Page 1

M24C16, M24C08
M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
16Kbit, 8Kbit, 4Kbit, 2Kbit and 1Kbit Serial I²C Bus EEPROM
FEATURES SUMMARY
■ Two-Wire I²C Serial Interface
Supports 400kHz Protocol
■ Single Supply Voltage:
– 2.5 to 5.5V for M24Cxx-W
– 1.8 to 5.5V for M24Cxx-R
■ Write Control Input
■ BYTE and PAGE WRITE (up to 16 Bytes)
■ RANDOM and SEQUENTIAL READ Modes
■ Self-Timed Programming Cycle
■ Automatic Address Incrementing
■ Enhanced ESD/Latch-Up Protection
■ More than 1 Million Erase/Write Cycles
■ More than 40-Year Data Retention
■ Packages
– ECOPACK® (RoHS compliant)
Table 1. Product List
Reference Part Number
M24C16-W
M24C16
M24C16-R
M24C08-W
M24C08
M24C08-R
M24C04-W
M24C04
M24C04-R
M24C02-W
M24C02
M24C02-R
M24C01-W
M24C01
M24C01-R
Figure 1. Packages
PDIP8 (BN)
SO8 (MN)
150 mil width
TSSOP8 (DW)
169 mil width
TSSOP8 (DS)
3x3mm² body size (MSOP)
UFDFPN8 (MB)
2x3mm² (MLP)
1/28January 2006
Page 2

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES SUMMARY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 1. Product List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 1. Packages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Figure 2. Logic Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Table 2. Signal Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Figure 3. 8-Pin Package Connections (Top View) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Serial Clock (SCL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Serial Data (SDA). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Chip Enable (E0, E1, E2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 4. Device Select Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Write Control (WC
Supply voltage (V
Operating supply voltage V
Internal Device Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Power-down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 5. Maximum RP Value versus Bus Parasitic Capacitance (C) for an I²C Bus . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 6. I²C Bus Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 3. Device Select Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
CC
CC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
DEVICE OPERATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Start Condition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Stop Condition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Acknowledge Bit (ACK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Data Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Memory Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4. Operating Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 7. Write Mode Sequences with WC
=1 (data write inhibited) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Write Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Byte Write. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Page Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 8. Write Mode Sequences with WC
=0 (data write enabled) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 9. Write Cycle Polling Flowchart using ACK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Minimizing System Delays by Polling On ACK. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 10.Read Mode Sequences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Read Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Random Address Read. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Current Address Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Sequential Read. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Acknowledge in Read Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
2/28
Page 3

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
INITIAL DELIVERY STATE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
MAXIMUM RATING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 5. Absolute Maximum Ratings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
DC and AC PARAMETERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 6. Operating Conditions (M24Cxx-W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 7. Operating Conditions (M24Cxx-R). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 8. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W, Device Grade 6). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 9. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W, Device Grade 3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 10. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-R) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 11. AC Measurement Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 11.AC Measurement I/O Waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 12. Input Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 13. AC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 14. AC Characteristics (M24Cxx-R). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 12.AC Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
PACKAGE MECHANICAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 13.PDIP8 – 8 pin Plastic DIP, 0.25mm lead frame, Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 15. PDIP8 – 8 pin Plastic DIP, 0.25mm lead frame, Package Mechanical Data . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 14.SO8 narrow – 8 lead Plastic Small Outline, 150 mils body width, Package Outline . . . .22
Table 16. SO8 narrow – 8 lead Plastic Small Outline, 150 mils body width,
Package Mechanical Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 15.UFDFPN8 (MLP8) 8-lead Ultra thin Fine pitch Dual Flat Package No lead 2x3mm²,
Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 17. UFDFPN8 (MLP8) 8-lead Ultra thin Fine pitch Dual Flat Package No lead 2x3mm²,
Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 16.TSSOP8 – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 18. TSSOP8 – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, Package Mechanical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 17.TSSOP8 3x3mm² – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, 3x3mm² body size,
Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 19. TSSOP8 3x3mm² – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, 3x3mm² body size,
Mechanical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
PART NUMBERING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 20. Ordering Information Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
REVISION HISTORY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 21. Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3/28
Page 4

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
These I²C-compatible electrically erasable programmable memory (EEPROM) devices are organized as 2048/1024/512/256/128 x 8 (M24C16,
M24C08, M24C04, M24C02 and M24C01).
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST
offers these devices in ECOPACK® packages.
ECOPACK® packages are Lead-free and RoHS
compliant.
ECOPACK is an ST trademark. ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com.
Figure 2. Logic Diagram
V
CC
3
E0-E2 SDA
SCL
WC
M24Cxx
V
SS
AI02033
I²C uses a two-wire serial interface, comprising a
bi-directional data line and a clock line. The devices carry a built-in 4-bit Device Type Identifier code
(1010) in accordance with the I²C bus definition.
The device behaves as a slave in the I²C protocol,
with all memory operations synchronized by the
serial clock. Read and Write operations are initiated by a Start condition, generate d by the bus master. The Start condition is followed by a Device
Select Code and Read/Write
bit (RW) (as described in Table 3.), terminated by an acknowledge bit.
When writing data to the memory, the device inserts an acknowledge bit during the 9
th
bit time,
following the bus master’s 8-bit transmission.
When data is read by the bus master, the bus
master acknowledges the receipt of the data byte
in the same way. Data transfers are terminated by
a Stop condition after an Ack for Writ e, and afte r a
NoAck for Read.
Table 2. Signal Names
E0, E1, E2 Chip Enable
SDA Serial Data
SCL Serial Clock
WC
V
CC
V
SS
Write Control
Supply Voltage
Ground
Figure 3. 8-Pin Package Connections (Top View)
M24Cxx
/2Kb/4Kb/8Kb16Kb
/1Kb
/ E0/ NC/ NCNC
/ E1/ E1/ NCNC
/ E2/ E2/ E2NC
Note: 1. NC = Not Connected
2. See PACKAGE MECHANICAL section for package dimensions, and how to identify pin-1.
4/28
/ E0
/ E1
/ E2
SS
1
2
3
4
V
8
CC
WC
7
SCL
6
SDAV
5
AI02034E
Page 5
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Serial Clock (SCL)
This input signal is used to strobe all data in and
out of the device. In applications where this signal
is used by slave devices to synchronize the bus to
a slower clock, the bus master must have an open
drain output, and a pull-up resistor can be connected from Serial Clock (SCL) to V
. (Figure 5.
CC
indicates how the value of the pull-up resistor can
be calculated). In most applicat ions, though, this
method of synchronization is not employed, and
so the pull-up resistor is not necessary, provided
that the bus master has a push-pull (rather than
open drain) output.
Serial Data (SDA)
This bi-directional signal is used to transfer data in
or out of the device. It is an open drain output that
may be wire-OR’ed with other open drain or open
collector signals on the bus. A pull up resistor must
be connected from Serial Data (SDA) to V
CC
. (Fig-
ure 5. indicates how the value of the pull-up resis-
tor can be calculated).
Chip Enable (E0, E1, E2)
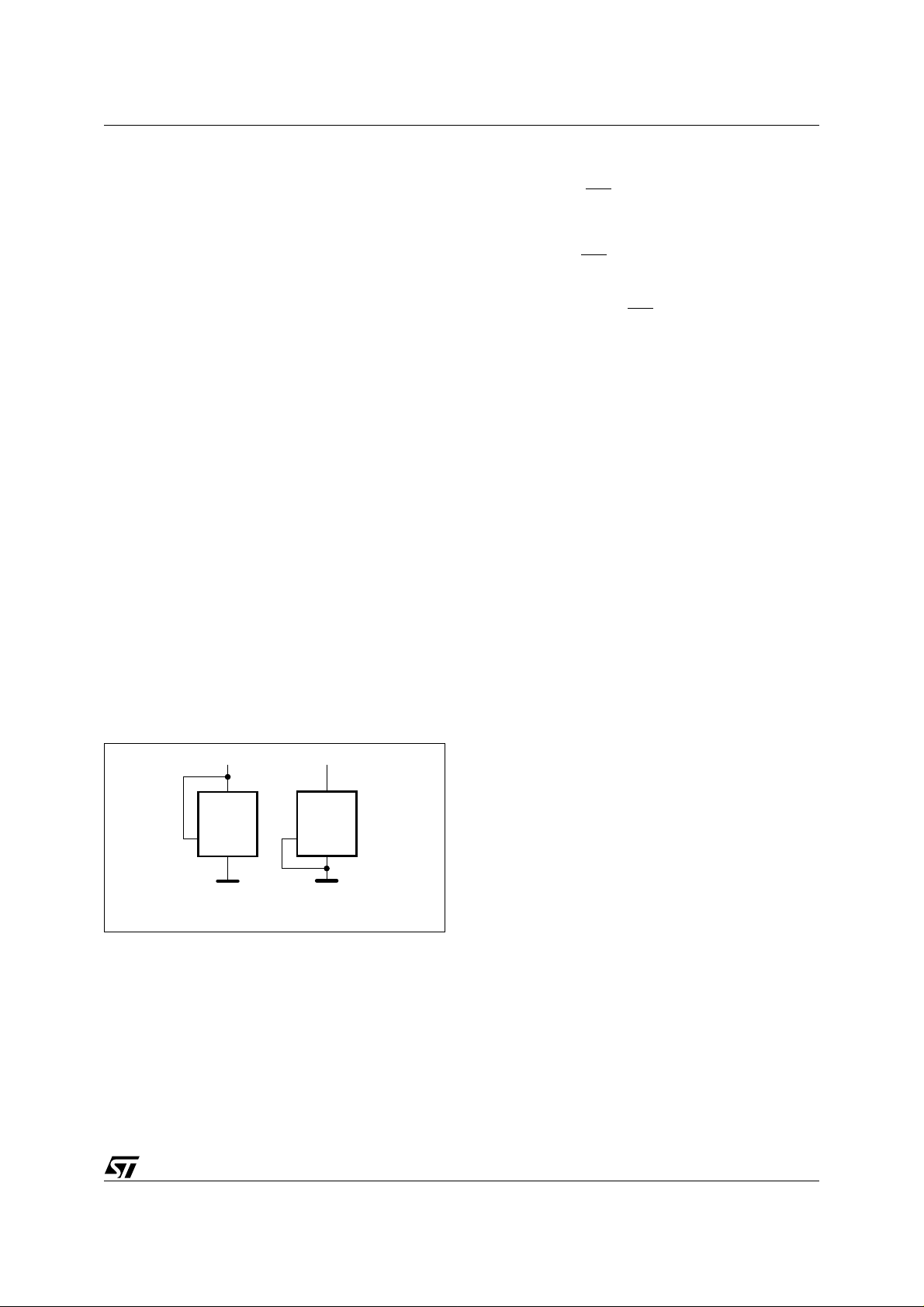
These input signals are used t o set the va lue that
is to be looked for on the three least significant bits
(b3, b2, b1) of the 7-bit De vice Select Code. These
inputs must be tied to V
or VSS, to establish the
CC
Device Select Code as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Device Select Code
V
CC
M24Cxx
E
i
V
SS
V
CC
M24Cxx
E
i
V
SS
Ai11650
Write Control (WC
). This input signal is useful
for protecting the entire contents of the memory
from inadvertent write operations. Write operations are disabled to the entire memory array when
Write Control (WC
nected, the signal is internally read as V
) is driven High. When uncon-
, and
IL
Write operations are allowed.
When Write Control (WC
) is driven High, Device
Select and Address bytes are acknowledged,
Data bytes are not acknowledged.
Supply voltage (V
Operating supply voltage V
CC
)
. Prior to select-
CC
ing the memory and issuing instructions to it, a valid and stable V
voltage must be applied: this
CC
voltage must be a DC voltage within the specified
(min), VCC(max)] range, as defined in Table
[V
CC
6. and Table 7. In order to secure a stable DC sup-
ply voltage, it is recommended to decouple the
line with a suitable capacitor (usually of the
V
CC
order of 10nF to 100nF) close to the V
CC/VSS
package pins.
The V
voltage must remain stable and valid until
CC
the end of the transmission of the instruction and,
for a Write instruction, until the completion of the
internal write cycle (t
).
W
Internal Device Reset. In order to pr event inadvertent Write operations during Power-up, a Power On Reset (POR) circuit is included. At Power-up
(continuous rise of V
spond to any instruction until V
), the device does not re-
CC
has reached the
CC
Power On Reset threshold voltage (this threshold
is lower than the minimum V
operating voltage
CC
defined in Table 6. and Table 7.).
When V
has passed the POR threshold, the de-
CC
vice is reset and in the Standby Power mode
Power-down. At Power-down (where V
creases continuously), as soon as V
drops from
CC
CC
de-
the operating voltage range below the Power On
Reset threshold voltage, the device stops responding to any instruction sent to it.
During Power-down, the device must be deselected and in the Standby Power mode (that is there
should be no internal Write cycle in progress).
5/28
Page 6

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 5. Maximum RP Value versus Bus Parasitic Capacita nce (C) for an I²C Bus
V
20
16
12
8
Maximum RP value (kΩ)
4
0
10
Figure 6. I²C Bus Protocol
SCL
fc = 400kHz
100
C (pF)
fc = 100kHz
1000
CC
MASTER
SDA
SCL
R
R
P
P
C
C
AI01665b
SDA
SCL
SDA
SCL
SDA
START
Condition
START
Condition
1 23 7 89
MSB
1 23 7 89
MSB ACK
SDA
Input
SDA
Change
STOP
Condition
ACK
STOP
Condition
AI00792B
6/28
Page 7
M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Table 3. Device Select Code
Device Type Identifier
1
Chip Enable
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
M24C01 Select Code 1 0 1 0 E2 E1 E0 RW
M24C02 Select Code 1 0 1 0 E2 E1 E0 RW
M24C04 Select Code 1 0 1 0 E2 E1 A8 RW
M24C08 Select Code 1 0 1 0 E2 A9 A8 RW
M24C16 Select Code 1 0 1 0 A10 A9 A8 RW
Note: 1. The most significant bit, b7, is sent first.
2. E0, E1 and E2 are compared against the respective external pins on the memory device.
3. A10, A9 and A8 represent most significant bits of the address.
2,3
RW
7/28
Page 8

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
DEVICE OPERATION
The device supports the I²C protocol. This is summarized in Figure 6.. Any device that sends data
on to the bus is defined to be a transmitter, and
any device that reads the data to be a receiver.
The device that controls the data transfer is known
as the bus master, and the other as the slave device. A data transfer can only be initiated by the
bus master, which will also provide the serial clock
for synchronization. The M24Cxx device is always
a slave in all communication.
Start Condition
Start is identified by a falling edge of Serial Data
(SDA) while Serial Clock (SCL) is stable in the
High state. A Start condition must precede any
data transfer command. The device continuously
monitors (except during a Write cycle) Serial Data
(SDA) and Serial Clock (SCL) for a Start condition,
and will not respond unless one is given.
Stop Condition
Stop is identified by a rising edge of Serial Data
(SDA) while Serial Clock (SCL) is stable and driven High. A Stop condition terminates communication between the device and the bus master. A
Read command that is followed by NoAck can be
followed by a Stop condition to force the device
into the Stand-by mode. A Stop condition at the
end of a Write command triggers the in ternal Write
cycle.
Acknowledge Bit (ACK)
The acknowledge bit is used to indicate a successful byte transfer. The bus transmitter, whether it be
bus master or slave device, releases Serial Data
(SDA) after sending eight bits of data. During the
th
clock pulse period, the receiver pulls Serial
9
Data (SDA) Low to acknowledge the receipt of the
eight data bits.
Data Input
During data input, the device samples Serial Data
(SDA) on the rising edge of Serial Clock (SCL).
For correct device operation, Serial Data (SDA)
must be stable during the rising edge of Serial
Clock (SCL), and the Serial Data (SDA) signal
must change only when Serial Clock (SCL) is driven Low.
Memory Addressing
To start communication between the bus master
and the slave device, the bus master must initiate
a Start condition. Following this, the bus master
sends the Device Select Code, shown in Table 3.
(on Serial Data (SDA), most significant bit first).
The Device Select Code consists of a 4-bit Device
Type Identifier, and a 3-bit Chip Enable “Address”
(E2, E1, E0). To address the memory ar ray, the 4bit Device Type Identifier is 1010b.
Each device is given a unique 3-bit code on the
Chip Enable (E0, E1, E2) inputs. When the Device
Select Code is received, the device only responds
if the Chip Enable Address is the same as the value on the Chip Enable (E0, E1, E2) inputs. However, those devices with larger memory capacities
(the M24C16, M24C08 and M24C04) need more
address bits. E0 is not available for u se on devices
that need to use address line A8; E1 is not available for devices that need to use address line A9,
and E2 is not available for devices that need to use
address line A10 (see Figure 3. and Table 3. for
details). Using the E0, E1 and E2 inputs, up to
eight M24C02 (or M24C01), four M24C04, two
M24C08 or one M24C16 devices can be connected to one I²C bus. In each case, and in the hybrid
cases, this gives a total memory capacity of
16 Kbits, 2 KBytes (except where M24C01 devices are used).
th
The 8
bit is the Read/Write bit (RW). This bit is
set to 1 for Read and 0 for Write operations.
If a match occurs on the Device Select code, the
corresponding device gives an acknowledgment
on Serial Data (SDA) during the 9
th
bit time. If the
device does not match the Device Select code, it
deselects itself from the bus, and goes into St andby mode.
8/28
Page 9

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Table 4. Operating Modes
Mode RW bit
Current Address Read 1 X 1 START, Device Select, RW
0X
Random Address Read
1 X reSTART, Device Select, RW
Sequential Read 1 X ≥ 1 Similar to Current or Random Address Read
Byte Write 0
Page Write 0
Note: 1. X = V
IH
or V
.
IL
Figure 7. Write Mode Sequences with WC=1 (data write inhibite d)
WC
Byte Write DEV SEL BYTE ADDR DATA IN
WC
(1)
Bytes Initial Sequence
START, Device Select, RW
1
V
IL
V
IL
ACK ACK NO ACK
1 START, Device Select, RW = 0
≤ 16 START, Device Select, RW = 0
= 1
= 0, Address
= 1
R/W
START
WC
ACK ACK NO ACK NO ACK
Page Write DEV SEL BYTE ADDR DATA IN 1 DATA IN 2
R/W
START
WC (cont'd)
NO ACK NO ACK
Page Write
(cont'd)
DATA IN N
STOP
STOP
DATA IN 3
AI02803C
9/28
Page 10

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Write Operations
Following a Start condition the bus master sends
a Device Select Code with the Read/Write
) reset to 0. The device acknowledges this, as
(RW
bit
shown in Figure 8., and waits for an addr ess byte .
The device responds to the address byte with an
acknowledge bit, and then waits for the data byte.
When the bus master generates a Stop condition
immediately after the Ack bit (in the “10
th
bit” time
slot), either at the end of a Byte Write or a Page
Write, the internal Write cycle is triggered. A Stop
condition at any other time slot does not trigger t he
internal Write cycle.
During the internal Write cycle, Serial Data (SDA)
and Serial Clock (SCL) are ignored, and the device does not respond to any requests.
Byte Write
After the Device Select code and the address byte,
the bus master sends one data byte. If the addressed location is Write-protected, by Write Control (WC
) being driven High (during the period from
the Start condition until the end of the address
byte), the device replies to the data byte with
NoAck, as shown in Figure 7., and the location is
not modified. If, instead, the addressed location is
not Write-protected, the device replies with Ack.
The bus master terminates the transfer by generating a Stop condition, as shown in Figure 8..
Page Write
The Page Write mode allows up to 16 bytes to be
written in a single Write cycle, provided that they
are all located in the same page in the memory:
that is, the most significant memory address bits
are the same. If more bytes are sent than will fit up
to the end of the page, a condition known as ‘rollover’ occurs. This should be avoided, as data
starts to become overwritten in an implementation
dependent way.
The bus master sends from 1 to 16 bytes of data,
each of which is acknowledged by the device if
Write Control (WC
tion is Write-protected, by Write Control (WC
) is Low. If the addressed loca-
) being driven High (during th e period from the Start
condition until the end of the address byte), the device replies to the data bytes with NoAck, as
shown in Figure 7., and the locations are not modified. After each byte is transferred, the internal
byte address counter (the 4 least significant address bits only) is incremented. The transfer is terminated by the bus master generating a Stop
condition.
10/28
Page 11

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 8. Write Mode Sequences with WC=0 (data write enabled)
WC
ACK
BYTE WRITE DEV SEL BYTE ADDR
R/W
START
WC
ACK ACK ACK ACK
PAGE WRITE DEV SEL BYTE ADDR
R/W
START
WC (cont'd)
ACKACK
PAGE WRITE
(cont'd)
DATA IN N
ACK ACK
DATA IN
DATA IN 1 DATA IN 2
STOP
DATA IN 3
STOP
AI02804B
11/28
Page 12

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 9. Write Cycle Polling Flowchart using ACK
WRITE Cycle
in Progress
START Condition
DEVICE SELECT
with RW = 0
ACK
NO
Returned
First byte of instruction
with RW = 0 already
decoded by the device
ReSTART
STOP
YES
Next
Operation is
Addressing the
Memory
DATA for the
WRITE Operation
Continue the
WRITE Operation
Minimizing System Delays by Polling On ACK
During the internal Write cycle, the device disconnects itself from the bus, and writes a copy of the
data from its internal latches to the memory cells.
The maximum Write time (t
) is shown in Table
w
13. and Table 14., but the typical time is shorter.
To make use of this, a polling sequence can be
used by the bus master.
The sequence, as shown in Figure 9., is:
YESNO
Send Address
and Receive ACK
START
Condition
YESNO
DEVICE SELECT
with RW = 1
Continue the
Random READ Operation
AI01847C
– Initial condition: a Write cycle is in progress.
– Step 1: the bus master issues a Start condition
followed by a Device Select Code (the first
byte of the new instruction).
– Step 2: if the device is busy with the internal
Write cycle, no Ack will be returned and the
bus master goes back to Step 1. If the device
has terminated the internal Write cycle, it
responds with an Ack, indicating that the
device is ready to receive the second part of
the instruction (the first byte of this i nstructi on
having been sent during Step 1).
12/28
Page 13

Figure 10. Read Mode Sequences
M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
CURRENT ADDRESS READ
RANDOM ADDRESS READ
SEQUENTIAL
CURRENT
READ
SEQUENTIAL
RANDOM
READ
ACK
DEV SEL DATA OUT
R/W
START
ACK
DEV SEL * BYTE ADDR
R/W
START
ACK ACK
DEV SEL DATA OUT 1
R/W
START
ACK ACK
DEV SEL * BYTE ADDR
NO ACK
STOP
ACK ACK
DEV SEL * DATA OUT
START
DEV SEL * DATA OUT 1
NO ACK
R/W
ACK NO ACK
DATA OUT N
ACK ACK
STOP
STOP
R/W
START
ACK NO ACK
DATA OUT N
STOP
Note: The seven most significant bits of the Device Select Code of a Random Read (in the 1st and 3rd bytes) must be identical.
Read Operations
Read operations are performed independently of
the state of the Write Control (WC
) signal.
START
edges this, and outputs the contents of the addressed byte. The bus master must not
acknowledge the byte, and terminates the transf er
with a Stop condition.
R/W
AI01942
The device has an internal address counter which
is incremented each time a byte is read.
Random Address Read
A dummy Write is first performed to load the address into this address counter (as shown in Fig-
ure 10.) but without sending a Stop condition.
Then, the bus master sends another Start condition, and repeats the Device Select Code, with the
Read/Write
bit (RW) set to 1. The device acknowl-
Current Address Read
For the Current Address Read operation, following
a Start condition, the bus master only sends a Device Select Code with the Read/Write
bit (RW) set
to 1. The device acknowledges this, and outputs
the byte addressed by the internal address
counter. The counter is then incremented. The bus
master terminates the transfer with a Stop condi-
13/28
Page 14

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
tion, as shown in Figure 10., without acknowledging the byte.
Sequential Read
This operation can be used after a Current Address Read or a Random Address Read. The bus
master does acknowledge the data byte output,
and sends additional clock pulses so that the device continues to output the next byte in sequence.
To terminate the stream of by tes, the bus master
must not acknowledge the last byte, and must
generate a Stop condition, as shown in Figure 10..
The output data comes from consecutive addresses, with the internal address counter automatica lly
incremented after each byte output. After the last
memory address, the address counter ‘rolls-over’,
and the device continues to output data from
memory address 00h.
Acknowledge in Read Mode
For all Read commands, the device waits, after
each byte read, for an acknowledgme nt during the
th
bit time. If the bus master does not drive Serial
9
Data (SDA) Low during this time, the device terminates the data transfer and switches to its Standby mode.
INITIAL DELIVERY STATE
The device is delivered with all bits in the memory
array set to 1 (each byte contains FFh).
14/28
Page 15

MAXIMUM RATING
M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Stressing the device outside the ratings listed in
Table 5. may cause permanent damage to the de-
vice. These are stress ratings only, and operation
of the device at these, or any other conditions outside those indicated in the Oper ating sections of
this specification, is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to
the STMicroelectronics SURE Program and other
relevant quality documents.
Table 5. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
T
A
T
STG
T
LEAD
V
IO
V
CC
V
ESD
Note: 1. T
LEAD
2. AEC-Q100-002 (compliant with JEDEC S td JESD22-A114A, C1=100pF, R1=1500Ω, R2=500Ω).
Ambient Operating Temperature –40 130 °C
Storage Temperature –65 150 °C
PDIP-Specific Lead Temperature during Soldering
260
(1)
Input or Output range –0.50 6.5 V
Supply Voltage –0.50 6.5 V
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Human Body model)
max must not be applied for more than 10s.
(2)
–4000 4000 V
°C
15/28
Page 16

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
DC AND AC PARAMETERS
This section summarizes the operating an d measurement conditions, and the DC and AC characteristics of the device. The parameters in the DC
and AC Characteristic tables that follow are derived from tests performed under the Measure-
ment Conditions summarized in the relevant
tables. Designers should check that the operating
conditions in their circuit match the measurement
conditions when relying on the quoted parameters.
Table 6. Operating Conditions (M24Cxx-W)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
V
CC
Supply Voltage 2.5 5.5 V
Ambient Operating Temperature (Device Grade 6) –40 85 °C
T
A
Ambient Operating Temperature (Device Grade 3) –40 125 °C
Table 7. Operating Conditions (M24Cxx-R)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
V
CC
T
A
Supply Voltage 1.8 5.5 V
Ambient Operating Temperature –40 85 °C
Table 8. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W, Device Grade 6)
Symbol Parameter
Input Leakage Current
I
LI
(SCL, SDA, E0, E1,and E2)
I
I
I
CC1
V
V
V
Note: 1. The voltage source driving only E0, E1 and E2 inputs must provide an impedance of less than 1kOhm.
Output Leakage Current
LO
Supply Current
CC
Stand-by Supply Current
IL
Input Low Voltage
IH
Input High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
OL
(1)
(1)
(in addition to those in Table 6.)
V
=5V, fc=400kHz (rise/fall time < 30ns)
CC
=2.5V, fc=400kHz (rise/fall time < 30ns)
V
CC
V
= VSS or VCC, for 2.5V < V
IN
IOL = 2.1mA when VCC = 2.5V or
Test Condition
V
= VSS or V
IN
V
= VSS or V
OUT
I
= 3mA when VCC = 5.5V
OL
SDA in Hi-Z
CC,
CC
= < 5.5V
CC
Min. Max. Unit
–0.45
0.7V
0.3V
CC
± 2 µA
± 2 µA
2mA
1mA
1µA
V
CC
VCC+1
V
0.4 V
16/28
Page 17

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Table 9. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W, Device Grade 3)
Symbol Parameter
Input Leakage Current
I
LI
(SCL, SDA, E0, E1,and E2)
I
I
I
CC1
V
V
V
Note: 1. The voltage source driving only E0, E1 and E2 inputs must provide an impedance of less than 1kOhm.
Output Leakage Current
LO
Supply Current
CC
Stand-by Supply Current
IL
Input Low Voltage
IH
Input High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
OL
(1)
(1)
(in addition to those in Table 6.)
=5V, fC=400kHz (rise/fall time < 30ns)
V
CC
IOL = 2.1mA when VCC = 2.5V or
Table 10. DC Characteristics (M24Cxx-R)
Symbol Parameter
Input Leakage Current
I
LI
(SCL, SDA, E0, E1,and E2)
I
I
I
CC1
V
V
V
Note: 1. The voltage source driving only E0, E1 and E2 inputs must provide an impedance of less than 1kOhm.
Output Leakage Current
LO
Supply Current
CC
Stand-by Supply Current
IL
Input Low Voltage
IH
Input High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
OL
(1)
(1)
(in addition to those in Table 7.)
V
V
=1.8V, fc=400kHz (rise/fall time < 30ns)
CC
V
IN
Test Condition
V
= VSS or V
IN
V
= VSS or V
OUT
V
=2.5V, fC=400kHz
CC
SDA in Hi-Z
CC,
(rise/fall time < 30ns)
= VSS or VCC, V
V
IN
= VSS or VCC, V
V
IN
I
= 3mA when VCC = 5.5V
OL
CC
CC
Test Condition
V
= VSS or V
= VSS or V
OUT
IN
CC
SDA in Hi-Z
CC,
= VSS or VCC, 1.8V < V
2.5 V ≤ V
1.8 V ≤ V
I
= 0.7 mA, VCC = 1.8 V
OL
< 2.5 V
CC
CC
CC
= 5 V
= 2.5 V
CC
–0.45
0.7V
Min. Max. Unit
< 5.5V
–0.45
–0.45
0.7V
Min. Max. Unit
± 2 µA
± 2 µA
3mA
3mA
5µA
2µA
CC
0.3V
VCC+1
CC
V
V
0.4 V
± 2 µA
± 2 µA
0.8 mA
1µA
CC
0.3 V
0.25 V
VCC+1
CC
CC
V
V
V
0.2 V
Table 11. AC Measurement Conditions
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
C
L
Load Capacitance 100 pF
Input Rise and Fall Times 50 ns
to 0.8V
Input Levels
Input and Output Timing Reference Lev els
0.2V
0.3V
CC
to 0.7V
CC
CC
CC
V
V
17/28
Page 18

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 11. AC Measurement I/O Waveform
Table 12. Input Parameters
Symbol
C
IN
C
IN
Z
WCL
Z
WCH
t
NS
Note: 1. TA = 25°C, f = 400kHz
2. Sampl ed only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance (SDA) 8 pF
Input Capacitance (other pins) 6 pF
WC Input Impedance
WC Input Impedance
Pulse width ignored
(Input Filter on SCL and SDA)
Parameter
Input Levels
0.8V
CC
0.2V
CC
1,2
Input and Output
Timing Reference Levels
0.7V
CC
0.3V
CC
AI00825B
Test Condition Min. Max. Unit
V
V
IN
< 0.3 V
IN
> 0.7V
CC
15 70 kΩ
500 kΩ
Single glitch 100 ns
18/28
Page 19

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Table 13. AC Characteristics (M24Cxx-W)
Test conditions specified in Table 6. and Table 11.
Symbol Alt. Parameter Min. Max. Unit
f
C
t
CHCL
t
CLCH
t
DL1DL2
t
DXCX
t
CLDX
t
CLQX
3
t
CLQV
1
t
CHDX
t
DLCL
t
CHDH
t
DHDL
4
t
W
Note: 1. For a reSTART condition, or following a Write cycle.
2. Sampl ed only, not 100% tested.
3. To avoid spurious START and STOP conditions, a minimum delay is placed between SCL=1 and the falling or rising edge of SDA.
4. Prev iou s de vic es beari n g the proc es s l ett er “L ” in t he pack age mar kin g gu ara nt ee a max i mum wri te t ime of 10 ms. Fo r mo re inf or mation about these devices and their device id entification, pl ease ask your ST Sales Office fo r Process Chang e Notices PCN MPG/
EE/0061 and 0062 (PCEE0061 and PCEE0062).
f
SCL
t
HIGH
t
LOW
2
t
t
SU:DAT
t
HD:DAT
t
DH
t
AA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
SU:STO
t
BUF
t
WR
Clock Frequency 400 kHz
Clock Pulse Width High 600 ns
Clock Pulse Width Low 1300 ns
SDA Fall Time 20 300 ns
F
Data In Set Up Time 100 ns
Data In Hold Time 0 ns
Data Out Hold Time 200 ns
Clock Low to Next Data Valid (Access Time) 200 900 ns
Start Condition Set Up Time 600 ns
Start Condition Hold Time 600 ns
Stop Condition Set Up Time 600 ns
Time between Stop Condition and Next Start Condition 1300 ns
Write Time 5 ms
Table 14. AC Characteristics (M24Cxx-R)
Test conditions specified in Table 7. and Table 10.
Symbol Alt. Parameter
f
C
t
CHCL
t
CLCH
t
DL1DL2
t
DXCX
t
CLDX
t
CLQX
3
t
CLQV
1
t
CHDX
t
DLCL
t
CHDH
t
DHDL
t
W
Note: 1. For a reSTART condition, or following a Write cycle.
2. Sampl ed only, not 100% tested.
3. To avoid spurious START and STOP conditions, a minimum delay is placed between SCL=1 and the falling or rising edge of SDA.
4. This is preliminary information.
f
SCL
t
HIGH
t
LOW
2
t
t
SU:DAT
t
HD:DAT
t
DH
t
AA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STA
t
SU:STO
t
BUF
t
WR
Clock Frequency 400 kHz
Clock Pulse Width High 600 ns
Clock Pulse Width Low 1300 ns
SDA Fall Time 20 300 ns
F
Data In Set Up Time 100 ns
Data In Hold Time 0 ns
Data Out Hold Time 200 ns
Clock Low to Next Data Valid (Access Time) 200 900 ns
Start Condition Set Up Time 600 ns
Start Condition Hold Time 600 ns
Stop Condition Set Up Time 600 ns
Time between Stop Condition and Next Start Condition 1300 ns
Write Time 10 ms
Min.
4
Max.
4
Unit
19/28
Page 20

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 12. AC Waveforms
SCL
SDA In
SCL
SDA In
SCL
tCHCL
tDLCL
tCHDX
START
Condition
tCHDH
STOP
Condition
tCLQV tCLQX
SDA
Input
tCLCH
SDA
Change
tW
Write Cycle
tDXCXtCLDX
tCHDH tDHDL
tCHDX
START
Condition
STOP
Condition
START
Condition
SDA Out
Data Valid
AI00795C
20/28
Page 21

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
PACKAGE MECHANICAL
Figure 13. PDIP8 – 8 pin Plastic DIP, 0.25mm lead frame, Package Outline
b2
A2
A1AL
be
D
8
E1
1
Note: Drawing is not to scale.
E
c
eA
eB
PDIP-B
Table 15. PDIP8 – 8 pin Plastic DIP, 0.25mm lead frame, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
A 5.33 0.210
A1 0.38 0.015
A2 3.30 2.92 4.95 0.130 0.115 0.195
b 0.46 0.36 0.56 0.018 0.014 0.022
b2 1.52 1.14 1.78 0.060 0.045 0.070
c 0.25 0.20 0.36 0.010 0.008 0.014
D 9.27 9.02 10.16 0.365 0.355 0.400
E 7.87 7.62 8.26 0.310 0.300 0.325
E1 6.35 6.10 7.11 0.250 0.240 0.280
e2.54––0.100––
eA 7.62 – – 0.300 – –
eB 10.92 0.430
L 3.30 2.92 3.81 0.130 0.115 0.150
millimeters inches
21/28
Page 22

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 14. SO8 narrow – 8 lead Plastic Small Outline, 150 mils body width, Package Outline
h x 45˚
A2
B
e
D
8
1
Note: 1. Drawing is not to scale.
2. The ‘1’ that appears in the top vie w of the package shows the position of pin 1 and the ‘N’ indicat es the total number of pins.
A
ddd
E
H
C
LA1 α
SO-A
Table 16. SO8 narrow – 8 lead Plastic Small Outline, 150 mils body width,
Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.35 1.75 0.053 0.069
A1 0.10 0.25 0.004 0.010
A2 1.10 1.65 0.043 0.065
B 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
D 4.80 5.00 0.189 0.197
ddd 0.10 0.004
E 3.80 4.00 0.150 0.157
e1.27– –0.050– –
H 5.80 6.20 0.228 0.244
h 0.25 0.50 0.010 0.020
L 0.40 0.90 0.016 0.035
α 0° 8° 0° 8°
N (number of
pins)
millimeters inches
88
22/28
Page 23

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 15. UFDFPN8 (MLP8) 8-lead Ultra thin Fine pitch Dual Flat Package No lead 2x3mm²,
Outline
e
D
b
L3
E
A
D2
ddd
A1
Note: 1. Drawing is not to scale.
2. The central pad (the area E2 by D2 in the above illustration) is pulled, internally, to VSS. It must not be allowed to be connected to
any other voltage or signal line on the PCB, for example during the soldering process.
3. The circle in the top view of the package indicates the position of pin 1.
L1
E2
L
UFDFPN-01
Table 17. UFDFPN8 (MLP8) 8-lead Ultra thin Fine pitch Dual Flat Package No lead 2x3mm²,
Data
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
A 0.55 0.50 0.60 0.022 0.020 0.024
A1 0.00 0.05 0.000 0.002
b 0.25 0.20 0.30 0.010 0.008 0.012
D 2.00 0.079
D2 1.55 1.65 0.061 0.065
ddd 0.05 0.002
E 3.00 0.118
E2 0.15 0.25 0.006 0.010
e0.50– –0.020– –
L 0.45 0.40 0.50 0.018 0.016 0.020
L1 0.15 0.006
L3 0.30 0.012
N (number of
pins)
millimeters inches
88
23/28
Page 24

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 16. TSSOP8 – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, Package Outline
D
8
1
CP
Note: 1. Drawing is not to scale.
2. The circle in the top view of the package indicates the position of pin 1.
5
EE1
4
α
A2A
A1
eb
L
L1
TSSOP8AM
Table 18. TSSOP8 – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, Packa ge Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.050 0.150 0.0020 0.0059
A2 1.000 0.800 1.050 0.0394 0.0315 0.0413
b 0.190 0.300 0.0075 0.0118
c 0 .090 0.200 0.0035 0.0079
CP 0.100 0.0039
D 3.000 2.900 3.100 0.1181 0.1142 0.1220
e 0.650 – – 0.0256 – –
E 6.400 6.200 6.600 0.2520 0.2441 0.2598
E1 4.400 4.300 4.500 0.1732 0.1693 0.1772
L 0.600 0.450 0.750 0.0236 0.0177 0.0295
L1 1.000 0.0394
α 0° 8° 0° 8°
millimeters inches
c
24/28
Page 25

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Figure 17. TSSOP8 3x3mm² – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, 3x3mm² body size,
Package Outline
D
8
1
CP
Note: 1. Drawing is not to scale.
2. The circle in the top view of the package indicates the position of pin 1.
5
EE1
4
A2A
A1
eb
L
L1
TSSOP8BM
c
α
Table 19. TSSOP8 3x3mm² – 8 lead Thin Shrink Small Outline, 3x3mm² body size,
Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
A 1.100 0.0433
A1 0.050 0.150 0.0020 0.0059
A2 0.850 0.750 0.950 0.0335 0.0295 0.0374
b 0.250 0.400 0.0098 0.0157
c 0 .130 0.230 0.0051 0.0091
D 3.000 2.900 3.100 0.1181 0.1142 0.1220
E 4.900 4.650 5.150 0.1929 0.1831 0.2028
E1 3.000 2.900 3.100 0.1181 0.1142 0.1220
e 0.650 – – 0.0256 – –
CP 0.100 0.0039
L 0.550 0.400 0.700 0.0217 0.0157 0.0276
L1 0.950 0.0374
α 0° 6° 0° 6°
millimeters inches
25/28
Page 26

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
PART NUMBERING
Table 20. Ordering Information Scheme
Example: M24C16 – W DW 3 T P /W
Device T ype
2
M24 = I
Device Function
16 = 16 Kbit (2048 x 8)
08 = 8 Kbit (1024 x 8)
04 = 4 Kbit (512 x 8)
02 = 2 Kbit (256 x 8)
01 = 1 Kbit (128 x 8)
Operating Voltage
W
R = V
Package
BN = PDIP8
MN = SO8 (150 mil width)
MB = UDFDFPN8 (MLP8)
DW = TSSOP8 (169 mil width)
DS = TSSOP8 (3x3mm² body size, MSOP8)
C serial access EEPROM
= VCC = 2.5 to 5.5V (400 kHz)
= 1.8 to 5.5V (400 kHz)
CC
Device Grade
6 = Industrial temperature range, –40 to 85 °C.
Device tested with standard test flow
3 = Device tested with High Reliability Certified Flow
Automotive temperature range (–40 to 125 °C)
Option
T = Tape and Reel Packing
Plating Technology
blank = Standard SnPb plating
P or G = ECOPACK® (RoHS compliant)
Process
/W or /S = F6SP36%
Note: 1. ST strongly recommends the use of the Automotive Grade devices for use in an automotive environment. The High Reliability Cer-
2
tified Flow (HRCF) is described in the quality note QNEE9801. Please ask your nearest ST sales office for a copy.
2. Used only for Device Grade 3.
For a list of available options (speed, package,
etc.) or for further information on any aspect of this
device, please contact your nearest ST Sales Office.
1
.
The category of second Level Interconnect is
marked on the package and on the inner box label,
in compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The
maximum ratings related to soldering conditions
are also marked on the inner box label.
26/28
Page 27

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
REVISION HISTORY
Table 21. Document Revision History
Date Version Description of Revision
10-Dec-1999 2.4
18-Apr-2000 2.5 Labelling change to Fig-2D, correction of values for ‘E’ and main caption for Tab-13
05-May-2000 2.6 Extra labelling to Fig-2D
23-Nov-2000 3.0
19-Feb-2001 3.1
20-Apr-2001 3.2 Revision of DC and AC characteristics for the -S series
08-Oct-2001 3.3 Ball numbers added to the SBGA connections and package mechanical illustrations
09-Nov-2001 3.4
30-Jul-2002 3.5
04-Feb-2003 3.6 Document title spelt out more fully. “W”-marked devices with tw=5ms added.
05-May-2003 3.7
07-Oct-2003 4.0
17-Mar-2004 5.0
7-Oct-2005 6.0
17-Jan-2006 7.0
TSSOP8 Turned-Die package removed (p 2 and order information)
Lead temperature added for TSSOP8 in table 2
SBGA package information removed to an annex document
-R range changed to being the -S range, and the new -R range added
SBGA package information put back in this document
Lead Soldering Temperature in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table amended
Write Cycle Polling Flow Chart using ACK illustration updated
References to PSDIP changed to PDIP and Package Mechanical data updated
Wording brought in to line with standard glossary
Specification of Test Condition for Leakage Currents in the DC Characteristics table
improved
Document reformatted using new template. SBGA5 package removed
TSSOP8 (3x3mm² body size) package (MSOP8) added. -L voltage range added
-R voltage range upgraded to 400kHz working, and no longer preliminary data.
5V voltage range at temperature range 3 (-xx3) no longer preliminary data.
-S voltage range removed. -Wxx3 voltage+temp ranged added as preliminary data.
Table of contents, and Pb-free options added. Minor wording changes in Summary
Description, Power-On Reset, Memory Addressing, Read Operations. V
-0.45V. t
MLP package added. Absolute Maximum Ratings for V
(max) value for -R voltage range corrected.
W
(min) and VCC(min) changed.
IO
(min) improved to
IL
Soldering temperature information clarified for RoHS compliant devices. Device grade
information clarified. Process identification letter “G” information added. 2.2-5.5V range is
removed, and 4.5-5.5V range is now Not f or New Design
Product List summary table added. AEC-Q100-002 compliance. Device Grade informaton
clarified. Updated Device internal reset section, Figure 4., Figure 5., Table 14. and Table
20. Added Ecopack® information. Updated tW=5ms for the M24Cxx-W.
Pin numbers removed from silhouettes (see Figure 1., Packages). Internal Device Reset
paragraph moved to below Supply voltage (V
SIGNAL DESCRIPTION. Test conditions for V
). Supply voltage (VCC) added below
CC
updated in Table 8. and Table 9. SO8N
OL
package specifications updated (see Table 16.)
New definition of I
over the whole VCC range (see Tables 8, 9 and 10).
CC1
27/28
Page 28

M24C16, M24C08, M24C04, M24C02, M24C01
Information furnished is believe d to be accura te and re liable. Howev er, STMi croelec tronics assumes n o resp onsibil ity for t he consequences
of use of such information nor f or any infringement of pa tents or other rights of third parties which may re sult from its use. N o license is granted
by implication or otherwise und er an y pa ten t or patent rights of STMicroelectr on ics . Sp ec ific ations mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2006 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
28/28
 Loading...
Loading...