
HF-D series
RF drive amplifiers for Ion Traps
HFD_Drives_Manual_2_1.doc
28 - April - 2013
User Manual
Rev. 2.1
Models HF-D 200, HF-D 425, HF-D 600
Main Features:
● RF drive amplifier for ion traps
● up to 600Vppinto 100pF load
● f = 360kHz to 1.5MHz, model dependent
● non resonant broadband design
● precision voltage stabilisation (device option)
www.stahl-electronics.com

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Safety Hints ………………………………….…………………………………… 3
2. General Information and Overview………………….………………………….. 4
2.1 Purpose and Description of the Device…………………………….. 4
2.2 Functional Principle and Block Diagram…………………………. 4
3. Installation ……………………………………………………………………..… 5
3.1. Mechanical and Electrical Installation……………………………… 5
4. Operation and Control Elements ……………………………………………….. 6
4.1 Elements on the Front Plate………………………………………… 6
4.2 Elements on Rear Side……………………………………………… 8
4.3 Output Characteristics……………………………………………… 9
4.3.1 Stability and Fast Turn-On/Off Feature……………… 9
4.3.2 Output Harmonics…………………………………… 10
4.3.3 Dipole Excitation…………………………………….. 10
4.4 Precision Output Amplitude Regulation …………………………… 11
5. Maintenance………………………………………….…………………………. 12
6. Specifications……………………………………………………………………. 13
Declaration of Conformity ………………………………………………………… 15

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
3
1. Safety Hints
Read all installation, operation, and safety
instructions
Prior to operation, thoroughly review all safety,
installation, and operating instructions accompanying
this equipment.
Rear side switch turns device completely
off
If the device is not in use for a longer time, it is
recommended to turn the mains switch at rear side off.
This equipment must be connected to an
earth safety ground
This product is grounded through the grounding
conductor of the power cord. To avoid electrical
hazard, the grounding conductor must be connected to
protective earth ground.
Do not modify the unit Do not make electrical or mechanical modifications to
this unit.
Change cabling only when device is off Changing the cabling, when voltages are present at the
outputs can lead to formation of harmful sparks.
Do not operate in wet/damp conditions To avoid electric shock hazard, do not operate this
product in wet or damp conditions. Protect the device
from humidity and direct water contact.
Beware of external magnetic fields External magnetic fields can impair, damage or even
destroy this device. A maximum external field strength
of no more than B = 5mT is admissible. Having placed
the device at any time into an external magnetic of
bigger B = 5mT (regardless if power was turned on or
off) can lead to severe overheating of the device and
severely increased hazard of fire.
Service is to be performed by qualified
service persons only
All servicing on this equipment must be carried out by
factory-qualified service personnel only.
Do not block chassis ventilation openings Slots and openings in the chassis are provided for
ventilation purposes to prevent overheating of the
equipment and must not be restricted.
All case vents should continuously be cleared (fan
inlets at rear side, air outlets on top side), in order to
prevent overheating. If mounted in a rack, allow 4cm
clearance at the top cover with respect to the next
device above.
Operate carefully with respect to risk of
electrical shock
This device can produce high voltages at its output
lines, which are harmful in case of direct touch with the
human body. Care must be taken to avoid unintentional
touching of any output line or connection to any device
which might be endangered by high voltages.
Routinely cleaning from dust After long operation, or operation in a dusty
environment it is strongly recommended to have the
internal parts of the device cleaned by the
manufacturer, or an appropriately qualified workshop
in order to reduce the hazard of overheating.
No outdoor operation Outdoor operation of the device is not admissible.
HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
4
2. General Information and Overview
2.1 Purpose and Description of the Device
Purpose of the RF drives HF-D 200, HF-D 425 and HF-D 600 is the supply of AC voltages to Paul Ion
Traps and other Quadrupole-type electrode setups for ion storage and manipulation. Unlike standard RF
(radio- frequency) power amplifiers, the device is capable to handle capacitive loads, which are related to
vacuum setups for ion trapping and storage. The devices feature a fast-turn-on/off capability to capture
ions in flight. Other common RF drives usually require a certain amount of time to build up the nominal
output voltage since they are based on a resonant voltage transformation. In contrast the RF drive HF-D
series consists of broadband devices which allow for instant turn-on and fast turn-off of the AC output
voltage. For example, the HF-D 200A is designed to deliver up to 200VppAC voltage of 600kHz to
1.5MHz frequency into a 100pF load on each output, the HF-D 600 is designed to deliver up to 600V
pp
AC voltage of 300kHz to 600kHz frequency into a 100pF load on each output. The devices are housed in a
standard 19-inch rack-mount case.
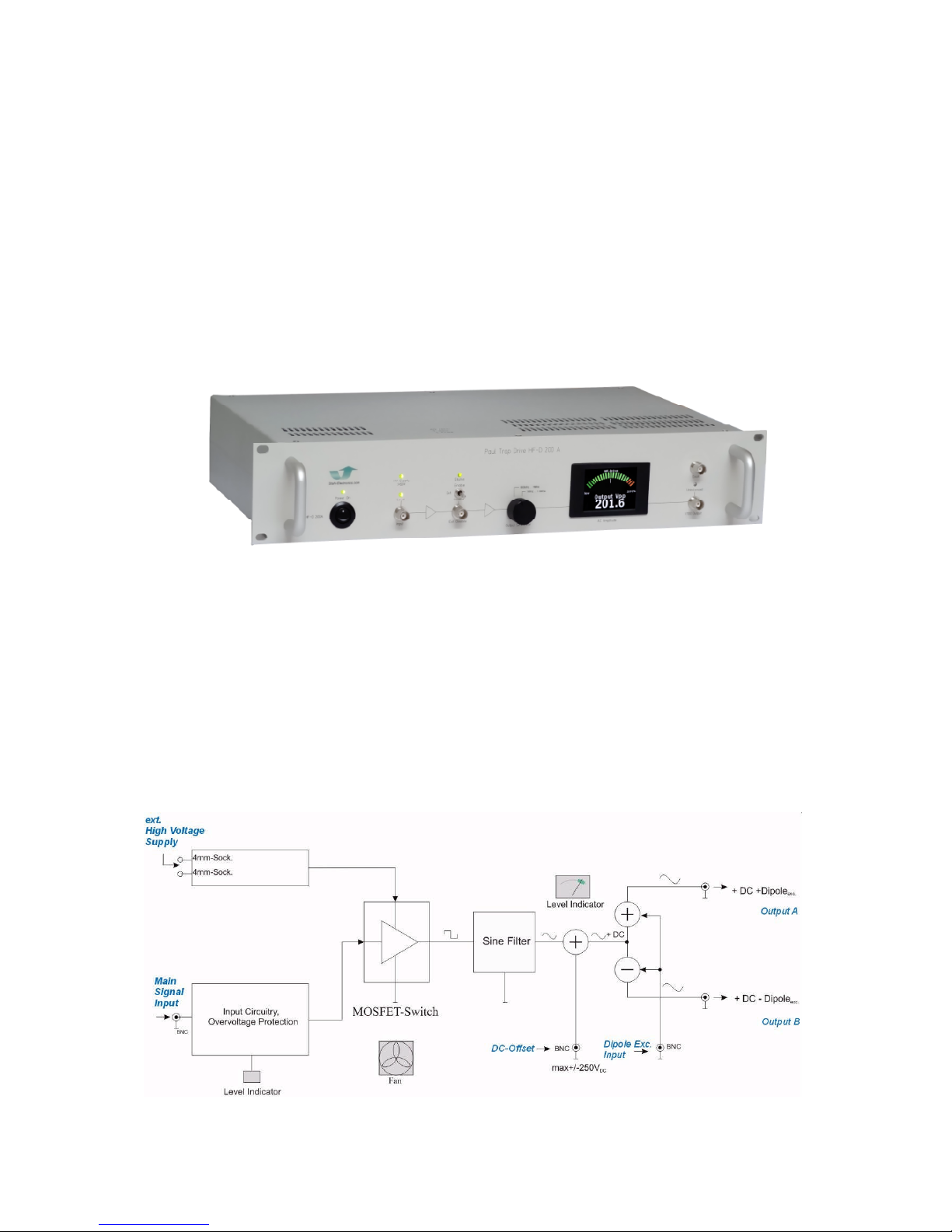
Fig. 2.1: RF drive HF-D 200A, trapping field generator in 19”-case.
2.2 Functional Principle and Block Diagram
The following picture displays a block diagram of the internal structure, illustrating the functional
principle. The voltage at the main signal input controls a fast electronic switch, which switches between
the high and low level of the external supply voltage, creating a rectangular shaped high voltage signal.
The rate at which this switching happens is defined by the frequency at the signal input (for instance
600kHz). A subsequent sine wave filter removes the higher harmonics, thus creating a sine-shaped high
voltage waveform. The DC level of the externally supplied DC voltage at rear input defines the devices
output AC level, since both voltages are in linear relation. This also means that output regulation of the
device AC level is done by choosing the appropriate input high voltage DC supply level.
Fig. 2.2: Block diagram of internal circuitry

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
5
As shown in the block diagram, an additional DC offset may be added to the output sine wave. This
voltage is applied at the rear side and adds linearly to the output sine, therefore shifting its DC level.
Furthermore an excitation signal may be applied, which also adds to the trapping field. This add-on signal
is split in to an in-phase and 180°-shifted part. Both parts are added to the trapping field, and the
sum/difference is subsequently available on the two BNC output plugs (denominated as outputs A and B)
on the rear side. This feature is specially suited for creating an AC dipolar field in the order of a few
Millivolts to a few Volts inside an attached ion trap. Note, that the dipolar excitation signal, being applied
on the front side of the device is attenuated or amplified to a certain degree. Figure 4.8 shows the
frequency response of this dipolar signal in terms of the voltage difference at the outputs A-B versus
frequency, at a given input excitation amplitude.
3. Installation
3.1 Mechanical and Electrical Installation
Positioning: Provide sufficient air cooling of the device and locate in normal horizontal position to allow
for defined air convection. Rack mounting into a standard 19” rack is as well possible as resting the device
on a table. If mounted in a rack, allow 4cm clearance at the top cover with respect to the next device
above. All case vents must permanently be cleared (inlet at rear side and air outlet at top side), in order to
prevent overheating. Please note that the device may experience serious damage in case
sufficient air ventilation is not given.
Fig.3.1 Air vents (marked blue) must all be kept clear to ensure sufficient ventilation. Under no circumstances the
vent slits must be blocked, since they are vital for device operation in order to prevent overheating.
Beware of external magnetic fields:
Strong external magnetic fields can impair, damage or even destroy this device (e.g. proximity to a
superconducting magnet). A maximum external field strength of no more than B = 5mT is admissible. Not
observing this important condition can lead to severe overheating of the device and increases the hazard of
fire.
Connecting to mains power:
Connect the device to the mains power supply by using an appropriate power cord, being properly wired
and providing a grounded outlet. The power cord must be suited with respect to possible load currents and
should be rated to 2A current.
Cabling of voltage outputs:
Always provide appropriate and safe cabling when connecting the device to other devices or
vacuum/experimental setups. Cabling is preferred using a high voltage low-capacitance cable with proper
shielding. A suitable choice of cable type is e.g. a RG62 type, which has a small parasitic capacitance of
approx. 48pF/m, half the value of standard RG58 BNC cable. The smaller parasitic capacitance allows a
higher degree of freedom since cable capacitance significantly contributes to the overall (terminal)
capacitance, which must not exceed 100pF (each output) to meet the device specifications.

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
6
4. Operation and Control elements
4.1 Elements on the front plate
Mains Supply Input Enable Range Selector Output Voltmeter Dipole Excitation
Input
Switch Fan/Temperature Warning
Figure 4.1: front plate and operating elements
The front plate contains the main control elements of the device:
Mains Supply Switch
The device is powered up after activating the rear-side mains supply switch and switching the power
button on the front plate into the “on” position. A Power-on-LED (green) indicates proper operation of
the internal circuitry. A warning beeper will temporarily sound, which is used for ventilation fan-speed
monitoring. If the warning beeper permanently sounds, the device must not be put into operation. In
general, if the device is not in use for a longer time, it is recommended deactivate the rear side mains
switch to cut the device completely off from mains supply. This is mainly for safety reasons.
Input
The input signal (sine wave) is fed into the BNC input at the front side (75 input impedance nominally).
An AC voltage level of nominally 5Vpp should be applied. The LED indicator above the BNC socket
lightens up green, if a sufficiently large signal level is applied, red otherwise (i.e. input AC voltage too
small). The waveform of the applied signal should be “sine” to allow for proper operation and meeting of
the specifications in chapter 6. This input may be fed by a common function generator or radio frequency
(RF) signal source. Please make sure that the device is not permanently operated with input voltage being
too low (LED indicator red). Note that the output voltage is not supposed to be controlled by the
amplitude value of this input, but by variation of the DC supply on rear side (see section 4.2). The latter
supply voltage is in good approximation proportional to the output AC voltage.
Once the device is installed and cabled in a given setup, it is recommended to choose the input voltage
level to be approx. 15% higher than the transition threshold (red-to-green) of the level indictor LED. A
second LED indicator above the one mentioned before lightens up green if the external DC supply voltage
exceeds approximately 150V to 180V, showing the presence of DC voltage at the rear side.
Enable
The “Enable” section of the device allows to turn the output power completely
on or off. This section consists of a manual switch, a disable BNC input and
status indicator. The output power of the device is either enabled or disabled
(LED indicator shows green or red light). The user may select this state by
choosing the desired switch position manually (putting it up or down), or by
applying an external signal of logic level to the corresponding BNC input.
When the manual switch lever is centered, a logic “LOW” level (0 Volts)
disables, a logic level “HIGH” (+5 Volts) enables the RF outputs. The
reaction time upon a change of this level is about 1 to 2 signal periods (see
also section 4.3.1)

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
7
Range Selector
For proper operation of the internal sine wave filter, the
frequency range selector knob must be placed in the
appropriate position, depending on the input frequency
chosen. Avoid running the device permanently in the wrong
position, since this may load the internal device circuitry after
some time due to excessive heat production.
Fan/Temperature Warning
In case there is a problem with the ventilation fans or signs of overheating inside the device, the latter is
indicated by red warning LEDs. In case they lighten up, the output is intentionally disabled for safety
reasons and a warning beeper will sound.
Output Voltmeter
The Output Voltmeter shows the output AC voltage in terms
of Volts-peak-peak. It averages over the two outputs A and B
(rear side of device). Note, that one always has to ensure by
choosing an appropriate DC supply level at the rear side, that
the output level does not constantly exceed its nominal value
of 200Vpp, 425Vpp or 600Vpp respectively. Note that
otherwise the device may overheat and get damaged.
Therefore always carefully watch this indicator when
changing the external DC supply voltage or changing other
conditions of devices attached (e.g. cabling).
Excitation Input and Test Output
At the BNC test output socket (placed on rear or front side), one can check the general functionality of
the device. 1/100 of the output amplitude, being averaged over the two outputs A and B is provided here.
This applies for AC components as well as the (optional) DC-Offset.
The excitation input allows for adding a voltage difference between the two outputs A and B. This
voltage is linearly superposed to the RF field. A voltage up to 20Vpp may be applied here. Please observe
the frequency response (fig. 4.7) i.e. the transfer function has a certain frequency-dependency.
The “unbalanced” LED indicator above the excitation socket lightens up if a large AC voltage difference
(greater roughly 15Vpp) between the outputs A and B is detected. It therefore lightens up in case of an
intentionally applied excitation signal, or if there is a malfunction, e.g. an unbalanced capacitive or
resistive load on the outputs A or B. This indicator may serve as coarse, but nevertheless important, check
for correctly attached cables and circuitry on the outputs. However, a thorough cabling check is
recommended before applying any signals to the outputs (see below, section 4.2).

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
8
4.2 Elements on rear side
Output A Output B DC Supply positive supply switch
Fuse DC Supply negative
Test Output Offset Input Case GND
Figure 4.2: rear plate elements. Not that the device may have an additional BNC output for installing a regulation
loop in order to keep the AC output voltage level constant (see text below).
The rear side contains the following elements:
Output A and B
Both outputs (BNC sockets) feature the same phase and amplitude of the created RF driving field, i.e.
voltages from 0 to 600Vpp at frequencies between 360kHz and 630kHz in case of the device HF-D 600.
Their only difference is an optional potential difference, regarded as dipolar excitation (see section 4.1 and
the overview in section 2.2). In case this feature is not needed, one may directly join outputs A and B
together at the rear side of the device and guide this trapping voltage with a single cable to the
experimental setup (this is not the case if one output is intentionally disabled). Otherwise two separate
cables are required, being connected to corresponding split trap or quadrupole electrodes.
Attention:
Before operating the device, a thorough check of the cables connected to the outputs A and B is
mandatory due to the high voltages and high associated electric power.
Therefore verify with a multimeter before connecting to the device, whether
● the attached cables on outputs A and B feature a high resistance to GND, i.e. >10MOhm including
the completely connected vacuum setup (ion trap, quadrupole setup),
● the attached cables have a capacitance to GND smaller 100pF each. In case both outputs are
connected together, the maximum capacitive load is 200pF1).
● the attached capacitance to GND of cables including connected vacuum setup should be equal, i.e. the
terminal capacitance should match by better than 5%
Device operation assumes that these boundary conditions are met. Otherwise, in case of a significant
resistive load or capacitive load greater 100pF per output, the device may not reach the desired output
voltages and furthermore may be damaged by thermal overload during permanent operation. Connect the
cables to the device and turn it on only if the above points have been checked and are fulfilled.
Remark1): Smaller capacitances are preferable in terms of long device life time and smaller power
consumption. The recommended load on each output is no more than 70pF.
Offset Input
The Offset Input allows for adding an additional (externally provided) offset to both output lines. This
offset is linearly added (superposed) and may reside in the range between -300V and +300V. Note, that

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
9
this input is not intended for fast changes (pulsing) of voltages. In case left open, an offset of zero volts is
added, i.e. the sine waveform of outputs A and B is centered around zero volts. Input impedance at this
input is nominally 1M + 25pF vs. GND. The applied voltage is internally diminished by roughly a factor
of 0.85 before being fed to the outputs.
Negative and positive external supply and GND
Connect these terminals to an external high voltage supply, being capable of delivering a stabilized
voltage and sustain a certain DC current, e.g. a stahl-electronics HVD-series supply or other suited. This
externally supplied voltage defines the AC output voltage of the device, and is therefore of decisive
importance. In case the external DC voltage supply has a GND line, connect the latter to the GND
terminal for minimizing of unwanted noise pickup. All three terminals are standard laboratory (4mm)
sockets. The required voltages and currents to achieve a certain AC output voltage depend on the
capacitive load on the outputs, the frequency and voltage. Figures 6.1 and following show typical
characteristics for HF-D series devices at capacitive loads. Note that the depicted data are obtained using a
symmetrically split supply voltage, e.g. 400VDCbeing split into + and - 200VDCat the red and black socket
on the rear side. Using a non-symmetric supply, e.g. positive or negative terminal grounded, is also
possible, but increases the current consumption typically by 15 to 20%.
Important:
When commissioning the device, it is recommended to start with a low DC supply voltage (e.g. 30V) on
the rear side terminals after completion of the cabling (see above) and gradually increase it. During this
time one should monitor, if the output voltage is built up as expected or if any problems occur. Essentially
the voltage/current characteristics like shown in figure 6.1 apply, and they scale linearly with supply
voltage. Therefor using a small supply voltage at the beginning will prevent excessive heat dissipation in
case of wrong cabling or other problems.
One should not take the risk to turn the device on to full power (maximum voltage) after the trap/electrode
setup had been changed substantially. Always perform a thorough cabling check like mentioned above
before trying to apply large voltages.
4.3 Output Characteristics
4.3.1 Stability and Fast Turn-On/Off Feature
The outputs A an B provide a sinusoidal waveform with identical amplitude and phase. Phase jitter and
amplitude jitter are in the order of < +/-1°, and about 2x 10-3relative to the output amplitude, respectively.
Note that instability of the externally supplied DC high voltage will add fluctuations to this intrinsic
amplitude instability.
Figure 4.3 Theoretical waveform: the non-resonant design allows for immediate response (turn-on / turn-off)
of the high frequency output

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
10
Figure 4.4 Experimentally measured waveforms during turn-on / turn-of events; f = 350kHz, U
out
= 380Vpp.
The HF-D amplifiers feature immediate turn-on characteristics as shown above, due to their inherent
broadband design. The remaining waveform tails during turn-on/off events typically last for about one
signal period.
The transient waveforms shown in the figure above were obtained using the “external enable” input on the
front plate.
Please note that the output amplitude at high amplitudes >150Vpp may show significant drift in time due
to internal heating effects with a typical time constant of 30 minutes. This drift (decreasing amplitude)
may be in the order of several percent after starting the device operation, unless an external correction
loop is implemented (see below).
4.3.2 Output Harmonics
The output waveform is essentially a sine wave
with some remains of higher harmonics. The
subsequent graphs depict the signal’s harmonics
content in dB with respect to the main
(fundamental) frequency, which are a left-over
from the sine-forming process.
Figure 4.5 Strength of residual signal harmonics in dB
with respect to fundamental frequency, HF-D 200A
device.
Figure 4.6
Strength of residual signal harmonics in dB with respect
to fundamental frequency, HF-D 600 device.

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
11
Figure 4.7
Strength of residual signal harmonics in dB with
respect to fundamental frequency, HF-D 425 device.
4.3.3 Dipole Excitation
The Dipole excitation input on the front plate can be used to create a voltage difference between the two
outputs A and B, see also fig. 2.2. This voltage, being in the order of a few volts, may be used to excite
motion or energy of trapped ions. Observe, that the internal circuitry features a certain transfer function,
which is shown in the subsequent figure. For instance applying a voltage of 10Vpp at 300kHz will create a
voltage difference of 15Vpp at the outputs. Maximum output voltage difference is approximately 20Vpp.
Beyond that value the circuitry will get into saturation.
figure 4.8
Dipole excitation transfer function, i.e. ratio of
output voltage-difference to excitation input
voltage, a sine wave is assumed.
4.4 Precision Output Amplitude Regulation
In case the corresponding option is installed, the device features a BNC
output at the rear side (marked in left picture) , at which a DC-voltage,
being proportional to the AC output amplitude is presented. The
corresponding scaling factor is approximately 1VDCper 200VACon the
AC outputs. By using this DC output voltage, an external correction loop
may adapt and continuously modify the supply high voltage to keep the
magnitude of AC output signal constant. This eliminates temporal and
temperature-related drifts of the AC amplitudes. Typically a stability on a
0.25%-level is reached that way. E.g. dedicated stahl-electronics HVD-series
supplies support this functionality. Please refer to their data sheets or manuals
for more details.
0,4
0,6
0,8
1,0
1,2
1,4
1,6
1,8
1 10 100 1000 10000
Frequency (k Hz)
Dipole transfer function

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
12
5. Maintenance
The HF-D 200A device is designed for long-term reliable operation. Under normal operating conditions, it
should not require electrical maintenance, except routine cleaning of dust. Exchange of ventilation fan is
strongly recommended every 50’000 operation hours (see below). If any question should arise, please
contact the manufacturer.
Routine cleaning
All ventilation openings – top, sides, and rear panel – should be checked periodically and must be kept
free of dust and other obstructions. A vacuum cleaner may be used to clean these vents when the unit is
powered off. The front panel may be cleaned periodically with a clean cloth and mild alcohol solution.
Fan life time and fire hazard
The air ventilation fans are parts which show unavoidable deterioration in time. Exchange is
recommended after 50’000 hours of operation. Please contact manufacturer for replacement. Complete
failure can lead to overheating of the device, causing malfunctions and risk of fire. Temperature fuses and
other protection measures provide a certain degree of safety against fire hazard, however a proper cooling
of the device is essential.
Please note that excessive accumulation of dust inside the device also can lead to overheating. This
increases the risk of fire. Routinely cleaning the device from dust minimizes this risk. It is therefore
recommended to routinely perform cleaning from dust in latest 2-year intervals, by an accordingly
qualified electronics workshop.
Decommissioning
Decommissioning of the device is recommended after 130’000 hours of operation. Please contact
manufacturer for appropriate waste disposal and observe applicable legal regulations.

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
13
6. Specifications
Input Specification
Input voltage level
nom. 5Vpp (Volts-peak-peak),
4.5Vpp to 8Vpp applicable without damage,
nom. 75 input, ac coupled
recommended signal level: 15% higher then LED indicator green-red
transition
Output Specifications
Output voltage
HF-D 200A
HF-D 425
HF-D 600
0 to 200Vpp (Volts-peak-peak) = 70.7V
rms
0 to 425Vpp (Volts-peak-peak) = 150.3V
rms
0 to 600Vpp (Volts-peak-peak) = 212.1V
rms
Frequency range
HF-D 200A
HF-D 425
HF-D 600
600kHz to 1.5MHz
450kHz to 900kHz
360kHz to 630kHz
Output connector type
(unless customized)
BNC
DC Offset max. +/-300V DC
(applied to rear side BNC offset input)
Capacitive load capability max. 100pF, ≤ 75pF recommended
typical maximum
35ns
1/100 Test Output
Delay with respect to
outputs A and B
Scaling Error
3 % 8%
Dipole Excitation
Input (front plate)
Output (rear side)
0 to 10Vpp, 50
see figure 4.6 (sine wave assumed )
< 12Vpp
20Vpp @ ≤100pF load
Front Plate Digital Voltmeter Reading (Volts-peak-peak)
Accuracy: typical maximum
Scale error 0.5% 2%
Offset error 2V 3V
Environmental Conditions
Magnetic Field max. 5mT admissible
Storage Temperature
-55 °C to +85 °C
Operating Humidity &
Temperature
noncondensing relative humidity up to 95%
temperatures between +10°C to +30°C.
Power Supply
AC Supply Rating
AC input voltage 230VACat 50Hz or 60Hz.
The power entry module is EMI/RFI-filtered.
Fuse: medium fast blow 2x 0.8A
typ. 12W consumption
External DC Supply typ. 200V to 600V DC, see figure 6.1, 6.2, 6.3

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
14
specifications continued
Case dimensions
19.00” wide x 10” deep. Front-panel mounting holes are configured for
M6 rack configurations
Weight approximately 5.6 kg
.
Figure 6.1 a and b: required externally supplied DC voltage and current consumption to obtain 200Vpp output
amplitude with 100pF load capacitance each output, device HF-D 200A. Both graphs are split in a lower and upper
frequencyband, according to the position of the range selector knob.
Figure 6.2 a and b: required externally supplied DC voltage and current consumption to obtain 600Vpp output
amplitude with 100pF load capacitance each output, device HF-D 600. Both graphs are split in a lower and upper
frequencyband, according to the position of the range selector knob.
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
400 600 800 1000
Fr equency (kHz)
Supply voltage (V)
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
400 600 800 1000
Fre que ncy (kHz)
Supply current (mA )
Figure 6.3 a and b: required externally supplied DC voltage and current consumption to obtain 425Vpp output
amplitude with 70pF load capacitance each output, device HF-D 425. Both graphs are split in a lower and upper
frequencyband, according to the position of the range selector knob.

HF-D User Manual, Rev 2.1
www.stahl-electronics.com phone: +49 6242-504882, fax: +49 6242 504884
15
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer's Name: Dr. Stefan Stahl
- Electronics for Science and Research -
Manufacturer's Address: Kellerweg 23
67582 Mettenheim
Germany.
Declares, that the product
Product Name: RF Drive for Paul Traps HF-D Series
Model Numbers: HF-D 200A, HF-D 425, HF-D 600
Product Options: This declaration covers all options of the above product(s)
Conforms with the following European Directives:
The product herewith complies with the requirements of the:
1. Low Voltage Directive 73/73EEC;
2. EMC Directive 89/336/EEC (including 93/68/EEC) and carries the CE Marking
accordingly
Date Of Issue __________________
5. January 2013 General Director
 Loading...
Loading...