Page 1

Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
Form : QCF42
Date : 11 February 2009
Unit / Module Description:
Quad ADC SLB Module
Unit / Module Number:
SMT941
Document Issue Number:
2
Issue Date:
Original Author:
PhSR
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House,
Waterside, Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS.
This document is the property of Sundance and may not be copied
nor communicated to a third party without prior written
permission.
© Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited 2009
User Manual
for
SMT941
User Manual SMT941 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 2
Revision History
Issue
Changes Made
Date
Initials
1
Original document ‘pre-released’.
06/11/2009
PhSR
2
Updates to match v2 PCB
23/03/2010
PhSR
User Manual SMT941 Page 2 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 3

Table of Contents
Precautions ................................................................................................................................ 5
Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 6
1 Related Documents ........................................................................................................ 7
1.1 Referenced Documents .............................................................................................. 7
1.2 Applicable Documents ............................................................................................... 7
2 Functional Description .................................................................................................. 8
2.1 Block Diagram.............................................................................................................. 8
2.2 Module Description .................................................................................................... 8
2.2.1 A/D converters ....................................................................................................... 9
2.2.2 Clock structure ..................................................................................................... 10
2.3 FPGA Design ............................................................................................................... 11
2.3.1 Control Register Settings .................................................................................... 11
2.3.2 Register Descriptions .......................................................................................... 13
Control Register – 0x1. ................................................................................................... 13
CLOCK Register 0 – 0x10. .............................................................................................. 14
CLOCK Register 1 – 0x11. .............................................................................................. 15
CLOCK Register 2 – 0x12. .............................................................................................. 15
CLOCK Register 3 – 0x13. .............................................................................................. 15
CLOCK Register 4 – 0x14. .............................................................................................. 16
CLOCK Register 5 – 0x15. .............................................................................................. 17
CLOCK Register 6 – 0x16. .............................................................................................. 17
CLOCK Register 7 – 0x17. .............................................................................................. 18
CLOCK Register 8 – 0x18. .............................................................................................. 18
CLOCK Register 9 – 0x19. .............................................................................................. 19
CLOCK Register A – 0x1A. ............................................................................................. 19
CLOCK Register B – 0x1B. .............................................................................................. 20
CLOCK Register C – 0x1C. ............................................................................................. 20
CLOCK Register D – 0x1D. ............................................................................................. 21
CLOCK Register E – 0x1E. .............................................................................................. 21
CLOCK Register F – 0x1F. .............................................................................................. 21
CLOCK Register 10 – 0x20. ............................................................................................ 22
CLOCK Register 11 – 0x21. ............................................................................................ 22
CLOCK Register 12 – 0x22. ............................................................................................ 22
CLOCK Register 13 – 0x23. ............................................................................................ 23
CLOCK Register 14 – 0x24. ............................................................................................ 23
CLOCK Register 15 – 0x25. ............................................................................................ 24
CLOCK Register 16 – 0x26. ............................................................................................ 24
CLOCK Register 17 – 0x27. ............................................................................................ 25
CLOCK Register 18 – 0x28. ............................................................................................ 26
CLOCK Register 19 – 0x29. ............................................................................................ 26
ADC Chab Register 0 – 0x30. ........................................................................................ 27
ADC Chab Register 1 – 0x31. ........................................................................................ 27
User Manual SMT941 Page 3 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 4

ADC Chab Register 2 – 0x32. ........................................................................................ 28
ADC Chab Register 3 – 0x33. ........................................................................................ 28
ADC Chab Register 4 – 0x34. ........................................................................................ 29
ADC Chab Register 5 – 0x35. ........................................................................................ 29
ADC Chab Register 6 – 0x36. ........................................................................................ 30
ADC Chab Register 7 – 0x37. ........................................................................................ 31
ADC Chab Register 8 – 0x38. ........................................................................................ 32
ADC Chab Register 9 – 0x39. ........................................................................................ 32
ADC Chcd Register 0 – 0x40. ........................................................................................ 33
ADC Chcd Register 1 – 0x41. ........................................................................................ 33
ADC Chcd Register 2 – 0x42. ........................................................................................ 34
ADC Chcd Register 3 – 0x43. ........................................................................................ 35
ADC Chcd Register 4 – 0x44. ........................................................................................ 35
ADC Chcd Register 5 – 0x45. ........................................................................................ 36
ADC Chcd Register 6 – 0x46. ........................................................................................ 37
ADC Chcd Register 7 – 0x47. ........................................................................................ 37
ADC Chcd Register 8 – 0x48. ........................................................................................ 38
ADC Chcd Register 9 – 0x49. ........................................................................................ 39
3 PCB Layout ..................................................................................................................... 40
3.1 Top View ..................................................................................................................... 40
3.2 Bottom View ............................................................................................................... 40
4 Connectors ..................................................................................................................... 41
4.1 Description ................................................................................................................. 41
4.2 Location on the board .............................................................................................. 42
5 Physical Properties ....................................................................................................... 43
6 Safety ............................................................................................................................... 43
7 Ordering Information .................................................................................................. 43
8 EMC .................................................................................................................................. 43
User Manual SMT941 Page 4 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 5

Table of Figures
Figure 1 - SMT942 Block diagram. .......................................................................................... 8
Figure 2 - Clock Structure - Block Diagram ........................................................................ 10
Figure 3 - Clock Architecture Main Characteristics. ......................................................... 11
Figure 4 – Setup Packet Structure. ....................................................................................... 12
Figure 5 – Control Register Read Sequence. ....................................................................... 12
Figure 6 – Register Memory Map. ......................................................................................... 13
Figure 7 - Connectors ............................................................................................................. 42
Precautions
In order to guarantee that Sundance’s boards function correctly and to protect the
module from damage, the following precautions should be taken:
- They are static sensitive products and should be handled accordingly.
Always place the modules in a static protective bag during storage and transition.
User Manual SMT941 Page 5 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 6

Introduction
The SMT941 is a single width expansion TIM that plugs onto an SLB base module,
the SMT351T (Virtex-5 LXT, SXT or even FXT FPGA) as an example and incorporates
2 Texas Instrument dual-channel Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADS62P49). The
SMT941 implements a comprehensive clock circuitry based on a distribution chip
(CDCE72010) from Texas Instrument that allows synchronisation among the
converters and the use of an internal/external reference clock or internal/external
sampling clock. It provides a complete conversion solution and stands as a platform
that can be part of a transmit/receive communication platform. The SMT941 has an
on-board VCXO of frequency 245.76MHz.
ADCs have a resolution of 14 bits and are able to update outputs at up to 250MHz.
All converters are 1.8/3.3-Volt. ADCs internal gain and offset can be adjusted as
well as the data format. ADCs are AC-coupled on the board using a doubletransformer structure. No DC-coupled version is currently available.
The Xilinx FPGA (Virtex-5 LXT or SXT series in the case of the SMT351T) on the base
module is responsible for handling data coming from one of the following sources:
Comports or Rocket Serial Link (RSL). These interfaces are compatible with a wide
range of Sundance’s modules.
The memory (DDR2 on SMT351T) on the base module can be used to store incoming
samples.
Converter configuration, sampling and transferring modes are set via internal
control registers stored inside the FPGA and accessible via Comport.
The SMT941 module is well-suited for multi-carrier, wide bandwidth communication
applications.
Note that the SMT941 requires to be coupled with an SLB base module set to work
with 2.5V FPGA IOs.
The main features of the SMT941 are listed below:
● Two Dual 14-bit 250MSPS ADC (ADS62P49),
● On-board low-jitter clock distribution chip (CDCE72010),
● On-board 245.76MHz VCXO,
● On-board 10MHz reference crystal,
● One external clock, and one reference clock inputs via MMCX connector,
● One external clock output via MMCX connector,
● One external trigger input via MMCX connector (can also be used as an
output),
● One SLB connector to link SMT941 and SMT351T as an example,
● All Analogue inputs to be connected to 50-Ohm sources.
● All Analogue outputs to be connected to 50-Ohm loads.
● A fan.
User Manual SMT941 Page 6 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 7

1 Related Documents
1.1 Referenced Documents
ADC datasheet: Texas Instrument ADS62P49.
Clock datasheet: Texas Instrument CDCE72010.
1.2 Applicable Documents
User Manual SMT941 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 8
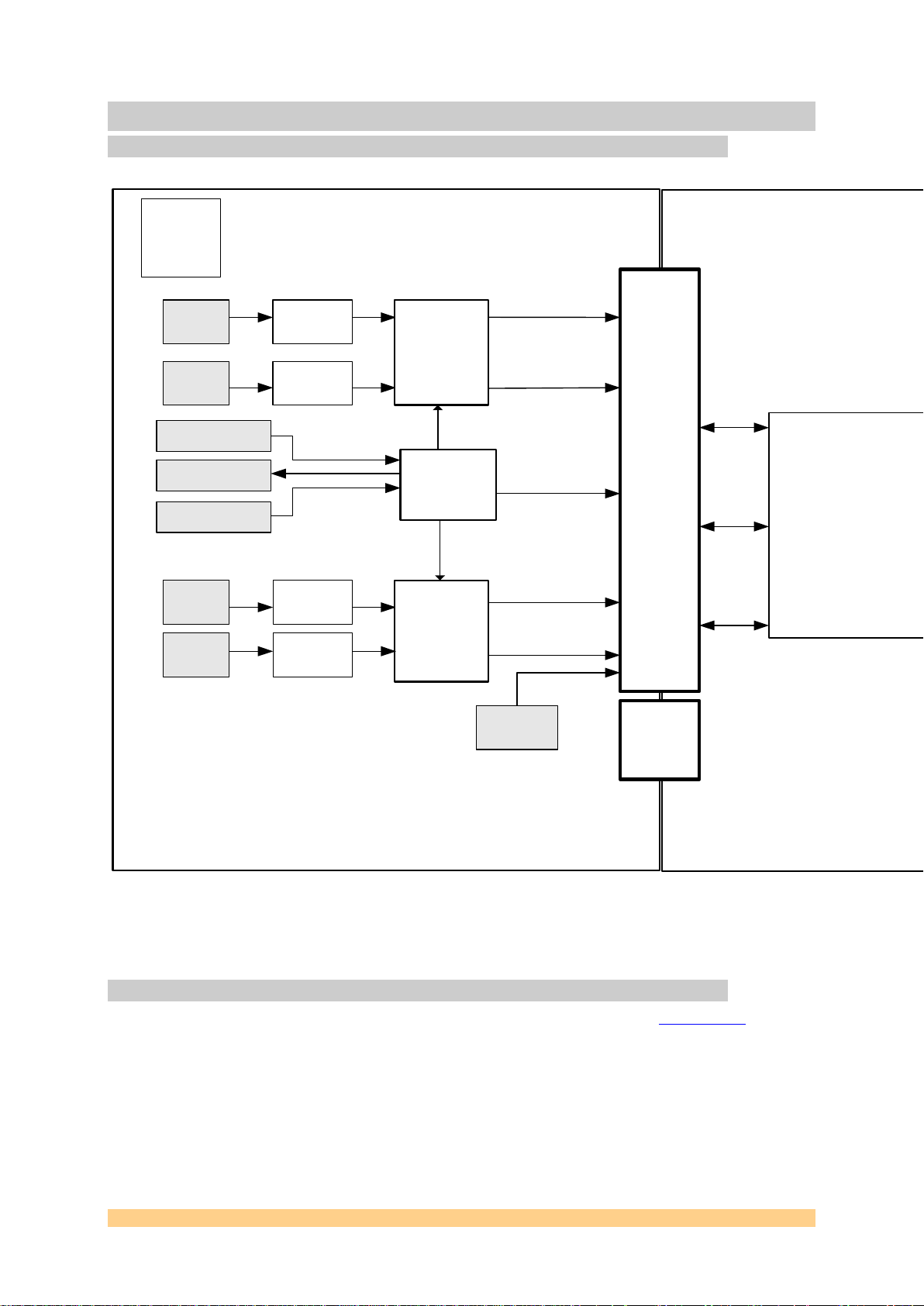
SLB Base Module (In this case SMT351T)
SMT941 (SLB Mezzanine Module)
Virtex-5
XC5VLX50T, SX50T, SX95T, LX110T
FF1136 Package
Channel A
Signal
Conditioning
(AC-coupling)
Channel B
Signal
Conditioning
(AC-coupling)
ADC Input
Ch A MMCX
50-Ohm
ADC Input
Ch B MMCX
50-Ohm
Daughter Card
interface
connector
SLB
ChA – 1.8V DDR LVDS,
Clock and Control
Data and Clocks
4xComports (0,1,3 and 4)
ADS62P49
Dual ADC ChA&B
14-bit 250MSPS
(2x675mW)
Channel C
Signal
Conditioning
(AC-coupling)
Channel D
Signal
Conditioning
(AC-coupling)
ADC Output
Ch C MMCX
50-Ohm
ADC Output
Ch D MMCX
50-Ohm
ADS62P49
Dual ADC ChA&B
14-bit 250MSPS
(2x675mW)
Power
Daughter Card
connector
SLB
ChD – 1.8V DDR LVDS,
Clock and Control
ChC – 1.8V DDR LVDS,
Clock and Control
Bank A
2.5V
Bank B
2.5V
Bank C
2.5V
Power
Supplies: 1.8
and 3.3 Volts
(Linear
Regulators)
External Trigger
Clock Synchronizer
and Jitter Cleaner
based on
CDCE72010 (1.8W)
ADCs External Clock In
- MMCX
External Reference
Clock In - MMCX
FPGA Clock
ChB – 1.8V DDR LVDS,
Clock and Control
ADCs External Clock
Out - MMCX
Data and Clocks
2 Functional Description
2.1 Block Diagram
2.2 Module Description
The SMT941 has got 2 dual channel Analog-to-Digital converters (ADS62P49 – Texas
Instrument) that have been designed for multi-carrier, wide bandwidth
communication applications. All 4 analog inputs are available on MMCX connectors.
They are 50-Ohm AC-coupled inputs (RF transformers - ration 1). DDR LVDS lines
are used to carry samples through the SLB connector to the FPGA (SLB base module
– FPGA IOs must be 2.5-Volt).
A clock distribution chip ensures that all converters sample synchronously to a
single clock source. The clock source can be external or internal (on-board 245.76-
Figure 1 - SMT942 Block diagram.
User Manual SMT941 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 9

MHz VCXO). The distribution chip also allows synchronising the on-board VCXO to a
Analogue Inputs
Input voltage range
0dB gain setting : 2.3Vpp - Full scale - AC
coupled
6dB gain setting : 1.15Vpp – Full Scale –
AC-coupled
Programmable input gain via register
(0…6dBs) by steps of 0.5dB (coarse gain)
and steps of 0.134dB (fine gain).
Impedance
Single-ended inputs – to be connected to a
50 (AC) source.
Bandwidth
Tbd – depends on ADC internal input gain.
ADC characteristics
Output Data Width per channel
14 Bits
Data Format
2’s Compliment or offset binary
(Changeable via control register)
SFDR
75 (0-db gain) / 82dBs (6-db gain)
maximum (manufacturer)
SNR
69 (0-db gain) / 66dBs (6-db gain)
maximum (manufacturer)
ENOB
11.3 bits maximum (manufacturer)
Maximum Sampling rate
250 MSPS
(1…100MSPS low speed mode)
(100…250MSPS high speed mode)
Minimum Sampling rate
1 MSPS
reference signal that can be external or internal (on-board 10-MHz crystal). External
reference, external sampling clock input and output are accessible on MMCX
connectors. An external trigger input is also available on the board (it is
implemented as an input in the default firmware provided but can also be
implemented as an output).
All control, data and clock lines are mapped onto an SLB connector so the card can
be fully controlled by an SLB FPGA base module (SMT351T for example, with 2.5Volt FPGA IOs).
Some green LEDs are available on the board. A group of four LEDs is driven directly
from the SLB base FPGA module and can be used to return status bits. Other
indivudual LEDs should be lit and show that local power supplies are on.
2.2.1 A/D converters
The main characteristics of the SMT941 are gathered into the following table.
ADC Analog inputs on the board are single-ended. A double RF transformer
structure is used to provide single-ended to differential conversion. Both
transformers are identical and have a ratio of 1. In order to match the 50-Ohm at
the connector, the output of the second transformer has two 25-Ohm resistors
terminated to the ADC common mode voltage.
User Manual SMT941 Page 9 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 10
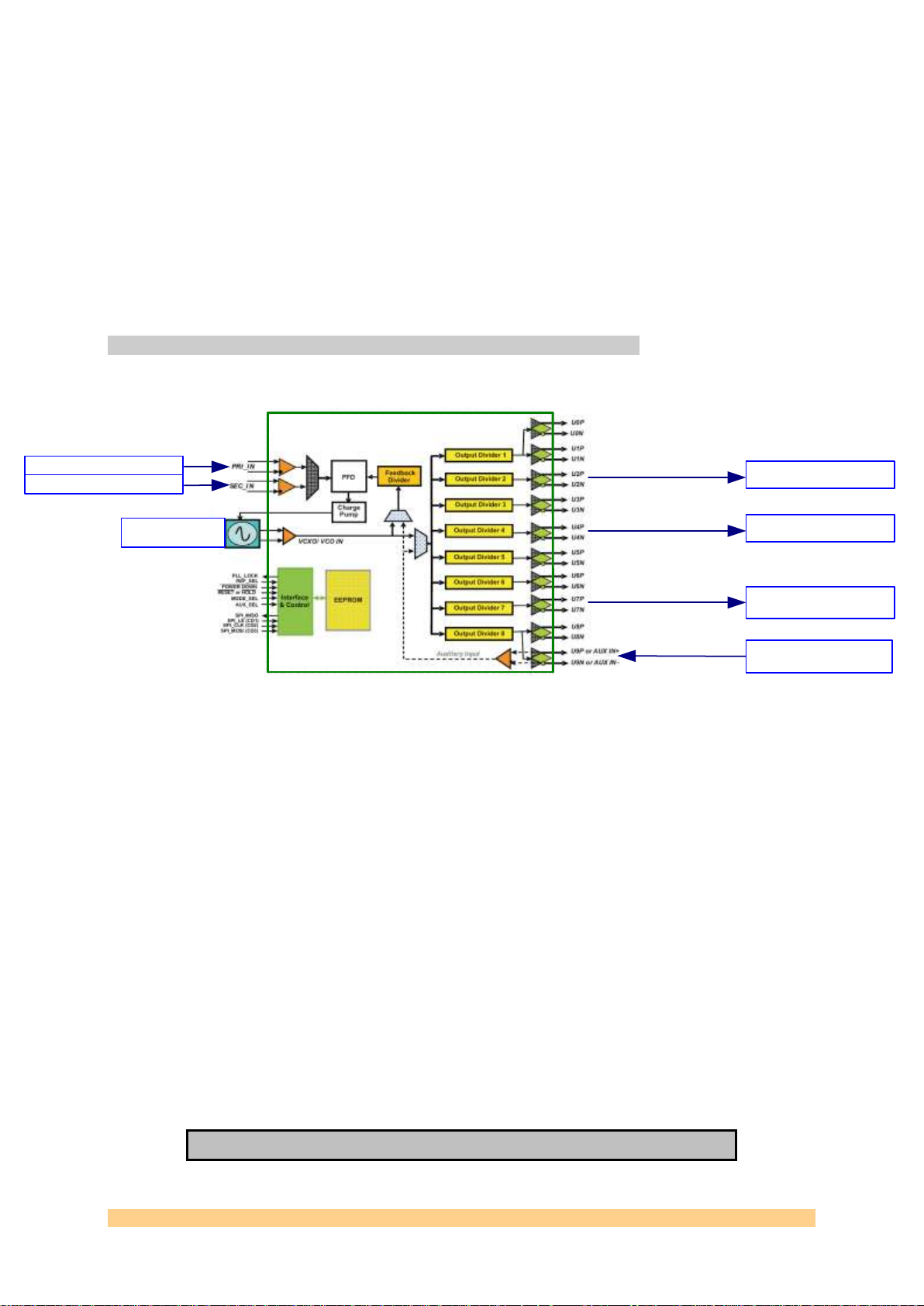
Clock Synthesizer and Jitter Cleaner - Texas Instrument CDCE72010
U2 - ADC Channel a&b
U7 - Clk Out and FPGA Clk Output (ExtClkOut)
FPGA (SLB)
Clk In
Clk Input (ExtClkIn)
On-board VCXO
254.76 MHz
On-board 10-MHz reference
External Reference (ExtRefIn)
ADC Chc&d – ADS62P49
14-bit 250MSPS
U4 - ADC Channel a&b
ADC Cha&b – ADS62P49
14-bit 250MSPS
External Reference Input
2.2.2 Clock structure
The following diagram shows the clock structure of the SMT941:
The clock distribution chip used on the SMT941 offers 2 reference inputs, a VCXO
differential input and a charge pump to drive the VCXO, as well as a second
differential clock input. ADCs and external clock are mapped to separate internal
output dividers in order to give more flexibility.
The CDCE72010 chip is designed to provide clean, phase related clocks to the
converters. The reference clock (on-board or external) is used to lock the on-board
VCXO using the clock chip PLL/charge pump. It is also possible to feed an external
sampling clock to the chip that can then be distributed the analog converters.
Note that when the board is mounted onto a PXI SLB carrier such as the SMT700
(with 2.5-Volt FPGA IOs), it is possible to feed the 10-MHz reference clock (PXI bus)
to the SMT941 order to lock the VCXO, then creating a local source synchronised to
the rest of the system.
Also to be noted is that a VCXO of a different frequency can be fitted to replace the
standard 245.76-MHz one. It is to be discussed prior to ordering as it is an
operation carried out in the factory.
The table below gathers the characteristics of all clock inputs/outputs:
Figure 2 - Clock Structure - Block Diagram
User Manual SMT941 Page 10 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 11
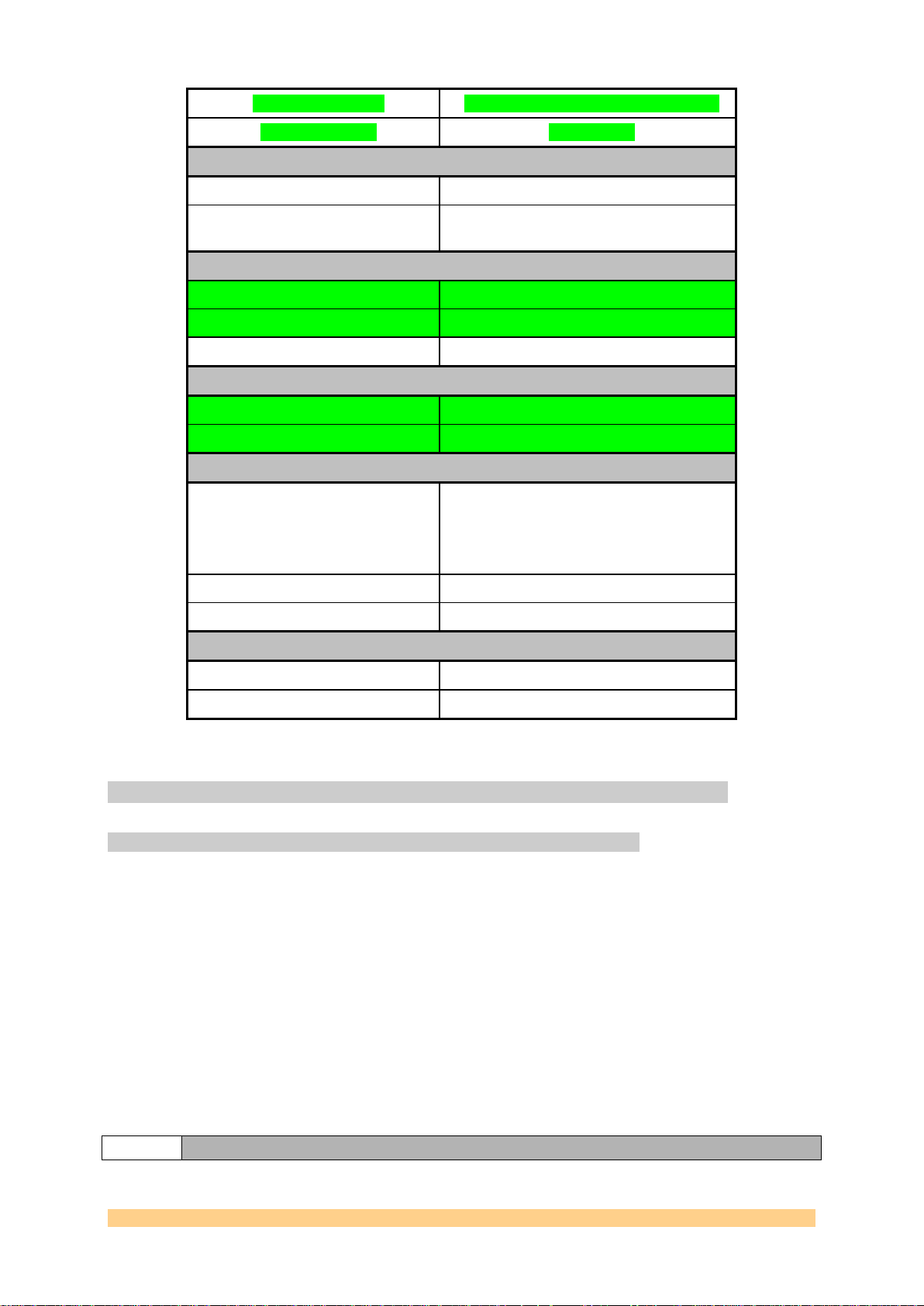
Input Voltage Level
1 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
Frequency Range
0 – 100 MHz.
External Reference Output
Output Voltage Level
1.6 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
Output Impedance
50-Ohm (Termination implemented at the
connector)
External Sampling Clock Input
Input Voltage Level
1.5 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
Input Format
Single-ended.
Frequency range
10-500 MHz
External Sampling Clock Output
Output Voltage Level
0-2.4 Volts fixed amplitude
Output Format
LVTTL
External Trigger Inputs
Input Voltage Level
1.5-3.3 Volts peak-to-peak.
Format
DC-coupled and Single-ended (Termination
implemented at the connector). Differential
on option (3.3 V PECL).
Impedance
50-Ohm.
Frequency range
62.5 MHz maximum
Delay
External Ref. Input to Ext Ref. Out
External Clk Input to Ext Clk Out
9ns (between J29 and J4)
Figure 3 - Clock Architecture Main Characteristics.
Byte Content
2.3 FPGA Design
2.3.1 Control Register Settings
The Control Registers control the complete functionality of the SMT941. They are
setup via the Comport3 (standard firmware provided). The settings of the ADCs,
triggers, clocks and the configuration of the interfaces and the internal FPGA data
path settings can be configured via the Control Registers.
2.3.1.1 Control Packet Structure
The data passed on to the SMT941 over the Comport must conform to a certain
packet structure. Only valid packets will be accepted and only after acceptance of a
packet will the appropriate settings be implemented. Each packet will start with a
command (4 bits – 0x1 for a write operation – 0x2 for a read operation) information,
followed by a register address (12 bits – see table Memory Map), followed by a 16-bit
data. This structure is illustrated in the following figure:
User Manual SMT941 Page 11 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 12
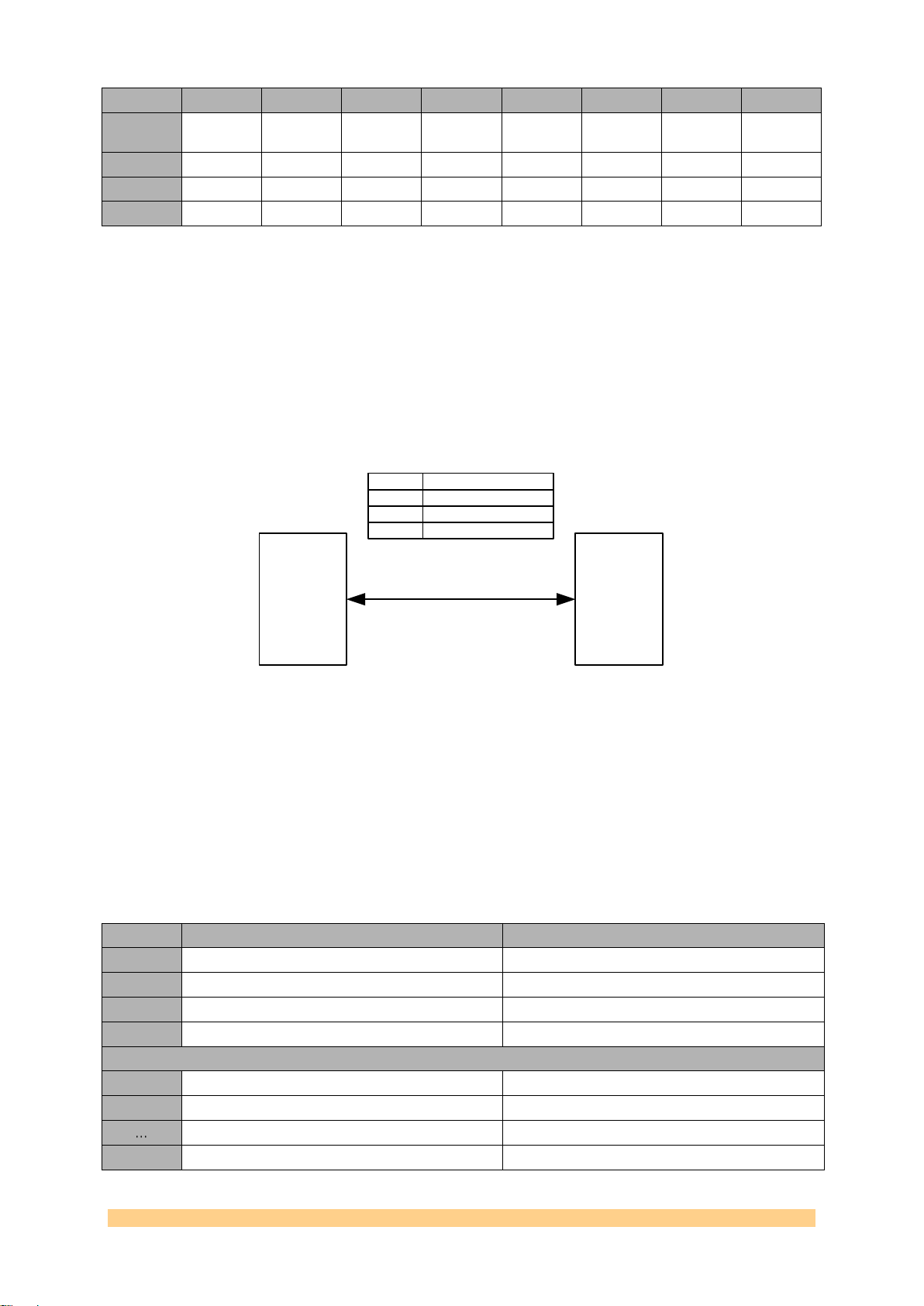
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
3
Command
3
Command
2
Command
1
Command
0
Address
11
Address
10
Address 9
Address 8
2
Address 7
Address 6
Address 5
Address 4
Address 3
Address 2
Address 1
Address 0
1
Data 15
Data 14
Data 13
Data 12
Data 11
Data 10
Data 9
Data 8
0
Data 7
Data 6
Data 5
Data 4
Data 3
Data 2
Data 1
Data 0
Figure 4 – Setup Packet Structure.
Host
Fixed Sequence
SMT941
ComPort 3
Byte 0
Read/Write AddressByte 1
Read/Write DataByte 3
Read/Write DataByte 4
1) Write Packet
Address
Writable Registers
Readable Registers
0x00
Reserved.
Reserved.
0x01
Board Control Register.
Firmware Version.
0x02
Reserved.
Clock Readback Register.
0x03
Reserved.
Board Status Register
Clock Section
0x10
Clock Register 0x0.
Read-back (FPGA Register) Clock Register 0x0.
0x11
Clock Register 0x1.
Read-back (FPGA Register) Clock Register 0x1.
…
…
0x28
Clock Register 0x18.
Read-back (FPGA Register) Clock Register 0x18.
2.3.1.2 Reading and Writing Registers
Control packets are sent to the SMT941 over Comport3. This is a bi-directional
interface. The format of a ‘Read Packet’ is the same as that of a write packet.
Figure 5 – Control Register Read Sequence.
2.3.1.3 Memory Map
The write packets must contain the address where the data must be written to and
the read packets must contain the address where the required data must be read.
The following figure shows the memory map for the writable and readable Control
Registers on the SMT941:
User Manual SMT941 Page 12 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 13
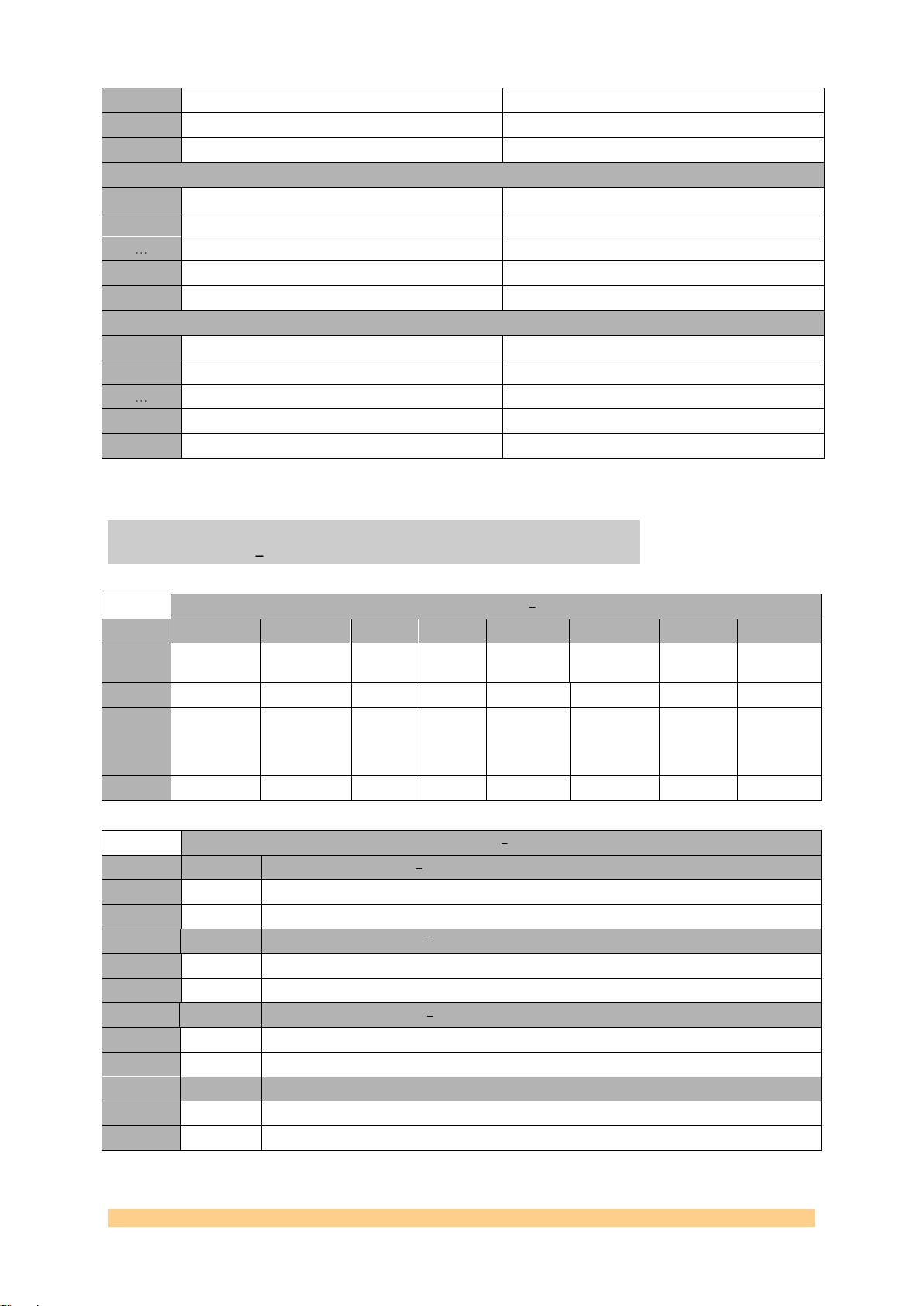
0x29
Clock Register 0x19.
Read-back (FPGA Register) Clock Register 0x19.
0x2A
Clock Readback Address Register (LSB)
0x2B
Clock Readback Address Register (MSB)
ADCab Section
0x30
ADCab Register 0x0.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCab Register 0x0.
0x31
ADCab Register 0x1.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCab Register 0x1.
…
...
0x38
ADCab Register 0x8.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCab Register 0x8.
0x39
ADCab Register 0x9.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCab Register 0x9.
ADCcd Section
0x40
ADCcd Register 0x0.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCcd Register 0x0.
0x41
ADCcd Register 0x1.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCcd Register 0x1.
…
...
0x48
ADCcd Register 0x8.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCcd Register 0x8.
0x49
ADCcd Register 0x9.
Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCcd Register 0x9.
Figure 6 – Register Memory Map.
Control Register 0x01
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Clk_Readb
ack
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Chcd
trigger
selection
Chdc
internal
trigger
Chab
trigger
selectio
n
Chab
internal
trigger
Chab reset
Chcd
update
(dac)
Chab
update
(adc)
clk update
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
Clock Register 0 0x10
Setting
Bit 0
Description clk update clock chip register update
0
0
No action.
1
1
All clock registers are sent to the clock chip via its serial interface.
Setting
Bit 1
Description chab update channel a and b register update
0
0
No action.
1
1
All registers (chab) are sent to the converter via its serial interface.
Setting
Bit 2
Description chcd update channel c and d register update
0
1
No action.
1
1
All registers (chcd) are sent to the converter via its serial interface.
Setting
Bit 4
Description chab Internal trigger
0
0
No action.
1
1
Starts the data flow (converter chab).
2.3.2 Register Descriptions
Control Register 0x1.
User Manual SMT941 Page 13 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 14

Setting
Bit 5
Description chab trigger selection
0
0
Trigger from control register selected.
1
1
Trigger from external source selected.
Setting
Bit 6
Description chcd Internal trigger
0
0
No action.
1
1
Starts the data flow (converter chcd).
Setting
Bit 7
Description chcd trigger selection
0
0
Trigger from control register selected.
1
1
Trigger from external source selected.
Clock Register 0 0x10
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Reserved
CP_DIR
CP_MODE
DELAY_PFD
REFSELCNTRL
VCXO_AUX_SEL
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘00’
‘0’
‘0’
0
SECSEL_PRISEL
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘00’
‘00’
‘0000’
Clock Register 0 0x10
Setting
Bit 7:6
Description SECSEL_PRISEL Reference Input Selection
0
00
Nothing Selected
1
01
On-board Reference selected
2
10
External Reference selected
3
11
Auto Selection (Not recommended)
Setting
Bit 8
Description VCXO_AUX_SEL VCXO/AUX Selection
0
0
On-board or External Reference. Selected (SECSEL_PRI_SEL)
1
1
On-board VCXO or External Clock selected.
Setting
Bit 9
Description REFSELCNTRL Reference selection mode
0
0
Reference selection made externally.
1
1
Reference selection made internally (using SECSEL_PRISEL.).
Setting
Bit 11:10
Description DELAY_PFD PFD pulse width
0
00
1 01
2 10
3 11
Setting
Bit 12
Description CP_MODE
0
0
3V. 1 1
5V
Setting
Bit 13
Description CP_DIR
0
0
Positive CP current output
1
1
Negative CP current output
CLOCK Register 0 0x10.
User Manual SMT941 Page 14 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 15

Clock Register 1 0x11
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Output0 (DAC chc&d clk1) Mode
PECLOHISWING
Reserved
Default
‘100000’
‘0’
‘0’ 0 Reserved
ICP
CP_PRE
Reserved
Default
‘00’
‘0000’
‘0’
‘0’
Reset Register 1 0x11
Setting
Bit 1
Description CP_PRE - Preset charge pump output voltage to vcc/2
0
0
OFF. 1 1
ON.
Setting
Bit 5:2
Description ICP Charge pump current setting
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 9
Description PECL0HISWING PECL output voltage swing (DAC chc&d clk1)
0
0
Normal Operation.
1
1
High PECL output voltage.
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Output0 (DAC chc&d clk1) mode
0
0
LVPECL only: ‘100000’.
Clock Register 2 0x12
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] (Output DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2)
Reserved
Default
‘000000’
‘00’
0
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘0011’
‘0001’
Reset Register 2 0x12
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2
0
0
1 1
Clock Register 3 0x13
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
CLOCK Register 1 0x11.
CLOCK Register 2 0x12.
CLOCK Register 3 0x13.
User Manual SMT941 Page 15 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 16

1
Output0 (DAC chc&d clk2) Mode
PECL1HISWING
Output
Divider
Enable
Default
‘100000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Output Divider Ratio DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2
Coarse Phase
Adjustment[6]
Default
‘0000000’
‘0’
Reset Register 3 0x13
Setting
Bit 0
Description - Coarse Phase Adjustment[6] DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 7:1
Description Output Divider Ratio DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2
0
0
1
1
Setting
Bit 8
Description Output Divider Enable DAC chc&d clk1 and clk2
0
0
Divider disabled.
1
1
Divider enabled.
Setting
Bit 9
Description PECL1HISWING PECL output voltage swing (DAC chc&d clk2)
0
0
Normal Operation.
1
1
High PECL output voltage.
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Output1 (DAC chc&d clk2) mode
0
0
LVPECL only: ‘100000’.
Clock Register 4 0x14
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] (Output DAC cha&b clk1)
Delay N[2:1]
Default
‘000000’
‘00’
0
Delay N[0]
Delay M
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0010’
Reset Register 4 0x14
Setting
Bit 6:4
Description Delay M
0
0
1
1
Setting
Bit 9:7
Description Delay N
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] DAC cha&b clk1
0
0
1 1
CLOCK Register 4 0x14.
User Manual SMT941 Page 16 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 17

CLOCK Register 5 0x15.
Clock Register 5 0x15
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Output0 (DAC cha&b clk1) Mode
PECL2HISWING
Output
Divider
Enable
Default
‘100000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Output Divider Ratio DAC cha&b clk1
Coarse Phase
Adjustment[6]
Default
‘0000000’
‘0’
Reset Register 5 0x15
Setting
Bit 0
Description - Coarse Phase Adjustment[6] DAC cha&b clk1
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 7:1
Description Output Divider Ratio DAC cha&b clk1
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 8
Description Output Divider Enable DAC cha&b clk1
0
0
Divider disabled.
1
1
Divider enabled.
Setting
Bit 9
Description PECL2HISWING PECL output voltage swing (DAC cha&b clk1)
0
0
Normal Operation.
1
1
High PECL output voltage.
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Output2 (DAC cha&b clk1) mode
0
0
LVPECL only: ‘100000’.
Clock Register 6 0x16
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] (Output DAC cha&b clk2)
BIAS_DIV23
Default
‘000000’
‘00’
0
BIAS_DIV01
Reserved
DIS_FDET_REF
Reserved
Default
‘00’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0011’
Reset Register 6 0x16
Setting
Bit 4
Description DIS_FDET_REF
0
0
Reference Clock detector is ON
1
1
Reference Clock detector is OFF
Setting
Bit 7:6
Description BIAS_DIV01 Current reduction output dividers 0 and 1
0
‘00’
No current output reduction
1
‘01’
20% output current reduction
CLOCK Register 6 0x16.
User Manual SMT941 Page 17 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 18

2
‘10’
30% output current reduction
Setting
Bit 9:8
Description BIAS_DIV23 Current reduction output dividers 2 and 3
0
‘00’
No current output reduction
1
‘01’
20% output current reduction
2
‘10’
30% output current reduction
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] DAC cha&b clk1
0
0
1 1
Clock Register 7 0x17
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Output0 (DAC cha&b clk2) Mode
PECL3HISWING
Output
Divider
Enable
Default
‘100000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Output Divider Ratio DAC cha&b clk1 and clk2
Coarse Phase
Adjustment[6]
Default
‘0000000’
‘0’
Reset Register 7 0x17
Setting
Bit 0
Description - Coarse Phase Adjustment[6] DAC cha&b clk2
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 7:1
Description Output Divider Ratio DAC cha&b clk2
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 8
Description Output Divider Enable DAC cha&b clk2
0
0
Divider disabled.
1
1
Divider enabled.
Setting
Bit 9
Description PECL3HISWING PECL output voltage swing (DAC cha&b clk2)
0
0
Normal Operation.
1
1
High PECL output voltage.
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Output3 (DAC cha&b clk2) mode
0
0
LVPECL only: ‘100000’.
Clock Register 8 0x18
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] (External Clock)
Reserved
HOLD_ON_LOR
Default
‘000000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘0000’
‘0011’
CLOCK Register 7 0x17.
CLOCK Register 8 0x18.
User Manual SMT941 Page 18 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 19

Reset Register 8 0x18
Setting
Bit 8
Description HOLD_ON_LOR
0
0
Normal mode of operation
1
1
Charge pump in tri-state mode
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Coarse Phase Adjustment[5:0] External Clock
0
0
1 1
Clock Register 9 0x19
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Output0 (External Clock) Mode
PECL4HISWING
Output
Divider
Enable
Default
‘100000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
Output Divider Ratio External Clock
Coarse Phase
Adjustment[6]
Default
‘0000000’
‘0’
Reset Register 9 0x19
Setting
Bit 0
Description - Coarse Phase Adjustment[6] External Clock
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 7:1
Description Output Divider Ratio External Clock
0
0
1 1
Setting
Bit 8
Description Output Divider Enable External Clock
0
0
Divider disabled.
1
1
Divider enabled.
Setting
Bit 9
Description PECL4HISWING PECL output voltage swing (External Clock)
0
0
Normal Operation.
1
1
High PECL output voltage.
Setting
Bit 15:10
Description Output4 (External Clock) mode
0
0
LVPECL only: ‘100000’.
Clock Register A 0x1A
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘000000’
‘00’
CLOCK Register 9 0x19.
CLOCK Register A 0x1A.
User Manual SMT941 Page 19 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 20

0
Reserved
BIAS_DIV45
Reserved
Default
‘00’
‘00’
‘0101’
Reset Register A 0x1A
Setting
Bit 5:4
Description BIAS_DIV01 Current reduction output dividers 0 and 1
0
‘00’
No current output reduction
1
‘01’
20% output current reduction
2
‘10’
30% output current reduction
Clock Register B 0x1B
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘01101000’
0
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
Clock Register C 0x1C
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3 Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
DET_STAR
T_BYPASS
FB_START
_BYPASS
Default
‘000000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
DIV2_DIS
DIV_SEL
Reserve
d
FB_FD_DESEL
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0110’
Reset Register C 0x1C
Setting
Bit 4
Description FB_FD_DESEL
0
‘0’
Feedback frequency detector is connected to the lock detector
1
‘1’
Feedback frequency detector is disconnected from the lock detector
Setting
Bit 6
Description DIV_SEL
0
‘0’
FB Clock divided by 1
1
‘1’
FB Clock divided by 2
Setting
Bit 7
Description DIV2_DIS
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation
1
‘1’
FB Div2 in reset
Setting
Bit 8
Description FB_START_BYPASS
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation
1
‘1’
FB Divider can be started with external REF_SEL (pin)
Setting
Bit 9
Description DET_START_BYPASS
CLOCK Register B 0x1B.
CLOCK Register C 0x1C.
User Manual SMT941 Page 20 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 21

0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation
1
‘1’
FB Divider can be started with external NRESET (pin)
Clock Register D 0x1D
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘01101000’
0
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
Clock Register E 0x1E
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3 Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
ADLOCK
LOCK_C[1]
Default
‘000000’
‘0’
‘0’
0
LOCK_C[0]
Reserved LOCK_WINDOW
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘00’
‘0111’
Reset Register E 0x1E
Setting
Bit 5:4
Description Lock detect window LOCK_WINDOW
0
‘0’
1 ‘1’
Setting
Bit 8:7
Description Number of coherent lock events LOCK_C
0
‘0’
1 ‘1’
Setting
Bit 9
Description ADLOCK
0
‘0’
Digital PLL Lock
1
‘1’
Analog PLL Lock
Clock Register F 0x1F
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘01101000’
0
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
CLOCK Register D 0x1D.
CLOCK Register E 0x1E.
CLOCK Register F 0x1F.
User Manual SMT941 Page 21 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 22

CLOCK Register 10 0x20.
Clock Register 10 0x20
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘00000001’
0
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘0111’
‘1000’
Clock Register 11 0x21
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘01101000’
0
Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
Clock Register 12 0x22
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
INDET_BP
START_B
YPASS
DIVSYNC
_DIS
Reserved
LOCKW
HOLD_CNT
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘00’
‘00’
0
Reserved
HOLD
Reserved
HOLDF
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘1001’
Reset Register 12 0x22
Setting
Bit 4
Description Frequency Hold Over (External) enable HOLDF
0
‘0’
Off 1 ‘1’
On
Setting
Bit 6
Description equals to HOLD pin HOLD
0
‘0’
Tri-state charge pump
1
‘1’
Setting
Bit 6
Description equals to HOLD pin HOLD
0
‘0’
Tri-state charge pump
1
‘1’
Setting
Bit 9:8
Description Hold function reactivates after a number of reference clock cycles HOLD_CNT
0
‘00’
64 clock cycles
1
‘01’
128 clock cycles
2
‘10’
256 clock cycles
3
‘11’
512 clock cycles
CLOCK Register 11 0x21.
CLOCK Register 12 0x22.
User Manual SMT941 Page 22 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 23

Setting
Bit 11:10
Description Extended lock detect window - LOCKW
0
‘00’
1 ‘01’
2 ‘10’
3 ‘11’
Setting
Bit 13
Description DIVSYNC_DIS
0
‘0’
Start signal is synchronised to N/M divider input clock
1
‘1’
Setting
Bit 14
Description START_BYPASS
0
‘0’
Start signal is synchronised to VCXO clock
1
‘1’
Start synch block is bypassed
Setting
Bit 15
Description INDET_BP
0
‘0’
Synch logic active when VCXO/AUX clocks are available
1
‘1’
Synch logic is independent from VCXO/AUX
Clock Register 13 0x23
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
0
Reserved
BIAS_DIV_FB
NPRESET
_MDIV
LOW_FD_
FB_EN
PLL_LOCK_B
P
Default
‘000’
‘00’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
Reset Register 13 0x23
Setting
Bit 0
Description PLL_LOCK_BP
0
‘0’
Synch logic waits for the first PLL lock state
1
‘1’
Synch logic independent from first PLL lock state
Setting
Bit 1
Description LOW_FD_FB_EN
0
‘0’
Synch logic is independent from VCXO/DIV_FB frequency
1
‘1’
Synch logic is started for VCXO/DIV_FB > 600khz
Setting
Bit 2
Description NPRESET_MDIV
0
‘0’
M-divider uses nHOLD as NPRESET
1
‘1’
M-divider not preset by nHOLD
Setting
Bit 4:3
Description BIAS_DIV_FB
0
‘00’
No current reduction
1
‘01’
20% current reduction
2
‘10’
30% current reduction
Clock Register 14 0x24
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reference Divider[11:4]
CLOCK Register 13 0x23.
CLOCK Register 14 0x24.
User Manual SMT941 Page 23 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 24

Default
‘00000000’
0
Reference Divider M[3:0]
Reserved
Default
‘0000’
‘1010’
Reset Register 14 0x24
Setting
Bit 11:4
Description Reference Divider M[11:0]
0
1
Clock Register 15 0x25
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
VCXO Divider N[13:6]
Default
‘000000’
0
VCXO Divider N[5:0]
Reference Divider
M[13:12]
Default
‘000000’
‘00’
Reset Register 15 0x25
Setting
Bit 1:0
Description Reference Divider M[13:12]
0
1
Setting
Bit 15:2
Description VCXO Divider N[13:0]
0
1
Clock Register 16 0x26
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
FB_COUNTER
FB_INCLK_I
NV
Default
‘0000000’
‘0’
0
FB_CML_SE
L
FB_DIS
SEC_DIV2
PRI_DIV2
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘1011’
Reset Register 16 0x26
Setting
Bit 4
Description PRI_DIV2
0
‘0’
Primary reference divider disabled
1
‘1’
Primary reference divider enabled
Setting
Bit 5
Description SEC_DIV2
0
‘0’
Secondary reference divider disabled
CLOCK Register 15 0x25.
CLOCK Register 16 0x26.
User Manual SMT941 Page 24 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 25

1
‘1’
Secondary reference divider enabled
Setting
Bit 6
Description FB_DIS
0
‘0’
FB Divider is active
1
‘1’
FB Divider is disabled
Setting
Bit 7
Description FB_CML_SEL
0
‘0’
FB is CMOS type
1
‘1’
FB is CML type
Setting
Bit 8
Description FB_INCLK_INV
0
‘0’
Input clock for FB not inverted (normal/low speed mode)
1
‘1’
Input for FB inverted (high speed mode)
Setting
Bit 15:9
Description FB_COUNTER
0
‘0’
FB Path integer counter
1
Clock Register 17 0x27
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
RESET_HO
LD
SEL_DELA
Y
RESHAPE
Reserved
OUT_MUX_S
EL
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
0
FB_MUX_
SEL
PD_PLL
FB_PHASE_ADJ
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘000000’
Reset Register 17 0x27
Setting
Bit 5:0
Description FB_PHASE_ADJ
0
‘0’
Feedback phase adjustment
Setting
Bit 6
Description PD_PLL
0
‘0’
PLL in normal mode
1
‘1’
PLL powered down
Setting
Bit 7
Description FB_MUX_SEL
0
‘0’
VCXO selected for clock tree and FB
1
‘1’
External Clock selected for clock tree and FB
Setting
Bit 8
Description OUT_MUX_SEL
0
‘0’
VCXO selected
1
‘1’
External clock selected
Setting
Bit 10
Description RESHAPE
0
‘0’
Reference clock reshaped
1
‘1’
Reference clock not reshaped
Setting
Bit 11
Description SEL_DELAY
0
‘0’
Enables short delay for fast operation
1
‘1’
Long delay – recommended for reference below 150mhz.
Setting
Bit 12
Description RESET_HOLD
0
‘0’
RESET or HOLD acts as nRESET pin
CLOCK Register 17 0x27.
User Manual SMT941 Page 25 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 26

1
‘1’
RESET or HOLD acts as nHOLD pin
Clock Register 18 0x28
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
nRESET_nHO
LD
nPD
Reserved
Default
‘000’
‘0’
‘1’
‘000’ 0 Reserved
Reserved
Default
‘0000’
‘1100’
Reset Register 18 0x28
Setting
Bit 11
Description nPD
0
‘0’
Power-down mode active
1
‘1’
Normal mode of operation
Setting
Bit 12
Description nRESET_nHOLD
0
‘0’
Forces RESET or HOLD
1
‘1’
Normal mode of operation
Clock Register 19 0x29
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Reset Register 19 0x29
Setting
Bit 11
Description nPD
0
1
Setting
Bit 12
Description nRESET_nHOLD
0
1
CLOCK Register 18 0x28.
CLOCK Register 19 0x29.
User Manual SMT941 Page 26 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 27

ADC Chab Register 0 0x30
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Enable Low
Speed
Mode
Reserved
Default
‘00000’
‘0’
‘00’
0
Software
Reset
Reserved
SerialRead
Out
Default
‘0’
‘000000’
‘0’
ADC Chab Register 0 0x30
Setting
Bit 0
Description SerialReadOut
0
‘0’
Serial readout disabled.
1
‘1’
Serial readout enabled.
Setting
Bit 7
Description - Software Reset
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation.
1
‘1’
Resets all internal registers and self-clears to ‘0’.
Setting
Bit 10
Description - Enable Low Speed Mode
0
‘0’
Low Speed Mode disabled. Sampling rates >100MSPS.
0
‘1’
Low Speed Mode enabled. Sampling rates <=100 MSPS.
ADC Chab Register 1 0x31
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Reference
Reserved
Standby
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘00’
‘000’
‘0’
‘0’
1
Reserved
PowerDownModes
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
ADC Chab Register 1 0x31
Setting
Bit 1
Description Standby.
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation.
ADC Chab Register 0 0x30.
ADC Chab Register 1 0x31.
User Manual SMT941 Page 27 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 28

1
‘1’
Both ADC channels are put into standby mode (internal ref and output buffers still
active).
Setting
Bit 6:5
Description Reference.
0
‘01’
Internal Reference enabled.
1
‘11’
External Reference enabled.
Setting
Bit 11:8
Description Power down modes.
0
‘0000’
Pins ctrl1, 2 and 3 determine power down modes.
1
‘1000’
Normal mode of operation.
2
‘1001’
Output buffers disabled for channelB.
3
‘1010’
Output buffers disabled for channelA.
4
‘1011’
Output buffers disabled for channelA and B.
5
‘1100’
Global power down.
6
‘1101’
ChannelB in standby.
7
‘1110’
ChannelA in standby.
ADC Chab Register 2 0x32
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
LVDS_CM
OS
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘0000000’
1
Clock Edge Control (rising edge)
Clock Edge Control (falling edge)
Reserved
Default
‘000’
‘000’
‘00’
ADC Chab Register 2 0x32
Setting
Bit 7
Description LVDS_CMOS
0
‘0’
Parallel CMOS interface.
1
‘1’
DDR LVDS interface.
Setting
Bit 12:10
Description Clock output Edge control (falling edge)
0
‘000’,’100’
Default output clock position.
1
‘101’
Falling edge shifted by +(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
2
‘110’
Falling edge shifted by -(6/26)/Sampling Frequency
3
‘111’
Falling edge shifted by -(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
Setting
Bit 15:13
Description Clock output Edge control (rising edge)
0
‘000’,’100’
Default output clock position.
1
‘101’
Rising edge shifted by +(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
2
‘110’
Rising edge shifted by -(6/26)/Sampling Frequency
3
‘111’
Rising edge shifted by -(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
ADC Chab Register 3 0x33
ADC Chab Register 2 0x32.
ADC Chab Register 3 0x33.
User Manual SMT941 Page 28 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 29

Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Channel
Control
Reserved
Data Format
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘0’
‘000’
‘00’
‘0’
1
Custom Pattern (lsb)
Default
‘00000000’
ADC Chab Register 3 0x33
Setting
Bit 2:1
Description Data Format
0
‘10’
2’s complement.
1
‘11’
Binary.
Setting
Bit 6
Description - Channel Control
0
‘0’
Common Control.
1
‘1’
Independent Control (Test pattern, Offset correction and SNR boost).
Setting
Bit 15:8
Description Custom Pattern (lsb)
0
ADC Chab Register 4 0x34
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Custom Pattern (msb)
Default
‘00’
‘000000’
1
Reserved
Offset
Correctio
n Enable
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘000000’
ADC Chab Register 4 0x34
Setting
Bit 5:0
Description Custom Pattern (msb).
0
Setting
Bit 14
Description Offset Correction Enable ChA.
0
‘0’
Offset Correction Disabled.
1
‘1’
Offset Correction Enabled.
ADC Chab Register 5 0x35
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Gain ChA (Common)
Offset Correction Time Constant ChA
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
1
Reserved
Fine Gain Adjustment ChA (Common)
ADC Chab Register 4 0x34.
ADC Chab Register 5 0x35.
User Manual SMT941 Page 29 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 30

Default
‘0’
‘0000000’
ADC Chab Register 5 0x35
Setting
Bit 3:0
Description Offset Correction Time Constant (number of clock cycles) ChA
0
‘0000’
256k 1 ‘0001’
512k 2 ‘0010’
1Meg 3 ‘0011’
2Meg 4 ‘0100’
4Meg 5 ‘0101’
8Meg 6 ‘0110’
16Meg
7
‘0111’
32Meg
8
‘1000’
64Meg
9
‘1001’
128Meg
10
‘1010’
256Meg
11
‘1011’
512Meg
Setting
Bit 7:4
Description Gain ChA (Common).
0
‘0000’
0dB gain
1
‘0001’
0.5dB gain
2
‘0010’
1.0dB gain
3
‘0011’
1.5dB gain
4
‘0100’
2.0dB gain
5
‘0101’
2.5dB gain
6
‘0110’
3.0dB gain
7
‘0111’
3.5dB gain
8
‘1000’
4.0dB gain
9
‘1001’
4.5dB gain
10
‘1010’
5.0dB gain
11
‘1011’
5.5dB gain
12
‘1100’
6.0dB gain
Setting
Bit 14:8
Description Fine Gain ChA (Common).
0
128 steps for a range of 0.134dB
ADC Chab Register 6 0x36
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Test Patterns ChA
Default
‘00000’
‘000’
1
Reserved
Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
Default
‘00’
ADC Chab Register 6 0x36.
User Manual SMT941 Page 30 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 31

ADC Chab Register 6 0x36
Setting
Bit 2:0
Description Test Patterns ChA
0
‘000’
Normal Mode of Operation
1
‘001’
Outputs all zeroes
2
‘010’
Outputs all ones
3
‘011’
Outputs toggle pattern (0x1555 and 0x2AAA)
4
‘100’
Outputs digital ramp (0->16383)
5
‘101’
Outputs custom pattern
Setting
Bit 13:8
Description Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
0
‘011111’
Pedestal=+31LSBs
1
‘011110’
Pedestal=+30LSBs
2
…
… 3 ‘000000’
Pedestal=0
4
…
… 5 ‘111111’
Pedestal=-1LSB
6
‘111110’
Pedestal=-2LSB
7
…
… 8 ‘100000’
-32LSBs
ADC Chab Register 7 0x37
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Offset
Correctio
n Enable
ChB
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘000000’
1
Gain ChB (Common)
Offset Correction Time Constant ChB
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
ADC Chab Register 7 0x37
Setting
Bit 6
Description Offset Correction Enable ChB.
0
‘0’
Offset Correction Disabled.
1
‘1’
Offset Correction Enabled.
Setting
Bit 11:8
Description Offset Correction Time Constant (number of clock cycles) ChB
0
‘0000’
256k 1 ‘0001’
512k 2 ‘0010’
1Meg 3 ‘0011’
2Meg 4 ‘0100’
4Meg 5 ‘0101’
8Meg
ADC Chab Register 7 0x37.
User Manual SMT941 Page 31 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 32

6
‘0110’
16Meg
7
‘0111’
32Meg
8
‘1000’
64Meg
9
‘1001’
128Meg
10
‘1010’
256Meg
11
‘1011’
512Meg
Setting
Bit 15:12
Description Gain ChB (Common).
0
‘0000’
0dB gain
1
‘0001’
0.5dB gain
2
‘0010’
1.0dB gain
3
‘0011’
1.5dB gain
4
‘0100’
2.0dB gain
5
‘0101’
2.5dB gain
6
‘0110’
3.0dB gain
7
‘0111’
3.5dB gain
8
‘1000’
4.0dB gain
9
‘1001’
4.5dB gain
10
‘1010’
5.0dB gain
11
‘1011’
5.5dB gain
12
‘1100’
6.0dB gain
ADC Chab Register 8 0x38
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Fine Gain Adjustment ChB
Default
‘0’
‘0000000’
1
Reserved
Test Patterns ChB
Default
‘00000’
‘000’
ADC Chab Register 8 0x38
Setting
Bit 6:0
Description Fine Gain ChB.
0
128 steps for a range of 0.134dB
Setting
Bit 10:8
Description Test Patterns ChB
0
‘000’
Normal Mode of Operation
1
‘001’
Outputs all zeroes
2
‘010’
Outputs all ones
3
‘011’
Outputs toggle pattern (0x1555 and 0x2AAA)
4
‘100’
Outputs digital ramp (0->16383)
5
‘101’
Outputs custom pattern
ADC Chab Register 9 0x39
ADC Chab Register 8 0x38.
ADC Chab Register 9 0x39.
User Manual SMT941 Page 32 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 33

Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Offset Pedestal ChB (Common)
Default
‘00’
1
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
ADC Chab Register 9 0x39
Setting
Bit 5:0
Description Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
0
‘011111’
Pedestal=+31LSBs
1
‘011110’
Pedestal=+30LSBs
2
…
… 3 ‘000000’
Pedestal=0
4
…
… 5 ‘111111’
Pedestal=-1LSB
6
‘111110’
Pedestal=-2LSB
7
…
… 8 ‘100000’
-32LSBs
ADC Chcd Register 0 0x40
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
1
Reserved
Enable Low
Speed
Mode
Reserved
Default
‘00000’
‘0’
‘00’
0
Software
Reset
Reserved
SerialRead
Out
Default
‘0’
‘000000’
‘0’
ADC Chcd Register 0 0x40
Setting
Bit 0
Description SerialReadOut
0
‘0’
Serial readout disabled.
1
‘1’
Serial readout enabled.
Setting
Bit 7
Description - Software Reset
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation.
1
‘1’
Resets all internal registers and self-clears to ‘0’.
Setting
Bit 10
Description - Enable Low Speed Mode
0
‘0’
Low Speed Mode disabled. Sampling rates >100MSPS.
0
‘1’
Low Speed Mode enabled. Sampling rates <=100 MSPS.
ADC Chcd Register 0 0x40.
ADC Chcd Register 1 0x41.
User Manual SMT941 Page 33 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 34

ADC Chcd Register 1 0x41
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Reference
Reserved
Standby
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘00’
‘000’
‘0’
‘0’
1
Reserved
PowerDownModes
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
ADC Chcd Register 1 0x41
Setting
Bit 1
Description Standby.
0
‘0’
Normal mode of operation.
1
‘1’
Both ADC channels are put into standby mode (internal ref and output buffers still
active).
Setting
Bit 6:5
Description Reference.
0
‘01’
Internal Reference enabled.
1
‘11’
External Reference enabled.
Setting
Bit 11:8
Description Power down modes.
0
‘0000’
Pins ctrl1, 2 and 3 determine power down modes.
1
‘1000’
Normal mode of operation.
2
‘1001’
Output buffers disabled for channelB.
3
‘1010’
Output buffers disabled for channelA.
4
‘1011’
Output buffers disabled for channelA and B.
5
‘1100’
Global power down.
6
‘1101’
ChannelB in standby.
7
‘1110’
ChannelA in standby.
ADC Chcd Register 2 0x42
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
LVDS_CM
OS
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘0000000’
1
Clock Edge Control (rising edge)
Clock Edge Control (falling edge)
Reserved
Default
‘000’
‘000’
‘00’
ADC Chcd Register 2 0x42
Setting
Bit 7
Description LVDS_CMOS
0
‘0’
Parallel CMOS interface.
1
‘1’
DDR LVDS interface.
Setting
Bit 12:10
Description Clock output Edge control (falling edge)
0
‘000’,’100’
Default output clock position.
1
‘101’
Falling edge shifted by +(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
2
‘110’
Falling edge shifted by -(6/26)/Sampling Frequency
ADC Chcd Register 2 0x42.
User Manual SMT941 Page 34 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 35

3
‘111’
Falling edge shifted by -(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
Setting
Bit 15:13
Description Clock output Edge control (rising edge)
0
‘000’,’100’
Default output clock position.
1
‘101’
Rising edge shifted by +(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
2
‘110’
Rising edge shifted by -(6/26)/Sampling Frequency
3
‘111’
Rising edge shifted by -(4/26)/Sampling Frequency
ADC Chcd Register 3 0x43
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Channel
Control
Reserved
Data Format
Reserved
Default
’0’
‘0’
‘000’
‘00’
‘0’
1
Custom Pattern (lsb)
Default
‘00000000’
ADC Chcd Register 3 0x43
Setting
Bit 2:1
Description Data Format
0
‘10’
2’s complement.
1
‘11’
Binary.
Setting
Bit 6
Description - Channel Control
0
‘0’
Common Control.
1
‘1’
Independent Control (Test pattern, Offset correction and SNR boost).
Setting
Bit 15:8
Description Custom Pattern (lsb)
0
ADC Chcd Register 4 0x44
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Custom Pattern (msb)
Default
‘00’
‘000000’
1
Reserved
Offset
Correctio
n Enable
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘000000’
ADC Chcd Register 4 0x44
Setting
Bit 5:0
Description Custom Pattern (msb).
0
Setting
Bit 14
Description Offset Correction Enable ChA.
ADC Chcd Register 3 0x43.
ADC Chcd Register 4 0x44.
User Manual SMT941 Page 35 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 36

0
‘0’
Offset Correction Disabled.
1
‘1’
Offset Correction Enabled.
ADC Chcd Register 5 0x45
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Gain ChA (Common)
Offset Correction Time Constant ChA
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
1
Reserved
Fine Gain Adjustment ChA (Common)
Default
‘0’
‘0000000’
ADC Chcd Register 5 0x45
Setting
Bit 3:0
Description Offset Correction Time Constant (number of clock cycles) ChA
0
‘0000’
256k 1 ‘0001’
512k 2 ‘0010’
1Meg 3 ‘0011’
2Meg 4 ‘0100’
4Meg 5 ‘0101’
8Meg 6 ‘0110’
16Meg
7
‘0111’
32Meg
8
‘1000’
64Meg
9
‘1001’
128Meg
10
‘1010’
256Meg
11
‘1011’
512Meg
Setting
Bit 7:4
Description Gain ChA (Common).
0
‘0000’
0dB gain
1
‘0001’
0.5dB gain
2
‘0010’
1.0dB gain
3
‘0011’
1.5dB gain
4
‘0100’
2.0dB gain
5
‘0101’
2.5dB gain
6
‘0110’
3.0dB gain
7
‘0111’
3.5dB gain
8
‘1000’
4.0dB gain
9
‘1001’
4.5dB gain
10
‘1010’
5.0dB gain
11
‘1011’
5.5dB gain
12
‘1100’
6.0dB gain
Setting
Bit 14:8
Description Fine Gain ChA (Common).
ADC Chcd Register 5 0x45.
User Manual SMT941 Page 36 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 37

0
128 steps for a range of 0.134dB
ADC Chcd Register 6 0x46
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Test Patterns ChA
Default
‘00000’
‘000’
1
Reserved
Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
Default
‘00’
ADC Chcd Register 6 0x46
Setting
Bit 2:0
Description Test Patterns ChA
0
‘000’
Normal Mode of Operation
1
‘001’
Outputs all zeroes
2
‘010’
Outputs all ones
3
‘011’
Outputs toggle pattern (0x1555 and 0x2AAA)
4
‘100’
Outputs digital ramp (0->16383)
5
‘101’
Outputs custom pattern
Setting
Bit 13:8
Description Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
0
‘011111’
Pedestal=+31LSBs
1
‘011110’
Pedestal=+30LSBs
2
…
… 3 ‘000000’
Pedestal=0
4
…
… 5 ‘111111’
Pedestal=-1LSB
6
‘111110’
Pedestal=-2LSB
7
…
… 8 ‘100000’
-32LSBs
ADC Chcd Register 7 0x47
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Offset
Correctio
n Enable
ChB
Reserved
Default
‘0’
‘0’
‘000000’
1
Gain ChB (Common)
Offset Correction Time Constant ChB
Default
‘0000’
‘0000’
ADC Chcd Register 6 0x46.
ADC Chcd Register 7 0x47.
User Manual SMT941 Page 37 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 38

ADC Chcd Register 7 0x47
Setting
Bit 6
Description Offset Correction Enable ChB.
0
‘0’
Offset Correction Disabled.
1
‘1’
Offset Correction Enabled.
Setting
Bit 11:8
Description Offset Correction Time Constant (number of clock cycles) ChB
0
‘0000’
256k 1 ‘0001’
512k 2 ‘0010’
1Meg 3 ‘0011’
2Meg 4 ‘0100’
4Meg 5 ‘0101’
8Meg 6 ‘0110’
16Meg
7
‘0111’
32Meg
8
‘1000’
64Meg
9
‘1001’
128Meg
10
‘1010’
256Meg
11
‘1011’
512Meg
Setting
Bit 15:12
Description Gain ChB (Common).
0
‘0000’
0dB gain
1
‘0001’
0.5dB gain
2
‘0010’
1.0dB gain
3
‘0011’
1.5dB gain
4
‘0100’
2.0dB gain
5
‘0101’
2.5dB gain
6
‘0110’
3.0dB gain
7
‘0111’
3.5dB gain
8
‘1000’
4.0dB gain
9
‘1001’
4.5dB gain
10
‘1010’
5.0dB gain
11
‘1011’
5.5dB gain
12
‘1100’
6.0dB gain
ADC Chcd Register 8 0x48
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Fine Gain Adjustment ChB
Default
‘0’
‘0000000’
1
Reserved
Test Patterns ChB
Default
‘00000’
‘000’
ADC Chcd Register 8 0x48
Setting
Bit 6:0
Description Fine Gain ChB.
ADC Chcd Register 8 0x48.
User Manual SMT941 Page 38 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 39

0
128 steps for a range of 0.134dB
Setting
Bit 10:8
Description Test Patterns ChB
0
‘000’
Normal Mode of Operation
1
‘001’
Outputs all zeroes
2
‘010’
Outputs all ones
3
‘011’
Outputs toggle pattern (0x1555 and 0x2AAA)
4
‘100’
Outputs digital ramp (0->16383)
5
‘101’
Outputs custom pattern
ADC Chcd Register 9 0x49
Byte
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Reserved
Offset Pedestal ChB (Common)
Default
‘00’
1
Reserved
Default
‘00000000’
ADC Chcd Register 9 0x49
Setting
Bit 5:0
Description Offset Pedestal ChA (Common)
0
‘011111’
Pedestal=+31LSBs
1
‘011110’
Pedestal=+30LSBs
2
…
… 3 ‘000000’
Pedestal=0
4
…
… 5 ‘111111’
Pedestal=-1LSB
6
‘111110’
Pedestal=-2LSB
7
…
… 8 ‘100000’
-32LSBs
ADC Chcd Register 9 0x49.
User Manual SMT941 Page 39 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 40

3 PCB Layout
3.1 Top View
3.2 Bottom View
User Manual SMT941 Page 40 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 41

Connector name
(silkscreen and
schematics)
Description
Location on the board
J16
ADCA Analog Input
Top / Left
J15
ADCB Analog Input
Top / Left
J1016
ADCC Analog Input
Top / Right
J1015
ADCD Analog Input
Top / Right
J30
External Reference Input
Bottom / Right
J29
External Clock Input
Bottom / Left
J4
External Clock Output
Bottom / Left
J24
External Trigger
Bottom / Left
4 Connectors
4.1 Description
The following table gathers all connectors on the board and describes their
function.
User Manual SMT941 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 42

4.2 Location on the board
Figure 7 - Connectors
User Manual SMT941 Page 42 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
Page 43

Dimensions
63.5mm x 106.7mm x 18mm
Weight
Tbc - 35 grams
Supply Voltages
Supply Current
+12V
N/A
+5V
tbd
+3.3V
tbd
-5V
N/A
-12V
N/A
MTBF
tbd
5 Physical Properties
6 Safety
This module presents no hazard to the user when in normal use.
7 Ordering Information
SMT941 (Standard Product): ADC inputs are AC-coupled.
8 EMC
This module is designed to operate from within an enclosed host system, which is
build to provide EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is not
guaranteed unless it is installed within an adequate host system.
This module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients originating from
outside the host system which may be introduced through the output cables.
Short circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up
or reboot.
User Manual SMT941 Page 43 of 43 Last Edited: 23/08/2011 17:24:00
 Loading...
Loading...