompted for Web Server Configuration during
installation.
4. When you are prompted, define a default Web Server instance.
Tip – Remember the port number you choose for this default Web Server instance.
This guide assumes that port 38000 is selected as the HTTP port for default
instance.
▼ To Install the Web Server for Stand-Alone Application
Server Installations
If you are using a stand-alone Application Server, or if you do not have access to the
Sun Java Enterprise System installer, install Web Server software using these steps:
Steps
1. Go to http://www.sun.com/downloads. Scroll down to the Web & Proxy
Servers heading and click Web Servers.
18 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 19

2. Download Web Server 6.1 Service Pack 2 or higher for the locale and platform of
your choice.
To download, you must log in with username and password registered with
MySunSM, Sun StoreSM, SunSolveSM, or the Online Support Center. If you do not
have a login account, you can register online.
3. Follow the instructions to install Web Server software. You must:
a. Extract the software from the compressed archive.
b. Run the setup program. If you need additional information, see the Web
Server installation instructions at http://docs.sun.com.
4. The Web Server installation process configures the Administration Server for
Web Server and prompts you to define a default Web Server instance.
Tip – Remember the port number you choose for this default web server instance.
This guide assumes that port 38000 is selected as the HTTP port for default
instance.
Installing the Load Balancer Plug-in
The section describes installing the load balancer plug-in for either a Sun Java
Enterprise System distribution or a stand-alone Application Server distribution.
▼ To Install the Load Balancer Plug-in
Steps
1. Run the installer for the software distribution you are using—Sun Java
Enterprise System software or the stand-alone Sun Java System Application
Server software.
2. When you are asked which components you want to install, select Load
Balancing Plug-in.
On the Sun Java Enterprise System installer, you must expand the Application
Server item to see the Load Balancing Plug-in. It is not selected for installation by
default.
Creating a Load Balancer Configuration
Now return to interacting with the Application Server ’s Domain Admin Server. You
need a shell execution environment for this section.
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 19
Page 20

▼ To Create an HTTP Load Balancer Configuration
Steps
1. Create a load balancer configuration called MyLbConfig targeted to the cluster
FirstCluster:
asadmin create-http-lb-config --target FirstCluster MyLbConfig
2. Enable the FirstCluster cluster and the clusterjsp application deployed in it for
HTTP load balancing:
asadmin enable-http-lb-server FirstCluster
asadmin enable-http-lb-application --name clusterjsp
FirstCluster
3. Create a health checker for the load balancer, which signals when an instance
that goes down recovers.
asadmin create-http-health-checker --interval 10 --config
MyLbConfig FirstCluster
The interval is the number of seconds the health checker waits between checks of
an unhealthy instance.
4. Export the configuration to a file loadbalancer.xml.
asadmin export-http-lb-config --config MyLbConfig
loadbalancer.xml
5. Copy loadbalancer.xml to:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname/config/loadbalancer.xml
Starting Load Balancing
Start load balancing by starting or restarting the Web Server.
■
If the Web Server instance serving as load balancer is not already running, start the
Web Server software by executing the start program in the following directory:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
■
If the Web Server instance serving as load balancer is already running, stop the
server and start it using the start and stop programs in the following directory:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
Verifying Load Balancing
Once the application is deployed and the load balancer is running, verify that the load
balancing is working.
20 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 21

▼ To Verify Load Balancing
Steps
1. To display the first page of the clusterjsp application, type this URL in your
browser:
http://localhost:web_server_port/clusterjsp
Replace the localhost variable with the name of the system that the Web Server is
running on.
Replace the web_server_port variable with the value of the port attribute of the LS
element in web_server_install_dir/https-hostname/config/server.xml. For this
example, port 38000 is used.
A page similar to what you saw in “To Verify the Application Deployment”
on page 16. appears.
2. Examine the Session and Host information displayed. For example:
■
Executed From Server: localhost
■
Server Port Number: 38000
■
Executed Server IP Address: 192.18.145.133
■
Session Created: Day Mon 05 14:55:34 PDT 2005
3. The Server Port Number is 38000, the Web Server’s port. The load balancer has
forwarded the request on the two instances in the cluster.
4. Using different browser software, or a browser on a different machine, create a
new session. Requests from the same browser are “sticky” and go to the same
instance.
These sessions should be distributed to the two instances in the cluster. You can
verify this by looking at the server access log files located here:
■
Solaris Java Enterprise System installation:
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs
/access/server_access_log
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs
/access/server_access_log
■
Linux Java Enterprise System installation:
/var/opt/sun/appserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs
/access/server_access_log
/var/opt/sun/appserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs
/access/server_access_log
■
Windows Java Enterprise System installation:
install-dir\nodeagents\nodeagent_name\i1\logs\access
\server_access_log
install-dir\nodeagents\nodeagent_name\i2\logs\access
\server_access_log
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 21
Page 22

■
Stand-alone Application Server installations:
install-dir/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs
/access/server_access_log
install-dir/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs
/access/server_access_log
5. Add a name and value pair (Name=Name Value=Duke) for storing in
HttpSession.
6. Click the “Add to Session Data” button.
7. Verify that the session data was added
Next Steps
▼ To Uninstall Completely
In this section you created an instance to use as a load balancer and set up a load
balancing configuration. You also verified load balancing.
To configure and verify HTTP session failover, continue to Chapter 2. Otherwise
continue on to “Cleaning Up” on page 22.
Cleaning Up
To clean up, you can uninstall the Application Server installation by completing the
steps in “To Uninstall Completely” on page 22, or you can simply delete the sample
cluster you have just created by completing the steps in “To Remove the Sample
Cluster Only” on page 23.
Caution – If you plan to complete Chapter 2 do not use these clean-up procedures.
Instead, go to Chapter 2 now and when you are done use the procedures you’ll find
there to clean up.
To completely uninstall Application Server and also uninstall the Web Server, use the
following procedure.
Steps
22 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
1. Stop the Application Server processes using these commands:
asadmin stop-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin stop-node-agent hostname
asadmin stop-domain domain1
Page 23

At this point all processes related to Application Server are stopped.
2. Uninstall the Application Server.
In a Solaris or Linux Java Enterprise System installation, run
var/sadm/prod/entsys/uninstall and follow the steps in the uninstallation
wizard.
In a Windows Java Enterprise System installation, use the Control Panel’s
Add/Remove Programs item. Choose Sun Java Enterprise Systems and click
Change/Remove.
In a Solaris or Linux stand-alone Application Server installation, run
install-dir/uninstall and follow the steps in the uninstallation wizard.
In a Windows stand-alone installation, from the Start menu, choose Programs ⇒
Sun Microsystems ⇒ Application Server EE ⇒ Uninstall.
3. If you installed Web Server for this exercise, stop the web server instance acting
as load balancer and uninstall the Web Server product. You can stop the instance
by executing the stop program in the following directory:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
4. If you want to unsinstall the Web Server product, run the uninstall program
from the web_server_install_dir.
▼ To Remove the Sample Cluster Only
To remove only the FirstCluster (the sample highly available cluster) and the sample
application used during this exercise, but retain the installed Application Server and
Web Server, use the following procedure.
Steps
1. Stop the Application Server processes and clean up configuration:
asadmin stop-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin disable-http-lb-server FirstCluster
asadmin delete-http-lb-ref --config MyLbConfig FirstCluster
asadmin delete-http-lb-config MyLbConfig
asadmin delete-instance i1
asadmin delete-instance i2
asadmin delete-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin undeploy clusterjsp
2. Stop the web server instance acting as load balancer by running the stop
program in the following directory:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
3. Rename the loadbalancer.xml file in web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
/config to loadbalancer.xml.sav
Chapter 1 • Quick Start 23
Page 24

Where to Go Next
Other resources for learning about and using Application Server are available. They
include:
■
Product details at install-dir/docs-ee/about.html.
See this document for the latest information on what is new, and pointers to
tutorials and other educational services.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Release Notes
See this document for late-breaking information regarding this release.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Administration Guide
See this document for information on performing administrative functions using
the Admin Console.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Reference Manual
See this document for reference information on Application Server ’s command-line
utilities, such as asadmin.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 High Availability
Administration Guide
See this document for information on the Sun Java System Application Server ’s
high availability features.
■
The J2EE 1.4 Tutorial
(http://java.sun.com/j2ee/1.4/docs/tutorial/doc/index.html)
See this document for a tutorial that covers the process for building and deploying
Java™ 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE™ platform) applications.
■
Java BluePrints (http://java.sun.com/blueprints) guidelines for the
Enterprise
See this document for a comprehensive set of examples that demonstrate
operations of the Application Server software and that can be used as application
templates.
24 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 25

CHAPTER 2
Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover
With the configuration used in the previous chapter, if a server instance goes down,
users lose session state. This section, the second of two advanced topics, provides the
steps for installing the high-availability database (HADB), creating a highly available
cluster, and testing HTTP session persistence.
Application Server supports both HTTP session persistence and persistence for
Stateful Session Beans. The procedures in this chapter cover HTTP session persistence.
These steps assume you have already performed the steps in the previous sections of
this Quick Start. The steps are presented in the order that you should complete them.
Note – Completing this section may require additional hardware resources.
This topic contains the following sections:
■
“About High Availability Clusters and HADB” on page 26
■
“HADB Preinstallation Steps” on page 26
■
“Installing HADB” on page 28
■
“Starting HADB” on page 28
■
“Configuring a Cluster and Application for High Availability” on page 30
■
“Restarting the Cluster” on page 31
■
“Verifying HTTP Session Failover” on page 32
■
“Cleaning Up” on page 33
■
“Where to Go Next” on page 37
25
Page 26

About High Availability Clusters and HADB
A highly availability cluster inSun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition
integrates a state replication service with the clusters and load balancer created earlier,
enabling failover of HTTP sessions.
HttpSession objects and Stateful Session Bean state is stored in HADB, a
high-availability database for storing session state. This horizontally scalable state
management service can be managed independently of the application server tier. It
was designed to support up to 99.999% service and data availability with load
balancing, failover and state recovery capabilities.
Keeping state management responsibilities separated from Application Server has
significant benefits. Application Server instances spend their cycles performing as a
scalable and high performance Java™ 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE™ platform)
containers delegating state replication to an external high availability state service.
Due to this loosely coupled architecture, application server instances can be easily
added to or deleted from a cluster. The HADB state replication service can be
independently scaled for optimum availability and performance. When an application
server instance also performs replication, the performance of J2EE applications can
suffer and can be subject to longer garbage collection pauses.
Because each HADB node requires 512 Mbytes of memory, you need 1 Gbyte of
memory to run two HADB nodes on the same machine. If you have less memory, set
up each node on a different machine. Running a two-node database on only one host
is not recommended for deployment since it is not fault tolerant.
HADB Preinstallation Steps
This procedure covers the most common preinstallation tasks. For information on
other preinstallation topics, including prerequisites for installing HADB, configuring
network redundancy, and file system support, see Chapter 2, “Installing and Setting
Up High Availability Database,” in Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise
Edition 8.1 2005Q2 High Availability Administration Guide.
The recommended system configuration values in this section are sufficient for
running up to six HADB nodes and do not take into consideration other applications
on the system that also use shared memory.
26 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 27

▼ To Configure Your System for HADB
Steps
1. Get root access.
2. Define variables related to shared memory and semaphores.
■
On Solaris:
a. Add these lines to the /etc/system file (or if these lines are in the file as
comments, uncomment them and make sure that the values match these):
set shmsys:shminfo_shmmax=0x80000000
set shmsys:shminfo_shmseg=36
set semsys:seminfo_semmnu=600
Set shminfo_shmmax to the total memory in your system (in hexadecimal
notation the value 0x80000000 shown is for 2 Gigabytes of memory).
If the seminfo_* variables are already defined, increment them by the
amounts shown. The default values for seminfo_semmni and
seminfo_semmns do not need to be changed. The variable
shminfo_shmeg is obsolete after Solaris 8.
b. Reboot, using this command:
sync; sync; reboot
■
On Linux:
a. Add these lines to the /etc/sysctl.conf file (or if they are in the file as
comments, uncomment them). Set the value to the amount physical
memory on the machine. Specify the value as a decimal number of bytes.
For example, for a machine having 2 GB of physical memory:
echo 2147483648 > /proc/sys/shmmax
echo 2147483648 > /proc/sys/shmall
b. Reboot, using this command:
sync; sync; reboot
■
On Windows: No special system settings are needed.
3. If you used existing JDK software when you installed a standalone Application
Server, check the JDK version.
HADB requires Sun JDK 1.4.1_03 or higher (for the latest information on JDK
versions, see the Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2
Release Notes). Check the version installed, and if it is not done already, set the
JAVA_HOME environment variable to the directory where the JDK is installed.
4. If necessary after the reboot, restart the domain, Web Server, and node agent.
To restart the domain, use the command asadmin start-domain domain1.
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 27
Page 28

To restart the Web Server, execute the start program in
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname.
To restart the node agent, use the command asadmin start-node-agent
hostname. Replace the variable hostname with the name of the host where the
Application Server is running.
Installing HADB
This section provides the steps for installing the high-availability database (HADB).
Note – If you plan to run the high-availability database on the Application Server
machine, and if you installed HADB when you installed Application Server, skip to
“Starting HADB” on page 28.
You can install the HADB component on the same machine as your Application Server
system if you have 2 Gbytes of memory and 1-2 CPUs. If not, use additional hardware.
For example:
■
Two 1 CPU systems with 512 Mbytes to 1 Gbyte memory each
■
One 1-2 CPU system with 1 Gbytes to 2 Gbytes memory
▼ To Install HADB
Steps
1. Run the Application Server or Java Enterprise System installer.
2. Choose the option to install HADB.
3. Complete the installation on your hosts.
Starting HADB
This section describes starting the HADB management agent in most cases by running
the ma-initd script. For a production deployment, start the management agent as a
service to ensure its availability. For more information, see “Starting the HADB
Management Agent” in Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2
High Availability Administration Guide.
28 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 29

If starting a database with HADB nodes on several hosts, start the management agent
on each host.
▼ To Start HADB in a Java Enterprise System
Installation on Solaris or Linux
Steps
1. Change to the /etc/init.d directory:
cd /etc/init.d
2. Run the command to start the agent:
./ma-initd start
▼ To Start HADB in a Java Enterprise System
Installation on Windows
HADB is started by default when Sun Java System is configured and running.
However, if you need to start it manually, follow these steps:
Steps
1. Go to Start⇒Settings⇒Control Panel, and double click Administrative Tools.
2. Double click Services shortcut.
3. Select HADBMgmtAgent Service from the Services list.
4. From the Action menu, select Start.
▼ To Start HADB in a Stand-Alone Installation on
Steps
Solaris or Linux
1. Change to the HADB bin directory in the Application Serverinstallation:
install-dir/hadb/4/bin
2. Run the command to start the agent:
./ma-initd start
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 29
Page 30

▼ To Start HADB in a Stand-Alone Installation on
Windows
Steps
1. In a terminal window, change to the HADB bin directory in the Application
Serverinstallation: install-dir\hadb\4.x\bin
The x represents the release number of HADB.
2. Run the command to start the agent:
ma -i ma.cfg
Configuring a Cluster and Application
for High Availability
The FirstCluster cluster must be configured to use HADB and high-availability must
be enabled for the clusterjsp application before you can verify HTTP session
persistence.
▼ To Configure a Cluster and Application for High
Availability
Steps
30 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
1. From the machine on which the Domain Administration Server is running,
configure FirstCluster to use HADB using this command:
asadmin configure-ha-cluster --hosts hadb_hostname,hadb_hostname
--devicesize 256 FirstCluster
Replace the hadb_hostname variable with the host name of the machine where
HADB is to run. If you are using just one machine, you must name it twice.
This simplified example runs two nodes of HADB on the same machine. In
production settings, use more than one machine.
Page 31

Note – To reduce the memory footprint of HADB for demonstration purposes,
execute the following hadbm command. You are prompted for the administration
password.
In Java Enterprise System installations:
/opt/SUNWhadb/4/bin/hadbm set
DataBufferPoolSize=64,LogBufferSize=25 FirstCluster
In standalone Application Server installations:
install_dir/hadb/4/bin/hadbm set
DataBufferPoolSize=64,LogBufferSize=25 FirstCluster
2. Configure the clusterjsp application for HTTP session persistence by enabling
high availability:
a. In the Admin Console, expand the Applications node.
b. Expand Enterprise Applications.
c. Click clusterjsp.
d. In the right pane, on the General tab, click the Availability Enabled
checkbox.
e. Click Save.
Availability is enabled at the server instance and container level by default.
Restarting the Cluster
Before the changes made in the previous section take effect, the cluster’s instances
must be restarted..
▼ To Restart the Cluster
Steps
1. In the Admin Console, expand the Clusters node.
2. Click FirstCluster.
3. In the right pane, click Stop Instances.
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 31
Page 32

4. Once the instances are stopped, click Start Instances.
Verifying HTTP Session Failover
The steps for testing session data failover are similar for testing load balancing as
described in the topic “Verifying Load Balancing” on page 20. This time Session Data
is preserved after failure. Failover is transparent to the user because the sample
application is configured for automatic retry after failure.
▼ To Verify HTTP Session Failover
Steps
1. To display the first page of the clusterjsp application, type this URL in your
browser:
http://localhost:web_server_port/clusterjsp
Replace the localhost variable with the name of the system that the Web Server is
running on.
Replace the web_server_port variable with the value of the port attribute of the LS
element in web_server_install_dir/https-hostname/config/server.xml. For this
example, port 38000 is used.
A page similar to what you saw in “To Verify the Application Deployment”
on page 16 appears.
2. Examine the Session and Host information displayed. For example:
■
Executed From Server: localhost
■
Server Port Number: 38000
■
Executed Server IP Address: 192.18.145.133
■
Session ID: 41880f618e4593e14fb5d0ac434b1
■
Session Created: Wed Feb 23 15:23:18 PST 2005
3. View the server access log files to determine which application server instance is
serving the application. The log files are located here:
■
Solaris Java Enterprise System installation:
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs/
access/server_access_log
/var/opt/SUNWappserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs/
access/server_access_log
■
Linux Java Enterprise System installation:
/var/opt/sun/appserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs/
access/server_access_log
32 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 33

/var/opt/sun/appserver/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs/
access/server_access_log
■
Windows Java Enterprise System installation:
install-dir\nodeagents\nodeagent_name\i1\logs\access\server_access_log
install-dir\nodeagents\nodeagent_name\i2\logs\access\
server_access_log
■
Standalone Application Server installations:
install-dir/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i1/logs/access/server_access_log
install-dir/nodeagents/nodeagent_name/i2/logs/access/
server_access_log
4. Stop the Application Server instance that is serving the page.
a. In the Admin Console, in the left pane, expand Clusters.
b. Click FirstCluster.
c. In the right pane, click the Instances tab.
d. Click the checkbox next to the server instance that served the request and
click the Stop button.
5. Reload the clusterjsp sample application page.
The session ID and session attribute data is retained.
6. Check the access log of the other Application Server instance, and notice that it
is now servicing the request.
The state failover features work because the HTTP session is stored persistently in
the HADB. In addition to the HTTP session state, the Application Server also can
store the state of EJB™ enterprise beans in the HADB.
Cleaning Up
To clean up, you can uninstall the Application Server installation by completing the
steps in “To Uninstall Completely” on page 34, or you can simply delete the sample
cluster you have just created by completing the steps in “To Remove the Sample
Cluster” on page 35
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 33
Page 34

▼ To Uninstall Completely
Steps
1. Stop the Application Server processes using these commands:
asadmin stop-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin remove-ha-cluster --hosts hadb_hostname,hadb_hostname
FirstCluster
Replace the hadb_hostname variable with the host name of the machine where
HADB is to run. If you are using just one machine, you must name it twice.
asadmin stop-node-agent hostname
asadmin stop-domain domain1
2. Stop the HADB Management Agent by one of the following methods:
■
In a Solaris or Linux Java Enterprise System installation:
a. Change to the /etc/init.d directory:
cd /etc/init.d
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
./ma-initd stop
■
In a Windows Java Enterprise System installation
a. Go to Start⇒Settings⇒Control Panel, and double click Administrative
Tools.
b. Double click the Services shortcut.
c. Select HADBMgmtAgent Service from the Services list.
d. From the Action menu, select Stop.
■
In a stand-alone Solaris or Linux Application Server installation:
a. Change to install-dir/hadb/4/bin
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
./ma-initd stop
■
In a stand-alone Windows Application Server Installation:
a. Change to install-dir\hadb\4.x\bin
The x represents the release number of HADB.
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
ma -r
At this point all processes related to Sun Java System Application Server are
stopped.
34 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 35

3. Uninstall the Application Server.
■
In a Solaris or Linux Java Enterprise System installation, run
var/sadm/prod/entsys/uninstall and follow the steps in the
uninstallation wizard.
■
In a Windows Java Enterprise System installation, use the Control Panel’s
Add/Remove Programs item. Choose Sun Java Enterprise Systems and click
Change/Remove.
■
In a Solaris or Linux standalone Application Server installation, run
install_dir/uninstall and follow the steps in the uninstallation wizard.
■
In a Windows standalone Application Server instance, from the Start menu,
choose Programs ⇒ Sun Microsystems ⇒ Application Server EE ⇒ Uninstall.
4. If you created a new Web Server instance for this exercise, delete it:
a. Log on to the Web Server’s Administration Console.
b. Stop the instance.
c. Delete the instance.
5. To unsinstall the Web Server product, run the uninstall program from the
web_server_install_dir.
▼ To Remove the Sample Cluster
Use this procedure to remove only the FirstCluster (the sample highly-available
cluster) and the sample application used during this exercise.
Steps
1. Stop the Application Server processes and clean up configuration:
asadmin stop-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin remove-ha-cluster --hosts hadb_hostname,hadb_hostname
FirstCluster
Replace the hadb_hostname variable with the host name of the machine where
HADB is to run. If you are using just one machine, you must name it twice.
asadmin disable-http-lb-server FirstCluster
asadmin delete-http-lb-ref --config MyLbConfig FirstCluster
asadmin delete-http-lb-config MyLbConfig
asadmin delete-instance i1
asadmin delete-instance i2
asadmin delete-cluster FirstCluster
asadmin undeploy clusterjsp
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 35
Page 36

2. Stop the web server instance acting as load balancer by running the stop
program in:
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname
3. Rename the loadbalancer.xml file in
web_server_install_dir/https-hostname/config to loadbalancer.xml.sav
4. Stop the HADB Management Agent by one of the following methods:
■
In a Solaris or Linux Java Enterprise System installation:
a. Change to the /etc/init.d directory:
cd /etc/init.d
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
./ma-initd stop
■
In a Windows Java Enterprise System installation:
a. Go to Start⇒Settings⇒Control Panel, and double click Administrative
Tools.
b. Double click the Services shortcut.
c. Select HADBMgmtAgent Service from the Services list.
d. From the Action menu, select Stop.
■
In a stand-alone Solaris or Linux Application Server installation:
a. Change to install-dir/hadb/4/bin
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
./ma-initd stop
■
In a stand-alone Windows Application Server Installation:
a. Change to install-dir\hadb\4.x\bin
The x represents the release number of HADB.
b. Run the command to stop the agent:
ma -r
Next Steps
Congratulations! You have now completed the Quick Start for Application Server.
In this section, you have installed, configured, and started HADB and configured a
cluster and an application to use high availability. You have also cleaned up so that
your system is ready for other work. See “Where to Go Next” on page 37 for
additional information on Application Server.
36 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
Page 37

Where to Go Next
Other resources for learning about and using Application Server are available. They
include:
■
Product details at install-dir/docs-ee/about.html.
See this document for the latest information on what is new, and pointers to
tutorials and other educational services.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Release Notes
See this document for late-breaking information regarding this release.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Administration Guide
See this document for information on performing administrative functions using
the Admin Console.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Reference Manual
See this document for reference information on Application Server command-line
utilities, such as asadmin.
■
Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 High Availability
Administration Guide
See this document for information on the Sun Java System Application Server ’s
high availability features.
■
The J2EE 1.4 Tutorial
(http://java.sun.com/j2ee/1.4/docs/tutorial/doc/index.html)
See this document for a tutorial that covers the process for building and deploying
Java™ 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE™ platform) applications.
■
Java BluePrints guidelines for the Enterprise
(http://java.sun.com/blueprints)
See this document for a comprehensive set of examples that demonstrate
operations of the Application Server software and that can be used as application
templates.
Chapter 2 • Quick Start for Setting Up High Availability Failover 37
Page 38

38 Sun Java System Application Server Enterprise Edition 8.1 2005Q2 Quick Start Guide
 Loading...
Loading...