Page 1
UM2682
User manual
300 W motor control power board based on STIPQ3M60T-H SLLIMM™-nano 2nd
series MOSFET IPM
Introduction
The STEV
module) 2nd series based on N-channel Power MOSFET MDmesh™ DM2 fast-recovery diode (STIPQ3M60T-HL). It provides
an affordable and easy-to-use solution for driving high power motors in a wide range of applications such as power white goods,
air conditioning, compressors, power fans and 3-phase inverters for motor drives in general.
The IPM itself consists of six MOSFETs, three high voltage half-bridge gate driver ICs and a wide range of features like
undervoltage lockout, smart shutdown, internal temperature sensor and NTC, overcurrent protection and internal op-amp.
The main characteristics of this evaluation board are small size, minimal BOM and high efficiency. It features an interface
circuit (BUS and VCC connectors), bootstrap capacitors, snubber capacitor, hardware short-circuit protection, fault event signal
and temperature monitoring. It is designed to work in single- or three-shunt configuration and with triple current sensing
options: three dedicated on-board op-amps, op-amps embedded on MCU or single internal IPM op-amp. The Hall/Encoder part
completes the circuit.
The system is designed to achieve accurate and fast conditioning of current feedback to satisfy the typical requirements for field
oriented control (FOC).
The STEVAL-IPMNM3Q is compatible with ST’s control board based on STM32, providing a complete platform for motor
control.
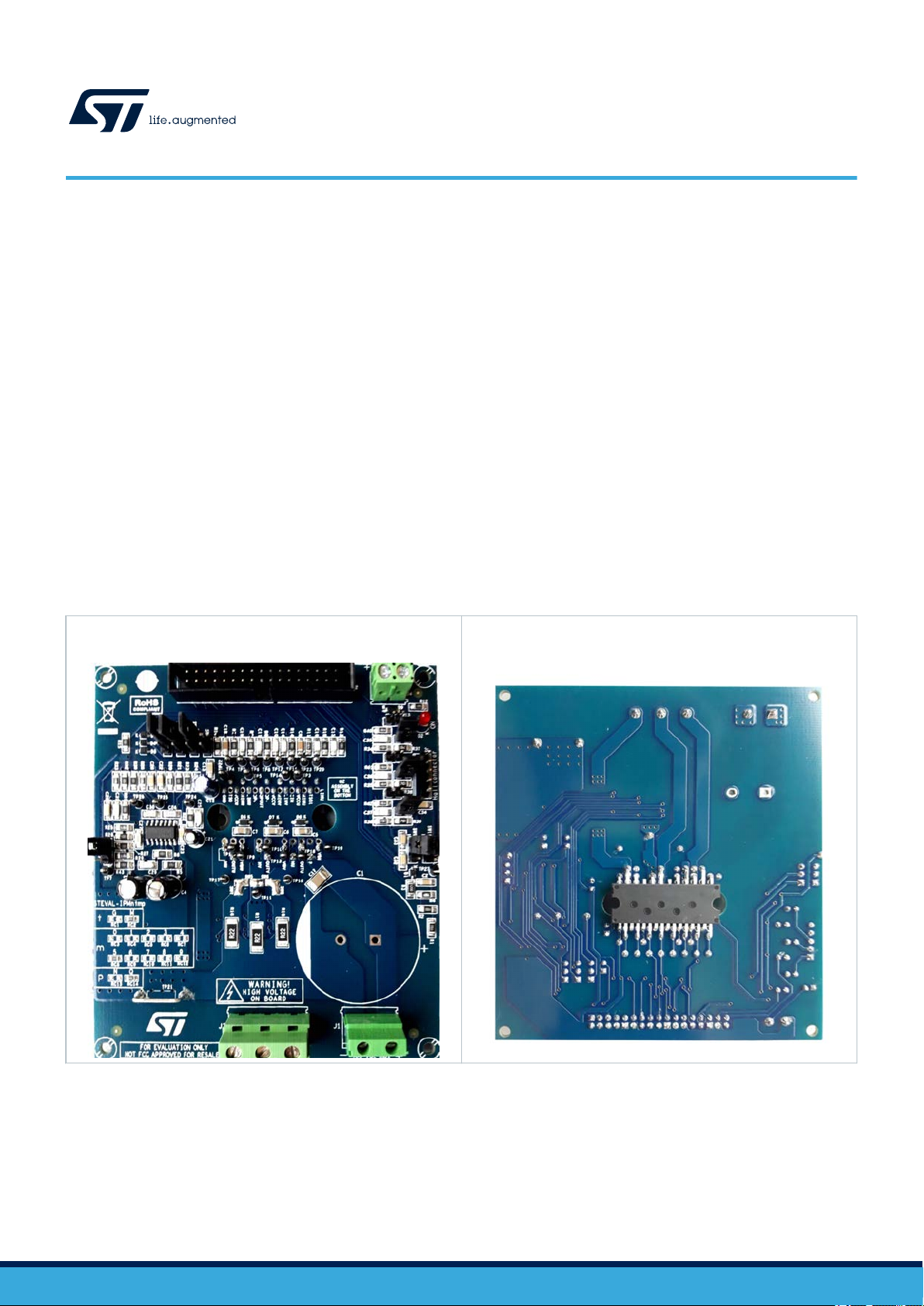
AL-IPMNM3Q is a compact motor drive power board equipped with SLLIMM-nano (small low-loss intelligent molded
Figure 1. Motor control board based on SLIMM-nano 2nd
series - top view
Figure 2. Motor control board based on SLIMM-nano 2nd
series - bottom view
UM2682 - Rev 2 - November 2020
For further information contact your local STMicroelectronics sales of
fice.
www.st.com
Page 2

1 Key features
UM2682
Key features
• Input voltage: from 125 to 400 V
•
Nominal power: up to 300 W
DC
– Allowable maximum power is related to the application conditions and cooling system
• Nominal current: up to 1.1 Arms
• Input auxiliary voltage: up to 20 V
DC
• Single- or three-shunt resistors for current sensing (with sensing network)
• Three options for current sensing: dedicated external op-amps, internal SLLIMM-nano or via MCU
• Overcurrent hardware protection
• IPM temperature monitoring and protection
• Hall sensor or encoder input
• MOSFETs intelligent power module
– SLLIMM-nano 2nd series IPM STIPQ3M60T-H - Full molded package
• Motor control connector (32 pins) interfacing with ST MCU boards
• Universal design for further evaluation with breadboard and testing pins
• Very compact size
• WEEE compliant
• RoHS compliant
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 2/31
Page 3

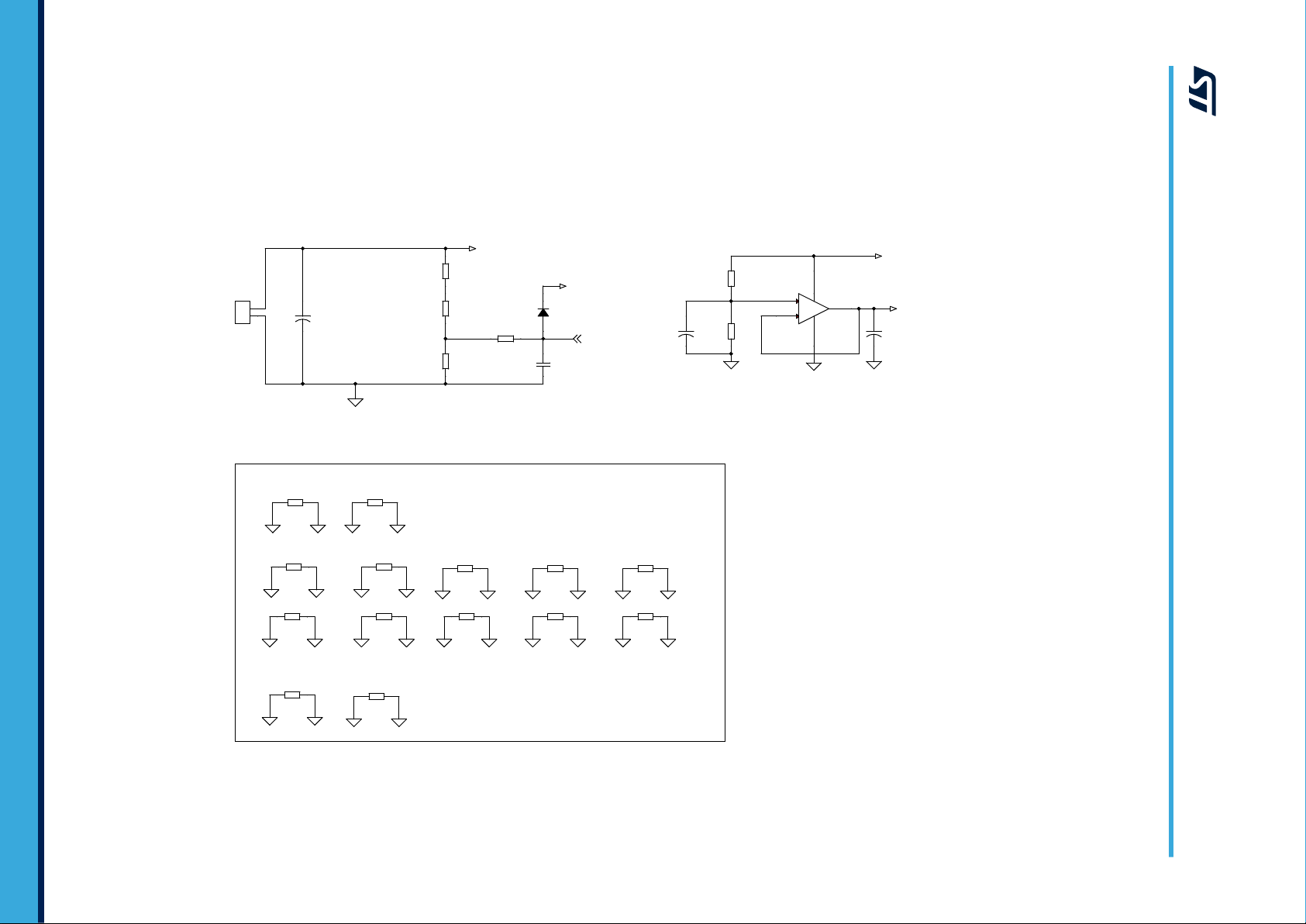
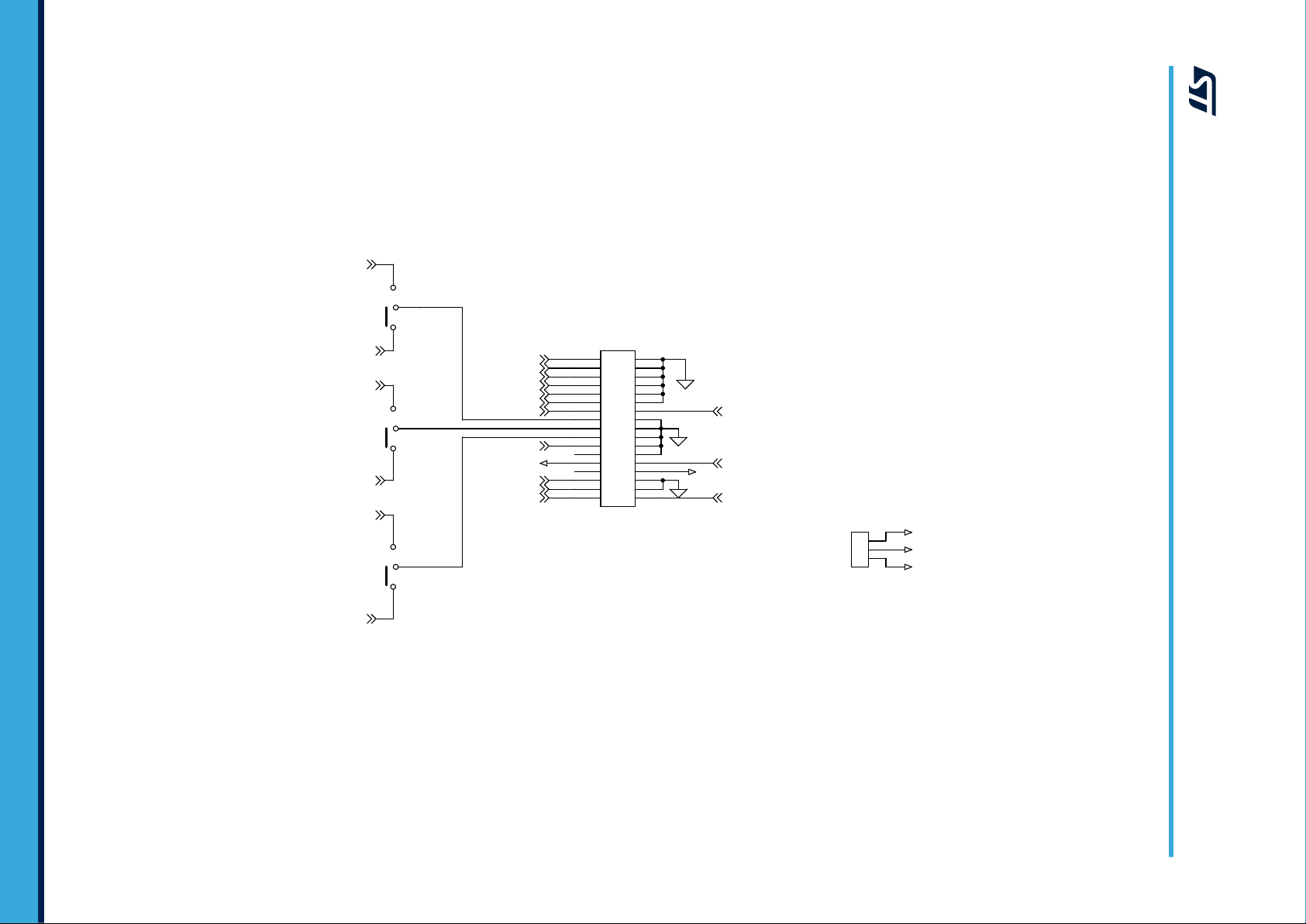
2 Circuit schematics
The full schematics for the SLLIMM-nano card for STIPQ3M60T-H IPM products is shown below. This card
consists of an interface circuit (BUS and VCC connectors), bootstrap capacitors, snubber capacitor
protection, fault output circuit, temperature monitoring, single-/three-shunt resistors and filters for input signals. It
also includes bypass capacitors for VCC and bootstrap capacitors. The capacitors are located very close to the
drive IC to avoid malfunction due to noise.
Three current sensing options are provided: three dedicated onboard op-amps, one internal IPM op-amp and the
embedded MCU op-amps; selection is performed through three jumpers.
The Hall/Encoder section (powered at 5 V or 3.3 V) completes the circuit.
UM2682
Circuit schematics
, short-circuit
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 3/31
Page 4
Input
DC_b us_vo ltage
STEVAL-IPMNntmp decoder
t
m
p
G M
0 1
2 3
5 6 7
4
8 9
N
Q
3.3 V
+Bus
3.3 V
1.6 5V
Bus_ voltage
RC60
RC12
0
RC14
0
RC20
D1
RC10
+
C4
47u/3 5V
J1
INPUT-dc
1
2
RC10
0
RC7
0
R2
470 K
R3 120 R
R1
470 K
R6
1k0
-
+
U1D
TSV994
12
13
14
411
RC130
RC3
0
RC80
RC11
0
RC4
0
+
C3
47u/3 5V
R4
7k5
C2
10n
RC5
0
RC9
0
+
C1
330 u/400V
R5
1k0
UM2682 - Rev 2
2.1 Schematic diagrams
Figure 3. STEV
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (1 of 5)
page 4/31
Schematic diagrams
UM2682
Page 5
ph a se_A
ph a se_B
ph a se_C
3.3 V
+5V
EM_S TOP
PW M-A-H
PW M-A-L
PW M-B-H
PW M-B-L
PW M-C-H
PW M-C-L
NTC_b ypas s_re lay
PW M_Vre f
M_pha se _A
M_pha se _B
Bus _voltage
M_pha se _C
NTC
Curre nt_B_a mp
E2
Curre nt_C_a mp
E3
Curre nt_A_am p
E1
J3
Motor Ou tput
1
2
3
SW 2
1
2
3
SW 3
1
2
3
J2
Con trol Conne ctor
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17
19
21
23
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
18
20
22
24
SW 1
1
2
3
Curre nt_A
Curre nt_B
Curre nt_C
UM2682 - Rev 2
Figure 4. STEV
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (2 of 5)
Schematic diagrams
UM2682
page 5/31
Page 6
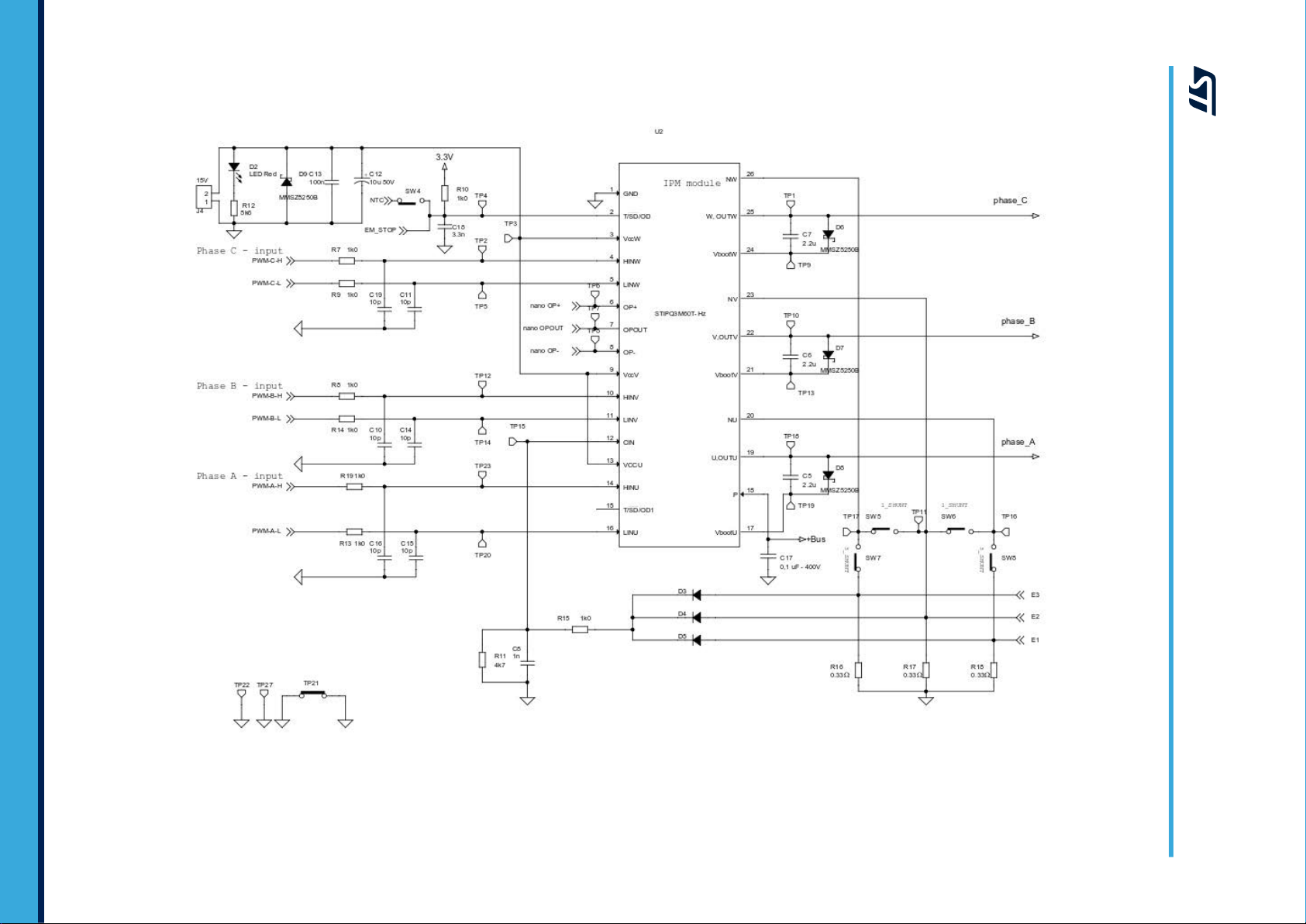
UM2682 - Rev 2
Figure 5. STEV
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (3 of 5)
page 6/31
Schematic diagrams
UM2682
Page 7
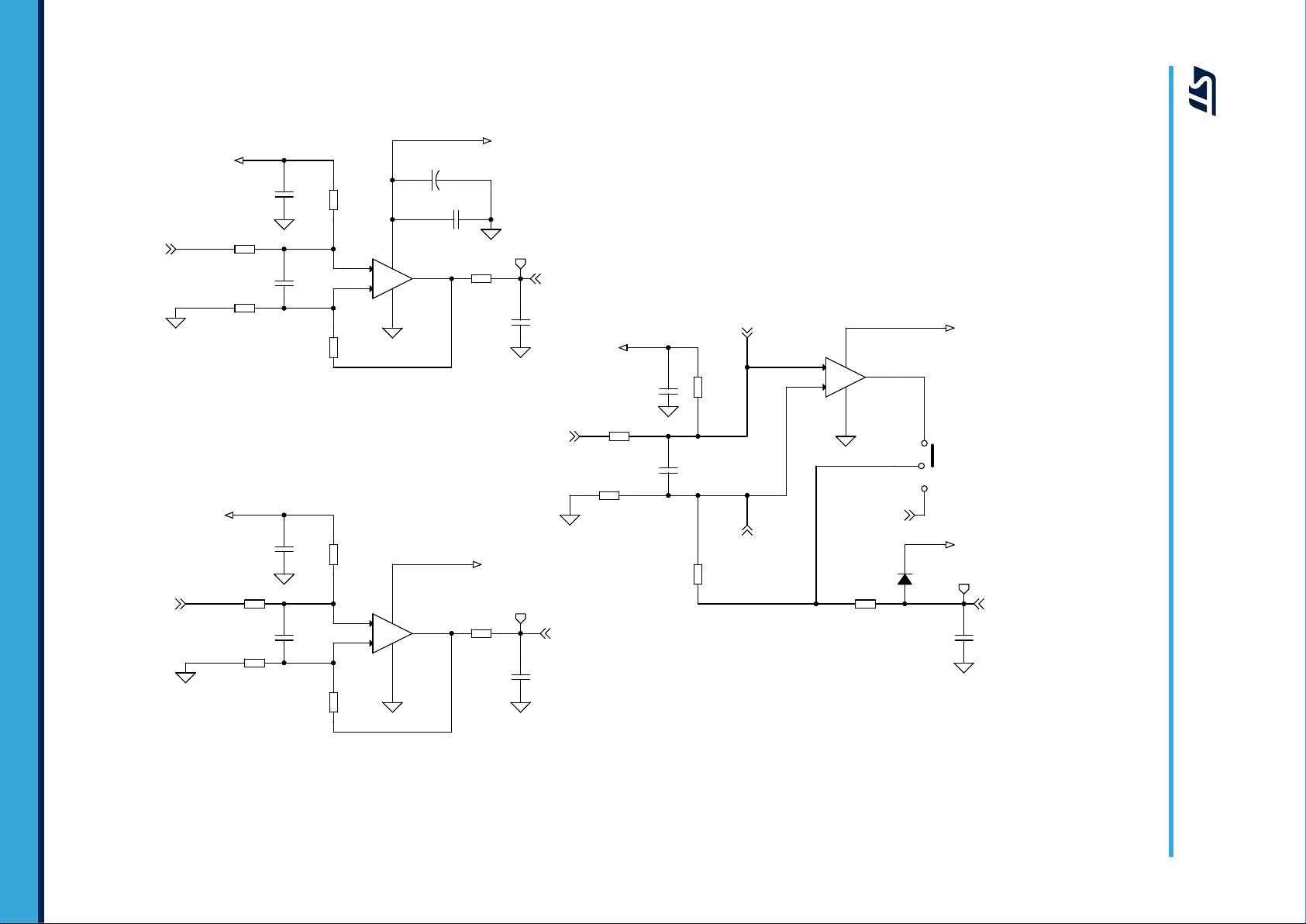
3.3 V
1.6 5V
1.6 5V
1.6 5V
3.3 V
3.3 V
3.3 V
E1
Curre nt_A_a mp
E2
Curre nt_B_ am pE3
Curre nt_C _a mp
na no OP +
na no OP -
na no OP OUT
R21 1k0
R20
1k9
-
+
U1A
TS V994
3
2
1
411
TP 24
R22
1k
R33
1k9
C30
100 p
R27 1k0
C29
330 p
R31
1k
C24
100 p
C28
10n
C25
330 p
TP 25
-
+
U1B
TS V994
5
6
7
411
R26 1k0
C23
100 n
C22
10n
R25
1k9
D10
R24
1k9
R32 1k0
C31
330 p
TP 26
SW 17
1
2
3
R23 1k0
R29
1k9
+
C21
4.7 u 50V
C27
100 p
-
+
U1C
TS V994
10
9
8
411
R30 1k0
R28
1k9
C26
10n
R43
1k
UM2682 - Rev 2
Figure 6. STEV
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (4 of 5)
page 7/31
Schematic diagrams
UM2682
Page 8
M_ph as e_ A
M_ph as e_ C
M_ph as e_ B
3.3V
+5V
3.3V
+5V
R42
4k7
R39 2k4
J 5
En code r/Hall
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
S W12
C37
10 p
S W15
C34
10 0n
S W13
S W10
R40
4k7
S W9
1
2
3
R34
4k7
R41
4k7
R35
4k7
C33
10 0n
C35
10 p
R37 2k4
S W14
R38 2k4
C32
10 0n
S W16
1
2
3
R36
4k7
S W11
C36
10 p
H1/A+
H2/B+
H3/Z+
+3.3/5V
GND
Hall/Encoder
UM2682 - Rev 2
Figure 7. STEV
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (5 of 5)
page 8/31
Schematic diagrams
UM2682
Page 9
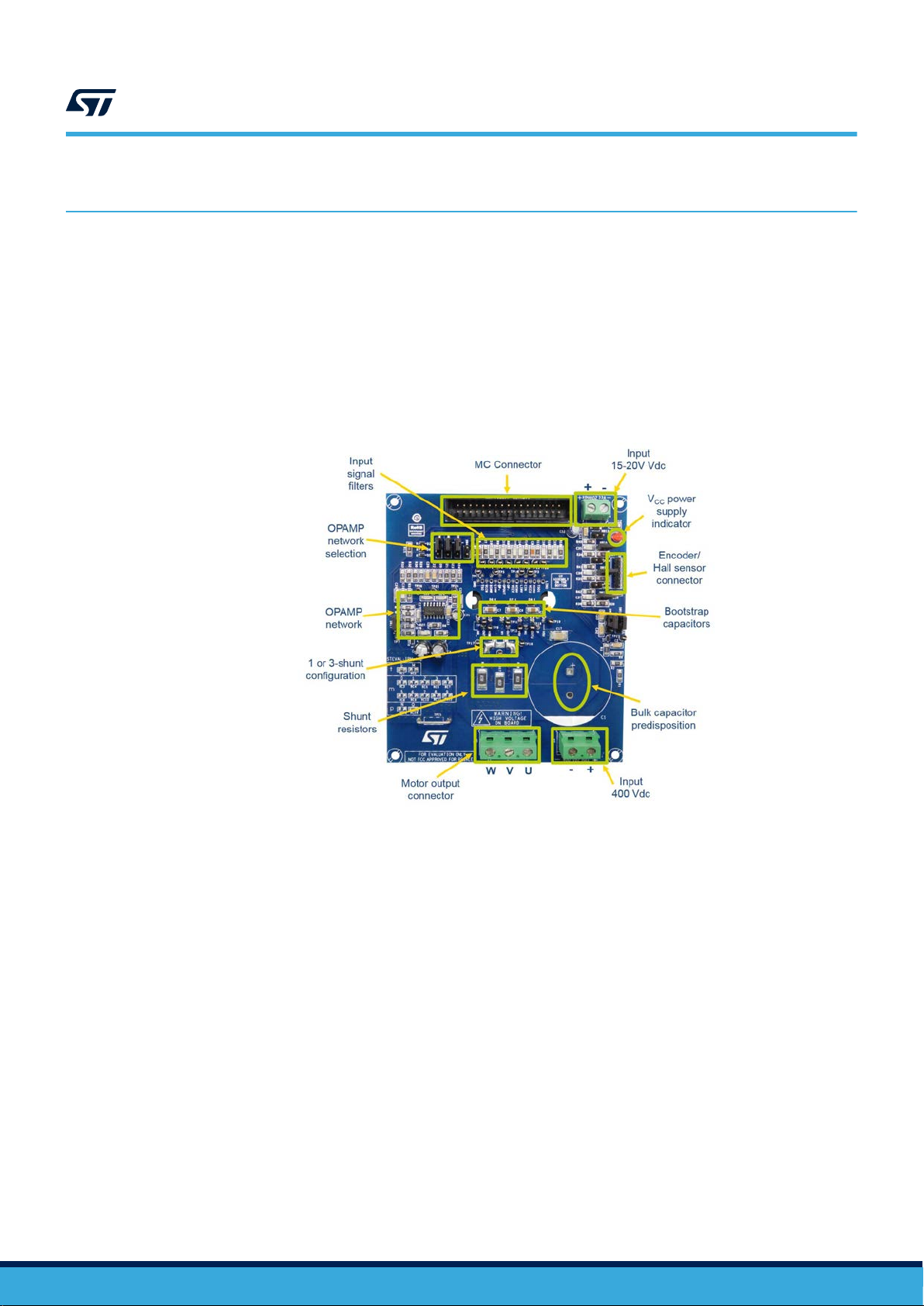
3 Main characteristics
The board is designed for a 125 VDC to 400 VDC supply voltage.
An appropriate bulk capacitor for the power level of the application must be mounted at the dedicated position on
the board.
The SLLIMM-nano integrates six MOSFET switches and high voltage gate drivers. Thanks to this integrated
module, the system of
increases reliability.
The board offers the added flexibility of being able to operate in single- or three-shunt configuration by modifying
solder bridge jumper settings (see Section 4.3.4 Single- or three-shunt selection).
fers power inversion in a simple and compact design that requires less PCB area and
UM2682
Main characteristics
Figure 8. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q architecture
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 9/31
Page 10
GADG221020181007IG
0
1
2
3
4
5
0 5 10 15 20
C
BOOT Calculated
(µF)
fsw(kHz)
STIPN2M50x-Hy
δ=50%
ΔV
CBOOT
=0.1V
ΔV
CBOOT
=0.3V
ΔV
CBOOT
=0.5V
UM2682
Filters and key parameters
4 Filters and key parameters
4.1 Input signals
The input signals (LINx and HINx) to drive the internal MOSFETs are active high. A 375 kΩ (typ.) pull-down
resistor is built-in for each input signal. T
close as possible to the IPM. The filter is designed using a time constant of 10 ns (1 kΩ and 10 pF).
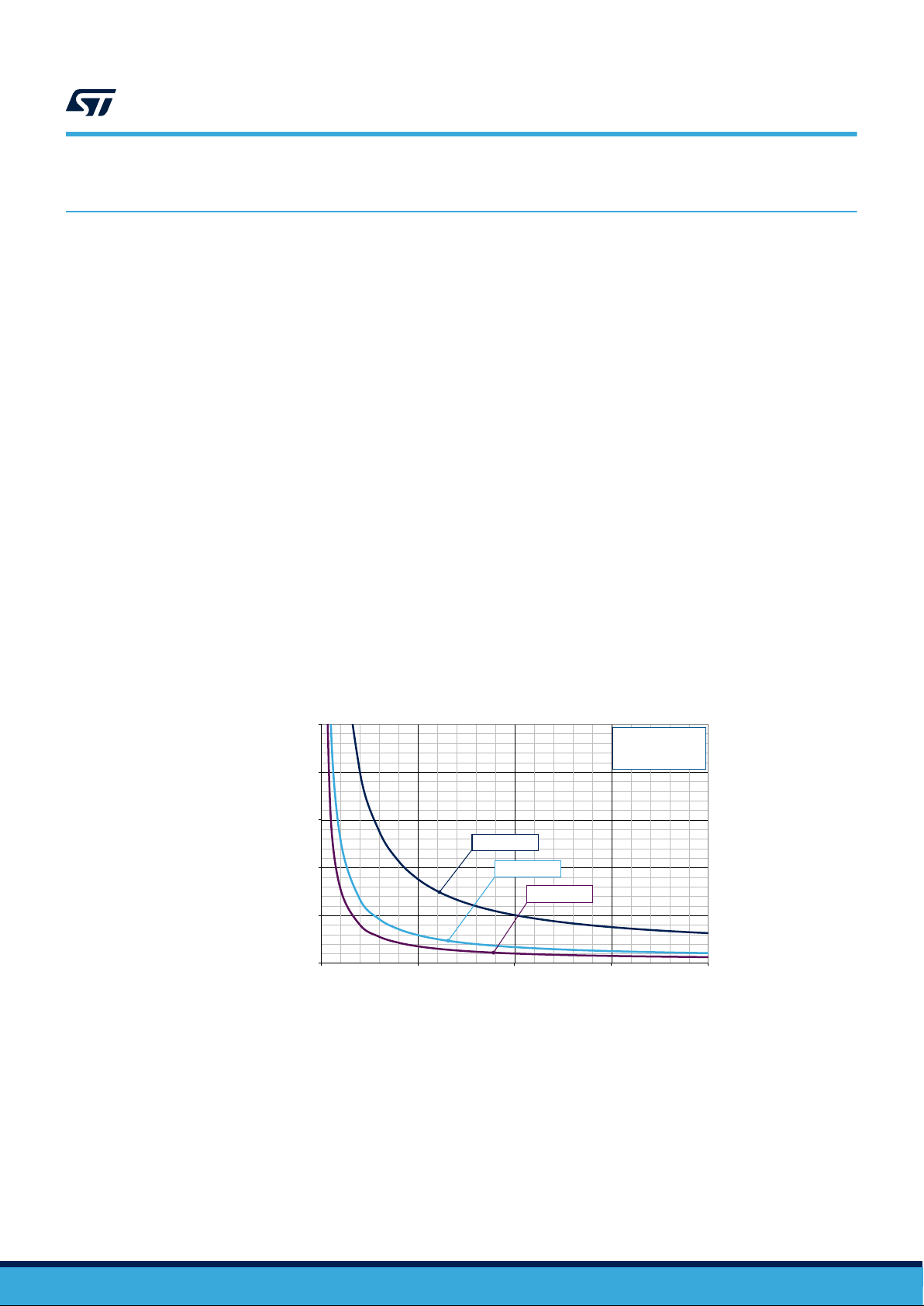
4.2 Bootstrap capacitor
In the 3-phase inverter, the emitters of the low side MOSFETs are connected to the negative DC bus (VDC-)
as common reference ground, which allows all low side gate drivers to share the same power supply, while the
emitter of the high side MOSFETs is alternatively connected to the positive (VDC+) and negative (VDC-) DC bus
during running conditions.
A bootstrap method is a simple and cheap solution to supply the high voltage section. This function is normally
accomplished by a high voltage fast recovery diode. The SLLIMM-nano MOSFET-based family includes a
patented integrated structure that replaces the external diode with a high voltage DMOS functioning as a diode
with series resistor. An internal charge pump provides the DMOS driving voltage.
The value of the CBOOT capacitor should be calculated according to the application requirements.
Figure 9. CBOOT graph selection shows the behavior of CBOOT (calculated) versus switching frequency (fsw),
with different values of ΔVCBOOT for a continuous sinusoidal modulation and a duty cycle δ = 50%.
Note: This curve is taken from application note AN5244 (available on www.st.com); calculations are based on the
STIPN2M50x-Hy device, which represents the worst case scenario for this kind of calculation.
The boot capacitor must be two or three times larger than the C
For this design, a value of 2.2 μF was selected.
o prevent input signal oscillation, an RC filter is added on each input as
calculated in the graph.
BOOT
4.3 Overcurrent protection
The SLLIMM-nano MOSFET-based integrates a comparator for fault sensing purposes. The comparator has an
internal voltage reference VREF (540 mV typ.) connected to the inverting input, while the non-inverting input on
the CIN pin can be connected to an external shunt resistor to implement the overcurrent protection function.
When the comparator triggers, the device enters the shutdown state.
The comparator output is connected to the SD pin in order to send the fault message to the MCU.
Figure 9. CBOOT graph selection
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 10/31
Page 11

4.3.1 SD pin
The SD is an input/output pin (open drain type if used as output) used for enable and fault; it is shared with NTC
thermistor
, internally connected to GND.
The pull-up resistor (R10) causes the voltage VSD-GND to decrease as the temperature increases. To maintain
the voltage above the high-level logic threshold, the pull-up resistor is sized at 1 kΩ (3.3 V MCU power supply).
The filter on
SD (R10 and C18) must be sized to obtain the desired re-starting time after a fault event and placed
as close as possible to the pin.
A shutdown event can be managed by the MCU; in which case, the SD functions as the input pin.
Conversely
, the SD functions as an output pin when an overcurrent or undervoltage condition is detected.
4.3.2 Shunt resistor selection
The value of the shunt resistor is calculated by the following equation:
Where V
The maximum OC protection level should be set to less than the pulsed collector current in the datasheet. In this
design the over current threshold level was fixed at IOC = 2.3 A in order to select a commercial shunt resistor
value.
Where VF is the voltage drop across diodes D3, D4 and D5.
The commercial value chosen was 0.33
The power rating of the shunt resistor is calculated by the following equation:
where:
• Maximum load current of inverter: I
• Shunt resistor value at TC = 25 °C
• Power derating ratio of shunt resistor at TSH =100 °C
• Safety margin of 30%
I
load(max)
Power shunt value is:
Considering available commercial values, a 1 W shunt resistor was selected.
Based on the previous equations and conditions, the minimum shunt resistance and power rating is summarized
below
is the internal comparator (CIN) (0.54 V typ.) and IOC is the overcurrent detection level.
ref
RSH=
is calculated considering the RMS value of the IPM nominal current including a safety margin:
.
UM2682
Overcurrent protection
V
f
RSH=
R23
V
re
f
+ R53
⋅
R53
I
OC
+ V
Ω to which corresponds a level of 2.6 A.
2
I
l
oad
1
I
oad
l
PSH=
max
PSH=
2
load(max)
I
=
1
2
⋅
nom@80°C
1.05² ⋅ 0.33 ⋅ 1.3
⋅
re
I
OC
0.54 ⋅
F
=
⋅
max
Derating ratio
2
0.8
(1)
1000 + 4700
4700
2.3
RSH⋅ margin
× 0.85 = 1.05Arms (4)
0.298W (5)
=
+ 0.18
0.367Ω (2)
=
(3)
Device OCP(peak) [A]
STIPQ3M60T-HL 2.6 1.05 0.33 1
4.3.3 CIN RC filter
An RC filter network on the CIN pin is required to prevent short-circuits due to the noise on the shunt resistor. In
this design, the R15-C8 RC filter has a constant time of about 1
UM2682 - Rev 2
Table 1. Shunt selection
I
[Arms] R
load(max)
μs.
SHUNT
[Ω]
Shunt
power rating PSH [W]
page 11/31
Page 12

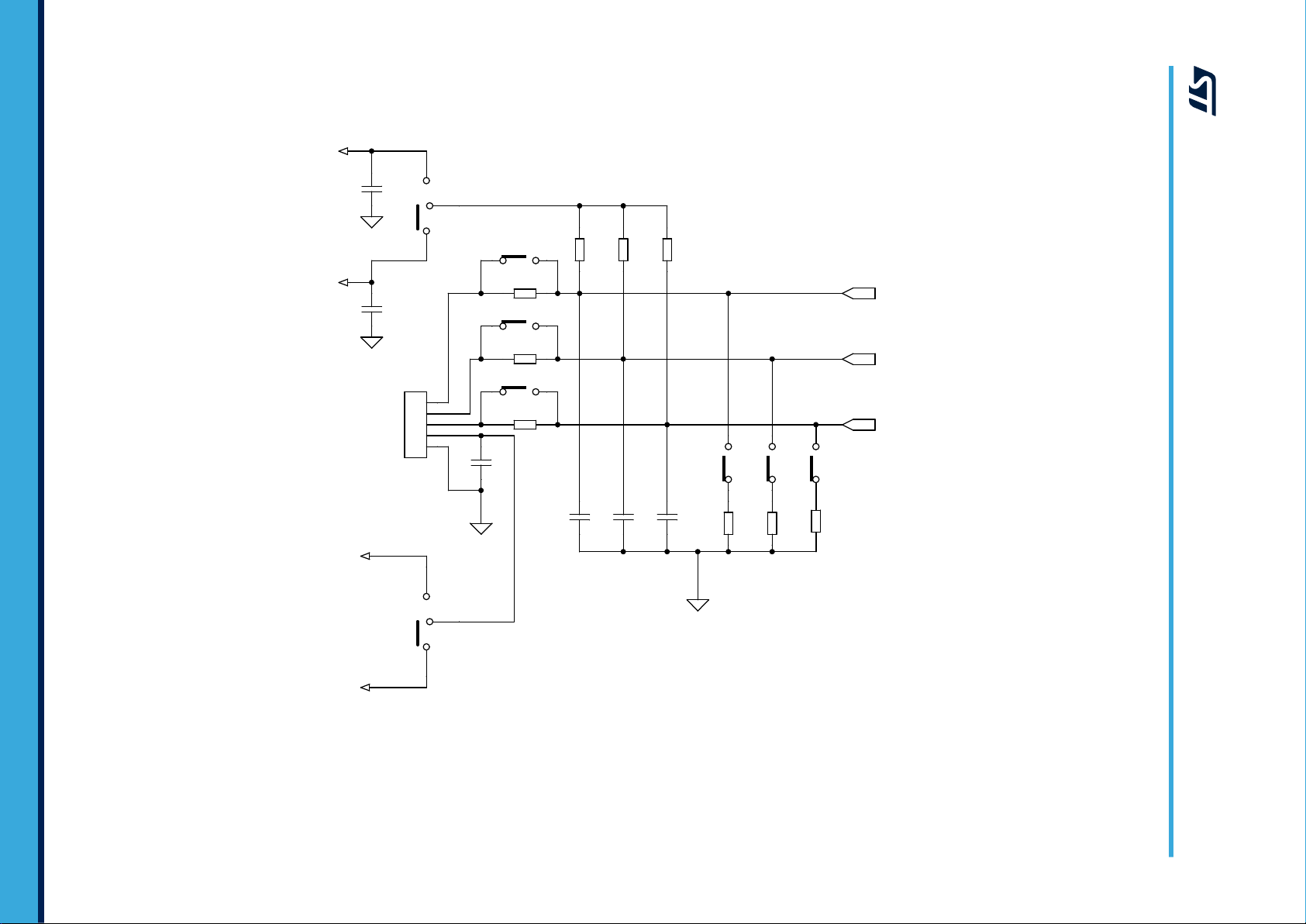
4.3.4 Single- or three-shunt selection
Single- or three-shunt resistor circuits can be adopted by setting the solder bridges SW5, SW6, SW7 and SW8.
The figures below illustrate how to set up the two configurations.
UM2682
Overcurrent protection
Figure 10. One-shunt configuration
Figure 11. Three-shunt configuration
Further details regarding sensing configuration are provided in the next section.
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 12/31
Page 13

5 Current sensing amplifying network
The STEVAL-IPMNM3Q motor control evaluation board can be configured to run in three-shunt or single-shunt
configurations for field oriented control (FOC).
The current can be sensed thanks to the shunt resistor and amplified by using the on-board operational amplifiers
or by the MCU (if equipped with op-amp).
Once the shunt configuration is chosen by setting solder bridge on SW5, SW6, SW7 and SW8 (as described in
Section 4.3.4 Section 5.3.4 Single- or three-shunt selection), the user can choose whether to send the voltage
shunt to the MCU amplified or not amplified.
Single-shunt configuration requires a single op amp so the only voltage sent to the MCU to control the sensing is
connected to phase V through SW2.
SW1, SW2, SW3 and SW17 can be configured to select which signals are sent to the microcontroller
following table.
Table 2. Op-amp sensing configuration
Configuration Sensing Bridge (SW1) Bridge (SW2) Bridge (SW3) Bridge (SW17)
IPM op-amp open 1-2 open 2-3
Single Shunt
Three Shunt
On board op-amp open 1-2 open 1-2
MCU op-amp open 2-3 open 1-2
On board op-amp 1-2 1-2 1-2 1-2
MCU op-amp 2-3 2-3 2-3 1-2
UM2682
Current sensing amplifying network
, as per the
The operational amplifier TSV994 used on the amplifying networks has a 20 MHz gain bandwidth from a single
positive supply of 3.3 V
.
The amplification network must allow bidirectional current sensing, so an output offset VO = +1.65 V represents
zero current.
For the STIPQ3M60T-H (I
OCP
= 2.6 A; R
= 0.33 Ω), the maximum measurable phase current, considering
SHUNT
that the output swings from +1.65 V to +3.3 V (MCU supply voltage) for positive currents and from +1.65 V to 0 for
negative currents is:
MaxMeasCurrent =
rm=
MaxMeas
ΔV
Current
ΔV
2.6A (6)
=
r
m
1.65
=
0.635Ω (7)
=
2.6
The overall trans-resistance of the two-port network is:
rm= R
AMP =
Finally choosing Ra=Rb and Rc=Rd, the dif
⋅ AMP = 0.33 ⋅ AMP = 0.635Ω (8)
S
HUNT
R
S
r
HUNT
0.635
m
=
=
1.924 (9)
0.33
ferential gain of the circuit is:
R
AMP =
c
=
1.9 (10)
R
a
An amplification gain of 1.9 was chosen. The same amplification is obtained for all the other devices, taking into
account the OCP current and the shunt resistance, as described in T
able 1. Shunt selection.
The RC filter for output amplification is designed to have a time constant that matches noise parameters in the
range of 1.5 μs:
4 ⋅
τ = 4 ⋅ Re⋅ Cc= 1.5µs (11)
1.5µs
CC=
4 ⋅ 1000
=
375pF
330p
Fselected
(12)
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 13/31
Page 14

Table 3. Amplifying networks
UM2682
Current sensing amplifying network
Phase
Phase A (U)
Phase B (V) R26 R27 R25 R29 R43 C29
Phase C (W) R30 R32 R28 R33 R31 C31
Ra Rb Rc Rd Re Cc
R21 R23 R20 R24 R22 C25
Amplifying network RC filter
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 14/31
Page 15

6 Temperature monitoring
The SLLIMM-nano MOSFET family integrates an NTC thermistor placed close to the power stage. The board is
designed to use it in sharing with the SD pin. Monitoring can be enabled and disabled via the SW4 switch.
6.1 NTC Thermistor
The built-in thermistor (85 kΩ at 25 °C) is inside the IPM and connected on SD /OD pin2 (shared with the SD
function).
Given the NTC characteristic and the sharing with the SD function, the network is designed to keep the voltage on
this pin higher than the minimum voltage required for the pull up voltage on this pin over the whole temperature
range.
Considering Vbias = 3.3 V
The figure below shows the typical voltage on this pin as a function of device temperature.
, a pull up resistor of 1 kΩ (R10) was used.
Figure 12. NTC voltage vs temperature
UM2682
Temperature monitoring
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 15/31
Page 16

Firmware configuration for STM32 PMSM FOC SDK
7 Firmware configuration for STM32 PMSM FOC SDK
The following table summarizes the parameters which customize the latest version of the ST FW motor
control library for permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM): STM32 PMSM FOC SDK for this STEV
IPMNM3Q.
Table 4. ST motor control workbench GUI parameters - STEVAL-IPMNM3Q
Block Parameter Value
⋅
Comparator threshold
Over current protection
Bus voltage sensing Bus voltage divider 1/125
Rated bus voltage info
Current sensing
Command stage
Overcurrent network offset 0
Overcurrent network gain
Min rated voltage 125 V
Max rated voltage 400 V
Nominal voltage 325 V
Current reading typology Single- or three-shunt
Shunt resistor value See T
Amplifying network gain 1.9
Phase U Driver HS and LS: Active high
Phase V Driver HS and LS: Active high
Phase W Driver HS and LS: Active high
V
f
re
Comparator threshold / Iocp (see
T
able 1. Shunt selection)
able 1. Shunt selection
R15
+ R11
R11
+ VF=
UM2682
AL-
0.83V (13)
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 16/31
Page 17

8 Connectors, jumpers and test pins
Table 5. Connectors
Connector Description / pinout
Supply connector (DC – 125 V to 400 V)
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
Positive +
•
• Negative -
Motor control connector
1 - emergency stop
3 - PWM-A-H
5 - PWM-A-L
7 - PWM-B-H
9 - PWM-B-L
1
1 - PWM-C-H
13 - PWM-C-L
15 - current phase A
17 - current phase B
19 - current phase C
21 - NTC bypass relay
23 - dissipative brake PWM
25 - +V power
27- PFC sync.
29 - PWM VREF
31 - measure phase A
33 - measure phase B
Motor connector
•
phase A (U)
• phase B (V)
• phase C (W)
VCC supply (20 VDC max)
•
Positive +
• Negative -
Hall sensors / encoder input connector
1. Hall sensors input 1 / encoder A+
2. Hall sensors input 2 / encoder B+
3. Hall sensors input 3 / encoder Z+
4. 3.3 or 5 Vdc
5. GND
UM2682
Connectors, jumpers and test pins
2 - GND
4 - GND
6 - GND
8 - GND
10 - GND
12 - GND
14 - HV bus voltage
16 - GND
18 - GND
20 - GND
22 - GND
24 - GND
26 - heat sink temperature
28 - VDD_m
30 - GND
32 - GND
34 - measure phase C
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 17/31
Page 18

UM2682
Connectors, jumpers and test pins
Table 6. Jumpers
Jumper Descripton
Choose current U to send to control board
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4 Enable or disable sending temperature information from NTC to microcontroller
SW5, SW6
SW7, SW8
SW9, SW16
SW10, SW13 Modify phase A hall sensor network
SW11, SW14 Modify phase B hall sensor network
SW12, SW15 Modify phase C hall sensor network
SW17
Jumper on 1-2: from amplification
Jumper on 2-3: directly from motor
output
Choose current V to send to control board
Jumper on 1-2: from amplification
Jumper on 2-3: directly from motor
output
Choose current W to send to control board
Jumper on 1-2: from amplification
Jumper on 2-3: directly from motor
output
Choose 1-shunt or 3-shunt configuration. (through solder bridge)
SW5, SW6 closed one shunt
SW7, SW8 open three shunt
Choose input power for Hall/Encoder
Jumper on 1-2: 5 V
Jumper on 2-3: 3.3 V
Choose on-board or IPM op-amp in one shunt configuration
Jumper on 1-2: on-board op-amp
Jumper on 2-3: IPM op-amp
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 18/31
Page 19

UM2682
Connectors, jumpers and test pins
Table 7. T
Test Pin Description
TP1 OUTW
TP2 HINW (high side W control signal input)
TP3 VccW
TP4 SD (shutdown pin)/NTC
TP5 LINW (high side W control signal input)
TP6 OP+
TP7 OPOUT
TP8 OP
TP9 VbootW
TP10 OUTV
TP11 NV
TP12 HINV (high side V control signal input)
TP13 VbootV
TP14 LINV (high side V control signal input)
TP15 CIN
TP16 NU
TP17 NW
TP18 OUTU
TP19 VbootU
TP20 LINU (high side U control signal input)
TP21 Ground
TP22 Ground
TP23 HinU (high side U control signal input)
TP24 Current_A_amp
TP25 Current_B_amp
TP26 Current_C_amp
TP27 Ground
est pins
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 19/31
Page 20

9 Bill of materials
UM2682
Bill of material
Table 8. STEV
Item Q.ty Ref. Part / Value Description Manufacturer Order code
1 - C1 330μF CPCYL_D1400 EPCOS B43501A9337M000
2 4
3 2 C3, C4 47μF PTH 2-pin any any
4 3 C5, C6, C7 2.2μF 1206 Murata
5 1 C8 1nF 1206 Kemet C1206C102K5RACTU
6 1 C12 10μF PTH 2-pin any any
7 9
8 1 C17 0.1μF 1812 Murata
9 1 C18 3.3nF 1206 Kemet C1206C332K5RACTU
10 1 C21 4.7μF PTH 2-pin any any
11 3
12 3
13 5
14 5
15 1 D2 LED Red PTH 2-pin Ledtech L4RR3000G1EP4
16 4
17 1 J1
18 1 J2 Connector 34P PTH 34-pin RS -
19 1 J3
C2, C22,
C26, C28
C10, C11,
C14,
C15, C16,
C19,
C35, C36,
C37
C24, C27,
C30
C25, C29,
C31
C13, C23,
C32,
C33, C34
D1, D3, D4,
D5,
D10
D6, D7, D8,
D9
10nF 1206 AVX 12065C103KAT2A
10pF 1206 AVX 12061A100JAT2A
100pF 1206 Kemet C1206C101J1GACTU
330pF 1206 AVX 12065A331JAT2A
100nF 1206 AVX 12065C104KAZ2A
Diode BAT48J SOD323 ST BAT48J
Diode ZENER SOD123
Conector 7.62
mm - 2P
Connector 7.62
mm - 3P
AL-IPMNM3Q bill of materials
Fairchild
Semiconduct
or
TE
PTH 2-pin
p.7,62mm
PTH 3-pin
p.7,62mm
Connectivity
AMP
Connectors
TE
Connectivity
AMP
Connectors
GCM31MR71E225KA57
L
GRM43DR72J104KW01
L
MMSZ5250B
282845-2
282845-3
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 20/31
Page 21

Bill of material
Item Q.ty Ref. Part / Value Description Manufacturer Order code
Conector 5 mm
20 1 J4
21 1 J5
22 2 R1, R2 470kΩ 1206 any any
23 1 R3 120 Ω 1206 any any
24 1 R4 7.5kΩ 1206 Panasonic ERJP08F7501V
R5, R6, R7,
R8,
R9, R10,
R13,
R14, R15,
25 19
26 1 R12 5.6kΩ 1206 any any
27 3
28 6
29 3
30 7
31 3
32 -
33 2 SW7, SW8 Solder Bridge SMD - -
34 2 SW5, SW6 open SMD - -
35 6
R19,
R21, R22,
R23,
R26, R27,
R30,
R31, R32,
R43
R16, R17,
R18
R20, R24,
R25,
R28, R29,
R33
R37, R38,
R39
R11, R34,
R35,
R36, R40,
R41,
R42
RC2, RC5,
RC14
RC1, RC3,
RC4,
RC6, RC7,
RC8,
RC9, RC10,
RC1
1,
RC12,
RC13
SW1, SW2,
SW3, SW9,
-
2P
Connector 2.54
mm - 5P
1kΩ 1206 any any
0.33Ω 2512 Panasonic ERJ1TRQFR33U
1.91kΩ 1206 Panasonic ERJ8ENF1911V
2.4kΩ 1206 any any
4.7kΩ 1206 any any
0 Ω 0805 any any
- Not mounted - -
Jumper 2.54 PTH 3-pin RS W81136T3825RC
PTH 2-pin p.5mm
PTH 5-pin
p.2,54mm
Phoenix
Contact
RS W81136T3825RC
1729128
UM2682
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 21/31
Page 22

Item Q.ty Ref. Part / Value Description Manufacturer Order code
SW16,
SW17
SW4,
SW10,
SW11,
36 7
37 26
38 1 TP21
39 10
40 1 U1 TSV994IDT SO14 ST TSV994
41 1 U2 STIPQ3M60T-H
SW12,
SW13,
SW14,
SW15
TP1, TP2,
TP3,
TP4, TP5,
TP6,
TP7, TP8,
TP9,
TP10, TP1
TP12,
TP13,
TP14,
TP15,
TP16,
TP17,
TP18,
TP19,
TP20,
TP22,
TP23,
TP24,
TP25,
TP26,
TP27
to close
SWxy
Jumper 2.54 PTH 2-pin RS W81136T3825RC
1,
PCB terminal
1mm
PCB terminal
12.7mm
Jumper female
straight, black,
2-way
, 2.54mm
PTH 1-pin KEYSTONE 5001
PTH 2-pin HARWIN D3083B-46
Jumper
IPM, 3-phase
inverter
, 3 A, 1.6
Ω max., 600 V Nchannel MDmesh
DM2, N2DIP-26L
package
TE
Connectivity
ST STIPQ3M60T-HL
881545-2
UM2682
Bill of material
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 22/31
Page 23
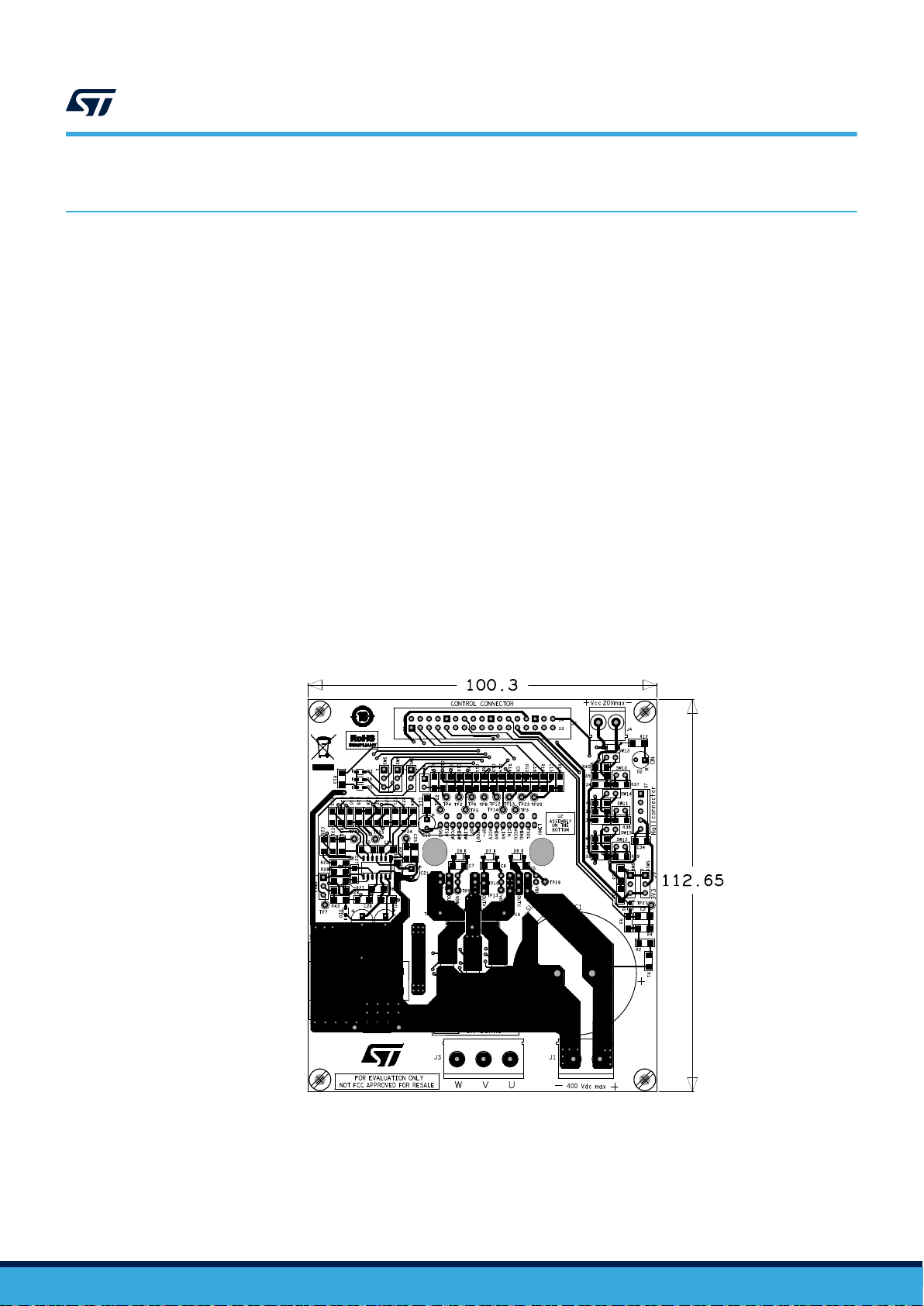
10 PCB design guide
Optimization of PCB layout for high voltage, high current and high switching frequency applications is a critical
point. PCB layout is a complex matter as it includes several aspects, such as length and width of track and circuit
areas, but also the proper routing of the traces and the optimized reciprocal arrangement of the various system
elements in the PCB area.
A good layout can help the application to properly function and achieve expected performance. On the other
hand, a PCB without a careful layout can generate EMI issues, provide overvoltage spikes due to parasitic
inductance along the PCB traces and produce higher power loss and even malfunction in the control and sensing
stages.
In general, these conditions were applied during the design of the board:
•
PCB traces designed as short as possible and the area of the circuit (power or signal) minimized to avoid the
sensitivity of such structures to surrounding noise
• Good distance between switching lines with high voltage transitions and the signal line sensitive to electrical
noise
• The shunt resistors were placed as close as possible to the low side pins of the SLLIMM. To decrease the
parasitic inductance, a low inductance type resistor was used
• RC filters were placed as close as possible to the SLLIMM pins in order to increase their efficiency
UM2682
PCB design guide
10.1 Layout of reference board
All the components are inserted on the top of the board. Only the IPM module is inserted on the bottom to allow
the insertion of a suitable heatsink for the application.
Figure 13. Silk screen and etch - top side
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 23/31
Page 24
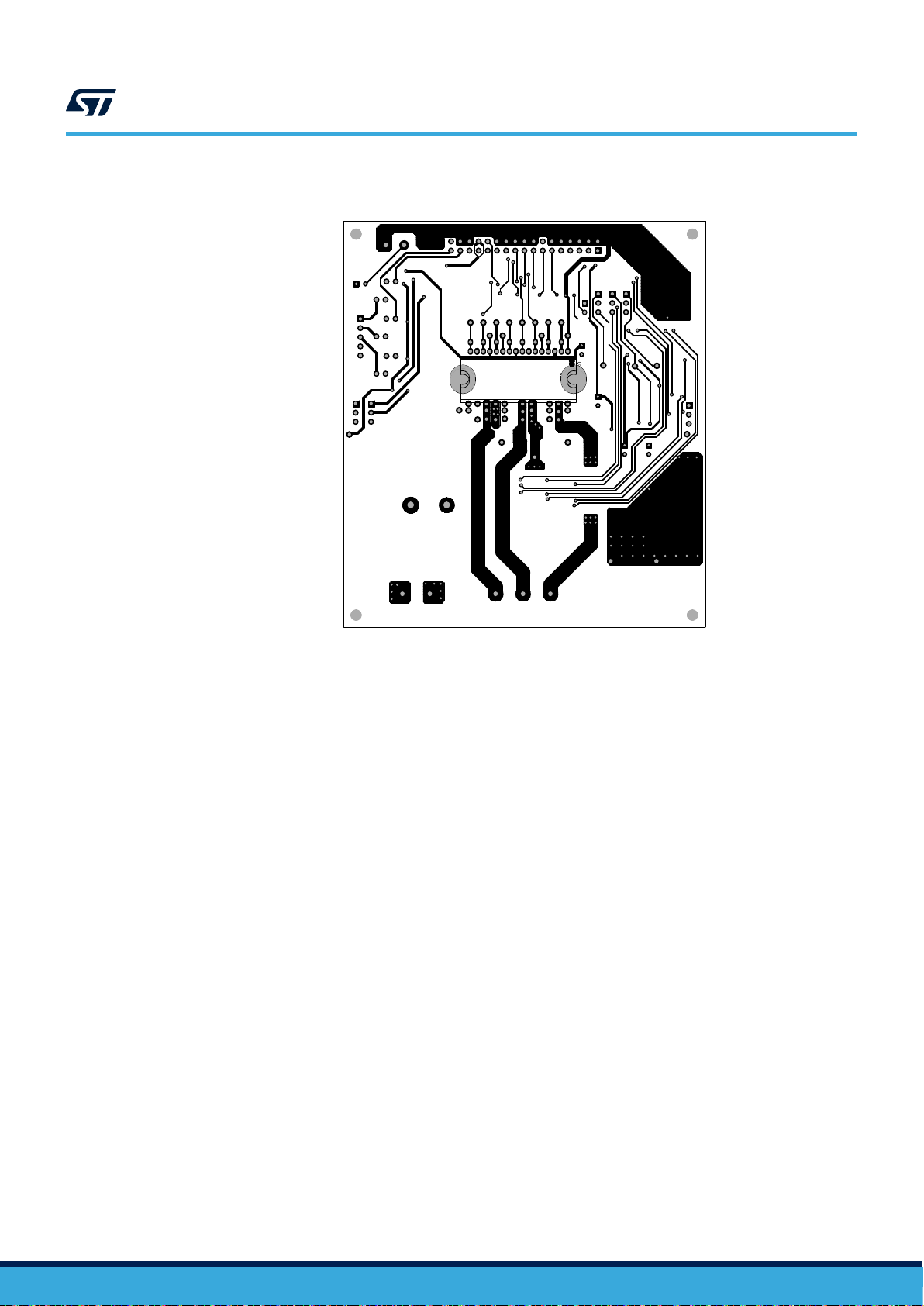
Figure 14. Silk screen and etch - bottom side
UM2682
Layout of reference board
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 24/31
Page 25

11 Recommendations and suggestions
• The BOM list is not provided with a bulk capacitor already inserted in the PCB. However, the necessary
space has been included (C1).In order to obtain a stable supply voltage, according to the application
conditions and current ripple requirements, it's advisable to use an adequate bulk capacitor
motor control applications, an electrolytic capacitor of at least 100 μF is suggested
• Similary, the PCB does not come with an heat sink, it can be placed above the IPM on the back of the
PCB with thermal conductive foil and screws. Heat sink RTH value is an important factor for good thermal
performance and depends on certain factors such as current phase, switching frequency, power factor and
ambient temperature.
• For an adequate heat sink dimensioning, it is suggest to use ST PowerStudio software (STSWPOWERSTUDIO), available on www.st.com.
• The board requires +5 V and +3.3 V to be supplied externally through the 34-pin motor control connector J2.
Please refer to the relevant board manuals for information on key connections and supplies.
UM2682
Recommendations and suggestions
. For general
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 25/31
Page 26

UM2682
General safety instructions
12 General safety instructions
Danger:
The evaluation board works with high voltage which could be deadly for the users. Furthermore
all circuits on the board are not isolated from the line input. Due to the high power density
components on the board as well as the heat sink can be heated to a very high temperature,
which can cause a burning risk when touched directly. This board is intended for use by
experienced power electronics professionals who understand the precautions that must be taken
to ensure that no danger or risk may occur while operating this board.
Caution: After the operation of the evaluation board, the bulk capacitor C1 (if used) may still store a high energy for
several minutes. So it must be first discharged before any direct touching of the board.
Important:
To protect the bulk capacitor C1, we strongly recommended using an external brake chopper after C1 (to discharge the high
brake current back from the induction motor).
, the
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 26/31
Page 27

Revision history
able 9. Document revision history
T
Date Version Changes
20-Mar-2020 1 Initial release.
Update figure in introduction.
17-Nov-2020 2
Updated Section 9 Bill of material
Updated Section 2.1 Schematic diagrams
Some edit changes to improve reabability
UM2682
.
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 27/31
Page 28

UM2682
Contents
Contents
1 Key features .......................................................................2
2 Circuit schematics.................................................................3
2.1 Schematic diagrams ............................................................4
3 Main characteristics ...............................................................9
4 Filters and key parameters........................................................10
4.1 Input signals..................................................................10
4.2 Bootstrap capacitor ............................................................10
4.3 Overcurrent protection .........................................................10
4.3.1 SD pin ................................................................ 1
4.3.2 Shunt resistor selection...................................................11
4.3.3 CIN RC filter ...........................................................11
4.3.4 Single- or three-shunt selection.............................................12
5 Current sensing amplifying network ..............................................13
6 Temperature monitoring ..........................................................15
6.1 NTC Thermistor...............................................................15
7 Firmware configuration for STM32 PMSM FOC SDK ...............................16
8 Connectors, jumpers and test pins................................................17
9 Bill of materials...................................................................20
10 PCB design guide ................................................................23
10.1 Layout of reference board ......................................................23
11 Recommendations and suggestions ..............................................25
12 General safety instructions .......................................................26
1
Revision history .......................................................................27
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 28/31
Page 29

UM2682
List of tables
List of tables
able 1. Shunt selection .................................................................... 11
T
Table 2. Op-amp sensing configuration ..........................................................13
Table 3. Amplifying networks .................................................................14
Table 4. ST motor control workbench GUI parameters - STEVAL-IPMNM3Q ................................ 16
Table 5. Connectors .......................................................................17
Table 6. Jumpers ......................................................................... 18
Table 7. Test pins ......................................................................... 19
Table 8. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q bill of materials ...................................................... 20
Table 9. Document revision history ............................................................. 27
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 29/31
Page 30

UM2682
List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Motor control board based on SLIMM-nano 2nd series - top view .................................1
Figure 2. Motor control board based on SLIMM-nano 2nd series - bottom view...............................1
Figure 3. STEV
Figure 4. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (2 of 5) ...............................................5
Figure 5. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (3 of 5) ...............................................6
Figure 6. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (4 of 5) ...............................................7
Figure 7. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (5 of 5) ...............................................8
Figure 8. STEVAL-IPMNM3Q architecture ........................................................9
Figure 9. CBOOT graph selection............................................................. 10
Figure 10. One-shunt configuration............................................................. 12
Figure 11. Three-shunt configuration ........................................................... 12
Figure 12. NTC voltage vs temperature.......................................................... 15
Figure 13. Silk screen and etch - top side ........................................................ 23
Figure 14. Silk screen and etch - bottom side...................................................... 24
AL-IPMNM3Q board schematic (1 of 5) ............................................... 4
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 30/31
Page 31

UM2682
IMPORTANT NOTICE – PLEASE READ CAREFULLY
STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and improvements to ST
products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on ST products before placing orders. ST
products are sold pursuant to ST’
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or the design of
Purchasers’ products.
No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. For additional information about ST trademarks, please refer to www
names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document.
s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order acknowledgement.
.st.com/trademarks. All other product or service
© 2020 STMicroelectronics – All rights reserved
UM2682 - Rev 2
page 31/31
 Loading...
Loading...