Page 1
OWNERS GUIDE TO INSTALLATION
AND OPERATION
FW0078
0813
Supersedes
0112
READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
Read these installation instructions in detail before installing your pump. Be sure to check the
following:
1. Be certain the motor is connected for the correct line voltage being used (check motor
nameplate).
2. Be certain the pump is completely primed before starting. Otherwise damage may occur to the
seal.
Every pump is tested before leaving the factory, and its performance depends largely on the
installation.
END SUCTION CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
IL0412
GENERAL SAFETY INFORMATION
1. Follow all local electrical and safety codes, as
well as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and
the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA).
2. Replace damaged or worn wiring cord
immediately.
3. Do not kink power cable and never allow the
cable to come in contact with oil, grease, hot
surfaces or chemicals.
4. Protect the power cable from coming in contact
with sharp objects.
5. Be careful when touching the exterior of an
operating motor - it may be hot enough to be
painful or cause injury.
6. Make certain that the power source conforms
to the requirements of your equipment.
7. Always disconnect power source before
performing any work on or near the motor or
its connected load. If the power disconnect
point is out-of-sight, lock it in the open position
and tag it to prevent unexpected application
of power. Failure to do so could result in fatal
electrical shock.
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
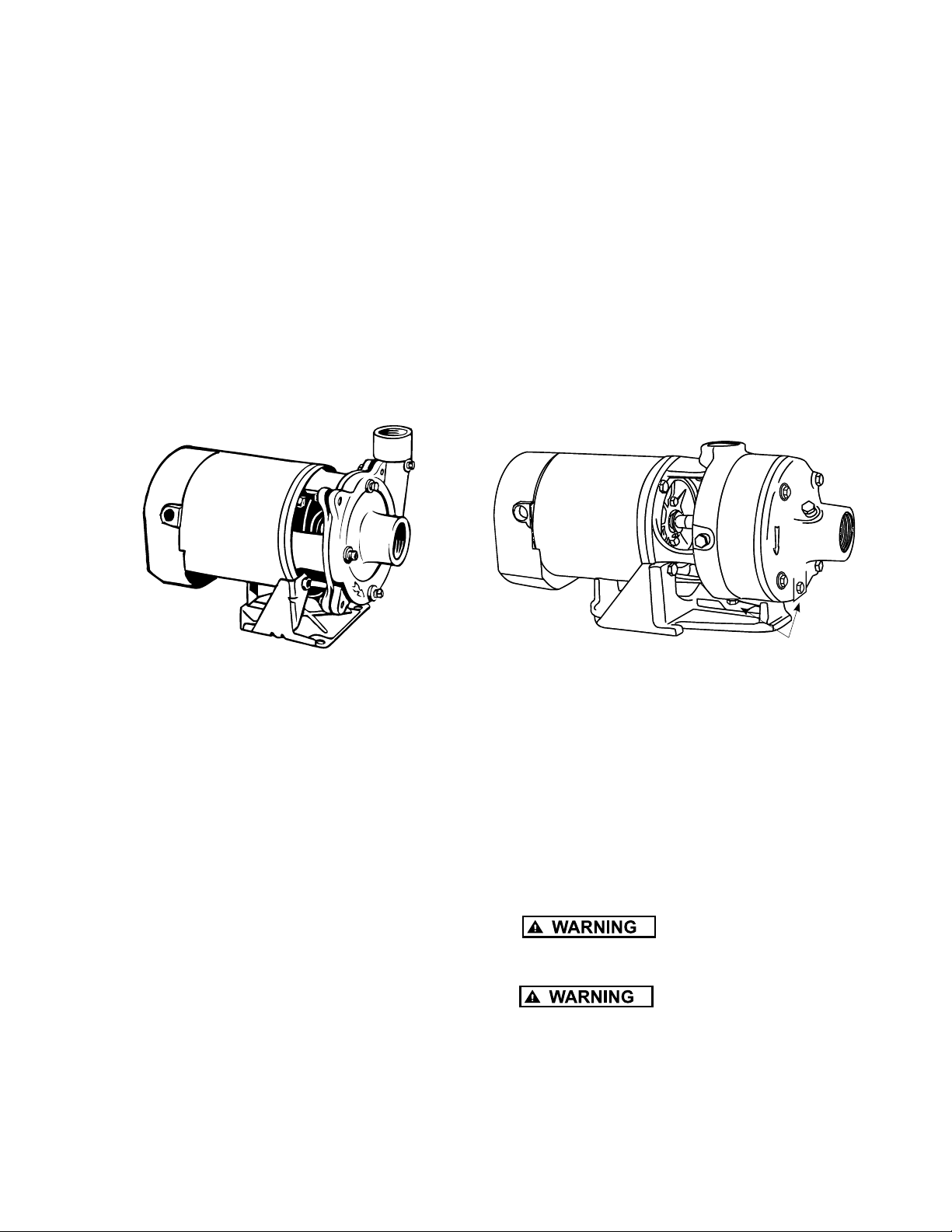
Drain Plug
Figure 2 - CJ101 SeriesFigure 1 - CJ103 Series
8. Do not handle the pump with wet hands or
when standing in water as fatal electrical shock
could occur. Disconnect main power before
handling unit for ANY REASON!
9. Unit must be securely and adequately
electrically grounded. This can be
accomplished by wiring the unit to a ground
metal-clad raceway system or by using a
separate ground wire connected to the bare
metal of the motor frame or other suitable
means.
10.
pump has not been investigated for use in
swimming pool areas.
11.
chemicals known to the State of California
to cause cancer and birth defects or other
reproductive harm.
NOTE: Pumps with the “CSA” mark are tested to
UL standard UL778 and certified to CSA standard
C22.2 No. 108.
1
Risk of electric shock. This
This product contains
130441
IL0201
Page 2

IL0413
IL0414
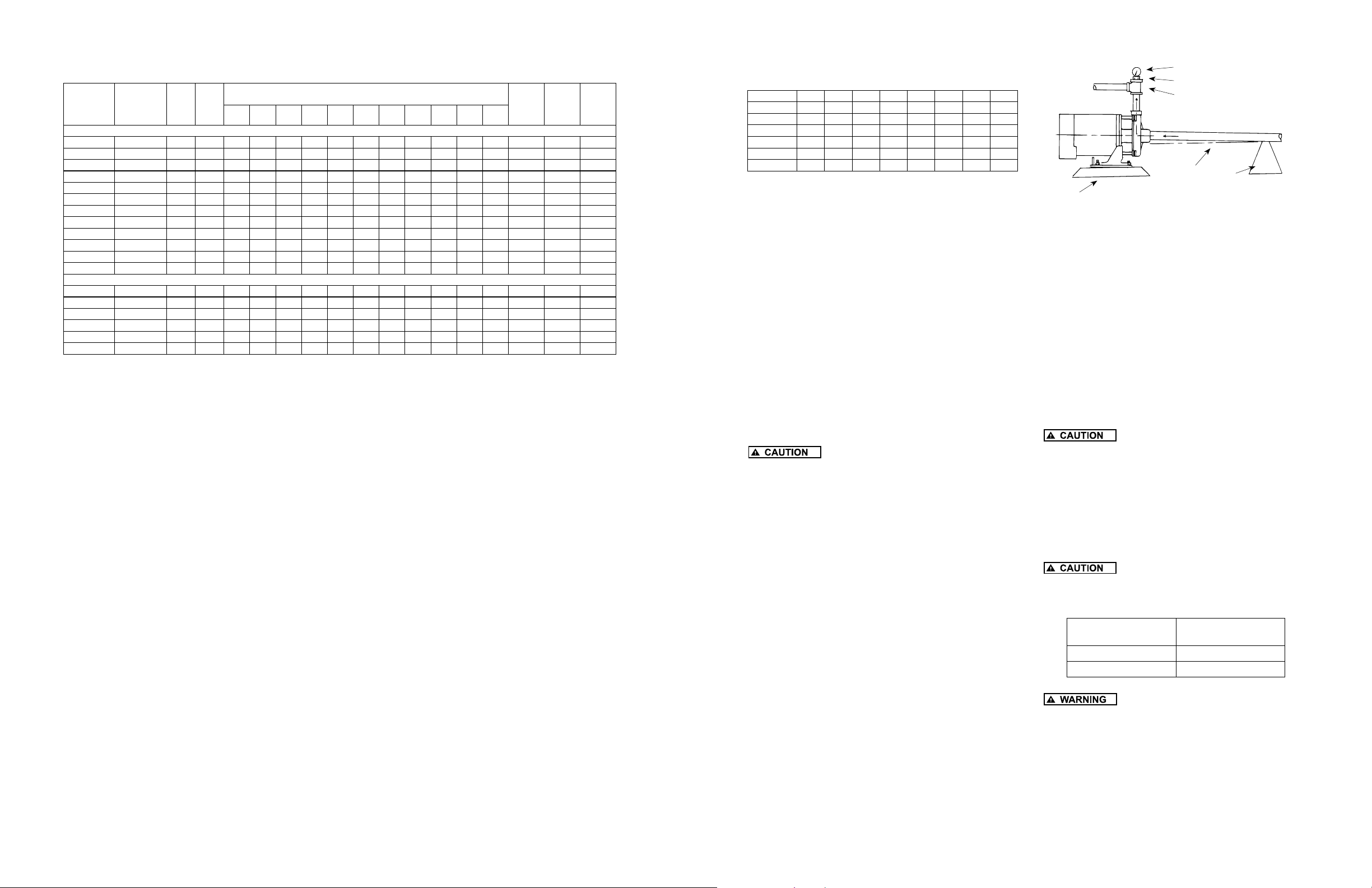
Dimensions (In Inches) CJ103 Series Chart A
HP A B C D E F G H J K
1/3 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/2 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/4 3-7/8
1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/2 3-7/8
3/4 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14 3-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14-1/2 3-7/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-1/8 3-7/8
2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-5/8 3-7/8
1-1/4” Discharge
H
A
J
Figure 3 - CJ103 Single Stage Booster Pump
1-1/2” Suction
F
E
D
C
IL0396
1-1/4” Discharge
K
H
A C
B
G
Figure 4 - CJ101B Two and Three Stage Booster Pump
J
F
1-1/2” Suction
E
D
B
G
IL0395
CJ101 Series Chart B
HP A B C D E F G H J
3/4 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 17-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 18-3/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19
2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19-1/2
2 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
3 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
(*) Three Stage
Motor Data Chart C
MOTOR
HP PH VOLTS HZ RPM
1/3 1 115/230 60 3450 115 V 8.6 4.3 — — 26.0 13.0 — — K
1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 115 V 13.0 6.5 — — 36.0 18.0 — — K
3/4 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 14.0 7. 0 — — 52.0 26.0 — — K
1 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 18.0 9.0 — — 70.0 39.0 — — L
1-1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 21.0 10.5 — — 98.0 49.0 — — J
2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 25.0 12.5 — — 116.0 58.0 — — H
3 1 230 60 3450 230V — 13.5 — — — 53.0 — — D
3/4 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 3.5 1.75 — — 19.0 9.5 K
1 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 4.5 2.25 — — 26.9 13.5 K
1-1/2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 5.7 2.85 — — 33.5 16.8 K
2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 7. 4 3.0 — — 44.0 22.0 K
3 3 208-230/460 60 3450 230V — — 9.8 4.9 — — 48.0 24.0 D
VOLTAGE
(FACTORY)
CONNECT.
SERVICE FACTOR MOTOR
AMPS
THREE
PHASE
115 V 230V 230V 460V 115 V 230V 230V 460V
PHASE
LOCKED ROTOR AMPS
SINGLE
PHASE
THREE
PHASE
KVASINGLE
Street Supply
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Line Strainer
or Filter
(Optional)
Union
Check Valve
Figure 5
To size pressure tank
properly, match the
drawdown of the tank
to the capacity of the
pump.
(*) For manual
operation, omit the
pressure tank and
pressure switch. Wire
motor direct to fuse
box.
Install
a pressure relief valve
on any installation
where pump pressure
can exceed the pressure
tank’s maximum working
pressure or on systems
where the discharge
line can be shut off or
obstructed. Extreme
over pressure can result
in personal injury or
property damage.
Typical Installations
Union
Pressure
Gauge
Figure 6
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Union
Pressure Switch
Drain
Vacuum
Gauge
Union
Check Valve
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Pressure Tank
Pressure
Switch
Pressure
Gauge
Pressure Switch
Foot Valve
with Strainer
Fuse Box
or Switch
Pressure Gauge
Pressure Relief Valve
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Union
Drain
Main Power Box
Union
Pressure Tank
Pressure
Switch
To size pressure tank
properly, match the
drawdown of the tank
to the capacity of the
pump.
(*) For manual
operation, omit the
pressure tank and
pressure switch. Wire
motor direct to fuse
box.
Install
a pressure relief valve
on any installation
where pump pressure
can exceed the pressure
tank’s maximum working
pressure or on systems
where the discharge
line can be shut off or
obstructed. Extreme
over pressure can result
in personal injury or
property damage.
Main Power Box
Fuse Box
or Switch
Union
Pressure Gauge
Pressure Relief Valve
2
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
3
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 3
Pump Performance Chart D
Single
Phase
Model No.
CJ103031 - 1/3 1 41 30 10 27 100 200°F
CJ103051 CJ103053 1/2 1 48 40 27 30 10 0 200°F
CJ103071 CJ103073 3/4 1 62 58 46 31 33 100 200°F
CJ103101 CJ103103 1 1 70 66 58 48 34 40 100 200°F
CJ103151 CJ103153 1-1/2 1 * 75 70 61 51 36 44 100 200°F
CJ103201 CJ103203 2 1 * * 79 77 68 57 45 100 200°F
CJ101B071 CJ101B073 3/4 2 * * 32 29 25 22 5 53 160 200°F
CJ101B101 CJ101B103 1 2 * * 35 32 29 27 23 3 62 160 200°F
CJ101B151 CJ101B153 1-1/2 2 * * 42 39 37 34 28 19 68 160 200°F
CJ101B201 CJ101B203 2 2 * * 45 44 43 40 34 26 70 160 200°F
CJ101C201 CJ101C203 2 3 * * 42 41 40 38 35 31 27 20 7 93 160 200°F
CJ101C301 CJ101C303 3 3 * * 51 50 49 43 41 40 35 29 21 95 160 200°F
CJ101P071 CJ101P073 3/4 2 * * 31 28 23 20 48 160 160°F
CJ101P101 CJ101P103 1 2 * * 34 31 30 29 19 60 160 160°F
CJ101P151 CJ101P153 1-1/2 2 * * 46 44 41 37 31 14 61 160 160°F
CJ101P201 CJ101P203 2 2 * * 45 44 42 39 31 21 65 160 160°F
CJ101D201 CJ101D153 2 3 * * 41 40 38 37 33 29 24 17 89 160 160°F
CJ101D301 CJ101D303 3 3 * * * 46 45 45 42 38 33 27 18 93 160 160°F
To convert to feet of head, multiply by 2.31.
* Operation of pump in this range may result in m
Do not exceed the maximum case pressure and maximum liquid temperature rating of the pump.
Suction & Discharge Tapping: 1-1/2” X 1-1/4”
Motor Voltage:
Three
Phase
Model No.
Single
Three
HP Stage
phase:
phase:
15 20 25 30 35 40 50 60 70 80 90
THERMOPLASTIC IMPELLER MODELS
1/3
1/2
- 115V; 1/2 thru 2 HP - 115/230V; 3 HP - 230V, 60HZ
thru 2 HP - 208-230/460V - 50/60HZ
HP - 208-230/460V - 60HZ
3
INSPECTION AND STORAGE
When unpacking the unit, inspect carefully for any
damage that may have occurred during shipment.
If the unit is received sometime before it can be
used, it should be inspected, recrated and stored
in a dry location.
LOCATION
IMPORTANT: In installations where property
damage might result from an inoperative or
leaking pump due to power outages, discharge
line blockage or any other reason, a back-up
system (s) and/or warning system (s) should be
used.Install a gate valve and union in the suction
and discharge lines. For removal of the pump for
service, close the gate valve and disconnect the
union.
1. Locate pump as close to the fluid source as
possible.
GPM at Total Pressure in PSI
BRASS IMPELLER MODELS
otor
damage.
4. Allow ample clearance around unit for free air
circulation.
5. CJ103 Series pumps incorporate a discharge
port on the pump casing that can be adjusted
in 90 increments. If necessary, adjust the
discharge port to accommodate the specific
application. Pump performance will not be
affected by the position of the discharge port.
SUCTION LIMITATIONS
1. Units are non self-priming. Normally after
being primed the total suction lift of the pump
is 25 feet. Suction lift varies depending upon
elevation (altitude) and water temperature. See
Practical Suction Lift chart.
2. Where liquids at or near their boiling points
are being handled, the supply must be located
above the suction, so that the available NPSH
will be greater than that required by the unit.
Press.
2. Place unit where the motor electrical
components and piping are protected from the
weather and extremes of heat, humidity and
below freezing temperatures.
3. Mount unit in a dry location that is easily
accessible for inspection and maintenance. If
a dry location is not available, mount it on a
foundation well above the wet floor.
Max.
PSI
Max.
Case
Press.
PSI
Max.
Liquid
Temp.
Practical Suction Lifts at Various Elevations and
Water Temperatures in Degrees Fahrenheit
Altitude 60º 80º 100º 120º 140º 160º 180º 200º
Sea Level -22 -21 -20 -18 -15 -10 -4 +5
2000 -20 -19 -18 -16 -12 -7 -1 +8
4000 -17 -16 -15 -13 -10 -4 +2 +12
6000 -15 -14 -13 - 11 -7 -2 +6 +16
8000 -13 -12 -10 -8 -4 +2 +9 —
10000 -10 -9 -8 -6 -2 +4 +13 —
This table gives the maximum permissible suction lift or
the minimum head permitted on the suction side of a pump
at various altitudes and liquid temperatures. A minus sign
before a number indicates suction lift. A plus sign before a
number indicates minimum head. These figures are to be
used as a guide.
PIPING
1. Use galvanized piping, rigid plastic or other
suitable pipe that will not collapse under
suction or rupture due to pressure.
2. The diameter of the suction and discharge pipe
should be no smaller than the corresponding
tappings of the pump (see Figure 3 & 4). If long
runs are encountered larger pipe should be
used. Smaller pipe will reduce the capacity of
the pump.
3. All joints and connections should have Teflon
tape or pipe sealing compound (male threads
only) applied and drawn up tightly.
The entire system must be air and
water tight for efficient operation.
PUMP INSTALLATION
Refer to Figures 5, 6, and 7 for typical installations.
Both the suction and discharge pipe should be
supported at a point near the pump to avoid
strains being placed on the pump.
1. If the pump is used as part of a permanent
installation, secure to a rigid foundation with
appropriate fasteners.
2. Locate the pump as close to the water as
possible, keeping the suction pipe as short as
conditions permit.
3. Avoid dips or pockets in offset piping or air
will accumulate at high points which will make
priming difficult.
4. The suction pipe should slope upward to the
pump inlet. A horizontal suction line must have
a gradual rise to the pump.
Pressure Gauge
Priming Plug
Discharge Tee
Suction Pipe Installed with
Gradual Rise to Pump Inlet
Level
Rigid
Foundation
Figure 7
Pipe
Support
5. On suction lift installations, a foot valve located
in the water or a check valve located as close
to the water as possible will reduce priming
time of the pump and help maintain prime. A
strainer must be used on the suction line to
filter out dirt and debris.
6. A priming tee installed in the pump discharge
port allows water to be poured into the pump
case and suction piping, which is required for
priming on suction lift installations.
7. Install a gate valve and union in the suction and
discharge lines. For removal of the pump for
service, close the gate valve and disconnect the
union.
Do not use a globe valve or other
restricting type of valve at the discharge. This will
seriously restrict the capacity of the pump.
8. Pressure Gauges - Properly sized vacuum or
pressure gauges can be installed in both the
suction and discharge pipe. The gauges will
enable observation of the pump’s performance
as well as detecting cavitation, vapor binding or
other unstable operation.
Use only components that are rated
higher than shut-off pressure of the system. Do not
exceed the pump’s maximum case pressure as listed in
the following table.
capacity must be installed on any installation where
the pump pressure can exceed the pressure tank’s
maximum working pressure or on systems where
the discharge line can be shut-off or obstructed.
Not providing a relief valve can cause extreme over
pressure which could result in personal injury and/or
property damage.
Models
CJ103 100 PSI
CJ101 160 PSI
Maximum Case
Pressure
A pressure relief valve of adequate
4
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
5
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 4

ELECTRICAL
Ground motor before connecting
to electrical power supply.
Connect the motor frame to
Hazardous voltage.
Can shock, burn
or cause death.
Failure to follow
warnings can
cause fatal or
severe shock
hazard or
equipment failure.
equipment grounding conductor by
using green screw. Do not connect
green ground wire to any of the motor
leads.
Do not ground to a gas supply
line.
Turn off power to motor before working on electrical
connections.
Supply voltage must be within ±10% of nameplate
voltage. If in doubt consult a licensed electrician.
Use wire size specified in wiring Chart E. If possible,
connect pump to a separate branch circuit with no other
appliances on it. If wiring diagram on motor model plate
differs from diagram shown in figures 8, 9 & 10, follow
diagram on motor.
All wiring should be performed by a qualified electrician
and in accordance with the national and local electric
codes.
WIRING
1. Motor voltages will vary depending upon the
motor horsepower and phase. Refer to the
motor nameplate and the Motor Data Chart
(Chart C) for voltage and electrical data.
Make certain that the power supply
conforms to the electrical specifications of the motor
supplied. Failure to do so may cause premature motor
failure and will void the warranty.
2. To change voltage, remove the rear access
cover, which is held in place with two (2)
screws. For proper electrical connection, refer
to the connection diagram located on the motor
nameplate or figures 8, 9, 10, 11 & 12.
indicates trouble in the motor or power lines
and immediate attention is needed.
Never examine, make wiring changes
or touch the motor before disconnecting the main
electrical supply switch. The thermal device may have
opened the electrical circuit.
2. Three phase motors do not have a built in
thermal protection. It is recommended that a
properly sized magnetic or manual starter (both
with properly sized heaters) be used with all
three phase motors. Install starters following
instructions of the starter manufacturer. See
Figure 13 for magnetic starter wiring diagram.
3. All motors (single and three phase) should be
equipped with a correctly fused disconnect
switch to provide protection. consult local
or national electric codes for proper fuse
protection based on motor data chart (see
Charts C & E).
115 VOLT
SINGLE PHASE
LINE
L1
L2A B
YELLOW
WHITE
GRAY
RED
TAN
Figure 8 - Wiring Diagram for Single Phase
1/3-2 HP
LOW VOLTAGE 230V HIGH VOLTAGE 460 V
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
L1 L3L2 L1 L3L2
IL0770
Figure 9 - Wiring Diagram for Three Phase
3-ø
230 VOLT
SINGLE PHASE
LINE
L1
YELLOW
WHITE
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
L2A B
GRAY
RED
TAN
IL0180
3 Phase
HIGH VOLTAGELOW VOLTAGE
5
5
6
9
3
IL1229
Figure 10 - Wiring Diagram for Baldor TEFC 3 Phase
motors
4
8
7
2
1
LINE LINE
6
9
3
3 Phase
HIGH VOLTAGELOW VOLTAGE
5
5
6
9
4
8
7
6
9
2
3
3
1
LINE
IL1230
Figure 11 - Wiring Diagram for Franklin Electric TEFC 1
Phase and 3 Phase motors
8
2
LINE
4
7
1
8
2
BROWN
VIOLET
BLACK
YELLOW
BLUE
BROWN
VIOLET
YELLOW
BLACK
BLUE
4
7
1
1 Phase
HIGH VOLTAGE
(10)
(9)
(2)
(3)
(4)
LOW VOLTAGE
(10)
(9)
(3)
(2)
(4)
LINE
LINE
3 Phase
HIGH VOLTAGELOW VOLTAGEGROUND
T5
T1
X2
T6
T9
T3
Lightning
Arrestor
L3
T3
T5
T6
(WHEN REQ)
T7
T8
T5
T6
T3
IL1231
Figure 12 - Wiring Diagram for Marathon TEFC 3 Phase
motors
Pressure
Switch
T2
03
02
T9
T1
T3
L1
MV W
T1
T8
LINE
T2
T4
T7
T2
L2
T2
T4
T8
T7
T2
T1
LINE
Fused
Disconnect
Switch
Replace rear access cover before
starting or operating pump. Failure to do so can result
in personal injury.
MOTOR PROTECTION
1. All single phase motors have built in thermal
protection for all voltages. The overload
protects the motor against burnout from
overload of low voltage, high voltage and other
causes. The device is automatic and resets
itself once the temperature has dropped to
a safe point. Frequent tripping of the device
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
T3
Motor
T1
IL0102
#10 or Heavier Copper Ground Wire, Connect
to 10 Ft. Ground Rod or Well Casing
Figure 13 - Magnetic Starter Wiring Diagram Three Phase
6
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
7
Page 5

PRIMING
1. Before starting any centrifugal pump, it is
absolutely necessary that both the casing and
suction pipe be completely filled with liquid.
This priming can be accomplished by any of
the following methods:
2. When the liquid supply level is above the center
line of the pump, it is primed by opening the
2. Proper rotation of pump impeller is critical for
three phase pumps. Pump motor should turn
counterclockwise (CCW) when facing pump
suction tapping. Momentarily “bump” (apply
power for less than a second) the motor to check
for proper rotation. To change rotation on three
phase units, interchange any two (2) incoming
line (power) leads.
suction and discharge valves. The inflowing
liquid will displace the air and fill the suction
line, pump casing, and discharge line up to the
level of supply.
3. Where the pump is operating with suction
lift and the suction line is equipped with a
foot valve, remove the priming plug from the
discharge tee (see Figures 5-8) and fill the
pump body and suction pipe completely with
water. No additional water will be needed for
Figure 14 - Correct Motor Rotation
IL0416
subsequent start-ups unless the pump body is
drained.
4. After the pump is turned on it will require 2-5
minutes before all air is evacuated from the
suction line and water begins to flow. If there
is no water after 5 minutes, turn the pump off
and check the following:
5. Any air leaks on the suction line must be
eliminated.
6. Suction pipe inlet should be a minimum of 5
feet below the water level.
7. Total suction lift cannot be greater than 25 feet.
8. Any restrictions in the discharge pipe, such as a
closed valve must be eliminated.
NOTE: Unit must be full of liquid before operating.
Never run dry, or against a closed discharge. Dry
running or running unit against a closed discharge
will cause damage to the shaft seal. Do not pump
dirty water or abrasive liquids, otherwise the same
may occur as if running dry.
MOTOR ROTATION
1. Single phase models are one (1) rotation only
(counterclockwise when facing the pump
suction tapping) and cannot be reversed.
MAINTENANCE
Lubrication
The pumps and motors require no lubrication.
The ball bearings of the motor have been greased
at the factory. Under normal operating conditions
they should require no further greasing.
Winterizing your Pump
Cracked pump housings caused by freezing are
not covered by warranty. To protect your pump
from freezing, for best results remove the pump
and store in a warm environment. If pump cannot
be removed from your system, remove both
drain plugs, one on the suction flange and one
at the bottom rear of the pump (see fig 2 in the
instructions.) Allow the water to completely drain
from the pump. Re-install both drain plugs and fill
pump with RV type antifreeze. Antifreeze also acts
as a rust inhibitor. It will help keep rust build up to
a minimum and seals lubricated inside the pump
while it is not in use.
ROTARY SEAL ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT
Disassembly
When disassembling the pump, care
should be taken not to damage the gaskets. If torn or
Chart E
DISTANCE FROM
MOTOR TO FUSE
BOX METER,
OR ELECTRICAL
OUTLET
0-50’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 10 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
50-100’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 8 12 8 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
100-150’ 14 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 6 12 6 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
150-200’ 12 14 12 14 10 12 8 12 * 10 * 10 10 14 14 14 14 12 14 12 14 12 14
200-300’ 12 14 10 14 8 12 6 10 * 10 * 10 8 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 12 10 12
Breaker Size
(Amps)
(*) Not economical to run in 115 volt, use 230 volts
1/3 HP 1/2 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP
115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 230V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V
15 15 20 15 20 15 30 15 30 20 30 20 30 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
MINIMUM COPPER WIRE SIZE CHART (GAUGE)
SINGLE PHASE MOTORS THREE PHASE MOTORS
8
damaged, replace with new gasket (see parts list).
1. Remove the four (4) pump through bolts that
connect the mounting ring to the pump body.
Remove the pump body, taking care not to
damage the gasket or o-ring.
2. Remove the impellers. CJ103 Models are
single stage units, having one impeller. Using
a 9/16” open end wrench, hold the motor shaft
flat and unthread the impeller by turning it
counterclockwise. The motor shaft flat area is
located in the middle of the mounting ring.
3. CJ101 models are multi stage units, having
two or more impellers and one or more
intermediate stages. Using an 11/16” open
end wrench on the motor shaft extension
flat, remove the first impeller by turning or
counterclockwise. Remove the intermediate
stage (stages) taking care not to damage the
gasket (gaskets) and unthread the remaining
impellers.
4. Remove the mechanical seal assembly. The
rotary portion of the seal assembly (carbon
ring, Buna-N gasket and spring) will easily slide
off the end of the shaft. The ceramic portion
can be pried out of the rubber seating using
two (2) screwdrivers (see Figure 15).
Reassembly
The precision lapped faces of the
mechanical seal are easily damaged. Handle the
replacement seal carefully. Short seal life will result if
seal faces (ceramic & carbon) are nicked, scratched or
dirty.
1. Clean the seal cavity of the mounting ring and
the motor shaft thoroughly.
2. Apply liquid soap (one drop only) to the outside
of the Buna-N gasket that houses the ceramic
seal seat. With thumb pressure, press the
ceramic seat, polished face up, squarely into
the seal cavity (see Figure 16).
3. If seal does not seat squarely, remove and
Figure 15 - Remove Mechanical Seal
IL0173
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
IL0168
Figure 16 - Press in Seal
reclean the seal cavity. Place a cardboard
washer over the polished seal face and carefully
press into place using a piece of pipe or tubing
(see Figure 17). Discard cardboard washer.
4. Apply liquid soap (one drop only) to the inside
diameter of the rubber drive ring. Slip rubber
drive ring (carbon face down) and the spring
over the shaft.
5. Reassemble the pump by following the reverse
order of the disassembly instructions.
MOTOR REPLACEMENT
1. Nema J motors can be replaced in the field
with any standard Nema J jet pump motor by
referring to the following instructions and the
attached parts list.
2. Follow steps as outlined under Rotary Seal
Replacement to remove the pump body,
diffuser, impeller and rotary seal.
3. Remove bolts that connect the motor to the
mounting ring and pull motor away.
4. Replace motor with standard Nema J jet
pump motor by positioning motor against the
mounting frame and assembling with four (4)
3/8” x 3/4” cap screws. The mounting base is
connected at the bottom of the mounting frame
with two (2) 3/8” x 1/2” cap screws.
5. Follow steps of Rotary Seal Assembly to
reassemble the remainder of the pump.
BECAUSE DAMAGE TO THE SHAFT SEAL IS
MOST LIKELY TO OCCUR IN DISASSEMBLY, A
NEW SEAL WILL BE NECESSARY.
3/4” Pipe
- Press
Carefully
IL0169
Figure 17- If Necessary, Press with
Cardboard and Pipe
9
NOTE:
Cardboard Washer
Protects Seal Face
Seal
Seal
Cavity
Page 6

Troubleshooting Chart
Symptom Possible Cause(s) Corrective Action
Little or no
discharge
Loss of suction 1. Air leak in suction line 1. Repair
Pump vibrates
and/or makes
excessive noise
Pump will not start
or run
Pumps leaks at
shaft
1. Pump not primed 1. Prime unit
2. Total head too high 2. Shorten suction lift and/or discharge head
3. Suction head higher than pump
3. Lower pump inlet
designed for
4. Impeller clogged 4. Clean
5. Incorrect rotation 5. Refer to wiring information
6. Leak in suction line 6. Repair or replace
7. Inadequate foot valve 7. Make needed adjustments
8. Impeller damaged 8. Replace
9. Foot valve or suction line not
9. Submerge lower in water
submerged deep enough in
water
10. Insufficient inlet pressure or
suction head
10. Increase inlet pressure by adding more
fluid to fluid source
11. Wrong size piping 11. Make needed adjustments
12. Casing gasket leaking 12. Replace gasket
13. Suction or discharge line
13. Open
valves closed
2. Suction head too high 2. Lower pump inlet
3. Insufficient inlet pressure or
suction head
3. Increase inlet pressure by adding more
fluid to fluid source
4. Clogged foot valve or strainer 4. Clean or replace
1. Mounting plate or foundation
1. Reinforce
not rigid enough
2. Foreign material in pump 2. Clean
3. Damaged impeller 3. Replace
4. Cavitation present 4. Check suction line for proper size and be
certain valve is open. Remove excessive
loops in suction line
5. Worn motor bearings 5. Replace
6. Bent impeller shaft 6. Replace
1. Improperly wired 1. Refer to wiring diagram
2. Blown fuse or open circuit
2. Replace fuse or close circuit breaker
breaker
3. Loose or broken wiring 3. Tighten connections and replace broken
wiring
4. Impeller clogged 4. Clean
5. Motor shorted out 5. Replace
1. Worn mechanical seal 1. Replace
2. Bent impeller shaft 2. Replace
10
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
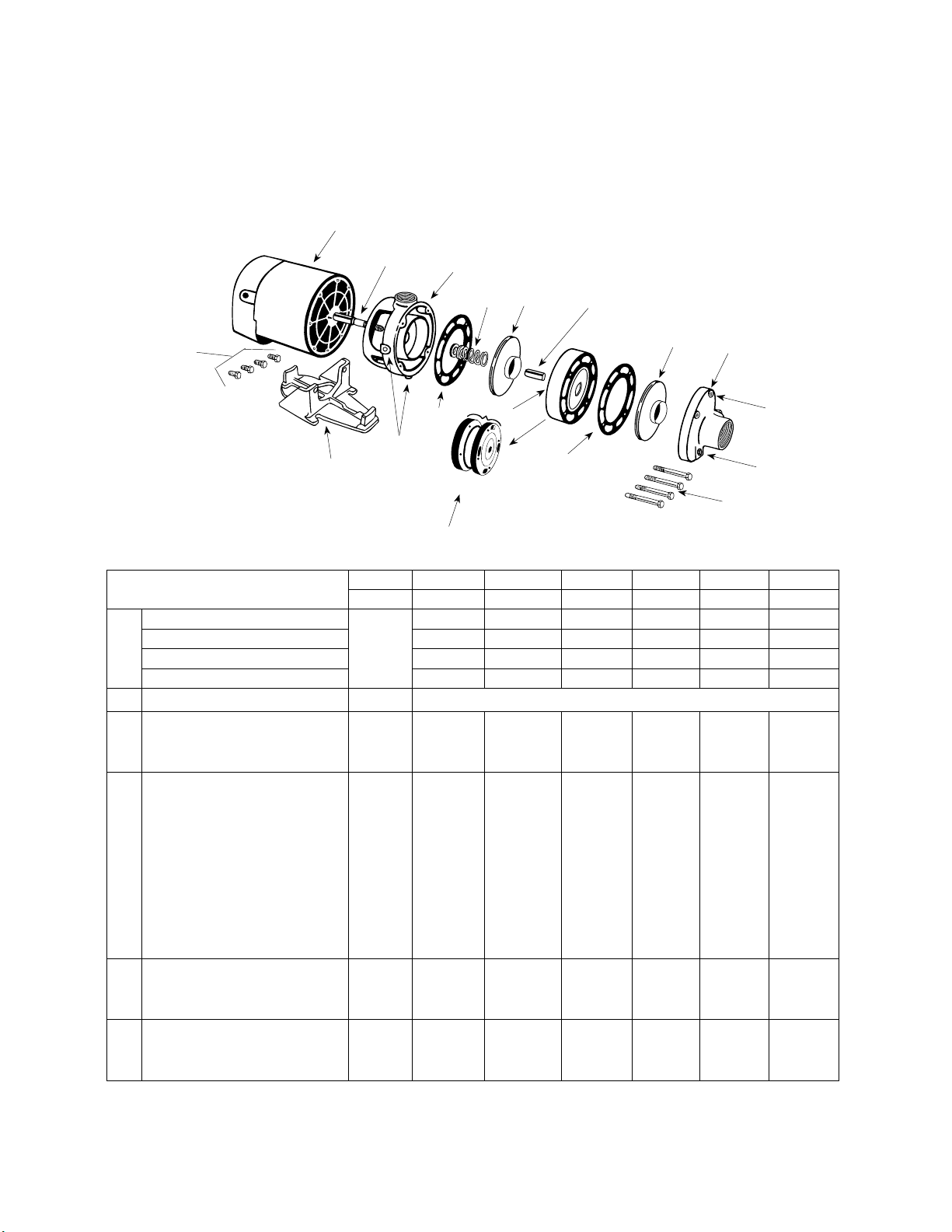
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP REPAIR PARTS
“CJ103” SERIES
(For Pricing Refer To Repair Parts Price List)
1
3
10
HP 1/3 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/2 2
STAGE 1 1 1 1 1 1
SINGLE PHASE
BRASS IMPELLER
THREE PHASE
BRASS IMPELLER
ITEM
11Motor, Nema J - 1PH
‡
2
3
4
5
5A
5B
6
7
‡
8
910Hex Hd. Cap Screws 3/8 x 1”
(*) Standard hardware item
(‡) Not shown
(†) For pumps wi h paper gasket, replace with part number 127782
(
∆) Kit Includes: Access Cover, Screws & Wiring Diagrams
SINGLE PHASE
PLASTIC IMPELLER
THREE PHASE
PLASTIC IMPELLER
DESCRIPTION
Motor, Nema J - 3 PH
Motor Access Cover
Screws, Access Cover
Slinger Washer
Mounting Ring
Hex Hd. Cap Screws 3/8 x 3/4”
Seal, Rotary w/Spring
Impeller - Brass
Impeller - Plastic
Clearance Ring
Ring, Square Cut †
Body Assembly - Brass Impeller
Body Assembly - Plastic Impeller
Suction Clearance Ring-Brass
Pipe Plugs, 1/8” NPT
Base
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
MODEL
NO.
PART
NO.
021301R
021302
126905
134107
131100
132583
021439
125855
CJ103031 CJ103051 CJ103071 CJ103101 CJ103151 CJ103201
CJ103P031 CJ103P051 CJ103P071 CJ103P101 CJ103P151 CJ103P201
*
*
*
98J103
—
1
2
1
1
4
1
130403A
133426
N/A
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
FORM NO. FW0039
SUPERSEDES 1009
PAGE 4-1A REPAIR PARTS
5A
2
4
6
9
CJ103053 CJ103073 CJ103103 CJ103153 CJ103203
CJ103P053 CJ103P073 CJ103P103 CJ103P153 CJ103P203
98J105
98J305
1
2
1
1
4
1
126900A
139222
138138
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
98J107
98J307
127805
021280
134240
127780
N/A
5B
7
5
8
IL0417
QTY.
98J110
1
2
1
1
4
1
1
1
4
4
1
98J310
1
2
1
1
4
1
127804
135248
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J115
98J315
1
2
1
1
4
1
127806
021279
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J120
98J320
127848
127780
11
0110
1
2
1
1
4
1
N/A
N/A
1
N/A
N/A
4
4
1
Page 7
FORM NO. FW0040
0813
SUPERSEDES 0811
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP REPAIR PARTS
“CJ101” SERIES
(For Pricing Refer To Repair Parts Price List)
1
2
4
13
12
3
6
5
8
9
Detail of
Intermediate Stage
Assembly
Square
Cut Ring
HP 3/4 1 1-1/2 2 2 3
STAGE 2 2 2 2 3 3
SINGLE PHASE - BRASS IMPELLER
ITEM
THREE PHASE - BRASS IMPELLER
SINGLE PHASE - PLASTIC IMPELLER
THREE PHASE - PLASTIC IMPELLER
MODEL
NO.
CJ101B071 CJ101B101 CJ101B151 CJ101B201 CJ101C201 CJ101C301
CJ101B073 CJ101B103 CJ101B153 CJ101B203 CJ101C203 CJ101C303
CJ101P071 CJ101P101 CJ101P151 CJ101P201 CJ101D201 CJ101D301
CJ101P073 CJ101P103 CJ101P153 CJ101P203 CJ101D203 CJ101D303
DESCRIPTION PART NO. QTY
11Motor, Nema J - 1 PH
Motor, Nema J - 3 PH
Motor Cover w/Screws
Screws, Cover
‡
Slinger Washer
2
Shaft
3
Mounting Ring
4
Hex Hd. Cap Screws 3/8 x 3/4”
5
Seal, Rotary w/Spring
6
Impeller, Brass
6
Impeller, Thermoplastic
7
Spacer, Shaft
8
Gasket
9
Intermediate Stage Assy-Brass**
9
Intermediate Stage Assy-Plastic**
‡
Suction Clearance Ring
‡
Hub Clearance Ring
‡
Square Cut Ring Interm. Stg.
10
Suction Flange Assembly-Brass
10
Suction Flange Assembly-Plastic
‡
Suction Clearance Ring
‡
Suction Bearing
11
Pump thru Bolts (Grade 5) 3/8” x 3-1/4”
11
Pump thru Bolts (Grade 5) 3/8” x 5”
12
Base w/ Bolts 3/8” x 1-1/4”
13
1/4" NPT Plug
(*) Standard hardware item
(†) For quantity required — See number of stages
(‡) Not shown
(**) Includes two castings, square cut ring, suction and hub clearance ring - See Detail Drawing
(∆) Kit Includes: Access Cover, Screws & Wiring Diagrams
021301R
021302
126905
125204
*
131100
133380
130968
131239B
023405
130957
131282
020240
125227A
023404
130957
020053
*
020054
*
98J107
98J307
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†135280A
†133425
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
4
98J110
98J310
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†135281A
†133427
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
4
8
†126900A
7
IL0159
98J115
98J315
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†139180
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
4
6
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†126901A
†128472
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
4
10
11
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†139126A
†139221
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
4
13
13
98J630
023251
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†136951A
†139104
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
4
12
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 8

GUÍA DEL PROPIETARIO PARA
INSTALACIÓN Y OPERACIÓN
FW0078
0813
Supersedes
0112
LEA ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES CON CUIDADO
Lea estas instrucciones de instalación por extenso antes de instalar su bomba. Verifique lo seguiente:
1. Aseqúrese de que el motor esté conectado con el voltaje correcto siendo usado (vea la placa de
fabricante en el motor).
2. Asegúrese de que la bomba esté completamente cebada antes de arrancarla. De otra manera daños
pueden ocurrir al sello.
Se prueba cada bomba antes de salir de la fábrica, y su eficiencia depende mucho de la manera en que será
instalada.
BOMBAS CENTRÍFUGAS CON ASPIRACIÓN DEL TÉRMINO
IL0412
INFORMACIÓN GENERAL DE SEGURIDAD
1. Siga todos los reglamentos eléctricos y de
seguridad locales.
2. Substituya o repare el cordón eléctrico dañado
o gastado inmediatamente.
3. No enrede el cable de fuerza y nunca deje que
entre en contacto con aceite, grasa, superficies
calientes, ni químicos.
4. Proteja el cable de fuerza de contactarse con
objectos agudos.
5. Tome cuidado al tocar la parte exterior de un
motor en funcionamiento porque puede estar
suficientemente caliente para causar dolores
personales.
6. Asegúrese de que el servicio de fuerza
conforme con los requisitos de su equipo.
7. Siempre desconecte el servicio de fuerza antes
de hacer cualquier trabajo en o cerca del motor
o su carga conectada. Si el interruptor para
desconectar la fuerza está fuera de vista,
ciérrelo en la posición abierta y lo marque
para evitar una aplicación inesperada de la
fuerza. Falta de hacerlo podría resultar en un
choque eléctrico fatal.
IL0201
Figura 2 - Series CJ101Figura 1 - Series CJ103
8. No toque en la bomba con las manos mojadas
o al estar de pie en aqua como puede ocourrir
un choque eléctrico fatal. ¡Desconecte la
fuerza eléctrica antes de tocar en la bomba
por CUALQUIER MOTIVO!
9. Asegúrese de que la bomba esté seguramente
conectada a tierra. Esto se puede hacer al
atarle con alambres a un sistema de canal de
tierra eléctrica con recubrimiento metálico o al
utilizar una tierra eléctrica separada conectada
a la parte metálica a la armazón del motor o
de otra manera adecuada.
10. ADVERTENCIA: Risque de choc électrique.
Cette pompe n’a pas été testée pour être
utilisée près de piscines.
11. ADVERTENCIA: Este producto contiene
sustancias químicas que de acuerdo al
estado de California pueden causar cancer y
defectos de nacimiento u otros daños en la
reproducción.
Aviso: Las bombas con la marca CSA han side
probadas de acuerdo al estandard UL778. Las
bombas “Certificadas” estan certificad de acuerdo al estandard CSA C22.2 No. 108.
1
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
130441S
Page 9
IL0413
IL0414
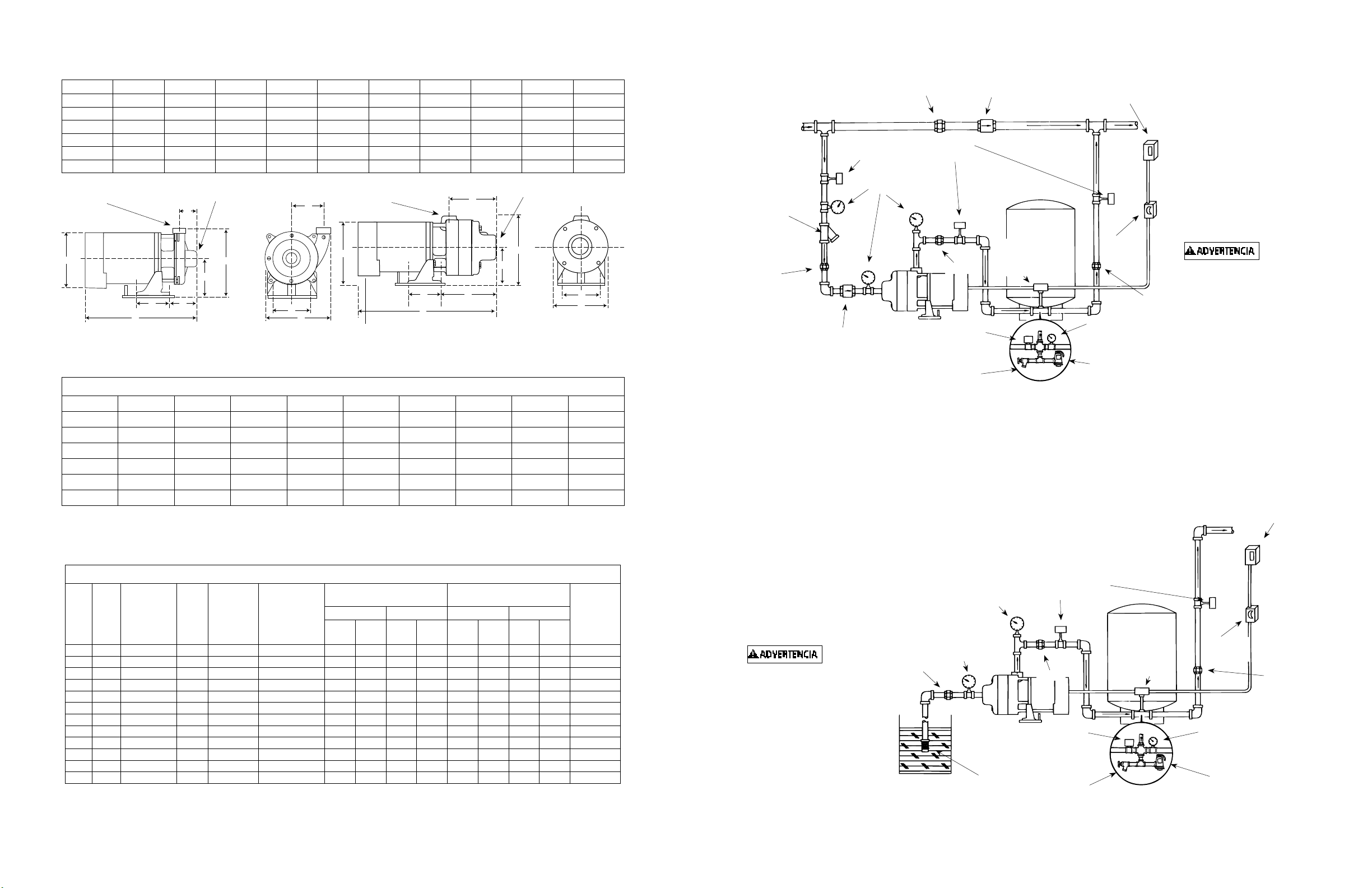
Dimensiones (En Pulgadas) Serie CJ103 Tabla A
HP A B C D E F G H J K
1/3 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/2 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/4 3-7/8
1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/2 3-7/8
3/4 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14 3-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14-1/2 3-7/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-1/8 3-7/8
2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-5/8 3-7/8
1-1/4” Descarga
H
A
J
Figura 3 - CJ103 - Bomba Reforzadora de Etapa Única
1-1/2” Succión
F
E
D
C
IL0396
K
B
G
1-1/4” Descarga
H
A C
J
Figura 4 - CJ101B - Bomba Reforzadora de Dos y Tres Etapas
F
1-1/2” Succión
E
D
B
G
IL0395
Serie CJ101 Tabla B
HP A B C D E F G H J
3/4 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 17-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 18-3/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19
2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19-1/2
2 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
3 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
(*) Tres Etapas
Datos De Motores Tabla C
VOLTIOS
DEL MOTOR
HP FASE VOLTIOS HZ RPM
1/3 1 115/230 60 3450 11 5V 8.6 4.3 — — 26.0 13.0 — — K
1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 11 5V 13.0 6.5 — — 36.0 18.0 — — K
3/4 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 14.0 7. 0 — — 52.0 26.0 — — K
1 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 18.0 9.0 — — 70.0 39.0 — — L
1-1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 21.0 10.5 — — 98.0 49.0 — — J
2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 25.0 12.5 — — 116.0 58.0 — — H
3 1 230 60 3450 230V — 13.5 — — — 53.0 — — D
3/4 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 3.5 1.75 — — 19.0 9.5 K
1 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 4.5 2.25 — — 26.9 13.5 K
1-1/2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 5.7 2.85 — — 33.5 16.8 K
2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 7. 4 3.0 — — 44.0 22.0 K
3 3 208-230/460 60 3450 230V — — 9.8 4.9 — — 48.0 24.0 D
(CONECTADO
EN LA
FÁBRICA)
AMPERIOS DEL MOTOR
FACTOR DE SERVICIO
FASE UNICA TRES FASES FASE UNICA TRES FASES
115 V 230V 230V 460V 115 V 230V 230V 460V
AMPERIOS DEL ROTOR
CERRADO
CÓDIGO
KVA
Suministró de Agua
Municipal
Válvula de Compuerta/Globo
(Normalmente Abierta)
Use Colador
o Filtro
(Opcional)
Unión
Válvula de
Retención
Figura 5
Para saber el tamaño
adecuado del tanque,
iguale la extracción
del tanque con la
capacidad de la bomba.
(*) Para una operación
manual, deje fuera el
tanque de presión y el
interruptor automático
por caída de presión.
Alambre el motor
directamente a la caja
de fusibles.
Instale
una válvula de alivio de
presión en cualquiera
instalación donde la
presión de la bomba
pueda exceder la presión
de trabajo máximo del
tanque de presión o en los
sistemas donde el tubo
de descarga puede estar
cerrado o obstruído. Una
sobrepresión extrema
puede resultar en daños
personales o danos a la
propiedad.
Instalaciones Típicas
Unión
Manómetro
Unión
Interruptor
Automático por
Caída de presión
Desagúe
Calibre
de Vacio
Unión
Figura 6
Válvula de
Retención
Tanque de
Presión
Interruptor
Automático
por Caída de
presión
Manómetro
Válvula
de Pie con
Colador
Válvula de
Compuerta/
Globo
(Normalmente
Abierta)
Unión
Interruptor
Automático por
Caída de presión
Desagúe
Caja de Fuerza
Principal
Caja de
Fusibles
Manómetro
Válvula de Alivio
de Presión
Tanque de
Presión
Interruptor
Automático
por Caída de
presión
Unión
Para saber el tamaño
adecuado del tanque,
iguale la extracción
del tanque con la
capacidad de la bomba.
(*) Para una operación
manual, deje fuera el
tanque de presión y el
interruptor automático
por caída de presión.
Alambre el motor
directamente a la caja
de fusibles.
Instale
una válvula de alivio de
presión en cualquiera
instalación donde la
presión de la bomba
pueda exceder la presión
de trabajo máximo del
tanque de presión o en los
sistemas donde el tubo
de descarga puede estar
cerrado o obstruído. Una
sobrepresión extrema
puede resultar en daños
personales o danos a la
propiedad.
Caja de Fuerza
Principal
Caja de
Fusibles
Unión
Manómetro
Válvula de Alivio
de Presión
2
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
3
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 10

Rendimiento de la Bomba Tabla D
Modelo
Cu.m/hr en Pressión Total en Kg/sq cm.
HP Etapas
Presión
Máxima kg/
Sq Cm
Monofásico Trifásico
CJ103031
CJ103051
CJ103071
CJ103101
CJ103151
CJ103201
CJ101B071
CJ101B101
CJ101B151
CJ101B201
CJ101C201
CJ101C301
---
CJ103053
CJ103073
CJ103103
CJ103153
CJ103203
CJ101B073
CJ101B103
CJ101B153
CJ101B203
CJ101C203
CJ101C303
1/3
1/2
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
2
3
1,06 1,41 1,76 2,11 2,81 3,52 4,22 4,92 5,62 6,33
Modelos con impulsores de bronce
--
--
--
--
2,3
6,8
9,3
1
--
--
--
--
6,1
9,1
10,9
1
--
--
--
7, 0
10,5
13,2
14,1
1
--
--
--
10,9
13,2
15,0
15,9
1
--
--
8,2
13,9
15,9
1 7, 0
*
1
--
--
13,0
1 7, 5
1 7, 9
*
*
1
--
1,1
5,0
6,6
7, 3
*
*
2
0,7
5,2
6,1
7, 3
7, 9
*
*
2
4,5
6,6
8,0
9,1
9,5
*
*
2
6,1
7, 7
9,1
10,0
10,2
*
*
2
6,1
7, 0
8,0
8,6
9,3
9,5
*
*
3
8,0
9,1
9,5
9,8
11,4
11,6
*
*
3
1,90
--
--
--
2,11
--
--
--
2,32
--
--
--
2,81
--
--
--
3,09
--
--
--
3,16
--
--
--
3,73
--
--
--
4,36
--
--
--
4,78
--
--
--
4,92
--
--
--
6,54
1,6
4,5
6,68
5,0
6,6
Modelos con impulsores de termoplástico
CJ101P071
CJ101P101
CJ101P151
CJ101P201
CJ101D201
CJ101D301
CJ101P073
CJ101P103
CJ101P153
CJ101P203
CJ101D203
CJ101D303
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
2
3
2
4,22
--
--
--
00
4,3
6,6
7, 0
7, 7
*
*
2
4,29
--
--
--
3,2
7, 0
8,4
10,0
10,5
*
*
2
4,57
--
--
--
4,8
7, 5
8,9
10,0
10,5
*
*
2
6,26
--
3,9
5,5
6,4
7, 7
8,4
9,5
9,3
*
*
3
6,33
4,1
6,1
7, 5
8,6
9,5
10,2
10,5
10,5
*
*
3
3,38
--
--
--
--
--
4,5
6,7
7, 0
*
*
( ) No exceda la presión mEaxima de la caja y la temperatura máxima liquida de capacidad nominal de la bomba.
(* ) La operación de la bomba en este rango puede disminuir la vida de la bomba y/o dañar el motor.
INSPECCIÓN Y ALMACENAJE
Al tirar la unidad de su embalaje, inspeccione
cuidadosamente por cualquier daño que pueda
haber ocurrido durante su transporte. Si Ud.
recibe la unidad un período de tiemp antes de que
vaya usarla, sería necesario inspeccionarla, volver
a encajarla y guardarla en un lugar seco.
LOCALIZACIÓN
IMPORTANTE: En las instalaciones en donde
daños a la propiedad pueden resultar de goteo
en la bomba o a una bomba inoperante debido a
paros eléctricos, atasco en el tubo de descarga, o
por cualquier otro motivo, es aconsejable tener un
otro sistema de reserva o sistema de aviso.
1. Es necesario localizar la bomba cerca de la
procedencia del flúido.
2. Se debe colocar la unidad donde el motor y
los componentes pueden estar protegidos del
tiempo y las extremas temperaturas de calor,
frío, y humedad.
3. Instale la unidad en un lugar seco que tiene fácil
4. Permita que haya bastante espacio alrededor de
la unidad para una mejor circulación de aire.
5. Las bombas de la Serie CJ103 tienen una
abertura para descarga en la caja de la bomba
que se puede ajustar en incrementos de 90
(grados). Cuando necesario, ajuste la abertura
de descarga para poder acomodar la aplicacón
específica. La posición de la abertura de
descarga no afectará el rendimiento de la
bomba.
LIMITACIONES DE SUCCIÓN
1. Las unidades no son de autocebado.
Normalmente, después de que la bomba está
cebada, el nivel total de succión es de 25 pies.
El nivel de succión varia dependiendo de la
altitud y la temperatura del agua. Refiérase a la
Tabla Práctica para Altura de Succión.
2. Cuando manosea líquidos cerca de o en sus
puntos de ebullición la procedencia del flúido
tiene que estar situada arriba de la succión para
que el NPSH disponsible será mayor que la
cantidad requerida por la unidad.
acceso para su mantenimiento e inspección. Si
un lugar seco no existe, móntela sobre una base
bastante arriba del suelo mojado.
4S
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Presión
Máxima de
Caja Kg/Sq
Cm
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
Temperatura
Máxima
Liquida
93,3ºC
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
71,1ºC
71,1
71,1
71,1
71,1
71,1
Tabla Práctica De Niveles De Succión En Varias
Altitudes Y Con Varias Temperaturas De Agua
Mostrado En Grados Fahrenheit
Altitud 60º 80º 100º 120º 140º 160º 180º 200º
Nivel Del
-22 -21 -20 -18 -15 -10 -4 +5
Mar
2000 -20 - 19 -18 -16 -12 -7 -1 +8
4000 -17 -16 -15 -13 -10 -4 +2 +12
6000 -15 -14 -13 - 11 -7 -2 +6 +16
8000 -13 -12 -10 -8 -4 +2 +9 —
10000 -10 -9 -8 -6 -2 +4 +13 —
Esta tabla muestra el nivel máximo permitido de succión o la
carga de bombeo mínima en el lado de succión de la bomba en
las varias altitudes y temperaturas del líquido. Un signo menos
antes de un número indica nivel de succión. Un signo más indica
carga mínima. Use estas figuras solo como guía.
TUBERÍA
1. Use tubería galvanizada, de plástico rígido u otro
tipo de tubería adecuada que no se va a aplastar
o doblar o reventar bajo succión presión.
2. El diámetro de los tubos de succión o de
descarga no deben ser menores que los
aterrajados correspondientes de la bomba (vea
las Figuras 3 & 4). Si las distancias son grandes,
es aconsejable usar tubería de tamaño mayor.
Tubos menores irán a reducir la capacidad de la
bomba.
3. Todas las juntas y conexiones deben de tener
cinta Teflon o un compuesto sellador (rosca
macho únicamente) aplicados y las juntas
aprietadas.
El sistema entero debe estar estanque e
impermeable para una operación eficiente.
INSTALACIÓN DE LA BOMBA
Refiérase a las Figuras 5, 6 y 7 para las
instalaciones típicas. Es necesario soportar tanto el
tubo de succión como el de descarga en un punto
cerca de la bomba para evitar esfuerzo adicional en
la bomba.
1. Si está usando la bomba como parte de una
instalación permanente, segúrela en una base
rígida con sujetadores apropiados.
2. Situe la bomba lo más cerca posible al agua,
manteniendo el tubo de succión tan corto como
permitan las condiciones.
3. Evite ángulos o bolsillo en tubería desplazada o
el aire acumulará en los puntos altos resultando
en un cebado dificil.
4. El tubo de succión debería inclinar hacia
arriba hasta la entrada de la bomba. Un tubo
horizontal de succión tiene que tener una
inclinación gradual hasta la bomba.
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Manómetro
Tapón de Cebado
Tubo “T” de Descarga
Tubo de Succión Instalada con
Una Inclinación Gradual Hacia la
Entrada de la Bomba
Nivel
Base
Soporte
del Tubo
Rígida
Figura 7
5. En las instalaciones para la carga de aspiración,
una válvula de pie o localizada en el agua o una
válvula de retención tan cerca al agua como
posible disminuirá el tiempo de cebado de
la bomba ayudando mantener el cebado. Es
necesario usar un colador en el tubo de succión
como filtro para suciedad.
6. Un tubo “T” para el cebado instalado en la
abertura de la descarga de la bomba permite
verter agua en la caja de la bomba y la tubería
de succión, lo cual es necesario para el cebado
en las instalaciones en la carga de succión.
7. Instale una válvula de compouerta y una unión
en el tubo de descarga. Para remoción de la
bomba para mantenimiento, cierre la válvula de
compuerta y desconecte la unión.
No use una válvula de globo u otro tipo
de válvula restrictora en la descarga. Esto restringirá
sériamente la capacidad de la bomba.
8. Manómetros — Los manómetros o
vacuómetros de tamaño adecuado pueden
estar instalados tanto en el tubo de succión
como en el de descarga. Los indicadores
permitirán la observación del rendimiento de la
bomba igual como la detección de cavitación
bloqueo de vapor u otra operación inestable.
Modelos
CJ103 100 PSI
CJ101 160 PSI
Utilice solamente componentes
asignados más altos que la presión de cierre del
sistema. Nunca exceda la presión máxima de la caja de
la bomba como alistada en la tabla abajo.
Es necesario instalar una válvula
reductora de tamaño adecuado en cualquier instalación
donde la presión de la bomba puede exceder la presión
máxima de trabajo del tanque o en sistemas donde se
puede cerrar la línea de descarga o puede estar obstruída.
El hecho de no usar una válvula reductora puede
resultar en una presión extrema que podría cuasar daños
personales o a la propiedad.
Presión Máxima De La
Caja
ELÉCTRICA
5
Page 11

IL0102
Haga una tierra eléctrica al motor
antes de conectarlo al sistema de
energía eléctrica.
Conecte la armazón del motor a
la tierra eléctrica del equipo usando el
Hazardous voltage.
Can shock, burn
or cause death.
Failure to follow
warnings can
cause fatal or
severe shock
hazard or
equipment failure.
tornillo verde. No conecte el alambre
verde de tierra eléctrica a los alambres
del motor.
No haga tierra eléctrica a un tubo
de suministro de gas.
Apague la corriente eléctrica al motor antes de
trabajar con las conexiones eléctricas.
El voltaje de suministro tiene que ser de 10% más o
menos del número de voltaje en la placa. Si existe duda,
consulte un electricista licensiado.
Use el tamaño de alambre especificado en la tabla
E de alambrado. Si posible, conecte la bomba a un
circuito lateral separado sin otros aparatos eléctricos. Si el
diagrama de instalación de la placa del motor es diferente
del diagrama mostrado en las figuras 9, 10, 11, 12 y 13,
entonces siga el diagrama del motor.
Todo el alambrado debe ser hecho por un electricista
calificado de acuerdo con los reglamentos locales.
ALAMBRADO
1. Los voltajes de los motores varian de acuerdo
al HP del motor y la fase. Refiérase a la placa
del motor y la Tabla de Datos del Motor (Tabla
C) para voltaje y datos eléctricos.
Asegúrese de que la fuerza eléctrica
esté conforme a las especificaciones eléctricas del
motor proporcionado. Falta de hacerlo puede resultar
en averías en el motor invalidando la garantía.
2. Para modificar el voltaje, remueva la cubierta
trasera que está fijada en su lugar con dos (2)
115 VOLTS
MONOFÁSICO
LÍNEA
L1
L2A B
AMARILLO
BLANCO
GRIS
ROJO
TOSTADO
NOTE: en el motor de voltaje dupla, cambie los
alambres de color rojo y gris al voltaje requerido
Figura 8 - Diagrama del Alambrado para
Monofásico de 1/3 - 2 HP
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
AMARILLO
230 VOLTS
MONOFÁSICO
L1
BLANCO
LÍNEA
GRIS
L2A B
ROJO
IL0180
tornillos. Para hacer una conexión eléctrica
correcta, vea el diagrama situado en la placa
del motor o en las figuras 9, 10, 11, 12 y 13.
Vuelva a poner la cubierta del aceso
trasero antes de encender u operar la bomba. Falta de
hacerlo podría resultar en daños personales.
PROTECCIÓN AL MOTOR
1. Todos los motores monofásicos tienen una
protección térmica integrada para todos los
voltajes. El sobrecarga protege el motor contra
quemado causado por sobrecarga de voltaje
bajo, alto, y por otras causas. El dispositivo es
automático y se restablece solo una vez que la
temperatura baje a un punto seguro. Disparos
frecuentes del dispositivo indican problemas
con el motor en las líneas de fuerza y requiere
atención inmediata.
Nunca examine, ni haga cambios al
alambrado, ni toque el motor antes de desconectar el
interruptor principal de la fuerza eléctrica. El dispositivo
térmico puede haber abierto el circuito eléctrico.
2. Los motores trifásicos no tienen una protección
térmica integrada. Se recomienda el uso
de un arrancador magnético o manual de
tamaño apropiado (ambos con calentadores
de tamaño correcto) con todos los motores
trifásicos. Instale los arrancadores siguiendo las
instrucciones del fabricante de los arrancadores.
Vea la figura 14 para el diagrama del alambrado
de arrancadores magnéticos.
3. Todos los motores (monofásicos y trifásicos)
deben ser equipados con un interruptor de
desconexión con fusibles correctos para
proporcionar protección. Consulte los
reglamentos locales para códigos eléctricos para
protección adecuada de los fusibles basada en las
tablas de datos de motores. (Vea las tablas C y E).
CEBANDO LA BOMBA
1. Antes de encender cualquier bomba centrífuga,
es absolutamente necesario que tanto la caja
como el tubo de succión estén completamente
llenos de líquido. Se puede llevar a cabo este
VOLTAJE BAJO VOLTAJE ALTO
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
TOSTADO
L1 L3L2 L1 L3L2
IL0770
CONEXIONES PARA TRIFÁSICO CON 9 ALAMBRES
NOTE: para invertir la rotación, intercambie
cualquier de dos alambres de la línea de fuerza
de entrada
Figura 9 - Diagrama de Alambrado para
Trifásico
6
3-ø
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
TRIFÁSICO
VOLTAJE BAJO VOLTAJE ALTO
5
5
6
9
3
LÍNEA
IL1229
Figura 10 - Diagrama del alambrado para motores trifásico
TEFC de Baldor
4
8
7
2
1
6
9
3
LÍNEA
TRIFÁSICO
VOLTAJE ALTOVOLTAJE BAJO
5
5
6
9
4
8
7
6
9
2
3
3
1
LÍNEA
IL1230
Figura 11 - Diagrama del alambrado para motores monofásicos y
trifásico TEFC de Franklin Electric
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
8
2
LÍNEA
4
7
1
8
2
Marrón
Violeta
Negro
Amarillo
Azul
Marrón
Violeta
Amarillo
Negro
Azul
4
7
1
MONOFÁSICO
VOLTAJE ALTO
(10)
(9)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(10)
(9)
(3)
(2)
(4)
LÍNEA
LÍNEA
TRIFÁSICO
LA TIERRA
ELÉCTRICA
(Cuando Requerido)
T7
T1
T8
T5
T6
T3
IL1231
Figura 12 - Diagrama del alambrado para motores trifásico
TEFC de Marathon
Interruptor
Automático
por Caída
de Presión
Figura 13 - Diagrama del Alambrado para Arrancador Magnético Trifásico
7
T2
L1
03
02
T1
T1
T5
T6
T9
T3
MV W
Motor
T4
T8
T7
T2
LÍNEA
L2
X2
T2
T2
T3
Alambre de Cobre Número 10
Para Tierra Eléctrica, Conecte a
una Varilla de Tierra o Tubo de
Revestimiento del Pozo.
VOLTAJE ALTOVOLTAJE BAJO
T6
T9
T3
T1
Interruptor de
Desconexión
Fundido
L3
Apartarrayos
T3
T5
T8
T2
LÍNEA
T4
T7
T1
Page 12

cebado al sequir cualquier de los seguientes
IL0416
métodos:
2. Cuando el nivel de líquido está arriba de la
línea del medio de la bomba, el cebado de
la bomba se realiza al abrir las válvulas de
succión y de descarga. El líquido que viene
entrando desplazará el aire y llenará el tubo
de succión, la caja de la bomba, y el tubo de
descarga hasta el nivel de suministro.
3. Mientras que la bomba está operando con
carga de aspiración y el tubo de succión está
equipado con una válvula de pie, remueva el
tapón de cebado del “T” de descarga (vea las
figuras 3-6) y llene el cuerpo de la bomba y
el tubo de succión completamente con agua.
No es necesario poner agua adicional para
arranques posteriores a no ser que el cuerpo de
la bomba esté vacia.
4. Después de encender la bomba de 2 hasta 5
minutos serán necesarios antes de que todo el
aire esté vaciado del tubo de succión y que el
agua esté fluindo. Se el agua no sale después
de 5 minutos, apaque la bomba y verifique el
seguiente.
5. Es necesario eliminar cualquier fuga de aire en
el tubo de succión.
6. La admision del tubo de succión debe estar a
un mínimo de 5 pies abajo del nivel del agua.
7. La altura total de aspiración no puede estar a
más de 25 pies.
8. Cualquiera restricción en el tubo de descarga,
como una válvula cerrada tiene que ser
eliminada.
NOTE: La unidad tiene que estar llena de líquido
antes de empezar su operación. Nunca opere
la unidad en seco o con la descarga cerrada.
manecillas del reloj al estar de frente con el
roscado interno de succión) y no puede ser
invertido.
2. Rotación correcta del impulsor de la bomba es
esencial para bombas trifásicas. El motor de la
bomba debe girar en sentido contrario al de las
manecilas del reloj al estar de frente al roscado
interno del tubo de succión de la bomba. Toque
momentaneamente (arranque el motor por
menos de un segundo) la fuerza del motor para
verificar rotación correcta. Para cambiar la
rotación en las bombas trifásicas, intercambie
cualquiera de dos líneas de entrada de fuerza.
MANTENIMIENTO
Lubricación
Las bombas y los motores no requieren lubricación.
Los cojinetes de bolas del motor vienen con grasa
desde la fábrica. Bajo condiciones normales de
operación, no deberán requerer grasa adicional.
Congelación
Hay que purgar el sistema entera si existe el peligro
de congelación. Un tapón de desagüe se localiza al
fondo de la caja de la bomba para este motivo.
SUBSTITUCIÓN DEL ENSAMBLAJE DEL SELLO
ROTATORIO
Desmontaje
Al desmontar la bomba , tome cuidado
de no dañar los empaques. Si está rasgada o dañada,
substitúyalos por empaques nuevos (vea la lista de piezas).
1. Remueva los cuatro (4) pernos pasantes que
conectan el anillo de montaje al cuerpo de la
bomba. Quite el cuerpo de la bomba tomando
cuidado para no dañar el empaque ni el arosello.
2. Remueva los impulsores. Los Modelos CJ103 son
de una sola etapa, con un impulsor. Use una llave
Operación en seco o con la descarga cerrada
causará daños al sello del eje. No vaya a bombear
agua sucia ni líquidos abrasivos, otramente lo
mismo puede ocurrir como si estuviera operando en
seco.
ROTACIÓN DEL MOTOR
1. Modelos monofásicos son de rotación de una
dirección única (En sentido contrario al de las
Figura 14 - Rotación Correcta Del Motor
Tabla E
Distancia del
Motor al contador
de la caja de
fusibles, o el
tamaño de
corriente.
0-50’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 10 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
50-100’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 8 12 8 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
100-150’ 14 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 6 12 6 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
150-200’ 12 14 12 14 10 12 8 12 * 10 * 10 10 14 14 14 14 12 14 12 14 12 14
200-300’ 12 14 10 14 8 12 6 10 * 10 * 10 8 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 12 10 12
Tamaño del
Interruptor
(amperios)
(*) No es económico operar en 115 Voltios, use 230 Voltios
1/3 HP 1/2 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP
115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 230V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V
15 15 20 15 20 15 30 15 30 20 30 20 30 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
TABLA DE MEDIDA MÍNIMA DE ALAMBRE (CALIBRE)
MOTORES MONOFÁSICOS MOTORES TRIFÁSICOS
8
de boca de 9/16” para segurar el eje al girarlo en
sentido contrario al de las manecillas del reloj. La
parte plana del eje del motor está en el medio del
anillo de montaje.
3. Los Modelos CJ101 son de varias etapas, con dos
o más impulsores y una o más etapas intermedias.
Usando una llave de boca de 11/16” en la parte
plana de la extensón del eje del motor, remueva
el primer impulsor al girarlo en sentido contrario
al de las manecillas del reloj. Remueva la etapa
intermedia tomando cuidado de no dañar el
empaque y desenrosque los otros impulsores.
4. Remueva el ensamblaje del sello mecánico. La
parte rotatoria del ensamblaje del sello (anillo de
carbono, el empaque Buna-N y resorte) facilmente
deslizarán del extremo del eje. La parte cerámica
separará del asiento de goma usando dos (2)
destornilladores (vea la figura 15).
REENSAMBLAJE
Es fácil dañar las superficies recubiertas con
presición de los sellos mecánicos. Manosee cuidadosamente
el sello de reemplazo. La vida útil del sello disminuirá si las
superficies del sello (carbono y níquel) si están melladas,
arañadas, o sucias.
1. Limpie la cavidad del sello del anillo de montaje y
el eje del motor por completo.
2. Aplique una gota de jabón en líquido al exterior
del empaque Buna-N que contiene el asiento del
sello de cerámica. Usando la presión del pulgar,
presione el asiento de cerámica, con la superficie
pulida hacia arriba, justamente dentro de la
cavidad del sello (vea la figura 16).
3. Si el sello no asienta correctamente, remueva y
vuelva a limpiar la cavidad del sello. Coloque
una arandela de cartón sobre la parte pulida de la
superficie del sello y con cuidado presione en su
lugar usando un pedazo de tubo o de tubería (vea
la Figura 17). Tire fuera la arandela de cartón.
4. Aplique jabón en líquido (solamente una gota) al
diámetro interior al anillo de goma de transmisión.
Deslice el anillo de goma de transmisión (con la
superficie de carbono hacia abajo) y el resorte
sobre el eje.
5. Vuelva a ensamblar la bomba al sequir las
instrucciones de desmontaje en orden invertida.
REEMPLAZO DEL MOTOR
1. Se puede reemplazar tanto los motores Nema
Figura 15 - Remueva el Sello Mecánico
IL0173
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
IL0168
Figura 16 - Presione el Sello
J como los de armazón simples en el campo
de operaciones al referirse a las sequientes
instrucciones de la lista anexada de piezas.
2. Siga los pasos delineados bajo Reemplazo del
Sello Rotatorio para remover el cuerpo de la
bomba, difusor, impulsor, y sello rotatorio.
3. Remueva los pernos que conectan el motor al
anillo de montaje y separe el motor.
4. Substituya el motor con motor Nema J estándar
a chorro al posicionar el motor contra la armazón
de montadura y ensamblarlo con cuatro tornillos
de cabeza de 3/8” x 3/4”. La base de montadura es
concetada al fondo de la armazón de montadura
con dos de los cuatro tornillos de cabeza 3/8” x
3/4”.
5. Siga los pasos del Ensamblaje del Sello del Rotor
para ensamblar el resto de la bomba.
PORQUE ES PROBABLE CAUSARLE DAÑOS AL
SELLO DEL EJE EN EL DESMONTAJE, SERÁ
NECESARIO PONER UN SELLO NUEVO.
NOTA:
Arandela de
Tubo de 3/4”
Presione con
Cuidado
IL0169
Figura 17 - Si Necesario, Presione con
Cartón o el Tubo
9
Cartón Proteje
la Superficie del
Sello
Sello
Cavidad
del Sello
Page 13

Tabla De Detección De Fallas
Síntoma Causa De Los Defectos(s) Correción Del Defecto
Poca o Ninguna Descarga 1. Bomba sin cebado 1. Cébela
2. Carga de Succión demasiada Alta 2. Acorte la altura de
succión o cambie la carga
de succión
3. Capacidad o Altura de Succión 3. Abaje la altura de la
demasiada Altas entrada
4. Impulsor Obturado 4. Limpie
5. Rotación errada en la línea de 5. Refiérase a la información
succión
6. Goteo en el tubo de succión 6. Repare o hace
substitución
7. Válvula de pie demasiado pequeño 7. Ajuste de acuerdo
8. Impulsor dañado 8. Substituya
9. Válvula de pie o tubo de succión 9. Sumerja más en agua
no sumergidos suficientemente
en agua
10. Falta de presión de entrada o de 10. Aumente la presión de
carga de succión entrada adicionando más
agua al tanque o
aumentando la
contrapresión
11. Tubería de succión demasiado 11. Aumente al mismo
pequeña tamaño del tubo de
entrada o para uno mayor
12. Empaque de la caja está goteando 12. Substituya empaque
13. Válvulas de succión o de 13. Abra
descarga cerradas
Pérdida de Succión 1. Goteo de aire en el tubo de 1. Reparar
succión
2. Altura de succión demasiada alta 2. Baje la altura de la entrada
3. La presión de la entrada está 3. Aumente la presión de
insuficiente y la carga de succión entrada adicionando más
está insuficiente agua al tanque o
aumentando la
contrapresión
4. La válvula de pie o criba están 4. Limpie o reemplace
obstruídas
La Bomba Vibra y/o hace 1. El plato de montadura o el 1. Reforzar
demasiado ruído basamento no son bastante rígidos
2. Material ajena en la bomba 2. Desarme y limpie la
bomba
3. Impulsor dañado 3. Substituir
4. Cavitación presente 4. Verifique el tubo de
succión para el tamaño
correcto y aségurese de
que la válvula esté
abierta. Quite las vueltas
excesivas
5. Cojinetes del motor gastados 5. Substituya
6. Eje del impulsor doblado 6. Substituya
La bomba no arranca ni funciona 1. Alambrado errado 1. Verifique el diagrama del
alambrado en el motor
2. Fusible fundido o interruptor 2. Substituya fusible o cierra
automático abierto el interruptor automático
3. Alambrado suelto o quebrado 3. Apriete todas las
conexiones, substituya el
alambrado quebrado
4. Piedra a partícula ajena 4. Limpie
5. Motor puesto en corto circuito 5. Substituya
introducida en el impulsor
La bomba gotea en el eje 1. Sello mecánico gastado 1. Substituya
2. Eje del impulsor doblado 2. Substituya
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO DE LA BOMBA
CENTRÍFUGA SERIE CJ103
1
3
10
Hp
Etapas
Monofásico
Impulsor de latón
Trifásico
Impulsor de latón
ITEM
Monofásico
Impulsor de plástico
Trifásico
Impulsor de plástico
Descripción
1
Motor, Nema J - 1 PH
1
Motor, Nema J - 3 PH
Cubierta del Acceso al Motor
‡
Tornillos, Cubierta
‡
Arandela del Lanzador
2
Anillo de Montadura
3
Tornillos de Cabeza Hexagonales 3/8 x 3/4”
4
Sello, Rotatorio con Resorte
5
Impulsor - latón
5A
Impulsor - plástico
5B
Anillo separador
6
Anillo de corte cuadrado†
7
Cuerpo de la Bomba - Impulsor de latón
Cuerpo de la Bomba - Impulsor de plástico
‡
Anillo para espacio l ibre de succión
8
Tapones para tubos, 1/8” NPT
910Tornillos de Cabeza Hexagonales 3/8 x 1”
Base
(*) Item de Herraje Estandar
(‡) No mostrado
(†) For pumps with paper gasket, replace with part number 127782
(∆) Kit Includes: Access Cover, Screws & Wiring Diagrams
Número
Del
Modelo
Número
De Pieza
021301R
021302
126905
134107
*
131100
132583
021439
*
*
125855
2
4
6
9
5A
5B
5
IL0417
7
8
1/3 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/2 2
1 1 1 1 1 1
CJ103031 CJ103051 CJ103071 CJ103101 CJ103151 CJ103201
CJ103053 CJ103073 CJ103103 CJ103153 CJ103203
CJ103P031 CJ103P051 CJ103P071 CJ103P101 CJ103P151 CJ103P201
CJ103P053 CJ103P073 CJ103P103 CJ103P153 CJ103P203
QTY.
98J103
—
1
2
1
1
4
1
130403A
133426
N/A
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
98J105
98J305
1
2
1
1
4
1
126900A
139222
138138
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
98J107
98J307
1
2
1
1
4
1
127805
021280
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J110
98J310
1
2
1
1
4
1
127804
135248
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J115
98J315
1
2
1
1
4
1
127806
021279
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
1
4
1
127848
N/A
N/A
1
127780
N/A
N/A
4
4
1
10
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
11
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 14

IL0159
PIEZAS DE REPUESTO DE LA BOMBA CENTRÍFUGA SERIE CJ101
1
2
4
8
3
6
5
9
Vista detallada
12
del conjunto de
etapa intermedia
Anillo de corte cuadrado
HP 3/4 1 1-1/2 2 2 3
Etapas
Monofásico No.-Impulsores de bronce
Trifásico No.-Impulsores de bronce
Ref.
Monofásico No.-Impulsores de plástico
No.
Trifásico No.-Impulsores de plástico
Descripción
1
Motor NEMA J Monofásico
1
Motor NEMA J Trifásico
Cubierta de acceso
‡
Tornillo de la cubierta de acceso
‡
Arandela del lanzador
2
Eje
3
Anillo de Montaje
4
Pernos de montaje de motor de 2-3/8 x 1-1/4”
5
Ensamblaje del sello mecánico
6
Impulsores de bronce
6
Impulsores de plástico
7
Manga espaciadora
8
Empaque
9
Etapa intermediaria de bronce**
9
Etapa intermediaria de plástico**
‡
Anillo separador de succión
‡
Anillo separador de cubo
‡
Anillo de corte cuadrado (etapa interm.)
10
Cuerpo de succión con anillo separador-bronce
10
Cuerpo de succión con anillo separador-plástico
‡
Anillo separador de succión
‡
Cojinetes (cuerpo de succión)
11
Pernos pasantes de la bomba de 3/8 x 31/4”
11
Pernos pasantes de la bomba de 3/8 x 5”
12
Base
(*) Pieza de herraje estándar, disponible localmente.
(†) Para la cantidad requerida, vea el número de etapes
(‡) No mostrado.
(**) Incluye dos piezas coladas, Anillo de corte cuadrado y anillo de desgaste de succion y cubo.
Modelo
Pieza
No.
021301R
021302
126905
125204
*
131100
133380
130968
131239B
023405
130957
131282
020240
125227A
023404
130957
020053
*
*
020054
2 2 2 2 3 3
CJ101B071 CJ101B101 CJ101B151 CJ101B201 CJ101C201 CJ101C301
CJ101B073 CJ101B103 CJ101B153 CJ101B203 CJ101C203 CJ101C303
CJ101P071 CJ101P101 CJ101P151 CJ101P201 CJ101D201 CJ101D301
CJ101P073 CJ101P103 CJ101P153 CJ101P203 CJ101D203 CJ101D303
98J107
98J307
1
2
1
135279A
135279A
1
2
1
†135280A
†133425
†135281A
†133427
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
8
98J110
98J310
1
2
1
1
2
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
7
Cantidad
98J115
98J315
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†126900A
†139180
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
6
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†126901A
†128472
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
10
11
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†139126A
†139221
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
98J630
023251
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†136951A
†139104
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
12
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 15
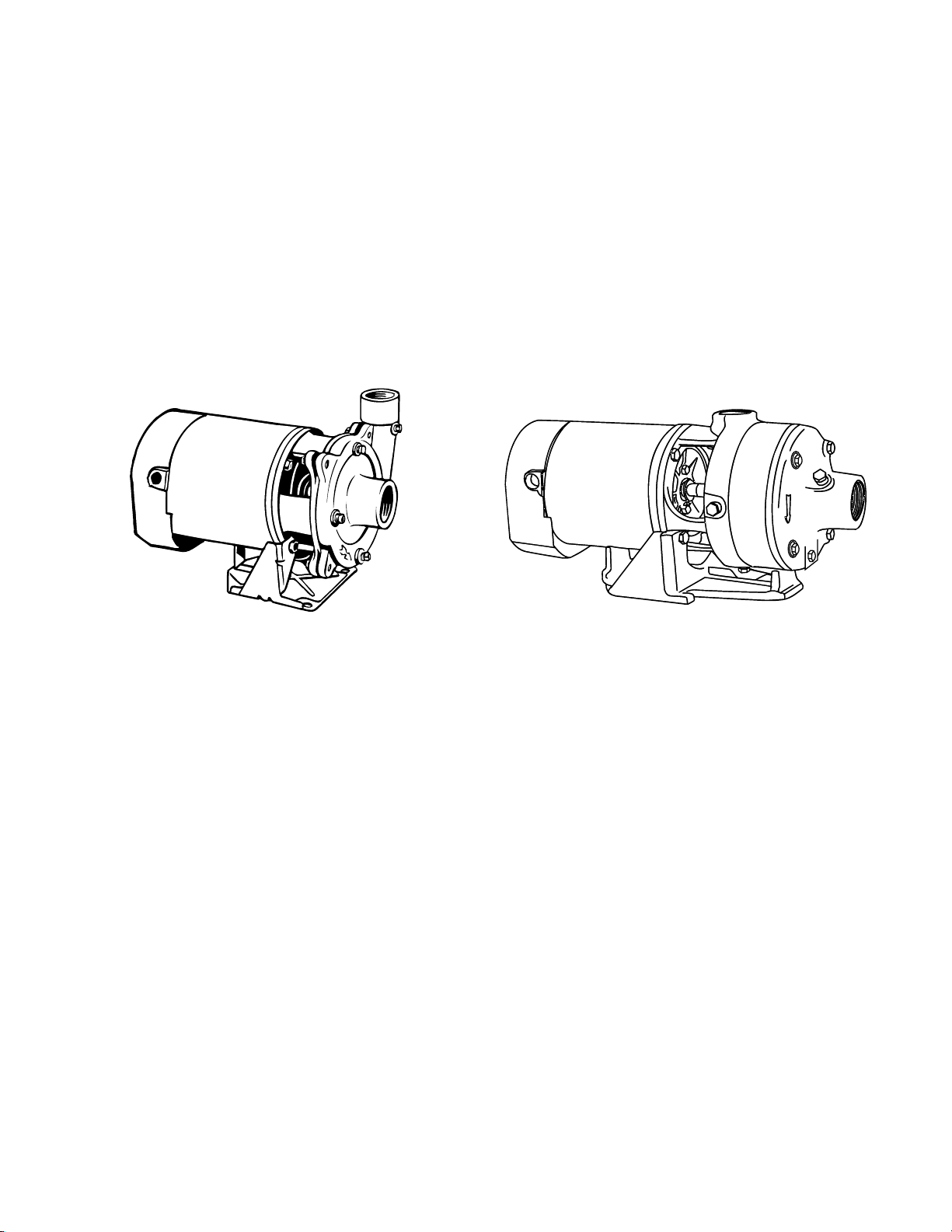
FW0078
0813Supersedes
GUIDE DE POSE ET DE
0112
FONCTIONNEMENT
LISEZ CES INSTRUCTIONS ATTENTIVEMENT
Lisez ces instructions de pose en détails avant d’installer votre pompe. Vérifiez ce qui suit:
1. Assurez-vous que le moteur est raccordé à la tension de secteur correcte (vérifiez la plaque signalétique sur
le moteur).
2. Assurez-vous d’amorcer complètement la pompe avant de la mettre en marche, sinon, le joint risque de
s’endommager.
Chaque pompe est vérifiée avant de sortir de la fabrique et son rendement dépend grandement de son
installation.
POMPES CENTRIFUGES À ASPIRATION LATÉRALE
Croquis 1 - Série CJ103
IL0412
RENSEIGNEMENTS DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRAUX
1. Observez tous les codes électriques et de sécurité
locaux, ainsi que la Réglementaion d’installations
électriques (NEC-É.-U.) et la loi concernant la
sécurité et la santé au travail (OSHA).
2. Remplacez immédiatement un cordon électrique
endommagé ou usé.
3. Ne coudez pas le câble d’alimentation et ne le
laissez jamais entrer en contact avec de l’huile,
de la graisse, des surfaces chaudes ou des
produits chimiques.
4. Protégez le câble d’alimentation pour qu’il ne soit
pas en contact avec des objets coupants.
5. Faites preuve de prudence si vous touchez
l’extérieur d’un moteur qui fonctionne, il peut
être suffisamment chaud pour causer une
douleur ou une blessure.
6. Assurez-vous que votre source d’alimentation
soit conforme aux exigences de votre
équipement.
7. Déconnectez toujours la source d’alimentation
avant d’effectuer toute réparation sur le moteur, à
proximité de celui-ci ou de sa charge connectée.
Si le point de débranchement de l’alimentation
électrique est hors de vue, bloquez-le en position
ouverte et fixez une étiquette pour éviter que le
IL0201
Croquis 2 - Série CJ101
courant soit mis en marche de façon inattendue,
sinon, il peut en résulter un choc électrique fatal.
8. Ne maniez pas la pompe avec les mains
mouillées ou si vous vous tenez dans de l’eau,
car il pourrait en résulter un choc électrique fatal.
Déconnectez la source d’alimentation principale
avant de manier l’appareil POUR N’IMPORTE
QUELLE RAISON!
9. Il faut mettre l’appareil à la terre de façon
appropriée. Ceci peut s’effectuer en raccordant
l’appareil à un système de canalisation revêtu de
métal mis à la terre ou en utilisant un fil de terre
séparé raccordé au métal nu du carter du moteur
ou à tout autre dispositif approprié.
10. AVERTISSEMENT : Risque de choc électrique.
Cette pompe n’a pas été testée pour être utilisée
près de piscines.
11. AVERTISSEMENT : Ce produit contient des
produits chimiques dont l’état de la Californie
a déterminer comme étant la cause de cancer
et de déficiences à la naissance ou autres
dommages reproductifs.
Les pompes avec annotations “CSA” sont vérifiées
d’après lanorme UL778. Les pompes certifiées CSA
sont vérifiées d’après la norme C22.2 no. 108.
1
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
130441F
Page 16
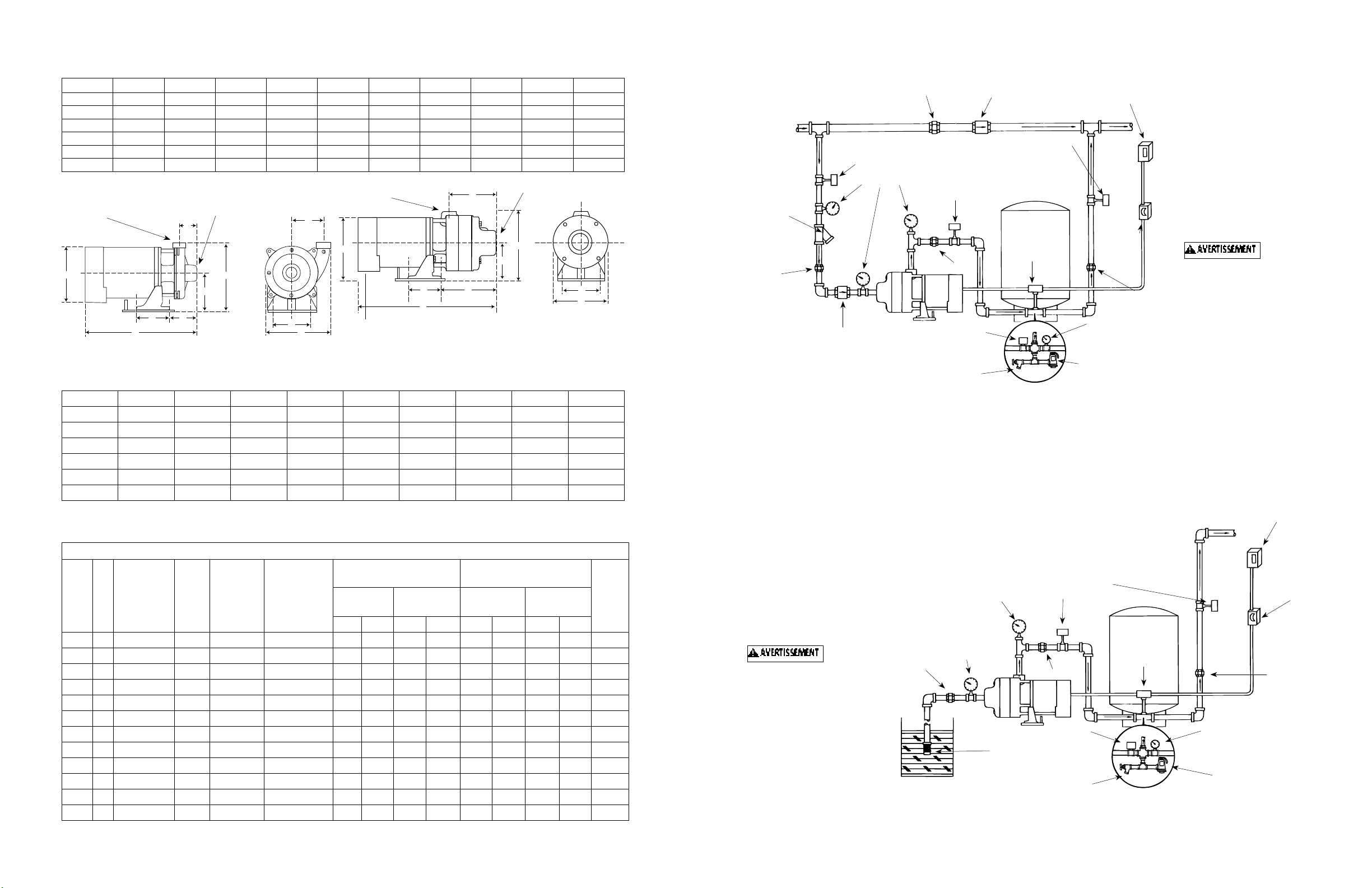
IL0413
IL0414
Dimensions (En Pouces) Série CJ103 Tableau A
HP A B C D E F G H J K
1/3 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/2 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/4 3-7/8
1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 13-1/2 3-7/8
3/4 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14 3-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 14-1/2 3-7/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-1/8 3-7/8
2 4 4-5/8 3-11/16 4-13/16 9-3/16 2-1/8 8-1/4 8-1/8 15-5/8 3-7/8
F
D
Aspiration 1-1/2”
E
B
G
IL0395
Évacuation 1-1/4”
H
A
J
Croquis 3 - CJ103 - Pompe d’appoint à un étage
Aspiration 1-1/2”
F
E
D
C
IL0396
Évacuation 1-1/4”
K
H
A C
J
B
G
Croquis 4 - CJ101B - Pompe d’appoint à deux et trois étages
Dimensions (En Pouces) Série CJ101 Tableau B
HP A B C D E F G H J
3/4 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 17-7/8
1 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 18-3/8
1-1/2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19
2 4 4-5/8 7-9/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 6-1/4 7 8-1/8 19-1/2
2 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
3 * 4 4-5/8 9-7/16 4-13/16 8-3/4 8-1/8 7 8-1/8 21-3/8
(*) 3 étages
Caractéristiques du Moteur Tableau C
TENSION
HP PH VOLTS HZ TR/MIN
1/3 1 115/230 60 3450 11 5 V 8,6 4,3 — — 26,0 13,0 — — K
1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 11 5 V 13,0 6,5 — — 36,0 18,0 — — K
3/4 1 115/230 60 3450 11 5 V 14,0 7, 0 — — 52,0 26,0 — — K
1 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 18,0 9,0 — — 70,0 39,0 — — L
1-1/2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 21,0 10,5 — — 98,0 49,0 — — J
2 1 115/230 60 3450 230V 25,0 12,5 — — 116,0 58,0 — — H
3 1 230 60 3450 230V — 13,5 — — — 53,0 — — D
3/4 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 3,5 1,75 — — 19,0 9,5 K
1 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 4,5 2,25 — — 26,9 13,5 K
1-1/2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 5,7 2,85 — — 33,5 16,8 K
2 3 208-230/460 60/50 3450/2850 230V — — 7, 4 3,0 — — 44,0 22,0 K
3 3 208-230/460 60 3450 230V — — 9,8 4,9 — — 48,0 24,0 D
DU MOTEUR
(RACCORDÉ
À L’USINE).
FACTEUR DE SERVICE DU
MOTEUR EN AMP
UNE PHASE
115 V 230V 230V 460V 115 V 230V 230V 460V
TROIS
PHASE
AMP., ROTOR BLOQUÉ
UNE PHASE
TROIS
PHASE
CODE
KVA
Conduite
Publicque
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Manomètre
Tamis de
Circuit
ou Filtre
(Facultatif)
Raccord
Clapet de
Retenue
Croquis 5
Pour un réservoir sous
pression de capacité
appropriée, agencez
l’abaissement du
niveau du réservoir à la
capacité de la pompe.
(*) Pour fonctionnement
manuel, ne tenez pas
compte du réservoir
sous pression et du
manomètre. Raccordez
le moteur directement
au coffret fusibles.
Posez
un purgeur de pression
sur toute installation où
la pression de la pompe
peut dépasser la pression
de fonctionnement
maximum du réservoir
sous pression ou sur les
systèmes dotés d’un tuyau
d’évacuation pouvant être
fermé ou obstrué. Une
surpression extrême peut
causer des blessure ou
l’endommagement des
biens.
Installations Typiques
Raccord
Gate/Ball Valve
(Normally Open)
Raccord
Manostat
Évacuation
Vacuomètre
Raccord
Croquis 6
Clapet de Retenue
RobinetVanne/Vanne
Sphérique
(Normalement
Ouverts)
Réservoir
Sous Pression
Manostat
Manomètre
Raccord
Clapet Inférieur
Avec Crépine
Boîte D’alimentation
Principale
Coffret à
Fusibles ou
Interrupte r
Manomètre
Purgeur de Pression
Robinet-Vanne/
Vanne Sphérique
(Normalement
Ouverts)
Manostat
Évacuation
Raccord
Réservoir
Sous Pression
Manostat
Pour un réservoir sous
pression de capacité
appropriée, agencez
l’abaissement du
niveau du réservoir à la
capacité de la pompe.
(*) Pour fonctionnement
manuel, ne tenez pas
compte du réservoir
sous pression et du
manomètre. Raccordez
le moteur directement
au coffret fusibles.
Posez
un purgeur de pression
sur toute installation où
la pression de la pompe
peut dépasser la pression
de fonctionnement
maximum du réservoir
sous pression ou sur les
systèmes dotés d’un tuyau
d’évacuation pouvant être
fermé ou obstrué. Une
surpression extrême peut
causer des blessure ou
l’endommagement des
biens.
Boîte
D’alimentation
Principale
Coffret à
Fusibles ou
Interrupteur
Raccord
Manomètre
Purgeur de Pression
2
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
3
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Page 17
IL0415
Rendement de la pompe Tableau D
2
Pression
de carter
max. kg/
2
cm
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
7, 01
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
11,3
Temp. de
liquide
max.
93,3ºC
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
93,3
71,1ºC
71,1
71,1
71,1
71,1
71,1
2
Pression
max. kg/
cm
--
--
--
--
1,6
5,0
1,90
--
2,11
--
2,32
--
2,81
--
3,09
--
3,16
--
3,73
--
4,36
--
4,78
--
4,92
6,54
6,68
--
--
6,1
8,0
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
-4,5
6,6
--
--
--
--
--
Modèle
Une phase Trois phase
CJ103031
CJ103051
CJ103071
CJ103101
CJ103151
CJ103201
CJ101B071
CJ101B101
CJ101B151
CJ101B201
CJ101C201
CJ101C301
--CJ103053
CJ103073
CJ103103
CJ103153
CJ103203
CJ101B073
CJ101B103
CJ101B153
CJ101B203
CJ101C203
CJ101C303
HP Étage
1/3
1/2
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
2
3
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
3
M3/h à pression totale en kg/cm
1,06 1,41 1,76 2,11 2,81 3,52 4,22 4,92 5,62 6,33
BRASS IMPELLER MODELS
9,3
6,8
2,3
--
--
8,2
13,0
5,0
6,1
8,0
9,1
8,6
9,8
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
1,1
5,2
0,7
6,6
4,5
7, 7
6,1
8,0
7, 0
9,5
9,1
10,9
14,1
15,9
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
9,1
13,2
15,0
1 7, 0
6,1
--
10,5
7, 0
13,2
10,9
15,9
13,9
*
1 7, 9
1 7, 5
*
7, 3
6,6
*
7, 9
9,5
10,2
9,5
11,6
7, 3
9,1
10,0
9,3
11,4
*
*
*
*
THERMOPLASTIC IMPELLER MODELS
CJ101P071
CJ101P101
CJ101P151
CJ101P201
CJ101D201
CJ101D301
CJ101P073
CJ101P103
CJ101P153
CJ101P203
CJ101D203
CJ101D303
3/4
1
1-1/2
2
2
3
2
*
*
7, 0
6,7
4,5
--
--
--
--
--
4,1
3,38
--
4,22
--
4,29
--
4,57
--
6,26
6,33
2
*
*
7, 7
7, 0
6,6
4,3
00
--
5,5
7, 5
--
--
--
--
-3,9
6,1
2
*
*
10,5
10,0
8,4
7, 0
2
*
*
10,5
10,0
3
*
*
3
*
9,3
*
10,5
9,5
10,5
8,9
8,4
10,2
7, 5
7, 7
9,5
3,2
4,8
6,4
8,6
( ) Ne dépassez pas la pression de carter maximum ni la température de li quide maximum indiquées pour la pompe.
(* ) Le fonctionnement de la pompe dans cette gamme peut raccourcir la durée de la pompe et/ou endommager le moteur.
INSPECTION ET ENTREPOSAGE
Lorsque vous déballez l’appareil, inspectez
attentivement qu’il n’a pas été endommagé en cours
d’expédition. S’il risque d’y avoir une période de
temps entre la réception de l’appareil et son utilisation,
inspectez-le dès la réception, emballez-le à nouveau et
entreposez-le dans un endroit sec.
EMPLACEMENT
IMPORTANT: Dans les endroits, où des biens peuvent
être endommagés si la pompe est inopérante ou fuit,
en cas de panne de courant, d’un blocage du tuyau
d’évacuation ou de toute autre raison, utilisez un (des)
système(s) auxiliaire(s) et/ou un (des) système (s)
d’avertissement.
1. Placez la pompe aussi près que possible de la
source du liquide à aspirer.
spécifique. La position de l’orifice d’évacuation
n’affectera pas le rendement de la pompe.
LIMITATIONS D’ASPIRATION
1. L’amorçage des pompes n’est pas automatique.
Normalement, après avoir amorcé la pompe, sa
hauteur d’aspiration totale est de 25 pieds. La
hauteur d’aspiration varie suivant l’élévation
(l’altitude) et la température de l’eau. Consultez le
tableau Hauteurs d’aspiration pratiques.
2. Dans le cas de liquides au point d’ébullition
ou proches de celui-ci, il faut que la source
d’approvisionnement soit située au-dessus du point
d’aspiration, pour que la charge nette absolue à
l’aspiration (NPSH) soit supérieure à celle exigée par
l’appareil.
2. Placez l’appareil de façon à protéger les éléments
électriques du moteur et les tuyaux des intempéries,
des températures très élevées ou en-dessous du
point de gel et de l’humidité.
3. Posez l’appareil dans un endroit sec, d’accès facile
pour l’inspecter et l’entretenir. Si un endroit sec
n’est pas possible, placez-le sur une fondation bien
au-dessus d’un sol mouillé.
4. Laissez un bon dégagement autour de l’appareil
pour laisser l’air circuler librement.
5. Les pompes de série CJ103 comportent un orifice
d’évacuation sur le carter de la pompe, réglable par
incréments de 90 . Si nécessaire, réglez l’orifice
d’évacuation pour répondre à une utilisation
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
4
Hauteurs D’aspiration Pratiques À Diverses
Élévations et Températures D’eau En Degrés
Fahrenheit
Altitude
Niveau De La Mer
10000 -10 -9 -8 -6 -2 +4 +13 —
Ce tableau indique la hauteur d’aspiration permise,
maximum ou la hauteur d’élévation minimum permise sur
le côté d’aspiration de la pompe, à des altitudes variées et
des températures de liquides variées. Le signe de moins
précédant un chiffre indique la hauteur d’aspiration; le signe
de plus précédent un chiffre indique la hauteur d’élévation
minimum. Utilisez ces chiffres à titre de guide.
60º 80º 100º 120º 140º 160º 180º 200º
-22 -21 -20 -18 -15 -10 -4 +5
2000 -20 -19 -18 -16 -12 -7 -1 +8
4000 -17 -16 -15 -13 -10 -4 +2 +12
6000 -15 -14 -13 - 11 -7 -2 +6 +16
8000 -13 -12 -10 -8 -4 +2 +9 —
TUYAUX
1. Utilisez des tuyaux galvanisés, en plastique rigide ou
tout autre tuyau approprié qui ne s’affaissera pas sous
l’effet de l’aspiration et qui ne sera pas soumis à une
rupture sous l’effet de la pression.
2. Le diamètre des tuyaux d’aspiration et d’évacuation
ne doit pas être inférieur à celui des branchements
correspondants sur la pompe (consultez les croquis
1 et 2). Si les tuyaux sont acheminés sur une longue
distance, utilisez des tuyaux d’un plus grand diamètre.
Des tuyaux trop petits réduiront la capacité de la
pompe.
3. Il faut poser du ruban au téflon ou une pâte
d’étanchéité pour tuyau sur tous les joints et les
raccords (filets mâles seulement) et bien les sceller.
Tout le système doit être étanche à l’air et à
l’eau pour fonctionner efficacement.
POSE DE LA POMPE
Reportez-vous aux croquis 5, 6 et 7 pour des
installations typiques. Il faut un point de soutien pour
les tuyaux d’aspiration et d’évacuation près de la
pompe pour éviter de la surcharger.
1. Si la pompe est installée de façon permanente,
fixez-la à une fondation rigide avec des attaches
appropriées.
2. Situez la pompe aussi près de l’eau que possible
et gardez le tuyau d’aspiration aussi court que
possible.
3. Évitez des inclinaisons ou des poches pour un tuyau
déporté, sinon, de l’air s’accumulera aux points
élevés, ce qui rendra l’amorçage difficile.
4. Inclinez le tuyau d’aspiration vers le haut jusqu’à
l’orifice d’entrée de la pompe. Un tuyau d’aspiration
horizontal doit être graduellement haussé jusqu’à la
pompe.
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
Manomètre
Bouchon D’amorçage
Té D’évacuation
Tuyau d’aspiration posé avec
une hausse graduelle jusqu’à
l’entrée de la pompe
Niveau
Fondation
Rigide
Soutien
Pour
Tuyau
Croquis 7
Dans le cas d’installations à hauteur d’aspiration, un
clapet inférieur placé dans l’eau ou un clapet de
retenue placé aussi près de l’eau que possible
réduiront le temps d’amorçage de la pompe et
aideront à maintenir l’amorçage. Il faut utiliser une
crépine sur le tuyau d’aspiration pour capter la saleté
et les débris.
6. Un té d’amorçage posé dans l’orifice d’évacuation
de la pompe permet de verser de l’eau dans le carter
de la pompe et dans le tuyau d’aspiration, ce qui est
requis pour l’amorçage dans le cas d’installations à
hauteur d’élévation.
7. Posez un robinet-vanne et un manchon de raccord
sur les tuyaux d’aspiration et d’évacuation. Pour
retirer la pompe, en cas d’entretien, fermez le
robinet-vanne et désassemblez le manchon de
raccord.
N’utilisez ni vanne sphérique ni tout autre
type de robinet limitant l’écoulement à la sortie. Ceci
limiterait grandement la capacité de la pompe.
8. Manomètres - on peut poser des manomètres ou
des indicateurs de vide appropriés sur les tuyaux
d’aspiration et d’évacuation. Ces dispositifs
permettront d’observer le rendement de la pompe
et indiqueront la cavitation, un blocage résultant de
vapeur ou tout fonctionnement anormal.
N’utilisez que des éléments d’une capacité
supérieure à celle de la pression d’arrêt du système. Ne
dépassez pas la pression de carter maximum de la pompe
telle qu’indiquée dans le tableau suivant.
Il faut poser un purgeur de pression de
capacité adéquate sur toute installation où la pression de
la pompe peut dépasser la pression de fonctionnement
maximum du réservoir ou sur les systèmes dotés d’un tuyau
d’évacuation pouvant être fermé ou obstrué. Le fait de
ne pas poser un purgeur de pression peut provoquer une
surpression extrême pouvant causer des blessures et/ou
l’endommagement des biens.
5
5.
Page 18
RACCORDS ÉLECTRIQUES
Mettez le moteur à la terre,
avant de le raccorder à une source de
courant électrique.
Raccordez le bâti du moteur
Tension dangereuse.
Peut provoquer un
choc électrique, des
brûlures ou la mort.
L’inobservation des
avertissements peut
causer le risque
d’un choc fatal ou
grave ou la panne
de l’équipement.
au fil de terre de l’équipment à l’aide
de la vis verte. Ne raccordez pas
le fil de terre vert à l’un des fils
conducteurs du moteur.
N’utilisez pas un tuyau
d’alimentation de gaz en guise de
terre.
Fermez le courant électrique alimentant le moteur avant
de toucher les raccords électriques.
La tension d’alimentation doit être de ±10% de la
tension sur la plaque signalétique. En cas de doute, adressezvous à un électricien qualifié.
Utilisez un calibre de fils tel qu’indiqué sur le tableau
de câblage E. Si possible, raccordez la pompe à un circuit
électrique séparé ne comportant aucun autre branchement
d’appareils. Si le plan de câblage sur la plaque signalétique
du moteur diffère des schémas montrés aux croquis 8, 9, 10,
11, et 12, suivez le schéma sur le moteur.
Tous les raccords électriques doivent être effectués par
un électricien qualifié et conformément aux codes électriques
locaux et nationaux.
CÂBLAGE
1. Les tensions du moteur varient suivant la puissance
en HP et le type de phase du moteur. Reportez-vous
à la plaque signalétique du moteur et au tableau
des caractéristiques du moteur (tableau C) pour les
renseignements sur la tension et le courant électrique.
Assurez-vous que l’alimentation de courant
électrique soit conforme aux caractéristiques électriques
du moteur fourni. Sinon, il peut en résulter une panne
prématurée du moteur et ceci annulerait la garantie.
2. Pour changer la tension, retirez le couvercle à l’arrière,
115 VOLT
UNE PHASE
CONDUCTEUR
L1
L2A B
JAUNE
BLANC
GRIS
ROUGE
TAN
N.B.: MOTEUR À BITENSION, CHANGEZ LE FIL
ROUGE ET GRIS À LA TENSION REQUISE.
Croquis 8 - Plan de câblage pour moteur
1/3-2 HP monophasé
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
JAUNE
230 VOLT
UNE PHASE
CONDUCTEUR
L1
BLANC
L2A B
GRIS
ROUGE
TAN
IL0180
retenu par deux (2) vis. Pour effectuer des raccords
électriques corrects, reportez-vous au schéma de
raccordement situé sur la plaque signalétique du
moteur ou sur les croquis 8, 9, 10, 11, et 12.
Replacez le couvercle à l’arrière avant de
mettre la pompe en marche, sinon, il peut en résulter des
blessures.
PROTECTION DU MOTEUR
1. Tous les moteurs à une phase sont dotés d’un coupe-
circuit thermique intégré pour toutes les tensions. Le
coupe-circuit thermique protège le moteur du grillage
en cas d’une surcharge de basse tension, de haute
tension ou de toute autre source. Ce dispositif est
automatique et effectue la remise en marche dès que
la température a atteint un niveau sûr. Une disjonction
fréquente du coupe-circuit signale un problème dans
le moteur ou les câbles électriques et une attention
immédiate doit y être apportée.
N’examinez et ne touchez jamais le moteur,
n’effectuez jamais de changement avec les fils avant d’avoir
déconnecté l’interrupteur principal d’alimentation électrique.
Le coupe-circuit thermique peut avoir ouvert le circuit
électrique.
2. Les moteurs à trois phases ne possèdent pas de
coupe-circuit thermique intégré. Il est conseillé
d’utiliser un starter magnétique ou manuel, de format
approprié (les deux dotés d’un élément chauffant
approprié) avec tous les moteurs à trois phases.
Installez le starter en suivant les instructions du
fabricant de starters. Consultez le croquis 13 pour le
plan de câblage d’un starter magnétique.
3. Il faut équiper tous les moteurs (à une ou trois
phases) d’un sectionneur à fusible approprié, à titre
de protection. Consultez le code d’électricité local
ou national concernant une protection appropriée
procurée par les fusibles, d’après le tableau des
caractéristiques du moteur (consultez les tableaux C et
E).
AMORÇAGE
1. Avant de mettre toute pompe centrifuge en marche, il
est absolument nécessaire que le carter de la pompe
et le tuyau d’aspiration soient remplis de liquide. On
peut effectuer l’amorçage de deux façons:
BASSE TENSION HAUTE TENSION
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
L1 L3L2 L1 L3L2
IL0770
RACCORDS POUR 3 PHASES, 9 CONDUCTEURS
N.B.: POUR INVERSER LA ROTATION, INTERCHANGEZ
N’IMPORTE LESQUELS DES DEUX FILS D’ENTRÉE (DU
COURANT).
Croquis 9 - Plan de câblage pour moteur
triphasé
6
3-ø
4 5 6
7 8 9
1 2 3
3 PHASES
HAUTE TENSIONBASSE TENSION
5
5
6
9
3
CONDUCTEUR CONDUCTEUR
IL1229
Croquis 10 - Schéma de montage pour moteurs Baldor
TEFC à trois phases
4
8
7
2
1
6
9
3
Triphasé
Haute tensionBasse tension
5
5
6
9
4
8
7
6
9
1
3
Conducteur
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
2
3
Conducteur
IL1230
Croquis 11 - Schéma de montage pour moteur Franklin Electric
TEFC à une et trois phases
4
8
7
2
1
8
2
Marron
Violette
Noir
Jaune
Bleu
Marron
Violette
Jaune
Noir
Bleu
4
7
1
Monophasé
Haute tension
(10)
(9)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Basse tension
(10)
(9)
(3)
(2)
(4)
Conducteur
Conducteur
7
3 PHASES
T1
X2
T3
HAUTE TENSIONBASSE TENSION
T5
T6
T8
T9
T2
T3
CONDUCTEUR
Sectionneur
À Fusible
Parafoudre
L3
T3
T4
T7
T1
Mise à la terre
(quand requis)
T7
T1
T8
T5
T6
T3
IL1231
Croquis 12 - Wiring Diagram for Marathon TEFC 3 Phase
motors
Manostat
T2
03
02
T5
T6
T8
T9
T2
T3
CONDUCTEUR
L1
L2
M
V
T1
T2
T1
Moteur
T4
T7
W
T2
IL0102
Fil De Terre En Cuivre N 10 Ou plus Épais. Le Raccorder À Un
Piquet De Terre De 10 Pi Ou Au Cuvelage du Puits.
Croquis 13 - Plan de câblage pour starter magnétique, Trois phases
Page 19

2. Lorsque le niveau d’approvisionnement du liquide
est au-dessus de la ligne centrale de la pompe, celleci est amorcée en ouvrant les robinets d’aspiration
et d’évacuation. L’arrivée du liquide déplacera l’air
pour vérifier si le moteur tourne dans le bon
sens. Pour changer la rotation sur les modèles à
trois phases, intervertissez deux (2) fils d’entrée
(n’importe lesquels).
et remplira le tuyau d’aspiration, le carter de la
pompe et le tuyau d’évacuation jusqu’au niveau de
l’approvisionnement du liquide.
3. Si la pompe fonctionne avec une hauteur d’aspiration
et que le tuyau d’aspiration est muni d’un clapet
inférieur, retirez le bouchon d’amorçage du té
d’évacuation (consultez les croquis 3-6) et remplissez
entièrement le corps de la pompe et le tuyau
d’aspiration avec de l’eau. Il ne sera plus nécessaire
d’ajouter à nouveau de l’eau pour mettre la pompe en
marche, à moins d’avoir vidé le corps de la pompe.
4. Après avoir mis la pompe en marche, il faudra de 2 à
5 minutes pour évacuer tout l’air du tuyau d’aspiration
et pour que l’eau commence à s’écouler. Si l’eau ne
s’écoule pas au bout de 5 minutes, mettez la pompe
hors circuit et vérifiez ce qui suit:
5. Y-a-t-il une entrée d’air dans le tuyau d’aspiration?
6. L’entrée du tuyau d’aspiration est-il à un minimum de 5
pieds au-dessous du niveau de l’eau?
7. La hauteur d’aspiration totale ne peut être supérieure à
25 pieds.
8. Y-a-t-il une obstruction dans le tuyau d’évacuation,
comme un robinet fermé?
REMARQUE: I’appareil doit être rempli de liquide
avant de le mettre en marche. Ne l’utilisez jamais à
sec ou si le tuyau d’évacuation est fermé. Ces facteurs
endommageraient le joint d’étanchéité de l’arbre.
N’aspirez pas de l’eau sale ou des liquides abrasifs,
car ceci endommagerait la pompe tout comme si elle
fonctionnait à sec.
Croquis 14 - Rotation Correcte du Moteur
ROTATION CORRECTE DU MOTEUR ENTRETIEN
Lubrification
Les pompes et les moteurs n’exigent aucune
lubrification. Les roulements à billes du moteur ont
été graissés à l’usine. Dans des conditions d’utilisation
normale, aucun graissage supplémentaire ne devrait
s’avérer nécessaire.
Gel
Videz tout le système s’il y a un danger de gel. À cette
fin, un bouchon de vidange est situé au bas du carter de
la pompe.
REMPLACEMENT DU DISPOSITIF D’ÉTANCHÉITÉ
ROTATIF
Démontage
Lors du démontage de la pompe , veillez à ne
pas endommager les joints. S’ils sont déchirés ou endommagés,
remplacez-les par un joint neuf (reportez-vous à la liste des
pièces).
1. Retirez les quatre (4) boulons qui retiennent l’anneau
de montage au corps de la pompe. Retirez le corps de
ROTATION DU MOTEUR
1. Les modèles à une phase ne tournent que dans un
(1) sens (sens antihoraire quand vous êtes face au
branchement de l’aspiration de la pompe) et on ne
peut en inverser la marche.
2. La rotation appropriée de la roue de la pompe est
essentielle pour les pompes à trois phases. Le
moteur de la pompe doit tourner dans le sens
antihoraire, face au branchement de l’aspiration
de la pompe. Mettez le moteur en marche
momentanément (pendant moins d’une seconde)
la pompe, en veillant à ne pas endommager les joints
d’étanchéité ou les joints toriques.
2. Retirez les roues. Les modèles CJ103 sont à un étage
et ne comportent qu’une roue. À l’aide d’une clé à
bout ouvert de 9/16”, maintenez la section plate de
l’arbre du moteur et dévissez la roue en tournant dans
le sens antihoraire. La section plate de l’arbre du
moteur est située au centre de l’anneau de montage.
3. Les modèles CJ101 sont à multi-étages et comportent
deux roues ou plus et un étage intermédiaire ou plus.
À l’aide d’une clé à bout ouvert de 11/16”, maintenez
la section plate de l’arbre du moteur et retirez la
Tableau E
DISTANCE DU
MOTEUR AU
COFFRET À
FUSIBLES, OU
À UNE PRISE
ÉLECTRIQUE
0-50’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 10 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
50-100’ 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 14 8 12 8 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
100-150’ 14 14 12 14 10 14 10 12 6 12 6 12 10 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
150-200’ 12 14 12 14 10 12 8 12 * 10 * 10 10 14 14 14 14 12 14 12 14 12 14
200-300’ 12 14 10 14 8 12 6 10 * 10 * 10 8 14 14 12 14 12 14 10 12 10 12
Breaker Size
(Amps)
(*) Le courant de 115 V n’est pas économique, utilisez 230 V
1/3 HP 1/2 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP 3/4 HP 1 HP 1-1/2 HP 2 HP 3 HP
115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 115V 230V 230V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V 230V 460V
15 15 20 15 20 15 30 15 30 20 30 20 30 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
TABLEAU DU CALIBRE MINIMUM DES FILS ÉLECTRIQUES
MOTEURS À UNE PHASE MOTEURS À TROIS PHASES
8
première roue en tournant dans le sens antihoraire.
Retirez l’étage (les étages) intermédiaire (s), en veillant
à ne pas endommager le(s) joint(s) d’étanchéité, puis
dévissez les roues restantes.
4. Retirez la garniture mécanique d’étanchéité. La
section rotative du dispositif d’étanchéité (bague au
carbone, joint Buna-N et ressort), glissera facilement
hors de l’extrémité de l’arbe. La section en céramique
peut être retirée hors du siège en caoutchouc à l’aide
de deux (2) tournevis (reportez-vous au croquis 15).
Remontage
Les faces de la garniture d’étanchéité
mécanique, qui se chevauchent avec précision, s’endommagent
facilement. Maniez la garniture d’étanchéité de rechange
délicatement. Sa durée sera raccourcie si les faces (céramique
et carbone) sont entaillées, égratignées ou sales.
1. Nettoyez à fond la section en retrait de l’anneau de
montage et l’arbre du moteur.
2. Appliquez du savon liquide (une goutte seulement)
sur l’extérieur du joint Buna-N qui loge le siège du
joint en céramique. À l’aide du pouce, pressez le
siège en céramique, la face polie vers le haut, de
niveau dans la section en retrait (reportez-vous au
croquis 16).
3. Si le joint n’est pas de niveau, retirez-le et nettoyez
à nouveau la section en retrait. Placez une rondelle
en carton sur la face polie du joint et pressez
délicatement en place à l’aide d’un morceau de tuyau
(reportez-vous au croquis 17). Jetez la rondelle en
carton.
4. Appliquez du savon liquide (une goutte seulement)
sur le diamètre intérieur de la bague d’entraînement
en caoutchouc. Faites-la glisser (face en carbone vers
le bas) et le ressort sur l’arbre.
5. Remontez la pompe en suivant l’ordre inverse des
instructions de démontage.
REMPLACEMENT DU MOTEUR
1. On peut remplacer, dans le commerce, les moteurs
NEMA J par tout moteur de pompe à jet standard
NEMA J, en se reportant aux instructions suivantes et
à la liste des pièces incluse.
2. Suivez les étapes indiquées sous la rubrique
Remplacement du dispositif d’étanchéité rotatif, pour
retirer le corps de la pompe, le diffuseur, la roue et le
dispositif d’étanchéité rotatif.
3. Retirez les boulons qui retiennent le moteur à l’anneau
de montage et sortez le moteur.
4. Remplacez le moteur par un moteur de pompe à jet
Croquis 15 - Retirez la garniture d’étanchéité
IL0173
mécanique
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
IL0168
Croquis 16 - Pressez le joint en place
standard NEMA J en le plaçant contre le châssis et en
le montant avec quatre (4) vis à chapeau de 3/8” x 3/4”.
La base de montage est retenue au bas du châssis par
deux (2) vis à chapeau de 3/8” x 1/2”.
5. Suivez les étapes de la rubrique Remplacement
du dispositif d’étanchéité rotatif, pour assembler à
nouveau le reste de la pompe.
ÉTANT DONNÉ QUE LE JOINT DE L’ARBRE SERA
TRÈS PROBABLEMENT ENDOMMAGÉ LORS DU
DÉMONTAGE, IL EST NÉCESSAIRE DE POSER UN
JOINT NEUF NECESSARY.
REMAQUE
Rondelle en
carton protégeant
la face du joint
Tuyau 3/4”
- Pressez
Délicatement
IL0169
Croquis 17 - Si nécessaire, pressez avec
9
une pièce de carton et un tuyau
Garniture
D’étanchéité
Section
en
Retrait
Page 20
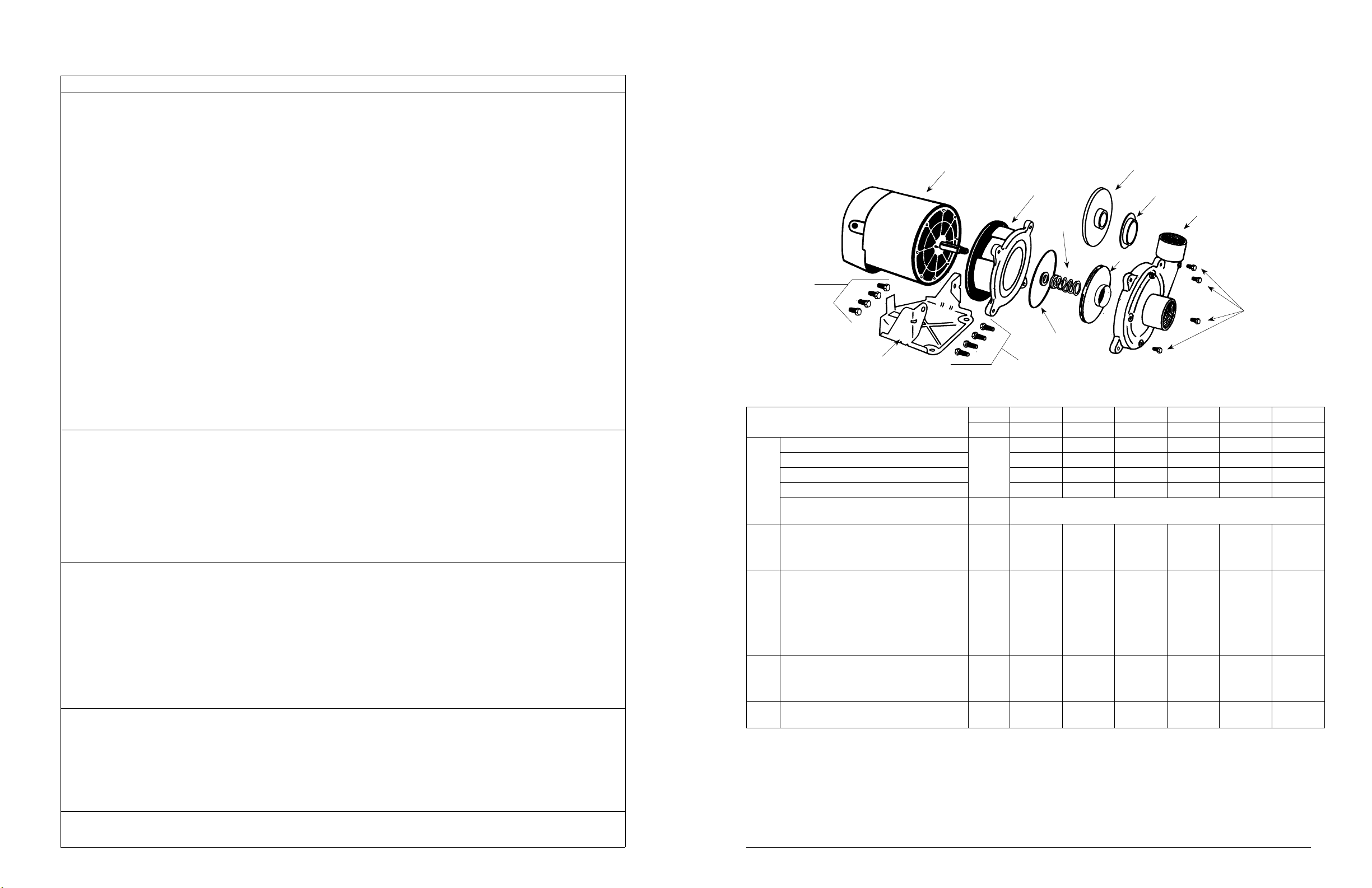
Guide De Dépannage
Symptômes Causes Possible(s) Mesures Correctives
Évacuation failble ou pas d’évacuation 1. La pompe n’a pas été amorcée 1. Amorcer la pompe
2. Hauteur manométrique trop élevée 2. Raccourcir la hauteur
d’aspiration et/ou celle
d’évacuation
3. Hauteur d’aspiration trop élevée 3. Baisser l’entrée de la
pour le modèle de pompe pompe
4. Roue bouchée 4. La nettoyer
5. Rotation incorrecte 5. Consulter les
renseignements de
câblage
6. Entrée d’air dans le tuyau 6. Le réparer ou le remplacer
d’aspiration
7. Clapet inférieur inapproprié 7. Faire les ajustements
nécessaires
8. Roue endommagée 8. La remplacer
9. Clapet inférieur ou tuyau 9. Submerger plus bas dans
d’aspiration pas submergés assez l’eau
profondément dans l’eau
10. Pression d’entrée ou hauteur 10. Augmenter la pression
d’aspiration insuffisantes d’entrée en ajoutant plus
de liquide dans la source
d’approvisionnement de
liquide
11. Tuyau de taille incorrecte 11. Faire les ajustements
nécessaires
12. Fuite au niveau du joint du corps 12. Remplacer le joint
13. Robinets du tuyau d’aspiration ou 13. Les ouvrir
d’évauation fermés
Perte d’aspiration 1. Entrée d’air dans le tuyau 1. Le réparer
d’aspiration
2. Hauteur d’aspiration trop élevée 2. Baisser l’entrée de la
pompe
3. Pression d’entrée ou hauteur 3. Augmenter la pression
d’aspiration insuffisantes d’entrée en ajoutant plus
de liquide à la source
d’approvisionnement de
liquide
4. Clapet inférieur ou crépine 4. Les nettoyer ou les
bouchés remplacer
La pompe vibre et/ou fait un bruit 1. Plaque de montage ou base pas 1. Les renforcer excessif
assez rigides
2. Corps étranger dans la pompe 2. Nettoyer
3. Roue endommagée 3. La remplacer
4. Présence de cavitation 4. Vérifier si le tuyau
d’aspiration est de la taille
appropriée et que le
robinet est ouvert. Retirer
un excès de boucles dans
le tuyau d’aspiration
5. Roulements du moteur usés 5. Les remplacer
6. Arbre de roue courbé 6. Le remplacer
La pompe ne se met pas en marche 1. Installation incorrecte des fils 1. Vérifier le plan de câblage
ou ne fonctionne pas électriques
2. Fusible sauté ou disjoncteur ouvert 2. Remplacer le fusible ou
fermer le disjoncteur
3. Fils électriques lâches ou cassés 3. Resserrer les connexions,
remplacer les fils cassés
4. Roue bouchée 4. La nettoyer
5. Court-circuit dans le moteur 5. Le remplacer
Fuite au niveau de l’arbre de la pompe 1. Garniture d’étanchéité mécanique 1. La remplacer
usée
2. Arbre de roue courbé 2. Le remplacer
10
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
PIÈCES DE RECHANGE POUR POMPE CENTRIFUGE
SÉRIE CJ103
1
3
10
HP 1/3 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/2 2
Étages
Une phase - Roues, Laiton
Trois phase - Roues, Laiton CJ103053 CJ103073 CJ103103 CJ103153 CJ103203
Art.
1
1
‡
2
3
4
5
5A
5B
6
7
‡
8
9
10
* Article de quincaillerie standard
Non montré
(†) For pumps with paper gasket, replace with part number 127782
(∆) Kit Includes: Access Cover, Screws & Wiring Diagrams
Une phase - Roues, plastique CJ103P031 CJ103P051 CJ103P071 CJ103P101 CJ103P151 CJ103P201
Trois phase - Roues, plastique CJ103P053 CJ103P073 CJ103P103 CJ103P153 CJ103P203
Désignation N Pièce
Moteur, Nema J - 1 PH
Moteur, Nema J - 3 PH
Couvercle d’accès au moteur
Vis, couvercle d’accès
Rondelle d’étanchéité
Anneau de montage
Vis à tête hex. 3/8” x 3/4”*
Dispositif d’étanchéité rotatif à ressort
Roue - Laiton
Roue - Plastique
Anneau de dégagement
Anneau à bord en équerre
Pièce de montage du corps - Roues, laiton
Pièce de montage du corps - Roues, plastique
Bague dégagement d’aspiration
Bouchon de tuyau, filet 1/8”
Vis à tête hex. 3/8” x 1”
Base
N
Modèle
021301R
021302
126905
134107
*
131100
132583
021439
*
*
125855
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
2
4
6
9
1 1 1 1 1 1
CJ103031 CJ103051 CJ103071 CJ103101 CJ103151 CJ103201
98J103
—
1
2
1
1
4
1
130403A
133426
N/A
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
98J105
98J305
1
2
1
1
4
1
126900A
139222
138138
1
127870
1
127869A
4
4
1
11
5A
5
98J107
98J307
127805
021280
134240
127780
N/A
IL0417
1
2
1
1
4
1
1
1
4
4
1
5B
QTY.
7
98J110
98J310
1
2
1
1
4
1
127804
135248
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
8
98J115
98J315
1
2
1
1
4
1
127806
021279
134240
1
127780
1
N/A
4
4
1
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
1
4
1
127848
N/A
N/A
1
127780
N/A
N/A
4
4
1
Page 21

PIÈCES DE RECHANGE POUR POMPE CENTRIFUGE
IL0159
SÉRIE CJ101
1
2
4
8
12
3
6
5
9
7
6
8
Détail de l’ensemble de
l’étage intermédiaire
Anneau à bord en équerre
HP 3/4 1 1-1/2 2 2 3
STAGE 2 2 2 2 3 3
Une phase - Roues, Laiton
Trois phases - Roues Laiton
o
N
Une phase - Roues, Plastique
de
Trois phases - Roues, Plastique
réf.
Description
1
Moteur NEMA J Une phase
1
Moteur NEMA J Trois phases
Couvercle d’accès au moteur
‡
Vis, couvercle d’accès
‡
Rondelle d’étanchéité
2
Arbre
3
Anneau de montage
4
Boulons 2-3/8x1-1/4 pour anneau de montage du moteur
5
Dispositif d’étanchéité mécanique
6
Turbine, Laiton
6
Turbine, Plastique
7
Manchon d’espacement
8
Joint
9
Étage interm. avec anneau de dégagement-laiton**
9
Étage interm. avec anneau de dégagement-plastique**
‡
Anneau de dégagement pour aspiration
‡
Anneau de dégagement pour moyeu
‡
Anneau à bord en équerre (etage interm.)
10
Corps d’aspiration avec anneau de dégagement-laiton
10
Corps d’aspiration avec anneau de dégagement-plastique
‡
Anneau de dégagement pour aspiration
‡
Roulement (corps d’aspiration)
11
Boulons 3/8 x 31/4” pour pompe
11
Boulons 3/8 x 5” pour pompe
12
Base
N
modèle
o
N
pièce
021301R
021302
126905
125204
121108
131100
133380
130968
131239B
023405
130957
131282
020240
125227A
023404
130957
130867
139483
CJ101B071 CJ101B101 CJ101B151 CJ101B201 CJ101C201 CJ101C301
o
CJ101B073 CJ101B103 CJ101B153 CJ101B203 CJ101C203 CJ101C303
de
CJ101P071 CJ101P101 CJ101P151 CJ101P201 CJ101D201 CJ101D301
CJ101P073 CJ101P103 CJ101P153 CJ101P203 CJ101D203 CJ101D303
de
*
*
98J107
98J307
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†135280A
†133425
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
98J110
98J310
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†135281A
†133427
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
98J115
98J315
135279A
†126900A
†139180
Qté
1
2
1
1
2
1
†126901A
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
(*) Article de quincaillerie standard, en vente dans les magasins locaux.
(†) Pour la quantité requise, voyez le nombre d’étages
(‡) Non montré.
(**) Comprend deux plaques coulées, Anneau à bord en équerre, anneau d’aspiration et de dégagement du moyeu.
12
95 North Oak Street • Kendallville, IN 46755 • Copyright © 2012. All rights reserved.
10
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
135279A
1
2
1
†128472
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
-1
11
98J120
98J320
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†139126A
†133427
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
98J630
023251
1
2
1
136612A
1
2
1
†136951A
†139104
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
-4
1
 Loading...
Loading...