
TSH340
320MHz Single Supply Video Buffer with Low In/Out Rail
■ Bandwidth: 320MHz
■ Single supply operation down to 3V
■ Low input & output rail
■ Very low harmonic distortion
■ Slew rate: 780V/µs
■ Voltage input noise: 7nV/√Hz
■ Specified for 150Ω and 100Ω loads
■ Internal gain of 6dB
■ Compatible with the PCB layout of a single
op-amp
■ Tested on 5V power supply
■ Data min. and max. are tested during
production
Description
The TSH340 is a single supply video buffer
featuring an internal gain of 6dB and a large
bandwidth of 320MHz for only 9.8mA of quiescent
current.
An advantage of this circuit is its input and output
negative rail feature, which is very close to GND in
single supply. This rail is teste d and guaranteed
during production at 60mV maximum from GND
on a 150Ω load. This al lows a good o utput swing
which fits perfectly when driving a v ideo sign al on
a 75Ω video line. Chapter 5 of this datasheet
gives technical support when using the TSH340
as a driver for video DAC output on a video line. In
particular, this chapter focuses on applying a
video signal DC shift to avoid any clamping of the
synchronization tip.
Pin Connections (top view)
OUT
OUT
NC
NC
NC
NC
IN
IN
GND
GND
GND
GND
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
1
1
2
2
3
3
SOT23-5
SOT23-5
SO8
SO8
5
5
4
4
+VCC
+VCC
NCIN
NCIN
8
8
7
7
6NCOUT
6NCOUT
5
5
NC
NC
+Vcc
+Vcc
Applications
■ High-end video systems
■ High Definition TV (HDTV)
■ Broadcast and graphic video
■ Multimedia products
The TSH340 is available in tiny SOT23-5 and
SO8 plastic packages.
Order Codes
Part Number Temperature Range Package Packaging Marking
TSH340ILT
TSH340ID
TSH340IDT Tape & Reel TSH340I
April 2005 Revision 2 1/13
-40°C to +85°C
SOT23-5 Tape & Reel K306
SO-8
Tube TSH340I

TSH340 Absolute Maximum Ratings
1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 1. Key parameters and their absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
T
T
Supply voltage
CC
V
Input Voltage Range
in
Operating Free Air Temperature Range
oper
Storage Temperature
std
T
Maximum Junction Temperature
j
Thermal Resistance Junction to Case
R
thjc
SOT23-5
SO8
Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient Area
R
thja
SOT23-5
SO8
Maximum Power Dissipation (@Ta=25°C) for Tj=150°C
P
max.
SOT23-5
SO8
CDM: Charged Device Model
ESD
HBM: Human Body Model
MM: Machine Model
1) All voltage values, except differential voltage, are with respect to network terminal.
2) The magnitude of input and output voltage must never exceed VCC +0.3V.
1
2
6V
-0.2 to +3 V
-40 to +85 °C
-65 to +150 ° C
150 °C
80
°C/W
75
250
°C/W
175
500
mW
715
2
1.5
200
kV
kV
V
Table 2. Operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
Power Supply Voltage
CC
Vicm Common Mode Input Voltage -0.4 to 3 V
1) Tested in full production at 0V/5V single power supply
3 to 5.5
1
V
2/13
Electrical Characteristics TSH340
2 Electrical Characteristics
Table 3. V
= +5V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
DC Performance
out
1
)
V
OS
I
ib
PSR
ICC
Output Offset Voltage
Input Bias Current T
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
20 log (∆V
/∆V
cc
Total Supply Current no Load, Vin=100mV
G DC Voltage Gain R
Input Resistance T
Rin
Input Capacitance T
Cin
no Load, T
-40°C < T
, V
amb
-40°C < T
=200mVp-p, F=1MHz
∆V
cc
icm
amb
< +85°C
amb
=0.6V
< +85°C
amb
-30 -5 +30
-6.8
616
7.2
-90 dB
9.8 12.8 mA
L = 150Ω 1.95 2 2.05 V/V
amb
amb
8MΩ
3.2 pF
Dynamic Performance and Output Characteristics
Bw
FPBW
SR
V
OH
V
OL
I
OUT
-3dB Bandwidth Small Signal V
=0.6V, RL = 150Ω
V
icm
Gain Flatness @ 0.1dB Small Signal V
=0.6V, RL = 150Ω
V
icm
Full Power Bandwidth V
icm
R
= 150Ω
L
=0.6V, V
Slew Rate Vicm=0.6V, V
= 150Ω
R
L
High Level Output Voltage RL = 150Ω
Low Level Output Voltage RL = 150Ω
Output Short Circuit Current (Isource) T
amb
-40°C < T
Output Current Vout=2Vp, T
OUT
OUT
< +85°C
amb
amb
out=20mVp
out=20mVp
= 2Vp-p,
= 2Vp-p,
190 320
MHz
63
130 200 MHz
780 V/µs
3.7 3.9 V
40 60 mV
100
90
45 87 mA
Noise and Distortion
eN Equivalent Input Noise Voltage F = 100kHz 7 nV/√Hz
iN Equivalent Input Noise Current F = 100kHz 1.5 pA/√Hz
HD2
HD3
1) Output Offset Voltage is determined from the following expression: V
2nd Harmonic Distortion V
3rd Harmonic Distortion V
= 2Vp-p, RL = 150Ω
OUT
F= 10MHz,
= 1Vp-p, RL = 150Ω
OUT
F= 10MHz,
=G.VIN+V
OUT
-85 dBc
-75 dBc
OS
mV
µA
mA
3/13
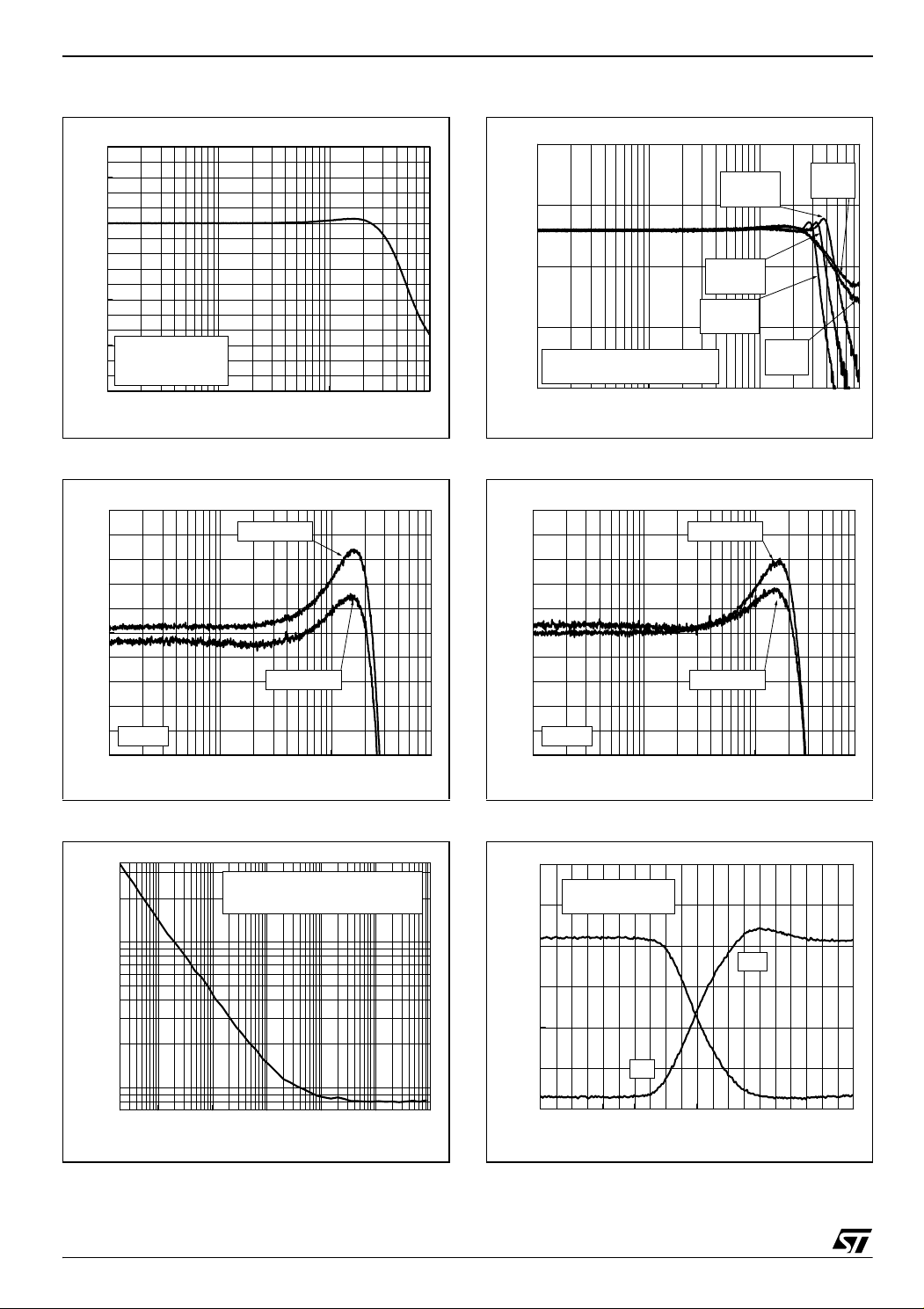
TSH340 Electrical Characteristics
M
Figure 1. Frequency response
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
-2
Gain (d B)
-4
-6
-8
-10
Vcc=5V
-12
Load=100 or 150
-14
SO8 and SOT23-5
-16
1M 10M 100M
Ω
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 2. Gain flatness - SOT23-5
7,0
6,8
6,6
6,4
6,2
6,0
5,8
Gain (dB)
5,6
5,4
5,2
Vcc=5V
5,0
1M 10M 100M
Load=150Ω
Load=100Ω
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 4. Frequency response on capa-load
20
C=10pF
10
0
Riso=22
C=22pF
Riso=22
Ω
C=1pF
Riso=0
Ω
C=47pF
-10
Frequency Response (dB)
Vcc=5V
Load=Riso + C//1k
-20
1M 10M 100M
Ω (to ground)
Riso=15Ω
C=0
Riso=0
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 5. Gain flatness - SO8
7,0
6,8
6,6
6,4
6,2
6,0
5,8
Gain (dB)
5,6
5,4
5,2
Vcc=5V
5,0
1M 10M 100M
Load=150Ω
Load=100Ω
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 3. T otal input noise vs. frequency
non-inverting input in short-circuit
Vcc=5V
100
Input Noise (nV/VHz)
10
100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10
Frequency (Hz)
4/13
Figure 6. Positive and negative slew rate
3,0
Vcc=5V
2,5
Load=100Ω or 150Ω
2,0
SR+
1,5
1,0
Output Response (V)
0,5
0,0
-5ns -4ns -3ns -2ns -1ns 0s 1ns 2ns 3ns 4ns 5ns
SR-
Time (ns)

Electrical Characteristics TSH340
Figure 7. Distortion on 100Ω load
-30
-35
-40
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
HD2 & HD3 (dBc)
-85
-90
-95
-100
01234
HD3
(30MHz)
HD2
(30MHz)
HD3
(10MHz)
HD2
(10MHz)
Output Amplitude (Vp-p)
Vcc=5V
Load=100
Figure 8. Output lower rail vs. frequency
500
Vcc=5V
Load=100
400
300
Ω or 150Ω
Figure 10. Distortion on 150Ω load
HD2
(30MHz)
HD2
(10MHz)
HD3
(30MHz)
Vcc=5V
Load=150
Ω
-30
-35
-40
-45
-50
-55
-60
-65
-70
-75
-80
HD2 & HD3 (dBc)
-85
-90
Ω
-95
-100
01234
HD3
(10MHz)
Output Amplitude (Vp-p)
Figure 11. Output voltage swing vs. Vcc
5
4
3
200
Vol (mV)
100
0
10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 9. Output voltage swing vs. frequency
5
4
3
2
Vout max. (Vp-p)
1
Vcc=5V
Load=100
0
1M 10M
Ω or Load=150Ω
Frequency (Hz)
2
Vout max (Vp-p)
1
F=30MHz
Load=100
0
3,00 3,25 3,50 3,75 4,00 4,25 4,50 4,75 5,00
Ω or 150Ω
Vcc (V)
Figure 12. Quiescent current vs. vcc
20
no load
15
10
Icc (mA)
5
0
1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5 5,0
Vcc (V)
5/13

TSH340 Electrical Characteristics
0
Figure 13. Isource
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
+3V
-50
-60
-70
Isource (mA)
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
0,0 0,5 1,0 1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5 5,
+5V
VOH
without loa d
Isource
V
0V
V (V)
Figure 14. Bandwidth vs. temperature
500
450
400
350
300
Bw (MHz)
250
200
150
Vcc=5V
Load=150
100
-40-200 20406080
Ω
Temperature (°C)
Figure 16. Reverse isolation vs. frequency
0
-20
-40
-60
Gain (dB)
-80
Small Signal
Vcc=5V
Ω
Load=100
-100
1M 10M 100M 1G
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 17. Voltage gain vs. temperature
2,05
2,04
2,03
2,02
2,01
2,00
1,99
Gain (dB)
1,98
1,97
Output: short-c ircuit
1,96
Vcc=5V
1,95
-40-200 20406080
Temperature (°C)
Figure 15. Output offset vs. temperature
0
-1
-2
Vos (mV)
-3
-4
Vcc=5V
Ω
Load=150
-5
-40-200 20406080
Temperature (°C)
6/13
Figure 18. Ibias vs. temperature
7,0
6,5
6,0
5,5
5,0
(µA)
BIAS
I
4,5
4,0
3,5
Vcc=5V
Load=150
3,0
-40-200 20406080
Ω
Temperature (°C)

Electrical Characteristics TSH340
V
(V)
V
(V)
Figure 19. Supply current vs. temperature
12
11
10
(mA)
CC
I
9
8
Vcc=5V
no Load
7
-40-200 20406080
Temperature (°C)
Figure 20. Output lower rail vs. temperature
0,10
0,08
Vcc=5V
Load=150
Ω
0,06
OL
0,04
0,02
0,00
-40-200 20406080
Temperature (°C)
Figure 21. Output higher rail vs. temperature
4,50
4,25
4,00
OH
3,75
Vcc=5V
Load=150
3,50
-40-200 20406080
Ω
Temperature (°C)
7/13

TSH340 Evaluation Boards
3 Evaluation Boards
An evaluation board kit optimized for high-speed operational amplifiers is available (order code:
KITHSEVAL/STDL). T he kit includes t he following evaluation boards, as well as a CD-ROM containing
datasheets, articles, application notes and a user manual:
z SOT23_SINGLE_HF BOARD: B oard for the eval uation of a singl e high-speed op-amp in SOT23-5
package.
z SO8_SINGLE_HF: Board for the evaluation of a single high-speed op-amp in SO8 package.
z SO8_DUAL_HF: Board for the evaluation of a dual high-speed op-amp in SO8 package.
z SO8_S_MULTI: Board for the evaluation of a single high-speed op-amp in SO8 package in inverting
and non-inverting configuration, dual and signle supply.
z SO14_TRIPLE: Board for the eval uation of a tri ple h igh-spe ed op -amp in SO 14 pack age with vide o
application considerations.
Board material:
z 2 layers
z FR4 (εr=4.6)
z epoxy 1.6mm
z copper thickness: 35µm
Figure 22: Evaluation kit for high speed op-amps
8/13

Power Supply Considerations TSH340
4 Power Supply Considerations
Correct power supply bypassin g is very impor tant for optimi zing performa nce in high -frequency r anges.
Bypass capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the IC pins to improve high-frequency
bypassing. A capacitor greater than 10µF is necessary to minimize the distortion. For better quality
bypassing, a capacit or of 10nF is added using the sam e implementation cond itions. Bypass capacito rs
must be incorporated for both the negative and the positive supply. On the SO8_SINGLE_HF board,
these capacitors are C8 and C6.
Figure 23: Circuit for power supply bypassing
+VCC
+VCC
TSH340
TSH340
10nF
10nF
CC
CC
+V
+V
GND
GND
10microF
10microF
+
+
9/13

TSH340 Using the TSH340 to Drive Video Signals
5 Using the TSH340 to Drive Video Signals
Figure 24. Implementation of the video driver on output video DACs
Volt
Volt
Video
Video
Signal
Signal
+5V
+5V
Reconstruction
Reconstruction
Filtering
Video
Video
DAC
DAC
1Vpp
1Vpp1Vpp
Filtering
LPF
LPF
6dB
6dB
VOL(100MHz) = 180mV (Figure 8)
To drive the video signal properly, the output of the driver must be at least equal to 250mV
(assuming V
z 1st solution:
and VOL variations).
OS
Set the video DAC 0-IRE output level to 125mV.
2.250V
2.250V
250mV
250mV
time
time
75Ω
75Ω
2Vpp
2Vpp
Volt
Volt
Volt
75Ω Cable
75Ω Cable
Video
Video
Signal
Signal
1.125V
1.125V
1.125V
1.125V
125mV
125mV
125mV
125mV
time
time
time
time
1Vpp
1Vpp1Vpp
75Ω
75Ω
100 IRE
White Level
White Level
Black Level
Black Level
z 2nd solution:
100 IRE
30 IRE
30 IRE
0 IRE
0 IRE
300mV
300mV
Synchronization Tip
Synchronization Tip
Image Content
Image Content
125mV
125mV
0V
0V
Implementation of a DC component in the input of the driver.
Volt
Video
Video
DAC
DAC
DC component
DC component
33uF
33uF
1Vpp
1Vpp1Vpp
=125mV
=125mV
Reconstruction
Reconstruction
Filtering
Filtering
LPF
LPF
1k
1k
+5V
+5V
6dB
6dB
Volt
Video
Video
Signal
Signal
2.250V
2.250V
time
time
1Vp-p
1Vp-p
250mV
250mV
2Vpp
2Vpp
75Ω
75Ω
Volt
Volt
Volt
75Ω Cable
75Ω Cable
Video
Video
Signal
Signal
1.125V
1.125V
1.125V
1.125V
125mV
125mV
125mV
125mV
time
time
time
time
1Vpp
1Vpp1Vpp
75Ω
75Ω
10/13

Package Mechanical Data TSH340
6 Package Mechanical Data
6.1 SO-8 package
SO-8 MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
A 1.35 1.75 0.053 0.069
A1 0.10 0.25 0.04 0.010
A2 1.10 1.65 0.043 0.065
B 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
D 4.80 5.00 0.189 0.197
E 3.80 4.00 0.150 0.157
e 1.27 0.050
H 5.80 6.20 0.228 0.244
h 0.25 0.50 0.010 0.020
L 0.40 1.27 0.016 0.050
k ˚ (max.)
ddd 0.1 0.04
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
mm. inch
8
0016023/C
11/13

TSH340 Package Mechanical Data
6.2 SOT23-5L (5-pin) package
SOT23-5L MECHANICAL DATA
DIM.
MIN. TYP MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
A 0.90 1.45 35.4 57.1
A1 0.00 0.15 0.0 5.9
A2 0.90 1.30 35.4 51.2
b 0.35 0.50 13.7 19.7
C 0.09 0.20 3.5 7.8
D 2.80 3.00 110.2 118.1
E 2.60 3.00 102.3 118.1
E1 1.50 1.75 59.0 68.8
e.95 37.4
e1 1.9 74.8
L 0.35 0.55 13.7 21.6
mm. mils
0
12/13

TSH340
7 Revision History
Date Revision Description of Changes
01 Jan. 2005 1 First release corresponding to Preliminary Data version of datasheet.
23 Mar. 2005 2 Datasheet of mature, full-specification product.
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patent s or other rights of third part ies which may result from its us e. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and repl aces all information previously supplied. ST Microelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critica l comp onents in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
13/13
 Loading...
Loading...