STMicroelectronics STM32MP157C, STM32MP157F Datasheet
Arm® dual Cortex®-A7 800 MHz + Cortex®-M4 MPU, 3D GPU,
LFBGA
TFBGA361 (12 × 12 mm)
TFBGA257 (10 × 10 mm)
min Pitch 0.5mm
TFBGA
LFBGA448 (18 × 18mm)
LFBGA354 (16 × 16mm)
Pitch 0.8mm
TFT/DSI, 37 comm. interfaces, 29 timers, adv. analog, crypto
Features
Core
• 32-bit dual-core Arm® Cortex®-A7
– L1 32-Kbyte I / 32-Kbyte D for each core
– 256-Kbyte unified level 2 cache
–Arm
• 32-bit Arm
– Up to 209 MHz (Up to 703 CoreMark
Memories
• External DDR memory up to 1 Gbyte
– up to LPDDR2/LPDDR3-1066 16/32-bit
– up to DDR3/DDR3L-1066 16/32-bit
• 708 Kbytes of internal SRAM: 256 Kbytes of
AXI SYSRAM + 384 Kbytes of AHB SRAM +
64 Kbytes of AHB SRAM in Backup domain
and 4 Kbytes of SRAM in Backup domain
• Dual mode Quad-SPI memory interface
• Flexible external memory controller with up to
16-bit data bus: parallel interface to connect
external ICs and SLC NAND memories with up
to 8-bit ECC
Security/safety
• Secure boot, TrustZone® peripherals, active
tamper
• Cortex
Reset and power management
• 1.71 V to 3.6 V I/Os supply (5 V-tolerant I/Os)
• POR, PDR, PVD and BOR
• On-chip LDOs (RETRAM, BKPSRAM, DSI
1.2 V, USB 1.8 V, 1.1 V)
• Backup regulator (~0.9 V)
• Internal temperature sensors
• Low-power modes: Sleep, Stop and Standby
®
NEON™ and Arm® TrustZone®
®
Cortex®-M4 with FPU/MPU
®
-M4 resources isolation
®
)
STM32MP157C/F
Datasheet - production data
• DDR memory retention in Standby mode
• Controls for PMIC companion chip
Low-power consumption
• Total current consumption down to 2 µA
(Standby mode, no RTC, no LSE, no
BKPSRAM, no RETRAM)
Clock management
• Internal oscillators: 64 MHz HSI oscillator,
4 MHz CSI oscillator, 32 kHz LSI oscillator
• External oscillators: 8-48 MHz HSE oscillator,
32.768 kHz LSE oscillator
• 6 × PLLs with fractional mode
General-purpose input/outputs
• Up to 176 I/O ports with interrupt capability
– Up to 8 secure I/Os
– Up to 6 Wakeup, 3 tampers, 1 active
tamper
Interconnect matrix
• 2 bus matrices
–64-bit Arm
266 MHz
–32-bit Arm
to 209 MHz
3 DMA controllers to unload the CPU
• 48 physical channels in total
• 1 × high-speed general-purpose master direct
memory access controller (MDMA)
®
AMBA® AXI interconnect, up to
®
AMBA® AHB interconnect, up
December 2020 DS12505 Rev 5 1/260
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com

STM32MP157C/F
• 2 × dual-port DMAs with FIFO and request
router capabilities for optimal peripheral
management
Up to 37 communication peripherals
• 6 × I2C FM+ (1 Mbit/s, SMBus/PMBus)
• 4 × UART + 4 × USART (12.5 Mbit/s, ISO7816
interface, LIN, IrDA, SPI slave)
• 6 × SPI (50 Mbit/s, including 3 with full duplex
2
I
S audio class accuracy via internal audio PLL
or external clock)
• 4 × SAI (stereo audio: I
• SPDIF Rx with 4 inputs
• HDMI-CEC interface
• MDIO Slave interface
• 3 × SDMMC up to 8-bit (SD / e•MMC
• 2 × CAN controllers supporting CAN FD
protocol, out of which one supports timetriggered CAN (TTCAN)
• 2 × USB 2.0 high-speed Host
+ 1 × USB 2.0 full-speed OTG simultaneously
– or 1 × USB 2.0 high-speed Host
+ 1 × USB 2.0 high-speed OTG
simultaneously
• 10/100M or Gigabit Ethernet GMAC
– IEEE 1588v2 hardware,
MII/RMII/GMII/RGMII
• 8- to 14-bit camera interface up to 140 Mbyte/s
2
S, PDM, SPDIF Tx)
™
/ SDIO)
– Pixel clock up to 90 MHz
– Two layers with programmable colour LUT
• MIPI
®
DSI 2 data lanes up to 1 GHz each
Up to 29 timers and 3 watchdogs
• 2 × 32-bit timers with up to 4 IC/OC/PWM or
pulse counter and quadrature (incremental)
encoder input
• 2 × 16-bit advanced motor control timers
• 10 × 16-bit general-purpose timers (including 2
basic timers without PWM)
• 5 × 16-bit low-power timers
• RTC with sub-second accuracy and hardware
calendar
• 2 × 4 Cortex
®
-A7 system timers (secure, non-
secure, virtual, hypervisor)
• 1 × SysTick M4 timer
• 3 × watchdogs (2 × independent and window)
Hardware acceleration
• AES 128, 192, 256, TDES
• HASH (MD5, SHA-1, SHA224, SHA256),
HMAC
• 2 × true random number generator
(3 oscillators each)
• 2 × CRC calculation unit
Debug mode
6 analog peripherals
• 2 × ADCs with 16-bit max. resolution (12 bits
up to 4.5 Msps, 14 bits up to 4 Msps, 16 bits up
to 3.6 Msps)
• 1 × temperature sensor
• Arm® CoreSight™ trace and debug: SWD and
• 8-Kbyte embedded trace buffer
3072-bit fuses including 96-bit unique ID,
up to 1184-bit available for user
• 2 × 12-bit D/A converters (1 MHz)
• 1 × digital filters for sigma delta modulator
All packages are ECOPACK2 compliant
(DFSDM) with 8 channels/6 filters
• Internal or external ADC/DAC reference V
REF+
Graphics
• 3D GPU: Vivante
®
- OpenGL
– Up to 26 Mtriangle/s, 133 Mpixel/s
• LCD-TFT controller, up to 24-bit // RGB888
– up to WXGA (1366 × 768) @60 fps or up to
Full HD (1920 × 1080) @30 fps
2/260 DS12505 Rev 5
®
ES 2.0
JTAG interfaces

STM32MP157C/F Contents
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3 Functional overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.1 Dual-core Arm® Cortex®-A7 subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.1.2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2 Arm® Cortex®-M4 with FPU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.3 Graphic processing unit (GPU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.4 Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.4.1 External SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.4.2 Embedded SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.5 DDR3/DDR3L/LPDDR2/LPDDR3 controller (DDRCTRL) . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.6 TrustZone address space controller for DDR (TZC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.7 Boot modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3.8 Power supply management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.8.1 Power supply scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.8.2 Power supply supervisor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
3.9 Low-power strategy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.10 Reset and clock controller (RCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.10.1 Clock management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.10.2 System reset sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.11 Hardware semaphore (HSEM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.12 Inter-processor communication controller (IPCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.12.1 IPCC main features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.13 General-purpose input/outputs (GPIOs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.14 TrustZone protection controller (ETZPC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.15 Bus-interconnect matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
3.16 DMA controllers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.17 Nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.18 Extended interrupt and event controller (EXTI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
DS12505 Rev 5 3/260
7

Contents STM32MP157C/F
3.19 Cyclic redundancy check calculation unit (CRC1, CRC2) . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.20 Flexible memory controller (FMC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.21 Dual Quad-SPI memory interface (QUADSPI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.22 Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.23 Temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.24 Digital temperature sensor (DTS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.25 V
operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
BAT
3.26 Digital-to-analog converters (DAC1, DAC2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.27 Voltage reference buffer (VREFBUF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3.28 Digital filter for sigma delta modulators (DFSDM1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3.29 Digital camera interface (DCMI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.30 LCD-TFT display controller (LTDC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.31 Display serial interface (DSI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3.32 True random number generator (RNG1, RNG2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3.33 Cryptographic and hash processors (CRYP1, CRYP2 and
HASH1, HASH2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.34 Boot and security and OTP control (BSEC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.35 Timers and watchdogs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.35.1 Advanced-control timers (TIM1, TIM8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3.35.2 General-purpose timers (TIM2, TIM3, TIM4, TIM5, TIM12, TIM13,
TIM14, TIM15, TIM16, TIM17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3.35.3 Basic timers TIM6 and TIM7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.35.4 Low-power timer (LPTIM1, LPTIM2, LPTIM3, LPTIM4, LPTIM5) . . . . . 49
3.35.5 Independent watchdog (IWDG1, IWDG2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.35.6 System window watchdog (WWDG1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.35.7 SysTick timer (Cortex-M4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.35.8 Generic timers (Cortex-A7 CNT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3.36 System timer generation (STGEN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3.37 Real-time clock (RTC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3.38 Tamper and backup registers (TAMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3.39 Inter-integrated circuit interface (I2C1, I2C2, I2C3, I2C4, I2C5, I2C6) . . . 53
3.40 Universal synchronous asynchronous receiver transmitter
(USART1, USART2, USART3, USART6 and UART4, UART5,
UART7, UART8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3.41 Serial peripheral interface (SPI1, SPI2, SPI3, SPI4, SPI5,
SPI6)– inter- integrated sound interfaces (I2S1, I2S2, I2S3) . . . . . . . . . . 54
4/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Contents
3.42 Serial audio interfaces (SAI1, SAI2, SAI3, SAI4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.43 SPDIF receiver interface (SPDIFRX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.44 Management data input/output (MDIOS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.45 Secure digital input/output MultiMediaCard interface
(SDMMC1, SDMMC2, SDMMC3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.46 Controller area network (FDCAN1, FDCAN2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.47 Universal serial bus high-speed host (USBH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.48 USB on-the-go high-speed (OTG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.49 Gigabit Ethernet MAC interface (ETH1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
3.50 High-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) – Consumer
electronics control (CEC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3.51 Debug infrastructure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4 Pinouts, pin description and alternate functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
5 Memory mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
6 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1 Parameter conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.1 Minimum and maximum values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.2 Typical values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.3 Typical curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.4 Loading capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.5 Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.1.6 Power supply scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
6.1.7 Current consumption measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
6.2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
6.3 Operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
6.3.1 General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
6.3.2 Operating conditions at power-up / power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
6.3.3 Embedded reset and power control block characteristics . . . . . . . . . . 131
6.3.4 Embedded reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
6.3.5 Embedded regulators characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
6.3.6 Supply current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
6.3.7 Wakeup time from low-power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
6.3.8 External clock source characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
DS12505 Rev 5 5/260
7

Contents STM32MP157C/F
6.3.9 External clock source security characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
6.3.10 Internal clock source characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
6.3.11 PLL characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
6.3.12 PLL spread spectrum clock generation (SSCG) characteristics . . . . . 161
6.3.13 Memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
6.3.14 EMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
6.3.15 Absolute maximum ratings (electrical sensitivity) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
6.3.16 I/O current injection characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
6.3.17 I/O port characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
6.3.18 NRST and NRST_CORE pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
6.3.19 FMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
6.3.20 QUADSPI interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
6.3.21 Delay block (DLYB) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
6.3.22 16-bit ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
6.3.23 DAC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
6.3.24 Voltage reference buffer characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
6.3.25 Temperature sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.26 DTS characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.27 VBAT ADC monitoring characteristics and charging characteristics . . 210
6.3.28 Temperature and VBAT monitoring characteristics for
tamper detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
6.3.29 VDDCORE monitoring characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.3.30 Voltage booster for analog switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.3.31 Compensation cell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.3.32 Digital filter for sigma-delta modulators (DFSDM) characteristics . . . . 211
6.3.33 Camera interface (DCMI) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
6.3.34 LCD-TFT controller (LTDC) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
6.3.35 Timer characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
6.3.36 Communications interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
6.3.37 USART interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
6.3.38 USB High-Speed PHY characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
6.3.39 DSI PHY characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
6.3.40 JTAG/SWD interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
7 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
7.1 TFBGA257 package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
7.2 LFBGA354 package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
6/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Contents
7.3 TFBA361 package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
7.4 LFBGA448 package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
7.5 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
7.5.1 Reference documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 254
8 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
9 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
DS12505 Rev 5 7/260
7

List of tables STM32MP157C/F
List of tables
Table 1. STM32MP157C/F features and peripheral counts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 2. Boot modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 3. System versus domain power mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 4. Timer feature comparison. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 5. USART features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 6. Legend/abbreviations used in the pinout table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Table 7. STM32MP157C/F pin and ball definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 8. Alternate function AF0 to AF7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Table 9. Alternate function AF8 to AF15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Table 10. Voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Table 11. Current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Table 12. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 13. General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 14. Operating conditions at power-up / power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Table 15. Embedded reset and power control block characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 16. Embedded reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Table 17. Embedded reference voltage calibration value. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Table 18. REG1V1 embedded regulator (USB_PHY) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Table 19. REG1V2 embedded regulator (DSI) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Table 20. REG1V8 embedded regulator (USB+DSI) characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Table 21. Current consumption (IDDCORE) in Run mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Table 22. Current consumption (IDD) in Run mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Table 23. Current consumption in Stop mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Table 24. Current consumption in LPLV-Stop mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Table 25. Current consumption in Standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Table 26. Current consumption in VBAT mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Table 27. Low-power mode wakeup timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Table 28. Wakeup time using USART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Table 29. High-speed external user clock characteristics
(digital bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Table 30. High-speed external user clock characteristics
(analog bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Table 31. Low-speed external user clock characteristics
(analog bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Table 32. Low-speed external user clock characteristics (digital bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Table 33. 8-48 MHz HSE oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Table 34. Low-speed external user clock characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Table 35. High-speed external user clock security system (HSE CSS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 36. HSI oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 37. CSI oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Table 38. LSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Table 39. PLL1_1600, PLL2_1600 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Table 40. PLL3_800, PLL4_800 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Table 41. USB_PLL characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Table 42. DSI_PLL characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Table 43. SSCG parameters constraint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Table 44. OTP characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Table 45. DC specifications – DDR3 or DDR3L mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
8/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F List of tables
Table 46. DC specifications – LPDDR2 or LPDDR3 mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Table 47. EMS characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Table 48. EMI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Table 49. ESD absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Table 50. Electrical sensitivities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Table 51. I/O current injection susceptibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Table 52. I/O static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Table 53. Output voltage characteristics for all I/Os except PC13, PC14, PC15 and PI8 . . . . . . . . 169
Table 54. Output voltage characteristics for PC13, PC14, PC15 and PI8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Table 55. Output timing characteristics (HSLV OFF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Table 56. Output timing characteristics (HSLV ON, _h IO structure) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Table 57. Output timing characteristics (HSLV ON, _vh IO structure) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Table 58. NRST and NRST_CORE pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Table 59. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR read timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Table 60. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR read - NWAIT timings . . . . . . . . . . 178
Table 61. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR write timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Table 62. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR write - NWAIT timings. . . . . . . . . . 180
Table 63. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR read timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Table 64. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR read-NWAIT timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Table 65. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR write timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Table 66. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR write-NWAIT timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Table 67. Synchronous multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Table 68. Synchronous multiplexed PSRAM write timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Table 69. Synchronous non-multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Table 70. Synchronous non-multiplexed PSRAM write timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Table 71. Switching characteristics for NAND Flash read cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Table 72. Switching characteristics for NAND Flash write cycles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Table 73. QUADSPI characteristics in SDR mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Table 74. QUADSPI characteristics in DDR mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Table 75. Dynamics characteristics: Delay block characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Table 76. ADC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Table 77. Minimum sampling time versus RAIN with 47 pF PCB capacitor
up to 125 °C and VDDA = 1.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Table 78. ADC accuracy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
Table 79. Minimum delay for interleaved conversion versus resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Table 80. DAC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Table 81. DAC accuracy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Table 82. VREFBUF characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Table 83. Temperature sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Table 84. Temperature sensor calibration values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Table 85. DTS characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Table 86. V
Table 87. V
ADC monitoring characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
BAT
charging characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
BAT
Table 88. Temperature and VBAT monitoring characteristics for temper detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
Table 89. V
DDCORE
monitoring characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Table 90. Voltage booster for analog switch characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Table 91. Compensation cell characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
Table 92. DFSDM measured timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Table 93. DCMI characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Table 94. LTDC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Table 95. TIMx characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Table 96. LPTIMx characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
DS12505 Rev 5 9/260
10

List of tables STM32MP157C/F
Table 97. Minimum i2c_ker_ck frequency in all I2C modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Table 98. I2C analog filter characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
Table 99. I2C FM+ pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
Table 100. SPI dynamic characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Table 101. I2S dynamic characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Table 102. SAI characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Table 103. MDIOS timing parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Table 104. Dynamic characteristics: SD / MMC / e•MMC characteristics,
VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Table 105. Dynamic characteristics: SD / MMC / e•MMC characteristics
VDD = 1.71 V to 1.9 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Table 106. USB OTG_FS electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Table 107. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC timings for MDIO/SMA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Table 108. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC timings for RMII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Table 109. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC timings for MII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Table 110. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC signals for GMII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Table 111. Dynamics characteristics: Ethernet MAC signals for RGMII . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Table 112. USART characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Table 113. USB High-Speed PHY characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Table 114. DSI PHY characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Table 115. Dynamics characteristics: JTAG characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Table 116. Dynamics characteristics: SWD characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Table 117. TFBGA257 - Mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
Table 118. TFBGA257 - Recommended PCB design rules (0.5/0.65 mm pitch, BGA) . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Table 119. LFBGA354 - Mechanical data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Table 120. LFBGA354 - Recommended PCB design rules (0.8 mm pitch, BGA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Table 121. TFBGA361 - Mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Table 122. TFBGA361 - Recommended PCB design rules (0.5/0.65 mm pitch BGA) . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
Table 123. LFBGA448 - Mechanical data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Table 124. LFBGA448 - Recommended PCB design rules (0.8 mm pitch, BGA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
Table 125. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Table 126. STM32MP157C/F ordering information scheme. . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
Table 127. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
10/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. STM32MP157C/F block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 2. Power-up/down sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 3. STM32MP157C/F bus matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 4. Voltage reference buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 5. STM32MP157C/FADxx TFBGA257 pinout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 6. STM32MP157C/FABxx LFBGA354 pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 7. STM32MP157C/FACxx TFBGA361 pinout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Figure 8. STM32MP157C/FAAxx LFBGA448 pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 9. Pin loading conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Figure 10. Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Figure 11. Power supply scheme. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Figure 12. Current consumption measurement scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Figure 13. VDDCORE rise time from reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Figure 14. VDDCORE rise time from LPLV-Stop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Figure 15. High-speed external clock source AC timing diagram (digital bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Figure 16. High-speed external clock source AC timing diagram (analog bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Figure 17. Low-speed external clock source AC timing diagram (analog bypass) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Figure 18. Low-speed external clock source AC timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Figure 19. Typical application with a 24 MHz crystal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Figure 20. Typical application with a 32.768 kHz crystal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Figure 21. PLL output clock waveforms in center spread mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Figure 22. PLL output clock waveforms in down spread mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Figure 23. VIL/VIH for FT I/Os . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Figure 24. Recommended NRST and NRST_CORE pin protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Figure 25. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR read waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Figure 26. Asynchronous non-multiplexed SRAM/PSRAM/NOR write waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Figure 27. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR read waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Figure 28. Asynchronous multiplexed PSRAM/NOR write waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Figure 29. Synchronous multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Figure 30. Synchronous multiplexed PSRAM write timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Figure 31. Synchronous non-multiplexed NOR/PSRAM read timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Figure 32. Synchronous non-multiplexed PSRAM write timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Figure 33. NAND controller waveforms for read access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Figure 34. NAND controller waveforms for write access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Figure 35. NAND controller waveforms for common memory read access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Figure 36. NAND controller waveforms for common memory write access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Figure 37. QUADSPI timing diagram - SDR mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Figure 38. QUADSPI timing diagram - DDR mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Figure 39. ADC accuracy characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Figure 40. Typical connection diagram using the ADC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Figure 41. 12-bit buffered /non-buffered DAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Figure 42. Channel transceiver timing diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
Figure 43. DCMI timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
Figure 44. LCD-TFT horizontal timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Figure 45. LCD-TFT vertical timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Figure 46. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
Figure 47. SPI timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA = 1
Figure 48. SPI timing diagram - master mode
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
DS12505 Rev 5 11/260
12

List of figures STM32MP157C/F
Figure 49. I2S slave timing diagram (Philips protocol)
Figure 50. I2S master timing diagram (Philips protocol)
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Figure 51. SAI master timing waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Figure 52. SAI slave timing waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Figure 53. MDIOS timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
Figure 54. SDIO high-speed mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Figure 55. SD default mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Figure 56. DDR mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Figure 57. Ethernet MDIO/SMA timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Figure 58. Ethernet RMII timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
Figure 59. Ethernet MII timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Figure 60. Ethernet GMII timing diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Figure 61. Ethernet RGMII timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Figure 62. JTAG timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Figure 63. SWD timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Figure 64. TFBGA257 - Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Figure 65. TFBGA257 - Recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
Figure 66. TFBGA257 marking (package top view). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Figure 67. LFBGA354 - Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 243
Figure 68. LFBGA354 - Recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 244
Figure 69. LFBGA354 marking (package top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Figure 70. TFBGA361 - Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Figure 71. TFBGA361 - Recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
Figure 72. TFBGA361 marking (package top view). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
Figure 73. LFBGA448 - Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 250
Figure 74. LFBGA448 - Recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 251
Figure 75. LFBGA448 marking (package top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
12/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Introduction
1 Introduction
This datasheet provides the ordering information and mechanical device characteristics of
the STM32MP157C/F microprocessors.
This document should be read in conjunction with the STM32MP157 reference manual
(RM0436), available from the STMicroelectronics website www.st.com.
For information on the Arm
and Cortex
®
-M4 Technical Reference Manuals.
®(a)
Cortex®-A7 and Cortex®-M4 cores, refer to the Cortex®-A7
a. Arm is a registered trademark of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the US and/or elsewhere.
DS12505 Rev 5 13/260
59

Description STM32MP157C/F
2 Description
The STM32MP157C/F devices are based on the high-performance dual-core Arm®
®
Cortex
includes a 32-Kbyte L1 instruction cache for each CPU, a 32-Kbyte L1 data cache for each
CPU and a 256-Kbyte level2 cache. The Cortex-A7 processor is a very energy-efficient
application processor designed to provide rich performance in high-end wearables, and
other low-power embedded and consumer applications. It provides up to 20% more single
thread performance than the Cortex-A5 and provides similar performance than the CortexA9.
-A7 32-bit RISC core operating at up to 800 MHz. The Cortex-A7 processor
The Cortex-A7 incorporates all features of the high-performance Cortex-A15 and CortexA17 processors, including virtualization support in hardware, NEON
™
, and 128-bit AMBA®4
AXI bus interface.
The STM32MP157C/F devices also embed a Cortex
to 209 MHz frequency. Cortex-M4 core features a floating point unit (FPU) single precision
which supports Arm
®
Cortex
-M4 supports a full set of DSP instructions and a memory protection unit (MPU)
®
single-precision data-processing instructions and data types. The
®
-M4 32-bit RISC core operating at up
which enhances application security.
The STM32MP157C/F devices also embed a 3D graphic processing unit
(Vivante
®
- OpenGL® ES 2.0) running at up to 533 MHz, with performances up to 26
Mtriangle/s, 133 Mpixel/s.
The STM32MP157C/F devices provide an external SDRAM interface supporting external
memories up to 8-Gbit density (1 Gbyte), 16 or 32-bit LPDDR2/LPDDR3 or DDR3/DDR3L
up to 533 MHz.
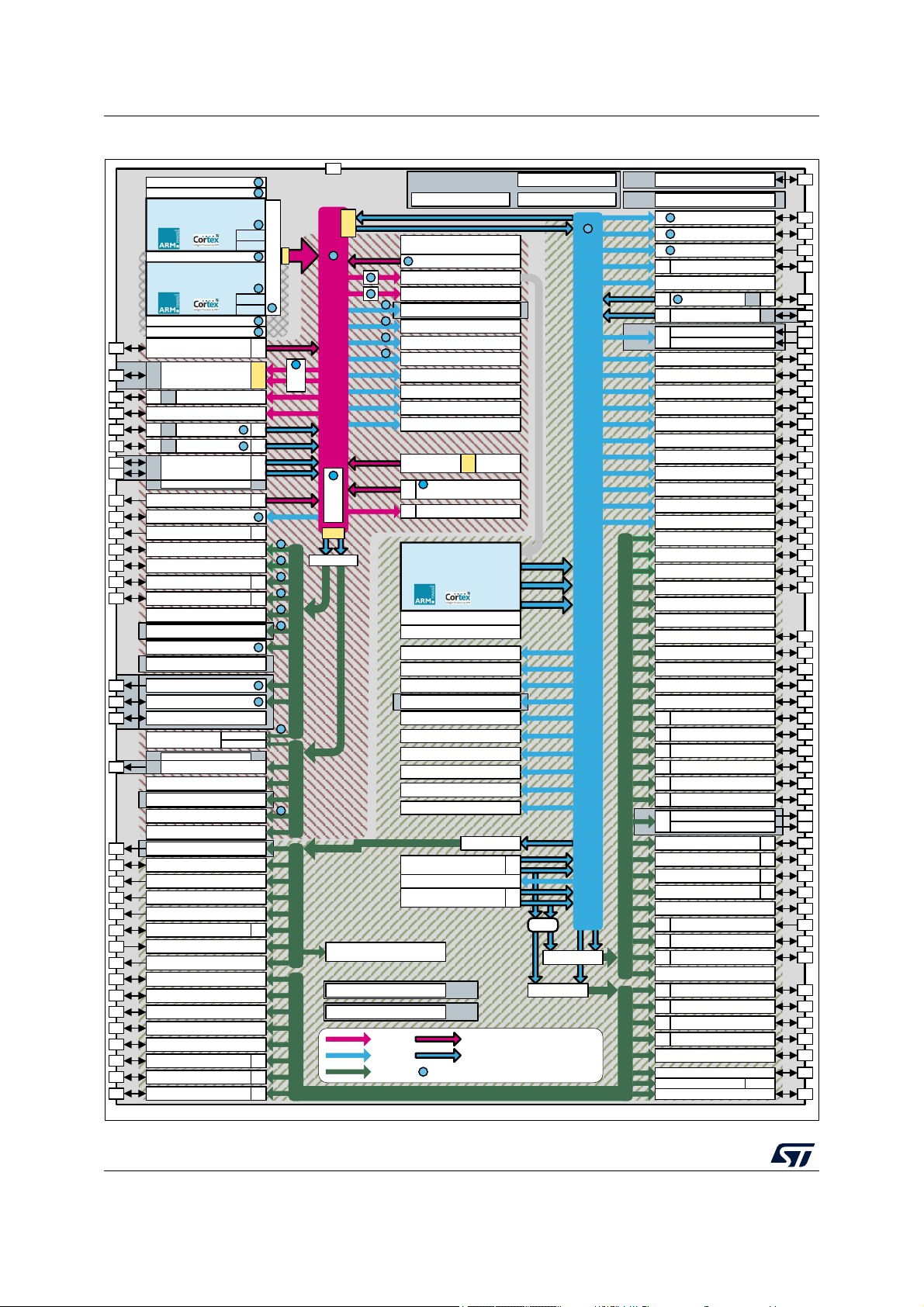
The STM32MP157C/F devices incorporate high-speed embedded memories with
708 Kbytes of Internal SRAM (including 256 Kbytes of AXI SYSRAM, 3 banks of 128 Kbytes
each of AHB SRAM, 64 Kbytes of AHB SRAM in backup domain and 4 Kbytes of SRAM in
backup domain), as well as an extensive range of enhanced I/Os and peripherals connected
to APB buses, AHB buses, a 32-bit multi-AHB bus matrix and a 64-bit multi layer AXI
interconnect supporting internal and external memories access.
14/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Description
All the devices offer two ADCs, two DACs, a low-power RTC, 12 general-purpose 16-bit
timers, two PWM timers for motor control, five low-power timers, a true random number
generator (RNG), and a cryptographic acceleration cell. The devices support six digital
filters for external sigma delta modulators (DFSDM). They also feature standard and
advanced communication interfaces.
• Standard peripherals
–Six I
2
Cs
– Four USARTs and four UARTs
– Six SPIs, three I
2
I
S peripherals can be clocked via a dedicated internal audio PLL or via an
2
Ss full-duplex master/slave. To achieve audio class accuracy, the
external clock to allow synchronization.
– Four SAI serial audio interfaces
– One SPDIF Rx interface
– Management data input/output slave (MDIOS)
– Three SDMMC interfaces
– An USB high-speed Host with two ports two high-speed PHYs and a USB OTG
high-speed with full-speed PHY or high-speed PHY shared with second port of
USB Host.
– Two FDCAN interface, including one supporting TTCAN mode
– A Gigabit Ethernet interface
– HDMI-CEC
• Advanced peripherals including
– A flexible memory control (FMC) interface
– A Quad-SPI Flash memory interface
– A camera interface for CMOS sensors
– An LCD-TFT display controller
– A DSI Host interface.
Refer to Tab le 1: STM32MP157C/F features and peripheral counts for the list of peripherals
available on each part number.
A comprehensive set of power-saving mode allows the design of low-power applications.
The STM32MP157C/F devices are proposed in 4 packages ranging from 257 to 448 balls
with pitch 0.5 mm to 0.8 mm. The set of included peripherals changes with the device
chosen.
These features make the STM32MP157C/F suitable for a wide range of consumer,
industrial, white goods and medical applications.
Figure 1 shows the general block diagram of the device family.
DS12505 Rev 5 15/260
59
Description STM32MP157C/F
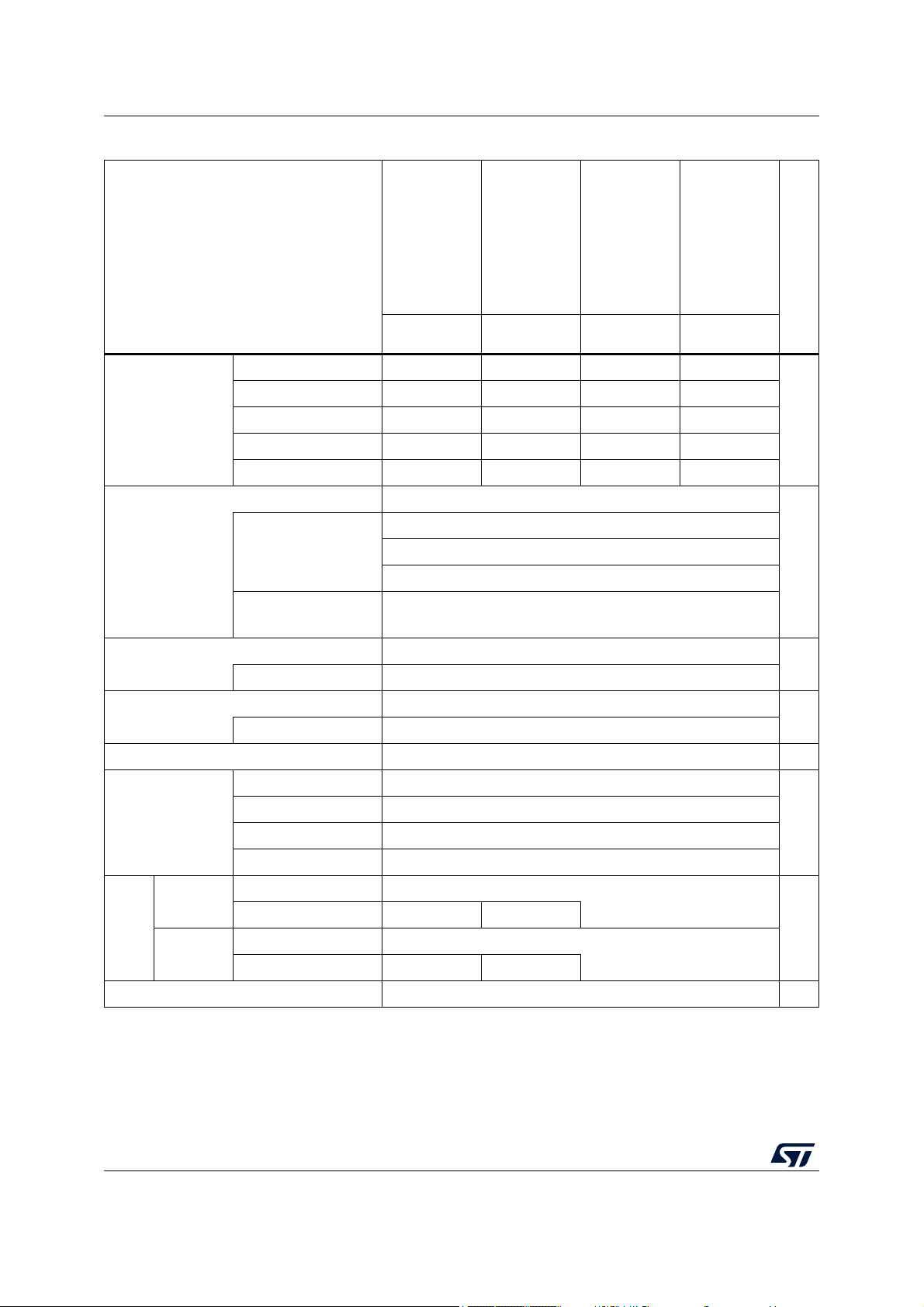
Table 1. STM32MP157C/F features and peripheral counts
Features
STM32MP157CADxx
STM32MP157FADxx
STM32MP157CABxx
STM32MP157FABxx
STM32MP157CACxx
STM32MP157FACxx
STM32MP157CAAxx
STM32MP157FAAxx
TFBGA257 LFBGA354 TFBGA361 LFBGA448
Body size (mm) 10x10 16x16 12x12 18x18
Package
Pitch (mm) 0.5
(1)
0.8 0.5
Ball size (mm) 0.30 0.40 0.30 0.40
(1)
0.8
Thickness (mm) <1.2 <1.4 <1.2 <1.4
Ball count 257 354 361 448
CPU Dual-core Cortex-A7 FPU Neon TrustZone
2 × 32-Kbyte L1 data cache
Caches size
2 × 32-Kbyte L1 instruction cache
256-Kbyte level 2 unified coherent cache
Frequency
STM32MP157C: 2 × 650 MHz
STM32MP157F: 2 × 800 MHz
GPU Vivante - Open GL ES 2.0
for 3D graphics Frequency 533 MHz
MCU core Cortex-M4 FPU
Frequency 209 MHz
ROM 128 Kbytes (secure) -
Miscellaneous
-
-
-
-
CPU system 256 Kbytes (securable)
MCU subsystem 384 Kbytes
Embedded SRAM
MCU retention 64 Kbytes
Backup 4 Kbytes (securable, tamper protected)
16-bit 533 MHz Up to 1 Gbyte, single rank
LPDDR2/3
32-bit 533 MHz - -
SDRAM
DDR3/3L
(securable)
16-bit 533 MHz Up to 1 Gbyte, single rank
32-bit 533 MHz - -
Backup registers 128 bytes (32x32-bit, securable, tamper protected) -
16/260 DS12505 Rev 5
708 Kbytes
-
STM32MP157C/F Description
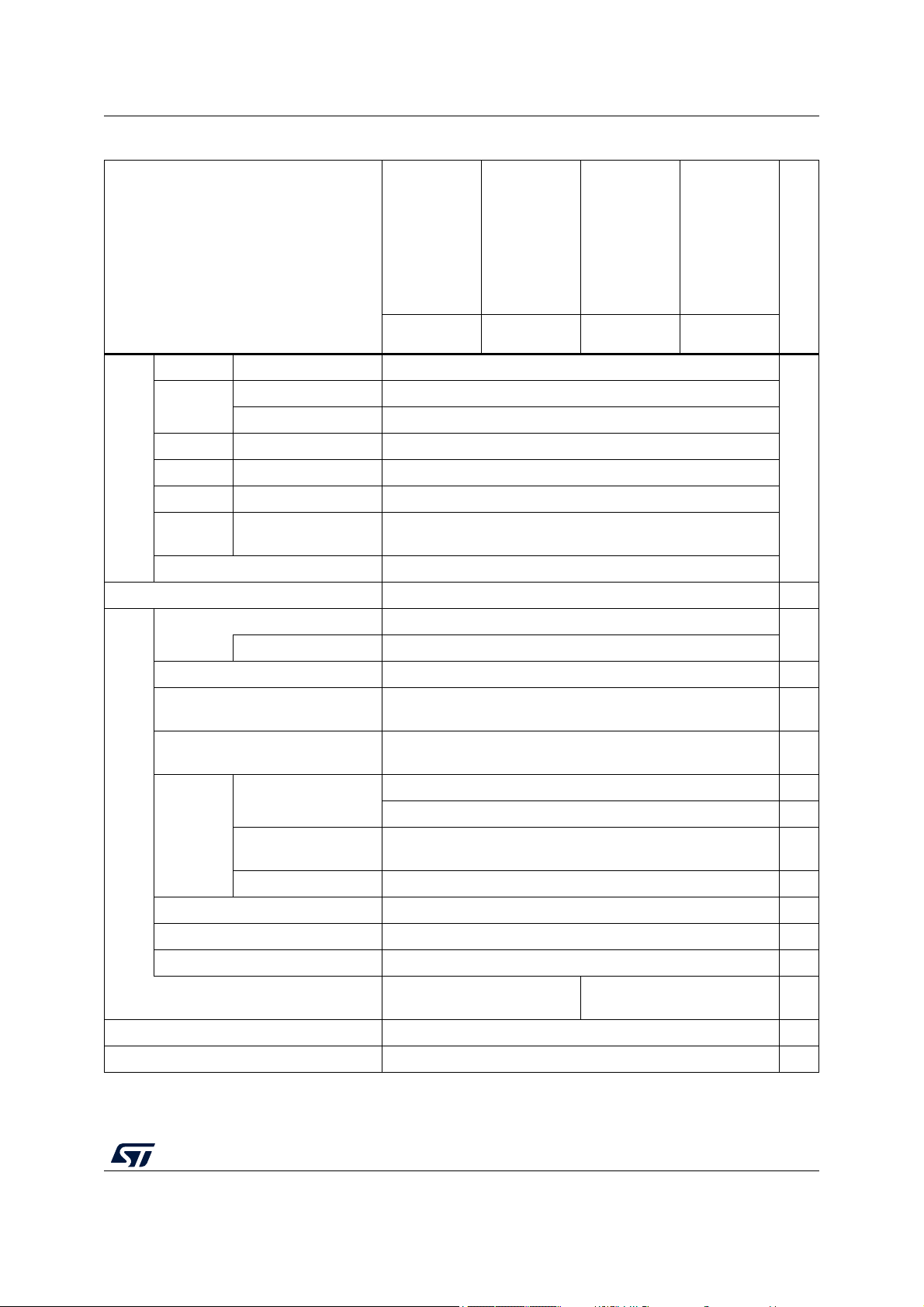
Table 1. STM32MP157C/F features and peripheral counts (continued)
Features
STM32MP157CADxx
STM32MP157FADxx
STM32MP157CABxx
STM32MP157FABxx
STM32MP157CACxx
STM32MP157FACxx
STM32MP157CAAxx
STM32MP157FAAxx
TFBGA257 LFBGA354 TFBGA361 LFBGA448
Advanced 16 bits 2
General
purpose
16 bits 8
32 bits 2
Basic 16 bits 2
Low power 16 bits 5
Timers
A7 timers 64 bits 2 × 4 (secure, non-secure, virtual, hypervisor)
M4
SysTick
24 bits 1
RTC/AWU 1 (securable)
Watchdog 3 (independent, independent secure, window) -
SPI 6 (1 securable)
Having I2S 3
I2C (with SMB/PMB support) 6 (2 securable) -
USART (smartcard, SPI, IrDA, LIN)
+ UART (IrDA, LIN)
SAI
4 (up to 8 audio channels), with I2S master/slave, PCM input,
4 + 4 (including 1 securable USART)
some can be a boot source
SPDIF-TX
Boot
Miscellaneous
29 timers
-
-
EHCI/OHCI Host
2 ports -
Embedded HS PHY with BCD -
USB
OTG HS/FS
(dual role port)
Yes, embedded FS or HS PHY with BCD, can be a boot source Boot
Embedded PHYs 3 (2 × high-speed + 1 × full-speed) -
Communication peripherals
SPDIF-RX 4 inputs -
FDCAN 2 (1 × TTCAN), clock calibration, 10 Kbyte shared buffer -
HDMI-CEC 1 -
Including the following securable 1 × USART, 1 × SPI, 2 × I2C
1 × USART, 1 × SPI, 2 × I2C
on securable GPIOs
-
SDMMC (SD, SDIO, e•MMC) 3 (8 + 8 + 4 bits), e•MMC or SD can be a boot source Boot
QuadSPI Yes (dual-quad), can be a boot source Boot
DS12505 Rev 5 17/260
59
Description STM32MP157C/F
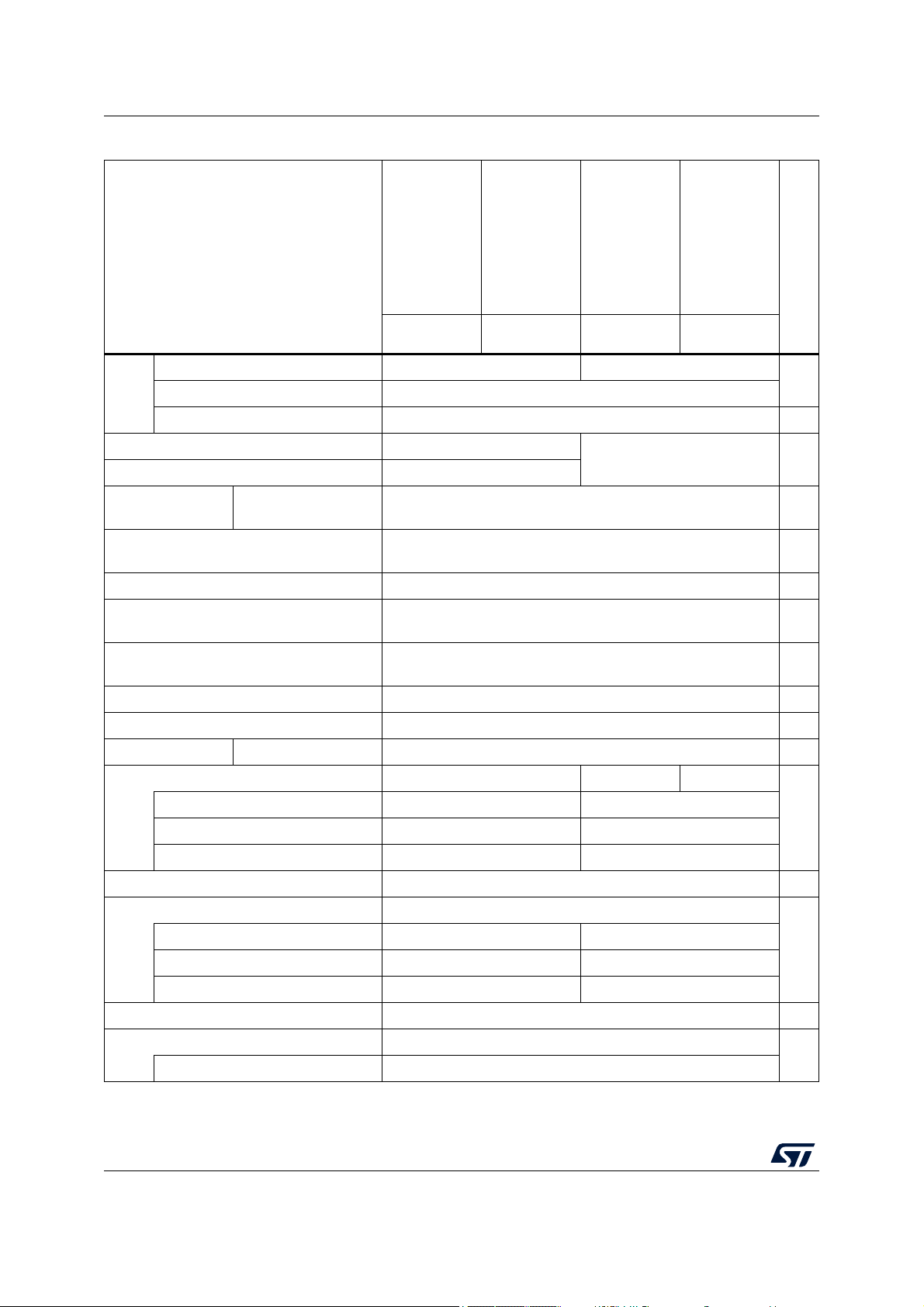
Table 1. STM32MP157C/F features and peripheral counts (continued)
Features
STM32MP157CADxx
STM32MP157FADxx
STM32MP157CABxx
STM32MP157FABxx
STM32MP157CACxx
STM32MP157FACxx
STM32MP157CAAxx
STM32MP157FAAxx
TFBGA257 LFBGA354 TFBGA361 LFBGA448
Parallel address/data 8/16-bit - 4 × CS, up to 4 × 64 Mbyte
FMC
Parallel AD-Mux 8/16-bit 4 × CS, up to 4 × 64 Mbytes
boot
NAND 8/16-bit Yes, 1 × CS, SLC, BCH4/8, can be a boot source Boot
Gigabit Ethernet -
10/100M Ethernet MII, RMII with PTP and EEE
LCD-TFT Parallel interface
Display serial interface (DSI)
Up to 24-bit data, up to 90 MHz pixel clock
(up to 1366 × 768 60 fps or up to 1920 × 1080 30 fps)
2 × data lanes 1 GHz each
(up to 1366 × 768 60 fps or up to 1920 × 1080 30 fps)
MII, RMII, GMII, RGMII with
PTP and EEE
DMA 3 instances (1 securable), 48 physical channels in total -
Cryptography
Hash
dual instances (secure and non-secure)
dual instances (secure and non-secure)
DES, TDES, AES-256
SHA-256, MD5, HMAC
True random number generator True-RNG, dual instances (secure and non-secure) -
Fuses (one-time programmable) 3072 effective bits (secure, >1500 bits available for user) -
Camera interface Bus width 14-bit -
Miscellaneous
No
-
-
-
-
-
GPIOs with interrupt (total count) 98 148 176
Securable GPIOs - 8
-
Wakeup pins 4 6
Tamper pins (active tamper) 2 (1) 3 (1)
DFSDM 8 input channels with 6 filters -
Up to 16-bit synchronized ADC 2 (up to 3.6/4/4.5/5/6 Msps on 16/14/12/10/8-bit each)
Low noise 16 bit (differential) - 2 (1)
-
16 bit (differential) 17 (7) 20 (9)
ADC channels in total
(2)
17 22
12-bit DAC 2-
Internal ADC/DAC VREF 1.5 V, 1.8 V, 2.048 V, 2.5 V or VREF+ input
-
VREF+ input pin Yes
1. With inner matrix balls having 0.65 mm pitch to allow optimized PCB routing for supplies.
18/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Description
2. In addition, there is also 6 internal channels for temperature, internal voltage reference, V
acquisitions.
DDCORE
, V
/4, DAC1 or DAC2
BAT
DS12505 Rev 5 19/260
59
Description STM32MP157C/F
MSv47445V4
@VDDA
@VDD_ANA
@VDDA
@VSW
@VDD
@VSW
@VDDA
@VSW
OTP Fuses
T
T
T
T
T
@VSW
SYSRAM 256KB
ROM 128KB
TIM3
ADC1
ADC2
64 bits
32 bits
32 bits
AXI
AHB
APB
64bits
AXI master
T
TrustZone
®
security protection
@VDD
Voltage Regulators
@VDD_ANA
Supply Supervision
32 bits
AHB master
BKPSRAM 4KB
STM
RETSRAM 64KB
DTS
(Digital temperature sensor)
@VDD_PLL
PLL1/2/3/4
@VDD
HSE (XTAL)
RCC
RNG2
DCMI
(Camera I/F)
MDIOS
CRC2
HSEM
PWR
SDMMC3
OTG
(HS/FS)
HASH2
T
USBPHYC
(USB 2 x PHY control)
FIFO
16b
16b
Interface
GPIOA
GPIOB
GPIOC
GPIOD
GPIOE
GPIOF
GPIOG
GPIOH
GPIOI
GPIOJ
GPIOK
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
16b
8b
SRAM1 128KB
SRAM2 128KB
SRAM3/SRAM4 64K/64K
HSI
CSI LSI
DMA1
8 Streams
DMA2
8 Streams
FIFO FIFO
2
17
4
20
14
9
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
8
5
TIM4
16b
5
TIM6
16b
TIM7
16b
TIM12
16b
2
TIM13
16b
1
TIM14
16b
1
TIM2
32b
5
TIM5
32b
5
LPTIM1
16b
4
2
USART2
Smartcard
IrDA
5
USART3
Smartcard
IrDA
5
PLLUSB
FIFOFIFO
5
T
4b
10
PHY
FIFO
I2C4 / SMBUS
SPI6
USART1
IWDG1
BSEC
ETZPC
3
4
5
Smartcard
IrDA
FIFO FIFO
RTC / AWU
LSE (32kHz XTAL)
TAMP / Backup Regs
T
2
2
3
RNG1
HASH1
CRC1
T
T
LTDC
(LCD)
SDMMC1
31
29
14
SDMMC2
14
8b
8b
FIFO FIFOFIFO
MDMA
32 Channels
T
QUADSPI (dual)
DDRCTRL
LPDDR2/3
DDR3/3L
FMC
async
37
13
77
GPIOZ
8b
8
16b
AHB2APB
Trace port
APB1 (104.5 MHz)
APB3 (104.5 MHz)
T
24b
8b
AHB2APB
2x2
Matrix
AHB2APB
IC Supplies
16b
AXIM: ARM 64-bit AXI interconnect (266 MHz)
async
DLYBSD1
(SDMMC1 DLY control)
DLYBSD2
(SDMMC2 DLY control)
DLYBSD3
(SDMMC3 DLY control)
async
DLYBQS
(QUADSPI DLY control)
17
16b
FIFOFIFO
14b
DMAMUX1
DDRPHYC
AXIMC
T
TT
T
8KB
FIFO
Sys. Timing
GENeration
APB5 (133MHz)
debug TimeStamp
GENerator TSGEN
DLYDLY DLY
DLY
(R)(G)MII
32b PHY
APB4
MLAHB: ARM 32-bit multi-AHB bus matrix (209 MHz)
T
@VSW
IWDG2
T
I2C6 / SMBUS
3
USBH
(2 x HS Host)
2
2
2 x PHY
FIFO
STGENC
STGENR
EXTI
176
16ext
T
T
T
T
SYSCFG
VREFBUF
TIM1 / PWM
TIM8 / PWM
10
10
16b
16b
TIM15
4
16b
TIM16
16b
TIM17
16b
3
3
1
LPTIM2
16b
4
LPTIM3
16b
1
LPTIM4
16b
1
LPTIM5
16b
1
SAI4
13
FIFO
3
HDP
8
8b
SAI1
13
FIFO
SAI2
8
FIFO
SAI3
8
FIFO
UART4
4
UART5
4
UART7
4
UART8
4
DAC1
DAC2
12b
12b
Interface
1
1
I2C1 / SMBUS
3
Filter
I2C2 / SMBUS
3
Filter
I2C3 / SMBUS
3
Filter
I2C5 / SMBUS
3
Filter
CEC (HDMI-CEC)
SPDIFRX
1
4
SPI2 / I2S2
SPI3 / I2S3
5
5
FIFOFIFOFIFOFIFOFIFOFIFOFIFO
SPI4
4
SPI5
4
USART6
5
Smartcard
IrDA
FIFO FIFOFIFO
SPI1 / I2S1
5
FIFO
WWDG1
4ch
DFSDM1
17
8ch
AHB2APB
BOOT
pins
T
T
T
128 bits
CNT (Timer)
T
ETM
T
Cortex-A7 CPU
650/800
(1)
MHz + MMU +
FPU + NEON
T
32K I$
32K D$
T
ETH1 GMAC
10/100/1000
FIFO
DAP
(JTAG / SWD)
T
T
DDRPERFM
async
CRYP2
DAP bus
CRYP1
IPCC
T
TZC
T
T
FIFO
GPU
async
Shader
(533 MHz)
FDCAN1 (TT)
FDCAN2
Buffer 10KB CCU
2
2
APB2 (104.5 MHz)
APB2 (104.5 MHz)
APB2 (104.5 MHz)
PLLDSI
DSI
PHY
6
I-Bus
D-Bus
S-Bus
SYSTICK
NVIC
Cortex-M4 CPU 209 MHz
+ MPU + FPU
GIC
ETM
CNT (Timer)
T
T
Cortex-A7 CPU
650/800
(1)
MHz + MMU +
FPU + NEON
T
32K I$
32K D$
256KB L2$ + SCU
T
T
1. STM32MP157C: 650 MHz, STM32MP157F: 800 MHz
Figure 1. STM32MP157C/F block diagram
20/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Functional overview
3 Functional overview
3.1 Dual-core Arm® Cortex®-A7 subsystem
3.1.1 Features
• ARMv7-A architecture
• 32-Kbyte L1 instruction cache for each CPU
• 32-Kbyte L1 data cache for each CPU
• 256-Kbyte level2 cache
• Arm
• Arm
• Arm
• DSP and SIMD extensions
• VFPv4 floating-point
• Hardware virtualization support
• Embedded trace module (ETM)
• Integrated generic interrupt controller (GIC) with 256 shared peripheral interrupts
• Integrated generic timer (CNT)
®
+ Thumb®-2 instruction set
®
TrustZone® security technology
®
NEON™ Advanced SIMD
3.1.2 Overview
The Cortex-A7 processor is a very energy-efficient applications processor designed to
provide rich performance in high-end wearables, and other low-power embedded and
consumer applications. It provides up to 20 % more single thread performance than the
Cortex-A5 and provides similar performance than the Cortex-A9.
The Cortex-A7 incorporates all features of the high-performance Cortex-A15 and CortexA17 processors, including virtualization support in hardware, NEON
AXI bus interface.
The Cortex-A7 processor builds on the energy-efficient 8-stage pipeline of the Cortex-A5
processor. It also benefits from an integrated L2 cache designed for low-power, with lower
transaction latencies and improved OS support for cache maintenance. On top of this, there
is improved branch prediction and improved memory system performance, with 64-bit loadstore path, 128-bit AMBA 4 AXI buses and increased TLB size (256 entry, up from 128 entry
for Cortex-A9 and Cortex-A5), increasing performance for large workloads such as web
browsing.
Thumb-2 technology
Delivers the peak performance of traditional Arm® code while also providing up to a 30 %
reduction in memory requirement for instructions storage.
TrustZone technology
Ensures reliable implementation of security applications ranging from digital rights
management to electronic payment. Broad support from technology and industry partners.
™
, and 128-bit AMBA®4
DS12505 Rev 5 21/260
59

Functional overview STM32MP157C/F
NEON
NEON technology can accelerate multimedia and signal processing algorithms such as
video encode/decode, 2D/3D graphics, gaming, audio and speech processing, image
processing, telephony, and sound synthesis. The Cortex-A7 provides an engine that offers
both the performance and functionality of the Cortex-A7 floating-point unit (FPU) and an
implementation of the NEON advanced SIMD instruction set for further acceleration of
media and signal processing functions. The NEON extends the Cortex-A7 processor FPU to
provide a quad-MAC and additional 64-bit and 128-bit register set supporting a rich set of
SIMD operations over 8-, 16- and 32-bit integer and 32-bit floating-point data quantities.
Hardware virtualization
Highly efficient hardware support for data management and arbitration, whereby multiple
software environments and their applications are able to simultaneously access the system
capabilities. This enables the realization of devices that are robust, with virtual environments
that are well isolated from each other.
Optimized L1 caches
Performance and power optimized L1 caches combine minimal access latency techniques
to maximize performance and minimize power consumption. There is also the option of
cache coherence for enhanced inter-processor communication, or support of a rich SMP
capable OS for simplified multicore software development.
Integrated L2 cache controller
Provides low-latency and high-bandwidth access to cached memory in high-frequency, or to
reduce the power consumption associated with off-chip memory access.
Cortex-A7 floating-point unit (FPU)
The FPU provides high-performance single and double precision floating-point instructions
compatible with the Arm VFPv4 architecture that is software compatible with previous
generations of Arm floating-point coprocessor.
Snoop control unit (SCU)
The SCU is responsible for managing the interconnect, arbitration, communication, cache to
cache and system memory transfers, cache coherence and other capabilities for the
processor.
This system coherence also reduces software complexity involved in maintaining software
coherence within each OS driver.
Generic interrupt controller (GIC)
Implementing the standardized and architected interrupt controller, the GIC provides a rich
and flexible approach to inter-processor communication and the routing and prioritization of
system interrupts.
Supporting up to 288 independent interrupts, under software control, each interrupt can be
distributed across A7 cores, hardware prioritized, and routed between the operating system
and TrustZone software management layer.
22/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Functional overview
This routing flexibility and the support for virtualization of interrupts into the operating
system, provides one of the key features required to enhance the capabilities of a solution
utilizing a hypervisor.
3.2 Arm® Cortex®-M4 with FPU
The Arm® Cortex®-M4 with FPU core is a 32-bit RISC processor that features exceptional
code-efficiency, delivering the high-performance expected from an Arm core in the memory
size usually associated with 8- and 16-bit devices.
The processor supports a set of DSP instructions which allow efficient signal processing and
complex algorithm execution.
Its single precision FPU (floating point unit) speeds up software development by using
metalanguage development tools, while avoiding saturation.
Note: Cortex-M4 with FPU core is binary compatible with the Cortex-M3 core.
Memory protection unit (MPU)
The memory protection unit (MPU) manages the Cortex®-M4 access rights and the
attributes of the system resources. It has to be programmed and enabled before use. Its
main purposes are to prevent an untrusted user program to accidentally corrupt data used
by the OS and/or by a privileged task, but also to protect data processes or read-protect
memory regions.
The MPU defines access rules for privileged accesses and user program accesses. It
allows the definition of up to 16 protected regions that can in turn be divided into up to 8
independent subregions, where region address, size, and attributes can be configured. The
protection area ranges from 32 bytes to 4
When an unauthorized access is performed, a memory management exception is
generated.
Gbytes of addressable memory.
3.3 Graphic processing unit (GPU)
The STM32MP157C/F includes a 3D graphics engine (Vivante).
The GPU is a dedicated graphics processing unit accelerating numerous 3D graphics
applications such as graphical user interface (GUI), menu display or animations.
It works together with an optimized software stack design for industry-standard APIs with
support for Android™ and Linux
®
embedded development platforms.
DS12505 Rev 5 23/260
59

Functional overview STM32MP157C/F
Hardware features:
• OpenGL ES 2.0 / 1.1 compliance, including extensions; OpenVG 1.1
• IEEE 32-bit floating-point pipeline
• Ultra-threaded, unified vertex and fragment (pixel) shaders
• Low memory bandwidth at both high and low data rates
• Low CPU loading
• Up to 12 programmable elements per vertex
• Dependent texture operation with high-performance
• Alpha blending
• Depth and stencil compare
• Support for 8 fragment shader simultaneous textures
• Support for 4 vertex shader simultaneous textures
• Point sampling, bi-linear sampling, tri-linear filtering, and cubic textures
• 8 k x 8 k texture size and 8 k x 8 k rendering target
• 4 Vertex DMA streams
API support:
• OpenGL ES 1.1 and 2.0
• OpenVG 1.1
• EGL 1.4
• OpenGL 2.1
Performance up to:
• 26 Mtriangle/s
• 133 Mpixel/s
24/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Functional overview
3.4 Memories
3.4.1 External SDRAM
The STM32MP157C/F devices embed a controller for external SDRAM which support the
following devices
• LPDDR2 or LPDDR3, 16- or 32-bit data, up to 1 Gbyte, up to 533 MHz clock.
• DDR3 or DDR3L, 16- or 32-bit data, up to 1 Gbyte, up to 533 MHz clock.
3.4.2 Embedded SRAM
All devices feature:
• SYSRAM in MPU domain: 256 Kbytes
• SRAM1 in MCU domain: 128 Kbytes
• SRAM2 in MCU domain: 128 Kbytes
• SRAM3 in MCU domain: 64 Kbytes
• SRAM4 in MCU domain: 64 Kbytes
• RETRAM (retention RAM): 64 Kbytes
The content of this area can be retained in Standby or V
• BKPSRAM (backup SRAM): 4 Kbytes
The content of this area is protected against possible unwanted write accesses, and
can be retained in Standby or V
BAT
mode.
BKPSRAM can be defined (in ETZPC) as accessible by secure software only.
BAT
mode.
DS12505 Rev 5 25/260
59

Functional overview STM32MP157C/F
3.5 DDR3/DDR3L/LPDDR2/LPDDR3 controller (DDRCTRL)
DDRCTRL combined with DDRPHYC provides a complete memory interface solution for
DDR memory subsystem.
• Two 64-bit AMBA 4 AXI4 ports interface (XPI)
• AXI clock asynchronous to the controller
• Supported standards:
– JEDEC DDR3 SDRAM specification, JESD79-3E for DDR3/3L with 32-bit
interface
– JEDEC LPDDR2 SDRAM specification, JESD209-2E for LPDDR2 with 32-bit
interface
– JEDEC LPDDR3 SDRAM specification, JESD209-3B for LPDDR3 with 32-bit
interface
• Advanced scheduler and SDRAM command generator
• Programmable full data width (32-bit) or half data width (16-bit)
• Advanced QoS support with 3 traffic class on read and 2 traffic classes on write
• Options to avoid starvation of lower priority traffic
• Guaranteed coherency for write-after-read (WAR) and read-after-write (RAW) on AXI
ports
• Programmable support for burst length options (4, 8,16)
• Write combine to allow multiple writes to the same address to be combined into a
single write
• Single rank configuration
• Supports automatic SDRAM power-down entry and exit caused by lack of transaction
arrival for programmable time
• Supports automatic clock stop (LPDDR2/3) entry and exit caused by lack of transaction
arrival
• Supports automatic low power mode operation caused by lack of transaction arrival for
programmable time via hardware low power interface
• Programmable paging policy
• Supports automatic or under software control self-refresh entry and exit
• Support for deep power-down entry and exit under software control (LPDDR2)
• Support for explicit SDRAM mode register updates under software control
• Flexible address mapper logic to allow application specific mapping of row, column,
bank bits
• User-selectable refresh control options
• DDRPERFM associated block to help for performance monitoring and tuning
DDRCTRL and DDRPHYC can be defined (in ETZPC) as accessible by secure software
only.
26/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Functional overview
3.6 TrustZone address space controller for DDR (TZC)
TZC is used to filter read/write accesses to DDR controller according to TrustZone rights
and according to non-secure master (NSAID) on up to 9 programmable regions.
• Configuration is supported by trusted software only
• 2 filter units working concurrently
• 9 regions:
– region 0 is always enabled and covers the whole address range.
– regions 1 to 8 have programmable base/end address and can be assigned to any
one or both filters.
• Secure and non-secure access permissions programmed per region
• Non-secure accesses are filtered according to NSAID
• Regions controlled by same filter must not overlap
• Fail modes with error and/or interrupt
• Acceptance capability = 256
• Gate keeper logic to enable and disable of each filter
• Speculative accesses
DS12505 Rev 5 27/260
59
Functional overview STM32MP157C/F
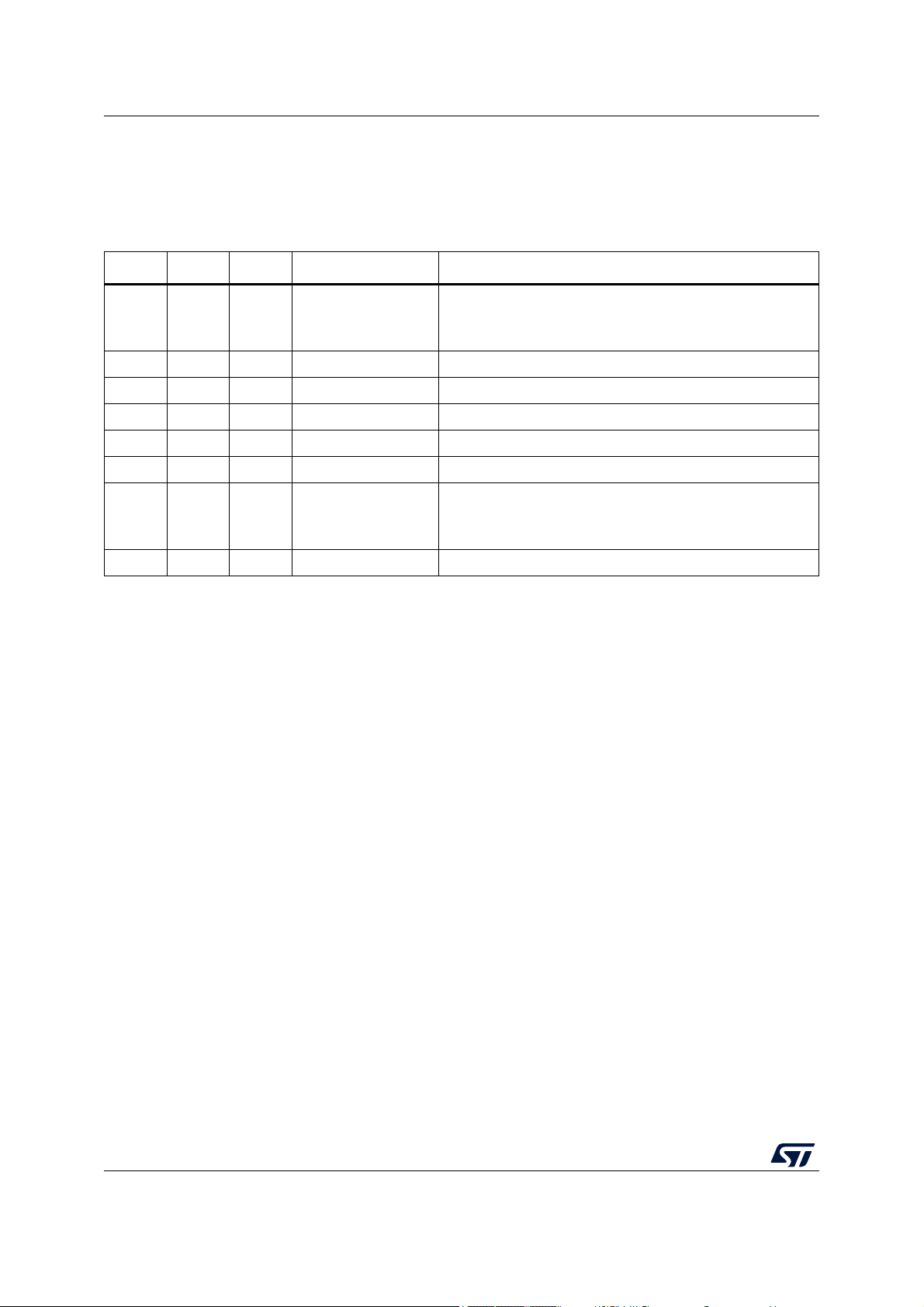
3.7 Boot modes
At startup, the boot source used by the internal BootROM is selected by the BOOT pin and
OTP bytes.
BOOT2 BOOT1 BOOT0 Initial boot mode Comments
Table 2. Boot modes
Wait incoming connection on:
(3)
(1)
– USART2/3/6 and UART4/5/7/8 on default pins
– USB high-speed device
(3)
Serial NOR Flash on QUADSPI
e•MMC on SDMMC2 (default)
(2)
(4)
(4)(5)
SLC NAND Flash on FMC
0 0 0 UART and USB
0 0 1 Serial NOR Flash
010e•MMC
(3)
011NAND Flash
1 0 0 Reserved (NoBoot) Used to get debug access without boot from Flash memory
101SD card
(3)
SD card on SDMMC1 (default)
(4)(5)
Wait incoming connection on:
1 1 0 UART and USB
(1)(3)
– USART2/3/6 and UART4/5/7/8 on default pins
– USB high-speed device on OTG_HS_DP/DM pins
1 1 1 Serial NAND Flash
1. can be disabled by OTP settings.
2. USB requires 24 MHz HSE clock/crystal if OTP is not programmed for different frequency.
3. Boot source can be changed by OTP settings (e.g. initial boot on SD card, then e•MMC with OTP settings).
4. Default pins can be altered by OTP.
5. Alternatively, another SDMMC1 or SDMMC2 interface than this default can be selected by OTP.
(3)
Serial NAND Flash on QUADSPI
(4)
(2)
28/260 DS12505 Rev 5

STM32MP157C/F Functional overview
3.8 Power supply management
3.8.1 Power supply scheme
Caution: V
• The V
is the main supply for I/Os and internal part kept powered during Standby
DD
mode. Useful voltage range is 1.71 V to 3.6 V (e.g. 1.8 V, 2.5 V, 3.0 V or 3.3 V typ.)
–V
• The V
DDCORE
DD_DSI
, V
DD_PLL
and V
DD_ANA
must be star-connected to VDD.
is the main digital voltage and is usually shutdown during Standby mode.
Voltage range during Run mode is 1.18 V to 1.25/1.38 V (1.2/1.34 V typ.), see
Table 13: General operating conditions.
• The VBAT pin can be connected to the external battery (1.2 V < V
external battery is used, it is mandatory to connect this pin to V
DD
BAT
.
< 3.6 V). If no
• The VDDA pin is the analog (ADC/DAC/VREF), supply voltage range is 1.71 V to 3.6 V.
DAC can only be used when V
requires V
equal to or higher than V
DDA
is above or equal 1.8 V. Using Internal V
DDA
REF+
+ 0.3 V.
REF+
• The VDDA1V8_REG pin is the output of internal regulator and connected internally to
USB PHY and USB PLL. Internal V
DDA1V8_REG
regulator is enabled by default and can
be controlled by software. It is always shut down during Standby mode.
There is specific BYPASS_REG1V8 pin that must be connected either to V
or VDD to
SS
activate or deactivate the voltage regulator. It is mandatory to bypass the 1.8 V
regulator when V
VDDA1V8_REG pin must be connected to V
is below 2.25 V (BYPASS_REG1V8 = V
DD
(if below 1.98 V) or to a dedicated
DD
. In that case,
DD)
1.65 V - 1.98 V supply (1.8 V typ.).
• V
DDA1V8_DSI
Should be connected to V
is the analog DSI supply. Voltage range is 1.65 V to 1.98 V. (1.8 V typ.)
DDA1V8_REG
.
• VDDA1V1_REG pin is the output of internal regulator connected internally to USB PHY.
Internal V
DDA1V1_REG
regulator is enabled by default and can be controlled by
software. It is always shut down during Standby mode.
• VDDA1V2_DSI_REG pin is the output of internal regulator and connected internally to
DSI PLL.
• V
DDA1V2_DSI_PHY
V
DDA1V2_DSI_REG
• V
DD3V3_USBHS
PHY supply. Voltage range is 3.07 V to 3.6 V. V
OTG_VBUS and ID pins. So, V
speed OTG device is used. If not used, must be connected to V
DD3V3_USBHS
must not be present unless V
is the analog DSI PHY supply and should be connected to
.
and V
DD3V3_USBFS
are respectively the USB high-speed and full-speed
is used to supply
DD.
DD3V3_USBFS
DDA1V8_REG
DD3V3_USBFS
must be supplied as well when USB high-
is present, otherwise permanent
STM32MP157C/F damage could occur. Must be ensured by PMIC ranking order or with
external component in case of discrete component power supply implementation.
• V
DDQ_DDR
is the DDR IO supply.
– Voltage range is 1.425 V to 1.575 V for interfacing DDR3 memories (1.5 V typ.).
– Voltage range is 1.283 V to 1.45 V for interfacing DDR3L memories (1.35 V typ.).
– Voltage range is 1.14 V to 1.3 V for interfacing LPDDR2 or LPDDR3 memories
(1.2 V typ.).
DS12505 Rev 5 29/260
59
Functional overview STM32MP157C/F
MSv47490V1
0.3
1
V
BOR0
3.6
Operating modePower-on Power-down time
V
V
DDX
(1)
V
DD
Invalid supply area V
DDX
< V
DD
+ 300 mV
V
DDX
independent from V
DD
During power-up and power-down phases, the following power sequence requirements
must be respected:
• When VDD is below 1 V, other power supplies (V
V
DDA1V8_DSI
V
+ 300 mV.
DD
• When V
During the power-down phase, V
, V
DDA1V1_REG
is above 1 V, all power supplies are independent.
DD
, V
DD3V3_USBHS/FS
can temporarily become lower than other supplies only
DD
, V
DDCORE
DDQ_DDR
, V
, V
DDA
DDA1V8_REG
) must remain below
,
if the energy provided to the STM32MP157C/F device remains below 1 mJ; this allows
external decoupling capacitors to be discharged with different time constants during the
power- down transient phase.
Figure 2. Power-up/down sequence
1. V
refers to any power supply among V
DDX
V
DD3V3_USBHS/FS
, V
DDQ_DDR
, V
.
DDCORE
DDA
, V
DDA1V8_REG
, V
DDA1V8_DSI
, V
DDA1V1_REG
,
30/260 DS12505 Rev 5
 Loading...
Loading...