Page 1

STM32H742xI/G STM32H743xI/G
Errata sheet
STM32H742xI/G and STM32H743xI/G device limitations
Applicability
This document applies to the part numbers of STM32H742/743xI/G devices listed in Table 1
and their variants shown in Tab le 2.
Section 1 gives a summary and Section 2 a description of workarounds for device
limitations, with respect to the device datasheet and reference manual RM0433.
Reference Part numbers
STM32H742xI/G
STM32H743xI/G
STM32H742VI, STM32H742ZI, STM32H742II, STM32H742BI,
STM32H742XI, STM32H742AI, STM32H742VG, STM32H742ZG,
STM32H742IG, STM32H742BG, STM32H742XG, STM32H742AG
STM32H743VI, STM32H743ZI, STM32H743II, STM32H743BI,
STM32H743XI, STM32H743AI, STM32H743VG, STM32H743ZG,
STM32H743IG, STM32H743BG, STM32H743XG, STM32H743AG
Table 1. Device summary
Reference
STM32H742xI/G V 0x2003
STM32H743xI/G Y 0x1003
STM32H743xI/G X 0x2001
STM32H743xI/G V 0x2003
1. Refer to the device datasheet for how to identify this code on different types of package.
2. REV_ID[15:0] bit field of DBGMCU_IDC register. Refer to the reference manual.
Table 2. Device variants
Silicon revision codes
Device marking
(1)
REV_ID
(2)
February 2021 ES0392 Rev 8 1/44
www.st.com
1
Page 2

Contents STM32H742/743xI/G
Contents
1 Summary of device limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Description of device limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1 Arm® 32-bit Cortex®-M7 core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1.1 Cortex®-M7 data corruption when using Data cache configured in
write-through . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1.2 Cortex®-M7 FPU interrupt not present on NVIC line 81 . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2 System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.2.1 Timer system breaks do not work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2.2 Clock recovery system synchronization with USB SOF does not work . 11
2.2.3 SysTick external clock is not HCLK/8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.4 Option byte loading can be done with the user wait-state configuration 12
2.2.5 Flash BusFault address register may not be valid when
an ECC double error occurs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.6 Flash ECC address register may not be updated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.7 PCROP-protected areas in Flash memory may be unprotected . . . . . . 13
2.2.8 Flash memory bank swapping might impact embedded
Flash memory interface behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2.9 Reading from AXI SRAM may lead to data read corruption . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2.10 Clock switching does not work when LSE failure is detected by CSS . . 13
2.2.11 RTC stopped when a system reset occurs while the LSI is used
as a clock source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2.12 USB OTG_FS PHY drive limit on DP/DM pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2.13 Unexpected leakage current on I/Os when VIN higher that VDD . . . . . 14
2.2.14 LSE oscillator driving capability selection bits are swapped . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2.15 HRTIM internal synchronization does not work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.16 Device stalled when two consecutive level regressions occur
without accessing from/to backup SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.17 Invalid Flash memory CRC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.18 GPIO assigned to DAC cannot be used in output mode when
the DAC output is connected to on-chip peripheral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.19 Unstable LSI when it clocks RTC or CSS on LSE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.2.20 480 MHz maximum CPU frequency not available on silicon revision Y . 16
2.2.21 VDDLDO is not available on TFBGA100 package
on devices revision Y and V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 3

STM32H742/743xI/G Contents
2.2.22 WWDG not functional when VDD is lower than 2.7 V and VOS0
or VOS1 voltage level is selected . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2.23 A tamper event does not erase the backup RAM when the
backup RAM clock is disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2.24 LSE CSS parasitic detection even when disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.3 FMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.3.1 Dummy read cycles inserted when reading synchronous memories . . . 18
2.3.2 Wrong data read from a busy NAND Flash memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.3.3 Missed clocks with continuous clock feature enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.4 QUADSPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.4.1 First nibble of data is not written after a dummy phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.4.2 QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.4.3 QUADSPI cannot be used in Indirect read mode when only
data phase is activated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.4.4 Memory-mapped read of last memory byte fails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.5 ADC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.5.1 Conversion overlap may impact the ADC accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.5.2 ADC resolution limited by LSE activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2.5.3 ADC maximum sampling rate when VDDA is lower than 2 V . . . . . . . . 21
2.5.4 ADC maximum resolution when VDDA is higher than 3.3 V . . . . . . . . . 21
2.5.5 First ADC injected conversion in a sequence may be corrupted . . . . . . 21
2.5.6 Writing the ADC_JSQR register when JADCSTART = 1 and JQDIS = 1
may lead to incorrect behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.5.7 Conversion may be triggered by context queue register update . . . . . . 22
2.5.8 Updated conversion sequence may be trigged by
context queue update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.6 VREFBUF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.6.1 Overshoot on VREFBUF output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.6.2 VREFBUF Hold mode cannot be used . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.7 OPAMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.7.1 OPAMP high-speed mode must not be used . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.8 LCD-TFT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.8.1 Device stalled when accessing LTDC registers while pixel clock
is disabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.9 TIM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.9.1 One-pulse mode trigger not detected in master-slave reset +
trigger configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.9.2 Consecutive compare event missed in specific conditions . . . . . . . . . . 24
ES0392 Rev 8 3/44
5
Page 4

Contents STM32H742/743xI/G
2.9.3 Output compare clear not working with external counter reset . . . . . . . 25
2.10 LPTIM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.10.1 MCU may remain stuck in LPTIM interrupt when entering Stop mode . 26
2.11 RTC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.11.1 RTC calendar registers are not locked properly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.12 I2C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.12.1 10-bit master mode: new transfer cannot be launched if first part
of the address is not acknowledged by the slave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.12.2 Wrong behavior in Stop mode when wakeup from Stop
mode is disabled in I2C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.12.3 Wrong data sampling when data setup time (t
one I2C kernel clock period . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2.12.4 Spurious bus error detection in Master mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2.12.5 Last-received byte loss in Reload mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.12.6 Spurious master transfer upon own slave address match . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.12.7 START bit is cleared upon setting ADDRCF, not upon address match . 31
) is shorter than
SU;DAT
2.13 USART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.13.1 Underrun flag is set when the USART is used in SPI Slave
receive mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.13.2 DMA stream locked when transferring data to/from USART/UART . . . . 31
2.14 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.14.1 Spurious DMA Rx transaction after simplex Tx traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.14.2 Master data transfer stall at system clock much faster than SCK . . . . . 32
2.14.3 Corrupted CRC return at non-zero UDRDET setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.14.4 TXP interrupt occurring while SPI/I2Sdisabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2.15 SDMMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.15.1 Busy not detected when a write operation suspended
during busy phase resumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.15.2 Wrong data line 2 generation between two blocks
during DDR transfer with Read wait mode enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.15.3 Unwanted overrun detection when an AHB error is reported
whereas all bytes have been received . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2.15.4 Consecutive multiple block transfers can induce incorrect data length . 34
2.15.5 Clock stop reported during Read wait mode sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.16 FDCAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.16.1 Writing FDCAN_TTTS during initialization corrupts FDCAN_TTTMC . . 34
2.16.2 Wrong data may be read from Message RAM by the CPU
when using two FDCANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 5

STM32H742/743xI/G Contents
2.16.3 Mis-synchronization in Edge filtering mode when the falling edge at
FDCAN_Rx input pin coincides with the end of the
integration phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2.16.4 Tx FIFO messages inverted when both Tx buffer and FIFO are used and
the messages in the Tx buffer have higher priority than
in the Tx FIFO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2.17 USB OTG_HS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2.17.1 Possible drift of USB PHY pull-up resistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
2.18 ETH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.18.1 Incorrect L4 inverse filtering results for corrupted packets . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.18.2 Rx DMA may fail to recover upon DMA restart following a bus error,
with Rx timestamping enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2.18.3 Tx DMA may halt while fetching TSO header under specific conditions 37
2.18.4 Spurious receive watchdog timeout interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.18.5 Incorrect flexible PPS output interval under specific conditions . . . . . . 38
2.18.6 Packets dropped in RMII 10Mbps mode due to fake dribble
and CRC error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.18.7 ARP offload function not effective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.19 HDMI-CEC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.19.1 Unexpected switch to Receive mode without automatic transmission
retry and notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
2.19.2 CEC header not received due to unjustified Rx-Overrun detection . . . . 40
3 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
ES0392 Rev 8 5/44
5
Page 6
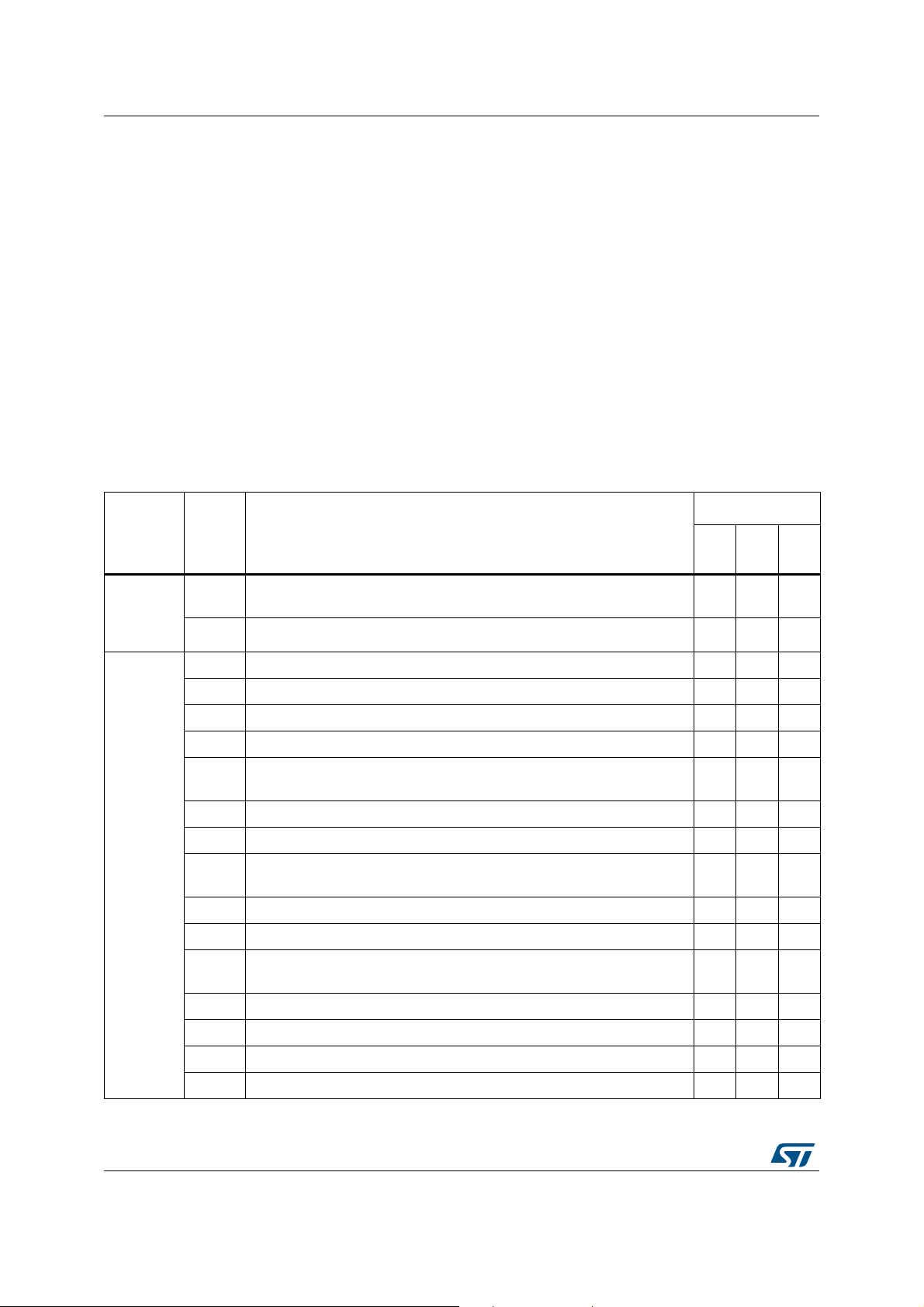
Summary of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
1 Summary of device limitations
The following table gives a quick references to all documented device limitations of
STM32H742/743xI/G and their status:
A = limitation present, workaround available
N = limitation present, no workaround available
P = limitation present, partial workaround available
“-” = limitation absent
Applicability of a workaround may depend on specific conditions of target application.
Adoption of a workaround may cause restrictions to target application. Workaround for a
limitation is deemed partial if it only reduces the rate of occurrence and/or consequences of
the limitation, or if it is fully effective for only a subset of instances on the device or in only a
subset of operating modes, of the function concerned.
Function Section Limitation
Table 3. Summary of device limitations
Status
Rev. YRev.
(1)
X
Rev.
V
Arm® 32-
bit
Cortex®-
M7 core
System
2.1.1
2.1.2 Cortex®-M7 FPU interrupt not present on NVIC line 81 AAA
2.2.1 Timer system breaks do not work N- -
2.2.2 Clock recovery system synchronization with USB SOF does not work A- -
2.2.3 SysTick external clock is not HCLK/8 A- -
2.2.4 Option byte loading can be done with the user wait-state configuration A- -
2.2.5
2.2.6 Flash ECC address register may not be updated N- -
2.2.7 PCROP-protected areas in Flash memory may be unprotected A- -
2.2.8
2.2.9 Reading from AXI SRAM may lead to data read corruption A- -
2.2.10 Clock switching does not work when LSE failure is detected by CSS A- -
2.2.11
2.2.12 USB OTG_FS PHY drive limit on DP/DM pins N- -
2.2.13 Unexpected leakage current on I/Os when VIN higher that VDD A- -
2.2.14 LSE oscillator driving capability selection bits are swapped A- -
Cortex®-M7 data corruption when using Data cache configured in
write-through
Flash BusFault address register may not be valid when an ECC double
error occurs
Flash memory bank swapping might impact embedded Flash memory
interface behavior
RTC stopped when a system reset occurs while the LSI is used as a
clock source
AAA
A- -
N- -
A- -
2.2.15 HRTIM internal synchronization does not work N- -
6/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 7
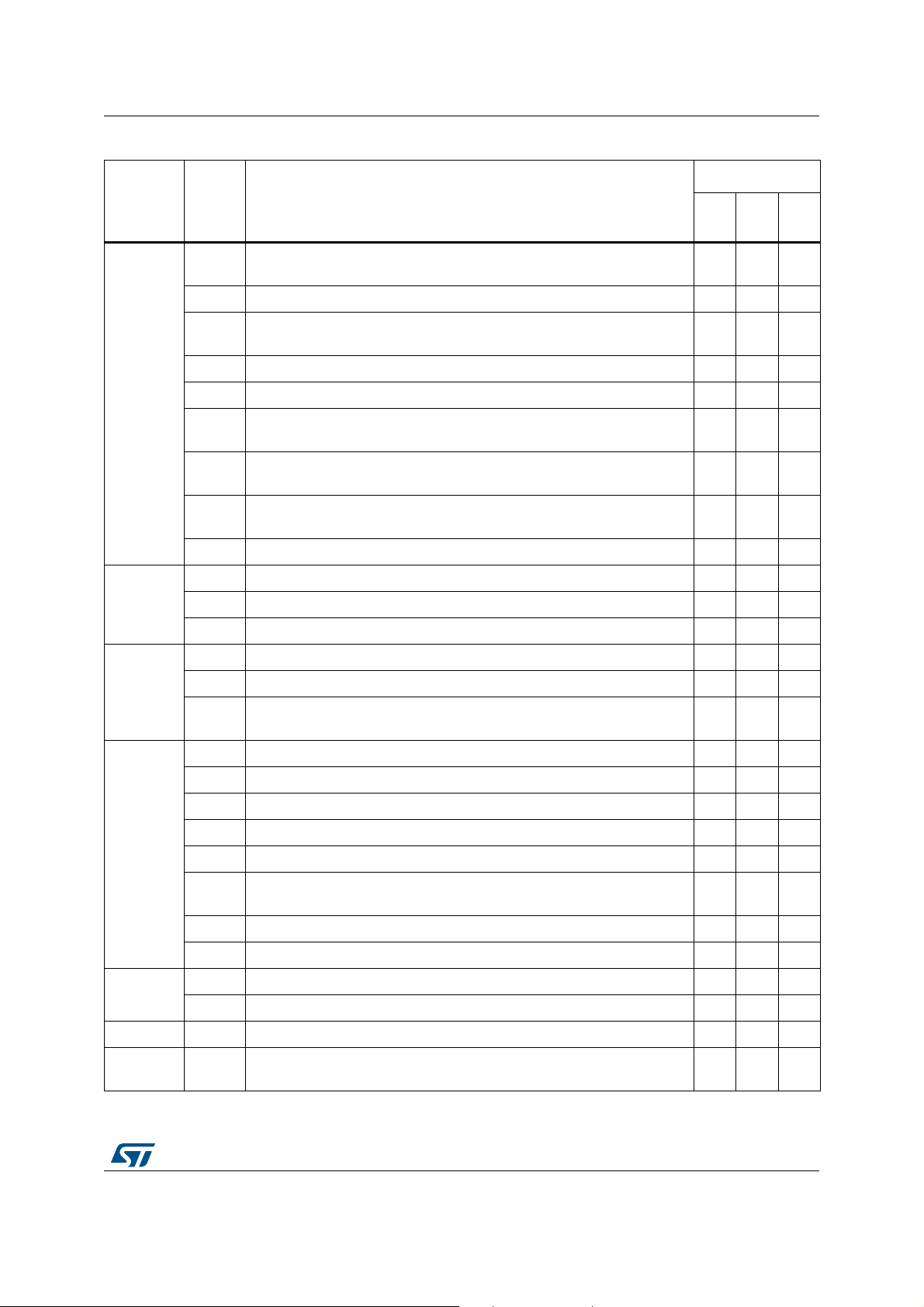
STM32H742/743xI/G Summary of device limitations
Table 3. Summary of device limitations (continued)
Status
Function Section Limitation
Rev. YRev.
(1)
X
Rev.
V
System
(continued)
FMC
QUADSPI
2.2.16
Device stalled when two consecutive level regressions occur without
accessing from/to backup SRAM
-AA
2.2.17 Invalid Flash memory CRC P- -
2.2.18
GPIO assigned to DAC cannot be used in output mode when the DAC
output is connected to on-chip peripheral
NNN
2.2.19 Unstable LSI when it clocks RTC or CSS on LSE AAA
2.2.20 480 MHz maximum CPU frequency not available on silicon revision Y PPP
2.2.21
2.2.22
2.2.23
VDDLDO is not available on TFBGA100 package on devices revision Y
and V
WWDG not functional when VDD is lower than 2.7 V and VOS0 or
VOS1 voltage level is selected
A tamper event does not erase the backup RAM when the backup RAM
clock is disabled
NNN
NNN
NNN
2.2.24 LSE CSS parasitic detection even when disabled NNN
2.3.1 Dummy read cycles inserted when reading synchronous memories NNN
2.3.2 Wrong data read from a busy NAND Flash memory AAA
2.3.3 Missed clocks with continuous clock feature enabled A- -
2.4.1 First nibble of data is not written after a dummy phase A- -
2.4.2 QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared AAA
2.4.3
QUADSPI cannot be used in Indirect read mode when only data
phase is activated
AAA
2.5.1 Conversion overlap may impact the ADC accuracy A- -
2.5.2 ADC resolution limited by LSE activity A- -
2.5.3 ADC maximum sampling rate when VDDA is lower than 2 V A- -
2.5.4 ADC maximum resolution when VDDA is higher than 3.3 V A- -
ADC
2.5.5 First ADC injected conversion in a sequence may be corrupted A- -
2.5.6
Writing the ADC_JSQR register when JADCSTART = 1 and JQDIS = 1
may lead to incorrect behavior
A- -
2.5.7 Conversion may be triggered by context queue register update AAA
2.5.8 Updated conversion sequence may be trigged by context queue update AAA
2.6.1 Overshoot on VREFBUF output AAA
VREFBUF
2.6.2 VREFBUF Hold mode cannot be used NNN
OPAMP 2.7.1 OPAMP high-speed mode must not be used N- -
LCD-
TFT
(2)
2.8.1
Device stalled when accessing LTDC registers while pixel clock is
disabled
AAA
ES0392 Rev 8 7/44
9
Page 8
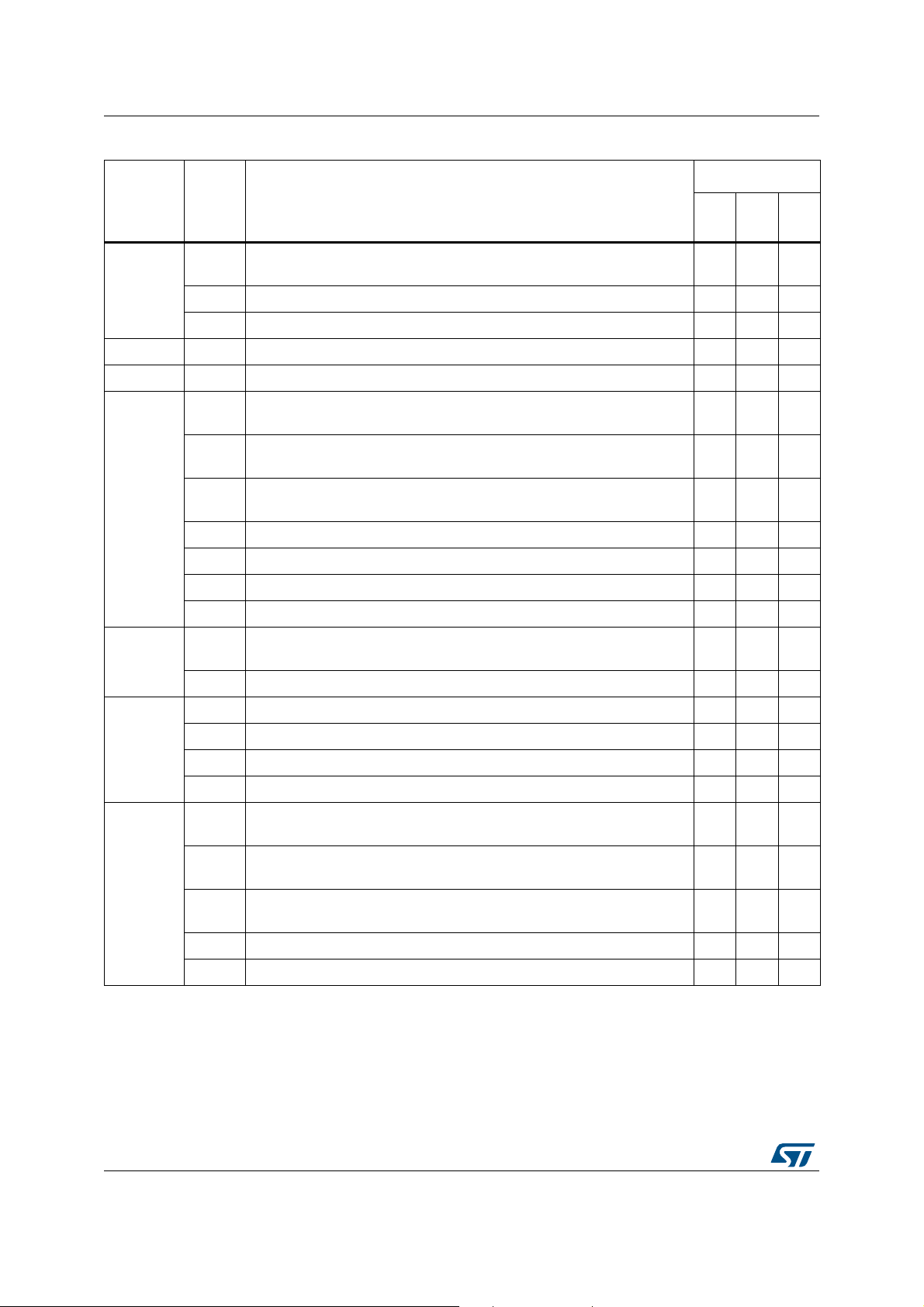
Summary of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
Table 3. Summary of device limitations (continued)
Status
Function Section Limitation
Rev. YRev.
(1)
X
Rev.
V
One-pulse mode trigger not detected in master-slave reset + trigger
configuration
PPP
TIM
2.9.1
2.9.2 Consecutive compare event missed in specific conditions NNN
2.9.2 Output compare clear not working with external counter reset PPP
LPTIM 2.10.1 MCU may remain stuck in LPTIM interrupt when entering Stop mode A- -
RTC 2.11.1 RTC calendar registers are not locked properly A- -
10-bit master mode: new transfer cannot be launched if first part of the
address is not acknowledged by the slave
Wrong behavior in Stop mode when wakeup from Stop mode is
disabled in I2C
Wrong data sampling when data setup time (t
) is shorter than
SU;DAT
one I2C kernel clock period
AAA
AAA
P- -
I2C
2.12.1
2.12.2
2.12.3
2.12.4 Spurious bus error detection in Master mode AAA
2.12.5 Last-received byte loss in Reload mode P- -
2.12.6 Spurious master transfer upon own slave address match PPP
2.12.7 START bit is cleared upon setting ADDRCF, not upon address match PPP
USART
2.13.1
Underrun flag is set when the USART is used in SPI Slave receive
mode
AAA
2.13.2 DMA stream locked when transferring data to/from USART/UART -AA
2.14.1 Spurious DMA Rx transaction after simplex Tx traffic A- -
SPI
2.14.2 Master data transfer stall at system clock much faster than SCK AAA
2.14.3 Corrupted CRC return at non-zero UDRDET setting PPP
2.14.4 TXP interrupt occurring while SPI/I2Sdisabled AAA
2.15.1
2.15.2
SDMMC
2.15.3
Busy not detected when a write operation suspended during busy
phase resumes
Wrong data line 2 generation between two blocks during DDR transfer
with Read wait mode enabled
Unwanted overrun detection when an AHB error is reported whereas all
bytes have been received
2.15.4 Consecutive multiple block transfers can induce incorrect data length A- -
2.15.5 Clock stop reported during Read wait mode sequence A- -
8/44 ES0392 Rev 8
A- -
A- -
A- -
Page 9
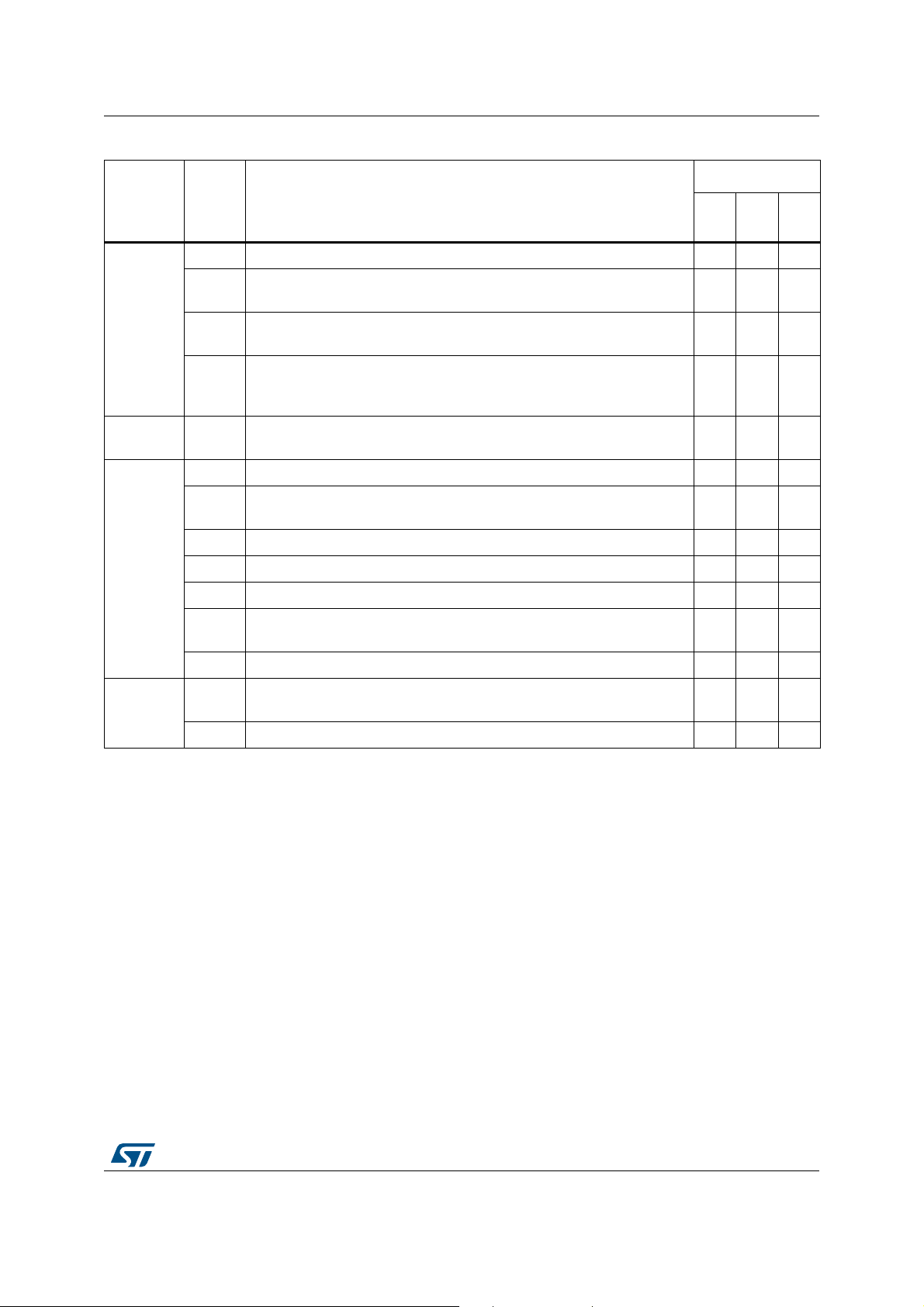
STM32H742/743xI/G Summary of device limitations
Table 3. Summary of device limitations (continued)
Status
Function Section Limitation
2.16.1 Writing FDCAN_TTTS during initialization corrupts FDCAN_TTTMC AAA
2.16.2
Wrong data may be read from Message RAM by the CPU when using
two FDCANs
Rev. YRev.
Rev.
(1)
X
V
A- -
FDCAN
2.16.3
Mis-synchronization in Edge filtering mode when the falling edge at
FDCAN_Rx input pin coincides with the end of the integration phase
Tx FIFO messages inverted when both Tx buffer and FIFO are used
2.16.4
and the messages in the Tx buffer have higher priority than in the Tx
FIFO
USB
OTG_HS
2.17.1 Possible drift of USB PHY pull-up resistor P- -
2.18.1 Incorrect L4 inverse filtering results for corrupted packets NNN
2.18.2
Rx DMA may fail to recover upon DMA restart following a bus error,
with Rx timestamping enabled
2.18.3 Tx DMA may halt while fetching TSO header under specific conditions AAA
ETH
2.18.4 Spurious receive watchdog timeout interrupt AAA
2.18.5 Incorrect flexible PPS output interval under specific conditions AAA
2.18.6
Packets dropped in RMII 10Mbps mode due to fake dribble and CRC
error
2.18.7 ARP offload function not effective AAA
HDMI-CEC
2.19.1
Unexpected switch to Receive mode without automatic transmission
retry and notification
2.19.2 CEC header not received due to unjustified Rx-Overrun detection AAA
1. Engineering samples only.
2. This limitation applies only to STM32H743xI/G microcontrollers.
AAA
AAA
PPP
AAA
AAA
ES0392 Rev 8 9/44
9
Page 10

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2 Description of device limitations
The following sections describe device limitations of the applicable Arm
provide workarounds if available. They are grouped by device functions.
(a)
core devices and
2.1 Arm® 32-bit Cortex®-M7 core
Errata notice for the Arm® processor Cortex®-M7 core revision r1p1 is available from
http://infocenter.arm.com.
2.1.1 Cortex®-M7 data corruption when using Data cache configured in write-through
Description
This limitation is registered under Arm® ID number 1259864 and classified into “Category
A”.
If a particular sequence of stores and loads is performed to write-through memory, and
so
me timing-based internal conditions are met, then a load might not get the last data stored
to that address.
This erratum can only occur if the loads and stores are to write-through memory. This could
due to any of the following:
be
• The
• The default memory map is being used and this address is write-through in that map.
• The memory is cacheable, and the CM7_CACR.FORCEWT bit is set.
• The memory is cacheable, shared, and the CM7_CACR.SIWT bit is set.
MPU has been programmed to set this address as write-through.
The following sequence is required for this erratum to occur:
1. The address of interest must be in the cache.
2. A write-through store to the same doubleword as the address of interest.
3. One of the following:
– A linefill is started (to a different cacheline to the address
to the same set as the address of interest.
– An ECC error.
– A cache maintenance operation without a following DSB.
4. A store to the address of interest.
5. A load from the address of interest.
If certain specific timing conditions are met,
from what was in the cache at the start of the sequence instead of the data from the second
store.
a. Arm is a registered trademark of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the US and/or elsewhere.
10/44 ES0392 Rev 8
the load will get the data from the first store, or
of interest) that allocates
Page 11

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
The effect of this erratum is that load operations can return incorrect data.
Workaround
There is no direct workaround for this erratum.
Where possible, Arm® recommends that you use the MPU to change the attributes on any
write-through memory to write-back memory. If this is not possible, it might be necessary to
disable the cache for sections of code that access write-through memory.
2.1.2 Cortex®-M7 FPU interrupt not present on NVIC line 81
Description
Arm® Cortex®-M7 FPU interrupt is not mapped on NVIC line 81.
Note: This limitation is due to an error of implementation of the Arm core on the die, as opposed to
a limitation of the core itself.
Workaround
None.
2.2 System
2.2.1 Timer system breaks do not work
Description
System break sources (processor LOCKUP output, PVD detection, RAM ECC error, Flash
ECC error or clock security system detection) do not generate a break event on TIM1, TIM8
and HRTIM.
Workaround
None
2.2.2 Clock recovery system synchronization with USB SOF does not work
Description
The clock recovery system (CRS) synchronization by USB start-of-frame signal (SOF) does
not work.
Workaround
When available, use the LSE oscillator as synchronization source.
ES0392 Rev 8 11/44
40
Page 12

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.2.3 SysTick external clock is not HCLK/8
Description
The SysTick external clock is the system clock, instead of the system clock divided by 8
(HCLK/8).
Workaround
Use the system clock (HCLK) as external clock and multiply the reload value by 8 in
STK_LOAD register (take care that the maximum value is 2
24
-1).
2.2.4 Option byte loading can be done with the user wait-state configuration
Description
After an option byte change, the option byte loading is performed with the user wait-state
configuration instead of the default configuration.
Workaround
When performing option byte loading (modification), configure the correct number of waitstates or use the default value (7 wait states).
2.2.5 Flash BusFault address register may not be valid when an ECC double error occurs
Description
When a first read operation is performed without ECC error and a master accesses data
with wait states, if a new access is done and contains an ECC double detection error, then
the error message returns the address of the first data which has not generated the error.
Workaround
When a double ECC error flag is raised, check the failing address in the Flash interface
(FAIL_ECC_ADDR1/2 in FLASH_ECC_FA1R/FA2R) and disregard the content of the
BusFault address register.
2.2.6 Flash ECC address register may not be updated
Description
When two consecutive ECC errors occur, the content of the FLASH_ECC_FA1/2 register
cannot be updated if the error correction flag (SNECCERR1/2 or DBECCERR1/2 in
FLASH_SR1/2 register) is cleared at the same time as a new ECC error occurs.
Workaround
None.
12/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 13

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.2.7 PCROP-protected areas in Flash memory may be unprotected
Description
In case of readout protection level regression from level 1 to level 0, the PCROP protected
areas in Flash memory may become unprotected.
Workaround
The user application must set the readout protection level to level 2 to avoid PCROPprotected areas from being unprotected.
2.2.8 Flash memory bank swapping might impact embedded Flash memory interface behavior
Description
When Flash memory bank swapping feature is enabled, the embedded Flash memory
interface behavior might become unpredictable.
Workaround
Do not enable the Flash memory bank swapping feature on devices revision Y.
2.2.9 Reading from AXI SRAM may lead to data read corruption
Description
Read data may be corrupted when the following conditions are met:
• Several read transactions are performed to the AXI SRAM,
• and a master delays its data acceptance while a new transfer is requested.
Workaround
Set the READ_ISS_OVERRIDE bit in the AXI_TARG7_FN_MOD register. This will reduce
the read issuing capability to 1 at AXI interconnect level and avoid data corruption.
2.2.10 Clock switching does not work when LSE failure is detected by CSS
Description
When a failure on the LSE oscillator is detected by a clock security system (CSS), the
backup domain clock source cannot be changed.
Workaround
When a clock security system detects a LSE failure, reset the backup domain and select a
functional clock source.
ES0392 Rev 8 13/44
40
Page 14

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.2.11 RTC stopped when a system reset occurs while the LSI is used as a clock source
Description
When the LSI clock is used as RTC clock source, the RTC is stopped (it does not received
the clock anymore) when a system reset occurs.
Workaround
1. Check the RTC clock source after each system reset.
2. If the LSI clock is selected, enable it again.
2.2.12 USB OTG_FS PHY drive limit on DP/DM pins
Description
To avoid damaging parts, the user application must avoid to load more than 5 mA on
OTG_FS_DP/DM pins.
Workaround
None
2.2.13 Unexpected leakage current on I/Os when VIN higher that VDD
Description
When VIN is higher than VDD and depending on the waveform applied to I/Os, an
unexpected leakage current might be observed when V
Note: This leakage does not impact the product reliability.
decreases.
IN
Workaround
The application must maintain VIN lower that VDD to avoid current leakage on I/Os.
2.2.14 LSE oscillator driving capability selection bits are swapped
Description
The LSEDRV[1:0] bits in the RCC_BDCR register, which are used to select LSE oscillator
driving capability, are swapped (see
LSEDRV[1:0]
Table 4. Expected vs effective LSE driving mode
01 Medium-low drive Medium-high drive
10 Medium-high drive Medium-low drive
Table 4).
LSE driving mode
Expected mode Effective mode
14/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 15

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
Workaround
• Use LSEDRV[1:0]=01 to select LSE medium-high drive
• Use LSEDRV[1:0]=10 to select LSE medium-low drive
2.2.15 HRTIM internal synchronization does not work
Description
HRTIM synchronization input source from internal event (SYNCIN[1:0]=10 in the
HRTIM_MCR register) does not work. Consequently, it is not possible to use the on-chip
TIM1_TRGO output as synchronization event for HRTIM.
Workaround
None.
2.2.16 Device stalled when two consecutive level regressions occur without accessing from/to backup SRAM
Description
The device might stall when two consecutive level regressions (switching from RDP level 1
to RDP level 0) are performed without accessing (reading/writing) from/to backup SRAM.
A power-on reset is required to recover from this failure.
Workaround
Perform a dummy access to backup SRAM before executing the level regression sequence
(switching from RDP level 1 to RDP level 0).
2.2.17 Invalid Flash memory CRC
Description
The CRC result might be corrupted when FLASH CRC end address register for bank 1/2
(FLASH_CRCEADD1/2R) targets last address in sector 7.
Workaround
Do not use the Flash memory CRC calculation feature.
2.2.18 GPIO assigned to DAC cannot be used in output mode when the DAC output is connected to on-chip peripheral
Description
When a DAC output is connected only to an on-chip peripheral, the corresponding GPIO is
expected to be available as an output for any other functions.
However, when the DAC output is configured for on-chip peripheral connection only, the
GPIO output buffer remains disabled and cannot be used in output mode (GPIO or alternate
function). It can still be used in input or analog mode.
ES0392 Rev 8 15/44
40
Page 16

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
This limitation applies to DAC1_OUT1 and DAC1_OUT2 connected to PA4 and PA5,
respectively.
Workaround
None.
2.2.19 Unstable LSI when it clocks RTC or CSS on LSE
Description
The LSI clock might become unstable (duty cycle different from 50 %) and its maximum
frequency can become significantly higher than 32
• The LSI oscillator clocks the RTC, or it clocks the clock security system (CSS) on LSE
(enabled when the LSECSSON bit of RCC_BDCR is set), and
• the V
–if V
–if V
power domain is reset while the backup domain is not reset, which happens:
DD
and VDD are separate and VDD is switched off and then on,
BAT
is tied to VDD (internally in the package for products that do not feature the
BAT
V
pin, or externally) and a short VDD drop under VDD(min) occurs (less than
BAT
1 ms).
Workaround
kHz, when:
Apply one of the following measures:
• Clock the RTC with LSE or HSE/RTCPRE, without using the CSS on LSE.
• If the LSI oscillator clocks the RTC or when the LSECSSON bit is set, reset the backup
domain upon each V
power-up (when the BORRSTF flag is set in RCC_RSR).
DD
2.2.20 480 MHz maximum CPU frequency not available on silicon revision Y
Description
VOS0 voltage scaling level is not available on silicon revision Y devices. This limits the
maximum CPU frequency to 400
MHz.
Workaround
Use silicon revision V devices to reach a maximum frequency of 480 MHz.
2.2.21 VDDLDO is not available on TFBGA100 package on devices revision Y and V
Description
On devices revision Y and V, VDDLDO pin is not available on TFBGA100 package. F4 ball
is internally connected to V
Workaround
DD
.
None.
16/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 17

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.2.22 WWDG not functional when VDD is lower than 2.7 V and VOS0 or VOS1 voltage level is selected
Description
The system window watchdog (WWDG) is not functional, that is, it does not generate a
correct system reset and/or the WWDG reset flag is not asserted, when V
2.7
V and VOS0 or VOS1 voltage level is selected. There is no dependency on V
is lower than
DD
DDLDO
.
Workaround
None.
2.2.23 A tamper event does not erase the backup RAM when the backup RAM clock is disabled
Description
Upon a tamper event, the backup RAM is normally reset and its content erased. However,
when the backup RAM clock is disabled (BKPRAMEN bit set to 0 in RCC_ AHB4ENR
register), the backup RAM reset fails and the memory is not erased.
Workaround
Enable the backup RAM clock by setting BKPRAMEN bit to 1 in the RCC_AHB4 clock
register (RCC_AHB4ENR). This can be done either during device initialization or during a
tamper service routine
2.2.24 LSE CSS parasitic detection even when disabled
Description
The LSECSSD flag in RCC_BDCR register can be spuriously set in case of ESD stress
when the device is in VBAT mode, even if the CSS on LSE is disabled. As long as the
LSECSSD flag is set, the LSE clock is no longer propagated to the RTC and the system,
even if the LSE is oscillating. LSECSSD can be cleared only by a backup domain reset.
During ST functional ESD tests, this failure was observed by stressing PC13, PC14, VBAT,
PE5 and PE6 pins. No failure was detected when both V
sensitivity observed on these five pins can be quantified through IEC1000-4-2 (ESD
immunity) standard with severity estimated between 1 (low immunity) and 2 (medium
immunity) according to the same standard.
DD
and V
were present. The
BAT
ES0392 Rev 8 17/44
40
Page 18

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
Workaround
To achieve a good overall EMC robustness, it is recommended to follow the general EMC
rules for hardening the equipment immunity. The robustness can be further improved for the
impacted pins other than VBAT by inserting close to the microcontroller, where possible,
serial resistors with a value as high as possible and lower or equal to 1
kΩ.
2.3 FMC
2.3.1 Dummy read cycles inserted when reading synchronous memories
Description
When performing a burst read access from a synchronous memory, two dummy read
accesses are performed at the end of the burst cycle whatever the type of AXI burst access.
The extra data values read are not used by the FMC and there is no functional failure.
Workaround
None.
2.3.2 Wrong data read from a busy NAND Flash memory
Description
When a read command is issued to the NAND memory, the R/B signal gets activated upon
the de-assertion of the chip select. If a read transaction is pending, the NAND controller
might not detect the R/B signal (connected to NWAIT) previously asserted and sample a
wrong data. This problem occurs only when the MEMSET timing is configured to 0x00 or
when ATTHOLD timing is configured to 0x00 or 0x01.
Workaround
Either configure MEMSET timing to a value greater than 0x00 or ATTHOLD timing to a value
greater than 0x01.
2.3.3 Missed clocks with continuous clock feature enabled
Description
When the continuous clock feature is enabled, the FMC_CLK clock can be switched OFF in
the following conditions:
• The FMC_CLK clock is divided by 2.
• An asynchronous byte transaction is performed on an FMC bank configured in 32-bit
memory data width.
Note: When the FMC_CLK clock is switched OFF on static memories, it can be switched ON by
issuing a synchronous transaction or any asynchronous transaction different from a byte
access on 32-bit data bus width.
18/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 19

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
Workaround
When the continuous clock feature is enabled, do not use the FMC_CLK clock divider ratio
of 2 when issuing a byte transaction to 32-bit asynchronous memories.
2.4 QUADSPI
2.4.1 First nibble of data is not written after a dummy phase
Description
The first nibble of data to be written to the external Flash memory is lost in the following
conditions:
• The QUADSPI is used in the Indirect write mode,
• and at least one dummy cycle is used.
Workaround
Use an alternate-bytes phase instead of a dummy phase in order to add a latency period
between the address phase and the data phase. This workaround works only if the number
of dummy cycles corresponds to a multiple of 8 bits of data.
As an example:
• To generate 1 dummy cycle, send 1 alternate-byte in 4 data line DDR mode or Dual-
Flash SDR mode.
• To generate 2 dummy cycles, send 1 alternate-byte in 4 data line SDR mode
• To generate 4 dummy cycles, send 2 alternate-bytes in 4 data line SDR mode or send
1 alternate-byte in 2 data line SDR mode
• To generate 8 dummy cycles, send 1 alternate-byte in 1 data line SDR mode.
2.4.2 QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared
Description
Writing 0x0000 0000 to the QUADSPI_CCR register causes the QUADSPI peripheral to
hang while the BUSY flag of the QUADSPI_SR register. remains set. Even an abort does
not allow exiting this status.
Workaround
Clear then set the EN bit in the QUADSPI_CR register.
ES0392 Rev 8 19/44
40
Page 20

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.4.3 QUADSPI cannot be used in Indirect read mode when only data phase is activated
Description
When the QUADSPI is configured in Indirect read with only the data phase activated (in
Single, Dual, Quad or Dual-quad I/O mode), the QUADSPI peripheral hangs and the BUSY
flag remains of the QUADSPI_SR register remains high. An abort must be performed to
reset the BUSY flag and exit from the hanging state.
Workaround
Insert a dummy phase with at least two dummy cycles.
2.4.4 Memory-mapped read of last memory byte fails
Description
Regardless of the number of I/O lines used (1, 2 or 4), a memory-mapped read of the last
byte of the memory region defined through the FSIZE[4:0] bitfield of the QUADSPI_DCR
register always yields 0x00, whatever the memory byte content is. A repeated attempt to
read that last byte causes the AXI bus to stall.
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Avoid reading the last byte of the memory region defined through FSIZE, for example
by taking margin in FSIZE bitfield setting.
• If the last byte is read, ignore its value and abort the ongoing process so as to prevent
the AXI bus from stalling.
• For reading the last byte of the memory region defined through FSIZE, use indirect
read.
2.5 ADC
2.5.1 Conversion overlap may impact the ADC accuracy
Description
The following conditions may impact the ADC accuracy
• Several ADC conversions are running simultaneously
• ADC and DAC conversions are running simultaneously
Workaround
Avoid conversion overlapping. The application should ensure that conversions are
performed sequentially.
20/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 21

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.5.2 ADC resolution limited by LSE activity
Description
The following ADC3 input pins may be impacted by adjacent LSE activity:
• ADC3 channels on pins PF3 to PF10
Workaround
16-bit and 14-bit data resolutions are not recommended on these pins. This limits data
resolution configuration to 8 bits, 10 bits or 12 bits
.
2.5.3 ADC maximum sampling rate when V
is lower than 2 V
DDA
Description
If V
sampling rate.
is lower than 2 V, the ADC conversion accuracy is not guaranteed over the full ADC
DDA
Workaround
The application should avoid a sampling rate higher than 1.5 MSPS when operating with
V
below 2 V.
DDA
2.5.4 ADC maximum resolution when V
is higher than 3.3 V
DDA
Description
If V
resolutions.
is higher than 3.3V, the ADC conversion accuracy is not guaranteed for all data
DDA
Workaround
16-bit, 14-bit and 12-bit data resolutions are not useful in this configuration. This limits
available data resolution configuration to 8 bits and 10 bits.
2.5.5 First ADC injected conversion in a sequence may be corrupted
Description
The ADC injected conversion that follows a regular conversion may be corrupted if the
following conditions are met:
• A regular conversion successive approximation is ongoing (sampling phase finished)
• An injected conversion sequence is triggered during the regular conversion successive
approximation phase.
In this case, the first injected conversion returns an invalid result. Other conversions are not
impacted.
ES0392 Rev 8 21/44
40
Page 22

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Use a sequence of at least two injected conversions, ignore the first injected value and
consider the other ones.
• Synchronize regular and injected conversion to prevent regular channels and injected
channels from overlapping.
2.5.6 Writing the ADC_JSQR register when JADCSTART = 1 and JQDIS = 1 may lead to incorrect behavior
Description
Writing the ADCx_JSQR register when an injected conversion is ongoing (JADCSTART=1)
may lead to unpredictable ADC behavior if the queue of context is not enabled (JQDIS=1).
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Use the context queue (JQDIS=0) to allow on-the-fly ADCx_JSQR modification
• Ensure that no injected conversion is ongoing (JADSTART=0) before modifying
ADC_JSQR register.
2.5.7 Conversion may be triggered by context queue register update
Description
Modifying the trigger selection or the edge polarity detection may trigger the conversion of
the new context without waiting for the trigger edge when the following conditions are met:
• The injected queue conversion is enabled (JQDIS = 0 in ADC_CGFR register) and
• the queue is never empty (JQM = 0 in ADC_CGFR register).
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Ignore the first converted sequence.
• Use the queue of context with JQM = 1 in ADC_CGFR.
• Use the queue of context with JQM = 0 in ADC_CGFR and change the sequence
without modifying the trigger and the polarity.
2.5.8 Updated conversion sequence may be trigged by context queue update
Description
Modifying the context queue for injected conversions may trigger the conversion of the new
context without waiting for the trigger edge when the following conditions are met:
• The injected queue conversion is enabled (JQDIS = 0 in ADC_CGFR register) and
• the queue is not empty (JQM = 0 in ADC_CGFR register) and
• the context queue is programmed five cycles before the JEOS flag is set to 1 in the
ADC_ISR register.
22/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 23

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Use the queue of context with JQM = 1 in ADC_CGFR.
• Synchronize the programming of the new context with the next trigger edge to make
sure it is performed after JEOS flag is set in ADC_ISR (for example at the trigger rising
edge).
2.6 VREFBUF
2.6.1 Overshoot on VREFBUF output
Description
An overshoot might occur on VREFBUF output if VREF+ pin has residual voltage when
VREFBUF is enabled (ENVR set to 1 in VREFBUF_CSR register).
Workaround
Let the voltage on the VREF+ pin drop to a level lower than 1 V below the target
VREFBUF_OUT. This can be achieved by switching VREFBUF buffer off (ENVR
HIZ
= 0 in VREFBUF_CSR register) during sufficient time to discharge the capacitor on the
VREF+ pin through VREFBUF pull-down resistor.
= 0 and
2.6.2 VREFBUF Hold mode cannot be used
Description
VREFBUF can be configured to operate in Hold mode to reduce current consumption.
When VREFBUF enters Hold mode (by setting both HIZ and ENVR bits of the
VREFBUF_CSR register), the VREF+ I/O transits to high impedance mode. If not
discharged externally, the capacitor on the VREF+ pin keeps its charge and voltage. Exiting
VREFBUF Hold mode (by clearing the HIZ bit) in this condition might lead to a voltage
overshoot on the VREF+ output.
Workaround
None.
2.7 OPAMP
2.7.1 OPAMP high-speed mode must not be used
Description
Signal limitations might be observed if the OPAMP high-speed mode is used (OPAHSM bit
set in OPAMPx_CSR register).
Workaround
None.
ES0392 Rev 8 23/44
40
Page 24

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.8 LCD-TFT
2.8.1 Device stalled when accessing LTDC registers while pixel clock is disabled
Description
The device might hang if an access to the LTDC register interface is performed while the
pixel clock (ltdc_ker_ck) is disabled.
Workaround
Enable the pixel clock before accessing LTDC registers. Apply the following sequence to
enable the LTDC clock:
1. Enable pll3_r_ck to feed the LTDC pixel clock (ltdc_ker_ck).
2. Enable the LTDC register interface clock by setting the LTDCEN bit in the
RCC_APB3ENR register.
2.9 TIM
2.9.1 One-pulse mode trigger not detected in master-slave reset + trigger configuration
Description
The failure occurs when several timers configured in one-pulse mode are cascaded, and the
master timer is configured in combined reset + trigger mode with the MSM bit set:
OPM = 1 in TIMx_CR1, SMS[3:0] = 1000 and MSM = 1 in TIMx_SMCR.
The MSM delays the reaction of the master timer to the trigger event, so as to have the
slave timers cycle-accurately synchronized.
If the trigger arrives when the counter value is equal to the period value set in the
TIMx_ARR register, the one-pulse mode of the master timer does not work and no pulse is
generated on the output.
Workaround
None. However, unless a cycle-level synchronization is mandatory, it is advised to keep the
MSM bit reset, in which case the problem is not present. The MSM = 0 configuration also
allows decreasing the timer latency to external trigger events.
2.9.2 Consecutive compare event missed in specific conditions
Description
Every match of the counter (CNT) value with the compare register (CCR) value is expected
to trigger a compare event. However, if such matches occur in two consecutive counter
24/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 25

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
clock cycles (as consequence of the CCR value change between the two cycles), the
second compare event is missed for the following CCR value changes:
• in edge-aligned mode, from ARR to 0:
– first compare event: CNT = CCR = ARR
– second (missed) compare event: CNT = CCR = 0
• in center-aligned mode while up-counting
value if the period is also changed) at the crest (that is, when TIMx_RCR = 0):
– first compare event: CNT = CCR = (ARR-1)
– second (missed) compare event: CNT = CCR = ARR
• in center-aligned mode while down-counting
TIMx_RCR = 0):
– first compare event: CNT = CCR = 1
– second (missed) compare event: CNT = CCR = 0
This typically corresponds to an abrupt change of compare value aiming at creating a timer
clock single-cycle-wide pulse in toggle mode.
As a consequence:
• In toggle mode, the output only toggles once per counter period (squared waveform),
whereas it is expected to toggle twice within two consecutive counter cycles (and so
exhibit a short pulse per counter period).
• In center mode, the compare interrupt flag does note rise and the interrupt is not
generated.
, from ARR-1 to ARR (possibly a new ARR
, from 1 to 0 at the valley (that is, when
Note: The timer output operates as expected in modes other than the toggle mode.
Workaround
None.
2.9.3 Output compare clear not working with external counter reset
Description
The output compare clear event (ocref_clr) is not correctly generated when the timer is
configured in the following slave modes: Reset mode, Combined reset + trigger mode, and
Combined gated + reset mode.
The PWM output remains inactive during one extra PWM cycle if the following sequence
occurs:
1. The output is cleared by the ocref_clr event.
2. The timer reset occurs before the programmed compare event.
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Use BKIN (or BKIN2 if available) input for clearing the output, selecting the Automatic
output enable mode (AOE = 1).
• Mask the timer reset during the PWM ON time to prevent it from occurring before the
compare event (for example with a spare timer compare channel open-drain output
connected with the reset signal, pulling the timer reset line down).
ES0392 Rev 8 25/44
40
Page 26

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.10 LPTIM
2.10.1 MCU may remain stuck in LPTIM interrupt when entering Stop mode
Description
This limitation occurs when disabling the low-power timer (LPTIM).
When the user application clears the ENABLE bit in the LPTIM_CR register within a small
time window around one LPTIM interrupt occurrence, then the LPTIM interrupt signal used
to wake up the MCU from Stop mode may be frozen in active state. Consequently, when
trying to enter Stop mode, this limitation prevents the MCU from entering low-power mode
and the firmware remains stuck in the LPTIM interrupt routine.
This limitation applies to all Stop modes and to all instances of the LPTIM. Note that the
occurrence of this issue is very low.
Workaround
In order to disable a low power timer (LPTIMx) peripheral, do not clear its ENABLE bit in its
respective LPTIMx_CR register. Instead, reset the whole LPTIMx peripheral via the RCC
controller by setting and resetting its respective LPTIMxRST bit in RCC_APByRSTRz
register.
2.11 RTC
2.11.1 RTC calendar registers are not locked properly
Description
When reading the calendar registers with BYPSHAD = 0, the RTC_TR and RTC_DR
registers may not be locked after reading the RTC_SSR register. This happens if the read
operation is initiated one APB clock period before the shadow registers are updated. This
can result in a non-consistency of the three registers. Similarly, the RTC_DR register can be
updated after reading the RTC_TR register instead of being locked.
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Use BYPSHAD = 1 mode (bypass shadow registers), or
• If BYPSHAD = 0, read SSR again after reading SSR/TR/DR to confirm that SSR is still
the same, otherwise read the values again.
26/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 27

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.12 I2C
2.12.1 10-bit master mode: new transfer cannot be launched if first part of the address is not acknowledged by the slave
Description
An I2C-bus master generates STOP condition upon non-acknowledge of I2C address that it
sends. This applies to 7-bit addresses as well as to each byte of 10-bit addresses.
When the device set as I2C-bus master transmits a 10-bit address of which the first byte (5bit header + 2 MSBs of the address + direction bit) is not acknowledged, the device duly
generates a STOP condition but it then cannot start any new I
spurious state, the NACKF flag of the I2C_ISR register and the START bit of the I2C_CR2
register are both set, while the START bit should normally be cleared.
Workaround
In 10-bit-address master mode, if both NACKF flag and START bit get simultaneously set,
proceed as follows:
1. Wait for the STOP condition detection (STOPF = 1 in I2C_ISR register).
2. Disable the I2C peripheral.
3. Wait for a minimum of three APB cycles.
4. Enable the I2C peripheral again.
2
C-bus transfer. In this
2.12.2 Wrong behavior in Stop mode when wakeup from Stop mode is disabled in I2C
Description
If the wakeup from Stop mode by I2C is disabled (WUPEN = 0), the correct use of the I2C
peripheral is to disable it (PE
Run mode.
Some reference manual revisions may omit this information.
Failure to respect the above while the MCU operating as slave or as master in multi-master
topology enters Stop mode during a transfer ongoing on the I
following:
1. BUSY flag is wrongly set when the MCU exits Stop mode. This prevents from initiating
a transfer in Master mode, as the START condition cannot be sent when BUSY is set.
2. If clock stretching is enabled (NOSTRETCH = 0), the SCL line is pulled low by I2C and
the transfer stalled as long as the MCU remains in Stop mode.
The occurrence of such condition depends on the timing configuration, peripheral clock
frequency, and I
This is a description inaccuracy issue rather than a product limitation.
2
Workaround
No application workaround is required.
= 0) before entering Stop mode, and re-enable it when back in
2
C-bus may lead to the
C-bus frequency.
ES0392 Rev 8 27/44
40
Page 28

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.12.3 Wrong data sampling when data setup time (t
one I2C kernel clock period
Description
The I2C-bus specification and user manual specify a minimum data setup time (t
• 250 ns in Standard mode
• 100 ns in Fast mode
• 50 ns in Fast mode Plus
The MCU does not correctly sample the I2C-bus SDA line when t
I2C kernel clock (I
instead of the current one. This can result in a wrong receipt of slave address, data byte, or
acknowledge bit.
Workaround
Increase the I2C kernel clock frequency to get I2C kernel clock period within the transmitter
minimum data setup time. Alternatively, increase transmitter’s minimum data setup time. If
the transmitter setup time minimum value corresponds to the minimum value provided in the
2
I
C-bus standard, the minimum I2CCLK frequencies are as follows:
• In Standard mode, if the transmitter minimum setup time is 250 ns, the I2CCLK
frequency must be at least 4 MHz.
• In Fast mode, if the transmitter minimum setup time is 100 ns, the I2CCLK frequency
must be at least 10 MHz.
• In Fast-mode Plus, if the transmitter minimum setup time is 50 ns, the I2CCLK
frequency must be at least 20 MHz.
2
C-bus peripheral clock) period: the previous SDA value is sampled
SU;DAT
SU;DAT
) is shorter than
SU;DAT
is smaller than one
) as:
2.12.4 Spurious bus error detection in Master mode
Description
In Master mode, a bus error can be detected spuriously, with the consequence of setting the
BERR flag of the I2C_SR register and generating bus error interrupt if such interrupt is
enabled. Detection of bus error has no effect on the I
any such transfer continues normally.
Workaround
If a bus error interrupt is generated in Master mode, the BERR flag must be cleared by
software. No other action is required and the ongoing transfer can be handled normally.
2
C-bus transfer in Master mode and
28/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 29

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.12.5 Last-received byte loss in Reload mode
Description
If in Master receiver mode or Slave receive mode with SBC = 1 the following conditions are
all met:
• I2C-bus stretching is enabled (NOSTRETCH = 0)
• RELOAD bit of the I2C_CR2 register is set
• NBYTES bitfield of the I2C_CR2 register is set to N greater than 1
• byte N is received on the I
• N - 1 byte is not yet read out from the data register at the instant TCR is raised,
then the SCL line is pulled low (I2C-bus clock stretching) and the transfer of the byte N from
the shift register to the data register inhibited until the byte N-1 is read and NBYTES bitfield
reloaded with a new value, the latter of which also clears the TCR flag. As a consequence,
the software cannot get the byte N and use its content before setting the new value into the
NBYTES field.
For I2C instances with independent clock, the last-received data is definitively lost (never
transferred from the shift register to the data register) if the data N
APB clock cycles preceding the receipt of the last data bit of byte N and thus the TCR flag
raising. Refer to the product reference manual or datasheet for the I2C implementation
table.
2
C-bus, raising the TCR flag
- 1 is read within four
Workaround
• In Master mode or in slave mode with SBC = 1, use the Reload mode with
NBYTES = 1.
• In Master receiver mode, if the number of bytes to transfer is greater than 255, do not
use the Reload mode. Instead, split the transfer into sections not exceeding 255 bytes
and separate them with repeated START conditions.
• Make sure, for example through the use of DMA, that the byte N - 1 is always read
before the TCR flag is raised. Specifically for I2C instances with independent clock,
make sure that it is always read earlier than four APB clock cycles before the receipt of
the last data bit of byte N and thus the TCR flag raising.
The last workaround in the list must be evaluated carefully for each application as the timing
depends on factors such as the bus speed, interrupt management, software processing
latencies, and DMA channel priority.
ES0392 Rev 8 29/44
40
Page 30

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.12.6 Spurious master transfer upon own slave address match
Description
When the device is configured to operate at the same time as master and slave (in a multimaster I
condition:
• Another master on the bus is in process of sending the slave address of the device (the
• The device initiates a master transfer by writing the I2C_CR2 register with its START
• After the ADDR flag is set:
In these circumstances, even though the START bit is automatically cleared by the circuitry
handling the ADDR flag, the device spuriously proceeds to the master transfer as soon as
the bus becomes free. The transfer configuration depends on the content of the I2C_CR2
register when the master transfer starts. Moreover, if the I2C_CR2 is written less than three
kernel clocks before the ADDR flag is cleared, the I2C peripheral may fall into an
unpredictable state.
2
C-bus application), a spurious master transfer may occur under the following
bus is busy).
bit set before the slave address match event (the ADDR flag set in the I2C_ISR
register) occurs.
– the device does not write I2C_CR2 before clearing the ADDR flag, or
– the device writes I2C_CR2 earlier than three I2C kernel clock cycles before
clearing the ADDR flag
Workaround
Upon the address match event (ADDR flag set), apply the following sequence.
Normal mode (SBC = 0):
1. Set the ADDRCF bit.
2. Before Stop condition occurs on the bus, write I2C_CR2 with the START bit low.
Slave byte control mode (SBC = 1):
1. Write I2C_CR2 with the slave transfer configuration and the START bit low.
2. Wait for longer than three I2C kernel clock cycles.
3. Set the ADDRCF bit.
4. Before Stop condition occurs on the bus, write I2C_CR2 again with its current value.
The time for the software application to write the I2C_CR2 register before the Stop condition
is limited, as the clock stretching (if enabled), is aborted when clearing the ADDR flag.
Polling the BUSY flag before requesting the master transfer is not a reliable workaround as
the bus may become busy between the BUSY flag check and the write into the I2C_CR2
register with the START bit set.
30/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 31

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.12.7 START bit is cleared upon setting ADDRCF, not upon address match
Description
Some reference manual revisions may state that the START bit of the I2C_CR2 register is
cleared upon slave address match event.
Instead, the START bit is cleared upon setting, by software, the ADDRCF bit of the I2C_ICR
register, which does not guarantee the abort of master transfer request when the device is
being addressed as slave. This product limitation and its workaround are the subject of a
separate erratum.
Workaround
No application workaround is required for this description inaccuracy issue.
2.13 USART
2.13.1 Underrun flag is set when the USART is used in SPI Slave receive mode
Description
When the USART is used in SPI Slave receive mode, the underrun flag (UDR bit in
USART_ISR register) may be set even if the transmitter is disabled (TE bit set to 0 in
USAR_CR1 register).
Workaround
Three workarounds are possible
• Ignore the UDR flag when the transmitter is disabled.
• Clear the UDR flag every time it is set, even if the Transmitter is disabled.
• Write dummy data in the USART_TDR register to avoid setting the UDR flag.
2.13.2 DMA stream locked when transferring data to/from USART/UART
Description
When a USART/UART is issuing a DMA request to transfer data, if a concurrent transfer
occurs, the requested transfer may not be served and the DMA stream may stay locked.
Workaround
Use the alternative peripheral DMA channel protocol by setting bit 20 of the DMA_SxCR
register.
This bit is reserved in the documentation and must be used only on the stream that
manages data transfers for USART/UART peripherals.
ES0392 Rev 8 31/44
40
Page 32

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.14 SPI
2.14.1 Spurious DMA Rx transaction after simplex Tx traffic
Description
With empty RXFIFO, SPI/I2S can spuriously generate a DMA read request upon enabling
DMA receive traffic (by setting RXDMAEN bit), provided that the preceding completed
transaction is a simplex transmission.
Workaround
Before enabling DMA Rx transfer following a completed Tx simplex transfer, perform
hardware reset of the SPI/I2S peripheral.
2.14.2 Master data transfer stall at system clock much faster than SCK
Description
With the system clock (spi_pclk) substantially faster than SCK (spi_ker_ck divided by a
prescaler), SPI/I2S master data transfer can stall upon setting the CSTART bit within one
SCK cycle after the EOT event (EOT flag raise) signaling the end of the previous transfer.
Workaround
Apply one of the following measures:
• Disable then enable SPI/I2S after each EOT event.
• Upon EOT event, wait for at least one SCK cycle before setting CSTART.
• Prevent EOT events from occurring, by setting transfer size to undefined (TSIZE = 0)
and by triggering transmission exclusively by TXFIFO writes.
2.14.3 Corrupted CRC return at non-zero UDRDET setting
Description
With non-zero setting of UDRDET[1:0] bitfield, the SPI/I2S slave can transmit the first bit of
CRC pattern corrupted, coming wrongly from the UDRCFG register instead of SPI_TXCRC.
All other CRC bits come from the SPI_TXCRC register, as expected.
Workaround
Keep TXFIFO non-empty at the end of transfer.
2.14.4 TXP interrupt occurring while SPI/I2Sdisabled
Description
SPI/I2S peripheral is set to its default state when disabled (SPE = 0). This flushes the FIFO
buffers and resets their occupancy flags. TXP and TXC flags become set (the latter if the
TSIZE field contains zero value), triggering interrupt if enabled with TXPIE or EOTIE bit,
respectively. The resulting interrupt service can be spurious if it tries to write data into
TXFIFO to clear the TXP and TXC flags, while both FIFO buffers are inaccessible (as the
peripheral is disabled).
32/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 33

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
Workaround
Keep TXP and TXC (the latter if the TSIZE field contains zero value) interrupt disabled
whenever the SPI/I2S peripheral is disabled.
2.15 SDMMC
2.15.1 Busy not detected when a write operation suspended during busy phase resumes
Description
When a card accepts a suspend command during a block write operation busy phase, the
card may drive the data line 0 (SDMMC_D0) when the write transfer is resumed. The
SDMMC does not detect that the data line 0 is Low when the write transfer resumes.
Workaround
To suspend a write transfer:
1. Set DTHOLD bit in the SDMMC_CMDR register.
2. Wait till the DHOLD status flag is set in SDMMC_STAR register to make sure the busy
line has been released.
3. Send a suspend command to the card (CMDSUSPEND = 1, CMDTRANS = 0 and
CPSMEN = 1 in SDMMC_CMDR).
2.15.2 Wrong data line 2 generation between two blocks during DDR transfer with Read wait mode enabled
Description
The Read wait mode allows suspending an SDIO multiple block read operation when the
host is not ready to receive the next bytes. The host can request the card to suspend
temporarily the transfer by driving data line 2 (SDMMC_D2) low between two blocks.
When a double data rate (DDR) read operation is ongoing, data line 2 is not driven low but
toggles constantly. Consequently, some bytes are not received and a CRC error failure is
reported.
Workaround
Use the clock stretching method (RWMOD = 1) instead of data line 2 to suspend temporarily
the transfer between two blocks.
2.15.3 Unwanted overrun detection when an AHB error is reported whereas all bytes have been received
Description
When the internal DMA is used and a write transfer initiated by the SDMMC on the AHB
fails, the IDMATE flag is set in SDMMC_STAR and the transfer is aborted by flushing the
FIFO.
ES0392 Rev 8 33/44
40
Page 34

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
When an AHB error occurs on the three last bursts of a successful read transfer, the FIFO is
considered as empty (DATAEND flag set in SDMMC_STAR) but some bytes, not yet
transferred to the FIFO, may still be present in the internal receive buffer. As a result, the
following read operation will fail and report an overrun error.
Workaround
1. When DATAEND = 1, check IDMATE flag.
2. If IDMATE = 1 and DTDIR = 1 in SDMMC_DCTRL, reset SDMMC.
2.15.4 Consecutive multiple block transfers can induce incorrect data length
Description
When a new transfer is started by setting the DTEN bit in SDMMC_DCTRL control register
while less than eight SDMMC clock cycles elapsed since the end of the previous transfer,
the second transfer is performed with the number of blocks configured for the previous
transfer. This is due to the fact that the new number of data to be transferred has not been
reloaded in the internal data block counter.
Workaround
The user application must ensure that at least 8 SDMMC clock cycles elapsed between the
successful completion of a transfer and the moment DTEN bit is set.
2.15.5 Clock stop reported during Read wait mode sequence
Description
When the SDMMC clock is stopped at low level, CKSTOP flag may be wrongly set in the
SDMMC_STAR register.
Workaround
When the multiple block transfer completes (DATAEND = 1 in SDMMC_STAR),
simultaneously set CKSTOPC and DATAENDC to 1 in SDMMC_ICR register.
2.16 FDCAN
2.16.1 Writing FDCAN_TTTS during initialization corrupts FDCAN_TTTMC
Description
During TTCAN initialization, writing to FDCAN TT Trigger Select Register (FDCAN_TTTS)
also affects FDCAN TT Trigger Memory Configuration Register (FDCAN_TTTMC).
Workaround
The user application must avoid writing to FDCAN_TTTS register during TTCAN
initialization phase.
Note: Outside of TTCAN initialization phase, write operations to FDCAN_TTTS do not impact
FDCAN_TTTMC since this register is write protected.
34/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 35

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.16.2 Wrong data may be read from Message RAM by the CPU when using two FDCANs
Description
When using two FDCAN controllers, and the CPU and FDCANs simultaneously request
read accesses from Message RAM, the CPU read request may return erroneous data.
The issue is not present if the CPU requests write access to Message RAM.
Workaround
To avoid concurrent read accesses between the CPU and FDCANs, use only one FDCAN at
a time.
2.16.3 Mis-synchronization in Edge filtering mode when the falling edge at FDCAN_Rx input pin coincides with the end of the integration phase
Description
The FDCAN may synchronize itself badly and may not correctly receive the first bit of the
frame when the following conditions are met:
• The edge filtering is enabled (EFBI bit of FDCAN_CCCR set to 1) and
• the end of the integration phase coincides with a falling edge detected at the
FDCAN_Rx input pin.
In this case the CRC detects that the first bit of the received frame is incorrect, flags the
received frame as faulty and responds with an error frame. This issue does not affect the
reception of standard frames.
Workaround
Disable edge filtering or wait for frame retransmission.
2.16.4 Tx FIFO messages inverted when both Tx buffer and FIFO are used and the messages in the Tx buffer have higher priority than in the Tx FIFO
Description
Two consecutive messages from the Tx FIFO may be inverted in the transmit sequence
when the following conditions are met:
• The FDCAN uses both a dedicated Tx buffer and a Tx FIFO (TFQM bit of
FDCAN_TXBC set to 0) and
• the messages contained in the Tx buffer have a higher internal CAN priority than the
messages in the Tx FIFO.
ES0392 Rev 8 35/44
40
Page 36

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
Workaround
Choose one of the following workarounds
• Ensure that only one Tx FIFO element is pending for transmission at any time:
The Tx FIFO elements may be filled at any time with messages to be transmitted, but
their transmission requests are handled separately. Each time a Tx FIFO transmission
has completed and the Tx FIFO gets empty (TFE bit of FDACN_IR set to 1) the next Tx
FIFO element is requested.
• Use only a Tx FIFO:
Send both messages from a Tx FIFO, including the message with the higher priority.
This message has to wait until the preceding messages in the Tx FIFO have been sent.
• Use two dedicated Tx buffers (e.g. use Tx buffer 4 and 5 instead of the Tx FIFO):
The pseudo-code below replaces the function in charge of filling the Tx FIFO:
Write message to Tx Buffer 4
Transmit Loop:
Request Tx Buffer 4 - write AR4 bit in FDCAN_TXBAR
Write message to Tx Buffer 5
Wait until transmission of Tx Buffer 4 complete (IR bit in FDCAN_IR),
read TO4 bit in FDCAN_TXBTO
Request Tx Buffer 5 - write AR5 bit of FDCAN_TXBAR
Write message to Tx Buffer 4
Wait until transmission of Tx Buffer 5 complete (IR bit in FDCAN_IR),
read TO5 bit in FDCAN_TXBTO
2.17 USB OTG_HS
2.17.1 Possible drift of USB PHY pull-up resistor
Description
When the V
3.6
V and ground) remains activated for a long period of time, the pull-up resistor value
DDUSB33
might drift, reaching the maximum value defined in USB Specification.
This issue occurs only during device Transmit and Reset states in device mode. Other
device states are not impacted.
The degradation can be observed after USB PHY pull-up continuous activation in the
following conditions:
• 10 years of continuous transmit operations or
• A 86 million reset operations (from the USB host) provided that the reset period is
2.5 ms (duration might vary depending on host reset duration).
The above results are based on design simulation.
Workaround
For USB OTG_HS1, use the external USB PHY instead of the internal PHY.
For USB OTG_HS2: no workaround is available.
equals 3.6 V and the USB Idle resistor (pull-up 1 connected between
36/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 37

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
2.18 ETH
2.18.1 Incorrect L4 inverse filtering results for corrupted packets
Description
Received corrupted IP packets with payload (for IPv4) or total (IPv6) length of less than two
bytes for L4 source port (SP) filtering or less than four bytes for L4 destination port (DP)
filtering are expected to cause a mismatch. However, the inverse filtering unduly flags a
match and the corrupted packets are forwarded to the software application. The L4 stack
gets incomplete packet and drops it.
Note: The perfect filtering correctly reports a mismatch.
Workaround
None
2.18.2 Rx DMA may fail to recover upon DMA restart following a bus error, with Rx timestamping enabled
Description
When the timestamping of Rx packets is enabled, some or all of the received packets can
have Rx timestamp which is written into a descriptor upon the completion of the Rx
packet/status transfer.
However, due to a defect, when bus error occurs during the descriptor read (that is
subsequently used as context descriptor to update the Rx timestamp), the context
descriptor write is skipped by DMA. Also, Rx DMA does not flush the Rx timestamp stored in
the intermediate buffers during the error recovery process and enters Stop state. Due to this
residual timestamp in the intermediate buffer, Rx DMA, after being restarted, does not
transfer packets.
Workaround
Issue a soft reset to drop all Tx packets and Rx packets present inside the controller at the
time of bus error. After the soft reset, reconfigure the controller and re-create the
descriptors.
Note: The workaround introduces additional latency.
2.18.3 Tx DMA may halt while fetching TSO header under specific conditions
Description
When fetching header bytes from the system memory by issuing a one-beat request in TSO
mode, Tx DMA may get into a deadlock state if
• address-aligned beats are enabled (AAL bit of the ETH_DMASBMR register is set),
• DMA start address of a burst transfer request (BUF1AP of TDES0 descriptor) is not
aligned on a boundary of the configured data width (64 bits), and
• DMA start address of a burst transfer request is not aligned on a boundary of the
programmed burst length (TxPBL bit of the ETH_DMACTXCR register).
ES0392 Rev 8 37/44
40
Page 38

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
Workaround
Ensure that Tx DMA initiates a burst of at least two beats when fetching header bytes from
the system memory, through one of the following measures:
• Disable address-aligned beats by clearing the AAL bit of the ETH_DMASBMR register.
• Align the buffer address pointing to the packet start to a data width boundary (set the
bits[2:0] of the address to zero, for 64-bit data width).
• Set the buffer address pointing to the packet start to a value that ensures a burst of
minimum two beats when AAL = 1.
2.18.4 Spurious receive watchdog timeout interrupt
Description
Setting the RWTU[1:0] bitfield of the ETH_DMACRXIWTR register to a non-zero value while
the RWT[7:0] bitfield is at zero leads to a spurious receive watchdog timeout interrupt (if
enabled) and, as a consequence, to executing an unnecessary interrupt service routine with
no packets to process.
Workaround
Ensure that the RWTU[1:0] bitfield is not set to a non-zero value while the RWT[7:0] bitfield
is at zero. For setting RWT[7:0] and RWTU[1:0] bitfields each to a non-zero value, perform
two successive writes. The first is either a byte-wide write to the byte containing the
RWT[7:0] bitfield, or a 32-bit write that only sets the RWT[7:0] bitfield and keeps the
RWTU[1:0] bitfield at zero. The second is either a byte-wide write to the RWTU[1:0] bitfield
or a 32-bit write that sets the RWTU[1:0] bitfield while keeping the RWT[7:0] bitfield
unchanged.
2.18.5 Incorrect flexible PPS output interval under specific conditions
Description
The use of the fine correction method for correcting the IEEE 1588 internal time reference,
combined with a large frequency drift of the driving clock from the grandmaster source
clock, leads to an incorrect interval of the flexible PPS output used in Pulse train mode. As a
consequence, external devices synchronized with the flexible PPS output of the device can
go out of synchronization.
Workaround
Use the coarse method for correcting the IEEE 1588 internal time reference.
2.18.6 Packets dropped in RMII 10Mbps mode due to fake dribble and CRC error
Description
When operating with the RMII interface at 10 Mbps, the Ethernet peripheral may generate a
fake extra nibble of data repeating the last packet (nibble) of the data received from the PHY
interface. This results in an odd number of nibbles and is flagged as a dribble error. As the
RMII only forwards to the system completed bytes of data, the fake nibble would be ignored
38/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 39

STM32H742/743xI/G Description of device limitations
and the issue would have no consequence. However, as the CRC error is also flagged when
this occurs, the error-packet drop mechanism (if enabled) discards the packets.
Note: Real dribble errors are rare. They may result from synchronization issues due to faulty clock
recovery.
Workaround
When using the RMII 10 MHz mode, disable the error-packet drop mechanism by setting
the FEP bit of the ETH_MTLRXQOMR register. Accept packets of transactions flagging both
dribble and CRC errors.
2.18.7 ARP offload function not effective
Description
When the Target Protocol Address of a received ARP request packet matches the device IP
address set in the ETH_MACARPAR register, the source MAC address in the SHA field of
the ARP request packet is compared with the device MAC address in ETH_MACA0LR and
ETH_MACA0HR registers (Address0), to filter out ARP packets that are looping back.
Instead, a byte-swapped comparison is performed by the device. As a consequence, the
packet is forwarded to the application as a normal packet with no ARP indication in the
packet status, and the device does not generate an ARP response.
For example, with the Address0 set to 0x665544332211:
• If the SHA field of the received ARP packet is 0x665544332211, the ARP response is
generated while it should not.
• If the SHA field of the received ARP packet is 0x112233445566, the ARP response not
is generated while it should.
Workaround
Parse the received frame by software and send the ARP response if the source MAC
address matches the byte-swapped Address0.
2.19 HDMI-CEC
2.19.1 Unexpected switch to Receive mode without automatic transmission retry and notification
Description
If the HDMI-CEC peripheral starts a transmit operation, and at the same time another CEC
initiator attempts to perform the same operation but with a wrong start-bit timing and/or
without following the signal free timing rules, the transmission is aborted and never restarts,
and the HDMI switch to Receive mode. The user application is not informed of the bus error.
Workaround
Use transmission timeout: when a timeout occurs, to enable again the transmission of the
pending message, disable and enable again the HDMI-CEC peripheral to clear TXSOM bit
in CEC_CR register.
ES0392 Rev 8 39/44
40
Page 40

Description of device limitations STM32H742/743xI/G
2.19.2 CEC header not received due to unjustified Rx-Overrun detection
Description
In a multinode CEC network, two messages are sent to two different followers. The CEC
device which is the destination of the second message should ignore the first message and
receive the second one. However, the header of the second message is not received and an
Rx-Overrun is wrongly detected and signaled by setting the RXOVR flag in the CEC_ISR
register and the RXOVRIE interrupt in the CEC_IER register.
The issue is not present:
• in Listen mode,
• when the first message is a broadcast message
• when the first message is a ping message (header only),
• or when the first message header is not acknowledged.
Workaround
Configure the HDMI-CEC to operate in Listen mode and apply message filtering based on
destination address. In this case all the messages sent over the CEC bus will be received
and it is up to the user application to discard the messages that are not sent to its address or
that are broadcast.
40/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 41

STM32H742/743xI/G Revision history
3 Revision history
Table 5. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
19-Jun-2017 1 Initial release.
Added STM32H743AI part number.
Removed JPEG limitation.
Updated Section 2.3.1: Dummy read cycles inserted when reading synchronous
02-Nov-2017 2
memories and Section 2.3.2: Wrong data read from a busy NAND Flash
memory.
Added Section 2.16.2: Wrong data may be read from Message RAM by the CPU
when using two FDCANs.
System limitations:
– Reorganized to group together Flash memory and RAM limitations
– Removed limitations “48 MHz RC oscillator user calibration values lost after
system reset” and “Flash memory wirte sequence error flag not set”
–Replaced “Accessing the system memory may stall the system when Flash
memory banks are swapped” and “Write flags are not swapped when Flash
memory banks are swapped” limitations by Section 2.2.8: Flash memory bank
swapping might impact embedded Flash memory interface behavior.
31-May-2018 3
ADC limitations:
– Moved all ADC limitations under Section 2.5: ADC.
– Added Section 2.5.5: First ADC injected conversion in a sequence may be
corrupted and Section 2.5.6: Writing the ADC_JSQR register when
JADCSTART = 1 and JQDIS = 1 may lead to incorrect behavior.
Added Section 2.11.1: RTC calendar registers are not locked properly.
Added Section 2.4.2: QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared and
Section 2.4.3: QUADSPI cannot be used in Indirect read mode when only data
phase is activated.
31-May-2018 3 (continued)
I2C limitations:
– Updated Section 2.12.1: 10-bit master mode: new transfer cannot be
launched if first part of the address is not acknowledged by the slave and
Section 2.12.3: Wrong data sampling when data setup time (t
SU;DAT
) is shorter
than one I2C kernel clock period.
– Added Section 2.12.2: Wrong behavior in Stop mode when wakeup from Stop
mode is disabled in I2C, Section 2.12.4: Spurious bus error detection in
Master mode, Section 2.12.5: Last-received byte loss in Reload mode,
Section 2.12.6: Spurious master transfer upon own slave address match and
Section 2.12.7: START bit is cleared upon setting ADDRCF, not upon address
match.
Removed limitation “NOSTRETCH setting may impact Master mode”.
SPI/I2S limitations:
– Removed limitation “Wrong DMA receive requests may be generated in Half-
duplex mode”
– Added Section 2.14.1: Spurious DMA Rx transaction after simplex Tx traffic,
Section 2.14.2: Master data transfer stall at system clock much faster than
SCK, Section 2.14.3: Corrupted CRC return at non-zero UDRDET setting and
Section 2.14.4: TXP interrupt occurring while SPI/I2Sdisabled.
ES0392 Rev 8 41/44
43
Page 42

Revision history STM32H742/743xI/G
Table 5. Document revision history (continued)
Date Revision Changes
Removed revision from document title.
Added revision X in Table 2: Device variantsTable 2: Device variants.Replaced
19-Jun-2018 4
27-Mar-2019 5
20-Jun-2019 6
“new silicon revision” by revision X in Table 3: Summary of device limitations.
Added Section 2.2.13: Unexpected leakage current on I/Os when VIN higher
that VDD.
Added STM32H742xI/G part numbers.
Added revision V for all devices.
Added Arm® 32-bit Cortex®-M7 core limitations.
System: added Section 2.2.16: Device stalled when two consecutive level
regressions occur without accessing from/to backup SRAM, Section 2.2.17:
Invalid Flash memory CRC and Section 2.2.18: GPIO assigned to DAC cannot
be used in output mode when the DAC output is connected to on-chip
peripheral.
Added OPAMP limitation.
Updated Section 2.4.2: QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared.
Updated Section 2.12.1: 10-bit master mode: new transfer cannot be launched if
first part of the address is not acknowledged by the slave
Added LCD-TFT limitation.
Added USB OTG_HS limitation.
Added Section 2.2.20: 480 MHz maximum CPU frequency not available on
silicon revision Y.
Added Section 2.5.7: Conversion may be triggered by context queue register
update and Section 2.5.8: Updated conversion sequence may be trigged by
context queue update.
Added Section 2.18: ETH.
Added Section 2.16.3: Mis-synchronization in Edge filtering mode when the
falling edge at FDCAN_Rx input pin coincides with the end of the integration
phase and Section 2.16.4: Tx FIFO messages inverted when both Tx buffer and
FIFO are used and the messages in the Tx buffer have higher priority than in the
Tx FIFO.
42/44 ES0392 Rev 8
Page 43

STM32H742/743xI/G Revision history
Table 5. Document revision history (continued)
Date Revision Changes
Changed Arm Cortex core revision to r1p1.
Added new system limitation Section 2.2.21: VDDLDO is not available on
TFBGA100 package on devices revision Y and V.
28-Feb-2020 7
12-Feb-2021 8
Added new DMA limitation Section 2.13.2: DMA stream locked when
transferring data to/from USART/UART.
Added new VREFBUF limitations:
– Section 2.6.1: Overshoot on VREFBUF output
– Section 2.6.2: VREFBUF Hold mode cannot be used
SYSTEM limitations:
– Added Section 2.2.22: WWDG not functional when VDD is lower than 2.7 V
and VOS0 or VOS1 voltage level is selected and Section 2.2.23: A tamper
event does not erase the backup RAM when the backup RAM clock is
disabled and Section 2.2.24: LSE CSS parasitic detection even when disabled
QUADSPI limitations:
– Added Section 2.4.4: Memory-mapped read of last memory byte fails.
– Updated Section 2.4.2: QUADSPI hangs when QUADSPI_CCR is cleared
title.
Added TIM limitations: Section 2.9.1: One-pulse mode trigger not detected in
master-slave reset + trigger configuration, Section 2.9.2: Consecutive compare
event missed in specific conditions and Section 2.9.3: Output compare clear not
working with external counter reset.
Moved Section 2.13.2: DMA stream locked when transferring data to/from
USART/UART from DMA to USART section.
ES0392 Rev 8 43/44
43
Page 44

STM32H742/743xI/G
IMPORTANT NOTICE – PLEASE READ CAREFULLY
STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and
improvements to ST products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on
ST products before placing orders. ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order
acknowledgement.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or
the design of Purchasers’ products.
No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. For additional information about ST trademarks, please refer to www.st.com/trademarks. All other
product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document.
© 2021 STMicroelectronics – All rights reserved
44/44 ES0392 Rev 8
 Loading...
Loading...