Page 1

Dot Matrix Printer
SP300 Series
Programmer’s Manual
Page 2

Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. CONTROL PANEL ..............................................................................1
1-1. Basic Operation ............................................................................1
1-2. Switch Operation (Combined Switch Operation) ........................2
2. SERIAL INTERFACE ..........................................................................7
2-1. Interface Specifications ................................................................7
2-2. Interface Circuit ...........................................................................8
2-2-1. RS-232C Serial Interface ..................................................8
2-2-2. Current Loop (option) .......................................................8
2-2-3. RS-422A Serial Interface (option) ....................................9
2-3. Connectors and Signals ..............................................................10
2-4. Interface Connections................................................................. 12
2-5. Installing the Optional Interface Board ......................................13
2-6. Data Structure.............................................................................14
2-6-1. DTR mode .......................................................................14
2-6-2. X-ON/X-OFF mode ........................................................16
2-6-3. STX-ETX mode ............................................................. 19
3. PARALLEL INTERFACE..................................................................22
3-1. Interface Specifications ..............................................................22
3-2. Interface Timing .........................................................................22
3-3. Connectors and Signals .............................................................. 24
4. Emergency Suspension........................................................................25
5. VALIDATION PRINTING (Models with validation function only) . 26
5-1. Operating Method ......................................................................26
5-2. Printing Format ..........................................................................27
5-3. Data format.................................................................................27
5-4. Other ........................................................................................... 27
6. AUTO CUTTER (Auto-cutting models only).....................................28
6-1. Cutting Method ..........................................................................28
6-2. Cutting position ..........................................................................28
6-3. Auto cutting control codes .........................................................28
6-4. Other position to be observed ....................................................28
Page 4

7. CONTROL CODES ............................................................................29
7-1. Control Codes Used for Character Setting .................................32
7-2. Control Codes Used for Line Spacing .......................................36
7-3. Control Codes Used for Page Layout......................................... 37
7-4. Control Codes Used for Graphics Printing ................................41
7-5. Control Codes Used for Download Characters ..........................46
7-6. Control Codes Used for Peripheral Units................................... 49
7-7. Other Control Codes .................................................................. 50
8. CHARACTOR CODE TABLES ...................................................... 55
8.1 U.S.A. & Europe (DIP SW2-1: ON, SW2-2: ON).....................55
8.2 IBM Character Set #1 (DIP SW2-1: OFF, SW2-2: ON) .......... 57
8.3 IBM Character Set #2 (DIP SW2-1: ON, SW2-2: OFF) ........... 59
8.4 JAPAN (DIP SW2-1:, OFF, SW2-2: OFF)................................61
8.5 International Character Sets .......................................................63
• For DIP switch settings, refer to Installation Manual.
• Models with validation function: SP312F, SP317F
Page 5

1. CONTROL PANEL
1-1. Basic Operation
1 “ON LINE” switch
POWER
3
ALARM
4
5
ON LINE
1
FEED
2
Fig. 1-1 Control panel
3 “POWER” lamp (green LED)
• Lights when the power for the printer is on.
4 “ALARM” lamp (red LED)
• Lights when the paper is out.
If the paper is out, load a new roll then press the “ON LINE” switch.
• Flashes when the front cover is open or a mechanical error (motor lock etc.)
occurs. The buzzer will give one short beep followed by a long beep.
Mount the front cover properly and press the “ON LINE” switch. If the
buzzer still sounds and the “ALARM” lamp flashes, this signifies that a
mechanical error has occurred. Locate the cause of the error and turn the
power for the printer off and back on again to reset the printer.
(In case of a mechanical error, the data will not be cleared even if the power
is turned off.)
5 “ON LINE” lamp (green LED)
LED lit: Printer is ON LINE
LED off: Printer is OFF LINE
LED flashes: Validation printing mode is set.
When all lamps 3 to 5 light simultaneously and the buzzer sounds continuously, a CPU error has occurred. In case of a CPU error, turn off the power then
turn it on again. When turning off the power, the data will be cleared.
Switches the printer between “ON
LINE” and “OFF LINE”. Whenever the printer switches between
“ON LINE” and “OFF LINE”, the
buzzer gives one short beep (“ON
LINE” and “OFF LINE”, switching
is possible only when the paper is
loaded in the printer.)
2 “FEED” switch
• When this switch is pressed and
then released within 0.5 sec.,the
paper feeds one line.
• When this switch is depressed for
more than 0.5 sec.,the paper feeds
continuously.
(The above paper feed operation
is possible for both “ON LINE”
and “OFF LINE” modes.)
– 1 –
Page 6

1-2. Switch Operation (Combined Switch Operation)
1 <SELF PRINT TEST>
FEED + POWER ON (Turn the power on while holding the FEED switch
depressed.)
Self-printing will be performed according to the VER. NO., DIP switch
settings and character order. When the FEED switch is held continuously
during self printing, only the characters will print out repeatedly.
In models with cutter, cutting will be done after self-printing is performed
according to the VER. NO., DIP switch setting and character order. When the
FEED switch is pressed after completed self-printing, character printing and
cutting will be repeatedly performed.
Fig. 1-2 Self printing sample (when using serial interface printer)
– 2 –
Page 7

2 <Hexadecimal dump mode>
ON LINE + POWER ON (Turn the power on while holding the ON LINE
switch depressed.)
Each of the signals sent from the computer to the printer will be printed out
in hexadecimal code.
This function allows you to check if a control code sent to the printer by the
program being used is correct or not. The buzzer will sound once to indicate
the printer is in hexadecimal dump mode.
After the program has been run, the last line buffer should be flushed by
pressing the ON LINE switch. To turn off the mode, it is necessary to turn off
the printer completely.
Fig. 1-3 Hexadecimal printing sample
3 <CLEAR PRINT BUFFER> (Single Head Only)
FEED + ON LINE + POWER ON (Turn the power on while holding both
the FEED and ON LINE switches depressed.)
This operation clears the printer buffer. (The buzzer gives two short beeps.)
When DIP switch 1-7 of this printer is set to ON (which is the factory presetting),
the RAM back-up function operates to maintain the data in the data buffer, even
if the power for the printer is shut off due to power failure, etc.
However, when the printer power is shut off for more than 10 hours, the data
content will become unstable and its content could degenerate and become unusable in the worst instances. For this reason, when the printer power is turned
off for more than 10 hours, perform the above operation to clear the data in the
data buffer.
Note that the data in the buffer can also be cleared by control code <CAN>.
4 <MICRO FEED>
ON LINE + FEED Press the FEED switch while holding the ON LINE
switch depressed when the printer is OFF LINE and the paper will feed in very
small increments.
– 3 –
Page 8

5 <PAGE TOP> (Sprocket-type Only)
ON LINE + FEED (Press the FEED button while holding the ON LINE
button depressed when the printer is ON LINE) The buzzer gives three short
beeps and the printer sets the page top.
6 <Dot alignment adjust mode> (Twin Head Only)
FEED + ON LINE + POWER ON
This mode enables adjustment of the forward and backward printed line alignment by 1/2-dot increments. The adjustment procedure is explained on the
following pages.
– 4 –
Page 9

1. Enter the Dot Alignment Adjust Mode by turning on the power while
pressing the ONLINE and FEED switches.
2. When Dot Alignment Adjust Mode starts, the buzzer will sound twice and
“Dot Alignment Adjust Mode” is printed.
3. Seven dot alignment patterns are printed as shown below. The patterns are
arranged with the backward printed lines more toward the left as the patterns
are printed down the page; the fourth pattern is the standard. The asterisk (*)
indicates the pattern printed with the current setting.
– 5 –
Page 10

4. To choose a pattern with a closer alignment of the forward and backward
printed lines, count from the top down to the desired pattern and press the
FEED switch the counted number of times. (The buzzer sounds each time the
FEED switch is pressed, up to a maximum of seven times. However, if the
FEED switch is pressed more than seven times, a warning sounds.)
5. Press the ONLINE switch after the setting is made. (If the power is turned off
before the ONLINE switch is pressed, the new setting becomes invalid.)
When the setting is entered, the buzzer sounds once and the chosen starting
position of the backward printed line is stored in the memory.
This setting does not change if the machine’s power is turned off.
A pattern using the selected setting and followed by “Adjust Completed!” is
printed.
If the ONLINE switch is pressed to end step 5 without changing the setting,
“Adjust Completed!” is printed and the mode is exited.
* To set the starting position of the backward printed line to 0, simultaneously
press the ONLINE and FEED switches in step 4. The mode automatically
continues on to step 5, then a pattern using the selected setting and followed
by “Adjust Completed!” is printed.
– 6 –
Page 11

2. SERIAL INTERFACE
2-1. Interface Specifications
1 Data transmission method: Asynchronous serial interface
2 Baud rate: Selectable from 150, 300, 600, 1200,
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 (Twin Head
only) bps (Refer to Installation
Manual.)
3 Word length Start bit: 1 bit
Data bit: 7 or 8 bits (selectable. Refer
to Installation Manual.)
Parity bit: Odd, even or none
(selectable. Refer to Installation
Manual.)
Stop bit: 1 or 2 bit length
4 Signal polarity RS-232C (Standard feature)
MARK : Logic “1”(–3V to –25V)
SPACE : Logic “0” (+3V to +25V)
Current loop (optional)
MARK : Logic “1”(current ON)
SPACE : Logic “0” (current OFF)
RS-422A (Optional)
MARK : Logic “1”
A is –0.2V or less than B
SPACE : Logic “0”
A is 0.2V or more than B
Mark [1]
Space [0]
b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 (b7)
ABCD
A: Start bit
B: Data bits
C: Vertical parity bit
D: Stop bit
– 7 –
Page 12

2-2. Interface Circuit
2-2-1.RS-232C Serial Interface
Input (RXD, CTS)
Printer Host computer
75189 or equivalent
Output (DTR, FAULT, TXD, RCH, RTS)
Printer Host computer
75188 or equivalent
Fig . 2-1 RS-232C interface circuit
2-2-2.Current Loop (option)
Input (TTY-RXD, TTY-RXDR)
Printer
Output (TTY-TXD, TTY-TXDR)
Printer
R
R
+V
+V
Host computer
Host computer
Note: Adjust “R” so that the loop current is set within 10 to 20 mA.
Fig. 2-2 Current loop interface circuit
– 8 –
Page 13

2-2-3.RS-422A Serial Interface (option)
Input (RD, RS)
Printer Host computer
A
B
Output (SD, CS)
Printer Host computer
A
B
Fig. 2-3 RS-422A interface circuit
– 9 –
Page 14

2-3. Connectors and Signals
RS-232C
Pin no. Signal name
1 F-GND — Frame ground
2 TXD OUT Transmitted data
3 RXD IN Received data
4 RTS OUT Data transmission request signal. This is al-
5 CTS IN This signal changes to “SPACE” when
6 N/C Not connected
7 S-GND — Signal ground
8 N/C Not connected
9-10 N/C This pin is used when using the optional
11 RCH OUT This signal changes to “SPACE” when the
12 N/C Not connected.
13 S-GND — Signal ground
14 FAULT OUT When printer error occurs (such as paper
15
16
Multi-printer TXD
Multi-printer DTR
17 to 19 N/C This pin is used when using the optional
20 DTR OUT Data terminal ready signal. When the printer
21-22 N/C Not connected
23 to 25 N/C This pin is used when using the optional
I/O
direction
ways “SPACE” when the printer is turned on.
host computer is ready to transmit data. (In
this instance, the printer does not check this
signal.)
interface board.
printer is ready to receive data. (The signal
line is same as pin 20.)
out, mechanical error, etc.), this signal is
set to “MARK”.
OUT Diode coupled TXD
OUT Diode coupled DTR
interface board.
is ready to receive data, this signal changes
to “SPACE”.
interface board.
Function
14
1
Fig. 2-4 Serial interface connector
– 10 –
25
13
Page 15

20 mA current loop (option)
Pin no. Signal name
9 TTY TXDR — Indicates the ground side of the data signal
10 TTY TXD OUT Transmitted data of 20 mA current loop.
17 TTY TXDR — Indicates the ground side of the data signal
18 TTY RXDR — Indicates the ground side of the data signal
19 TTY RXD IN Received data of 20 mA current loop.
23 TTY RXDR — Indicates the ground side of the data signal
24 TTY TXD OUT Transmission data of 20 mA current loop.
25 TTY RXD IN Reception data of 20 mA current loop.
I/O
direction
Function
of 20 mA loop current.
of 20 mA loop current.
of 20 mA loop current.
at 20 mA loop current.
RS-422A (option)
Pin no. Signal name
9 SD (+) OUT Transmitted data
10 SD (–) OUT Transmitted data
17 RD (+) IN Received data
18 RD (–) IN Received data
19 CS (+) IN When the host computer is set to standby
23 CS (–) IN When the host computer is set to standby
24 RS (+) OUT Data transmission request signal. When the
25 RS (–) OUT Data transmission request signal. When the
I/O
direction
Function
for data transmission, this signal changes to
“SPACE”.
(In this instance, the printer does not check
the signal.)
for data transmission, this signal changes to
“SPACE”.
(In this instance, the printer does not check
the signal.)
printer is ready to receive data, this signal
changes to “SPACE”.
printer is ready to receive data, this signal
changes to “SPACE”.
– 11 –
Page 16

2-4. Interface Connections
The following is a basic example of interface connections. (For interface
connections, refer to the specifications for the respective interface.) IBM PC type
serial port is shown as example.
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
S-GND
FAULT
DTR
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
S-GND
FAULT
DTR
Board side
1
2
3
4
5
7
14
20
Board side
1
2
3
4
5
7
14
20
Shield
IBM PC side
25Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
IBM PC side
9 Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DSR
S-GND
DCD
DTR
DCD
RXD
TXD
DTR
S-GND
DSR
RTS
CTS
RI
Fig. 2-5 Example of interface connections for IBM PC
– 12 –
Page 17
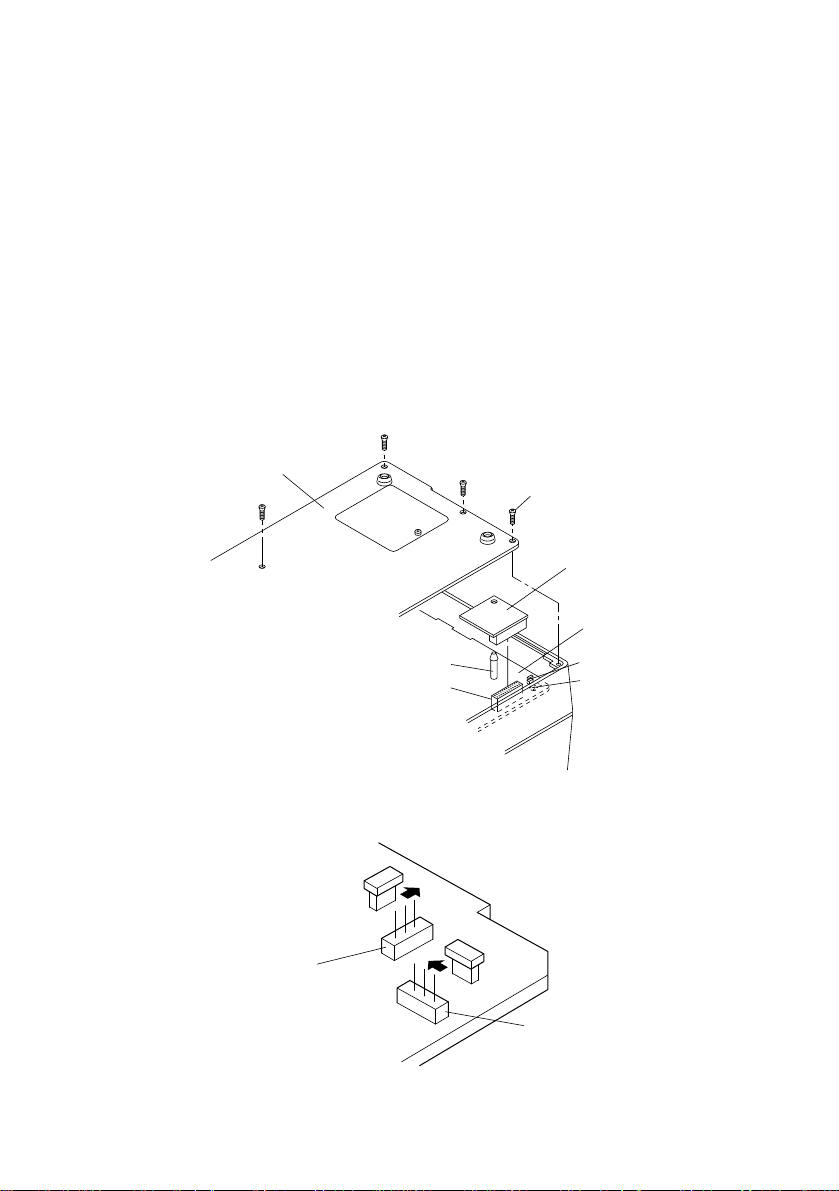
2-5. Installing the Optional Interface Board
Bottom cover
Screw
Optional interface board
Main logic board
SW5
SW6
Board support
CN9
When using the optional 20 mA current loop interface or the RS-422A interface,
the optional interface board must be mounted to the printer’s main logic board.
The following is the method of mounting the interface board to the printer’s main
logic board.
1 Remove the 6 screws on the bottom cover of the printer, then remove the
bottom cover.
2 Connect the optional interface board connector to connector CN9 on the
printer’s main logic board.
3 At the same time, insert the plastic board support of the main logic board into
the hole on the interface board.
4 Switch SW5 and SW6 on the main logic board from A-C to B-C.
5 Mount the bottom cover to the printer and fasten the 6 screws to fix it in place
on the printer.
Fig. 2-6 Installing the optional interface board
A C B
SW5
Fig. 2-7 Switch SW5 and SW6
A C B
– 13 –
SW6
Page 18

2-6. Data Structure
2-6-1.DTR mode
This mode is accessed when the DIP switch 3-5 is ON.
Signals are controlled using the DTR line as BUSY flag.
RXD
DTR
Printing
RXD
DTR
Printing
PAPER OUT signal
Power ON
When paper is out
Data Data Data
Buffer full Buffer empty
OFF LINE ON LINE
Paper out
Press the ON LINE switch after
loading paper.
Power ON
If a printer errors do not occur after the power is turned on, the DTR signal line
changes to “SPACE”.
When the host computer confirms that the DTR signal line is set to “SPACE”, the
host computer sends the data text via the RXD signal line to the printer. Also, the
printer will set the DTR signal line to “MARK” when the empty space in the data
buffer is below 256 bytes. After the host computer detects that the DTR signal line
is at “MARK”, transmission of the data text is sopped. In this instance, data can
still be received up until the data buffer becomes completely full.
When the empty space in the data buffer is increased following printing (when the
data in the data buffer is reduced to 256 bytes or less), the printer sets the DTR
signal line to “SPACE”.
– 14 –
Page 19

Data buffer
Full
Remainder
256 bytes
DTR “MARK” DTR “SPACE”
Near Full
Near Empty Empty
256 bytes
[Paper out]
When the “paper out’ detector senses the end of the paper, the printer stops
printing after printing a maximum of two more lines or on feeding the paper.
Immediately after a “paper out” condition is detected, the printer sets to OFF
LINE and the DTR changes to “MARK”. (To reset printer after a “paper out’, load
paper into the printer and press the ON LINE switch to set the printer to ON
LINE.)
[Mechanical error]
Mechanical errors are detected when the front cover is opened during printing, or
when the motor locks and the unit will not print. Immediately after a mechanical
error occurs, the printer sets the DTR to “MARK” and then sets the printer to OFF
LINE. To cancel a mechanical error, close the front cover properly and press the
ON LINE switch. If the buzzer sounds and the ALARM lamp flashes at this time,
then locate the cause of the error and turn the power for the printer off and back
on again to reset the printer.
[Status]
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Constantly
set at “0”
– 15 –
Vertical parity error
1: error
Framing error
1: error
Mechanical error
1: error
Paper empty
1: empty
Buffer empty
1: empty
Buffer overflow
1: overflow
Compulsion switch
High level
(Switch is set to ON)
Page 20

[Framing error]
A framing error occurs when SPACE is detected at the stop bit. When a framing
error or a vertical parity error occurs for the data which is received, the printer
prints out a “?” mark to indicate that the error occurred.
[Compulsion switch]
When pin 6 of the peripheral unit drive circuit connector is set “HIGH”, status bit
7 becomes “1”.
2-6-2.X-ON/X-OFF mode
This mode accessed when the DIP switch 3-5 is OFF.
X–ON X–OFF X–OFF X–ON X–OFF X–OFF
X–OFF
TXD
X–OFF
X–ON
RXD
Printing
Paper out
signal
ON LINE
lamp
ON
OFF
Power ON Load paper and press
Data Data Data
Paper out
the ON LINE switch.
If printer errors do not occur after the power is turned on, the printer outputs an
X-ON (DC1 by control code; 11H by hexadecimal data) signal on the TXD signal
line which sends it to the host computer. When the host computer receives the XON signal, the host computer transmits the data to the RXD signal line for the
printer. If data text is not sent from the host computer (even after transmitting the
X-ON signal to the host computer), the printer outputs an X-ON signal at 3 second
intervals until the printer receives data.
The printer starts outputting an X-OFF (DC3, 13H) signal when the empty space
in the buffer reduces below 256 bytes. When the host computer receives the XOFF signal, it halts output of data. (however, the printer can continue receiving
data until the buffer becomes completely full.)
Output of the X-ON signal is resumed when the data in the buffer is printed out
and drops to below 256 bytes.
– 16 –
Page 21

Data buffer
Full
Remainder
256 bytes
X-OFF X-ON
Near Full
Near Empty Empty
256 bytes
[Paper out]
When the “paper out” detector senses the end of the paper, the printer stops
printing after printing a maximum of two more lines or on feeding the paper. The
printer will set the DTR to “MARK” and set the printer to OFF LINE five seconds
after a “paper out” condition is detected. To reset the printer after a “paper out”,
load a new roll of paper into the printer and press the OFF LINE switch to set the
printer ON LINE.
[Mechanical error]
Mechanical errors occur when the front cover is opened during printing and
printing stops or when the motor locks and printing stops. After the error occurs,
the printer outputs an X-OFF signal and stops printing. The printer sets the DTR
signal to “MARK” and sets to OFF LINE five seconds after a mechanical error
occurs. To reset the printer after a mechanical error occurs, close the front cover
properly and press the ON LINE switch. If a buzzer sounds and the ALARM lamp
flashes at this point, locate the cause of the error and turn the power off and then
back on to reset the printer.
– 17 –
Page 22

[Status]
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
0
Constantly
set at “0”
[Framing error]
A framing error occurs when SPACE is detected at the stop bit. When a framing
error or a vertical parity error occurs for the data which is received, the printer
prints out a “?” mark to indicate that the error occurred.
Vertical parity error
1: error
Framing error
1: error
Mechanical error
1: error
Paper empty
1: empty
Buffer empty
1: empty
Buffer overflow
1: overflow
Compulsion switch
High level
(Switch is set to ON)
[Compulsion switch]
When pin 6 of the peripheral unit drive circuit connector is set at “HIGH”, status
bit 7 becomes “1”.
– 18 –
Page 23

2-6-3.STX-ETX mode
This mode is accessed from whichever DTR mode or X-ON/X-OFF mode.
To set this mode, the data buffer must be empty.
The host computer sends an ENQ code to the printer and acknowledges the printer
status. Then, the host computer checks if the printer buffer is empty. After the host
computer detects that the buffer is empty, a STX code and data are transmitted.
After 1 block of data is transmitted, the host computer sends an ENQ code to the
printer and then receives the printer status and check byte (horizontal parity for
the printer.)
At this points, the host computer performs a status and horizontal parity check.
When the host computer determines that there was no error, it transmits an ETX
code which serves as text end code. After the printer receives the ETX code, data
in the data buffer is printed out. If an error occurs, a CAN code is transmitted by
the host computer. (In this instance, the data which was previously sent to the
buffer is cleared, thus, the host computer must retransmit the same data to the
printer.)
A flowchart of this operation is illustrated on the following page.
[Status]
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
0
Constantly
set at “0”
Vertical parity error
1: error
Framing error
1: error
Mechanical error
1: error
Paper empty
1: empty
Buffer empty
1: empty
Buffer overflow
1: overflow
Compulsion switch
High level
(Switch is set to ON)
[Framing error]
A framing error occurs when SPACE is detected at the stop bit. When a framing
error or a vertical parity error occurs for the data which is received, the printer
prints out a “?” mark to indicate that the error occurred.
– 19 –
Page 24

[Compulsion switch]
When pin 6 of the peripheral unit drive circuit connector is set at “HIGH”, status
bit 7 becomes “1”.
– 20 –
Page 25

Starts the
STX-ETX mode.
Sends an <ENQ>
Sends <ENQ>
Receives status byte.
NO
Is the data buffer
empty?
YES
Sends <STX>
Is an odd parity
check?
YES
(FF) H is set for the text
byte.
Acquires the exclusive OR of the content
of the text byte and the data to sent, then
it is used as the content of the test byte.
NO
The test byte is set at (0)H.
Receives status signal.
Receives a check byte.
Is the status an
error?
Horizontal
parity check
Ends the
STX-ETX mode.
NO
Check byte =
test byte?
YES
Sends <ETX>
(Printing)
YES
NO
Sends <CAN>
Transmits the data to
the printer.
NO
Is this the last data in
a block?
Is there a data block in
the STX-ETX mode?
YES
Check byte:
Horizotal parity of the printer.
Test byte:
Horrizontal parity of the host
computer.
YES
STX-ETX mode flow diagram for host computer
– 21 –
NO
RET
Page 26

3. PARALLEL INTERFACE
3-1. Interface Specifications
This printer has a parallel interface to communicate with the computer. The
operating specifications of the parallel interface are as follows.
(1) Data transfer rate : 1000 to 6000 characters per second
(2) Synchronization : Via externally supplied STROBE pulses
(3) Handshaking : ACK and BUSY signals
(4) Logic level : Compatible with TTL level
3-2. Interface T iming
A C K
About 9ms
Data
STROBE
BUSY
TTT
T:more than 0.5 microsec.
Fig. 3-1 Interface timing diagram
– 22 –
Page 27

Signal Name Circuit Example
74 HC Compatible4.7KW
DATA 1 – DATA 8
(To Printer)
4.7KW
INPUT
OUTPUT
STROBE
(To Printer)
BUSY, ACK
(From Printer)
74 HC Compatible4.7KW
100W
470pF
74 HC Compatible4.7KW
Fig. 3-2 Typical interface circuit
– 23 –
Page 28

3-3. Connectors and Signals
Pin no Signal name
1 STROBE IN Signals when data is ready to be read. Signal
2-9 DATA 1-8 IN These signals provide the information of the
10 ACK OUT A 9 microsecond LOW pulse acknowledges
11 BUSY OUT When this signal goes LOW, the printer is
12 PAPER OUT OUT This signal is normally LOW. It will go
13 SELECTED OUT This signal is HIGH when the printer is online.
14-15 N/C Unused
16
17
SIGNAL GND
CHASSIS GND
18 +5VDC +5VDC (Max 50mA)
19-30 GND Twisted pair return signal ground level.
31 RESET IN When this signal goes LOW, the printer is
32 ERROR OUT This signal is normally HIGH. This signal
33 EXT GND External ground.
34
COMPULSION
35-36 N/C Unused.
(19) (36)
Direction
goes from HIGH to LOW (for at least 0.5
microsec.) when data is available.
first to eighth bits of parallel data. Each signal
is at HIGH level for a logical 1 and at a LOW
level for a logical 0.
receipt of data.
ready to accept data. When the printer is in
one of the conditions below. “HIGH” is set.
1. Data being entered.
2. Off line.
3. Error condition.
HIGH if the printer runs out of paper.
Signal ground.
Chassis ground, isolated from logic ground.
reset to its power-on condition.
goes LOW to signal that the printer cannot
print due to an error condition.
Refer to Item 8-4 Emergency Suspension.
OUT Compulsion signal
Function
(1) (18)
Fig. 3-3 Parallel interface connector (printer side)
This connector mates with an
Amphenol 57-30360 connector
– 24 –
Page 29

4. EMERGENCY SUSPENSION
If any of the following errors is detected while the printer is operating, the printer
halts and ERROR signal turns to “LOW” level.
1 Mechanical errors
• Motor lock
• Defective of timing detector (signal not issued)
• Abnormal home position check.
• Defective cutter movement (paper jam, etc.)
• Timing error of Reset sig of the auto cutter during the auto cutter operation
(Auto-cutting models only)
• Abnormality of thermistor
To reset the emergency suspension, rectify the cause of trouble & adopt one of
the following 2 methods.
• Turn the printer power off and on again.
• Push ON LINE switch.
Even while in the status of no backed up RAM with DIP SW1-7, the RAM is
not cleared when power is turned OFF. Printing resumes from the line being
printed when the mechanism stopped. (Single Head Only)
2 If the front cover is opened while printing
If the front cover is opened while printing, the same operation as given in
above item “1 Mechanical errors” takes place. To restart printing, close the
front cover and push ON LINE switch.
3 CPU error
If CPU goes erratic due to external noise, etc., the printer halts, treating it as
CPU error. Normal operation can be resumed by turning ON the power supply
again, but the data contained in RAM gets cleared.
4 RAM Check Function
Before self-printing and when clearing the buffer, a RAM check is performed.
5 Procedures at Time of Power Interruption (Single Head Only)
When using the backed up RAM function in valid status, the data in the buffer
will be preserved even when there is a power interruption. When the power is
turned ON again, the power interruption message “
and printing will be resumed from the line where it was stopped.
– 25 –
” will be printed,
Page 30

5. VALIDATION PRINTING (Models with validation function only)
This printer can print one line of validation printing.
5-1. Operating Method
B
A
Adjust lever
A: Standard position (one sheet)
B: Validation printing or copying
Fig. 5-1 Position of the adjust lever
Rear cover
Front cover
1 Open the front cover, pull the adjust
lever one notch from standard position A toward the operation panel
side position B.
When you cannot find standard position A, push the lever as far as
possible toward the rear cover, and
pull it 2 notches after having pressed
it down. The lever is now in standard
position A.
2 Mount the front cover.
3 Set the printer for the validation
print mode. In this instance, the
buzzer gives tow short beeps.
4 Make sure that the ON LINE lamp
is flashing.
5 Align the right edge of paper with
the right end of the tear bar then
insert the paper from the top.
POWER
ALARM
ON LINE
FEED
Fig. 5-2 Loading the paper
6 The printer starts printing approx. 1
second after the paper is loaded.
7 When printing is completed, pull
the paper upward and remove it
from the printer.
Right end
of the tear bar
Note: When printing a roll paper, also
set the adjust lever at position B.
– 26 –
Page 31

5-2. Printing Format
Prints one line in 7 × 9 font normal printing.
32 columns (from the 5th to 36th columns)
Even if the setting for the paper width is changed by the DIP switch, the 32column format will not change.
5-3. Data format
<GS> <data> <LF>
5-4. Other
• The FEED and ON LINE switches will not operate normally during validation
printing.
• When the printer receives an immediate execution command for peripheral
units during validation printing, it executes the command when the validation
print mode is canceled.
• Modes in effect before the validation printing (such as emphasized printing,
inverted printing, expanded printing, and underlining) are invalid during
validation printing. But these become valid again after validation printing.
• Data received before a <GS> code is printed out when the printer receives the
<GS> code.
Paper sensor
position
Print area
52.8
100
Min. 120
Fig. 5-3 Print area
– 27 –
Approx.
17
Approx.
18
Approx.12
: m m
Min. 70
Page 32

6. AUTO CUTTER (Auto-cutting models only)
6-1. Cutting Method
Cuts recording paper into continuous forms connected at only one point remaining uncut between adjacent forms.
Only one sheet of paper can be cut each time.
6-2. Cutting position
The paper is cut approximately 21.7 mm above the printing head.
Center of printer
Partial cutting
with one uncut
point left
Fig. 6-1 Cutting method Fig. 6-2 Cutting position
Cutting position
Approx. 21.7mm
Printing head
position
6-3. Auto cutting control codes
<ESC> “d” “0” or <ESC> “d” <0>
<ESC> “d” “1” or <ESC> “d” <1>
Refer to the control codes of chapter 10.
6-4. Other position to be observed
1 When continuously cutting for more than 12 minutes, make a maximum of 10
cuttings per minute.
2 When using for a long time, paper dust will gather around the cutter.
Therefore, make sure to clean periodically. If paper dust is not removed,
normal paper feeding may become impossible.
– 28 –
Page 33

7. CONTROL CODES
Control Codes Used for Character Setting
Control codes
<ESC> “R” n 1B 52 n Select international character set 32
<ESC> “6” 1B 36 Select IBM character set #2 32
<ESC> “7” 1B 37 Select IBM character set #1 32
<ESC> “M” 1B 4D Select 7 × 9 (half dot) font 33
<ESC> “P” 1B 50 Select 5 × 9 (2 pulses + 1 dot) font 33
<ESC> “:” 1B 3A Select 5 × 9 (3 pulses + 1 dot) font 33
<SO> 0E Select expanded character mode 33
<DC4> 14 Cancel expanded character mode 34
<ESC> “W” “1” 1B 57 31
<ESC> “W” <1> 1B 57 31
<ESC> “W” “0” 1B 57 30
<ESC> “W” <0> 1B 57 30
<ESC> “E” 1B 45 Select emphasized print mode 34
<ESC> “F” 1B 46 Cancel emphasized print mode 34
<ESC> “-” “1” 1B 2D 31
<ESC> “-” <1> 1B 2D 01
<ESC> “-” “0” 1B 2D 30
<ESC> “-” <0> 1B 2D 00
<ESC> “_” “1” 1B 5F 31
<ESC> “_” <1> 1B 5F 01
<ESC> “_” “0” 1B 5F 30
<ESC> “_” <0> 1B 5F 00
<ESC> “4” 1B 34 Select highlighted print mode 35
<ESC> “5” 1B 35 Cancel highlighted print mode 36
<SI> 0F Select inverted print mode 36
<DC2> 12 Cancel inverted print mode 36
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Select expanded character mode 34
Cancel expanded character mode 34
Select underline mode 35
Cancel underline mode 35
Select upperline mode 35
Cancel upperline mode 35
Control Codes Used for Line Spacing
Control codes
<LF> 0A Line feed 36
<CR> 0D Line feed (same as LF) 36
<ESC> “z” “1” 1B 7A 31
<ESC> “z” <1> 1B 7A 01
<ESC> “0” 1B 30 Set 1/8-inch line feed 37
<ESC> “a” n 1B 61 n Feed paper n lines 37
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Set 1/6-inch line feed 36
– 29 –
Page 34

Control Codes Used for Page Layout
Control codes
<FF> 0C Page feed (form feed) 37
<ESC> “C” n 1B 43 n Set page length at n lines 37
<ESC> “C” <0> n 1B 43 00 n Set page length at n inches 37
<ESC> “B” n1 n2 1B 42 n1 n2 Set vertical tab positions 38
<VT> 0B Execute vertical tab 38
<ESC> “N” n 1B 4E n Set bottom margin 38
<ESC> “O” 1B 4F Cancel bottom margin 39
<ESC> “1” n 1B 6C n Set left margin 39
<ESC> “Q” n 1B 51 n Set right margin 39
<ESC> “D” n1 n2 1B 44 n1 n2 Set horizontal tab position 40
<HT> 09 Execute the horizontal tab 40
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Control Code Used for Graphics Printing
Control codes
<ESC> “1” 1B 31 Set 7/72-inch line feed 41
<ESC> “A” n 1B 41 n Define n/72-inch line feed 41
<ESC> “2” 1B 32 Set n/72-inch line feed 41
<ESC> “J” n 1B 4A n One time line feed of n/72-inch 41
<ESC> “z” “0” 1B 7A 30
<ESC> “z” <0> 1B 7A 00
<ESC> “3” n 1B 33 n Set n/216-inch line feed simulation 42
<ESC> “y” n 1B 79 n Set n/144-inch line feed (Models with 1/44”
<ESC> “K” n1 <0> 1B 4B n1 00 8 dot single density bit image 42
<ESC> “L” n1 n2 1B 4C n1 n2 8 dot double density bit image 44
<ESC> “h” “1” 1B 68 31
<ESC> “h” <1> 1B 68 01
<ESC> “h” “0” 1B 68 30
<ESC> “h” <0> 1B 68 00
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Set 1/12-inch line feed 41
-pitch paper feed mechanism only)
Select vertical expanded character mode 45
Cancel vertical expanded character mode 45
42
Control Codes Used for Download Characters
Control codes
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 1B 26 00 n1 n2 Definition of down load characters 46
<ESC> “%” “1” 1B 25 31
<ESC> “%” <1> 1B 25 01
<ESC> “%” “0” 1B 25 30
<ESC> “%” <0> 1B 25 00
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Enable download character set 47
Disable download character set 47
– 30 –
Page 35

Control Codes Used for Peripheral Units
Control codes
<ESC> <BEL> n1 n2 1B 07 n1 n2 Adjust drive pulse width for peripheral unit 1 49
<BEL> 07 Deferred drive command for peripheral unit 1 49
<FS> 1C Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 1 49
<SUB> 1A Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 2 50
<EM> 19 Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 1 50
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Other Control Codes
Control codes
<RS> 1E Sound buzzer 50
<CAN> 18 Cancel print data in buffer & Initialize printer 50
<DC3> 13 Set deselect mode 51
<DC1> 11 Set select mode 51
<ESC> “U” “1” 1B 55 31
<ESC> “U” <1> 1B 55 01
<ESC> “U” “0” 1B 55 30
<ESC> “U” <0> 1B 55 00
<ESC> “@” 1B 40 Initialize printer 52
<ENQ> 05 Enquiry 53
<STX> 02 Enter STX-ETX mode 53
<ETX> 03 Terminate STX-ETX mode 53
<ESC> “d” “0” 1B 64 30
<ESC> “d” <0> 1B 64 00 Trigger auto-cutter drive
<ESC> “d” “1” 1B 64 31 (Auto-cutting models only)
<ESC> “d” <1> 1B 64 01
<GS>...<LF> 1D...0A Selection of validation characters
Hexadecimal
codes
Function Page
Select uni-directional print mode 52
Select bi-directional print mode 52
(Models with validation function only)
54
54
– 31 –
Page 36

7-1. Control Codes Used for Character Setting
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
NOTE
Select international character set
<ESC> “R” n
(1B)H (52)H n
(00)H n (08)H
Select the international character set corresponding to the
value set for n.
n =(00)
(01)
(02)
H: U.S.A. (03)H: England (06)H: Italy
H: France (04)H: Denmark (07)H: Spain
H: Germany (05)H: Sweden (08)H: Japan
The default international characters can also be set with DIP
switches, however, setting by control code takes priority over
setting by DIP switches.
Refer to chapter 11-5 “Code Table”
Select IBM character set #2
<ESC> “6”
H (36)H
(1B)
Selects IBM character set #2.
This code is only valid when the character code table set by
DIP switches 2-1 and 2-2 is IBM character set #1 or #2.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
NOTE
Select IBM character set #1
<ESC> “7”
H (37)H
(1B)
Selects IBM character set #1.
This code is only valid when the character code table set by
DIP switches 2-1 and 2-2 is IBM character set #1 or #2.
– 32 –
Page 37

FUNCTION
CODE
Select 7 × 9 (half dot) font
<ESC> “M”
H (4D)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Selects 7 × 9 (half dot) font.
Refer to User’s manual for the maximum number of print
columns.
When the power of the printer is turned on, 7 × 9 (half dot)
printing is automatically selected.
This code valid only when received at the beginning of a line.
Select 5 × 9 (2 pulses = 1 dot) font
<ESC> “P”
H (50)H
(1B)
Selects 5 × 9 (2 pulses = 1 dot) font.
This code is valid only when received at the beginning of a
line.
Select 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot) font
<ESC> “:”
H (3A)H
(1B)
Selects 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot) font.
This code is invalid when using SP311F SP341F SP321S.
This code is valid only when received at the beginning of a
line.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Select expanded character mode
<SO>
H
(0E)
Data following this code is printed in double-width charac-
ters.
Same as <ESC> “W” “1” or <ESC> “W” <1>.
– 33 –
Page 38

FUNCTION
CODE
Cancel expanded character mode
<DC4>
H
(14)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Cancels expanded character mode set by <SO> or <ESC>
“W” “1” or <ESC> “W” <1> code. Data following this code
is printed out in normal size characters.
Same as <ESC> “W” “0” or <ESC> “W” <0>.
Select expanded character mode
<ESC> “W” “1” or <ESC> “W” <1>
H (57)H (31)H or (1B)H (57)H (01)H
(1B)
Data following this code is printed in double-width charac-
ters.
Same as <SO>.
Cancel expanded character mode
<ESC> “W” “0” or <ESC> “W” <0>
H (57)H (30)H or (1B)H (57)H (00)H
(1B)
Cancels expanded character mode set by <ESC> “W” “1” or
<ESC> “W” <1> or <SO> code. Data following this code is
printed out in normal size characters.
Same as <DC4>.
Select emphasized print mode
<ESC> “E”
H (45)H
(1B)
Data following this code is printed in the emphasized print
mode. In this mode, only uni-directional printing is performed.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Cancel emphasized print mode
<ESC> “F”
H (46)H
(1B)
Cancels emphasized print mode.
– 34 –
Page 39

FUNCTION
CODE
Select underline mode
<ESC> “-” “1” or <ESC> “-” <1>
H (2D)H (31)H or (1B)H (2D)H (01)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
Data following this code is printed out underlined. (However,
the spaces generated by horizontal tab are not underlined.)
Cancel underline mode
<ESC> “-” “0” or <ESC> “-” <0>
H (2D)H (30)H or (1B)H (2D)H (00)H
(1B)
Cancels underlined mode.
Select upperline mode
<ESC> “_” “1” or <ESC> “_” <1>
H (5F)H (31)H or (1B)H (5F)H (01)H
(1B)
Data following this code is printed out with an upperline.
(However the spaces generated by horizontal tab are not
upperlined.)
Cancel upperline mode
<ESC> “_” “0” or <ESC> “_” <0>
H (5F)H (30)H or (1B)H (5F)H (00)H
(1B)
Cancels upperline mode.
Select highlighted print mode
<ESC> “4”
H (34)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
Prints with highlighted characters.
If an underline, upperline or inverted print command is input
while the highlighted print mode is in effect, the highlighted
mode will be canceled and the newly input command will be
executed. If a highlighted print command is received while
the underline, upperline or inverted print mode is in effect, the
previously set mode is canceled and the highlighted print
mode will be set.
– 35 –
Page 40

FUNCTION
CODE
Cancel highlighted print mode
<ESC> “5”
H (35)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Cancels highlighted print mode.
Select inverted print mode
<SI>
H
(0F)
Data following this code is printed out in inverted characters.
This code is valid only when input at the beginning of a line,
thus, normal and inverted characters cannot be mixed in on
the same line.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Cancel inverted print mode
<DC2>
H
(12)
Cancels the inverted character mode. This code is valid only
when input at the beginning of a line.
7-2. Control Codes Used for Line Spacing
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Line feed
<LF>
H
(0A)
Data in the line buffer is printed out and one line is fed. If data
does not exist before this code is received, the printer only
feeds one line.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Line feed (Same as LF)
<CR>
H
(0D)
Functions the same as an LF code.
When DIP SW 1-3 is set to ON, this code becomes invalid.
Set 1/6-inch line feed
<ESC> “z” “1” or <ESC> “z” <1>
H (7A)H (31)H or (1B)H (7A)H (01)H
(1B)
Line feed is set at 1/6-inch after this code is received.
– 36 –
Page 41

FUNCTION
CODE
Set 1/8-inch line feed
<ESC> “0”
H (30)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANG
OUTLINE
Line feed is set at 1/8-inch after this code is received.
Feed paper n lines
<ESC> “a” n
H (61)H n
(1B)
1 n 127
After data in the line buffer is printed out, feeds the paper
n lines.
7-3. Control Codes Used for Page Layout
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANG
Page feed (form feed)
<FF>
H
(0C)
After data in the line buffer is printed out, feeds the paper to
the top of the next page.
Set page length at n lines
<ESC> “C” n
H (43)H n
(1B)
1 n 255 (default value friction: n =33
Sprocket: n =42)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANG
OUTLINE
Sets page length at n lines.
Set page length at n inches
<ESC> “C” <0> n
H (43)H (00)H n
(1B)
1 n 127
Sets page length at n inches.
– 37 –
Page 42

FUNCTION
CODE
Set vertical tab positions
<ESC> “B” n1 n2...nk <0>
H (42)H n1 n2...nk (00)H
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
NOTE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
1 n1 < n2 < n3 <....< nk 255, 1 k 16
Cancels all current vertical tab positions and sets new vertical
tab positions at lines n1, n2, etc., where n1, n2, etc. are
numbers between 1 and 255. A maximum of 16 vertical tab
positions can be set. Tab positions must be specified in
ascending order; any violation of ascending order terminates
the tab position list. Standard termination is by the <0>
control code. Vertical tab positions are set in terms of the
current line spacing and do not move if the line spacing is
changed later.
If a tab set position <nk> is equivalent or smaller than
<nk–1> just preceding the tab set position, setting of vertical
tab is assumed as complete.
Execute vertical tab
<VT>
H
(0B)
Feeds the paper to the next vertical tab set position.
When a vertical tab is not set, line feed is not performed. If the
current line is at or below the last vertical tab set position, the
paper feeds to the top of the next page.
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
Page length
Set bottom margin
<ESC> “N” n
(1B)H (4E)H n
0 n 255 (Default n = 0)
Sets bottom margin to n lines.
Feeds the paper
automatically.
Bottom margin of n lines.
– 38 –
Page 43

FUNCTION
CODE
Cancel bottom margin
<ESC> “O”
H (4F)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
Cancels bottom margin.
Set left margin
<ESC> “1” n
H (6C)H n
(1B)
0 n (right margin –2)
Sets the left margin at column n in the current character pitch.
The left margin does not move if the character pitch is
changed later. The left margin must be at least two columns
to the left of the right margin and within the limits above.
Set right margin
<ESC> “Q” n
H (51)H n
(1B)
2 n (maximum no. of print columns)
Sets the right margin at column n in the current character
pitch. Column n becomes the last character position the line.
The right margin does not move if the character pitch is
changed later. The right margin must be within the limits
above.
Left end
Left margin n
Printing area
Right margin n columns
– 39 –
Page 44

FUNCTION
CODE
Set horizontal tab position
<ESC> “D” n1 n2...nk <0>
H (44)H n1 n2...nk (00)H
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
NOTE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
1 n1 < n2 < n3...< nk (Maximum print columns –1),
k 16
1
Cancels all current horizontal tab positions and sets new tab
positions at columns n1, n2, etc. in the current character pitch,
where n1, n2, etc. are numbers between 1 and (Maximum
print columns–1). The maximum number of horizontal tab
positions allowed is 16. The tab positions must be specified
in ascending order; any violation of ascending order terminates the tab position list. Standard termination is by the <0>
control code. To clear all tab positions, specify <ESC> “D”
<0>.
When the horizontal tab set position <nk> is equivalent or
smaller than <nk-1> which is the column just preceding the set
tab position, horizontal tab setting is assumed as complete.
Execute horizontal tab
<HT>
H
(09)
The print position skips to the next horizontal tab position in
line. If the current position is after the final horizontal tab
position that can be executed, this code is ignored. (Underlining and overlining do not take place in the spaces between
characters set with the horizontal tab function.)
– 40 –
Page 45

7-4. Control Codes Used for Graphics Printing
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
Set 7/72-inch line feed
<ESC> “1”
H (31)H
(1B)
Line feed is set at 7/72-inch after this code is received.
Define n/72-inch line feed
<ESC> “A” n
(1B)H (41)H n
0 n 85 (Default n = 12)
Line feed is defined at n/72-inch after this code is received.
This code sets the feed at n/72-inch with the <ESC> “2” code.
Set n/72-inch line feed
<ESC> “2”
H (32)H
(1B)
This code sets the line feed at a defined value with the <ESC>
“A” previously described.
One time line feed of n/72-inch
<ESC> “J” n
H (4A)H n
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
1 n 255
This code activates the n/72-inch paper feed once.
Set 1/12-inch line feed
<ESC> “z” “0” or <ESC> “z” <0>
H (7A)H (30)H or (1B)H (7A)H (00)H
(1B)
Line feed is set at 1/12-inch after this code is received.
– 41 –
Page 46

FUNCTION
CODE
Set n/216-inch line feed simulation
<ESC> “3” n
H (33)H n
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
1 n 255
Line feed is set at n/216-inch after this code is received.
According to the minimum paper feed pitch of the connected
mechanism, the amount of line feed is set as follows:
For 1/72”-pitch mechanisms: INT {(n/3)}/72-inch.
For 1/144”-pitch mechanisms: INT {(2n/3)+0.5}/144-inch.
FUNCTION
CODE
Set n/144-inch line feed
<ESC> “y” n
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
1 n 255
Line feed is set at n/144-inch after this code is received.
* 1/72-inch type mechanism only
FUNCTION
CODE
8 dot single density bit image
<ESC> “K” n1 <0> m1 m2 ...
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
1 n1 200
Excutes 8 dot bit image print determined by “n1”. The total
number of bit image data bytes in one line is equal to n1.
The printer ignores any data bytes over the specified amount
allowed in one line. When the bit image print is finished the
printer automatically returns to the character mode.
H (79)H n
H (4B)H n1 (00)H m1 m2 ...
Dot Position
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 (Not Used)
– 42 –
Image data
MSB LSB
D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D
1
Page 47

m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7 m8 m9
m10 m11 m12 m13 m14 m15 m16 m17 m18 m19 m20 m21 m22 m23 m24 m25 m26 m27 m28 m29 m30
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
EXAMPLE
Actually, let us consider printing as a means of bit image. We
will create the design below using bit image.
Printing Samples
First, since the volume of data is 30, n1 = (1E)
H. If the data m1
~ m30 is converted to hexadecimal, it appears as shown
below.
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
m1 00000001 01
m2 00011110 1E
m3 00111110 3E
m4 01011111 5F
m5 00011111 1F
m6 01011110 5E
m7 00011110 1E
m8 00111111 3F
m9 00101111 2F
m10 00111110 3E
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
m11 00111110 3E
m12 00000010 02
m13 00000010 02
m14 00111110 3E
m15 00111110 3E
m16 00101111 2F
m17 00101111 2F
m18 00111110 3E
m19 00101110 2E
m20 00101110 2E
Data Binary
m21 00111110 3E
m22 00101110 2E
m23 00101110 2E
m24 00111110 3E
m25 00101111 2F
m26 00101111 2F
m27 00111110 3E
m28 00111110 3E
m29 00000010 02
m30 00000010 02
Hexa-
decimal
– 43 –
Page 48

FUNCTION
CODE
8 dot double density bit image
<ESC> “L” n1 n2 m1 m2...
H (4C)H n1 n2 m1 m2...
(1B)
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
NOTE
1 n1 + 256 × n2 400
Executes double density bit image printing (half-dot print-
ing) determined by “n1” and “n2”. The total number of bit
image data bytes in one line is equal to n1 + n2 × 256. Refer
to <ESC> K as to the relation between the dot position and the
bit number. The printer ignores any data bytes over the
specified amount allowed in one line.
The printer does not print adjacent dots. When the bit image
printing is finished, the printer automatically returns to the
character mode.
For double density bit image printing, dots cannot be printed
overlapping each other in the horizontal direction.
The following is an example of this.
Printing Possible
m2 m4 m6 m8 m10
m1 m3 m5 m7 m9m11
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
Printing not Possible
m2 m4 m6 m8 m10
m1 m3 m5 m7 m9m11
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
Over lapping
horizontally
Over lapping
horizontally
When printing one graphic image of a minimum of two lines
with <ESC> K or <ESC>L, feed the paper a minimum of one
line before printing so that the line spacing becomes identical
between the lines.
– 44 –
Page 49

FUNCTION
CODE
Select vertical expaned character mode
<ESC> “h” “1” or <ESC> “h” <1>
H (68)H (31)H or (1B)H (68)H (01)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
NOTE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Prints characters two times the normal vertical size after the
code is received.
However, the bit image mode <ESC> “K” and <ESC> “L”
are excluded.
(1) When combined with the <SO> code, this code enables
printing of the characters in two times the normal vertical
and horizontal size.
(2) This code is not combined with the inverted print mode
<SI> code.
(3) For the 6 × 12 dots IBM block graphic (the characters
code table (B0)
H-(DF)H and (F4)H-(F5)H of IBM charac-
ter set #1 and #2) of the font construction, vertical
enlargement is not available.
(4) The relationship of the vertically enlarged character and
the normal character is matched at the lower level.
(5) Feed the paper a minimum of one line before printing
with this code.
Cancel vertical expanded character mode
<ESC> “h” “0” or <ESC> “h” <0>
H (68)H (30)H or (1B)H (68)H (00)H
(1B)
Cancels vertical expanded character mode
– 45 –
Page 50

7-5. Control Codes Used for Download Characters
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Definition of download characters
When the 7 × 9 (half dot) font is set (default setting):
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7]
n2 – n1 + 1
(1B)H (26)H (00)H n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7]
n2 – n1 + 1
When the 5 × 9 font is set:
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5]
n2 – n1 + 1
(1B)H (26)H (00)H n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5] n2 – n1 + 1
(21)H n1 n2 (7F)H, m0 = (00)H or m0 = (80)H
Defines download characters
Up to 10 download characters can be defined and the defined
character patterns can be stored in the printer’s RAM.
Defining of download characters begins with character code
n1 and completes with n2. When only one character is
defined, n1 = n2.
m0 indicates the relationship between the character pattern
and print head.
m1 = m2...Indicate the character pattern
When m0=(00)H
MSB
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
(Not Used)
LSB
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 (Not Used)
When m0=(80)H
MSB
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
LSB
NOTE
When the 7 × 9 (half dot) font is set (the default setting),
printing of adjacent horizontal dots is not allowed.
Printing possible
m2 m4 m6
m1 m3 m5 m7
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
– 46 –
Printing not possible
m2 m4 m6
m1 m3 m5 m7
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
Over lapping
horizontally
Over lapping
horizontally
Page 51

FUNCTION
CODE
Enable download character set
<ESC> “%” “1” or <ESC> “%” <1>
H (25)H (31)H or (1B)H (25)H (01)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
EXAMPLE
Enables the download character set
Download characters defined by the ESC & 0 code cannot be
printed until enabled by this command.
Disable download character set
<ESC> “%” “0” or <ESC> “%” <0>
H (25)H (30)H or (1B)H (25)H (00)H
(1B)
Disables the selected download character set and selects the
built-in character set. When the power of the printer is
initially turned on, the built-in character set is selected.
To print a download character when the 7 × 9 (half dot) font
character size is set.
(1) Design the download character to be used at code posi-
tions (21)
H, (22)H, and (23)H.
m2 m4 m6
m1 m3 m5 m7
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
Char. Code=(21)H Char. Code=(22)H Char. Code=(23)H
m1 m3 m5 m7
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
m2 m4 m6
m1 m3 m5 m7
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
m2 m4 m6
(2) Define the download characters.
When character codes where the download character is
written are specified as (21)H, (22)H, (23)H, n1 = (21)H, n2
H are obtained.
=(23)
If the relationship between the character pattern data and
printing head is specified to “not use pin 9”, m0 = (80)
H is
obtained. When data m1 to m7 are converted into hexadecimal data, they are indicated as follows.
– 47 –
Page 52

Data Binary
m1 10100000 A0
m2 00000000 00
m3 10100000 A0
m4 00011111 1F
m5 10100000 A0
m6 00000000 00
m7 10100000 A0
Example of transmitting data
Hexa-
Data Binary
decimal
m1 10011000 98
m2 01100100 64
m3 10000010 82
m4 00000001 01
m5 10000010 82
m6 01100100 64
m7 10011000 98
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
m1 00111000 3C
m2 01000010 42
m3 10100101 A5
m4 00000000 00
m5 10100101 A5
m6 01000010 42
m7 00111000 3C
Printing Samples
(1) Definition of down-
load characters
(2) Selecting the down-
load character set
(3) Character codes
(4) Canceling the down-
load character set
(5) Character codes
(1B)H (26)H (00)H (21)H (23)H (80)H
(A0)H (00)H (A0)H (1F)H (A0)H (00)H
(A0)H (80)H (98)H (64)H (82)H (01)H
(82)H (64)H (98)H (80)H (3C)H (42)H
(A5)H (00)H (A5)H (42)H (3C)H
(1B)H (25)H (31)H
(21)H (22)H (23)H (0A)H
H (25)H (30)H
(1B)
(21)H (22)H (23)H (0A)H
– 48 –
Page 53

7-6. Control Codes Used for Peripheral Units
ON
OFF
10 × n1 (ms) 10 × n2 (ms)
Printing and paper feed
are prohibited.
FUNCTION
CODE
DEFINITION RANGE
OUTLINE
NOTE
Adjust drive pulse width for peripheral unit 1
<ESC> <BEL> n1 n2
H (07)H n1 n2
(1B)
1 n1 127, 1 n2 127 (default setting n1 = n2 = 20)
Adjusts drive pulse width for peripheral devices requiring
other than standard 200 ms pulse time and delay time
Energizing time = 10 × n1 (ms)
Delay time = 10 × n2 (ms)
Executed by <BEL>, <FS> codes.
Adjustment is not necessary for standard cash drawers in the
U.S.A. market.
FUNCTION
CODE
Deferred drive command for peripheral unit 1
<BEL>
(07)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
Executes drive pulse for peripheral unit 1 (deferred).
Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 1
<FS>
(1C)
OUTLINE
Executes drive pulse for peripheral unit 1 (immediate).
This code differs from the <BEL> code as follows:
When the printer receives an <FS> code, the command is
executed immediately. The <BEL> code is stored in the data
buffer in the same manner as other codes, and executed in the
order in which they are received.
H
H
– 49 –
Page 54

FUNCTION
CODE
Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 2
<SUB>
H
(1A)
OUTLINE
Drives peripheral unit 2. Pulse width is fixed at 200ms with
a fixed delay time of 200 ms.
When the printer receives a <SUB> code, the command is
executed immediately. Same as <EM>
NOTE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Peripheral units 1 and 2 cannot be driven simultaneously.
Immediate drive command for peripheral unit 2
<EM>
H
(19)
Dives peripheral unit 2. Pulse width is fixed at 200 ms with
a fixed delay time of 200 ms.
When the printer receives a <EM> code, the command is
executed immediately. Same as <SUB>.
NOTE
Peripheral units 1 and 2 cannot be driven simultaneously.
7-7. Other Control Codes
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Sound buzzer
<RS>
H
(1E)
A short alarm is generated by the printer.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Cancel print data in buffer & Initialize printer
<CAN>
H
(18)
Clears the data buffer and line buffer and initializes (<ESC>
“@”) all commands already set. However, the following
parameters are not initialized: external device drive pulse
width setting, operation switch valid/invalid selection, online
switch valid/invalid selection.
For a serial interface printer, the select/deselect state for
addressable mode and DC1/DC3 mode is not affected.
In STX-ETX mode, this CAN code clears the data between
STX and ETX and the line buffer, but does not initialize the
commands.
– 50 –
Page 55

FUNCTION
CODE
Set deselect mode
<DC3>
H
(13)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
(1) When using serial interface printer:
This function differs depending on the setting of DIP
switch 4.
a) When the DC1, DC3 invalid mode is set (DIP switches
4-1 to 4-4 are all set to ON), the printer ignores this code.
b) In the DC1, DC3 valid mode (with DIP switches 4-1
to 4-4 set to OFF), data following this code is ignored
when the printer receives a <DC3> code.
The deselect mode is canceled by <DC1> code.
c) If the printer receives a <DC3> code during an
addressable mode (with DIP switches 4-1 to 4-4 set to
settings other than a) and b) above,), the data following this code is ignored.
Deselect mode can be canceled by a <DC1> n code.
Note that addressable mode is valid only when the RS422A interface option is installed.
(2) When using parallel interface printer;
Data following this code is ignored when the printer
receives a <DC3> code.
The deselect mode is canceled by <DC1> code.
Set select mode
When using serial interface printer;
<DC1> or <DC1>n
H or (11)H n
(11)
When using parallel interface printer
<DC1>
H
(11)
OUTLINE
(1) When using serial interface printer;
This function differs depending on the setting of DIP
switch 4.
a) When the DC1, DC3 invalid mode is set (DIP switches
4-1 to 4-4 are all set to ON), the printer ignores this code.
b) In the DC1, DC3 valid mode (with DIP switches 4-1
to 4-4 set to OFF), when the printer receives a <DC1>
code, the deselect mode is canceled and data following this code is input to the buffer.
– 51 –
Page 56

c) If the printer receives a <DC1> n code (n is the DIP
switch controlled address) during the addressable
mode (with DIP switches 4-1 to 4-4 set other than
settings a) and b) above,), the deselect mode is canceled
and data following this code is input to the buffer.
Note that addressable mode is valid only when optional RS-422A interface is installed.
(2) When using parallel interface printer;
When the printer receives a <DC1> code, the deselect
mode is canceled and data following this code is input to
the buffer.
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
Select uni-directional print mode
<ESC> “U” “1” or <ESC> “U” <1>
H (55)H (31)H or (1B)H (55)H (01)H
(1B)
Prints only when the print head moves from left to right.
Select bi-directional print mode
<ESC> “U” “0” or <ESC> “U” <0>
H (55)H (30)H or (1B)H (55)H (00)H
(1B)
Returns to the standard bi-directional print mode. (This mode
is set automatically when the printer power is turned on.)
Initialize printer
<ESC> “@”
H (40)H
(1B)
Initializes all the commands already set. However the follow-
ing parameters are not initialized: eternal device drive pulse
width setting, operation switch valid/invalid selection, online
switch valid/invalid selection. Also, the line and data buffers
are not cleared and the DIP switches are not read in again.
For a serial interface printer, the select/deselect state for
addressable mode and DC1/DC3 mode is not affected.
– 52 –
Page 57

FUNCTION
CODE
Enquiry
<ENQ>
H
(05)
OUTLINE
NOTE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
This code is valid when using serial interface printer.
Online in STX-ETX mode: The printer sends the status data
and the check byte to the host computer.
Online in any other mode: The printer sends only the status
data to the host computer.
Offline in any mode: The printer only sends the status data to
the host computer if there is a mechanical error in the status
bit, or if the paper out or power down bit is set.
When IBM character set #2 is selected by character code,
codes <ENQ> does not exist. (In this instance, select another
code.)
U.S.A. & Europe IBM #1 IBM #2 Japan
(05)H <ENQ> <ENQ> ♣ <ENQ>
Enter STX-ETX mode
<STX>
H
(02)
This code is valid when using serial interface printer.
STX-ETX mode is set.
Terminate STX-ETX mode
<ETX>
(03)H
This code is valid when using serial interface printer.
Terminates the STX-ETX mode and prints out the text data.
NOTE
When IBM character set #2 is selected by character code,
codes <ETX> does not exist. (In this instance, select another
code).
U.S.A. & Europe IBM #1 IBM #2 Japan
(03)H <ETX> <ETX> ♥ <ETX>
– 53 –
Page 58

FUNCTION
CODE
Trigger auto-cutter drive (Auto-cutting models only)
<ESC> “d” “0” or <ESC> “d” <0>
H (64)H (30)H or (1B)H (64)H (00)H
(1B)
<ESC> “d” “1” or <ESC> “d” <1>
H (64)H (31)H or (1B)H (64)H (01)H
(1B)
OUTLINE
FUNCTION
CODE
OUTLINE
NOTE
This code causes the printer to trigger auto-cutter.
Select validation printing (Models with validation function
only)
<GS> data <LF>
H data (0A)
(1D)
Prints up to 32 columns of the 7 × 9 (half dot) font size
characters on one line.
(1) Character data and immediate execution command
<CAN> <SUB> <LF> are valid for data.
(2) Printing modes (such as emphasized, inverted, expanded
character modes, etc.) which were set before validation
printing are invalid during validation printing. (These
modes become valid again after validation printing is
completed.)
(Refer to “5. VALIDATION PRINTING”)
– 54 –
Page 59

8. CHARACTER CODE TABLES
8.1 U.S.A. & Europe (DIP SW2-1: ON, SW2-2: ON)
– 55 –
Page 60

– 56 –
Page 61

8.2 IBM Character Set #1 (DIP SW2-1: OFF, SW2-2: ON)
– 57 –
Page 62

– 58 –
Page 63

8.3 IBM Character Set #2 (DIP SW2-1: ON, SW2-2: OFF)
– 59 –
Page 64

– 60 –
Page 65

8.4 JAPAN (DIP SW2-1:, OFF, SW2-2: OFF)
– 61 –
Page 66

– 62 –
Page 67

8.5 International Character Sets
– 63 –
Page 68

MEMO
Page 69

Page 70

ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS DIVISION
STAR MICRONICS CO., LTD.
536 Nanatsushinnya, Shimizu, Shizuoka,
424-0066 Japan
Tel: 0543-47-0112, Fax: 0543-48-5013
OVERSEAS SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
STAR MICRONICS AMERICA, INC.
1150 King Georges Post Road, Edison,
NJ 08837-3729 U.S.A.
Tel: 732-623-5555, Fax: 732-623-5590
Please access the following URL
http://www.star-micronics.co.jp/service/frame_sp_spr_e.htm
for the lastest revision of the manual.
STAR MICRONICS U.K. LTD.
Star House, Peregrine Business Park, Gomm Road,
High Wycombe, Bucks, HP13 7DL, U.K.
Tel: 01494-471111, Fax: 01494-473333
Printed in Japan, 80872005
2000.11.30
 Loading...
Loading...