Strebel S-CB+ Series, S-CB+80, S-CB+60, S-CB+100, S-CB+120 Installation Operating & Maintenance Manual
...
STREBEL
S-CB+ Boiler Range
Models +60 - +80 - +100 - +120 - +150 - +180
Wall hung high efficiency condensing boiler
Installation, Operating & Maintenance Manual
2015-07-21 v1



4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION…………………………………………………………………………………………….….…...7
1 SAFETY GUIDELINES ................................................................................................................................ 7
2 TECHNICAL DATA S-CB+ BOILERS ......................................................................................................... 9
2.1 FUNCTIONAL INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................. 9
2.2 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS DATASHEET......................................................................................... 10
3 DIMENSIONS .............................................................................................................................................12
3.1 S-CB
3.2 S-CB
+
60-120 .............................................................................................................................. 12
+
150-180 ............................................................................................................................ 13
4 ACCESSORIES AND UNPACKING ..........................................................................................................14
4.1 ACCESSORIES ............................................................................................................................... 14
4.2 UNPACKING ................................................................................................................................... 14
5 INSTALLATION OF THE S-CB+ ................................................................................................................15
5.1 GENERAL NOTES ........................................................................................................................... 15
5.2 MOUNTING THE BOILER .................................................................................................................. 16
6 CONNECTIONS WATER SIDE .................................................................................................................17
6.1 BOILER CONNECTIONS ................................................................................................................... 17
6.2 CONDENSATE DRAIN CONNECTION .................................................................................................. 17
6.3 FLOW AND RETURN CONNECTIONS .................................................................................................. 18
6.4 THE EXPANSION VESSEL................................................................................................................. 18
6.5 PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE ............................................................................................................... 18
6.6 BYPASS ........................................................................................................................................ 18
6.7 PUMP FUNCTIONALITY .................................................................................................................... 18
6.8 FROST PROTECTION ...................................................................................................................... 19
6.9 INSTALLING A STRAINER AND/OR DIRT SEPARATOR ........................................................................... 19
6.10 WATER QUALITY ............................................................................................................................ 19
6.11 PLASTIC PIPING IN THE HEATING SYSTEM ......................................................................................... 20
6.12 AUTOMATIC AIR VENT ..................................................................................................................... 20
6.13 AUTOMATIC WATER FILLING SYSTEMS ............................................................................................. 20
6.14 WATER PRESSURE ......................................................................................................................... 20
6.15 CHEMICAL WATER TREATMENT ....................................................................................................... 21
6.16 UNDER FLOOR HEATING ................................................................................................................. 21
6.17 FLUSH THE SYSTEM WITH FRESH WATER ......................................................................................... 21
6.18 INSTALLATION EXAMPLES ............................................................................................................... 21
6.18.1 Example of a standard single boiler heating circuit with low loss header ......................... 21
6.18.2 Example of a multiple boiler heating circuit with low loss header ..................................... 23
7 PUMP CHARACTERISTICS ......................................................................................................................24
7.1 HYDRAULIC GRAPHS ...................................................................................................................... 24
7.2 PUMPS: MAXIMUM ELECTRICAL POWER............................................................................................ 27
8 FLUE GAS AND AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM ..................................................................................................27
8.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................................................... 27
8.2 AIR SUPPLY ................................................................................................................................... 28
8.2.1 Combustion air quality ...................................................................................................... 28
8.2.2 Air supply through humid areas ........................................................................................ 28
8.3 FLUE TERMINAL ............................................................................................................................. 28
8.4 S-CB+ 60 TWIN PIPE VERSION ........................................................................................................ 28
8.5 PIPE HEIGHTS AND MUTUAL DISTANCES ON A FLAT ROOF .................................................................. 29
8.6 B23P CERTIFIED ............................................................................................................................ 29
8.7 C63 CERTIFIED .............................................................................................................................. 29
8.8 FLUE GAS AND AIR SUPPLY RESISTANCE TABLE ................................................................................ 30
8.9 FIVE TYPICAL EXAMPLES ................................................................................................................ 31
8.9.1 Example A: Twin pipe system ........................................................................................... 31
8.9.2 Example B: Twin pipe system with concentric roof terminal ............................................. 31
8.9.3 Example C: Single flue gas outlet. Air supply from boiler room ........................................ 33
8.9.4 Example D: Concentric flue gas/air supply pipe (roof-mounted) ...................................... 35
8.9.5 Example E: Concentric flue gas/air supply pipe (wall-mounted) ...................................... 35
9 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................37
9.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................................................... 37
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

5
9.2 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS ............................................................................................................ 37
9.3 EXPLANATION OF THE CONNECTIONS .............................................................................................. 37
9.4 ELECTRICAL SCHEMATICS .............................................................................................................. 39
9.5 SENSOR VALUES ............................................................................................................................ 42
10 USER INTERFACE ....................................................................................................................................43
10.1 CONTROL PANEL / DISPLAY UNIT ..................................................................................................... 43
10.2 CONTROL PANEL MENU STRUCTURE................................................................................................ 44
10.3 DISPLAY DURING OPERATION .......................................................................................................... 46
10.4 MONITOR SCREENS ....................................................................................................................... 47
10.5 SERVICE FUNCTION ........................................................................................................................ 49
10.6 SCHORNSTEINFEGER FUNCTION ..................................................................................................... 50
10.7 PROGRAMMING IN STANDBY MODE .................................................................................................. 51
10.8 SETTING THE TIME & DATE ............................................................................................................. 51
10.9 SET POINTS ................................................................................................................................... 52
10.10 SETTING THE TIMER PROGRAMS ..................................................................................................... 53
10.11 SETTING THE OUTDOOR SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................ 56
10.12 CHECKING THE OPERATING HISTORY ............................................................................................... 60
10.13 CHECKING THE FAULT HISTORY ...................................................................................................... 61
10.14 SETTING THE MAINTENANCE SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................................. 62
10.15 SETTING THE USER LOCK ............................................................................................................... 66
10.16 SETTING THE PARAMETERS AT THE CONTROL PANEL ........................................................................ 67
10.17 FAULT CODES DISPLAY ................................................................................................................... 74
10.17.1 Lock-out codes .................................................................................................................. 74
10.17.2 Blocking codes .................................................................................................................. 76
10.17.3 Messages .......................................................................................................................... 77
11 CONTROLLING OPTIONS AND SETTINGS ............................................................................................78
11.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................................................... 78
11.1.1 Extra boiler control ............................................................................................................ 78
11.1.2 Max cooling time ............................................................................................................... 78
11.1.3 Temperature display on/off ............................................................................................... 78
11.1.4 Water pressure ................................................................................................................. 78
11.1.5 Gas type selection ............................................................................................................ 78
11.1.6 Soft start option ................................................................................................................. 79
11.1.7 Pump mode (EC technology) ............................................................................................ 79
11.2 HEATING ....................................................................................................................................... 80
11.2.1 Controlling behaviour settings........................................................................................... 80
11.2.2 Room thermostat on/off .................................................................................................... 81
11.2.3 Room thermostat OPEN-THERM ..................................................................................... 81
11.2.4 Outdoor temperature related flow control ......................................................................... 81
11.2.5 0-10 Vdc remote flow temperature set point ..................................................................... 81
11.2.6 0-10 Vdc Remote burner input control .............................................................................. 82
11.2.7 Timer contact function ....................................................................................................... 82
11.3 INDIRECT HOT WATER/CALORIFIER .................................................................................................. 83
11.3.1 Pump and 3-way valve control .......................................................................................... 83
11.3.2 Tank thermostat ................................................................................................................ 83
11.3.3 Tank sensor ...................................................................................................................... 83
11.3.4 Low/high flow temperature to tank coil ............................................................................. 84
11.3.5 Heating and hot water switching time ............................................................................... 85
11.3.6 Heating and hot water switching at sudden temperature drop ......................................... 85
11.3.7 Anti-Legionnaires’ disease function (pasteurisation) ........................................................ 86
11.4 CASCADE CONTROL ....................................................................................................................... 87
11.4.1 Parameter settings for cascaded boilers .......................................................................... 87
11.4.2 Monitor screens ................................................................................................................ 89
11.4.3 Output control and boiler sequence .................................................................................. 89
12 COMMISSIONING THE BOILER ...............................................................................................................90
12.1 FIRST: FLUSHING THE BOILER WITH WATER ...................................................................................... 90
12.2 SECOND: FILLING & VENTING THE BOILER AND THE SYSTEM .............................................................. 90
12.3 THIRD: CHECK THE WATER FLOW .................................................................................................... 90
13 STARTING THE BOILER ..........................................................................................................................92
13.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................................................... 92
13.2 FIRING FOR THE FIRST TIME ............................................................................................................ 92
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

6
14 ADJUSTING AND SETTING THE BURNER ............................................................................................93
14.1 INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................................................. 93
14.1.1 Adjustment tables ............................................................................................................. 93
14.1.2 Setting screws gas valve(s): drawings .............................................................................. 95
14.1.3 Gas valve classes A+C and B+J (B+J only for Poland) .................................................... 96
14.1.4 Adjustment actions: general scheme ................................................................................ 97
14.2 ADJUSTING IN CASE OF A NEW BOILER, OR AFTER MAINTENANCE (CASE A) ........................................ 98
14.2.1 General remark ................................................................................................................. 98
14.2.2 Checking and adjusting at maximum load ........................................................................ 98
14.2.3 Checking and adjusting at minimum load ......................................................................... 98
14.3 ADJUSTING IN CASE OF VALVE REPLACEMENT OR GAS CONVERSION (CASE B) ................................... 98
14.3.1 General remarks ............................................................................................................... 98
14.3.2 Checking and adjusting at maximum load A+60 / A+80 / A+100 ....................................... 98
14.3.3 Checking and adjusting at minimum load A+60 / A+80 / A+100......................................... 98
14.3.4 Checking and adjusting at maximum load A+120 / A+150 / A+180 ................................... 99
14.3.5 Checking and adjusting at minimum load A+120 / A+150 / A+180 .................................... 99
14.4 ADJUSTING PROCEDURES ............................................................................................................ 100
15 PUTTING THE BOILER OUT OF OPERATION ......................................................................................101
15.1 OUT OF OPERATION: ON/OFF FUNCTION ........................................................................................ 101
15.2 OUT OF OPERATION: POWER OFF .................................................................................................. 101
16 FAULT CODES. BLOCKING CODES .....................................................................................................102
16.1 FAULT CODES .............................................................................................................................. 102
16.2 BLOCKING CODES: ....................................................................................................................... 109
16.3 MAINTENANCE ATTENTION FUNCTION ............................................................................................ 112
17 MAINTENANCE .......................................................................................................................................113
17.1 GENERAL .................................................................................................................................... 113
17.2 INSPECTION & MAINTENANCE........................................................................................................ 113
18 USER INSTRUCTIONS ...........................................................................................................................117
19 INSTALLATION EXAMPLES ..................................................................................................................118
20 INDEX .......................................................................................................................................................123
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

7
INTRODUCTION
Warning: important information concerning the safety of persons and/or the appliance.
The manufacturer/supplier is not liable for any damage caused by inaccurately following these mounting
instructions. Only original parts may be used when carrying out any repair or service work.
This appliance is not intended for use by persons (including children) with reduced physical, sensory or
mental capabilities, or lack of experience and knowledge, unless they have been given supervision or
instruction concerning use of the appliance by a person responsible for their safety. Children should be
supervised to ensure that they do not play with the appliance.
This manual is written for:
The installer
System design engineer
The service engineer
The following symbol is used in this manual:
Strebel Ltd is not accountable for any damage caused by incorrect following the mounting instructions. For service
and repair purposes use only original Strebel spare parts.
All documentation produced by the manufacturer is subject to copyright law.
1 SAFETY GUIDELINES
Carefully read all the instructions before commencing installation.
Keep these instructions near the boiler for quick reference.
The appliance should be installed by a skilled installer such as GAS SAFE registered person, electrical work car-
ried out by a qualified person, all according to national and regional standards.
Failure to comply with these regulations could deem the warranty invalid. This appliance must be installed in ac-
cordance with the rules that apply and only be used in an adequately ventilated space conforming to standards in
place.
Without written approval of the manufacturer the internals of the boiler may not be changed. When changes are
executed without approval, the boiler certification becomes invalid.
Commissioning, maintenance and repair must be done by a skilled installer/engineer, according to all applicable
standards and regulations.
What should one do when there is the smell of gas: -
Don't use any electrical equipment.
Don't press any switches.
Close the gas supply.
Ventilate the room (open the windows and/or outdoor boiler room doors).
Immediately warn the responsible person.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

8
These instructions are written for the installer of Strebel products and contain all necessary information on the installation and adjustment of S-CB+ Ranges of boilers. Please read these instructions fully before installation to ensure that all work is carried out correctly.
We suggest that you keep a copy of these instructions near the boiler.
These instructions together with those in any supplemental instruction booklet cover the basic principles to ensure
the satisfactory installation of the boiler, although detail may need slight modification to suit particular local site
conditions.
It is the law that all gas appliances and fittings are installed by a competent person (such as a Gas Safe registered
installer) and in accordance with The Gas Safety (installation and Use) Regulations.
The relevant British standards for installation, codes of practice or rules in force and in accordance with the Manufactures’ instructions.
The installation must be carried out in accordance with the following regulations plus relevant codes & standards:
- Due consideration must be given to current Health & Safety Legislation while this product is being installed.
- Key Approved Documents to the Building Regulations, in the region of the United Kingdom that this product is
being installed.
- The Local Building Regulations and Local water by-laws, the gas services area and the Local Authority recommendations.
- The appropriate British & European Standards for the type of installation and fuel used, including but not exclusively the following standards: -
o BS 5440: Parts 2 (Flues and Ventilation).
o BS 6644: Installation of gas-fired hot water boilers of rated inputs between 70kW & 1.8MW
- The clean air act as defined by the local authority.
- The appropriate documents as produced by the Institution of Gas Engineers and Managers Documents
(IGEM) for the type of installation and fuel used, including but not exclusively the following documents: -
o IGE/UP1
o IGE/UP2
o IGE/UP4
o IGE/UP10
- If the product is being fuelled with LPG then the appropriate UKLPG Codes of Practice (CoP) should be referred to.
- Wiring to the appliance must be in accordance with the IEE (BS 7671) Wiring Regulations the Health and
Safety Document No 635 “The Electricity at Work Regulations 1989” and any local regulations that apply.
- CP 342: Part 2, 1994. Code of practice for centralised hot water supply – buildings other than individual dwellings.
- CIBSE, Guides A, B and C.
Adhere to all regulations that are in force at the time of installation or service.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

9
2 TECHNICAL DATA S-CB+ BOILERS
2.1 Functional introduction
The S-CB+ boilers are central heating boilers with a maximum high efficiency. Such a performance can be reached
by, amongst other things, using a special heat exchanger made of stainless steel. This allows the flue gases to cool
down below the condensation point, and so release extra heat. This has an immediate positive impact on the efficiency, exceeding the 100%.
The S-CB+ boiler is standard set for Natural gas G20
Gases used must meet the European standard EN 437.
Fuel used should have sulphur rates according to the European standard, a maximum annual peak over a short
period of time of 150 mg/m3 and an annual average of 30 mg/m3.
Boiler control includes:
Cascade control for up to twelve boilers
Remote operation and heat demand indication from each boiler
Weather compensation control
Hot water cylinder control
Connections for:
0-10 VDC remote flow temperature (set point) control
0-10 VDC remote burner input control
Outdoor temperature sensor
External hot water cylinder pump or diverter valve
Cascade control
When using the integrated cascade control, a maximum of twelve boilers can be controlled in a cascade configuration. By the use of an appropriate external control, this number may be increased at will.
0-10 VDC connection available
The boiler flow temperature or power input can be controlled by an external 0-10 VDC signal. When a number of
boilers are cascaded, and controlled by the integrated cascade control, the signal should be directed to the master
boiler only. If an alternative control is used, more than one boiler may be controlled by a 0-10 VDC signal. A signal
of 1,48 Volt will switch on the boiler(s), less than 1,4 Volt will switch off the boiler(s).
Time program
For both central heating and hot water function of the boiler, time programs with three programmable periods per
day are available. These time programs are set and activated by entering the desired settings directly at the boiler
control panel.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

10
2.2 Technical specifications datasheet
GENERAL
Product Identification Number
-
CE 0063 BP3254
Classification
-
II2H3P (for NL II2L3P)
Gas Appliance Type
-
B23, B23P; C13X, C23X, C33X, C43X, C53X, C63X, C83X
Type boiler
S-CB+60
S-CB+80
S-CB+100
S-CB+120
S-CB+150
S-CB+180
Dimensions (h x w x d)
mm
842 x 476 x 486
898 x 476 x 677
Water content estimated
litre
3,9
5,0
6,5
8,3
10,4
12,9
Weight (empty)
kg
46
73
78
83
92
101
Flow/return connection (boiler)
inch
R 1”
R 1”
R 1”
R 1”
R 1¼”
R 1¼”
Flow/return connection (T-piece)
inch
Rp 1¼”
Rp1¼”
Rp 1¼”
Rp 1¼”
Rp 1½”
Rp 1½”
Gas connection
inch
R ¾”
R ¾”
R ¾”
R ¾”
R 1”
R 1”
Flue duct flue/air inlet (* as supplied)
mm
80/125*
80/125*
100/150*
100/150*
100/150
100/150
Parallel connection (* as supplied)
mm
80-80
80-80
100-100
100-100
130-130*
130-130*
HEATING Values min-max:
Nominal input (Net)
kW
12,5 - 55,6
14,6 - 74,3
17,2 - 92,2
26,0 - 111
34,0 - 138
45,0 - 166
Nominal input (gross) (G20, G25)
kW
13,9 - 61,8
16,2 - 82,5
19,1 - 102
28,9 - 123
37,8 - 153
50,0 - 184
Nominal input (gross) (G31)
kW
13,6 - 60,4
15,9 - 80,8
18,7 - 100
28,3 - 121
37,0 - 150
48,9 - 180
Nominal input (gross) (G30)
kW
13,5 - 60,3
15,8 - 80,2
18,6 - 99,7
34,7 - 120
36,8 - 150
48,8 - 180
Nom. output 80/60°C
kW
12,0 - 53,5
14,0 - 71,2
16,5 - 88,4
24,7 - 106
32,6 - 132
43,3 - 160
Nom. output 50/30°C
kW
12,9 - 57,4
15,2 - 77,5
18,0 - 96,2
27,2 - 116
35,5 - 144
47,3 - 175
Nom. output 37/30°C
kW
13,5 - 59,8
15,7 - 80,1
18,6 - 99,5
28,1 - 120
36,7 - 149
48,5 - 179
Efficiency 40/30°C DIN 4702-8
%
up to 110,6 % within the S-CB+ range
GAS CONSUMPTION [EN437] Values min-max:
Natural gas G25
m³st/h
1,54 - 6,84
1,80 - 9,14
2,12 - 11,4
3,20 - 13,7
4,18 - 17,0
5,54 - 20,4
Natural gas G20
m³st/h
1,32 - 5,88
1,54 - 7,86
1,82 - 9,76
2,75 - 11,8
3,60 - 14,6
4,76 - 17,6
Propane gas G31 1
m³st/h
0,51 - 2,27
0,60 - 3,04
0,70 - 3,77
1,06 - 4,54
1,39 - 5,65
1,84 - 6,79
Butane gas (B/P) G30 1
m³st/h
0,39 - 1,72
0,45 - 2,29
0,53 - 2,85
0,99 - 3,44
1,05 - 4,28
1,40 - 5,15
Gas supply pressure
nom. 2
G25
mbar
25
G20
mbar
20
G31 1
mbar
30/37
G30 1
mbar
50
NOTES
1
Using propane or butane/propane mixtures (B/P), maximum fan speed needs to be reduced (parameter P4BD)
2
Min. and max. gas supply pressures according to EN437:
p nominal [mbar]
p min [mbar]
p max [mbar]
G25
25
20
30
G20
20
17
25
G31
30
25
35
37
25
45
G30
50
43
57
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
11
Type boiler
S-CB+60
S-CB+80
S-CB+100
S-CB+120
S-CB+150
S-CB+180
EMISSION [EN437] Values min-max:
CO2 flue gas 3
G25/G20
%
8,7 - 9,0
8,7 - 9,0
8,7 - 9,0
8,7 - 9,0
8,7 - 9,0
8.7 - 9.0
G31
%
9,3 - 10,3
9,3 - 10,3
9,3 - 10,3
9,3 - 10,3
9,3 - 10,4
9.3 - 10.5
G30 (B/P)
%
9,3 - 10,4
9,3 - 10,4
9,3 - 10,4
9,3 - 10,4
9,3 - 10,5
9.3 - 10.6
NOx at 0% O2, year emission
ppm
21,0
31,5
24,6
27,4
25,3
16,5
mg/kWh
37,7
56,6
44,2
49,2
45,4
29,7
NOx class [EN483 / EN15420]
-
5
Flue gas temperature at combustion
air temperature = 20°C
°C
~ 85-95
Available pressure for the flue system 4
Pa
200
INSTALLATION
Available pressure for
the installation at
T = 20 K
mWC
3,8
1,3
1,5
1,0
0,7
0,1
T = 25 K
mWC
5,1
3,7
3,7
3,0
3,2
2,5
Pressure boiler min-max.
bar
1,0 - 4,0 5
Max. flow temperature
°C
90
ELECTRIC
Power consumption
W
355
355
355
370
600
Power supply
V/Hz
230/50
Protection class
-
IPX4D
NOTES
3
CO2 of the unit measured/set without the boiler
front panel in place
4
Maximum allowed combined resistance of flue
gas and air supply piping at high fire
5
When the built-in water pressure sensor is replaced
by a water pressure switch, water pressure may go
up to 6,0 bar
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
12
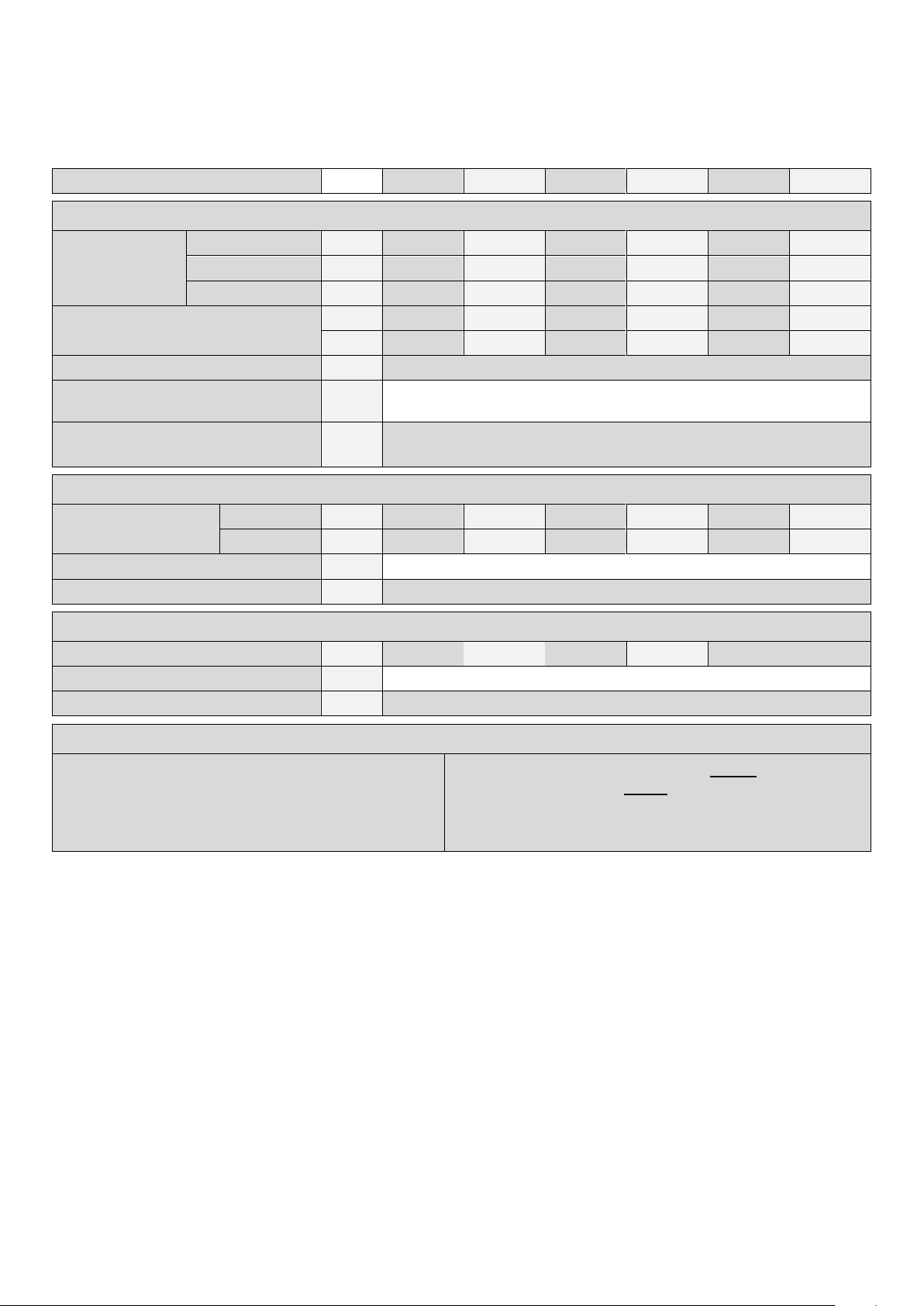
3 DIMENSIONS
Connections
twin pipe
Concentric
(Standard Delivery)
+
60 +80 +100 +120 +60 +80 +100 +120
FG
AI
flue gas
air inlet
80-80
100-100
80/125
100/150
size "A"
112
155
112
size "B"
135
150
135
size "C"
308
N.A.
F
C
R
G
flow
condensate
return
gas
R 1¼" (male)
flexible hose Ø25/21 x 750 mm
R 1¼" (male)
R ¾" (male)
3.1 S-CB+ 60-120
TWIN PIPE CONCENTRIC (Standard Delivery)
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
13
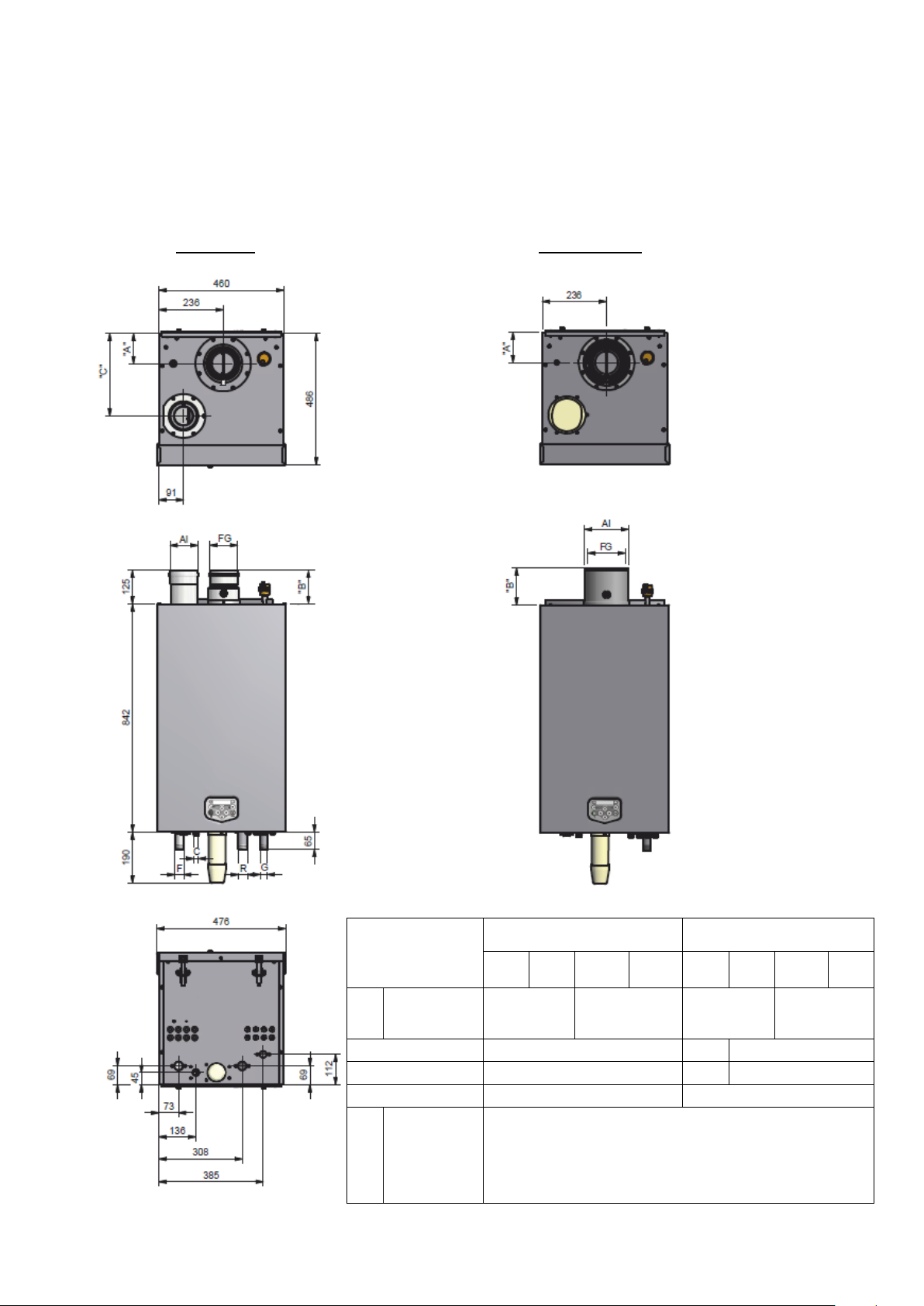
Connections
twin pipe
(Standard Delivery)
concentric
FG
AI
flue gas
air inlet
130-130
100/150
F
C
R
G
flow
condensate
return
gas
R 1½" (male)
flexible hose Ø25/21 x 750 mm
R 1½" (male)
R 1” (male)
3.2 S-CB+ 150-180
TWIN PIPE (Standard Delivery) CONCENTRIC
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
14
4 ACCESSORIES AND UNPACKING
Item
Part Nº.
Outdoor (air) temperature sensor: 12kOhm@25°C (to be connected to the boiler connections)
E04.016.585
External flow temperature sensor for system side of the low loss header: 10kOhm@25°C (to
be mounted to the boiler connections)
E04.016.304
Calorifier temperature sensor: 10kOhm@25°C (to be connected to the boiler connections)
S04.016.303
Conversion sets flue and air terminals
S-CB+60: concentric to twin pipe 80/125→80-80
E61.001.162
S-CB+60: twin pipe to concentric 80-80→80/125
E61.001.187
S-CB+80: concentric to twin pipe 80/125→80-80
E61.001.163
S-CB+80: twin pipe to concentric 80-80→80/125
E61.001.170
S-CB+100-120: concentric to twin pipe 100/150→100-100
E61.001.164
S-CB+100-120: twin pipe to concentric 100-100→100/150
E61.001.171
S-CB+150-180: concentric to twin pipe 100/150→130-130
E61.001.165
S-CB+150-180: twin pipe to concentric 130-130→100/150
E61.001.172
Room Controller “OpenTherm” RC (Modulating) with room sensor
S04.016.355
Room Controller “OpenTherm” RC (Modulating) no room sensor/to be used with E04.016.359
S04.016.358
External room sensor for the RC and RCH controller: 5kOhm@25°C
E04.016.359
Room thermostat (modulating) RCH with e-bus interface, to control one heating zone (Thermostat includes room sensor).
S04.016.357
EBC heating zone controller to control 2 different heating zones. This EBC will include the wall
housing unit, for an easy installation and connection.
S04.016.550
Interface IF to convert an OpenTherm signal to an E-bus signal (One interface for each boiler
or one interface for cascaded boilers).
S04.016.552
External flow sensor for one heating zone: 5 kOhm@25°C
E04.016.363
Software + interface cable for programming the boiler with a computer/laptop
S04.016.586
4.1 Accessories
Depending on the selected controlling behaviour for the central heating system and/or the optional use of a calorifier, the following items can be supplied with the boiler. Ask your supplier for the specifications.
4.2 Unpacking
The S-CB+ boiler will be supplied with the following documents and accessories:
One “Mounting Instructions” manual for the installer
One suspension bracket with locking plate and bolts
Three spare nuts for mounting the burner plate, two spare fuses for the boiler control and a gas conversion
sticker (all in a bag attached to the front of the gas valve)
Bottom part of the siphon
Two T-pieces for the flow and return connections of the boiler
After delivery, always check the boiler package to see if it is complete and without any defects. Report any imperfections immediately to your supplier.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

15
5 INSTALLATION OF THE S-CB+
5.1 General notes
At every side of the boiler at least 50 mm of clearance should be applied to walls or wall units, 350 mm above the
top side of the boiler and 250 mm from the bottom of the boiler.
The installation area/room must have the following provisions:
230 V - 50 Hz power source socket with earth connection.
Open connection to the sewer system for draining condensing water.
A sound-deadening wall.
Note:
The wall used for mounting the boiler must be able to hold the weight of the boiler. If not, it is recommended to
mount the boiler by means of a (cascade) frame.
Other considerations related to the boiler location.
The ventilation of the boiler room must meet local and national standards and regulations, regardless of the
selected supply of fresh air to the boiler.
Both the air supply and the flue gas pipes must be connected to the outside wall and/or the outside roof.
The installation area must be dry and frost-free.
The boiler has a built-in fan that will generate noise, depending on the total heat demand. The boiler loca-
tion should minimise any disturbance this might cause. Preferably mount the boiler on a brick wall.
There must be sufficient lighting available in the boiler room to work safely on the boiler.
When a boiler is positioned at the highest point of the installation, the supply and return pipes must first
protrude 0.5 m above the top of the boiler, before these pipes go to the installation side. In other words, the
water level must always be 0.5 meter above the top of the boiler and an automatic air vent must be installed in the supply or return pipe. A low-water level protection should also be installed at the installation
side.
Remind the positioning of electrical components in relation to the temperature sensitivity.
Make sure there is an open connection with the sewer to drain the condensate. This connection should be
lower than the condensate drain level of the boiler.
The boiler must be positioned and installed by a skilled installer in accordance with all applicable standards and
regulations. Commissioning of the boiler must be done by a skilled service/commissioning engineer, who is trained
for this type of boiler.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
16
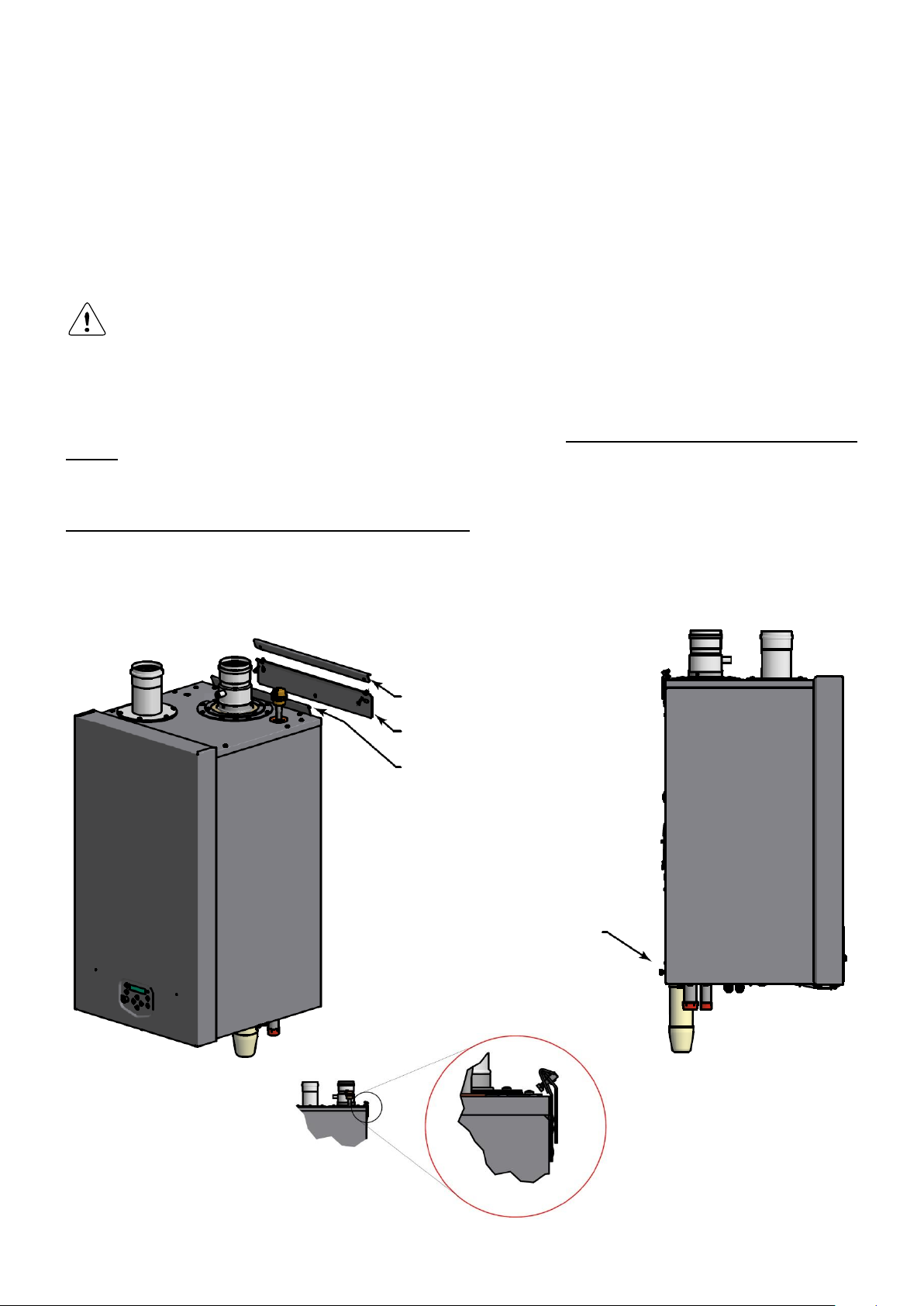
5.2 Mounting the boiler
All lines/piping must be mounted free of tension. The weight of the installation components should be supported separately from the boiler so there will be no standing forces on the connections.
This might influence the mounting position of the boiler.
1. Attach mounting bracket to wall
with inclined side facing upwards
3. Lock boiler with locking plate
and two bolts
2. Suspend boiler with suspension
bracket on mounting bracket
4. Level boiler using
adjusting bolts
Before mounting and installing the boiler the following connections should be considered:
Flue gas system and the flue gas pipe connections
Air supply system and connections
Flow and return pipe connection
Condensate and pressure relief valve drainage
Power supply (preferably the power connection positioned above the boiler)
Determine the position of the flow and return pipes by using the included suspension bracket or a suspension
frame (when supplied).
While marking the holes, ensure that the suspension bracket or frame is perpendicular and the boiler does not lean
forward. If necessary adjust the position with the adjusting bolts at the lower rear side of the back panel (see drawing). When the adjusting bolts aren’t sufficient, fill the gap behind the bolts to get the boiler in position. The exact
boiler position lies between the boiler hanging level and hanging slightly backwards.
The boiler should not lean forward in the mounted position.
Lock the suspension bracket with the security cover before making any other connections to the boiler. This secu-
rity cover will prevent the boiler from falling off the bracket. Don't use excessive force during the mounting of the
boiler connections.
suspension detail
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
17
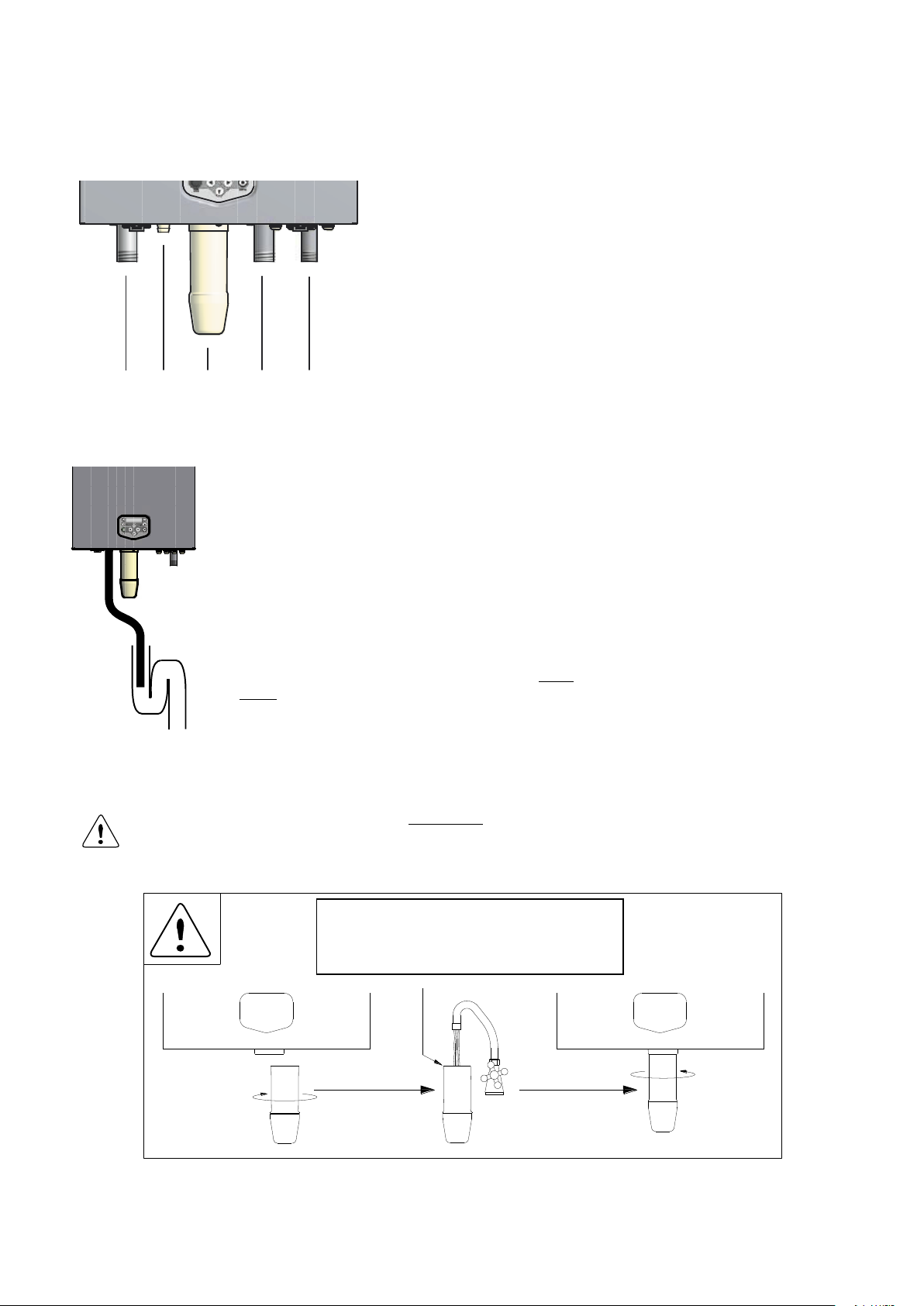
6 CONNECTIONS WATER SIDE
FRONT VIEW
1 2 3 4 5
6.1 Boiler connections
1 – Flow CH
2 – Condensate drain
3 – Siphon cleaning point
4 – Return CH
5 – Gas
Open connection
to the sewer.
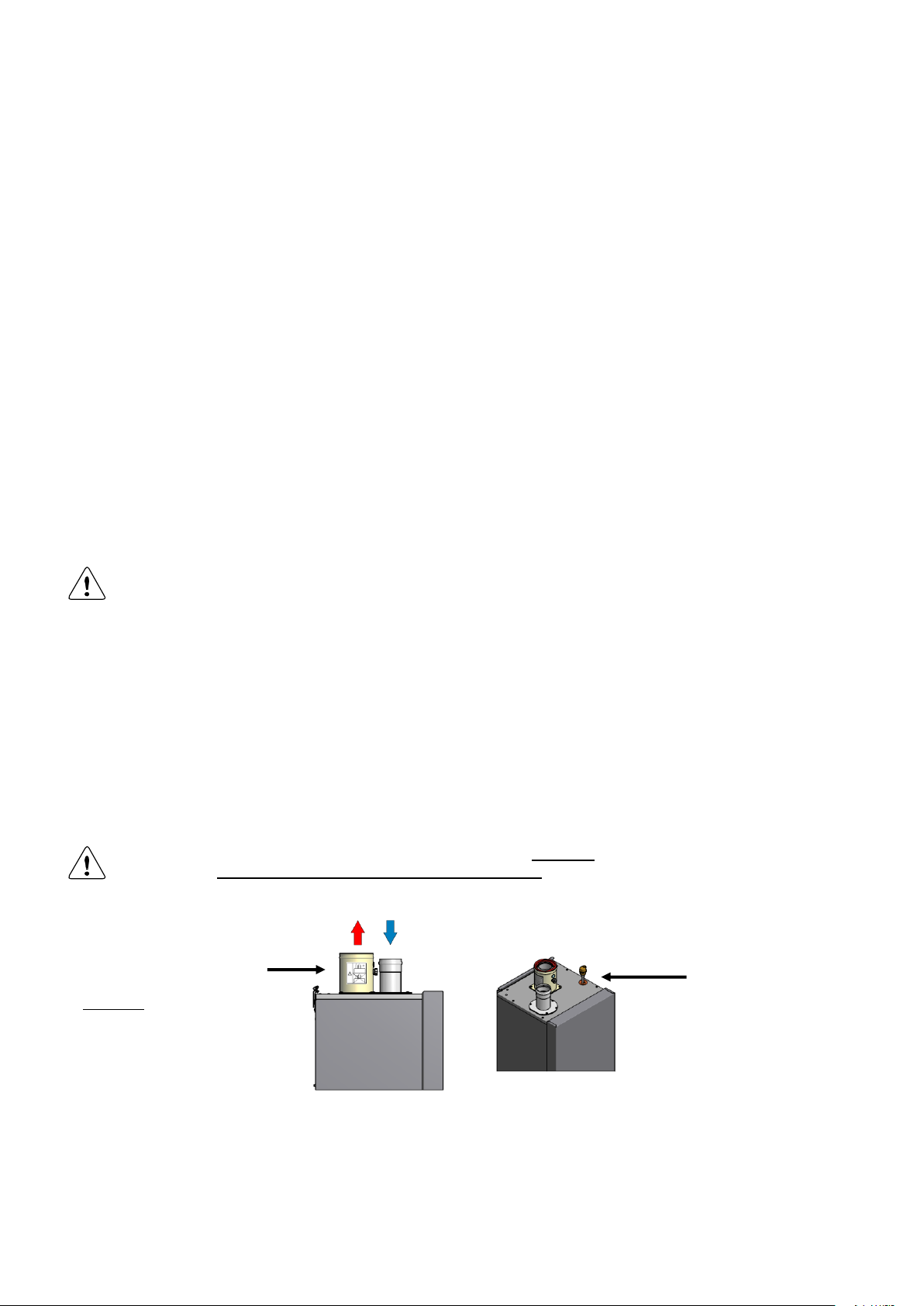
6.2 Condensate drain connection
The condensate drain is placed at the centre and at the bottom of
the boiler and has a ¾ inch hose discharge. Connect this flexible
hose to the sewer system.
Use only plastic parts with the condensate drain. Metal lines are not
allowed.
Blockage of this drain might damage the boiler. The drain connection is correct when the condensate can be seen flowing away, e.g.
using a funnel. Any damage that might occur, when the drain is not
installed correctly, is not covered by the warranty of the boiler.
There should be an open connection of the condensate hose into
the sewage system. A possible vacuum in the sewage system must
never give the opportunity to suck on the boiler’s condensate drain
hose.
When mounting the bottom part of the siphon, before commissioning the boiler and/or after maintenance, the siphon must ALWAYS be completely filled with water.
This is a safety measure: the water in the siphon keeps the flue gases from leaking out of the
heat exchanger via the condensate drain.
The siphon must always be filled to the
edge with water, before placing back on
the unit.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
18
6.3 Flow and return connections
Two separate T-pieces are shipped with the boiler.
These are applied for externally mounting the pressure
relief valve and the boiler bleed valve for servicing the
boiler. We advise to install two service valves in the
flow and return pipes underneath the boiler, so the
boiler can be isolated from the heating system and
eventually disconnected, when needed.
When using a system pump, this pump should always
be mounted in the return pipe of the heating system.
Do not use chloride-based fluxes for soldering any
pipes of the water system.
6.4 The expansion vessel
The capacity of the expansion vessel must be selected
and based on the capacity of the central heating system
and the static pressure. Suggested is to fit the expansion vessel in the return pipe of the central heating system. It can be combined with the drain valve for service.
See the above drawing.
P1
supplied
with
boiler
supplied
with
boiler
BOILER
boiler bleed
valve for service
boiler service valves
pressure
relief valve
expansion
vessel
6.5 Pressure relief valve
The boiler has no internal pressure relief valve. This should be installed close to the boiler in the flow pipe of the
heating system. When having cascaded boilers, each boiler should have its own pressure relief valve. It is advised
to use the T-piece that is supplied with the boiler, for this.
Advice is always to install service valves, so the boiler can be isolated from the heating system, when needed.
Make sure that the pressure relief valve is mounted between the boiler and the service valves.
The specifications and size of the relief valve should be determined by the installer and must comply with all applicable regulations and boiler capacity.
6.6 Bypass
The boiler has no internal bypass. When many thermostatic valves are being used, the system should have a bypass to allow an adequate flow when all thermostatic valves are closed. Instead of a bypass also a low-loss header
can be used for this function.
The boiler flow will also be influenced when a pipe of the heating system is frozen / blocked. Make sure all heating
pipes are free from the risk of frost. If there is the risk of freezing of the heating system, all the pipe section must be
insulated and/or protected with the help of a tracing.
6.7 Pump functionality
Controlling the pump:
The pump speed is controlled by a PWM signal provided by the burner controller at a value causing a Delta T
across the heat exchanger of 20°C at the whole burner modulation range.
When the boiler modulates down or up, also the pump speed decreases or increases, keeping delta T at 20°C until
it reaches the end of its modulation range.
Delta T monitoring:
The delta T monitoring parameters are active. A malfunctioning of the pump, burner controller or a high resistance
in the hydraulic system will cause a high Delta T and will therefore be detected by the burner controller. The display
shows “dT Block” or “FlowReturn dTfault”.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
19
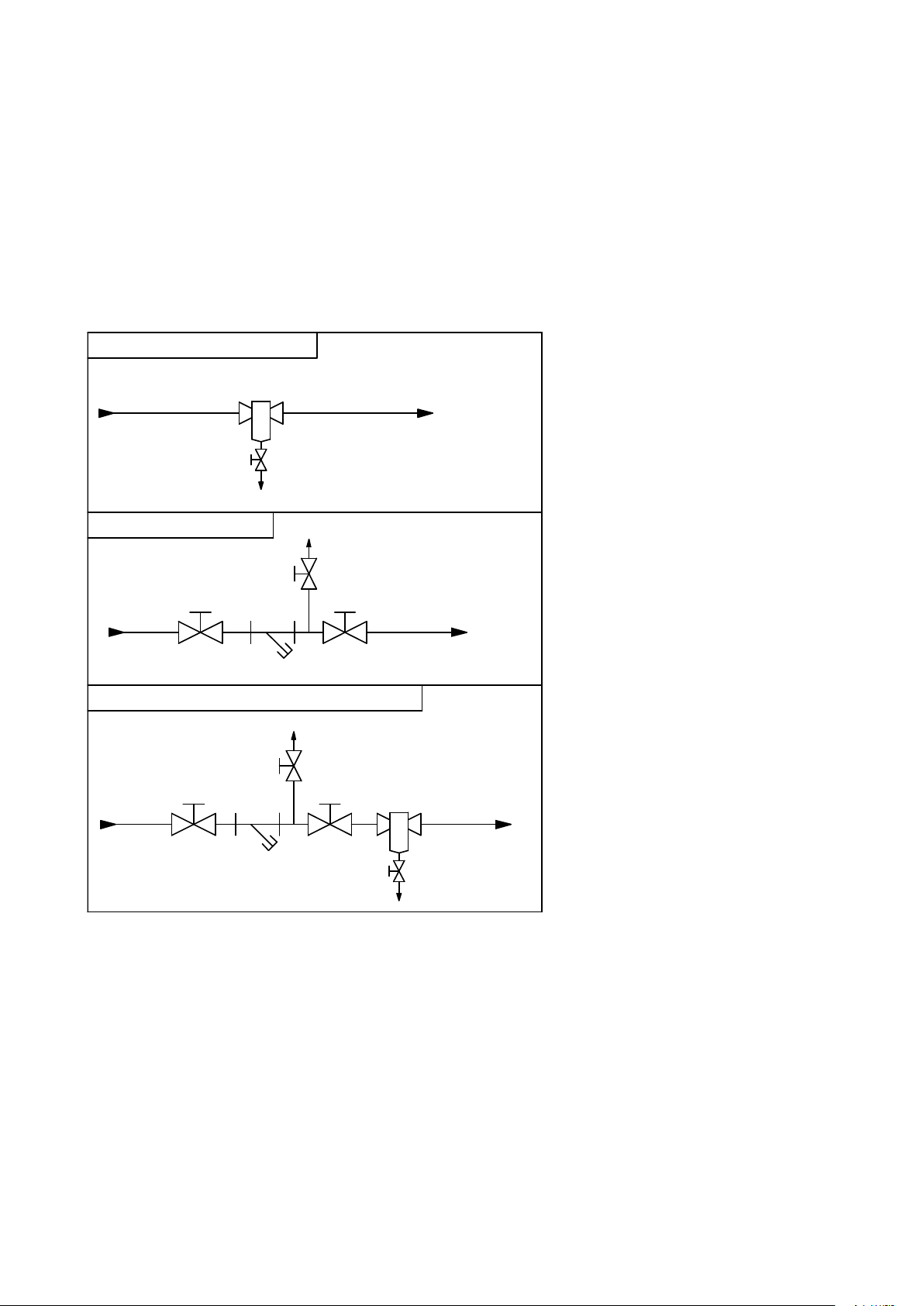
6.8 Frost protection
Always install a strainer (water filter)
and/or a dirt separator in the return pipe
of the boiler; in such a way that the water going to the boiler is free of any debris/particles. When using a water filter
always check a week after installation to
determine the strainer cleaning interval.
Advice is to mount valves before and
after the strainer, including an air bleed
valve, so the strainer can be isolated
from the heating circuit for service operations. Clean water is very important,
blocked and/or polluted heat exchangers, including failures and/or damages
caused by this blockage are not covered
by the warranty.
SYSTEM WITH DIRT SEPARATOR
SYSTEM WITH STRAINER
SYSTEM WITH STRAINER AND DIRT SEPARATOR
DIRT SEPARATOR
DIRT SE-
PARATOR
WATER RETURN FROM
SYSTEM
WATER
RETURN
FROM
SYSTEM
WATER
RETURN
FROM
SYSTEM
WATER FLOW
TO BOILER(S)
WATER FLOW
TO BOILER(S)
WATER
FLOW TO
BOILER(S)
DIRT
BLEED
VALVE
DIRT
BLEED
VALVE
AIR
BLEED
VALVE
AIR
BLEED
VALVE
VALVE
VALVE
VALVE
VALVE
STRAINER
(WATER FILTER)
STRAINER
(WATER FILTER)
The boiler has a built-in frost protection that is automatically activating the central heating pump when the boiler
return (water) temperature drops below the 5°C (programmable). When the boiler return temperature drops below
the 3°C (programmable), the burner is also ignited. The pump and/or burner will shut down as soon as the return
temperature has reached the 10°C (programmable). The mentioned temperatures are related to the temperatures
measured by the RETURN sensor of the boiler. This frost protection function will not fire up the boiler in case of a
“general blocking” of the burner demand.
NOTICE: This “Frost Protection” function is only useable for the boiler and not for the whole central heating system.
Because it concerns a programmable setting, a boiler damaged by frost is not covered under warranty.
6.9 Installing a strainer and/or dirt separator
6.10 Water quality
The pH value of the water must be within the following limits: 7,5 < pH < 9,5. This pH value is reached with the
steady conditions. These steady conditions will occur, when after filling the heating system (pH around 7) with fresh
water, the water will lose its air because of the air bleeding operation and heating up (dead water conditions).
Water hardness must be within the following limits:
3,5° Clark (50 ppm CaCO3) < total hardness < 10,5° Clark (150 ppm CaCO3)
When the water might contain aluminium particles, this should be of a maximum of 0.2 mg/litre. If there is the risk of
contamination of the water by any kind of debris/chemicals in the period after installing, a plate heat exchanger
should be used to separate the boiler circuit from the heating circuit (see drawing below).
It is advised to prevent the possible air intake and water leakage of the central heating system. Fresh oxygenated
water might damage the heat exchanger of the boiler and should therefore be prevented! Usual spots where air is
most likely to seep in are: suction gaskets, pumps, air valve working as a venting pipe, O-rings / gaskets in stuffing
box, under floor heating pipes.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
20
6.11 Plastic piping in the heating system
BOILER
BOILER
BOILER
BOILER
HEATING
ZONE
HEATING
ZONE
PLATE HEAT EX-
CHANGER
PLATE HEAT
EXCHANGER
When plastic pipes are used in the central heating system, these should be separated from the boiler system by
using a plate heat exchanger. Diffusion (through the plastic) can cause air to enter the heating system. This could
damage the boiler, pumps and other components in the system. Be aware that plastic piping is often used in under
floor heating systems. When no measures have been taken to prevent the entrance of air into the boiler system,
the warranty of the boiler and any boiler part may be deemed invalid.
6.12 Automatic air vent
An automatic air vent is mounted on the boiler to remove the air from the water circuit.
NOTICE: This automatic air vent is only used for bleeding the air in the heat exchanger of the boiler. One or more
external automatic air vent(s) and/or air separators must always be mounted in the heating system to take out the
air trapped in the heating circuit.
DE-AERATION PROGRAM. When the unit is fired for the first time the unit starts a de-aeration program. One cycle
means 5 seconds pump running and 5 seconds pump off. A complete de-aeration program consists out of three
cycles. The de-aeration program can be interrupted/stopped by briefly pressing the service button.
6.13 Automatic water filling systems
When using an automatic water refill system some precautions should be taken (fresh water is bringing fresh oxygen into the system), like installing a water meter to measure and evaluate the total water volume that is added to
the system. This to detect and eliminate any water leakage as soon as possible.
When an automatic water refill system is used, some form of logging should take place to prevent continuously
filling of the system with large amounts of oxygenated fresh water. This can happen when a leak in the system is
not detected and the total added water amount is not being logged.
6.14 Water pressure
First and for all, the installation should be designed and built conform all applicable regulations and standards, including the right safety valves. IMPORTANT: Always keep the pressure in the boiler lower than the value at which
its safety valve opens.
Sensor
A water pressure sensor has been built into the boiler. With this sensor, the minimum water pressure in the boiler is
0,8 bar and the maximum pressure is 4,0 bar (sensor values). The normal water pressure is supposed to be between 1,5 and 2,0 bar.
The pressure sensor will stop the boiler from firing when the water pressure drops below 0,8 bar, and start the
boiler firing again when the water pressure reaches above the 1,0 bar. These values can be changed in the boiler
control settings.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
21
valve
air separator
dirt separator
strainer (water filter)
pressure relief valve
siphon
pump
automatic air vent
expansion vessel
low loss header
BOILER
HEATING ZONE
Higher pressure systems (e.g. in high buildings)
If pressures higher than 4,0 bar occur in the heating system, the best solution is to separate the system from the
boiler by means of a plate heat exchanger. Now the boiler pressure can still be under 4,0 bar and the boiler control
remains as described above.
Without plate heat exchanger, above 4,0 bar, a water pressure switch has to be built into the boiler instead of the
water pressure sensor - the maximum allowed value in the boiler now is 6,0 bar and the boiler control needs to be
adjusted.
6.15 Chemical water treatment
The chemical compatibility of several products for treatment of the central heating equipment has been tested on
the heat exchangers and the boilers. A list with the corrosion inhibitors in preventative and curative treatment for
gas fired central heating boilers can be supplied by Strebel Ltd.
6.16 Under floor heating
When using an under floor heating system, the boiler circuit must be separated from the heating circuit with a plate
heat exchanger.
6.17 Flush the system with fresh water
The water of the boiler and heating circuit should be free of any particles, debris and pollution. Therefore the complete installation must always be thoroughly flushed with clean water before installing and using the boiler(s).
6.18 Installation examples
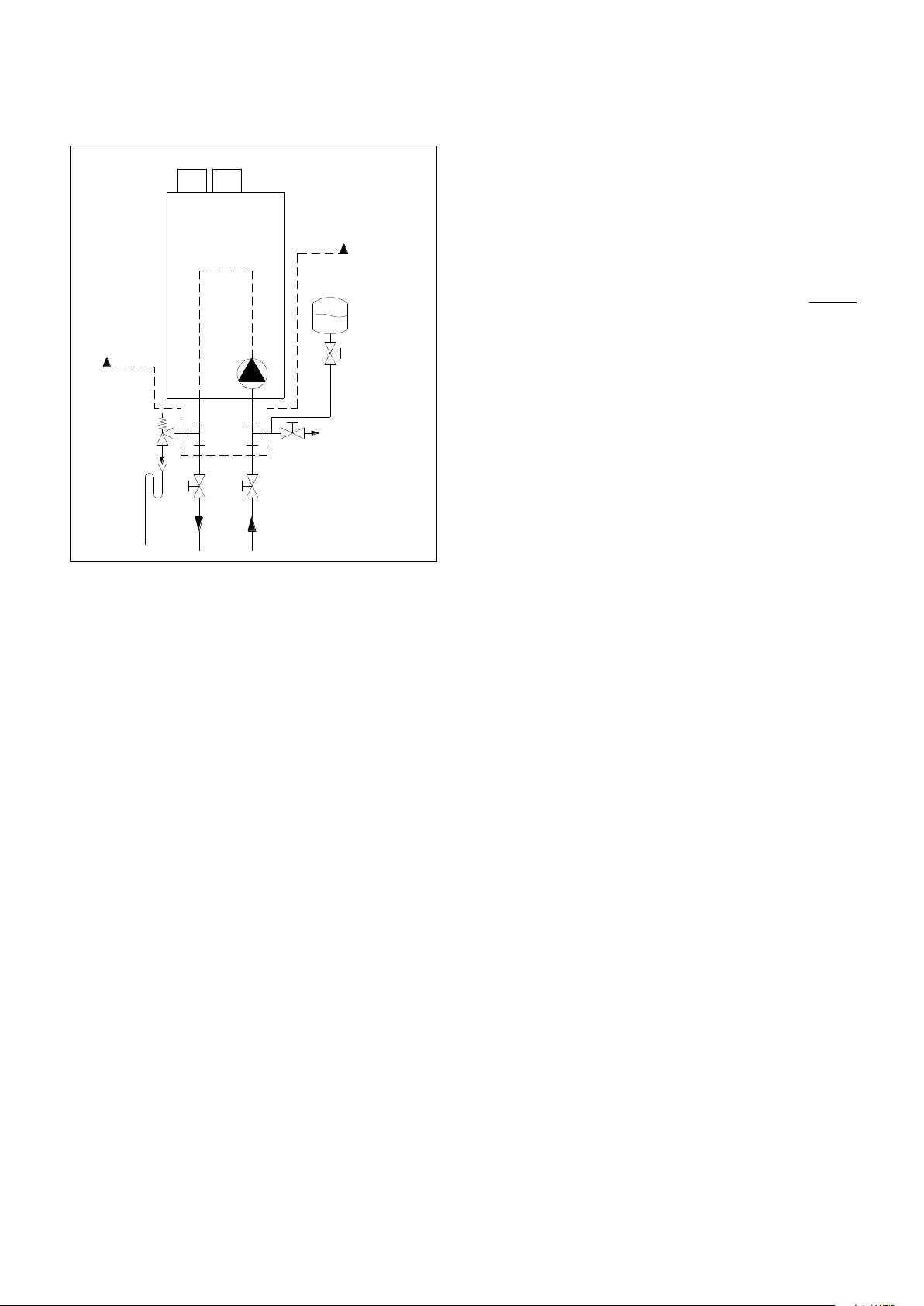
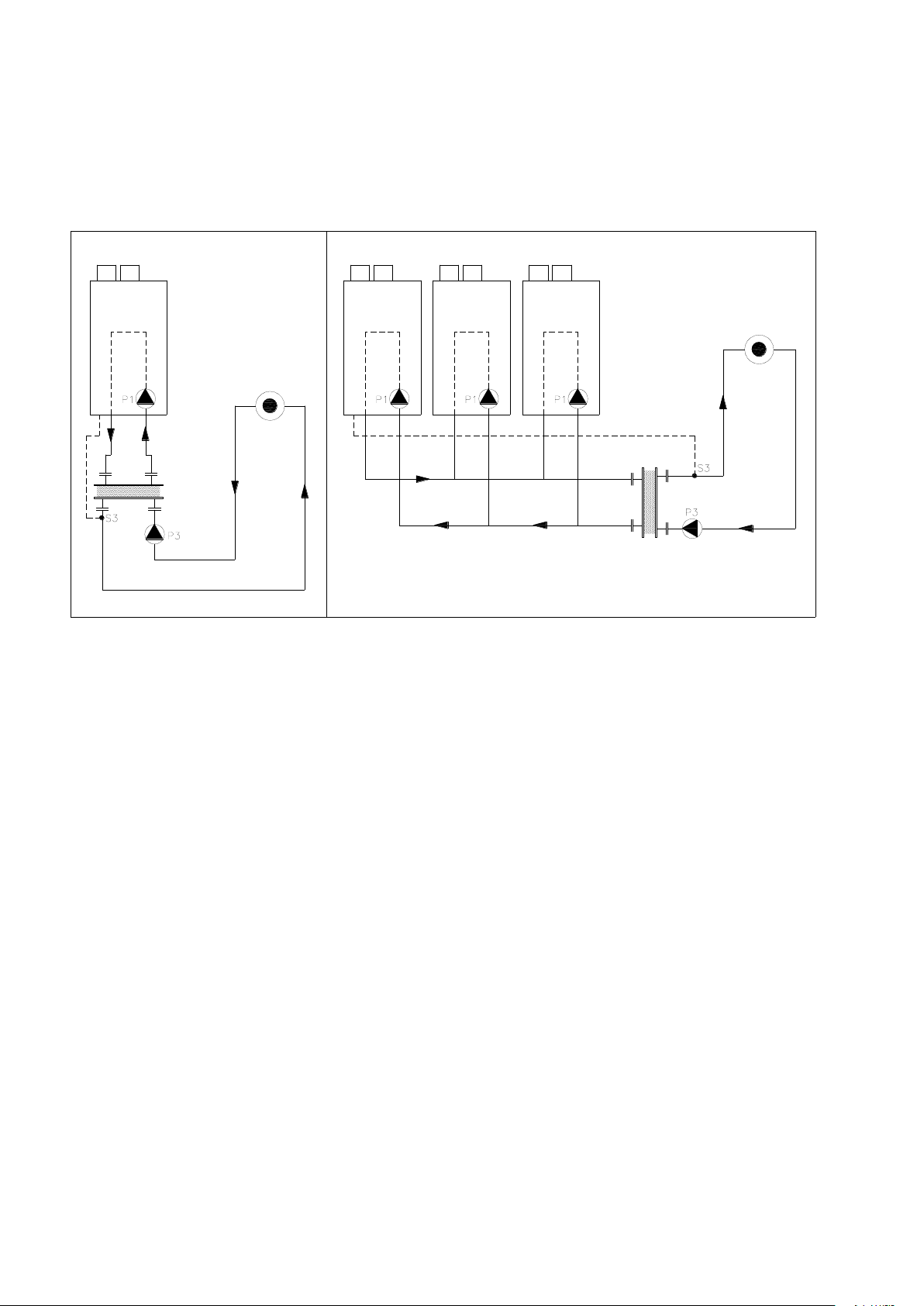
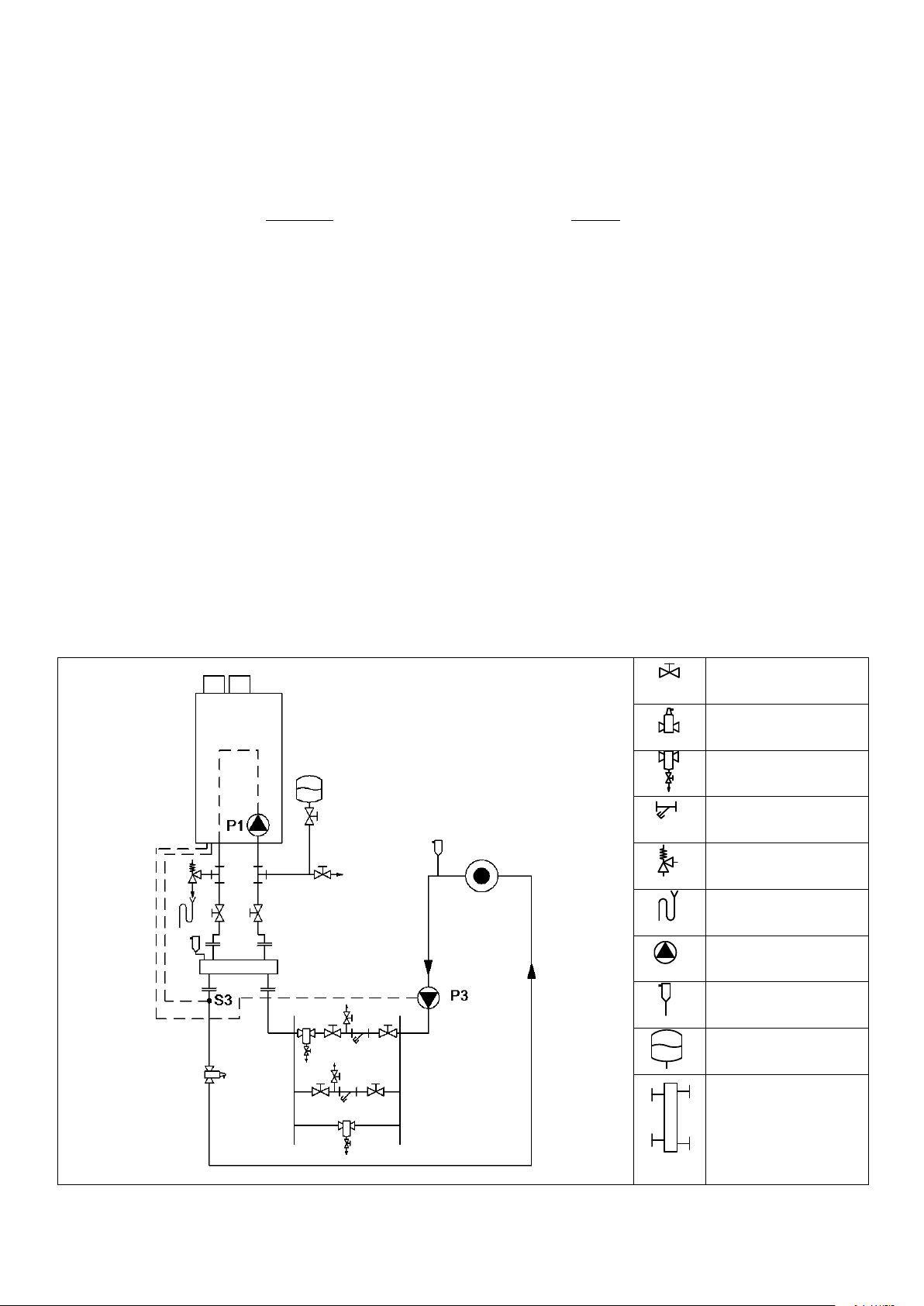
6.18.1 EXAMPLE OF A STANDARD SINGLE BOILER HEATING CIRCUIT WITH LOW LOSS HEADER
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

22
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
23
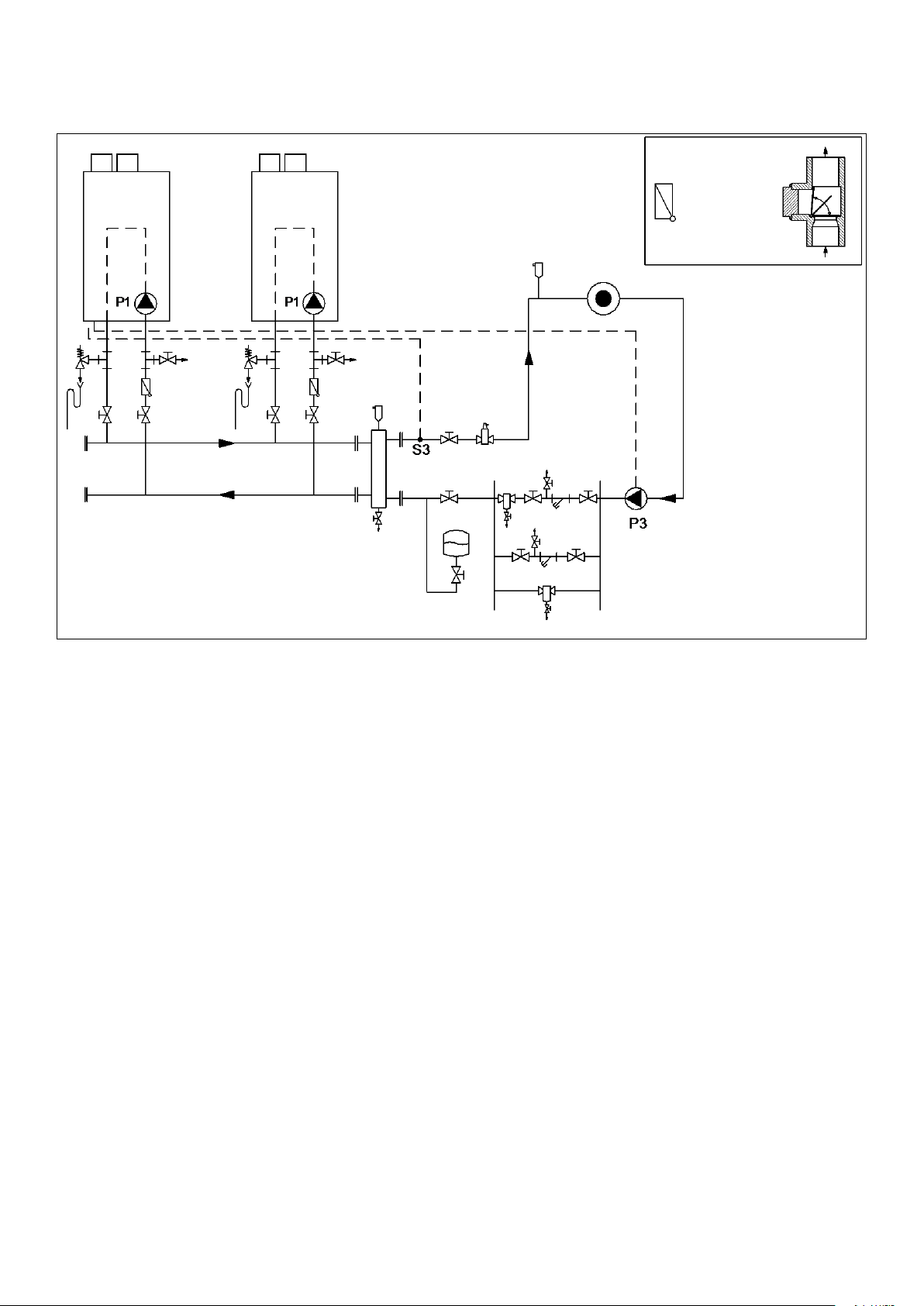
6.18.2 EXAMPLE OF A MULTIPLE BOILER HEATING CIRCUIT WITH LOW LOSS HEADER
NON RETURN
VALVE
(low resistance
type)
NOT SPRING
LOADED
HEATING
ZONE
BOILER
BOILER
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
24
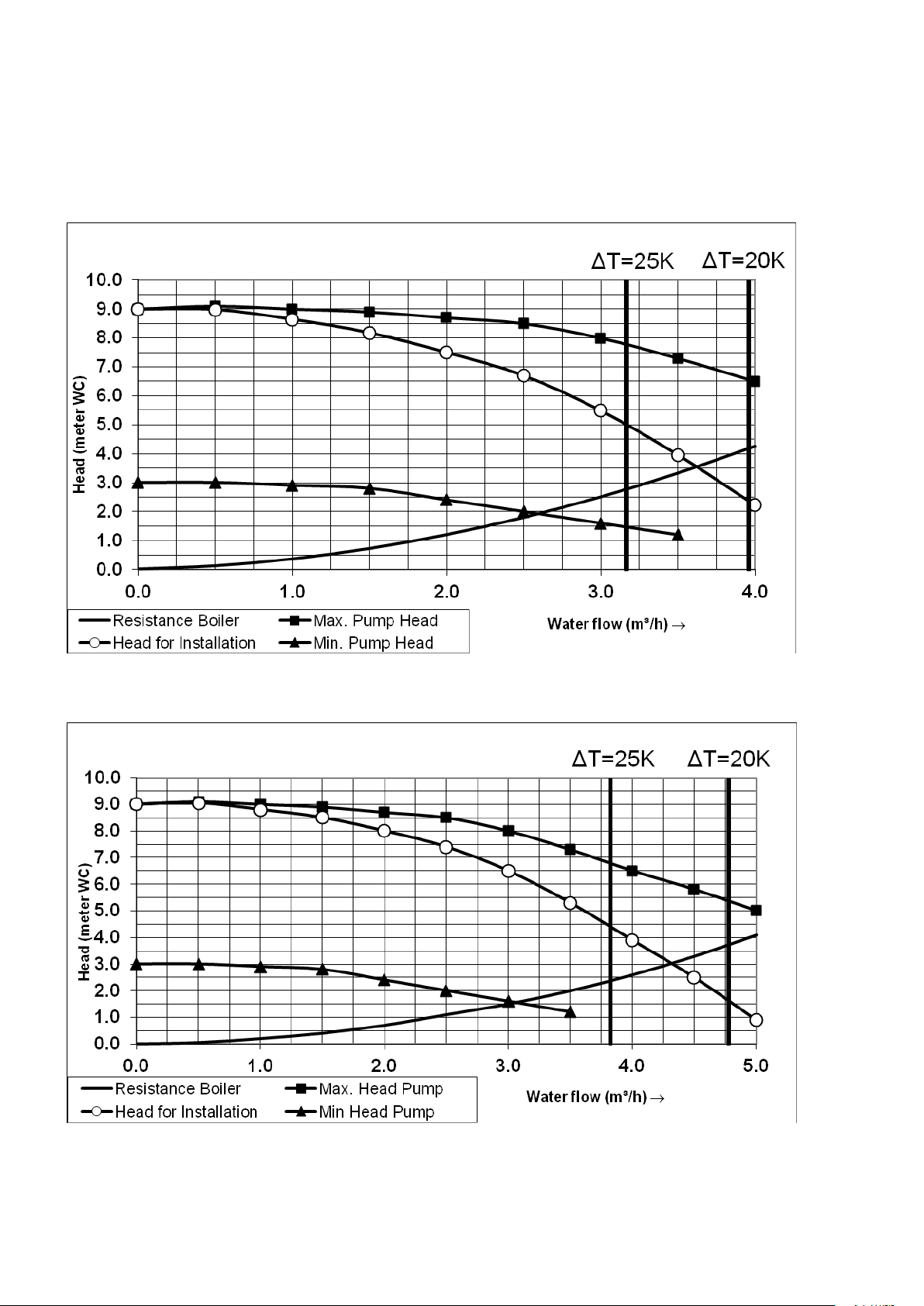
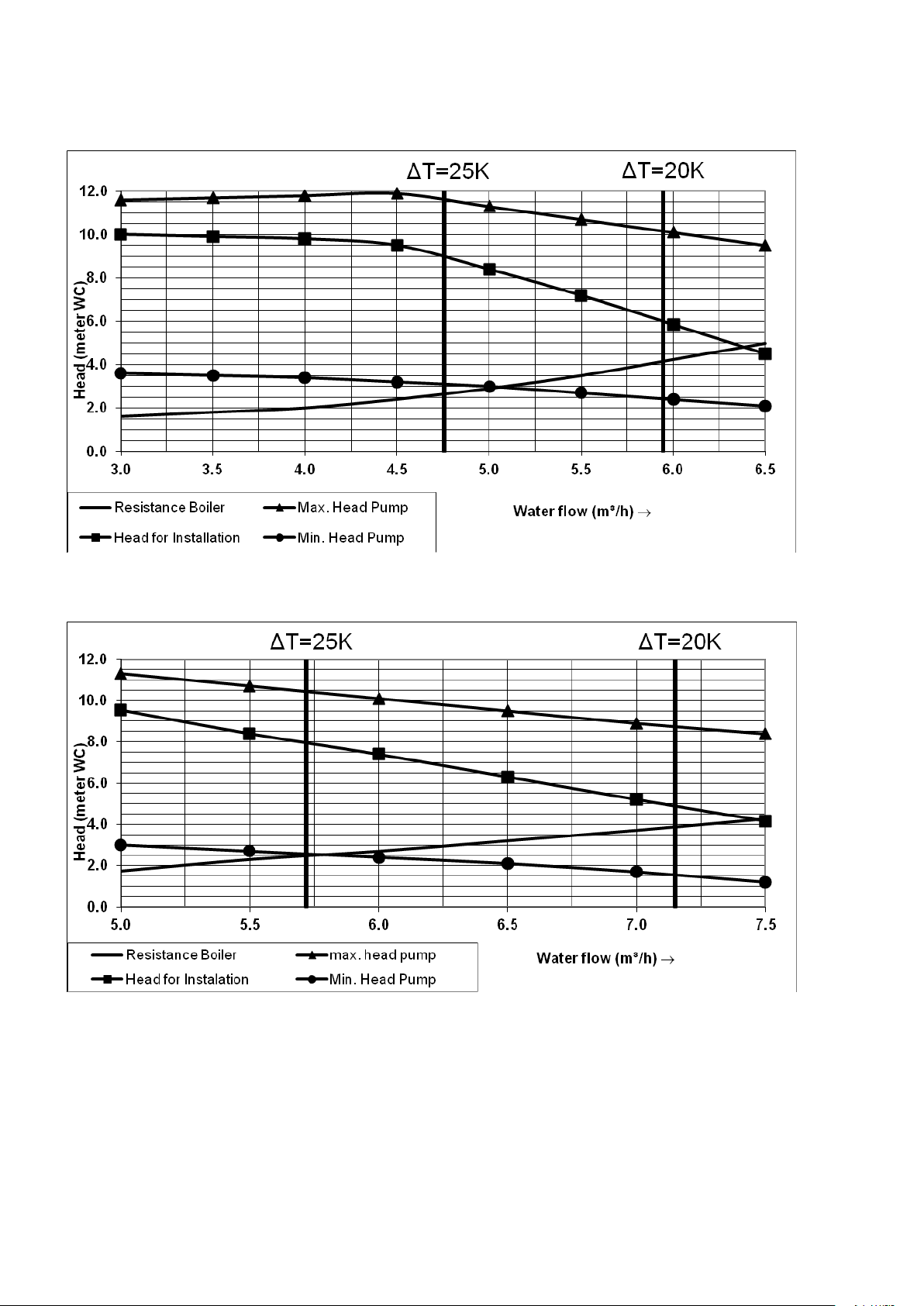
7 PUMP CHARACTERISTICS
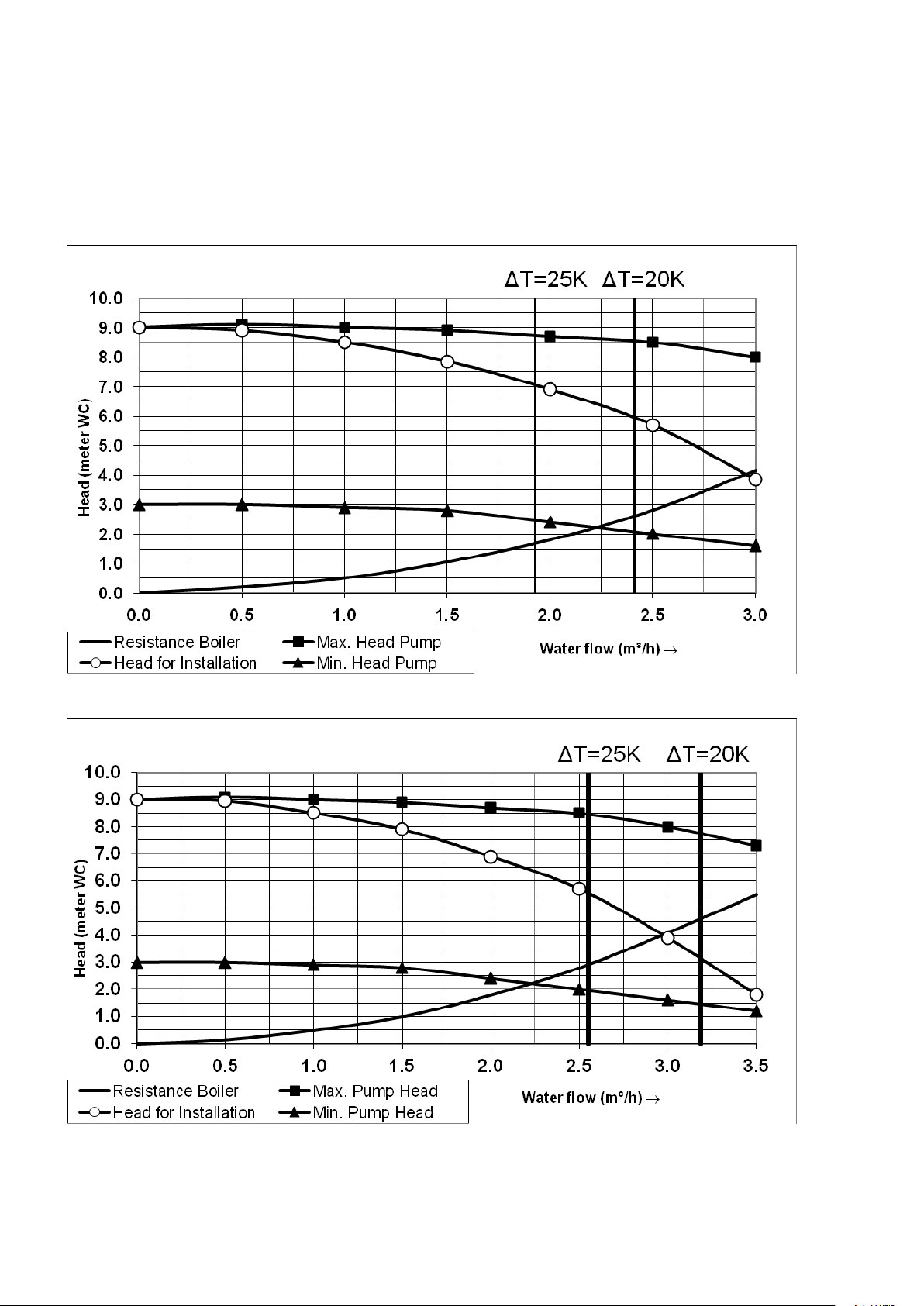
7.1 Hydraulic graphs
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
60. UPML 25-105PWM:
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
80. UPML 25-105PWM:
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
25
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
100. UPML 25-105PWM:
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
120. UPML25-105 PWM:
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
26
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
150. Wilo Stratos Para 30/1-12 PWM:
Boiler and pump graph S-CB
+
180. Wilo Stratos Para 30/1-12 PWM:
Explanation pump graph:
The S-CB+ range is equipped with high efficiency pumps, in the hydraulic graph there is a minimum and maximum
head for the pump. This is the range in which the pump will modulate.
The pump speed is controlled by a PWM signal provided by the burner controller at a value causing a Delta T
across the heat exchanger of 20°C at the whole burner modulation range.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual

27
7.2 Pumps: maximum electrical power
General
- The start current of a conventional pump is approximately 2½ x its nominal current.
- The maximum switch current of the PCB is 5 A.
When the two statements are combined, the conclusion is that nominal currents of pumps, controlled by the PCB,
may not exceed 2 A.
Pump P1 - boiler pump.
This modulating pump is part of the appliance. The speed and power consumption depends on the Delta T across
the heat exchanger and is controlled by the burner controller.
Pump P2 - calorifier pump.
Pump P2 is a DHWi pump and is used when P4AA = 1, meaning the appliance is an indirect calorifier.
Pumps P1 and P2 are connected to one fuse of 5 A, so their total nominal current may not exceed 5 A. To limit the
inrush current, the switching sequence has been modified so pump P2 always switches 100 ms later than pump
P1.
The maximum nominal current of pump P2 must also be 2 A, again due to the inrush current.
3 way valve.
The combined nominal current of pump P1 and the 3 way valve must be smaller than 5 A.
So, the inrush current of the 3 way valve must be lower than 3 A.
Pump P3 - system pump.
The nominal current of pump P3 must be equal to or lower than 2 A.
Warning (EC pumps):
In case of using an electronic commutating pump, the relays 1, 2 or 3 may not be used for the power connection,
because of the inrush current of the electronics of the pump.
Directly connect the pump to an external power supply.
Control connections of an EC pump can be established in several ways, set by parameter P5BN.
See § 11.1.7 on page 79.
8 FLUE GAS AND AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM
8.1 General
The boiler has a positive pressure flue system. The available combined pressure drop for the inlet and outlet system is 200 Pa for the complete boiler range.
Notice:
Install the horizontal flue components with an angle of 3° downwards in the direction of the boiler (roughly
equal to five centimetres for every linear meter). When not installed accordingly, it may result in condensate
building-up in the flue gas tube, eventually causing component failure.
Wall flue terminals are generally used up to 60-80 kW. Using these terminals with larger capacities will give
unpleasant large condensate clouds.
When using a wall terminal, there is the possible risk of ice building-up on surrounding parts/structures, be-
cause the condensate will freeze. This risk should be taken into account during the design phase of the heating installation.
Note
Because the flue gases can have a low temperature, the boiler needs to have a high efficiency approved stainless
steel or plastic flue system. These materials, including the gaskets, should be usable for positive pressure flue gas
systems and have a temperature class of T120.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
28
8.2 Air supply
Never use aluminium (containing) flue gas materials for this boiler.
The S-CB+ 60 boiler as shown in the picture below, is a twin pipe boiler with separate air inlet and flue
outlet pipes. Do NOT connect a concentric pipe to this boiler.
Note the sticker on the flue
pipe, indicating that this is
a twin pipe boiler.
The twin pipe version
is recognized by the
two pipes, one of
which has a RED ring
cap.
When an air supply duct is connected from the outside of the building to the boiler, the boiler will operate as a
room-independent boiler (closed boiler).
The air supply duct can be made of:
PVC / PP
Thin-walled aluminium
Stainless steel
8.2.1 COMBUSTION AIR QUALITY
Combustion air must be free of contaminants. For example: chlorine, ammonia and/or alkali agents, dust, sand and
pollen. Remind that installing a boiler near a swimming pool, a washing machine, laundry or chemical plants does
expose combustion air to these contaminants.
8.2.2 AIR SUPPLY THROUGH HUMID AREAS
When the supply duct will be placed in a boiler room with moist air (for example: greenhouses), a double walled
supply duct or an insulated duct must be used to prevent the possible condensation at the outside of the duct. It is
not possible to insulate the internal air pipes of the boiler and therefore condensation at the internal air canals must
be prevented.
When roof mounted, the air supply duct needs to be protected against rain, so no water will be entering the boiler.
8.3 Flue terminal
The flue terminal duct can be made of:
Stainless steel in combination with T120 gaskets
PP temperature class T120
Multiple boilers can be connected to a common duct. These flue gas systems for multiple boiler installations must
always be engineered as zero or negative pressure systems; this to prevent the risk of recirculation of the flue
gases. Consult the flue gas supplier for detailed information and engineering. See also the cascade manual for
these multiple boiler installations.
8.4 S-CB+ 60 Twin pipe version
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
29
8.5 Pipe heights and mutual distances on a flat roof
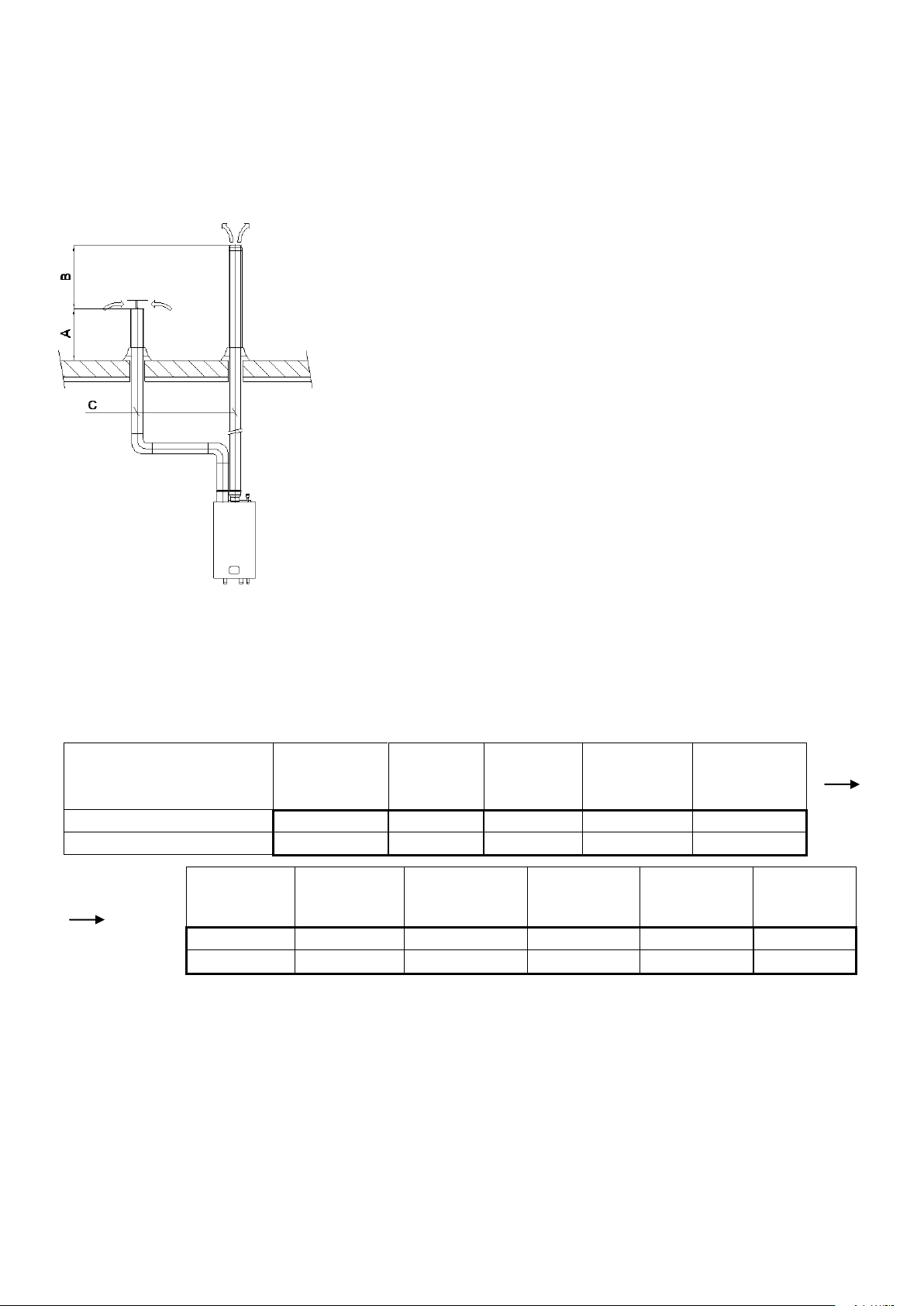
Height A
This is the height of the air inlet. A rain hood should prevent
rainwater entering the air supply system.
When the inlet and outlet are mounted on a flat roof, the inlet should
be at least 60 cm above the roof surface and at least 30 cm above the
maximum snow level.
Example 1:
When the maximum snow level on the roof surface is 45 cm then the
air inlet should be at 45+30=75 cm. 75 cm is more than the minimum
60 so the height will be 75 cm.
Example 2:
When the maximum snow level on the roof surface is 15 cm then the
air inlet should be at 15+30=45 cm. 45 cm is less than the minimum
60 cm so the height will be 60 cm.
Height difference B
This is the distance between the flue outlet and the air inlet.
The flue gas outlet should be at least 70 cm above the air inlet. It is
advised to be equipped with a conical outlet.
When no air inlet connection is applied on the roof, the flue outlet should be situated at least 100 cm above the roof surface.
Distance C
The horizontal mutual distance at roof level.
This distance should be at least 70 cm.
CE string flue gas
material (B23P)
European standard
Temperature class
Pressure
class
Resistance to
condensate
Corrosion resistance class
min. requirement PP
EN 14471
T120
P1 W 1
min. requirement StS
EN 1856-1
T120
P1 W 1
Metal: liner
specifications
Soot fire resistance class
Distance to
combustible
material
Plastics:
location
Plastics: fire
behaviour
Plastics:
enclosure
O 30
I or E
C/E
L
L20040 O 40
8.6 B23P certified
Overpressure flue gas systems
For boiler classification B23P and for overpressure flue gas systems the minimum requirements of the flue gas
material for Eco Boilers can be determined in a designation string according to the EN1443 (see table):
A few examples of flue gas material suitable for ECO boilers:
CE String for Plastic PPs: EN14471 T120 P1 W 2 O(30) I C/E L
CE String for Stainless Steel: EN1856-1 T250 P1 W V2-L50040 O (50)
When selecting flue gas systems, be aware that the minimum requirements are met. So only select flue gas materials having the same or better properties than this table.
8.7 C63 certified
In general, boilers are certified with their own flue gas material. If a boiler is C63 certified, no specific type flue gas
material has been certified in combination with the boiler. In this case the flue gas material does not need to be
certified in combination with the boiler but should be fit for purpose, and comply with the applicable European standards. It must be able to handle the condensate forming and transport, overpressure and must have a minimum
temperature class of T120.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
30
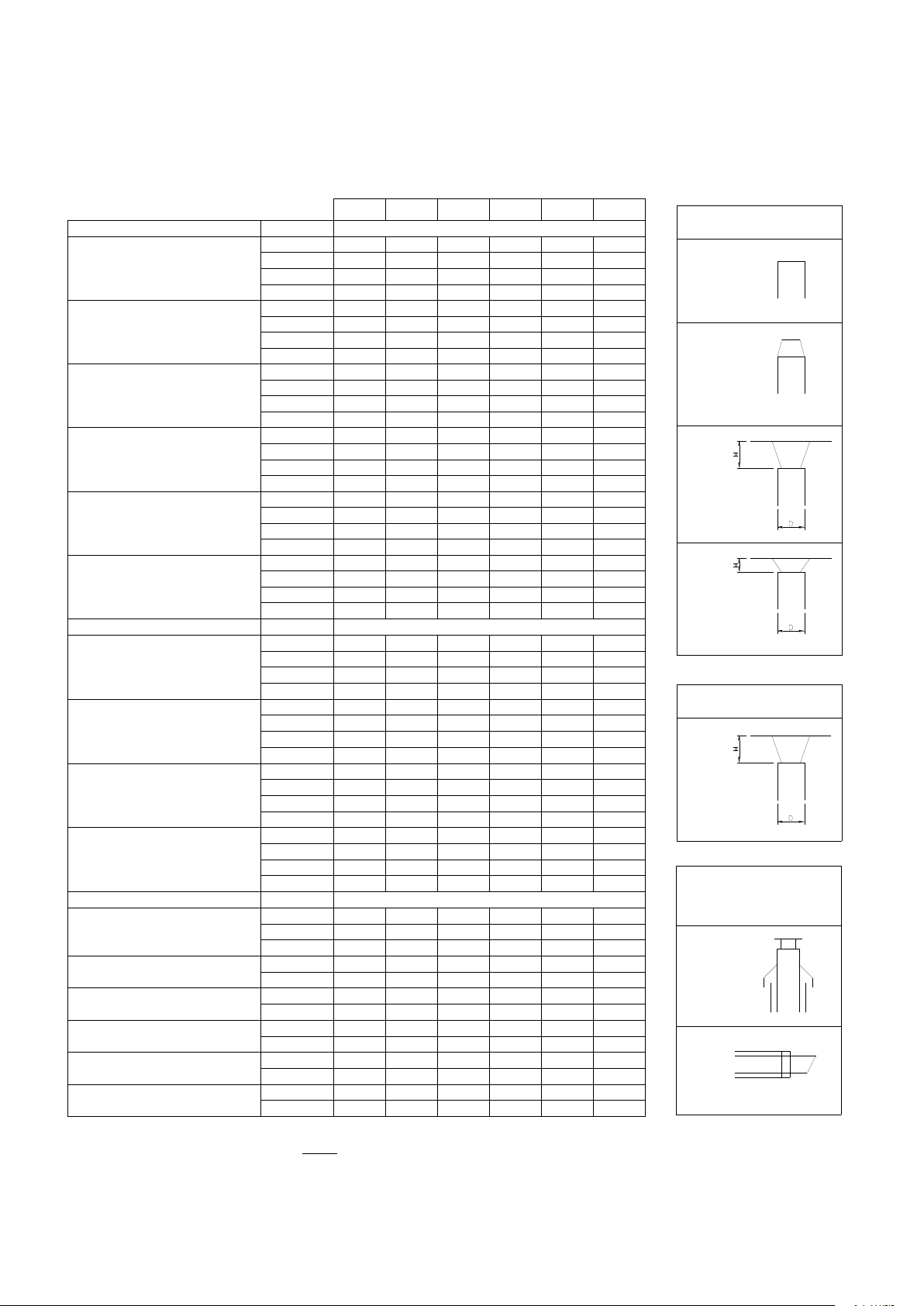
8.8 Flue gas and air supply resistance table
* Never reduce pipe diameters relative to boiler connections
Values printed in grey applicable for larger pipe diameters than boiler connection
+60 +80 +100 +120 +150 +180
FLUE GAS PIPING
Ø [mm] *
RESISTANCE [Pa]
straight tube/m
80
5,0
8,0
-
-
-
-
100
2,0
3,5
4,0
6,5
-
-
130
0,45
0,8
1,2
1,8
3,8
6,0
150
-
-
0,5
0,8
1,7
3,0
45° bend
80
2,5
4,0
-
-
-
-
100
1,0
1,7
2,0
3,2
-
-
130
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1,9
3,0
150
-
-
0,2
0,4
0,8
1,5
90° bend
80
5,0
8,0
-
-
-
-
100
2,0
3,5 4 6,5
-
-
130
0,4
0,8
1,2
1,8
3,8
6,0
150
-
-
0,5
0,7
1,7
3,0
Flue outlet zeta=0,05
80
0,7
1,2
-
-
-
-
100
0,3
0,5
0,8
1,1
-
-
130
0,1
0,18
0,3
0,4
0,6
0,9
150
-
-
0,15
0,2
0,35
0,5
Flue outlet zeta=1
80
13,8
24,0
-
-
-
-
100
5,6
9,8
15,2
22,1
-
-
130
2,0
3,5
5,3
7,8
12,0
17,3
150
-
-
3,0
4,4
6,8
9,8
Flue outlet zeta=1,5
80
20,6
36,0
-
-
-
-
100
8,5
14,8
22,8
33,2
-
-
130
3,0
5,2
8,0
11,6
18,0
26,0
150
-
-
4,5
6,6
10,2
14,7
AIR SUPPLY PIPING
Ø [mm] *
RESISTANCE [Pa]
straight tube/m
80
4,0
7,5
-
-
-
-
100
1,2
3,0
3,5
4,0
-
-
130
0,35
0,75
0,8
1,1
1,2
2,0
150
-
-
0,3
0,4
0,6
1,2
45° bend
80
2,0
3,5
-
-
-
-
100
0,6
1,5
1,7 2 -
-
130
0,2
0,4
0,4
0,5
0,6
1,0
150
-
-
0,15
0,2
0,3
0,6
90° bend
80
4,0
7,0
-
-
-
-
100
1,2
3,0
3,5
4,0
-
-
130
0,3
0,7
0,8
1,1
1,2
2,0
150
-
-
0,3
0,4
0,6
1,2
Air inlet zeta =1
80
10,4
18,1
-
-
-
-
100
4,2
7,4
11,4
16,7
-
-
130
1,5
2,6
4,0
5,8
9,1
13,1
150
-
-
2,3
3,3
5,1
7,4
CONCENTRIC PARTS
Ø [mm] *
RESISTANCE [Pa]
roof terminal
80/125
34
61
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
39
45
69
86
130/200
-
-
-
-
15
23
outside wall terminal
80/125
13
22
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
19
24
40
48
straight tube/m
80/125
9
12
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
8
10
14
16
45° bend concentric
80/125
5
7
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
8
9
14
16
90° bend concentric
80/125
8
13
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
11
13
22
28
conc./par. adaptor
80/125
10
14
-
-
-
-
100/150
-
-
16
22
40
56
CONCENTRIC
FLUE GAS OUTLET
AIR INLET
ROOF
WALL
AIR INLET
H/D=1,0
zeta=1,0
FLUE GAS OUTLET
zeta=0
open outlet
zeta=0,05
conical outlet
H/D=1,0
zeta=1,0
H/D=0,5
zeta=1,5
In the next section, for five typical flue gas outlet & air inlet configurations the maximum lengths of the straight
pipes will be calculated. First all component resistance values are given in the next table:
NOTICE: This table may only be used for a single flue/air system for one boiler. Do NOT use this table for common
flue systems with cascaded boilers.
S-CB+ Boiler Range Manual
 Loading...
Loading...