Page 1

USER’S MANUAL
PCI Express
RS-422/485
Communication Board
Third Edition, December 2011
English Version
SUNIX Co., Ltd.
Tel : +886-2-8913-1987
Fax: +886-2-8913-1986
Http://www.sunix.com.tw
info@sunix.com.tw
Page 2

___________________________________________________________________________________
PCI Express RS-422/485 Communication Board
User’s Manual
Copyright
Copyright© 2010 SUNIX Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into any language,
or transmitted in any from or by any means, photocopying, manual, or otherwise, without prior written permission from
SUNIX.
Disclaimer
SUNIX shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential damages resulting from the performance or use of this
equipment.
SUNIX makes no representations or warranties regarding the contents of this manual. Information in this manual has
been carefully checked for reliability; however, no guarantee is given as to the correctness of this content. In the
interest of continued product improvement, this company reserves the right to revise the manual or include change in
the specifications of the product described within it at any time without notice and without obligation to notify a ny
person of such revision or changes. The information contained in this manual is provided for general use by the
customers.
Trademarks
SUNIX is a registered trademark of SUNIX Group.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective owners.
Safety Information
1. Keep this User’s Manual for future reference.
2. Always read the safety information carefully.
3. Keep this equipment away from direct sunlight, or in humid or damp places.
4. Do not place this equipment in an unstable position, or on vibrating surface before setting it up.
5. Do not use or place this equipment near magnetic fields, televisions, or radios to avoid electronic
interface that affects device performance.
1
Page 3

___________________________________________________________________________________
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction...............................................................................................4
Overview..........................................................................................................5
Package Checklist...........................................................................................5
Product Features.............................................................................................6
Product Specifications.....................................................................................7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation................................................................................8
Hardware Installation......................................................................................9
Pin Assignment.............................................................................................10
Jumper Settings...........................................................................................15
Chapter 3 Driver Installation....................................................................................17
Windows Driver Installation…………………………………………..................18
Windows Driver Uninstallation.......................................................................23
Linux Driver Installation.................................................................................24
Verify Installation...........................................................................................26
Chapter 4 Port Configuration...................................................................................27
Configure Serial Port Settings........................................................................28
COM Port Number Settings...........................................................................29
COM I/O Resource........................................................................................29
FIFO Settings............................................................................................... 30
Advanced Settings for RS-422/485 Communication.................................... 31
Chapter 5 Appendix .................................................................................................35
Troubleshooting.............................................................................................36
Product Family…..........................................................................................38
Contact Information.......................................................................................43
2
Page 4

___________________________________________________________________________________
WHQL Certification Approval
The Designed for Microsoft Windows 32/64-bit operation system WHQL logo
identifies products that meet Microsoft’s quality standards, SUNIX I/O products
carry with this logo and listed on Windows Catalog. WHQL logo includes below
operation system version
Microsoft Windows Client: Windows 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 (X86/X64)
Microsoft Windows Server: Windows 2003 / 2008 (X86/X64)
3
Page 5

___________________________________________________________________________________
1.
Introduction
______________________________________________
RS-422/485 Golden I/O series, a line of PCI Express Multi-port Serial
Communication Board, is designed to meet PCI Express Base Specification
Ver1.1 (Compliable with PCI Express General 2 Specification). Its can be
installed in virtually any available PC system and compatible with all major
operating systems. Users do not need to manually set jumpers to configure I/O
addresses and IRQ locations.
This board offers independent RS-422 and RS-485 ports for connecting kinds
of serial terminals on the PC based systems. This board is industrial stand
which offers a reliable and high performance solution for serial multi-port
communications.
The following topics covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Product Features
Product Specifications
4
Page 6

___________________________________________________________________________________
Overview
Thanks for purchasing SUNIX PCI Express Multi-Port Communication Board; it
is compatible with RS-422 and RS-485 standard serial interfaces. User can
expand Multi RS-422/485 ports on PC-based system by installing in PCI
Express x1, x2, x4, x8 and x16 lane slots. Each port has on-chip hardware and
software flow control, a built-in 128-byte Tx/Rx FIFO, and WHQL certificated
device drivers. This board is designed with SUNIX 16C950 UART controller
and as well built with many of SUNIX advanced features and technologies,
making it the best solution for commercial and industrial automation
applications.
Package Checklist
Please check if the following items are present and in good condition upon
opening your package. Contact your vendor if any item is damaged or missing.
1. Hardware:
Serial Communication Board:
PCI Express RS-422/485 Multi-Port Communication Board × 1
Cable: (Depend on what product you bought)
* 4 ports PCI Express series: DB44M to 4 ports DB9 Male Cable × 1
* 8 ports PCI Express series: DB44M to 8 ports DB9 Male Cable × 1
* 16 ports PCI Express series: DB78M to 16 ports DB9 Male Cable × 1
2. CD Driver
3. User's Manual (This document)
4. Termination Resistor Jumper
5
Page 7

___________________________________________________________________________________
Product Features
Expands Multi RS-422/485 serial ports on the system
High performance SUNIX 16C950 compatible UART controller on-board.
Ultra low power consumption design for Green Environment.
Designed to meet PCI Express Base Specification Revision 1.1
Supports x1, x2, x4, x8, x16 (lane) PCI Express Bus connector keys.
Data transmission speeds up to 921.6Kbps.
On-chip hardware auto flow control to guarantee no data loss.
RS-422 and RS-485 auto detect and switching technology.
AHDC/CS™ technology for collision free communication.
Built-in ± 15KV ESD protection for all serial signals.
2.0 KV optical isolation protection for all signal and power. (SI Version Only)
500W peak surge protection for all signal lines. (SI Version Only)
Plug-n-Play, I/O address and IRQ assigned by BIOS.
Certified by CE, FCC, RoHS, and Microsoft WHQL approval.
Support Microsoft Windows, Linux, and DOS.
Note:
SUNIX RS-422/485 Card with Surge and Isolation (SI Version) is available
with certain models which include TVSS (Transient Voltage Surge Suppressor)
technology to help prevent damage due to lightning or high potential voltage.
Optical isolation (2000V) and embedded protection (max. ESD of 16 KV, max.
EFT of 2 KV). These features help provide protection in critical or harsh
factory-type environments.
6
Page 8

___________________________________________________________________________________
Product Specifications
Serial Communication
Interface RS-422/485 Baud rate 50bps ~921.6Kpbs
Controller
BUS PCI Express one lane (x1) Parity even, odd, none, mark, space
No. of Port 1/2/4/8/16-port
IRQ & IO Assigned by System FIFO 128byte Hardware
Signal
ESD
Protection
Surge
Protection
Isolation
Protection
Connector DB9 / 25 Male
SUNIX SUN1999
(16C950 UART Compatible)
RS-422: TxD+, TxD-, RxD+, RxD-, GND
4-wire RS-485: TxD+, TxD-, RxD+, RxD-, GND
2-wire RS-485: Data+, Data-, GND
±15KV ESD protection for each signal Human Body Model (HBM)
±15KV IEC1000-4-2 Air Gap Discharge
±8KV IEC1000-4-2 Contact Discharge
500W peak surge protection for all signal lines meet IEC 61000-4-5
(SI Version Only)
2.5 KV Isolation Protection for all signal and power
(SI Version Only)
Stop bit 1, 1.5, 2
Flow
Control
None, Xon/Xoff, RTS/CTS
Driver Support
Microsoft Client
Microsoft Server
Microsoft Embedded XP Embedded / POS Ready 2009 / Embedded System 2009
Linux Linux 2.4.x / 2.6.x
DOS DOS
XP / Vista / 7 (X86/X64)
2000 / 2003 / 2008 (X86/X64)
Regulatory Approvals
Hardware
Software
EN55022 Class B, EN55024, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3,
FCC Part 15 Class B, RoHS
Microsoft WHQL Windows
Microsoft Client: XP / Vista / 7 (X86/X64)
Microsoft Server: 2000 / 2003 / 2008 (X86/X64)
Environment
Operation Temperature 0 to 60°C (32 to 140°F)
Operation Humidity 5 to 95% RH
Storage Temperature -20 to 85°C (-4 to 185°F)
7
Page 9

___________________________________________________________________________________
2.
Hardware Installation
______________________________________________
This chapter includes information about hardware installation for PCI Express
RS-422/485 Multi-Port Communication Board. The following topics are
covered:
Hardware Installation
Pin Assignments
Jumper Settings
8
Page 10
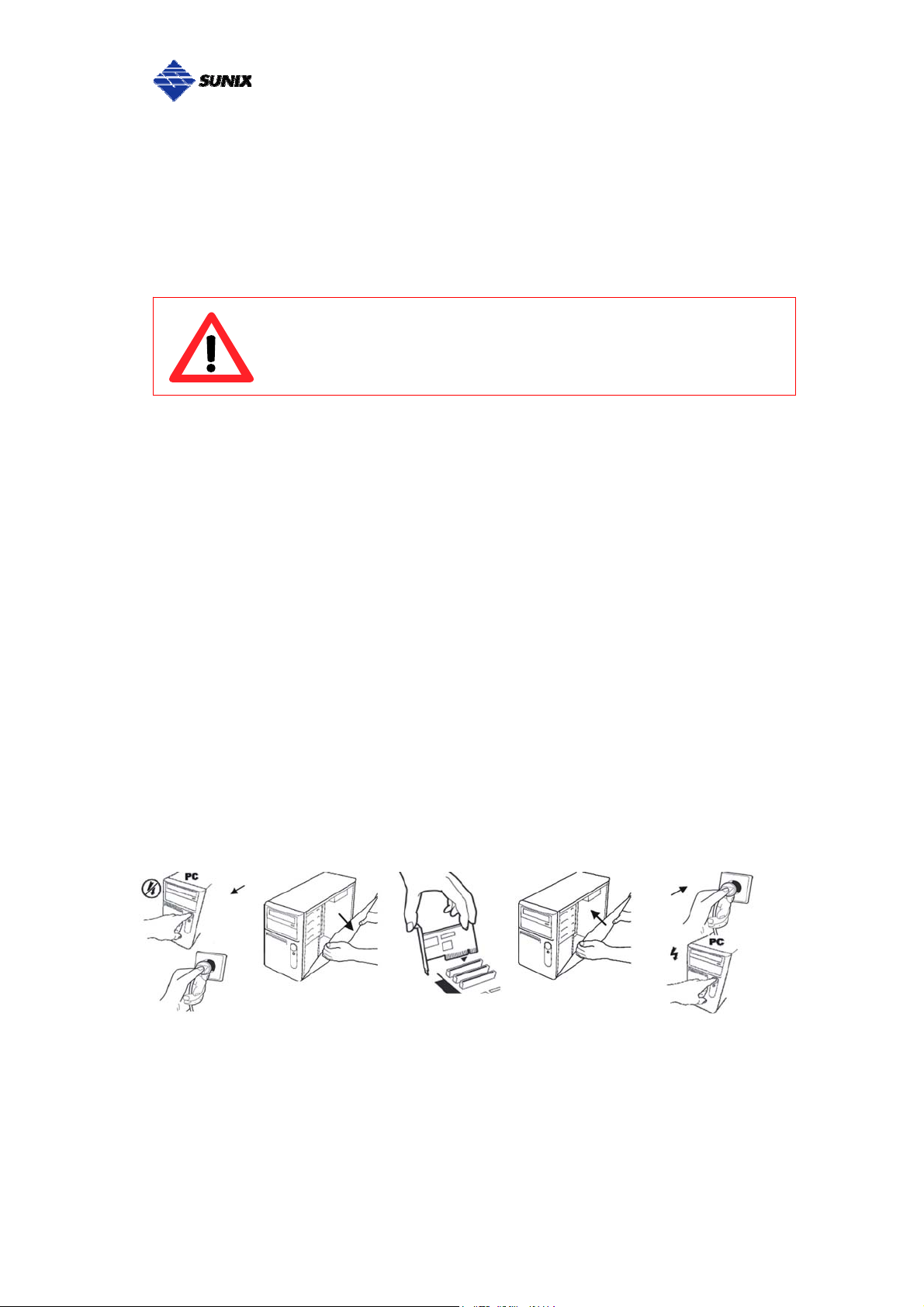
___________________________________________________________________________________
Hardware Installation
The hardware installation of PCI Express serial boards is easy to carry out.
Before inserting the card into the PCI Express bus, please follow the detailed
steps given below to install the PCI Express serial board in your computer.
Safety First
Step 1: Turn your PC’s power off, and shut off the power to any peripheral.
Step 2: Remove the power plug from the plug socket.
To avoid damaging your system and boards, make sure your
PC’s power is turned off before installing PCI Express card.
Step 3: Remove the cover from the computer case.
Step 4: If fitted. Remove the metal cover plate on the rear of a free PCI-E slot.
Step 5: Insert PCI Express Multi-Port Communication Board into the free PCI
Express slot and screw it firmly on the bracket side.
Step 6: Place the cover back onto the computer.
Step 7: Insert the plug into the plug socket.
9
Page 11
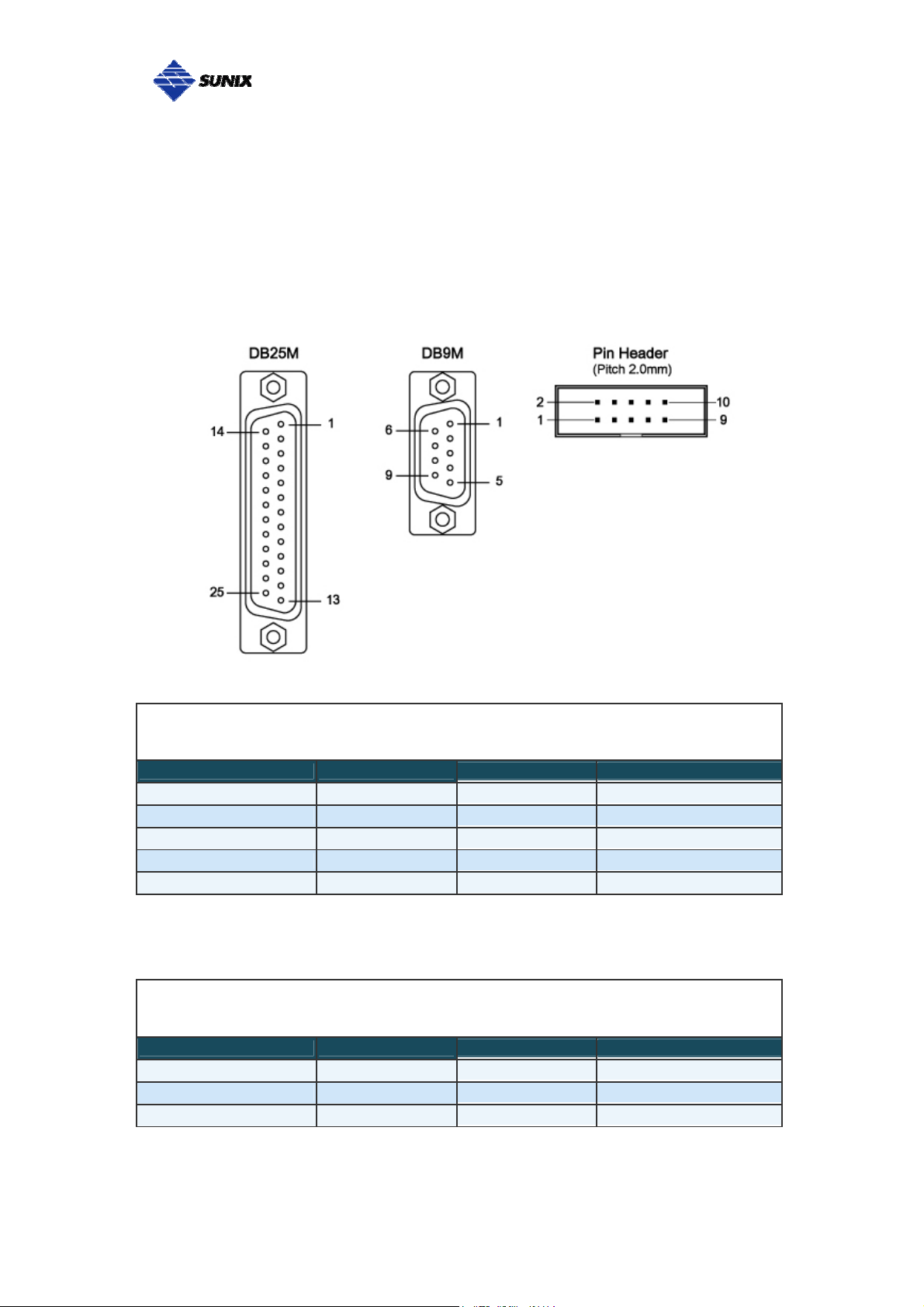
___________________________________________________________________________________
Pin Assignment
This chapter provides the pin assignments for SUNIX PCI Express
RS-422/485 Multi-Port Communication Board, as well as the pin assignments
for the optional accessories.
RS-422 or 4-Wire RS-485
PIN DB9M DB25M Pin Header
Tx+ 2 3 3
Tx- 1 8 1
Rx+ 3 2 5
Rx- 4 20 7
GND 5 7 9
2-Wire RS-485
PIN DB9M DB25M Pin Header
Tx+ 2 3 3
Tx- 1 8 1
GND 5 7 9
10
Page 12
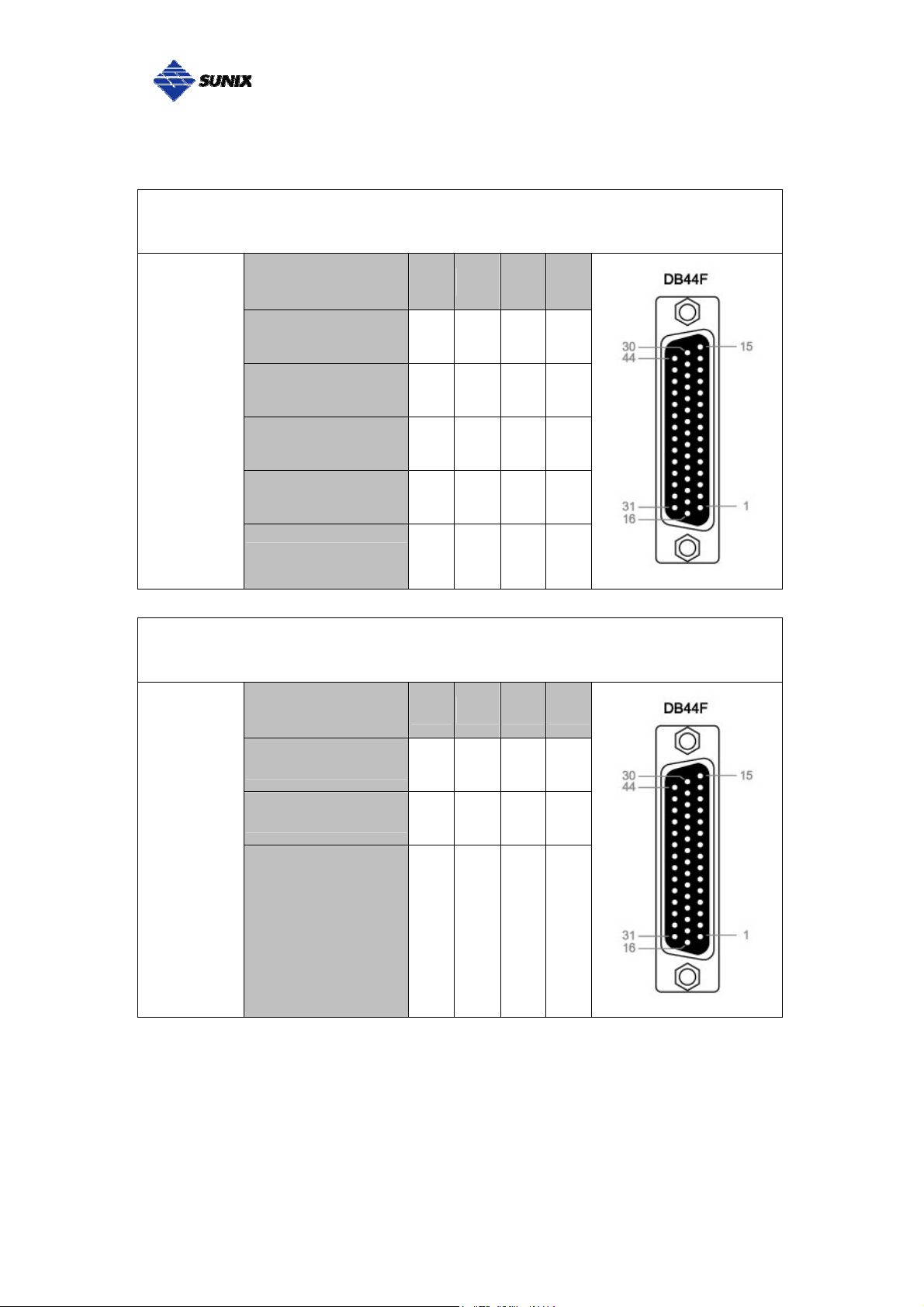
___________________________________________________________________________________
SUNIX 4-port RS-422/485 Card builds DB44F connector on board.
SUNIX DB44 Female 4 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
1 2 3 4
Signal
Tx+ 32 36 40 44
RS-422
Tx- 17 22 26 30
or
4-Wire
Rx+ 3 7 11 15
RS-485
Rx- 1 5 9 13
GND GND GND GND GND
SUNIX DB44 Female 4 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
1 2 3 4
Signal
2-Wire
RS-485
D+ 32 36 40 44
D- 17 22 26 30
GND GND GND GND GND
11
Page 13
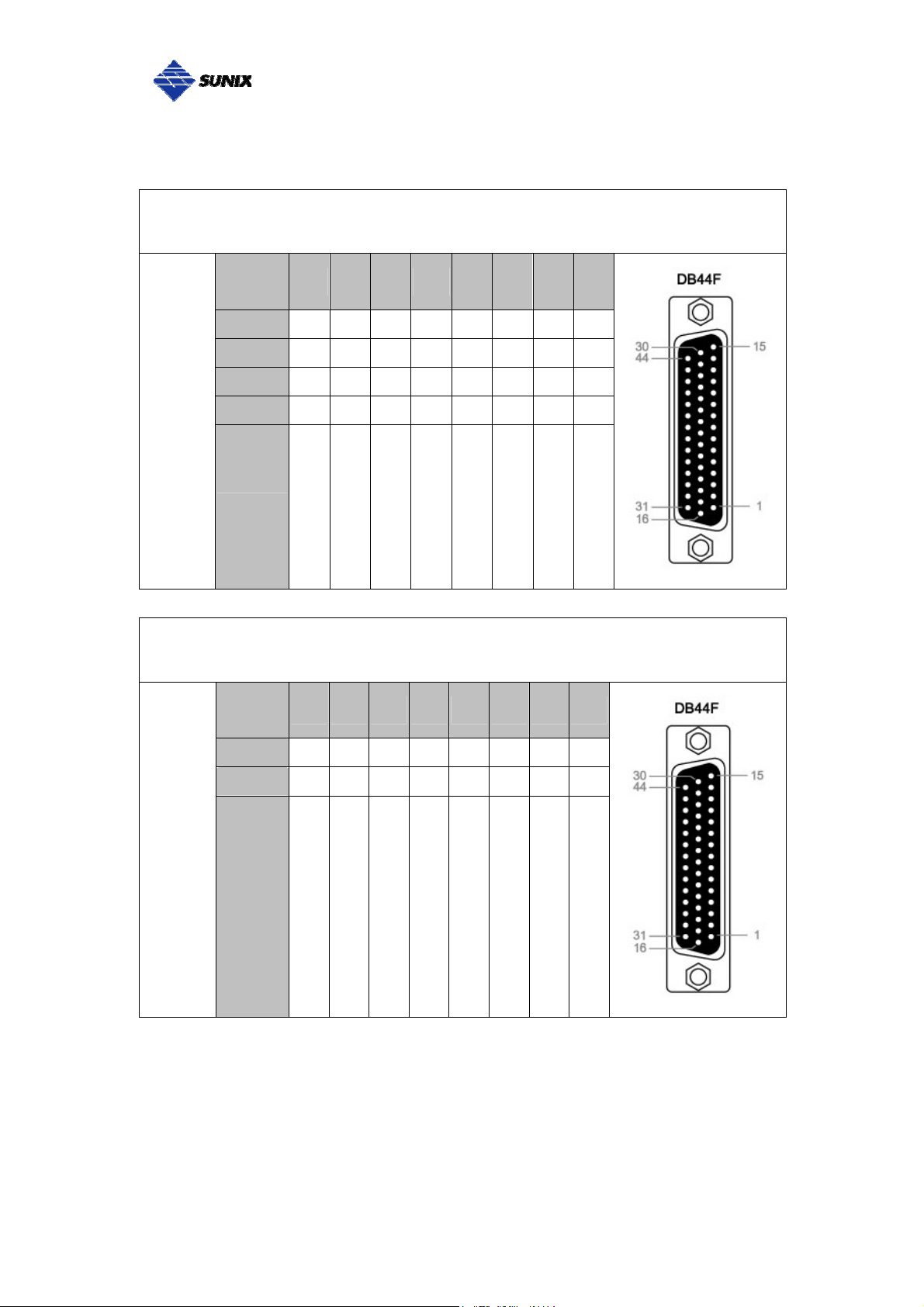
___________________________________________________________________________________
SUNIX 8-port RS-422/485 Card builds DB44F connector on board.
SUNIX DB44 Female 8 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
Signal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Tx+ 32 2 36 6 40 10 44 14
Tx- 17 18 22 34 26 38 30 42
RS-422
or
Rx+ 3 31 7 35 11 39 15 43
Rx- 1 16 5 20 9 24 13 28
4-Wire
RS-485
GND
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
SUNIX DB44 Female 8 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
Port
Signal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Tx+ 32 2 36 6 40 10 44 14
Tx- 17 18 22 34 26 38 30 42
2-Wire
RS-485
GND
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
12
Page 14
___________________________________________________________________________________
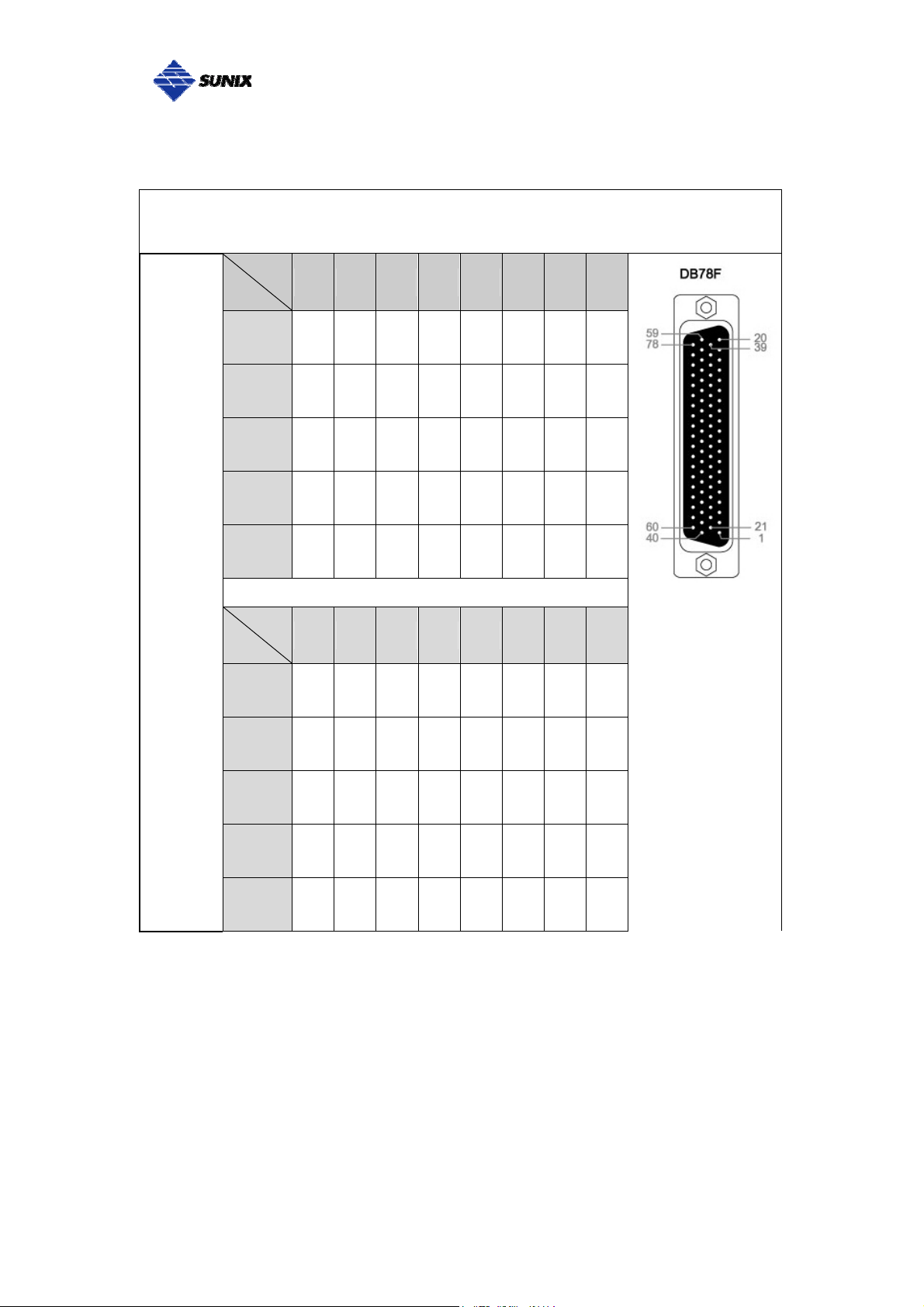
SUNIX 16-port RS-422/485 Card builds DB78F connector on board.
SUNIX DB78 Female 16 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
RS-422
or
4-Wire
RS-485
Port
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Signal
Tx+ 60 21 43 4 65 26 48 9
Tx- 40 1 62 23 45 6 67 28
Rx+ 61 22 44 5 66 27 49 10
Rx- 41 2 63 24 46 7 68 29
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
Port
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Signal
Tx+ 70 31 53 14 75 36 58 19
Tx- 50 11 72 33 55 16 77 38
Rx+ 71 32 54 15 76 37 59 20
Rx- 51 12 73 34 56 17 78 39
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
13
Page 15

___________________________________________________________________________________
SUNIX DB78 Female 16 ports Serial Communication Boards Pin Assignment
2-Wire
RS-485
Port
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Signal
Tx+ 60 21 43 4 65 26 48 9
Tx- 40 1 62 23 45 6 67 28
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
Port
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Signal
Tx+ 70 31 53 14 75 36 58 19
Tx- 50 11 72 33 55 16 77 38
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND GND
14
Page 16

___________________________________________________________________________________
Jumper Settings
For RS-422/485 serial communications, when an electrical signal travels
through two different resistance junctions in a transmission line, the impedance
mismatch will sometimes cause signal reflection. Signal reflection causes
signal distortion, which in turn will contribute communication errors. The
solution to this problem is to establish the same impedance at the line ends as
in the line itself by terminating them with resistors.
Ideally, the two ends of the cable will have a termination resistor connected
across the two wires. Without termination resistors, reflections of fast driver
edges can cause multiple data edges that can cause data corruption.
Termination resistors also reduce electrical noise sensitivity due to the lower
impedance, and bias resistors (120 ohms for twisted pairs) are required. The
value of each termination resistor should be equal to the cable impedance.
15
Page 17

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-422 or 4-Wire RS-485 working model with termination resistor:
SUNIX Host Card Device
Tx +
Tx –
Rx +
Rx –
2-Wire RS-485 working model with termination resistor:
SUNIX Host Card Device
D + (Tx+)
D – (TX-)
Rx +
Rx –
Tx +
Tx –
D +
D –
SUNIX RS-422/485 PCI Express Serial board equips independent TX and RX
termination resistors for each serial port. User can modify the jumper setting
(short the pins) to avoid impedance mismatched problem when operate under
Multi-drop transmission. Resistors should be added near the receiving side.
Note: Stands for termination resistor near the receiving side.
Manufactory default jumper setting is OPEN (disable 120 ohms termination
resistors across the two wires).
16
Page 18

___________________________________________________________________________________
3.
Driver Installation
______________________________________________
After installing the PCI Express RS-422/485 Multi-Port Communication Board
in your system successfully, please follow the step by step software installation
guide to confirm how to install appropriate driver and configure the serial port
settings.
The driver for PCI Express serial board supports Windows and Linux operating
systems, and you can select your requirement in the following chapter:
The following topics covered in this chapter:
Windows Driver Installation
Windows Driver Uninstallation
Linux Driver Installation
Verify Installation
17
Page 19

___________________________________________________________________________________
Windows Driver Installation
Please refer to following instructions to install the driver for the first time under
Windows operation system. You will need to plug the board in an available PCI
Express slot first, before installing the driver.
(1) After the board is physically installed and the PC boots up, system will
detect the PCI Express Serial card and prompt for driver installation wizard,
please choose cancel.
(2) Put CD driver bound with product in your CD / DVD ROM drive.
Please select autorun.exe., then select “Driver Installation”.
18
Page 20

___________________________________________________________________________________
(3) Please select the product interface you bought, such as PCI Express.
(4) Please select the O.S. version you are using, such as Windows Vista.
Then system will process the driver installation step automatically.
19
Page 21

___________________________________________________________________________________
(5) Please select driver language for your operation system.
(6) Click “Next” to continue driver installation steps.
20
Page 22

___________________________________________________________________________________
(7) Click “Install” to continue driver installation steps.
(8) System will install driver automatically. It takes about one minute.
21
Page 23

___________________________________________________________________________________
(9) Click “Finish” to end installation steps.
22
Page 24

___________________________________________________________________________________
Windows Driver Uninstallation
Please refer to following instructions uninstall Multi-I/O card driver.
(1) Click on the “Programs and Features” tab in the Windows Control Panel.
Start > Controller Panel > Programs and Features
(2) Entry Uninstall or change a program page, and double click “Windows
Driver Package – SUNIX Co., Ltd SUNIX Multi-I/O Controller” to process
driver uninstallation procedure.
23
Page 25

___________________________________________________________________________________
Linux Driver Installation
This installation guide describes the procedures to install the PCI Express
serial board in Linux kernel 2.4.x and 2.6.x. Please refer to
“snx_Vx.x.x.x.tar.gz” for driver installation detail in CD Driver (Linux folder)
directory.
: \ PCI_IO \ Linux
(1) Driver install
Please create a directory under root directory, e.g /temp, do commands:
# cd /
# mkdir temp
After get driver file "snx_Vx.x.x.x.tar.gz". Copy file to /temp
directory, then extract and install, do commands:
# cp snx_Vx.x.x.x.tar.gz /temp
# cd /temp
# tar xvfz snx_Vx.x.x.x.tar.gz
# cd /temp/snx
# make clean ; make install
*************************************************************
* If system is Suse 9.0 and errors occur when
* "make clean ; make install", do commands:
*
* # cd /usr/src/linux/
* # make cloneconfig
* # make dep
*
* then do "make clean ; make install" again in /temp/snx
*************************************************************
Load driver module, do command:
# modprobe snx
or
24
Page 26

___________________________________________________________________________________
# insmod /temp/snx/driver/snx.ko (snx.o for kernel 2.4)
Check driver module, do command:
# lsmod | grep snx
Unload driver, do command:
# rmmod snx
(2) Device node creation
Each serial port has one device node which is named "ttySNX?",
maximum up to 32 serial ports.
Each parallel port has two device node which is name "lp?" and
"parport?". This step will backup lp2~lp3 and parport2~parport3
to lp?.bak and parport?.bak in /dev for your system first. Then,
create lp2~lp3 and parport2~parport3 in /dev for sunix driver,
maximum up tp 2 parallel ports.
This setp will be done when do "make clean ; make install", if
device nodes aren't in /dev, do commands:
# cd /temp/snx/snxmknod
# ./snxmknod
This will create device nodes in /dev.
If there are more than two boards installed, serial port device
nameing convention please refer to F1.
25
Page 27

___________________________________________________________________________________
Verify Installation
You can use Windows “Device Manager” to verify proper installation.
(1) Click on the “Programs and Features” tab in the Windows Control Panel.
Start > Controller Panel > Device Manager
(2) In the Device Manager window, you should see this board under
Multifunction adapters (4-port RS-422/485 Serial Card in this example).
You should also see SUNIX COM port under Ports (COM & LPT).
26
Page 28

___________________________________________________________________________________
4.
Port Configuration
______________________________________________
This chapter shows all Serial COM port settings that user came with usually,
such as COM port number, FIFO length(size), baud rate, IO address and
others.
The following topics covered in this chapter:
Configure Serial Port Settings
COM Port Number Settings
COM I/O Resource
FIFO Settings
Advanced Settings for RS-422/485 Communication
27
Page 29

___________________________________________________________________________________
Configure Serial Port Settings
After the board and serial port drivers are installed, please refer to following
instructions to configure Serial COM settings.
(1) Please launch the “Device Manager”.
(2) Right click the “SUNIX Serial Card” item from the “Multifunction
adapters” sub-tree and click “Properties”.
(3) On the “Port Control” tab, select a port to configure.
* Click “OK” to approve the settings for the selected port.
* Click “Set to All” to approve the settings for all COM ports.
28
Page 30
___________________________________________________________________________________
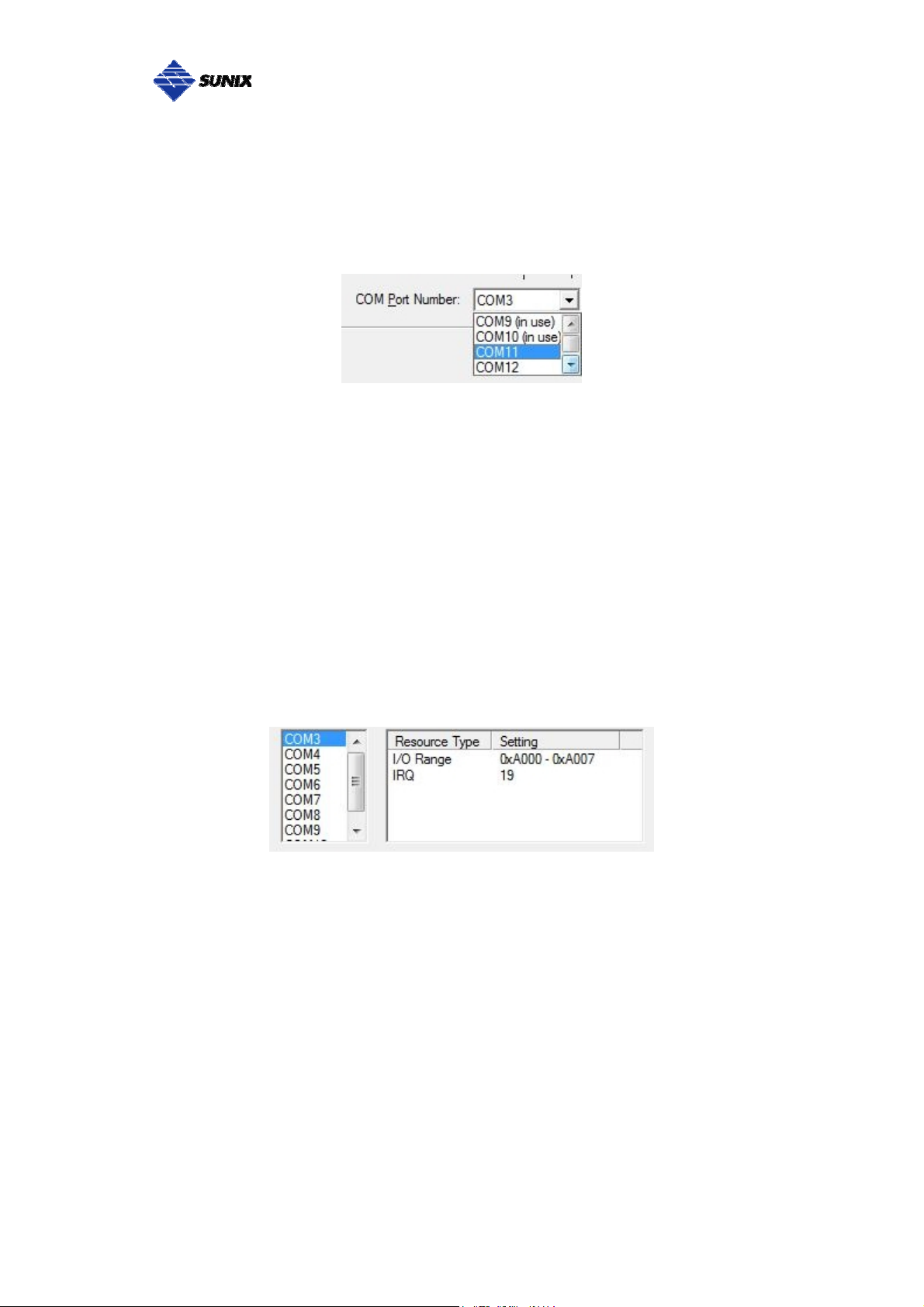
COM Port Number Settings
Under Port Number, select a COM number to assign to the serial port. Click
“OK” to approve the settings for the selected port.
Note: In order to prevent system resource conflict, do not select “in use” port.
COM I/O Resource
User can read the COM “IO Range” and “IRQ” located in system by selecting
COM port.
IRQ and I/O address is automatically assigned by the mainboard PCI (PCI
Express) BIOS automatically (before COM card driver installing). User can
NOT assign legacy ISA address (3F8, 3E8, 2F8, 2E8) for the specific COM
port. But for IRQ setting, user can set specific IRQ value for this PCI Express
bus slot via mainboard’s BIOS settings (not via SUNIX driver). But all COM
ports will share one IRQ value.
29
Page 31

___________________________________________________________________________________
FIFO Settings
Select an Rx FIFO Trigger and Tx FIFO Size.
The default Rx FIFO Trigger is 112 bytes. The default Tx FIFO Size is 128
bytes. Click “Set to All” to change this setting for all serial ports on the board.
Then click “OK” to save the settings.
Receive FIFO interrupt trigger level:
When the level of data in the receiver FIFO reaches this value, a receiver data
interrupt is triggered.
Transmit FIFO interrupt trigger level:
When the level of data in the transmit FIFO falls below this value, a transmitter
interrupt is triggered. Setting this value to zero will not trigger an interrupt until
the transmitter is completely idle.
The FIFO trigger levels can be fine tuned to gain optimum performance,
depending on system performance, baud rate used, levels of serial traffic etc.
30
Page 32

___________________________________________________________________________________
Advanced Settings for RS-422/485 Communication
User can control RS-422/485 communication in Advanced Port Control page
through “Advanced” settings.
1.
2.
3.
31
Page 33

___________________________________________________________________________________
Clock Rate
This is the “Data Rate" value for on board crystal frequency of input clock. The
baud rate can optionally be adjusted according to the data rate required. The
clock pre-divisor is used to divide the input clock prior to baud rate generation.
This parameter must matches with the oscillator (crystal) frequency on the
board. System default is 14745600 Hz. We do NOT recommend for
modification without SUNIX instruction. User can click “Defaults” button back
to manufactory settings.
UART Type (Default: Auto RS-422/485 )
User can select RS-422 or RS-485 interface for each COM port of this board.
1). Auto RS-422/485
SUNIX developed a unique technology “ Auto Detect & Switching
RS-422/485, which can automatically detect the state of RS-422 full duplex or
RS-485 half duplex and control the data transmitting and receiving wires at the
same port without any hardware or software settings.
2). RS-422 (4-Wire RS-485)
This COM port forces to run RS-422 full duplex mode.
(RS-485 ACS function can not open under this mode.)
3). RS-485
This COM port forces to run RS-485 half duplex mode.
32
Page 34

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-485 ACS™ Technology (Default: Enable)
Auto Carrier Sense (ACS™) technology is the data flow control under RS-485
half duplex (one-way traffic) communicating. It manages data flow between
computers or devices or between nodes in a RS-485 network, so that the data
can be handled at an efficient pace
Auto Carrier Sense (ACS™) technology will check the status of RS-485
communication bus. If the bus is idle, it starts transmission. If the bus is not idle
(some data flows in the bus), then it will postpone the transmission of UART
until the bus is idle. Due to the reduction of TX/RX packet conflicting on
RS-485 one-way traffic bus, it will enhance better system performance and
RS-485 communication ability.
33
Page 35

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-485 AHDC™ Technology
Since RS-485 is bidirectional which means the driver is turned on only when it
needs to transmit some data, otherwise it is floating. SUNIX developed a new
design to control the direction of driver (On or off) automatically which is called
Auto Hardware Direction Control/Carrier Sense. AHDC/CS™ works on the
same principle and only turns on the driver when UART needs to transmits
some data; but the advantage is that AHDC/CS™.
Auto Hardware Direction Control (AHDC™) technology makes it easier to
manage 2-wire RS-485 half-duplex communications, eliminating the need for
software interference. User does not necessary to write extra code for
Windows applications to control the half-duplex protocol. Auto Hardware
Direction Control (AHDC™) technology is the key feature of SUNIX UART, and
this function is default enabling.
34
Page 36

___________________________________________________________________________________
5.
Appendix
______________________________________________
This chapter shows some problems that user came with usually. Also you can
check it if the PCI Express serial board can not work properly in your system
after following hardware and software installation steps. In addition, you could
contact with us for detail technical product information.
In this appendix, we cover the following topics.
Troubleshooting
Product Family
Contact Information
35
Page 37

___________________________________________________________________________________
Troubleshooting
1. System fails to find the PCI Express serial board or COM port.
A: It may cause by following issue:
a. The board is not properly plugged into the PCI Express slot.
b. Please clean the golden finger.
c. The PCI Express slot is defective. Please try other slots until you find one
that works.
d. The mainboard does not have an available IRQ for the PCI Express
serial board. Enter the PC.s BIOS and make sure an IRQ setting is
available in the PCI/PnP settings.
e. The board itself might be defective. You can try another mainboard
testing this board working or not.
2. There is a blue screen when I entry operation system.
A: The possible reason is an IRQ or I/O address conflict with other PCI
Express or PCI bus adapters, such as LAN or serial boards, or with the
system BIOS. Refer to the corresponding problem in the previous FAQ for
solutions.
3. There are some exclamation marks in device manager and serial ports
can not work properly.
A: It caused by the wrong driver installing or hardware settings. Please turn off
your computer firtly and re-install hardware and software, especially
re-install the correct driver.
4. Should I enable auto flow control features?
A: Enable Auto CTS/RTS Flow Control means the CTS/RTS flow control is
controlled by hardware automatically. System will be more stable if the
function is enabled. Please make sure your serial device and cable wiring
before enabling the hardware flow control function.
36
Page 38

___________________________________________________________________________________
5. How large FIFO length I should set?
A: FIFO (First-in-First-out) buffers are used to reduce the frequency of interrupt
processes for UART chips. The size of the buffer will determines the
number of times the cards need to interrupt the computer’s CPU in order to
process a string of data. With larger FIFO buffer size; there is more data
flow and less interruption to the CPU, therefore allowing the CPU to be free
to handle other more crucial tasks.
Set the Receive/Transmit Buffer to higher value will get faster performance
because the interrupts will be reduced, but the time for interrupt service
routine will become shorter. The receive buffer overflow will be easily
happened if the CPU speed is not enough to handle. If the system is not
stable, select the lower value to correct problems.
37
Page 39

___________________________________________________________________________________
Product Family
SUNIX provides kinds of RS-232/422/485 interface cards for customer
selection, including PCI Express, PCI, PCI/104, CardBus, and ExpressCard.
Please refer to the product family table for reference.
RS-422/485 PCI Express Interface
Port Connecter
8
4
2 DB9 Male 921.6Kbps
DB44
Female
DB44
Female
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
RS-422/485 PCI Interface
Port Connecter
16
8
4
2 DB9 Male 921.6Kbps
DB79
Female
DB44
Female
DB44
Female
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±15KV
±15KV
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±15KV
±15KV
±15KV
Surge
Protection
600W 2.5KV IPC-E2108SI
- - IPC-E2108
600W 2.5KV IPC-E2104SI
- - IPC-E2104
600W 2.5KV IPC-E2102SI
- - IPC-E2102
Surge
Protection
- - IPC-P21 16
600W 2.5KV IPC-P2108SI
- - IPC-P2108
600W 2.5KV IPC-P2104SI
- - IPC-P2104
600W 2.5KV IPC-P2102SI
- - IPC-P2102
Isolation
Protection
Isolation
Protection
Model NO.
Model NO.
RS-422/485 PCI/104 Interface
Port Connecter
8
4
2
5x2 Pin
Header
5x2 Pin
Header
5x2 Pin
Header
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±15KV
±15KV
38
Surge
Protection
600W 2.5KV IPC-B2108SI
- - IPC-B2108
600W 2.5KV IPC-B2104SI
- - IPC-B2104
600W 2.5KV IPC-B2102SI
- - IPC-B2102
Isolation
Protection
Model NO.
Page 40

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-232/422/485 PCI Express Interface
Port Connecter
8
4
DB44
Female
DB44
Female
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
RS-232/422/485 PCI Interface
Port Connecter
8
4
DB44
Female
DB44
Female
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
921.6Kbps
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±15KV
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±15KV
Surge
Protection
600W 2.5KV IPC-E3108SI
- - IPC-E3108
600W 2.5KV IPC-E3104SI
- - IPC-E3104
Surge
Protection
600W 2.5KV IPC-P3108SI
- - IPC-P3108
600W 2.5KV IPC-P3104SI
- - IPC-P3104
Isolation
Protection
Isolation
Protection
Model NO.
Model NO.
39
Page 41

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-232 PCI Express Interface
Port Connecter
16
8
4 DB44 Female
Mini SCSI 68
Female
DB62 Female 115.2 kbps
Mini SCSI 68
Female
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps - Standard SER1640A
921.6Kbps
1 15.2 kbp s
921.6Kbps
ESD
Protection
±15KV
Power
output
- Standard SER5466A
- Low profile SER5466AL
- Standard SER5466H
- Low profile SER5466HL
- SER5456A
5V/12V
- SER5456AL
5V/12V
- SER5456H
5V/12V
- SER5456HL
5V/12V
Bracket Model NO.
Standard
SER5456P
Low profile
SER5456PL
Standard
SER5456PH
Low profile
SER5456PHL
DB9 Male
1 15.2 kbp s
DB44 Female
2
DB9 Male
921.6Kbps
DB44 Female
5x2 Pin Header
- SER5437A
5V/12V
- SER5437AL
5V/12V
- SER5437H
5V/12V
- SER5437HL
5V/12V SER5437PHL
-
Standard
SER5437P
Low profile
SER5437PL
Standard
SER5437PH
Low profile
SER5037UHL
40
Page 42

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-232 PCI Interface
Port Connecter
Mini SCSI 68
DB62 Female - Standard SER5066A
Mini SCSI 68
5x2 Pin Header
8
DB62 Female - Standard SER5066H
Mini SCSI 68
5x2 Pin Header
DB44 Female
5x2 Pin Header
4
DB44 Female
5x2 Pin Header
DB44 Female
DB9 Male
5x2 Pin Header -
DB44 Female
5x2 Pin Header
2
DB9 Male
5x2 Pin Header -
DB44 Female
5x2 Pin Header
1 DB9 Male
Baud
Rate
921.6Kbps
1 15.2Kbps
921.6Kbps
1 15.2Kbps
921.6Kbps
1 15.2Kbps
921.6Kbps
1 15.2Kbps
921.6Kbps
ESD
Protection
±15KV
±2KV
±15KV
±2KV
±15KV
±2KV
±15KV
±2KV
±15KV
Power
output
- Standard SER1600A
- Low profile SER5066AL
Standard SER5066U
- Low profile SER5066UL
- Low profile SER5066HL
- Standard SER5066UH
- Low profile SER5066UHL
- SER5056A
5V/12V
- SER5056AL
5V/12V
- Standard SER5056U
- Low profile SER5056UL
- Standard SER5056H
- Low profile SER5056HL
5V/12V SER5056PH
-
- SER5056UHL
5V/12V
- SER5037A
5V/12V SER5037P
- SER5037AL
5V/12V SER5037PL
-
- SER5037H
5V/12V SER5037PH
- SER5037HL
5V/12V SER5037PHL
-
- SER5027A
5V/12V
- SER5027AL
5V/12V
- SER5027H
5V/12V
- SER5027HL
5V/12V
Bracket Model NO.
Standard
Low profile
Standard
Low profile
Standard
Low profile
Standard
Low profile
Standard
Low profile
Standard
Low profile
SER5056P
SER5056PL
SER5056UH
SER5056PHL
SER5037U
SER5037UL
SER5037UH
SER5037UHL
SER5027P
SER5027PL
SER5027PH
SER5027PHL
41
Page 43

___________________________________________________________________________________
RS-232 ExpressCard Interface
Port Connecter Baud Rate ESD Protection Bracket Model NO.
4 34mm ECS4000
DB44 Female
2
921.6Kbps
±15KV
34mm ECS2000
1 DB9 Male
34mm ECS1000
RS-232 CardBus Interface
Port Connecter Baud Rate ESD Protection Bracket Model NO.
4 54mm CBS4000
DB44 Female
2
1 DB9 Male
1 15.2Kbps
±15KV
54mm CBS2000
54mm CBS1000
RS-232 PCI/104 Interface
Port Connecter Baud Rate ESD Protection Model NO.
8 SER5337A
5x2 Pin Header 115.2Kbps
4 SER5356A
±2KV
2
SER5366A
42
Page 44

___________________________________________________________________________________
Contact Information
Customer satisfaction is our number one concern, and to ensure that
customers receive the full benefit of our products, SUNIX services has been
set up to provide technical support, driver updates, product information, and
user’s manual updates.
The following services are provided
E-mail for technical support
................................... info@sunix.com.tw
World Wide Web (WWW) Site for product information:
............................http://www.sunix.com.tw
43
Page 45

___________________________________________________________________________________
This page is blank
44
 Loading...
Loading...