Page 1

SMT8090
User Manual
User Manual (QCF42); Version 3.0, 8/11/00; © Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd. 1999
Page 2
Version 0.9 Page 2 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Revision History
Date Comments Engineer Version
18/02/04 First release PSR 0.9
Page 3

Version 0.9 Page 3 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Table of Contents
Revision History.......................................................................................................... 2
Table of Contents ....................................................................................................... 3
Contacting Sundance. ................................................................................................ 4
Notes. ......................................................................................................................... 4
Precautions................................................................................................................. 4
Outline description...................................................................................................... 5
Architecture. ............................................................................................................... 6
Hardware involved...................................................................................................... 7
Hardware installation. ................................................................................................. 7
Software applications. ................................................................................................ 9
3L application.......................................................................................................... 9
Description of the functions in the test software menu............................................ 9
“Resetting SMT390 FPGA”.................................................................................. 9
“SMT390 FPGA DLLs Reset” .............................................................................. 9
“Configuring Clock Synthesizers” ........................................................................ 9
“Clock Selection” ............................................................................................... 10
“ADC Output Format” ........................................................................................ 10
“Capture Data – Both Channels” ....................................................................... 10
Matlab application ............................................................................................. 10
Pegasus application (to be done).......................................................................... 10
Page 4

Version 0.9 Page 4 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Contacting Sundance.
You can contact Sundance for additional information by sending email to
support@sundance.com
.
Notes.
- SHB stands for Sundance High-speed Bus.
- CommPort denotes an 8-bit communication port following the TI C4x
standards.
Precautions
In order to guarantee that Sundance’s boards function correctly and to protect the
module from damage, the following precautions should be taken:
- They are static sensitive products and should be handled accordingly.
Always place the modules in a static protective bag during storage and
transition.
- When operating, make sure that the heat generated by the system is
extracted e.g. a fan extracting heat or air blower. It is vital for the SMT390
daughter module.
Page 5

Version 0.9 Page 5 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Outline description.
The SMT8090 is a dual-C6713 based module (SMT374) combined with a dual highspeed ADC module (SMT390).
SMT374 characteristics:
⇒ Dual TMS320C6713 processor running at 225MHz
⇒ Six 20MB/s communication ports (comm.-ports)
⇒ 128MBytes of SDRAM (100MHz)
⇒ 8MByte Flash ROM for boot code and FPGA programming
⇒ Global expansion connector
⇒ General purpose I/O connector
⇒ High bandwidth data I/O via 2 Sundance High-speed Buses (SHB).
SMT390 characteristics:
⇒ Two 12-bit ADCs (AD9430-210
) sampling at up to 210MHz,
⇒ Two Sundance High-speed Bus (SHB) connectors,
⇒ Two 4-channel Rocket Serial Link (RSL
) connector – 2.5Gbits/second each,
⇒ Two 20 MegaByte/s communication ports,
⇒ Low-jitter on-board system clock,
⇒ Xilinx Virtex-II Pro FPGA,
⇒ 50-Ohm terminated analogue inputs and outputs, external triggers and
clocks via MMCX (Huber and Suhner) connectors,
⇒ User defined pins for external connections,
⇒ Compatible with a wide range of Sundance SHB modules,
⇒ TIM standard compatible.
The SMT8090 is a demonstration software for the evaluation of the SMT374 and
rd
SMT390 modules. It can be used for prototyping 3G (3
generation) systems and
high-speed data acquisition system with or without digital processor. This document
is an installation guide for the SMT8090 demonstration system.
The SMT8090 application gets the DSP on the SMT374 to configure the SMT390
FPGA and control clock frequencies, clock routings, data format and data capture.
The DSP grabs data from both channels and stores them into a file, which can be
read by a Matlab application for data displaying and FFT processing.
Page 6

Version 0.9 Page 6 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Architecture.
The following diagram shows the architecture of the SMT8090 system:
Analogue
Connection
SMT374
Module #1
Global Bus
Connection
DSP
TIM site 1
Data
SMT516
Data
SHB
Connection
SMT390
DAQ
Module #2
TIM site 2
Control
Comm
Port
Data
SDB
Connection
Spare
TIM site 3
Data
Comm
Port
Spare
MMCX to BNC cables
Processing
SMT310Q
TIM site 4
PC
Host
Page 7

Version 0.9 Page 7 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Hardware involved.
The SMT8090 is built around two main modules but also involves a carrier board and
some cables to interconnect them and allow them to communicate with each other
and to access the PC.
⇒ 1x SMT310Q: PCI carrier
⇒ 1x SMT374: Dual-C6713 based module; to be plugged on site 1 of
SMT310Q.
⇒ 1x SMT390: Dual-ADC module; to be plugged on site 2 of SMT310Q.
⇒ 1x FMS cable (20cm): to connect T1C0 to T2C3 at the back of the
SMT310Q.
⇒ 1x SMT516 (SHB to SHB PCB): to connect SHBA (SMT374) to SHBA
(SMT390).
⇒ 4x MMCX to BNC cables to connect an external analogue signal source to
J1 to J4 and an external clock source (when using external sampling clock) to J5 and
J6.
Hardware installation.
Here are the steps to follow to install the SMT8090 system.
1 – Place the SMT374 on TIM site 1 of the carrier board (SMT310Q).
2 – Place the SMT390 on TIM site 2 of the carrier board (SMT310Q).
3 – Make sure that the boards are firmly seated, then provide the 3.3V to the boards
by screwing in the bolts and screws through one of the mounting holes on the
SMT374 and SMT390.
4 – Connect CommPort 0 of the SMT374 to CommPort 3 of the SMT390 (T1C0 to
T2C3) via an FMS cable at the back of the SMT310Q.
5 – Connect SHBA on the SMT374 to SHBA on the SMT390 via the SMT516.
6 – Connect external sources to J1, J4, J5 and J6 via MMCX-BNC cables. Make sure
that the external signal meet the input characteristics of the SMT390 described in the
SMT390 User Manual.
7 – Place the carrier board in the host system.
Page 8
Version 0.9 Page 8 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
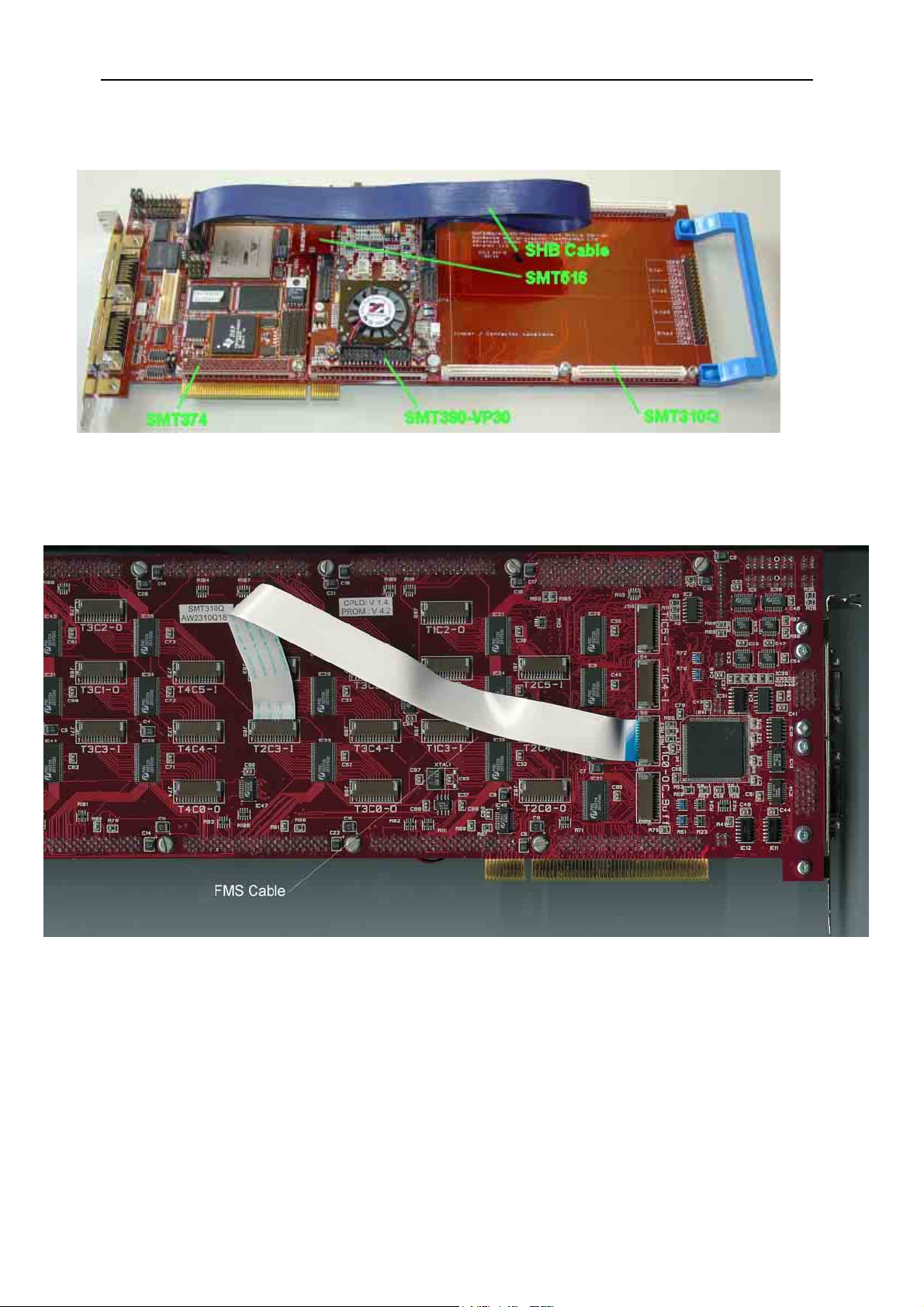
The following picture shows how connections are made at the top of the system:
The following picture shows the CommPort connection at the back of the SMT310Q.
Note that the FMS are ‘twisted’, i.e. one end should be blue and the other should
show silver pins.
Page 9

Version 0.9 Page 9 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
Software applications.
3L application.
In a sub-folder labelled 3L, you will find a C (Test.c), a configuration (Test.cfg) and a
make (nmake) files.
In a DOS prompt window, simply type nmake to generate the 3L application file,
which can be loaded into the SMT374 by using the 3L Server (3L Diamond needs to
be installed first).
This application allows the user to execute simple commands such as configuring the
ADC (output format and scale), the clock synthesizers, clock routing, capturing data,
etc.
Description of the functions in the test software menu.
The 3L application provided with the system allows the following option. Some will
prompt for a value. Before sending the control word to the SMT390. In some case
and where available, the internal control register is not only set up but also read-back
straight after to make sure it has been programmed properly. The value read-back is
displayed in the main window.
“Resetting SMT390 FPGA”
This command keeps the configuration of the FPGA but resets all its internal
registers.
“SMT390 FPGA DLLs Reset”
The FPGA implements two DLLs (one per ADC channel). When the sampling
frequency or the clock routing is being changed, DLLs can run out of step. To avoid
that problem and re-lock them, a DDL Reset operation is necessary. Writing any
value into the reset register will reset both DDLs.
“Configuring Clock Synthesizers”
This function loads with the value specified (in decimal, not hexadecimal) and starts
the on-board clock synthesizer.
Fsynthesized = M / N, with 200 < M < 400 and N=0 (div by 2), 1 (div by 4), 2 (div by
8) or 3 (div by 1).
For example, to generate 100 MHz: 400/4=100, which gives M=400 and N=4
M is coded on 9 bits and N on 2 bits. Here (400)d=(110010000)b and N=(2)d=(10)b
The value in binary is obtained by gathering N and M : 10110010000
Simply convert this value into decimal (1424) and enter it when prompted.
Page 10

Version 0.9 Page 10 of 10 SMT8090 User Manual
“Clock Selection”
This command routes the clocks to the ADC depending on whether they are external
or internal. Enter 0 for External, 1 for Internal or 2 for External from Opposite
Channel. The selection is prompted for Channel A first and then Channel B
“ADC Output Format”
The ADC can output the data in either binary or 2’s Complement format. The function
allows the selection and also the scale (half or full).
“Capture Data – Both Channels”
This command captures data from both channels, one after the other (not
simultaneously). Data are then stored into two separate files into the directory where
the application has been started. Files are called CAPTUREA0.txt and
CAPTUREB0.txt
Matlab application
In the same folder as the 3L application, you can find a Matlab application (test.m).
Under Matlab set up the current folder into the path in order for the application to
open the two data files and run the application.
It will open 4 windows, which are respectively ChannelA – Time Domain, ChannelA –
Frequency Domain, ChannelB – Time Domain and Channel B - frequency domain.
Once data are captured, you can launch the Matlab application, located on
Pegasus application (to be done).
The SMT8090 is also provided with a Pegasus application (Pegasus folder), which
shows the user the dynamic performance of the system.
 Loading...
Loading...