®
HIGH EFFICIENCY ULTRAFAST DIODE
Table 1: Main Product Characteristics
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
T
(max) 175°C
j
V
(max) 0.78 V
F
(max) 20 ns
t
rr
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
■ Very low conduction losses
■ Negligible switching losses
■ Low forward and reverse recovery times
■ High junction temperature
DESCRIPTION
The STTH102, which is using ST’s new 200V
planar technology, is specially suited for switching
mode base drive and transistor circuits.
The device is also intended for use as a free
wheeling diode in power supplies and other power
switching applications.
1 A
200 V
SMA
(JEDEC DO-214AC)
STTH102A
Table 2: Order Codes
Part Number Marking
STTH102A U12
STTH102 STTH102
STTH102RL STTH102
STTH102
DO-41
STTH102
Table 3: Absolute Ratings (limiting values)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
T
T
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 200 V
Average forward current
Surge non repetitive forward
current
Storage temperature range -65 to + 175 °C
stg
Maximum operating junction temperature 175 °C
j
DO-41 T
SMA
DO-41 50
SMA T
= 148°C δ = 0.5
L
= 130°C δ = 0.5
L
tp = 10 ms Sinusoidal
1A
40
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage 10000 V/µs
June 2005
REV. 4
A
1/6
STTH102
Table 4: Thermal Resistance
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th(j-l)
Junction to lead
Lead length = 10 mm DO-41 50
Table 5: Static Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Tests conditions Min. Typ Max. Unit
= 25°C
T
I
*
R
V
F
Reverse leakage current
**
Forward voltage drop
j
T
= 125°C
j
= 25°C
T
j
= 125°C IF = 1A
T
j
Pulse test: * tp = 5 ms, δ < 2%
** tp = 380 µs,
δ < 2%
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation: P = 0.65 x I
V
= V
R
= 700 mA
I
F
(SMA)
= 1A
I
F
F(AV)
SMA 30
RRM
0.68 0.78
+ 0.130 I
F2(RMS)
°C/W
1
125
0.90
0.97
µA
V
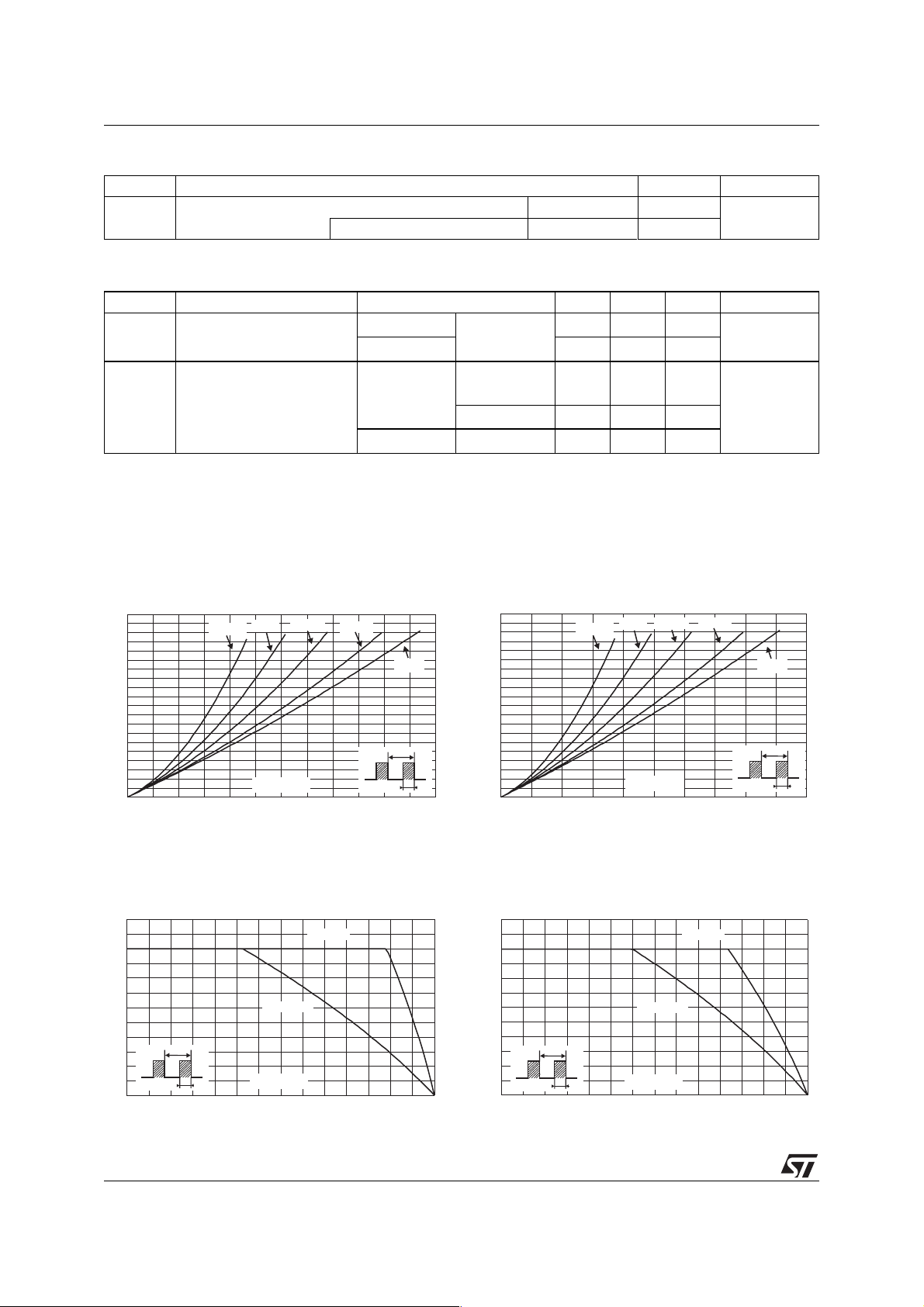
Figure 1: Average forward power dissipation
versus average forward current (SMA)
P (W)
F(AV)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
I (A)
F(AV)
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 3: Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (δ = 0.5) (SMA)
I (A)
F(AV)
1.2
1.0
0.8
R=R
th(j-a) th(j-I)
Figure 2: Average forward power dissipation
versus average forward current (DO-41)
P (W)
F(AV)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
I (A)
F(AV)
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 4: Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (δ = 0.5) (DO-41)
I (A)
F(AV)
1.2
1.0
0.8
R=R
th(j-a) th(j-I)
R =120°C/W
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
th(j-a)
T (°C)
amb
2/6
R =110°C/W
0.6
0.4
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
0.2
0.0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
th(j-a)
T (°C)
amb

STTH102
Figure 5: Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient versus pulse
duration (epoxy printed circuit board,
e(Cu)=35µm, recommended pad layout) (SMA)
Z/R
th(j-c) th(j-c)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
δ = 0.5
0.5
0.4
δ = 0.2
0.3
δ = 0.1
0.2
0.1
Single pulse
0.0
1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03
t (s)
p
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
Figure 7: Forward voltage drop versus forward
current
I (A)
FM
100.0
T =125°C
j
(maximum values)
10.0
1.0
T =125°C
j
(typical values)
T =25°C
j
(maximum values)
Figure 6: Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient versus pulse
duration (DO-41)
Z/R
th(j-c) th(j-c)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
δ = 0.5
0.5
0.4
0.3
δ = 0.2
0.2
δ = 0.1
0.1
Single pulse
0.0
1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03
t (s)
p
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
Figure 8: Junction capacitance versus reverse
voltage applied (typical values)
C(pF)
100
10
F=1MHz
V =30mV
OSC RMS
T =25°C
j
V (V)
0.1
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2 2.4
FM
Figure 9: Reverse recovery time versus dI
(90% confidence)
t (ns)
rr
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
1 10 100 1000
T =125°C
j
T =25°C
j
dI /dt(A/µs)
F
I =1A
F
V =100V
R
T =125°C
j
V (V)
1
1 10 100 1000
/dt
F
Figure 10: Peak recovery current versus dIF/dt
R
(90% confidence)
I (A)
RM
3.5
I =1A
F
V =100V
R
T =125°C
3.0
j
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
1 10 100 1000
T =125°C
j
dI /dt(A/µs)
F
T =25°C
j
3/6

STTH102
Figure 11: Reverse recovery charges versus
/dt (90% confidence)
dI
F
Q (nC)
rr
35.0
32.5
I =1A
F
V =100V
R
30.0
27.5
25.0
22.5
20.0
17.5
15.0
12.5
10.0
7.5
5.0
2.5
0.0
1 10 100 1000
T =125°C
j
dI /dt(A/µs)
F
T =25°C
j
Figure 13: Thermal resistance junction to
ambient versus copper surface under each
lead (Epoxy printed circuit board FR4, copper
thickness: 35µm) (SMA)
R (°C/W)
th(j-a)
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
S(cm²)
Figure 12: Relative variations of dynamic
parameters versus junction temperature
I;t;Q[T] /
RM rr rr j
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
I=I
F F(AV)
dI /dt=200A/µs
F
V =100V
R
25 50 75 100 125 150 175
I ; t ; Q [T =25°C]
RM rr rr j
T (°C)
j
Q
RR
t
rr
I
RM
Figure 14: Thermal resistance versus lead
length (DO-41)
R (°C/W)
th
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
5 10152025
R
th(j-a)
R
th(j-I)
L (mm)
leads
4/6

Figure 15: SMA Package Mechanical Data
STTH102
DIMENSIONS
E1
D
E
A1
C
L
A2
Figure 16: SMA Foot Print Dimensions
(in millimeters)
REF.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
A1 1.90 2.03 0.075 0.080
A2 0.05 0.20 0.002 0.008
b 1.25 1.65 0.049 0.065
c 0.15 0.41 0.006 0.016
E 4.80 5.60 0.189 0.220
E1 3.95 4.60 0.156 0.181
b
D 2.25 2.95 0.089 0.116
L 0.75 1.60 0.030 0.063
1.45 1.45
2.40
1.65
5/6

STTH102
Figure 17: DO-41 Package Mechanical Data
CA
O
/
D
C
O
/
D
/
BO
DIMENSIONS
REF.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Max. Min. Max.
A 4.07 5.20 0.160 0.205
B 2.04 2.71 0.080 0.107
C28 1.102
D 0.712 0.863 0.028 0.034
Table 6: Ordering Information
Ordering type Marking Package Weight Base qty Delivery mode
STTH102A U12 SMA 0.068 g 5000 Tape & reel
STTH102 STTH102 DO-41 0.34 g 2000 Ammopack
STTH102RL STTH102 DO-41 0.34 g 5000 Tape & reel
■ Band indicates cathode
■ Epoxy meets UL94, V0
Table 7: Revision History
Date Revision Description of Changes
Jul-2003 2A Last update.
1. SMA package dimensions update. Reference A1 max.
Aug-2004 3
changed from 2.70mm (0.106inc.) to 2.03mm (0.080).
2. SMA and DO-41 datasheets merged
27-Jun-2005 4 Corrected error in title.
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
6/6
 Loading...
Loading...