Page 1

SMT384
User Manual
Page 2
Version 1.4 Page 2 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Revision History
Date Comments Engineer Version
02/05/06 Original Version PhSR 1.0
15/06/06 Added DC-coupling input stage diagram PhSR 1.1
26/01/07 Connector description and location added PhSR 1.2
25/05/07 FPGA Registers are read-back from FPGA. PhSR 1.3
25/11/09 Clarification AC/DC version PhSR 1.4
Page 3

Version 1.4 Page 3 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Table of Contents
Revision History............................................................................................................ 2
Table of Contents ......................................................................................................... 3
Table of Figures............................................................................................................ 5
Physical Properties ....................................................................................................... 7
Precautions................................................................................................................... 8
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 9
Overview ................................................................................................................... 9
Module features ........................................................................................................ 9
Possible applications .............................................................................................. 10
Related Documents ................................................................................................ 10
Functional Description ................................................................................................ 11
Block Diagram......................................................................................................... 11
Module Description ................................................................................................. 11
ADC Channels. ....................................................................................................... 13
ADC Main Characteristics. .................................................................................. 13
ADC Input Stage (standard SMT384). ................................................................ 14
Clock Structure........................................................................................................ 15
Power Supply and Reset Structure......................................................................... 17
Green LEDs. ........................................................................................................... 17
Mezzanine module Interface................................................................................... 17
Control Register Settings............................................................................................ 25
Control Packet Structure......................................................................................... 25
Reading and Writing Registers ............................................................................... 25
Memory Map ........................................................................................................... 26
Register Descriptions.............................................................................................. 27
Reset Register – 0x0........................................................................................... 27
Test Register – 0x1. ............................................................................................ 28
ADCA Register 0 – 0x2. ...................................................................................... 28
ADCA Register 1 – 0x3. ...................................................................................... 28
ADCA Register 2 – 0x4. ...................................................................................... 29
ADCB Register 0 – 0x5. ...................................................................................... 29
Page 4

Version 1.4 Page 4 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
ADCB Register 1 – 0x6. ...................................................................................... 30
ADCB Register 2 – 0x7. ...................................................................................... 30
ADCC Register 0 – 0x8. ...................................................................................... 30
ADCC Register 1 – 0x9. ...................................................................................... 31
ADCC Register 2 – 0xA....................................................................................... 31
ADCD Register 0 – 0xB....................................................................................... 32
ADCD Register 1 – 0xC. ..................................................................................... 32
ADCD Register 2 – 0xD. ..................................................................................... 32
Main Module Temperature – 0x18 ...................................................................... 33
Main Module FPGA Temperature – 0x19 ........................................................... 33
Mezzanine Module Temperature – 0x1A ............................................................ 33
Mezzanine Module Converters Temperature – 0x1B ......................................... 33
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C........................................................................... 33
Updates, Read-back and Firmware Version Registers – 0x1D .......................... 35
Decimator Register – 0x1E. ................................................................................ 35
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x30. ................................................................................. 36
AD9510 Register 1 – 0x31. ................................................................................. 36
AD9510 Register 2 – 0x32. ................................................................................. 36
AD9510 Register 3 – 0x33. ................................................................................. 36
AD9510 Register 4 – 0x34. ................................................................................. 37
AD9510 Register 5 – 0x35. ................................................................................. 37
AD9510 Register 6 – 0x36. ................................................................................. 37
AD9510 Register 7 – 0x37. ................................................................................. 37
AD9510 Register 8 – 0x38. ................................................................................. 38
AD9510 Register 9 – 0x39. ................................................................................. 38
AD9510 Register A – 0x3A. ................................................................................ 38
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x3B.................................................................................. 38
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x3C. ................................................................................ 39
AD9510 Register D – 0x3D. ................................................................................ 39
AD9510 Register E – 0x3E. ................................................................................ 39
AD9510 Register F – 0x3F.................................................................................. 39
AD9510 Register 10 – 0x40. ............................................................................... 40
AD9510 Register 11 – 0x41. ............................................................................... 40
Page 5

Version 1.4 Page 5 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 12 – 0x42. ............................................................................... 40
AD9510 Register 13 – 0x43. ............................................................................... 40
AD9510 Register 14 – 0x44. ............................................................................... 41
AD9510 Register 15 – 0x45. ............................................................................... 41
AD9510 Register 16 – 0x46. ............................................................................... 41
AD9510 Register 17 – 0x47. ............................................................................... 41
AD9510 Register 18 – 0x48. ............................................................................... 42
AD9510 Register 19 – 0x49. ............................................................................... 42
PCB and Firmware Version Registers ................................................................ 42
FPGA Design.............................................................................................................. 43
Serial Interfaces ...................................................................................................... 43
Block of registers .................................................................................................... 44
Space available in FPGA ........................................................................................ 44
PCB Layout................................................................................................................. 44
Connectors ................................................................................................................. 46
Description .............................................................................................................. 46
Location on the board ............................................................................................. 47
Table of Figures
Figure 1 – Fan across PCI............................................................................................ 8
Figure 2 - Block Diagram............................................................................................ 11
Figure 3 - Main features. ............................................................................................ 14
Figure 4 - ADC Input Stage (AC coupling). ................................................................ 14
Figure 5 - ADC Input Stage (DC Coupling) ................................................................ 15
Figure 6 - Clock Structure........................................................................................... 15
Figure 7 - External Clock. ........................................................................................... 16
Figure 8 - Clock Architecture Main Characteristics.................................................... 17
Figure 9 – Mezzanine module Connector Interface (SLB data and power connectors).
.................................................................................................................................... 18
Figure 10 – Mezzanine Module Interface Power Connector and Pinout. .................. 20
Figure 11 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank
A). ............................................................................................................................... 21
Page 6

Version 1.4 Page 6 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Figure 12 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank
B). ............................................................................................................................... 23
Figure 13 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank
C). ............................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 14 – Setup Packet Structure. .......................................................................... 25
Figure 15 – Control Register Read Sequence. .......................................................... 25
Figure 16 – Register Memory Map............................................................................. 27
Figure 17 - Firmware Block Diagram.......................................................................... 43
Figure 18 – Main Module Component Side................................................................ 44
Figure 19 - Main Module (SMT368) Solder Side........................................................ 45
Figure 20 - Daughter Module Component Side. ........................................................ 45
Figure 21 - Daughter Module Solder Side.................................................................. 46
Figure 22 - Connectors Location. ............................................................................... 47
Page 7
Version 1.4 Page 7 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Physical Properties
Dimensions 63.5mm x 106.7mm x 18mm
Weight 35 grams
Supply Voltages
Supply Current +12V
+5V
+3.3V
-5V
-12V
MTBF
Page 8

Version 1.4 Page 8 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Precautions
In order to guarantee that Sundance’s boards function correctly and to protect the
module from damage, the following precautions should be taken:
- They are static sensitive products and should be handled accordingly.
Always place the modules in a static protective bag during storage and transition.
- When operated in a closed environment make sure that the heat generated
by the system is extracted e.g. a fan extracting heat or blowing cool air. Sundance
recommends and uses PAPST 12-Volt fans (Series 8300) producing an air flow of 54
cubic meters per hour (equivalent to 31.8 CFM). Fans are placed so they blow across
the PCI bus as show on the following picture:
Figure 1 – Fan across PCI.
Page 9
Version 1.4 Page 9 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Introduction
Overview
The SMT384 is a single width expansion TIM that plugs onto an SLB
(for instance SMT368
, SMT338-VP or SMT398-VP) and incorporates 4 Texas
base module
Instrument Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADS5500). The SMT384 implements a
comprehensive clock circuitry based on a AD9510
chip that allows synchronisation
among the converters and cascading modules for multiple receiver systems as well
as the use of an external reference clock. It provides a complete conversion solution
and stands as a platform that can be part of a receive base station.
ADCs are 14-bit and can sample at up to 125 MHz. All converters are 3.3-Volt. As a
standard, the ADCs are all AC-coupled (RF Transformers), but can also be optionally
DC-coupled (TI opamp THS4509
The Xilinx FPGA
on the base module is responsible for handling data or control
commands coming from the TI converters, Comports (TIM-40 standard
High-speed Bus (SHB
). These interfaces are compatible with a wide range of
).
), Sundance
Sundance’s modules.
Converter configuration, sampling and transferring modes are set via internal control
registers stored inside the FPGA and accessible via Comport.
Module features
The main features of the SMT384 are listed below:
● Quad 14-bit 125MSPS ADC (ADS5500
),
MMCX
● On-board low-jitter clock generation (AD9510
),
● One external clocks, two external triggers and one reference clock via
connector,
● One SLB
connector to link SMT384 and the base SLB module,
● Synchronisation signals,
● All Analogue inputs to be connected to 50-Ohm sources/loads.
● Temperature sensors.
Page 10

Version 1.4 Page 10 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Possible applications
The SMT384 can be used for the following application (this non-exhaustive list
should be taken as an example):
● High Intermediate-Frequency (IF) sampling architecture,
● Cellular base station such as CDMA and TDMA,
● Baseband I&Q systems,
● Wireless communication systems,
● Communication instrumentation,
● ...
Related Documents
ADS5500 Datasheet – Texas Instrument:
http://focus.ti.com/docs/prod/folders/print/ads5500.html
AD9510 Datasheet – Analog Devices:
http://www.analog.com/en/prod/0,2877,AD9510,00.html
Sundance High-speed Bus (SHB) specifications – Sundance.
ftp://ftp2.sundance.com/Pub/documentation/pdffiles/SHB_Technical_Specification.pdf
Sundance LVDS Bus (SLB) specifications – Sundance.
http://www.sundance.com/docs/SLB%20-%20Technical%20Specifications.pdf
TIM specifications.
ftp://ftp2.sundance.com/Pub/documentation/pdf-files/tim_spec_v1.01.pdf
MMCX Connectors – Hubert Suhner.
MMCX Connectors
Surface Mount MMCX connector
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd.
SMT368
SMT338-VP
SMT398-VP
Page 11
Version 1.4 Page 11 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Functional Description
In this part, we will see the general block diagram and some comments on some the
SMT384 entities.
Block Diag ram
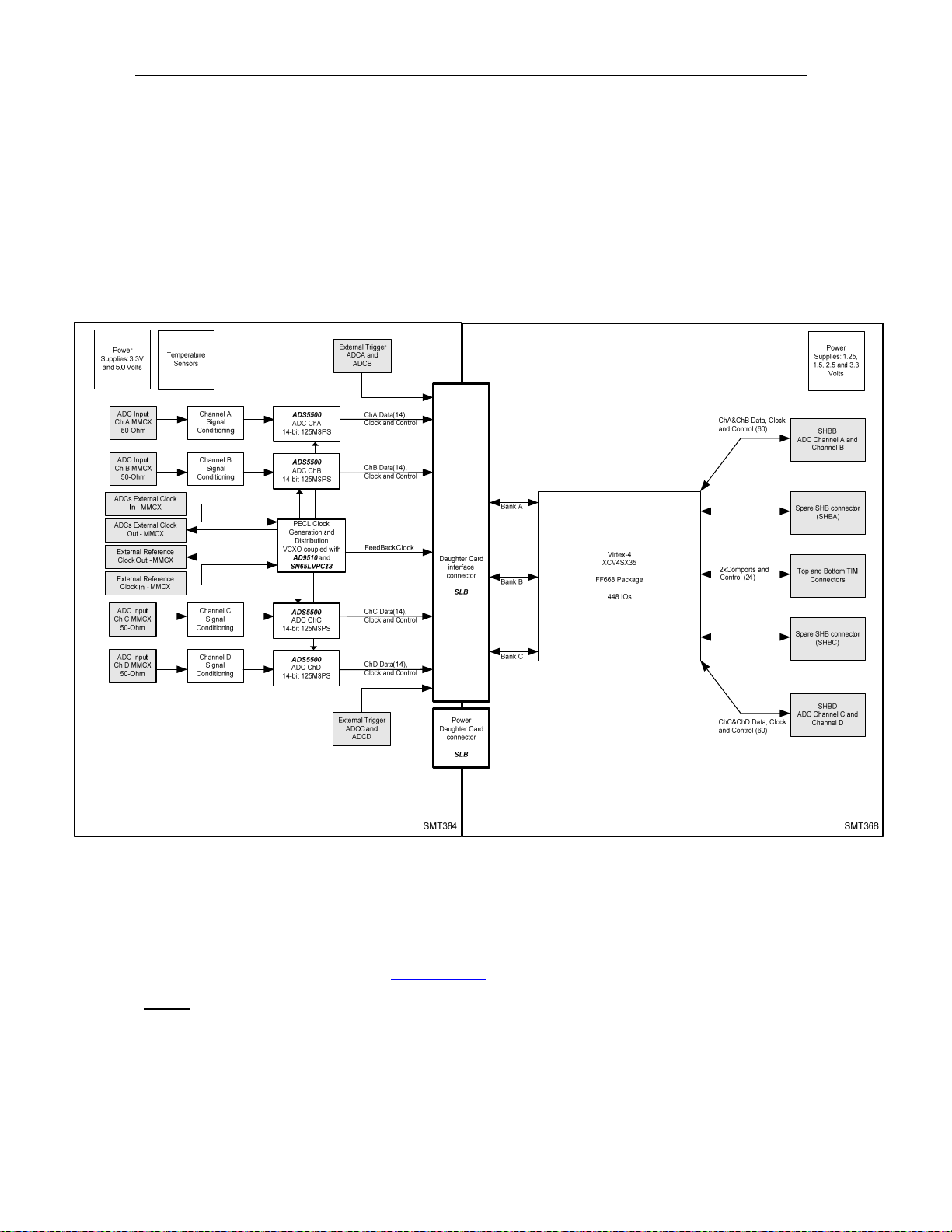
The following diagram describes the architecture of the SMT384, coupled – as an
example – with an SMT368 to show how mezzanine and base modules are
connected together:
Figure 2 - Block Diagram.
Module Description
The module is built around four TI ADS5500
ADCs
: Analog data enters the module via four MMCX connectors, one for each
14-bit sampling analog-to-digital.
channel. Both signals are then conditioned (AC coupling as standard via RF
transformers; DC optional via Texas Instrument amplifier THS4509) before being
Page 12
Version 1.4 Page 12 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
digitized. ADCs get their own sampling clock, which can be either on-board
generated or from an external reference or an external clock, common to all ADCs
(MMCX connector). Digital samples travel to the FPGA on the base module via the
inter-module connector (SLB
– Sundance LVDS Bus, used in this case as ‘single-
ended’).
Clock generator and distribution
: All samplings clocks are generated by the same
chip. It allows having them all synchronized to a single reference clock. The on-board
clock uses the VCXO locked on an on-board 10MHz reference. The reference also
can be external, in that case the VCXO is still used. In the case of an external clock,
the VCXO is no longer used as the AD9510 then acts as a clock multiplexer. In all
cases, all sampling clocks are synchronized to the same clock source.
Multi-module Synchronization
: SMT384s can be cascaded and still be synchronized
as either the external reference or the external clock can be passed the next module
in the chain. The external reference goes through a 0-delay buffer and is then output.
Please note that symchronisation is in frequency and not in phase.
Inter-module Connector
pins). It is called Sundance LVDS Bus. Please refer to the SLB specifications
: it is made of a power (33 pins) and data connectors (120
for
more details. In the case of the SMT384, the SLB is used as ‘single-ended’.
A global reset signal is mapped to the FPGA from the bottom TIM connector.
External Clock signals
, used to generate Sampling clocks. There is one external
clock, common to all four ADCs. When used, the AD9510 is used as a clock
multiplexer. Also available, an external reference clock that can be passed to an
other SMT384 (cascaded modules) module with ‘0-delay’.
External Trigger
: passed directly to the base module. There are two, one for each
pair of ADCs (Channel A & B and Channel C & D).
Temperature Sensor
: available for constant monitoring.
Page 13
Version 1.4 Page 13 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
ADC Channels.
ADC Main Characteristics.
The main characteristics of the SMT384 ADCs are gathered into the following table.
Analogue Inputs
AC coupled option. 2.4 Vp-p (11.5 dbm –
50 Ohm) Full scale - AC coupled via RF
transformer.
Input voltage range
Impedance
Bandwidth
External Reference Input
DC coupled option. 1.15 Vp-p (Gain
amplifier 6dB) centered around 0. DC
coupled via amplifier. Gai n can be adjust ed
to a required input amplitude centered
around 0. Minimm gain 6dBs, which should
allow input swing +/-0.575V as full scale.
AC Coupled option. ADC single-ended
inputs are to be connected to an AC 50-Ω
source. Source impedance matching
implemented between RF transformers and
ADC.
DC Coupled option. Impedance matching
done at the connector. To be connected to a
Dc 50-Ω source.
ADC bandwidth: 750 MHz.
Input Voltage Level
Input Impedance
Frequency Range
Output Voltage Level
Output Impedance
External Sampling Clock Input
Input Voltage Level
Input Format
Frequency range
Input Voltage Level
Format
0.5 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
50-Ohm (Termination implemented at the
connector)
0 – 100 MHz.
External Reference Output
1.6 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
50-Ohm (Termination implemented at the
connector)
0.5 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
Single-ended or differential on option (3.3V
LVPECL).
10-125 MHz
External Trigger Inputs
1.5-3.3 Volts peak-to-peak.
DC-coupled and Single-ended (Termination
implemented at the connector). Differentia l
Page 14
Version 1.4 Page 14 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
on option (3.3 V PECL).
Impedance
Frequency range
Output Data Width
Data Format
SFDR
SNR
Minimum Sampling Clock
Maximum Sampling Frequency
Figure 3 - Main features.
ADCs Output
14-Bits
2’s Complement or offset binary
(Changeable via control register)
82dBs maximum (manufacturer)
70dBs maximum (manufacturer)
10 MHz (ADC DLL off)
125 MHz (ADC DLL on)
50-Ohm.
62.5 MHz maximum
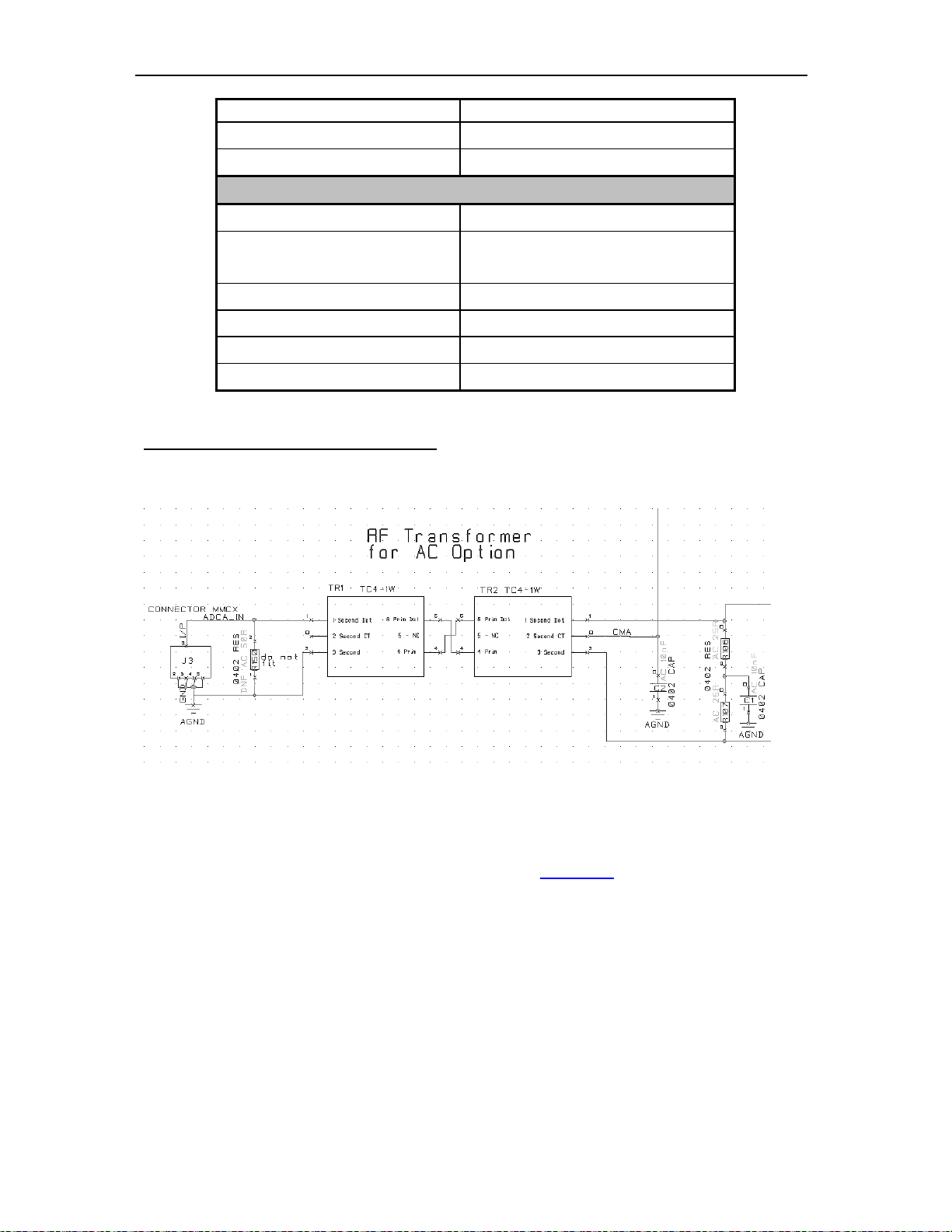
ADC Input Stage (standard SMT384).
Each ADC Analogue input is AC-coupled via and RF transformer. Both sides of the
transformers are balanced so the input is 50-Ohm single-ended.
Figure 4 - ADC Input Stage (AC coupling).
The SMT384 can also receive an DC-coupling input stage on request as shown
below :
It is based around a Texas Instrument amplifier (THS4509
), which gain is set to 6
dBs and is to match a 50-Ohm signal source.
Page 15
Version 1.4 Page 15 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Figure 5 - ADC Input Stage (DC Coupling)
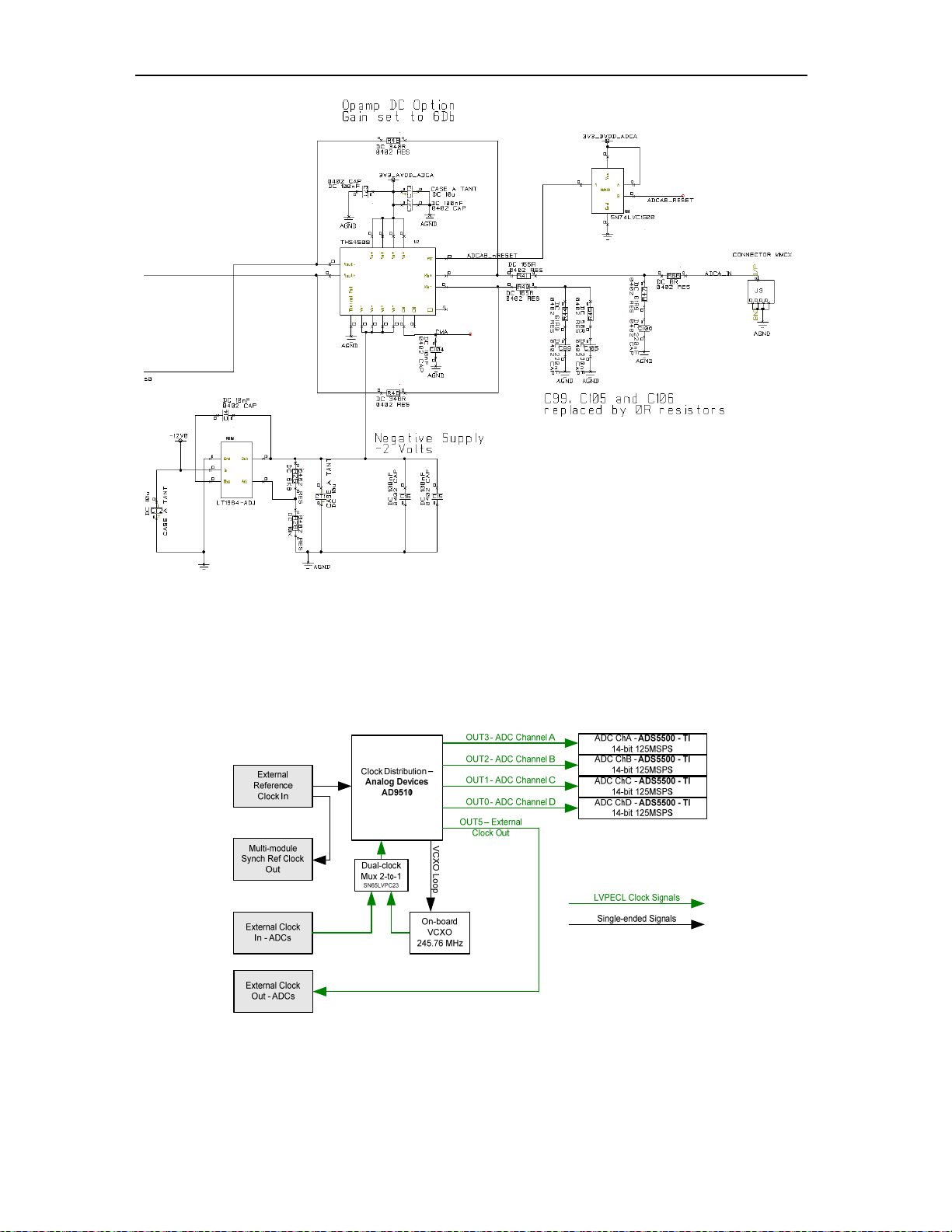
Clock Structure
There is one integrated clock generator on the module (AD9510 – Analog Devices).
The user can either use this clock (on-board) or provide the module with an external
clock (input via MMCX connector).
Figure 6 - Clock Structure.
Page 16

Version 1.4 Page 16 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
ADCs can all receive the same clock or the integer multiple of it (x2, x3, …x32), the
maximum being 125MHz for each ADC. This clock can be coming from the on-board
VCXO or from an external source.
An extra connector outputs the reference clock for multiple-module systems.
Below is shown how the external clock is fed to the system. By default it is singleended and AC-coupled before being converted into LVPECL format. The option of
having a differential external clock is still possible on the hardware by the way of
fitting or not some of the components.
Figure 7 - External Clock.
The main characteristics of the SMT384 Clocks are gathered into the following table.
External Reference Input
Input Voltage Level
Input Impedance
Frequency Range
External Reference Output
Output Voltage Level
Output Impedance
External Sampling Clock Input
Input Voltage Level
Format
0.5 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
50-Ohm (Termination implemented at the
connector)
0 – 100 MHz.
1.6 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
50-Ohm (Termination implemented at the
connector)
0.5 – 3.3 Volts peak-to-peak (AC-coupled)
Single-ended or differential on option (3.3V
LVPECL).
Page 17

Version 1.4 Page 17 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Frequency range
External Sampling Clock Output
10-125 MHz
Output Voltage Level
Output Format
External Trigger Inputs
Input Voltage Level
DC-coupled and Single-ended (Termination
Format
Impedance
Frequency range
External Ref. Input to Ext Ref. Out
External Clk Input to Ext Clk Out
Figure 8 - Clock Architecture Main Characteristics.
implemented at the connector ). Differential
Delay
0-2.4 Volts fixed amplitude.
LVTTL
1.5-3.3 Volts peak-to-peak.
on option (3.3 V PECL).
50-Ohm.
62.5 MHz maximum
11ns between J29 and J4
Power Supply and Reset Structure
The SMT384 gets two power sources from the base module: 3.3 and 5 Volts. Linear
regulators are used to provide a clean and stable voltage supply to the analog
converters. The DC-coupling option uses also -12 Volts.
Green LEDs.
There are some LEDs on the Daughter Module. Three are dedicated for the power
supplies (3.3-Volt Channel A, B, C and D, as well as clock circuitry). Green LEDs
being ON meaning that the supply is under power.
Mezzanine module Interface
The daughter module interface is made up of two connectors (data and power). The
first one is a 0.5mm-pitch differential Samtec connector. This connector is for
transferring data such as ADC samples to the FPGA on the main module. The
second one is a 1mm-pitch Samtec header type connector. This connector is for
providing power to the daughter-card.
Sundance defines these two connectors as the Sundance LVDS Bus (SLB). It has
originally been made for data transfers using LVDS format but can also be used with
single-ended lines, which is the case for the SMT384. To know more about the SLB,
please refer to the SLB specifications
.
The figure underneath illustrates this configuration. The bottom view of the daughter
card is shown on the right. This view must the mirrored to understand how it connects
to the main module.
Page 18

Version 1.4 Page 18 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Data
Bank A
Bank B Bank C
Power
connectors
Figure 9 – Mezzanine module Connector Interface (SLB data and power connectors).
The female differential connector is located on the base module. The Samtec Part
Number for this connector is QTH-060-01-F-D-DP-A.
The female power connector is located on the base module. The Samtec Part
Number for this connector is BKS-133-03-F-V-A
The male differential connector is located on the mezzanine card. The Samtec Part
Number for this connector is QSH-060-01-F-D-DP-A
The male power connector is located on the mezzanine card. The Samtec Part
Number for this connector is BKT-133-03-F-V-A
The mated height between the main module and the daughter card is 5 mm.
Page 19

Version 1.4 Page 19 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Some JTAG Lines are also mapped onto this connector to be used in case the
Daughter module would have a TI Processor. They would allow debugging and
programming via JTAG.
The following table shows the pin assignment on the power connector:
2
1
33
Pin Number Pin Name Description of Signal
1 D+3V3 Digital 3.3 Volts
2 DGND Digital Ground
3 D+3V3 Digital 3.3 Volts
4 DGND Digital Ground
5 D+3V3 Digital 3.3 Volts
6 DGND Digital Ground
7 D+3V3 Digital 3.3 Volts
8 DGND Digital Ground
9 D+5V0 Digital 5.0 Volts
10 DGND Digital Ground
11 D+5V0 Digital 5.0 Volts
12 DGND Digital Ground
13 D+5V0 Digital 5.0 Volts
14 DGND Digital Ground
15 D+5V0 Digital 5.0 Volts
16 DGND Digital Ground
17 D+12V0 Digital +12.0 Volts – not used on the SMT384
18 DGND Digital Ground
19 D+12V0 Digital +12.0 Volts – not used on the SMT384
20 DGND Digital Ground
21 D-12V0 Digital –12.0 Volts – used on the SMT384 only for DC option.
Page 20

Version 1.4 Page 20 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
22 DGND Digital Ground
23 D-12V0 Digital –12.0 Volts –used on the SM384 only for DC option.
24 DGND Digital Ground
25 DGND Digital Ground
26 EMU0 Emulation Control 0 – not used on SMT384
27 EMU1 Emulation Control 1 – not used on SMT384
28 TMS JTAG Mode Control – not used on SMT384
29 nTRST JTAG Reset – not used on SMT384
30 TCK JTAG Test Clock – not used on SMT384
31 TDI JTAG Test Input – not used on SMT384
32 TDO JTAG Test Output – not used on SMT384
33 DGND Digital Ground
Figure 10 – Mezzanine Module Interface Power Connector and Pinout.
The following few pages describes the signals on the data connector between the
main module and the daughter card. Bank A on the connector is used for the ADC
Channels A and B. Bank C is used for the ADC channels C and D. Bank B is used for
system clock and trigger signals, ADCs/Clock control signal.
Page 21

Version 1.4 Page 21 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Bank A Bank B Bank C
1 3 5 7 41 43 81 83
2 4 6 8
Bank A (ADC A and B)
Pin No Pin Name Signal Description Pin No Pin Name Signal Description
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
1 DOAI0p Data Out 0, Channel A. 2 DOBI0p Data Out 1, Channel A.
3 DOAI0n Data Out 2, Channel A. 4 DOBI0n Data Out 3, Channel A.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
5 DOAI1p Data Out 4, Channel A. 6 DOBI1p Data Out 5, Channel A.
7 DOAI1n Data Out 6, Channel A. 8 DOBI1n Data Out 7, Channel A.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
9 DOAI2p Data Out 8, Channel A. 10 DOBI2p Data Out 9, Channel A.
11 DOAI2n Data Out 10, Channel A. 12 DOBI2n Data Out 11, Channel A.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
13 DOAI3p Data Out 12, Channel A. 14 DOBI3p Data Out 13, Channel A.
15 DOAI3n Over Range, Channel A. 16 DOBI3n Data Out 0, Channel B.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
17 DOAI4p Data Out 1, Channel B. 18 DOBI4p Data Out 2, Channel B.
19 DOAI4n Data Out 3, Channel B. 20 DOBI4n Data Out 4, Channel B.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
21 DOAI5p Data Out 5, Channel B. 22 DOBI5p Data Out 6, Channel B.
23 DOAI5n Data Out 7, Channel B. 24 DOBI5n Data Out 8, Channel B.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
25 DOAI6p Data Out 9, Channel B. 26 DOBI6p Data Out 10, Channel B.
27 DOAI6n Data Out 11, Channel B. 28 DOBI6n Data Out 12, Channel B.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
29 DOAI7p Data Out 13, Channel B. 30 DOBI7p Over Range, Channel B.
31 DOAI7n Led ADC A and B. 32 DOBI7n Status Lock AD9510
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
33 ClkOIp Data Clock Out, Channel A. 34 DOIRIp Status Ref AD9510
35 ClkOIn Data Clock Out, Channel B. 36 DOIRIn Status VCXO AD9510
Dir Reserved. Dir Reserved.
37 Reserved. Reserved. 38 Reserved ADC A and B External Trigger, P.
39 Reserved. Reserved. 40 Reserved ADC A and B External Trigger, N.
Figure 11 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank A).
Page 22

Version 1.4 Page 22 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Bank A Bank B Bank C
1 3 5 7 41 43 81 83
2 4 6 8
Bank B
Pin No Pin N a me Signal Description Pin No Pin Nam e Signal Description
Type Clock and Trigger System Signals Type Clock and Trigger System Signals
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
41 SMBClk Temperature Sensor Clock. 42 SMBData Temperature Sensor Data.
43 SMBnAlert Temperature Sensor Alert. 44 SerialNo Reserved
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Reserved
45 AdcVDacI Reserved 46 AdcVDacQ Reserved
47 AdcVRes Reserved 48 AdcReset AD9510 Function
Dir Main Module to Daughter Card Dir Main Module to Daughter Card
49 D3v3Enable Reserved 50 D2v5Enable Reserved
51 AdcMode ADCA Serial Clock. 52 AdcClock ADCA Serial Data.
Type ADC Specific Signals Type ADC Specific Signals
Dir Main Module to Daughter Card Dir Reserved
53 AdcLoad ADCA Serial Enable. 54 AdcData ADCB Serial Clock.
55 AdcCal ADCB Serial Data. 56 AdjClkCntr0 ADCB Serial Enable.
Dir Main Module to Daughter Card Dir Main Module to Daughter Card
57 AdjClkCntr1 ADC A and B Format (binary,
2’s).
59 AdjClkCntr3 ADC A and B Output Enable. 60 PllCntr0 AD9510 serial Enable.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
61 PllCntr1 AD9510 serial Clock. 62 PllCntr2 AD9510 serial Data.
63 PllCntr3 AD9510 Clock Selection. 64 AdcAClkSel ADCC Serial Clock.
Type Module Control Signals Type Module Control Signals
Dir Main Module to Daughter Card Dir Main Module to Daughter Card
65 AdcBClkSel ADCC Serial Data. 66 IntClkDivEn ADCC Serial Enable.
67 IntClkDivnReset ADCD Serial Clock. 68 IntExtClkDivEn ADCD Serial Data.
Dir Main Module to Daughter Card Dir Main Module to Daughter Card
69 IntExtClkDivnReset ADCD Serial Enable. 70 FpgaVRef Reserved
71 FpgaTck Reserved 72 FpgaTms Reserved
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Reserved
73 FpgaTdi Reserved 74 FpgaTdo Reserved
75 MspVRef Reserved 76 MspTck Reserved
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Reserved
58 AdjClkCntr2 ADC A and B Reset.
Page 23

Version 1.4 Page 23 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
77 MspTms Reserved 78 MspTdi Reserved.
79 Msptdo Reserved 80 MspnTrst Reserved
Figure 12 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank B).
Page 24

Version 1.4 Page 24 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Bank A Bank B Bank C
1 3 5 7 41 43 81 83
2 4 6 8
Bank C (ADC C and D)
Pin No Pin Name Signal Description Pin No Pin Name Signal Description
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
81 DOAQ0p Data Out 0, Channel C. 82 DOBQ0p Data Out 1, Channel C.
83 DOAQ0n Data Out 2, Channel C. 84 DOBQ0n Data Out 3, Channel C.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
85 DOAQ1p Data Out 4, Channel C. 86 DOBQ1p Data Out 5, Channel C.
87 DOAQ1n Data Out 6, Channel C. 88 DOBQ1n Data Out 7, Channel C.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
89 DOAQ2p Data Out 8, Channel C. 90 DOBQ2p Data Out 9, Channel C.
91 DOAQ2n Data Out 10, Channel C. 92 DOBQ2n Data Out 11, Channel C.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
93 DOAQ3p Data Out 12, Channel C. 94 DOBQ3p Data Out 13, Channel C.
95 DOAQ3n Over Range, Channel C. 96 DOBQ3n Data Out 0, Channel D.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
97 DOAQ4p Data Out 1, Channel D. 98 DOBQ4p Data Out 2, Channel D.
99 DOAQ4n Data Out 3, Channel D. 100 DOBQ4n Data Out 4, Channel D.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
101 DOAQ5p Data Out 5, Channel D. 102 DOBQ5p Data Out 6, Channel D.
103 DOAQ5n Data Out 7, Channel D. 104 DOBQ5n Data Out 8, Channel D.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
105 DOAQ6p Data Out 9, Channel D. 106 DOBQ6p Data Out 10, Channel D.
107 DOAQ6n Data Out 11, Channel D. 108 DOBQ6n Data Out 12, Channel D.
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
109 DOAQ7p Data Out 13, Channel D. 110 DOBQ7p Over Range, Channel D.
111 DOAQ7n Led ADC C and D. 112 DOBQ7n ADC C and D Format (binary, 2’s).
Dir Daughter Card to Main Module Dir Daughter Card to Main Module
113 ClkOIp Data Clock Out, Channel C. 114 DOIRIp ADC C and D Reset.
115 ClkOIn Data Clock Out, Channel D. 116 DOIRIn ADC A and B Output Enable.
Dir Reserved. Dir Reserved.
117 Reserved. Reserved. 118 Reserved ADC C and D External Trigger, P.
119 Reserved. Reserved. 120 Reserved ADC C and D External Trigger, N.
Figure 13 – Daughter Module Interface: Data Signals Connector and Pinout (Bank C).
Page 25

Version 1.4 Page 25 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Control Register Settings
The Control Registers control the complete functionality of the SMT384. They are
setup via the Comport0 or 3 (the default firmware implements Comport3 only). The
settings of the ADCs, triggers, clocks and the configuration of the SHB interfaces and
the internal FPGA data path settings can be configured via the Control Registers.
Control Packet Structure
The data passed on to the SMT384 over the Comports must conform to a certain
packet structure. Only valid packets will be accepted and only after acceptance of a
packet will the appropriate settings be implemented. Each packet will start with a
certain sequence indicating the start of the packet (0xFF). The address to write the
data payload into will follow next. After the address the data will follow. This structure
is illustrated in the following figure:
Byte Content
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
1
3
4
‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’
Address 7 Address 6 Address 5 Address 4 Address 3 Address 2 Address 1 Address 0
Data 15 Data 14 Data 13 Data 12 Data 11 Data 10 Data 9 Data 8
Data 7 Data 6 Data 5 Data 4 Data 3 Data 2 Data 1 Data 0
Figure 14 – Setup Packet Structure.
Reading and Writing Registers
Control packets are sent to the SMT384 over Comport 0 or 3. This is a bi-directional
interface. The format of a ‘Read Packet’ is the same as that of a write packet.
1) Write Packet
Byte 0
Host
Fixed Sequence
Read/Write AddressByte 1
Read/Write DataByte 3
Read/Write DataByte 4
ComPort 0 or 3
SMT350
Figure 15 – Control Register Read Sequence.
Page 26

Version 1.4 Page 26 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Memory Map
The write packets must contain the address where the data must be written to and
the read packets must contain the address where the required data must be read.
The following figure shows the memory map for the writable and readable Control
Registers on the SMT384:
Address Writable Registers Readable R e g isters
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
0x06
0x07
0x08
0x09
0x0A
0x0B
0x0C
0x0D
0x0E
0x0F
0x18
0x19
0x1A Reserved Mezzanine Module Temperature
0x1B
0x1C Misc Register (Trigger, Clock Selection, etc…). Read- Misc Register.
0x1D
0x1E
0x30
0x31
0x32
0x33
0x34
0x35
0x36
0x37
0x38
0x39
0x3A
Reset Register. Reserved.
Test Register. Reserved.
ADCA Register 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCA Register 0.
ADCA Register 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCA Register 1.
ADCA Register 2. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCA Register 2.
ADCB Register 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCB Register 0.
ADCB Register 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCB Register 1.
ADCB Register 2. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCB Register 2.
ADCC Register 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCC Register 0.
ADCC Register 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCC Register 1.
ADCC Register 2. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCC Register 2.
ADCD Register 0. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCD Register 3.
ADCD Register 1. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCD Register 4.
ADCD Register 2. Read-back (FPGA Register) ADCD Register 5.
Reserved Main Module Temperature
Reserved Main Module FPGA Temperature
Reserved Mezzanine Module Converter Temperature
Update and Read-back command Register Firmware Version and Status bits.
Decimator Register Decimator Register
AD9510 Register 0x0. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 0.
AD9510 Register 0x1. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 1.
AD9510 Register 0x2. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 2.
AD9510 Register 0x3. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 3.
AD9510 Register 0x4. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 4.
AD9510 Register 0x5. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 5.
AD9510 Register 0x6. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 6.
AD9510 Register 0x7. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 7.
AD9510 Register 0x8. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 8.
AD9510 Register 0x9. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 9.
AD9510 Register 0xA. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register A.
Page 27

Version 1.4 Page 27 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
0x3B
0x3C
0x3D
0x3E
0x3F
0x40
0x41
0x42
0x43
0x44
0x45
0x46
0x47
0x48
0x49
AD9510 Register 0xB. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register B.
AD9510 Register 0xC. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register C.
AD9510 Register 0xD. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register D.
AD9510 Register 0xE. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register E.
AD9510 Register 0xF. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register F.
AD9510 Register 0x10. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 10.
AD9510 Register 0x11. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 11.
AD9510 Register 0x12. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 12.
AD9510 Register 0x13. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 13.
AD9510 Register 0x14. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 14.
AD9510 Register 0x15. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 15.
AD9510 Register 0x16. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 16.
AD9510 Register 0x17. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 17.
AD9510 Register 0x18. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 18.
AD9510 Register 0x19. Read-back (FPGA Register) AD9510 Register 19.
Figure 16 – Register Memory Map.
Register Descriptions
Reset Register – 0x0.
Reset Register – 0x0
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
SHB ChC
and D
Reset
‘1’ ‘1’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘1’ ‘1’ ‘1’
SHB ChA
and B
Reset
Reserved Reserved Reserved AD9510
Reset
ADC C&D
Reset
Reset Register – 0x0
Setting Bit 0 Description – ADC A&B Reset
0 0 Normal Operation.
1
Setting Bit 1 Description – ADC C&D Reset
0
1
Setting Bit 2 Description – AD9510 Reset
0
1
Setting Bit 6 Description – SHB ADC A&B Reset
0
1 Resets both ADC devices as well as their corresponding Serial Interfaces.
0 Normal Operation.
1 Resets both ADC devices as well as their corresponding Serial Interfaces.
0 Normal Operation.
1 Resets Clock device as well as its Serial Interfaces.
0 Normal Operation.
ADC A&B
Reset
Page 28

Version 1.4 Page 28 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
1
Setting Bit 7 Description - SHB ADC C&D Reset
0
1
1 Resets SHB (ADC ChA&B) interfaces.
0 Normal Operation.
1 Resets SHB (ADC ChC&D) interfaces.
Note: The Reset bits don’t get cleared automatically, so a device can remain reset
while not used to reduce the global power consumption.
Test Register – 0x1.
Any 16-bit value written in this register can be read-back to check that the Comport
used works properly.
Test Register – 0x1
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
1
ADCA Register 0 – 0x2.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCA Register 0 – 0x2
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting Bit 1 Description
0
1
0 PLL ON – for sampling frequencies between 60 and 125 MHz
1 PLL OFF – for sampling frequencies between 10 and 80 MHz
Reserved PLL Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’
ADCA Register 0 – 0x2
Reserved
‘0000000’
ADCA Register 1 – 0x3.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCA Register 1 – 0x3
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Reserved TP1 TP0 Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCA Register 1 – 0x3
Page 29

Version 1.4 Page 29 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Setting TP1 TP0 Description
0
1
2
3
0 0 Normal Mode of Operation
0 1 All outputs are zeroes
1 0 All outputs are ones
1 1 Continuous stream of ‘10’
ADCA Register 2 – 0x4.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCA Register 2 – 0x4
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting PDN Description
0
1
0 Normal Mode of Operation
1 Device in Power Down Mode
Reserved PDN Reserved
‘0000’ ‘0’ ‘000’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCA Register 2 – 0x4
ADCB Register 0 – 0x5.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCB Register 0 – 0x5
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting Bit 1 Description
0
1
0 PLL OFF – for sampling frequencies between 10 and 80 MHz
1 PLL ON – for sampling frequencies between 60 and 125 MHz
Reserved
‘0000000’
Reserved PLL Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’
ADCB Register 0 – 0x5
1
Default
Reserved
‘0000000’
Page 30

Version 1.4 Page 30 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
ADCB Register 1 – 0x6.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCB Register 1 – 0x6
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting TP1 TP0 Description
0
1
2
3
0 0 Normal Mode of Operation
0 1 All outputs are zeroes
1 0 All outputs are ones
1 1 Continuous stream of ‘10’
Reserved TP1 TP0 Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCB Register 1 – 0x6
ADCB Register 2 – 0x7.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCB Register 2 – 0x7
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting PDN Description
0
1
0 Normal Mode of Operation
1 Device in Power Down Mode
Reserved PDN Reserved
‘0000’ ‘0’ ‘000’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCB Register 2 – 0x7
ADCC Register 0 – 0x8.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCB Register 0 – 0x8
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Default
Default
1
0
Reserved
‘0000000’
Reserved PLL Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’
1
Default
Reserved
‘0000000’
Page 31

Version 1.4 Page 31 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Setting Bit 1 Description
0
1
0 PLL OFF – for sampling frequencies between 10 and 80 MHz
1 PLL ON – for sampling frequencies between 60 and 125 MHz
ADCC Register 0 – 0x8
ADCC Register 1 – 0x9.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCB Register 1 – 0x9
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting TP1 TP0 Description
0
1
2
3
0 0 Normal Mode of Operation
0 1 All outputs are zeroes
1 0 All outputs are ones
1 1 Continuous stream of ‘10’
Reserved TP1 TP0 Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCC Register 1 – 0x9
ADCC Register 2 – 0xA.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCC Register 2 – 0xA
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting PDN Description
0
1
0 Normal Mode of Operation
1 Device in Power Down Mode
Reserved PDN Reserved
‘0000’ ‘0’ ‘000’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCC Register 2 – 0xA
Page 32

Version 1.4 Page 32 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
ADCD Register 0 – 0xB.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCD Register 0 – 0xB
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Reserved 1 Reserved
Default
0 Reserved PLL Reserved
Default
Setting Bit 1 Description
0
1
0 PLL OFF – for sampling frequencies between 10 and 80 MHz
1 PLL ON – for sampling frequencies between 60 and 125 MHz
‘0000000’
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’
ADCD Register 0 – 0xB
Default
‘0000000’
ADCD Register 1 – 0xC.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCD Register 1 – 0xC
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Setting TP1 TP0 Description
0
1
2
3
0 0 Normal Mode of Operation
0 1 All outputs are zeroes
1 0 All outputs are ones
1 1 Continuous stream of ‘10’
Reserved TP1 TP0 Reserved
‘000000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved
‘00000000’
ADCD Register 1 – 0xC
ADCD Register 2 – 0xD.
For more details, refer to ADS5500 datasheet.
ADCD Register 2 – 0xD
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Reserved PDN Reserved
‘0000’ ‘0’ ‘000’
Reserved
‘00000000’
Page 33

Version 1.4 Page 33 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Setting PDN Description
0
1
0 Normal Mode of Operation
1 Device in Power Down Mode
ADCD Register 2 – 0xD
Main Module Temperature – 0x18
Main Module Temperature – 0X18
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
Temperature in Degrees Celsius
‘00000000’
Main Module FPGA Temperature – 0x19
Main Module FPGA Temperature – 0X19
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
Temperature in Degrees Celsius
‘00000000’
Mezzanine Module Temperature – 0x1A
Mezzanine Module Temperature – 0X1A
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
Temperature in Degrees Celsius
‘00000000’
Mezzanine Module Converters Temperature – 0x1B
Mezzanine Module Converters Temperature – 0X1B
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
Temperature in Degrees Celsius
‘00000000’
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C.
Miscellaneous Register – 0X1C
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
1
Default
Reserved
ADC C and D Trigger
‘000’ ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved ADC C
‘00’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘00’ ‘00’
and D
Data
Format
ADC A and
B Data
Format
ADC A and B Trigger Clock
Selection
SHB Selection ChC&D SHB Selection ChA&B
Reference
Selection
Page 34

Version 1.4 Page 34 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 0 Description – Reference Clock Selection
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 1 Descri ption – Clock Source Selection
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 2 Description – Software Trigger ChA&B (Internal Trigger)
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 3 Descr iption – Trigger ChA&B Polarity
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 4 Descr iption – Trigger ChA&B Selection
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 5 Description – Software Trigger ChC&D (Internal Trigger)
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 6 Descr iption – Trigger ChC&D Polarity
0
1 1 Inverting.
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 7 Descri pt io n – Tr i gger ChC&D Selection
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 9/8 Description – SHB Selection ADC Channels A and B
0
1
2
3
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 11/10 Description – SHB Selecti on ADC Channels C and D
0
0 On-Board 10-MHz Reference Clock selected.
1 External Reference Selected.
0 VCXO selection.
1 External Source Selected.
0 Not Active.
1 Active.
0 Non Inverting.
1 Inverting.
0 Internal Trigger Selected.
1 External Trigger Selected
0 Not Active.
1 Active.
0 Non Inverting.
0 Internal Trigger Selected.
1 External Trigger Selected
00 ADC Channel A and B ; 1 sample of each ADC channel packed onto one 32-bit word. [ChB ChA]
01 ADC Channel A only ; 2 samples packed onto one 32-bit word [word(t+1) word(t)]
10 ADC Channel B only ; 2 samples packed onto one 32-bit word [word(t+1) word(t)]
11 ADC Channel A and B ; 1 sample of each ADC channel packed onto one 32-bit word. [ChB ChA]
00 ADC Channel C and D ; 1 sample of each ADC channel packed onto one 32-bit word. [ChD ChC]
Page 35

Version 1.4 Page 35 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
1
2
3
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 12 Description – ADC A and B Data Format
0
1
Miscellaneous Register – 0x1C
Setting Bit 13 Description – ADC C and D Data Format
0
1
01 ADC Channel C only ; 2 samples packed onto one 32-bit word [word(t+1) word(t)]
10 ADC Channel D only ; 2 samples packed onto one 32-bit word [word(t+1) word(t)]
11 ADC Channel C and D ; 1 sample of each ADC channel packed onto one 32-bit word. [ChD ChC]
0 ADC A and B output binary samples
1 ADC A and B output 2’s complement samples
0 ADC C and D output binary samples
1 ADC C and D output 2’s complement samples
Updates, Read-back and Firmware Version Registers – 0x1D
The Update bit activates the corresponding Serial Interface to pass registers
previously written in the FPGA, into the corresponding device (ADCA, ADCB, ADCC,
ADCD or CLK devices).
Update and Read-back commands – 0x1D
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
1 Reserved Reserved
Default
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved CLK
Update
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Reserved ADCC&D
Update
ADCA&B
Update
Reading-back this register returns the Firmware version as well as some Status
signals coming from theAD9510.
Firmware Version – 0x1D
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
1
Default
Reserved AD9510
‘00000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Firmware Version
‘00000000’
Status
Lock
AD9510
Status
Ref
AD9510
Status
VCXO
Decimator Register – 0x1E.
Decimator Register – 0x1E
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
Default
1
Default
Decimation Factor ADC ChannelC&D Decimation Factor ADC ChannelA&B
‘0000’ ‘0000’
Reserved
‘00000000’
Page 36

Version 1.4 Page 36 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x30.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x30
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1 Not Used
Default
0 SDO
Default
Inactive
LSB First Soft Reset Long Inst. Not Used
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘1’ ‘0000’
‘00000000’
AD9510 Register 1 – 0x31.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 1 – 0x31
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used
‘00000000’
Not Used
‘00000000’
AD9510 Register 2 – 0x32.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 2 – 0x32
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used 13-bit B Counter (12…8)
‘000’ ‘00000’
Not Used 6-bit A Counter
‘00’ ‘000000’
AD9510 Register 3 – 0x33.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 3 – 0x33
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used LOR Lock_Del Not Used LOR Enable Not Used
‘0’ ‘00’ ‘00’ ‘0’ ‘00’
13-bit B Counter (7…0)
‘00000000’
Page 37

Version 1.4 Page 37 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 4 – 0x34.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 4 – 0x34
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default ‘0’ ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
0
Default ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’ ‘00’
Not Used CP Current Not Used Reset R
Counter
Not Used PFD Polarity PLL Mux Select CP Mode
Reset N
Counter
Reset all
Counters
AD9510 Register 5 – 0x35.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 5 – 0x35
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default ‘00’ ‘000000’
0
Default
Not Used 14-bit R Divider (13…8)
Not Used B Bypass Not Used Prescaler P Power Down
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘000’ ‘01’
AD9510 Register 6 – 0x36.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x30
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used Digital Lock
Det Enable
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘000’ ‘00’
Digital
Lock Det.
Window
Not Used Antibacklash
14-bit R Divider (7…0)
‘00000000’
AD9510 Register 7 – 0x37.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 7 – 0x37
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default ‘0000000’ ‘1’
Not Used Ramp Capacitor 5 Ramp Current 5
‘0’ ‘000’ ‘000’
Not Used Bypass 5
Page 38

Version 1.4 Page 38 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 8 – 0x38.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 8 – 0x38
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used 5-bit Fine Delay 5 Must be ‘0’
‘00’ ‘00000’ ‘0’
Not Used
‘00000000’
AD9510 Register 9 – 0x39.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 9 – 0x39
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used Ramp Capacitor 6 Ramp Current 6
‘0’ ‘000’ ‘000’
Not Used Bypass 6
‘0000000’ ‘1’
AD9510 Register A – 0x3A.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register A – 0x3A
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used 5-bit Fine Delay 6 Must be ‘0’
‘00’ ‘00000’ ‘0’
Not Used
‘00000000’
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x3B.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register B – 0x3B
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used Output Level 1 Power Down 1
‘0000’ ‘00’ ‘00’
Not Used Output Level 0 Power Down 0
‘0000’ ‘00’ ‘00’
Page 39

Version 1.4 Page 39 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 0 – 0x3C.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register C – 0x3C
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used Output Level 3 Power Down 3
‘0000’ ‘00’ ‘00’
Not Used Output Level 2 Power Down 2
‘0000’ ‘00’ ‘00’
AD9510 Register D – 0x3D.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register D – 0x3D
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘01’ ‘0’
0
Default ‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘01’ ‘0’
Not Used CMOS Inv 5 Logic
Select 5
Not Used CMOS Inv 4 Logic
Select 4
Output Level 5 Output
Power 5
Output Level 4 Output
Power 4
AD9510 Register E – 0x3E.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register E – 0x3E
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used CMOS Inv 7 Logic
Select 7
‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘01’ ‘0’
Not Used CMOS Inv 6 Logic
Select 6
‘000’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘01’ ‘0’
Output Level 7 Output
Power 7
Output Level 6 Output
Power 6
AD9510 Register F – 0x3F.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register F – 0x3F
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Not Used CLKs in
PD
‘00’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘1’
REF IN
PD
Prescaler
Not Used
‘00000000’
PD
CLK2 PD CLK1 PD Sel CLKIN
Page 40

Version 1.4 Page 40 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 10 – 0x40.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 10 – 0x40
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 0 No Synch 0 Force 0 Start H/L 0 Phase Offset 0
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 0 High Cycles 0
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 11 – 0x41.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 11 – 0x41
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 1 No Synch 1 Force 1 Start H/L 1 Phase Offset 1
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 1 High Cycles 1
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 12 – 0x42.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 12 – 0x42
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 2 No Synch 2 Force 2 Start H/L 2 Phase Offset 2
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 0 High Cycles 2
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 13 – 0x43.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 13 – 0x43
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 3 No Synch 3 Force 3 Start H/L 3 Phase Offset 3
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 3 High Cycles 3
‘0000’ ‘0000’
Page 41

Version 1.4 Page 41 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 14 – 0x44.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 14 – 0x44
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 4 No Synch 4 Force 4 Start H/L 4 Phase Offset 4
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 4 High Cycles 4
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 15 – 0x45.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 15 – 0x45
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 5 No Synch 5 Force 5 Start H/L 5 Phase Offset 5
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 5 High Cycles 5
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 16 – 0x46.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 16 – 0x46
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 6 No Synch 6 Force 6 Start H/L 6 Phase Offset 6
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 6 High Cycles 6
‘0000’ ‘0000’
AD9510 Register 17 – 0x47.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 17 – 0x47
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default
Bypass 7 No Synch 7 Force 7 Start H/L 7 Phase Offset 7
‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0000’
Low Cycles 7 High Cycles 7
‘0000’ ‘0000’
Page 42

Version 1.4 Page 42 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
AD9510 Register 18 – 0x48.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 18 – 0x48
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default ‘0’ ‘00’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’
Not Used Set Function pin PD Synch PD all Ref Synch
Not Used
‘00000000’
Software
Synch
Select
Synch
Enable
AD9510 Register 19 – 0x49.
For more details, refer to AD9510 datasheet.
AD9510 Register 19 – 0x49
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
1
Default
0
Default ‘00000000’
Not Used Update
Registers
‘0000000’ ‘0’
Not Used
PCB and Firmware Version Registers
The PCB and Firmware Version registers can only be read by the Host. These
registers indicate the PCB and Firmware versions of the SMT384.
Page 43

Version 1.4 Page 43 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
FPGA Design
The following block diagram shows how the default FPGA design is structured
targeting the SMT368 SLB base Module:
Figure 17 - Firmware Block Diagram.
Serial Interfaces
All serial interfaces have been designed in accordance with manufacturers
datasheets and validated by probing and checking against timing provided.
Page 44

Version 1.4 Page 44 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Block of registers
This implements what has previously been described in this document.
Space available in FPGA
Here is an example of the logic resource used by the default SMT384 FPGA design
targeting a XC2VP30 (SMT338-VP):
Number of RAMB16s 20 out of 136 14%
Number of SLICEs 4749 out of 13696 34%
PCB Layout
The following figures show the top and bottom view of the main module, the top view
of the daughter-card and the module composition viewed from the side.
Figure 18 – Main Module Component Side.
Page 45

Version 1.4 Page 45 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Figure 19 - Main Module (SMT368) Solder Side.
Figure 20 - Daughter Module Component Side.
Page 46

Version 1.4 Page 46 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Figure 21 - Daughter Module Solder Side.
Connectors
Description
The following table gathers all connectors on the board and describes their function.
Connector name (silkscreen
and schematics)
J3
J11
J6
J7
J30
J29
J34
J4
ADCA Analog Input Middle / Left
ADCB Analog Input Middle / Left
ADCC Analog Input Middle / Right
ADCD Analog Input Middle / Right
External Reference Input Top / Left
External Clock Input Top / Left
External Reference
Output
External Clock Output Top / Right
Description Location on the board
Top / Right
J24 External Trigger ADCA&B Bottom / Left
J25
External Trigger
Bottom / Left
ADCC&D
Page 47

Version 1.4 Page 47 of 47 SMT384 User Manual
Location on the board
Figure 22 - Connectors Location.
 Loading...
Loading...