Page 1
L5973AD
Fi
2A SWITCH STEP DOWN SWITCHING REGULATOR
1 GENERAL FEATURES
■ 2A INTERNAL SWITCH
■
OPERATING INPUT VOLTAGE FROM 4.4V TO 36V
■ 3.3V / (±2%) REFERENCE VOLTAGE
■ OUTPUT VOLTAGE ADJUSTABLE FROM
1.235V TO 35V
■ LOW DROPOUT OPERATION: 100% DUTY
CYCLE
■ 500KHz INTERNALLY FIXED FREQUENCY
■ VOLTAGE FEEDFORWARD
■ ZERO LOAD CURRENT OPERATION
■ INTERNAL CURRENT LIMITING
■ INHIBIT FOR ZERO CURRENT
CONSUMPTION
■ SYNCHRONIZATION
■ PROTECTION AGAINST FEEDBACK
DISCONNECTION
■ THERMAL SHUTDOWN
1.1 APPLICATIONS:
■ CONSUMER: STB, DVD, TV, VCR,CAR
RADIO, LCD MONITORS
■ NETWORKING: XDSL, MODEMS,DC-DC
MODULES
■ COMPUTER: PRINTERS, AUDIO/GRAPHIC
CARDS, OPTICAL STORAGE, HARD DISK
DRIVE
■ INDUSTRIAL: CHARGERS, CAR BATTERY
DC-DC CONVERTERS
2 DESCRIPTION
The L5973AD is a step down monolithic power
gure 1. Package
HSOP8 (Exposed pad)
Table 1. Order Codes
Part Number Package
L5973AD HSOP8
L5973ADTR HSOP8 in Tape & Reel
switching regulator with a switch current limit of 2A so
it is able to deliver more than 1.5A DC current to the
load depending on the application conditions.
The output voltage can be set from 1.235V to 35V.
The high current level is also achieved thanks to an
SO8 package with exposed frame, that allows to reduce the R
th(j-amb)
down to approximately 40°C/W
The device uses an internal P-Channel D-MOS transistor (with a typical of 200m
Ω
) as switching element
to avoid the use of bootstrap capacitor and guarantee
high efficiency.
An internal oscillator fixes the switching frequency at
500KHz to minimize the size of external components.
Having a minimum input voltage of 4.4V only, it is
particularly suitable for 5V bus, available in all computer related applications.
Pulse by pulse current limit with the internal frequency modulation offers an effective constant current
short circuit protection.
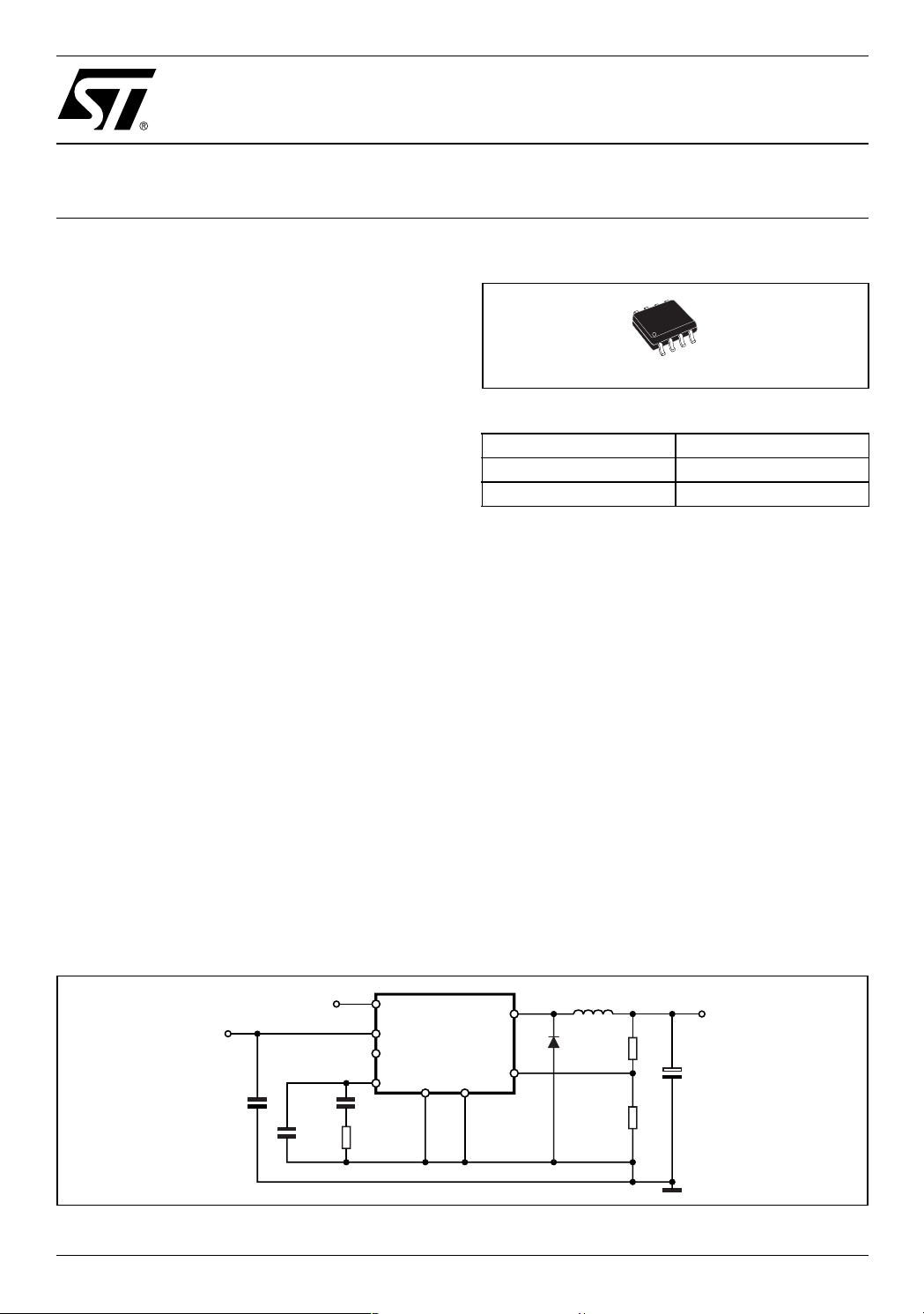
Figure 2. Test and Application Circuit
VREF
3.3V
C4
22nF
C3
220pF
VCC
SYNC.
COMP
December 2004
VIN = 4.4V to 35V
C1
10µF
35V
CERAMIC
R3
4.7K
6
8
L5973AD
2
4
L1 15µH
OUT
1
D1
STPS340U
7
GNDINH
D03IN1453
5
FB
3
R1
5.6K
R2
3.3K
VOUT=3.3V
C2
330µF
10V
Rev. 3
1/14
Page 2
L5973AD
Table 2. Thermal Data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
th (j-amb)
(*) Package mounted on board
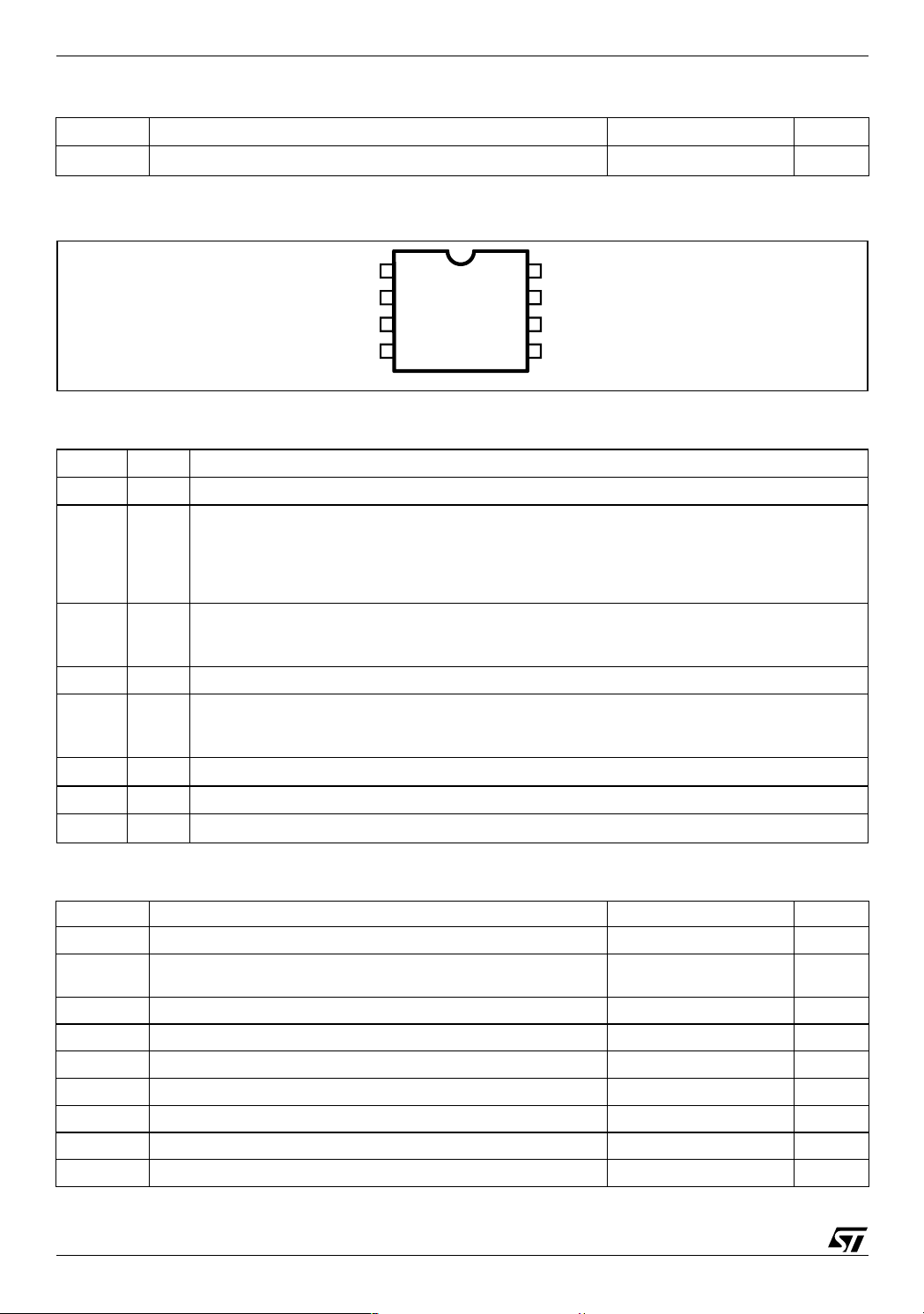
Figure 3. Pin Connection (top view)
Table 3. Pin Description
N. Name Description
1 OUT Regulator Output.
2 SYNC Master/Slave Synchronization. When it is open, a signal synchronous with the turn-off of the inter-
3INH
4 COMP E/A output to be used for frequency compensation.
5 FB Stepdown feedback input. Connecting the output voltage directly to this pin results in an output
6V
7 GND Ground.
8V
Thermal Resistance Junction to ambient Max. 40 (*) °C/W
VCC
OUT
SYNC
INH
COMP
1
2
3
4
D98IN955
8
GND
7
VREF
6
FB
5
nal power is present at the pin. When connected to an external signal at a frequency higher than
the internal one, then the device is synchronized by the external signal.
Connecting together the SYNC pin of two devices, the one with the higher frequency works as
master and the other one, works as slave.
A logical signal (active high) disables the device. With IHN higher than 2.2V the device is OFF and with
INH lower than 0.8V, the device is ON.
If INH is not used the pin must be grounded. When it is open, an internal pull-up disables the device.
voltage of 1.235V. An external resistor divider is required for higher output voltages (the typical
value for the resistor connected between this pin and ground is 4.7K).
Reference voltage of 3.3V. No filter capacitor is needed to stability.
REF
Unregulated DC input voltage.
CC
Table 4. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
2/14
V
V
I
1
, V
V
4
V
V
P
tot
T
T
stg
Input Voltage 40 V
8
Output DC voltage
1
Output peak voltage at t = 0.1µs
-1 to 40
-5 to 40
Maximum output current int. limit.
Analog pins 4 V
5
INH -0.3V to V
3
SYNC -0.3 to 4 V
2
Power dissipation at T
Operating junction temperature range -40 to 150 °C
j
≤ 60°C 2.25 W
amb
Storage temperature range -55 to 150 °C
CC
V
V
Page 3
L5973AD
Table 5. Electrical Characteristics (Tj = 25°C, VCC = 12V, unless otherwise specified.)
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
R
DSON
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS (see test circuit ).
V
DC CHARACTERISTICS
I
qop
I
qst-by
INHIBIT
ERROR AMPLIFIER
V
V
I
o source
I
o sink
gm Transconductance I
SYNC FUNCTION
REFERENCE SECTION
Note: 1. Guaranteed by design
Operating input voltage range Vo = 1.235V; Io = 2A 4.4 36 V
CC
Mosfet on Resistance 0.250 0.5 Ω
Maximum limiting current VCC = 4.4V to 36V 2 2.3 A
I
l
Switching frequency 500 KHz
f
s
Duty cycle 0 100 %
Voltage feedback 4.4V < VCC < 36V 1.220 1.235 1.25 V
5
η Efficiency V
= 5V, VCC = 12V 90 %
O
Total Operating Quiescent Current 5 7 mA
Quiescent current Duty Cycle = 0; VFB = 1.5V 2.7 mA
I
q
Total stand-by quiescent current V
> 2.2V 50 100 µA
inh
INH Threshold Voltage Device ON 0.8 V
Device OFF 2.2 V
High level output voltage VFB = 1V 3.5 V
OH
Low level output voltage VFB = 1.5V 0.4 V
OL
Source output current V
Sink output current V
Source bias current 2.5 4 µA
I
b
DC open loop gain R
High Input Voltage V
Low Input Voltage V
Slave Sink Current
Master Output Amplitude I
Output Pulse Width no load, V
= 1.9V; VFB = 1V 200 300 µA
COMP
= 1.9V; VFB = 1.5V 1 1.5 mA
COMP
= ∞ 50 57 dB
L
= -0.1mA to 0.1mA
comp
V
= 1.9V
COMP
= 4.4V to 36V 2.5 V
CC
= 4.4V to 36V 0.74 V
CC
= 0.74V
V
sync
V
= 2.33V
sync
= 3mA 2.75 3 V
source
(1)
= 1.65V 0.20 0.35 µs
sync
0.11
0.21
2.3 mS
Reference Voltage 3.234 3.3 3.366 V
I
= 0 to 5mA
REF
3.2 3.3 3.399 V
VCC = 4.4V to 36V
Line Regulation I
REF
= 0mA
510mV
VCC = 4.4V to 36V
Load Regulation I
= 0 to 5mA 8 15 mV
REF
Short Circuit Current 10 18 30 mA
REF
0.25
0.45mAmA
V
3/14
Page 4
L5973AD
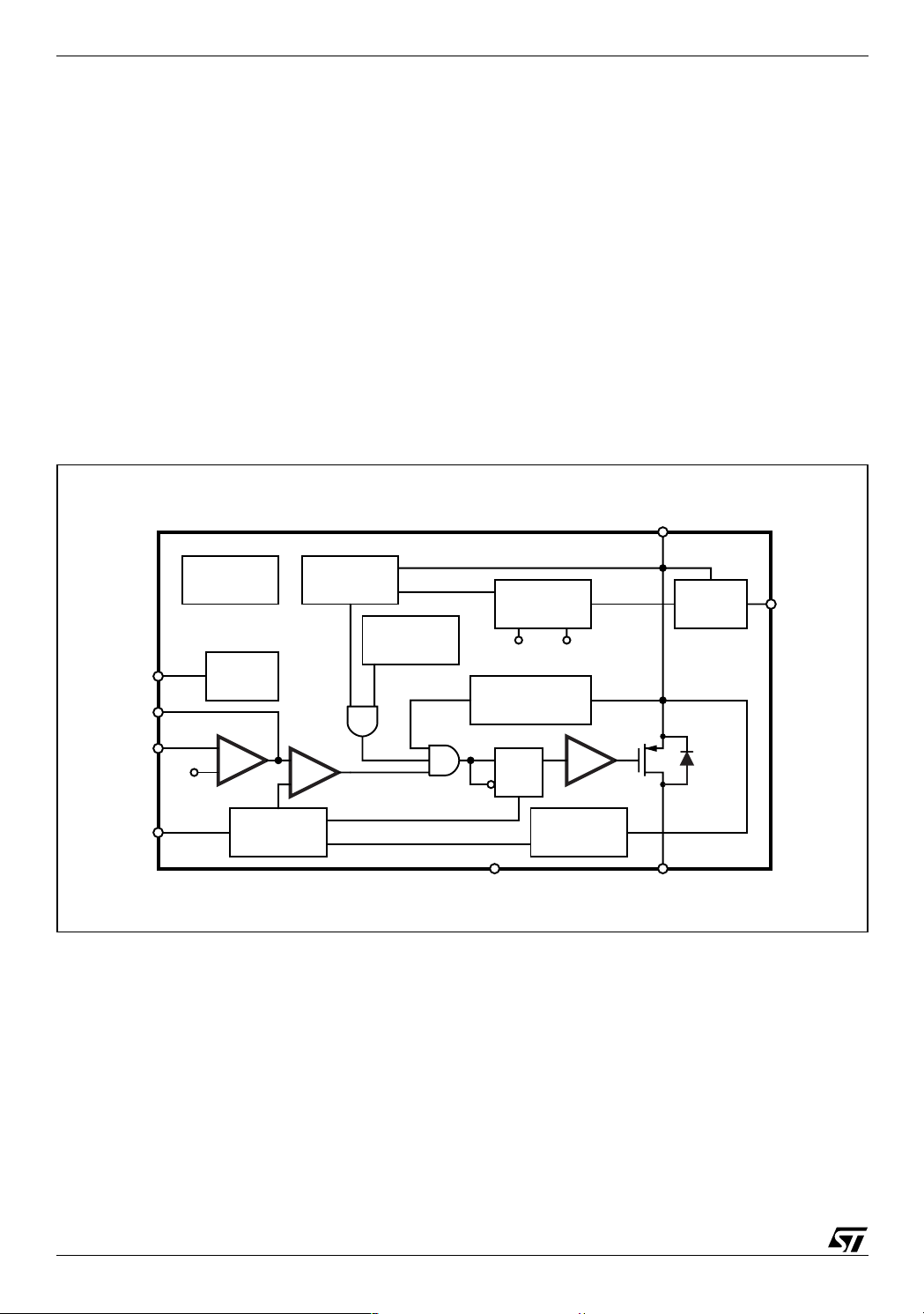
3 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The main internal blocks are shown in Fig. 1, where is reported the device block diagram. They are:
● A voltage regulator that supplies the internal circuitry. From this regulator, a 3.3V reference
voltage is externally available.
● A voltage monitor circuit that checks the input and internal voltages.
● A fully integrated sawtooth oscillator whose frequency is500KHz
● Two embedded current limitations circuitries which control the current that flows through the
power switch. The Pulse by Pulse Current Limit forces the power switch OFF cycle by cycle
if the current reaches an internal threshold, while the Frequency Shifter reduces the switching frequency in order to strongly reduce the duty cycle.
● A transconductance error amplifier.
● A pulse width modulator (PWM) comparator and the relative logic circuitry necessary to drive
the internal power.
● An high side driver for the internal P-MOS switch.
● An inhibit block for stand-by operation.
● A circuit to realize the thermal protection function.
Figure 4. Block Diagram
VCC
VOLTAGES
MONITOR
PWM
+
-
THERMAL
SHUTDOWN
SUPPLY
1.235V 3.5V
PEAK TO PEAK
CURRENT LIMIT
DCkQ
DRIVER
FREQUENCY
SHIFTER
GND OUT
V
REF
BUFFER
LPDMOS
POWER
D00IN1125
V
REF
INH
COMP
FB
SYNC
TRIMMING
1.235V
INHIBIT
E/A
-
+
OSCILLATOR
3.1 POWER SUPPLY & VOLTAGE REFERENCE
The internal regulator circuit (shown in Figure 2) consists of a start-up circuit, an internal voltage Preregulator, the Bandgap voltage reference and the Bias block that provides current to all the blocks.
The Starter gives the start-up currents to the whole device when the input voltage goes high and the device is enabled (inhibit pin connected to ground).
The Preregulator block supplies the Bandgap cell with a preregulated voltage V
that has a very low
REG
supply voltage noise sensitivity.
4/14
Page 5
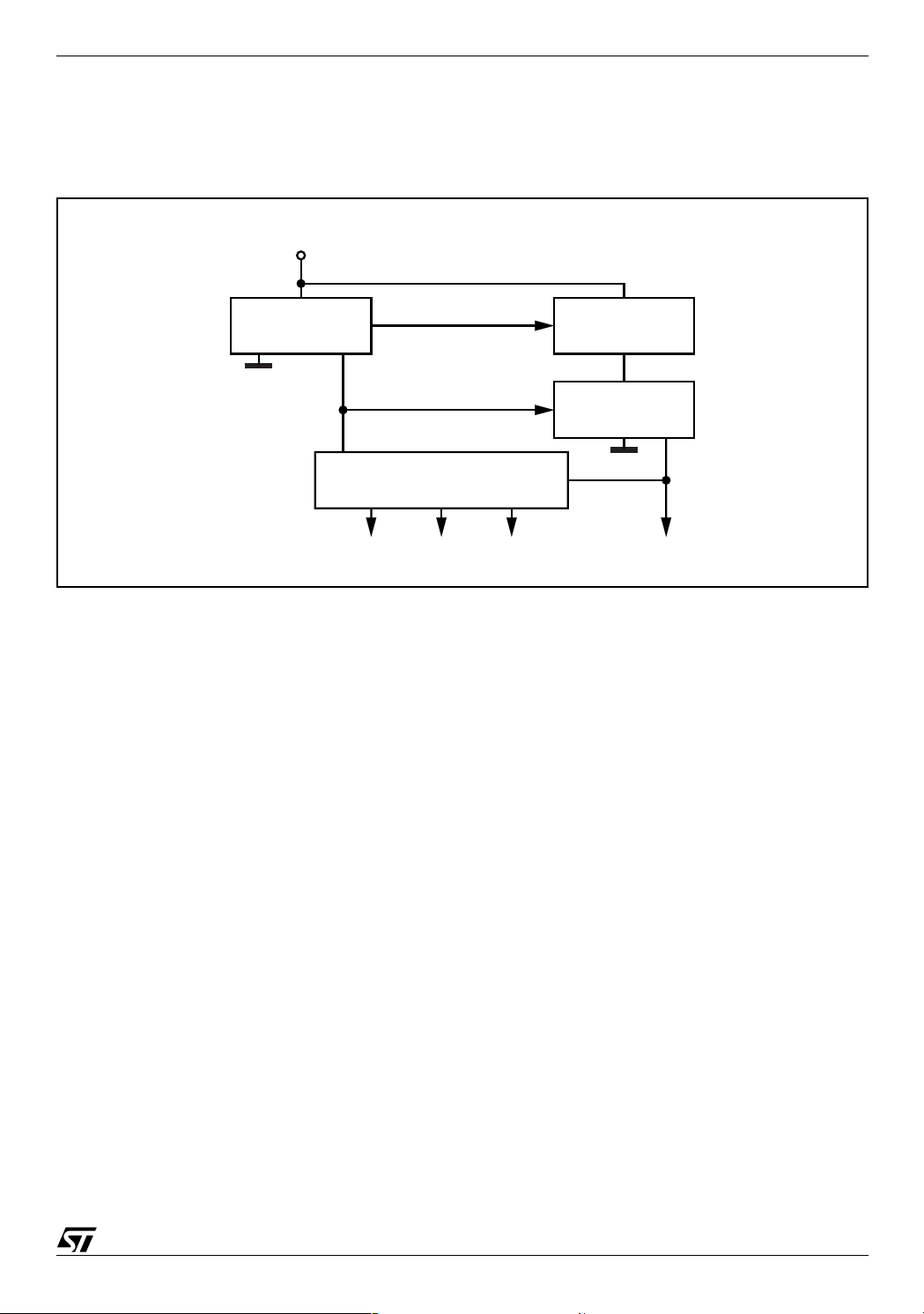
3.2 VOLTAGES MONITOR
An internal block senses continuously the Vcc, V
and Vbg. If the voltages go higher than their thresholds, the
ref
regulator starts to work. There is also an hysteresis on the V
Figure 5. Internal Regulator Circuit
V
CC
(UVLO).
CC
L5973AD
STARTER
IC BIAS
D00IN1126
PREREGULATOR
VREG
BANDGAP
VREF
3.3 OSCILLATOR & SYNCHRONIZATOR
Figure 6 shows the block diagram of the oscillator circuit.
The Clock Generator provides the switching frequency of the device that is internally fixed at 500KHz. The frequency
shifter block acts reducing the switching frequency in case of strong overcurrent or short circuit. The clock signal is
then used in the internal logic circuitry and is the input of the Ramp Generator and Synchronizator blocks.
The Ramp Generator circuit provides the sawtooth signal, used to realize the PWM control and the internal voltage feed forward, while the Synchronizator circuit generates the synchronization signal. Infact the device has a
synchronization pin that can works both as Master and Slave.
As Master to synchronize external devices to the internal switching frequency.
As Slave to synchronize itself by external signal.
In particular, connecting together two devices, the one with the lower switching frequency works as Slave and
the other one works as Master.
To synchronize the device, the SYNC pin has to pass from a low level to a level higher than the synchronization
threshold with a duty cycle that can vary approximately from 10% to 90%, depending also on the signal frequency and amplitude.
The frequency of the synchronization signal must be at least higher than the internal switching frequency of the
device (500KHz).
5/14
Page 6

L5973AD
Figure 6. Oscillator Circuit
Ibias_osc
FREQUENCY
SHIFTER
CLOCK
t
CLOCK
GENERATOR
D00IN1131
RAMP
GENERATOR
SYNCHRONIZATOR
RAMP
SYNC
3.4 CURRENT PROTECTION
The L5973AD has two current limit protections, pulse by pulse and frequency fold back.
The schematic of the current limitation circuitry for the pulse by pulse protection is shown in figure 7.
The output power PDMOS transistor is split in two parallel PDMOS. The smallest one has a resistor in series,
R
. The current is sensed through Rsense and if reaches the threshold, the mirror is unbalanced and the
SENSE
PDMOS is switched off until the next falling edge of the internal clock pulse.
Due to this reduction of the ON time, the output voltage decreases.
Since the minimum switch ON time (necessary to avoid false overcurrent signal) is not enough to obtain a suf-
ficiently low duty cycle at 500KHz, the output current, in strong overcurrent or short circuit conditions, could increase again. For this reason the switching frequency is also reduced, so keeping the inductor current under its
maximum threshold. The Frequency Shifter (see fig. 6) depends on the feedback voltage. As the feedback voltage decreases (due to the reduced duty cycle), the switching frequency decreases too.
Figure 7. Current Limitation Circuitry
6/14
VCC
DRIVER
OUT
A1/A2=95
I
OFF
PWM
RSENSE
A1
A2
II
RTH
I
NOT
D00IN1134
L
Page 7

L5973AD
3.5 ERROR AMPLIFIER
The voltage error amplifier is the core of the loop regulation. It is a transconductance operational amplifier whose
non inverting input is connected to the internal voltage reference (1.235V), while the inverting input (FB) is connected to the external divider or directly to the output voltage. The output (COMP) is connected to the external
compensation network.
The uncompensated error amplifier has the following characteristics:
Transconductance 2300µS
Low frequency gain 65dB
Minimum sink/source voltage 1500µA/300µA
Output voltage swing 0.4V/3.65V
Input bias current 2.5µA
The error amplifier output is compared with the oscillator sawtooth to perform PWM control.
3.6 PWM COMPARATOR AND POWER STAGE
This block compares the oscillator sawtooth and the error amplifier output signals generating the PWM
signal for the driving stage.
The power stage is a very critical block cause it has to guarantee a correct turn on and turn off of the PDMOS.
The turn on of the power element, or better, the rise time of the current at turn on, is a very critical parameter to compromise.
At a first approach, it looks like the faster it is the rise time, the lower are the turn on losses.
But there is a limit introduced by the recovery time of the recirculation diode.
In fact when the current of the power element equals the inductor current, the diode turns off and the drain
of the power is free to go high. But during its recovery time, the diode can be considered as an high value
capacitor and this produces a very high peak current, responsible of many problems:
Spikes on the device supply voltage that cause oscillations (and thus noise) due to the board parasitics.
Turn on overcurrent causing a decrease of the efficiency and system reliability.
Big EMI problems.
Shorter freewheeling diode life.
The fall time of the current during the turn off is also critical. In fact it produces voltage spikes (due to the
parasitics elements of the board) that increase the voltage drop across the PDMOS.
In order to minimize all these problems, a new topology of driving circuit has been used and its block diagram is shown in fig. 8.
The basic idea is to change the current levels used to turn on and off the power switch, according with the
PDMOS status and with the gate clamp status.
This circuitry allow to turn off and on quickly the power switch and to manage the above question related
to the freewheeling diode recovery time problem. The gate clamp is necessary to avoid that Vgs of the
internal switch goes higher than Vgsmax. The ON/OFF Control block avoids any cross conduction between the supply line and ground.
7/14
Page 8

L5973AD
Figure 8. Driving Circuitry
Vgs
max
I
VCC
OFF
STOP
DRIVE
DRAIN
D00IN1133
CLAMP
ON/OFF
CONTROL
GATE
OFF
ON
DRAIN
I
ON
PDMOS
L
ESR
C
VOUT
I
LOAD
3.7 INHIBIT FUNCTION
The inhibit feature allows to put in stand-by mode the device. With INH pin higher than 2.2V the device is disabled and the power consumption is reduced to less than 100
µ
A. With INH pin lower than 0.8V, the device is
enabled. If the INH pin is left floating, an internal pull up ensures that the voltage at the pin reaches the inhibit
threshold and the device is disabled. The pin is also Vcc compatible.
3.8 THERMAL SHUTDOWN
The shutdown block generates a signal that turns off the power stage if the temperature of the chip goes higher
than a fixed internal threshold (150°C). The sensing element of the chip is very close to the PDMOS area, so
ensuring an accurate and fast temperature detection. An hysteresis of approximately 20°C avoids that the devices turns on and off continuously
4 ADDITIONAL FEATURES AND PROTECTIONS
4.1 FEEDBACK DISCONNECTION
In case of feedback disconnection, the duty cycle increases versus the maximum allowed value, bringing the
output voltage close to the input supply. This condition could destroy the load.
To avoid this dangerous condition, the device is turned off if the feedback pin remains floating.
4.2 OUTPUT OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION
The overvoltage protection, OVP, is realized by using an internal comparator, which input is connected to the
feedback, that turns off the power stage when the OVP threshold is reached. This threshold is typically 30%
higher than the feedback voltage.
When a voltage divider is requested for adjusting the output voltage (see test application circuit), the OVP intervention will be set at:
+
R
1R2
1.3
--------------------
⋅⋅=
R
V
2
FB
Where R
is the resistor connected between the output voltage and the feedback pin, while R2 is between the
1
feedback pin and ground.
8/14
V
OVP
Page 9

L5973AD
4.3 ZERO LOAD
Due to the fact that the internal power is a PDMOS, no boostrap capacitor is required and so, the device works properly also with no load at the output. In this condition it works in burst mode, with random repetition rate of the burst.
4.4 APPLICATION CIRCUIT
In figure 9 is shown the demo board application circuit, where the input supply voltage, Vcc, can range from 4.4V
to 25V due to the rated voltage of the input capacitor and the output voltage is adjustable from 1.235V to V
Figure 9. Demo board Application Circuit
.
cc
VIN = 4.4V to 25V
C1
10µF
25V
CERAMIC
3.3V
C4
22nF
C3
220pF
VREF
VCC
SYNC.
COMP
4.7K
R3
6
8
L5973AD
2
4
OUT
1
3
7
5
FB
GNDINH
D03IN1454
L1 15µH
D1
STPS2L25U
Table 6. Component List
Reference Part Number Description Manufacturer
C1 10µF, 25V TOKIN
C2 POSCAP 6TPB330M 330µF, 6.3V Sanyo
C3 C1206C221J5GAC 220pF, 5%, 50V KEMET
R1
5.6K
R2
3.3K
VOUT=3.3V
C2
330µF
6.3V
C4 C1206C223K5RAC 22nF, 10%, 50V KEMET
R1 5.6K, 1%, 0.1W 0603 Neohm
R2 3.3K, 1%, 0.1W 0603 Neohm
R3 4.7K, 1%, 0.1W 0603 Neohm
D1 STPS2L25U 2A, 25V ST
L1 DO3316P-153 15µH, 3A COILCRAFT
9/14
Page 10

L5973AD
V
V
Figure 10. Junction Temperature vs. Output
Current
Tj ( °C)
Tj ( °C)
100
100
90
90
Vi n= 5V
Vi n= 5V
80
80
Tamb=25° C
Tamb=25° C
70
70
60
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Io(A)
Io(A)
Vo=3 . 3V
Vo=3 . 3V
Vo=1. 8V
Vo=1. 8V
Vo=2. 5
Vo=2. 5
Figure 11. Junction Temperature vs Output
Current
Tj( C)
Tj( C)
110
110
Vo=3 . 3 V
Vo=2. 5V
Vo=2. 5V
Vo=3 . 3 V
100
100
Vin=12V
Vin=12V
90
90
Tamb=25°C
Tamb=25°C
80
80
70
70
60
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Io(A)
Io(A)
Vo=5V
Vo=5V
Figure 12. Efficiency vs. Output Current
95
95
90
90
Vout=3.3V
85
85
80
80
75
75
Efficiency (%)
Efficiency (%)
70
70
65
65
Vin=5V
Vin=5V
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Io(A)
Io(A)
Vout=3.3V
Vout=2.5V
Vout=2.5V
Vout=1.8V
Vout=1.8V
Figure 13. Efficiency vs. Output Current
95
95
90
90
85
85
80
80
Efficiency (%)
Efficiency (%)
75
75
Vin=12V
70
70
65
65
Vin=12V
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
Io(A)
Io(A)
Vout=5V
Vout=5V
Vout=2.5V
Vout=2.5V
Vout=3.3V
Vout=3.3V
10/14
Page 11

5 APPLICATION IDEAS
Figure 14. Positive Buck-Boost regulator
L5973AD
C3
22nF
R3
4.7k
Vcc
COMP
SYNC
8
4
2
VREF
VIN=5V
C1
10uF
10V
Ceramic
C2
220pF
Figure 15. Buck-Boost regulator
3.3V
VIN = 5V
C1
10µF
10V
CERAMIC
C2
10µF
25V
CERAMIC
C4
22nF
C3
220pF
L5973AD
6
GND
3.3V
VREF
VCC
SYNC.
COMP
4.7K
R3
7
1
5
3
INH
6
8
L5973AD
2
4
OUT
FB
3
D1
STPS2L25U
7
GNDINH
D03IN1455
1
5
L1
15uH
OUT
D1
STPS2L25U
FB
2.7K
24K
D2
STPS2L25U
M1
STN4NE03L
L1 15µH
C5
100µF
16V
24k
2.7k
VOUT=-12V/
VOUT=12V/0.6A
C4
100uF
16V
0.6A
Figure 16. Dual output voltage with auxiliary winding
D2
C4
100µF
10V
1N4148
VOUT1=5V/
50mA
VOUT=3.3V/
0.5A
C5
47µF
10V
VIN = 5V
C1
10µF
25V
CERAMIC
3.3V
C3
22nF
C2
220pF
VREF
VCC
SYNC.
COMP
R3
4.7K
6
8
L5973AD
2
4
N1/N2=2
OUT
1
Lp 22µH
D1
7
5
GNDINH
D03IN1456
3
STPS25L25U
FB
Refer to L5973AD application note (AN1723) to have additional information, details, and more application
ideas.
L5973AD belongs to L597x family.
Related part numbers are:
● L5970D: 1.5A (I
● L5972D: 2A (I
● L5973D: 2.5A (I
), 250KHz Step Down DC-DC Converter in SO8
sw
), 250KHz Step Down DC-DC Converter in SO8
sw
), 250KHz Step Down DC-DC Converter in HSOP8
sw
In case higher current is needed, the nearest DC-DC Converter family is L497x.
11/14
Page 12

L5973AD
6 PACKAGE INFORMATION
Figure 17. HSOP8 (Exposed Pad) Mechanical Data & Package Dimensions
DIM.
A 1.350 1.750 0.531 0.069
A1
A2
B
C
D
E
e
H
h
L
k 0˚ (min), 8˚ (max)
ddd 0.100 0.010
Dimension D does not include mold flash, protusions
(1)
or gate burrs shall not exeed 0.15mm (both side).
mm inch
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
0.100 0.250 0.004 0.010
1.100 1.650 0.043 0.065
0.330 0.510 0.013 0.020
0.190 0.250 0.07 0.010
4.800 5.000 0.189 0.197
3.800 4.000 0.150 0.157
1.270 0.05
5.800 6.200 0.228 0.244
0.250 0.500 0.010 0.020
0.400 1.270 0.016 0.05
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
HSOP8
(Exposed Pad)
Exposed Pad:
D1 = 3.1mm
E1 = 2.41mm
7195016
12/14
Page 13

7 REVISION HISTORY
Table 7. Revision History
Date Revision Description of Changes
December 2003 1 First Issue
January 2004 2 Migration to EDOCS dms
December 2004 3 Added D1 & E1 dimensions in HSOP8 package information.
L5973AD
13/14
Page 14

L5973AD
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2004 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
14/14
 Loading...
Loading...