Page 1

Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited
User Manual
Unit / Module Description: User Manual
Unit / Module Number: SMT348
Document Issue Number:
Issue Date:
Original Author: E.P
User Manual
Form : QCF42
Date : 6 July 2006
Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd, Chiltern House, Waterside,
Chesham, Bucks. HP5 1PS.
This document is the property of Sundance and may not be copied nor
communicated to a third party without prior written permission.
© Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Limited 2006
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 2
Revision History
Issue Changes Made Date Initials
1.0.0 First release 06/11/06 E.P
1.0.1 Minor inconsistency about comports removed from
block Diagram
1.0.2 Clarification about the elements in the JTAG chain 15/11/07 E.P
1.0.3 Updated JTAG header information. Wrong marking
of position.
Added chapters about bitstream formatting, FPGA
configuration
26/02/07 E.P
29/02/08 E.P
User Manual SMT348 Page 2 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 3

Table of Contents
1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 6
2 Related Documents..................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Referenced Documents .............................................................................................7
2.2 Applicable Documents ..............................................................................................7
3 Acronyms, Abbreviations and Definitions ................................................................. 8
3.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations ...................................................................................8
3.2 Definitions .................................................................................................................8
4 Functional Description ............................................................................................... 9
4.1 Block Diagram...........................................................................................................9
4.2 Module Description.................................................................................................10
4.2.1 FPGA...................................................................................................................10
4.2.2 CPLD...................................................................................................................10
4.2.3 FLASH MEMORY..............................................................................................10
4.2.4 JTAG Header......................................................................................................10
4.2.5 FPGA Configuration schemes............................................................................11
4.2.6 FPGA Reset Scheme...........................................................................................12
4.2.7 FPGA Bitstream formatting ..............................................................................13
4.2.8 QDR2 SRAM.......................................................................................................14
4.2.9 Sundance High speed Bus .................................................................................15
4.2.10 Sundance Low voltage Bus ................................................................................15
4.2.11 TIM Connectors..................................................................................................16
4.2.12 DIP Switches ......................................................................................................16
4.2.13 Clocking scheme .................................................................................................17
4.2.14 LEDs ...................................................................................................................17
4.2.15 Performance........................................................................................................17
4.3 Interface Description ..............................................................................................17
4.3.1 Power Budget .....................................................................................................17
5 Footprint ....................................................................................................................22
5.1 Top View..................................................................................................................22
5.2 Bottom View............................................................................................................23
6 Pinout.........................................................................................................................24
6.1 FPGA Pin allocation by bank .................................................................................24
6.2 SHB..........................................................................................................................24
6.3 SLB ..........................................................................................................................24
6.4 JTAG........................................................................................................................25
User Manual SMT348 Page 3 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 4

7 Qualification Requirements ......................................................................................25
7.1 Qualification Tests..................................................................................................25
7.1.1 Meet Sundance standard specifications............................................................25
7.1.2 Speed qualification tests ....................................................................................26
7.1.3 Integration qualification tests ...........................................................................26
8 Support Packages ......................................................................................................26
9 Physical Properties....................................................................................................27
10 Safety .........................................................................................................................28
11 EMC ...........................................................................................................................29
User Manual SMT348 Page 4 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 5

Table of Figures
Figure 1: Block Diagram ........................................................................................................9
Figure 2: CPLD state machine.............................................................................................13
Figure 3: FPGA connections to Bank1 of QDRII.................................................................14
Figure 4: Top View................................................................................................................22
Figure 5: Bottom view ..........................................................................................................23
Figure 6: JTAG Connector, top view....................................................................................25
Table of Tables
Table 1: DIP switch SW1 position for special reset feature ...............................................16
Table 2: DIP switch SW1 position for the selection of the configuration bitstream source
.......................................................................................................................................16
Table 3: DIP switch SW1 position for the selection of the Flash erase & program
operations. .....................................................................................................................16
Table 4: Total available power. ............................................................................................18
Table 5: Power budget on 1.2v .............................................................................................18
Table 6: Power budget on 2.5v .............................................................................................18
Table 7: Power budget on 1.8v. ............................................................................................19
Table 8: Power budget on QDRII 0.9v Termination voltage. .............................................19
Table 9: Power budget on QDRII and FPGA 0.9v reference voltage. ................................20
Table 10: Power budget on 3.3v. ..........................................................................................20
Table 11: Coolrunner II resources summary.......................................................................21
Table 12:Coolrunner II pin resources. .................................................................................21
Table 13: Pin allocation by Bank .........................................................................................24
User Manual SMT348 Page 5 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 6

1 Introduction
The SMT348 is an FPGA TIM module designed to be integrated in modular
systems.
It is designed to connect to the huge range of other TIM modules and carriers
developed by Sundance.
Sundance modular solutions provide flexible and upgradeable systems.
The SMT348 is a TIM module aimed at completing the range of Sundance Virtex4
modules like SMT368, SMT362, SMT339.
It provides a communications platform between an XC4VSX55 or XC4VLX160
FPGA and
• 4 banks of QDR2 SRAM at a frequency of up to 250Mhz.
• 2 32-bit SHBs.
• TIM Global Bus.
• LVDS connections for high speed parallel connections
• LVTTL connections and connectors.
This variety of connectors and interfaces provides a wide range of development
options for designers to explore the capabilities of the comprehensive Sundance
TIM modules family.
User Manual SMT348 Page 6 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 7

2 Related Documents
2.1 Referenced Documents
SUNDANCE SDB specification.
SUNDANCE SHB specification
SUNDANCE SLB specification
Samsung QDRII Datasheet
Spansion S29GLXXXN flash
2.2 Applicable Documents
TI TIM specification & user’s guide.
Samtec QSH Catalogue page
Virtex 4 Datasheet
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 8

3 Acronyms, Abbreviations and Definitions
3.1 Acronyms and Abbreviations
TIM Texas Instruments Module
TI© DSP Texas Instrument Digital Signal Processor
Xilinx©
FPGA
QDR Quad Data Rate
CP ComPort. Communication interface
SDB Sundance Digital Bus. Communication interface
SHB Sundance High-Speed Bus. Communication interface
Xilinx© Field Programmable Gate Array.
3.2 Definitions
DSP Module
FPGA-only Module A TIM with no on-board DSP, where the FPGA provides all
Firmware A proprietary FPGA design providing some sort of functionality.
Typically a TIM module hosting a TI DSP and, a Xilinx FPGA.
functionality.
Sundance Firmware is the firmware running in an FPGA of a DSP
module.
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 9
4 Functional Description
This module conforms to the TIM standard (Texas Instrument Module, See TI TIM
specification & user’s guide) for single width modules.
It sits on a carrier board.
The carrier board provides power (5V, 3.3V, +/-12V), ground, communication links
(Comport links) between all the modules fitted and a pathway to the host, for a non
stand-alone system.
The SMT348 requires a 3.3V power supply (as present on all Sundance TIM carrier
boards), which must be provided by the two diagonally opposite mounting holes.
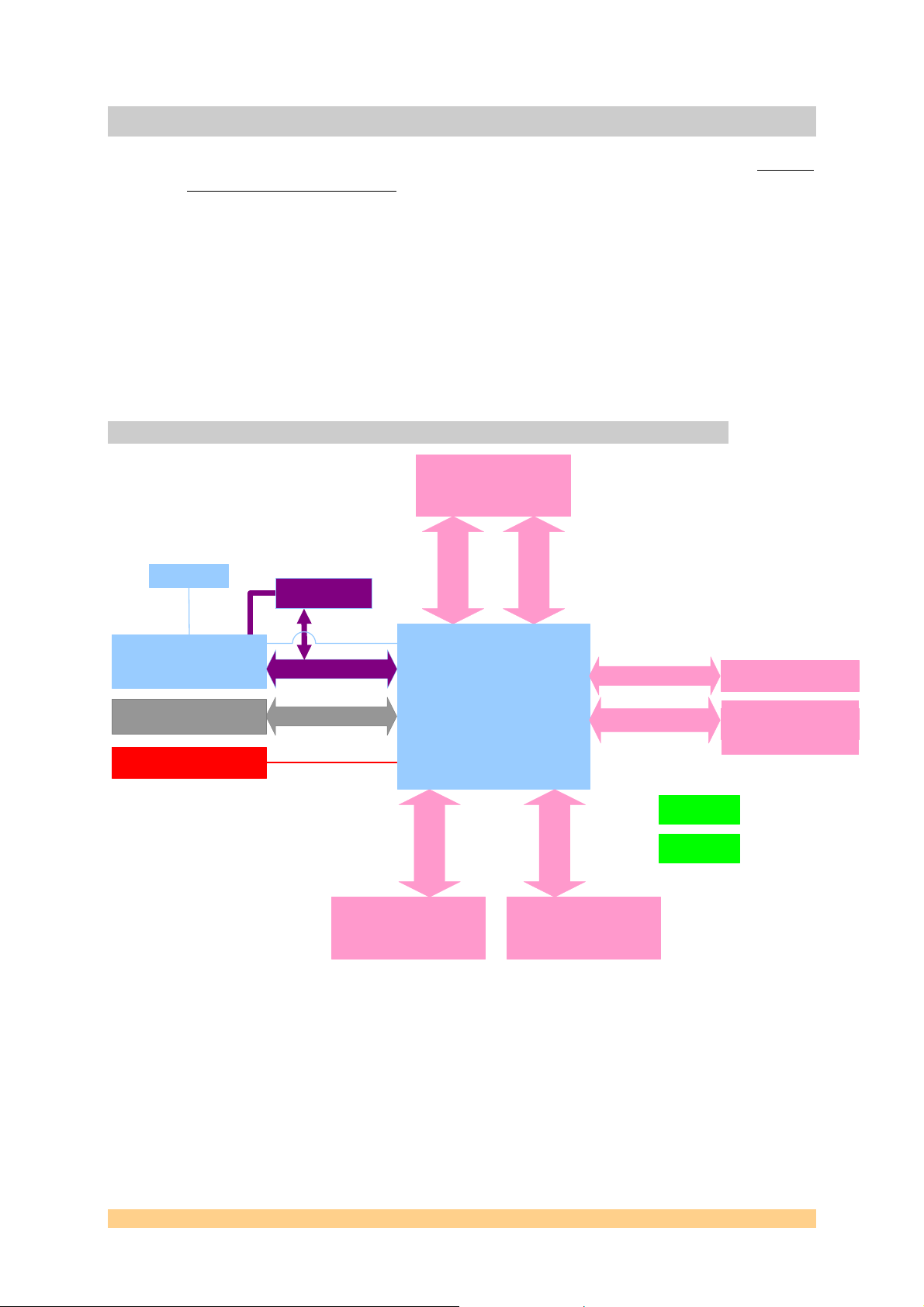
4.1 Block Diagram
J1 Top Primary TIM
Connector
ComPort/SDL 0 & 3
JTAG Header
J
T
A
G
Xilinx Coolrunner II CPLD
XC2C256VQ100 on
Comport3 and
Config&control
4 banks of QDR2 SRAM
4x (2Mx18)
4 LEDs and
Figure 1: Block Diagram
Flash memory
11 I/O pins
260 I/O pins
2x ComPorts/SDL
JTAG
Virtex-4 FF1148
XC4VSX55/LX160
1.8V/2.5V/3.3V I/O
24 I/O pins
2x ComPort/SDL
J2 Bottom Secondary TIM
Connector
ComPort/SDL 1 & 4
24 I/O pins
FPGA
1.5V Core
5I/Opins
Interrupts & Reset
80 I/O pins
20 differential pa irs
40 TTL IOs
72 I/O pins
Add, Data, Control
J3 Global Bus TIM Connector
Sundance High-speed Bus
(2 Conn.)
Sundance Low-voltage Bus
(1 Conn.)
ONLY with
LX160
External clock
Local clock
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 10

4.2 Module Description
• Block1 and Block6 Xilinx Virtex 4 XC4VSX55/LX160 and configuration scheme.
• Block2: QDR2 SRAM memory.
• Block3: IO connectors for general purpose or dedicated interfaces.
• Block4: 50MHz or 200MHz local clocks, and external clock input.
• Block5: LEDs for development and in-use monitoring and general purpose use.
4.2.1 FPGA
Xilinx Virtex 4 XC4VSX55FF1148 or XC4VLX160FF1148 FPGA.
This device is packaged in a 1148-pin BGA package.
4.2.2 CPLD
Xilinx Coolrunner II device XC2C256-6CP132C. This device is packaged in a 132-ball BGA
type package with a -6 speed grade.
It can be used to configure the FGPA via Comport 3, or from a configuration stored in flash
memory.
The flash memory is programmed using the CPLD and data via the ComPort3.
4.2.3 FLASH MEMORY
S29GL256N11TFI01 is a 256Mbit flash from Spansion
It can be used to configure the FPGA at power up.
Flash accessed using Comport3 via the CPLD.
Flash programming selection via switch SW1 (See Table 3)
Software Library Support available from Sundance.
The code can run on Sundance DSP TIM or a Host.
All the flash functionalities are available.
4.2.4 JTAG Header
The JTAG header is compatible with Xilinx Parallel-IV cable signals.
It supports code download (for the FPGA), FPGA configuration, Hardware and Software
Debugging tools for the Virtex-4.
This cable connects the parallel port of an engineer's Workstation/PC to the JTAG chain of the
SMT348 Module.
All the Xilinx devices from block1 are chained and accessible via this JTAG header.
User Manual SMT348 Page 10 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 11

4.2.5 FPGA Configuration schemes
Different schemes are available to provide maximum flexibility in systems where the SMT348
is involved:
The FPGA configuration bitstream source is
• On Comport 3:
The CPLD is connected to the Comport 3 link of the SMT348 TIM connector. (See block1).
A switch is used to select Comport 3 as the link that will be used to receive the bitstream.
The CPLD allows for FPGA configuration in slave SelectMAP mode.
• Using the on-board Flash memory.
The CPLD monitors the configuration data between the Flash and the FPGA.
The FPGA configuration is operated in Slave SelectMap mode.
A switch is used to select the Flash as the source for the configuration bitstream.
• Using the on-board JTAG header and Xilinx JTAG programming tools.
The JTAG header is a Parallel-IV Header.
Note: Using JTAG to configure the FPGA bypasses the CPLD which controls configuration.
The following section describes the CPLD role and the reset scheme used.
As the CPLD is bypassed when JTAG is used to configure the FPGA, it is necessary to adopt
one of the three following ways:
• If your FPGA design does not implement comport3,
o do not use the Reset signal generated by the CPLD but use the TIM reset signal
as your design’s reset. You can use JTAG to configure your FPGA with your
application and the design will reset and run everytime you issue a new TIM
reset.
• If your design implements comport3
o Set the switch to configure the FPGA from flash after reset. In this way a default
bitstream being stored in flash will be loaded in the FPGA by the CPLD.
In this manner the CPLD has gone trhough the cycle of configuring the
FPGA and releases the reset (FPGAresetn)
Then you can reconfigure the FPGA via JTAG with your application.
o Set the switch to configure from comport 3. After reset, configure the FPGA via
JTAG and provide an end key word on comport 3 to the CPLD so that it releases
the Reset. (FPGAresetn).
User Manual SMT348 Page 11 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 12

4.2.6 FPGA Reset Scheme
The CPLD is connected to a TIM global Reset signal provided to the SMT348 via its primary
TIM connector pin 30. (See TI TIM specification & User’s guide).
This signal goes to the CPLD and the FPGA.
Nevertheless as a general rule for good practice, the FPGA should not use this reset but should
use the reset signal generated by the CPLD.
The CPLD provides another signal called FPGAResetn that offers a better Reset control over
the FPGA.
At power up or on reception of a low TIM global Reset pulse, the CPLD drives the
FPGAResetn signal low and keeps it low.
This is used to keep the FPGA design in reset.
A new FPGA configuration bitstream can then be downloaded.
When the ENDKEY has been received, the CPLD drives FPGAResetn high.
Use FPGAResetn for the Global Reset signal of your FPGA
designs.
In this manner, you can control your FPGA design Reset activity and you will also avoid
possible conflicts on ComPort 3 if your FPGA design implements it.
(Comport3 is a communication resource shared by the CPLD and the FPGA. But only 1 entity
is allowed to use it at a time).
If you implement comport 3 in the FPGA you have to use
Fpgaresetn generated by the CPLD, as the comport is shared
between the two.
The Reset control is operated by the CPLD line FPGAResetn.
The following diagram shows the CPLD states after Reset.
User Manual SMT348 Page 12 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 13

Figure 2: CPLD state machine
4.2.7 FPGA Bitstream formatting
If you generated you FPGA bitstream using Diamond FPGA, you do not need any other handling.
The .app file created can be used as is to configure the FPGA.
If you used Xilinx ISE and created a .bit file, you need to use the Sundance executable
“Getrawdata.exe” provided for free in the SMT6001 package.
Please read the SMT6001 help file at chapter: “Saving FPGA configuration data to file”.
The resulting file can be used as is to configure the FPGA.
User Manual SMT348 Page 13 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 14

4.2.8 QDR2 SRAM
Up to 4 Mbytes of QDR2 SRAM per bank.
The memory is available as 4 independent banks.
The QDR2 memory runs at 250MHz.
Each bank is fully independent with separate address, control and data busses and arranged as
follows:
Figure 3: FPGA connections to Bank1 of QDRII
The devices used are Samsung K7R321884M. Alternative part numbers, fully compatible can
be fitted depending on availability at time of order.
User Manual SMT348 Page 14 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 15

4.2.9 Sundance High speed Bus
2 x 60 pin connectors provide 80 IO connections between the FPGA and the outside word.
They allow interfacing to other Sundance modules providing that you implement an SHB
interface in the FPGA. (See 2.1)
The SHB interface is available in Sundance SMT6500 support package. Either two 16-bit, or 1
32-bit interface can be implemented per connector.
They allow interfacing to the outside world by implementing your own interface in the FPGA.
The FPGA IO banks hosting the SHB signals are powered using Vcco = 3.3V.
4.2.10 Sundance Low voltage Bus
This bus is present on the LX160 version of the module only.
This is an LVDS bus comprising data (2 x 16 bit buses, I & Q), clock, and control signals.
They allow interfacing to Sundance mezzanine modules providing that you implement an SLB
interface in the FPGA. (See 2.1)
They allow interfacing to the outside world by implementing your own LVDS interface in the
FPGA.
All LVDS data pins (both I and Q) are connected to a 2.5/3.3V powered FPGA banks (link
selectable by jumper JP3).
The FPGA LVDS DIFF_TERM standard should be used instead of the DCI terminations when
LVDS standard is selected.
DCI terminations are only available when a 2.5v standard is selected.
The LVDS Clock signals are also in these banks.
All LVTTL signals are connected to a 3.3V powered FPGA bank.
User Manual SMT348 Page 15 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 16

4.2.11 TIM Connectors
TIM connectors provide 4 communication links (Comports) and a Global Bus to the FPGA.
The comports which are available on the SMT348 are CP0, CP1, CP3, and CP4.
They allow interfacing to Sundance TIM modules or to a Host PC providing that you
implement a Comport Interface inside the FPGA. (See 2.1)
The Comport interface is available in Sundance SMT6500 support package.
The FPGA io banks hosting the Comport signals are powered using Vcco = 3.3v.
The TIM connectors also provide power/ground, reset and various control signals.
References and specifications for these connectors are available in
user’s guide
4.2.12 DIP Switches
One four-position DIP switch is connected to the CPLD to provide control over the selection of
the configuration bitstream source and a special reset feature called “TIM Confign”.
SW1 pos 4 TIM Config
ON ENABLED
OFF DISABLED
Table 1: DIP switch SW1 position for special reset feature
SW1 pos 3,2, 1 JPC3 JPC2 JPC1
C3P OFF OFF OFF
TI TIM specification &
Flash OFF OFF ON
Table 2: DIP switch SW1 position for the selection of the configuration bitstream source
SW1 pos 3,2, 1 JPC3 JPC2 JPC1
Flash accesses ON OFF OFF
Table 3: DIP switch SW1 position for the selection of the Flash erase & program operations.
The Flash erase & program operations are operated by the CPLD.
Commands are provided via Comport3 from an application running on a Host or DSP.
Status information from the Flash is given over Comport3 as well.
User Manual SMT348 Page 16 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 17

4.2.13 Clocking scheme
The SMT348 module contains a 50MHz LVTTL clock, a 200MHz clock, and a connector for
an external LVTTL clock input/output.
50 MHz LVTTL oscillator: Main system clock. Clocks the CPLD and the FPGA. Can be input
in a DCM.
200MHz LVTTL oscillator: QDRII clock. Can also be used as a main FPGA clock. Can be
input in a DCM.
An external clock input is provided to the Virtex 4 FPGA via an MMCX connector. This
connector is NOT fitted by default or if a mezzanine is required. YOU MUST ask Sundance if
needed for your application.
4.2.14 LEDs
4 Red LEDs connect to the FPGA and are available to the User: D4, D5, D6, D7.
1 Green Led: D1, connects to the DONE pin of the FPGA and is lit to show that the FPGA is
configured. (depending on supply from manufacturer a red led can be fitted instead).
4.2.15 Performance
The FPGA features like speed grade and density dictate most performances.
The performances achievable by the other components are given in the chapters above and
the components respective data sheets.
4.3 Interface Description
For the TIM to carrier board or external world interfacing, see in
can download from the Sundance Wizzard)
4.3.1 Power Budget
The SMT348 draws its power from the 3.3v rail of the PCI.
The PCI specification stipulates that the maximum power for one card is 25W.
Therefore, the maximum current that the SMT348 could draw from +3.3V is 7.6A, assuming
zero current on all the other supply voltages.
Sundance Help file (that you
But this limit is "system dependent," so a given system might not have the full 7.6A available
for a slot even if it is the only PCI card in the system.
A system might balance the power capabilities differently between the +5V and +3.3V (and +/12V) supplies, rather than making 25W available from +5V and 25W available from +3.3V.
User Manual SMT348 Page 17 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 18

As a result, check your main power supply ratings.
If your system is likely to reach 25W per power rail we advice that you provide extra power to
the carrier board using an external power supply.
Device
3.3v power supply V33 1 3.3 7600 25 PCI specifications
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Current(mA) Power(W) Source
Table 4: Total available power.
Device
XC4VLX160FF1148-11
Vccint=1.2v
Fpga Vccint power plane
capacity
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Curren
t(mA)
Vfpga 1 1.2 1.805 2.166
Vfpga 1 1.2 14000 16.8 TI TPS50410
Power(W) Source
Virtex-4
(design implementation of 4
independent qdrii controllers)
power
estimator
Table 5: Power budget on 1.2v
Device
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Current(mA) Power(W) Source
XC4VLX160FF1148-11
Vcco=2.5v (LVDS TX
pairs on SLB bus)
XC4VLX160FF1148-11
Vcco=2.5v (LVCMOS
TX on SLB bus)
Total power consumed V25 1.81
Fpga 2.5v power plane
capacity
Excess power 1.94
V25 40 2.5 10 1 Virtex-4 power
V25 27 2.5 12 0.81 Virtex 4 ds302 v1.17
V25 1 2.5 1.5 3.75 LT1963-1.5A Linear
Table 6: Power budget on 2.5v
estimator
p.7
Regulator 3.3v to
2.5v/1.5A
User Manual SMT348 Page 18 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 19

Device
Name Quantity Voltage
(V)
Current(mA) Power(W) Source
Samsung QDR II burst
4 (18-bit interface)
ML6554CU DC/DC
converter
Coolrunner
XC2C256CP132
XC4VLX160FF1148-11
HSTL II
Total power consumed V18 7.27599
HSTL power plane
(1.8v) capacity
Excess power 3.525
V18 4 1.8 800 5.76 Samsung QDRII (-
V18 1 1.8 0.01 0.018 Fairchild
V18 1 1.8 0.55 0.00099 Ise 8.2.03i Xpower
V18 1
(design
implementation of 4
independent qdrii
controllers)
V18 1 1.8 6000 10.8 TI TPS54611PWP
1.8 829 1.497 Virtex-4 power
Table 7: Power budget on 1.8v.
25), datasheet rev1.1
p.9
ML6554CU
(obsolete)
software version:
I.34
estimator
Device
QDRII Vtt
termination resistor
(50 ohms) (See
details)
Total power
consumed
HSTL Vtt
termination Power
Plane (0.9v) capacity
Excess power 1.87
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Current(mA) Power(W) Source
V09 240 0.9 18.0 3.89 Samsung QDRII (-25), datasheet
V09 3.89
V09 1 0.9 3000 5.76 Fairchild ML6554CU (obsolete)
Table 8: Power budget on QDRII 0.9v Termination voltage.
rev1.1 p.9
User Manual SMT348 Page 19 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 20

Device
QDRII Vref VR09 8 0.9 0 0 Samsung QDRII (-
XC4VLX160FF1148-11 HSTL
Vref
Total power consumed VR09 0.000144
HSTL Vref plane (0.9v)
capacity
Excess power 0.002556
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Current(mA) Power(W) Source
25), datasheet
rev1.1 p.9
VR09 16 0.9 0.01 0.000144 DS302 (v1.17)
table 3 p.3
VR09 1 0.9 3 0.0027 Fairchild
ML6554CU
(obsolete)
Table 9: Power budget on QDRII and FPGA 0.9v reference voltage.
Device
25 Mhz Clock oscillator V33 1 3.3 15 0.05 Jauch VX3 Quartz
200 Mhz Clock
oscillator
Name Quantity Voltage(V) Current(mA) Power(W) Source
crystal oscillators
datasheet
V33 1 3.3 20 0.066 Jauch VX3 Quartz
crystal oscillators
datasheet
Linear Regulator 3.3v
to 2.5v/1.5A
DC/DC converter 3.3v
to 0.9v
DC/DC converter 3.3v
to 1.2v
DC/DC converter 3.3v
to 1.8v
DIP Switch V33 1 3.3 0.7 0.002 Four 4.7 Kohm pullup
Flash memory V33 1 3.3 90 0.297 S29GL256N
XC4VLX160FF1148-11
LVTTL Vcco=3.3v
3.3v power plane V33 1 3.3 7600 25W TI TPS50410
V33 1 3.3 1.136 3.75 LT1963-1.5A
V33 13.75 N/A Fairchild ML6554CU
(obsolete)
V33 14000 N/A TI TPS50410
V33 6000 N/A TI TPS54611PWP
V33 1 3.3 Depends on
implemented
design
Virtex-4 power
estimator
Table 10: Power budget on 3.3v.
User Manual SMT348 Page 20 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 21

Details:
Coolrunner XC2C256-6-CP132 power requirements based on design:
Macrocells
Used
218/256 (86%) 531/896 (60%) 190/256 (75%) 69/106 (66%) 445/640 (70%)
Pterms Used Registers Used Pins Used
Function Block
Inputs Used
Table 11: Coolrunner II resources summary.
Signal Type Required Mapped
Input 8 8
Output 40 40
Bidirectional 20 20
GCK 1 1
GTS 0 0
GSR 0 0
Pin Type Used Total
I/O 65 96
GCK/IO 3 3
GTS/IO 0 4
GSR/IO 1 1
CDR/IO 0 1
DGE/IO 0 1
Table 12:Coolrunner II pin resources.
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 22

5 Footprint
5.1 Top View
Figure 4: Top View
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 23

5.2 Bottom View
Figure 5: Bottom view
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 24

6 Pinout
6.1 FPGA Pin allocation by bank
Bank I/O Vr* QDR2 SHB CP SLB GB Other Total
1 48 0
2 48 0 8xConfig 8
3 16 0
4 16 0
5 64 4
6 64 4
7 64 6 SLB LVTTL 13 Control
8 64 6
9 64 4
10 64 4
11 64 6 1xSHB 2xCP 64
12 64 6 1xSHB 2xCP 64
13 64 6
14 64 6
Clocks & DLL
control
Bank C Data +
Control
Bank B Data +
Control
Bank D Data &
Control
Bank A Data &
Control
2
Clocks &
Reset &
Switches
64
64
PXI, TTL,
INTs, LEDs,
Misc.
32 Data &
31 Address &
1 Control
64
64
16 Diff Data &
4 Diff Clocks
16 Diff Data &
4 Diff Clocks
46
64
46
13
64
Vr* = Vrp + Vrn + Vref
Table 13: Pin allocation by Bank
6.2 SHB
SUNDANCE SHB specification
6.3 SLB
SUNDANCE SLB specification
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 25

6.4 JTAG
TDO
TDI
TMS
JP1
TCK
GND
3.3V
34
25
16
Figure 6: JTAG Connector, top view
7 Qualification Requirements
7.1 Qualification Tests
7.1.1 Meet Sundance standard specifications
• Meet the TIM standard specifications
• Meet the SLB specifications (LVDS standard).
• Meet the SHB specifications.
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 26

7.1.2 Speed qualification tests
• QDR2 memory accesses at 250MHz.
7.1.3 Integration qualification tests
• Must work on ALL Sundance platforms as a root TIM module or as part of
a network of TIMs on carriers.
• Must be able to work stand-alone.
8 Support Packages
User Manual SMT348 Page 26 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 27

9 Physical Properties
Dimensions
Weight
Supply Voltages
Supply Current +12V
+5V
+3.3V
-5V
-12V
MTBF
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 28

10 Safety
This module presents no hazard to the user when in normal use.
User Manual SMT348 Page 28 of 29 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
Page 29

11 EMC
This module is designed to operate from within an enclosed host system, which is build
to provide EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is not guaranteed
unless it is installed within an adequate host system.
This module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients originating from outside
the host system which may be introduced through the output cables.
Short circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up or
reboot.
User Manual SMT348 Last Edited: 29/02/2008 17:52:00
 Loading...
Loading...