Stanley MSD 1000, MSD 1500, MSD 2500, MSD 3000, MSD 4000 Safety, Operation & Maintenance Manual
...Page 1

MSD
Saber Series™
Shears
Part Number 512141
Safety, Operation & Maintenance Manual
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY – PATENT INFORMATION
This product is covered by one or more of the following patents.
U.S. PATENT NUMBERS:
5,474,242 7,240,869
5,531,007 7,487,930
5,992,023 7,578,461
7,322,273 7,832,130
8,146,256 8,104,384
EPO Patent Numbers
435,702
737,107
1,682,299
1,789,225
PREFACE
This manual contains information for the safe and proper operation
and maintenance of MSD Mobile Shears. Read the entire manual before the
initial start-up of the attachment. It is important to know the correct operating
procedures of the attachment and all safety precautions to prevent the possibility
of property damage and personal injury.
The LaBounty attachment has been designed and manufactured with
high quality materials and care in workmanship. The instructions in this manual
have been prepared to ensure that, when followed properly, the attachment
will provide effi cient and reliable service. Continuing product development and
improvement may have caused changes in the attachment that are not refl ected
in this manual. If a question arises regarding the operation or maintenance of the
attachment, contact a LaBounty dealer for the most current information available.
COPYRIGHT © 2012
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION TO SAFETY
Introduction ................................................................................................................................1-2
Understand Signal Words ...........................................................................................................1-2
Safety Summary .........................................................................................................................1-3
Attachment Decals .....................................................................................................................1-5
SECTION 2 ABOUT THE ATTACHMENT
Model Description ......................................................................................................................2-2
Features ......................................................................................................................................2-2
Attachment Terms...................................................................................................................... 2-3
Attachment Glossary ................................................................................................................. 2-4
Flow and Pressure Requirements ..............................................................................................2-7
SECTION 3
Shear Mounting Procedure ......................................................................................................... 3-2
Mobile Shear Start-Up Procedure ...............................................................................................3-4
Shear Removal Procedure ..........................................................................................................3-5
Shear Storage .............................................................................................................................3-5
Internal Rotation Control System Installation (if equipped) .........................................................3-6
Electrical Installation - Internal Rotation Control System .............................................................3-6
Electrical Schematic - Internal Rotation Control System .............................................................3-7
Hydraulic Return Line Installation Instructions - Internal Rotation Control System .....................3-8
Hydraulic Schematic - Internal Rotation Control System ............................................................3-9
INSTALLATION
SECTION 4 OPERATION
Before You Start ..........................................................................................................................4-2
First Things First .........................................................................................................................4-2
Safety Devices You’ll Need .........................................................................................................4-2
General Rules for Safe Operation ...............................................................................................4-3
Mobile Shear Controls ................................................................................................................4-4
Operating the Rotator .................................................................................................................4-6
Backdriving the Rotator ..............................................................................................................4-6
Operating the Internal Rotation Control System .........................................................................4-6
Recharging the Accumulator with Fluid ......................................................................................4-6
Speed Valve Operating Characteristics .......................................................................................4-7
Getting the Feel of the Attachment ............................................................................................4-7
SECTION 5
Scheduled Maintenance ..............................................................................................................5-2
Recommended Spare Parts List ..................................................................................................5-3
Maintenance Safety Procedures ..................................................................................................5-4
General Rules for Maintenance ...................................................................................................5-4
8-Hour Service Recommended ...................................................................................................5-5
80-Hour Service Recommended .................................................................................................5-5
2000-Hour Service Recommended ..............................................................................................5-5
8-Hour Inspection Checklist ........................................................................................................5-6
80-Hour Inspection Checklist ......................................................................................................5-7
8-Hour Inspection Rotator Checklist ............................................................................................5-8
MAINTENANCE
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5 MAINTENANCE continued
Lubrication ...................................................................................................................................5-9
Bolt Torque Guidelines ................................................................................................................5-10
Metric Capscrew Size Guide ......................................................................................................5-10
Torque Values for Metric Fasteners............................................................................................. 5-11
Slide Screw Maintenance ...........................................................................................................5-12
Blade Removal ............................................................................................................................ 5-14
Blade Bolt Torque Specifi cations ................................................................................................. 5-15
Torque Values for Blade Bolts......................................................................................................5-15
Guide Blade Shimming and Rotation ..........................................................................................5-16
Cutting Blade Rotation Procedure .............................................................................................. 5-17
Weld-in Tip Cutting Blade Rotation Procedure ............................................................................ 5-21
Cutting Blade Shimming ............................................................................................................. 5-22
General Guidelines for Build-up and Hardsurfacing ....................................................................5-23
Build-up Recommendations .......................................................................................................5-24
Hardsurfacing Recommendations ..............................................................................................5-24
Critical Wear Areas ......................................................................................................................5-26
Upper Shear Build-up and Hardsurfacing .................................................................................... 5-27
Weld-in Tip Maintenance ............................................................................................................5-28
Weld-in Tip Replacement ............................................................................................................5-30
Front Wear Plate Replacement ...................................................................................................5-32
Lower Wear Plate Replacement .................................................................................................5-33
Lower Shear Build-up and Hardsurfacing ....................................................................................5-34
Hydraulic System Maintenance ..................................................................................................5-37
Flange Type Hose Fittings ........................................................................................................... 5-37
Torque Values for Four-Bolt Flange Fittings .................................................................................5-38
Applying Split Flange Clamps .....................................................................................................5-39
Cylinder Gap Check ....................................................................................................................5-40
Hydraulic Schematic - Standard Rotating Shears ......................................................................... 5-41
Hydraulic Schematic - Standard Non-rotating Shears ..................................................................5-41
Speed Valve Adjustment .............................................................................................................5-42
Decal Maintenance .....................................................................................................................5-54
SECTION 6 ROTATOR MAINTENANCE
Major Components of Typical Rotation Systems ........................................................................6-2
The Rotator .................................................................................................................................6-3
Bolt Torque ..................................................................................................................................6-3
Torque Values for Turntable Bolts ................................................................................................6-3
Torque Values for Rotation Assembly Bolts .................................................................................6-3
Planetary Gearbox Lubrication (if equipped) ...............................................................................6-4
Lubricant Change-out Procedure ................................................................................................6-4
Planetary Gearbox Lubricants .....................................................................................................6-5
Synthetic Specifi cation ...............................................................................................................6-5
Gearbox Fill Capacities ...............................................................................................................6-5
Turntable Bearing ........................................................................................................................6-6
Turntable Bearing Lubricants .......................................................................................................6-6
Hydraulic Requirements ............................................................................................................. 6-7
Rotation Control Valve Manifold .................................................................................................. 6-7
Case Drain .................................................................................................................................. 6-7
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 6 ROTATOR MAINTENANCE continued
Rotation Control Valve Assembly Schematics and Descriptions .................................................6-8
Internal Rotation Control System (if equipped) ...........................................................................6-9
Accumulator Control Valve Assembly (if equipped) ...................................................................6-10
Maintenance Intervals for Internal Rotation (if equipped) ..........................................................6-11
Accumulator Maintenance ......................................................................................................... 6-11
Testing the Accumulator Pre-charge .......................................................................................... 6-12
Pressure Release ....................................................................................................................... 6-12
Accumulator Pre-charging..........................................................................................................6-12
Operating Flow for Internal Rotation ......................................................................................... 6-13
Operating Pressure for Internal Rotation ................................................................................... 6-13
SECTION 7 TROUBLESHOOTING
Cutting Performance Troubleshooting Guide ............................................................................... 7-2
Rotation Circuit Troubleshooting Guide ........................................................................................ 7-5
Internal Rotation Control System Troubleshooting Guide (if equipped) ........................................ 7-7
Speed Valve Troubleshooting Guide ............................................................................................ 7-10
Appendices
Bolt Torque Charts .................................................................................................................A-1 (8-25)
Warranty .....................................................................................................................................A-3
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 7

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION TO SAFETY
Introduction ................................................................................................................................1-2
Understand Signal Words ...........................................................................................................1-2
Safety Summary .........................................................................................................................1-3
Attachment Decals .....................................................................................................................1-4
Introduction to Safety Section 1 Page 1
Page 8

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
INTRODUCTION
Your safety and the safety of others is a direct result
of how you operate and maintain your equipment.
Read and understand this manual and other safety
information provided with the base machine and be
sure that you understand all controls and operating
instructions before attempting to operate this
equipment. Failure to follow the safety precautions
can result in personal injury, death or property
damage.
Carefully read all safety messages in this manual
and on your equipment safety signs. Keep safety
signs in good condition; replace missing or
damaged safety signs.
Because LaBounty cannot foresee all hazardous
circumstances, the precautions listed in this manual
and on the equipment are not all-inclusive. If a
procedure, method, tool or part is not specifi cally
recommended by LaBounty, determine whether it
is safe for you and others, and that the equipment
will not be damaged or made unsafe as a result of
your decision to implement it.
The basic rules are summarized in this section
of the manual. They also appear throughout the
manual along with additional specifi c rules for safety
and operation.
UNDERSTAND SIGNAL
WORDS
When you see the following symbols and signal words
on your equipment or in this manual, be alert to
the potential for personal injury or equipment
or property damage. Follow recommended
precautions and safe operating practices.
Indicates immediate hazards that WILL result in
severe personal injury or death.
Indicates hazards or unsafe practices that CAN
result in severe personal injury or death.
Indicates hazards or unsafe practices that could
result in damage to the machine or personal
injury.
NOTICE
Indicates notes of importance to a procedure or
part.
Page 2 Section 1 Introduction to Safety
Page 9

SAFETY SUMMARY
If the attachment is not functioning properly,
you MUST shut the machine down and follow
proper lock-out, tag-out and repair procedures.
NEVER operate equipment without the original
equipment safety guards in place. If the cab
glass is missing or damaged, check with your
dealer or manufacturer for proper replacement.
Ensure that the cab is equipped with the proper
safety guards for LaBounty applications. In
addition, it is required that the cab be equipped
with an approved Falling Object Protection
Structure (FOPS) when processing materials.
The FOPS must meet the requirements of SAE
standard J1356. A transparent shatter-resistant
shield covering the front of the cab is also
required. Contact your base machine equipment
dealer or manufacturer for more information on
the availability of FOPS. Lack of proper FOPS
may result in injury or death.
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
DO NOT close the attachment on a structure and
reverse the excavator in an attempt to pull down
material.
Clear all persons and equipment from the area of
operation and machine movement. NEVER move
loads over people or equipment. When viewing
the operation of the attachment, maintain a safe
distance of at least 75 feet (22.9 meters).
NEVER approach power lines with any part of
the machine. Keep clear at a minimum of 15 feet
(5 meters).
Avoid tipping. The attachment will alter the
lift capacities of the base machine. DO NOT
overload the excavator or serious injury could
result. Lift capacities will vary if the base
machine is not on level ground. Carry loads in
recommended positions for maximum stability.
Use the recommended excavator counterweight.
Use short slings and lift the load only as high as
necessary.
DO NOT process or handle material with the
attachment over the operator’s cab.
DO NOT attempt to shear brittle materials such
as axles and railroad rail. Brittle material breaks
or shatters instead of shearing. The material
being processed could become a projectile
and cause injury or death. DO NOT process
any material in any position that may propel it
toward operator, other workers, buildings or
equipment.
DO NOT allow riders on the machine.
NEVER remove any pins unless the attachment
is on the ground and blocked up or serious
injury or death could result. Metal chips
or debris may fl y when a connecting pin is
struck. Use a brass drift when striking pins and
always wear protective clothing and proper eye
protection. Pins may fl y when struck with force
to drive them in or out. Keep people clear when
removing or installing pins.
Introduction to Safety Section 1 Page 3
Page 10

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SAFETY SUMMARY continued
Under no circumstances should any
modifi cations be made to LaBounty equipment
without factory authorization.
ALWAYS lower the boom to the ground before
leaving the cab. If it is necessary to work on an
attachment off the ground, securely support the
machine and attachment. DO NOT support the
machine on cinder blocks, hollow tiles, or props
that may crumble under continuous load. DO
NOT rely on a cylinder to hold the attachment
in the air. DO NOT work under a machine that is
supported only by a jack.
DO NOT weld on any structural member
unless specifi cally authorized by LaBounty. Any
unauthorized welding or welding procedures
will void the warranty, and may cause structural
failure or result in personal injury.
ALWAYS wear close-fi tting clothing and safety
equipment appropriate to the job. Safety
equipment should be worn at all times
when viewing, operating, or maintaining the
attachment to prevent injury. Safety equipment
includes eye protection, hard hat, steel toe shoes,
gloves, and hearing protection.
DO NOT let hot hydraulic oil get in contact
with the skin as it could cause severe burns.
Wear adequate protective clothing and safety
equipment. DO NOT tamper with any hydraulic
line or component while it is pressurized.
Escaping fl uid under pressure can penetrate the
skin, causing serious injury. Relieve pressure
before unhooking hydraulic or other lines.
Tighten all connections before applying pressure.
Keep hands
nozzles which eject fl uids under high pressure. Use
a piece of cardboard to search for leaks. If ANY fl uid
is injected into the skin, seek immediate medical
assistance.
and body away from pinholes and
Keep clear of all potential pinch points, including
the moving upper jaw, cylinder connections,
bucket linkages or other moving parts.
Before operating the attachment, read and
observe all safety instructions in the Operation
and Maintenance sections of this manual. If
you are unfamiliar with any operation or
maintenance procedure, seek instruction before
proceeding.
Page 4 Section 1 Introduction to Safety
Page 11

ATTACHMENT DECALS
STANLEY LABOUNTY BRAND DECALS
(REPLACEMENT DECALS AVAILABLE UPON REQUEST)
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
FIGURE 1-1
MODEL DECAL
FIGURE 1-2
SAFETY FIRST DECAL PART NUMBER 503590
(INCLUDED WITH MANUALS)
FIGURE 1-3
Introduction to Safety Section 1 Page 5
Page 12

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ATTACHMENT DECALS continued
GREASE DECAL
PART NUMBER 116338
FIGURE 1-4
1538 HIGHWAY 2
TWO HARBORS, MN 55616
tel 1-800-522-5059
fax 1-218-834-3879
www.stanleyhydraulic.com
Attachment Model:
Serial Number:
Year of Manufacture:
PATENT PLATE
PART NUMBER 116404
FIGURE 1-5
Weight (lb./ kg):
Made in the U.S.A. with Global Materials
MODEL/SERIAL NUMBER PLATE
PART NUMBER 511045
FIGURE 1-7
U.S. PATENT NUMBERS EPO PATENT NUMBERS
5,474,242 7,240,869 435,702
5,531,007 7,487,930 737,107
5,992,023 7,578,461 1,682,299
7,322,273 7,832,130 1,789,225
8,146,256 8,104,384
STANLEY LABOUNTY
1538 Highway 2 1-800-522-5059
Two Harbors, MN 55616 www.stanleyhydraulic.com
FOREIGN PATENTS AND OTHER PATENTS PENDING
SAFE VIEWING DISTANCE DECAL
PART NUMBER 116389
FIGURE 1-6
Page 6 Section 1 Introduction to Safety
116404
SAFETY DECAL
PART NUMBER 503647
FIGURE 1-8
Page 13

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 2 ABOUT THE ATTACHMENT
Model Description ......................................................................................................................2-2
Features ......................................................................................................................................2-2
Attachment Terms...................................................................................................................... 2-3
Attachment Glossary ................................................................................................................. 2-4
Flow and Pressure Requirements ..............................................................................................2-7
About the Attachment Section 2 Page 1
Page 14

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
MODEL DESCRIPTION
Since LaBounty® mobile shear technology was introduced, many
changes have taken place. A wide selection of models and sizes are
now available. Product refi nements like 360º continuous rotation, highperformance reversed cylinders, tougher steels, and bolt-on replaceable wear parts have altered the look and improved the performance of
LaBounty® Mobile Shears.
MSD Saber Series™ shear models are currently available for base
machines with operating weights from 20,000 - 280,000 lbs (9091
– 130,000 kg) with a range of cutting depths. Both rotating and non-
rotating models are available. Rotating models feature hydraulicallypowered 360º continuous rotation. This option allows the shear jaws to
be positioned to cut at virtually any angle.
MSD Saber Series™ models feature a cylinder-mounted speed valve to
decrease cycle times and increase effi ciency. This patented, spool-type
valve design has proven signifi cantly more dependable than cartridgetype regenerative systems favored by other mobile shear manufactur-
ers. These shears feature high-strength, abrasion-resistant steel
FEATURES
• Patented wear parts system for increased effi ciency
and less downtime for
maintenance
• Dependable spool-type
speed valve technology to
decrease cycle times
• Maximum cutting
strength and reach with
minimal weight
• Optimum reach reduces
machine movement and
wear; greatly reduces the
need for stick mounting and
increases safety
• Made with high-strength,
abrasion-resistant steel for
durability
• Four-way indexable blades
• Installs in as little as two
hours
• At-factory upgrading and
rebuilding services available
for extended life
OPTIONS
• 360˚ continuous rotation
• Magnet lifting eye
• Auxiliary hydraulic kit for
rotation circuit
construction to assure long, uninterrupted service – even in the harshest conditions. The main pivot shaft
of every model is manufactured for long life and pivots on Stanley LaBounty’s specially designed bearings.
These shears are designed to draw the material into the jaws to the point where the shear force is greatest,
making them the most effi cient cutting tool possible.
Mobile shears can cut a wide variety of materials including I-beams, H-beams, channel iron, steel plate, pipe,
round stock, wire, rebar, concrete, etc. They are ideal for scrap processing, demolition work, road and bridge
reconstruction, and jobs where torching is not feasible or possible.
Page 2 Section 2 About the Attachment
Page 15
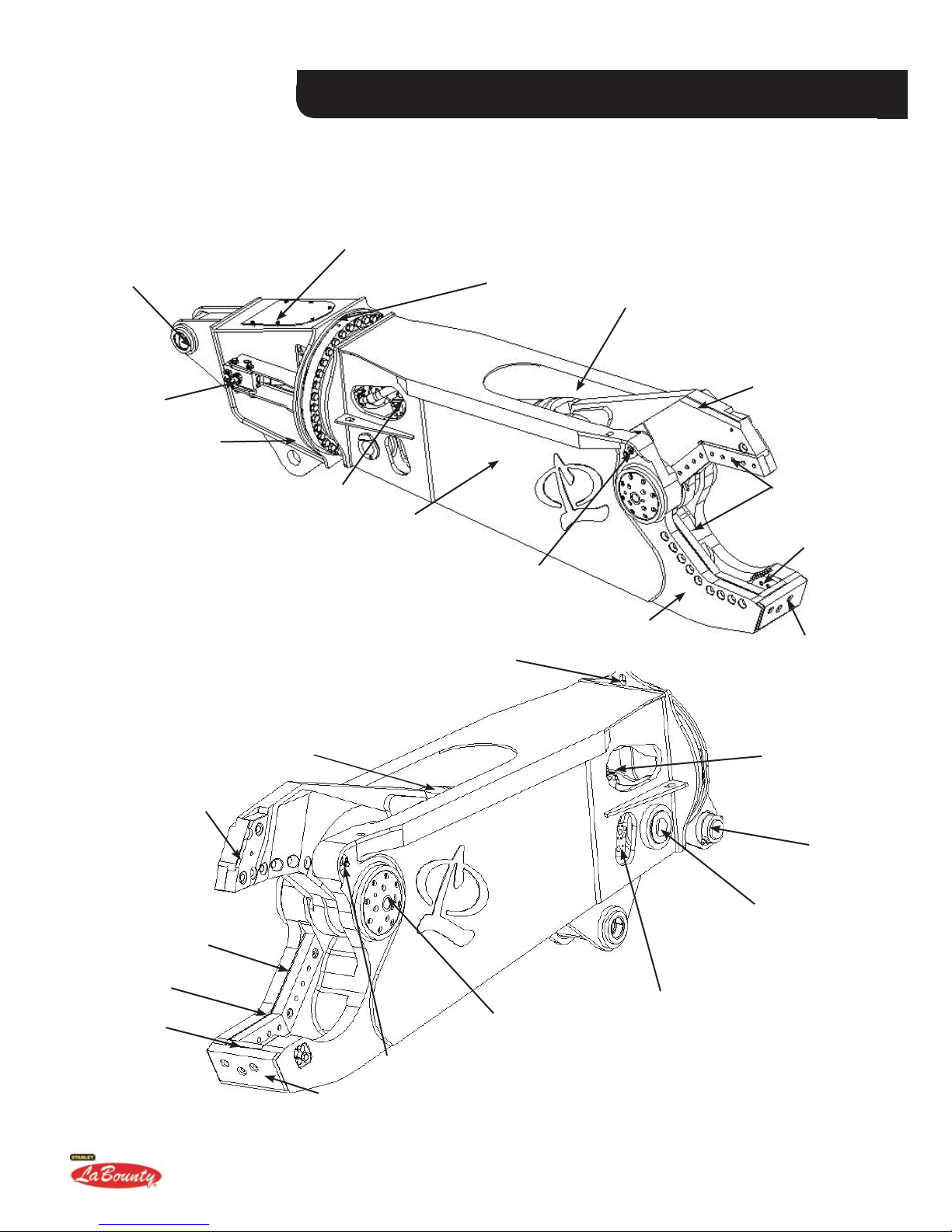
ATTACHMENT TERMS
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ROTATOR
CYLINDER
CONNECTION
HYDRAULIC
MANIFOLD
BLOCK
BOOM PIVOT
ROTATING HEAD
SPEED VALVE
(INSIDE SHEAR)
TURNTABLE BEARING
SHEAR STICK
(SHEAR BODY)
LIFTING POINT
TURNTABLE BEARING
FRONT CYLINDER PIN
FRONT CYLINDER PIN
SLIDE SCREW
RIGHT
LOWER
SHEAR
UPPER SHEAR
CUTTING
BLADES
GUIDE
BLADE
WEAR PLATE
NON-ROTATOR
SHEAR
CYLINDER
SABER TIP
ADJUSTMENT
PLATES
APEX
CROSS
BLADE
SPEED VALVE
(INSIDE SHEAR)
MOUNTING
BRACKET
REAR
CYLINDER
PIN
HYDRAULIC MANIFOLD BLOCK
MAIN PIVOT GROUP
SLIDE SCREW (LEFT)
CROSS PLATE
About the Attachment Section 2 Page 3
Page 16

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ATTACHMENT GLOSSARY
Accumulator Used in a hydraulic rotation kit to store hydraulic fl uid to drive the rotation motor.
Adjustment Custom-made plates that precisely adjust the lower cutting blades to the upper blades. These plates
Plates make it possible to achieve a uniform blade gap on the shear.
Apex The point where the primary and secondary cutting blades come together.
Blade Gap The gap between the upper and lower cutting blades as the blades bypass. A very important item that
must be maintained regularly to prevent material from jamming in the blades.
Blade Shims Thin metal shims used to adjust the position of the lower cutting blades to maintain a proper blade gap.
Blades should never be shimmed out farther than 0.13" (3.3 mm).
Boom Pivot Part of the shear mounting bracket that attaches to the excavator’s boom tip (second member mounts).
Build Up Welding process where worn off parent material is replaced with new metal. A very important
maintenance procedure that must be performed regularly throughout the life of the shear.
Control Valve Used in the hydraulic rotation kit to direct fl ow to the accumulator and back to the hydraulic motor.
Manifold
Cross Blade A replaceable component located on the inside of the lower shear cross plate. The cross blade is an
easy-to-replace wear part that reduces maintenance time in the piercing area.
Cross Plate Plate located at the front of the lower shear which ties the two halves of the lower shear together. The
cross blade is contained in the cross plate. Requires regular build-up and hardsurface.
Crossover A hydraulic component used in a rotating shear that limits the amount of hydraulic pressure sent to the
Relief Valve rotation assembly. The crossover is preset at the factory and must not be tampered with.
Cutting The blades in the upper and lower shear jaws that shear materials as they bypass. The primary blades are
Blades those in the upper and lower jaws that are nearest to the shear throat. The secondary blades are those
that are farthest from the shear throat.
Cylinder Part of the shear mounting bracket that articulates the tip-up function of the shear. The cylinder
Connection connection attaches to the excavator’s stick cylinder (second member mounts).
End Cap Protects and adjusts the main pivot group of the shear. The end cap is a vital component to the
adjustment of the main pivot group and must not be removed without fi rst consulting the LaBounty
Customer Service Department.
Flow Control A hydraulic component used in a rotating shear that meters out the hydraulic fl uid from the rotation
Valve motor. The fl ow control should be set to limit the rotator from spinning faster than 1 - 2 revolutions per
minute.
Front Cylinder The pin that attaches the shear cylinder barrel end to the upper shear.
Pin
Grain of The direction that the parent material was initially rolled at the steel mill. It is very important when
Material hardsurfacing any part of the shear to weld with the grain of the steel. Cross-grained hardsurfacing has
the tendency to start cracks in the base material.
Page 4 Section 2 About the Attachment
Page 17

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ATTACHMENT GLOSSARY continued
Guide Blade A replaceable component located opposite the cutting blades in the lower shear. The main purpose of
the guide blade is to support the upper shear during the cutting cycle. This is a very important
maintenance item.
Guide Blade Thin metal shims used to adjust the guide blade out to maintain the proper guide blade gap. Shims come
Shims in a designated set that determines when the guide blade will be indexed or replaced.
Guide Blade The gap between the front wear plate and the guide blade as the upper shear is cycled into the lower.
Gap This is an important maintenance item to ensure longevity of the shear’s structure.
Hardsurface Welding process for protecting the parent material of the shear jaws. The hardsurface acts as a wear
surface.
Hub Shims Thin metal, circular shims used in the main pivot group of LaBounty shears. Hub shims provide factory
adjustment of the upper shear for close blade tolerance.
Lifting Points Small holes in the top of the shear to be used when mounting or transporting the shear. There are two
holes near the front of the shear and one lug at the rear. These points must never be used for cable
hanging the shear for cutting operations.
Lower The frontal area of the lower shear through which the upper piercing tip passes. This area contains the
Piercing Area guide blade and the cross blade.
Lower Shear The lower stationary jaw of the shear. The lower shear contains the lower cutting blades, the guide blade,
and the cross blade.
Lower Wear Replaceable, abrasion-resistant wear plates that protect the cross plate of the lower shear.
Plates
Main Bearing Hardened bushings that the main shaft of the shear rotates on during operation. There are two main
bearings, bolted in on both sides of the main pivot group.
Main Pivot High tolerance area of the shear that contains the two main bearings, two thrust washers, main shaft,
Group hub shims and two end caps.
Main Shaft The shaft on which the upper shear pivots causing the shearing action of the attachment.
Manifold Hydraulic block that directs the excavator’s hydraulic fl ow to the shear cylinder and rotation
Block assembly.
Motor Hydraulic rotation component that drives the turntable bearing or planetary gear box on rotating shears.
Mounting The bracket at the rear of the shear that allows it to be attached to the excavator. For a typical second
Bracket member mount, the mounting bracket pins to the excavator boom tip and stick cylinder.
Planetary Hydraulic rotation component on larger rotating shears. The planetary gear box rotates the body of the
Gear Box shear with hydraulic motor. The output shaft of the component directly drives the turntable bearing of the
rotating shear.
Rear Cylinder Pin that connects the rod end of the shear cylinder to the rear of the shear. The rear cylinder pin must be
Pin greased according to the required maintenance.
About the Attachment Section 2 Page 5
Page 18

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ATTACHMENT GLOSSARY continued
Rotation Hydraulic drive assembly allows full 360° continuous rotation of the shear. This option gives greater
Assembly positioning capabilities when processing with the mobile shear.
Saber Tip Bolt-on, two-way indexable piercing tip/wear plate found at the top of the upper jaw.
Shear Hydraulic cylinder that powers the cutting action of the shear. The barrel end of the cylinder attaches to
Cylinder the shear’s upper jaw and the rod end attaches to the rear cylinder lugs. The cylinder rod stays
protected from damage inside the shear.
Shear Stick The main body of the shear that includes the lower shear. This weldment must be regularly inspected for
damage.
Slide Screw Adjustable components installed through both sides of the stick. Aligns and supports the upper shear for
a uniform blade gap.
Speed Valve Regenerative hydraulic valve mounted on the cylinder of LaBounty® MSD Saber Series shears that
increases the shear closing speed (cylinder extend function) when the shear is not under a load, thereby
reducing cycle times and increasing effi ciency. Stanley LaBounty uses a spool-type speed valve design for
better durability over cartridge-type regenerative valves.
Swivel Allows continuous hydraulic fl ow to the shear cylinder during rotation of shear without twisting hoses.
Manifold
Thrust Main pivot group component that is located inside the end caps as a wear part for the main shaft.
Washer
Tie Rod Rod that extends through the center of the main pivot group. The tie rod adds lateral support to the main
pivot group.
Throat Area of both the upper and lower jaw near the main pivot where the primary blades are located. The
throat area is the optimum area for shearing material. The shear is most powerful on the primary blades
nearest the pivot point.
Turntable Rotary gear bearing used in rotating shears. It is mounted to the shear stick and is driven by hydraulic
Bearing components in the upper head or mounting bracket. This bearing is sometimes called a slewing ring.
Upper Head Mounting bracket portion of a rotating shear. Attaches to the turntable bearing that attaches to the rear of
the shear stick. The upper head contains the hydraulic manifolds and the swivel manifold.
Upper Shear Movable jaw of the shear that contains cutting blades, the Saber Tip™, and the wear area for the slide
pucks. The shear cylinder articulates the upper shear into the lower shear to perform the cutting action of
the shear.
Wear Parts Consists of the cutting blades, guide blade, cross blade, and Saber Tip™. These parts can be easily
replaced to refresh the System wear areas of the shear jaws. Dramatically increased surface areas on
these wear parts provide better wear and less downtime for maintenance.
Page 6 Section 2 About the Attachment
Page 19
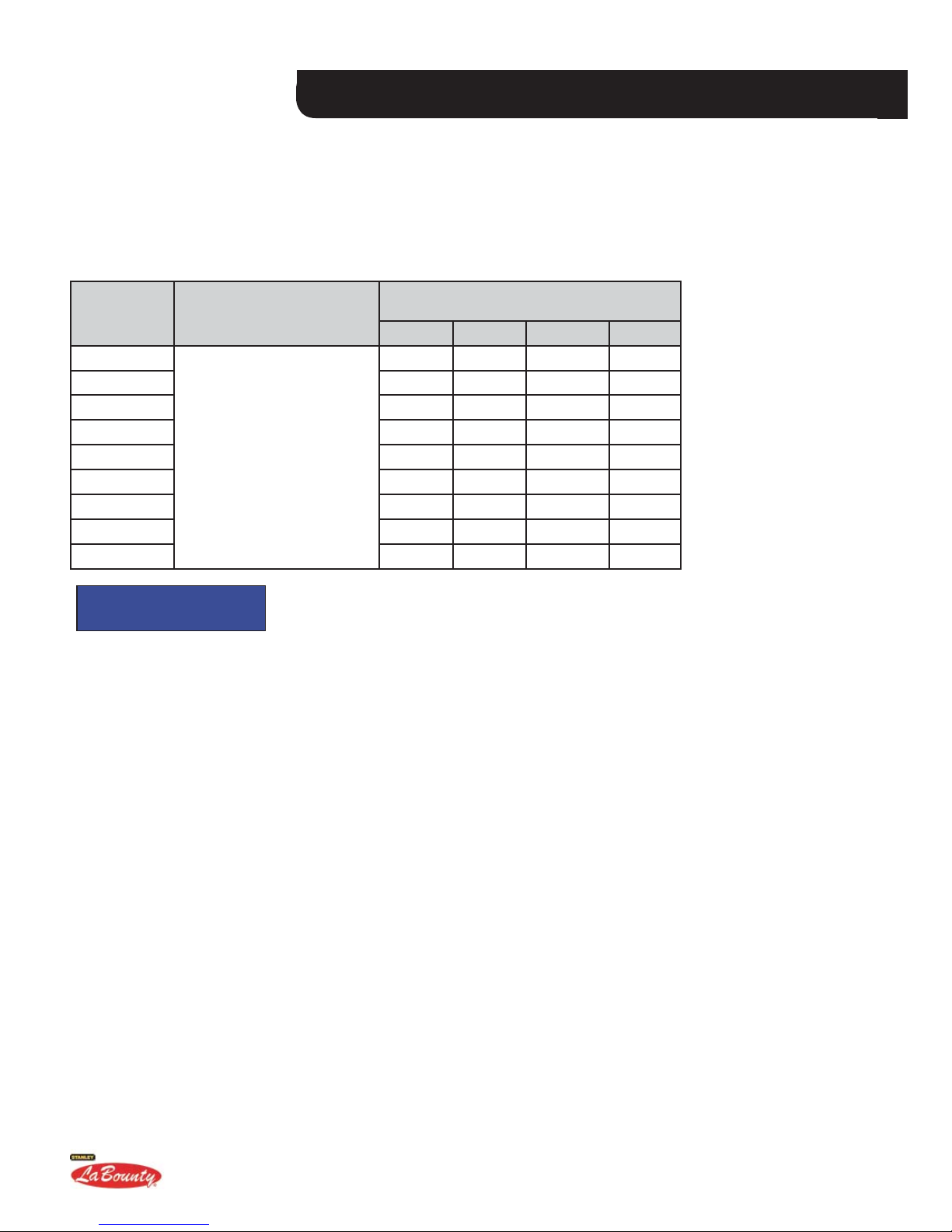
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
FLOW AND PRESSURE REQUIREMENTS
The following table prvodes the MSD Saver Series Mobile Shear fl ow and pressure requirements for the open and close
function. Please note that all models include speed valves; also note that these calculations are theoretical and that actual
cycle times will vary depending upon the specifi c excavator’s hydraulic effi ciency, possible back pressure in the system,
operator competency, etc. These cycle times are calculated with not material in the jaws. The cycle times will be longer
when maximum shear force is required (shear will go out of “speed valve mode”).
REQUIRED FLOW (GPM) TO MEET
SHEAR
MODEL
MSD 1000
MSD 1500 60 48 40 -MSD 2000 110 90 70 60
MSD 2500 150 130 110 94
MSD 3000 160 140 120 103
MSD 4000 -- 170 150 128
MSD 4500 -- 175 150 128
MSD 7500 -- 241 201 172
MSD 9500 -- 350 292 250
RECOMMENDED
PRESSURE RANGE
4000 - 5500 PSI
(276-379 BAR)
8, 10, 12, AND 14 SECOND CYCLE TIMES
8 SEC 10 SEC 12 SEC 14 SEC
50 40 -- --
NOTICE
• Rotation Circuit - 8-12 GPM @ 2000 - 2500 PSI. A 1/2" case drain line going from the hydraulic rotation
motor to the excavator’s hydraulic tank is required to relieve back pressure.
• Pump summation or dual pump fl ow is recommended for shear munting second-member on most
excavators. Due to the increase in fl ow, there may be a requirement to add larger hydraulic lines or dual
lines up the boom to minimize back pressure, reduce heat and maximize shear performance.
About the Attachment Section 2 Page 7
Page 20

Page 21

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 3 INSTALLATION
Shear Mounting Procedure ........................................................................................................ 3-2
Mobile Shear Start-up Procedure ............................................................................................... 3-4
Shear Removal Procedure ......................................................................................................... 3-5
Shear Storage ............................................................................................................................ 3-5
External Rotation Control System Installation (if equipped) ....................................................... 3-6
Electrical Installation - Internal Rotaiton Control System ............................................................ 3-6
Electrical Schematic - Internal Rotation Control System ............................................................ 3-7
Hydraulic Return Line Installation Instructions Interal Rotation Control System ........................ 3-8
Hydraulic Schematic - Internal Rotation Control System ............................................................ 3-9
Installation Section 3 Page 1
Page 22
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SHEAR MOUNTING
PROCEDURE
Take note whether yours is a second member or a
third member installation. A second member mount
is where the shear replaces the excavator stick; a
third member mount is where the shear replaces
the bucket.
1. Place the shear upside down on the ground with
blocking to keep the shear level. Locate fl at, hard
ground for installation.
2. For a second member mount, remove the excavator stick following the manufacturer’s recommended
procedure.
3. For a third member mount, remove the bucket or
other attachment following manufacturer’s recommended procedure. To prevent contamination of the
hydraulic system, plug the hydraulic hose when they
are disconnected.
NOTICE
It may be necessary to lift the rear of the shear
into position to allow boom pivot pin installation
on second member mounts.
4. With the jaws of the shear facing the excavator,
walk the excavator into position, aligning the excavator’s boom or stick into the boom pivot or stick connection of the shear bracket (see Figure 3-1).
5. For second member mounts, pin the shear boom
pivot to the excavator boom using the excavator
boom pin (second member). For third member
mounts, pin the stick tip to the stick connection using the pin provided by LaBounty.
6. Instruct the operator to slowly pick the shear up
into a position where there will be enough clearance
to pin the other connection of the shear mounting
bracket (see Figure 3-2).
FIGURE 3-1
FIGURE 3-2
Page 2 Section 3 Installation
Page 23
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SHEAR MOUNTING PROCEDURE continued
7. Extend the cylinder rod or bucket linkage and move into position as necessary to pin this connection. Install
shear supplied pin. It may be necessary to use a lifting device (overhead hoist, forklift, etc.) to position the
cylinder or linkage correctly.
8. Connect the hydraulic hoses to the manifold located on each side of the head. Remember to cap all hydraulic hoses and fi ttings immediately to prevent contamination of the hydraulic system. Tighten the bolts to the
proper torque (refer to Split Flang Fitting Torque Tables on page 8-26).
9. On rotating models the following procedures are to be followed.
a. After installing a hydraulic circuit on the excavator, install additional hydraulic lines up the boom—
these will include two 1/2” (13 mm) diameter feed lines and one 1/2” (13 mm) diameter case drain
line. These will terminate at the end of the boom.
b. Install jump lines from the above hydraulic lines to the shear bulkhead or manifold fi ttings. Please
refer to the parts catalog for specifi c fl ow and pressure requirements; if in doubt, call Service (800-522-
5059).
10. Check to make sure all collars, fasteners, and other connecting hardware are secure before proceeding.
11. Lift the boom and slowly try the shear rotate function and shear open and close function (see Figure 3-3).
Watch for hydraulic oil leaks.
NOTICE
When installation is complete, slowly curl the
shear to tuck it under the boom. Check for
interference. Contact factory immediately if
any interference occurs.
FIGURE 3-3
Installation Section 3 Page 3
Page 24

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
MOBILE SHEAR START-UP PROCEDURE
Air must be bled out of the cylinder prior to operation of the shear. Trapped air in the system leads to cavitation, oxidation of the oil, and excessive heat. These conditions promote hydraulic oil break down, contamination, noise, sluggish operation, reduced component life and potential cylinder damage. This procedure will
need to be followed upon installation, after hydraulic repairs have been made, or when a shear has been
stored or idle for an extended period of time. Make sure the shear cylinder is either fully retracted or extended—if not, mechani-cally place into either of these positions (loosen end plugs or caps on the manifold or fi ttings to relieve air pressure to the shear cylinder. Position the shear so the cylinder is as horizontal as possible.
Sett the excavator at idle speed or slightly above idle speed.
WITH CYLINDER FULLY RETRACTED
1. Slowly fi ll the rod end of the cylinder (open the shear) until a noticeable change in tone of the excavator is
heard, indicating full cylinder. Do not operate to the machine’s full operating pressure.
2. Change direction of oil fl ow; slowly fi ll the bore end of the cylinder (close the shear) until the rod is extended
approximately 1/4 of stroke.
3. Retract the cylinder rod all the way.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3, extending rod to approximately 1/2 stroke, then 3/4 stroke, then full stroke.
5. When cylinder is full of oil, slowly cycle cylinder rod back and forth at least fi ve times through full stroke. Do
not operate to the machine’s full operating pressure.
WITH CYLINDER FULLY RETRACTED
1. Slowly fi ll the bore end of the cylinder (close the shear0 until a noticeable change in tone of the excavator is
heard, indicating full cylinder. Do not operate to the machine’s full operating pressure.
2. Change direction of oil fl ow; slowly fi ll the rod end of the cylinder (open the shear) until the cylinder rod is
retracted approximately 1/4 stroke.
3. Extend the cylinder rod all the way.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3, retracting cylinder rod to appoximately 1/2 stroke, then 3/4 stroke, then full stroke.
5. When cylinder is full of oil, slowly cycle cylinder rod back and forth at least fi ve times through full storke. Do
not operate to machine’s full operating pressure.
6. Slowly cycle the cylinder fi ve or more times reaching machine’s normal operating pressure at end of each
stroke, open or close. Listen for unusual noise and check for any hydraulic leaks.
NOTICE
After the cylinder has been bled and drained of air,
check the excavator hydraulic fl uid and fi ll to the
proper level.
Page 4 Section 3 Installation
Page 25

MOBILE SHEAR REMOVAL
PROCEDURE
1. Position shear under the boom of the excavator as
far as the stick cylinder will extend and lower shear
to the ground.
2. Use blocking to support the stick cylinder from
the excavator boom.
3. Remove the stick cylinder pin from the shear
mounting bracket.
4. Fully retract the stick cylinder as it is unattached
from the shear mounting bracket.
5. Cycle the upper jaw closed far enough to allow
the upper to lay fl at on the ground with the rest of
the shear. The object of this is to create as many
possible shear contact points with the ground.
6. Cycle all controls with the excavator off to relieve
any trapped pressure.
7. Carefully remove the jump-lines at the shear manifold.
8. Plug the open manifold ports and hose ends with
pressure plugs to prevent contamination of the hydraulic system.
9. At this point, be extremely sure that the shear is
stable and tension to the boom pivot pin is released
before unpinning the boom pivot pin and releasing
the weight of the shear.
10. Remove the boom pivot pin from the shear.
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
Figure 3-4
See Figure 3-4. Trapped hydraulic pressure may
be present after the base machine is shut off.
Extreme caution must be taken when removing
attachment hydraulic hoses or possible injury or
death could result.
SHEAR STORAGE
1. Block the shear up off the ground using wood
blocking.
2. Grease the pins and machined bores of the
mounting bracket of the attachment. Apply a generous amount of grease to the shear blades, cylinder
rod and all other exposed unpainted surfaces.
NOTICE
Watch the boom to attachment pivot for any interference. If interference is present DO NOT force the
attachment under any further. Block the attachment
up before it interferes with the boom, or stop.
Installation Section 3 Page 5
Page 26
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
INTERNAL ROTATION
CONTROL SYSTEM
INSTALLATION
if equipped
BEFORE GETTING STARTED
1. Have the Parts Catalog for the shear and the
installation manual on hand for reference. The parts
information for the Internal Rotation Control System
is included in it.
2. Check if the following items exist on the base
machine:
a. A preferred control switch other than the
foot switch provided (see Foot Pedal Switch Installation).
b. One -8 (1/2” SAE JIC type) adapter to tap
into base machine reservoir or return line.
c. One -8 (1/2” SAE) hydraulic line plumbed
from the base machine’s hydraulic return to the end
of the boom (if the shear is mounted in place of the
stick) or the stick if the shear is mounted in place of
the bucket.
d. One 15 amp circuit breaker or fuse.
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
INTERNAL ROTATION
CONTROL SYSTEM
if equipped
LaBounty provides a three-position foot switch with
the Internal Rotation Control System. Alternative
types of switches may be used in place of the provided foot switch, if preferred. Contact your LaBounty dealer for information on operating the control
valve. Any of the following can be used:
a. Joystick handle equipped with a single
pole/double throw momentary three-position rocker
switch;
b. Two joystick handles each equipped with a
single pole/single throw momentary rocker switch or
push button switch;
c. a single pole/double throw three-position
momen-tary toggle switch mounted to the control
lever with a fabricated bracket.
INSTALLATION
1. Place the foot switch or other preferred control
switch inside the cab in a convenient location for
operating.
2. Route the electrical cord with the plug up the
boom (and stick if the shear replaces the bucket).
Secure the cord to an existing hydraulic line using
tie straps. Attach the green wire of this cord to the
base machine chassis to ground the system.
3. Run a 14-gauge wire from the base machine’s DC
voltage power supply and connect it to a 15-amp
circuit breaker fuse. The power source should be
accessory side or a similar source that provides voltage only when the starter key switch is in the “ON”
position, and should have a 5-amp minimum rating.
4. Connect a 14-gauge wire from the circuit breaker
or fuse to the red wire of the electrical cord running
up the boom to the electrical plug. Connect another
14-gauge wire from the circuit breaker or fuse to
this red wire of the electrical cord coming from the
foot switch. The red wire from the electrical plug
and the red wire from the foot switch can be connected.
5. Connect the black wire from the boom cord to
the black wire from the foot switch cord. Connect
the white wires in the same way. The green wire
from the foot switch cord will not be used.
To prevent electrical shock, short, or accidental
start-up, do not connect to the power source
until the entire system is installed.
NOTICE
Make sure to complete all installation procedures described in this section before starting the machine.
Operating the shear before proper installation is
complete may cause damage to the base machine.
Page 6 Section 3 Installation
Page 27
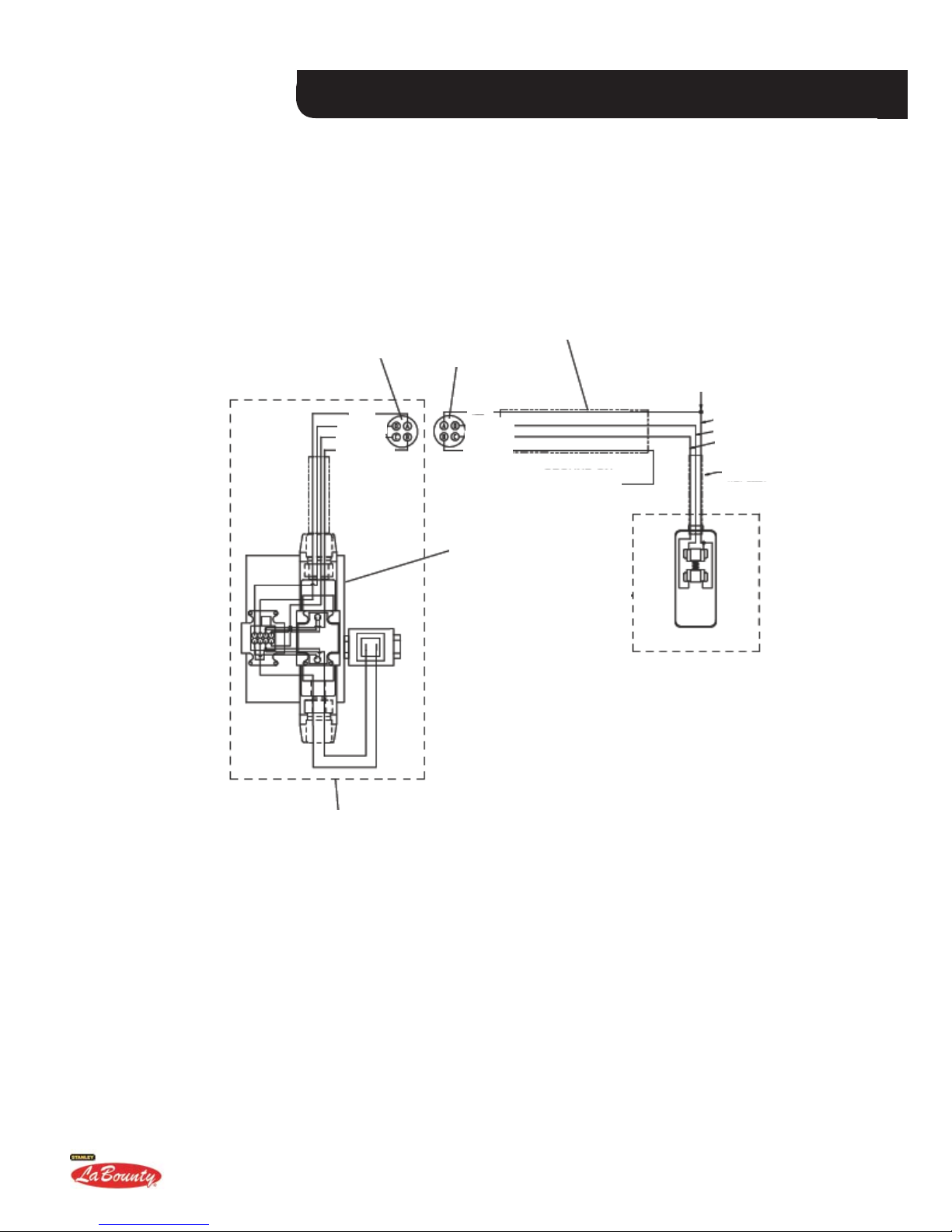
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ELECTRICAL SCHEMATIC
INTERNAL ROTATION CONTROL SYSTEM
if equipped
RECEPTACLE
RED
WHITE
BLACK
GREEN
ELECTRICAL CORD
PLUG
RED
WHITE
BLACK
GREEN
GROUND ON
CHASSIS
CONTROL VALVE
ASSEMBLY
12V OR 24V DC
POWER SUPPLY
15-AMP FUSE OR
BREAKER
RED
WHITE
BLACK
GREEN
FOOT SWITCH
(INSIDE OPERATOR’S CAB)
INSIDE ATTACHMENT
(INSTALLED AT FACTORY)
FIGURE 3-5
Installation Section 3 Page 7
Page 28

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
HYDRAULIC RETURN LINE
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
INTERNAL ROTATION
CONTROL SYSTEM
1. Always relieve all hydraulic pressure of the base machine
by working the controls in all directions with the engine off
before beginning work on any hydraulic component. See
Figure 3-6.
2. Shut off the base machine and check the hydraulic sys-
tem pressure. It should be zero PSI.
3. Hydraulic oil becomes hot during operation. DO NOT
let hydraulic oil get in contect with the skin as it will cause
severe burns.
FIGURE 3-6
4. Whenever hydraulic lines are disconnected, hoses must
be capped and ports much be plugged to prevent contamination of the hydraulic system.
5. Install a 1/2” diameter hydraulic line (customer supplied)
from the attachment’s return fi tting, located in the right
hand hydraulic manifold, to the base machine’s hydraulic
reservoir or return line. Secure the line properly to the excavator boom and stick.
Escaping fl uid under pressure can penetrate the skin
causing serious injury. Relieve pressure before disconnecting hydraulic lines. Tighten all connections before
applying pressure. Use a piece of cardboard to search
for leaks. If ANY fl uid is injected into the skin, seek immediate medical assistance.
Page 8 Section 3 Installation
Page 29
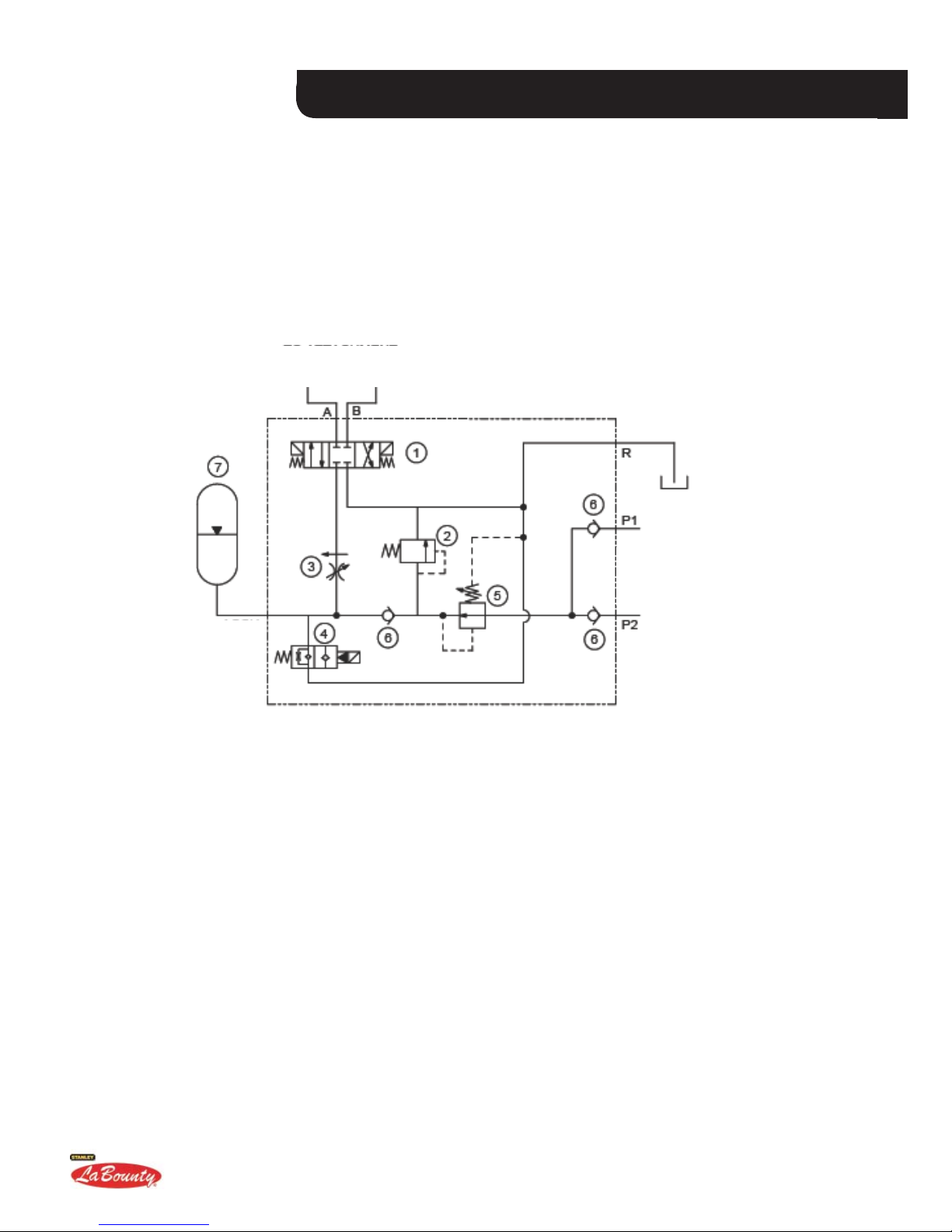
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC
INTERNAL ROTATION CONTROL SYSTEM
Check your internal rotation control system regularly.
TO ATTACHMENT
ROTATION CIRCUIT
INPUT FLOW FROM HY-
DRAULIC MANIFOLDS
ACCUMULATOR
FIGURE 3-7
1. DIRECTIONAL CONTROL VALVE
2. RELIEF VALVE - SET AT 3000 PSI (200 BAR)
3. FLOW CONTROL
4. UNLOADING VALVE
5. PRESSURE REDUCING VALVE - SET AT 2500
PSI (170 BAR)
6. CHECK VALVE
7. ACCUMULATOR - SET GAS CHARGE AT
1100 PSI (76 BAR)
Installation Section 3 Page 9
Page 30

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
Page 10 Section 3 Installation
Page 31

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 4 OPERATION
Before You Start ..........................................................................................................................4-2
First Things First .........................................................................................................................4-2
Safety Devices You’ll Need .........................................................................................................4-2
General Rules for Safe Operation ...............................................................................................4-3
Mobile Shear Controls ................................................................................................................4-4
Operating the Rotator .................................................................................................................4-6
Backdriving the Rotator ..............................................................................................................4-6
Operating the Internal Rotation Control System .........................................................................4-6
Recharging the Accumulator with Fluid ......................................................................................4-6
Speed Valve Operating Characteristics .......................................................................................4-7
Getting the Feel of the Attachment ............................................................................................4-7
Operation Section 4 Page 1
Page 32

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BEFORE YOU START
KNOW YOUR SAFETY PROGRAM
1. Read and understand the safety section of this
manual and the base machine manual.
2. Know the employer’s safety rules for your job.
Consult your foreman for specifi c instructions and
safety equipment required.
3. Learn the traffi c rules at the work site.
4. Know the hand signals used on the job and who
is responsible for signaling. Take signals from only
ONE person.
KNOW YOUR EQUIPMENT
• Learn the location and function of all controls.
Test all controls to ensure proper operation. If any
malfunctions are found, shut the machine down and
report the malfunction for repair.
• Be familiar with the safety devices on the machine,
indicators, warning devices and caution instructions.
They will alert you to conditions that may make it
hazardous to continue operating.
• Wear proper protective clothing including hard
hat, safety shoes, ear protectors, refl ective clothing,
safety goggles and work gloves. Loose clothing
can get caught in machinery and cause injury.
Wrist watches, rings and other accessories can be
dangerous, as well.
• Know the clearances in the work area.
FIRST THINGS FIRST
1. Ensure all safe viewing distance decals are
installed and legible; contact LaBounty for
replacements as required.
2. Have a DAILY Safety Dialog with all those with
whom you work. Inform them of any out-of-theordinary work that may be planned for the day.
Remind them of the safe working distance.
3. Clear the area; inspect. ALWAYS look out for
others. In any work area, people constitute a
serious safety hazard. Before operating, walk
completely around the machine to be sure there
are no workers next to, under or on it. Warn nearby
workers that you are starting up; DO NOT start up
until they are out of danger.
4. Each day before starting, visually inspect the
machine by walking around it entirely; check the
location of cables, gas lines, and water mains
before any operations. Make sure work site
footing has suffi cient strength to fi rmly support
the machine. When working close to an excavation,
position machine with the propel motors at the rear.
5. Once started, keep bystanders clear, especially
before moving the boom, swinging the upper
structure, or traveling. ALWAYS be alert for
bystanders in or near the operating area.
SAFETY DEVICES YOU’LL
NEED
Seat belts
Canopies
Falling Objects Protective Structures (FOPS)
Shields and guards
Safety decals
Visual or audible warning devices
Flags and fl ares
Barricades
Signs and other markings
Warning lights
Page 2 Section 4 Operation
Page 33

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
GENERAL RULES FOR SAFE
OPERATION
1. Read the Operator’s Manual for the base machine
on which the shear is mounted.
2. KNOW the capacity of the excavator and its
attachments. DO NOT overload the machine or
serious injury could result. The attachment may
have altered the base machine’s lift capabilities.
3. It is required that a Falling Objects Protection
Structure be installed surrounding the excavator cab
for all material handling applications.
4. The shear is for processing materials. DO NOT
use the attachment for unapproved purposes or
warranty may be voided.
5. DO NOT continuously process oversized
materials by forcing them into the shear throat with
the downward force of the excavator. This practice
is detrimental to the life of the shear and is strongly
discouraged.
6. If the shear stalls during processing, scale back
the amount of material being processed at one time.
Continuously overloading the shear and cycling
the excavator to full system pressure can cause
overheating and have adverse effects on the shear
and the excavator hydraulic system.
7. Whenever possible, cycle the shear cylinder
completely during processing. Fully opening and
closing the shear allows more hydraulic fl uid to
circulate through the system to help prevent
overheating.
8. Inspect and lubricate the shear daily. Tighten
any loose bolts or fi ttings to the proper torque as
specifi ed in this manual.
9. Maintain a safe distance and avoid contact
between the excavator and the shear or any
material held by the shear jaws.
10. NEVER leave the shear suspended or pass it
over people, occupied vehicles, or buildings.
11. When working in confi ned spaces, keep a
watchful eye on exposed parts, such as cylinder
rods and hoses, to avoid damage.
12. Maintain at least 15 feet (5 meters) between the
shear and any nearby power lines.
13. ALWAYS lower the shear to the ground and turn
the base machine off when leaving the machine
unattended.
14. DO NOT close the shear on a structure and
reverse the excavator in an attempt to pull down
material. This is not only dangerous, but will likely
damage the excavator and shear.
15. Avoid collision of the boom or shear, especially
when working with limited visibility or inside
buildings. Know the height and reach of the shear
during operation, transport, and when swinging the
excavator.
16. Use machine swing for positioning only. DO
NOT use the shear as a jack hammer or wrecking
ball.
17. Avoid contact between boom arm or shear stick
and overhead obstacles when you operate, move, or
haul the machine.
18. DO NOT alter factory preset hydraulics of the
shear or vary from the excavator manufacturer
specifi cations. This may void the warranty.
19. DO NOT shear high tensile steel such as railroad
rail, spring steel, axles and some types of wire as
blade, Saber Tip, and/or upper damage will result.
This type of material breaks when processed and
can become a projectile which could cause injury or
death.
20. To prevent bending the upper shear, DO NOT
attempt to shear material stuck through the lower
jaw.
21. Before attempting to shear thin material, make
sure that the shear blades are sharp and properly
adjusted. Otherwise, such material may become
jammed in the shear blades.
22. The lifting lugs are to be used for shipping and
installation. They are not for use in cable-hung
applications.
23. The shear rotation function is for positioning only.
DO NOT use it for bending, breaking or prying.
24. DO NOT use the force of the excavator to force
the shear into a pile.
25. DO NOT apply excavator force or weight at
either end of the upper shear in an attempt to unjam the shear or to cut materials that are too large
for the shear.
Operation Section 4 Page 3
Page 34

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
MOBILE SHEAR CONTROLS
There are four basic movements of a mobile shear plus one for rotating the shear if it is equipped with
the rotation option. Mobile shear controls will vary slightly depending on the type of base machine and
whether the shear is mounted as a second or third member. The shear open/close and rotation systems
are customized to each machine. Review the shear operations with an authorized dealer or the installation
technician before operating. The functions for a typical shear third-member installation are illustrated below
(see Figure 4-1). and on page 4-5 (second-member installation).
Determine the control for each movement of the
shear before attempting to operate. Practice the
machine movements as described in Getting the
Feel of the Shear instructions in this section.
THIRD- MEMBER INSTALLATION
Shear replaces bucket
FIGURE 4-1
Bucket CURL = Shear IN
Bucket DUMP = Shear OUT
Page 4 Section 4 Operation
Page 35

MOBILE SHEAR CONTROLS
(CONTINUED)
SECOND MEMBER INSTALLATION
Shear replaces stick
FIGURE 4-2
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BUCKET CURL = SHEAR CLOSE
ARM IN = SHEAR IN
ARM OUT= SHEAR OUT
Operation Section 4 Page 5
Page 36

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
OPERATING THE ROTATOR
if equipped
The rotator gives the shear 360˚ of continuous rotation in both directions for easy, accurate processing at
all angles. The rotator requires special attention when operating the shear. The rotator is to be used only to
position the shear, not as a means of bending, twisting, or breaking material.
DO NOT use the shear rotator for any other purpose except to position the shear for a cut. Using
the rotator for any other purpose, such as bending or twisting material, will damage the rotation
components and may void the shear warranty.
BACKDRIVING THE ROTATOR
Backdriving occurs when an excessive, off-center force is applied to the shear. Examples of this are closing
the jaws on a rigid member without the jaws being square to the member or handling a heavy load off-center
in the jaws. Backdriving puts undue stress on the rotation system and, if done continually, can lead to
rotation component problems. Follow the tips below to minimize backdriving as much as possible.
1. When handling a load in the jaws, try to grip it as close to its center of gravity as possible
2. When processing a long member that is suspended, make several shorter cuts rather than one long cut
where the member can come loose and backdrive the rotator.
3. When processing any rigid member, use the rotator to square the jaws to the cut. If the jaws are not
square, the rotator will backdrive to adjust to the cut.
OPERATING THE INTERNAL ROTATION CONTROL SYSTEM
if equipped
The foot switch installed in the operator’s cab is used to operate the Internal Rotation Control System,
assuming an alternative customer provided switch is not used. The foot switch provided by LaBounty has
three positions—center, front (toe), and back (heel). The switch will automatically move to the neutral center
position when it is not being used. No rotation occurs in this position. The other two positions will cause
the shear to rotate. One position will cause clockwise rotation and the other will cause counterclockwise
rotation.
RECHARGING THE ACCUMULATOR WITH FLUID
When using the Internal Rotation Control System, the shear will typically rotate between 100º and 270º each
time the accumulator is charged with fl uid. When the accumulator runs out of fl uid charge, it is necessary to
recharge the system before rotating the shear again. To recharge the system, simply open or close the shear.
The system draws hydraulic fl uid from the jaw circuit when the jaws are operated.
Page 6 Section 4 Operation
Page 37

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
NOTICE
• The amount of rotation your shear will achieve per fl uid charge depends on the shear model.
• Continuous rotation can be achieved by cracking an excavator function that charges the accumulator.
• The accumulator needs to be charged with fl uid when the base machine is fi rst started up. The unloading
valve is designed to drain to the accumulator whenever the base machine is shut off.
SPEED VALVE OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
The function of the speed valve is to increase the shear closing speed (cylinder extend function) when the
shear is not under a load, thereby reducing cycle times and increasing effi ciency. The speed valve directs
return fl ow from the rod side of the cylinder to the bore side as the cylinder extends. This function occurs
only when the cylinder is extending in a “low to medium load” condition, which occurs as the upper shear
jaw is moving toward the material to be cut. As the shear jaws close down on the material to be cut, the
cylinder meets resistance and requires more operating pressure. The pilot valve on the speed valve senses
this increased pressure and shifts the valve spool out of the speed mode. The rod side fl uid is now directed
back to the base machine reservoir and full system operating pressure can now be directed to the bore side
of the cylinder, allowing the shear to cut the material with maximum force.
GETTING THE FEEL OF THE SHEAR
Before starting the fi rst job with a new machine, it is suggested that the operator fi nd an open spot on fi rm,
level ground that’s free of obstructions such as trees, buildings, people, and other equipment. Move the
machine to this area, and spend some time just getting to know the “operating feel” of the machine and the
shear. The machine is extremely powerful. Be concerned about safety when preparing to operate the new
machine. Ensure safe operation by inspecting the machine as stated in Getting Started Safely. Read the
Getting Started Safely section of this manual and understand it.
The control levers should be moved in a gradual, deliberate way rather than with jerky, abrupt movements.
Jerky operation can cause damage and early wear to various parts on the machine, and can also overheat
the hydraulic system. For example, as each control lever is moved forward or backward from the center,
or neutral position, the oil fl ows to the cylinder or motor controlling a function. The component (boom,
attachment, etc.) starts to move. The component moves faster as the control lever is moved further forward
or backward. Holding the lever in the forward or backward position will hold that movement at a given rate
of speed. To slow the movement down, gradually move the lever toward the neutral position. Movement is
stopped at the neutral position. The position is maintained until the control lever is moved again. Feathering
the controls is a technique that will increase output and make operating the shear easier. When starting any
motion of the machine, move the control slightly from neutral until it starts to move, then smoothly move
the control to increase motion to desired speed. Do the same when stopping a motion.
Operation Section 4 Page 7
Page 38

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
Page 8 Section 4 Operation
Page 39

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 5 MAINTENANCE
Scheduled Maintenance ..............................................................................................................5-2
Recommended Spare Parts List ..................................................................................................5-3
Maintenance Safety Procedures ..................................................................................................5-4
General Rules for Maintenance ...................................................................................................5-4
8-Hour Service Recommended ...................................................................................................5-5
80-Hour Service Recommended .................................................................................................5-5
2000-Hour Service Recommended ..............................................................................................5-5
8-Hour Inspection Checklist ........................................................................................................5-6
80-Hour Inspection Checklist ......................................................................................................5-7
8-Hour Inspection Rotator Checklist ............................................................................................5-8
Lubrication ...................................................................................................................................5-9
Bolt Torque Guidelines ................................................................................................................5-10
Metric Capscrew Size Guide ......................................................................................................5-10
Torque Values for Metric Fasteners............................................................................................. 5-11
Slide Screw Maintenance ...........................................................................................................5-12
Blade Removal ............................................................................................................................ 5-14
Blade Bolt Torque Specifi cations ................................................................................................. 5-15
Torque Values for Blade Bolts......................................................................................................5-15
Guide Blade Shimming and Rotation ..........................................................................................5-16
Cutting Blade Rotation Procedure .............................................................................................. 5-17
Weld-in Tip Cutting Blade Rotation Procedure ............................................................................ 5-21
Cutting Blade Shimming ............................................................................................................. 5-22
General Guidelines for Build-up and Hardsurfacing ....................................................................5-23
Build-up Recommendations .......................................................................................................5-24
Hardsurfacing Recommendations ..............................................................................................5-24
Critical Wear Areas ......................................................................................................................5-26
Upper Shear Build-up and Hardsurfacing .................................................................................... 5-27
Weld-in Tip Maintenance ............................................................................................................5-28
Weld-in Tip Replacement ............................................................................................................5-30
Front Wear Plate Replacement ...................................................................................................5-32
Lower Wear Plate Replacement .................................................................................................5-33
Lower Shear Build-up and Hardsurfacing ....................................................................................5-34
Hydraulic System Maintenance ..................................................................................................5-37
Flange Type Hose Fittings ........................................................................................................... 5-37
Torque Values for Four-Bolt Flange Fittings .................................................................................5-38
Applying Split Flange Clamps .....................................................................................................5-39
Cylinder Gap Check ....................................................................................................................5-40
Hydraulic Schematic - Standard Rotating Shears ......................................................................... 5-41
Hydraulic Schematic - Standard Non-rotating Shears ..................................................................5-41
Speed Valve Adjustment .............................................................................................................5-42
Decal Maintenance .....................................................................................................................5-54
Maintenance Section 5 Page 1
Page 40

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SERVICE AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES 8 HOURS 80
HOURS
Visually inspect shear for damage
Inspect all safety decals
Inspect cab protection on excavator
Confi rm all excavator warning systems are operational
Lubricate each side of main pivot group (2 each side)
Lubricate end slide puck assemblies (each side)
Lubricate end of front cylinder pin
Lubricate end of rear cylinder pin
Lubricate boom pivot connection of mounting bracket
Lubricate cylinder connection of mounting bracket
Inspect pinheads and pinkeepers
Inspect all bolts for looseness or damage
Check slide puck /back wear plate gap; refer to manual if gap
exceeds .010" (.25mm)
Check guide blade/Saber Tip gap; refer to manual is gap
exceeds .030" (.75mm)
Check cutting blade gap; refer to manual is gap exceeds
.030" (.75mm)
Inspect Saber Tip; ensure it fi ts squarely in upper jaw
Inspect cross blade for any looseness or damage
Inspect hoses for wear and potential failure
Inspect cylinder for leaks
If rotator equipped:
Grease turntable bearing
Inspect rotation hoses (and hose connections) for wear, leaks,
potential failure
Check rotation assembly bolts
Inspect all bolts connecting turntable bearing to upper head and shear;
replace as needed
Rotate or replace cutting blades, Saber Tip, cross and guide blades
Check slide screw wear; replace if necessary
Inspect upper shear: check build up and hardsurface around blade edges; build
up if needed
Replace wear plates on lower shear if necessary
Check split fl anges and fi tting for looseness; tighten if necessary
Inspect and maintain the lower secondary blade buffer or build-up strip
Replace shear cylinder seals (including Nylock lock ring)
Replace swivel manifold seals (if equipped)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
2,000 HOURS
•
•
Page 2 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 41

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
RECOMMENDED SPARE PARTS LIST
The following is a description of the parts Stanley LaBounty recommends to have on hand for these benefi ts.
1. Less downtime for lack of a part.
2. Original equipment manufacturer parts are inspected to Stanley LaBounty standards for proper fi t and
function.
3. Eliminate the possibility of a part being unavailable for immediate delivery.
4. Eliminate overnight air freight costs.
5. The accessibility of replacement parts assures the proper shear maintenance will be followed and there-
fore increase the effi ciency of the shear.
UPPER AND LOWER JAWS OF THE
SHEAR:
BASIC ASSEMBLY
Cutting blades
Guide blade
All bolts and washers used to fasten blades
Blade shims for lower shear blades (not supplied
with new blades)
Complete blade kits
UPPER SHEAR
Saber Tip™
One extra upper secondary blade
All bolts & washers used to fasten tip
NOTICE
Do not substitute parts unless you know they are
the same in ALL characteristics. Your warranty could
be compromised by using parts other than original
LaBounty parts.
NOTICE
Refer to the shear parts catalog for specifi c part
numbers. Be sure to reference the attachment serial
number.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
All hydraulic hoses
O-ring face seal adapters (ORS)
CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
Cylinder seal kit (ordered by cylinder part
number and serial number)
ROTATION ASSEMBLY if equipped
Crossover relief or motion control valve (one
is applicable to each rotation assembly)
MANIFOLD ASSEMBLY if equipped
O-ring seals
Crown seals
STANLEY LABOUNTY BLADE MAINTENANCE TOOL KIT
P/N 184238.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 3
Page 42

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
MAINTENANCE SAFETY
PROCEDURES
During maintenance of the shear, it is imperative
that the excavator is turned OFF to prevent injury.
• Inspect the shear daily. DO NOT operate a poorly
maintained or damaged shear or major structural
damage could result.
• ALWAYS lower the shear to the ground before
leaving the cab. If it is necessary to work on a shear
off the ground, securely support the base machine
and shear. DO NOT support the shear on cinder
blocks, hollow tiles, or props that may crumble
under continuous load. DO NOT rely on the cylinder
to hold the shear in the air. If a control is moved or
hydraulic pressure is otherwise released, the shear
will drop. DO NOT work under a machine that is
supported solely by a jack.
• NEVER operate the machine if an unsafe
condition exists. Attach a “DO NOT OPERATE” tag
to the machine.
• If more than one person is working on a machine,
each must be familiar with the controls and aware
of what the others are doing. Before working on a
machine, BE SURE TO TAG THE CONTROLS SO
NO ONE ELSE WILL START IT.
• ALWAYS use two people when making checks
with the engine running.
• Keep hands away from moving parts. NEVER
lubricate or work on a machine while it is moving.
• ALWAYS wear proper safety equipment when
maintaining the shear including safety glasses with
side shields, hard hat, steel toe shoes, gloves, and
hearing protection.
GENERAL RULES FOR
MAINTENANCE
1. Read the maintenance manual. Be sure all
maintenance personnel read and understand all
maintenance procedures before they attempt them.
2. Use factory approved parts. Use of parts that
are not factory approved may cause damage or
unnecessary downtime and may void the warranty.
3. Lubricate every four hours; follow the lubrication
schedule as outlined on page 5-9.
4. Use the included Inspection Checklists during
shear inspections to make sure all maintenance is
complete.
5. In extremely cold temperatures, work the shear
on lighter materials fi rst before working up to
heavier materials. DO NOT operate at temperatures
below -10º F (-23ºC).
6. To get maximum life from the shear blades,
rotate to utilize all four edges.
7. DO NOT enter the pivot group of the shear
without fi rst consulting your dealer or the Stanley
LaBounty Customer Service Department.
8. The machined adjustment plates behind the
cutting blades in the lower shear have been custom
machined for each shear. If they should come loose,
be sure to replace them properly.
9. ALWAYS connect the welding ground cable
directly to the attachment component that you are
welding on. DO NOT allow ground current to run
through the pivot group, the rotation group, or the
hydraulic cylinder.
10. DO NOT weld guide blades, and/or the other
blades, into their blade seats. The guide blade is
needed for proper adjustment of the shear. DO
NOT allow excessive gap between guide blade and
Saber Tip.
11. DO NOT weld or hardsurface across the grain of
the steel at any time. When hardsurfacing, do not
exceed two passes of hardsurface rod.
12. DO NOT weld on the excavator boom or stick
without fi rst consulting the excavator manufacturer
for proper welding procedures.
13. Rotate or replace the blades when edges have
rounded to approximately ¼" (6 mm) radius or after
80 hours, whichever comes fi rst.
14. DO NOT adjust the slide screws when the
upper shear is in either the full-open or full-closed
position. Be sure the slide screw will contact the
rear wear plate when adjusting. Lubricate the slide
screw assembly every eight hours of operation.
15. DO NOT weld on blades.
16. Torque bolted connections as prescribed in this
manual.
17. DO NOT disconnect any hydraulic hoses or
fi ttings without fi rst relieving the excavator system
hydraulic pressure.
18. DO NOT exert the weight of the excavator
on the shear in order to free the upper shear if it
becomes jammed. Please consult the factory.
Page 4 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 43

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
GENERAL RULES FOR
MAINTENANCE
19. DO NOT let hot hydraulic oil get in contact with
the skin as it could cause severe burns.
20. DO NOT operate a rotating shear without a
case drain line connected back to the tank or return
line fi lter (rotating shears only), or the rotation
component will be damaged. Smaller shears (MSD
1000) do not require a case drain.
continued
8-HOUR SERVICE
RECOMMENDED
Inspect the Shear: Look over the shear for damage
or any clues that might indicate a potential problem.
Inspect Safety Devices: Make sure all decals are
installed and legible. Inspect the condition of the
cab protection and make sure visual and audible
warning devices are working properly. Make all
repairs before using the equipment.
Grease Fittings: Lubricate according to the shear
Lubrication section. Replace broken fi ttings.
Connecting Pins: Inspect the mounting bracket pins
and shear cylinder pins for looseness or damage.
Check pinheads and pin keepers.
Bolts: Check for looseness or damage. Torque if
necessary according to the proper torque chart in
this manual.
Slide Screws: Inspect for damage. Refer to the
adjustment procedure on page 5-12. Lubricate the
puck assembly and contact area.
Saber Tip/Guide Blade Gap: Inspect for damage.
If gap exceeds 0.030" (0.76mm) refer to the
shimming instructions in this manual.
Cutting Blade Gap: Inspect. Shimming is
necessary if the gap exceeds recommendations;
see page 5-17. For most applications, this gap
should be maintained at 0.010" to 0.020" (0.25 to
0.50 mm). This gap may be shimmed down to
0.005" (0.13 mm) if jamming becomes a problem
when processing thin materials.
Hoses, Connections, Cylinders: Inspect for leaks,
wear and damage. Tighten, repair or replace.
Rotator (if equipped): Check all turntable bearing
bolts for looseness or damage. Bolts may be
retorqued only once and then must be replaced.
Refer to the Turntable Bearing Bolt Torque Chart
on page 6-3 for proper torque values. Lubricate
according to instructions in this manual.
80-HOUR SERVICE
RECOMMENDED
Cutting Blades: Measure blade gap, rotate blades
and shim blades according to procedures in this
manual.
Upper Shear: Inspect cutting blades, Saber Tip,
and parent material around blade edges. Refer
to manual for build-up, hardsurface or blade
replacement instructions.
Lower Shear: Inspect guide blade, nose blade,
and lower shear. Refer to manual for build-up,
hardsurface or replacement instructions.
Rotator (If equipped): Inspect all bolts connecting
the turntable bearing to the head and shear for
looseness or damage. Bolts must be replaced if retorque is necessary. Refer to the Turntable Bearing
Bolt Torque Chart on page 6-3 for proper torque
values.
2,000-HOUR SERVICE
RECOMMENDED
Shear Cylinder Seals: It is recommended that
the shear cylinder seals be replaced every 2,000
hours. Operating the shear with worn-out seals
will decrease shear performance and may cause
internal damage to the cylinder. Please note that
cylinder seal life is highly dependent on the care
taken to properly maintain the hydraulic fl uid. Fluid
with higher levels of contaminants and particulates
will wear down cylinder seals faster than fl uid that
is properly fi ltered and changed out regularly. It
is necessary to replace the cylinder seals more
frequently if the shear works regularly in severeduty applications or if the hydraulic fl uid is not
properly maintained.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 5
Page 44

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
8-HOUR INSPECTION CHECKLIST
Shear Model _____________________Excavator Hour Meter________________________
Shear Serial Number ______________________________ Date______________________
_______ 1. Visually inspect shear for any damage
_______ 2. Inspect safety devices
_______ a. All safety decals in place and legible - seal decal and label maintenance section
_______ b. All cab protection in good condition
_______ c. All excavator warning systems working
_______ 3. Lubricate all points. Refer to shear lubrication in this section
_______ a. Each side of main pivot group (two each side)
_______ b. End of slide puck assemblies (each side)
_______ c. End of front cylinder pin
_______ d. End of rear cylinder pin
_______ e. Boom pivot connection of mounting bracket
_______ f. Cylinder connection of mounting bracket
_______ 4. Inspect connecting pins and pin retaining hardware
_______ a. Boom pivot pin of mounting bracket
_______ b. Cylinder connection pin of mounting bracket
_______ c. Front shear cylinder pin
_______ d. Rear shear cylinder pin
_______ e. Pinheads and pinkeepers
_______ 5. Inspect all bolts
_______ a. Visually inspect all bolts and replace any that are loose or damaged
_______ 6. Check slide puck/wear plate gap
_______ a. Refer to manual if gap exceeds recommendations; see page 5-21
_______ 7. Check guide blade/Saber Tip gap
_______ a. Refer to manual if gap exceeds recommendations; see page 5-21
_______ 8. Check cutting blade gap
_______ a. Refer to manual if gap exceeds 0.030” (0.75 mm)
_______ 9. Inspect Saber Tip
_______ a. Saber Tip fi ts squarely in upper jaw
_______ 10. Inspect cross blade for looseness or damage
_______ 11. Inspect Hydraulic System
_______ a. Inspect hoses for wear and potential failure
_______ b. Inspect hose connections for leaks
_______ c. Inspect cylinder for leaks
Inspected by: __________________________________________________________________________
Page 6 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 45

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
80-HOUR INSPECTION CHECKLIST
Attachment Model _____________________Excavator Hour Meter________________________
Attachment Serial Number ______________________________ Date______________________
_______ 1. Inspect blades
_______ a. Rotate or replace upper cutting blades
_______ b. Rotate or replace Saber Tip, nose blade, and guide blade
_______ c. Measure blade gap, refer to manual for shimming procedure and tolerance range
_______ 2. Inspect slide screw and slide screw gaps, each side
_______ a. Check for slide screw wear, replace if necessary
_______ b. Measure slide screw gap, adjust if necessary
_______ 3. Inspect upper shear
_______ a. Build-up and hardsurface upper shear
_______ 4. Inspect lower shear
_______ a. Replace wear plates if necessary
_______ 5. Inspect hydraulic components
_______ a. Check split fl anges and fi ttings for looseness, tighten if necessary
_______ b. Check hoses for wear or cracking
If Rotator equipped:
_______ 1. Inspect all bolts connecting the turntable bearing to the upper head and shear
_______ a. Replace bolts if retorque is necessary
Inspected by: __________________________________________________________________________
NOTICE
IMPORTANT
It is recommended that the shear cylinder and swivel seals be replaced every 2,000 hours. Operating the
shear with worn-out seals will decrease shear performance and may cause internal damage to the cylinder.
It is recommended that this work by performed by an authorized Stanley LaBounty Dealer. The Nylock lock
ring must be replaced each time a new seal kit is installed.
It is recommended that the cylinder shear seals be replaced by an authorized Stanley LaBounty dealer. The
Nylock lock ring must be replaced each time the cylinder seals are installed.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 7
Page 46

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
8-HOUR INSPECTION ROTATOR CHECKLIST
Shear Model _____________________Excavator Hour Meter________________________
Shear Serial Number ______________________________ Date______________________
_______ 1. Visually check all turntable bearing bolts and replace any that are loose or damaged
_______ 2. Grease the turntable bearing - refer to the Rotator Maintenance section for instructions
_______ 3. Inspect the rotation hydraulics system
_______ a. Inspect rotation hoses for wear and potential failure
_______ b. Inspect rotation hose connections for leaks
_______ 4. Visually check all rotation assembly bolts
Inspected by: __________________________________________________________________________
Page 8 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 47

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
LUBRICATION
Regular lubrication of the attachment is absolutely vital to proper operation and long life of the attachment.
The speed valve feature accelerates the shear cycle time and allows the shear to open and close more often
throughout the day. This makes it necessary to lubricate the shear more frequently than was required with
older models. Use premium grease No. 2EP or equivalent and lubricate all points every 4 hours of operation.
Grease fi tting locations are indicated in Figure 5-1 and by the “GREASE” decals on the attachment. Grease
all fi ttings at the main pivot group with the shear jaws open AND with the shear jaws closed to evenly dis-
tribute the grease throughout the pivot group.
4
3
4
2
3
7
1
FIGURE 5-1
ROTATOR DESIGNS VARY BY MODEL. LOOK FOR GREASE DECALS WHEN LUBRICATING THE ATTACHMENT.
LOCATION ON ATTACHMENT NUMBER OF SHOTS
1. Rear cylinder connection 6
2. Front cylinder connection 6
3. Main jaw pivot (2 zerks each side) 6
a. Jaw Open 6
b. Jaw closed 6
4. Slide screw
a. Left side 6 at each grease fi tting
b. Right side 6 at each grease fi tting
5. Turntable bearing (rotators only) 6 at each grease fi tting
LOCATION ON BRACKET
6. Boom pivot connection - consult excavator maintenance manual
7. Linkage connection (3rd member mount) or cylinder pivot connection (2nd member mount)
Maintenance Section 5 Page 9
Page 48

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BOLT TORQUE GUIDELINES
Proper bolt installation is critical to ensure the safe and effi cient operation of the shear. Carefully follow the
steps below to properly install bolts.
1. Always replace bolts and nuts with the same size and class of fastener. Replacement fasteners can be
ordered from the Stanley LaBounty Parts Department to ensure the correct part is used (refer to Figure 5-2).
Unless otherwise specifi ed, use class 10.9 metric hex head capscrews, class 10.9 metric fl at head cap-
screws, and class 12.9 metric socket head capscrews.
2. Make sure bolts, nuts and bolt holes are free of dirt, oil, grease and other contaminants.
3. If necessary, use the Capscrew Size Guide on this page to help determine the size of the bolt being in-
stalled.
4. The torque values in this manual are for use with non-plated fasteners with clean, dry threads. These values are suitable for use with or without thread adhesives, such as Loctite products. Please note that proper
torque values may vary depending on the specifi c area of the shear.
METRIC CAPSCREW SIZE GUIDE
A
HEX HEAD
B
SOCKET HEAD
FIGURE 5-2
CAP-
SCREW
SIZE
M10 0.63" (16mm) 0.63" (16mm)
M12 0.71" (18mm) 0.71" (18mm)
M14 0.83" (21mm) 0.83" (21mm)
M16 0.94" (24mm) 0.94" (24mm)
M20 1.18" (30mm) 1.18" (30mm)
M24 1.42" (36mm) 1.42" (36mm)
M30 1.81" (46mm) 1.77" (45mm)
Always replace bolts and nuts with the same
size and class of fastener. Inferior fasteners can
fail and cause injury or death and damage to the
equipment.
A
HEX HEAD
SOCKET HEAD
B
Page 10 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 49

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
TORQUE VALUES FOR METRIC FASTENERS
IMPORTANT
Please note that some parts of the shear require special torque values. These parts are listed below with the
page number where the proper torque values for that area can be found. They include:
• Blade Bolts Page 5-15
• Hydraulic Connection Bolts (split fl ange connections) Page 5-40
• Speed Valve Bolts
• Turntable Bearing Bolts Page 6-3, 8-26
• Rotation Assembly Bolts Page 6-3, 8-26
• End Cap Bolts Page 8-26
• SAE Straight Thread Port Hex Head Bolts Page 8-25
• Nation Pipe Thread (NPT) Page 8-26
For all other bolts used in the LaBounty shear, use the Generic Torque Table, below.
CLASS 10.9 CLASS 12.9
SIZE FT-LBS N-M FT-LBS N-M
M1041554967
M12719685116
M16 173 235 207 281
M20 335 454 403 547
M24 579 785 693 939
M30 1164 1579 1391 1887
Page 5-44-55, 8-26
Always replace bolts and nuts with the
same size and class of fastener. Inferior
fasteners can fail and cause injury or
death and damage to the equipment.
NOTICE
It is preferred to apply torque to the nut
rather than the bolt head wherever possible.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 11
Page 50

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SLIDE SCREW MAINTENANCE
Maintenance of the slide screw area is very important for keeping the cutting blades in line and for proper
operation of the shear. This critical area should be inspected and adjusted every 80 hours. Use the following
instructions to maintain and adjust the slide screw.
1. See Figure 5-3. To check and/or replace the slide screw, remove the bolts and lock plate (see Figure 5-5,
page 5-13). Use a crescent wrench on the square end of the slide screw and turn it clockwise to adjust,
counterclockwise to remove.
2.
Look at the face of the slide screw to determine if there are still grease grooves (see Figure 5-4). If the
grease grooves are worn away, it will be necessary to replace the slide screw. If the slide screw needs to be
replaced, continue on with step 3.
3. To remove the slide screw, turn counterclockwise and back it completely out. To adjust the slide screws,
cycle the upper jaw until the slide screw is centered on the wear plate. Clean the inside threads, if necessary, and thread in the new slide screw until it just makes contact with the wear plate (both sides). Reinstall the lock plate and lock bolts, and lock the adjusted slide screw into position.
4. Apply grease to the entire assembly through the grease fi tting in the slide screw. Also, apply a layer of
grease to the rear wear plates on the upper shear with a brush or grease gun. Do not apply grease by hand!
5. It is recommended that the slide screws be completely removed every 80 hours of operation, the threads
(both internal an external) be cleaned, and then coated with 2-EP Lithium grease. Failure to do so will result
in the slide puck jamming and becoming ineffective.
SLIDE SCREW
FIGURE 5-3 FIGURE 5-4
DO NOT cycle or move the shear while unthread-
ing the slide screw by hand. This will result in
severe injury.
SQUARE END
GREASE GROOVES
Keep clear when the shear is in motion. Avoid
pinch points, such as the upper shear or the
shear cylinder, or severe injury could result.
Page 12 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 51

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SLIDE SCREW MAINTENANCE continued
NOTICE
• Some models (2500) have a spacer beneath the
lock plate.
• MSD 1000/1500 and 1000/1500R do not have slide
screws on the right (cutting blade) side.
SLIDE SCREW
FIGURE 5-5
LOCK PLATE
Maintenance Section 5 Page 13
Page 52

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BLADE REMOVAL
Removing and handling shear blades can be hazardous if done incorrectly. To ensure your safety and to
prevent damaging the shear, please read the following warnings and instructions when removing a
blade from its seat.
To prevent injury, wear safety equipment at
all times when maintaining the attachment.
Safety equipment includes eye protection, hard
hat, steel toe shoes, work gloves and hearing
protection.
Make sure the blade is well supported before
removing the blade bolts. When the bolts are
removed, the blade may drop and cause severe
injury.
1. Loosen all blade bolts but leave them partially
installed and threaded into the blade.
2. The blades may come loose from their seats
without much effort. If the blades are loose, make
sure they are well supported before removing the
blade bolts.
3. If the blades are not loose, tap on the blade face
with a soft-faced mallet to loosen the bond between
the blade and seat. Use a pry bar between the top
of the blade and the blade seat to loosen the blade.
5. If you are unable to dislodge the blades using
these methods, please contact your Stanley LaBounty dealer for further assistance. Also note that blade
replacement kits are available. For best service,
please have the serial number of your shear on hand
when calling for blade replacement kits.
NOTICE
Do not strike directly on the blade bolts with a hammer or other hard object. This may cause damage to
the blade threads.
NOTICE
Full blade kits are available by calling Stanley
LaBounty Customer Service at 800-522-5059. For
best service, please have the shear serial number
on hand when calling.
PRY HERE IF
NECESSARY
BLADE
Never strike against any blade with a hardened
steel tool of any kind. The blade may chip and
cause severe injury.
4. If the blade is still jammed in its seat, place a
wood block or similar object against the head of
one of the blade bolts and strike with a mallet (see
Figure 5-6). The bolt being struck should be within
1/2” (13 mm) of being fully threaded into the blade
to prevent thread damage.
Page 14 Section 5 Maintenance
WOOD
BLOCK
FIGURE 5-6
ALL BOLTS
PARTIALLY
UNTHREADED
Page 53

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BLADE BOLT TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS
Proper torque of the LaBounty shear blade bolts is
a crucial factor in extending the life of the shear and
blade components. Maintaining the proper torque
according to the specifi cations in this manual will
help prevent loosening of blades and possible damage to the blade seats.
LaBounty shear blades can be rotated to utilize all
four blade edges (see Figure 5-7 for the compo-
nents of a typical blade replacement kit). Blade bolts
and washers can typically be used for the life of the
accompanying blade set. Due to the critical nature
of these fasteners, Stanley LaBounty requires that
blade fasteners (bolts and washers) be replaced
with each set of new blades.
When using existing blade fasteners during blade
rotations, always inspect the hardware for any imperfections or damage and replace as necessary. If
a bolt has become elongated or a washer has spun,
it will be diffi cult or impossible to achieve proper
torque to secure the blade in the seat.
NOTICE
Earlier model blades have a counter-bore and removable dowels to do the same function as the updated
four-bolt tip design.
Proper torque values for blade bolts are listed below.
These values should only be used for blade bolts.
TORQUE VALUES FOR BLADE
BOLTS
CLASS 10.9
SIZE FT-LBS N-M
M20 500 678
M24 900 1220
M30 1200 1627
ASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
Your new Saber shear has a raised area on the Saber
Tip™ that fi ts into the Secondary Blade of the upper
jaw. This helps provide uniform support and loading of blade seats when piercing items that do not
extend totally across the piercing tip.
FIGURE 5-7
Maintenance Section 5 Page 15
Page 54

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
GUIDE BLADE SHIMMING AND ROTATION
The guide blade gap is another adjustment that keeps the shear blades in line and ensures the proper opera-
tion of the shear. This adjustment should be checked daily.
1. Close the shear until the Saber Tip on the upper shear begins to bypass the guide blade (see Figure 5-8).
Use a feeler gauge to check the gap and record it. Close the shear in steps and check the gap at different
spots along the Saber Tip surface.
2. Find the smallest gap along the Saber Tip and mark it. The gap at this spot should not exceed 0.030" (0.76
mm). If the gap is more than this, it will be necessary to shim the guide blade.
3. Guide blade shims are provided with a new shear. The shim kit includes four shims that are 0.024" (0.61
mm) thick and one that is 0.12" (3 mm) thick.
4. To determine the amount of shims to use, subtract the desired gap of 0.010" (0.25 mm) from the smallest
gap that was recorded earlier. See the example at the right side of this page.
Do not check gaps while the shear is in motion.
Stay clear when closing the shear or severe injury could result.
Wear gloves at all times during blade
maintenance.
NOTICE
• If the guide blade is stuck in its seat, refer to the
Blade Removal procedure in this section.
• If the shear has been operated for more than 80
hours since the last blade rotation, it is recommended that all blades be rotated at this time. Follow the
instructions on this page and the following pages.
MEASURE
SABER TIP
GUIDE BLADE
FIGURE 5-8
Example:
Recorded Gaps:
0.035" (0.89mm)
0.040" (1.02 mm)
0.045" (1.14 mm)
Smallest Gap = 0.035"
Minus Desired Gap - 0.010"
Shim Amount = 0.025"
For this example, one of the 0.024" (0.61 mm) thick
shims would be used to achieve the desired guide
blade gap.
GAP HERE
Page 16 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 55

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
GUIDE BLADE SHIMMING AND ROTATION continued
5. To shim the blade, loosen the guide blade bolts and move the guide blade out far enough to slide the
shims between the blade seat and the guide blade. If all fi ve shims are installed and the gap still exceeds
0.030" (0.76 mm), it will be necessary to rotate or replace the guide blade.
6. The guide blade can be rotated once so the whole face of the blade can be used to increase its life. When
it is time to rotate the blade, remove it and turn it end for end, and place it back in its seat. The same face
should be used for the entire life of the blade. Use the steps above to shim the guide blade to the correct
gap. When the whole face of the blade is worn and it cannot be shimmed anymore, it is time to replace it
with a new one.
7. If a gap greater than 0.030" (0.76 mm) still exists with a new guide blade and a full set of shims, the Saber
Tip will need to be replaced. Refer to Cutting Blade Rotation in this section.
Always wear proper safety equipment when doing blade maintenance. This includes eye protection,
hard hat, steel toe shoes, work gloves and hearing protection. Wear an approved respirator when
grinding.
CUTTING BLADE ROTATION PROCEDURES
Proper rotation and adjustment of the cutting blades is very important for the best shear performance and
longer shear life. It is recommended that the blades be rotated after every 80 hours of use. Regular blade
rotation keeps the blades and blade gaps uniform, which allows the blades to be shimmed properly. Regular
blade maintenance is especially important when processing thinner materials. It may be necessary to rotate
and adjust the cutting blades more often when processing thin or non-ferrous materials. Frequent rotation
and adjustment of the cutting blades is not as critical when processing larger materials, but it will extend the
life of the blades. Use the following instructions to properly rotate the cutting blades:
1. Use the Blade Removal instructions from this section to remove the upper shear blades. Take care to keep
track of all parts and their positions as you remove them. This will be important when reinstalling.
2. Once the blades are removed, use a small grinder to clean up the edges. Remove sharp burrs and smooth
out deformations. Clean out the blade seats in the same way, removing any debris or burrs.
NOTICE
For optimal Saber Tip performance, and to assure that two fl at surfaces are torqued together, the upper
secondary blade should always be new at each blade position change. To accomplish this, do the following:
Use fi rst edge of new shear (all blades new), rotate all blades end-for-end in original location. Use second
edge and then discard lower primary blade. Move upper secondary blade to lower primary position and
install new blade in the upper secondary position. Swap positions of the upper primary and lower secondary.
Continue this sequence, discarding the lower primary and installing a new upper secondary at each blade
position swap. This results in an optimal Saber Tip performance at the one time cost of an additional upper
secondary blade (after two edges are used). See Figures 5-9 and 5-10 on page 5-18.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 17
Page 56

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
CUTTING BLADE ROTATION
continued
The startup kit for every new shear contains two
extra blades. Keep these blades for the second time
you rotate edges and replace blades. For the fi rst
rotation, you’ll only need the original four blades; the
second time, you’ll be using new blades.
If you follow these directions correctly, each
time you order a new set of four blades you’ll be
setting aside two blades for a second rotation—
at every second blade fl ip, two new blades
will be inserted in the top blade seats. NEVER
ROTATE USED LOWER BLADES INTO UPPER
BLADE SEATS.
NOTICE
Never operate a shear when the blade edges have
rounded to a 1/4” (6 mm) radius or more. Operating
the shear with badly worn blades greatly decreases
shear performance and can eventually cause
structural and hydraulic damage to the shear.
FIRST AND THIRD BLADE EDGE ROTATION
1. Remove each blade.
2. Turn end for end.
3. Reinstall in same seat.
4. Replace Saber Tip as required.
FIGURE 5-9
SECOND BLADE EDGE ROTATION
NEW BLADES
1. See Figure 5-9. Turn each original blade end-for-
end and return each one to its original seat. When
done, you have completed the procedure for the
fi rst blade edge rotation.
2. See Figure 5-10. For the second blade edge
rotation (when edges have rounded to a 1/4” radius),
remove and discard the lower blades. Next, remove
the two upper blades, swap end-for-end, and install
in the lower seats. Now install two new blades in
the open upper seats.
3. Whenever you rotate or replace cutting blade
edges, make sure all blades are seated properly and
use a new set of blade bolts and torque according
to the Dry Bolt Torque Chart in this section. Always
use the same size and class of bolts. Refer to your
Parts Catalog to order replacement bolts from your
authorized Stanley LaBounty dealer.
4. Cross blade and guide blade maintenance should
be performed when lower blades are being rotated.
Keep track of all parts and their positions as you
remove them to make reinstallation easier.
DISCARD
DISCARD
1. Discard lower blades.
2. Rotate upper blades to lower blade seats.
3. Install two new blades in upper seats.
FIGURE 5-10
Page 18 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 57

CUTTING BLADE ROTATION
continued
NOTICE
The holes in the front of the cross plate can be used
to dislodge the cross blade from its seat. Place a
soft metal punch or pin through these holes and up
against the blade. Strike the punch with a mallet to
dislodge the blade.
6. Use a small grinder to clean up the blade edges.
Remove sharp burrs and smooth out deformations.
Clean out the blade seats in the same way, remov-
ing any debris or burrs.
7. The cross blade can be rotated one time to increase its life. If the current cross blade has not
already been rotated once, turn it end for end and
place it back in its seat. If the cross blade has already been rotated once, it will need to be replaced.
8. If there were shims behind the cross blade when
it was removed, make sure to reinstall them (see
Figure 5-12). Replace any damaged shims. Tap the
face of the blade with a soft-faced mallet to make
sure that it seats fi rmly.
9. Like the cross blade, the guide blade can be
rotated one time to increase its life. If the current
guide blade has not already been rotated once, turn
it end for end and place it back in its seat. Only use
one face of the guide blade before replacing.
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ASSURE THAT NO GAP
EXISTS HERE BEFORE
APPLYING TORQUE TO
BLADE AND SABER TIP
BOLTS
FIGURE 5-11
CROSS BLADE CROSS BLADE SHIMS
FIGURE 5-12
Maintenance Section 5 Page 19
Page 58

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
CUTTING BLADE ROTATION
continued
10. After rotation or replacement, place the guide
blade back in its seat without shims. Use a new set
of guide blade bolts and tighten them until snug. Do
not apply torque to the bolts yet. Make sure the
blade is seated snugly.
11. Rotate the lower cutting blades according to the
Blade Rotation Sequence diagrams on page 5-18.
12. Make sure the adjustment plate is reinstalled
properly and then place the blades into their proper
positions without shims. Use a new set of blade
bolts and tighten until snug. Do not apply torque
to the bolts yet. Ensure the blades are seated
snugly.
NOTICE
The adjustment plate behind the lower cutting
blades must be reinstalled properly for the blades to
be aligned. The notched end of the adjustment plate
should be toward the throat (Figure 5-13).
13. The guide blade and lower cutting blades are
now ready for shimming. DO NOT operate the
shear without shimming the guide blade and cutting
blades to the proper blade gaps.
ADJUSTMENT PLATE NOTCH TOWARD SHEAR
THROAT
FIGURE 5-13
Page 20 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 59

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
WELD-IN TIP CUTTING BLADE ROTATION PROCEDURE
Proper rotation and adjustment of the cutting blades is very important for the best shear performance and
longer shear life. It is recommended that the blades be rotated after every 80 hours of use.
FIRST AND THIRD BLADE EDGE ROTATION
FIGURE 5-16
1. Remove each blade.
2. Turn end for end.
3. Reinstall in same seat.
4. Replace Weld-In Tip as required.
SECOND AND FOURTH BLADE EDGE ROTATION
FIGURE 5-17
UPPER SECONDARY
LOWER PRIMARY
1. Remove all blades.
2. Swap the blade positions.
3. Replace Weld-In Tip as required.
NOTICE
Never operate a shear when the blade edges have round to a 1/4” (6 mm) radius or more. Operating the
shear with badly worn blades greatly decreases shear performance and can eventually cause structural and
hydraulic damage to the shear.
1. Keep track of all parts and their positions as you remove them. This will be important when reinstalling.
2. Once the blades are removed, use a small grinder to clean up the edges and blade seats, remove sharp
burrs and smooth out deformations.
3. See Figure 5-16. Turn each original blade end-for-end and return each one to its original seat. When done,
you have completed the procedure for the fi rst blade edge rotation.
4. See Figure 5-17. For the second blade edge rotation (when edges have rounded to a 1/4” radius), swap
the blade positions (primary to secondary and secondary to primary).
5. Whenever you rotate or replace cutting blade edges, make sure all blades are seated properly and use a
new set of blade bolts and torque according to the Dry Bolt Torque Chart in the SOM. Always use the same
size and class of bolts. Refer to your Parts Catalog to order replacement bolts from your authorized Stanley
LaBounty dealer.
6. Cross blade and guide blade maintenance should be performed when lower blades are being rotated.
Keep track of all parts and their positions as you remove them to make reinstallation easier.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 21
Page 60

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
CUTTING BLADE SHIMMING
After blade rotation, use the following instructions to shim to the proper blade gap. Shimming is necessary
if the gap exceeds 0.030” (0.75 mm). For most shearing applications, this gap should be maintained at 0.010
to 0.020" (0.25 to 0.50 mm), but see the table below for the specifi c gap for your shear. The gap may be
shimmed down to 0.005” (0.13 mm) if jamming becomes a problem, especially when processing thin mate-
rials. Shim only the lower blades.
1. To check for blade gap, close the shear until the secondary blades in the upper and lower shear begin to
bypass (see Figure 5-18). Start with the thickest shims and check to see how many shims can be slipped
between the blades and record this amount. Another method is to use a feeler gauge to check the blade gap
and record it.
2. The whole shim set adds up to 0.125” (3.2 mm). If all shims can be slipped between the blades it will
be necessary to replace the blades. Do not shim the lower blades out more than 0.125" (3.2 mm). This may
cause structural damage to the shear.
3. Close the shear further until the primary blades begin to bypass (see Figure 5-19). Again, check to see
how many shims can be slipped between the blades (or use the feeler gauge). Record this gap also. If the
blades have been rotated properly at the correct intervals, the blade gap should be even over the entire span
of the blades. If the gap is not even, contact your Stanley LaBounty dealer.
4. Once the blade gap is checked and recorded, open the shear. Shim the lower blades by using the same
amount of shims that you were able to slip between the blades earlier.
5. To install the shims, loosen the lower blade bolts and move the blades out slightly. Slide the shims be-
tween the lower blades and the existing adjustment plate. Tighten the blade bolts until snug.
6. Cycle the shear slowly to the full-closed position. Check the gap at different points to make sure it is be-
tween 0.010" and 0.020" (0.25 and 0.50 mm). If it is too tight, you may need to remove a shim.
7. When the gap is correct, apply the correct torque to the blade bolts. Refer to the Dry Bolt Torque Charts in
this section for the proper torque value.
CHECK GAP HERE
PRIMARY BLADES
FIGURE 5-1
Keep hands away from moving shear. Be sure the shear will not move while checking the blade gaps
or severe injury could result.
8
SHEAR MODEL BLADE GAP
MSD1000 .010”
MSD1500 .010”
MSD2000 .010”
MSD2500 .010”
MSD3000 .010”
MSD4000
MSD4500 .020”
MSD7500 .040”
MSD9500 .060”
.020”
CHECK GAP HERE
SECONDARY BLADES
FIGURE 5-19
Page 22 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 61

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR
BUILD UP AND
HARDSURFACING
The steel used in LaBounty Saber Series™ shears is
stronger and more durable than ever. However, this
steel requires special attention during maintenance.
Pay special attention to the preheat and post-heat
instructions and follow them exactly. Review the following guidelines for build-up and hardsurfacing the
shear. Detailed instructions on maintaining specifi c
areas of the shear are on the following pages.
PREHEAT
Preheat the general surrounding area to at least
200°F (100°C) to remove moisture from the base
material.
NOTICE
Before ANY thermal process is applied to the shear
steel, including welding, tack welding, torch cutting,
and air-arcing, preheat the area within 6" (150 mm) of
the local area to a minimum of 400°F (200°C) and a
maximum of 450°F (230°C). This includes adding and
removing lifting lugs.
HANDLING AND STORAGE
OF WELD MATERIALS
Follow the weld manufacturer’s handling and storage instructions closely. Make sure the electrodes
or wire are free of moisture. Moisture can cause
cracks and porosity in the weld and the base metal
beneath the weld.
WELD QUALITY
Quality and attention to detail in welding can signifi cantly affect the life of the shear. Stanley LaBounty
strongly recommends that only qualifi ed and certifi ed welders perform this work. Make sure the weld
consumables and base material are clean, dry, and
free of grease, paint, dirt, or any other foreign substance that may harm the weld.
NOTICE
Preheat and post-heat instructions must be followed
exactly. Failure to do so can compromise warranty
coverage.
NOTICE
Preheat must be uniform throughout the material
thickness and maintained until all welding has been
completed. Avoid cyclic heating and large temperature swings. Preheating may be done by localized
gas torches, or thermal strip blankets.
POST HEAT
If preheat has dropped below 400°F (200°C) within
6 inches (150 mm) of the weld area, post heat to
400° (200°C) and wrap with heat blanket to allow
it to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. Plan
to perform build-up and hardsurfacing at the end of
the day or when there will be adequate time for the
welded areas to cool before placing the shear back
into service.
Using improper build up and hardsurfacing products
may result in premature wear or increased potential
for cracking and may compromise warranty
coverage.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 23
Page 62

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
BUILD UP
RECOMMENDATIONS
Refer to the list of AWS classifi cations below to select a suitable build-up material for LaBounty shears.
Weld products within these classifi cations meet the
combined requirements for strength, toughness,
and ductility that are essential for LaBounty applications.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding - Stick Electrodes
• E7018
• E8018-C 3
Gas Metal Arc Welding - Solid Wire Electrodes
• ER 70S-6
Gas Metal Arc Welding - Flux Cored Electrodes
• E71 T- 1
• E71T-1M
• E80T1-Ni1
• E80T1-Ni1M
• Innershield NR-233
Gas Metal Arc Welding - Metal Powder Cored
Electrodes
• E70C-6M
• E80C-Ni1
HARDSURFACING
RECOMMENDATIONS
For hardsurfacing, Stanley LaBounty recommends
Amalloy 814H rod or equivalent. It is important to always use a hardsurfacing weld material with a chromium content of less than .10 percent and a severe
impact-resistance rating to prevent cracking. If you
have questions about what hardsurface material to
use, please contact the Stanley LaBounty Customer
Service Department.
Failure to adhere to LaBounty hardsurfacing recommendations may compromise the attachment
warranty. Hardsurfacing should be applied directly
on top of the build-up welds. The build up acts as
a bonding or underlayment for the hardsurfacing,
which reduces the chances that the hardsurfacing
will crack.
Contact Information for
Amalloy Welding and Industrial Supply
Phone: 800-735-3040 (toll free)
Fax: 763-753-8263
Web site: amalloy.com
NOTICE
Welding suppliers can assist in identifying products
that meet these AWS classifi cations.
Page 24 Section 5 Maintenance
DO NOT use stainless hardsurface rod. It will crack
the base metal which can cause a major structural
failure of your shear jaws.
Page 63

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
CRITICAL WEAR AREAS
NOTICE
The area shown in Figure 5-20 must be inspected daily, and maintained whenever the crosshatch pattern is
almost worn down to the base metal surface. If you have any questions regarding this information, please call
the Stanley LaBounty Service Department at (218)-834-6901.
Close attention must be paid to the “crosshatch” hardsurfacing. This area should be inspected daily. When
the crosshatch is worn down almost to the base metal surface, clean the surface by wire brushing, preheat
to 400°, and apply new underlayment beads to the pattern using E-7018 welding rod, or E-70 series wire.
After the pattern has been established with underlayment beads, apply hardsurface to the pattern. It is rec-
ommended that only one pass (bead) of hardsurfacing be applied. After welding, wrap the upper in a heat
blanket and allow to cool slowly. Apply hardsurfacing on top of each of the underlayment beads. DO NOT
APPLY HARDSURFACE DIRECTLY TO THE PARENT MATERIAL. It is important to use an air operated slag
peener on each pass of weld to relieve stress.
If, as a result of production considerations, the crosshatch pattern has been worn down into the base metal
of the shear upper jaw, the Saber Tip can be used as a guide for build-up to proper profi le prior to applying
new hardsurfacing. If the edge of the Saber Tip has been worn, it will be necessary to remove the tip, rotate
to the new front edge, and bolt into place. The surface of the upper shear face should be built up (using
E-7018 welding rod, or E-70 series wire-following pre-heat procedures) to conform in profi le to the new
Saber Tip edge. Depending upon the model, this surface should be fl ush with the Saber Tip edge to 1/16"
above the edge. Once the surface has been built up and ground to profi le, the crosshatch hardsurface pattern can be applied. Use 1½” spacing in the crosshatch hardsurface pattern, as shown in Figure 5-20.
NOTICE
Recommended Hardsurfacing Welding Rod for this
application: Amalloy 814-H
CROSSHATCH AREA
B
A
FIGURE 5-20
Maintenance Section 5 Page 25
Page 64

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
CRITICAL WEAR AREAS
continued
CROSSHATCH HARDSURFACING
See Figure 5-21.
A. In some applications, this area can be built up
for added wear resistance. Taper and blend the top
edge of the weld procedure.
B. Maintain build-up in this critical area. Area to be
built up fl ush with the top edge of the blade. Use
E-7018 or E-70 series wire.
C. Maintain profi le and build-up in this area. Blend
the bottom edge. This area must be maintained to
prevent wear into the Saber Tip reverse edge, which
rests just behind it.
D. Use E-7018 or E-70 series wire. Apply hardsurface allowing 1/16" space in from the edge both
sides. Do not apply hardsurface directly on an edge.
E. Apply the crosshatch pattern using 1.50” spacing.
F. Build up this area so that the bottom edge pro-
trudes 1/16" beyond the end of the blade. Taper and
blend the top edge; use E-7018 or E-70 series wire.
C
D
E
A
B
FIGURE 5-21
FIGURE 5-17
F
BUILD UP TEMPLATE
NOTICE
Apply hardsurfacing on top of the underlayment
beads. DO NOT APPLY HARD SURFACE DIRECTLY
TO THE PARENT MATERIAL. It is important to use
an air operated slag peener on each pass of weld to
relieve stress.
FIGURE 5-22
FIGURE 5-18
NOTICE
• Figure 5-22 is not to scale; it has been enlarged for the purpose of illustration.
• Apply hardsurfacing on top of the underlayment beads. DO NOT APPLY for all build-up and welding
procedures; use E-7018 welding rod, or E-70 series wire, following the welding procedures outlined on pages
5-19 through 5-20 of this manual.
• Use build-up template provided in the maintenance kit, to profi le upper.
• If restoring the profi le of the tip pocket is unattainable through welding and grinding, please contact
LaBounty Service Department: (800) 522-5059. There is a tip grinding tool that follows a template that will
restore the seat to factory specifi cations.
Page 26 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 65

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
UPPER SHEAR BUILD UP AND HARDSURFACING
1. Apply a bead of hardsurface rod on top of each of the underlayment beads. It is important to use an air
operated slag peener on each pass to relieve weld stress.
2. To determine how much build up is required along the blade seats, place a straightedge across the blades.
Repeat steps 4 and 5 to build this area fl ush with the blade (see Figure 5-23).
3. If necessary, build-up along the top and front edges of the secondary blade seat fl ush with the blade (see
Figure 5-24). The blade should not stick out beyond the edge of the seat in this area.
4. To hardsurface the area alongside the upper blades, establish the pattern with three or four passes of
build-up. These beads should run parallel to the blades from behind the Saber Tip to approximately the midpoint of the primary blade (see Figure 5-25).
NOTICE
• Keep the outside passes at least 1/4" (6 mm) back from the blade seat and outer edges.
• Stagger the ends of the welds and do not end a weld adjacent to a blade bolt hole.
• Use a grinder to taper the ends of each weld down to the base material. Grind marks should go with the
grain.
• Do not undercut the ends of the weld with the grinder.
5. Apply hardsurfacing on top of each of the underlayment beads. Do not apply hardsurface directly to the
parent material. It is important to use an air operated slag peener on each pass of weld to relieve stress.
6. If the temperature within 6" (150 mm) of the weld area has dropped below 400°F (200°C) during the weld
process, post heat this area to 400°F (200°C).
7. Wrap with a heat blanket and allow the welded area to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. The shear
should not be put back into service until it has cooled completely.
STAGGER WELDS
BUILD UP AREA FLUSH
WITH BLADES
FIGURE 5-23
BUILD UP AREA FLUSH
WITH BLADE
FIGURE 5-24
GRAIN DIRECTION
FIGURE 5-25
Maintenance Section 5 Page 27
Page 66

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
WELD-IN TIP MAINTENANCE
if equipped
Check the condition of the piercing tip daily. It should
be square and fi t closely between the blades of the
lower shear. All blade maintenance should be completed before building up the piercing tip. The condition
of the piercing tip has a large effect on the piercing
ability of the shear. If the tip is worn, it is suggested
that the tip be built up and hardsurfaced. If the tip is
badly worn, it is recommended that a new piercing tip
be installed. Instructions for replacing the tip are on
the following pages. This maintenance should be done
at the end of the work day to allow adequate cooling
time before putting the shear back into production.
1. Use a straight edge to determine how much buildup is needed along the sides of the piercing tip. Place
the straightedge along the cutting blades and extend
it beyond the tip (see Figure 5-26). The tip should be
fl ush with the blades.
2. Now do the same on the other side of the upper
shear. The tip should be fl ush with the front wear plate
(see Figure 5-27). If there is a gap, this area needs to
be built up.
3. Use the build-up template provided by Stanley
LaBounty to determine the amount of build-up needed
on the front and bottom surfaces of the tip. Line up
the template with the edges of the cutting blade and
check the wear (see Figure 5-28 on page 31).
4. Clean all dirt and grease from area to be built up.
5. Preheat the area surrounding the tip to about 200°F
(100°C) to remove moisture. Preheat the area within 6
inches (150 mm) of the weld location to a minimum of
400°F (200°C) and a maximum of 450° (230°C). Maintain this temperature range throughout the process.
PIERCING TIP
FLUSH WITH BLADE
FIGURE 5-26
PIERCING TIP
FLUSH WITH WEAR
PLATE
STRAIGHT EDGE
The upper shear must be grounded when welding on
the upper shear to prevent the possibility of electric
shock and arcing through the cylinder or main pivot
components.
Page 28 Section 5 Maintenance
STRAIGHT EDGE
FIGURE 5-27
Page 67

WELD-IN TIP MAINTENANCE
continued
6. Apply build up to the worn areas (see General Rules
for Build Up and Hardsurfacing). Peen each pass vigorously to relieve weld stress and remove slag.
NOTICE
Check temperature frequently during this procedure.
Maintain 400-450ºF (200-230ºC). Do not exceed 450º
(230ºC).
7. To hardsurface the built up area, apply single passes, side by side. Peen each pass.
8. When welding is complete, grind the tip smooth
and square with wear plate and cutting blades. Check
it again with the straight edge and build-up template.
9. To check the fi t of the tip, close the shear until the
piercing tip begins to enter the lower shear (see Fig-
ure 5-29). The piercing tip should fi t squarely into the
lower jaw.
10. When fi nished reworking the tip, work harden it
by peening the welded area until it is shiny or until the
peener cannot dent the weld anymore (approximately
fi ve minutes).
11. If the temperature within 6" (150 mm) of the weld
area has dropped below 400°F (200°C) during the
weld process, post heat this area to 400°F (200°C).
12. Wrap with a heat blanket and allow the welded
area to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. The
shear should not be put back into service until cooled.
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
UPPER BUILD-UP
TEMPLATE
LINE UP TEMPLATE
WITH BLADE EDGES
FIGURE 5-28
CHECK FOR CLOSE
AND SQUARE FIT
FIGURE 5-29
Maintenance Section 5 Page 29
Page 68

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
WELD-IN TIP REPLACEMENT
if equipped
If the piercing tip is badly worn, it is advisable to
install a new piercing tip using the following
instructions.
NOTICE
If the front wear plate is also worn, replace it at the
same time as the piercing tip.
1. Preheat the surrounding area to about 200°F
(100°C) to remove moisture. Preheat the area within
6" (150 mm) of the tip to a minimum of 400°F (200°C)
and a maximum of 450°F (230°C). Maintain this temperature range throughout the process.
2. Air-arc the old tip to remove it. Be sure to remove
the old tip completely. Please note that a notch or
seat for the tip is present in the upper shear.
3. To completely prepare the surface for the new tip,
the upper must be chamfered as shown (see Figure
5-30). The chamfer size should be approximately onehalf the thickness of the new tip.
NOTICE
Before installing the new piercing tip, grind the area
fl at and smooth. Remove carbon residue with the
air-arc.
4. Place the new tip into the seat. Use a straightedge
to position the tip before tacking it into place. The
side edge of the new tip should be fl ush with the
face of the blade (see Figure 5-31).
5. Make sure the tip is squarely against the edge.
Once the tip is positioned properly, bring the preheat
back up to 400°F (200°C) and tack the tip in place.
6. Check the tip profi le with the build up template
supplied by Stanley LaBounty (see Figure 5-32).
7. Close the shear until the tip begins to enter the
lower shear and check the clearance of the new tip.
If clearance is correct, proceed with the following
steps. If not, adjust the position of the tip as needed.
FIGURE 5-30
TIP FLUSH WITH BLADE
FIGURE 5-31
BUILD-UP TEMPLATE
45º CHAMFERS
Page 30 Section 5 Maintenance
FIGURE 5-32
Page 69

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
WELD-IN TIP REPLACEMENT continued
The upper shear must be grounded when
welding on the upper shear to prevent the
possibility of electric shock and arcing through
the cylinder or main pivot components.
NOTICE
Check temperature frequently during this procedure. Maintain 400-450ºF (200-230ºC). Do not exceed 450º (230ºC).
8. Once it is tacked in the proper position, preheat the tip area to a minimum of 400°F (200°C) and a maximum of
450°F (230°C).
9. Use the recommended build-up weld rod to fi ll the chamfered areas with multiple passes. Do the sides fi rst
and stress relieve each pass by peening. A weld is required on both sides of the tip (see Figure 5-33).
10. Weld the back and front to the upper shear, following the same procedure.
11. Grind the welds fl ush on the sides. The weld on the wear plate side should be ground fl ush with the front
wear plate.
12. If the temperature within 6
post heat this area to 400°F (200°C).
13. Wrap with a heat blanket and allow the welded area to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. The shear
should not be put back into service until it has cooled.
"
(150 mm) of the area has dropped below 400°F (200°C) during the weld process,
FIGURE 5-33
Maintenance Section 5 Page 31
Page 70

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
FRONT WEAR PLATE
REPLACEMENT
if equipped
The front wear plate bears against the guide blade to
support the upper shear during operation (see Figure
5-34). To prevent damage to the shear, it is crucial to
replace this wear part when it is worn. Replace the
front wear plate when the guide blade gap is greater
than 0.030" (0.75 mm) with a new guide blade and a
full set of shims installed. Whenever the front wear
plate is replaced, also replace the piercing tip. Use the
following instructions to replace the front wear plate.
1. Preheat the area surrounding the wear plate to
about 200°F (100°C) to remove moisture. Preheat
the area within 6" (150 mm) of the wear plate to a
minimum of 400°F (200°C) and a maximum of 450°
(230°C). Maintain this temperature range throughout
the process. Temperature/melt sticks are available
from Stanley LaBounty.
2. Air-arc the old wear plate to remove it completely.
Please note that the upper shear has a machined surface for the wear plate.
3. Use a grinder to make sure the area is fl at and
smooth with all carbon residue removed.
4. Place the new wear plate into the machined area
existing on the upper. Position the new wear plate so
there is approximately 1/2" (12.7 mm) gap between
the wear plate and the piercing tip, and equal distances on the other sides of the seat. Clamp the wear
plate into position.
5. Bring the preheat back up to 400°F (200°C) and tack
the tip in place.
NOTICE
Check temperature frequently during this procedure.
Maintain 400-450ºF (200-230ºC). Do not exceed 450º
(230ºC).
FRONT WEAR PLATE
The upper shear must be grounded when
welding on the upper shear to prevent the
possibility of electric shock and arcing through
the cylinder or main pivot components.
Page 32 Section 5 Maintenance
FIGURE 5-34
Page 71

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
LOWER WEAR PLATE
REPLACEMENT
The lower wear plates protect the lower cross plate
from excessive wear. Inspect these plates every 80
hours and replace them before the cross plate is in
danger of being exposed to wear. Use the following
instructions to replace the lower wear plates.
1. Preheat the surrounding area to about 200°F
(100°C) to remove moisture. Preheat the area within
six inches (150 mm) of the lower wear plates to a
minimum of 400°F (200°C) and a maximum of 450°
(230°C). Maintain this temperature range throughout
the process. Temperature/melt sticks are available
from Stanley LaBounty.
2. Air-arc the old wear plates to remove them com-
pletely from the nose plate.
3. Use a grinder to make sure the surfaces are fl at
and smooth with all weld and carbon residue removed. If necessary, build up the edges of the cross
plate before installing the new wear plates. See the
lower shear build-up instructions in this chapter.
4. Position the new front wear plate so it is centered
across the width of the cross plate. The holes in the
wear plate should be aligned with the holes in the
nose plate. This should leave a gap between the
top of the wear plate and the top of the nose plate
that will be fi lled with weld later (see Figure 5-35).
Clamp the wear plate into position, bring the pre-
heat back up to 400°F (200°C). Tack weld in place.
NOTICE
Check temperature regularly during this procedure.
Maintain 400-450°F (200-230°C). Do not exceed
450°F (230°C).
The lower shear must be grounded when weld-
ing on the lower shear to prevent the possibility
of electric shock.
TOP WEAR PLATE
CROSSPLATE
FRONT WEAR PLATE
NOTICE
Lower wear plates have been added to the sides of
the cross plate in 1000, 1500 and 2000 Saber Shears.
SIDE VIEW FRONT VIEW
FIGURE 5-35
Maintenance Section 5 Page 33
Page 72

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
LOWER WEAR PLATE REPLACEMENT continued
5. Position the new top wear plate so it is also centered across the width of the cross plate. This wear plate
should overhang the front edge of the cross plate to be fl ush with the face of the front wear plate. Clamp the
wear plate into position, bring the preheat back up to 400°F (200°C) and tack weld in place.
6. Use the recommended build-up weld rod to fi ll the area between the wear plates. Then weld an approxi-
mate 3/8" (10 mm) fi llet on all remaining sides around the wear plates. Also weld a fi llet around the inside of
the holes on the front. Stress relieve each pass by peening. Grind welds smooth.
7. If the temperature within 6" (150 mm) of the weld area has dropped below 400°F (200°C) during the weld
process, post-heat this area to 400°F (200°C).
8. Wrap with a heat blanket and allow the welded area to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. The shear
should not be put back into service until it has cooled completely.
LOWER SHEAR BUILD UP AND HARDSURFACING
For maximum performance and long life, all edges on the lower shear should be kept square and fl ush with
the blades. Check the lower shear every 80 hours and maintain it when necessary. All blade maintenance
must be done before building up and hardsurfacing the lower shear. It is recommended that this maintenance be done at the end of the working day to allow adequate cooling time before putting the shear back
into service.
1. Remove all existing hardsurfacing by grinding down to the base metal. Do not weld on top of the existing
hardsurfacing.
2. Clean all dirt and grease from area to be maintained.
3. Use a straight edge to determine how much build-up is required on the cross plate. If the lower wear
plates on the nose plate are worn, these should be replaced at this time (see previous page for instructions).
4. Use the straight edge across the top of the blades to fi nd the build-up requirements on the top side of the
lower shear. All edges should be square.
5. Preheat the area surrounding the tip to about 200°F (100°C) to remove moisture. Preheat the area within 6"
(150 mm) of the weld location to a minimum of 400°F (200°C) and a maximum of 450° (230°C). Maintain this
temperature range throughout the process.
The lower shear must be grounded when weld-
ing on the lower shear to prevent the possibility
of electric shock and arcing through the cylinder
or main pivot components.
Page 34 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 73

LOWER SHEAR BUILD UP
AND HARDSURFACING
continued
6. Apply build up to the worn areas in single passes,
side-by side, running with the grain of the base
material (see General Rules for Build Up and Hardsurfacing). Use the air-operated slag peener to peen
each pass to relieve weld stress and remove slag.
Grind all edges to 90°.
NOTICE
Check temperature regularly during this procedure.
Maintain 400-450°F (200-230°C). Do not exceed
450°F (230°C).
7. If necessary, build up the area beneath the edge
of the secondary blade so it is fl ush with the blade
(see Figure 5-37). The blade should not stick out
beyond the edge of the seat in this area.
8. To hardsurface the top sides of the lower shear,
establish the pattern with three or four passes of
build-up. These beads should run parallel to the
blades from the nose plate back to about the midpoint of the primary blade. Do this on the guide
blade side also. This will establish the hardsurfacing
pattern and serve as an underlayment.
9. Apply a bead of hardsurface rod on top of each
of the underlayment beads. DO NOT apply hardsurface directly to the parent material. It is important
to use an air operated slag peener on each pass of
weld to relieve stress.
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
USE STRAIGHT EDGE
ACROSS SURFACES
FIGURE 5-36
BUILD UP AREA FLUSH WITH
BLADE
FIGURE 5-37
Maintenance Section 5 Page 35
Page 74

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
LOWER SHEAR BUILD UP
AND HARDSURFACING
continued
NOTICE
• Keep the outside passes at least 1/4"(6 mm) back
from the blade seat and outer edges.
• Stagger the ends of the welds and do not end a
weld adjacent to a blade bolt hole. See Figure 5-38.
• Use a grinder to taper the ends of each weld down
to the base material. Grind marks should go with the
grain.
• Do not undercut the ends of the weld with the
grinder.
10. Use a similar technique to hardsurface the sides
of the nose plate. Establish a 45º diamond pattern
of approximately 1-1/2" (38 mm) (see Figure 5-39).
Again, use the build-up rod to lay down the pattern
and use the hardsurface rod on top. Use the airoperated slag peener to peen each pass to relieve
weld stress and remove slag.
11. If the temperature within 6" (150 mm) of the
weld area has dropped below 400°F (200°C) during the weld process, post heat this area to 400°F
(200°C).
12. Wrap with a heat blanket and allow the welded
area to cool slowly to the ambient temperature. The
shear should not be put back into service until it has
cooled completely.
STAGGER WELDS
DO NOT WELD EDGES
FIGURE 5-38
Page 36 Section 5 Maintenance
CROSSHATCH PATTERN
FIGURE 5-39
Page 75

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
MAINTENANCE
Use the following instructions to safely perform
hydraulic checks and maintenance on the shear.
1. Always relieve all excavator hydraulic pressure
before working on any hydraulic component. Relieve
hydraulic pressure before working on the machine
by working the controls in all directions with the
engine off.
2. In order to test the hydraulic system, a diagnostic
fi tting will need to be installed into the shear hydrau-
lic manifold block. To do this, shut off the excavator
and relieve the system pressure. Make sure the system pressure is at zero (0) psi and remove the dash-
4 (1/ 4") O-ring boss plug from the diagnostic port on
the hydraulic manifold block.
a diagnostic fi tting for your test gauge. Maintaining
proper operating pressure will result in the best cutting performance. This is also a quick check to make
sure that the excavator is performing up to specifi cations.
3. Check all hydraulic components (split fl anges,
hoses, fi ttings, mounting hardware, etc.) every 80
hours.
4. Have the shear cylinder seals replaced by an au-
thorized Stanley LaBounty dealer every 2,000 hours.
5. Whenever hydraulic lines are disconnected,
hoses must be capped and ports must be plugged
to prevent contamination of the hydraulic system.
Replace this plug with
MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
Relieve pressure before disconnecting hydraulic
lines. Tighten all connections before applying
pressure. Keep hands and body away from pin
holes and nozzles, which can eject fl uids under
high pressure. Use a piece of cardboard to search
for leaks.
penetrate the skin and cause serious injury.
If ANY fl uid is injected into the skin, seek
immediate medical attention.
NEVER adjust pressure relief valves to get
higher operating pressures. The manufacturer’s
recommended pressures give the safest
performance with the longest life.
Escaping fl uid under pressure can
NOTICE
Maintenance Section 5 Page 37
Page 76

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
FLANGE TYPE HOSE FITTINGS
Check fl ange fi ttings for smooth, tight fi t of matching surfaces. If any cap screws are loose or matching sur-
faces are not tight, tighten the loose cap screw then tighten the diagonally opposite cap screw. Tighten the
two remaining cap screws then torque all four screws as specifi ed in the Torque Chart in this manual.
Tolerance is ± 10%. The torques given are enough for the given size connection with the recommended work-
ing pressure. Torques can be increased to the maximum shown for each screw size if desired. DO NOT use
these values if a different torque value or tightening procedure is listed for a specifi c application. Torque values
listed are for general use only. Check tightness of cap screws periodically.
Shear bolts are designed to fail under predetermined loads. Always replace shear bolts with identical grade. To
prevent them from failing when tightening, make sure fastener threads are clean and properly engaged.
TORQUE VALUES FOR FOUR-BOLT FLANGE FITTINGS
CODE 62 FLANGES
NOMINAL
FLANGE
SIZE
1" M12x1.75 70 95
1 1/4" M12x1.75 70 95
1 1/4" M14x2.00 112 152
1 1/2" M16x2.00 224 304
2" M20x2.50 435 590
CAPSCREW
SIZE
TORQUE
FT-LBS
TORQUE
N-M
CODE 61 FLANGES
NOMINAL
FLANGE
SIZE
3/4" M10x1.50 42 57
1" M10x1.50 42 57
1 1/4" M12x1.75 70 95
1 1/2" M12x1.75 70 95
2" M12x1.75 70 95
CAPSCREW
SIZE (CLASS
10.9)
TORQUE
FT-LBS
TORQUE
N-M
Use only metric tools on metric
hardware. Other tools may not fi t
properly. They may slip and cause
injury.
NOTICE
Do not use air wrenches. Tighten each
bolt equally in an alternating pattern.
Do not over tighten.
Page 38 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 77

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
APPLYING SPLIT FLANGE
CLAMPS
1. Clean sealing surfaces and make certain they are
free from nicks, scratches and burrs. Foreign material prevents a proper seal (see Figure 5-40).
FIGURE 5-40
2. Lubricate the o-ring and ensure that it is properly
installed so as to prevent damage during installation.
3. Push the fl ange clamps toward the fl ange head
and screw fasteners into fl ange pad. Continue to
screw the fasteners until their heads just meet the
split fl ange surface (see Figure 5-41).
4. Torque the fasteners in diagonal sequence, in
small increments, until fi nal torque level is achieved.
Torque values for fl ange connections are listed on
page 34. Notice that the torque values vary accord-
ing to the size and fastener type.
FIGURE 5-42
FIGURE 5-41
Maintenance Section 5 Page 39
Page 78

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
X
CYLINDER GAP CHECK
FIGURE 5-43
Periodically check (minimum once per week) the gap between the rod eye shoulder and head face (X) with
the cylinder fully retracted (see Figure 5-43). If the gap exceeds the dimensions given in the table, below, by
more than .06", it could be an early indication of required maintenance. Stop shear operations and call the
LaBounty Service Department: (218)-834-6901.
MODEL X-DIMENSION
1500 0.50"
2000 1.50"
2500 0.50"
3000 0.50"
4000 0.50”
4500 1.00"
7500 0.75"
9500 0.75"
Page 40 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 79

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC - STANDARD ROTATING SHEARS
TO EXCAVATOR
SPEED VALVE
ASSEMBLY
HYDRAULIC
MANIFOLD
BLOCKS (ON
SHEAR)
TEST PORT
ROTATION
CASE DRAIN LINE
CONTROL VALVE
ASSEMBLY
MOTOR
TEST PORT
TO EXCAVATOR
FIGURE 5-44
MOTOR
HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC - STANDARD NON-ROTATING SHEARS
SHEAR CYLINDER
TO EXCAVATOR
HYDRAULIC
MANIFOLD
BLOCKS (ON
SHEAR)
SPEED VALVE
ASSEMBLY
TO EXCAVATOR
FIGURE 5-45
Maintenance Section 5 Page 41
Page 80

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT
The speed valve on LaBounty® shears is factory
adjusted by Stanley LaBounty technicians prior to
shipment. Field adjustments of the valve should
only be necessary if the operator senses that the
valve is not functioning properly. Some indicators of
a poorly functioning valve are:
• The shear does not consistently shift into speed
mode when closing the jaw
• The shear jaw continues to close after the operator
has let go of the controls
• The shear shifts into speed mode, but seems to
lack power
Follow the procedure below if speed valve adjustment is necessary.
TOOLS NEEDED
The following tools are recommended for speed
valve adjustment on any Stanley LaBounty Saber
Series Hydraulic Cylinder:
1. Open-end or box end wrenches (12-19 mm sizes)
2. Digital gauge kit (Stanley LaBounty P/N 169832)
3. Allen wrenches (4-12 mm sizes)
3. Insulating gloves for low and high temperatures.
4. Overalls or other uniform—no loose fi tting cloth-
ing that may become entangled in machinery
5. Hearing protection—ear muffs or plugs.
Relieve pressure before disconnecting hydraulic
lines. Tighten all connections before applying
pressure. Keep hands and body away from pin
holes and nozzles, which can eject fl uids under
high pressure. Use a piece of cardboard to
search for leaks. Escaping fl uid under pressure
can penetrate the skin and cause serious
injury. If ANY fl uid is injected into the skin, seek
immediate medical attention.
DO NOT let hydraulic oil get in contact with the
skin as it could cause severe burns. Hydraulic oil
becomes hot during operation. Wear adequate
protective clothing and safety equipment.
SAFETY POINTS
Stanley LaBounty recommends that the following
safety precautions be followed when adjusting the
speed valve on any Stanley LaBounty Saber Series
Hydraulic Cylinder.
Reminder: Always wear the proper personal protection equipment including the following:
1. Steel toe safety shoes or boots.
2. Shatter proof safety glasses and head wear such
as a hard hat.
Page 42 Section 5 Maintenance
Chemicals used on Stanley LaBounty Saber
Series hydraulic cylinders include hydraulic
oil; refer to the excavator operator’s manual
and have MSDS sheets and proper treatment
equipment available.
Page 81

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
REGENERATIVE VALVE DESIGN
The design of the regenerative fl ow valve used in Stanley LaBounty Mobile Shears consists of a pilot valve
mounted onto a spool valve. The pilot valve is used for regulating the movement of the spool valve in shifting the valve into and out of regenerative mode. See Figure 5-46. The only component that is in the working
fl ow path of the fl uid to the shear cylinder is the valve spool. The valve spool is of similar construction to that
of the excavator’s main control valve spool. Therefore, it is considerably larger than the components found in
a typical cartridge type regenerative valve.
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
The function of the regenerative valve is to provide for rapid advance of the shear hydraulic cylinder during
the closing phase of the shear cycle. The valve accomplishes this function by shifting a valve spool to open
the rod side of the cylinder to the bore side of the cylinder, thus allowing the fl uid in the rod side to fi ll the
bore side when the cylinder is extending. This function only occurs when the cylinder is advancing in a “low
load” condition, which occurs as the shear jaw is closing down onto the material that it is about to be cut. As
the shear enters the cutting phase, the operating pressure requirements increase. The pilot valve portion of
the regenerative valve, which in turn causes the valve spool to shift out of regenerative mode, senses the
increased pressure. During this phase, the rod-side fl uid is directed to the work line and back to the base
machine’s reservoir (low pressure). Meanwhile, only the fl ow from the excavator’s control valve is directed
to the bore side of the cylinder, allowing it to reach full system operating pressure. This allows the shear to
cut by utilizing the full power of the excavator with resistance coming only from the material being cut by the
shear.
TROUBLESHOOTING
There are two operating conditions that affect the
performance of the speed valve and will require
some troubleshooting by an equipment mechanic or
service representative. These conditions are:
a. The speed valve does not seem to shift out of
regenerative mode at the appropriate time resulting
in the shear appearing to lose cutting power, or
b. The speed valve does not appear to shift into
regenerative mode resulting in a slow closing movement of the shear jaw. Both of these conditions can
be remedied by following the speed valve adjustment procedure discussed on the following pages.
NOTICE
If making the appropriate adjustments does not
remedy the above conditions, refer to page 6-11 of
this manual for further troubleshooting guidelines. If
further diffi culties are encountered, the speed valve
may require replacement of the hydraulic seals.
Seal kits are available from the Stanley LaBounty
Customer Service Department. Shear serial number
will be required when ordering.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 43
Page 82

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
C
B
D
FIGURE 5-46*
Page 44 Section 5 Maintenance
A
A. MAIN SPOOL VALVE ADJUSTMENT
B. PILOT VALVE
C. PILOT VALVE HOUSING
D. MAIN SPOOL HOUSING
*Your speed valve may vary slightly from this
isometric illustration, which is not to scale.
Page 83

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT
continued
The following procedure is recommended by Stanley
LaBounty for speed valve adjustment on any fully
assembled and installed Saber Series Hydraulic
Cylinder. Prior to making any adjustments to the
valve, verify whether the valve is operating properly
by checking the following operational conditions. For
condition “a” (as described on page 5-43), install a
pressure gauge into the MAZ test port to see if the
pressure drops to zero when fully closing the shear
jaw. For condition “b” (as described on page 43),
compare the closing speed of the shear to the opening speed. If the closing speed is equal to, or less
than the opening speed, then the valve is shifting
properly into the regenerative speed mode.
This procedure requires more than one individual
in close proximity to the shear and shear
operation. Keep within sight when operating the
shear. Ensure all persons are clear before cycling
the shear. This procedure requires adjustments
to be performed with the hydraulic system
pressurized.
1. Position the attachment on fi rm, level ground so
the speed valve is easily accessible.
2. Turn the excavator off and release all hydraulic
pressure to the shear by working the excavator
controls in all directions. Be certain to relieve the
air pressure in the excavator reservoir. Refer to the
excavator operator’s manual for proper excavator
hydraulic pressure relief procedures.
3. Slowly remove the plugs from the MBS port and
the MAZ port on the speed valve. Turn the plugs
counterclockwise until fl uid begins to seep from the
port. Allow the fl uid seepage to slow before continuing.
4. Continue to slowly turn the plugs counterclock-
wise, pausing momentarily in 1/4 to 1/2 turn intervals until the plug is removed. This ensures all
residual pressure is relieved from the speed valve.
Refer to the illustration on page 5-44 of this section
for port locations. Place a drainage basin below the
ports to capture all escaping fl uid.
5. I
nstall the test fi ttings supplied with the Stanley
LaBounty Digital Gauge Kit, P/N 169832 into the
MBS and MAZ ports on the Speed Valve. If the MAZ
port is too diffi cult to access for test fi tting installation, the MX port on the speed valve may also be
used to monitor valve pressure.
6. Attach the digital gauge and pressure line to the
MAZ test port on the speed valve. If two gauges are
available, install the second digital gauge and pressure line to the MBS test port on the speed valve. If
only one digital gauge is available, the MBS test port
on the speed valve must be plugged at this time
with the MBS port plug. Mechanical, liquid fi lled dial
gauges may be used to monitor pressure in place of
the digital gauges.
7. Reset the main spool valve adjustment by loosening the 19mm lock nut on the main spool valve, and
turning the 6mm socket head adjustment screw
counter-clockwise. Continue to turn the socket
head adjustment screw until the end of its travel is
reached, then turn the adjustment clockwise until
you feel the spring tension of the main spool, after tension is felt turn the adjustment one full turn
clockwise. Re-tighten the 19mm lock nut.
8. Loosen the 19mm lock nut on the pilot valve,
but DO NOT turn the 6mm socket head pilot valve
adjustment screw.
9. Have a co-worker restart the excavator. Check for
leaks in the test fi ttings by using a piece of cardboard or other rigid material. Repair all leaks before
proceeding.
NOTICE
Note that turning the pilot valve adjustment screw
past the locking nut could cause severe damage to
the pilot valve.
Maintenance Section 5 Page 45
Page 84

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT
continued
10. Have the excavator operator cycle the shear to
the fully closed position and set the pilot valve to
its maximum setting. Turn the pilot valve adjustment screw clockwise until the cylinder just fails
to shift out of speed mode. You may need to open
and close the shear multiple times to reach the
pilot valve maximum setting. The pressure gauge
attached to the MAZ port should read approximately
400 psi or higher when in speed mode.
NOTICE
DO NOT make adjustments to the speed valve while
the cylinder is extending.
11. Have the excavator operator cycle the shear to
the fully closed position then set the pilot valve to
its minimum setting. Turn the pilot valve adjustment
screw counter-clockwise until the cylinder just fails
to shift into speed mode. You may need to open
and close the shear multiple times to reach the
pilot valve minimum setting. The pressure gauge
attached to the MBS port should read approximately
full system pressure when not in speed mode. Pay
careful attention to the number of turns required to
reach this setting.
12. Have the excavator operator return the shear to
the fully open position a second time. Re-adjust the
pilot valve adjustment screw to the fi nal setting by
turning the adjustment screw clockwise 1/2 of the
number of turns required to reach the minimum setting and tighten the lock nut. This brings the valve
to its median setting, which is optimum for most
operating conditions.
13. Test the adjustments by cycling the shear to the
closed position six times normally and six times
with the shear stalled in the closed position. Monitor the gauge attached to the MAZ carefully. During
normal cycling, the gauge should read 400psi (26
bar) or higher. When stalling the shear, gauge pressure should drop to zero.
14. Verify the shift pressure. Have the excavator
operator cycle the shear to the fully closed position
and carefully monitor the pressure gauge attached
to the MAZ test port. Note the pressure reading
immediately before the shear stalls. This pressure is
the shift pressure required to shift the speed valve
out of speed mode. Shift pressure should be 3600 –
3700 PSI. (248 - 255 BAR).
15. Turn the excavator off and release all hydraulic
pressure to the shear by working the excavator
controls in all directions. Be certain to relieve the
air pressure in the excavator reservoir. Refer to the
excavator operator’s manual for proper excavator
hydraulic pressure relief procedures. Detach the
digital pressure gauge(s) and pressure line(s) from
the MBS and /or MAZ test fi tting(s). Slowly remove
the test fi tting(s) from the test port(s) as in step 3
of this procedure and replace the MBS and/or MAZ
port plug(s).
16. Restart the excavator. Check for leaks by using a
piece of cardboard or other rigid material. Repair all
leaks before using the shear. Re-apply the correct
torque to all speed valve fasteners including split
fl anges if found leaking. Use the table on page 8-26
for correct torque values.
17. Speed valve troubleshooting procedures can be
found on page 7-10 in the Troubleshooting section in
the back of this manual.
Page 46 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 85

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: MSD 1500 - 4500 SHEARS
Proper bolt installation is critical to ensure the safe and effi cient operation of the speed valve.
Carefully follow the steps below to properly install bolts.
NOTICE
Please note that the parts illustrated below (Figure 5-47) and on pages 5-50 through 5-51 are for
#513029, which is used in MSD 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 4000 and 4500 shears. For MSD 7500
and above, refer to your parts catalog for the speed valve part number and call Stanley LaBounty for
torque values. MSD 1000 models do not have speed valves.
1. Always replace bolts and nuts with the same size and class of fastener. Replacement fasteners
can be ordered from the Stanley LaBounty Parts Department to ensure the correct part is used.
Unless otherwise specifi ed, use class 10.9 metric hex head capscrews, class 10.9 metric fl at head
capscrews, and class 12.9 metric socket head capscrews.
2. Make sure bolts, nuts and bolt holes are free of dirt, oil, grease and other contaminants. .
3. The torque values in this manual are for use with non-plated fasteners with clean, dry threads.
These values are suitable for use with or without thread adhesives, such as Loctite™ products.
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY
P/N 513029 USED IN
MSD 1500,2000, 2500,
3000,4000 AND 4500
SHEARS
FIGURE 5-47
PILOT VALVE ASSEMBLY
SEE PAGE 5-51
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
5 512210 Socket Head Screw M8X35 4 32 ft lb/43 Nm
6 513133 Socket Head Screw M10X45 6 62 ft lb/84 Nm
5
6
CHECK VALVE
ASSEMBLY
SEE PAGE 5-52
MAIN VALVE
ASSEMBLY
SEE PAGE 5-50
Maintenance Section 5 Page 47
Page 86

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: MAIN VALVE ASSEMBLY
14
7
9
8
MAIN VALVE
ASSEMBLY
P/N 513080 USED IN
MSD 1500,2000, 2500,
3000, 4000, AND 4500
SHEARS
FIGURE 5-48
7
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
7 511515 Hex Nut 5 15 ft lbs/20 Nm
8 513086 Hex Nut 2 15 ft lbs/20 Nm
9 513087 Screw Plug (Allen) 7 7 ft lbs/10 Nm
14 511504 Hex Nut 1 22 ft lbs/30 Nm
9
8
7
Page 48 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 87

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES:
24
4
PILOT VALVE
P/N 512288 USED IN
MSD 1500,2000, 2500,
3000, 4000, AND 4500
SHEARS
FIGURE 5-49
PILOT VALVE ASSEMBLY
11
11
31
11
12
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
2 512317 Valve Seat 1 73 ft lbs/100 Nm
4 512318 Spring Cap 1 162 ft lbs/220 Nm
11 512323 Capscrew 8 1.5 ft lbs/2 Nm
12 511514 Screw Plug 10 7.5 ft lbs/10 Nm
24 511504 Seallock Nut 1 22 ft lbs/30 Nm
31 511563 Screw 1 18 ft lbs/25 Nm
12
12
12
2
Maintenance Section 5 Page 49
Page 88

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: CHECK VALVE ASSEMBLY
CHECK VALVE
ASSEMBLY
P/N 511540 USED IN
MSD 1500,2000, 2500,
3000, 4000, AND 4500
SHEARS
FIGURE 5-50
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
5 511579 Screw Plug 1 103 ft lbs/140 Nm
Page 50 Section 5 Maintenance
5
Page 89

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: MSD 7500, 9500 SHEARS
Proper bolt installation is critical to ensure the safe and effi cient operation of the speed valve. Carefully follow
the steps below to properly install bolts.
NOTICE
Please note that the parts illustrated below (Figure 5-51) and on pages 5-54 through 5-55 are for speed valve
#511461, which is used in MSD 7500 and 9500 shears.
1. Always replace bolts and nuts with the same size and class of fastener. Replacement fasteners can be
ordered from the Stanley LaBounty Parts Department to ensure the correct part is used. Unless otherwise
specifi ed, use class 10.9 metric hex head capscrews, class 10.9 metric fl at head capscrews, and class 12.9
metric socket head capscrews.
2. Make sure bolts, nuts and bolt holes are free of dirt, oil, grease and other contaminants. .
3. The torque values in this manual are for use with non-plated fasteners with clean, dry threads. These val-
ues are suitable for use with or without thread adhesives, such as Loctite products.
SPEED VALVE
ASSEMBLY
P/N 511461 USED IN
MSD 7500 AND 9500
SHEARS
FIGURE 5-51
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
6 512210 Socket Head Screw
6
4 31 ft lbs/43 Nm
M8X1.25X35
Maintenance Section 5 Page 51
Page 90

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: MSD 7500, 9500 SHEARS
MAIN BLOCK ASSEMBLY
P/N 512330 USED IN MSD
7500 AND 9500 SHEARS
FIGURE 5-52
5
5
5
5
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
5 512338 Screw Plug M8X1 4 7.5 ft lbs/10Nm
Page 52 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 91

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SPEED VALVE ADJUSTMENT continued
SPEED VALVE ASSEMBLY TORQUE VALUES: MSD 7500, 9500 SHEARS
14
REGEN VALVE
P/N 512327 USED
IN MSD 7500 AND
9500 SHEARS
FIGURE 5-53
13
25
12
13
13
25
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION QTY TORQUE
12 512338 Screw Plug M8X1 4 7.5 ft lbs/10 Nm
13 511515 Screw Plug 7/16-20 5 15 ft lbs/20 Nm
14 512339 Seallock Nut M20X1.5 1 73 ft lbs/100 Nm
25 512342 Socket Head Capscrew M14X70 12 51 ft lbs/70 Nm
26 512343 Socket Head Capscrew M14X50 8 51 ft lbs/70 Nm
26
Maintenance Section 5 Page 53
Page 92

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
DECAL AND LABEL MAINTENANCE
Be sure that all safety decals are installed and visible (see Figure 5-54). Replacement decals are available
from your Stanley LaBounty dealer. Complete label installation kits are available upon request.
7
3
1
4
5
2
FIGURE 5-54
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 116388 Grease Decal - one at each grease fi tting
2 116389 DANGER Decal - on both sides (Keep 75 feet away during opera-
tion)
3 503647 DANGER Decal - on both sides (top and front cab guarding
required)
4 511045 Model and Serial Number Plate - on right side only
5 116404 Stanley LaBounty Decals - on both sides toward rear of shear
6 BY MODEL Stanley LaBounty Decals - on both sides toward rear of shear
7 BY MODEL Model Decals - on both sides
6
1
Page 54 Section 5 Maintenance
Page 93

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
SECTION 6 ROTATOR MAINTENANCE
Major Components of Typical Rotation Systems ........................................................................6-2
The Rotator .................................................................................................................................6-3
Bolt Torque ..................................................................................................................................6-3
Torque Values for Turntable Bolts ................................................................................................6-3
Torque Values for Rotation Assembly Bolts .................................................................................6-3
Planetary Gearbox Lubrication (if equipped) ...............................................................................6-4
Lubricant Change-out Procedure ................................................................................................6-4
Planetary Gearbox Lubricants .....................................................................................................6-5
Synthetic Specifi cation ...............................................................................................................6-5
Gearbox Fill Capacities ...............................................................................................................6-5
Turntable Bearing ........................................................................................................................6-6
Turntable Bearing Lubricants .......................................................................................................6-6
Hydraulic Requirements ............................................................................................................. 6-7
Rotation Control Valve Manifold .................................................................................................. 6-7
Case Drain .................................................................................................................................. 6-7
Rotation Control Valve Assembly Schematics and Descriptions .................................................6-8
Internal Rotation Control System (if equipped) ...........................................................................6-9
Accumulator Control Valve Assembly (if equipped)....................................................................6-10
Maintenance Intervals for Internal Rotation (if equipped) .......................................................... 6-11
Accumulator Maintenance ......................................................................................................... 6-11
Testing the Accumulator Pre-charge .......................................................................................... 6-12
Pressure Release ....................................................................................................................... 6-12
Accumulator Pre-charging .......................................................................................................... 6-12
Operating Flow for Internal Rotation .........................................................................................6-13
Operating Pressure for Internal Rotation ................................................................................... 6-13
Rotator Maintenance Section 6 Page 1
Page 94

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
MAJOR COMPONENTS OF TYPICAL ROTATION SYSTEMS
Typical second member upper head assembly (see Figure 6-1, below), with an internal drive rotator, a gearbox
and standard rotation.
CONTROL VALVE
MANIFOLD
FIGURE 6-1
HYDRAULIC PORT
ROTATION PORT
GREASE FITTING
(BEHIND RING)
Typical third member upper head assembly (see Figure 6-2, below), with an external drive rotator, no gearbox
and optional internal rotation control system.
ACCUMULATOR
CONTROL VALVE
MANIFOLD
GREASE FITTING
GREASE FITTING
FOOT SWITCH
RETURN LINE FITTING AND ELECTRICAL
PLUG (FAR SIDE)
MOTOR
GEARBOX
TURNTABLE BEARING
MOTOR
ACCUMULATOR
Page 2 Section 6 Rotator Maintenance
CONTROL VALVE
MANIFOLD
TURNTABLE BEARING
Page 95

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
THE ROTATOR
The rotator gives the shear 360 degrees of continuous rotation in both directions for easy, accurate processing at all angles. The hydraulic rotation circuit consists of the hydraulic motor driving a turntable bearing, either
directly or through a planetary gearbox. It is necessary to regularly maintain this system to ensure long life and
good performance. The maintenance requirements of the rotator are outlined in the following pages.
BOLT TORQUE
The bolts connecting the turntable bearing are a critical structural area. The bolts must be inspected after the
initial eight hours of operation and weekly thereafter. Damaged fasteners must always be replaced with the
same size and grade of fastener. If bolts are found to be loose after operation, they should never be retorqued
more than one time before they are replaced. Please contact the Stanley LaBounty Service Department for
specifi c information about replacement.
TORQUE VALUES FOR
TURNTABLE BOLTS
SIZE CLASS FT-LBS N-M
M20 10.9 435 590
M20 12.9 523 710
M24 10.9 752 1020
M24 12.9 900 1220
M30 10.9 1511 2049
M30 12.9 1800 2450
1.00" L-9 900 1220
1.50" ZN-L-9 2600 3520
TORQUE VALUES FOR
ROTATION ASSEMBLY BOLTS
SIZE CLASS FT-LBS N-M
M10 12.9 49 67
Always replace bolts and nuts with the same
size and class fastener. Inferior fasteners can fail
and cause injury or death and damage to the
equipment.
NOTICE
• Use of the rotation feature for any other purpose
may damage the rotation components and may void
the shear warranty.
• It may be necessary to rotate the shear to access
all the bolts connecting the shear, turntable bearing
and rotating head.
• Be sure to use the proper torque value for the size,
class, and type of bolt.
M12 10.9 71 96
M16 10.9 173 235
M20 10.9 335 454
.38" Gr.8 63 85
.50" Gr.8 106 209
.75" Gr.8 380 515
Rotator Maintenance Section 6 Page 3
Page 96

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
PLANETARY GEARBOX LUBRICATION if equipped
The planetary gearbox is used if changes in gear ratios are required between the hydraulic motor and turntable bearing to rotate the shear. Correct lubricant and change-out procedures are critical to maintain dependable gearbox operation. The Planetary Gearbox Lubricants chart on the following page specifi es correct lubricants for various operating temperature.
The gearbox lubricant must be changed after the fi rst 50 hours of operation to remove metal fi lings from the
gearbox break-in period. Thereafter, refer to the following change-out schedule:
GRADE TIME
SAE 80W-90 500 hours or one year
Synthetic ISO 150 @ 104ºF 1000 hours or two years
Synthetic ISO 460 @ 104ºF 1000 hours or two years
Recommended inspection of the gearbox fl uid level is every 250 hours or six months.
• Cold weather lubrication is critical. If the temperature is below 5ºF (-14ºC), change out lubricant to synthetic
specifi cation.
• Slow rotation of the shear is recommended with all grades of lubricant at temperatures below 20ºF (-7ºC) to
warm up the rotation system prior to working the shear.
• All rotating shears leaving the factory have synthetic ISO 150 @ 104ºF grade lubricant in the gearbox.
LUBRICATION CHANGE-OUT PROCEDURE
1. Position the shear at a comfortable working height and in a position where gearbox is near level (gearbox
rotation axis should be horizontal).
2. Remove the upper head to access cover.
3. Place a lubricant catch basin below the drain plug capable of hold more than 2 quarts.
4. Remove the drain plug (bottom) and the visible top plug. These plugs are magnetic and will attract metal
fi lings from inside the gearbox. These fi lings should be removed from the plugs before reinstalling.
5. Reinstall the drain plug once the gearbox is fully drained.
6. Add the applicable gearbox lubricant through top plug hole. Refer to the chart on the following page for
proper fi ll capacity for your gearbox.
7. Remove lubricant catch basin.
8. Reinstall top plug and gearbox access cover.
Support the shear with blocking or cribbing during this procedure.
Be sure the excavator is shut off.
Page 4 Section 6 Rotator Maintenance
Page 97

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
PLANETARY GEARBOX LUBRICANTS
OPERATING AMBIENT TEMPERATURE RANGE RECOMMENDED GRADES
5ºF to 120°F (-14ºc to 49ºC) SAE 80W - 90
-50ºF to 120ºF (-46°C to 49°C) Synthetic ISO 150 @ 104ºF
-25°F to 180°F (-32°C to 82°C) Synthetic ISO 460 @ 104ºF
APPROVED SOURCE/GRADE GRADE
Manufacturers of approved SAE lubricants SAE 80W - 90
Mobile Oil Corp - Mobilube SHC 75W-90 Synthetic ISO 150 @ 104ºF
Mobile Oil Corp - Mobilube SHC 80W-140 Synthetic ISO 460 @ 104ºF
SYNTHETIC SPECIFICATION
MOBILUBE SHC 75W - 90 80W - 140
Product Number
SAE Number
Gravity API
Flash PT °C (°F), Min.
Flash PT °C (°F), Max.
Viscosity
cP @ - 40°C
cP @ -26°C
cST @ 40°C
cST @ 100°C
Viscosity Index
51100-6
75W - 90
29.8
204 (400)
-48 (-55)
109,000
---117
15.5
139
51101-4
80W - 140
30.2
218 (425)
-42 (-45)
---80,000
312
31.3
139
GEARBOX FILL CAPACITIES
PART NUMBER FILL CAPACITY MODEL NUMBER
510783 17 fl uid ounces (0.5 liter) MSD 1500R, MSD2000R
511491 68 fl uid ounces (2.0 liters) MSD 2500R
511493 68 fl uid ounces (2.0 liters) MSD3000R, MSD4500R
511373 68 fl uid ounces (2.0 liters) MSD7500R, MSD9500R
512565 22 fl uid ounces (0.66 liter) MSD1500R, MSD2000R
Rotator Maintenance Section 6 Page 5
Page 98

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
TURNTABLE BEARING
LUBRICATION FREQUENCY
Equipment operating frequently in extreme environments should be lubricated at least every eight hours. If the
old grease is noted to be in good condition and free of contamination, the interval may be extended. Conversely, if the old grease is contaminated or deteriorated, the interval should be shortened. Rotating shears in storage
should be lubricated at least every six months.
LUBRICATION PROCEDURES
Bearings are equipped with one to four grease fi ttings, depending upon the model. The grease fi ttings will be
located either on the outside of the bearing (if it is an internal drive rotator) or on the upper head side plate (external drive). To lubricate the bearing, grease a fi tting and then stand clear to rotate the shear. This will uniformly
distribute the grease and effectively fl ush out the old grease and contaminants. Grease the same fi tting again
after rotating before moving on to the next fi tting. Grease each fi tting a total of eight pumps of the grease gun
or until grease escapes through the bearing seals.
Stand clear of the shear while rotating. Grease
a fi tting and then stand clear to rotate the bearing to distribute the grease. DO NOT attempt to
grease the bearing while the shear is rotating or
severe injury could occur.
TURNTABLE BEARING LUBRICANTS
For normal operating conditions, periodic lubrication with lithium Grade 2 extreme pressure grease is recommended. For operation below 32°F (0°C), Grade 0 is recommended. the following table lists typical lubricants
for turntable bearings (comparable lubricants by other manufacturers may also be used):
APPROVED SOURCE TRADE NAME OPERATION BELOW 32°F OPERATION ABOVE 32°F
Amoco Rycon EPO EP2
Chevron Dura Lith EPO EP2
Exxon Lidok EPO EP2
Mobil Mobilux EPO EP2
Shell Alvania EPRO EP2
Sohio Bearing Guard LTO 2
Sun Prestige 740EP 742EP
Texaco Multifak EPO EP2
Union Unoba EPO EP2
Page 6 Section 6 Rotator Maintenance
Page 99

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
HYDRAULIC REQUIREMENTS
The rotating shear requires an auxiliary hydraulic circuit in order to operate the rotator. This circuit will need
to be a medium pressure (2000 - 2500 PSI/138 - 172 BAR), low fl ow (8 - 10 GPM/30 - 39 LPM) hydraulic circuit.
There are minimum and maximum pressure and fl ow requirements that may vary depending upon the shear
model. These requirements are listed in the Hydraulic Installation Requirements sheet in the Parts Catalog for
the shear. The rotation control manifold my vary depending upon the type of the rotation system and the particular requirements for the rotation circuit. Adjustment procedures for the rotation control valve are given on
the following pages.
ROTATION CONTROL VALVE MANIFOLD
One of two rotation control valves is installed on the shear depending upon the model. The rotation control
valve manifold provides overload protection and a load control system for the rotator with two crossover relief
valves and two brake valves. The crossover relief valve and brake valves have been preset at the factory and
require no adjustment. Do not tamper with these valves. If a malfunction is suspected due to a lack of performance in the rotator, a pressure check should be performed. Diagnostic fi ttings (which require a Parker PD
Series coupler or gauge) are installed in the manifold to provide a means of checking pressure. Contact the
Stanley LaBounty Service Department for the proper procedure for performing this check.
CASE DRAIN
A case drain is required because back pressure can develop in the hydraulic motor case as a result of metering
fl ow out of the motor. Depending upon the shear model, this port will either be a bulkhead in the upper head
side plate or will be located in the hydraulic port block. A 1/2" hydraulic line should be connected to this port and
routed back directly to the tank via a return-line fi lter or a fi lter of its own. The maximum allowable back pressure in this line should not exceed 300 PSI.
NOTICE
The case drain line must be connected to prevent
failure to the case or motor seals.
Rotator Maintenance Section 6 Page 7
Page 100

MSD SABER SERIES SHEARS
ROTATION CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY SCHEMATICS
AND DESCRIPTIONS
Please refer to the Parts Catalog to identify the control valve assembly in your specifi c attachment.
ROTATION CONTROL VALVE USED ON MODELS MSD 1500R AND MSD 2000R
MOTOR
WORK PORTS (A & B)
SAE #8 O-Ring Boss Ports
GAUGE PORTS (G1 & G2)
SAE #4 O-Ring Boss Ports
RELIEF
VALVES
BRAKE
VALVES
FIGURE 6-3
ROTATION CONTROL VALVE USED ON MODELS MSD 2500R, 3000R, 4000R, 4500R
MOTOR
RELIEF
VALVES
BRAKE
VALVES
FIGURE 6-4
WORK PORTS (A & B)
SAE #10 O-Ring Boss Ports
GAUGE PORTS (G1 & G2)
SAE #4 O-Ring Boss Ports
Page 8 Section 6 Rotator Maintenance
 Loading...
Loading...