Page 1

TS4985
2 X 1.2W Stereo Audio Power Amplifier with
Dedicated Standby Pins
■ Operating from V
■ 1.2W output power per channel @ V
=2.2V to 5.5V
CC
CC
=5V,
THD+N=1%, RL=8Ω
■ 10nA standby current
■ 62dB PSRR @ 217Hz with grounded inputs
■ High SNR: 106dB(A) typ.
■ Near zero pop & click
■ Lead-free 15 bumps, flip-chip package
Description
The TS4985 has been designed for top-class
stereo audio applications. Thanks to its compact
and power-dissipation efficient flip-chip package,
it suits various applications.
With a BTL configuration, this audio power
amplifier is capable of delivering 1.2W per
channel of continuous RMS output power into an
8Ω load @ 5V.
Each output channel (left and right), has an
external controlled standby mode pin (STDBYL &
STDBYR) to reduce the supply current to less
than 10nA per channel. The device also features
an internal thermal shutdown protection.
The gain of each channel can be configured by
external gain setting resistors.
Flip-chip - 15 bumps
Pin Connection (top view)
VCC2
VCC2
VCC1
VCC1
IN-L
IN-L
VO+L
VO+L
IN+L
IN+L
STDBYL
STDBYL
BYPASS
BYPASS
STDBYR
STDBYR
Applications
■ Cellular mobile phones
■ Notebook & PDA computers
■ LCD monitors & TVs
■ Portable audio devices
IN+R
IN+R
VO+R
VO+R
GND2
GND2
IN-R
IN-R
VO-RVO-L
VO-RVO-L
GND1
GND1
Order Codes
Part Number Temperature Range Package Packaging Marking
TS4985EIJT
TS4985EKIJT
-40, +85°C
May 2005 1/29
Lead free flip-chip
Lead free flip-chip +
back coating
Tape & Reel A85
Rev 2
www.st.com
29
Page 2

Typical Application Schematic TS4985
1 Typical Application Schematic
Figure 1
shows a typical application schematic for the TS4985.
Figure 1. Application schematic
Cin-LInput L
100n
Cin-R
100n
Rin-L
22k
VCC
1
2
3
+
Cb
1u
Rin-R
22k
VCC
1
2
3
Input R
GND
GND
Cfeed-L
Rfeed-L
22k
A1
B2
C5
C3
D6
E5
C1
IN-L
IN+L
Standby L
Bypass
IN+R
IN-R
Standby R
VCC
+
Cs
1u
B6A5
VCC1
-
+
Bias
+
-
-
AV = -1
+
-
AV = -1
+
VO-L
VO+L
VO-R
VO+R
A3
B4
E3
D4
Neg. Output L
Pos. Output L
Neg. Output R
Pos. Output R
Cfeed-R
Rfeed-R
22k
Table 1. External component descriptions
Components Functional Description
Inverting input resistors which sets the closed loop gain in
R
IN L,R
C
IN L,R
R
FEED L,R
C
C
A
V L, R
S
B
conjunction with Rfeed. These resistors also form a high pass
filter with C
(fc = 1 / (2 x Pi x RIN x CIN))
IN
Input coupling capacitors which blocks the DC voltage at the
amplifier input terminal
Feedback resistors which sets the closed loop gain in
conjunction with R
Supply Bypass capacitor which provides power supply filtering
Bypass pin capacitor which provides half supply filtering
Closed loop gain in BTL configuration = 2 x (R
each channel
GND1
E1 D2
IN
GND2 VCC2
TS4985
FEED
/ RIN) on
2/29
Page 3

TS4985 Absolute Maximum Ratings
2 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 2. Key parameters and their absolute maximum ratings
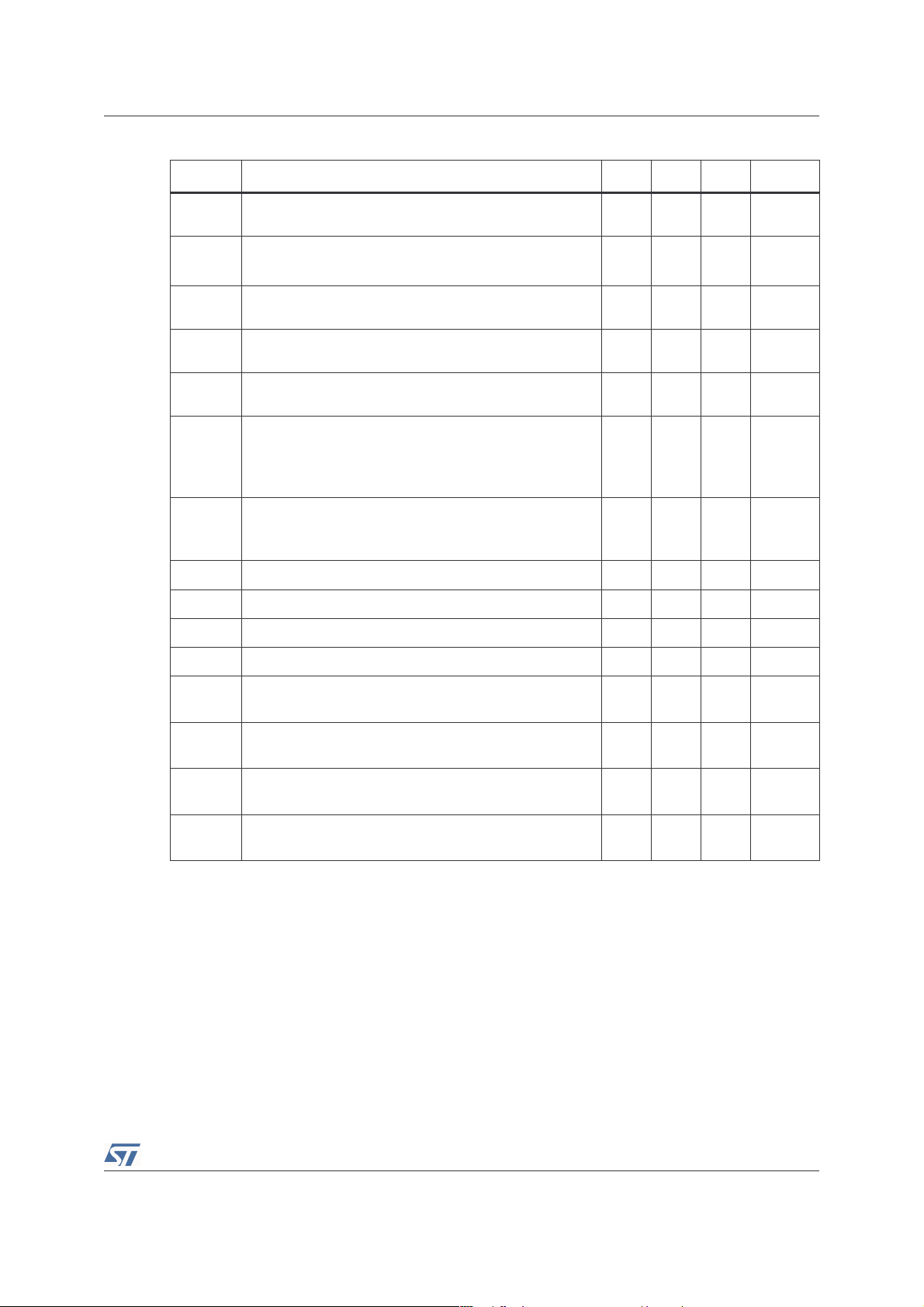
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
VCC
V
T
oper
T
stg
T
R
thja
(1)
(2)
i
Supply voltage
Input Voltage
Operating Free Air Temperature Range -40 to + 85 °C
Storage Temperature -65 to +150 °C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150 °C
j
Flip-chip Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient 180 °C/W
6V
GND to V
CC
Pd Power Dissipation Internally Limited
ESD
Human Body Model
(3)
2kV
ESD Machine Model 200 V
Latch-up Immunity 200 mA
1. All voltages values are measured with respect to the ground pin.
2. The magnitude of input signal must never exceed VCC + 0.3V / GND - 0.3V
3. All voltage values are measured from each pin with respect to supplies.
Table 3. Operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
VCC Supply Voltage 2.2 to 5.5 V
V
ICM
Common Mode Input Voltage Range
1.2V to V
CC
V
V
Standby Voltage Input:
VSTB
Device ON
Device OFF
1.35 ≤ V
GND ≤ V
STB
STB
≤ V
≤ 0.4
CC
RL Load Resistor ≥ 4 Ω
ROUTGND
Resistor Output to GND (V
STB
= GND)
≥ 1MΩ
TSD Thermal Shutdown Temperature 150 °C
RTHJA
1. When mounted on a 4-layer PCB.
Flip-chip Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient
(1)
110
V
°C/W
3/29
Page 4

Electrical Characteristics TS4985
3 Electrical Characteristics
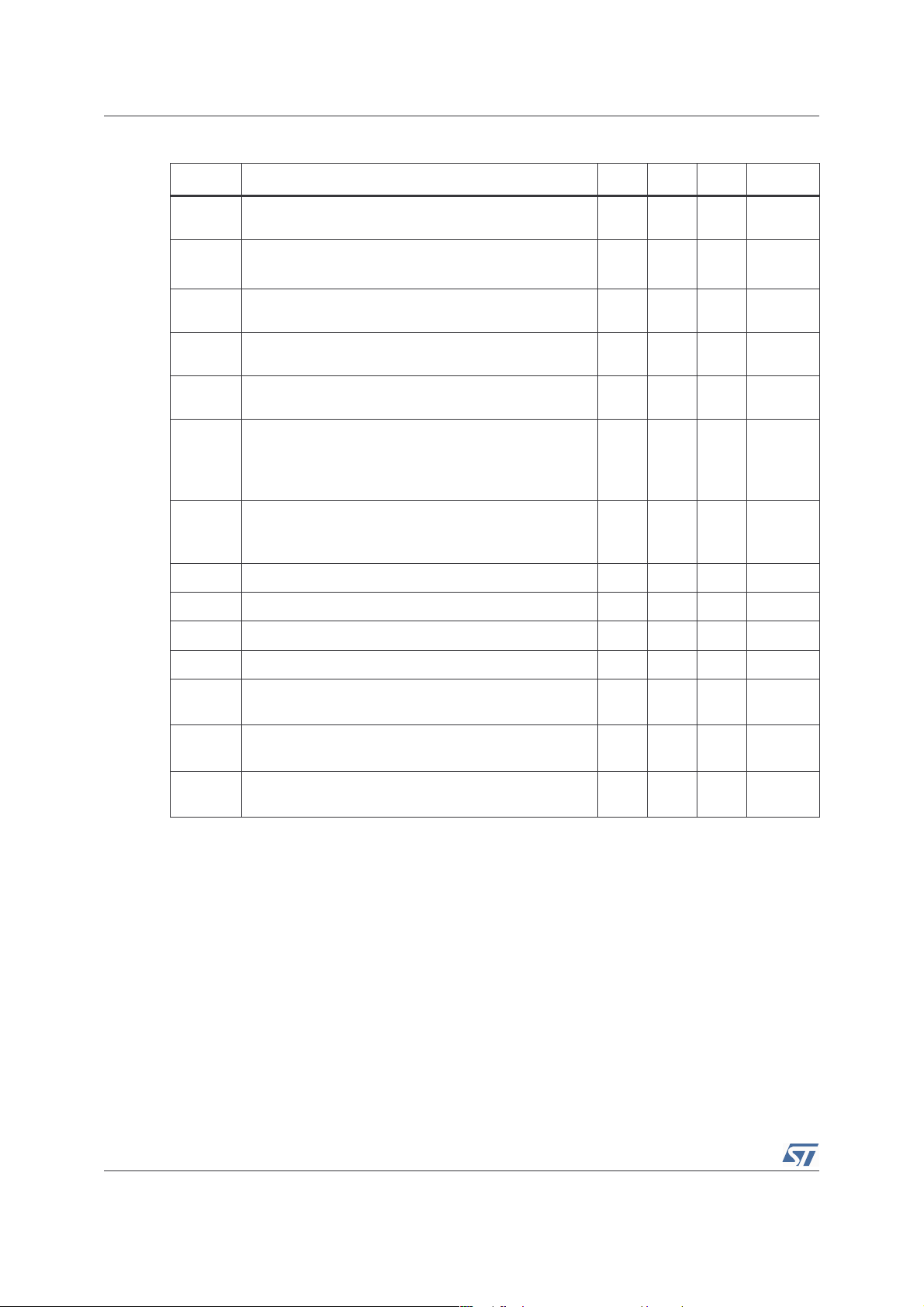
Table 4. VCC = +5V, GND = 0V, T
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
I
STANDBY
Voo
Po
THD + N
PSRR
Crosstalk
T
T
STDB
V
STDBH
V
STDBL
Φ
GM
GBP
1. Standby mode is activated when Vstdby is tied to Gnd.
2. All PSRR data limits are guaranteed by production sapling tests.
Dynamic measurements - 20*log(rms(Vout)/rms(Vripple)). Vripple is the sinusoidal signal superimposed upon
Vcc
Supply Current
CC
No input signal, no load 7.4 12
Standby Current
No input signal, Vstdby = GND, RL = 8Ω
(1)
10 1000 nA
Output Offset Voltage
No input signal, RL = 8Ω 110
Output Power
THD = 1% Max, F = 1kHz, RL = 8Ω
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
Po = 1Wrms, Av = 2, 20Hz ≤ F ≤ 20kHz, RL = 8Ω
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(2)
0.9 1.2 W
0.2 %
RL = 8Ω, Av = 2, Vripple = 200mVpp, Input Grounded
F = 217Hz
F = 1kHz
Channel Separation, R
= 8Ω
L
55
55
F = 1kHz
F = 20Hz to 20kHz
Wake-Up Time (Cb = 1µF) 90 130 ms
WU
62
64
-107
-82
Standby Time (Cb = 1µF) 10 µs
Standby Voltage Level High 1.3 V
Standby Voltage Level Low 0.4 V
Phase Margin at Unity Gain
M
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Margin
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
L
= 8Ω
65 Degrees
15 dB
1.5 MHz
mA
mV
dB
dB
4/29
Page 5
TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Table 5. VCC = +3.3V, GND = 0V, T
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
I
STANDBY
Voo
Po
THD + N
PSRR
Crosstalk
T
T
STDB
V
STDBH
V
STDBL
Φ
GM
GBP
GBP
1. Standby mode is activated when Vstdby is tied to Gnd.
2. All PSRR data limits are guaranteed by production sampling tests.
Dynamic measurements - 20*log(rms(Vout)/rms(Vripple)). Vripple is the sinusoidal signal superimposed upon
Vcc
Supply Current
CC
No input signal, no load 6.6 12
Standby Current
No input signal, Vstdby = GND, RL = 8Ω
(1)
10 1000 nA
Output Offset Voltage
No input signal, RL = 8Ω 110
Output Power
THD = 1% Max, F = 1kHz, RL = 8Ω
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
Po = 400mWrms, Av = 2, 20Hz ≤ F ≤ 20kHz, RL = 8Ω
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(2)
375 500 mW
0.1 %
RL = 8Ω, Av = 2, Vripple = 200mVpp, Input Grounded
F = 217Hz
F = 1kHz
Channel Separation, R
= 8Ω
L
55
55
F = 1kHz
F = 20Hz to 20kHz
Wake-Up Time (Cb = 1µF) 110 140 ms
WU
61
63
-107
-82
Standby Time (Cb = 1µF) 10 µs
Standby Voltage Level High 1.2 V
Standby Voltage Level Low 0.4 V
Phase Margin at Unity Gain
M
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Margin
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
L
= 8Ω
Gain Bandwidth Product
L
= 8Ω
R
65 Degrees
15 dB
1.5 MHz
1.5 MHz
mA
mV
dB
dB
5/29
Page 6
Electrical Characteristics TS4985
Table 6. VCC = +2.6V, GND = 0V, T
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
I
STANDBY
Voo
Po
THD + N
PSRR
Crosstalk
T
T
STDB
V
STDBH
V
STDBL
Φ
GM
GBP
1. Standby mode is activated when Vstdby is tied to Gnd.
2. All PSRR data limits are guaranteed by production sampling tests.
Dynamic measurements - 20*log(rms(Vout)/rms(Vripple)). Vripple is the sinusoidal signal superimposed upon
Vcc
Supply Current
CC
No input signal, no load 6.2 12
Standby Current
No input signal, Vstdby = GND, RL = 8Ω
(1)
10 1000 nA
Output Offset Voltage
No input signal, RL = 8Ω 110
Output Power
THD = 1% Max, F = 1kHz, RL = 8Ω
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
Po = 200mWrms, Av = 2, 20Hz ≤ F ≤ 20kHz, RL = 8Ω
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
(2)
220 300 mW
0.1 %
RL = 8Ω, Av = 2, Vripple = 200mVpp, Input Grounded
F = 217Hz
F = 1kHz
Channel Separation, R
= 8Ω
L
55
55
F = 1kHz
F = 20Hz to 20kHz
Wake-Up Time (Cb = 1µF) 125 150 ms
WU
60
62
-107
-82
Standby Time (Cb = 1µF) 10 µs
Standby Voltage Level High 1.2 V
Standby Voltage Level Low 0.4 V
Phase Margin at Unity Gain
M
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Margin
R
= 8Ω, CL = 500pF
L
Gain Bandwidth Product
R
L
= 8Ω
65 Degrees
15 dB
1.5 MHz
mA
mV
dB
dB
6/29
Page 7

TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Table 7. Index of graphics
Description Figure Page
Open Loop Frequency Response
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) vs. Frequency
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) vs. DC Output Voltage
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) at F=217Hz vs. Bypass
Capacitor
Output Power vs. Power Supply Voltage
Output Power vs. Load Resistor
Power Dissipation vs. Output Power
Clipping Voltage vs. Power Supply Voltage and Load Resistor
Current Consumption vs. Power Supply Voltage
Current Consumption vs. Standby Voltage
Output Noise Voltage, Device ON
Output Noise Voltage, Device in Standby
THD+N vs. Output Power
Figure 2
Figure 8
Figure 14
to
7 page 8
to
13 page 9
to
22
page 10
page 11
Figure 23 page 11
Figure 24
Figure 27
Figure 30
Figure 33
Figure 34
to
26
to
29 page 12
to
32
,
page 11
page 12
page 12
page 13
page 13
Figure 35 page 13
Figure 36
to
38
page 13
page 14
Figure 39 page 14
Figure 40 page 14
Figure 41
to
49
page 14
page 15
to
to
to
to
to
THD+N vs. Frequency
Crosstalk vs. Frequency
SIgnal to Noise Ratio vs. Power Supply with Unweighted Filter
(20Hz to 20kHz)
SIgnal to Noise Ratio vs. Power Supply with A-weighted Filter
Power Derating Curves
Figure 50
Figure 53
to
to
Figure 56
Figure 57
Figure 58
Figure 59
52 page 16
55 page 16
,
,
page 17
page 17
Figure 60 page 17
7/29
Page 8
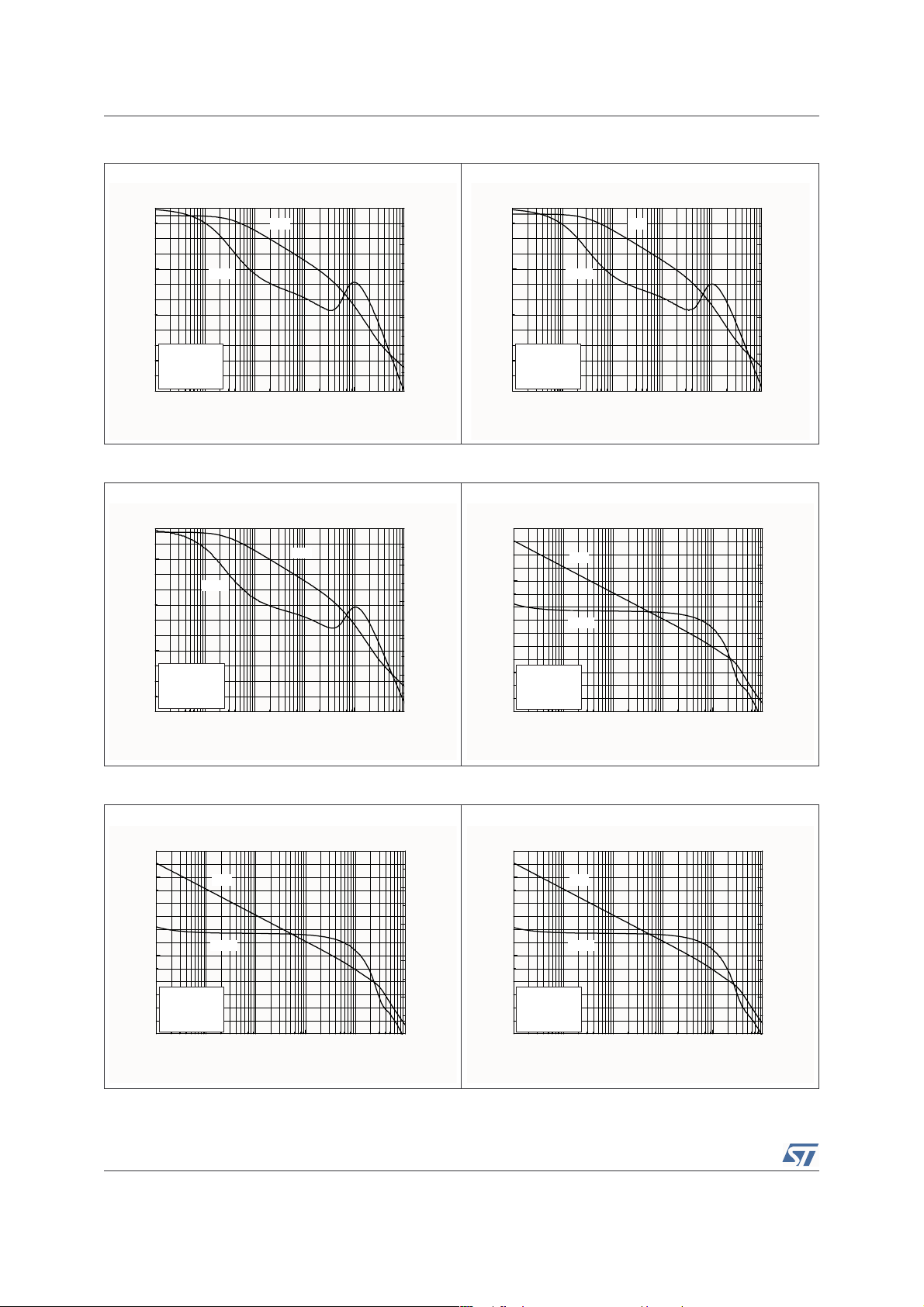
Electrical Characteristics TS4985
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
-200
-160
-120
-80
-40
0
Gain
Phase
Gain (dB)
Frequency (kHz)
Vcc = 3.3V
RL = 8
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
Phase (°)
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
-200
-160
-120
-80
-40
0
Gain
Phase
Gain (dB)
Frequency (kHz)
Vcc = 2.6V
CL = 560pF
Tamb = 25°C
Phase (°)
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
-200
-160
-120
-80
-40
0
Gain
Phase
Gain (dB)
Frequency (kHz)
Vcc = 5V
CL = 560pF
Tamb = 25°C
Phase (°)
Figure 2. Open loop frequency response Figure 3. Open loop frequency response
60
40
20
0
Gain (dB)
-20
-40
-60
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
Vcc = 2.6V
RL = 8
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
Phase
Gain
Frequency (kHz)
0
-40
-80
-120
-160
-200
Phase (°)
Figure 4. Open loop frequency response Figure 5. Open loop frequency response
60
40
20
0
Gain (dB)
-20
-40
-60
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
Phase
Vcc = 5V
RL = 8
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
Frequency (kHz)
Gain
0
-40
-80
-120
-160
-200
Phase (°)
Figure 6. Open loop frequency response Figure 7. Open loop frequency response
100
80
60
40
20
Gain (dB)
0
Vcc = 3.3V
-20
CL = 560pF
Tamb = 25°C
-40
0.1 1 10 100 1000 10000
8/29
Gain
Phase
Frequency (kHz)
0
-40
-80
Phase (°)
-120
-160
-200
Page 9
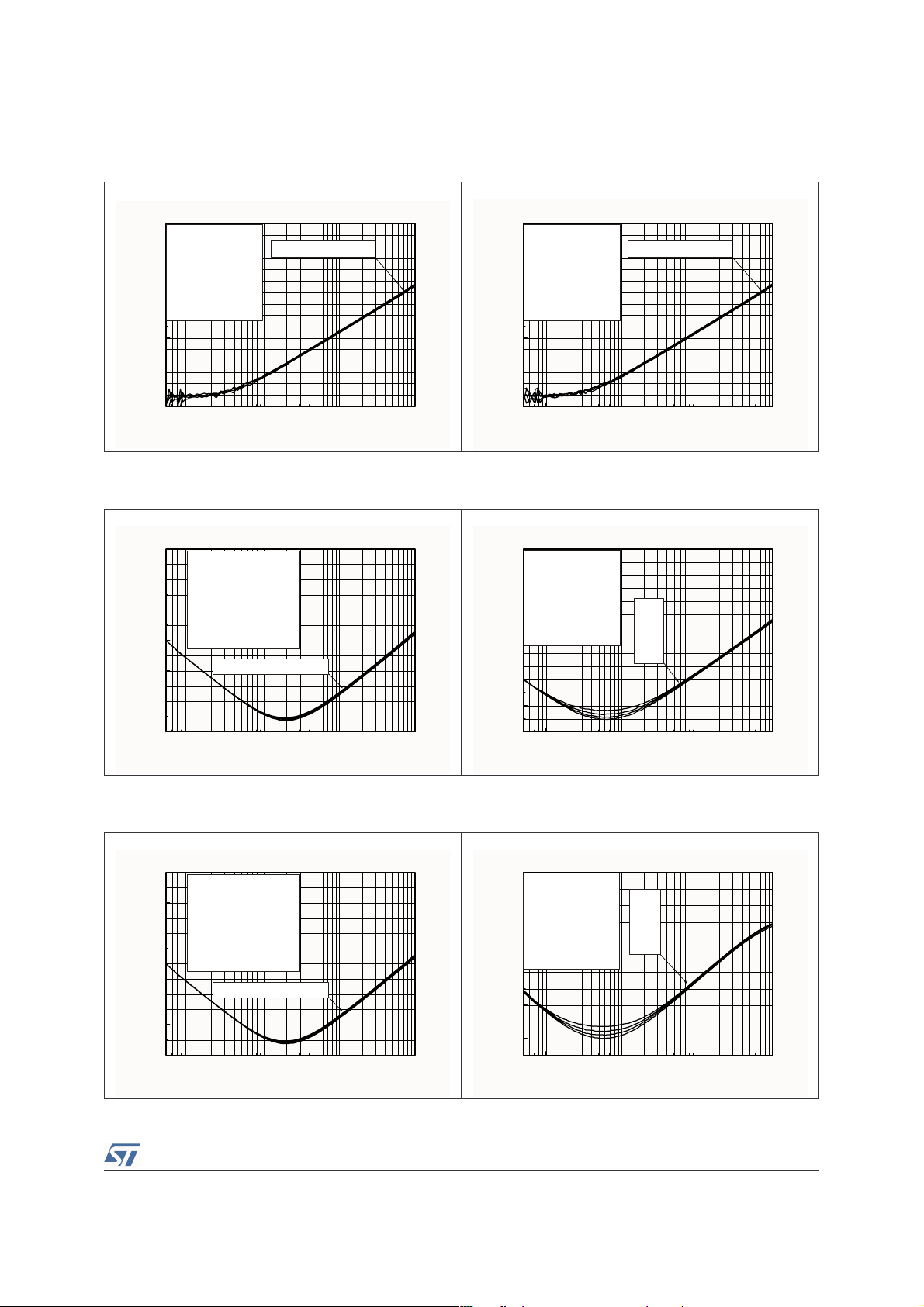
TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 8. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
Vripple = 200mVpp
-10
Rfeed = 22kΩ
Input = Floating
-20
Cb = 0.1µF
RL >= 4
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-80
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
100 1000 10000 100000
Vcc = 2.2, 2.6, 3.3, 5V
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 10. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
-10
-20
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-60
Vripple = 200mVpp
Av = 2
Input = Grounded
Cb = 0.1µF, Cin = 1µF
RL >= 4
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
Vcc = 5, 3.3, 2.5 & 2.2V
100 1000 10000 100000
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 9. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
Vripple = 200mVpp
-10
Rfeed = 22kΩ
Input = Floating
-20
Cb = 1µF
RL >= 4
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-80
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
100 1000 10000 100000
Vcc = 2.2, 2.6, 3.3, 5V
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 11. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
Vripple = 200mVpp
-10
Av = 2
Input = Grounded
-20
Cb = Cin = 1µF
RL >= 4
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
100 1000 10000 100000
Vcc :
2.2V
2.6V
3.3V
5V
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 12. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
-10
-20
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-60
Vripple = 200mVpp
Av = 2
Input = Grounded
Cb = 0.1µF, Cin = 1µF
RL >= 4
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
Vcc = 5, 3.3, 2.5 & 2.2V
100 1000 10000 100000
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 13. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. frequency
0
Vripple = 200mVpp
Av = 10
-10
Input = Grounded
Cb = Cin = 1µF
-20
RL >= 4
Ω
Tamb = 25°C
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
100 1000 10000 100000
Vcc :
2.2V
2.6V
3.3V
5V
Frequency (Hz)
9/29
Page 10

Electrical Characteristics TS4985
-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
Vcc = 2.6V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 5
Tamb = 25°C
PSRR (dB)
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
-3.0 -2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
Vcc = 3.3V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 2
Tamb = 25°C
PSRR (dB)
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
-3.0 -2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
Vcc = 3.3V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 10
Tamb = 25°C
PSRR (dB)
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 14. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Vcc = 2.6V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 2
Tamb = 25°C
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 16. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
Vcc = 2.6V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 10
Tamb = 25°C
Figure 15. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
Figure 17. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 18. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
10/29
Vcc = 2.6V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Cb = 1µF
AV = 10
Tamb = 25°C
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 19. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
Ω
Page 11

TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 20. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
PSRR (dB)
-50
-60
-70
-5-4-3-2-1012345
Vcc = 5V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 2
Tamb = 25°C
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 22. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-5-4-3-2-1012345
Vcc = 5V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 10
Tamb = 25°C
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 21. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
vs. DC output voltage
0
-10
-20
-30
PSRR (dB)
-40
-50
-60
-5-4-3-2-1012345
Vcc = 5V
Vripple = 200mVpp
RL = 8
Ω
Cb = 1µF
AV = 5
Tamb = 25°C
Differential DC Output Voltage (V)
Figure 23. Power supply rejection ratio (PSRR)
at f=217Hz vs. bypass capacitor
-30
-40
-50
Av=2
Vcc:
-60
2.6V
PSRR at 217Hz (dB)
3.3V
5V
-70
-80
0.1 1
Av=5
Vcc:
2.6V
3.3V
5V
Bypass Capacitor Cb ( F)
Av=10
Vcc:
2.6V
3.3V
5V
Tamb=25°C
Figure 24. Output power vs. power supply
voltage
Figure 25. Output power vs. power supply
voltage
11/29
Page 12

Electrical Characteristics TS4985
Figure 26. Output power vs. power supply
voltage
Figure 28. Output power vs. load resistor Figure 29. Output power vs. load resistor
Figure 27. Output power vs. load resistor
Figure 30. Power dissipation vs. output power
per channel
12/29
Figure 31. Power dissipation vs. output power
per channel
Page 13

TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
012345
0
2
4
6
8
Only One channel active
Both channels active
No Loads
Tamb=25 C
Icc (mA)
Vcc (V)
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Only one channel active
Both channels active
Vcc = 3.3V
No Loads
Tamb=25 C
Icc (mA)
Vstdb (V)
Figure 32. Power dissipation vs. output power
per channel
Figure 34. Clipping voltage vs. power supply
voltage and load resistor
Figure 33. Clipping voltage vs. power supply
voltage and load resistor
Figure 35. Current consumption vs. power
supply voltage
Figure 36. Current consumption vs. power
supply voltage
6
Vcc = 2.6V
No Loads
Tamb=25 C
5
4
3
Icc (mA)
2
1
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Figure 37. Current consumption vs. standby
voltage
Both channels active
Only one channel active
Vstdb (V)
13/29
Page 14

Electrical Characteristics TS4985
Figure 38. Current consumption vs. standby
voltage
8
7
6
5
4
Icc (mA)
3
2
1
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
Both channels active
Only one channel active
Vstdb (V)
Vcc = 5V
No Loads
Tamb=25 C
Figure 40. Output noise voltage device in
Standby
Figure 39. Output noise voltage device ON
Figure 41. THD + N vs. output power
Figure 42. THD + N vs. output power Figure 43. THD + N vs. output power
14/29
Page 15

TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 44. THD + N vs. output power Figure 45. THD + N vs. output power
Figure 46. THD + N vs. output power Figure 47. THD + N vs. output power
Figure 48. THD + N vs. output power Figure 49. THD + N vs. output power
15/29
Page 16

Electrical Characteristics TS4985
Figure 50. THD + N vs. frequency Figure 51. THD + N vs. frequency
Figure 52. THD + N vs. frequency Figure 53. Crosstalk vs. frequency
Figure 54. Crosstalk vs. frequency Figure 55. Crosstalk vs. frequency
16/29
Page 17

TS4985 Electrical Characteristics
Figure 56. Signal to noise ratio vs. power
supply with unweighted filter (20Hz
to 20kHz)
Figure 58. Signal to noise ratio vs. power
supply with unweighted filter (20Hz
to 20kHz)
Figure 57. Signal to noise ratio vs. power
supply with unweighted filter (20Hz
to 20kHz)
Figure 59. Signal to noise ratio vs. power
supply with A weighted filter (20Hz
to 20kHz)
Figure 60. Power derating curves
17/29
Page 18

Application Information TS4985
4 Application Information
The TS4985 integrates two monolithic power amplifiers with a BTL (Bridge Tied Load) output
type (explained in more detail in
will be referred to.
Section 4.1
). For this discussion, only the left-channel amplifier
Referring to the schematic in
=IN-L
V
in
V
=VO-L
out1
V
=VO+R
out2
R
= Rin-L,
in
R
=Rfeed-L
feed
C
=Cfeed-L
feed
Figure 61
, we assign the following variables and values:
Figure 61. Typical application schematic - left channel
Cfeed = Cfeed-L
GND
VCC
Cin = Cin-LInput L
Rin = Rin-L
Vin-
Vin+
+
Cb
1u
IN-L
=
IN+L
=
Bypass
VCC1
-
+
Bias
VCC2
-
AV = -1
+
+
Cs
1u
TS4985
Rfeed = Rfeed-L
VO-L
=
Vout 1
VO+L
=
Vout 2
RL
4.1 BTL configuration principle
BTL (Bridge Tied Load) means that each end of the load is connected to two single-ended
output amplifiers. Thus, we have:
Single-ended output 1 =
Single-ended output 2 =
The output power is:
For the same power supply voltage, the output power in a BTL configuration is four times higher
than the output power in a single-ended configuration.
18/29
V
out1=Vout
V
=-V
out2
2V
()
P
------------------------------------=
out
(V),
out
outRMS
R
L
(V),
2
V
out1-Vout2
=2V
out
(V)
Page 19

TS4985 Application Information
4.2 Gain in typical application schematic
The typical application schematic (
C
In the flat region (no
For the second stage:
effect), the output voltage of the first stage is:
in
V
out2
V
=-V
Figure 61
=
out1
out1
V
–in()
(V)
) is shown on
R
feed
--------------
(V)
R
in
The differential output voltage is:
R
V
out2Vout1
The differential gain, referred to as
G
v
V
is in phase with
out2
V
and
in
V
out1
–
=
G
for greater convenience, is:
v
–
V
out2Vout1
----------------------------------- 2
V
is phased 180° with
feed
2V
--------------
in
R
in
in
terminal of the loudspeaker should be connected to
4.3 Low and high frequency response
In the low frequency region,
a -3dB cut-off frequency:
C
starts to have an effect.
in
1
--------------------------
F
=
CL
2
π
RinC
(Hz)
in
page 18
(V)
R
feed
--------------==
R
in
V
. This means that the positive
in
V
and the negative to
out2
C
forms with
in
.
V
out1
R
a high-pass filter with
in
.
In the high frequency region, you can limit the bandwidth by adding a capacitor (
parallel with
The following graph (
Figure 62. Frequency response gain versus Cin & C
R
. It forms a low-pass filter with a -3dB cut-off frequency.
feed
1
-------------------------------------
=
F
CH
2
π
R
feedCfeed
Figure 62
10
5
0
-5
-10
Gain (dB)
-15
-20
-25
10 100 1000 10000
Cin = 82nF
) shows an example of
Cfeed = 330pF
Cfeed = 680pF
Cin = 470nF
Cin = 22nF
Rin = Rfeed = 22k
Tamb = 25°C
Frequency (Hz)
(Hz)
Cfeed = 2.2nF
C
Ω
and
in
feed
C
influence.
feed
F
CH
is in Hz.
C
feed
) in
19/29
Page 20

Application Information TS4985
4.4 Power dissipation and efficiency
Hypotheses:
● Voltage and current in the load are sinusoidal (V
● Supply voltage is a pure DC source (V
cc
).
Regarding the load we have:
V
out
= V
PEAK
sinωt
(V)
and
V
out
I
=
------------R
(A)
L
out
and
2
PEAK
2R
L
(W)
V
P
=
-------------------------
out
Therefore, the average current delivered by the supply voltage is:
V
I
CC
AVG
= 2
PEAK
---------------------
π
R
L
out
(A)
and I
out
).
The power delivered by the supply voltage is:
P
supply
VCCI
=
⋅
CC
AVG
W()
Then, the power dissipated by each amplifier is:
P
=
dissPsupply
22V
diss
-----------------------
=
π
P
R
CC
L
P
–
out
P
outPout
W()
–⋅
W()
and the maximum value is obtained when:
∂
P
diss
--------------------- = 0
∂
P
out
and its value is:
2
2V
cc
P
dissmax
--------------= W()
π2R
L
Note: This maximum value is only depending on power supply voltage and load values.
The efficiency, η, is the ratio between the output power and the power supply:
η
=
P
-------------------- =
P
supply
out
π
V
PEAK
------------------------4V
CC
The maximum theoretical value is reached when
π
----- = 78.5%
4
20/29
V
PEAK
=
V
, so that:
CC
Page 21

TS4985 Application Information
The TS4985 has two independent power amplifiers, and each amplifier produces heat due to its
power dissipation. Therefore, the maximum die temperature is the sum of the each amplifier’s
maximum power dissipation. It is calculated as follows:
P
P
To t al P
= Power dissipation due to the left channel power amplifier
diss L
= Power dissipation due to the right channel power amplifier
diss R
diss=Pdiss L+Pdiss R
(W)
In most cases,
P
diss L
= P
diss R
, giving:
Total P
or, stated differently:
Total P
diss
4.5 Decoupling the circuit
Two capacitors are needed to correctly bypass the TS4985. A power supply bypass capacitor
C
and a bias voltage bypass capacitor
S
C
has particular influence on the THD+N in the high frequency region (above 7kHz) and an
S
indirect influence on power supply disturbances. With a value for
similar THD+N performances to those shown in the datasheet. For example:
● In the high frequency region, if
on the power supply rail are less filtered.
● On the other hand, if
more filtered.
C
has an influence on THD+N at lower frequencies, but its function is critical to the final result
b
of PSRR (with input grounded and in the lower frequency region), in the following manner:
● If C
● If C
is lower than 1µF, THD+N increases at lower frequencies and PSRR worsens.
b
is higher than 1µF, the benefit on THD+N at lower frequencies is small, but the benefit
b
to PSRR is substantial.
C
is higher than µF, those disturbances on the power supply rail are
S
2P
=
diss
42V
CC
-----------------------P
=
π
R
L
C
B
C
is lower than 1µF, it increases THD+N and disturbances
S
dissL
–
out2Pout
.
(W)
W()
C
of 1µF, you can expect
S
Note that
C
in
C
has a non-negligible effect on PSRR at lower frequencies. The lower the value of
in
, the higher the PSRR.
4.6 Wake-up time, T
When the standby is released to put the device ON, the bypass capacitor
immediately. As
until the
C
specified in electrical characteristics table with
C
has a value other than 1µF, please refer to the graph in
If
b
time value.
C
is directly linked to the bias of the amplifier, the bias will not work properly
voltage is correct. The time to reach this voltage is called wake-up time or TWU and
b
b
WU
C
= 1µF.
b
Figure 63
C
will not be charged
b
to establish the wake-up
21/29
Page 22

Application Information TS4985
Due to process tolerances, the maximum value of wake-up time could be establish by the graph
in
Figure 64
.
Figure 63. Typical wake-up time vs. C
600
Tamb=25°C
500
400
300
200
Startup Time (ms)
100
0
0.1
Vcc=2.6V
1234
Bypass Capacitor Cb ( F)
Vcc=3.3V
Vcc=5V
b
4.7
Figure 64. Maximum wake-up time vs. C
Tamb=25°C
600
500
400
300
200
Max. Startup Time (ms)
100
0
Vcc=2.6V
1234
Bypass Capacitor Cb ( F)
Vcc=3.3V
Vcc=5V
b
4.70.1
Note: Bypass capacitor Cb as also a tolerance of typically +/-20%. To calculate the wake-up time with
this tolerance, refer to the previous graph (considering for example for C
0.8µF
≤
1µF≤1.2µF).
= 1µF in the range of
b
4.7 Shutdown time
When the standby command is set, the time required to put the two output stages in high
impedance and the internal circuitry in shutdown mode is a few microseconds.
Note: In shutdown mode, Bypass pin and Vin- pin are short-circuited to ground by internal switches.
This allows for the quick discharge of the C
and Cin capacitors.
b
4.8 Pop performance
Pop performance is intimately linked with the size of the input capacitor
bypass capacitor
The size of
size of
Moreover,
C
is dependent on THD+N and PSRR values requested at lower frequencies.
b
C
C
.
b
C
is dependent on the lower cut-off frequency and PSRR values requested. The
in
determines the speed with which the amplifier turns ON. In order to reach near
b
zero pop and click, the equivalent input constant time is:
τ
=(Rin+2kΩ)xCin (s)
in
must not reach the τ
maximum value as indicated in the graph below in
in
with
R
≥
5k
Ω
in
C
and the bias voltage
in
Figure 65
.
22/29
Page 23

TS4985 Application Information
Figure 65. τ
160
120
80
in max. (ms)
40
max. versus bypass capacitor
in
Tamb=25°C
Vcc=3.3V
Vcc=2.6V
0
1234
Bypass Capacitor Cb ( F)
Vcc=5V
By following previous rules, the TS4985 can reach near zero pop and click even with high gains
such as 20dB.
Example calculation:
With
R
=22kΩ and a 20Hz, -3db low cut-off frequency,
in
standard value which gives a lower cut-off frequency equal to 18.5Hz. In this case,
(
R
+2kΩ)x
in
C
= 9.36ms. When referring to the previous graph, if
in
read 20ms max. This value is twice as high as our current value, thus we can state that pop and
click will be reduced to its lowest value. Minimizing both
phenomena, and the cost and size of the application.
C
= 361nF. So,
in
C
and the gain benefits both the pop
in
C
=1µF and
b
C
=390nF with
in
Vcc
=5V, we
4.9 Dedicated standby control
TS4985 has two standby control inputs to allow to put each channel in standby mode
independently. In case a channel is active and another one in standby mode It’s very important
to be in line with a following recommendation to reach near zero pop. When left (right) channel
is active and right (left) channel is in standby mode it's necessary to put active channel in
standby mode first and then immediately (with regard to Standby time) activate right (left)
channel or both channels together in at the same moment.
4.10 Application example: differential-input BTL power stereo amplifier
The schematic in
For this discussion, only the left-channel amplifier will be referred to.
Let:
R
C
The gain of the amplifier is:
Figure 65
1R=R2L=R1
= C
inR
inL=Cin
shows how to design the TS4985 to work in differential-input mode.
, R2R=R2L=R
2
Gvdif = 2
R2
-------
×
R1
23/29
Page 24

Application Information TS4985
In order to reach the optimal performance of the differential function,
matched at 1% maximum.
Figure 66. Differential input amplifier configuration
Neg. I nput LEFT
Pos. Input LEFT
Pos. Input RIGHT
Neg. Inpu t RIGH T
CinR
CinR
StandBy L
Control
StandBy R
Control
R1LCinL
R1LCinL
R1R
R1R
R2L
R2R
+
Cb
R2L
IN-L
IN+L
StandBy L
Bypass
IN+R
IN-R
StandBy R
R2R
VCC
VCC1GND1
-
+
Bias
+
-
-
+
-
+
GND2 VCC2
AV = -1
AV = -1
U1
TS498 5
VO-L
VO+L
VO-R
VO+R
R
1
+
Cs
LEFT Spe aker
8 Ohms
RIGHT Speaker
8 Ohms
and
R
should be
2
The value of the input capacitor
lower frequency required (where
Note: This formula is true only if:
is 5 times lower than FL.
The following bill of materials (
a gain of 2 and a -3dB lower cut-off frequency of about 80Hz.
Table 8. Example of a bill of materials
Designator Part Type
R
= R
1L
1R
= R
R
2L
2R
= C
C
inR
inL
C
b=CS
U1 TS4985
C
can be calculated with the following formula, using the -3dB
IN
F
is the lower frequency required):
L
1
C
F
CB
Tabl e 8
≈
IN
π
=
) is provided as an example of a differential amplifier with
)F(
FR2
L1
1
+π
)Hz(
C)RR(2
B21
20kΩ / 1%
20kΩ / 1%
100nF
1µF
24/29
Page 25

TS4985 Application Information
4.11 Demoboard
A demoboard for the TS4985 in flip-chip package is available.
For more information about this demoboard, please refer to Application Note AN2152, which
can be found on www.st.com.
Figure 67
shows the schematic of the demoboard.
Figure 68, Figure 69
component locations, top layer and bottom layer respectively.
Figure 67. Demoboard schematic
C2
1 2
R2
21
22K
VCC
Cn9
1
Vcc
InputL
InputR
GND
GND
GND
neg.
GND
pos.
2
GND
C1
Cn1
1
neg
2
Cn3
1
pos.
2
Cn4
1
2
Cn6
1
2
1 2
100nF
C3
1 2
C4
1 2
100nF
C6
1 2
R1
21
22K
R3
21
Cn7
Jumper J1
StandByL
Cn8
Jumper J2
StandByR
R4
21
22K
R6
21
21
R8
R7
2 1
IN-L
6
-
5
IN+L
+
VCC
1
STDB YL
2
15
3
STDBYR
IN-R
IN+R
Bypass
Bias
-
+
VCC
1
8
2
3
13
14
7
VCC1GND1
12
C7
1uF
210
-
AV = -1
+
-
AV = -1
+
12
C8
100nF
TS4985_FC_ADAPTER
VO-L
VO+L
VO-R
VO+R
and
U1
4
3
11
12
Figure 70
show the
Cn2
2
neg.
1
pos.
OUTL
Cn5
2
neg.
1
pos.
OUTR
12
C9
1uF
R5
21
22K
C5
1 2
GND2 VCC2
9 1
25/29
Page 26

Application Information TS4985
Figure 68. Component locations
Figure 69. Top layer
Figure 70. Bottom layer
26/29
Page 27

TS4985 Package Mechanical Data
5 Package Mechanical Data
Figure 71. Pinout (top view)
6
6
5
5
VCC1
VCC1
VCC1
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
IN-L
IN-L
IN-L
VCC2
VCC2
VCC2
VO+L
VO+L
VO+L
IN+L
IN+L
IN+L
STDBYL
STDBYL
STDBYL
BYPASS
BYPASS
BYPASS
STDBYR
STDBYR
STDBYR
IN+R
IN+R
IN+R
VO+R
VO+R
VO+R
GND2
GND2
GND2
IN-R
IN-R
IN-R
VO-RVO-L
VO-RVO-L
VO-RVO-L
GND1
GND1
GND1
ABCDE
ABCDE
Figure 72. Marking (top view)
XXX
XXX
YWW
YWW
Note: Balls are underneath
E
E
Marking shows:
■ ST Logo
■ Product & assembly code: XXX
- A85 from Tours
- 858 from Singapore
- 85K from Shenzhen
■ 3-digit datecode: YWW
■ “E” lead-free symbol
■ The dot marks position of pin A1
27/29
Page 28

Package Mechanical Data TS4985
Figure 73. Package mechanical data for 15-bump flip-chip
2.40 mm
2.40 mm
■ Die size: 2.40 x 1.90 mm ±30µm
0.25m
0.25m
m
m
0.5mm
0.5mm
1.90 mm
1.90 mm
∅ 0.3mm
∅ 0.3mm
0.86mm
0.86mm
60 µm Back coating *
60 µm Back coating *
600 µm
600 µm
* Optional
* Optional
Figure 74. Tape & Reel specification (top view)
■ Die height (including bumps): 600µm
■ Back coating height (optional): 60µm
■ Bump diameter: 315µm ±50µm
■ Bump diameter before reflow: 300µm
±10µm
■ Bump height: 250µm ±40µm
■ Die height: 350µm ±20µm
■ Pitch: 500µm ±50µm
■ Coplanarity: 60µm max.
1.5
4
4
1
1
1
A
A
8
8
Die size Y + 70µm
Die size Y + 70µm
Die size X + 70µm
Die size X + 70µm
4
4
All dimensi ons are in mm
All dimensi ons are in mm
User direction of feed
User direction of feed
1
A
A
1.5
28/29
Page 29

TS4985 Revision History
6 Revision History
Date Revision Changes
November 2004 1 First Release corresponding to the product preview version
May 2005 2 Product in full production
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringe ment of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is
granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are
subject to change withou t notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products
are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All righ ts reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
29/29
Page 30

 Loading...
Loading...