Page 1

SMT498
User Manual
User Manual; Version 1.2, 11/01/05; © Sundance Digital Signal Processing Inc. 2004
Page 1
Page 2
Revision History
Changes Made Issue Initials
5/31/05 First release 1.0 PTM
6/1/05 Updates based on feedback 1.1 PTM
11/1/05 Update on System ACE and JTAG 1.2 SM
Page 2
Page 3
List of Abbreviations
Abbreviation Explanation
ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
BOM Bill Of Materials
CMC Common Mezzanine Card
Comport Communications Port
DSP Digital Signal Processor
FPDP Front Panel Data Port
FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
NA Not Applicable
OTP One-Time Programmable
PC Personal Computer
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect
PMC PCI Mezzanine Card
PrPMC Processor PMC
SDB Sundance Digital Bus
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
SHB Sundance High-speed Bus
SMT Sundance Multiprocessor Technology
TBD To Be Determined
TI Texas Instruments
Page 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Introduction........................................................................................................................... 7
Overview............................................................................................................................. 7
Module Features................................................................................................................. 7
Related Documents ............................................................................................................ 7
Block Diagram.......................................................................................................................8
Mechanical Standard............................................................................................................ 8
SMT498 Support.................................................................................................................... 9
SMT498 Installation .............................................................................................................. 9
QL5064................................................................................................................................. 10
Local bus........................................................................................................................... 10
Virtex FPGA configuration ................................................................................................ 11
Virtex FPGA design .......................................................................................................... 11
Virtex II FPGA...................................................................................................................... 12
FPGA Block Diagram........................................................................................................12
Configuration..................................................................................................................... 12
Memory............................................................................................................................. 12
SHBs................................................................................................................................. 13
SHB Connectors ........................................................................................................... 13
SHB Cable Assembly.................................................................................................... 14
SHB Inter Modules solutions......................................................................................... 14
Half Word Interface (16-bit SHB Interface) ................................................................... 14
RSLs .................................................................................................................................15
RSL Connector.............................................................................................................. 15
RSL Cable Assembly.................................................................................................... 15
Miscellaneous I/O’s........................................................................................................... 16
System ACE SC................................................................................................................... 17
PROM ...............................................................................................................................17
Configuration Controller.................................................................................................... 17
Flash.................................................................................................................................17
Power Supplies ................................................................................................................... 18
DC/DC converter............................................................................................................... 18
Linear Voltage regulator.................................................................................................... 18
Daughter Module................................................................................................................. 19
PMC Standard ..................................................................................................................... 20
Voltage keying .................................................................................................................. 20
Connectors........................................................................................................................ 20
Page 4
Page 5

Component heights........................................................................................................... 20
Board Weight .................................................................................................................... 20
Standoffs........................................................................................................................... 20
Bezel and I/O capability .................................................................................................... 20
Power consumption .......................................................................................................... 20
Grounding ......................................................................................................................... 21
Conduction Cooling........................................................................................................... 21
Power Supply.................................................................................................................... 21
Standalone operation........................................................................................................ 21
Only use this connector for standalone operation (i.e. when not plugged into a PCI slot)!21
Reset Structure................................................................................................................. 21
Header Pinout...................................................................................................................... 22
PCI.................................................................................................................................... 22
SHBs................................................................................................................................. 24
RSL Header ...................................................................................................................... 26
RSL Side 1 Pinout (LVDS only) .................................................................................... 26
RSL Side 2 Pinout (LVDS only) .................................................................................... 26
JTAG headers................................................................................................................... 27
Power connector............................................................................................................... 28
PCB Layout.......................................................................................................................... 28
Safety................................................................................................................................... 29
EMC...................................................................................................................................... 30
Appendix.............................................................................................................................. 30
Configuring the FPGA....................................................................................................... 31
PCI Mode...................................................................................................................... 31
JTAG/Boundary Scan ................................................................................................... 32
System ACE SC............................................................................................................ 33
Status Bit Encoding:.................................................................................................. 34
Creating System ACE programming file (.MPM)............................................................... 35
Page 5
Page 6

Table of Figures
Figure 1 - Block diagram of the SMT498................................................................................8
Figure 2 – Single-Size PMC card (from IEEE 1386-2001)...................................................... 8
Figure 3 – QL5064 Connection............................................................................................. 10
Figure 4 - Default FPGA Configuration................................................................................. 12
Figure 5 – SHB Connector.................................................................................................... 13
Figure 6 – RSL Top Connector............................................................................................. 15
Figure 7 - RSL Bottom Connector........................................................................................ 15
Figure 8 – Location of JTAG IN, OUT and DIP Switches ..................................................... 27
Figure 9 - Module Side 1 View............................................................................................. 29
Figure 10 – Module Side 2 View........................................................................................... 29
Figure 11 – Module Side View.............................................................................................. 29
Figure 12 - Location of the DIP Switches and the PROM..................................................... 31
Table of Tables
Table 1 - SHB configuration Matrix....................................................................................... 14
Table 2 – RSL Speed VS FPGA Speed Grade..................................................................... 16
Table 3 – Board Clocks......................................................................................................... 16
Table 4 – PMC P11/P12 Interface........................................................................................23
Table 5 – PMC P13/P14 Interface........................................................................................24
Table 6 – SHB Interface........................................................................................................ 25
Table 7 – RSL Side 1 Pinout................................................................................................. 26
Table 8 – RSL Side 2 Pinout................................................................................................. 26
Table 9 – JTAG Header Pinout............................................................................................. 27
Table 10 – Status Bits Encoding........................................................................................... 34
Page 6
Page 7

Introduction
Overview
The SMT498 is Sundance’s latest FPGA PrPMC module. This module uses a Xilinx Virtex II
Pro XC2VP100, which is configured to provide two comport links, five SHB’s, two RSL’s and
other functions.
Module Features
The main features of the SMT498 are listed below:
Xilinx
128MB of DDR2 SDRAM
Five
In System Configuration using System ACE Soft Controller
Tall single-size PrPMC module
66MHz 64-bit PCI interface with over 500MB/s data rate
Virtex II Pro XC2VP100 (FF1704 package)
SHB, two RSL, and two 8-bit Comport interfaces for easy interconnection to
Sundance products
Related Documents
[1] PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC) Spec – IEEE.
http://shop.ieee.org/store/product.asp?prodno=SS94922
[2] Sundance High-speed Bus (SHB) specifications – Sundance.
http://sundance.com/docs/SHB%20Technical%20Specification.pdf
[3] Rocket Serial Link (RSL) specifications – Sundance.
http://sundance.com/docs/RSL%20%20Technical%20Specification%20Rev01%20Iss03.pdf
[4] Processor PMC (PrPMC) Spec – VITA.
http://www.vita.com/
[5] System ACE SC Solution Datasheet – Xilinx.
http://direct.xilinx.com/bvdocs/publications/ds088.pdf
Page 7
Page 8
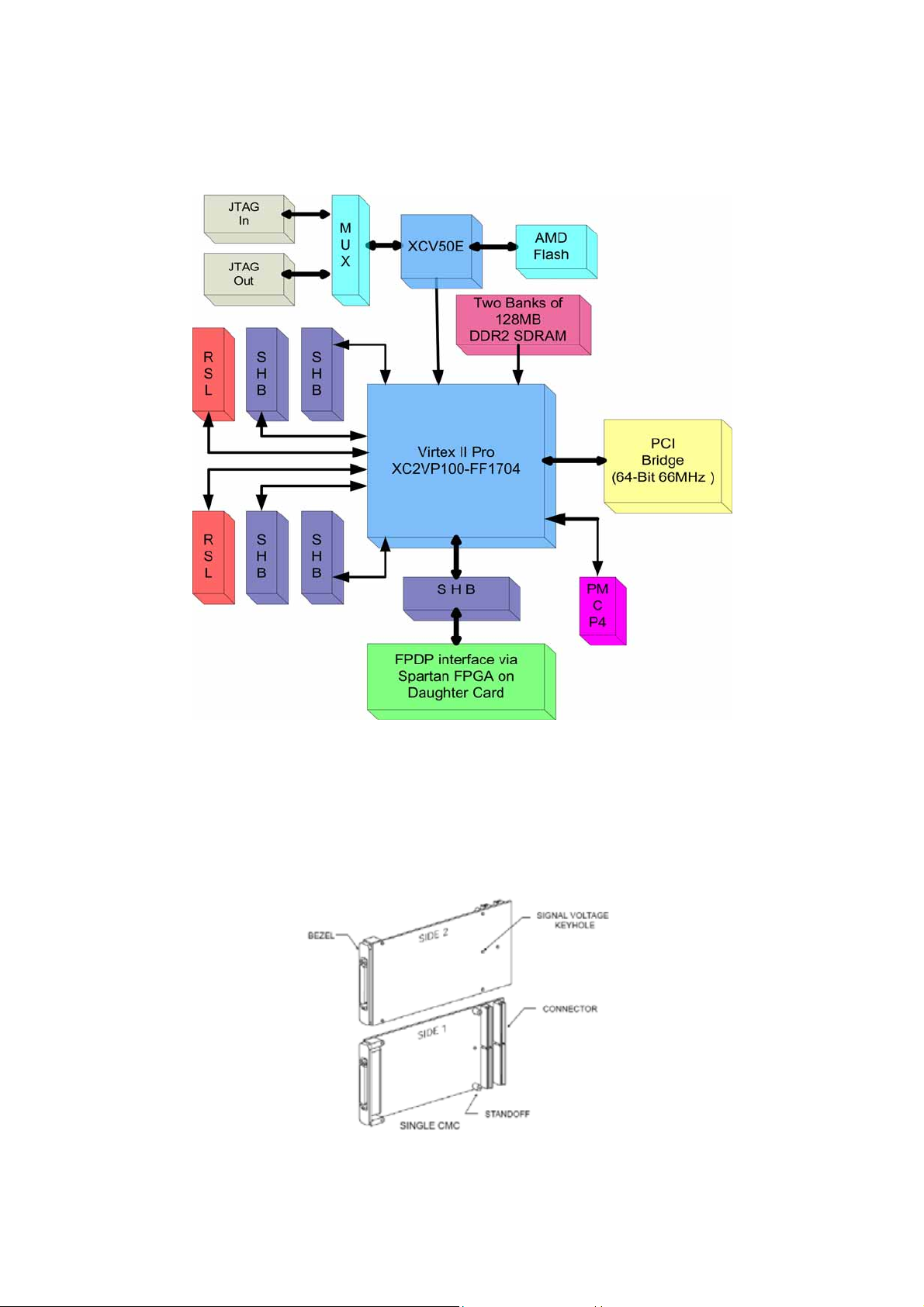
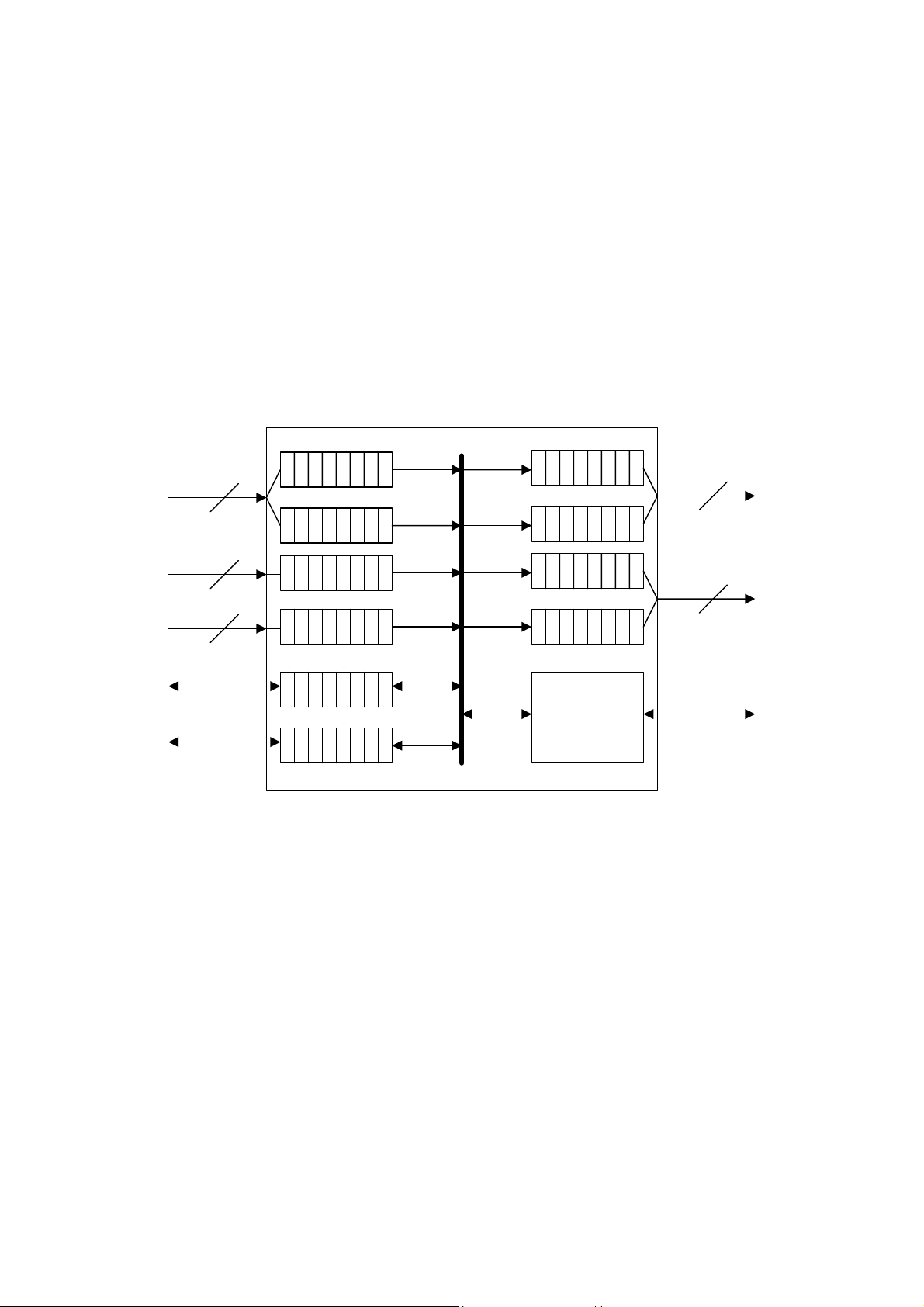
Block Diagram
The following diagram shows the block diagram of the SMT498.
Figure 1 - Block diagram of the SMT498.
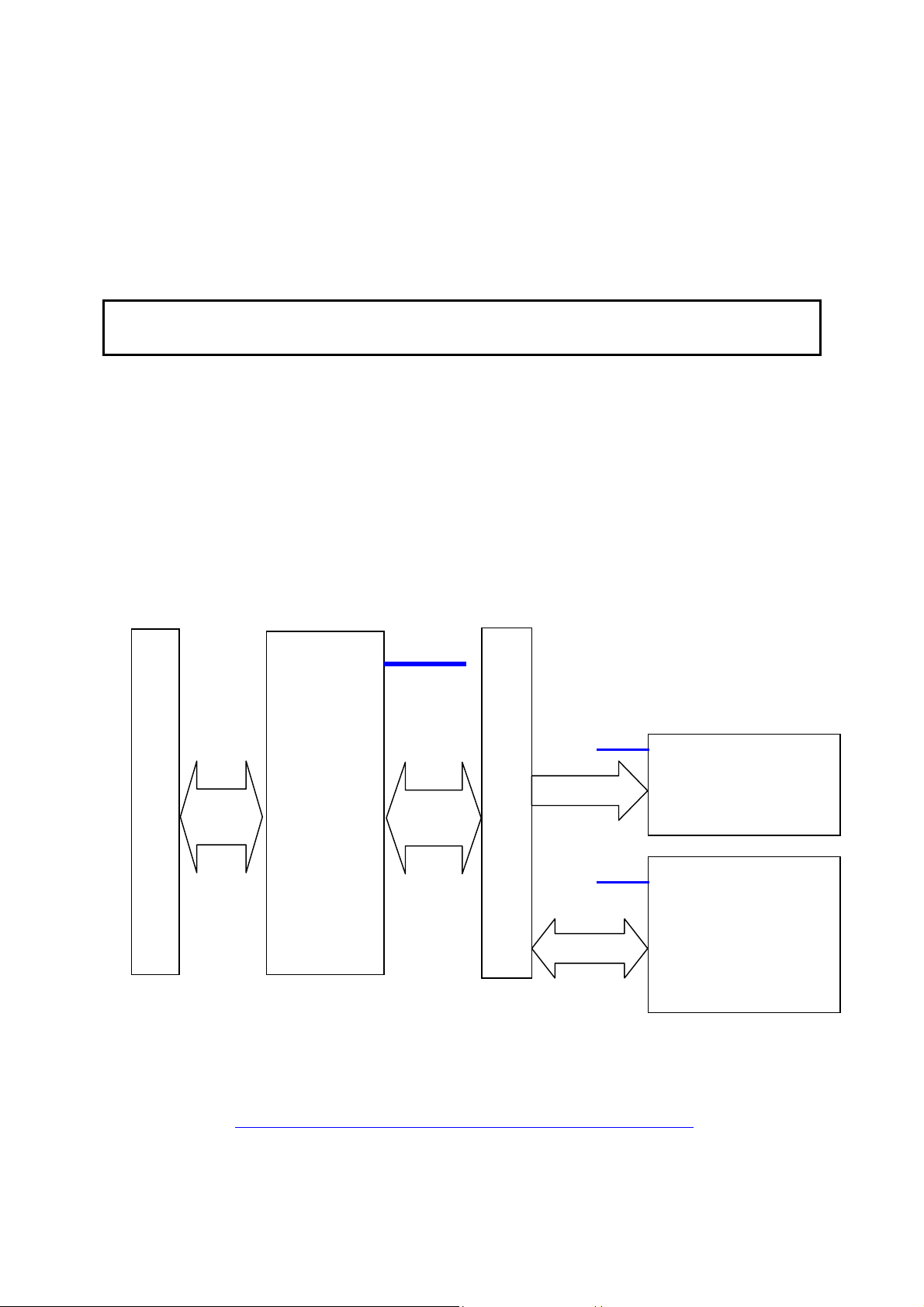
Mechanical Standard
PMC is a variant of CMC that uses PCI to communicate over the backplane. The
IEEE CMC standard describes both single- and double-size mezzanine cards.
SMT498 will be a single-size card.
Figure 2 – Single-Size PMC card (from IEEE 1386-2001)
Page 8
Page 9

Dimensions of the single-size CMC are 74.0mm wide by 149.0mm deep.
SMT498 Support
The SMT498 is supported by the SMT6041-498 software package available from
SUNDANCE. Please register on the SUNDANCE Support Forum if not yet
registered. Then enter your company’s forum and you can request the SMT6041-498
from there.
SMT498 Installation
Do NOT connect any external TTL (5v) signals to the SMT498 I/Os, which
connect directly to the FPGA, as the FPGA is NOT 5v tolerant. However the
lines on connector P14 of the carrier board are made 5V tolerant for some
applications.
You can fit the SMT498 on its own on any PMC compatible carrier board. When
mated with a carrier board such as Twin Industries Xtend1000, it may then be
plugged into a host computer (e.g. Windows PC).
Please, follow these steps to install the SMT498 module on a Host system:
1. Remove the carrier board from the host system.
2. Place the SMT498 module on a PMC site. (See your carrier board User
Manual.)Make sure that the board is firmly seated before screwing the
SMT498 to the two main mounting holes. Use 10mm M3 Standoffs (Digikey
4391K-ND) and M3 5mm bolts (Digikey H742-ND) to secure the module to
any carrier card.
3. Connect the SHB and/or RSL cables to the SMT498 (if required by your
application).
4. Install the carrier board in the host system and start the PC.
5. The SMT498 can also be used as a standalone FPGA board. Connect a
molex power connector similar to the one used for the hard disk to provide 5V.
(Note only 5V should be provided, do not provide 12 V)
Page 9
Page 10
QL5064
The PCI bridge chip from QuickLogic is installed on a SMT498.
This device combines a 66MHz/64-bit PCI Master/Target ASIC core with a one-time
programmable (OTP) FPGA fabric.
The configuration of the FPGA fabric in the QL5064 is performed prior to
manufacturing of the module and cannot be changed by the user.
Local bus
QL5064 provides a bridge between the PCI bus of the host system and the Local
bus of the SMT498. This interface will allow software on the host PC to transfer data
to and from the other interfaces in this design. The interface between the FPGA and
PCI bridge is clocked at a speed of 64MHz with a data bus width of 64 bits.
There are two primary functions of the Local bus on SMT498:
1) Configuration of the Virtex FPGA
2) Communication with logic designs loaded in the Virtex FPGA
CS[3..0]
CS[0]
64-Bit/
66 MHz
PCI BUS
QL5064
64-Bit/
64 MHz
8/64-Bit
Local Bus
Virtex FPGA
Config / User
Defined
CS[3..1]
64-Bit
User Defined
Figure 3 – QL5064 Connection
More information about the Local bus interface and protocols can be obtained from
QuickLogic at:
http://www.quicklogic.com/images/QL5064_CD_UM.pdf
Page 10
Page 11

Virtex FPGA configuration
Programming of the Virtex FPGA can be achieved over the PCI bus using the
SelectMAP interface. This interface is 8-bits wide and runs at the full speed of the
Local bus. By simply writing a stream of configuration bytes to the location at CS[0]
the FPGA can be programmed.
An example of this is provided in the SMT6041-498 software package available from
SUNDANCE.
Virtex FPGA design
Once the FPGA has been programmed the user may then communicate with the
design by means of CS regions 1, 2 and 3. 12 address lines allow for a total
addressable space of 4kB per CS region. Accesses to these regions may be up to
64-bits wide.
An example of this is provided in the SMT6041-498 software package available from
SUNDANCE
Page 11
Page 12
Virtex II FPGA
The module can be fitted with an XC2VP70 or XC2VP100 FPGA. Only flip-chip
FF1152 package will fit on this board. The choice of FPGA will be price/performance
driven.
This Xilinx Virtex II Pro, is responsible for the provision of 5 SHBs, 2 Comports via
the SHB user IO pins, a PCI Local bus interface, and 14 RSLs (see Ordering
Information).
FPGA Block Diagram
SHBA
16-bit SDB
60
16-bit SDB
16-bit SDB
16-bit SDB
SHBC
60
SHBB
60
32-bit SDB
SHBE
32-bit SDB
60
16-bit SDB
16-bit SDB
SHBD
60
Com p o r t A
Com p o r t B
Comport
Local Bus
Interface
QuickLogic
Comport
Figure 4 - Default FPGA Configuration
Configuration
The FPGA can be configured in three different ways:
•Loading the FPGA on power up from flash on the board using System ACE SC.
•Using the SMT6041-498 utility to load the FPGA over the PCI bus.
•Using the on-board JTAG header and Xilinx JTAG programming tools.
(See the Appendix for full details)
Memory
Two banks of DDR SDRAM are attached directly to the FPGA for storage of
incoming data. Each bank consists of two 133 MHz DDR SDRAM components
(Micron MT46V32M16FN or equivalent) providing a total of 128 MB of storage
capacity on the module.
Page 12
Page 13

SHBs
SHB Connectors
The SMT498 includes five 60-pin connectors to provide SHB communication to the
outside world.
All 60 pins of each SHB connector are routed to the FPGA.
Figure 5 – SHB Connector
Features:
High-speed socket strip: QSH-030-01-L-D-A-K on the SMT498, mates with QTH-
030-01-L-D-A-K
QTH are used for cable assembly or PCB connecting 2 PMCs.
Centreline: 0.5mm (0.0197”) QSH Connector
An adapter is available for Agilent probes for the 16760A Logic Analyser.
The 2 probes supported are the E5378A 100-pin Single-ended Probe and the
E5386A Half Channel Adapter with E5378A.
The SMT498 can include five Sundance High-speed Bus (SHB) interfaces, three on
PMC Side 1 and two on PMC Side 2. They are connected directly to the FPGA
device, and can support data rates of 100MHz.
Two of the SHBs on Side 1 are wired to support LVDS. Each of these connectors
can support 28 pairs of LVDS data including 1 pair for clock input. Due to a lack of
clock inputs on the FPGA, only SHBA fully supports 2x16-bit SDB mode. All SHBs
fully support 32-bit mode. See Table 1 for details.
SHB 16-bit SDB
capable?
32-bit SDB
capable?
LVDS capable?
A 2xTX/RX TX/RX No
B 2xTX, 1xRX TX/RX TX/RX
C 2xTX, 1xRX TX/RX No
Page 13
Page 14

D 2xTX, 1xRX TX/RX No
E 2xTX, 1xRX TX/RX TX/RX
Table 1 - SHB configuration Matrix
The demo logic will configure SHBA, SHBB, SHBE as receivers, while SHBC and
SHBD are transmitters. As SHBA is the only SHB that can support two 16-bit SDB
receivers, it will be configured for that implementation. The rest of the SHBs either
support 32-bit SDBs or 16-bit SDB transmitters. See Figure 4 for details.
SHB Cable Assembly
The cable is custom made by Precision Interconnect and a cable assembly solution
builder can be found at:
http://www.precisionint.com/tdibrsb/content/howtouse.asp
SHB Inter Modules solutions
High-speed data transfer can be achieved between PMC modules thanks to the use
of a 60-way flat ribbon micro-coax cable or via PCB connections.
As a result, NO DIFFERENTIAL lines are required to transfer data on long distances
and at speeds in excess of 100MHz, which allows the full use of the SHB connector
60 pins.
Half Word Interface (16-bit SHB Interface)
The SHB connectors provide connections to the external world. You can implement
your own interface to transfer data over using these connectors, but if you want to
communicate with other Sundance modules, you can implement a Half Word (Hw)
interface sitting on 25 pins of an SHB connector.
The SHBs are parallel communication links for synchronous transmission. An SHB
interface is derived from the SDB interface which is a 16-bit wide synchronous
communication interface. (SUNDANCE SDB specification)
The differences are:
• The SHB interface can be made Byte (8 bits), Half Word (16 bits) or Word (32
bits) wide.
• The transfer rate can be increased thanks to better quality interconnect.
As an example, let us consider the Half Word (Hw) SHB interface.
You can implement 2 x 16-bit SHB interfaces per SHB connector, and have some
spare signals for User defined functions. (no differential lines are needed thanks to
our SHB cable assembly described in SHB Cable Assembly).
You must refer to the latest SUNDANCE SDB specification for technical information
on how it works.
Page 14
Page 15
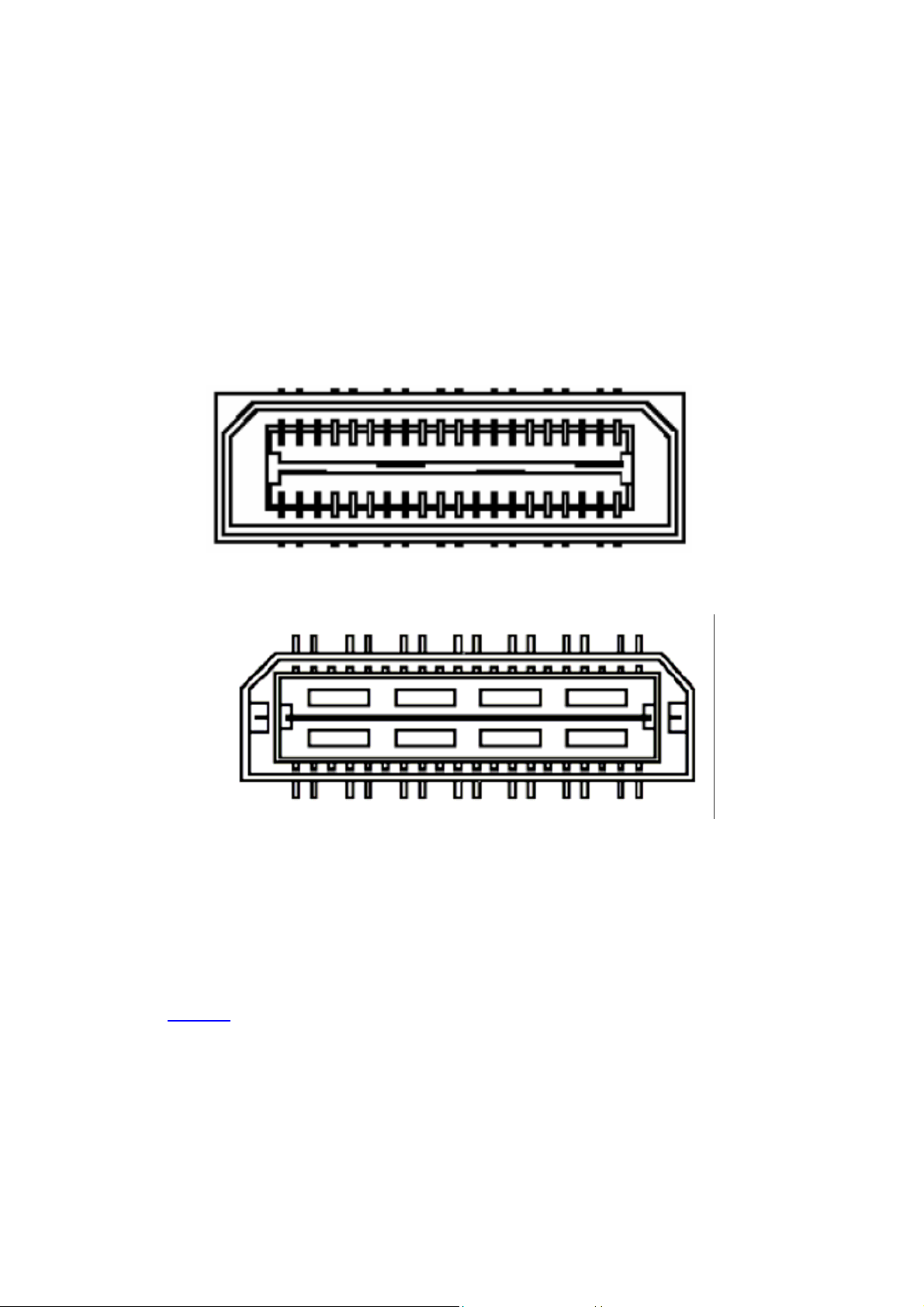
RSLs
RSL Connector
The SMT498 includes two 28-pin (7-pair) RSL connectors.
28 pins (7 pairs) of each RSL connector (52 total) are routed to the FPGA
Figure 6 – RSL Top Connector
Figure 7 - RSL Bottom Connector
Features:
• High-speed socket strip: QSE-014-xx-DP on the SMT407 Side 1, mates with
QTE-014-xx-DP
• High-speed socket strip: QTE-014-xx-DP on the SMT407 Side 2, mates with
QSE-014-xx-DP
•
Samtec for details.
RSL Cable Assembly
Cable assemblies with QTE connectors on one side and QSE on the other are like
the flexible versions of the PCB adapters mentioned above.
RSL Interface
Page 15
Page 16

The RSL connectors are the fastest FPGA connections available on SMT498.
As RSL are based on RocketIO transceiver blocks, the speed is limited by the speed
grade of FPGA installed:
Table 2 – RSL Speed VS FPGA Speed Grade
Based on the above, the 14 bi-directional links of SMT498 can provide a combined
bandwidth of up to 37.5Gbps.
Refer to the latest SUNDANCE RSL specification for technical information on how it
works.
Local bus
http://www.quicklogic.com/images/QL5064_CD_UM.pdf
Clocks
The FPGA is provided with the following clocks:
Description Speed
QL5064 Local bus clock 64MHz
SHB clock 100MHz
RSL LVDS clock 125MHz
Table 3 – Board Clocks
Miscellaneous I/O’s
The following external interfaces will be provided for user-defined functions:
• PMC P14 (64-bits 5V tolerant)
• 4 LEDs
• 4 DIP switches
Page 16
Page 17

System ACE SC
The SMT498 FPGA PMC module is equipped with In System FPGA configuration
solution called System ACE SC. As soon as the board is powered up the FPGA is
configured from the flash. The System ACE SC has a PROM, Configuration
controller, and a Flash. For more information on System ACE look at: System ACE
PROM
The System ACE SC solution has a OTP PROM XC17V01. The PROM is
programmed with the configuration controller before it is installed on the board.
Configuration Controller
The XCV50E is used as the configuration controller. The PROM on power up
configures the Virtex-E chip (XCV50E). After configuration the XCV50E is seen as a
XCCACE64M (System ACE chip) in the JTAG chain. The controller forms a link
between the Flash and the target FPGA. Four status LEDs are connected to the
controller to monitor its state. (See the Appendix for status bit encoding table).
Flash
A 8MB Flash ROM device is connected to the XCV50E configuration controller. The
target FPGA bitstream is loaded in to this Flash via JTAG to configure the FPGA on
power up.
Page 17
Page 18

Power Supplies
Due to the close packing of components between PMC Side 1 and the host module,
power consumption is limited to 4.0W for 10.0mm standoffs (this increases to 6.0W
for 13.0mm standoffs). The total consumption for Side 1 and Side 2 of the module
shall not exceed 7.5W, and represents the total power drawn from all power rails
provided at the connector (+5V, +3.3v, +VI/O, +12V,-12V, +3.3Vaux).
For this reason it is recommended that you analyse the total FPGA device power
drawn by using Xilinx XPOWER before implementing your design in the FPGA.
This module must have 5V and 3.3V supplied through the PMC connectors. Either
5V or 3.3V may be supplied for PCI I/O voltage and should be consistent with the
signaling standard of the PCI host bus. +12V and -12V are optional and may be
supplied to the PMC connectors as per PMC specifications.
Contained on the module are linear regulators for the FPGA VCCAUX and FPGA
RocketIO. A DC/DC converter supplies the core voltage for the FPGA and DSPs.
DC/DC converter
An International Rectifier IP1201 Power Block is used to supply the 1.5V core
voltage to the FPGA. The current limits are configured for 10A and 5A, respectively.
The DC/DC converter is powered from the 5V supply.
Linear Voltage regulator
The FPGA VCCAUX and FPGA RocketIO voltages are supplied through linear
voltage regulators drawn from 3.3V.
Page 18
Page 19

Daughter Module
SMT498 has been designed to incorporate the option for a daughter module that can
interface to the FPGA and provide external I/O functions. SMT498 has one location
for a daughter module. The daughter module interfaces to SMT498 via SHBE,
therefore this SHB will not be available when the daughter module is installed.
Page 19
Page 20

PMC Standard
Voltage keying
The QuickLogic 5064 bridge is both 3.3V and 5V compliant. Both keying holes are
provided.
Connectors
According to IEEE 1386.1-2001 connectors Pn1 through Pn3 are provided for 64-bit
PCI connectivity. Additionally, connector Pn4 is provided for 64 bits of user-defined
I/O. Given that SMT498 is a single-size card, these connectors are referenced from
P11 through P14.
Component heights
This module obeys the PrPMC Tall module specs for component heights. Heights of
components on PMC Side 1 (see Figure 10) are limited to 4.7mm except in the I/O
Area (where they may extend to the host module surface). Components on PMC
Side 2 (see Figure 10) are limited to 23.5mm minus PCB thickness, or about
22.0mm (assuming 1.5mm PCB thickness).
Board Weight
The SMT498 weighs approximately 85 grams
Standoffs
There are two standoffs as part of the module. The standoffs are of standard 10mm
height in order to support the broadest range of host modules.
Bezel and I/O capability
Access to the right-angle FPDP port is provided through the front panel. For
purposes of mechanical rigidity and EMC compliance a customised bezel is provided
through which the FPDP is accessed.
Power consumption
Due to the close packing of components between PMC Side 1 and the host module,
power consumption is limited to 4.0W for 10.0mm standoffs (this increases to 6.0W
for 13.0mm standoffs). For Tall PrPMC modules an additional cooling method such
as a heat sink and fan should be considered if the total module power exceeds 25W.
Page 20
Page 21

The following information shall be provided on the PMC card:
5V current drawn, peak and average
3.3V current drawn, peak and average
Note: While it may appear that a stacking height of 13.0mm is desirable, some hosts
may not accept this.
Grounding
Per section 4.14 of IEEE 1386-2001.
Conduction Cooling
As the SMT498 adheres to PrPMC standards, the entire active and hot parts are on
the back of the module, which is suitable to place a conduction plate at the back of
the module to provide conduction coolong.
Power Supply
The SMT498 shall conform to the PMC standard for single-size modules. The PCI
connectors supply the module with 5.0V and 3.3V power supply. The 3.3V will be
used to supply all LVTTL digital I/O voltages directly. The FPGA Core Voltage
(V
= 1.5V) is generated from the 5.0V. FPGA Auxiliary voltage (V
CCINT
CCAUX
= 2.5V) is
derived from 3.3V to minimise losses.
Note: Due to restrictions of the Virtex II Pro, the FPGA Auxiliary voltage (V
must be provided before V
V
CCAUX
is generated locally, there will need to be a means to switch V
(3.3V). Given that V
CCO
is generated externally and
CCO
built into the
CCO
CCAUX
)
hardware.
Standalone operation
A 4-pin 0.200” power connector such as the type used to power PC hard disks will
be provided on Side 2 of the module. This connector provides 5V, 12V power, and
ground. SMT498 will generate 3.3V on board from the 5V supply.
Only use this connector for standalone operation (i.e. when not plugged into a PCI slot)!
Reset Structure
The SMT498 shall obey the reset signal provided by the PCI connector. In the
absence of an external reset signal, the module will bring itself out of reset once all
supplies are in compliance.
Page 21
Page 22

Header Pinout
PCI
A 66MHz 64-bit PCI bridge will allow SMT498 to communicate with the host system.
As the Local Bus has a maximum clock speed of 64MHz, the maximum theoretical
speed data can be transferred between the host and FPGA is 512MB/s.
PMC PCI connectors are directly connected to the QuickLogic 5064 bridge chip.
PMC P14 must be 5V tolerant.
P11 P12
Pin # Signal name Signal name Pin # Pin # Signal name Signal name Pin #
1 TCK -12V 2 1+12V TRSTN 2
3 GND INTAN 4 3 TMS TDO 4
5 INTBN INTCN 6 5 TDI GND 6
7 BUSMODE1N +5V 8 7 GND PCI-RSVD* 8
9 INTDN PCI-RSVD* 10 9 PCI-RSVD* PCI-RSVD* 10
11 GND 3.3Vaux 12 11 BUSMODE2N +3.3V 12
13 CLK GND 14 13 RSTN BUSMODE3
N
15 GND GNTN 16 15 +3.3V BUSMODE4
N
17 REQN +5V 18 17 PMEN GND 18
19 VIO AD31 20 19 AD30 AD29 20
21 AD28 AD27 22 21 GND AD26 22
23 AD25 GND 24 23 AD24 +3.3V 24
25 GND C/BE3N 26 25 IDSEL AD23 26
27 AD22 AD21 28 27 +3.3V AD20 28
29 AD19 +5V 30 29 AD18 GND 30
31 VIO AD17 32 31 AD16 C/BE2N 32
33 FRAMEN GND 34 33 GND PMC-RSVD 34
35 GND IRDYN 36 35 TRDYN +3.3V 36
14
16
37 DEVSELN +5V 38 37 GND STOPN 38
39 GND LOCKN 40 39 PERRN GND 40
41 PCI-RSVD* PCI-RSVD* 42 41 +3.3V SERRN 42
43 PAR GND 44 43 C/BE1N GND 44
Page 22
Page 23

45 VIO AD15 46 45 AD14 AD13 46
47 AD12 AD11 48 47 M66EN AD10 48
49 AD9 +5V 50 49 AD8 +3.3V 50
51 GND C/BE0N 52 51 AD7 PMC-RSVD 52
53 AD6 AD5 54 53 +3.3V PMC-RSVD 54
55 AD4 GND 56 55 PMC-RSVD GND 56
57 VIO AD3 58 57 PMC-RSVD PMC-RSVD 58
59 AD2 AD1 60 59 GND PMC-RSVD 60
61 AD0 +5V 62 61 ACK64N +3.3V 62
63 GND REQ64N 64 63 GND PMC-RSVD 64
Table 4 – PMC P11/P12 Interface
P13 P14
Pin # Signal name Signal
Pin # Pin # Signal name Signal name Pin #
name
1 PCI-RSVD GND 2 1 I/O I/O 2
3 GND C/BE7N 4 3 I/O I/O 4
5 C/BE6N C/BE5N 6 5 I/O I/O 6
7 C/BE4N GND 8 7 I/O I/O 8
9 VIO PAR64 10 9 I/O I/O 10
11 AD63 AD62 12 11 I/O I/O 12
13 AD61 GND 14 13 I/O I/O 14
15 GND AD60 16 15 I/O I/O 16
17 AD59 AD58 18 17 I/O I/O 18
19 AD57 GND 20 19 I/O I/O 20
21 VIO AD56 22 21 I/O I/O 22
23 AD55 AD54 24 23 I/O I/O 24
25 AD53 GND 26 25 I/O I/O 26
27 GND AD52 28 27 I/O I/O 28
29 AD51 AD50 30 29 I/O I/O 30
31 AD49 GND 32 31 I/O I/O 32
33 GND AD48 34 33 I/O I/O 34
35 AD47 AD46 36 35 I/O I/O 36
37 AD45 GND 38 37 I/O I/O 38
Page 23
Page 24

39 VIO AD44 40 39 I/O I/O 40
41 AD43 AD42 42 41 I/O I/O 42
43 AD41 GND 44 43 I/O I/O 44
45 GND AD40 46 45 I/O I/O 46
47 AD39 AD38 48 47 I/O I/O 48
49 AD37 GND 50 49 I/O I/O 50
51 GND AD36 52 51 I/O I/O 52
53 AD35 AD34 54 53 I/O I/O 54
55 AD33 GND 56 55 I/O I/O 56
57 VIO AD32 58 57 I/O I/O 58
59 PCI-RSVD PCI-RSVD 60 59 I/O I/O 60
61 PCI-RSVD GND 62 61 I/O I/O 62
63 GND PCI-RSVD 64 62 I/O I/O 64
Table 5 – PMC P13/P14 Interface
SHBs
The SHB signals have been named to match 2 16-bit SDB interfaces (or Hw SHB
interface) pinout according to the SUNDANCE SHB specification Half Word
configuration. SMT498 will be equipped with 4 SHBs. Two SHBs will be wired to the
FPGA to support LVDS.
Hw QSH Pin
number
QSH Pin
number
Hw
SHBxCLK0 1 2 SHBxD0(0)
SHBxD0(1) 3 4 SHBxD0(2)
SHBxD0(3) 5 6 SHBxD0(4)
SHBxD0(5) 7 8 SHBxD0(6)
SHBxD0(7) 9 10 SHBxD0(8)
SHBxD0(9) 11 12 SHBxD0(10)
SHBxD0(11) 13 14 SHBxD0(12)
SHBxD0(13) 15 16 SHBxD0(14)
SHBxD0(15) 17 18
SHBxUSER0(1
7)
Hw0
19 20
Page 24
SHBxUSER0(1
6)
SHBxUSER0(1
8)
Hw0
Page 25

SHBxUSER0(1
9)
21 22 SHBxWEN1
SHBxREQ1 23 24
SHBxUSER1(2
3)
SHBxUSER1(2
5)
SHBxUSER1(2
7)
SHBxUSER1(2
9)
SHBxUSER1(3
1)
SHBxUSER1(3
3)
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
SHBxACK1
SHBxUSER1(2
4)
SHBxUSER1(2
6)
SHBxUSER1(2
8)
SHBxUSER1(3
0)
SHBxUSER1(3
2)
SHBxUSER1(3
4)
SHBxCLK3 37 38 SHBxD1(0)
SHBxD1(1) 39 40 SHBxD1(2)
SHBxD1(3) 41 42 SHBxD1(4)
SHBxD1(5) 43 44 SHBxD1(6)
SHBxD1(7) 45 46 SHBxD1(8)
SHBxD1(9) 47 48 SHBxD1(10)
SHBxD1(11) 49 50 SHBxD1(12)
SHBxD1(13) 51 52 SHBxD1(14)
SHBxD1(15) 53 54
SHBxUSER2(5
3)
SHBxUSER2(5
5)
SHBxREQ4 59 60
Hw1
55 56
57 58 SHBxWEN4
Table 6 – SHB Interface
SHBxUSER2(5
2)
SHBxUSER2(5
4)
SHBxACK4
Hw1
Due to height constraints of components on the PMC module, vertical SHB cables
will not be possible. Luckily, there is a right-angle cable available:
http://www.precisionint.com/tdibrsb/images/drawings/D043850NNNLLLDD20.pdf
Page 25
Page 26

RSL Header
Headers are per RSL Spec.
RSL Side 1 Pinout (LVDS only)
Table 7 – RSL Side 1 Pinout
RSL Side 2 Pinout (LVDS only)
Table 8 – RSL Side 2 Pinout
Page 26
Page 27

JTAG headers
The JTAG header is used to access the XC2VP FPGA scan chain and configure the System
ACE configuration solution.
RSL Connectors SHB Connectors
JTAG IN
DIP Switch S2
JTAG OUT
Figure 8 – Location of JTAG IN, OUT and DIP Switches
The JTAG/Multilinx header has the following pinout:
Table 9 – JTAG Header Pinout
Page 27
Page 28

A JTAG In port and JTAG Out port are provided for chaining multiple modules
together. A DIP switch is provided to activate the JTAG Out port.
Power connector
A power connector is provided on the board for stand-alone operation. This
connector is a 4-pin male header similar to the type used to power PC hard disk
drives. Although the standard pinout for these connectors provides 5V and 12V
power; only 5V will be required to power the module.
PCB Layout
Page 28
Page 29

The following figures show a preliminary concept of the Side 1, Side 2, and side view
of the module. Subject to change based on final design details.
Figure 9 - Module Side 1 View
10
mm
Safety
FPDP
I/ O Area
Figure 10 – Module Side 2 View
SHB
SHB
FPGA
Figure 11 – Module Side View
Page 29
PCI Connx
QL 5064
PCB Plane
Page 30

This module presents no hazard to the user.
EMC
This module is designed to operate from within an enclosed host system, which is
build to provide EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is not
guaranteed unless it is installed within an adequate host system.
Appendix
Page 30
Page 31

Configuring the FPGA
The module will be provided with the default VHDL core burned in the Flash. On
power up, the FPGA will be configured with the default bitstream. In case the user
wants to use his own custom design the following method can be used to configure
the FPGA.
It is assumed that the user is familiar with Xtend1000 PMC carrier card and is aware
of the procedure for mounting the PMC on the Xtend1000 and powering it up within a
PC environment.
PCI Mode
To configure the FPGA (Virtex II Pro – VP 100) using the PCI interface, switchswitch 4 of S3 to ‘ON’ position and use the PCI driver for SMT407/498 to download
the firmware to the FPGA.
PROM (there is a
S3 jumper near this PROM S2
which is not shown in this picture)
Figure 12 - Location of the DIP Switches and the PROM
Page 31
Page 32

JTAG/Boundary Scan The JTAG header is provided to enable device programming via suitable software.
(See board header table for JTAG pin details). Typically, this will be Xilinx iMPACT.
Xilinx iMPACT supports Parallel Cable IV download cable for communication
between the PC and FPGA(s).
The JTAG header on the board was designed to mate directly with the 2mm
ribbon cable provided with the MultiLINX Cable IV. BE SURE TO ATTACH
THE RIBBON CABLE PROPERLY.
To directly configure the FPGA via the JTAG, remove the jumper near the PROM
chip as shown on the picture below. Turn switch 1 of S2 to ‘ON’ position and switch 2
of S2 to ‘OFF’ position. The switch 4 of S3 should be in ‘OFF’ position for the JTAG
to work.
To initialize the JTAG chain, connect the Xilinx Parallel cable to JTAG IN connector
JA2. Using the Xilinx impact software initialize the JTAG chain, this will show two
devices as shown in the figure below
The first device will be the XC2VP100 and the second device will be XCV50E.
Assign the intended .BIT file to the XC2VP100 and program it. This will configure the
FPGA directly via the JTAG. To test the approaches please use the LED_FLASH.bit,
which is provided.
Page 32
Page 33

System ACE SC To configure the FPGA from the Flash on power up, install the jumper pin near the
PROM chip. Turn the switch 1 of S2 to ‘ON’ position and switch 2 of S2 to ‘OFF’
position. Switch 4 of S3 should be in ‘OFF’ position for the JTAG to work and
switches 1, 2, and 3 should be in the ‘ON’ position.
To initialize the JTAG chain, connect the Xilinx Parallel cable to JTAG IN connector
JA2. Using the Xilinx impact software initialize the JTAG chain, this will show two
devices as shown in the figure below
The first device will be the XC2VP100 and the second device will be XCCACEM64
SC (this is the System ACE chip that allows the bitstream to be loaded into the flash
via JTAG). Assign the .MPM file (Generation of the .MPM file is given at the end) to
the System ACE chip and program it. To check the configuration of the VP100 via
the Flash, toggle the switch 4 of S3 this will reset the system ACE and configure the
FPGA from the Flash. You will see the done pin (LED D5, which is not populated on
the prototype) of the Target FPGA go low. This confirms the FPGA is configured and
you will see the status LED’s D12, D13 lit. From now onwards as soon as the board
is powered up the VP100 will be configured from Flash.
Note: In this mode the VP100 cannot be configured directly via the JTAG.
Page 33
Page 34

Status Bit Encoding:
Status bits (3..0)
D14 D13 D12 D11
Status Definition
1 1 1 1 System busy. Cannot process JTAG
commands
1 1 1 0 Successful slave-serial or select map
configuration (CFG_DONE High). System
Busy.
1 1 0 1 Configuration Error (CFG_DONE did not go
high). System Busy.
1 1 0 0 Decompressor error. System Busy.
1 0 1 1 Invalid controller state. System Buy.
1 0 1 0 Flash memory blank or invalid configuration
data in Flash memory. System Busy.
1 0 0 1 Invalid configuration option. System Busy.
1 0 0 0 Flash Chip erase successful. System Busy.
0 1 1 1 System ready to accept commands through
JTAG port.
0 1 1 0
Successful Slave-serial/ Slave Select
MAP configuration (CFG_DONE high).
System ready to accept commands
through JTAG port.
0 1 0 1 Configuration Error (CFG_DONE did not go
high). System ready to accept commands
through JTAG port.
0 1 0 0 Decompressor error. System ready to
accept commands through JTAG port.
0 0 1 1 Invalid controller state. System ready to
accept commands through JTAG port.
0 0 1 0 Flash memory blank or invalid configuration
data in Flash memory. System ready to
accept commands through JTAG port.
0 0 0 1 Invalid configuration option. System ready to
accept commands through JTAG port.
0 0 0 0 Flash Chip erase successful. System ready
to accept commands through JTAG port.
Table 10 – Status Bits Encoding
Page 34
Page 35

Creating System ACE programming file (.MPM)
Once the .BIT file is generated using the normal procedure open Xilinx iMPACT
software. Under mode select ‘File mode’. In the blank space right click to launch
wizard.
a) Select ‘System ACE MPM/SC’. Click Next.
Page 35
Page 36

b) Select size as 64Mbits as the flash can hold 64Mbits.
c) Specify the name of the .MPM file and the location to store it.
Page 36
Page 37

d) Select ‘In Select MAP mode’.
e) Select ‘CS0’ as there is only one Target FPGA on the board
Page 37
Page 38

f) Select ‘Configuration Addr 0’. Click Next. If multiple bitstreams are stored
under different configuration addresses. The bitstream select switches must
be set to the particular address before the board is powered up, in order to
configure the target FPGA with the respective bitstream.
g) Click Next
h) Add the respective .BIT file, with which you intend to configure the target
FPGA.
Page 38
Page 39

i) Click on Finish.
j) Click on Yes to Generate file.
k) Do not compress the file. Click OK.
Once the file is generated, it will be stored in the location specified.
Page 39
 Loading...
Loading...