Page 1

SMT335
SMT375
User Manual
User Manual (QCF42); Version 3.0, 5/2/01; © Sundance Multiprocessor Technology Ltd. 2001
Page 2
Version 3.0 Page 2 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Revision History
Date Comments Engineer Version
08/05/00 Comm port J.V. 0.1
12/06/00 SDB J.V. 0.2
10/07/00 Pre-release version J.V. 0.9
26/07/00 First version J.V. 1.0
27/07/00 Typing error corrected. (Comm Port status) J.V. 1.1
08/08/00 New Burst mode selection from CP status
J.V. 1.2
Global register display the interrupt status
09/08/00 Output FIFO status displays how many words
J.V. 1.3
can be sent
14/08/00 Global register and Interrupt control register
J.V. 1.4
reordered. (Need Bootv1.2)
03/09/00 SDB naming corrected to A and B.
J.V. 1.5
Global Bus modification for DMA use.
Comm port drawing modified
Boot code Version 1.4
FPGA Firmware Version 2.0
(top335V2_0_6.dat)
14/09/00 NMI routing selection added. J.V. 1.6
18/09/00 Global Bus transfer example corrected J.V. 1.7
10/10/00 Global Bus wait state and bus sharing feature
J.V. 1.8
added.
Comm-port status register: OCPRDY and
ICPRDY moved to allow FIFO depth
expansion.
Firmware version 2.5.6
27/10/00 Global Bus wait state increased to 15. Cf.
Control register.
Comm-port status register: Full reset bit added
for crash recovery.
Firmware version 2.7.6
J.V. 1.9
Page 3
Version 3.0 Page 3 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
09/11/00 Documentation added for DMA transfers
FPGA I/O Slew rate changed to S_12.
Firmware version 2.8.6
07/12/00 SDB interrupt flags modified.
Global bus tri-state signal not latched.
Global bus flag cleared when transfer direction
is changed.
Comm-port reply disabled during token
exchange.
Firmware version 2.9.6
11/12/00 SDB Memory mapping updated.
Firmware version 3.0.6
24/01/01 Manual updated with quality template.
Timer routing detailed.
J.V. 2.0
J.V. 2.1
J.V. 2.2
J.V. 2.3
Comm-port drawing corrected.
Reprogramming and version control described.
SDB Interrupt Bug fixed. SDB handling
detailed.
Comm-port bug reported.
Firmware version 3.3.6
13/4/01 General overhaul and clarificati o n PSR 3.0
30/8/01 Power consumption and reset timing added.
J.V. 3.1
Value of Bit 12-13 of the global control register
explained.
11/04/02 Global bus additional feature. Synchronisation
J.V. 3.2
with carrier board on SMT328 and SMT310.
External trigger for ADC acquisition for
SMT118.
Fix for Comm-port Burst mode selection
between threads in bi-directional transfer.
Firmware version 3 .11.6
Page 4
Version 3.0 Page 4 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
15/05/02 IIOF Interrupt description.
J.V. 3.3
Global bus BUSY bit description
Interrupt control register 6 address corrected.
Global bus transfers description for SMT310
family.
Firmware version 3 .11.6
30/01/03 Restructure of the document.
J.V. 3.4
Double buffered global bus. Will require code
change if transfer via dma were used.
SDB dma synchronisation changed no
software change required.
Firmware version 3 .13.6
It is important that you use the correct version of the firmware; you should use
firmware version 3.13.6 or later.
Check your firmware revision number with the program read_version_335.out and
ask for a more recent version if necessary.
E-mail: support@sundance.com
Page 5

Version 3.0 Page 5 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Table of Contents
Revision History............................................................ Error! Bookmark not define d.
Contacting Sundance................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Notational Conventions................................................ Error! Bookmark not defined.
SMT335....................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Register Descriptions...............................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Outline Description....................................................... Error! Bookmark not define d.
Block Diagram............................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Architecture Description.............................................. Error! Bookmark not de fine d.
TMS320C6201/6701....................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Boot Mode................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
EMIF Control Registers................................................ Error! Bookmark not define d.
SBSRAM..................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
SDRAM....................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
FLASH......................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Version control ............................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Reprogramming the firmware and boot code ............ Error! Bookmark not defined.
Interrupts....................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Communication ports................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Data rates ...................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
SDB................................................................................ Error! Bookmark not define d.
SDB................................................................................ Error! Bookmark not define d.
SDB update..............................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
SDB Clock selection.................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Global bus..................................................................... Error! Bookmark not d e fine d.
Note for SMT310, SMT310Q, SMT300, SMT300Q..Error! Bookmark not defined.
Clock Speed.................................................................. Error! Bookmar k not d efined.
LED Setting ................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
LED Register............................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
CONFIG & NMI............................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Timer.............................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
IIOF interrupt................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Page 6

Version 3.0 Page 6 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Code Composer............................................................ Error! Bookmark not de fine d.
Application Development............................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Operating Conditions................................................... Error! Bookmar k not d e fine d.
Safety.......................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
EMC.........................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
General Requirements.............................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Power Consumption.................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Serial Ports.................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
C6201 Memory Map...................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Flash Access ................................................................. Error! Bookmark not define d.
Virtex Memory Map....................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Jumpers......................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
JP1: Clock speed select...........................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
JP2: Serial port header.............................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
SDB Pin-Out .................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Virtex layout.................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Virtex Pin-Out................................................................ Error! Bookmark not defined.
Bibliography.................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Index .............................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
Contacting Sundance
You can contact Sundance for additional information by sending email to
support@sundance.com
Page 7

Version 3.0 Page 7 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Notational Conventions
SMT335
Throughout this document the term SMT335 will usually be used to refer to both the
SMT335 and the SMT375. It should be clear from the context when a distinction is
being drawn between the two types of module.
Register Descriptions
The format of registers is described using diagrams of the following form:
31–24 23–16 15–8 7–0
OFLAGLEVEL
R,00000000 RW,10000000 R,00000000 R,10000000
The digits at the top of the diagram indicate bit positions within the register and the
central section names bits or bit fields. The bottom row describes what may be done
to the field and its value after reset. Shaded fields are reserved and should only ever
be written with zeroes.
R Readable by the CPU
W Writeable by the CPU
RW Readable and writeable by the CPU
Binary digits indicate the value of the field after reset.
Page 8

Version 3.0 Page 8 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Outline Description
The SMT335 is a C6000-based size 1 TIM offering the following features:
SMT335: TMS320C6201 processor running at 200MHz
SMT375: TMS320C6701 processor running at 166MHz
Six 20MB/s communication ports (comm.-ports)
512KB of fast SBSRAM, 16MB of SDRAM
512KB Flash ROM for boot code and FPGA programming
Global expansion connector
High bandwidth data I/O via 2 Sundance Digital Buses (SDB).
Page 9
Version 3.0 Page 9 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
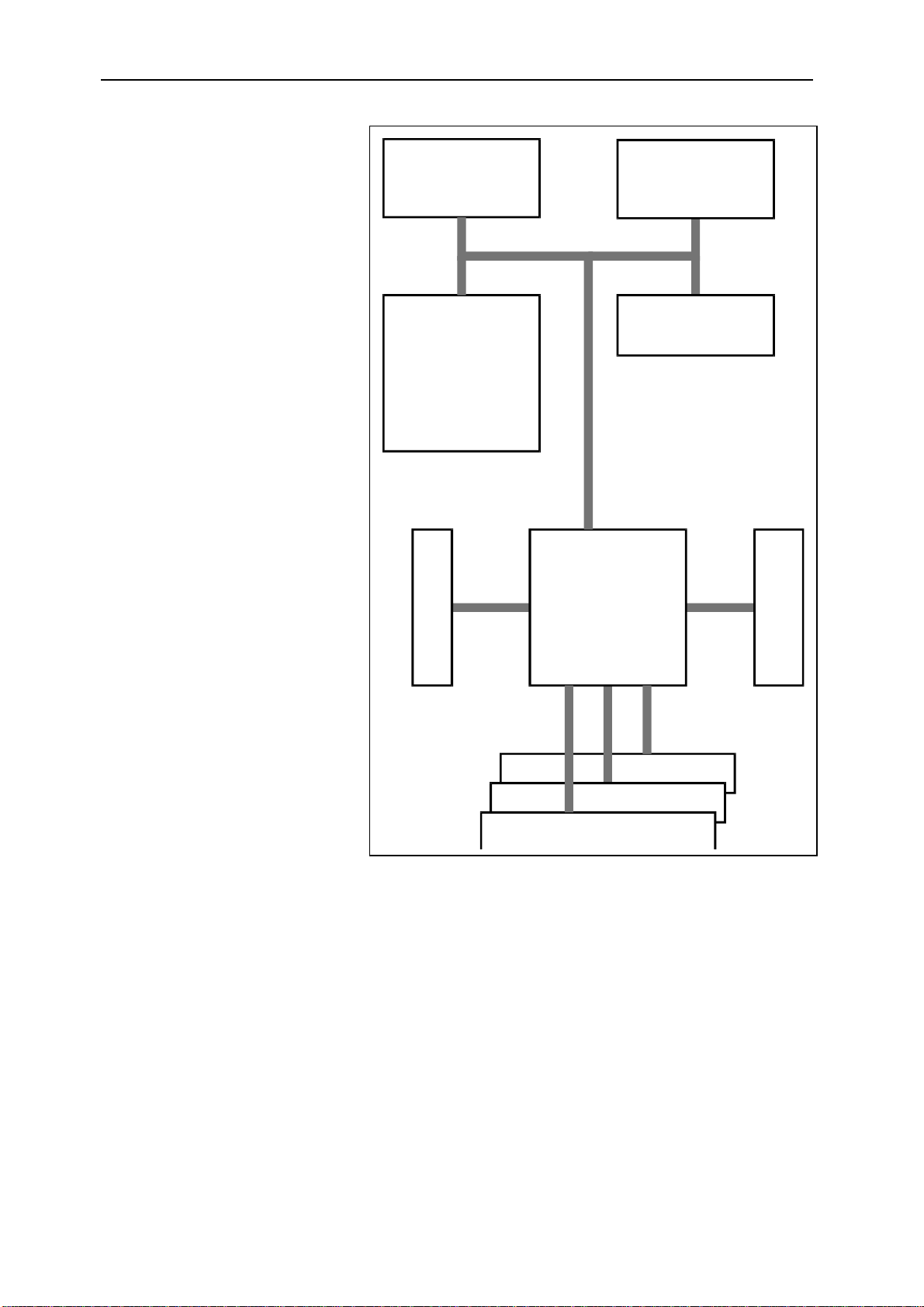
Block Diagram
SDRAM
4M x 32
C6201
1600MIPS
23pins 23pins
SDB
SBSRAM
Address(16),Data(32),Control=12
Virtex
GLOBAL BUS
COMM PORTS
SDB
User applications
128K x 32
FLASH
512K x 8
SDB
Address,Data,Control=75pins
4xComms=48pins
2xComms,Tclk,Clocks,Ints=33pins
GLOBAL
SECONDARY
PRIMARY
Page 10

Version 3.0 Page 10 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Architecture Description
The SMT335 TIM consists of a Texas Instruments TMS320C6201 running at
200MHz while the SMT375 has a TMS320C6701 running at 166MHz. Modules are
populated with 512KB of synchronous burst SRAM (SBSRAM) and 16MB of
synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), giving a total memory capacity of 16.5MB.
A Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) is used to manage global bus accesses
and implement six communication ports and two Sundance Digital Buses.
Page 11

Version 3.0 Page 11 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
TMS320C6201/6701
Bother processors will run with zero wait states from internal SRAM, the
TMS320C6201 at 200MHz and the TMS320C6701 at 166MHz.
An on-board synthesiser from MicroClock provides the clock used for the C6000;
jumpers on the TIM allow you to select clock speeds from 118MHz to 200MHz.
Unlike similar TIMs based on the TMS320C4x, there is no option to provide an
external clock source.
The TIM configuration feature is fully implemented. This provides a single opencollector line that can be held low until software configuration has been completed.
Boot Mode
The SMT335 is configured to use the following boot sequence each time it is taken
out of reset:
1. The processor copies a bootstrap program from the first 32KB of the flash
memory into internal program RAM starting at address 0.
2. Execution starts at address 0.
The standard bootstrap supplied with the SMT335 then performs the following
operations:
1. All relevant C6000 internal registers are set to default values;
2. The FPGA is configured from data held in flash memory and sets up the
communication ports, the global bus and the Sundance Digital Buses. This
step must have been completed before data can be sent to the comm-ports
from external sources such as the host or other TIMs;
3. A C4x-style boot loader is executed. This will continually examine the six
communication ports until data appears on one of them. The bootstrap will
then load a program in boot format from that port; the loader will not read data
arriving on other ports. See “Application Development” on page Error!
Bookmark not defined. for details of the boot loader format;
4. Finally, control is passed to the loaded program.
The delay between the release of the board reset and the FPGA configuration is
around 280ms for a SMT335 (200MHz clock) and 330ms for a SMT375 (166MHz).
The worse case is with a board clocked at 118MHz (no jumper fitted) in which case
the FPGA will be configured 480ms after the rese t is released.
A typical time to wait after releasing the board reset is 500ms.
Page 12

Version 3.0 Page 12 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
EMIF Control Registers
The C6000 contains several registers that control the external memory interface
(EMIF). There is one global control register and a separate register for each of the
memory spaces CE0 to CE3. A full description of these registers can be found in the
C60000 Peripherals Reference GuideError! Reference source not found.Error!
Reference source not found.[Error! Reference source not found.].
The standard bootstrap will initialise these registe rs to the following values:
GC (global control)
0x00003779
0x0000377D
For half speed SBSRAM
For full speed SBSRAM (default)
CE0 0x00000040 Indicates SBSRAM
CE1 0x30FF3F03 Defines asynchronous memory timing s
CE2 0x00000030 Indicates SDRAM
CE3 0x00000030 VIRTEX FPGA
Note: Bits 12&13 of the Global control register are listed as 'reserved' in the current
TI documentation . With earlier version s of the C6000 silicon, these 2 bits co ntrolled
the polarity of two clock outputs from the device. To maintain code compatib ility for all
of our version modules, we have left our documentation with bits 12&13 set.
SBSRAM
Memory space CE0 is used to access 512KB of zero wait-state SBSRAM over the
C6000 external memory interface (EMI).
SBSRAM is normally set to run at the speed of the C6000 core clock, but the GC
register can be used to reduce this to one half of the core clock speed. The
appropriate setting has to be determined in conjunction with the C6000 core speed
and the external memory speed; refer to Clock Speed on page Error! Bookmark
not defined. for further details.
SDRAM
Memory space CE2 is used to access 16MB of SDRAM over the EMI. The SDRAM
operates at one half of the core clock speed.
FLASH
A 512KB Flash ROM device is connected to the C6000 EMI. This device is
accessed, a byte at a time, with word addresses from 0x0140 0000 to 0x015F FFFF
using strobe CE1 in 32-bit asynchronous mode. Each 32-bit load will give 8 bits of
data in bits 7–0 of the result; the state of bits 31–8 is undefined.
Page 13

Version 3.0 Page 13 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
The ROM holds boot code for the C6000, configuration data for the FPGA, and
optional user-defined code.
A software protection algorithm is in place to prevent programs accidentally altering
the ROM’s contents. Please contact Sundance for further information about reprogramming this device [Error! Reference source not found.Error! Reference
source not found.Error! Reference source not found.Error! Reference source
not found.].
Version control
Revision numbers for both the boot code and FPGA firmware are stored in the Flash
ROM during programming as zero-terminated ASCII strings. These revision numbers
are located using byte offsets from the base of the Flash ROM (0x01400000). The
offsets are held as 4-byte words at the end of the ROM: 0x015FFFF8 for the FPGA
firmware offset and 0x0147FFFC for the boot code offset.
The distribution disk contains a program, read_version_335.out, in the directory
Reprogramming\version_control. You can load and run this program from
code composer to display both the FPGA and boot code version numbers.
Reprogramming the firmware and boot code
The Reprogramming\flash directory of the distribution disk contains a utility that
will run under code composer and program the flash ROM. The utility is called
pflashx_y_z.out, where x_y_z is the FPGA version number.
You load the utility with the code composer “Load Program” option from the “File”
menu. Once the program has loaded, you should select “Run” from the “Debug”
menu. The reprogramming process takes a minute or so and should display “Flash
programming complete” when it has finished. After the program has run you should
“Halt” the processor from the “Debug” menu and select “Run Free”. To confirm that
the programming has been successful you should use the Sundance Server to reset
the board and execute one of the supplied test programs.
A detailed description of the reprogramming process is available as an Application
Note [Error! Reference source not found.], which will also help you to develop your
own core in the FPGA.
Page 14

Version 3.0 Page 14 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Interrupts
See general firmware description
Communication ports
The SMT335 provides six comm-ports.
See general firmware description
Data rates
When using the communication links of a C6000 you must remember that the links
share a single bus, so the performance you get will depend on the way you sequence
bus accesses.
C6201 can read at 100MHz from external to internal memory; the rate for the C6701
is 83MHz. If you want to store in external memory then the rate achievable are
divided by two as the read and writes share the same bus, which means respectively
50MHz and 41MHz.
The C6000 DMA channels are not efficient when moving data between two external
memory areas sharing a commo n bus; the transfer will take place a word at a time
and not in more efficient bursts. This is why it may not be advisable to use DMA to
transfer data directly between external memory and a communication link.
Performance can be greatly improved by using an intermediate buffer in internal
memory.
SDB
The SMT335 provides two Sundance Digital Buses (SDBs).
See general firmware description
SDB update
You should be aware that revisions of the SDB before V3.0.6 have a significantly
different treatment of the status flags and a different address is used to program the
SDB flag leve ls for input and output. When upgradi ng from versions before V3.0.6,
you will need to change the code for flag programming and accessing the status bits.
You should use version V3.3.6 or above because previous versions could generate
spurious interrupts on input.
SDB Clock selection
At any time you can change the speed of an SDB clock by altering SDBCLK.
Page 15

Version 3.0 Page 15 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Module SDBCLK Clock Speed
SMT335
0 50MHz
1 100MHz
0 41MHz
SMT375
1 83MHz
Global bus
The SMT335 provides one global bus interface.
See general firmware description
The latest global bus interface is double buffered for dma so that it can read ahead
the next buffer while the first one is being read by the DSP. Similarly a buffer is being
written while the previous one is being sent.
The important thing is to set the global bus operation register before enabling the
global bus interrupt on an external interrupt line so that the interrupt generated is the
one relevant to the operation (read/write).
This has changed for the SMT335 firmware as it used to need the dma event to be
forced for a write and that the external interrupt was enabled before the operation
register was set. This is the only change needed when updating from a version of the
SMT335 prior to 3.13.6.
Note for SMT310, SMT310Q, SMT300, SMT300Q
Burst Transfer across a 1KBytes page boundary is only supported from version
3.13.6 of the firmware.
To transfer over the PCI the global bus is set-up to be able to perform burst transfer
across the PCI bridge chip. A burst transfer is happening whenever the global bus
transfer size register is set to transfer more than one word at a time. During a burst a
word is transferred on every clock cycle.
The PC memory can be accessed through aperture 0 of the PCI Bridge but a burst
transfer must not cross a 1KBytes boundary (256 words). This is because the page
size of the bridge chip is 1KBytes.
In other words burst transfer must always be ended on a page boundary. For
example you should never burst from the pci address XXXXX3FCH to XXXXX400H.
Address XXXXX400H would actually be targeting address XXXXX000H in the pci
address space as the page accessed by this burst was in the address range
XXXXX000H - XXXXX3FCH.
To make sure a page crossing does not happen during burst access an address
alignment has to be performed. The global bus transfer size has to be reduced not to
Page 16

Version 3.0 Page 16 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
cross a page. For DMA it is advised to align the transfer on 256 words and then setup the DMA to transfer by bursts of 256 words to ensure no page boundary is
crossed during burst.
Page 17

Version 3.0 Page 17 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Clock Speed
You must consider EMIF device speeds when choosing the appropriate C6000 clock
speed. Under most circumstances, the C6201 would be set to 200MHz and have an
SBSRAM speed equal to the core speed; the C6701 would be set to 166MHz. See
the description of jumper JP1 on page Error! Bookmark not defined..
C6000 clock SBSRAM SDRAM FPGA
133 133 67 67
166 166 83 83
200 100 100 100
200 200 100 100
LED Setting
The SMT335 has 5 LEDs.
LED 1 always displays the state of the FPGA DONE pin. This LED is off when the
FPGA is configured (DONE=1) and on when it is not configured (DONE=0).
This LED should go on when the board is first powered up and go off when the FPGA
has been successfully programmed. If the LED does not light at power-on, check that
you have the mounting pillars and screws fitted prope rly. If it stays on, the DSP is not
booting correctly.
The remaining LEDs can b e controlled with the LED register. W riting 1 will illuminate
the LED; writing 0 will turn it off.
See general firmware description
CONFIG & NMI
See general firmware description
Timer
See general firmware description
IIOF interrupt
From version 3.11.6 of the firmware it is possible to generate pulses on the external
interrupt lines of the TIM.
See general firmware description
Page 18

Version 3.0 Page 18 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Code Composer
This module is fully compatible with the Code Composer debug environment. This
extends to both the software and JTAG debugging hardware including the
SMT320V4, SMT327, SMT328 and TI’s XDS- 510.
Application Development
You can develop code for SMT335/375 modules in several ways. The simplest is to
use the Sundance SMT6000 Server Loader and its associated libraries.
The Server Loader is an application that runs on a host PC under either Windows 98
or NT and allows you to run COFF-format applications. Modified forms of the TI rts
library, one for the C6201 and one for the C6701, support standard C I/O.
The Server Loader will read a .out file and convert it into C4x-style boot code which
is then transmitted down a comm-port to the SMT335.
The boot code is in the following format:
Word1 1
6-word
header
Words 2, 3, 4 0, 0, 0
Word 5 start address
Word 6 0
Word 1 4*N: Length of load block (in bytes)2
Load Block
Word 2 Destination address (external memory only)
Next N words N data words
0 or more
Load Blocks
Terminator Word 1 03
0x00003779 half speed SBSRAM
0x0000377D full speed SBSRAM (recommended)
1
A word is 32 bits
2
The length of each data block will be rounded up to a multiple of 4 bytes if necessary.
3
Effectively a zero-length Load Block
Page 19

Version 3.0 Page 19 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Operating Conditions
Safety
The module presents no hazard to the user.
EMC
The module is designed to operate within an enclosed host system that provides
adequate EMC shielding. Operation within the EU EMC guidelines is only guaranteed
when the module is installed within an appropriate host system.
The module is protected from damage by fast voltage transients introduced along
output cables from outside the host system.
Short-circuiting any output to ground does not cause the host PC system to lock up
or reboot.
General Requirements
The module must be fixed to a TIM40-compliant carrier board.
The SMT335 TIM is in a range of modules that must be supplied with a 3.3v power
source. In addition to the 5v supply specified in the TIM specification, these new
generation modules require an additional 3.3v supply to be presented on the two
diagonally-opposite TIM mounting holes. The lack of this 3.3v power supply should
not damage the module, although it will obviously be inoperable; prolonged operation
under these circumstances is not recommended.
This module is not directly compatible with earlier generations of TIM motherboards,
although the 3.3v supply can be provided from a separate source. It is, however,
compatible with the latest generation of Sundance TIM carrier boards such as the
SMT320V4 and subsequent versions (PCI), and SMT328 (VME), which present the
3.3v via conductive mounting pillars.
Use of the TIM on SMT327 (cPCI) motherboards may require a firmware upgrade. If
LED #1 on the SMT335 rem ains illumi nated once the T IM is plugged in and powered
up, the SMT327 needs the upgrade. The latest firmware is supplied with all new
boards shipped. Please contact Sundance directly if you have an older board and
need the upgrade.
A SMT320V3 motherboard can be used providing a SMT335 TIM is not located in the
first slot; putting one there prevents the SMT320V3 from coming out of reset. Any
other type of TIM must be placed in the first slot of this motherboard to ensure correct
operation.
The external ambient temperature must remain between 0°C and 40°C, and the
relative humidity must not exceed 95% (non-condensing).
Power Consumption
The power consumption of this TIM is dependent on the operating conditions in terms
of core activity and I/O activity. The maximum power consumption is 6W.
Page 20

Version 3.0 Page 20 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Serial Ports
The C6000 contains two multichannel buffered serial ports (McBSP). The signals
involved are connected to a 0.1” pitch DIL pin header (JP2). For a full description of
signal activity and the serial protocols available, please refer to Chapter 11 of [Error!
Reference source not found.].
Signal Pin Pin Signal
FSX1 1 2 FSX0
FSR1 3 4 FSR0
DX1 5 6 DX0
DR1 7 8 DR0
CLKX1 9 10 CLKX0
CLKR1 11 12 CLKR0
CLKS1 13 14 CLKS0
GND 15 16 GND
Page 21

Version 3.0 Page 21 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
C6201 Memory Map
Starting Address RESOURCE Refer to
00000000 Internal Program RAM
00010000 Reserved
00400000 – 0047FFFF
01400000 – 015FFFFF
01800000 Internal Peripherals
01C00000 Reserved
02000000 -02FFFFFF
03000000 – 03FFFFFF
04000000 Reserved
80000000 Internal Data RAM
80010000 Reserved
80400000 Reserved
External Memory Space CE0
512KB SBSRAM
External Memory Space CE1
512KB Flash
External Memory Space CE2
16MB SDRAM
External Memory Space CE3
See Virtex memory map
SBSRAM
Flash
SDRAM
Comm-ports,
SDB, Global bus
Flash Access
Address Resource
01400000 – 015FFFFF
ED31 ED30 CE1
0 0 Read Flash / Write Flash
0 1 Read Flash / Pulse PROG
1 0 Read Flash / Write CCLK
1 1 Read Flash / Write Flash
Page 22

Version 3.0 Page 22 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Virtex Memory Map
See general firmware description with i = 18
The memory mapping is as follows:
#define CP0 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03000000
#define CP1 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03080000
#define CP2 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03100000
#define CP3 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03180000
#define CP4 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03200000
#define CP5 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03280000
#define CP0_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03040000
#define CP1_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x030C0000
#define CP2_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03140000
#define CP3_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x031C0000
#define CP4_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03240000
#define CP5_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x032C0000
#define GBSTAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03340000
#define SDBSTAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03380000
#define STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x033C0000
#define SDBA (volatile unsigned int *)0x03400000
#define SDBB (volatile unsigned int *)0x03500000
#define SDBA_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03480000
#define SDBB_STAT (volatile unsigned int *)0x03580000
#define SDBA_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x03440000
#define SDBB_INPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x03540000
#define SDBA_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x034C0000
#define SDBB_OUTPUTFLAG (volatile unsigned int *)0x035C0000
#define GLOBAL_BUS (volatile unsigned int *)0x03A00000
#define GLOBAL_BUS_CTRL (volatile unsigned int *)0x03800000
#define GLOBAL_BUS_START (volatile unsigned int *)0x03880000
#define GLOBAL_BUS_LENGTH (volatile unsigned int *)0x03900000
#define TCLK (volatile unsigned int *)0x03C00000
#define TIMCONFIG (volatile unsigned int *)0x03C80000
#define LED (volatile unsigned int *)0x03D00000
#define IIOF (volatile unsigned int *)0x03D80000
#define INTCTRL4 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03E00000
#define SDBINTCTRL4 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03E40000
Page 23

Version 3.0 Page 23 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
#define INTCTRL5 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03E80000
#define SDBINTCTRL5 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03EC0000
#define INTCTRL6 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03F00000
#define SDBINTCTRL6 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03F40000
#define INTCTRL7 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03F80000
#define SDBINTCTRL7 (volatile unsigned int *)0x03FC0000
Page 24

Version 3.0 Page 24 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Jumpers
JP1: Clock speed select
S2 S1 S0 C6000 CLK
(MHz)
IN IN IN 200
IN IN OUT 182
IN OUT IN 167
IN OUT OUT 154
OUT IN IN 143
OUT IN OUT 133
OUT OUT IN 125
OUT OUT OUT 118
S0, S1 and S2 refer to the
following link positions on JP1.
S2 S1 S0
JP2: Serial port header
Refer to the TMS320C6201 Peripheral Reference Guide [Error! Reference source
not found.] for a description of the signals and their usage.
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
FSX0 FSR0 DX0 DR0 CLKX0 CLKR0 CLKS0 GND
FSX1 FSR1 DX1 DR1 CLKX1 CLKR1 CLKS1 GND
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
Page 25

Version 3.0 Page 25 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
SDB Pin-Out
Pin Signal Signal Pin
1 CLK GND 2
3 D0 GND 4
5 D1 GND 6
7 D2 GND 8
9 D3 GND 10
11 D4 GND 12
13 D5 GND 14
15 D6 GND 16
17 D7 GND 18
19 D8 GND 20
21 D9 GND 22
23 D10 GND 24
25 D11 GND 26
27 D12 GND 28
29 D13 GND 30
31 D14 GND 32
33 D15 GND 34
35 UD0 DIR 36
37 WEN REQ 38
39 UD1 ACK 40
Page 26

Version 3.0 Page 26 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
A
Virtex layout
CLOCK SDB B
C60 CLOCK / 2
SDB B + CP 0
C
6
X
B
U
S
CP 4 + CP 5
VIRTEX
300
FG456
G
L
O
B
L
B
U
S
SDB A + CP 3
CLOC K SDB A
CP 1 + CP 2
C60 CLOCK / 2
Page 27

Version 3.0 Page 27 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Virtex Pin-Out
A1 B1 ED0 C1 ED1 D1 ED16
A2 C0S10 B2 C2 ED15 D2 /AWE
A3 SDBD15 B3 SDBBWEN C3 D3
A4 SDBD12 B4 C0S5 C4 D4
A5 SDBD9 B5 SDBBUD0 C5 C0S8 D5 SDBBD2
A6 C0S11 B6 SDBBUD1 C6 C0S6 D6 SDBBD5
A7 SDBD6 B7 SDBBD13 C7 C0S9 D7 SDBBD8
A8 SDBD3 B8 SDBBD10 C8 DIRB D8 SDBBD11
A9 C0S4 B9 SDBBD7 C9 D9 SDBBD14
A10 SDBD0 B10 SDBBD4 C10 CLKB D10 SDBBREQ
A11 CLK100 B11 SDBBD1 C11 CLKB D11 C4S0
A12 C5S5 B12 C5S9 C12 C5S0 D12 C4S1
A13 C5S6 B13 C4S10 C13 C5S1 D13 C4S2
A14 C5S7 B14 C5S10 C14 C5S2 D14 C4S3
A15 /C60NMI B15 C5S11 C15 C5S3 D15 C4S4
A16 C5S8 B16 /TIMIACK C16 C5S4 D16 C4S5
A17 /C60IACK B17 IIOF2 C17 D17 C4S6
A18 B18 /TIMNMI C18 D18 GA29
A19 B19 CONFIG C19 D19
A20 B20 C20 D20 Config D0
A21 B21 C21 D21 GA26
A22 B22 CCLK C22 GA27 D22 STAT0
Comm-ports are numbered C0 to C5. Each has 12 elements (i.e. CnS[0..11]).
CnS0 STRB
CnS1 RDY
CnS2 REQ
CnS3 ACK
CnS[4..11] Data[0..7]
Page 28

Version 3.0 Page 28 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
E1 ED2 F1 ED5 G1 ED10 H1 ED14
E2 /RAS F2 ED6 G2 ED17 H2 ED22
E3 ED3 F3 ED7 G3 ED11 H3 ED23
E4 ED4 F4 ED8 G4 ED12 H4 /CAS
E5 F5 ED9 G5 ED13 H5 ED24
E6 SDBBACK F6 G6 H6
E7 C0S0 F7 G7 H7
E8 C0S7 F8 G8 H8
E9 C0S1 F9 G9 H9
E10 C0S2 F10 G10 H10
E11 C0S3 F11 G11 H11
E12 C4S7 F12 G12 H12
E13 /TIMNMI F13 G13 H13
E14 C4S11 F14 G14 H14
E15 C4S8 F15 G15 H15
E16 C4S9 F16 G16 H16
E17 /RESET F17 G17 H17
E18 F18 GA22 G18 GA18 H18 STAT2
E19 GA30 F19 GA21 G19 GA17 H19 GA13
E20 GA25 F20 GA20 G20 GA16 H20
E21 GA24 F21 STAT1 G21 GA15 H21 GA12
E22 GA23 F22 GA19 G22 GA14 H22
Page 29

Version 3.0 Page 29 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
J1 ED18 K1 ED28 L1 ED31 M1 EA2
J2 ED25 K2 ED20 L2 ED21 M2 EA17
J3 ED26 K3 /SDRAMWE L3 /SDRAMCS M3 EA3
J4 ED19 K4 ED29 L4 /ARE M4 EA4
J5 ED27 K5 ED30 L5 /ARDY M5 EA5
J6 K6 L6 /AOE M6 EA6
J7 K7 L7 M7
J8 K8 L8 M8
J9 K9 L9 M9
J10 K10 L10 M10
J11 K11 L11 M11
J12 K12 L12 M12
J13 K13 L13 M13
J14 K14 L14 M14
J15 K15 L15 M15
J16 K16 L16 M16
J17 K17 L17 GA9 M17
J18 GA28 K18 GA6 L18 /AE M18
J19 GA11 K19 GA5 L19 GA3 M19 /DE
J20 GA10 K20 L20 GA2 M20 GD31
J21 GA8 K21 STAT3 L21 GA1 M21 GD30
J22 GA7 K22 GA4 L22 GA0 M22 GD29
Page 30

Version 3.0 Page 30 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
N1 EA18 P1 EA19 R1 EA13 T1 EA16
N2 TIN0 P2 EA10 R2 EA14 T2 /BE0
N3 EA7 P3 EA11 R3 EA21 T3 TCLK0
N4 EA8 P4 EA12 R4 TIN1 T4 /BE1
N5 EA9 P5 EA20 R5 EA15 T5 /BE2
N6 P6 R6 T6
N7 P7 R7 T7
N8 P8 R8 T8
N9 P9 R9 T9
N10 P10 R10 T10
N11 P11 R11 T11
N12 P12 R12 T12
N13 P13 R13 T13
N14 P14 R14 T14
N15 P15 R15 T15
N16 P16 R16 T16
N17 P17 R17 T17
N18 GD28 P18 GD24 R18 GD19 T18 GD15
N19 GD27 P19 GD23 R19 GD18 T19 GD14
N20 GD26 P20 GD22 R20 GD17 T20 GD13
N21 GD25 P21 GD21 R21 T21 GD12
N22 P22 GD20 R22 GD16 T22
Page 31

Version 3.0 Page 31 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
U1 /BE3 V1 LED1 W1 DMAC3 Y1 TCLK1
U2 DMAC0 V2 LED2 W2 Y2 TOUT1
U3 DMAC1 V3 LED3 W3 TOUT0 Y3
U4 DMAC2 V4 LED4 W4 Y4 M2=V33
U5 M1=V33 V5 W5 C3S6 Y5
U6 V6 W6 C3S7 Y6 SDBAUD0
U7 V7 C3S1 W7 C3S8 Y7 SDBAD8
U8 V8 C3S2 W8 SDBAWEN Y8 SDBAD5
U9 V9 C3S3 W9 SDBAD14 Y9 SDBAD2
U10 V10 C3S4 W10 SDBAD13 Y10
U11 C3S0 V11 C3S5 W11 SDBAD11 Y11 CLKA
U12 C1S0 V12 C1S1 W12 CLK100 Y12 C1S11
U13 V13 C1S2 W13 /TIMCE1 Y13
U14 V14 C1S3 W14 C1S7 Y14 /TIMRW1
U15 V15 C1S4 W15 /TIMLOCK Y15 /TIMSTRB1
U16 V16 C1S5 W16 C1S8 Y16 INT4
U17 V17 C1S6 W17 C1S9 Y17 INT5
U18 GD11 V18 W18 C1S10 Y18 INT6
U19 GD10 V19 INIT W19 Y19 DONE
U20 GD9 V20 GD6 W20 /PROG Y20
U21 GD8 V21 GD5 W21 GD3 Y21
U22 GD7 V22 GD4 W22 GD2 Y22 GD1
Page 32

Version 3.0 Page 32 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
AA1 AB1
AA2 AB2 M0=V33
AA3 SDBAD10 AB3 SDBAD15
AA4 C3S9 AB4 SDBAD12
AA5 SDBAUD1 AB5 SDBAD9
AA6 C3S10 AB6 SDBAD6
AA7 C3S11 AB7 SDBAREQ
AA8 DIRA AB8 SDBAACK
AA9 SDBAD7 AB9 SDBAD3
AA10 SDBAD4 AB10 SDBAD0
AA11 SDBAD1 AB11 CLKA
AA12 INT7 AB12 TIMPAGE1
AA13 C2S8 AB13 C2S4
AA14 IIOF0 AB14 H3
AA15 IIOF1 AB15 C2S5
AA16 /TIMRDY1 AB16 C2S9
AA17 C2S0 AB17 C2S6
AA18 C2S1 AB18 C2S7
AA19 C2S2 AB19 C2S10
AA20 C2S3 AB20 C2S11
AA21 AB21 H1
AA22 GD0 AB22
Page 33

Version 3.0 Page 33 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Bibliography
1. TMS320C6201/C6701 Peripherals Reference Guide (literature number
SPRU190) describes common peripher als available o n the TMS320C62 01/C6701 dig ital signal
processors. This book includes information on the internal data and program memories, the
external memor y interface (EMIF), the h ost port, m ultichann el-buff ered serial por ts, direct m emory
access (DMA), clocking and phase-locked loop (PLL), and the power-down modes.
2. Application Note: Flash Programming
3. TIM-40 MODULE SPECIFICATION Including TMS320C44 Addendum
4. SDB Technical Specification V2.1 or above
5. TMS320C4x User's Guide (literature number SPRU063) describes the C4x 32-bit
floating-point processor, developed for digital signal processing as well as parallel processing
applications. Covered are its architecture, internal register structure, instruction set, pipeline,
specifications, an d operation of its six DMA c hannels and s ix comm unication ports. Sof tware and
hardware applications are included.
6. Application Note: Creating New Firmware
Page 34

Version 3.0 Page 34 of 34 SMT335 User Manual
Index
Application Development.............. 17
server-loader................................ 17
Architecture Description............... 10
Bibliography................................... 32
Block Diagram.................................. 9
Board not working
firmware revision............................ 4
firmware version numbers............ 13
LED 1 illuminated......................... 16
no 3.3v supply.............................. 18
old version of SDB........................14
boot code format............................ 17
Boot Mode ...................................... 11
bootstrap program......................... 11
carrier boards................................. 18
Clock
speed ........................................... 16
speed select................See Jumpers
Code Composer............................. 17
Comports
performance................................. 14
config line....................................... 11
Contacting Sundance...................... 6
email address................................... 6
EMIF Control Registers................. 12
field values after reset..................... 7
Flash ............................................... 12
access.......................................... 20
protection algorithm...................... 12
FPGA............................................... 10
configuration................................. 11
Jumpers.......................................... 23
JP1............................................... 16
LEDs................................................16
FPGA DONE pin...........................16
McBSP.............................................19
Memory Map...................................20
memory space (CE0 to CE3).........12
motherboards.................................18
NMI .................................................. 16
Notational Conventions ................... 7
Operating Conditions .................... 18
Power
3.3v...............................................18
power consumption......................18
register descriptions........................7
revision numbers
boot code......................................13
FPGA firmware.............................13
SBSRAM ......................................... 12
SDB ................................................. 14
clock speed ..................................14
pin-out .......................................... 24
spurious interupts.........................14
versions........................................14
SDRAM............................................12
Serial Ports.....................................19
serial port header..........................23
SMT335 ............................................. 7
SMT375 ............................................. 7
Sundance TIM carrier boards........18
Timer............................................... 16
TMS320C6201.................................11
Virtex
layout ............................................ 25
pin-out .......................................... 26
 Loading...
Loading...