Page 1

SMT365
User Manual
User Manual (QCF42); Version 3.0, 5/2/01; © Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd. 2001
Page 2
Version 2.3 Page 2 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Revision History
Date Comments Engineer Version
18/7/02 First rev, based on 361 GP 1.0.0
06/01/03 User manual updated, 2 SHBs YC 1.0.1
16/1/03 Revised board layout, control registers, paging GP 1.0.2
20/1/03 Added FPGA pin-out GP 1.0.3
27/01/03 Updated interrupt registers, global status register JPA 1.0.4
30/01/03 Corrected CPLD header pin-out. GP 1.0.5
14/03/03 Added location of SDBs on the board JPA 1.0.6
11/04/03 Corrected I/O connector block pin-out GP 1.0.7
08/05/03 Added link to General firmware specification, SHB and
SDB specification, added fpga pinout convention
19/08/03 Page 30: NSDRAMCS mapped on emif_ctrl<5>
Updated Reprogramming chapter
20/10/03 Added information about SHB-Word (SHB32x) firmware
version.
01/12/03 SHB-Word (SHB32x) firmware version available for both
SMT365-1 and –2 modules
SDL interface availability
FPGA space availability
11/03/04 Updated Flash section
Added board’s weight
04/05/04 Corrected figure 1 (Flash logical sections).
Updated EMIFB CE3 space control register value.
Updated EMIFA CE1 address range.
Updated FPGA space availability section.
25/10/04 Create the FPGA configuration section SM 1.1.4
04/08/05 Update: the user manual supports the new firmware
implementation
JPA 1.0.8
JPA 1.0.9
JPA 1.1.0
JPA 1.1.1
JPA 1.1.2
JPA 1.1.3
SM 2.0
13/12/05 Details added on EMIF registers settings JV 2.1
15/02/06 Changed GEL file contents. GP 2.2
09/05/06 Minor changes SM 2.3
Page 3

Version 2.3 Page 3 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Table of Contents
Revision History....................................................................................................... 2
Table of Contents ..................................................................................................... 3
Contacting Sundance............................................................................................... 4
Notational Conventions ........................................................................................... 5
DSP ........................................................................................................................ 5
SDB ........................................................................................................................ 5
SHB ........................................................................................................................ 5
Register Descriptions.............................................................................................. 5
Outline Description .................................................................................................. 6
Intended Audience ................................................................................................... 6
Block Diagram .......................................................................................................... 7
Architecture Description.......................................................................................... 8
DSP............................................................................................................................ 8
Boot Mode............................................................................................................... 8
EMIF Control Registers........................................................................................... 9
ZBTRAM .................................................................................................................. 11
FLASH ..................................................................................................................... 12
Virtex FPGA............................................................................................................. 13
Version control...................................................................................................... 13
Firmware versions.................................................................................................. 13
Reprogramming the firmware and boot code ...................................................... 13
Comports................................................................................................................. 14
SHB.......................................................................................................................... 14
Architecture........................................................................................................... 14
Global bus............................................................................................................... 14
LED Setting............................................................................................................. 14
LED Register......................................................................................................... 15
CONFIG & NMI ........................................................................................................ 16
Config Register..................................................................................................... 16
Timer........................................................................................................................ 17
Page 4

Version 2.3 Page 4 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
IIOF interrupt........................................................................................................... 18
FPGA space availability......................................................................................... 18
Code Composer...................................................................................................... 19
Application Development....................................................................................... 19
SMT6400 .............................................................................................................. 19
3L Diamond........................................................................................................... 19
SMT6500 .............................................................................................................. 19
Operating Conditions............................................................................................. 20
Safety.................................................................................................................... 20
EMC...................................................................................................................... 20
General Requirements.......................................................................................... 20
Power Consumption.............................................................................................. 20
Weight................................................................................................................... 20
Connector Positions .............................................................................................. 21
Serial Ports & Other DSP I/O ................................................................................. 22
FPGA and CPLD JTAG........................................................................................... 22
FPGA configuration................................................................................................ 22
Virtex Memory Map................................................................................................. 23
SHB pinout.............................................................................................................. 25
SHB generic pin-out.............................................................................................. 25
32-bits SDB interface:........................................................................................... 26
Bibliography............................................................................................................ 27
Index........................................................................................................................ 28
Contacting Sundance
You can contact Sundance for additional information by login onto the Sundance
support forum.
Page 5

Version 2.3 Page 5 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Notational Conventions
DSP
The terms DSP, C64xx and TMS320C64xx will be used interchangeably throughout
this document.
SDB
The term SDB will be used throughout this document to refer to the Sundance Digital
Bus interface.
SHB
The term SHB will be used throughout this document to refer to the Sundance Highspeed Bus interface.
Register Descriptions
The format of registers is described using diagrams of the following form:
31–24 23–16 15–8 7–0
OFLAGLEVEL
R,00000000 RW,10000000 R,00000000 R,10000000
The digits at the top of the diagram indicate bit positions within the register and the
central section names bits or bit fields. The bottom row describes what may be done
to the field and its value after reset. Shaded fields are reserved and should only ever
be written with zeroes.
R Readable by the CPU
W Writeable by the CPU
RW Readable and writeable by the CPU
Binary digits indicate the value of the field after reset
Page 6

Version 2.3 Page 6 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Outline Description
The SMT365 is a DSP module, size 1 TIM offering the following features:
TMS320C6416 processor running at 600MHz
Six 20MB/s comports
8MB of ZBTRAM (133MHz)
8MBytes Flash ROM
Global Bus connector
2 SHB connectors for high-speed data transfer
Intended Audience
There are two existing versions of the firmware for the SMT365. These two versions
differ by the number and the type of communication resources (comport and SDB
interfaces) provided.
For each of the versions of the different firmware is loaded in the FPGA:
- Firmware version 1.0 or
- Firmware version 2.0
This user manual covers the version 2.0 of the firmware for the SMT365 implemented
with the model described in the
The changes between the firmware version 1.0 and version 2.0 are described in the
section Firmware versions.
SMT6500 help file.
Page 7
Version 2.3 Page 7 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
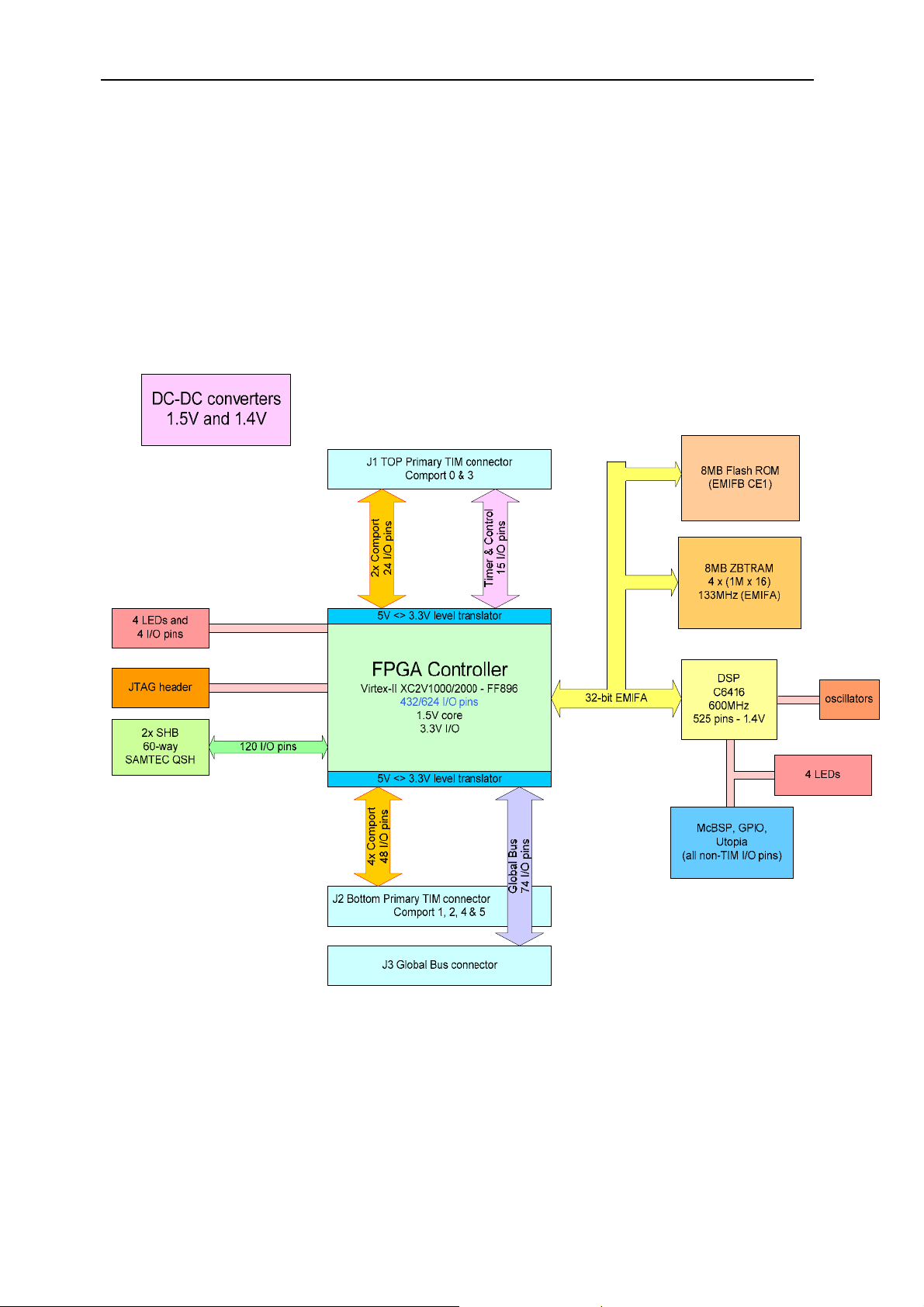
Block Diagram
The following drawing shows the block diagram of the SMT365 module.
The main components of the SMT365 are:
- a Texas Instruments DSPs
- One Xilinx FPGA Virtex-II device
- 8MB of ZBTRAM
Page 8

Version 2.3 Page 8 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Architecture Description
DSP
The Texas Instruments DSP can run at up to 600MHz. The DSP is doted of 8MBytes
of Zero Bus Turnaround RAM (ZBTRAM).
The DSP is a TMS320C6416 type.
This is a fixed-point digital signal processor provided by Texas Instruments. The
processor will run with zero wait states from internal SRAM. The internal memory is
1MB in size and can be partitioned between normal SRAM and L2 cache.
An on-board crystal oscillator provides the clock used for the DSP which them
multiplies this by twelve internally.
Boot Mode
The DSP is connected to the on-board flash ROM that contains the Sundance
bootloader and the FPGA bitstream.
Following reset, the DSP will automatically load the data from the flash ROM into its
internal program memory at address 0 and then start executing from there. All this
code is the Sundance bootloader, and it is made up of two parts: FPGA configuration
and processor configuration. FPGA configuration uses data in the ROM to configure
the FPGA. A processor configuration sets the processor into a standard state by
writing into the DSP internal registers of the EMIF. Then it configures the FPGA from
the data held in the flash ROM.
Note that two control register bits are needed for this purpose, one to put the FPGA
into a ‘waiting for configuration’ state, and another to actually transfer the
configuration data. The PROG pin (causes the FPGA to enter the non-configured
state) is accessed at address 0x6C02000X. Writing to address 0x6C020000 will
assert this pin, and address 0x6C0200001 will de-assert this pin.
The configuration data clock is accessed at address 0x6C080001. Each bit of the
FPGA’s configuration bit-stream must be serially clocked through this address.
The bootloader is executed. It will continually check the six comports until data
appears on one of them. This will next load a program in boot format from this
comport. Note that the bootloader will not read data arriving on other comports.
Finally the control is passed to the loaded DSP application.
The DSP will take approximately about 1000ms to configure the FPGA following
reset, assuming a 600MHz clock. The external devices implemented in the FPGA
(such as comports) must not be used during this configuration.
Page 9
Version 2.3 Page 9 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
It is safest to wait for the configuration to complete. Note that comports will appear to
be "not ready" until the FPGA has been configured.
The FPGA programming algorithm is not described here. It can be found in the boot
code.
EMIF Control Registers
The DSP has two external memory interfaces (EMIF) that are 64 bits wide and 16
bits wide.
The DSP contains several registers that control the external memory interface
(EMIF). A full description of these registers can be found in the
DSP C6000
Peripherals Reference Guide.
The standard bootstrap will initialise these registers to use the following resources:
Memory space
(EMIFA)
Internal program memory (1MB) 0x00000000 - 0x000FFFFF
CE0 ZBTRAM (2x 8MB sections) 0x80000000 - 0x807FFFFF
CE1 Virtex 0x90000000 - 0x900FFFFF
Memory space
(EMIFB)
CE1 1st/3rd section of flash
CE2 2nd/4th section of flash
Resource Address range
Resource Address range
0x64000000 – 0x641FFFFF
(2MB each)
0x68000000 – 0x681FFFFF
(2MB each)
Page 10

Version 2.3 Page 10 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
The EMIF settings are set by the boot code so no GEL file is necessary. See TI
documentation for help on creating GEL file.
A GEL file example:
Menuitem "SMT365_Init";
hotmenu SMT365_Reset()
{
GEL_Reset();
SMT365_emif_init();
}
hotmenu SMT365_emif_init()
{
*(int *) 0x01800000 = 0x0001277C; // EMIFA_GCTL
*(int *) 0x01800008 = 0x000000E0; // EMIFA_CE0
*(int *) 0x01800004 = 0x00000030; // EMIFA_CE1
*(int *) 0x01800018 = 0x55227000; // EMIF_SDRAMCTL
*(int *) 0x01800048 = 0x0000001A; // EMIF_CE0_SEC
}
Page 11

Version 2.3 Page 11 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
ZBTRAM
Memory space CE0 is used to access 8MB of ZBTRAM over the EMIFA. It is mapped
as a 64-bit memory.
The speed of the ZBTRAM is dependent on the processor variant. Using the C6416,
the ZBTRAM will operate at 133MHz maximum. It operates at one quarter or one
sixth of the core clock speed.
The EMIFA CE0 memory space control register should be programmed with the
value 0x000000E0.
Note that depending upon the application; the best performance may be obtained
whilst running the DSP at a lower clock speed. I.e. at 600MHz, the external EMIF will
only run at 100MHz (core clock/6, as we are constrained by the TI imposed limit of
133MHz). But if the core were running at 533MHz, then the EMIF would be at the
maximum limit possible of 133MHz (a quarter of 533). This speed adjustment is not a
user option, but must be adjusted during manufacture.
Note also that the DSP only has 20 address pins on the EMIFA and cannot therefore
directly address more than 8MB of SRAM (the ZBTRAM is a type of SRAM with nonmultiplexed address pins). It requires the use of a paging mechanism to access
more. On the SMT365 there is a single page bit which is connected directly to the
most significant bit of the ZBTRAM (bit 20). This bit is controlled by a register
accessed on EMIFB CE3 address space (0x6C04000X). A write to the addresses
shown below (data = don’t care) will have the following effect:
Address
ZBTRAM Address
bit 20 state
0x6C040000 0
0x6C040001 1
Note that for smaller ZBTRAM chipsets there is no need to set this bit as all memory
will be directly accessible to the DSP.
Page 12

Version 2.3 Page 12 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
FLASH
An 8MB Flash ROM is connected to the DSP in the EMIFB CE1 & CE2 memory
spaces. The ROM holds boot code for the DSP, configuration data for the FPGA, and
optional user-defined code.
The flash is 16-bit wide. The boot code is stored in 8-bit mode as this is the way the
DSP boots. The FPGA data and user application are stored in 16-bit.
The EMIFB CE1 and CE2 space control registers should be programmed with the
value 0xFFFFFF03 to access the flash in 8-bit mode and 0xFFFFFF13 in 16-bit
mode.
As the DSP only provides 20 address lines on its EMIFB, both CE1 & CE2 are used
to access this device. This in itself allows the direct access of 4MB. A paging
mechanism is used to select which half of the 8MB device is visible in this 4MB
window.
As the EMIFB CE1 & CE2 memory spaces alias throughout the available range, the
flash device can be accessed using the address range 0x67E00000-0x681FFFFF.
This gives a 4MB continuous memory space.
The flash can be divided into the four logical sections shown in the following figure
(paging bit is bit 21).
Page0
(2 MBytes)
CE1
Page1
(2 MBytes)
Page0
(2 MBytes)
CE2
Page1
(2 MBytes)
Figure 1: Flash logical sections
0x67C00000
Section 1
0x67E00000
Section 2
0x68000000
Section 3
0x68200000
Section 4
0x68400000
To change the state of the page bit, you need to write to the following address as
shown (the data written is irrelevant):
Address Flash page selected
0x6C000000 Page 0 (1st and 3rd
sections enabled)
0x6C000001 Page 1 (2nd and 4th
sections enabled)
The EMIFB CE3 space control register should be programmed with the value
0x00CFFF03 for optimum access speed to the CPLD.
Page 13

Version 2.3 Page 13 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
This mechanism is identical in operation to that needed for the largest ZBTRAM
chipsets.
Virtex FPGA
The FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is a Xilinx Virtex-II device XC2V2000 (or
XC2V1000). Is is mapped on EMIFA CE1 as a 32-bit SDRAM.
It implements the following communication resources:
• Six comport interfaces
• Two 32-bit Sundance digital bus interfaces
• One global bus interface
Version control
Revision numbers for both the boot code and FPGA firmware are stored in the Flash
ROM during programming as zero-terminated ASCII strings.
The
SMT6001 utility can be used to display the version numbers of the bootloader
and the FPGA data.
Firmware versions
The SMT6001 utility includes the latest version of the bootloader and the latest
version of the FPGA data that implements the FPGA architecture described in the
SMT6500 help file.
Note that the new firmware does not support the 16-bit SDB interfaces. Only two 32bit SDB interfaces are presented on the TIM connectors. Customers who wish to use
the old firmware that supported 16-bit options can obtain it
from our support web
forum.
Reprogramming the firmware and boot code
The contents of the flash ROM are managed using the SMT6001 utility. This includes
the latest firmware and bootloader along with complete documentation on how to
reprogram the ROM. The utility assumes that you have Code Composer Studio
installed and that it has been configured correctly for the installed TIMs. The
Sundance Wizard can help you with this.
To confirm that the ROM has been programmed correctly, you should run the
confidence test in the BoardInfo utility (SMT6300).
Page 14

Version 2.3 Page 14 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Comports
The DSP has six comports, numbered 0 to 5.
The addresses of the ComPort registers are described in the
SMT6400 help file.
SHB
The SMT365 has two SHB connectors, both of which are connected to the DSP to
give 32-bit SDB interfaces. These interfaces operate with a fixed clock rate of
100MHz.
Architecture
SDB0 and SDB2 on the DSP are presented on the TIM's SHB connectors, SHBA and
SHBB respectively.
SDB 2 SDB 0
The addresses of the SDB registers are shown in the Virtex Memory Map, and are
described in the
SMT6400 help file.
Global bus
The SMT365 provides a single global bus interface. This is only accessible from the
DSP. The addresses of the global bus registers are shown in the
and are described in the
SMT6400 help file.
Virtex Memory Map,
LED Setting
The SMT365 has 9 LEDs. One shows the FPGA configuration status and the other 8
are under DSP control.
Page 15

Version 2.3 Page 15 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Four output TTL I/O pins are available on connector JP1 for control or debugging.
Their values can be controlled by bits in the LED register. The GPIO pins 12 to 15
are connected to the leds D2 to D5 respectively.
Four of the LEDs (D7 to D10) are controlled by bits in the LED register. Writing ‘1’
illuminates the LEDs; writing ‘0’ turn it off.
The TTL I/O are available on the connector JP2 for control or debugging. They can
be controlled by bits in the same register.
LED D6 always displays the state of the FPGA DONE pin. This LED is off when the
FPGA is configured (DONE=1) and on when it is not configured (DONE=0).
This LED should go on when the board is first powered up and go off when the FPGA
has been successfully programmed (this is the standard operation of the boot code
resident in the flash memory device). If the LED does not light at power-on, check
that you have the mounting pillars and screws fitted properly. If it stays on, the DSP
is not booting correctly, or is set to boot in a non-standard way.
LED Register
(0x900D0000)
31–4 3 2 1 0
LED
D10
RW,0 RW,0 RW,0 RW,0
LED
D9
LED
D8
LED
D7
Page 16

Version 2.3 Page 16 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
CONFIG & NMI
The TIM specification describes the operation of an open-collector type signal
CONFIG that is driven low after reset.
This signal, on a standard C4x based TIM, is connected to the processor’s IIOF3 pin.
On the SMT365, the CONFIG signal is asserted after power on, and can be released
by writing the value (1<<6) to the config register. Conversely, CONFIG may be reasserted by writing 0 to this bit. It is not possible for software to read the state of the
CONFIG signal.
The NMI signal from the TIM connector can be routed to the DSP NMI pin.
WARNING: Several software components include code sequences that assume
setting GIE=0 in the DSP CSR will inhibit all interrupts; NMI violates that assumption.
If an NMI occurs during such code sequences it may not be safe to return from the
interrupt. This may be particularly significant if you are using the compiler’s software
pipelining facility.
Config Register
31–8 7 6 5–0
NMI CONFIG
Field Description
0 drive CONFIG low
CONFIG
1 tri-state CONFIG
0 Disconnect NMI from the DSP
NMI
1 Connect NMI from TIM to the DSP.
Config and NMI DSP lines are described in the
SMT6400 help file.
Page 17

Version 2.3 Page 17 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Timer
The TIM TCLK0 and TCLK1 signals can be routed to the DSP’s TOUT/TINP pins.
The signal direction must be specified, together with the routing information in the
timer control register:
31–6 5 4 3–0
Reserved TCLK1 TCLK0 Reserved
Field Description
TCLK0
0 TIM TCLK0 is an input
1 Enable TIM TCLK0 as an output
0 TIM TCLK1 is an input
TCLK1
1 Enable TIM TCLK1 as an output
If the TIM TCLKx pin is selected as an output, the DSP TOUTx signal will be used to
drive it. The TIM TCLKx pin will always drive the DSP TINPx input.
TCLK0EN
C6x
TOUT0 TCLK0
TINP0
FPGA
The Timer control register is described in the
SMT6400 help file.
Page 18

Version 2.3 Page 18 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
IIOF interrupt
The firmware can generate pulses on the external interrupt lines of the TIM.
Only the interrupt line IIOF1 and IIOF2 are connected from/to the DSP and the
HOST.
• IIOF1 is connected from the DSP side to the HOST side: so, the DSP
interrupts the HOST
• IIOF2 is connected from the HOST side to the DSP side: so, the HOST
interrupts the DSP
The IIOF interrupt lines are described in the
SMT6400 help file.
FPGA space availability
Latest firmware version is designed in VHDL following the model described in the
SMT6500 help file.
Depending on the FPGA fitted on board, two firmware versions are available:
• SMT365_32_2: Virtex-II 2000, 32-bit SDB interfaces
• SMT365_32_1: Virtex-II 1000, 32-bit SDB interfaces
The table below gives the device utilization summary after place and route:
Number of RAMB16s
Number of SLICEs
Number of BUFGMUXs
Number of TBUFs
SMT365-v1000-32 SMT365-v2000-32
55% (22 out of 40) 39% (22 out of 56)
64% (3309 out of 5120) 32% (3547 out of 10752)
6% (1 out of 16) 6% (1 out of 16)
22% (576 out of 2560) 10% (576 out of 5376)
Page 19

Version 2.3 Page 19 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Code Composer
This module is fully compatible with the Code Composer Studio debug and
development environment. This extends to both the software and JTAG debugging
hardware. The driver to use is the tixds64xx_11.dvr. CCS version 3.0 or later is
required as the reprogramming utility (SMT6001) requires it.
Troubleshooting
Our
Knowledge data base and FAQ sections may help you to resolve some known
issues.
Application Development
Depending on the complexity of your application, you can develop code for SMT365
modules in several ways.
SMT6400
For simple applications, the Sundance
SMT6400 software support package (project
examples) and its associated header files (SmtTim.h and ModSup.h) can suffice.
The SMT6400 product is installed by the Sundance Wizard and it is free of charge.
3L Diamond
This module is fully supported by 3L Diamond, which Sundance recommends for all
but the simplest of applications. An SMT365 has to be declared as appropriate in
configuration files as one processors of type:
• SMT365_4_1 (4MB ZBTRAM, XC2V1000) or SMT365_4_2 (4MB ZBTRAM,
XC2V2000)
• SMT365_8_1 (8MB ZBTRAM, XC2V1000) or SMT365_8_2 (8MB ZBTRAM,
XC2V2000)
• SMT365_16_1 (16MB ZBTRAM, XC2V1000) or SMT365_16_2 (16MB
ZBTRAM, XC2V2000)
SMT6500
This is the
support package for the FPGA. It may be used to develop your application
in the FPGA of the module.
Page 20

Version 2.3 Page 20 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Operating Conditions
Safety
The module presents no hazard to the user.
EMC
The module is designed to operate within an enclosed host system that provides
adequate EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is only guaranteed
when the module is installed within an appropriate host system.
The module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients introduced along
output cables from outside the host system.
Short-circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up
or reboot.
General Requirements
The module must be fixed to a TIM40-compliant carrier board.
The SMT365 TIM is in a range of modules that must be supplied with a 3.3V power
source. In addition to the 5V supply specified in the TIM specification, these new
generation modules require an additional 3.3V supply to be presented on the two
diagonally-opposite TIM mounting holes. The lack of this 3.3V power supply should
not damage the module, although it will obviously be inoperable; prolonged operation
under these circumstances is not recommended.
The SMT365 is compatible with all Sundance TIM carrier boards. It is a 5V tolerant
module, and as such, it may be used in mixed systems with older TIM modules,
carrier boards and I/O modules.
Use of the TIM on SMT327 (cPCI) motherboards may require a firmware upgrade. If
LED D6 on the SMT365 remains illuminated once the TIM is plugged in and powered
up, the SMT327 needs the upgrade. The latest firmware is supplied with all new
boards shipped. Please contact Sundance directly if you have an older board and
need the upgrade.
The external ambient temperature must remain between 0°C and 40°C, and the
relative humidity must not exceed 95% (non-condensing).
Power Consumption
The power consumption of this TIM is dependent on the operating conditions in terms
of core activity and I/O activity. The maximum power consumption is 10W.
Weight
SMT365 weigh approximately 56.25 grams.
Page 21

Version 2.3 Page 21 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Connector Positions
Page 22

Version 2.3 Page 22 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Serial Ports & Other DSP I/O
The DSP contains various I/O ports. These signals are connected to a 0.1” pitch DIL
pin header. The pin-out of this connector is shown here:
P O TTL1 TTL0 GND GND GPIO7 GPIO6 GPIO5 GPIO4 GPIO3 GPIO2
CLK / 6
L A TTL3 TTL2 V33 V33 GPIO15 GPIO14 GPIO13 GPIO12 GPIO11 GPIO10 GPIO9 NC
R I URD0 URD1 URD2 URD3 URD4 URD5 URD6 URD7 URCLK URENB URCLAV URSOC
S A UXD0 UXD1 UXD2 UXD3 UXD4 UXD5 UXD6 UXD7 UXCLK UXENB UXCLAV UXSOC
GPIO1
CLK / 4
GPIO0
T I UXA0 DR1
UXA1
O N URA0 URA1 CLKR1
FSR1
UXA2
URA2
FSX1
UXA3
CLKX1
URA4
DX1
UXA4
CLKS1
URA3
CLKS2
GPIO8
CLKS0 CLKX0 CLKR0 FSX0 DX0 FSR0 DR0
CLKX2 CLKR2 FSX2 DX2 FSR2 DR2
FPGA and CPLD JTAG
The following shows the pin-outs for JP2 (CPLD) and JP3 (FPGA) JTAG connectors:
Signal Pin Pin Signal
V33 1 2 TMS
TCK 3 4 TDO
GND 5 6 TDI
FPGA configuration
The CPLD and the FPGA have two different JTAG chains. You can configure the
FPGA by the JTAG connector using for instance the Xilinx parallel cable IV.
The lines M0, M1 and M2 are not connected to the CPLD. These lines are hardwired
connected to the FPGA at high-logic level ‘1’. So, the FPGA is configured in Slave
Serial mode.
Page 23

Version 2.3 Page 23 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Virtex Memory Map
See general firmware description.
The memory mapping is as follows:
#define SMT365CP0 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90000000
#define SMT365CP1 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90008000
#define SMT365CP2 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90010000
#define SMT365CP3 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90018000
#define SMT365CP4 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90020000
#define SMT365CP5 (volatile unsigned int *)0x90028000
#define SMT365CP0_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90004000
#define SMT365CP1_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x9000C000
#define SMT365CP2_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90014000
#define SMT365CP3_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x9001C000
#define SMT365CP4_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90024000
#define SMT365CP5_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x9002C000
#define SMT365GB_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90034000
#define SMT365SDB_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90038000
#define SMT365STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x9003C000
#define SMT365SDBA (volatile unsigned int *)0x90040000
#define SMT365SDBB (volatile unsigned int *)0x90050000
#define SMT365SDBC (volatile unsigned int *)0x90060000
#define SMT365SDBD (volatile unsigned int *)0x90070000
#define SMT365SDBA_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90048000
#define SMT365SDBB_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90058000
#define SMT365SDBC_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90068000
#define SMT365SDBD_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x90078000
#define SMT365SDBA_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x90044000
#define SMT365SDBB_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x90054000
#define SMT365SDBC_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x90064000
#define SMT365SDBD_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x90074000
#define SMT365SDBA_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x9004C000
#define SMT365SDBB_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x9005C000
#define SMT365SDBC_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x9006C000
#define SMT365SDBD_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x9007C000
#define GLOBAL_BUS (volatile unsigned int *)0x900A0000
#define GLOBAL_BUS_CTRL (volatile unsigned int *)0x90080000
Page 24

Version 2.3 Page 24 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
#define GLOBAL_BUS_START (volatile unsigned int *)0x90088000
#define GLOBAL_BUS_LENGTH (volatile unsigned int *)0x90090000
#define SMT365TCLK (volatile unsigned int *)0x900C0000
#define SMT365TIMCONFIG (volatile unsigned int *)0x900C8000
#define SMT365LED (volatile unsigned int *)0x900D0000
#define SMT365INTCTRL4 (volatile unsigned int *)0x900E0000
#define SMT365INTCTRL4_EXT (volatile unsigned int *)0x900E4000
#define SMT365INTCTRL5 (volatile unsigned int *)0x900E8000
#define SMT365INTCTRL5_EXT (volatile unsigned int *)0x900EC000
#define SMT365INTCTRL6 (volatile unsigned int *)0x900F0000
#define SMT365INTCTRL6_EXT (volatile unsigned int *)0x900F4000
#define SMT365INTCTRL7 (volatile unsigned int *)0x900F8000
#define SMT365INTCTRL7_EXT (volatile unsigned int *)0x900FC000
Page 25

Version 2.3 Page 25 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
SHB pinout
SHB generic pin-out
W Hw QSH Pin number QSH Pin number W Hw
CLK CLK 1 2 D0 D0
D1 D1 3 4 D2 D2
D3 D3 5 6 D4 D4
D5 D5 7 8 D6 D6
D7 D7 9 10 D8 D8
D9 D9 11 12 D10 D10
D11 D11 13 14 D12 D12
D13 D13 15 16 D14 D14
D15 D15 17 18 USERDEF0
USERDEF1 19 20 USERDEF2
USERDEF3 21 22 WEN WEN
REQ
D17 D1 39 40 D18 D2
D19 D3 41 42 D20 D4
D21 D5 43 44 D22 D6
D23 D7 45 46 D24 D8
D25 D9 47 48 D26 D10
D27 D11 49 50 D28 D12
D29 D13 51 52 D30 D14
D31 D15 53 54 USERDEF0
USERDEF1 55 56 USERDEF2
USERDEF3 57 58 WEN
Hw0
REQ 23 24 ACK
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
Hw1
35 36
CLK 37 38 D16 D0
REQ 59 60
Hw0
ACK
Hw1
ACK
Note: - W is a short for Full Word (i.e. 32-bit Word)
- Hw is a short for Half-word (i.e. 16-bit Word)
Page 26

Version 2.3 Page 26 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
32-bits SDB interface:
Pin Signal Signal Pin
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
SDBA_CLK SDBA_DATA0
SDBA_DATA1 SDBA_DATA2
SDBA_DATA3 SDBA_DATA4
SDBA_DATA5 SDBA_DATA6
SDBA_DATA7 SDBA_DATA8
SDBA_DATA9 SDBA_DATA10
SDBA_DATA11 SDBA_DATA12
SDBA_DATA13 SDBA_DATA14
SDBA_DATA15 SDBA_U0
SDBA_U1 -
- SDBA_WEN
SDBA_REQ SDBA_ACK
- -
- -
- -
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
31
33
35
37
39
41
43
45
47
49
51
53
55
57
59
- -
- -
- -
SDBA_CLK SDBA_DATA16
SDBA_DATA17 SDBA_DATA18
SDBA_DATA19 SDBA_DATA20
SDBA_DATA21 SDBA_DATA22
SDBA_DATA23 SDBA_DATA24
SDBA_DATA25 SDBA_DATA26
SDBA_DATA27 SDBA_DATA28
SDBA_DATA29 SDBA_DATA30
SDBA_DATA31 SDBA_U0
SDBA_U1 -
- SDBA_WEN
SDBA_REQ SDBA_ACK
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
50
52
54
56
58
60
Not implemented
Page 27

Version 2.3 Page 27 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Bibliography
1. Sundance Help file
SMT6400 help file (DSP support package) and SMT6500 help file (FPGA support package)
2.
TMS320C6000 Peripherals Reference Guide (literature number SPRU1 90)
3.
It describes common peripherals available on the TMS320C6000 digital signal processors. This
book includes information on the internal data and program memories, the external memory
interface (EMIF), the host port, multichannel-buffered serial ports, direct memory access (DMA),
clocking and phase-locked loop (PLL), and the power-down modes.
TIM-40 MODULE SPECIFICATION Including TMS320C44 Addendum
4.
SDB Technical Specification
5.
6. SHB Technical Specification
TMS320C4x User's Guide (literature number SPRU063)
7.
It describes the C4x 32-bit fixed-point processor, developed for digital signal processing as well as
parallel processing applications. Covered are its architecture, internal register structure, instruction
set, pipeline, specifications, and operation of its six DMA channels and six communication ports.
Software and hardware applications are included.
Xilinx Virtex-II datasheet
8.
TMSC6416 datasheet
9.
Page 28

Version 2.3 Page 28 of 28 SMT365 User Manual
Index
A
Application Development · 19
Architecture Description · 8
B
Bibliography · 27
Block Diagram · 7
Boot Mode · 8
C
Code Composer · 19
Comports · 14
CONFIG & NMI · 16
E
EMIF Control Registers · 9
F
Firmware versions · 13
Flash · 12
FPGA space availability · 18
N
Notational Conventions · 5
O
Operating Conditions · 20
P
Power consumption · 20
R
Register Descriptions · 5
S
Serial Ports · 22
SHB · 14
SHB pinout · 25
SMT6400 · 19
SMT6500 · 19
T
G
Global Bus · 14
I
IIOF lines · 18
J
JTAG chains · 22
L
LED register · 15
LEDs · 14
Table of contents · 3
Timer · 17
V
Version Control · 13
Virtex
memory map · 23
W
Weight · 20
Z
ZBTRAM · 11
 Loading...
Loading...