Page 1
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
Unit / Module Description: Multi-output DDS based SLB Mezzanine
Unit / Module Number: SMT399-160
Document Issue Number: 3
Issue Date: 24/05/2007
Original Author: PSR
Form : QCF42
Date : 6 July 2006
User Manual
for
SMT399-160
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House, Waterside,
Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS.
This document is the property of Sundance and may not be copied nor
communicated to a third party without prior written permission.
© Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited 2006
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 2
Revision History
Issue Changes Made Date Initial
1 Original Document 08/01/2007 PSR
2 Power consumption added 12/01/2007 PSR
3 Modification: MMBX connectors fitted 24/05/2007 SM
s
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 2 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction............................................................................................... 6
2 Related Documents .................................................................................... 7
3 Examples of application. ............................................................................8
4 Functional Description............................................................................... 9
4.1 Block Diagram ................................................................................................................9
4.2 Module Description........................................................................................................9
4.3 SMT399-160 characteristics. .......................................................................................10
4.4 Power Supply structure. ...............................................................................................10
4.5 On-board crystal. ...........................................................................................................11
4.6 Output Variable Gain Amplifier....................................................................................11
4.7 Dau ghter sub-module interface. ...................................................................................11
4.8 Cascading modules.......................................................................................................11
4.9 Dual-tone Mode............................................................................................................12
4.10 External Trigger............................................................................................................ 12
4.11 LEDs..............................................................................................................................13
5 Control Register Settings...........................................................................13
5.1 Control Packet Structure .............................................................................................. 13
5.2 Reading and Writing Registers ....................................................................................14
5.3 Memory Map.................................................................................................................14
5.4 Register Descriptions ...................................................................................................16
5.4.1 Reset and Update Register – 0x0............................................................................16
5.4.2 Profile Register – 0x1. .............................................................................................18
5.4.3 VGA0 Register – 0x2...............................................................................................18
5.4.4 VGA1 Register – 0x3................................................................................................19
5.4.5 VGA2 Register – 0x4 ...............................................................................................19
5.4.6 VGA3 Register – 0x5. ..............................................................................................19
5.4.7 DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register............................................... 20
5.4.8 DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register................................................22
5.4.9 DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register................................................23
5.4.10 DDS0 Register – 0x9 – Amplitude Scale Factor. ...................................................25
5.4.11 DDS0 Regis ter – 0xA – Amplitude Ramp Ra te. .....................................................25
5.4.12 DDS0 Register – 0xB – Frequency Tuning Word 0...............................................25
5.4.13 DDS0 Register – 0xC – Frequency Tuning Word 0...............................................26
5.4.14 DDS0 Register – 0xD – Phase Offset Word. ..........................................................26
5.4.15 DDS0 Register – 0xE – Frequency Tuning Word 1. ..............................................26
5.4.16 DDS0 Register – 0xF – Frequency Tuning Word 1................................................27
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 3 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 4

5.4.17 DDS0 Register – 0x10 – RAM Segment Control Word 0. .....................................27
5.4.18 DDS0 Register – 0x11 – RAM Segment Control Word 0.......................................27
5.4.19 DDS0 Register – 0x12 – RAM Segment Control Word 0. .................................... 28
5.4.20 DDS0 Register – 0x13 – RAM Segment Control Word 1...................................... 28
5.4.21 DDS0 Register – 0x14 – RAM Segment Control Word 1...................................... 28
5.4.22 DDS0 Register – 0x15 – RAM Segment Control Word 1...................................... 28
5.4.23 DDS0 Register – 0x16 – RAM Segment Control Word 2.......................................29
5.4.24 DDS0 Register – 0x17 – RAM Segment Control Word 2.......................................29
5.4.25 DDS0 Register – 0x18 – RAM Segment Control Word 2. .....................................29
5.4.26 DDS0 Register – 0x19 – RAM Segment Control Word 3.......................................29
5.4.27 DDS0 Register – 0x1A – RAM Segment Control Word 3. .................................... 30
5.4.28 DDS0 Register – 0x1B – RAM Segment Control Word 3. .................................... 30
5.4.29 DDS0 Register – 0x1C – Falling Delta Frequency Tuning.................................... 30
5.4.30 DDS0 Register – 0x1D – Falling Delta Frequency Word.......................................31
5.4.31 DDS0 Register – 0x1E – Falling Sweep Ramp Rate Word. ................................... 31
5.4.32 DDS0 Register – 0x1F – Rising Delta Frequency Tuning...................................... 31
5.4.33 DDS0 Register – 0x20 – Rising Delta Frequency Word........................................32
5.4.34 DDS0 Register – 0x21 – Rising Sweep Ramp Rate Word......................................32
6 PCB Layout............................................................................................... 33
6.1 Top View .......................................................................................................................33
6.2 Bottom View..................................................................................................................34
7 Connector Location.................................................................................. 35
8 Support Packages..................................................................................... 36
9 Physical Properties .................................................................................. 37
10 Safety .......................................................................................................38
11 EMC ......................................................................................................... 39
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 4 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 5

Table of Figures
Figure 1 - Examples of applications..............................................................................................8
Figure 2 - SMT399-160 Block Diagram. ......................................................................................9
Figure 3 - Output main characteristics. .....................................................................................10
Figure 4 - Connections for cascading modules. ..........................................................................11
Figure 5 - Multi module synchronisation connectors................................................................12
Figure 6 - Dual-Tone Mode. .......................................................................................................12
Figure 7 – Setup Packet Structure..............................................................................................13
Figure 8 – Control Register Read Sequence. .............................................................................14
Figure 9 – Register Memory Map. .............................................................................................16
Figure 10 - Layout - Top Side. ....................................................................................................33
Figure 11 - Layout - Bottom Side. ...............................................................................................34
Figure 12 - Connector Location. ................................................................................................ .35
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 5 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 6

1 Introduction
The SMT399-160 is a multi-output mezzanine single width module, which is able to generate
sine waves at up to 160MHz. This mezzanine board is to be fitted on one of Sundance SLB
(Sundance LVDS Bus) base modules, such as
cannot be used on its own. It is built around two
Analog Devices) featuring
are separately programmable, can contain up to 4 profiles and have the possibility of being
synchronised. The architecture allows generating single-tone or dual-tone signals. DDS
outputs are split into two legs, each of them featuring a programma ble amplifier (VGA). The
SMT399-160 has got in total two pairs of outputs.
A Xilinx FPGA Virtex-II Pro (or Virtex4) from the base module, is used to control DDSs and
Variable Gain Amplifiers (VGAs) of the SMT399-160, after receiving command words via a
Comport.
SMT399-160 modules can be cascaded and work into the AD9954 Master/Slave mode.
14-bit DAC operating/sampling at up to 400 MHz. Both devices
SMT338-VP or SMT398-VP or SMT368 and
AD9954s, Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS –
PCB connectors are
It can be used in the following application:
- Radio systems, as a clock generator (fine tuning),
- Test systems (dual tone and fast hopping),
- Programmable system (software programmable),
- Etc…
MMBXs from Hubert Suhner.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 6 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 7

2 Related Documents
AD9954 Datasheet - Analog Devices:
http://www.analog.com/Analog_Root/productPage/productHome/0,2121,AD9954,00.html
Sundance High-speed Bus (SHB) specifications – Sundance.
ftp://ftp2.sundance.com/Pub/documentation/pdf-files/SHB_Technical_Specification.pdf
Sundance LVDS Bus (SLB) – Sundance.
http://www.sundance.com/docs/SLB%20-%20Technical%20Specifications.pdf
TIM specifications - TI.
ftp://ftp2.sundance.com/Pub/documentation/pdf-files/tim_spec_v1.01.pdf
Xilinx Virtex-II PRO FPGA - Xilinx.
http://direct.xilinx.com/bvdocs/publications/ds083.pdf
MMBX Connectors – Hubert Suhner.
MMBX Connectors
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 8
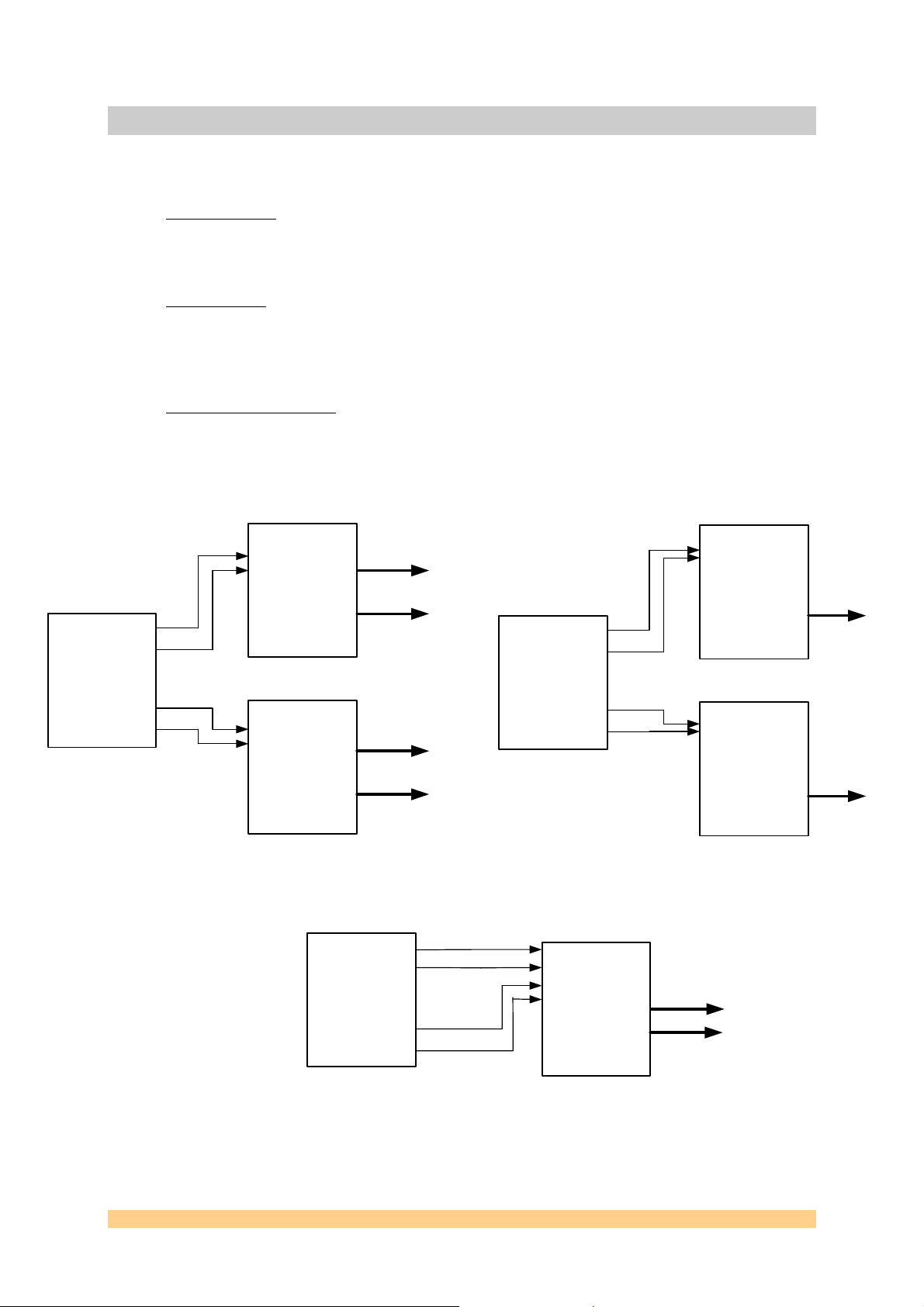
3 Examples of application.
The SMT399-160 module can be used in the following application:
- Radio systems
. Compatible with Sundance’s TIM Modules, it can be combined with
DAQ modules such as ADCs and DACs, as a clock generator. The SMT399-160 finetuning makes it even more suitable for such platform to generate up-to-four
synchronised and/or quadrature signals.
- Test systems
. It is sometimes very helpful to have a signal generator capable of
generators various frequencies to evaluate some radio system. Fast hopping is the key
word here. Dual tone signals are useful to characterise a receiver system to evaluate
its capabilities of receiving signals close to each other in frequency. DDSs also to
generate a ramp, a pattern or a frequency sweep.
- Programmable system
. As most of system, it a very important top control every part
of a system. The SMT399-160 is fully controllable via software.
- Etc…
As both pairs of DDSs are synchronised and coupled master/slave, the module can generate
90-degree phase shift signals and be part of a quadrature modulator system.
Ext. Clk ADCs
Ext. Clk DAC
SMT370
Dual ADC/DAC
Analogue Converters
ChA0
ChA1
Up to 160MHz
Quadrature
Ext.
Clock
SMT390-VP
Dual 210-MSPS ADC
Analogue Converters
I
Q
ChA0
Up to 160MHz
ChA1
SMT399-160
ChB0
ChB1
Channel A and Channel B
synchronised
Dual Quadrature Sampling
Up to 160MHz
Quadrature
Ext.
Clock
SMT390-VP
Dual 210-MSPS ADC
Analogue Converters
SMT399-160
SMT399-160
ChB0
I
All channels synchronised
ChB1
Q
Multi-DAQ synchronisation
ChA0
ChA1
ChB0
ChB1
Up to 160MHz
Up to 160MHz
or test pattern
Ext.
Clocks
Analog
Inputs
SMT390-VP
Dual 210-MSPS ADC
Analogue Converters
Sampling with test pattern
Up to 160MHz
Ext. Clk ADCs
Ext. Clk DAC
SMT370
Dual ADC/DAC
Analogue Converters
Figure 1 - Examples of applications.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 9
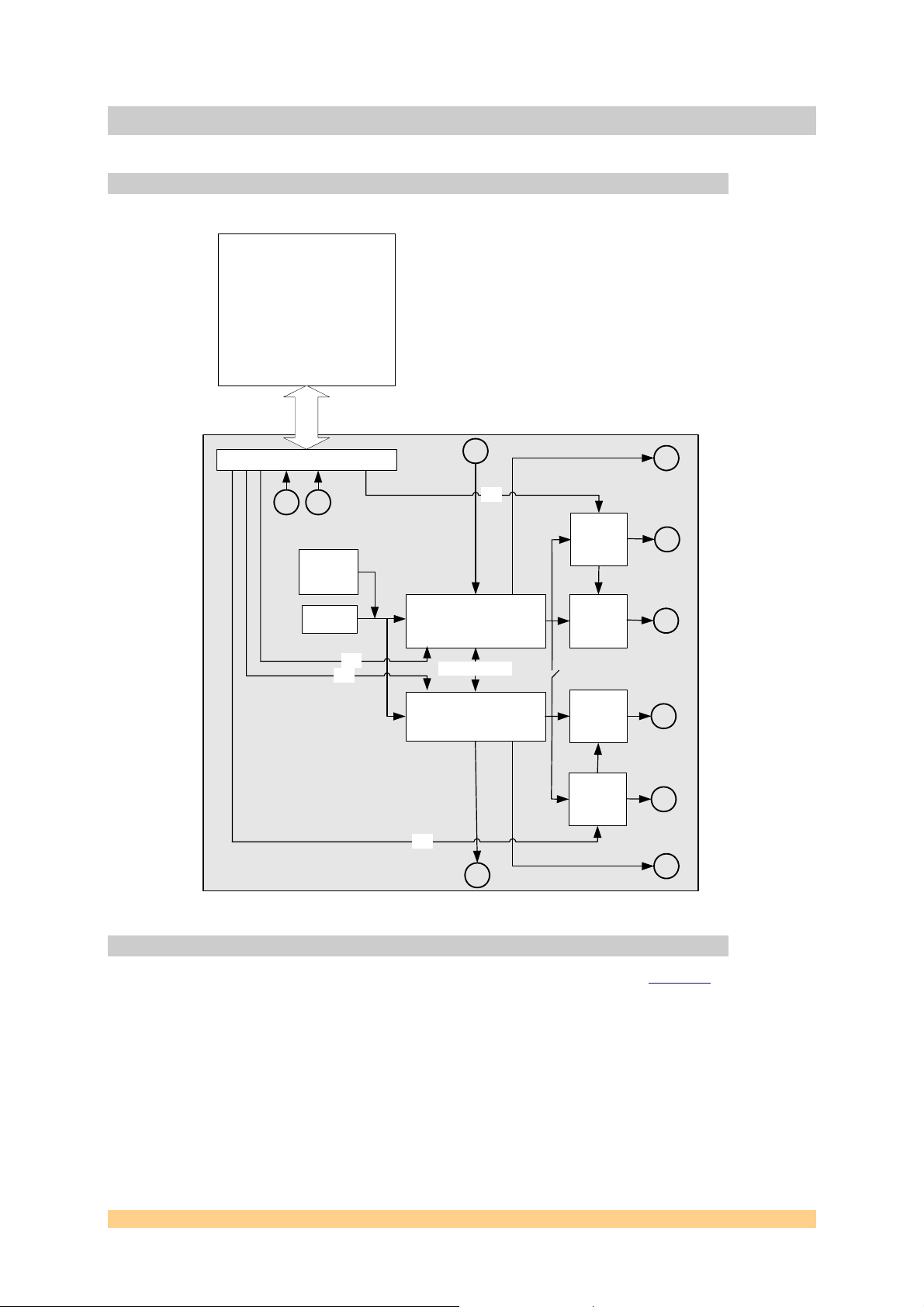
4 Functional Description
In this part, we will see the general block diagram and some comments on the main entities.
4.1 Block Diagram
The following diagram shows the block diagram of the SMT399-160.
Sundance SLB base
module (SMT338-VP,
SMT398-VP or SMT368
for example)
68 I/O pins
+3.3V, +5V
SMT399-160 SLB
Syn
in
squ
are
A
TrigATrig
B
External
Reference
(Option)
On-board
Crystal
I/Os
I/Os
Daughter Module - SMT399-160
Figure 2 - SMT399-160 Block Diagram.
I/Os
1xAD9954 DDS (Channel A)
14-bit @ 400MSPS
48-pin TQFP
Synchronisation
1xAD9954 DDS (Channel B)
14-bit @ 400MSPS
48-pin TQFP
I/Os
Syn
out
AD8370
VGA
AD8370
VGA
AD8370
VGA
AD8370
VGA
A0
A1
B0
B1
squ
are
B
4.2 Module Description
The module is built around two Direct Digital Synthesizers (DDS): two AD9954.
The AD9954 is a DDS featuring 14-bit DAC operating at up to 400MSPS. It forms a digitally
programmable high frequency synthesizer capable of generating an analog output sinusoidal
waveform at up to 160MHz. The AD9954 provides fast frequency hopping and fine-tuning
resolution (32-bit frequency tuning word). The AD9954 includes an integrated 1024x32 static
RAM to support flexible frequency sweep capability in several modes. It also supports a user
defined linear sweep mode of operation. The frequency resolution of the AD9954 is 0.0931
Hz when clocked at 400MHz. Both analog outputs can be linked together via jumpers in
order to generate a dual tone signal.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 10

DDS outputs are doubled and combined with Variable Gain Amplifiers (VGA).
Analog signals are all single-ended and output on MMBX connec tors (J13, J14, J15 and J20)
for connection to a 50-Ohm load.
Output Sine waves can be turned into ‘sharp’ square signals using the AD9954 built-in
comparator. Square signals (one per DDS) are also available on MMBX connectors (J24 and
J25) on LVTTL format.
All DDS settings travel via the FPGA present on SLB base module. Information comes from a
Comport and the FPGA stores it first into internal registers and interfaces it to the DDS chips
via the SLB connector. Comports follow the Texas Instrument C4x standard.
4 green LEDs are also available and driven by the FPGA to report working or failing
conditions to the user. Other green LEDs show that all power supplies are ON and working.
Two external triggers (J11 and J23) are also available.
4.3 SMT399-160 characteristics.
Analog Outputs (J13, J14, J15 and J20).
0 to 2.12 Volts without saturation (sine wave)
Analog Output Voltage Range
Output Impedance
Frequency range
Frequency resolution
Square Outputs (J24 and J25).
Output Format
Frequency range
Frequency Resolution
External Triggers (J11 and J23).
Input Range
Frequency Range
Input Reference (Option – J21)
Frequency range
Figure 3 - Output main characteristics.
0 to 3.0 Volts with saturation
(Output level set via Control Register - VGA)
Terminated to be connected to a 50-Ohm load.
Up to 160 MHz
0.0931 Hz
LVTTL
Up to 160 MHz
0.0931 Hz
LVTTL (default FPGA PAD setting)
Up to 160 MHz
0 to 400 MHz.
4.4 Power Supply structure.
The SMT399-160 conforms to the TIM standard for single width modules. The TIM
connectors supply 5 Volts to the base module, which also requires an additional 3.3-Volt
power supply, which must be provided by the two diagonally opposite mounting holes. This
3.3-volt is present on all Sundance TIM carrier boards. From these two power rails, are
generated a filtered 3.3-volt as well as a 1.8-volt source for both
Greens LEDs placed on the board report the state of the power supplies.
The SMT399-160 requires 2 power rails from the SLB power connector: +3.3 and +5 Volts.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 10 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
AD9954s.
Page 11
4.5 On-board crystal.
The AD9954 are clocked from a crystal (20MHz). The master DDS then passes the sampling
clock to the slave DDS to ensure synchronisation. Synchronisation can also be achiev ed when
cascading several SMT399-160 daughter modules. There is an automatic synchronisation
available from the DDS registers.
4.6 Output Variable Gain Amplifier.
Each output is driven by a Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA – AD8370), digitally controlled that
uses 8 bits to code the gain and provides a power-down mode. Two ranges of gains are
available: from –11 to +17dBs or from +6 to +34dBs.
4.7 Daughter sub-module interface.
The link between the main and the daughter sub-module is made via two Samtec connec tors.
There is no fast signal travelling between both cards. The first connector passes control
signals and the second one passes a 3.3-volt and 5-volt s upplies and a ground between submodules.
The female differential connector is located on the m ain module. The Samtec Part Number
for this connector is QTH-060-01-F-D-DP-A.
The female power connector is located on the main module. The Samtec Part Numbe r for this
connector is BKS-133-03-F-V-A
The male differential connector is located on th e daughter card. The S amtec Part Nu mber for
this connector is QSH-060-01-F-D-DP-A
The male power connector is located on the daughter card. The Samtec Part Nu mber for this
connector is BKT-133-03-F-V-A
The mated height between the main module and the daughter card is 5 mm.
4.8 Cascading modules
Several SMT399-160s can be cascaded. All DDSs can be synchronised by linking the modul es
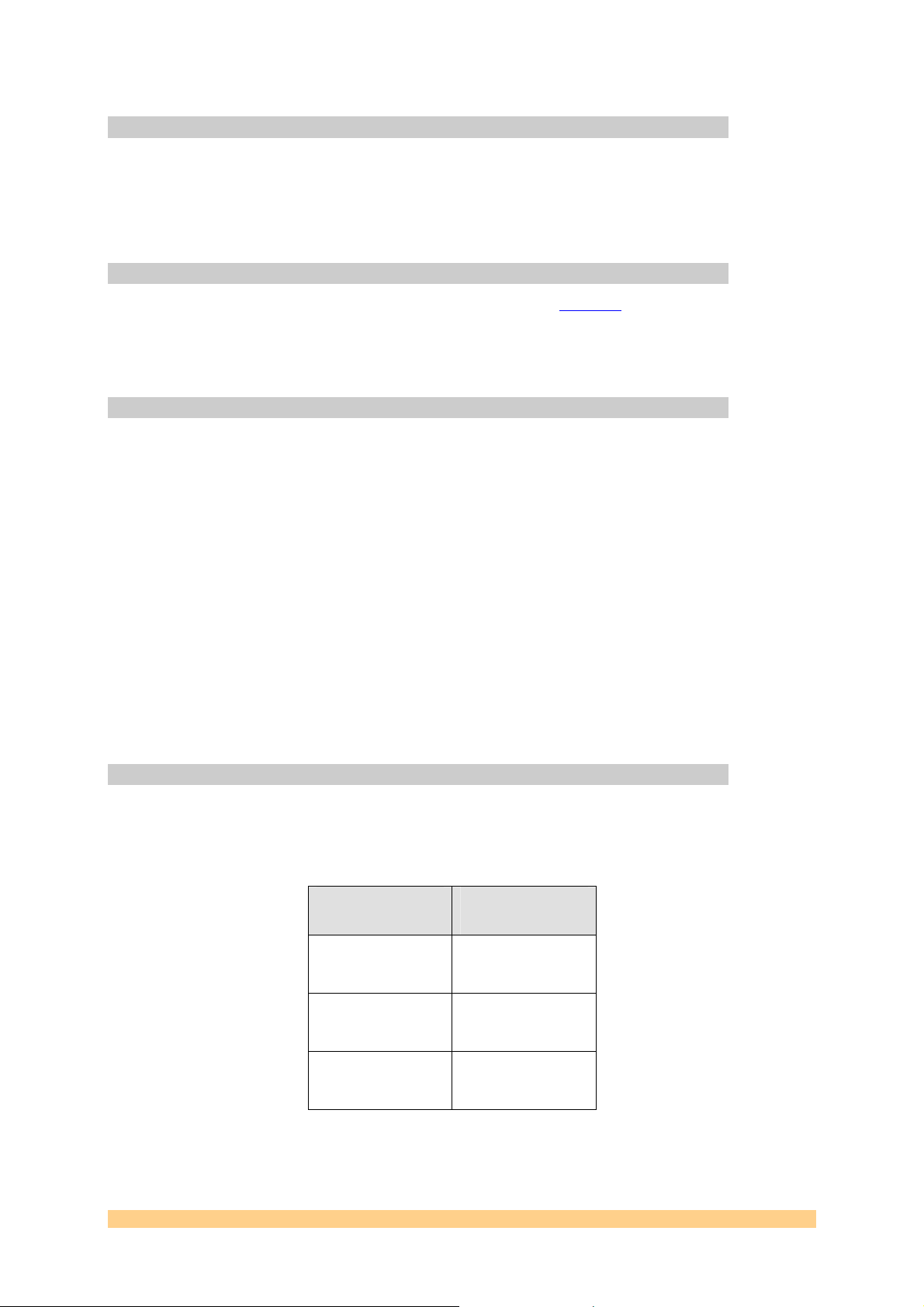
via connectors J1 and J3, both are 2-mm 3-pin head ers. J1 of the master module should be
connected to J3 of the slave module as follows:
SMT399-160
Master (J1)
Crystal Out
(J1 – pin 1)
Gnd
SMT399-160
Slave (J3)
Crystal In
(J3 – pin 3)
Gnd
(J1 – pin 2)
Synch In
(J1 – pin 3)
Figure 4 - Connections for cascading modules.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 11 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
(J3 – pin 2)
Synch Out
(J3 – pin 1)
Page 12
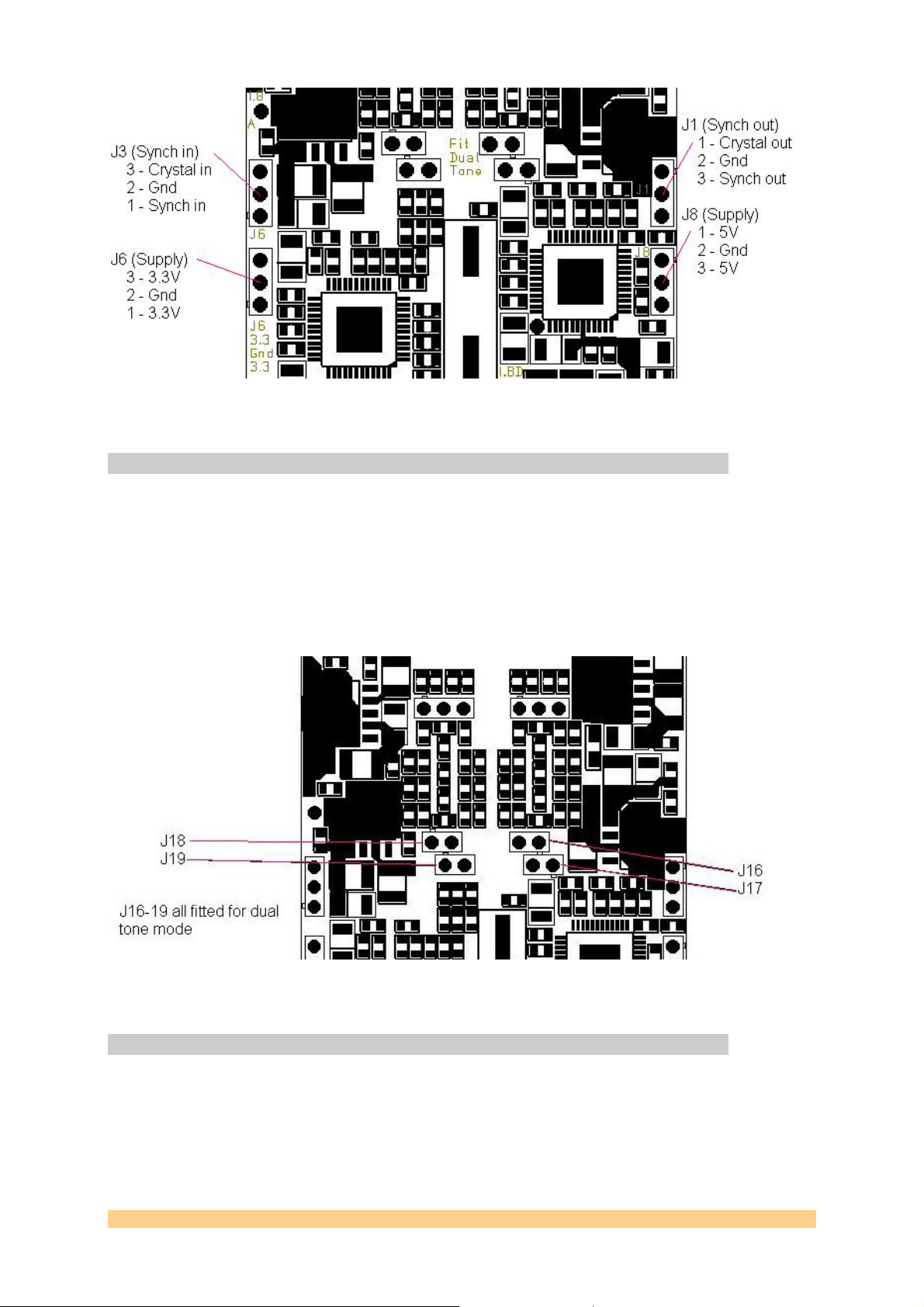
Figure 5 - Multi module synchronisation connectors.
4.9 Dual-tone Mode.
The SMT399-160 can used as a dual-tone generator. Both DDS outputs can be mixed
together. In this case, all four analog outputs (J13, J14, J15 and J20) would show the same
signal, at relevant amplitudes.
To configure the SMT399-160 into the dual-tone mo de, simply fit J16, J17, J18 and J19 in
place.
The normal mode of operation is obtained by leaving J16, J17, J18 and J19 open.
Figure 6 - Dual-Tone Mode.
4.10 External Trigger.
Two external triggers are available on J23 and J11. Both are straight through, i.e. the
connector is directly connected to the FPGA. There is no protection so it is to the user to
make sure levels present on the connector are compatible with th e pad implemented in the
FPGA. In the default firmware provided, J23 is connected to LED1 and J11 to LED3 (see
silkscreen for LED locations).
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 12 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 13

4.11 LEDs.
There are 8 LEDs on the board. Only 4 are user d efined, i.e. accessible from the FPGA on the
SLB base module. These 4 leds are la belled on silkscreen LED1, LED2, LED3 and LED4. In
the standard firmware provided with the board, LED0 and LED2 are flashing in opposite
phase as soon as the FPGA is configured and the on-board crystal of the SLB based module is
working. LED1 is connected directly to the trigger signal coming from J11. LED3 is connected
directly to the trigger signal coming from J23. External triggers have no more action than
driving LED1 and LED3.
The other 4 LEDs are connected on power rails and should be ON at all time. If not it is
strongly recommended to put the module off power and to contact Sundance.
5 Control Register Settings
The Control Registers control the complete f unctionality of the SMT399-160. They are setup
via the Comport3 in the standard FPGA firmware provided.
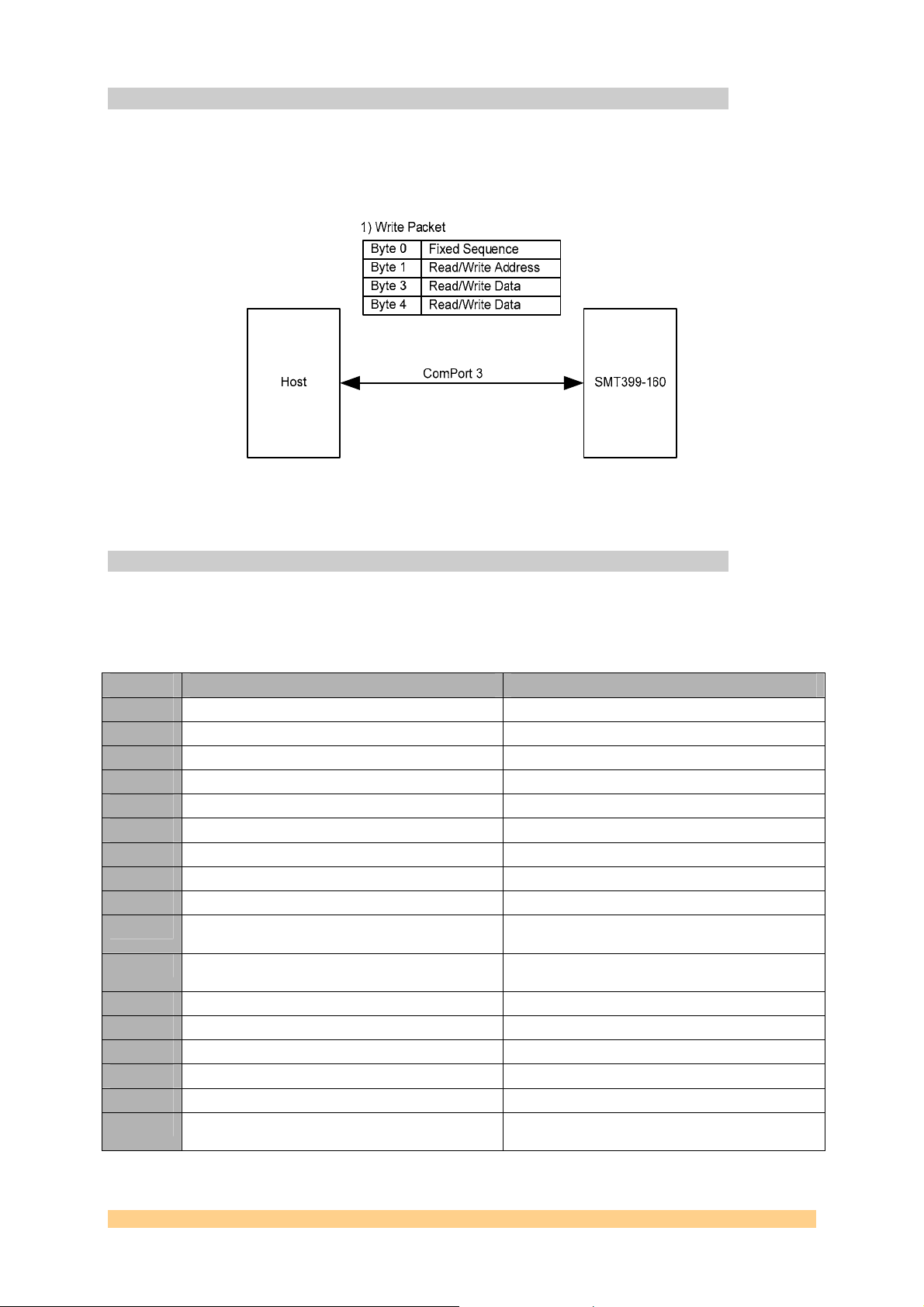
5.1 Control Packet Structure
The data passed on to the SMT399-160 over the Comports must conform to a certain packet
structure. Only valid packets will be accepted and only after acceptanc e of a packet will the
appropriate settings be implemented. Each packet will start with a certain sequence
indicating the start of the packet (0xFF). The address to write the data payload into will
follow next. After the address the data will follow. This structure is illustrated in the following
figure:
Byte Content
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’
1 Address 7 Address 6 Address 5 Address 4 Address 3 Address 2 Address 1 Address 0
3 Data 15 Data 14 Data 13 Data 12 Data 11 Data 10 Data 9 Data 8
4 Data 7 Data 6 Data 5 Data 4 Data 3 Data 2 Data 1 Data 0
Figure 7 – Setup Packet Structure.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 13 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 14
5.2 Reading and Writing Registers
Control packets are sent to the SMT399-160 over Comport3 only in the standard firmware.
This is a bi-directional interface. The format of a ‘Read Packet’ is the s ame as that of a write
packet.
Figure 8 – Control Register Read Sequence.
5.3 Memory Map
The write packets must contain the address where the data must be written to and the read
packets must contain the address where the req uired data must be read. Th e following figure
shows the memory map for the writable and readable Control Registers on the SMT399-160:
Address Writable Registers Readable Registers
0x00 Reset and Update Register. Reserved.
0x01 DDS0 and 1 Profile Register. DDS0 and DDS1 Profile Register.
0x02 VGA0. Read-back (FPGA Register) VGA0.
0x03 VGA1. Read-back (FPGA Register) VGA1.
0x04 VGA2. Read-back (FPGA Register) VGA2.
0x05 VGA3. Read-back (FPGA Register) VGA3.
0x06 DDS0 – Register 0 (0x0) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 0 (0x0).
0x07 DDS0 – Register 1 (0x1) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 1 (0x1).
0x08 DDS0 – Register 2 (0x2) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 2 (0x2).
0x09 DDS0 – Register 3 (0x3) – Amplitude Scale Factor
Register.
0x0A DDS0 – Register 4 (0x4) – Amplitude Ramp Rate
Register.
0x0B DDS0 – Register 5 (0x5) – Frequency Tuning Word 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 5 (0x5).
0x0C DDS0 – Register 6 (0x6) – Frequency Tuning Word 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 6 (0x6).
0x0D DDS0 – Register 7 (0x7) – Phase Offset Word. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 7 (0x7).
0x0E DDS0 – Register 8 (0x8) – Frequency Tuning Word 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 8 (0x8).
0x0F DDS0 – Register 9 (0x9) – Frequency Tuning Word 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 9 (0x9).
0x10 DDS0 – Register A (0xA) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 3 (0x3).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 4 (0x4).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register A (0xA).
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 14 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 15

0x11 DDS0 – Register B (0xB) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
0x12 DDS0 – Register C (0xC) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
0x13 DDS0 – Register D (0xD) – RAM Segment Control
Word 1.
0x14 DDS0 – Register E (0xE) – RAM Segment Control
Word 1.
0x15 DDS0 – Register F (0xF) – RAM Segment Control
Word 1.
0x16 DDS0 – Register 10 (0x10) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x17 DDS0 – Register 11 (0x11) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x18 DDS0 – Register 12 (0x12) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x19 DDS0 – Register 13 (0x13) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x1A DDS0 – Register 14 (0x1A) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x1B DDS0 – Register 15 (0x1B) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x1C DDS0 – Register 16 (0x1C) – Falling Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x1D DDS0 – Register 17 (0x1D) – Falling Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x1E DDS0 – Register 18 (0x1E) – Falling Sweep Ramp rate
Word.
0x1F DDS0 – Register 19 (0x1F) – Rising Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x20 DDS0 – Register 20 (0x20) – Rising Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x21 DDS0 – Register 21 (0x21) – Rising Sweep Ramp rate
Word.
0x26 DDS1 – Register 0 (0x0) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 0 (0x0).
0x27 DDS1 – Register 1 (0x1) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 1 (0x1).
0x28 DDS1 – Register 2 (0x2) – Control Function Register. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 2 (0x2).
0x29 DDS1 – Register 3 (0x3) – Amplitude Scale Factor
Register.
0x2A DDS1 – Register 4 (0x4) – Amplitude Ramp Rate
Register.
0x2B DDS1 – Register 5 (0x5) – Frequency Tuning Word 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 5 (0x5).
0x2C DDS1 – Register 6 (0x6) – Frequency Tuning Word 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 6 (0x6).
0x2D DDS1 – Register 7 (0x7) – Phase Offset Word. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 7 (0x7).
0x2E DDS1 – Register 8 (0x8) – Frequency Tuning Word 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 8 (0x8).
0x2F DDS1 – Register 9 (0x9) – Frequency Tuning Word 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 9 (0x9).
0x30 DDS1 – Register A (0xA) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
0x31 DDS1 – Register B (0xB) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
0x32 DDS1 – Register C (0xC) – RAM Segment Control
Word 0.
0x33 DDS1 – Register D (0xD) – RAM Segment Control Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register D (0xD).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register B (0xB).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register C (0xC).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register D (0xD).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register E (0xE).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register F (0xF).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 10
(0x10).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 11 (0x11).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 12 (0x12).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 13 (0x13).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 14 (0x14).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 – Register 15 (0x15).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Falling Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Falling Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Falling Sweep
Ramp rate Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Rising Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Rising Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS0 - Rising Sweep
Ramp rate Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 3 (0x3).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 4 (0x4).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register A (0xA).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register B (0xB).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register C (0xC).
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 15 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 16

Word 1.
0x34 DDS1 – Register E (0xE) – RAM Segment Control
Word 1.
0x35 DDS1 – Register F (0xF) – RAM Segment Control
Word 1.
0x36 DDS1 – Register 10 (0x10) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x37 DDS1 – Register 11 (0x11) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x38 DDS1 – Register 12 (0x12) – RAM Segment Control
Word 2.
0x39 DDS1 – Register 13 (0x13) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x3A DDS1 – Register 14 (0x14) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x3B DDS1 – Register 15 (0x15) – RAM Segment Control
Word 3.
0x3C DDS1 – Register 16 (0x1C) – Falling Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x3D DDS1 – Register 17 (0x1D) – Falling Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x3E DDS1 – Register 18 (0x1E) – Falling Sweep Ramp rate
Word.
0x3F DDS1 – Register 19 (0x1F) – Rising Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x40 DDS1 – Register 20 (0x20) – Rising Delta Frequency
Tuning Word.
0x41 DDS1 – Register 21 (0x21) – Rising Sweep Ramp rate
Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register E (0xE).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register F (0xF).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 10 (0x10).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 11 (0x11).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 12 (0x12).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 13 (0x13).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 14 (0x14).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 – Register 15 (0x15).
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Falling Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Falling Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Falling Sweep
Ramp rate Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Rising Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Rising Delta
Frequency Tuning Word.
Read-back (FPGA Register) DDS1 - Rising Sweep
Ramp rate Word.
Figure 9 – Register Memory Map.
Analog Devices provides an Interactive Web Tool to calculate Tuning words. It can be found
at the following URL:
http://designtools.analog.com/dtDDSWeb/dtDDSMain.aspx?part=AD9954
5.4 Register Descriptions
5.4.1 Reset and Update Register – 0x0.
Reset Register – 0x0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 DDS1
IO_Update
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
0 Reserved Reserved DDS1
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’
DDS0
IO_Update
DDS1
Update
Reset
DDS0
Update
DDS0
Reset
VGA3
Update
VGA3
Reset
VGA2
Update
VGA2
Reset
VGA1
Update
VGA1
Reset
VGA0
Update
VGA0
Reset
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 16 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 17

Reset Register – 0x0
Setting Bit 0 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep VGA0 in Power Down mode (Gain settings preserved).
Setting Bit 1 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep VGA1 in Power Down mode (Gain settings preserved).
Setting Bit 2 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep VGA2 in Power Down mode (Gain settings preserved).
Setting Bit 3 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep VGA3 in Power Down mode (Gain settings preserved).
Setting Bit 4 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep DDS0 in Power Down mode.
Setting Bit 5 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Keep DDS1 in Power Down mode.
Setting Bit 8 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 VGA0 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 9 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 VGA1 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 10 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 VGA2 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 11 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 VGA3 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 12 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 DDS0 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 13 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 DDS1 gets updated with current register settings.
Setting Bit 14 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Forces DDS0 to reload its registers. Self-clear. To be used in conjunction of bit 15 to synchronise
Setting Bit 15 Description
0 0 Normal Operation.
1 1 Forces DDS0 to reload its registers. Self-clear. To be used in conjunction of bit 14 to synchronise
both DDS chips.
both DDS chips
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 17 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 18

Note 0
: Reset bits don’t get cleared automatically, so a device can remain reset while not
used to reduce the global power consumption.
Note 1
: Update and IO_Update bits get cleared automatically.
5.4.2 Profile Register – 0x1.
Any 16-bit value written in this register can be read-back to check that the Comport used
works properly.
Profile Register – 0x1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Not Used Profile Selection DDS1 Profile Selection DDS0
Default ‘0000’ ‘00’ ‘00’
Reset Register – 0x0
Setting Bit 1&0 Description
0 ‘00’ Profile 0 Selected – DDS0.
1 ‘01’ Profile 1 Selected – DDS0.
2 ‘10’ Profile 2 Selected – DDS0.
3 ‘11’ Profile 3 Selected – DDS0.
Setting Bit 3&2 Description
0 ‘00’ Profile 0 Selected – DDS1.
1 ‘01’ Profile 1 Selected – DDS1.
2 ‘10’ Profile 2 Selected – DDS1.
3 ‘11’ Profile 3 Selected – DDS1.
5.4.3 VGA0 Register – 0x2.
For more details, refer to AD8370 datasheet.
VGA0 Register – 0x2
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Reserved
Default ‘0000000’
0 Gain Mode Gain
Default ‘0’ ‘0000000’
Setting Gain
Mode
(Bit 7)
0 0 LG Mode: Low Gain. The Gain can be from -11 to +17dBs.
1 1 HG Mo de: Low Gain . The Gain c an be from +6 to +34dB s.
VGA0 Register – 0x2
Setting Bits 6-0 Description
0 Gain value (Binary). The scale is from -11 to +17dBs (LG Mode) or from +6 to +34dBs (HG Mode).
VGA0 Register – 0x2
Description
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 18 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 19

5.4.4 VGA1 Register – 0x3.
For more details, refer to AD8370 datasheet.
VGA1 Register – 0x3
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Reserved
Default ‘0000000’
0 Gain Mode Gain
Default ‘0’ ‘0000000’
Setting Gain
Mode
(Bit 7)
0 0 LG Mode: Low Gain. The Gain can be from -11 to +17dBs.
1 1 HG Mo de: Low Gain . The Gain c an be from +6 to +34dB s.
VGA1 Register – 0x3
Setting Bits 6-0 Description
0 Gain value (Binary). The scale is from -11 to +17dBs (LG Mode) or from +6 to +34dBs (HG Mode).
VGA1 Register – 0x3
Description
5.4.5 VGA2 Register – 0x4
For more details, refer to AD8370 datasheet.
VGA2 Register – 0x4
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Reserved
Default ‘0000000’
0 Gain Mode Gain
Default ‘0’ ‘0000000’
VGA2 Register – 0x4
Setting Gain
0 0 LG Mode: Low Gain. The Gain can be from -11 to +17dBs.
1 1 HG Mo de: Low Gain . The Gain c an be from +6 to +34dB s.
VGA2 Register – 0x4
Setting Bits 6-0 Description
0 Gain value (Binary). The scale is from -11 to +17dBs (LG Mode) or from +6 to +34dBs (HG Mode).
Mode
(Bit 7)
Description
5.4.6 VGA3 Register – 0x5.
For more details, refer to AD8370 datasheet.
VGA3 Register – 0x5
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Reserved
Default ‘0000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 19 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 20

0 Gain Mode Gain
Default ‘0’ ‘0000000’
Setting Gain
Mode
(Bit 7)
0 0 LG Mode: Low Gain. The Gain can be from -11 to +17dBs.
1 1 HG Mo de: Low Gain . The Gain c an be from +6 to +34dB s.
VGA3 Register – 0x5
Setting Bits 6-0 Description
0 Gain value (Binary). The scale is from -11 to +17dBs (LG Mode) or from +6 to +34dBs (HG Mode).
VGA3 Register – 0x5
Description
5.4.7 DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Digital
Power
Down
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
1 Load SRR
@ IO UD
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Setting Load SRR
@IO UD
(Bit 15)
0 0 The Linear Sweep Ramp Rate timer is loaded only upon timeout and is not loaded due to an Io
1 1 The Linear Sweep Ramp Rate timer is loaded only upon timeout and is loaded due to an Io
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Auto Clear
Freq
Accum
(Bit 14)
0 0 The state of the frequency accumulator remains unchanged.
1 1 Clears the frequency accumulator for one cycle on an IO Update signal.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Auto Clear
Phase
Accum
(Bit 13)
0 0 The state of the phase accumulator remains unchanged.
1 1 Clears the phase accumulator for one cycle on an IO Update signal.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Enable Description
Comp
Power
Down
AutoClear
Freq
Accum
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Update input signal.
Update input signal.
DAC
Power-
Down
AutoClear
Phase
Accum
Clock
Input
Power-
down
Enable
Sine
Output
External
Power-
down
Mode
Clear Freq
Accum
Description
Description
Description
Linear
Sweep No
Dwell
Clear
Phase
Accum
SYNC_CLk
Out
Disable
SDIO
Input Only
Not Used
LSB First
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 20 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 21

Sine output
(Bit 12)
0 0 Cosine Function.
1 1 Sine Function.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Clear Freq
0 0 The frequency accumulator functions as normal.
1 1 The frequency accumulator is cleared until this bit is cleared.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Clear
0 0 The phase accumulator functions as normal.
1 1 The phase accumulator is cleared until this bit is cleared.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting SDIO
0 0 SDIO is bidirectional.
1 1 SDIO is unidirectional.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting LSB first
0 0 MSB first format is active.
1 1 LSB first format is active
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Digital
0 0 All Digital functions and clocks are active.
1 1 All non-IO digital functions is suspended.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Comp
0 0 The comparator is enabled for operation.
1 1 The comparator is disabled.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting DAC
0 0 The DAC is enabled for operation
1 1 The DAC is disabled.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Clk Input
Accum
(Bit 11)
Phase
Accum
(Bit 10)
Input only
(Bit 9)
(Bit 8)
Power
Down (Bit
7)
Power
Down (Bit
6)
Power
Down (Bit
5)
Power
Down (Bit
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 21 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 22

4)
0 0 The clock input circuitry is enabled.
1 1 The Clock input circuitry is disabled.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting External
0 0 Only digital logic and DAC are powered down when PWRDWNCTL pin is high.
1 1 All functions are powered down when PWRDWNCTL pin is high.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting Linear
0 0 The linear sweep no dwell function is inactive.
1 1 The linear sweep no dwell function is active.
DDS0 Register – 0x6 – Control Function Register
Setting SYNC_CLK
0 0 The SYNC_CLK pin is active.
1 1 The SYNC_CLK pin assumes a static 0.
Power
Down (Bit
3)
Sweep
(Bit 2)
out disable
(Bit 1)
Description
Description
Description
5.4.8 DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Autoatic
Sync
Enable
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘00000’
1 RAM
Enable
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Setting RAM
Enable
(Bit 15)
0 0 The RAM disabled.
1 1 The RAM is active for operation.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting RAM
Destination
(Bit 14)
0 0 The RAM drives the phase accum u lator.
1 1 Th e RAM drive s the phase-of fs et add er.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Software
Manual
Sync
RAM Dest
is Phase
Word
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Linear
Sweep
Enable
Internal Profile Control Load ARR OSK
Description
Description
Not Used
Enable
Auto OSK
Keying
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 22 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 23

Setting Internal
Internal Profile control.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting Load ARR
0 0 The Amplitude Ramp Rate timer is loaded only upon timeout and is not loaded due to an Io
1 1 The Amplitude Ramp Rate timer is loaded only upon timeout and is loaded due to an Io Update
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting OSK
0 0 Shaped on-off keying is bypassed.
1 1 Shaped on-off keying is enabled.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting Auto OSK
0 0 Manual on-off keying operation selected.
1 1 Automatic on-off keying operation selected.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting Auto Synch
0 0 The auto synchronisation of multiple AD9954 is inactive.
1 1 The auto synchronisation of multiple AD9954 is active.
DDS0 Register – 0x7 – Control Function Register
Setting Soft
0 0 The manual synchronisation of multiple AD9954 is inactive.
1 1 The manual synchronisation of multiple AD9954 is active.
DDS0 Register – 0x7– Control Function Register
Setting Linear
0 0 The linear frequency sweep capabilities are inactive.
1 1 The linear frequency sweep capabilities are active.
Profile
Control
(Bit 13-11)
@IO UD
(Bit 10)
Enable
(Bit 9)
Keying
(Bit 8)
Enable
(Bit 7)
Manual
Synch (Bit
6)
Sweep
Enable
(Bit 5)
Description
Description
Update input signal.
input signal.
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
5.4.9 DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RefClk Multiplier VCO Range Charge Pump Current
Default ‘00000’ ‘0’ ‘00’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 23 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 24

1 Not Used High speed
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Setting High
Speed
Sync (Bit
11)
0 0 The high-speed enhancement is off.
1 1 The high-speed enhancement is on.
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Setting Hardware
Manual
Synch
(Bit 10)
0 0 The hardware synch function is off.
1 1 The hardware synch function is on.
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Setting Crystal
out pin
active
(Bit 9)
0 0 CRYSTAL OUT pin is inactive.
1 1 CRYSTAL OUT pin is active.
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Setting Ref Clock
Multiplier
(Bit 7-3)
Valid values are decimal 4-20 (0x4 to 0x14).
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Setting VCO
Range
(Bit 2)
0 0 The VCO operates in a range of 100MHz to 250MHz.
1 1 The VCO operates in a range of 250MHz to 400MHz.
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
Setting Charge
Pump
Current
(Bit 1-0)
0x0 (75uA), 0x1 (100uA), 0x2 (125uA) or 0x3 (150uA).
DDS0 Register – 0x8 – Control Function Register
synch
enable
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
Description
Hardware
Manual
Sync
enable
Crystal
Output Pin
active
Not Used
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 24 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 25

5.4.10 DDS0 Register – 0x9 – Amplitude Scale Factor.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x9 – Amplitude Scale Factor
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Amplitude Scale Factor Register[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Auto Ramp Rate Speed Amplitude Scale Factor Register[13:8]
Default ‘00’ ‘000000’
Setting Auto Ramp
0 0 Tell the OSK block how many amplitude steps to each increase.
DDS0 Register – 0x9 – Amplitude Scale Factor
Setting Amplitude
Rate Speed
(Bit 15-14)
Scale
Factor
(Bit 13-0)
Programs the maximum value achievable by the OSK.
DDS0 Register – 0x9 – Amplitude Scale Factor
Description
Description
5.4.11 DDS0 Register – 0xA – Amplitude Ramp Rate.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xA – Amplitude Ramp Rate
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Amplitude Ramp Rate
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Amplitude
Ramp
Rate (Bit
7-0)
The 8-bit amplitude ramp rate used in the auto OSK mode.
DDS0 Register – 0xA – Amplitude Ramp Rate
Description
5.4.12 DDS0 Register – 0xB – Frequency Tuning Word 0.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xB – Frequ ency Tuning Word 0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Frequency Tuning Word 0[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Frequency Tuning Word 0[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 25 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 26

DDS0 Register – 0xB – Frequency Tuning Word 0
Setting Frequency
Tuning
Word 0
Description
The frequency tuning word is a 32-bit register that controls the rate of accumulation in the phase
accumulator of the DDS core.
5.4.13 DDS0 Register – 0xC – Frequency Tuning Word 0.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xC – Frequency Tuning Word 0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Frequency Tuning Word 0[23:16]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Frequency Tuning Word 0[31:24]
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Frequency
Tuning
Word
DDS0 Register – 0xC – Frequency Tuning Word 0
Description
The frequency tuning word is a 32-bit register that controls the rate of accumulation in the phase
accumulator of the DDS core.
5.4.14 DDS0 Register – 0xD – Phase Offset Word.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xD –Phase Offset Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Phase Offset Word[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used Phase Offset Word[13:8]
Default ‘00’ ‘000000’
Setting Phase
Offset
Word
The phase offset word is a 14-bit register that stores a phase offset value.
DDS0 Register – 0xD – Phase Offset Word
Description
5.4.15 DDS0 Register – 0xE – Frequency Tuning Word 1.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xE – Frequency Tuning Word 1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Frequency Tuning Word 1[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 26 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 27

1 Frequency Tuning Word 1[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Frequency
Tuning
Word 1
DDS0 Register – 0xE – Frequency Tuning Word 1
Description
The frequency tuning word is a 32-bit register that controls the rate of accumulation in the phase
accumulator of the DDS core.
5.4.16 DDS0 Register – 0xF – Frequency Tuning Word 1.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0xF – Frequency Tuning Word 1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Frequency Tuning Word 1[23:16]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Frequency Tuning Word 1[31:24]
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Frequency
Tuning
Word 1
DDS0 Register – 0xF – Frequency Tuning Word 1
Description
The frequency tuning word is a 32-bit register that controls the rate of accumulation in the phase
accumulator of the DDS core.
5.4.17 DDS0 Register – 0x10 – RAM Segment Control Word
0.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x10 – RAM Segment Control Word 0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 0 Mode Control No Dwell
Active
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
1 RAM Segment 0 Beginning Address[5:0] RAM Segment 0 Final
Default ‘000000’ ‘00’
RAM Segment 0 Beginning Address[9:6]
Address[9:8]
5.4.18 DDS0 Register – 0x11 – RAM Segment Control Word
0.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x11 – RAM Segment Control Word 0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 0 Final Address[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 27 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 28

1 RAM Segment 0 Address Ramp Rate[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.19 DDS0 Register – 0x12 – RAM Segment Control Word
0.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x12 – RAM Segment Control Word 0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 0 Address Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.20 DDS0 Register – 0x13 – RAM Segment Control Word
1.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x13 – RAM Segment Control Word 1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 1 Mode Control No Dwell
Active
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
1 RAM Segment 1 Beginning Address[5:0] RAM Segment 1 Final
Default ‘000000’ ‘00’
RAM Segment 1 Beginning Address[9:6]
Address[9:8]
5.4.21 DDS0 Register – 0x14 – RAM Segment Control Word
1.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x14 – RAM Segment Control Word 1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 1 Final Address[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 RAM Segment 1 Address Ramp Rate[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.22 DDS0 Register – 0x15 – RAM Segment Control Word
1.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x15 – RAM Segment Control Word 1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 1 Address Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 28 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 29

5.4.23 DDS0 Register – 0x16 – RAM Segment Control Word
2.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x16 – RAM Segment Control Word 2
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 2 Mode Control No Dwell
Active
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
1 RAM Segment 2 Beginning Address[5:0] RAM Segment 2 Final
Default ‘000000’ ‘00’
RAM Segment 2 Beginning Address[9:6]
Address[9:8]
5.4.24 DDS0 Register – 0x17 – RAM S egment Control Word
2.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x17 – RAM Segment Control Word 2
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 2 Final Address[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 RAM Segment 2 Address Ramp Rate[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.25 DDS0 Register – 0x18 – RAM Segment Control Word
2.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x18 – RAM Segment Control Word 2
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 2 Address Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.26 DDS0 Register – 0x19 – RAM Segment Control Word
3.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x19 – RAM Segment Control Word 3
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 3 Mode Control No Dwell
Active
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
1 RAM Segment 3 Beginning Address[5:0] RAM Segment 3 Final
Default ‘000000’ ‘00’
RAM Segment 3 Beginning Address[9:6]
Address[9:8]
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 29 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 30
5.4.27 DDS0 Register – 0x1A – RAM Segment Control Word
3.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1A – RAM Segment Control Word 3
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 3 Final Address[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 RAM Segment 3 Address Ramp Rate[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.28 DDS0 Register – 0x1B – RAM Segment Control Word
3.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1B – RAM Segment Control Word 3
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 RAM Segment 3 Address Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
5.4.29 DDS0 Register – 0x1C – Falling Delta Frequency
Tuning.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1C – Falling Delta Frequency Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Falling Delta Frequency Word[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Falling Delta Frequency Word[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Falling
Delta
Frequency
Word
DDS0 Register – 0x1C – Falling Delta Frequency Word
Description
The Falling Delta Frequency word is a 32-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 30 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 31

5.4.30 DDS0 Register – 0x1D – Falling Delta Frequency
Word.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1D – Falling Delta Frequency Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Falling Delta Frequency Word[23:16]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Falling Delta Frequency Word[31:24]
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Falling
Delta
Frequency
Word
DDS0 Register – 0x1D – Falling Delta Frequency Word
Description
The Falling Delta Frequency word is a 32-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
5.4.31 DDS0 Register – 0x1E – Falling Sweep Ramp Rate
Word.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1E – Falling Sweep Ramp rate Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Falling Sweep Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Falling
Delta
Frequency
Word
DDS0 Register – 0x1E – Falling Sweep Ramp rate Word
Description
The Falling Sweep Ramp Rate is a 7-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
5.4.32 DDS0 Register – 0x1F – Rising Delta Frequency
Tuning.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x1F – Ris ing Delta Frequency Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Rising Delta Frequency Word[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Rising Delta Frequency Word[15:8]
Default ‘00000000’
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 31 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 32

DDS0 Register – 0x1F – Rising Delta Frequency Word
Setting Rising
Delta
Frequency
Word
Description
The Rising Delta Frequency word is a 32-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
5.4.33 DDS0 Register – 0x20 – Rising Delta Frequency
Word.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x20 – Rising Delta Frequency Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Rising Delta Frequency Word[23:16]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Rising Delta Frequency Word[31:24]
Default ‘00000000’
DDS0 Register – 0x20 – Rising Delta Frequency Word
Setting Rising
Delta
Frequency
Word
Description
The Rising Delta Frequency word is a 32-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
5.4.34 DDS0 Register – 0x21 – Rising Sweep Ramp Rate
Word.
For more details, refer to AD9954 datasheet.
DDS0 Register – 0x21 – Rising Sweep Ramp rate Word
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 Rising Sweep Ramp Rate[7:0]
Default ‘00000000’
1 Not Used
Default ‘00000000’
Setting Falling
Delta
Frequency
Word
DDS0 Register – 0x21 – Rising Sweep Ramp rate Word
Description
The Rising Sweep Ramp Rate is a 7-bit register that is used in the sweeping mode.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 32 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 33

6 PCB Layout
6.1 Top View
Figure 10 - Layout - Top Side.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 34

6.2 Bottom View
Figure 11 - Layout - Bottom Side.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 34 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 35

7 Connector Location
The following diagram shows where connectors are located on the board:
Figure 12 - Connector Location.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 36

8 Support Packages
An example code is provided with the SMT399-160, often part of one of Sundance’s software
packages.
The example code, if not targeting exactly the h ardware platform used can b e used as a base
for an other platform.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 37

9 Physical Properties
Dimensions maximum height
12.8 mm
Weight 35 gramms
Supply Voltages 3.3 and 5 Volts
through SLB
power connector.
Supply Current +12V N/A
+5V 0.3A Max
+3.3V 0.5A Max
-5V N/A
-12V N/A
MTBF
It is strongly recommended to allow some air flow around the SMT399-160 module,
especially when used in a closed PC case, in order to avoid it to reach high temperature.
0.02A under Reset
0.35A under Reset
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 38

10 Safety
This module presents no hazard to the user when in normal use.
User Manual SMT399-160 Page 38 of 39 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
Page 39

11 EMC
This module is designed to operate from within an enclosed host system, which is build to
provide EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is not guaranteed unless it
is installed within an adequate host system.
This module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients originating from outside th e
host system which may be introduced through the output cables.
Short circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up or reboot.
User Manual SMT399-160 Last Edited: 24/05/2007 17:12:00
 Loading...
Loading...