Page 1
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
Unit / Module Description: Virtex 4 FPGA module
Unit / Module Number: SMT368
Document Issue Number: 2.5
Issue Date:
Original Author: Sebastien Maury
User Manual
for
Form : QCF42
Date : 6 July 2006
SMT368
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House, Waterside,
Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS.
This document is the property of Sundance and may not be copied nor
communicated to a third party without prior written permission.
© Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited 2006
User Manual SMT368 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 2
Revision History
Issue Changes Made Date Initials
2.0 New release 04/09/2006 SM
2.1 Added: weight characteristic 21/09/2006 SM
2.2 Added detailed ZBT banks arrangement 04/10/06 E.P
2.3 Corrected wrong sw1 positions for flash
configuration
2.4 Added section about programming the Xilinx
PROM
2.5 Added positioning and names of switches on
SW1 and SW2 in figure 13, PCB top view
03/04/07 E.P
28/11/07 E.P
31/12/08 E.P
User Manual SMT368 Page 2 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction............................................................................................... 6
2 Related Documents ....................................................................................6
2.1 Referenced Documents ..................................................................................................6
2.2 Applicable Documents....................................................................................................6
3 Acronyms, Abbreviations and Definitions.................................................. 7
3.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations.........................................................................................7
3.2 Definitions ......................................................................................................................7
4 Functional Description...............................................................................8
4.1 Block Diagram ................................................................................................................8
4.1.1 Major features............................................................................................................8
4.1.2 Communication resources.........................................................................................8
4.1.3 FPGA ..........................................................................................................................9
4.1.4 CPLD ..........................................................................................................................9
4.1.5 PROM.........................................................................................................................9
4.1.6 ZBTRAM ....................................................................................................................9
4.1.7 Sundance High-speed bus.......................................................................................10
4.1.8 Sundance Low voltage differential signals Bus........................................................11
4.1.9 TIM Connectors .......................................................................................................12
4.1.10 DIP Switches ............................................................................................................12
4.1.11 Clocking scheme ......................................................................................................12
4.1.12 LEDs.........................................................................................................................13
4.1.13 I/Os ..........................................................................................................................13
4.2 Module Description......................................................................................................13
4.2.1 FPGA Configuration ................................................................................................13
4.2.2 FPGA Reset Scheme.................................................................................................14
4.2.3 TIM config................................................................................................................ 15
4.3 Interface Description.................................................................................................... 15
4.3.1 Mechanical Interface ...............................................................................................15
4.3.2 Electrical Interface................................................................................................... 15
4.3.3 Programming the Xilinx PROM ..............................................................................16
5 Footprint..................................................................................................20
5.1 Top View ...................................................................................................................... 20
5.2 Bottom View..................................................................................................................21
6 Pinout .......................................................................................................21
6.1 DIP switch SW2............................................................................................................21
6.2 SHB Header ..................................................................................................................21
User Manual SMT368 Page 3 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 4

6.3 JTAG Header ................................................................................................................21
6.4 I/Os Header..................................................................................................................23
6.5 Fan Header ...................................................................................................................23
7 Support Packages..................................................................................... 23
8 Physical Properties .................................................................................. 24
9 Safety .......................................................................................................24
10 EMC ......................................................................................................... 24
User Manual SMT368 Page 4 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 5

Table of Figures and Tables
Figure 1: Block Diagram................................................................................................................8
Figure 2:FPGA connections to Bank1 of ZBT...............................................................................9
Figure 3: ZBT Constraints file signal names ..............................................................................10
Figure 4: SHB Constraints file control signal names.................................................................10
Figure 5: SHB Constraints file data signal names ......................................................................11
Figure 6: ComPort Constraints file signal names ......................................................................12
Figure 7: Schematics of the External Clock I/O......................................................................... 13
Figure 8: CPLD state machine....................................................................................................14
Figure 9: PROM file selection.....................................................................................................16
Figure 10: Program Options .......................................................................................................17
Figure 11: PROM programming..................................................................................................18
Figure 12: Programming succeeded ...........................................................................................19
Figure 13: PCB – Top view......................................................................................................... 20
Figure 14: PCB – Bottom view....................................................................................................21
Figure 15: Pinout JTAG header – JP1 ........................................................................................22
Figure 16: Pinout JTAG header – JP1 ........................................................................................22
Figure 17: Boundary JTAG chain (Xilinx iMPACT)...................................................................23
Figure 18: Pinout TTL I/Os – JP3..............................................................................................23
Figure 19: Pinout TTL I/Os– JP3...............................................................................................23
Table 1: External Clock specification.......................................................................................... 12
Table 2: LEDs connections .........................................................................................................13
Table 3: SW1 DIP switch for the configuration mode selection ................................................14
Table 4: SW1 DIP switch for the configuration mode selection................................................ 15
Table 5:SW2 DIP switch settings................................................................................................ 21
User Manual SMT368 Page 5 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 6

1 Introduction
The SMT368 is a single-size module based on a Virtex-4 FPGA (XC4VSX35) and provides the
following features:
• On-board ZBTRAM memory,
• Four Sundance High-speed Bus connections,
• One Sundance LVDS Bus connections allowing pairing with daughter modules,
• Four ComPort connections,
• One external clock I/O,
• LEDs and user defined I/O pins.
This variety of connectors and interfaces provides a wide range of development opti ons for
designers to explore the capabilities of the comprehensive family of Sundan ce modules and
carrier boards.
2 Related Documents
2.1 Referenced Documents
Sundance help file
Sundance SHB specification document
Sundance SDB specification document
Sundance SLB specification document
Sundance SDL specification document
TI TIM specification & user’s guide
Sundance’s documentation and user guides
2.2 Applicable Documents
Texas Instruments specification & user’s guide
ComPort specification document (Refer to Chapter 12)
Xilinx PROM XCF32PVOG48C
SAMSUNG ZBTRAM datasheet
XC2C128 CoolRunner-II CPLD
Virtex-4 user guide
Xilinx Xapp136
User Manual SMT368 Page 6 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 7

3 Acronyms, Abbreviations and Definitions
3.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations
TIM Texas Instruments Module
DSP Digital Signal Processor
FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
NtRAM No Turnaround Random Access Memory
ZBTRAM Zero Bus Turnaround Random Access Memory
CP ComPort, Communication interface
SDB Sundance Digital Bus, Communication interface
SHB Sundance High-Speed Bus, Communication interface
SLB Sundance LVDS Bus, Communication interface
3.2 Definitions
DSP Module
FPGA-only Module A TIM with no on-board DSP, where the FPGA provides all functionality
Firmware A proprietary FPGA design providing some sort of functionality.
A TIM module hosting a TI DSP, and a Xilinx FPGA
Sundance Firmware is the firmware running into a FPGA of a DSP
module.
User Manual SMT368 Page 7 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 8
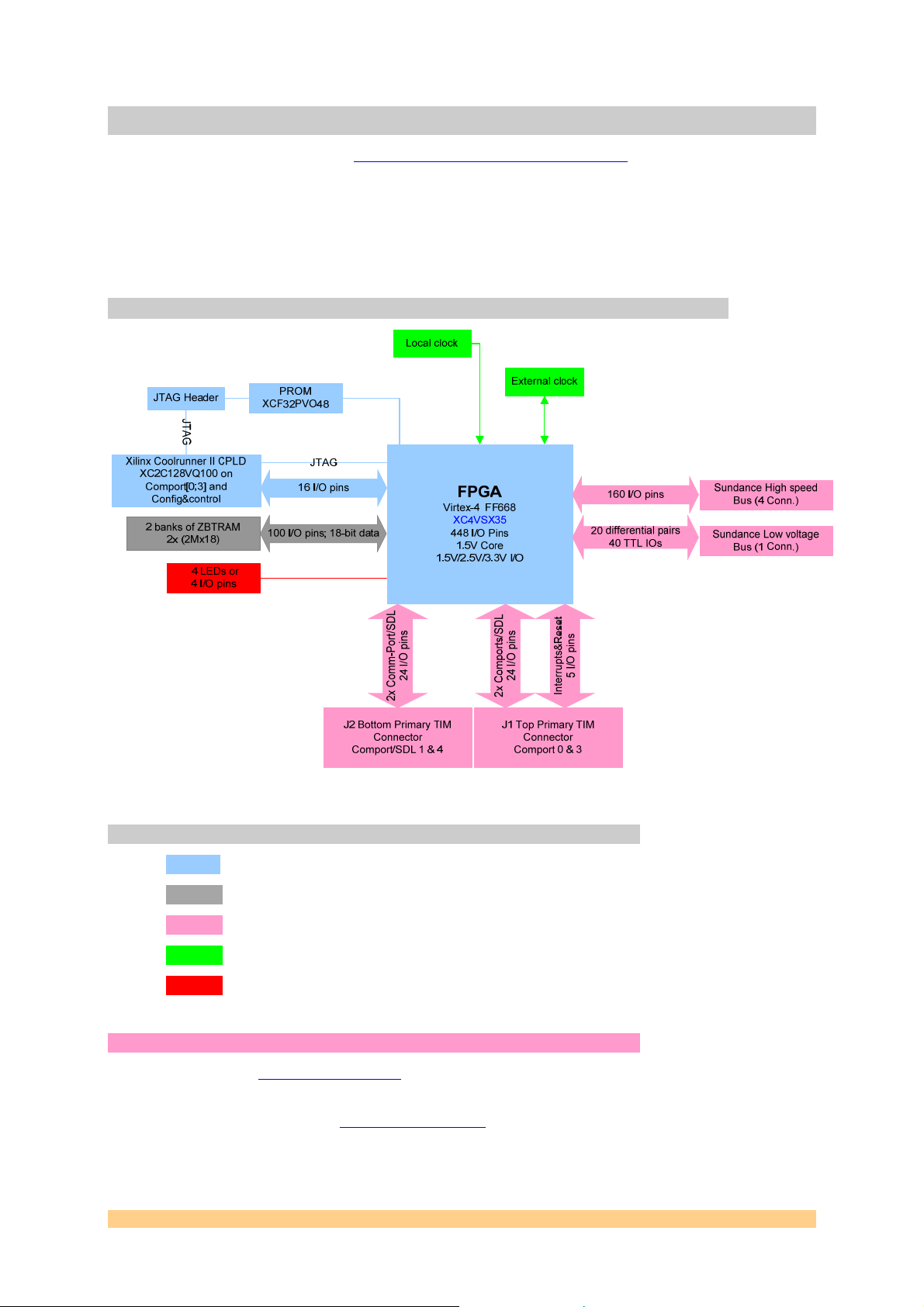
4 Functional Description
The module is conformed to the Texas Instruments Module standard for single-size modules.
It sits on a carrier board that provides electrical connections (power, ground) and
communication links (ComPort) between all the modules fitted. It is also a pathway to the
host, for a non stand-alone system.
4.1 Block Diagram
Figure 1: Block Diagram
4.1.1 Major features
• Block1: Xilinx Virtex-4 XC4VSX35, configuration and reset schemes,
• Block2: ZBTRAM memory,
• Block3: I/O connectors for general purpose or dedicated interfaces,
• Block4: Clocking scheme,
• Block5: LEDs for development, in-use monitoring and general purpose use.
4.1.2 Communication resources
Please refer to the
from the TIM to the carrier board and the external world interfacing.
Please refer to the Sundance
resources provided by Sundance and available onto the SMT368.
User Manual SMT368 Page 8 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Sundance help file for the general description of the Sundance’s boards
SMT6400 help file for the description of the communication
Page 9

4.1.3 FPGA
Xilinx Virtex-4 XC4VSX35™ - Device package FFG668.
This device has 448 I/O-pin BGA package with a -10 speed grade.
It contains up to 34,560 logic cells and 192 XtremeDSP™ Slices.
4.1.4 CPLD
Xilinx CoolRunner-II XC2C128™ - Device package 6VQG100C.
This device has 100 I/O-pin QFP package with a -6 speed grade.
It provides the option to configure the FPGA via ComPort_3 or ComPort_0.
This is ideal for fast in systems debugging/prototyping and development of your FPGA
design.
The CPLD programming code is NOT to be modified without the Sunda nce prior
approval.
4.1.5 PROM
Xilinx Flash PROM XCF32™ - Device package VOG48
This device contains 128 m acro-cells.
This device is programmed via JTAG.
The PROM automatically configures the FPGA at power-up or reset.
It uses parallel FPGA configuration interface performing at up to 33MHz, and it has a built-in
data decompressor compatible with the Xilinx advanced compression technology.
4.1.6 ZBTRAM
Samsung NtRAM – Device part number
K7N321801M-PC20
Up to 8MB of pipeline ZBT memory is provided with direct access to the FPGA.
Figure 2:FPGA connections to Bank1 of ZBT
User Manual SMT368 Page 9 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 10

The ZBTRAM is designed to sustain 100% bus bandwidth by eliminating turnaround cycle
when there is transition from Read to Write, or vice-versa.
The device is well suited for SDR applications that experience frequent bus turnarounds,
needs to operate on small data chunks (especially one-word ch unks), and needs to operate at
higher frequencies than permitted by the flow-through version.
The memory is split in 2x18-bit-wide banks, and is expected to be clocked at 166MHz with a
speed grade -16.
The 2 banks present independent address/data and control busses.
To ensure high performance, the FPGA design should generate de-skewed controller and
board-level clocks using the clock feedback signal provided . The result is a high-speed, deskewed clock driving the controller and the ZBT SRAM.
For more complete information, please refer to the
datasheet and to Xilinx application note
xapp136.
Constraints File signal names:
Figure 3: ZBT Constraints file signal names
4.1.7 Sundance High-speed bus
4 x 60-pin connectors provide 4 x 40 I/O connections between the FPGA and the outside
world. Note that there is no USER I/O pins implemented for the SHB.
The SHB interface is available in the SMT6500 support package.
The FPGA I/O banks hosting the SHB signals are powered using Vcco=3.3V.
Constraints File signal names:
Figure 4: SHB Constraints file control signal names
User Manual SMT368 Page 10 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 11

Figure 5: SHB Constraints file data signal names
4.1.8 Sundance Low voltage differential signals Bus
1 x 60 LVDS pairs I/O connections between the FPGA and the outside world.
They allow interfacing to the Sundance mezzanine modules by implementing a SLB interface
in the FPGA.
Sundance provides the interfaces to the mezzanines supported on this module.
For the mezzanines supported, please contact Sundance technical support, as
more mezzanines are supported over time.
They allow interfacing to the outside world by implementing your own LVDS interf ace in the
FPGA.
The FPGA I/O banks hosting the SLB signals are powered using Vcco=2.5V.
User Manual SMT368 Page 11 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 12

4.1.9 TIM Connectors
TIM connectors provide 4 ComPorts to the FPGA: ComPort_0, 1, 3 and 4.
They allow interfacing to Sundance modules or to a host by implementing a ComPort
interface in the FPGA.
The ComPort interface is available in the
SMT6500 support package.
The FPGA I/O banks hosting the ComPort signals are powered using Vcco=3.3V.
The TIM connectors also provide the power and ground rails, reset and various control
signals.
The references and the specification documents for these connectors are availa ble from our
website.
Constraints file signal names:
Figure 6: ComPort Constraints file signal names
4.1.10 DIP Switches
Two four-position DIP switches are connected to the CPLD: SW1 provides control over the
selection of the configuration bitstream source, and SW2 can be used as I/Os. They are
referenced
SW1 and SW2.
4.1.11 Clocking scheme
The SMT368 module provides an on-board oscillator and an external clock I/O:
• The on-board oscillator provides a free running clock to the FPGA and CPLD. The
default is a 50MHz oscillator, but other frequencies can be provided upon request to
Sundance.
Note: Please ask your Sundance technical or sale person when ordering if you
need other frequencies.
• An external clock input/output (J2) is provided directly to the FPGA via a 50 ohms
MMBX coax connector.
Specification
Description
V
IL
V
OL
V
IH
V
OH
Maximum voltage 0.8V 0.4V 3.8V
Minimum voltage -0.5V 2.0V 2.4V
Impedance 50 ohms
Frequency
The frequency limitations are the ones of the
FPGA. Refer to the Xilinx’s user guide.
Table 1: External Clock specification
User Manual SMT368 Page 12 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 13

Figure 7: Schematics of the External Clock I/O
Constraints file signal names:
BOARDCLK On-board oscillator input to the FPGA (pin AF10)
EXT_CLK External Clock input to the FPGA (pin AF11: IO_L4P_GC_LC_4)
4.1.12 LEDs
There are six LEDs on the SMT368:
• Four LEDs are connected to the FPGA and they are available as I/Os:
UCF name
FPGA pin LED
LED0 H3 D3
LED1 H4 D4
LED2 H5 D5
LED3 H6 D6
Table 2: LEDs connections
• One LED (D1) is connected to the DONE pin of the FPGA to show that the FPGA is
configured.
• One LED (D2) is connected to a I/O (pin 99) of the CPLD.
4.1.13 I/Os
There are four TTL I/Os that are directly conn ected to the FPGA. They are connected to the
pin-socket header
JP3.
4.2 Module Description
4.2.1 FPGA Configuration
The general FPGA configuration is described in the
chapter Configuring the FPGA section FPGA type TIM. To illustrate the FPGA
configuration, please refer to the
animated slideshow from the Knowledge Base in the
Support forum.
SMT6500 help file. Please refer to the
Different schemes are available to provide a maximum flexibility in systems where the
SMT368 is involved. The FPGA can be configured in three different ways:
• Using the ComPort_3 (CP_3) or ComPort_0 (CP_0) to provide the bitstream,
• Using the on-board JTAG header (JP1) and the JTAG programming tools,
• Using the on-board Xilinx PROM.
User Manual SMT368 Page 13 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 14

The following table describes the settings fo r the jumper SW1 according to the various FPGA
configuration modes:
Configuration
SW1 Position
POS3 POS2 POS1
From CP_0 ON ON ON
From CP_3 OFF OFF OFF
From PROM OFF OFF ON
Table 3: SW1 DIP switch for the configuration mode selection
At power-up the FPGA is not configured.
LED D1 (see Figure 7: Components placement - Top view) will be lit upon the
FPGA configuration.
4.2.2 FPGA Reset Scheme
The CPLD is connected to the TIM global reset si gnal provided to th e SMT368 via its primary
TIM connector (P1) pin 30.
The CPLD provides another signal called FPGAResetn that offers a better Reset control
over the FPGA.
At power-up or on reception of a low TIM global reset pulse, the CPLD drives the
FPGAResetn signal low and it keeps it low.
When the ENDKEY has been received, the CPLD drives the FPGAResetn high.
Sundance recommends you to use the FPGAResetn signal for the Global Reset signal of
your FPGA designs.
In this manner, you can control your FPGA design Reset activity and you will also avoid
possible conflicts on the ComPort_3 if your FPGA design implements it.
The Reset control is operated by the CPLD line FPGAResetn.
Figure 8: CPLD state machine
Note: The Reset level on the SMT368 is active low.
User Manual SMT368 Page 14 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 15

4.2.3 TIM config
The TIM config is a special reset feature. This signal comes from the TIM connector (P1), pin
74, and it is available to the CPLD.
TIM Config is driven by another module on the same carrier board, for instance from a DSP
module running an application (see the Chapter
Config & NMI DSP lines in the
SMT6400)
It can be enabled with the DIP swith SW1:
TIM Config
SW1 Position
POS4
ENABLED ON
DISABLED OFF
Table 4: SW1 DIP switch for the configuration mode selection
4.3 Interface Description
4.3.1 Mechanical Interface
This module conforms to the TIM standard (Texas Instrument Module, See
TI TIM
specification & user’s guide) for single width modules.
It sits on a carrier board.
The carrier board provides power, Ground, communication links (ComPort links) between all
the modules fitted and a pathway to the HOST, for a non stand-alone system.
The SMT368 requires an additional 3.3V power supply (as present on all Sundance TIM
carrier boards), which must be provided by the two diagonally opposite mounting holes.
4.3.2 Electrical Interface
Do NOT connect any external TTL (5V) signals to the SMT368 I/Os as the FPGA
is NOT 5V compliant. This implies that the ComPorts and global bus lines of the
carrier board MUST be LVTTL and that any device driving signals on the SHB
connectors must drive at LVTTL (3.3V).
This module must have the +5V supplied through the TIM connectors. The SMT368 requires
an additional 3.3V power rail (compatible and present on all the Sundance ’s carrier boards),
which must be provided by the two diagonally opposite mounting holes.
DC/DC Converter:
An on-board DC-DC converter is used to supply power to the FPGA core.
Linear Voltage regulator:
Linear regulation is provided for the Vcco banks of the FPGA that are connected to the SLB
when used in 2.5V mode (LVDS_25).
User Manual SMT368 Page 15 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 16

4.3.3 Programming the Xilinx PROM
DO NOT fit the SLB mezzanine before programming the PROM via JTAG.
It makes the JTAG fail. (It does not damage the board).
Plug the JTAG cable on JP1. The cable mus t be ordered from Sundance. A standard
Xilinx cable does not fit on JP1.
Run Xilinx JTAG software (Impact) and connect to the target up to the stag e showed
Figure 9.
on
Proceed by selecting the PROM.
Browse to a PROM file of your choice (filename.mcs) which is the configuration to be
downloaded in the PROM.
Filename.mcs should now be assigned to the PROM as per
Figure 9: PROM file selection
Figure 9.
User Manual SMT368 Page 16 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 17

Right click on the PROM icon and select Program from the menu.
Next, select the same options as per
Figure 10.and click O.K. on the 2 dialog windows.
Beware to leave unchecked verify (as it takes ages to verify) and to TICK LoadFPGA
and Parallel Mode boxes.
The PROM option will not work if these latter 2 boxes are not ticked.
Figure 10: Program Options
User Manual SMT368 Page 17 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 18

Figure 11: PROM programming.
It can take more than 2 minutes…
User Manual SMT368 Page 18 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 19

A successful programming is indicated as per Figure 12.
Figure 12: Programming succeeded
User Manual SMT368 Page 19 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 20

Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
5 Footprint
5.1 Top View
Form : QCF42
Date : 6 July 2006
Figure 13: PCB – Top view
User Manual SMT368 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 21

Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
5.2 Bottom View
Form : QCF42
Date : 6 July 2006
Figure 14: PCB – Bottom view
6 Pinout
6.1 DIP switch SW2
The DIP switch SW2 is not used in the default firmware. It is therefore connected to the
CPLD for custom applications.
The following table describes the settings for the positions of the SW2:
Configuration
Pin of CPLD 53 52 51 50
SW2 Pos
Type I/O I/O I/O I/O
6.2 SHB Header
The SHB connectors support LVTTL standard only. They are referenced SHBA, SHBB, SHBC
and SHBD.
POS1 POS2 POS3 POS4
Table 5:SW2 DIP switch settings
6.3 JTAG Header
The JTAG header is a 2mm pitch pin-socket, and it is referenced JP1. It is compliant with the
Xilinx Parallel cable IV.
User Manual SMT368 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 22

Note: An adapter is necessary to connect the JTAG Header JP1 to the Xilinx
Parallel cable IV. Please ask your Sundance technical or sales person for
ordering information.
All devices from the Block_1 (FPGA, CPLD, PROM) are chained, and they are accessible via
this JTAG header.
Signal
Pin Pin Signal
VCC 1 4 TMS
GND 2 5 TDI
TCK 3 6 TDO
Figure 15: Pinout JTAG header – JP1
Figure 16: Pinout JTAG header – JP1
User Manual SMT368 Page 22 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 23

Figure 17: Boundary JTAG chain (Xilinx iMPACT)
6.4 I/Os Header
The TTL I/Os header is a 2mm pitch pin-socket, and it is referenced JP3.
Signal
VCC 1 4 TTL2
TTL0 2 5 TTL3
TTL1 3 6 GND
Figure 18: Pinout TTL I/Os – JP3
Figure 19: Pinout TTL I/Os– JP3
Note: Those TTL I/O pins are not easily accessible if you wish to plug a Sundance
daughter module via the SLB interface onto this module. Please ask your
Sundance technical or sale person when ordering.
Pin Pin Signal
6.5 Fan Header
A fan coupled with a heat sink can be mounted on the FPGA to provide heat dissipation; but a
permanent airflow should always be maintained inbox to provide enough cooling for the
system.
The fan header is a 2-pin 1.25mm, and it is referenced JP2.
Note: Please ask your Sundance technical or sale person when ordering.
7 Support Packages
The SMT368 is supported by the SMT6500 software package available from SUNDANCE
under Non-Disclosure Agreement.
Please register on SUNDANCE
company’s forum to request the SMT6500 product.
Host side software to communicate with the SMT368 can be developed with the SMT6025
for Windows, and the SMT6036 for Linux.
The SMT368 can be configured from a DSP module via a ComPort link. The SMT6500
support package provide host interface to download the bitstream from the host, and a
library of software functions to run on the DSP (See
“Configuration library”).
Support Forum if you are not registered yet. Then enter your
SMT6500 help file section
User Manual SMT368 Page 23 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
Page 24

8 Physical Properties
Dimensions 106.68mm x 63.5mm
Weight 50g.
Supply Voltages
Supply Current +12V
+5V
+3.3V
-5V
-12V
MTBF
Power consumption:
ZBT 2.7Watts
CPLD 0.2Watts
FPGA depending on the implemented design, the power consumption can reach a
maximum of 15Watts (approx.)
4.2’’ x 2.5’’
Sundance recommends you to analyse the FPGA power drawn by using
before implementing your design in the FPGA. This will tell you if you need to use the
external power connector provided on our carrier boards.
Xilinx XPOWER
9 Safety
This module presents no hazard to the user when in normal use.
10 EMC
This module is designed to operate from within an enclosed host system, which is build to
provide EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is not guaranteed unless it
is installed within an adequate host system.
This module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients originating from outside th e
host system which may be introduced through the output cables.
Short circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up or reboot.
User Manual SMT368 Page 24 of 24 Last Edited: 31/12/2008 13:53:00
 Loading...
Loading...