Page 1
STSC1718
English(Original) Page 4
French Page 15
Portuguese Page 26
Russian Page 37
Ukrainian Page 50
Page 2
ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
FIG. A FIG. B
FIG. C FIG. D
FIG. E
1
2
7
8
4
10
6
11
FIG. F FIG. G
13 12
4
3
9
5
2
Page 3
(Original instructions)
ENGLISH
FIG. H FIG. I
4
9
14
FIG. J
FIG. K
5
11
15
16
10
8
FIG. L
FIG. M
15
11
8
10
19
17
19
8
18
3
Page 4

ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
Technical Data
Specifications STSC1718
Voltage 230V
Frequency 50Hz
Power 1700W
No-Load Speed 5500/min (rpm)
Maximum cutting depth 62mm AT 90°
46mm AT 45°
Intended Use
Your STANLEY saw has been designed for sawing wood
and wood products. This tool is intended for consumer use
only
• For tools intended to cut wood, instruction on correct
use of the dust collection system.
• For tools intended to cut wood, instruction to wear a
dust mask.
• Instrcution to only use saw blades recommended.
• Instruction to always wear hearing protection.
DO NOT RETURN THIS PRODUCT TO THE STORE,
first contact your local STANLEY Office
or nearest authorized service center.
General Safety Rules
Warning! Read and understand all instructions.
Failure to follow all instructions listed below, may
result in electric shock, fire and/or serious
personal injury.
Save These Instructions
Safety instructions
General power tool safety warnings
Warning! Read all safety warnings and all
instructions. Failure to follow the warnings and
instructions listed below may result in electric
shock, fire and/or serious injury.
Save all warnings and instructions for future reference.
The term "power tool" in all of the warnings listed below
refers to your mains operated (corded) power tool or battery
operated (cordless) power tool.
1. Work area safety
a. Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered or dark
areas invite accidents.
b. Do not operate power tools in explosive
atmospheres, such as in the presence of flammable
liquids, gases or dust. Power tools create sparks which
may ignite the dust or fumes.
c. Keep children and bystanders away while operating
a power tool. Distractions can cause you to lose control.
2. Electrical safety
a. Power tool plugs must match the outlet. Never
modify the plug in any way. Do not use any adapter
plugs with earthed (grounded) power tools.
Unmodified plugs and matching outlets will reduce risk of
electric shock.
b. Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded
surfaces such as pipes, radiators, ranges and
refrigerators. There is an increased risk of electric
shock if your body is earthed or grounded.
c. Do not expose power tools to rain or wet conditions.
Water entering a power tool will increase the risk of
electric shock.
d. Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for
carrying, pulling or unplugging the power tool. Keep
cord away from heat, oil, sharp edges or moving
parts. Damaged or entangled cords increase the risk of
electric shock.
e. When operating a power tool outdoors, use an
extension cord suitable for outdoor use. Use of a cord
suitable for outdoor use reduces the risk of electric
shock.
f. If operating a power tool in a damp location is
unavoidable, use a residual current device (RCD)
protected supply. Use of an RCD reduces the risk of
electric shock. Note: The term “Residual Curent Device
(RCD)” can be replaced by “Ground Fault Circuit
Interrupter (GFCI)” or by “Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
(ELCB)”.
3. Personal safety
a. Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use
common sense when operating a power tool. Do not
use a power tool while you are tired or under the
influence of drugs, alcohol or medication. A moment
of inattention while operating power tools may result in
serious personal injury.
b. Use personal protective equipment. Always wear eye
protection. Protective equipment such as dust mask,
non-skid safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection
used for appropriate conditions will reduce personal
injuries.
c. Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the switch is
in the off-position before connecting to power
source and/or battery pack, picking up or carrying
the tool. Carrying power tools with your finger on the
switch or energising power tools that have the switch on
invites accidents.
4
Page 5

(Original instructions)
ENGLISH
d. Remove any adjusting key or wrench before turning
the power tool on. A wrench or a key left attached to a
rotating part of the power tool may result in personal
injury.
e. Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance
at all times. This enables better control of the power
tool in unexpected situations.
f. Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or
jewellery. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves away
from moving parts. Loose clothes, jewellery or long
hair can be caught in moving parts.
g. If devices are provided for the connection of dust
extraction and collection facilities, ensure these are
connected and properly used. Use of dust collection
can reduce dust-related hazards.
4. Power tool use and care
a. Do not force the power tool. Use the correct power
tool for your application. The correct power tool will do
the job better and safer at the rate for which it was
designed.
b. Do not use the power tool if the switch does not turn
it on and off. Any power tool that cannot be controlled
with the switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
c. Disconnect the plug from the power source and/or
the battery pack from the power tool before making
any adjustments, changing accessories, or storing
power tools. Such preventive safety measures reduce
the risk of starting the power tool accidentally.
d. Store idle power tools out of the reach of children
and do not allow persons unfamiliar with the power
tool or these instructions to operate the power tool.
Power tools are dangerous in the hands of untrained
users.
e. Maintain power tools. Check for misalignment or
binding of moving parts, breakage of parts and any
other condition that may affect the power tools
operation. If damaged, have the power tool repaired
before use. Many accidents are caused by poorly
maintained power tools.
f. Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly
maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges are
less likely to bind and are easier to control.
5. Service
a. Have your power tool serviced by a qualified repair
person using only identical replacement parts. This
will ensure that the safety of the power tool is
maintained.
6. Labels on tool
The label on your tool may include the following symbols:
Read
Instructions
Manual
Use Eye
Protection
Use Ear
Protection
V ........ Volts
A ........ Amperes
Hz ....... Hertz
W ........ Watts
min ..... minutes
..... Alternating
Current
..... Direct
Current
n
....... No-Load
0
Speed
...... Class II
Construction
.... Earthing
Terminal
.... Safety Alert
Symbol
.../min.. Revolutions
or Reciprocation per
minute
Position of date barcode
The Date Code, which also includes the year of
manufacture, is printed into the housing.
Example:
2014 XX JN
Year of manufacturing
7. Electrical safety
Your tool is double insulated; therefore no earth wire
is required. Always check that the main voltage
corresponds to the voltage on the rating plate.
Warning! If the power cord is damaged, it must
be replaced by the manufacturer, authorized
STANLEY Service Center or an equally qualified person in
order to avoid damage or injury. If the power cord is replaced
by an equally qualified person, but not authorized by
STANLEY, the warranty will not be valid.
Additional power tool safety warnings
Warning! Safety instructions for all saws
Cutting procedures
Danger! Keep hands away from cutting area
and the blade. Keep your second hand on
auxiliary handle, or motor housing. If both hands are
holding the saw, they cannot be cut by the blade.
b. Do not reach underneath the workpiece. The guard
cannot protect you from the blade below the workpiece.
5
Page 6

ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
c. Adjust the cutting depth to the thickness of the
workpiece. Less than a full tooth of the blade teeth
should be visible below the workpiece.
d. Never hold piece being cut in your hands or across
your leg. Secure the workpiece to a stable platform.
It is important to support the work properly to minimize
body exposure, blade binding, or loss of control.
e. Hold the power tool by insulated gripping surfaces
only, when performing an operation where the
cutting tool may contact hidden wiring. Contact with
a "live" wire will also make exposed metal parts of the
power tool "live" and could give the operator an electric
shock.
f. When ripping, always use a rip fence or straight
edge guide. This improves the accuracy of cut and
reduces the chance of blade binding.
g. Always use blades with correct size and shape
(diamond versus round) of arbour holes. Blades that
do not match the mounting hardware of the saw will run
eccentrically, causing loss of control.
h. Never use damaged or incorrect blade washers or
bolt. The blade washers and bolt were specially
designed for your saw, for optimum performance and
safety of operation.
Kickback Causes And Related Warnings
• Kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched, bound or
misaligned saw blade, causing an uncontrolled saw tolift
upandoutoftheworkpiecetowardtheoperator.
• When the blade is pinched or bound tightly by the kerf
closing down, the blade stalls and the motor reaction
drives the unit rapidly back toward the operator.
• If the blade becomes twisted or misaligned in the cut,
the teeth at the back edge of the blade can dig into the
top surface of the wood causing the blade to climb out of
the kerf and jump back toward operator.
• Kickback is the result of tool misuse and/or incorrect
operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided
6
by taking proper precautions as given below.
a. Maintain a firm grip with both hands on the saw and
position your body and arm to allow you to resist
kickback forces. Kickback forces can be controlled by
the operator, if proper precautions are taken.
b. When blade is binding, or when interrupting a cut for
any reason, release the trigger and hold the saw
motionless in the material until the blade comes to a
complete stop. Never attempt to remove the saw
from the work or pull the saw backward while the
blade is in motion or kickback may occur. Investigate
and take corrective actions to eliminate the cause of
blade binding.
c. When restarting a saw in the workpiece, center the
saw blade in the kerf and check that the saw teeth
are not engaged into the material. If saw blade is
binding, it may walk up or kickback from the workpiece
as the saw is restarted.
d. Support large panels to minimize the risk of blade
pinching and kickback. Large panels tend to sag under
their own weight. Support must be placed under the
panel on both sides, near the line of cut and near the
edge of the panel.
e. Do not use dull or damaged blade. Unsharpened or
improperly set blades produce narrow kerf causing
excessive friction, blade binding, and kickback.
f. Blade depth and bevel adjusting locking levers must
be tight and secure before making cut. If blade
adjustment shifts while cutting, it may cause binding and
kickback.
g. Use extra caution when making a “Pocket Cut” into
existing walls or other blind areas. The protruding
blade may cut objects that can cause kickback.
Lower guard function
a. Check lower guard for proper closing before each
use. Do not operate the saw if lower guard does not
move freely and close instantly. Never clamp or tie
the lower guard into the open position. If saw is
Page 7

(Original instructions)
ENGLISH
accidentally dropped, lower guard may be bent. Raise
the lower guard with the retracting handle and make
sure it moves freely and does not touch the blade or any
other part, in all angles and depths of cut.
b. Check the operation of the lower guard spring. If the
guard and the spring are not operating properly,
they must be serviced before use. Lower guard may
operate sluggishly due to damaged parts, gummy
deposits, or a build-up of debris.
c. Lower guard may be retracted manually only for
special cuts such as "plunge cuts" and "compound
cuts". Raise lower guard by retracting handle and as
soon as blade enters the material, the lower guard must
be released. For all other sawing, the lower guard
should operate automatically.
d. Always observe that the lower guard is covering the
blade before placing saw down on bench or floor. An
unprotected, coasting blade will cause the saw to walk
backwards, cutting whatever is in its path. Be aware of
the time it takes for the blade to stop after switch is
released.
Residual risks
Additional residual risks may arise when using the tool
which may not be included in the enclosed safety warnings.
These risks can arise from misuse, prolonged use etc.
Even with the application of the relevant safety regulations
and the implementation of safety devices, certain residual
risks can not be avoided. These include:
• Injuries caused by touching any rotating/moving parts.
• Injuries caused when changing any parts, blades or
accessories.
• Injuries caused by prolonged use of a tool. When using
any tool for prolonged periods ensure you take regular
breaks.
• Impairment of hearing.
• Health hazards caused by breathing dust developed
when using your tool (example:- working with wood,
especially oak, beech and MDF.)
Safety Guidelines/definitions
It is important for you to read and understand this manual.
The information it contains relates to protecting Your Safety
and Preventing Problems. The symbols below are used to
help you recognize this information.
Danger! Indicates an imminently hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, will result in death
or serious injury.
Warning! Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could result in
death or serious injury.
Caution! Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor
or moderate injury.
Caution! Used without the safety alert symbol
indicates potentially hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, may result in property damage.
Additional Safety Rules For Circular Saws
Warning! Some dust created by power
sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities contains chemicals known to
cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints,
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other
masonry products,
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber
(CCA).
7
Page 8

ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how
often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to
these chemicals:
• Work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved
safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are
specially designed to filter out microscopic particles.
• Avoid prolonged contact with dust from power
sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities. Wear protective clothing and
wash exposed areas with soap and water. Allowing
dust to get into your mouth, eyes, or lay on the skin may
promote absorption of harmful chemicals.
Caution! Wear appropriate hearing protection
during use. Under some conditions and duration
of use, noise from this product may contribute to
hearing loss.
• Snagging the lower guard on a surface below the
material being cut can momentarily reduce operator
control. The saw can lift partially out of the cut
increasing the chance of blade twist. Ensure there is
sufficient clearance under the workpiece.
• When necessary to raise lower guard manually, use
the retracting lever.
• Keep the Blades Clean and Sharp. Sharp blades
minimize stalling and kickback. The use of dull and/ or
dirty blades can increase the saw loading causing the
operator to push harder which promotes twisting.
Caution! Laceration Hazard. Keep hands away from
cutting areas. Keep hands away from blades. Never place
hands in front of or behind the path of the blade while
cutting. Do not reach underneath work while blade is
rotating. Do not attempt to remove cut material when blade
is moving.
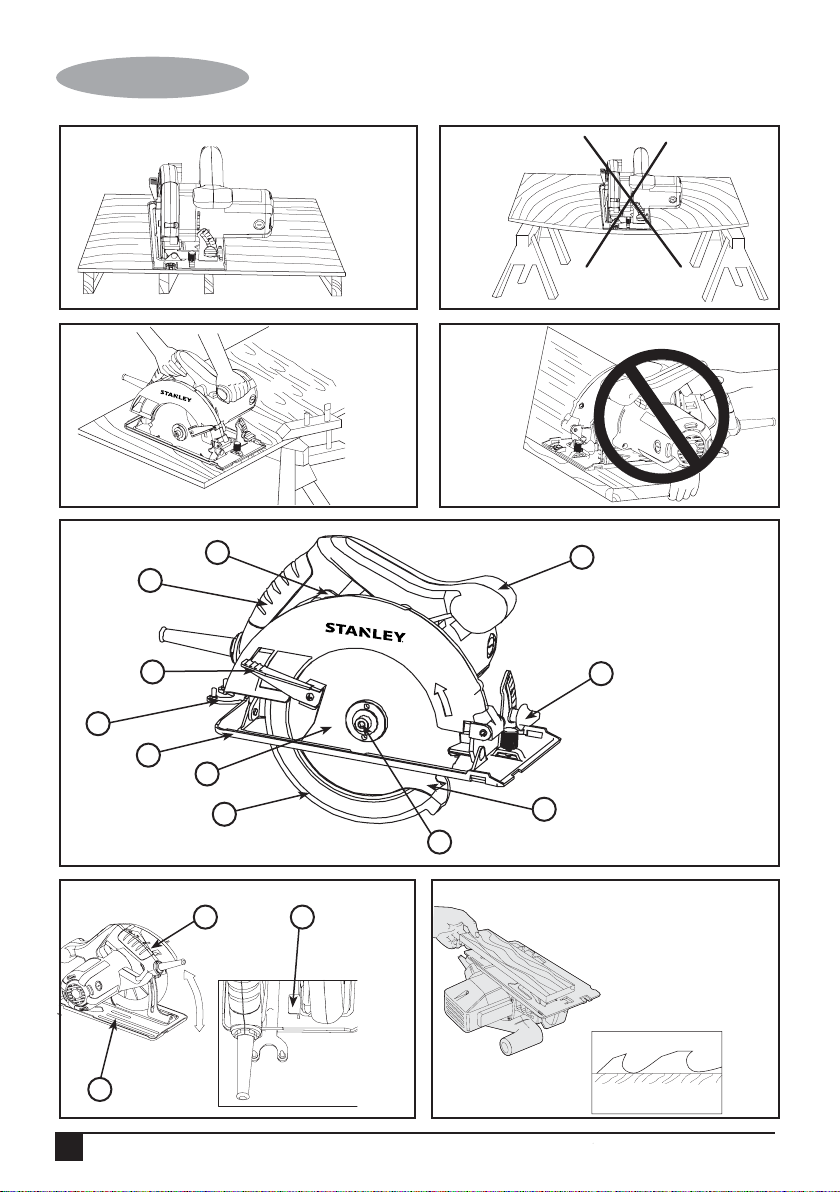
• Support large panels. Large panels must be supported
as shown (Fig. A) in this manual to minimize the risk of
blade pinching and kickback. Material supported only at
the ends (Fig. B) will lead to blade pinching. When
cutting operation requires the resting of the saw on the
workpiece, the saw shall be rested on the larger portion
and the smaller piece cut off.
• Use only correct blades and blade assembly
components when mounting blades. Do not use
blades with incorrect size holes. Never use defective or
8
incorrect blade washers or bolts. Follow blade assembly
procedures.
Saw blades
• Do not use blades of larger or smaller diameter than
recommended. For the proper blade rating refer to the
technical data. Use only the blades specified in this
manual, complying with EN 847-1.
Warning! Never use abrasive wheels.
Safety of others
• This appliance is not intended for use by persons
(including children) with reduced physical, sensory or
mental capabilities, or lack of experience and knowledge,
unless they have been given supervision or instruction
concerning use of the appliance by a person responsible
for their safety.
• Children should be supervised to ensure that they do not
play with the appliance.
Vibration
The declared vibration emission values stated in the
technical data and the declaration of conformity have been
measured in accordance with a standard test method
provided by EN 60745 and may be used for comparing one
tool with another. The declared vibration emission value may
also be used in a preliminary assessment of exposure.
Warning! The vibration emission value during actual use of
the power tool can differ from the declared value depending
on the ways in which the tool is used. The vibration level
may increase above the level stated.
When assessing vibration exposure to determine safety
measures required by 2002/44/EC to protect persons
regularly using power tools in employment, an estimation of
vibration exposure should consider, the actual conditions of
use and the way the tool is used, including taking account of
all parts of the operating cycle such as the times when the
tool is switched off and when it is running idle in addition to
the trigger time.
• Adjustments. Before cutting be sure depth and bevel
adjustments are tight.
• Support and secure the work properly. Insure that the
material to be cut is clamped (Fig. C), and solidly
Page 9

(Original instructions)
ENGLISH
supported and balanced on a strong, stable and level
work surface. Support the work so that the wide portion
of the saw shoe is on the portion of the material that
doesn’t fall after the cut is made. Never hold cut off
piece by hand (Fig. D). Kickback from blade pinch can
result. Keep both hands on saw at all times.
• Stay alert and exercise control. Keep body positioned
to one side of blade. Always maintain a firm grip and
control of saw with both hands. Do not change hand grip
or body position while saw is running. Take precaution to
avoid injury from cut off pieces and other falling material
during operation.
Danger! Release switch immediately if blade
binds or saw stalls.
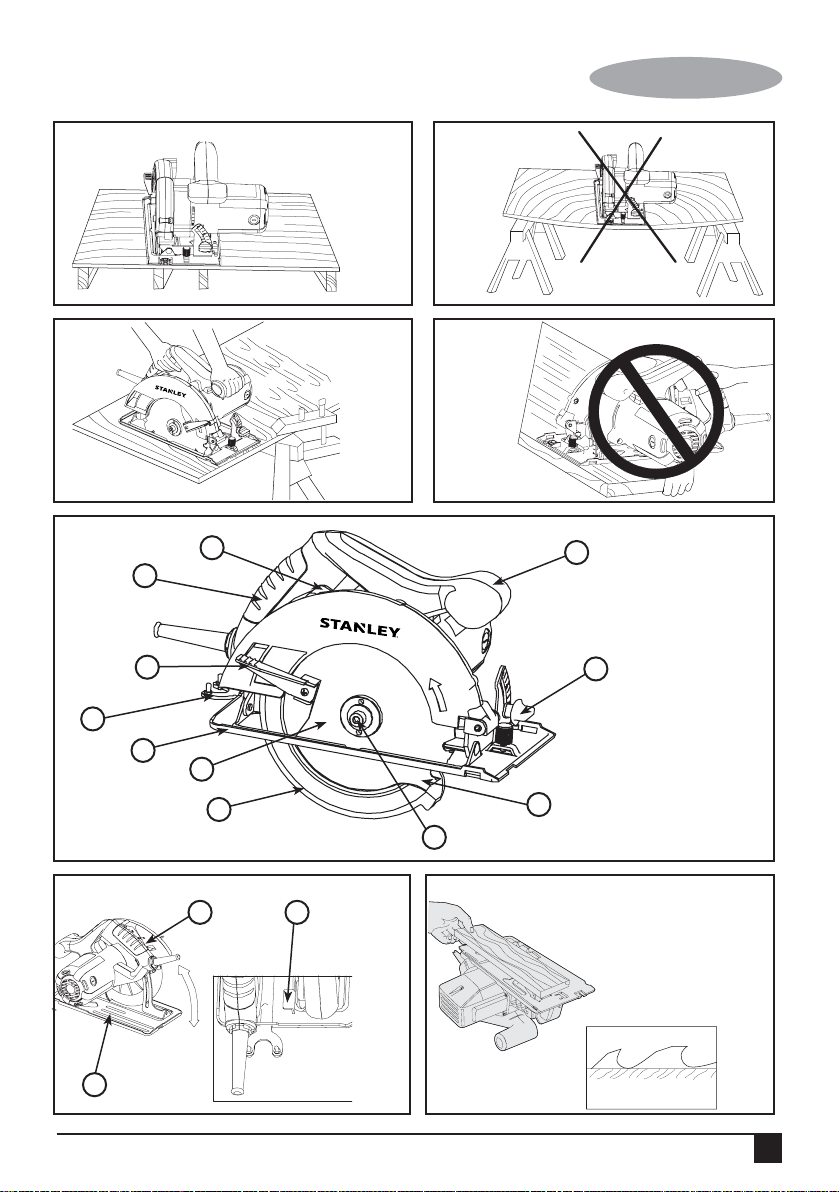
Features (Fig. E)
This tool includes some or all of the following features.
1. On/Off Switch
2. Main Handle
3. Secondary Handle
4. Shoe
5. Saw Blade
6. Saw Blade Guard
7. Blade Guard Retracting Lever
8. Saw Blade Spanner Wrench
9. Bevel Adjustment Knob
10. Outer Washer
11. Blade Retaining Screw
Saw Blade Hex Wrench (Shown on Fig.I)
18. Rip Fence (Shown on Fig. M)
Inner Flange (Shown on Fig. J)
Assembly/adjustment Set-up
Warning! Always unplug saw from power supply
before any of the following operations.
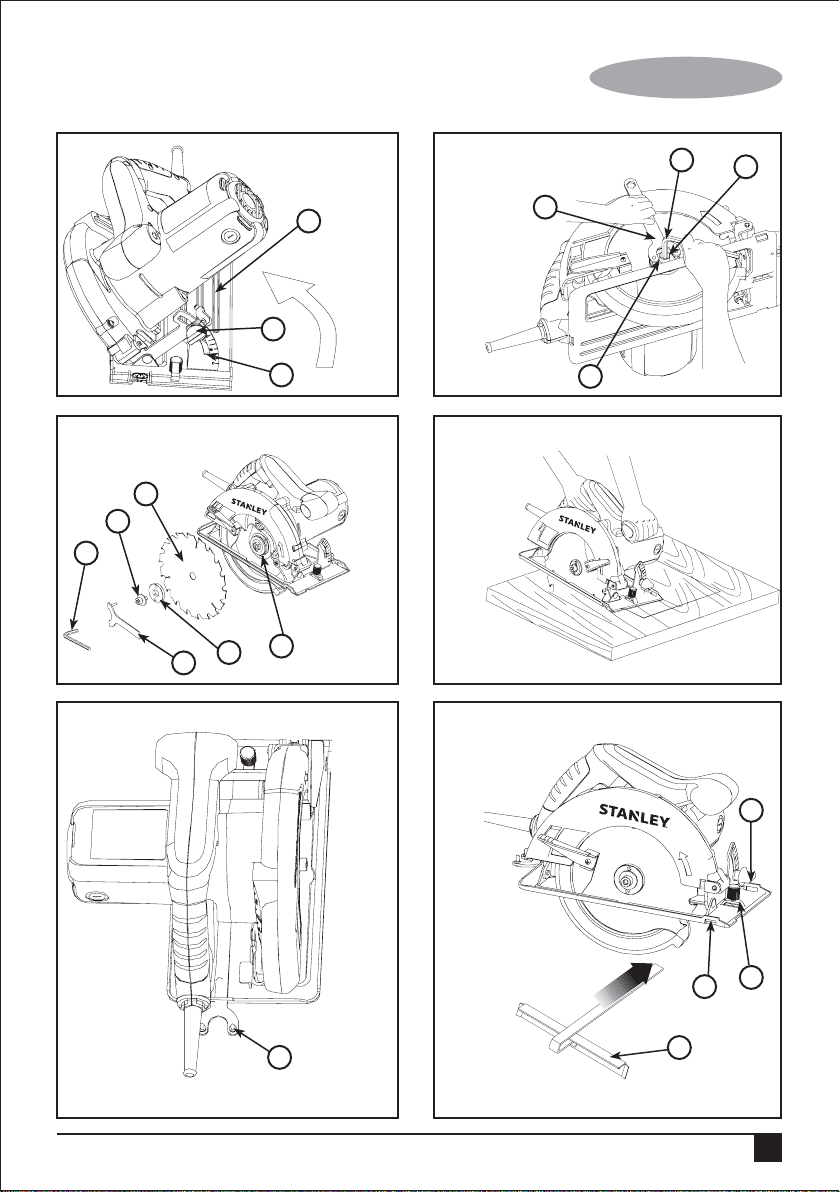
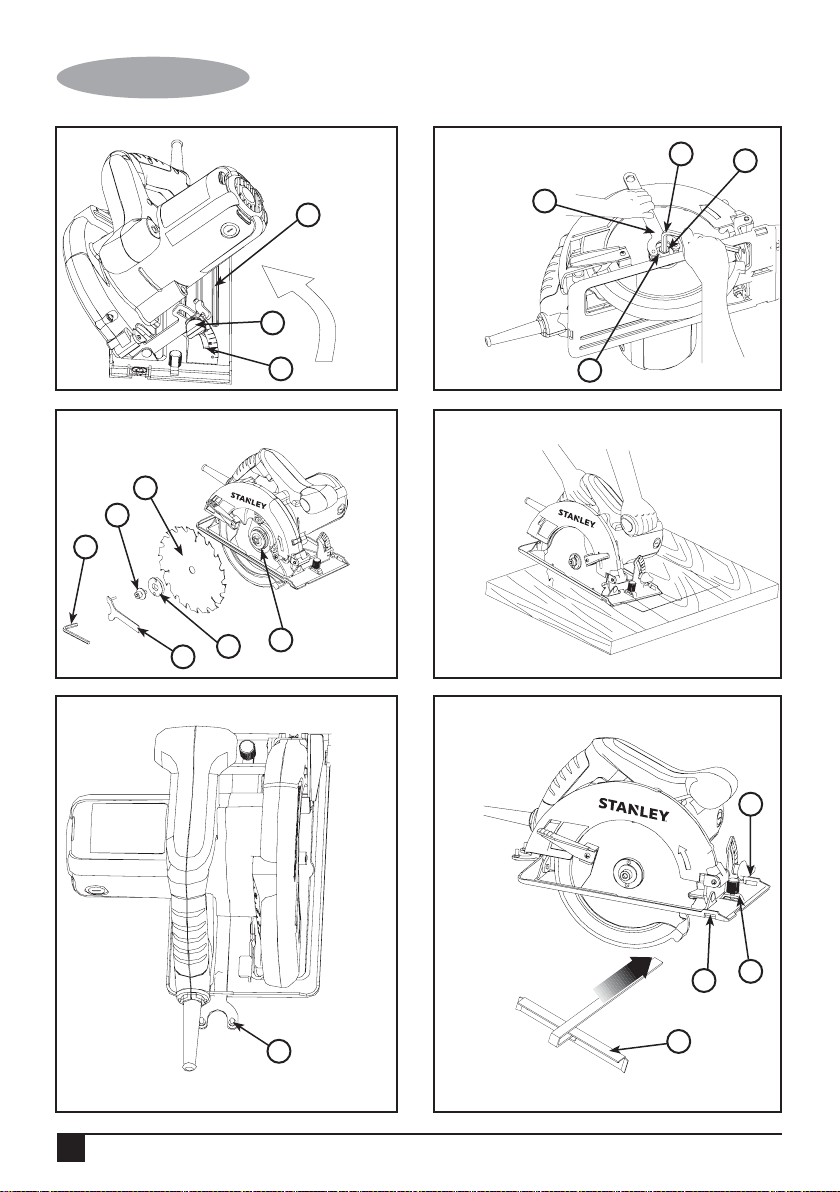
Adjusting the depth of cut (Fig. F and G)
The depth of cut should be set according to the thickness of
the workpiece.
• Loosen the lever (12) to unlock the saw shoe.
• Move the saw shoe (4) into the desired position. The
corresponding depth of cut can be read from the scale (13).
• Tighten the lever to lock the saw shoe in place.
• Set depth adjustment of saw such that one tooth of the
blade projects below the workpiece as shown in Fig. G.
Adjusting the bevel angle (Fig. H)
This tool can be set to bevel angles between 0° and 45°
• Loosen the locking knob (9) to unlock the saw shoe.
• Move the saw shoe (4) into the desired position. The
corresponding bevel angle can be read from the scale
(14).
• Tighten the locking knob to lock the saw shoe in place.
Attaching the blade (Fig. I and J)
• To prevent spindle rotation engage the protrusions of the
spanner wrench (8) into the holes in the outer washer
(10) as shown in Fig. I.
• Loosen and remove the blade retaining screw (11) by
turning the hex wrench (15) counter- clockwise.
• Remove the outer washer.
• Check and re-assembly inner flange (20) on spindle (16).
Insure the correct side of inner flange (20) faces outward
and match saw blade with diameter arbor well.
• Place the saw blade (5) onto the inner flange (20),
making sure that the arrow on the blade points in the
same direction as the arrow on the tool.
• Fit the outer washer (10) on the spindle.
• Insert the blade retaining screw (11) into the hole in the
spindle.
• Prevent spindle rotation by engaging the spanne wrench
into the holes of the outer washer.
• Securely tighten the blade retaining screw by holding the
spanner wrench and turning hex wrench clockwise to
tighten the blade retaining screw.
Warning! Inner flange (20) respectively marked
with “19” and “20”, match the saw blade (5) with
19mm and 20mm diameter arbor.
Removing the blade
To prevent spindle rotation, engage the protrusions of the
spanner wrench (8) into the holes in the outer washer (10).
9
Page 10
ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
• Loosen and remove the blade retaining screw (11) by
turning it counterclockwise using the hex wrench (15).
• Remove the outer washer (10).
• Remove the saw blade (5). Warning! To reduce the risk
of serious personal injury, read, understand and follow
all important safety warnings and instructions prior to
using tool.
General Cuts
Guard against kickback
With unit unplugged, follow all assembly, adjustment and set
up instructions. Make sure lower guard operates. Select the
proper blade for the material to be cut.
• Measure and mark work for cutting.
• Support and secure work properly (See Safety Rules
and Instructions).
• Use appropriate and required safety equipment (See
Safety Rules).
• Secure and maintain work area (See Safety Rules).
• With plug inserted and guard closed, make sure switch
turns saw on and off.
Warning! It is important to support the work
properly and to hold the saw firmly to prevent loss
of control which could cause personal injury. Fig.
C illustrates recommended hand position.
Operation
Switch
• To operate the tool, depress the trigger switch (1). The
tool will continue to run as long as the trigger is
depressed.
• To turn the tool off, release the trigger switch (1). There
is no provision for locking the tool on, and the switch
should never be locked on by any other means.
Sawing
Warning! To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury,always hold the tool with both hands.
• Let the blade run freely for a few seconds before starting
the cut.
• Apply only a gentle pressure to the tool while performing
the cut.
• Work with the shoe pressed against the workpiece.
Hints For Optimum Use
• As some splintering along the line of cut on the top side
of the workpiece cannot be avoided, cut on the side
where splintering is acceptable.
• Where splintering is to be minimized, e.g. when cutting
laminates, clamp a piece of plywood onto the top of the
workpiece.
Pocket cutting (Fig. K)
Pocket cutting is used to cut a hole in a piece of material
without cutting from the side.
• Measure and mark work.
• Tilt saw forward and rest front of the shoe on material to
be cut. Align so that cut will begin at the back of the
drawn rectangle shown in Fig. K.
• Using the retracting lever, retract blade guard to an
upward position, with the blade just clearing the material,
start motor and gradually lower the saw into the material.
Warning! As blade starts cutting the material,
release the retracting lever immediately.
• Never tie the blade guard in a raised position.
• When the shoe rests flat on the material being cut,
complete the cut in forward direction.
• Allow the blade to come to a complete stop before lifting
saw from material.
• When starting each new cut, repeat the above steps
Wrench storage (Fig. L)
The spanner wrench (8) can be stored on the saw shoe as
shown in Fig. L.
Attaching and removing the rip fence (Fig. M)
The rip fence is used to saw in a straight line parallel to the
edge of the working piece.
Attaching
• Loosen the locking knob (17).
• Insert the rip fence (18) through the openings (19).
• Slide the rip fence into the desired position.
10
Page 11

(Original instructions)
ENGLISH
• Tighten the locking knob.
Removing
• Loosen the locking knob.
• Pull the rip fence out of the tool. Note: If you do not have
a proper fitting fence, use a straight edge guide in
contact with the edge of the shoe to improve accuracy of
cut and reduce the possibility of binding and kickback.
Dust extraction
An adaptor is required to connect a vacuum cleaner or dust
extractor to the tool.
• Insert the dust extraction adaptor into the saw dust
outlet (9).
• Connect the vacuum cleaner hose to the adaptor.
Accessories
The performance of your tool depends on the accessory
used. Stanley and Piranha accessories are engineered to
high quality standards and designed to enhance the
performance of your tool. By using these accessories you
will get the very best from your tool.
Warning! The use of any accessory not
recommended for use with this tool could be
hazardous. Use only 185mm blades with 19mm
or 20mm diameter arbor.
Maintenance
Your tool has been designed to operate over a long period
of time with a minimum of maintenance. Continuous
satisfactory operation depends upon proper tool care and
regular cleaning.
Warning! Before performing any maintenance,
switch off and unplug the tool.
• Regularly clean the ventilation slots in your tool using a
soft brush or dry cloth.
• Regularly clean the motor housing using a damp cloth.
Do not use any abrasive or solvent-based cleaner.
Important! To assure product SAFETY and
RELIABILITY, repairs, maintenance and adjustment
(other than those listed in this manual) should be
performed by authorized service centers or other
qualified service personnel, always using identical
replacement parts.
Lubrication
Stanley tools are properly lubricated at the factory and are
ready for use.
Service Information
STANELY offers a full network of company-owned and
authorized service locations. All STANLEY Service Centers
are staffed with trained personnel to provide customers with
efficient and reliable power tool service. For more
information about our authorized service centers and if you
need technical advice, repair, or genuine factory
replacement parts, contact the STANLEY location nearest
you.
LpA (sound pressure) dB(A) 92.5
Uncertainty (K) dB(A) 3
LWA (sound power) dB(A) 103.5
Uncertainty (K) dB(A) 3
Vibration total values (triax vector sum) according to
EN 60745:
Cutting wood (a
uncertainty (K) = 1.5 m/s2
The vibration emission level given in this information sheet
has been measured in accordance with a standardised test
given in EN 60745 and may be used to compare one tool
with another. It may be used for a preliminary assessment of
exposure.
applications, with different accessories or poorly maintained,
the vibration emission may differ. This may significantly
increase the 1.5exposure level over the total working period.
An estimation of the level of exposure to vibration should
also take into account the times when the tool is switched
off or when it is running but not actually doing the job. This
may significantly reduce the exposure level over the total
working period.
Identify additional safety measures to protect the operator
from the effects of vibration such as: maintain the tool and
the accessories, keep the hands warm, organisation of work
patterns.
h, W
Warning: The declared vibration emission level
represents the main applications of the tool.
However if the tool is used for different
2
) = 3.3 m/s
11
Page 12

ENGLISH
(Original instructions)
Protecting the environment
Separate collection. This product must not be
disposed of with normal household waste.
Should you find one day that your Stanley product needs
replacement, or if it is of no further use to you, do not
dispose of it with household waste. Make this product
available for separate collection.
Separate collection of used products and packaging
allows materials to be recycled and used again.
Re-use of recycled materials helps prevent
environmental pollution and reduces the demand for raw
materials.
Local regulations may provide for separate collection of
electrical products from the household, at municipal waste
sites or by the retailer when you purchase a new product.
Stanley provides a facility for the collection and recycling of
Stanley products once they have reached the end of their
working life. To take advantage of this service please return
your product to any authorised repair agent who will collect
them on our behalf.
You can check the location of your nearest authorised repair
agent by contacting your local Stanley office at the address
indicated in this manual. Alternatively, a list of authorised
Stanley repair agents and full details of our after-sales
service and contacts are available on the Internet at:
www.2helpU.com
Two years full warranty
If your Stanley product becomes defective due to faulty
materials or workmanship within 24 months from the date of
purchase, Stanley Europe guarantees to replace all defective
parts free of charge or – at our discretion – replace the unit
free of charge provided that:
• The product has not been misused and has been used in
accordance with the instruction manual.
• The product has been subject to fair wear and tear;
• Repairs have not been attempted by unauthorised
persons;
• Proof of purchase is produced.
• The Stanley product is returned complete with all original
components
If you wish to make a claim, contact your seller or check the
location of your nearest authorised Stanley repair agent in
the Stanley catalogue or contact your local Stanley office at
the address indicated in this manual. A list of authorised
Stanley repair agents and full details of our after sales
service is available on the internet at:www.stanleytools.com
12
Page 13
(Instructions initiales)
FIG. A FIG. B
FIG. C FIG. D
FRANÇAIS
FIG. E
1
2
7
8
4
10
6
11
FIG. F FIG. G
13 12
4
3
9
5
13
Page 14
FRANÇAIS
(Instructions initiales)
FIG. H FIG. I
4
9
14
FIG. J
FIG. K
5
11
15
16
10
8
FIG. L
FIG. M
15
11
8
10
14
19
17
19
8
18
Page 15

Fiche technique
Spécifications STSC1718
Tension 230V
Fréquence 50Hz
Puissance 1700W
Vitesse à vide 5500/min (rpm)
Profondeur de coupe maximale 62mm À 90°
46mm À 45°
Utilisation
Votre scie STANLEY est conçue pour scier le bois et les
produits à base de bois. Cet outil est destiné à un usage
privé uniquement.
• Pour les outils destinés à couper le bois, instructions
pour l’utilisation correcte du système capteur de
poussière.
• Pour les outils destinés à couper le bois, instructions
pour porter un masque antipoussières.
• Instructions pour n’utiliser que les lames de scie
recommandées.
• Instructions pour toujours porter des protecteurs auditifs.
NE RETOURNEZ PAS CET APPAREIL AU MAGASIN,
contactez d’abord le bureau local Stanley ou le centre de
service agréé le plus proche.
Règles générales de sécurité
Attention! Lire et assimiler toutes les
instructions. Le non-respect de toutes les
instructions mentionnées ci-dessous peut
entraîner un choc électrique, un incendie et/ou des
blessures graves.
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS
Consignes de sécurité
Consignes générales de sécurité concernant les outils
électroportatifs
Attention! Lire avec attention tous les
avertissements et toutes les instructions. Le
non-respect des avertissements et des
instructions indiquées ci-dessous peut entraîner un choc
électrique, un incendie et/ou des blessures graves
Conservez ces consignes et ces instructions pour
référence ultérieure.
La notion "d’outil électroportatif" mentionnée par la suite se
rapporte à des outils électriques raccordés au secteur (avec
câble) ou fonctionnant avec piles (sans fil).
(Instructions initiales)
1. Sécurité de la zone de travail
a. Maintenir la zone de travail propre et bien éclairée.
Un lieu de travail en désordre ou mal éclairé augmente le
risque d’accidents.
b. Ne pas utiliser d’outils électroportatifs dans un
environnement présentant des risques d’explosion
ni en présence de liquides, gaz ou poussières
inflammables. Les outils électroportatifs génèrent des
étincelles risquant d’enflammer les poussières ou les
vapeurs.
c. Pendant l’utilisation d’un outil électroportatif, les
enfants et autres personnes présentes doivent rester
éloignés. En cas d’inattention, vous risquez de perdre le
contrôle de l’outil.
2. Sécurité électrique
a. La fiche de l’outil électrique doit être compatible
avec la prise d’alimentation, Ne modifiez la fiche en
aucun cas. N’utilisez pas d’adaptateurs avec des
outils ayant une prise de terre. Le respect de ces
consignes réduit le risque de choc électrique.
b. Eviter le contact physique avec des surfaces mises à
la terre telles que tuyaux, radiateurs, fours et
réfrigérateurs. Le risque de choc électrique augmente si
votre corps est relié à la terre.
c. Ne pas exposer les outils électroportatifs à la pluie
ou à l’humidité. La pénétration d’eau dans un outil
électroportatif augmente le risque de choc électrique.
d. Ne pas maltraiter le câble d’alimentation. Ne jamais
utiliser le câble pour porter l’outil, et ne le tirez pas
pour débrancher l’outil. Maintenir le câble éloigné
des sources de chaleur, de la graisse, des bords
coupants et des pièces en rotation. Un câble
endommagé ou emmêlé augmente le risque de choc
électrique.
e. Lorsque vous utilisez l’outil électroportatif à
l’extérieur, utilisez une rallonge homologuée pour
une utilisation à l’extérieur. L’utilisation d’une rallonge
électrique homologuée pour les travaux à l’extérieur
réduit le risque de choc électrique.
f. Si l’outil doit être utilisé dans un endroit humide,
utilisez un dispositif différentiel à courant résiduel
(DDR). L’utilisation d’un tel dispositif réduit le risque de
choc électrique. Remarque: Le terme “dispositif
différentiel à courant résiduel (DDR)” peut être remplacé
par “disjoncteur de fuite à la terre (DDFT)” ou par
“interrupteur différentiel de sécurité (ELCB)”.
3. Sécurité personnelle
a. Restez vigilant, surveillez ce que vous faites et faites
preuve de bon sens quand vous utilisez un outil.
N’utilisez pas un outil électroportatif lorsque vous
êtes fatigué ou après avoir consommé de l’alcool ou
pris des médicaments. Un moment d’inattention en
utilisant l’outil peut entraîner de graves blessures.
FRANÇAIS
15
Page 16
FRANÇAIS
(Instructions initiales)
b. Portez un équipement de protection. Portez toujours
des lunettes de protection. Selon le travail à
effectuer, le port d’un équipement de protection tel que
masque anti-poussières, chaussures de sécurité
antidérapantes, casque ou protection auditive, réduit le
risque de blessures.
c. Evitez tout démarrage imprévu. L’interrupteur de
l’outil doit être en position d’arrêt (off) avant
d’effectuer le branchement à l’alimentation et/ou au
bloc batterie, de ramasser l’outil ou de le porter.
Porter ou brancher un outil électrique dont l’interrupteur
est en position Marche (on) est une invite à l’accident.
d. Retirez les outils ou les clés de réglage avant de
mettre l’outil en marche. Une clé ou un outil se
trouvant sur une partie en rotation peut causer des
blessures.
e. Adoptez une position confortable. Adoptez une
position stable et gardez votre équilibre en
permanence. Vous contrôlerez mieux l’outil dans des
situations inattendues.
f. Portez des vêtements appropriés. Ne portez pas de
vêtements amples ou de bijoux. N’approchez pas les
cheveux, vêtements ou gants des pièces en
mouvement. Les vêtements amples, les bijoux ou les
cheveux longs peuvent s’accrocher dans les pièces en
mouvement.
g. En cas d’utilisation d’appareils servant à aspirer ou
à recueillir les poussières, assurez-vous qu’ils sont
correctement raccordés et utilisés. L’utilisation de tels
dispositifs réduit les dangers dus aux poussières.
4. Utilisation des outils électroportatifs et précautions
a. Respectez la capacité de l’outil. Utilisez l’outil
approprié pour le travail à effectuer. Avec un outil
approprié, vous travaillerez mieux et en toute sécurité.
b. N’utilisez pas un outil électroportatif dont
l’interrupteur marche/arrêt est défectueux. Un outil
électroportatif qui ne répond pas à la commande
marche/arrêt est dangereux et doit être réparé.
c. Retirez la fiche de la prise de courant et/ou
débranchez le bloc-batterie avant d’effectuer des
réglages, de changer les accessoires ou de ranger
l’outil. Cette mesure de précaution empêche de mettre
l’outil en marche accidentellement.
d. Rangez les outils électroportatifs hors de la portée
des enfants et les personnes ne connaissant pas
l’outil ne doivent en aucun cas l’utiliser. Les outils
électroportatifs sont dangereux lorsqu’ils sont utilisés par
des personnes non initiées.
e. Entretenez les outils électroportatifs. Vérifiez que
les parties en mouvement fonctionnent
correctement et qu’elles ne sont pas coincées.
Vérifiez qu’il n’y a pas de pièces cassées ou
endommagées susceptibles de nuire au bon
fonctionnement de l’outil. S’il est endommagé, faites
réparer l’outil avant de l’utiliser. De nombreux
16
accidents sont la conséquence d’outils mal entretenus.
f. Les outils de coupe doivent toujours être aiguisés et
propres. Des outils soigneusement entretenus avec des
bords tranchants bien aiguisés se coincent moins
souvent et peuvent être guidés plus facilement.
5. Réparations
a. Faites réparer votre outil électroportatif uniquement par
du personnel qualifié et seulement avec des pièces de
rechange appropriées. Cela garantira le maintien de la
sécurité de votre outil.
6. Etiquettes apposées sur l’outil
L’étiquette apposée sur votre outil peut contenir les
symboles suivants:
Lire le manuel
d’instructions
Utiliser une
protection
oculaire
Utiliser des
protections
auditives
V ........ Volts
A ........
Ampères
W ........
min .....
.....
.....
n
.......
0
Hertz
Watts
minutes
Courtant
alternatif
Courant
continu
Vitesse à
vide
......
Construction
de classe II
....
Borne de
Symbole d’alerte
de sécurité
Rotations
par minute
terre
....
.../min..
Hz .......
Position of date barcode
Le code de la date, comprenant aussi l’année de fabrication,
est imprimé sur le boîtier de l’outil.
Exemple:
2014 XX JN
Année de fabrication
7. Sécurité électrique
Cet outil est doublement isolé; par conséquent,
aucun câble de mise à la terre n’est nécessaire.
Vérifiez si l’alimentation mentionnée sur la plaque
signalétique de l’appareil correspond bien à la tension
présente sur le lieu.
Attention! Si le câble d’alimentation est
endommagé, il doit être remplacé par le fabricant,
par un centre de réparation Stanley agréé ou par
un électricien qualifié, de façon à éviter les dommages
matériels et corporels. En cas de remplacement du câble
d’alimentation par un électricien qualifié mais non agréé par
Stanley, la garantie ne sera pas valable.
Mises en garde supplémentaires pour les
outils électriques
Attention! Consignes de sécurité pour toutes les
scies
Page 17

(Instructions initiales)
FRANÇAIS
Procédures de coupe
Danger! Gardez vos mains en dehors de la zone de
coupe et de la lame. Gardez votre seconde main sur la
poignée auxiliaire, ou sur le boîtier du moteur. Si vos
deux mains tiennent la scie, elles ne peuvent pas être
coupées par la lame.
b. Ne passez pas vos mains en dessous de la pièce. La
protection ne peut pas vous protéger de la lame en
dessous de la pièce.
c. Réglez la profondeur de coupe à l’épaisseur de la
pièce. Seulement moins d’une dent de la lame doit être
visible en dessous de la pièce.
d. Ne tenez jamais la pièce que vous coupez dans vos
mains ou sur votre cuisse. Attachez la pièce sur une
plateforme stable. Il est important de soutenir
correctement la pièce sur laquelle vous travaillez pour
minimiser l’exposition du corps, un blocage de la lame
ou une perte de contrôle.
e. Tenez l’outil électrique par les surfaces de prise
isolées quand vous faites un travail où l’accessoire
de coupe risque d’entrer en contact avec un fil
électrique caché ou son propre cordon. Si
l’accessoire de coupe entre en contact avec un fil sous
tension il peut « électrifier » les parties métalliques
exposées et donner une décharge électrique à
l’utilisateur.
f. Quand vous fendez, servez-vous toujours d’un
guide de coupe longitudinale ou d’un tasseau. Cela
améliore la précision de la coupe et réduit le risque que
la lame se coince.
g. Utilisez toujours des lames avec la dimension et la
forme correcte (diamant versus rond) des trous de
fixation. Les lames qui ne correspondent pas au
dispositif de fixation de la scie tourneront de façon
excentrique, provoquant une perte de contrôle.
h. N’utilisez jamais des rondelles ou des boulons de
lame endommagés ou incorrects. Les rondelles et le
boulon de la lame sont spécialement conçus pour votre
scie, pour une performance optimale et la sécurité de
l’opération.
Causes du recul et mises en garde
• Le recul est la réaction soudaine d’une lame de scie
pincée, coincée ou mal alignée, faisant qu’une scie non
contrôlée se soulève hors de la pièce sur laquelle vous
travaillez vers l’utilisateur.
• Quand la lame est pincée ou coincée par la saignée qui
se referme, la lame s’arrête de tourner et la réaction du
moteur pousse rapidement l’unité vers l’utilisateur.
• Si la lame se tord ou est mal alignée dans la coupe, les
dents sur le bord arrière de la lame peuvent mordre la
surface supérieure du bois faisant que la lame sort de la
saignée et saute en arrière vers l’utilisateur.
• Un recul est le résultat d’une mauvaise utilisation de
l’outil et/ou de procédures ou conditions de
fonctionnement incorrectes et il peut être évité en
prenant les précautions ci-dessous.
a. Tenez fermement la scie avec les deux mains et
positionnez votre corps et votre bras de façon à ce
que vous puissiez résister à la force du recul. La
force du recul peut être contrôlée par l’utilisateur si les
précautions adéquates sont prises.
b. Quand la lame est coincée, ou quand vous
interrompez la coupe pour une raison quelconque,
relâchez la gâchette et tenez la scie dans le matériau
sans la bouger jusqu’à ce que la lame s’arrête
complètement. N’essayez jamais d’enlever la scie de
la pièce ou de retirer la scie en arrière alors que la
lame est encore en mouvement sinon un recul peut
se produire. Investiguez et prenez les mesures
correctives pour éliminer la cause du blocage de la lame.
c. Quand vous redémarrez la scie dans la pièce,
centrez la lame de scie dans la saignée et vérifiez
que les dents de la scie ne mordent pas dans le
matériau. Si la lame de scie est coincée, elle peut sortir
de la pièce ou provoquer un recul lorsque l’outil est
redémarré.
d. Soutenez les panneaux pour minimiser le risque que
la lame soit pincée et d’un recul. Les panneaux de
grande taille ont tendance à plier sous leur propre poids.
Un support doit être placé sous le panneau des deux
côtés, près du trait de coupe et près du bord du
panneau.
e. N’utilisez pas une lame usée ou endommagée. Les
lames non aiguisées ou incorrectement réglées
produisent une saignée étroite causant une friction
excessive, un blocage de la lame et un recul.
f. Les leviers de verrouillage du réglage de la
profondeur et de l’angle de la lame doivent être
fermement serrés avant de commencer la coupe. Si
le réglage de la lame change pendant que vous coupez,
cela peut causer un blocage et un recul.
g. Faites particulièrement attention quand vous faites
une découpe avec évidemment dans des murs
existants ou d’autres surfaces aveugles. La lame
saillante risque de couper des objets qui peuvent causer
un recul.
Fonction de la protection inférieure
a. Vérifiez la bonne fermeture de la protection
inférieure avant chaque utilisation. Ne vous servez
pas de la scie si la protection inférieure ne bouge
pas aisément et ne se ferme pas instantanément. Ne
jamais fixer ni attacher la protection inférieure dans la
position ouverte. Si vous faites tomber la scie
accidentellement, la protection inférieure risque de se
fausser. Soulevez la protection inférieure avec la
poignée rétractable et vérifiez qu’elle bouge librement et
ne touche pas la lame ou une autre pièce de la scie,
dans tous les angles et profondeurs de coupe.
17
Page 18

FRANÇAIS
(Instructions initiales)
b. Vérifiez le fonctionnement du ressort de la
protection inférieure. Si la protection et le ressort ne
fonctionnent pas correctement, vous devez les réviser
avant de vous servir de la scie. Il se peut que la
protection inférieure fonctionne mollement à cause de
pièces endommagées, de dépôts collants ou d’une
accumulation de débris.
c. La protection inférieure peut être rétractée
manuellement uniquement pour les coupes
spéciales comme les coupes plongeantes et les
coupes composées. Soulevez la protection inférieure
en rétractant la poignée et dès que la lame mord le
matériau, la protection inférieure doit être relâchée. Pour
tous les autres types de coupe, la protection inférieure
doit pouvoir fonctionner automatiquement.
d. Regardez toujours si la protection inférieure couvre
la lame avant de poser la scie sur un établi ou par
terre. Quand la lame non protégée continue de tourner
la scie se déplace en arrière, coupant tout sur son
passage. Sachez combien de temps il faut à la lame
pour s’arrêter de tourner après avoir relâché la gâchette.
Risques résiduels
Des risques résiduels supplémentaires qui ne sont peut-être
pas mentionnés dans les consignes de sécurité ci-incluses
peuvent exister quand vous vous servez de l’outil. Ces
risques peuvent être dus à un mauvais usage, une
utilisation trop prolongée etc.
Même en appliquant les règles de sécurité et en mettant en
place les dispositifs de sécurité, certain risques résiduels ne
peuvent pas être complètement éliminés. Ils comprennent :
• Se blesser en touchant les parties tournantes/mobiles.
• Se blesser en changeant les pièces, les lames ou les
accessoires.
• Se blesser en travaillant trop longtemps avec un outil.
Quand vous vous servez d’un outil pendant de longues
périodes pensez à faire des pauses régulières.
• Perte de l’acuité auditive.
• Problèmes de santé dus à l’inhalation de la poussière
produite par votre outil (exemple : travail sur du bois,
plus particulièrement le chêne, le hêtre et les panneaux
MDF).
Consignes de sécurité / définitions
Il est important de lire et comprendre ce mode d’emploi. Les
informations qu’il contient expliquent les précautions à
prendre pour votre sécurité et éviter les problèmes. Les
symboles ci-dessous sont utilisés pour vous aider à
reconnaître ces informations.
Danger! Indique une situation immédiatement
dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée,
provoquera la mort ou des blessures graves.
Attention! Indique une situation potentiellement
dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, peut
entraîner la mort ou des blessures graves.
Précaution! Indique une situation potentiellement
dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, peut
entraîner des blessures légères ou modérées.
Précaution! Utilisé sans le symbole
d’avertissement de sécurité, indique une situation
potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas
évitée, peut entraîner des dégâts matériels.
Règles de sécurité supplémentaires pour les
scies circulaires
Attention ! La poussière créée par le ponçage,
le sciage, le meulage, le perçage électrique et
d’autres activités de construction contient des produits
chimiques reconnus comme pouvant causer un cancer,
des malformations congénitales ou d’autres troubles de
l’appareil reproducteur. Quelques exemples des ces
produits chimiques sont :
• Le plomb dans les peintures à base de plomb,
• La poussière de silice cristalline dans la brique et le
ciment et d’autres produits de maçonnerie,
• L’arsenic et le chrome dans le bois chimiquement traité
(CCA).
Les risques que vous courez avec ces types d’exposition
varient, suivant la fréquence avec laquelle vous faites ce
type de travaux. Pour réduire votre exposition à ces produits
chimiques :
18
Page 19

(Instructions initiales)
FRANÇAIS
• Travaillez dans un endroit bien ventilé et avec un
équipement de sécurité aux normes, comme le masque
antipoussières spécialement conçu pour filtrer les
particules microscopiques.
• Évitez le contact prolongé avec la poussière émise
par ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage électriques
et autres activités de construction. Portez des
vêtements de protection et lavez la peau exposée à
l’eau et au savon. En laissant la poussière pénétrer
dans votre bouche, vos yeux, ou rester sur la peau
favorise l’absorption des produits chimiques nocifs.
Précaution ! Portez des protecteurs auditifs
appropriés. Dans certaines conditions et durées
d’utilisation, le bruit de cet outil peut contribuer à
une perte de l’acuité auditive.
• Quand la protection inférieure accroche une surface
en dessous du matériau que vous sciez cela peut
réduire momentanément votre contrôle de l’outil. La
scie peut partiellement se soulever en dehors de la
coupe, augmentant le risque que la lame se torde.
Assurez-vous qu’il y a suffisamment d’espace sous la
pièce sur laquelle vous travaillez.
• Quand il est nécessaire de soulever la protection
inférieure manuellement, servez-vous du levier de
rétraction.
• Gardez les lames propres et aiguisées. Des lames
bien coupantes minimisent le risque de caler et de recul.
L’utilisation de lames usées et/ou sales accroît la charge
sur la scie si bien que l’utilisateur appuie plus fort et la
lame peut se tordre plus facilement.
Précaution ! Risque de lacération. Gardez les mains loin
de la zone de coupe. Gardez les mains éloignées de la
lame. Ne placez jamais les mains devant ou derrière la
trajectoire de la lame pendant que vous sciez. Ne passez
pas les mains en dessous de la pièce quand la lame tourne.
N’essayez pas d’enlever le matériau découpé quand la lame
est en mouvement.
• Soutenez les panneaux de grande taille. Les
panneaux de grande taille doivent être soutenus comme
illustré (Fig. A) dans ce manuel pour minimiser le risque
de pincement et de recul de la lame. Un matériau
soutenu seulement aux extrémités (Fig. B) facilitera le
pincement de la lame. Quand l’opération de sciage
demande que la scie repose sur la pièce, la scie devra
reposer sur la plus grande portion, et la portion plus
petite est celle qui sera coupée.
• N’utilisez que des lames et des éléments de fixation
de lame corrects quand vous montez les lames.
N’utilisez pas des lames avec des trous de la
mauvaise dimension. N’utilisez jamais des rondelles ou
boulons de lame défectueux ou incorrects. Suivez la
procédure de montage de la lame.
Lames de scie
• N’utilisez pas des lames d’un diamètre plus grand ou
plus petit que celui recommandé. Pour la bonne
dimension de lame reportez-vous à la fiche technique.
N’utilisez que les lames spécifiées dans ce mode
d’emploi, conformes à la norme EN 847-1.
Attention! N’utilisez jamais des roues abrasives.
Sécurité des autres
• Cet outil n’est pas fait pour être utilisé par des personnes
(y compris les enfants) avec des capacités physiques,
sensorielles ou mentales réduites, ou un manque
d’expérience et de connaissances, sauf si elles
bénéficient, par l’intermédiaire d’une personne
responsable de leur sécurité, d’une supervision ou
d’instructions concernant l’utilisation de l’appareil.
• Les enfants doivent être surveillés pour s’assurer qu’ils
ne jouent pas avec l’appareil.
Vibrations
Les valeurs d’émission des vibrations déclarées
mentionnées dans la fiche technique et la déclaration de
conformité ont été mesurées conformément à la méthode de
test standard fournie par la norme EN 60745 et peuvent être
utilisées pour comparer avec d’autres outils. La valeur
d’émission des vibrations déclarée peut aussi servir pour
une estimation préliminaire de l’exposition.
Attention! La valeur d’émission des vibrations pendant
l’utilisation actuelle de l’outil électrique peut différer de la
valeur déclarée suivant la manière dont l’outil est utilisé. Le
niveau des vibrations peut augmenter au dessus du niveau
déclaré.
Quand une estimation de l’exposition aux vibrations est faite
afin de déterminer les mesures de sécurité requises par la
norme 2002/44/EC pour protéger les personnes employées
utilisant régulièrement des outils électriques, cette estimation
doit considérer les conditions actuelles d’utilisation et la
manière dont l’outil est utilisé, et tenir compte également de
tous les stades du cycle de fonctionnement, comme les
périodes où l’outil est éteint et celles où il tourne au ralenti,
en plus des périodes de fonctionnement à plein régime.
• Réglages : Avant de scier assurez-vous que les réglages
de profondeur et d’inclinaison sont resserrés.
19
Page 20

FRANÇAIS
(Instructions initiales)
• Soutenez et fixez correctement la pièce à scier.
Assurez-vous que le matériau qui doit être coupé est
fixé (Fig. C) et fermement soutenu, en bon équilibre sur
une surface de travail solide, stable et plane. Soutenez
la pièce sur laquelle vous travaillez de façon à ce que la
portion large de la semelle de guidage de la scie repose
sur la partie du matériau qui ne tombe pas quand la
coupe est terminée. Ne tenez jamais le morceau à scier
à la main (Fig. D).Il peut y avoir un recul dû au
pincement de la lame. Gardez tout le temps les deux
mains sur la scie.
• Soyez alerte et gardez le contrôle. Veillez à ce que
votre corps soit positionné d’un côté de la lame.
Tenez toujours fermement et gardez le contrôle de la
scie avec les deux mains. Ne changez pas de main ni la
position du corps quand la scie tourne. Prenez la
précaution d’éviter de vous blesser avec les chutes
sciées et les autres morceaux de matériau qui tombent
pendant l’opération.
Danger! Relâchez immédiatement le bouton si la lame se
bloque ou si la scie cale.
Caractéristiques (Fig. E)
Cet outil comprend certains ou tous les éléments suivants.
1. Bouton Marche/Arrêt
2. Poignée à main
3. Poignée secondaire
4. Semelle
5. Lame de scie
6. Protection de la lame de scie
7. Levier de rétraction de la protection de la lame
8. Clé de serrage de la lame de scie
9. Bouton de réglage de l’angle
10. Rondelle extérieure
11. Vis de fixation de la lame
Clé hexagonale de la lame de scie (voir Fig.I)
18. Guide de coupe longitudinale (voir Fig. M)
Bride intérieure (voir Fig. J)
Montage / Réglage
Attention! Débranchez toujours la scie de sa source
d’alimentation avant les opérations suivantes.
Régler la profondeur de la coupe (Fig. F et G)
La profondeur de la coupe doit être réglée à l’épaisseur de
la pièce.
• Desserrez le levier (12) pour déverrouiller la semelle de
la scie.
• Placez la semelle de la scie (4) dans la position désirée.
La profondeur correspondante de la coupe peut être lue
sur la règle graduée (13).
• Resserrez le levier pour verrouiller la semelle de la scie
en place.
• Faites le réglage de la profondeur de la scie de façon à
ce qu’une dent de la lame dépasse sous la pièce comme
illustré à la Fig. G.
Régler l’angle d’inclinaison (Fig. H)
Sur cet outil l’angle d’inclinaison peut être réglé entre 0° et
45°
• Desserrez le bouton de verrouillage (9) pour
déverrouiller la semelle de la scie.
• Placez la semelle de la scie (4) dans la position désirée.
L’angle d’inclinaison correspondant peut être lu sur la
règle graduée (14).
• Serrez le bouton de verrouillage pour verrouiller en place
la semelle de la scie.
Attacher la lame (Fig. I et J)
• Pour empêcher la rotation de la broche engagez les
protubérances de la clé (8) dans les trous de la rondelle
extérieure (10) comme illustré à la Fig. I.
• Desserrez et enlevez la vis de fixation (11) de la lame en
tournant la clé hexagonale (15) dans le sens antihoraire.
• Déposez la rondelle extérieure.
• Vérifiez et remontez la bride intérieure (20) sur la broche
(16). Assurez-vous que le bon côté de la bride intérieure
(20) est face à l’extérieur et fait correspondre la lame de
scie avec le diamètre de la broche.
• Placez la lame de scie (5) sur la bride intérieure (20), en
vérifiant que la flèche sur la lame pointe dans la même
direction que la flèche sur l’outil.
• Installez la rondelle extérieure (10) sur la broche.
• Insérez la vis de fixation (11) de la lame dans le trou
aménagé dans la broche.
• Empêchez la rotation de la broche en engageant la clé
dans les trous de la rondelle extérieure.
• Serrez à fond les vis de fixation de la lame en la tenant
avec la clé et en tournant dans le sens horaire avec la
clé hexagonale pour serrer la vis de fixation de la lame.
20
Page 21

(Instructions initiales)
FRANÇAIS
Attention! Les brides intérieures (20)
respectivement marquées « 19 » et « 20 »
correspondent aux lames de scie (5) avec un
diamètre de broche de 19mm et 20mm.
Enlever la lame
Pour empêcher la rotation de la broche engagez les
protubérances de la clé (8) dans les trous de la rondelle
extérieure (10).
• Desserrez et enlevez la vis de fixation (11) de la lame
en la tournant dans le sens antihoraire à l’aide d’une clé
hexagonale (15).
• Enlevez la rondelle extérieure (10).
• Enlevez la lame de scie (5). Attention ! Pour réduire le
risque de vous blesser grièvement, lisez, comprenez et
observez toutes les importantes mises en garde et les
instructions avant de vous servir de l’outil.
Coupes générales
Protection contre un recul
Avec l’unité débranchée, suivez toutes les instructions de
montage, réglage et configuration. Vérifiez que la protection
inférieure fonctionne. Sélectionner la lame adéquate pour le
matériau que vous devez scier.
• Mesurez et marquez la pièce à scier.
• Soutenez et fixez correctement la pièce sur laquelle
vous allez travailler (voir Règles de sécurité et
Instructions).
• Utilisez l’équipement de sécurité approprié et requis
(voir Règles de sécurité).
• Sécurisez et maintenez la zone de travail (voir Règles
de sécurité).
• Avec la prise branchée et la protection fermée, vérifiez
que l’interrupteur gâchette démarre et arrête la scie.
Attention! Il est important de soutenir la pièce
correctement et de tenir la scie fermement pour
éviter une perte de contrôle qui pourrait entraîner
des blessures. La Fig. C montre la position recommandée
des mains.
Fonctionnement
Gâchette
• Pour faire fonctionner l’outil, appuyez sur la gâchette
(1). L’outil continuera de tourner tout le temps que la
gâchette est enfoncée.
• Pour arrêter l’outil, relâchez la gâchette (1). Il n’y a pas
de provision pour verrouiller l’outil et la gâchette ne doit
jamais être bloquée par un quelconque moyen.
Sciage
Attention! Pour réduire le risque de vous blesser
grièvement, tenez toujours l’outil avec les deux mains.
• Laissez la lame tourner librement pendant quelques
secondes avant de commencer à scier.
• N’exercez qu’une légère pression sur l’outil pendant que
vous sciez.
• Travaillez avec la semelle appuyée contre la pièce.
Astuces pour un usage optimal
• Puisque les éclats le long du trait de coupe sur le dessus
de la pièce ne peuvent pas être évités, sciez le matériau
du côté où les éclats sont acceptables.
• Là où les éclats doivent être un minimum, par ex. quand
vous sciez un panneau mélaminé, attachez un morceau
de contreplaqué sur le dessus de la pièce.
Découpe avec évidements (Fig. K)
La découpe avec évidements est utilisée pour découper
un trou dans une pièce de matériau sans couper depuis
le bord.
• Mesurez et marquez la pièce à scier.
• Inclinez la scie vers l’avant et posez l’avant de la semelle
sur le matériau que vous devez couper. Alignez de façon
à ce que le trait de coupe commence à l’arrière du
rectangle dessiné comme illustré à la Fig. K.
• Avec le levier de rétraction, rétractez la protection de
lame en position dressée vers le haut, avec la lame
dépassant juste le matériau, démarrez le moteur et
abaissez progressivement la scie dans le matériau.
Attention! Dès que la lame commence à couper
le matériau, relâchez immédiatement le levier de
rétraction.
• N’attachez jamais la protection de lame en position
dressée.
• Quand la semelle repose à plat sur le matériau que vous
découpez, terminez la coupe vers l’avant.
• Laissez la lame s’arrêter complètement avant de relever
la scie hors du matériau.
• Pour chaque nouvelle coupe, répétez les étapes
ci-dessus.
Rangement de la clé (Fig. L)
La clé de serrage (8) peut être rangée sur la semelle de la
scie comme illustré à la Fig. L.
21
Page 22

FRANÇAIS
(Instructions initiales)
Attacher et enlever le guide de coupe longitudinale
(Fig. M)
Le guide de coupe longitudinale est utilisé pour scier en
ligne droite parallèlement au bord de la pièce.
Attacher
• Desserrez le bouton de verrouillage (17).
• Insérez le guide de coupe longitudinale (18) à travers
les ouvertures (19).
• Faites glisser le guide de coupe longitudinale dans la
position désirée.
• Resserrez le bouton de verrouillage.
Enlever
• Desserrez le bouton de verrouillage.
• Tirez le guide de coupe longitudinale hors de l’outil.
Remarque : Si vous n’avez pas un rail de guidage
correct, utilisez un tasseau en contact avec le bord de
la semelle pour une plus grande précision du trait de
coupe et réduire la possibilité de caler et d’un recul.
Capteur de poussière
Il vous faut un adaptateur pour brancher un aspirateur ou un
capteur de poussière sur l’outil.
• Insérez l’adaptateur du capteur de poussière sur la
sortie de poussière (9) de la scie.
• Branchez le tuyau de l’aspirateur sur l’adaptateur.
Accessoires
La performance de votre outil dépend de l’accessoire utilisé.
Les accessoires STANLEY et Piranha sont fabriqués en
respectant un standard de qualité élevé et conçus pour
améliorer la performance de votre outil. En utilisant ces
accessoires vous obtiendrez le maximum de votre outil.
Attention! L’utilisation d’un accessoire qui n’est
pas recommandé pour cet outil peut être
dangereuse. N’utilisez que les lames de 185mm
avec une tige de 19mm ou 20mm de diamètre.
Entretien
Votre outil a été conçu pour fonctionner longtemps avec un
minimum d’entretien. Un fonctionnement continuellement
satisfaisant de l’outil dépend de son utilisation appropriée et
d’un nettoyage régulier.
Attention! Avant de faire l’entretien, mettez
l’outil hors tension et débranchez la prise
électrique.
• Nettoyez régulièrement les fentes de ventilation de votre
outil avec une brosse douce ou un chiffon sec.
22
• Nettoyez régulièrement le boîtier du moteur avec un
chiffon humide. N’utilisez pas de produit nettoyant abrasif
ou à base de solvant. Important ! Pour assurer la
SÉCURITÉ et la FIABILITÉ du produit, les réparations,
l’entretien et les réglages (autres que ceux mentionnés
dans ce mode d’emploi) doivent être effectués dans les
centres de service agréés ou des personnels de service
qualifiés, et en utilisant toujours des pièces de rechange
identiques.
Lubrification
Les outils Stanley sont correctement lubrifiés avant la sortie
d’usine et prêts à l’emploi.
Informations de service
STANLEY possède un réseau complet de points de services
dans ses propres établissements et chez des représentants
agréés. Tous les Centres de Service STANLEY disposent
d’un personnel qualifié pour offrir clients un service efficace
et fiable de leurs outils électriques. Pour plus de
renseignements sur nos centres de service agréés et si vous
avez besoin de conseils techniques, de réparations ou de
pièces de rechange d’origine, contactez le représentant
STANLEY le plus proche.
LpA (pression acoustique) dB(A) 92,5
Incertitude (K) dB(A) 3
LWA (puissance acoustique) dB(A) 103,5
Incertitude (K) dB(A) 3
Valeurs des vibrations totales (somme vectorielle triaxiale)
conformes à la norme EN 60745:
Sciage du bois (a
Incertitude (K) = 1,5 m/s
Le niveau d’émission de vibrations mentionné dans la fiche
technique a été mesuré conformément à la méthode de test
standard fournie par la norme EN 60745 et peut être utilisé
pour comparer avec d’autres outils. Il peut aussi être utilisé
pour une estimation préliminaire de l’exposition.
applications différentes, avec des accessoires différents ou
si l’entretien n’est pas fait correctement, l’émission de
vibrations peut différer. Cela peut augmenter le niveau
d’exposition de 1,5 sur la durée totale de travail.
Une estimation du niveau d’exposition aux vibrations doit
aussi tenir compte des périodes pendant lesquelles l’outil
est hors tension ou au ralenti. Cela peut réduire de façon
non négligeable le niveau d’exposition sur la période de
travail totale.
Identifiez les mesures de sécurité supplémentaires pour
protéger l’utilisateur des effets des vibrations tels que :
entretien de l’outil et des accessoires, garder les mains
chaudes, organisation des rythmes de travail.
h, W
Attention: Le niveau d’émission de vibrations
déclaré est celui des applications principales de
l’outil. Toutefois si l’outil est utilisé pour des
2
) = 3,3 m/s
2
Page 23

(Instructions initiales)
FRANÇAIS
Protection de l’environnement
Collecte sélective. Ne pas jeter cet appareil avec les
ordures ménagères.
Si vous devez remplacer un appareil Stanley ou si vous ne
l’utilisez plus, ne le jetez pas avec les ordures ménagères,
mais dans les conteneurs de collecte sélective.
La collecte sélective des produits et des emballages
usagés permet de recycler et de réutiliser leurs
matériaux. La réutilisation de matériaux recyclés
aide à protéger l’environnement contre la pollution et à
réduire la demande en matières premières.
Les réglementations locales peuvent proposer la collecte
sélective des appareils électriques ménagers, dans des
déchetteries municipales ou par le revendeur lorsque vous
achetez un nouvel appareil. Stanley dispose d’installations
pour la collecte et le recyclage des produits Stanley en fin de
vie. Pour profiter de ce service, veuillez rapporter votre
appareil auprès d’un centre de réparation agréé qui se
chargera de le collecter en notre nom.
Pour connaître l’adresse d’un centre de réparation agréé
près de chez vous, contactez votre distributeur Stanley à
l’adresse indiquée dans ce manuel, ou consultez la liste des
centres de réparation agréés Stanley et tout renseignement
complémentaire sur notre service après-vente sur le site
internet à l’adresse: www.2helpU.com.
Garantie deux
Si votre appareil STANLEY s’avère défectueux en raison
d’un vice de matériau ou de fabrication dans les 24 mois à
compter de sa date d’achat, STANLEY Europe garantit le
remplacement gratuit de toute pièce défectueuse ou – à
notre entière discrétion – le remplacement gratuit de
l’appareil, à condition que:
• L’appareil n’ait pas été utilisé avec négligence et qu’il ait
été utilisé en suivant les instructions contenues dans ce
manuel.
• L’appareil ait été soumis à une usure normale;
• Aucune réparation n’ait été effectuée par du personnel
non autorisé;
• Une preuve d’achat soit fournie.
• L’appareil STANLEY soit retourné complet, avec
l’ensemble de ses composants originaux.
Pour avoir recours à la garantie, contactez votre revendeur
ou consultez l’emplacement du centre de réparation agréé
Stanley le plus proche dans le catalogue, ou contactez le
service clientèle Stanley à l’adresse indiquée dans ce
manuel. Une liste des centres de réparation agréés Stanley
et tout détail complémentaire concernant notre service
après-vente sont à votre disposition sur notre site internet
:www.stanleytools.com
23
Page 24

PORTUGUESE
(Instruções Originais)
FIG. A FIG. B
FIG. C FIG. D
FIG. E
1
2
7
8
4
10
6
11
FIG. F FIG. G
13 12
4
3
9
5
24
Page 25

(Instruções Originais)
PORTUGUESE
FIG. H FIG. I
4
9
14
FIG. J
FIG. K
5
11
15
16
10
8
FIG. L
FIG. M
15
11
8
10
19
17
19
8
18
25
Page 26

PORTUGUESE
(Instruções Originais)
Dados técnicos
SEspecificações STSC1718
Tensão 230V
Frequência 50Hz
Potência 1700W
Velocidade sem carga 5500/min (rpm)
Profundidade máxima de corte 62mm AT 90°
46mm AT 45°
Utilização pretendida
A sua serra STANLEY foi projetada para serrar madeira e
produtos de madeira. Esta ferramenta destina-se somente
para utilização do consumidor.
• Para ferramentas com o objetivo de cortar madeira,
instrução sobre a utilização correta do sistema de
retenção de poeira.
• Para ferramentas com o objetivo de cortar madeira,
instrução para usar uma máscara de poeira.
• Instrução para utilizar somente lâminas de serra
recomendadas.
• Instrução para usar sempre proteção auricular.
NÃO DEVOLVER ESTE PRODUTO À LOJA,
Contacte primeiro com o seu escritório STANLEY ou centro
de serviços autorizado mais próximo.
Regras de Segurança Geral
Aviso! Ler e compreender todas as instruções. A
falha em seguir todas as instruções listadas em
baixo podem resultar em choque, incêndio e/ou
grave lesão pessoal.
GUARDAR ESTAS INSTRUÇÕES
Instruções de Segurança
Aviso de segurança geral de ferramenta elétrica
Aviso! Ler e compreender todas as
instruções. A falha em seguir todas as instruções
listadas em baixo podem resultar em choque,
incêndio e/ou grave lesão pessoal.
Guarde todos estes avisos para futura consulta.
O termo “ferramenta elétrica” em todos os avisos em baixo
listados refere-se aos meios operados (por cabo) da
ferramenta elétrica ou ferramenta elétrica alimentada a
bateria (sem fios).
1. Segurança de área de trabalho
a. Manter a área de trabalho limpa e bem iluminada.
Áreas desordenadas ou escuras são propícias a
acidentes.
b. Não operar as ferramentas elétricas em atmosferas
explosivas, tais como na presença de materiais,
gases ou poeiras. Ferramentas elétricas podem causar
faíscas que acendam a poeira ou fumos.
c. Manter as crianças e transeuntes longe quando
operar uma ferramenta elétrica. Distrações podem-no
fazer perder o controlo.
2. Segurança elétrica
a. As fichas das ferramentas elétricas devem ser iguais
às das tomadas. Nunca modifique de qualquer forma
a ficha. Não usar quaisquer fichas com ferramentas
elétricas com ligação à terra (terra). Fichas não
modificadas e tomadas condizentes reduziram o risco de
choque elétrico.
b. Evite o contacto físico com superfícies ligadas à
terra tais como tubos, radiadores, conteúdos e
frigoríficos. Existe um risco maior de choque elétrico se
o seu corpo estiver ligado à terra ou chão.
c. Não exponha as ferramentas elétricas a condições
chuvosas ou húmidas. Água que entre numa
ferramenta elétrica aumentará o risco de choque elétrico.
d. Não abuse do fio. Nunca use o fio para carregar,
puxar ou desligar a ferramenta elétrica. Mantenha o
fio longe do calor, óleo, pontas afiadas ou partes
móveis. Fios danificados ou entrelaçados aumentam o
risco de choque elétrico.
e. Quando operar uma ferramenta elétrica no exterior,
use um fio de extensão adequado para uso exterior.
O uso de um fio apropriado para uso exterior reduz o
risco de choque elétrico.
f. Se o uso de uma ferramenta elétrica num local
húmido não for inevitável, use uma fonte protegida
de dispositivo de corrente residual (DCR). O uso de
DCR reduz o risco de choque elétrico. Aviso: O termo
“Dispositivo de Corrente Residual (DCR)” pode ser
substituído por Disjuntor (D)” ou por “Disjuntor
Diferencial (DD)”.
3. Segurança pessoal
a. Esteja atento, tenha atenção ao que está a fazer e
use o senso comum quando operar uma ferramenta
elétrica. Não use ferramentas elétricas quando
estiver cansado ou sob influência de drogas, álcool
ou medicação. Uma desatenção enquanto opera uma
ferramenta elétrica pode causar graves danos pessoais.
26
Page 27

(Instruções Originais)
PORTUGUESE
b. Use equipamento de proteção pessoal. Use sempre
proteção ocular. Equipamento protetor tal como
mascara de poeiras, calçado anti derrapagem,
capacete, ou proteção auditiva usada para as condições
apropriadas de poeiras, calçado anti derrapagem,
capacete, ou proteção auditiva usada para as condições
apropriadas reduzirá o risco de lesões pessoais.
c. Previna arranque indesejado. Assegure-se que o
interruptor está na posição “off” antes de ligar à
fonte de energia e/ou pilhas, ao pegar ou carregar a
ferramenta. Carregar ferramentas elétricas com o seu
dedo no interruptor ou alimentar ferramentas elétricas
que têm o interruptor ligado propiciam os acidentes.
d. Remova qualquer chave de ajuste ou chave antes
de ligar a ferramenta elétrica. Uma chave deixada
presa à peça em rotação pode resultar em lesões
pessoais.
e. Não se exceda. Mantenha sempre a posição de pés
adequada e equilíbrio. Isto permite um melhor controlo
da ferramenta elétrica em situações inesperadas.
f. Vista-se apropriadamente. Não use roupas largas ou
joias. Mantenha o seu cabelo, vestuário e luvas
longe das partes em movimento. Vestuário largo, joias
ou cabelo comprido podem ficar presos nas peças em
movimento.
g. Se são fornecidos dispositivos para a coleção ou
extração de poeiras e instalações de coleção,
assegure-se que estes estão ligados e são usados
apropriadamente. Uso da recolha de poeira pode reduzir
o risco de perigos relacionados com a poeira.
4. Uso e cuidado da ferramenta elétrica
a. Não forçar a ferramenta elétrica. Use a ferramenta
elétrica correta para a sua tarefa. A ferramenta elétrica
correta fará o trabalho melhor de forma mais segura à
medida para a qual foi desenhada.
b. Não use a ferramenta elétrica se o interruptor não a
ligar ou desligar. Qualquer ferramenta elétrica que não
possa ser controlada com o interruptor é perigosa e
deve ser reparada.
c. Desligue a fiche da fonte de energia e/ou pilha da
ferramenta elétrica antes de fazer qualquer ajuste
mudar acessórios ou guardar as ferramentas
elétricas. Tais medidas preventivas reduzem o risco de
ligar a ferramenta elétrica acidentalmente.
d. Guarde ferramentas elétrica inativas fora do alcance
das crianças e não permita a pessoas não
familiarizadas com as ferramentas elétricas a operar
a ferramenta elétrica. Ferramentas elétricas são
perigosas nas mãos de utilizadores não preparados.
e. Reveja as ferramentas elétricas. Verifique se há
desalinhamento ou ligação das peças móveis, se as
peças quebraram e quaisquer outras condições que
possam afetar a operação das ferramentas elétricas.
Muitos acidentes são causados por ferramentas elétricas
mal revistas.
f. Mantenha as ferramentas de corte afiadas e limpas.
Ferramentas de corte devidamente revistas com
superfícies de corte afiadas têm menos probabilidades
de ligar e mais fáceis de controlar.
5. Manutenção
a. Mantenha a sua ferramenta elétrica revista por uma
pessoa especializada de reparações usando só
peças de substituição idênticas. Isto assegurará que a
segurança da ferramenta elétrica está mantida.
6. Etiquetas na ferramenta
A etiqueta na sua ferramenta pode incluir os
seguintes símbolos:
Ler Manual
de Instruções
Usar proteção
ocular
Usar proteção
auditiva
V ........ Volts
A ........ Amperes
Hz ....... Hertz
W ........ Watts
min ..... minutos
.....
Corrente
Alternada
.....
Corrente
Direta
n
.......
Velocidade
0
em vazio
Classe II
......
Construção
Símbolo de
....
Aviso de
Terminal de
....
Ligação à
Terra
.../min..
Rotações ou
Reciprocações
por minuto
Posição do código de barras de dados
O código de Dados, que também inclui o ano de fabrico,
é impresso na carcaça.
Exemplo:
2014 XX JN
Ano de Fabrico
7. Segurança elétrica
A sua ferramenta é duplamente isolada; por isso
não necessita de fio de terra. Verifique sempre
que a voltagem principal corresponde à placa sinalética.
Aviso! Se o fio de alimentação está danificado,
deverá ser trocado pelo fabricante, Centro de
Serviços autorizado da STANLEY ou uma pessoa
igualmente qualificada de forma a evitar danos ou lesões.
Se o fio de alimentação for trocado por uma pessoa
igualmente qualificada, mas não autorizada pela STANLEY,
a garantia não será válida.
Avisos de segurança adicionais para a
ferramenta elétrica
Aviso! Instruções de segurança para todas as
serras
27
Page 28

PORTUGUESE
(Instruções Originais)
Procedimentos de corte
Perigo! Mantenha as mãos afastadas da área de corte e
da lâmina. Mantenha a sua segunda mão no manípulo
auxiliar ou no corpo do motor. Se ambas as mãos
estiverem a segurar a serra não podem ser cortadas pela
lâmina.
b. Não se exponha à parte inferior da peça de trabalho.
A proteção não pode protegê-lo da lâmina na parte
inferior da peça de trabalho.
c. Ajuste a profundidade do corte à espessura da peça
de trabalho. Menos do que um dente completo dos
dentes da lâmina deve estar visível por baixo da peça
de trabalho.
d. Nunca segure a peça a cortar com as mãos ou na
sua perna. Fixe a peça de trabalho a uma plataforma
estável. É importante apoiar o trabalho corretamente
para minimizar a exposição do corpo, ligação da lâmina
ou perda de controlo.
e. Mantenha a ferramenta elétrica somente em
superfícies aderentes isoladas quando executar
uma operação em que a ferramenta de corte pode
entrar em contacto com fios escondidos. O contacto
com um fio «sob tensão» também coloca as peças de
metal da ferramenta elétrica «sob tensão» e poderá dar
ao operador um choque elétrico.
f. Quando rasgar utilize sempre uma guia de corte ou
guia de aresta reta. Isto melhora a precisão do corte e
reduz a hipótese da ligação da lâmina.
g. Utilize sempre lâminas com a dimensão correta e
forma (diamante versus redonda) de furos da árvore.
As lâminas que não correspondem ao hardware de
montagem da serra funcionarão descentradas
provocando perda de controlo.
h. Nunca utilize anilhas da lâmina danificadas ou
erradas ou parafuso. As anilhas da lâmina e parafuso
foram especialmente concebidos para a sua serra, para
o desempenho ótimo e segurança de operação.
Causa do ressalto e avisos relacionados
• O ressalto é uma reação súbita a uma lâmina de serra
apertada, ligada ou desalinhada causando uma serra
descontrolada para proteger o operador.
• Quando a lâmina está presa ou ligada com firmeza pelo
encerramento da largura de corte, as cabinas da lâmina
e a reação do motor fazem recuar rapidamente a
unidade na direção do operador.
• Se a lâmina torcer ou desalinhar no corte, os dentes na
borda traseira da lâmina podem penetrar na superfície
superior da madeira fazendo com que a lâmina saia do
corte e salte na direção do operador.
• O ressalto é o resultado da má utilização da ferramenta
e/ou procedimentos errados de operação ou condições
28
e pode ser evitado se tomar as precauções adequadas
abaixo indicadas.
a. Mantenha um aperto firme com as duas mãos na
serra e posicione o seu corpo e braços de modo a
resistir às forças do ressalto. As forças de ressalto
podem ser controladas pelo operador se as precauções
adequadas forem tomadas.
b. Quando a lâmina está ligada ou quando interromper
um corte por qualquer razão, solte o gatilho e segure
a serra imóvel no material até que a lâmina chegue a
uma paragem completa. Nunca tente remover a serra
do trabalho ou puxar a serra para trás enquanto a
lâmina estiver em movimento ou pode ocorrer um
ressalto. Investigue e tome as ações de correção para
eliminar a causa de ligação da lâmina.
c. Quando reiniciar uma serra na peça de trabalho,
centre a lâmina da serra na largura do corte e
verifique que os dentes da serra não estão
engatados no material. Se a lâmina de serra está
ligada, pode subir ou ressaltar da peça quando a serra é
reiniciada.
d. Apoie os painéis grandes para minimizar o risco de
a lâmina apertar e ressaltar. Os painéis grandes
tendem a arquear sob o seu próprio peso. O apoio
deve ser colocado sobre o painel em ambos os lados,
perto da linha da aresta do painel.
e. Não utilize lâmina cega ou danificada. Conjuntos de
lâminas não afiadas ou indevidas produzem uma largura
de corte estreita provocando uma fricção excessiva,
ligação da lâmina e ressalto.
f. A profundidade da lâmina e alavancas de ajuste de
travamento do chanfro devem estar apertadas e
seguras antes de realizar o corte. Se o ajuste da
lâmina muda durante o corte, pode causar ligação e
ressalto.
g. Tenha cuidado extra quando realiza um «Corte de
Bolso» em paredes existentes ou outras áreas
cegas. A lâmina saliente pode cortar objetos que podem
causar ressalto.
Função de proteção inferior
a. Verifique se a proteção inferior fecha devidamente
antes de cada utilização. Não utilize a serra se a
proteção inferior não se mover livremente e fechar
instantaneamente. Nunca prenda ou amarre a
proteção inferior na posição aberta. Se a serra caiu
acidentalmente, a proteção inferior pode estar dobrada.
Levante a proteção inferior com o manípulo de retração
e certifique-se que se move livremente e não toca na
lâmina ou em qualquer outra parte, em todos os ângulos
e profundidades de corte.
Page 29

(Instruções Originais)
PORTUGUESE
b. Verifique o funcionamento da mola da proteção
inferior. Se a proteção e a mola não estão a
funcionar corretamente, elas devem receber
manutenção antes da utilização. A proteção inferior
pode funcionar lentamente devido a peças danificadas,
depósitos de goma ou a um acúmulo de resíduos.
c. A proteção inferior pode ser recolhida manualmente
apenas para cortes especiais como «cortes de
mergulho» e «cortes compostos. Levante a proteção
inferior com o manípulo de retração assim que a lâmina
penetra no material, a proteção inferior deve estar
libertada. Para todos os outros tipos de serramento, a
proteção inferior deverá funcionar automaticamente.
d. Observe sempre se a proteção inferior está a cobrir
a lâmina antes de baixar a serra na bancada ou no
chão. Uma lâmina sem proteção e velocidade reduzida
fará com que a serra recue, cortando o que estiver no
seu percurso. Esteja consciente do tempo que leva para
a lâmina parar depois do interruptor ser libertado.
Riscos residuais
Os riscos residuais podem surgir quando utiliza a
ferramenta que pode não estar incluída nos avisos de
segurança anexos. Estes riscos podem surgir da má
utilização, utilização prolongada, etc.
Mesmo com a aplicação dos regulamentos de segurança
relevantes e a implementação de dispositivos de
segurança, certos riscos de segurança não podem ser
evitados. Estes incluem:
• Lesões causadas por tocar em peças rotativas/móveis.
• Lesões causadas quando substitui quaisquer peças,
lâminas ou acessórios.
• Os perigos de saúde causados por respirar pó
desenvolvido quando utiliza a sua ferramenta (por
exemplo: trabalhar com madeira, especialmente
carvalho, faia e MDF.)
Diretrizes/definições de segurança
É importante para que você possa ler e compreender este
manual. A informação que ele contém refere-se a proteger a
sua segurança e prevenção de problemas. Os símbolos
abaixo indicados são utlizados para ajudar a reconhecer
esta informação.
Perigo! Indica uma situação de perigo eminente
que, se não for evitada, resultará em morte ou
ferimentos graves.
Aviso! Indica uma situação de perigo potencial
que, se não for evitada, resultará em morte ou
ferimentos graves.
Atenção! Indica uma situação de perigo potencial
que, se não for evitada, pode resultar em
ferimentos menores ou moderados.
Atenção! Utilizado sem o símbolo de alerta de
segurança indica situação potencialmente
perigosa que, se não for evitada, pode resultar
em danos à propriedade.
Regras de segurança adicionais para Serras
Circulares
Aviso! Algum pó criado pela lixadeira elétrica,
serragem, retificadora, perfuração e outras
atividades de construção contém produtos
químicos conhecidos por causar cancro, defeitos de
nascimento ou outros danos reprodutivos. Alguns exemplos
destes produtos químicos são:
• Lesões causadas pela utilização prolongada de uma
ferramenta. Quando utiliza uma ferramenta por períodos
prolongados, certifique-se de que faz intervalos
regulares.
• Perda de audição.
• O chumbo de tintas à base de chumbo,
• Sílica cristalina de tijolos e cimento e outros produtos de
alvenaria,
• Arsénio e cromo de madeiras tratadas quimicamente
(CCA).
29
Page 30

PORTUGUESE
(Instruções Originais)
O risco dessas exposições varia, dependendo de quantas
vezes faz este tipo de trabalho. Para reduzir a sua
exposição a estes produtos químicos:
• Trabalhe numa área bem ventilada e trabalhe com
equipamento de segurança aprovado, como por
exemplo, máscaras de pó que são projetadas
especialmente para filtrar partículas microscópicas.
• Evite o contacto prolongado com o pó da lixadeira,
serragem, retificação, perfuração e outras atividades
de construção. Use roupas de proteção e lave as
áreas expostas com água e sabão. Permitindo que o
pó penetre na sua boca, olhos ou na pele pode provocar
a absorção de substâncias químicas nocivas.
Atenção! Use proteção auditiva adequada
durante a utilização. Sob algumas condições e
tempo de utilização, o ruído deste produto pode
contribuir para a perda de audição.
• Impedir a proteção inferior numa superfície por
baixo do material a ser cortado, pode reduzir
momentaneamente o controlo do operador. A serra
pode levantar parcialmente fora do corte aumentando a
hipótese de torção da lâmina. Verifique se há folga
suficiente sob a peça.
• Quando necessário aumente a proteção inferior
manualmente, utilize a alavanca de retração.
• Mantenha as lâminas limpas e afiadas. As lâminas
afiadas minimizam a paragem e o ressalto. A utilização
de lâminas cegas e/ou sujas podem aumentar a carga
da serra fazendo com que o operador empregue mais
força ao empurrar o que promove a torção.
Atenção! Perigo de laceração. Mantenha as mãos longe
das áreas de corte. Mantenha as mãos longe das lâminas.
Nunca coloque as mãos na frente ou atrás do percurso da
lâmina durante o corte. Não se exponha debaixo do
trabalho enquanto lâmina está a rodar. Não tente remover o
material de corte quando a lâmina estiver em movimento.
• Apoio dos painéis grandes. Os painéis devem estar
apoiados como mostrado (Fig. A) neste manual para
minimizar o risco de aperto da lâmina e ressalto. O
material apoiado somente nas extremidades (Fig. B)
conduzirá ao aperto da lâmina. Quando a operação de
corte exige o repouso da serra na peça de trabalho, a
serra deve permanecer imóvel na porção maior e a peça
menor cortada.
• Utilize apenas lâminas corretas e componentes de
montagem da lâmina ao montar lâminas. Não utilize
lâminas com orifícios de dimensões incorretas. Nunca
utilize anilhas da lâmina com defeito ou erradas ou
parafusos. Siga os procedimentos de montagem da
lâmina.
Lâminas de serra
• Não utilize lâminas de diâmetro maior ou inferior ao
recomendado. Para a classificação adequada da lâmina
consulte os dados técnicos. Utilize apenas as lâminas
especificados neste manual, cumprindo com a norma EN
847-1.
Aviso! Nunca utilize mós abrasivas.
Segurança de outras pessoas
• Este aparelho não se destina a ser utilizado por pessoas
(incluindo crianças) com deficiência física ou mental ou
falta de experiência e conhecimento, salvo se receberam
supervisão ou instruções relativas à utilização do
aparelho por parte da pessoa responsável pela sua
segurança.
• As crianças deverão ser vigiadas de modo a garantir
que não brincam com o aparelho.
Vibração
Os valores de emissão da vibração indicados nos dados
técnicos e da declaração de conformidade foram medidos
de acordo com um método de teste padrão fornecido pela
norma EN 60745 e pode ser utilizado para comparar uma
ferramenta com outra. O valor da emissão da vibração
indicado também pode ser utilizado numa avaliação
preliminar de exposição.
Aviso! O valor de emissão da vibração durante a utilização
real da ferramenta elétrica pode ser diferente do valor
declarado, dependendo dos meios em que a ferramenta é
utilizada. O nível de vibração pode aumentar acima do nível
indicado.
Quando a exposição da avaliação da vibração para
determinar as medidas de segurança necessárias pela
norma 2002/44/EC para proteger as pessoas que utilizam
ferramentas elétricas com regularidade no emprego, uma
estimativa da exposição da vibração deverá considerar as
condições reais de utilização e o modo como a ferramenta é
utilizada, incluindo ter em conta todas as partes do ciclo de
funcionamento como por exemplo, as vezes em que a
ferramenta é desligada e em que está a funcionar inativa
além do tempo de disparo.
• Ajustes. Antes de cortar tenha a certeza de que os
ajustes de profundidade e de chanfro estão apertados.
• Apoie e segure corretamente o trabalho. Certifique-se
de que o material a ser cortado está apertado (Fig. C) e
solidamente apoiado e equilibrado numa superfície de
trabalho forte, estável e de nível. Apoie o trabalho de
modo a que a parte mais larga da sapata da serra esteja
sobre a parte do material que não cai depois do corte ser
30
Page 31

(Instruções Originais)
PORTUGUESE
feito. Nunca segure o corte da peça com a mão (Fig. D).
O ressalto do aperto da lâmina pode resultar. Mantenha
as duas mãos na serra em todos os momentos.
• Fique atento e exerça o controlo. Mantenha o corpo
posicionado para um lado da lâmina. Mantenha sempre
um aperto firme e controlo da serra com as duas mãos.
Não altere o aperto da mão ou a posição do corpo
enquanto a serra está em execução. Tome precauções
para evitar lesões provocadas pelo corte de peças e
outro material que cai durante a operação.
Perigo! Solte imediatamente o interruptor se a
lâmina liga ou a serra atrasa.
Características (Fig. E)
Esta ferramenta inclui algumas ou todas as seguintes
características.
1. Interruptor On/Off (Ligar/Desligar)
2. Manípulo principal
3. Manípulo secundário
4. Sapata
5. Lâmina de serra
6. Proteção da lâmina de serra
7. Alavanca de retração da proteção da lâmina
8. Chave inglesa da lâmina da serra
9. Botão de ajuste do chanfro
10. Anilha exterior
11. Parafuso de retenção da lâmina
Chave de boca hexagonal da lâmina da serra (Mostrado
na Fig.I)
18. Guia de corte (Mostrado na Fig. M)
flange interna (Mostrado na Fig. J)
Configuração montagem/ajuste
Aviso! Desligue sempre a serra da fonte de
alimentação antes de qualquer uma das
seguintes operações.
Ajustar a profundidade de corte (Fig. F e G)
A profundidade de corte deve ser configurada de acordo
com a espessura da peça de trabalho.
• Desaperte a alavanca (12) para desbloquear a sapata
da serra.
• Mova a sapata da serra (4) para a posição desejada. A
profundidade de corte correspondente pode ser lida a
partir da escala (13).
• Aperte a alavanca para travar a sapata da serra no
lugar.
• Configure o ajuste de profundidade da serra de tal forma
que um dente dos projetos da lâmina abaixo da peça de
trabalho tal como mostrado na Fig. G.
Ajustar o ângulo do chanfro (Fig. H)
Esta ferramenta pode ser configurada para chanfrar ângulos
entre os 0° e os 45°.
• Desaperte o botão de bloqueio (9) para desbloquear a
sapata da serra.
• Mova a sapata da serra (4) para a posição desejada. O
ângulo de chanfro correspondente pode ser lido a partir
da escala (14).
• Aperte o botão de bloqueio para travar a sapata da serra
no lugar.
Anexar a lâmina (Fig. I e J)
• Para evitar a rotação da árvore engate as saliências da
chave inglesa (8) nos orifícios da anilha externa (10)
como mostrado na Fig. I.
• Desaperte e remova o parafuso de retenção da lâmina
(11) virando a chave hexagonal (15) no sentido
anti-horário.
• Remova a anilha exterior.
• Verifique e monte de novo a flange interior (20) na
árvore (16). Segure o lado correto da flange interior (20)
faces para o exterior e faça coincidir a lâmina de serra
com o diâmetro da árvore.
• Coloque a lâmina da serra (5) na flange interior (20),
certificando-se de que a seta na lâmina aponta na
mesma direção que a seta na ferramenta.
• Encaixe a anilha exterior (10) na árvore.
• Insira o parafuso de retenção da lâmina (11) no orifício
da árvore.
• Para evitar a rotação da árvore engate a chave inglesa
nos orifícios da anilha externa.
• Aperte com segurança o parafuso de retenção da lâmina
segurando a chave inglesa e virando a chave hexagonal
no sentido dos ponteiros do relógio para apertar o
parafuso de retenção da lâmina.
31
Page 32

PORTUGUESE
(Instruções Originais)
Aviso! A flange interior (20) respetivamente
marcada com “19” e “20” coincide com a lâmina
da serra (5) com diâmetro da árvore 19 mm e 20
mm.
Remoção da lâmina
Para evitar a rotação da árvore engate as saliências da
chave inglesa (8) nos orifícios da anilha externa (10).
• Desaperte e remova o parafuso de retenção da lâmina
(11) virando-o no sentido anti-horário utilizando a chave
hexagonal (15).
• Retire a anilha exterior (10).
• Retire a lâmina de serra (5). Aviso! Para reduzir o risco
de ferimentos graves, leia, compreenda e siga todos os
avisos de segurança e instruções importantes antes de
utilizar a ferramenta.
Cortes gerais
Proteção contra ressalto
Com a unidade desligada, siga toda a montagem, ajuste e
instruções de configuração. Certifique-se de que a proteção
inferior funciona. Selecione a lâmina apropriada para o
material a ser cortado.
• Meça e marque o trabalho para corte.
• Apoie e segure o trabalho corretamente (Consulte as
normas de segurança e instruções).
• Utilize equipamento de segurança apropriado e
necessário (Consulte as regras de segurança).
• Segure e mantenha a área de trabalho (Consulte as
regras de segurança).
• Com o tampão inserido e a proteção fechada,
certifique-se de que o interruptor liga e desliga a serra.
Aviso! É importante apoiar o trabalho
corretamente e segurar a serra com firmeza para
evitar a perda de controlo que pode causar
ferimentos pessoais. A Fig. C ilustra a posição da mão
recomendada.
Operação
Interruptor
• Para trabalhar a ferramenta, pressione o interruptor de
disparo (1). A ferramenta continuará a executar assim
que o gatilho é pressionado.
• Para desligar a ferramenta, solte o interruptor de
disparo (1). Não há fornecimento para bloquear a
ferramenta e o interruptor nunca deve ser bloqueado por
qualquer outro meio.
32
Serra
Aviso! Para reduzir o risco de ferimentos
pessoais graves, segure sempre a ferramenta
com ambas as mãos.
• Deixe que a lâmina funcione livremente durante alguns
segundos antes de iniciar o corte.
• Aplique apenas uma ligeira pressão na ferramenta
enquanto executa o corte.
• Trabalhe com a sapata pressionada contra a peça de
trabalho.
Sugestões para uma utilização ótima
• Como algumas lascas ao longo da linha de corte no lado
do topo da peça de trabalho não podem ser evitadas,
corte no lado onde a lascagem é aceitável.
• Onde a lascagem deve ser minimizada, isto é aquando
do corte em lâminas, aperte uma peça de madeira
compensada no topo da peça de trabalho.
Corte de bolso (Fig. K)
O corte de bolso é utilizado para cortar um orifício numa
peça de material sem cortar a partir do lado.
• Meça e marque o trabalho.
• Incline a serra para a frente e descanse a frente da
sapata no material a ser cortado. Alinhe para que o corte
inicie na parte de trás do retângulo desenhado mostrado
na Fig. K.
• Utilize a alavanca de retração, retraia a proteção da
lâmina para uma posição para cima, com a lâmina
apenas limpe o material, inicie o motor e desça
gradualmente a serra na direção do material.
Aviso! Assim que a lâmina inicia o corte do
material, liberte imediatamente a alavanca de
retração.
• Nunca amarre a proteção da lâmina numa posição
elevada.
• Quando a sapata repousa plana sobre o material a ser
cortado, complete o corte na direção de avanço.
• Permita que a lâmina chegue a uma paragem completa
antes de levantar a serra do material.
• Repita os passos acima sempre que inicia cada novo
corte.
Armazenamento de chaves de boca (Fig. L)
A chave inglesa (8) pode ser armazenada na sapata de
serra conforme mostrado na Fig. L.
Page 33

(Instruções Originais)
PORTUGUESE
Fixação e remoção da guia de corte (Fig. M)
A guia de corte é utilizada para serrar numa linha reta
paralela à aresta da peça de trabalho.
Anexo
• Solte o botão de bloqueio (17).
• Insira a guia de corte (18) através das aberturas (19).
• Deslize a guia de corte para a posição desejada.
• Aperte o botão de bloqueio.
Remoção
• Solte o botão de bloqueio.
• Puxe a guia de corte para fora da ferramenta. Nota: Se
não tem um esquadro de guia apropriado, utilize uma
guia de aresta reta em contacto com a guia da sapata
para melhorar a precisão do corte e reduzir a
possibilidade de ligação e ressalto.
Extração de pó
É necessário um adaptador para ligar um aspirador ou
extrator de pó para a ferramenta.
• Insira o adaptador de extração de pó para a saída de pó
de serra (9).
• Ligue a mangueira de aspirador ao adaptador.
Acessórios
O desempenho da sua ferramenta depende do acessório
utilizado. Os acessórios Stanley e Piranha foram fabricados
para elevados padrões de qualidade e foram concebidos
para melhorar o desempenho da sua ferramenta. Ao utilizar
estes acessórios obterá o melhor da sua ferramenta.
Aviso! A utilização de qualquer acessório não
recomendado para utilizar com esta ferramenta
pode ser perigoso. Utilize apenas lâminas de 185
mm com 19 mm ou 20 mm de diâmetro da árvore.
Manutenção
A sua ferramenta foi concebida para operar durante um
longo período de tempo com um mínimo de manutenção.
Um funcionamento satisfatório permanente depende de um
cuidado adequado da ferramenta e de uma limpeza regular.
Aviso! Antes de realizar qualquer manutenção,
desligue a ferramenta, inclusive da tomada.
• Limpe regularmente as ranhuras de ventilação da sua
ferramenta utilizando uma escova macia ou um pano
seco.
• Limpe regularmente o corpo do motor com um pano
húmido. Não utilize nenhum agente de limpeza abrasivo
ou à base de solvente. Importante! Para garantir a
SEGURANÇA e a CONFIABILIDADE, as reparações,
manutenção e ajustes (exceto aqueles listados neste
manual) devem ser realizados por centros de serviços
autorizados ou outros técnicos de serviço qualificados,
utilizando sempre peças de substituição idênticas.
Lubrificação
As ferramentas Stanley são devidamente lubrificadas na
fábrica e estão prontas a serem utilizadas.
Serviço de informação
A STANLEY proporciona uma rede completa de filiais e
locais de serviço autorizados da empresa. Todos os Centros
de Serviço STANLEY são equipados com pessoal treinado
para oferecer aos clientes um serviço de ferramentas
elétricas eficiente e confiável. Para obter mais informações
sobre os nossos centros de serviços autorizados e se
precisar de aconselhamento técnico, reparação ou peças de
reposição genuínas de fábrica, entre em contacto com o
local STANLEY mais próximo de si.
LpA (pressão sonora) dB(A) 92.5
Incerto (K) dB(A) 3
LWA (potência sonora) dB(A) 103.5
Incerto (K) dB(A) 3
Valores totais de vibração (soma do vetor triáxico)
de acordo com a norma EN 60745:
Corte de madeira (a
incerto (K) = 1.5 m/s2
O nível de emissão da vibração dado nesta ficha de
informação foi medido de acordo com um teste normalizado
fornecido na EN 60745 e pode ser utilizado para comparar
uma ferramenta com outra. Pode ser utilizado para uma
avaliação preliminar da exposição.
em aplicações diferentes, com acessórios diferentes ou com
fraca manutenção, a emissão da vibração pode diferir. Isto
pode aumentar significativamente o nível 1,5 de exposição
sobre o período de trabalho total.
Uma estimativa do nível de exposição à vibração também
deve ter em conta os tempos em que a ferramenta está
desligada ou quando está a funcionar mas não está
realmente a trabalhar. Isto pode reduzir significativamente o
nível de exposição sobre o período de trabalho total.
Identificar medidas de segurança adicionais para proteger
operador dos efeitos de vibração tais como: manter a
ferramenta e os acessórios, manter as mãos quentes,
organização dos modelos de trabalho.
h, W
Aviso: O nível de emissão de vibração indicado
representa as principais aplicações da
ferramenta. Contudo se a ferramenta é utilizada
2
) = 3.3 m/s
33
Page 34

PORTUGUESE
(Оригинальные инструкции)
Protegendo o ambiente
Recolha separada. Este produto não deve ser
descartado com o resto do lixo caseiro normal.
Se encontrar que um dia o seu produto Stanley precisa de
substituição, ou se já não tem mais uso para si, não o
descarte com o resto de lixo caseiro normal. Disponibilize
este produto para recolha separada.
Recolha separada dos produtos usados e embalagens
permite que os materiais sejam reciclados e usados de
novo. Reutilizar materiais reciclados ajuda a prevenir
poluição ambiental e reduz a necessidade de
matéria-prima.
Leis locais podem fornecer recolha separada de
produtos elétricos das casas, em sítios de
resíduos municipais ou no vendedor quando você
compra um novo produto. Stanley oferece uma instalação
para a recolha e reciclagem de produtos Stanley uma vez
que estes atingiram o fim da sua vida útil. Para desfrutar
deste serviço por favor devolva o seu produto a qualquer
agente autorizado de reparações que os recolherá em
nosso nome.
Você pode verificar a localização do seu agente de
reparações autorizado mais próximo contactando o seu
escritório local Stanley no endereço indicado neste manual.
Alternativamente, uma lista de agentes de reparações
autorizados pela Stanley e detalhes completes dos nossos
serviços pós-venda e contactos estão disponíveis na
Internet em: www.2helpU.com
dois ano de garantia total
Se o seu produto STANLEY ficar defeituoso devido a
materiais ou mão-de-obra defeituosos em 24 meses a
contra da data da compra, STANLEY Europe garante a
substituição de todas as peças defeituosas sem custos – por
nossa conta – substitui a unidade sem custos dado que:
• O produto não foi mal usado e foi usado de acordo com
o manual de instruções.
• O produto foi sujeito a uso e desgaste justo;
• Não foram tentadas reparações feitas por pessoas não
autorizadas;
• É fornecida um comprovativo de compra.
• O produto STANLEY é devolvido com todos os seus
componentes originais.
Se quiser apresentar uma reclamação, contacte o seu
vendedor ou verifique a localização do agente de
reparações Stanley autorizado no catálogo ou contacte com
o seu escritório local nos endereços indicados neste
manual. Uma lista de agentes autorizados de reparação
Stanley e detalhes completes dos nossos serviços
pós-venda estão disponíveis na internet em:
www.stanleytools.com
34
Page 35

(Оригинальные инструкции)
FIG. A FIG. B
FIG. C FIG. D
РУССКИЙ
FIG. E
1
2
7
8
4
10
6
11
FIG. F FIG. G
13 12
4
3
9
5
35
Page 36

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
FIG. H FIG. I
4
9
14
FIG. J
FIG. K
5
11
15
16
10
8
FIG. L
FIG. M
15
11
8
10
36
19
17
19
8
18
Page 37

(Оригинальные инструкции)
РУССКИЙ
Технические данные
Спецификации STSC1718
Напряжение 230V
Частота 50Hz
Мощность 1700W
Скорость без нагрузки 5500/мин (об/мин)
Максимальная глубина резания 62 мм при 90°
46 мм при 45°
Использование по назначению
Ваша пила STANLEY предназначена для распиловки
древесины и изделий из нее. Этот инструмент
предназначен только для бытового использования
• Для инструментов, предназначенных для
распиловки леса, инструкция по правильному
использованию системы сбора пыли.
• Для инструментов, предназначенных для
распиловки леса, инструкции по ношению защитной
маски.
• Инструкция для использования только
рекомендованных циркулярных пил.
• Инструкция для обязательного использования
средств защиты органов слуха.
НЕ ВОЗВРАЩАЙТЕ ЭТО ИЗДЕЛИЕ В МАГАЗИН,
сначала обратитесь в ваш местный офис STANLEY или
в ближайший авторизованный сервисный центр.
Общие правила техники
безопасности
Внимание! Прочитайте и поймите все
инструкции. Несоблюдение любых инструкций,
указанных ниже, может привести к поражению
электрическим током, пожару и/или серьезной травме.
СОХРАНИТЕ ЭТИ ИНСТРУКЦИИ
Правила техники безопасности
Общие предупреждения по технике безопасности
электроинструментов
Внимание! Ознакомьтесь со всеми правилами
безопасности и инструкциями. Несоблюдение
предупреждений и инструкций, указанных ниже, может
привести к поражению электрическим током, пожару
и/или серьезной травме.
Сохраните все предупреждения и инструкции для
будущего использования.
Термин "электроинструмент" во всех предупреждениях,
указанных ниже, относится к вашему сетевому (с
кабелем) электроинструменту или аккумуляторному
электроинструменту (без кабеля питания).
1. Безопасность рабочего места
а. Содержите рабочее место в чистоте и хорошо
освещенным. Беспорядок на рабочем месте или
отсутствие освещения рабочего места может
привести к аварии.
b. Не работайте с электроинструментом в месте
хранения взрывоопасных материалов, например,
в присутствии огнеопасных жидкостей, газов или
пыли. Электрические инструменты создают искры,
которые могут воспламенить пыль или пары.
с. Дети и посторонние лица должны находиться как
можно дальше во время работы с
электроинструментом. Вы можете отвлечься и
потерять контроль.
2. Электробезопасность
а. Вилка электроинструмента должна
соответствовать розетке. Никогда не
модифицируйте вилку каким-либо образом. Не
используйте никакие вилки-переходники с
заземленными (замкнутыми на землю)
электроинструментами. Вилки и розетки, которые
не подвергались никаким изменениям снижают риск
поражения электрическим током.
b. Избегайте контакта тела с заземленными
поверхностями, такими как трубы, радиаторы,
плиты и холодильники. Существует повышенный
риск поражения электрическим током, если ваше
тело заземлено.
с. Избегайте любого воздействия дождя или влаги
на электроинструменты. Вода, попавшая в
электроинструмент, увеличивает риск поражения
электрическим током.
d. Аккуратно обращайтесь со шнуром питания.
Никогда не используйте шнур питания для
переноски, перемещения или извлечения вилки
из розетки. Держите шнур вдали от источников
тепла, масла, острых краев или движущихся частей.
Поврежденные или запутанные шнуры увеличивают
риск поражения электрическим током.
е. При работе с электроинструментом на улице,
используйте удлинитель, подходящий для
наружного использования. Использование кабеля,
пригодного для использования на открытом воздухе,
снижает риск поражения электрическим током.
f. При необходимости работы с
электроинструментом во влажной среде,
используйте устройство защитного отключения
(УЗО). Использование УЗО снижает риск поражения
электрическим током. Примечание: Термин
“устройство защитного отключения (УЗО)” может
быть заменен на "аварийный прерыватель
заземления" или "автоматический выключатель тока
утечки".
37
Page 38

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
наружного использования. Использование кабеля,
пригодного для использования на открытом воздухе,
снижает риск поражения электрическим током.
f. При необходимости работы с
электроинструментом во влажной среде,
используйте устройство защитного отключения
(УЗО). Использование УЗО снижает риск поражения
электрическим током. Примечание: Термин
“устройство защитного отключения (УЗО)” может
быть заменен на "аварийный прерыватель
заземления" или "автоматический выключатель тока
утечки".
3. Личная безопасность
a. Будьте внимательны, смотрите, что вы делаете,
используйте здравый смысл при работе с
электроинструментом. Не используйте
электроинструмент, если вы устали или находитесь
под влиянием наркотиков, алкоголя или лекарств.
Малейшая неосторожность при работе с
электроинструментом может привести к серьезным
травмам.
b. Используйте средства индивидуальной защиты.
Всегда надевайте защитные очки. Другое
защитное оборудование, включая респиратор,
ботинки на нескользящей подошве, защитный
шлем или средства защиты органов слуха,
используемые в надлежащих условиях, уменьшат
риск получения травмы.
с. Для предотвращения случайного запуска,
убедитесь, что переключатель находится в
выключенном положении перед подключением к
источнику питания и/или аккумуляторной
батарее, поднятия или переноски инструмента.
Не переносите электроинструмент с пальцем на
выключателе и не включайте питание на инструмент
с включенным выключателем, что может привести к
несчастному случаю.
d. Перед включением электроинструмента
снимайте регулировочный или гаечный ключ.
Гаечный или регулировочный ключ, оставленный на
вращающейся части электроинструмента, может
привести к травме.
е. Не тянитесь. Сохраняйте правильную стойку и
баланс все время. Это позволяет лучше
контролировать инструмент в неожиданных
ситуациях.
f. Одевайтесь правильно. Не надевайте свободную
одежду или украшения. Держите волосы, одежду
и перчатки вдали от движущихся частей.
Свободная одежда, украшения или длинные
волосы могут попасть в движущиеся части.
g. Если имеются устройства для подключения
пылесборника или вытяжки, убедитесь в том, что
они подсоединены и используются правильно.
Использование пылесборника снижает вероятность
возникновения рисков, связанных с пылью.
4. Использование и уход за электроинструментом
a. Не перегружайте электроинструмент.
Используйте подходящий электрический
инструмент для соответствующего применения.
Правильно подобранный электроинструмент
позволит выполнить работу лучше и безопаснее при
скорости, для которой он был разработан.
b. Не используйте электроинструмент, если
переключатель не может его включить и
выключить. Любой электроинструмент, который
нельзя контролировать с помощью переключателя,
опасен и должен быть отремонтирован.
c. Отключите кабель питания от источника питания
и/или аккумуляторный блок от электрического
инструмента перед выполнением любых
регулировок, замены принадлежностей или при
хранении электроинструмента. Такие
профилактические меры безопасности уменьшают
риск непреднамеренного запуска электрического
инструмента.
d. Храните неиспользуемые электроинструменты в
недоступном для детей месте и не позволяйте
лицам, не знакомым с электроинструментом или
данными инструкциями, работать с
электроинструментом. Электроинструменты опасны
в руках неопытных пользователей.
е. Поддержание электроинструмента. Проверяйте
разрегулированность или cоединение
подвижных частей, поломки частей и любые
другие условия, которые могут повлиять на
работу электроинструмента. При наличии
повреждения, отремонтируйте
электроинструмент перед использованием.
Многие несчастные случаи являются следствием
плохого ухода за электроинструментом.
f. Держите режущий инструмент острым и чистым.
Хорошо ухоженный режущий инструмент с острыми
режущими кромками легче контролировать.
5. Обслуживание
а. Обеспечьте, чтобы обслуживание и ремонт
вашего электроинструмента проводился в
авторизованном сервисном центре по ремонту с
использованием только оригинальных запасных
частей. Это станет гарантией безопасности
электроинструмента.
38
Page 39

(Оригинальные инструкции)
РУССКИЙ
6. Этикетки на инструменте
Этикетка на вашем инструменте может включать
следующие символы:
Читайте
инструкции по
эксплуатации
Используйте
средства
защиты глаз
Используйте
средства
защиты
органов слуха
В ........ Вольт
A ........ Ампер
Гц ....... Герц
Вт ........ Ватт
мин...... минуты
Перемен-
.....
ный ток
Постоян-
.....
ный ток
Скорость
n
.......
0
без нагрузки
Конструкция
......
класса II
Терминал
....
заземления
Символ
предупреж-
....
дения об
опасности
обороты или
...мин..
возвратнопоступательное движение
в минуту
Положение даты штрих-кода
Дата кода, который также включает год изготовления,
печатается на корпусе.
Пример:
2014 XX JN
Год изготовления
7. Электрическая безопасность
Ваш инструмент имеет двойную изоляцию, именно в
этой связи заземляющий провод не требуется. Всегда
проверяйте, что напряжение сети соответствует
напряжению, указанному на заводской табличке.
Внимание! Если шнур питания поврежден, он должен
быть заменен производителем в авторизованном
сервисном центре STANLEY или квалифицированным
специалистом для того, чтобы избежать повреждения
или травмы. Если шнур питания заменен
квалифицированным специалистом, не
уполномоченным STANLEY, гарантия не будет
действовать.
Дополнительные меры безопасности для
электроинструмента
Warning! Safety instructions for all saws
Предостережение! Инструкции по технике безопасности
для всех пил
Процедуры резания
Опасность! Держите руки подальше от зоны
резания и диска пилы. Держите вторую руку
на вспомогательной рукоятке или корпусе
руками, руки не пострадают от работающего диска.
b. Не прикасайтесь к нижней части заготовки. Кожух не
двигателя. Если держать пилу обеими
сможет защитить вас от диска ниже заготовки.
c. Отрегулируйте глубину резания согласно толщине
заготовки. Над заготовкой должно быть видно
немногим меньше полного зубца зубчатого диска
пилы.
d. Никогда не держите заготовку, которую необходимо
распилить в руках и не придерживайте ногами.
Закрепите заготовку на устойчивой платформе.
Важно поддерживать заготовку таким образом, чтобы
свести к минимуму воздействие на тело, застревание
диска или потерю контроля.
e. Держите электроинструмент за изолированные
поверхности при выполнении действий, при которых
режущий инструмент может задеть скрытую
проводку. Контакт с "работающим" проводом также
обнажит металлические части работающего
электроинструмента, в результате чего оператора
может ударить электрическим током.
f. При продольной распиловке всегда используйте
направляющую планку или прямую боковую
направляющую. Это повышает точность реза и
уменьшает вероятность сдерживания пильного
диска.
g. Всегда используйте пильные диски с правильным
размером и формой со шпиндельными отверстиями.
Диски, которые не соответствуют монтажному
оборудованию пилы будут работать эксцентрически,
что приведет к потере контроля.
h. Никогда не используйте поврежденные или
неправильные шайбы или болты для пильных
дисков. Дисковые шайбы и болты были специально
разработаны для вашего типа пилы для обеспечения
оптимальной производительности и безопасности
работы.
Причины отдачи и связанные с нею
предупреждения
• Отдача это – внезапная реакция на защемление или
застревание или перекос пильного диска,
вызывающая неконтролируемое движение пилы
вверх и вниз от заготовки и в сторону оператора.
• Когда диск зажимается или застревает, двигательная
реакция заставляет инструмент сделать быстрый
толчок назад к оператору.
• Если диск становится изогнутым или смещенным в
разрезе, зубцы задней кромки диска могут врезаться
в поверхность древесины в результате чего диск
выскочит из пропила и отлетит назад к оператору.
• Отдача является результатом неправильного
использования инструмента и/или неправильных
действий оператора или условий, ее можно
39
Page 40

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
избежать, приняв соответствующие меры
предосторожности, как указано ниже.
a. Крепко держите пилу обеими руками и убедитесь,
что положение вашего тела и рук позволит вам
противостоять воздействию обратного удара
(отдачи). Оператор может контролировать силу
отдачи, если приняты соответствующие меры
предосторожности.
b. Когда диск пилы застревает или по какой-либо
причине происходит сбой во время распила,
отпустите курок и удерживайте пилу неподвижно в
материале, пока диск полностью не остановится.
Никогда не пытайтесь удалить пилу во время работы
и не тяните ее назад в то время, когда диск
находится в движении, так как это может привести к
отдаче. Следует понять причину и предпринять
корректирующие действия с целью устранения
причин застревания диска.
c. При перезапуске пилы, когда диск находится в
заготовке, убедитесь, что пильный диск находится в
пропиле и зубья пилы не застряли в материале.
Если диск застрял, он может выскочить или
произвести реакцию отдачи от заготовки, как только
пила будет перезапущена.
d. Поддерживайте большие панели для сведения к
минимуму риска ущемления диска и отдачи.
Большие панели, как правило, прогибаются под
собственным весом. Поддержка должна быть
помещена под панелью с обеих сторон, рядом с
линией реза и у края панели.
e. Не используйте тупые или поврежденные диски.
Незаточенные или неправильно установленные
диски производят узкий пропил вызывая чрезмерное
трение, ущемление диска и отдачу.
f. Глубина диска и конические установочные
запирающие рычаги должны быть надежно затянуты
прежде чем начать резку. Если регулировка диска
сдвигается во время резки, это может привести к
ущемлению и отдаче.
g. Будьте особенно осторожны при выполнении
"карманной резки" в существующих стенах или
других слепых зонах. Выступающие диски могут
отрезать объекты, которые могут привести к
возникновению отдачи.
Функция нижнего защитного кожуха
a. Проверьте хорошо ли закрыт нижний защитный
кожух перед каждым использованием. Не
используйте пилу, если нижний защитный кожух не
перемещается свободно и не закрывается
мгновенно. Никогда не закрепляйте и не
привязывайте нижний защитный кожух в открытом
положении. Если пила случайно упала, нижний кожух
может быть согнут. Поднимите нижний защитный
кожух с ручкой втягивания и убедитесь, что он
свободно перемещается и не касается лезвия или
любой другой части, при всех углах и глубине
40
резания.
b. Проверьте работу пружины нижнего защитного
кожуха. Если кожух и пружина не работают должным
образом, они должны пройти техническое
обслуживание перед использованием. Нижний
защитный кожух может работать медленно из-за
наличия поврежденных частей, смолистых
отложений или мусора.
c. Нижний защитный кожух может быть втянут вручную
только для особых видов резки, таких как “погружная”
и “сложная”. Поднимите нижний защитный кожух
путем втягивания ручки и, как только пильный диск
входит в материал, нижний кожух должен быть
освобожден. Для всех остальных видов распиловки,
нижний кожух должен работать в автоматическом
режиме.
d. Всегда следите за тем, чтобы нижний кожух
покрывал диск до размещения пилы на верстаке или
на полу. Незащищенный, движущийся по инерции
диск заставляет пилу двигаться назад и резать все,
что есть на пути. Вы должны знать сколько времени
необходимо для остановки пильного диска после
отпускания выключателя.
Остаточные риски
Дополнительные остаточные риски могут возникнуть при
использовании инструмента, которые не включены в
описанные здесь правила техники безопасности. Эти
риски могут возникнуть при неправильном или
продолжительном использовании изделия и т.п.
Несмотря на соблюдение соответствующих правил
техники безопасности и использование
предохранительных устройств, некоторых остаточных
рисков невозможно избежать. Они включают в себя:
• Травмы в результате касания
вращающихся/движущихся частей.
• Риск получения травмы во время смены деталей
инструмента, ножей или насадок
• Травмы, вызванные продолжительным
использованием инструмента. При использовании
инструмента в течение продолжительного периода
времени делайте регулярные перерывы в работе.
• Плохой слух.
• Ущерб здоровью в результате вдыхания пыли при
использовании инструмента (пример: работа с
деревом, в особенности, древесиной дуба, бука и
древесноволокнистой плитой средней плотности).
Правила техники безопасности/определения
Важно, чтобы вы прочитали и поняли данное
руководство. Содержащаяся в нем информация
относится к защите вашей безопасности и
предотвращению проблем. Приведенные ниже символы
используются, чтобы помочь вам распознать эту
информацию.
Page 41

(Оригинальные инструкции)
РУССКИЙ
используются, чтобы помочь вам распознать эту
информацию.
Опасность! Указывает на потенциально
опасную ситуацию, которая, если ее не
травмам.
смерти или серьезным травмам.
легкой или средней травме.
избежать, может привести к повреждению имущества.
избежать, приведет к смерти или серьезным
Предупреждение! Указывает на
потенциально опасную ситуацию, которая,
если ее не избежать, могла бы привести к
Предостережение! Указывает на
потенциально опасную ситуацию, которая,
если ее не избежать, может привести к
Предостережение! Используется без знака
опасности указывает на потенциально
опасную ситуацию, которая, если ее не
Дополнительные правила техники
безопасности для циркулярных пил
Предостережение! Часто пыль,
пиления, шлифования, сверления и других
строительных работ содержит химические вещества,
которые могут вызвать рак, врожденные дефекты или
другие нарушения репродуктивной функции. Некоторые
примеры этих химикатов:
• Свинец из свинцовых красок,
• Кристаллический кремнезем от кирпичей, цемента и
• Мышьяк и хром из химически обработанной
Риск от воздействия данных веществ зависит от того,
как часто вы производите этот тип работы. Чтобы
снизить воздействие этих химикатов:
• Работайте в хорошо проветриваемом помещении с
• Избегайте длительного контакта с пылью во время
образовавшаяся после грубой шлифовки,
других кладочных продуктов
древесины.
соответствующими средствами обеспечения
безопасности, включая респираторы, которые
специально разработаны для фильтрации
микроскопических частиц.
шлифования, пиления, сверления и других
строительных работ. Носите защитную одежду и
мойте открытые участки тела водой с мылом.
Попадание пыли в рот, глаза или на кожу может
способствовать усвоению вредных химических
веществ.
Внимание! Носите соответствующие средства
для защиты органов слуха во время
использования. При некоторых условиях и
продолжительности использования, шум от этого
продукта может способствовать потере слуха.
• Если нижний защитный кожух зацепляется на
поверхности ниже разрезаемого материала, это
может кратковременно снизить контроль оператора.
Пила может подняться из разреза частично, что
может увеличить возможность искривления диска.
Убедитесь, что под заготовкой имеется достаточный
зазор.
• При необходимости поднять нижний защитный кожух
вручную, используйте рычаг втягивания.
• Держите диски чистыми и острыми. Острые диски
минимизируют опрокидывание и отдачу.
Использование испорченных и/или грязных дисков
может увеличить нагрузку на пилу, в результате чего
оператору надо будет сильнее толкать пилу, что
может привести к искривлению.
Предостережение! Опасность повреждения. Держите
руки подальше от места распила. Держите руки
подальше от пильных дисков. Никогда не помещайте
руки перед или сзади пути движения диска во время
резки. Не прикасайтесь к заготовке во время вращения
пильного диска. Не пытайтесь удалить срезанный
материал во время движения диска.
• Поддержка больших панелей. Большие панели
должны быть поддержаны как показано на рисунке
(рис. А) в данном руководстве, чтобы
минимизировать риск защемления диска и отдачи.
Материал поддерживается только по краям (рис. В) и
может привести к защемлению диска. Если во время
резки требуется дать отдых пиле на заготовке, пилу
следует положить на большей части, а меньший
кусок отрезать.
• Используйте только правильные диски и компоненты
дисков для установки. Не используйте диски с
отверстиями неправильного размера. Никогда не
используйте диски с дефектами или шайбы и болты
для диска неправильного размера. Четко следуйте
процедурам установки диска.
Пильные диски
• Не используйте диски больше или меньше
рекомендуемого диаметра. Для правильного размера
диска, обратитесь к техническим данным.
Используйте только диски, указанные в данном
руководстве, соответствующие стандарту EN 847-1.
Предостережение! Никогда не используйте абразивные
диски.
41
Page 42

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
Безопасность посторонних лиц
• Этот инструмент не предназначен для
использования лицами (включая детей) с
ограниченными физическими, чувствительными или
умственными способностями или с недостатком
опыта или знаний, если они не были под контролем
и руководством лица, контролирующего
использование инструмента или ответственным за
их безопасность.
• Дети должны быть под присмотром взрослых, чтобы
не допустить никаких игр с инструментом.
Вибрация
Заявленные значения уровня вибрации, указанные в
технических характеристиках инструмента и декларации
соответствия, были измерены в соответствии со
стандартным методом определения EN 60745 и могут
использоваться для сравнения одного инструмента с
другим. Объявленное значение вибрационного
воздействия также может быть использовано для
предварительной оценки воздействия.
Предостережение! Значения вибрационного
воздействия при фактическом использовании
электроинструмента может отличаться от заявленного
значения в зависимости от способов, при помощи
которых используется инструмент. Уровень вибрации
может превышать заявленное значение.
При оценке степени вибрационного воздействия для
определения необходимых защитных мер, требуемых
согласно закону 2002/44/EC для защиты людей,
постоянно использующих электроинструмент, оценка
воздействия вибрации должна рассматривать
фактические условия использования и способ, при
помощи которого используется инструмент, в том числе
с учетом всех сегментов рабочего цикла, включая
время, когда инструмент находится в выключенном
состоянии, и когда он работает в холостом режиме в
дополнение к времени срабатывания.
• Регулировки. Перед распилом убедитесь, что
корректировки глубины и наклона установлены
надлежащим образом.
• Поддержка и обеспечение надлежащей
безопасности работы. Убедитесь, что материал для
распиливания зажат (рис. C), надежно
поддерживается и сбалансирован на прочной,
устойчивой и ровной рабочей поверхности.
Проводите работу так, чтобы широкая часть
подошвы находилась на части материала, который
не упадет после распила. Никогда не держите
отрезаемый кусок рукой (рис. D). Это может
привести к отдаче от защемления диска. Всегда
держите обе руки на пиле.
• Будьте внимательны и осуществляйте постоянный
контроль. Займите положение у одной стороны
лезвия. Всегда крепко держите пилу обеими руками.
Не изменяйте положение рук или положение тела во
время работы пилы. Необходимо принять меры
предосторожности, чтобы избежать травм от
отрезанных кусков и другого падающего материала
во время работы.
Опасность! Отпустите переключатель немедленно, если
диск застрянет или пила остановится.
Особенности (рис. Е)
Этот инструмент включает в себя некоторые или все из
следующих признаков:
1. Включатель/выключатель питания
2. Главная ручка
3. Вспомогательная ручка
4. Башмак
5. Пильный диск
6. Кожух пильного диска
7. Рычаг втягивания защитного кожуха диска
8. Гаечный ключ пильного диска
9. Ручка регулировки наклона
10. Внешняя шайба
11. Регулировочный винт диска
Шестигранный ключ пильного диска (как показано на
рисунке I)
18. Параллельный упор (как показано на рис. М)
Внутренний фланец (как показано на рис. J)
Монтаж/регулировка
Предостережение! Всегда отключайте пилу от источника
питания до любой из следующих операций:
Регулировка глубины реза (рис. F и G)
Глубина резания должна быть установлена в
соответствии с толщиной заготовки.
• Ослабьте рычаг (12), чтобы разблокировать
подошву.
• Переместите подошву (4) в требуемое положение.
Соответствующая глубина резания может быть
прочитана по шкале (13).
• Затяните рычаг, чтобы зафиксировать подошву на
месте.
• Установите глубину резки пилы таким образом, что
один зубец диска был ниже заготовки, как показано
на рисунке G.
42
Page 43
(Оригинальные инструкции)
РУССКИЙ
Регулировка угла скоса (рис. H)
Этот инструмент может быть установлен на скос углов
от 0° до 45°.
• Ослабьте ручку блокировки (9), чтобы
разблокировать подошву.
• Переместите подошву (4) в требуемое положение.
Соответствующий угол наклона можно прочитать по
шкале (14).
• Затяните ручку блокировки, чтобы зафиксировать
подошву на месте.
Установка диска (рис. I и J)
• Для предотвращения вращения шпинделя, зацепите
выступы на гаечном ключе (8) в отверстия в
наружной шайбе (10), как показано на рис. I.
• Ослабьте и снимите крепежный винт диска (11),
повернув шестигранный ключ (15) против часовой
стрелки.
• Снимите внешнюю шайбу.
• Проверьте и произведите повторную сборку
внутреннего фланца (20) на шпиндель (16).
Убедитесь, чтобы правильная сторона внутреннего
фланца (20) смотрит наружу и соответствует
пильному диску с диаметром отверстий шпинделя.
• Поместите пильный диск (5) на внутренний фланец
(20), убедившись, что стрелка на диске находится в
том же направлении, что и стрелка на инструменте.
• Установите внешнюю шайбу (10) на шпиндель.
• Вставьте крепежный винт диска (11) в отверстие в
шпинделе.
• Не допускайте вращения шпинделя, вставив
гаечный ключ в отверстия на внешней шайбе.
• Надежно затяните крепежный винт диска, удерживая
гаечный ключ и поворачивая шестигранный ключ по
часовой стрелке, чтобы затянуть крепежный винт
диска.
Предостережение! Внутренний фланец (20),
соответственно маркированный цифрами
"19" и "20", соответствуют пильному диску (5)
с диаметром шпинделя 19 мм и 20 мм.
Снятие пильного диска
• Для предотвращения вращения шпинделя зацепите
выступы на гаечном ключе (8) в отверстия в
наружной шайбе (10).
• Ослабьте и снимите крепежный винт диска (11),
повернув шестигранный ключ (15) против часовой
стрелки.
• Снимите внешнюю шайбу (10).
• Снимите пильный диск (5). Предостережение! Чтобы
снизить риск получения серьезной травмы,
необходимо прочесть, понять и соблюсти все важные
правила безопасности и инструкции перед
использованием инструмента.
Общая резка�
Защита против отдачи
С устройством, отключенным от электрической сети,
выполните все инструкции по монтажу, наладке и
настройке. Убедитесь, что нижний защитный кожух
работает. Выберите нужный диск для разрезаемого
материала.
• Измерьте и сделайте отметки на заготовке для резки.
• Проведите все меры по поддержке и безопасности
работы (см. Правила и инструкции по технике
безопасности).
• Используйте соответствующее и необходимое
оборудование безопасности (см. Правила техники
безопасности).
• Обеспечьте поддержку и безопасность рабочей зоны
(см. Правила техники безопасности).
• С установленным разъемом и закрытым кожухом,
убедитесь, что переключатель включает и выключает
пилу.�
Предостережение! Важно поддерживать
работу должным образом и надежно
удерживать пилу, чтобы предотвратить
потерю контроля, что может привести к травме. Рис. C
иллюстрирует рекомендованное положение рук.
Функциональный �переключатель
• Чтобы включить инструмент, нажмите на курковый
выключатель (1). Инструмент будет продолжать
работать до тех пор, пока курковый выключатель
утоплен.
• Для выключения инструмента, отпустите курковый
выключатель (1). В инструменте отсутствует
положение для фиксации, поэтому переключатель
никогда не должен быть заблокирован никакими
другими средствами.
Распиловка
Предостережение! Чтобы снизить риск получения
серьезной травмы, всегда держите инструмент обеими
руками.
• Дайте диску свободно перемещаться в течение
нескольких секунд, прежде чем начать резку.
43
Page 44

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
• Применяйте только легкое надавливание на
инструмент при выполнении разреза.
• Работайте с башмаком, прижатым к
обрабатываемой детали.
Советы по оптимальному использованию
• Поскольку некоторых расколов вдоль линии
разреза на верхней стороне заготовки не возможно
избежать, производите резку по той стороне, где
раскалывания являются приемлемыми.
• Там, где раскалывания должны быть сведены к
минимуму, например, при резки ламината, прижмите
кусок фанеры к верхней части заготовки.
Карманная резка (рис. К)
Карманная резки используется для вырезки
отверстий в куске материала без разрезания со
стороны.
• Сделайте измерения и пометки на заготовке.
• Наклоните вперед пилу и переднюю часть башмака
на материале, который будет вырезан. Выравняйте
таким образом, чтобы разрез начался с заду,
нарисованного прямоугольника, показанного на рис.
К.
• Используя рычаг втягивания, уберите защитный
кожух диска в верхнюю позицию, запустите
двигатель и постепенно двигайте пилу вниз в
материале.
Предостережение! По мере того, как диск
начинает резать материал, немедленно
освободите рычаг втягивания.
• Никогда не закрепляйте защитный кожух в поднятом
положении.
• Когда башмак лежит на разрезаемом материале,
закончить распил в прямом направлении.
• Дайте диску полностью остановиться прежде, чем
поднять пилу от материала.
• Когда начинаете каждую новую резку, повторите
описанные выше шаги
Хранение гаечного ключа (рис. L)
Гаечный ключ (8) может храниться на башмаке пилы,
как показано на рис. L
44
Установка и снятие параллельного упора (рис. M)
Параллельный упор используется для распила по
прямой линии, параллельной краю заготовки.
Приложения
• Ослабьте ручку блокировки (17).
• Вставьте параллельный упор (18) через отверстия
(19).
• Вставьте параллельный упор в нужное положение.
• Затяните ручку блокировки.
Снятие
• Ослабьте ручку блокировки.
• Снимите параллельный упор с инструмента.
Примечание: если у вас нет правильно подобранного
упора, используйте прямую боковую направляющую
в контакте с краем башмака, чтобы повысить
точность резки и уменьшить вероятность
застревания и отдачи.
Аксессуары
Производительность вашего инструмента зависит от
используемых аксессуаров. Аксессуары STANLEY
разработаны согласно высоким стандартам качества, и
они способны увеличить производительность вашего
электроинструмента. Используя эти принадлежности, вы
сможете наиболее эффективно использовать
ваш инструмент.
Предостережение! Использование каких-либо
аксессуаров не рекомендуется для использования с
этим инструментом и может быть опасным. Используйте
только 185 мм диски с диаметром шпинделя 19 мм или
20 мм.
Обслуживание�
Ваш инструмент был разработан для работы в течение
длительного периода времени при минимальном
техническом обслуживании. Для обеспечения
удовлетворительной работы, инструмент должен
правильно храниться и подвергаться регулярной чистке.
Предостережение! Перед выполнением
любых работ по обслуживанию, выключите и
отсоедините инструмент.
Page 45

(Оригинальные инструкции)
РУССКИЙ
• Регулярно очищайте вентиляционные прорези
инструмента мягкой щеткой или сухой тканью.
• Регулярно очищайте корпус двигателя влажной
тканью. Не используйте абразивные вещества или
чистящие растворы на основе растворителя. Важно!
Для обеспечения БЕЗОПАСНОСТИ и НАДЕЖНОСТИ
оборудования, ремонт, техническое обслуживание и
регулировка (кроме тех, которые перечислены в
настоящем руководстве) должны выполняться
квалифицированным персоналом в авторизованных
сервисных центрах с использованием оригинальных
запасных частей.
Смазка
Инструменты Stanley были надлежащим образом
смазаны на заводе и готовы к использованию. �
Информационная служба
STANLEY предлагает полную сеть авторизированных
сервисных центров, принадлежащих компании. Все
сервисные центры STANLEY укомплектованы
персоналом, прошедшим обучение, чтобы предоставить
клиентам эффективный и надежный сервис по
обслуживанию электроинструментов. Для получения
дополнительной информации о авторизированных
сервисных центрах или если вам нужен технический
совет, ремонт или оригинальные запасные части, вам
необходимо обратиться в ближайший сервисный центр
STANLEY.
применений инструмента. Однако, если инструмент
используется для различных применений, с
разнообразными аксессуарами или не подвергался
надлежащему обслуживанию, уровень вибрации может
отличаться. Это может повысить уровень воздействия в
1,5 раза в течение всего рабочего периода.
При оценке уровня воздействия вибрации необходимо
также учитывать время, когда инструмент выключен или
когда он включен, но на самом деле не делает свою
работу. Это может значительно уменьшить уровень
воздействия в течение всего периода работы.
Определите дополнительные меры предосторожности
для защиты оператора от воздействия вибрации, такие
как: тщательный уход за инструментом и аксессуарами,
содержание рук в тепле, организация режимов работы и
пр.
LpA (давление звука) dB(A) 92.5
Изменчивость (K) dB(A) 3
LWA (мощность звука) dB(A) 103.5
Изменчивость (K) dB(A) 3
Общие значения вибрации согласно
Резки дерева (a
Изменчивости (K) = 1.5 m/s2
Уровень вибрации, указанный в настоящем
информационном листке, был рассчитан в соответствии
со стандартизированным испытанием, содержащимся в
EN 60745 и может использоваться для сравнения
одного инструмента с другим. Он может быть
использован для предварительной оценки воздействия.
h, W
Предостережение: Указанный уровень
вибрации представлен для основных
) = 3.3 m/s
2
45
Page 46

РУССКИЙ
(Оригинальные инструкции)
Защита окружающей среды
Раздельный сбор и утилизация. Этот продукт
не следует утилизировать вместе с бытовым
мусором.
Если вы поймете, что ваш продукт Stanley нуждается в
замене, или если он не имеет никакого дальнейшего
применения для вас, не выбрасывайте его вместе с
бытовыми отходами. Предоставьте этот продукт для
раздельного сбора/утилизации.
Раздельный сбор продуктов и упаковок
позволяет осуществить их переработку и
использовать их повторно. Повторное
использование переработанных материалов помогает
защищать окружающую среду от загрязнения и снижает
расход сырьевых материалов.
Местное законодательство может обеспечить сбор
старых электроинструментов отдельно от бытового
мусора на муниципальных свалках отходов или в
торговом предприятии при покупке нового изделия.
Stanley обеспечивает возможность для сбора и
утилизации продуктов Stanley, как только они достигли
конца своего срока службы. Для того чтобы
воспользоваться этой услугой, вы можете сдать ваше
изделие в любой авторизованный сервисный центр,
который собирает их по нашему поручению.
Вы можете узнать место нахождения вашего
ближайшего авторизованного сервисного центра,
обратившись в местное отделение Stanley по адресу,
указанному в данном руководстве. Кроме того, список
авторизованных ремонтных агентов Stanley и полную
информацию о нашем послепродажном обслуживании и
контактах вы можете найти в Интернете:
www.2helpU.com10
Два год полной гарантии
Если ваш продукт STANLEY выходит из строя из-за
дефектных материалов или изготовления в течение 24
месяцев с даты покупки, STANLEY Europe гарантирует
замену всех неисправных деталей бесплатно или - по
своему усмотрению - замену продукта бесплатно при
условии, что:
• Продукт использовался правильно, его эксплуатация
проводилась строго в соответствии с инструкцией по
эксплуатации.
• Продукт подвергался естественному износу;
• Ремонт не проводился посторонними лицами;
• Представлены документы, подтверждающие покупку.
• Продукт STANLEY возвращается в полном комплекте
со всеми оригинальными компонентами
Если вы хотите сделать заявку, свяжитесь с продавцом
или узнайте место нахождения вашего ближайшего
авторизованного сервисного агента Stanley в каталоге
Stanley или обратитесь в местное представительство
Stanley по адресу, указанному в данном руководстве.
Список авторизованных сервисных агентов Stanley и
полную информацию о нашем послепродажном
обслуживании можно найти в Интернете по адресу:
www.stanleytools.com
46
Page 47

(Оригинальные инструкции)
Гарантийные условия
Уважаемый покупатель!
1. Поздравляем Вас с покупкой высококачественного
изделия STANLEY и выражаем признательность за Ваш
выбор.
2. При покупке изделия требуйте проверки его комплектности
и исправности в Вашем присутствии, инструкцию по
эксплуатации и заполненный гарантийный талон на
русском языке.
В гарантийном талоне должны быть внесены: модель,
дата продажи, серийный номер, дата производства
инструмента; название, печать и подпись торговой
организации. При отсутствии у Вас правильно заполненного гарантийного талона, а также несоответствия
указанных в нем данных мы будем вынуждены откло- нить
Ваши претензии по качеству данного изделия.
3. Во избежание недоразумений убедительно просим Вас
перед началом работы с изделием внимательно
ознакомиться с инструкцией по его эксплуатации.
Правовой основой настоящих гарантийных условий
является действующее Законодательство. Гарантийный
срок на данное изделие составляет 24 месяца и
исчисляется со дня продажи. В случае устранения
недостатков изделия, гарантийный срок продлевается на
период его нахождения в ремонте. Срок службы изделия
составляет 5 лет со дня продажи.
4. В случае возникновения каких-либо проблем в про- цессе
эксплуатации изделия рекомендуем Вам обра- щаться
только в уполномоченные сервисные центры STANLEY,
адреса и телефоны которых Вы сможете найти в
гарантийном талоне, на сайте www.2helpU.com или узнать
в магазине. Наши сервисные станции - это не только
квалифицированный ремонт, но и широкий ассортимент
запчастей и принадлежностей.
5. Производитель рекомендует проводить периодическую
проверку и техническое обслуживание изделия в
уполномоченных сервисных центрах.
Изготовитель
Блэк энд Деккер Холдингс ГмбХ
Германия, 65510, Идштайн,
ул. Блэк энд Деккер, 40
РУССКИЙ
6. Наши гарантийные обязательства распространяются
только на неисправности, выявленные в течение гарантийного срока и вызванные дефектами производства и \
или материалов.
7. Гарантийные условия не распространяются на
неисправности изделия, возникшие в результате:
7.1. Несоблюдения пользователем предписаний инструкции по
эксплуатации изделия, применения изделия не по
назначению, неправильном хранении, использования
принадлежностей, расходных материалов и запчастей, не
предусмотренных производителем.
7.2. Механического повреждения (сколы, трещины и разрушения) внутренних и внешних деталей изделия,
основных и вспомогательных рукояток, сетевого электрического кабеля, вызванного внешним ударным или
любым иным воздействием
7.3 Попадания в вентиляционные отверстия и проникновение внутрь изделия посторонних предметов,
материалов или веществ, не являющихся отходами,
сопровождающими применение изделия по назначению,
такими как: стружка, опилки, песок, и пр.
7.4. Воздействий на изделие неблагоприятных атмосферных и
иных внешних факторов, таких как дождь, снег,
повышенная влажность, нагрев, агрессивные среды,
несоответствие параметров питающей электросети,
указанных на инструменте.
7.5. Стихийного бедствия. Повреждение или утрата изделия,
связанное с непредвиденными бедствиями, стихийными
явлениями, в том числе вследствие действия
непреодолимой силы (пожар, молния, потоп и другие
природные явления), а так же вследствие перепадов напряжения в электросети и другими причинами, которые
находятся вне контроля производителя.
8. Гарантийные условия не распространяются:
8.1. На инструменты, подвергавшиеся вскрытию, ремонту или
модификации вне уполномоченного сервисного центра.
8.2. На детали и узлы, имеющие следы естественного износа,
такие как:
приводные ремни и колеса, угольные щетки, смазка,
подшипники, зубчатое зацепление редукторов, резиновые уплотнения, сальники, направляющие ролики,
муфты, выключатели, бойки, толкатели, стволы, и т.п.
8.3. На сменные части: патроны, цанги, зажимные гайки и
фланцы, фильтры, аккумуляторные батареи, ножи,
шлифовальные подошвы, цепи, звездочки, пильные шины,
защитные кожухи, пилки, абразивы, пильные и
абразивные диски, фрезы, сверла, буры и т.п.
8.4. На неисправности, возникшие в результате перегрузки
инструмента (как механической, так и электрической),
повлекшей выход из строя одновременно двух и более
деталей и узлов, таких как: ротора и статора, обеих
обмоток статора, ведомой и ведущей шестерни редуктора или других узлов и деталей. К безусловным
признакам перегрузки изделия относятся, помимо прочих:
появление цветов побежалости, деформация или
оплавление деталей и узлов изделия, потемнение или
обугливание изоляции проводов электродвигателя под
воздействием высокой температуры.
47
Page 48

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
FIG. A FIG. B
FIG. C FIG. D
FIG. E
1
2
7
8
4
10
6
11
FIG. F FIG. G
13 12
4
3
9
5
48
Page 49

(Оригінальні інструкції)
УКРАЇНСЬКА
FIG. H FIG. I
4
9
14
FIG. J
FIG. K
5
11
15
16
10
8
FIG. L
FIG. M
15
11
8
10
19
19
17
49
Page 50

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
Технічні дані
Спецификації STSC1718
Напруга 230V
Частота 50Hz
Потужність 1700W
Швидкість без навантаження 5500/хвил. (об/хвил.)
Максимальна глибина різання 62 мм при 90°
46 мм при 45°
Використання за призначенням
Ваша пила STANLEY призначена для розпилювання
деревини та виробів з неї. Цей інструмент призначений
тільки для побутового використання
• Для інструментів, призначених для розпилювання
лісу, інструкція по правильному використанню
системи збору пилу.
• Для інструментів, призначених для розпилювання
лісу, інструкція по носінню захисної маски.
• Інструкція для використання тільки рекомендованих
циркулярних пилок.
• Інструкція для обов'язкового використання засобів
захисту органів слуху.
НЕ ПОВЕРТАЙТЕ ЦЕЙ ВИРІБ В МАГАЗИН,
спочатку зверніться у місцевий офіс STANLEY або в
найближчий авторизований сервісний центр.
Загальні правила техніки безпеки
Увага! Прочитайте і зрозумійте всі інструкції.
Недотримання будь-яких інструкцій,
зазначених нижче, може призвести до
та/або серйозної травми.
ураження електричним струмом, пожежі
ЗБЕРЕЖІТЬ ЦІ ІНСТРУКЦІЇ
Правила техніки безпеки
Загальні попередження з техніки безпеки
електроінструментів
Увага! Ознайомтеся з усіма правилами
безпеки та інструкціями. Недотримання
може призвести до ураження електричним струмом,
пожежі та/або серйозної травми.
Збережіть всі попередження та інструкції для
майбутнього використання.
Термін "електроінструмент" у всіх попередженнях,
зазначених нижче, відноситься до мережевого (з
кабелем) електроінструменту або акумуляторної батареї
(без кабелю живлення).
1. Безпека робочого місця
а. Утримуєте робоче місце в чистоті і добре
50
попереджень та інструкцій, зазначених нижче,
освітленим. Безлад на робочому місці або
відсутність освітлення робочого місця може
призвести до аварії.
b. Не працюйте з електроінструментом в місці
зберігання вибухонебезпечних матеріалів,
наприклад, у присутності легкозаймистих рідин,
газів або пилу. Електричні інструменти створюють
іскри, що можуть запалити пил або пари.
с. Діти і сторонні особи повинні знаходитися
якнайдалі під час роботи з електроприладами. Ви
можете відволіктися і втратити контроль.
2. Електробезпека
а. Вилка електроінструмента повинна відповідати
розетці. Ніколи не змінюйте вилку будь-яким
чином. Не використовуйте ніякі
вилки-перехідники з заземленими (замкнутими на
землю) електроінструментами. Вилки і розетки, які
не піддавалися ніяким змінам знижують ризик
ураження електричним струмом.
b. Уникайте контакту тіла з заземленими
поверхнями, такими як труби, радіатори, плити та
холодильники. Існує підвищений ризик ураження
електричним струмом, якщо ваше тіло заземлене.
с. Уникайте будь-якого впливу дощу або вологи на
електроінструменти. Вода, що потрапила в
електроінструмент, збільшує ризик ураження
електричним струмом.
d. Обережно поводьтеся зі шнуром живлення.
Ніколи не використовуйте шнур живлення для
перенесення, переміщення або вилучення вилки з
розетки. Тримайте шнур подалі від джерел тепла,
масла, гострих країв або рухомих частин.
Пошкоджені або заплутані шнури збільшують ризик
ураження електричним струмом.
е. При роботі з електроінструментом на вулиці,
використовуйте подовжувач, відповідний для
зовнішнього використання. Використання кабелю,
придатного для використання на відкритому повітрі,
знижує ризик ураження електричним струмом.
f. При необхідності роботи з електроінструментом у
вологому середовищі, використовуйте пристрій
захисного відключення (ПЗВ). Використання ПЗВ
знижує ризик ураження електричним струмом.
Примітка: Термін "пристрій захисного відключення
(ПЗВ)" може бути замінений на "аварійний переривач
заземлення" або "автоматичний вимикач струму
витоку".
3. Особиста безпека
a. Будьте уважні, дивіться, що ви робите,
використовуйте здоровий глузд при роботі з
електроприладами. Не використовуйте
електроінструмент, якщо ви втомилися або
перебуваєте під впливом наркотиків, алкоголю або
ліків. Найменша необережність при роботі з
електроінструментом може призвести до серйозних
травм.
b. Використовуйте засоби індивідуального захисту.
Завжди надягайте захисні окуляри. Інше захисне
обладнання, включаючи респіратор, черевики на
нековзній підошві, захисний шолом або засоби
Page 51

(Оригінальні інструкції)
УКРАЇНСЬКА
захисту органів слуху, використовувані в належних
умовах, зменшать ризик отримання травми.
с. Для запобігання випадкового запуску,
переконайтеся, що перемикач знаходиться у
вимкненому положенні перед підключенням до
джерела живлення та/або акумуляторної батареї,
підняття або перенесення інструменту. Не
переносьте електроінструмент з пальцем на
вимикачі і не включайте електроживлення на
інструмент з увімкненим вимикачем, що може
призвести до нещасного випадку.
d. Перед включенням електроінструменту знімайте
регулювальний або гайковий ключ. Гайковий або
регулювальний ключ, залишений на обертовій
частині електроінструменту, може призвести до
травми.
е. Не тягніться. Зберігайте правильну стійку і
баланс весь час. Це дозволяє краще контролювати
інструмент в несподіваних ситуаціях.
f. Одягайтеся правильно. Не надягайте вільний
одяг або прикраси. Тримайте волосся, одяг і
рукавички далеко від рухомих частин. Вільний
одяг, прикраси або довге волосся можуть потрапити
в рухомі частини.
g. Якщо є пристрої для підключення пилозбірника
або витяжки, переконайтеся в тому, що вони
під'єднані і використовуються правильно.
Використання пилозбірника знижує ймовірність
виникнення ризиків, пов'язаних з пилом.
4. Використання та догляд за електроінструментом
a. Не перевантажуйте електроінструмент.
Використовуйте відповідний електричний
інструмент для відповідного застосування.
Правильно підібраний електроінструмент дозволить
виконати роботу краще і безпечніше при швидкості,
для якої він був розроблений.
b. Не використовуйте електроінструмент, якщо
перемикач не може його включити і вимкнути.
Будь-який електроінструмент, який не можна
контролювати за допомогою перемикача, є
небезпечний і повинен бути відремонтований.
c. Від'єднайте кабель живлення від джерела
живлення та/або акумулятора від електричного
інструменту перед виконанням будь-яких
регулювань, заміни приладдя або при зберіганні
електроінструменту. Такі профілактичні заходи
безпеки зменшують ризик ненавмисного запуску
електричного інструменту.
d. Зберігайте електроприлади в недоступному для
дітей місці і не дозволяйте особам, які не знайомі
з електричним інструментом або даними
інструкціями, працювати з електроприладами.
Електроінструменти небезпечні в руках
недосвідчених користувачів.
е. Підтримання електроінструменту. Перевіряйте
разрегульованість або з'єднання рухомих частин,
поломки частин і будь-які інші умови, які можуть
вплинути на роботу електроінструменту. При
наявності пошкодження, відремонтуйте
електроінструмент перед використанням. Багато
нещасних випадків є наслідком поганого догляду за
електроінструментом.
f. Тримайте ріжучий інструмент гострим і чистим.
Добре доглянутий ріжучий інструмент з гострими
ріжучими крайками легше контролювати.
5. Обслуговування
а. Забезпечте, щоб обслуговування і ремонт вашого
електроінструменту проводився в
авторизованому сервісному центрі по ремонту з
використанням тільки оригінальних запасних
частин. Це стане гарантією безпеки
електроінструменту.
6. Етикетки на інструменті
Етикетки на вашому інструменті можуть включати
такі символи:
Читайте
інструкції з
експлуатації
Використовуйте
засоби захисту
очей
Використовуйте
засоби захисту
органів слуху
В ........ Вольт
A ........ Ампер
Гц ....... Герц
Вт ........
мин .....
n
Ватт
хвилини
Змінний
.....
струм
Постійний
.....
струм
.......
Швидкість
0
без навантаження
......
....
....
хв..
Конструкція
класу II
Термінал
заземлення
Символ
попередження про
небезпеку
обороти або
зворотно
поступальний рух в
хвилину
Положення дати штрих-коду
Дата коду, який також включає рік виготовлення,
друкується на корпусі.
Приклад:
2014 XX JN
Рік виготовлення
7. Електрична безпека
Ваш інструмент має подвійну ізоляцію, саме в
цьому зв'язку заземлюючий провід не потрібен.
Завжди перевіряйте, що напруга мережі
відповідає напрузі, вказаній на табличці.
Увага! Якщо шнур живлення пошкоджений, він
повинен бути замінений виробником в
авторизованому сервісному центрі STANLEY
або кваліфікованим фахівцем для того, щоб уникнути
пошкодження або травми. Якщо шнур живлення
замінений кваліфікованим фахівцем, не уповноваженим
STANLEY, гарантія не діятиме.
Додаткові заходи безпеки для
електроінструменту
Застереження! Інструкції з техніки безпеки для всіх видів
пил
Процедури різання
a. Небезпека! Тримайте руки подалі від зони різання і
диска пили. Тримайте другу руку на допоміжній
рукоятці або корпусі двигуна. Якщо тримати пилу
обома руками, руки не постраждають від працюючого
диска.
51
Page 52

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
b. Не торкайтесь нижньої частини заготовки. Кожух не
зможе захистити вас від диска нижче заготовки.
c. Відрегулюйте глибину різання згідно товщині
заготовки. Над заготівлею повинно бути видно трохи
менше повного зубця зубчастого диска пили.
d. Ніколи не тримайте заготовку, яку необхідно
розпиляти в руках і не притримуйте ногами. Закріпіть
заготовку на стійкій платформі. Важливо
підтримувати заготовку таким чином, щоб звести до
мінімуму вплив на тіло, застрявання диска або
втрату контролю.
e. Тримайте електроінструмент за ізольовані поверхні
при виконанні дій, при яких ріжучий інструмент може
зачепити приховану проводку. Контакт з
"працюючим" проводом також оголить металеві
частини працюючого електроінструменту, в
результаті чого оператора може вдарити
електричним струмом.
f. При поздовжньому розпилюванні завжди
використовуйте направляючу планку або пряму бічну
напрямну. Це підвищує точність різу і зменшує
ймовірність стримування пильного диску.
g. Завжди використовуйте пилкові диски з правильним
розміром і формою зі шпиндельними отворами.
Диски, які не відповідають монтажному обладнанню
пили працюватимуть ексцентрично, що призведе до
втрати контролю.
h. Ніколи не використовуйте пошкоджені або
неправильні шайби або болти для пильних дисків.
Дискові шайби і болти були спеціально розроблені
для вашого типу пили для забезпечення оптимальної
продуктивності і безпеки праці.
Причини віддачі і пов'язані з нею
попередження
• Віддача це - раптова реакція на защемлення або
застрявання або перекіс пилкового диска, що
викликає неконтрольований рух пили вгору і вниз від
заготівлі і в бік оператора.
• Коли диск затискається або застряє, рухова реакція
змушує інструмент зробити швидкий поштовх назад
до оператора.
• Якщо диск стає зігнутим або зміщеним в розрізі,
зубці задньої кромки диска можуть врізатися в
поверхню деревини в результаті чого диск вискочить
з пропила і відлетить назад до оператора.
• Віддача є результатом неправильного використання
інструменту та/або неправильних дій оператора або
умов, її можна уникнути, прийнявши відповідні
52
запобіжні заходи, як зазначено нижче.
a. Міцно тримайте інструмент обома руками і
переконайтеся, що положення вашого тіла і рук
дозволить вам протистояти впливу зворотного удару
(віддачі). Оператор може контролювати силу віддачі,
якщо прийняті відповідні запобіжні заходи.
b. Коли диск пилки стримується з якої-небудь причини
відбувається збій під час розпилу, відпустіть курок і
утримуйте пилку нерухомо в матеріалі, поки диск
повністю не зупиниться. Ніколи не намагайтеся
видалити пилку під час роботи і не тягніть її назад в
той час як диск знаходиться в русі, так як це може
призвести до віддачі. Слід зрозуміти причину і вжити
корегуючі дії з метою усунення причин застрявання
диска.
c. При перезапуску пили, коли диск знаходиться у
заготівлі, переконайтеся, що пильний диск
знаходиться в пропилу і зубци диска не застрягли в
матеріалі. Якщо диск застряг, він може вискочити або
призвести реакцію віддачі від заготовки, як тільки
пилу буде перезапущено.
d. Підтримуйте великі панелі для зведення до мінімуму
ризику утиску диска і віддачі. Великі панелі, як
правило, прогинаються під власною вагою. Підтримка
повинна бути поміщена під панеллю з обох сторін,
поруч з лінією різу і біля краю панелі.
e. Не використовуйте тупі або пошкоджені диски.
Незаточені або неправильно встановлені диски
роблять вузький пропил, викликаючи надмірне тертя,
утиск диска і віддачу.
f. Глибина диска і конічні установочні замикаючі важелі
повинні бути надійно затягнуті перш ніж почати
різання. Якщо регулювання диска зсувається під час
різання, це може призвести до ущемлення і віддачі.
g. Будьте особливо обережні при виконанні
"кишенькового різання" в існуючих стінах або інших
сліпих зонах. Виступаючі диски можуть відрізати
об'єкти, які можуть призвести до виникнення віддачі.
Функція нижнього захисного кожуха
a. Перевірте чи добре закритий нижній захисний кожух
перед кожним використанням. Не використовуйте
пилу, якщо нижній захисний кожух не рухається
вільно і не закривається миттєво. Ніколи не
закріплюйте і не прив'язуйте нижній захисний кожух у
відкритому положенні. Якщо пила випадково впала,
нижній кожух може бути зігнутий. Підніміть нижній
захисний кожух з ручкою втягування і переконайтеся,
що він вільно переміщується і не торкається диска
або будь-якої іншої частини, при всіх кутах і глибині
різання.
Page 53

(Оригінальні інструкції)
УКРАЇНСЬКА
b. Перевірте роботу пружини нижнього захисного
кожуха. Якщо кожух і пружина не працюють
належним чином, вони повинні пройти технічне
обслуговування перед використанням. Нижній
захисний кожух може працювати повільно через
наявність пошкоджених частин, смолистих
відкладень або сміття.
c. Нижній захисний кожух може бути втягнутий вручну
тільки для особливих видів різання, таких як
"погружне" або "складне" різання. Підніміть нижній
захисний кожух шляхом втягування ручки і, як тільки
пильний диск входить в матеріал, нижній кожух
повинен бути звільнений. Для всіх інших видів
розпилювання, нижній кожух повинен працювати в
автоматичному режимі.
d. Завжди стежте за тим, щоб нижній кожух покривав
диск до розміщення пили на верстаті або на підлозі.
Незахищений діск, що рухається за інерцією, змушує
пилку рухатися назад і різати все, що є на шляху. Ви
повинні знати скільки часу необхідно для зупинки
пильного диска після відпускання вимикача.
Iнші ризики
Додаткові залишкові ризики можуть виникнути при
використанні інструменту, який не може бути включений
в описані тут правила техніки безпеки. Ці ризики можуть
виникнути при неправильному або тривалому
використанні виробу і т.д. Незважаючи на дотримання
відповідних правил техніки безпеки та використання
запобіжних пристроїв, деяких залишкових ризиків
неможливо уникнути. Вони включають в себе:
• Травми в результаті торкання обертових/рухомих
частин.
• Ризик отримання травми під час зміни деталей
інструменту, ножів або насадок.
• Травми, викликані тривалим використанням
інструменту. При використанні інструменту протягом
тривалого часу робіть регулярні перерви в роботі.
• Поганий слух
• Збиток здоров'ю внаслідок вдихання пилу при
використанні інструменту (приклад: робота з
деревом, особливо, з деревиною дуба, бука і
деревоволокнистими плитами середньої щільності)
Правила техніки безпеки/визначення
Важливо, щоб ви прочитали і зрозуміли цей посібник. В
ньому міститься інформація відносно захисту вашої
безпеки та запобігання проблемам. Наведені нижче
символи використовуються, щоб допомогти вам
розпізнати цю інформацію.
Небезпека! Вказує на потенційно небезпечну
ситуацію, яка, якщо її не уникнути, призведе
до смерті або серйозних травм.
Попередження! Вказує на потенційно
небезпечну ситуацію, яка, якщо її не уникнути,
могла б призвести до смерті або серйозних
травм.
Застереження! Вказує на потенційно
небезпечну ситуацію, яка, якщо її не уникнути,
може призвести до легкої або середньої травми.
Застереження! Використовується без знака
небезпеки, вказує на потенційно небезпечну
ситуацію, яка, якщо її не уникнути, може призвести до
пошкодження майна.
Додаткові правила техніки безпеки для
циркулярних пилок
Застереження! Часто пил, що утворився після
грубої шліфовки, пиляння, шліфування,
свердління та інших будівельних робіт містить хімічні
речовини, які можуть викликати рак, вроджені дефекти
або інші порушення репродуктивної функції. Деякі
приклади цих хімікатів:
• Свинець з свинцевих фарб
• Кристалічний кремнезем від цегли, цементу та інших
продуктів кладки
• Миш'як і хром з хімічно обробленої деревини.
53
Page 54

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
Ризик від впливу даних речовин залежить від того, як
часто ви проводите цей тип робіт. Щоб знизити вплив
цих хімікатів:
• Працюйте в добре провітрюваному приміщенні з
відповідними засобами забезпечення безпеки,
включаючи респіратори, які спеціально розроблені
для фільтрації мікроскопічних часток.
• Уникайте тривалого контакту з пилом під час
шліфування, пиляння, свердління та інших
будівельних робіт. Носіть захисний одяг і мийте
відкриті ділянки тіла водою з милом. Потрапляння
пилу в рот, очі або на шкіру може сприяти засвоєнню
шкідливих хімічних речовин.
Увага! Носіть відповідні засоби для захисту
органів слуху під час використання. При
деяких умовах і тривалості використання, шум від цього
продукту може сприяти втраті слуху.
• Якщо нижній захисний кожух зачіпається на поверхні
нижче матеріалу, що розрізається, це може
короткочасно знизити контроль оператора. Пила
може піднятися з розрізу частково, що може
збільшити можливість викривлення диска.
Переконайтеся, що під заготівлею є достатній зазор.
• При необхідності підняти нижній захисний кожух
вручну, використовуйте важіль втягування.
• Тримайте диски чистими і гострими. Гострі диски
мінімізують перекидання і віддачу. Використання
зіпсованих та/або брудних дисків може збільшити
навантаження на пилу, в результаті чого оператору
треба буде сильніше штовхати пилку, що може
призвести до викривлення.
Застереження! Небезпека ушкодження. Тримайте руки
подалі від місця розпилу. Тримайте руки подалі від
пильних дисків. Ніколи не кладіть руки перед або позаду
шляху руху диска під час різання. Не торкайтеся до
заготівлі під час обертання пилкового диска. Не
намагайтеся видалити зрізаний матеріал під час руху
диска.
• Підтримка великих панелей. Великі панелі повинні
бути підтримані як показано на малюнку А у цьому
посібнику, щоб мінімізувати ризик защемлення диска
і віддачі. Матеріал підтримується тільки по краях
(мал. В) і може призвести до затискання диска. Якщо
під час різання потрібно дати відпочинок пилі на
заготівлі, пилку слід покласти на більшій частині, а
менший шматок відрізати.
• Використовуйте тільки правильні диски і компоненти
дисків для установки. Не використовуйте диски з
отворами неправильного розміру. Ніколи не
використовуйте диски з дефектами або шайби і болти
для диска неправильного розміру. Чітко
дотримуйтесь процедури установки диска.
Пильні диски
• Не використовуйте диски більше або менше
рекомендованого діаметру. Для правильного розміру
диска, зверніться до технічних даних. Використовуйте
тільки диски, зазначені в цьому посібнику, що
відповідають стандарту EN 847-1.
Застереження! Ніколи не використовуйте абразивні
диски.
Безпека сторонніх осіб
• Цей інструмент не призначений для використання
особами (включаючи дітей) з обмеженими фізичними,
чутливими або розумовими здібностями або з браком
досвіду чи знань, якщо вони не були під контролем і
керівництвом особи, яка контролює використання
приладу або відповідальна за їх безпеку.
• Діти повинні бути під наглядом дорослих, щоб не
допустити ніяких ігор з приладом.
Вібрація
Заявлені значення рівня вібрації, зазначені в технічних
характеристиках інструменту та декларації відповідності,
були виміряні відповідно до стандартних методов
визначення EN 60745 і можуть використовуватися для
порівняння одного інструмента з іншим. Оголошене
значення вібраційного впливу також може бути
використано для попередньої оцінки впливу.
Застереження! Значення вібраційного впливу при
фактичному використанні електроінструменту може
відрізнятися від заявленого значення залежно від
способів, за допомогою яких використовується
інструмент. Рівень вібрації може перевищувати заявлене
значення.
При оцінці ступеня вібраційного впливу для визначення
необхідних захисних заходів, необхідних згідно із
54
Page 55

(Оригінальні інструкції)
УКРАЇНСЬКА
законом 2002/44/EC для захисту людей, постійно
використовують електроінструмент, оцінка впливу
вібрації повинна розглядати фактичні умови
використання і спосіб, за допомогою якого
використовується інструмент, в тому числі з
урахуванням всіх сегментів робочого циклу, включаючи
час, коли інструмент знаходиться у вимкненому стані, і
коли він працює в холостому режимі на додаток до часу
спрацьовування.
• Регулювання. Перед розпилом переконайтеся, що
коригування глибини і нахилу встановлені належним
чином.
• Підтримка та забезпечення належної безпеки
роботи. Переконайтеся, що матеріал для
розпилювання затиснутий (рис. C), надійно
підтримується і збалансований на міцній, стійкій і
рівній робочій поверхні. Проводьте роботу так, щоб
широка частина підошви перебувала на частині
матеріалу, який не впаде після розпилу. Ніколи не
тримайте відрізаний шматок рукою (рис. D). Це може
призвести до віддачі від защемлення диска. Завжди
тримайте обидві руки на пилі.
• Будьте уважні і здійснюйте постійний контроль.
Займіть положення з однієї сторони леза. Завжди
міцно тримайте інструмент обома руками. Не
змінюйте положення рук або положення тіла під час
роботи пили. Необхідно вжити заходів обережності,
щоб уникнути травм від відрізаних шматків та іншого
падаючого матеріалу під час роботи.
Небезпека! Відпустіть перемикач негайно, якщо диск
застрягне або пила зупиниться.
Особливості (мал. Е)
Цей інструмент включає в себе деякі або всі з таких
ознак:
1. Вмикач/вимикач живлення
2. Головна ручка
3. Допоміжна ручка
4. Башмак
5. Пільний диск
7. Важіль втягування захисного кожуха диска
8. Гучний ключ пилкового диска
9. Ручка регулювання нахилу
10. Зовнішня шайба
11. Регулювальний гвинт диска
Шестигранний ключ пилкового диска (як показано на
малюнку I)
18. Паралельний упор (як показано на мал. М)
Внутрішній фланець (як показано на мал. J)
Монтаж/регулювання
Застереження! Завжди відключайте пилку від джерела
живлення до будь-якої з таких операцій:
Регулювання глибини різу (мал. F і G)
Глибина різання повинна бути встановлена відповідно до
товщини заготовки.
• Послабте важіль (12), щоб розблокувати підошву.
• Перемістіть підошву (4) в необхідне положення.
Відповідна глибина різання може бути прочитана за
шкалою (13).
• Затягніть важіль, щоб зафіксувати підошву на місці.
• Встановіть глибину різання пилки таким чином, що
один зубець диска був нижче заготовки, як показано
на малюнку
Діапазон кутів повороту (мал. H)
• Цей інструмент може бути встановлений на скіс кутів
від 0° до 45°.
• Послабте ручку блокування (9), щоб розблокувати
підошву.
• Перемістіть підошву (4) в необхідне положення.
Відповідний кут нахилу можна прочитати за шкалою
(14).
• Затягніть ручку блокування, щоб зафіксувати підошву
на місці.
6. Кожух пилкового диска
55
Page 56

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
Установка диска (мал. I і J)
• Для запобігання обертання шпинделя, зачепить
виступи на гайковому ключі (8) в отвори в зовнішній
шайбі (10), як показано на мал. I.
• Послабте і зніміть кріпильний гвинт диска (11),
повернувши шестигранний ключ (15) проти
годинникової стрілки.
• Зніміть зовнішню шайбу.
• Перевірте і зробіть повторну збірку внутрішнього
фланця (20) на шпиндель (16). Переконайтеся, що
правильна сторона внутрішнього фланця (20)
дивиться назовні і відповідає пильному диску з
діаметром отворів шпинделя.
• Помістіть пильний диск (5) на внутрішній фланець
(20), переконавшись, що стрілки на диску
знаходяться в тому ж напрямку, що і стрілка на
інструменті.
• Встановіть зовнішню шайбу (10) на шпиндель.
• Вставте кріпильний гвинт диска (11) в отвір в
шпинделі.
• Не допускайте обертання шпинделя, вставивши
гайковий ключ в отвори на зовнішній шайбі.
• Надійно затягніть кріпильний гвинт диска, утримуючи
гайковий ключ і повертаючи шестигранний ключ за
годинниковою стрілкою, щоб затягнути кріпильний
гвинт диска.
Застереження! Внутрішній фланець (20),
відповідно маркований цифрами "19" і "20",
відповідає пильному диску (5) з діаметром
шпинделя 19 і 20 мм.
Зняття пилкового диска
• Для запобігання обертання шпинделя зачепить
виступи на гайковий ключ (8) в отвори в зовнішній
шайбі (10).
• Послабте і зніміть кріпильний гвинт диска (11),
повернувши шестигранний ключ (15) проти
годинникової стрілки.
• Зніміть зовнішню шайбу (10).
• Зніміть пильний диск (5). Застереження! Щоб знизити
ризик отримання серйозної травми, необхідно
прочитати, зрозуміти і дотримуватися важливіх
правил безпеки та інструкцій перед використанням
інструменту.
Загальне різання
Захист проти віддачі
З пристроєм, відключеним від електричної мережі,
виконайте всі інструкції з монтажу, налагодження та
налаштування. Переконайтеся, що нижній захисний
кожух працює. Виберіть потрібний диск для розрізаємого
матеріалу.
• Виміряйте і зробіть позначки на заготівлі для різання.
• Проведіть всі заходи з підтримки та безпеки роботи
56
(див. Правила та інструкції з техніки безпеки).
• Використовуйте відповідне і необхідне обладнання
безпеки (див. Правила техніки безпеки).
• Забезпечте підтримку і безпеку робочої зони (див.
Правила техніки безпеки).
• З встановленим роз'ємом і закритим кожухом,
переконайтеся, що перемикач вмикає і вимикає
пилку.
Застереження! Важливо підтримувати роботу належним
чином і надійно утримувати пилку, щоб запобігти втраті
контролю, що може призвести до травми. Мал. C
ілюструє рекомендоване положення рук.
Функціональний перемикач
• Щоб включити інструмент, натисніть на курок
вимикача (1). Інструмент буде продовжувати
працювати до тих пір, поки курок вимикача
втоплений.
• Щоб вимкнути інструмент, відпустіть курок вимикача
(1). У інструменті відсутнє положення для фіксації,
тому перемикач ніколи не має бути заблокований
жодними іншими засобами.
Розпилювання
• Застереження! Щоб знизити ризик отримання
серйозної травми, завжди тримайте інструмент обома
руками.
• Дайте диску вільно переміщатися протягом декількох
секунд, перш ніж почати різання.
• Вживайте лише легке натиснення на інструмент при
виконанні розрізу.
• Працюйте з башмаком, притиснутим до
оброблюваної деталі. �
Поради по оптимальному використанню
• Оскільки деяких розколів уздовж лінії розрізу на
верхній стороні заготовки не можливо уникнути, ріжте
по тій стороні, де розколювання є прийнятними.
• Там, де розколювання повинні бути зведені до
мінімуму, наприклад, при різанні ламінату, притисніть
шматок фанери до верхньої частини заготовки.
Кишенькове різання (мал. К)
Кишенькове різання використовується для вирізки
отворів у матеріалі без розрізання з боку.
• Зробіть вимірювання та позначки на заготівлі.
• Нахиліть вперед пилку і передню частину башмака на
матеріалі, який буде вирізаний. Вирівняйте таким
чином, щоб розріз почався з заду намальованого
прямокутника, як показано на мал. К.
• Використовуючи важіль втягування, приберіть
захисний кожух диска у верхню позицію, запустіть
двигун і поступово рухайте пилку вниз в матеріалі.
Застереження! У міру того, як диск починає різати
матеріал, негайно звільніть важіль втягування.
Page 57

(Оригінальні інструкції)
УКРАЇНСЬКА
• Ніколи не закріплюйте захисний кожух в піднятому
положенні.
• Коли башмак лежить на матеріалі, закінчити розпил
в прямому напрямку.
• Дайте диску повністю зупинитися перш, ніж підняти
пилку від матеріалу.
• Коли починаєте кожне нове різання, повторіть
описані вище кроки
Зберігання гайкового ключа (мал. L)
Гайковий ключ (8) може зберігатися на башмаку пили, як
показано на рис. L
Установка і зняття паралельного упору (мал. M)
Паралельний упор використовується для розпилу по
прямій лінії, паралельної краю заготовки.
Додатки
• Послабте ручку блокування (17).
• Вставте паралельний упор (18) через отвори (19).
• Вставте паралельний упор в потрібне положення.
• Затягніть ручку блокування.
Зняття
• Послабте ручку блокування.
• Зніміть паралельний упор з інструменту. Примітка:
якщо у вас немає правильно підібраного упору,
використовуйте пряму бічну напрямну в контакті з
краєм башмака, щоб підвищіти точність різання и
зменшити ймовірність застрявання и віддачі.
Аксесуари
Продуктивність вашого електроінструменту залежить від
використовуваних аксесуарів. Аксесуари STANLEY
розроблено відповідно високим стандартам якості, і вони
здатні збільшити продуктивність вашого
електроінструменту. Використовуючи ці приналежності,
ви зможете найбільш ефективно використовувати ваш
інструмент.
Застереження! Використання будь-яких
аксесуарів не рекомендовано для
використання з цим інструментом і може бути
диски з діаметром шпинделя 19 або 20 мм.
небезпечним. Використовуйте тільки 185 мм
Обслуговування
Ваш інструмент був розроблений для роботи протягом
тривалого періоду часу при мінімальному технічному
обслуговуванні. Для забезпечення задовільної роботи,
інструмент повинен правильно зберігатися і піддаватися
регулярному чищенню.
Застереження! Перед виконанням будь-яких
робіт з обслуговування вимкніть і відключіть
інструмент.
• Регулярно очищайте вентиляційні прорізи
інструменту м'якою щіткою або сухою тканиною.
• Регулярно очищайте корпус двигуна вологою
тканиною. Не використовуйте абразивні речовини або
чистящи розчини на основі розчинника. Важливо! Для
забезпечення безпеки і надійності обладнання,
ремонт, технічне обслуговування і регулювання (крім
тих, які перераховані в цьому посібнику) повинні
виконуватися кваліфікованим персоналом в
авторизованих сервісних центрах з використанням
оригінальних запасних частин.
Змазування
Інструменти Stanley були належним чином змащені на
заводі і готові до використання.
Інформаційна служба
STANLEY пропонує повну мережу авторизованих
сервісних центрів, що належать компанії. Всі сервісні
центри STANLEY укомплектовані персоналом, який
пройшов навчання, щоб надати клієнтам ефективний і
надійний сервіс з обслуговування електроінструментів.
Для отримання додаткової інформації про авторизовані
сервісни центри або якщо вам потрібна технічна рада,
ремонт або оригінальні запасні частини, вам необхідно
звернутися в найближчий сервісний центр STANLEY.
LpA (тиск звуку) dB(A) 92.5
Мінливість (K) dB(A) 3
LWA (потужність звуку) dB(A) 103.5
Мінливість (K) dB(A) 1.5 m/s
Загальні значення вібрації згідно
Різки дерева (ah, W) = 3.3 m/s2
Мінливості (K) = 1.5 m/s
Рівень вібрації, зазначений у цьому інформаційному
листку, був розрахований відповідно зі
стандартизованим випробуванням, що міститься в EN
60745 і може використовуватися для порівняння одного
інструмента з іншим. Він може бути використаний для
попередньої оцінки впливу.
належному обслуговуванню, рівень вібрації може
відрізнятися. Це може підвищити рівень впливу в 1,5
рази протягом усього робочого періоду.
При оцінці рівня впливу вібрації необхідно також
враховувати час, коли інструмент вимкнений або коли він
включений, але насправді не робить свою роботу. Це
може значно зменшити рівень впливу протягом усього
періоду роботи.
Визначте додаткові запобіжні заходи для захисту
оператора від впливу вібрації, такі як: ретельний догляд
за інструментом і аксесуарами, зміст рук в теплі,
організація режимів
2
Застереження: Зазначений рівень вібрації
представлений для основних застосувань
інструменту. Однак, якщо інструмент
використовується для різних застосувань з
різноманітними аксесуарами або піддавався
2
57
Page 58

УКРАЇНСЬКА
(Оригінальні інструкції)
Захист навколишнього середовища
Роздільний збір і утилізація. Цей продукт не
слід утилізувати разом з побутовим сміттям.
Якщо ви зрозумієте, що ваш продукт Stanley потребує
заміни, або якщо він не має ніякого подальшого
застосування для вас, не викидайте його разом з
побутовими відходами. Надайте цей продукт для
роздільного збору/утилізації.
Роздільний збір продуктів і упаковок дозволяє
здійснити їх переробку і використати їх
повторно. Повторне використання перероблених
матеріалів допомагає захищати довкілля від
забруднення і знижує витрату сировинних матеріалів.
Місцеве законодавство може забезпечити збір старих
електроінструментів окремо від побутового сміття на
муніципальних звалищах відходів або в торговому
підприємстві при купівлі нового виробу. Stanley
забезпечує можливість для збору і утилізації продуктів
Stanley, як тільки вони досягли кінця свого терміну
служби. Для того, щоб скористатися цією послугою, ви
можете здати ваш виріб у будь-який авторизований
сервісний центр, який збирає їх за нашим дорученням.
Ви можете упізнати місце знаходження вашого
найближчого авторизованого сервісного центру,
звернувшись в місцеве відділення Stanley за адресою,
вказаною в цьому керівництві. Крім того, список
авторизованих ремонтних агентів Stanley і повну
інформацію про наше післяпродажне обслуговування і
контакти ви можете знайти в Інтернеті:
www.2helpu.com10
Два рік повної гарантії
Якщо ваш продукт STANLEY виходить з ладу із-за
дефектних матеріалів або виготовлення впродовж 24
місяців з дати купівлі, STANLEY Europe гарантує заміну
усіх несправних деталей безкоштовно або - на власний
розсуд - заміну продукту безкоштовно за умови, що:
• Продукт використовувався правильно, його
експлуатація проводилася строго відповідно до
інструкції з експлуатації.
• Продукт піддавався звичайному зносу;
• Ремонт не проводився сторонніми особами;
• Представлені документи, що підтверджують купівлю.
• Продукт STANLEY повертається в повному комплекті
з усіма оригінальними компонентами
Якщо ви хочете зробити заявку, зв'яжіться з продавцем
або з’ясуйте місце знаходження вашого найближчого
авторизованого сервісного агента Stanley в каталозі
Stanley або зверніться в місцеве представництво Stanley
за адресою, вказаною в цьому посібнику. Список
авторизованих сервісних агентів Stanley і повну
інформацію про наше післяпродажне обслуговування
можна знайти в Інтернеті за адресою:
www.stanleytools.com
58
Page 59

(Оригінальні інструкції)
Гарантійні умови
Шановний покупець!
1. Вітаємо Вас з покупкою високоякісного виробу
STANLEY і висловлюємо вдячність за Ваш вибір.
2. При покупці виробу вимагайте перевірки його
комплектності і справності у Вашій присутності,
інструкцію з експлуатації та заповнений гарантійний
талон українською мовою
В гарантійному талоні повинні бути внесені: модель,
дата продажу, серійний номер, дата виробництва
інструменту; назва, печатка і підпис торгової
організації. За відсутності у Вас правильно
заповненого гарантійного талону, а також при
невідповідності зазначених у ньому даних ми
будемо змушені відхилити Ваші претензії щодо
якості даного виробу.
3. Щоб уникнути непорозумінь, переконливо просимо
Вас перед початком роботи з виробом уважно
ознайомитися з інструкцією з його експлуатації.
Правовою основою справжніх гарантійних умов є
чинне Законодавство. Гарантійний термін на даний
виріб складає 24 місяці і обчислюється з дня
продажу. У разі усунення недоліків виробу,
гарантійний строк продовжується на період його
перебування в ремонті. Термін служби виробу
становить 5 років з дня продажу.
4. У разі виникнення будь-яких проблем у процесі
експлуатації виробу рекомендуємо Вам звертатися
тільки в уповноважені сервісні центри STANLEY,
адреси та телефони яких Ви зможете знайти в
гарантійному талоні, на сайті www.2helpU.com або
дізнатися в магазині. Наші сервісні станції - це не
тільки кваліфікований ремонт, але і широкий
асортимент запчастин і аксесуарів.
5. Виробник рекомендує проводити періодичну
перевірку і технічне обслуговування виробу в
уповноважених сервісних центрах.
6. Наші гарантійні зобов'язання поширюються тільки
на несправності, виявлені протягом гарантійного
терміну і викликані дефектами виробництва та \ або
матеріалів.
7. Гарантійні умови не поширюються на несправності
виробу, що виникли в результаті:
7.1 Недотримання користувачем приписів інструкції з
експлуатації виробу, застосування виробу не за
призначенням, неправильного зберігання,
використання приладдя, витратних матеріалів і
запчастин, що не передбачені виробником.
7.2 Механічного пошкодження (відколи, тріщини і
руйнування) внутрішніх і зовнішніх деталей виробу,
основних і допоміжних рукояток, мережевого
кабелю, що викликані зовнішнім ударним або
будь-яким іншим впливом
УКРАЇНСЬКА
7.3 Потрапляння у вентиляційні отвори та проникнення
всередину виробу сторонніх предметів, матеріалів
або речовин, що не є відходами, які супроводжують
застосування виробу за призначенням, такими як:
стружка, тирса, пісок, та ін.
7.4 Впливу на виріб несприятливих атмосферних і
інших зовнішніх факторів, таких як дощ, сніг,
підвищена вологість, нагрівання, агресивні
середовища, невідповідність параметрів
електромережі, що зазначені на інструменті.
7.5 Стихійного лиха. Пошкодження або втрати виробу,
що пов'язані з непередбаченими лихами,
стихійними явищами, у тому числі внаслідок дії
непереборної сили (пожежа, блискавка, потоп і інші
природні явища), а також внаслідок перепадів
напруги в електромережі та іншими причинами, які
знаходяться поза контролем виробника.
8. Гарантійні умови не поширюються:
8.1. На інструменти, що піддавались розкриттю, ремонту
або модифікації поза уповноваженим сервісним
центром.
8.2. На деталі, вузли та матеріали, що мають сліди
природного зносу, такі як: приводні ремені і колеса,
вугільні щітки, мастило, підшипники, зубчасті
зчеплення редукторів, гумові ущільнення, сальники,
направляючі ролики, муфти, вимикачі, бойки,
штовхачі, стволи тощо.
8.3. На змінні частини: патрони, цанги, затискні гайки і
фланці, фільтри, акумуляторні батареї, ножі,
шліфувальні підошви, ланцюги, зірочки, пильні
шини, захисні кожухи, пилки, абразиви, пильні і
абразивні диски, фрези, свердла, бури тощо
8.4. На несправності, що виникли в результаті
перевантаження інструменту (як механічного, так і
електричного), що спричинили вихід з ладу
одночасно двох і більше деталей і вузлів, таких як:
ротора і статора, обох обмоток статора, веденої і
ведучої шестерень редуктора або інших вузлів і
деталей. До безумовних ознак перевантаження
виробу відносяться, крім інших: поява кольорів
мінливості, деформація або оплавлення деталей і
вузлів виробу, потемніння або обвуглювання
ізоляції проводів електродвигуна під впливом
високої температури.
90618245 01/2015
59
Page 60

Names & Addresses for STANLEY Service Concessionaries - MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
ALGERIA: Sarl Outillage Corporation, 08 Rue Med Boudiaf - Cheraga - Algiers, Algeria. Tel: (213-21) 375130, Fax: (213-21) 369667. ANGOLA: Angoferraria,
Lda., Rua Robert Shields, No. 61, Luanda, Angola, Tel: 00244-222-395837 / 222-395034, Fax: 00244-222-394790. AZERBAIJAN: Royalton Holdings Ltd. 41
Khagani St. Apt. 47 AZ 1001, Baku. Tel: (994-12) 4935544, Fax: (994-12) 5980378. BAHRAIN: Kavalani & Sons W.L.L., P.O. Box 71, Sitra, Manama, Tel: (973)
17732888, Fax: (973) 17737379. Alfouz Services Co. WLL., P.O. Box 26562, Tubli, Manama. Tel: (973) 17783562, Fax: (973) 17783479. EGYPT: El Farab
S.A.E., 15-Nabil El Wakkad Street, Dokki, Giza, Egypt, Tel: 00202-37603946 / 002-010-2582544, Fax: 00202-33352796. ETHIOPIA: Seif Tewfik Sherif, Arada
Sub-City, Kebele 01/02, Global Insurance Building, 2nd Floor, Room 43, P.O. Box 2525, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Tel: (251-11) 1563968/ 1563969, Fax: (251-11)
1558009. IRAQ: Financial Links, Kazzaz Building Arasat Al-Hindia Block No: 629 Street: 31Building No: 1 Baghdad – Iraq. Tel: 00964 (0)780 195 2223/ 00964
(0)781 3763044. Al Sard Co. for General Trading Ltd. Jbara Bldg. 3Flr, Al Rasheed St. Bagdad. Tel: (964) 18184102. Sakhar Group, Arrassat al-hindya Al
Masbah, Bagdad. (964) 7400144446. JORDAN: Palestine Bldg. Matl. (Bashiti Hardware), 93 King Abdullah 2nd Street, Opp. ELBA House, P.O. Box 3005,
Amman 11953, Tel: (962-6) 5349098, Fax: (962-6) 5330731. KENYA: Dextron Tools Ltd., P.O. Box 20121-00200, Shariff House, Kimathi Street, Nairobi. Tel:
(254-20) 6905000/ 2358021, Fax: (254-20) 6905111/ 6905112. KUWAIT: Al Omar Technical Co., P.O. Box 4062, 13041 Safat, Kuwait. Tel: (965) 24848595/
24840039, Fax: (965) 24845652. Fawaz Al Zayani Establishment, P.O. Box 42426, Shop No. 18, Al Humaizi Commercial Complex, Khalifa Al Jassim,
Shuwaikh, Kuwait. Tel: (965) 24828710, Fax: (965) 24828716. Fawaz Al Zayani Establishment, P.O. Box 42426, Shop No.18, Al Humaizi Commercial
Complex, Khalifa Al Jassim, Shuwaikh, Kuwait, Tel: (965) 24828710, Fax: (965) 24828716. Fawaz Al Zayani Establishment, Fahaheel Industrial Area, Main St.,
Sanaya, Kuwait, Tel: (965) 23925830, Fax: (965) 24828716. LEBANON: Est. Shaya & Azar S.A.R.L., Boulvard Jdeideh - Mar Takla - Bouchrieh .P.O. Box
90545 Jdeideh.Beirut - Lebanon, Tel: 00961 1 872305 / 306 , Fax: 00961 1 872303. LIBYA: North Africa Trading ( El Ghoul Brothers), AlHilal Service Center
Tawergha St. Misurata, Tel: 00218-091-3221408. (Benghazi) Sniydel st., Amr Ibn EL-Aas Rd. Tel: (+218) 92 5771120. (Tripoli) Al Barniq Service Center,
Mokhazin elsukar st., ElFallah. Tel: (+218) 21 4808019. (Misrata) Al Hilal Service Center, Tawergha st. Tel: (+218) 51 2626743. MAURITIUS: Robert Le Marie
Limited, Old Moka Road, Bell Village, P.O. Box 161, Port Louis, Tel: 00230-212 1865/ 212 2847, Fax: 00230-2080843. MOROCCO: Ets Louis Guillaud & Cie,
149, Quartier Industriel, Moulay Rachid, Casablanca, Postal Code 20450, Morocco, Tel: 00212-522729233, Fax: 00212-522729096. NIGERIA: Meridian
Power Tools Ltd., Gr.Floor, #1 Alhaji Masha Rd, Next toTeslim Balogun Stadium, Near National Stadium Surulere, Lagos, Nigeria, Tel: 00234-1-7740431 /
7740410, Fax: 00234-1-7913798. OMAN: Al Jizzi Company LLC, P.O. Box 1704,PC 112 Ruwi, Oman, Tel: (968) 24832618/ 24835153, Fax: (968)
24831334/24836460. Al Hassan Technical & Construction Supplies Co. LLC, P.O. Box 1948, P.C. 112, Ruwi, Tel: (968) 24810575 / 24837054, Fax: (968)
24810287/ 24833080. Oman Hardware Co. LLC, P.O. Box 635, Ruwi Postal Code 112, Te: (968) 24815131, Fax: (968) 24816491. Khimji Ramdas, P.O. Box
19, Post Code 100, Ghala, Muscat, Oman. Tel: (968) 24595906/ 907, Fax: (968) 24852752. Oman Marketing & Service Co. (Omasco), P.O. Box 2734, Behind
Honda Showroom, Wattayah, Oman. Tel: (968) 24560232/ 24560255, Fax: (968) 24560993. Oman Marketing & Service Co. (Omasco), Al Ohi, Sohar, Oman.
Tel: (968) 26846379, Fax: (968) 26846379. Oman Marketing & Service Co. (Omasco), Sanaya, Salalah, Oman. Tel: (968) 23212290, Fax: (968) 23210936.
PAKISTAN: ZIT Co - Nasir & Bros., 2nd Floor, Qadri Center, Chowk Dalgran Railway Road, Lahore, Pakistan, Tel: 0092 42 37670839, Fax: 0092 42
37652989. Ammar Service & Spares, 60-Bank Arcade, Serai Road, Karachi, Pakistan. Tel: (92-21) 32426905, Fax: (92-21) 32427214. QATAR: Teyseer
Industrial Supplies & Services Co. WLL, 55, Al Wakalat St. (Between St. 18 & 19) Salwa Industrial Area, P.O. Box 40523 Doha,Qatar, Te: (974) 44581536, Fax:
(974) 44682024. Shaheen Electrical Works & Trading Co. WLL, Gate 34, St. 44 Industrial Area P.O. Box 9756, Doha, Tel: (974) 44600230 /44600525, Fax:
(974) 44601338. Al Muftah Service Centre, Al Wakrah Road, P.O. Box 875, Doha,Qatar, Tel: (974) 44650880/ 44650110/ 44446868, Fax: (974) 44441415 /
44662599. SAUDI ARABIA: (Al Bahr) Mohamed Ahmed Bin Afif Est., P.O. Box 530, Yanbu, Al Bahr. Tel: (966-4) 3222626/ 3228867, Fax: (966-4) 3222210.
(Al Khobar) Fawaz Ebrahim Al Zayani Trading Est., P.O. Box 76026, Al Khobar # 31952, Tel: (966-3) 8140914, Fax: (966-3) 8140824. MSS (Al-Mojil Supply &
Services) P.O. Box 450, Jubail 31951, Opp. Gulf Bridge Library & Riyadh House. Tel: (966-3) 3612850/ 3624487/ 3621729, Fax: (966-3) 3623589/ 3620783.
(Dammam) MSS (Al-Mojil Supply & Services), P.O. Box 450, Jubail 31951.Opp-Gulf Bridge Library & Riyadh House, Tel: (966-3) 3612850 / 3624487 /
3621729, Fax: (966-3) 3623589 / 3620783. Al Bawardi Tools & Hardware, P.O. Box 112, Dammam, Tel: (966-3) 8330780 Ext.24 / 8348585 Ext. 24 /
+966-3-8335555, Fax: (966-3) 8336303. (Al Hassa) Mutawa Trading & Gen. Services, Maliki road Hafuf city, Al Hassa, KSA. Tel: (966) 502846275 (Jeddah) Al
Bawardi Tools & Hardware, P.O. Box 16905, Jeddah 21474, Tel: (966-2) 6444547 / 6439035 / 6456095, Fax: (966-2) 6439024. EAC (Al Yousef Contg. & Trdg.
Est.), P.O. Box 30377, Jeddah -21477, Tel: (966-2) 6519912, Fax: (966-2) 6511153. (Madina) Garziz Trading for Bldg Mat & Decoration, P.O. Box 3364,
Madina, Tel: (966-4) 826 14 90 / 8227636, Fax: (966-4) 8265741. (Riyadh) Industrial Material Organization (IMO), P.O. Box 623, Rail Street ,Riyadh, Tel:
(966-1) 4028010 Ext 26 / 8001245757, Fax: (966-1) 4037970. Sultan Garment Factory (RSC), P.O. Box 29912, Riyadh 11467, KSA, Tel: (966-1) 4055148 /
4042889, Fax: (966-1) 4055148. Al Bawardi Tools & Hardware, P.O. Box 68, Riyadh 11411, Tel: (966-1) 4484999, Fax: (966-1) 4487877. (Yanbu) Fawaz
Ebrahim Al Zayani, Opposite to Al Fouzan, Jeddah highway or King Abdul Aziz road, Yanbu. Tel: (966-4) 3960980, Fax: (966-4) 3961980. Mohamed Ahmed
Bin Afif Est., P.O. Box 530, Yanbu, Al Bahr, Tel: (966-4) 3222626/ 3228867, Fax: (966-4) 3222210. SOUTH AFRICA: Stanley Black & Decker - RSA, 199
Winze Drive Stormill Ext 9 Roodepoort, Tel: (2711) 472 0454, Fax: (2711) 472 0482. Trevco Power Tool Service 14 Steenbok Street, Koedoespoort, 0186,
Pretoria, South Africa. Tel: (27-86) 1873826, Fax: (27-86) 5001771. TANZANIA: General Motors investment Ltd., P.O. Box 16541, 14 Nyerere Road,
Vingunguti, Dar-es-Salaam. Tel: (255 22) 2862661/ 2865022, Fax: (255 22) 2862667. TUNISIA: Societe Tunisienne De Maintenance (STM), Rue de la
Physique. Nouvelle Zone Industrielle Ben Arous., 2013 Ben Arous, Tunisia. Tel: (+216) 79 389687, Fax: (+216) 71 385154. UAE: (Abu Dhabi) Light House
Electrical, P.O. Box 120, Abu Dhabi, Tel: (971-2) 6726131, Fax: (971-2) 6720667. Galaxy Equipment Trading, Madinath Zayed (Baada Zaid), Abu Dhabi P.C.
58910, Tel: (971-2) 8844279, Fax: (971-2) 8844297 (Ajman) Al Sukoon Gen. Trdg. Co. LLC, P.O. Box 2975, Ajman. Tel: (971-6) 7435725/ 7438317, Fax:
(971-6) 7437350. Al Sukoon Gen. Trdg. Co. LLC, P.O. Box 2975, Ajman, Tel: (971-6) 7435725 / 7438317, Fax: (971-6) 7437350 (Al Ain) Zillion Equipment and
Spare Parts Trading LLC, P.O. Box 19740, Opp. Bin Sadal/ Trimix Redymix Sanaiya, Al Ain. Tel: (971-3) 7216690, Fax: (971-3) 7216103. (Dubai) Black &
Decker (Overseas) GmbH, P.O. Box 5420, Dubai, Tel: (971-4) 8127400/ 8127406, Fax: (971-4)2822765. Ideal Star Workshop Eqpt.Trading LLC, P.O. Box
37116, Al Quoz, Dubai, Tel: (971-4) 3474160, Fax: (971-4) 3474157, Fine Tools, P.O.Box 30139 , Al Quoz, Dubai, Tel: (971-4) 3385240, Fax: (971-4) 3385239,
Alebrah Engineering Service, P.O. Box 78954, Al Qusais , Dubai, Tel: (971-4) 2850044, Fax: (971-4) 2844802. (Musaffah) Light House Electrical, P.O. Box
120, Abu Dhabi, Tel: (971-2) 5548315, Fax: (971-2) 5540461. (Sharjah) Mc Coy Middle East LLC, P.O. Box 25793, Sharjah, Tel: (971-6) 5395931, Fax:
(971-6) 5395932. Burj Al Madeena, Industrial Area No.1, Opp. Pakistani Masjid, P.O. Box 37635, Sharjah. Tel: (971-6) 5337747, Fax: (971-6) 5337719. Burj Al
Madeena, , Industrial Area No 1,opp Pakistani Masjid P.O. Box 37635, Sharjah, Tel: (971-6) 5337747, Fax: (971-6) 5337719 (Ras Al Khaimah) Mc Coy Middle
East LLC, P.O. Box 10584, Ras Al Khaimah, Tel: (971-7) 2277095, Fax: (971-7) 2277096. UGANDA: The Building Center (U) Ltd., 52 Station Road, Kitgum
House, P.O. Box 7436, Kampala, Uganda. Tel: (256-41) 4234567/ 4259754, Fax: (256-41) 4236413. YEMEN: (Aden) Middle East Trad. Co. Ltd. (METCO),
Mualla Dakka, Aden, Yemen. Tel: (967-2) 222670, Fax: (967-2) 222670. (Sana'a) Middle East Trad. Co. Ltd. (METCO), Hayel St., Sana'a, Yemen. Tel: (967-1)
204201, Fax: (967-1) 204204. (Taiz) Middle East Trading Co. (METCO), P.O. Box 12363, 5th Flr, Hayel Saeed Anam Bldg, Al-Mugamma St. Taiz, Yemen. Tel:
(967-4) 213455, Fax: (967-4) 219869.
 Loading...
Loading...