
TS4621B
High-performance class-G stereo headphone amplifier
with I
2
C volume control
Features
■ Power supply range: 2.3 V to 4.8 V
■ 0.6 mA/channel quiescent current
■ 2.1 mA current consumption with
100 µW/channel (10 dB crest factor)
■ 0.006% typical THD+N at 1 kHz
■ 100 dB typical PSRR at 217 Hz
■ 100 dB of SNR A-weighted at G = 0 dB
■ Zero pop and click
2
■ I
C interface for volume control
■ Digital volume control range from -60 dB to
+4 dB
■ Independent right and left channel shutdown
control
■ Integrated high-efficiency step-down converter
■ Low software standby current: 5 µA max
■ Output-coupling capacitors removed
■ Thermal shutdown
■ Flip-chip package: 1.65 mm x 1.65 mm,
400 µm pitch, 16 bumps
Applications
■ Cellular phones, smart phones
■ Mobile internet devices
■ PMP/MP3 players
Description
The TS4621B is a class-G stereo headphone
driver dedicated to high audio performance, high
power efficiency and space-constrained
applications.
It is based on the core technology of a low power
dissipation amplifier combined with a highefficiency step-down DC/DC converter for
supplying this amplifier.
TS4621BEIJT - flip-chip
Pinout (top view)
SCL
SCL
SDA
PVSS
PVSS
C1
C1
AVDD
AVDD
SDA
C2
C2
AGND
AGND
SW
SW
D
D
C
C
B
B
A
A
INR-
INR-
VOUTR
VOUTR
INR+
INR+
CMS
CMS
HPVDD
INL+
HPVDD
INL+
VOUTL
VOUTL
INL-
INL-
4321
4321
Balls are underneath
When powered by a battery, the internal stepdown DC/DC converter generates the appropriate
voltage to the amplifier depending on the
amplitude of the audio signal to supply the
headsets. It achieves a total 2.1 mA current
consumption at 100 µW output power (10 dB
crest factor).
THD+N is 0.02 % maximum at 1 kHz and PSRR
is 100 dB at 217 Hz, which ensures a high audio
quality of the device in a wide range of
environments.
The traditionally bulky output coupling capacitors
can be removed.
A dedicated common-mode sense pin removes
parasitic ground noise.
The TS4621B is designed to be used with an
output serial resistor. It ensures unconditional
stability over a wide range of capacitive loads.
The TS4621B is packaged in a tiny 16-bump
flip-chip package with a pitch of 400 µm.
September 2011 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 1/48
www.st.com
48

Contents TS4621B
Contents
1 Absolute maximum ratings and operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Typical application schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.1 I2C bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.1.1 I²C bus operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.1.2 Control register CR1 - address 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4.1.3 Control register CR2 - address 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.4 Control register CR3 - address 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.5 Summary of output impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.2 Wake-up and standby time definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.3 Overview of the class-G, 2-level headphone amplifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.4 External component selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.4.1 Step-down inductor selection (L1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.4.2 Step-down output capacitor selection (Ct) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.4.3 Full capacitive inverter capacitors selection (C12 and Css) . . . . . . . . . 34
4.4.4 Power supply decoupling capacitor selection (Cs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4.4.5 Input coupling capacitor selection (Cin) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4.4.6 Low-pass output filter (Rout and Cout) and
IEC 61000-4-2 ESD protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.4.7 Integrated input low-pass filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.5 Single-ended input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4.5.1 Layout recommendations for single-ended operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.6 Startup phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.6.1 Auto zero technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.6.2 Input impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.7 Layout recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.7.1 Common mode sense layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.8 Demonstration board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
2/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Contents
6 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 3/48

List of figures TS4621B
List of figures
Figure 1. Typical application schematics for the TS4621B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 2. SCL and SDA timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 3. Start and stop condition timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 4. Current consumption vs. power supply voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 5. Standby current consumption vs. power supply voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 6. Maximum output power vs. loadin-phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 7. Maximum output power vs. loadout-of-phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 8. Maximum output power vs. power supply voltage, RL = 16 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 9. Maximum output power vs. power supply voltage, RL = 32 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 10. Maximum output power vs. power supply voltage, RL = 47 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 11. Maximum output voltage vs. power supply voltage, in-phase. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 12. Maximum output voltage vs. power supply voltage, out-of-phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 13. Current consumption vs. total output power, RL = 16 Ω. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 14. Current consumption vs. total output power, RL = 32 Ω. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 15. Current consumption vs. total output power, RL = 47 Ω. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 16. Current consumption vs. total output power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 17. Power dissipation vs. total output power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 18. Output impedance vs. frequency in HiZ mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 19. Differential input impedance vs. gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 20. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 21. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 22. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 23. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 24. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 25. THD+N vs. output power RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 26. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 27. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 28. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 29. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 30. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 31. THD+N vs. output power RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 32. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 33. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 34. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 35. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 36. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 37. THD+N vs. output power RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 38. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 39. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 40. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 41. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 42. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 43. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 44. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Figure 45. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 46. THD+N vs. frequencyRL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
CC
Figure 47. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 48. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CC
4/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B List of figures
Figure 49. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 50. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
CC
Figure 51. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 52. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
CC
Figure 53. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Figure 54. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
CC
Figure 55. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CC
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
CC
Figure 56. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 10 kΩ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 57. THD+N vs. frequency RL = 600 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 58. THD+N vs. output voltage RL = 10 kΩ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 59. THD+N vs. output voltage RL = 600 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 60. THD+N vs. input voltage, HiZ left and right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 61. CMRR vs. frequency. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 62. PSRR vs. frequencyV
Figure 63. PSRR vs. frequencyV
Figure 64. PSRR vs. frequencyV
= 2.5 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
CC
= 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
CC
= 4.8 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
CC
Figure 65. Output signal spectrum. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 66. Crosstalk vs. frequencyRL = 16 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 67. Crosstalk vs. frequencyRL = 32 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 68. Crosstalk vs. frequencyRL = 47 Ω . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 69. Crosstalk vs. frequencyRL = 10 kΩ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 70. Wake-up time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 71. Shutdown time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 72. I²C write operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 73. I²C read operations1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 74. Flowchart for short-circuit detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 75. TS4621B architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 76. Efficiency comparison. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 77. Class-G operating with a music sample . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 78. Typical application schematic with IEC 61000-4-2 ESD protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 79. Single-ended input configuration1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 80. Single-ended input configuration 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 81. Incorrect ground connection for single-ended option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 82. Correct ground connection for single-ended option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 83. Common mode sense layout example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 84. Demonstration board schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 85. Copper layers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 86. Copper layer and overlay layers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 87. TS4621B footprint recommendation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 88. Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 89. Marking (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 90. Flip-chip - 16 bumps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 91. Device orientation in tape pocket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 5/48
Absolute maximum ratings and operating conditions TS4621B
1 Absolute maximum ratings and operating conditions
Table 1. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
V
in+,Vin-
T
R
P
ESD
CC
stg
T
thja
Supply voltage
Input voltage referred to ground +/- 1.2 V
Storage temperature -65 to +150 °C
Maximum junction temperature
j
Thermal resistance junction to ambient
Power dissipation Internally limited
d
Human body model (HBM)
All pins
VOUTR, VOUTL vs. AGND
Machine model (MM), min. value
Charge device model (CDM)
All pins
VOUTR, VOUTL
IEC61000-4-2 level 4, contact
IEC61000-4-2 level 4, air discharge
(1)
during 1ms.
(5)
(7)
(2)
(6)
(7)
(3)
5.5 V
150 °C
200 °C/W
(4)
2
4
100 V
500
750
+/- 8
+/- 15
kV
V
kV
Lead temperature (soldering, 10 sec) 260 °C
1. All voltage values are measured with respect to the ground pin.
2. Thermal shutdown is activated when maximum junction temperature is reached.
3. The device is protected from over-temperature by a thermal shutdown mechanism, active at 150° C.
4. Exceeding the power derating curves for long periods may provoke abnormal operation.
5. Human body model: a 100 pF capacitor is charged to the specified voltage, then discharged through a
1.5 kΩ resistor between two pins of the device. This is done for all couples of connected pin combinations
while the other pins are floating.
6. Machine model: a 200 pF capacitor is charged to the specified voltage, then discharged directly between
two pins of the device with no external series resistor (internal resistor < 5 Ω). This is done for all couples of
connected pin combinations while the other pins are floating.
7. The measurement is performed on an evaluation board, with ESD protection EMIF02-AV01F3.
6/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
TS4621B Absolute maximum ratings and operating conditions
Table 2. Operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CC
Supply voltage 2.3 to 4.8 V
internal step-down DC output voltages
HPVDD
High rail voltage
Low rail voltage
1.9
1.2
SDA, SCL Input voltage range GND to V
T
R
R
C
oper
thja
L
L
Load resistor ≥ 16 Ω
Load capacitor
Serial resistor of 12 Ω minimum, R
≥ 16 Ω 0.8 to 100
L
Operating free air temperature range -40 to +85 °C
Flip-chip thermal resistance junction to ambient 90 °C/W
V
cc
V
nF
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 7/48
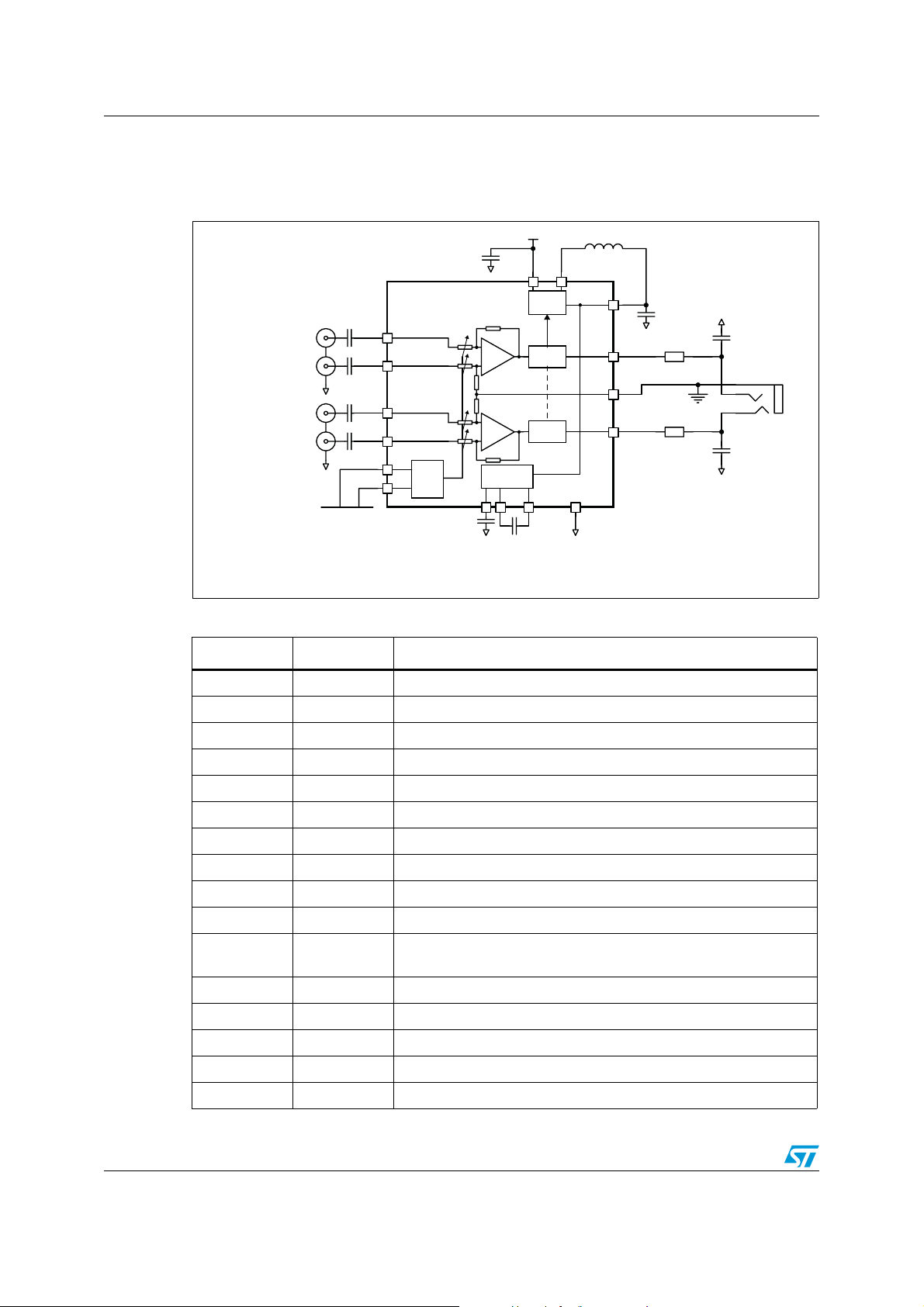
Typical application schematics TS4621B
2 Typical application schematics
Figure 1. Typical application schematics for the TS4621B
Negative left in put
Positive left input
Negative rig ht input
Positive right input
I²C bus
Cin
1 uF
Cin
1 uF
Cin
1 uF
Cin
1 uF
InL+
InR-
SDA
SCL
InL-
InR+
I2C
Cs
2.2 uF
PVss
Css
2.2 uF
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
AVdd
Vbat
Positive
detector
detector
C12
2.2 uF
supply
Level
Level
Sw
3.3 uH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGndC1 C2
L1
Ct
10 uF
Rout
12 ohms min.
Rout
12 ohms min.
Cout
0.8 nF min.
3
J1
2
1
Cout
0.8 nF min.
Table 3. TS4621B pin description
Pin number Pin name Pin definition
A1 SW Switching node of the buck converter
A2 AVDD Analog supply voltage, connect to battery
A3 VOUTL Output signal for left audio channel
A4 INL- Negative input signal for left audio channel
B1 AGND Device ground
B2 C1 Flying capacitor terminal for internal negative supply generator
B3 HPVDD Buck converter output, power supply for amplifier
B4 INL+ Positive input signal for left audio channel
C1 C2 Flying capacitor terminal for internal negative supply generator
C2 PVSS Negative supply generator output
C3 CMS
Common mode sense, to be connected as close as possible to the
ground of headphone/line out plug
C4 INR+ Positive input signal for right audio channel
D1 SDA I²C data signal, up to V
D2 SCL I²C clock signal, up to V
tolerant input
CC
tolerant input
CC
D3 VOUTR Output signal for right audio channel
D4 INR- Negative input signal for right audio channel
AM06119
8/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
TS4621B Typical application schematics
Table 4. TS4621B component description
(1)
Component Value Description
Decoupling capacitors for V
. A 2.2 µF capacitor is sufficient for proper
CC
decoupling of the TS4621B. An X5R dielectric and 10 V rating voltage is
Cs 2.2 µF
recommended to minimize ΔC/ΔV when V
Must be placed as close as possible to the TS4621B to minimize parasitic
inductance and resistance.
Capacitor for internal negative power supply operation. An X5R dielectric
and 6.3 V rating voltage is recommended to minimize ΔC/ΔV when
C12 2.2 µF
HPVDD = 1.9 V.
Must be placed as close as possible to the TS4621B to minimize parasitic
inductance and resistance.
Filtering capacitor for internal negative power supply. An X5R dielectric and
C
SS
2.2 µF
6.3 V rating voltage is recommended to minimize ΔC/ΔV when
HPVDD = 1.9 V.
Cin
C
in
C
out
R
out
----------------------------------------- -=
2 π Rin Fc×××
0.8 to 100 nF
12 Ω min.
L1 3.3 µH
1
Input coupling capacitor that forms with Rin ≈ Rindiff/2 a first-order highpass filter with a -3 dB cutoff frequency Fc. For example, at maximum gain
G=4dB, Rin=12.5kΩ, C
= 1 µF, therefore Fc = 13 Hz.
in
Output capacitor of 0.8 nF minimum to 100 nF maximum. This capacitor is
mandatory for operation of the TS4621B.
Output resistor in-series with the TS4621B output. This 12 Ω minimum
resistor is mandatory for operation of the TS4621B.
Inductor for internal DC/DC step-down converter.
References of inductors: refer to Section 4.4.1 for more information.
Tank capacitor for internal DC/DC step-down converter. An X5R dielectric
C
t
10 µF
and 6.3 V rating voltage is recommended to minimize ΔC/ΔV when
HPVDD = 1.9 V. Refer to Section 4.4.2 for more information.
1. Refer to Section 4.4 for a complete description of each component.
CC
=4.8V.
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 9/48
Electrical characteristics TS4621B
3 Electrical characteristics
Table 5. Electrical characteristics of the I²C interface
for V
= +3.6 V, AGND = 0 V, T
CC
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
V
V
Table 6. Electrical characteristics of the amplifier
Low level input voltage on SDA, SCL pins 0.6 V
IL
High level input voltage on SDA, SCL pins 1.2 V
IH
Low level output voltage, SDA pin, I
OL
Input current on SDA, SCL 10 µA
I
in
for V
= +3.6 V, AGND = 0 V, RL= 32 Ω + 15 Ω, T
CC
= 3mA 0.4 V
sink
V
SDA SCL,
------------------------------ -- -
600k Ω
= 25° C
amb
(unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
I
STBY
V
V
V
Quiescent supply current, no input signal, both channels
CC
enabled
Supply current, with input modulation, both channels enabled,
HPVDD = 1.2 V, output power per channel, F=1kHz
Pout = 100 µW at 3 dB crest factor
I
s
Pout = 500 µW at 3 dB crest factor
Pout = 1mW at 3dB crest factor
Pout = 100 µW at 10 dB crest factor
Pout = 500 µW at 10 dB crest factor
Pout = 1 mW at 10 dB crest factor
Standby current, no input signal, I²C CR1 = 01h
= 0 V, V
V
SDA
Input differential voltage range
in
SCL
= 0 V
(1)
Output offset voltage
oo
No input signal
Maximum output voltage, in-phase signals
= 16 Ω, THD+N = 1% max, f = 1 kHz
R
L
= 47 Ω, THD+N = 1% max, f = 1 kHz
out
R
L
RL = 10 kΩ, Rs = 15 Ω, CL = 1 nF, THD+N = 1% max,
f = 1 kHz
1.2 1.5 mA
2.3
3.7
4.7
3.5
5
6.5
2.1
3.1
3.9
0.6 5 µA
1V
-500 +500 µV
0.6
1.0
1.0
0.8
1.1
1.3
mA
V
rms
rms
Total harmonic distortion + noise, G = 0 dB
THD+N
PSRR
= 700 mVrms, F = 1 kHz
V
out
= 700 mVrms, 20 Hz < F < 20 kHz
V
out
Power supply rejection ratio
inputs
F = 217 Hz, G = 0 dB, R
F = 10 kHz, G = 0 dB, R
L
L
(1)
, V
≥16 Ω
≥16 Ω
= 200 mVpp, grounded
ripple
10/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
0.006
0.05
90 100
70
0.02 %
dB
TS4621B Electrical characteristics
Table 6. Electrical characteristics of the amplifier
for V
= +3.6 V, AGND = 0 V, RL= 32 Ω + 15 Ω, T
CC
amb
= 25° C
(unless otherwise specified) (continued)
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Common mode rejection ratio
CMRR
F = 1 kHz, G = 0 dB, V
F = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, G = 0 dB, Vic = 200 mV
= 200 mV
ic
pp
65
pp
45
Channel separation
Crosstalk
SNR
ONoise
= 32 Ω + 15 Ω , G = 0 dB, F = 1 kHz, Po = 10 mW
R
L
= 10 kΩ, G = 0 dB, F = 1 kHz, V
R
L
Signal-to-noise ratio, A-weighted, V
F = 1 kHz
(1)
out
out
= 1 V
=1 Vrms
G = +4 dB
G = +0 dB
Output noise voltage, A-weighted
(1)
G = +4 dB
, THD+N < 1%,
rms
60
80
99
100
100
110
9119µVrms
G = +0 dB
G Gain range with gain (dB) = 20 x log[(V
Mute InL/R+ - InL/R- = 1 V
rms
L/R)/(InL/R+ - InL/R-)] -60 +4 dB
out
- Gain step size error -0.5 +0.5
-80 dB
dB
dB
dB
step-
size
- Gain error (G = +4 dB) -0.45 +0.42 dB
R
Differential input impedance 25 34 kΩ
indiff
Input impedance during wake-up phase (referred to ground) 2 kΩ
Output impedance when CR1 = 00h (negative supply is ON and
amplifier output stages are OFF)
Z
out
F < 40 kHz
F = 6 MHz
F = 36 MHz
t
t
stby
t
t
1. Guaranteed by design and parameter correlation.
2. Refer to the application information in Section 4.2 on page 30.
Wake-up time
wu
Standby time 100 µs
Attack time. Setup time between low rail and high rail voltages
atk
of internal step-down DC/DC converter
Decay time 50 ms
dcy
(2)
(1)
10
500
75
12 16 ms
100 µs
kΩ
Ω
Ω
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 11/48
Electrical characteristics TS4621B
Table 7. Timing characteristics of the I²C interface for I²C interface signals over
recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
f
SCL
t
d(H)
t
d(L)
t
t
t
t
t
Frequency, SCL 400 kHz
Pulse duration, SCL high 0.6 µs
Pulse duration, SCL low 1.3 µs
Setup time, SDA to SCL 100 ns
st1
Hold time, SCL to SDA 0 ns
h1
Bus free time between stop and start condition 1.3 µs
t
f
Setup time, SCL to start condition 0.6 µs
st2
Hold time, start condition to SCL 0.6 µs
h2
Setup time, SCL to stop condition 0.6 µs
st3
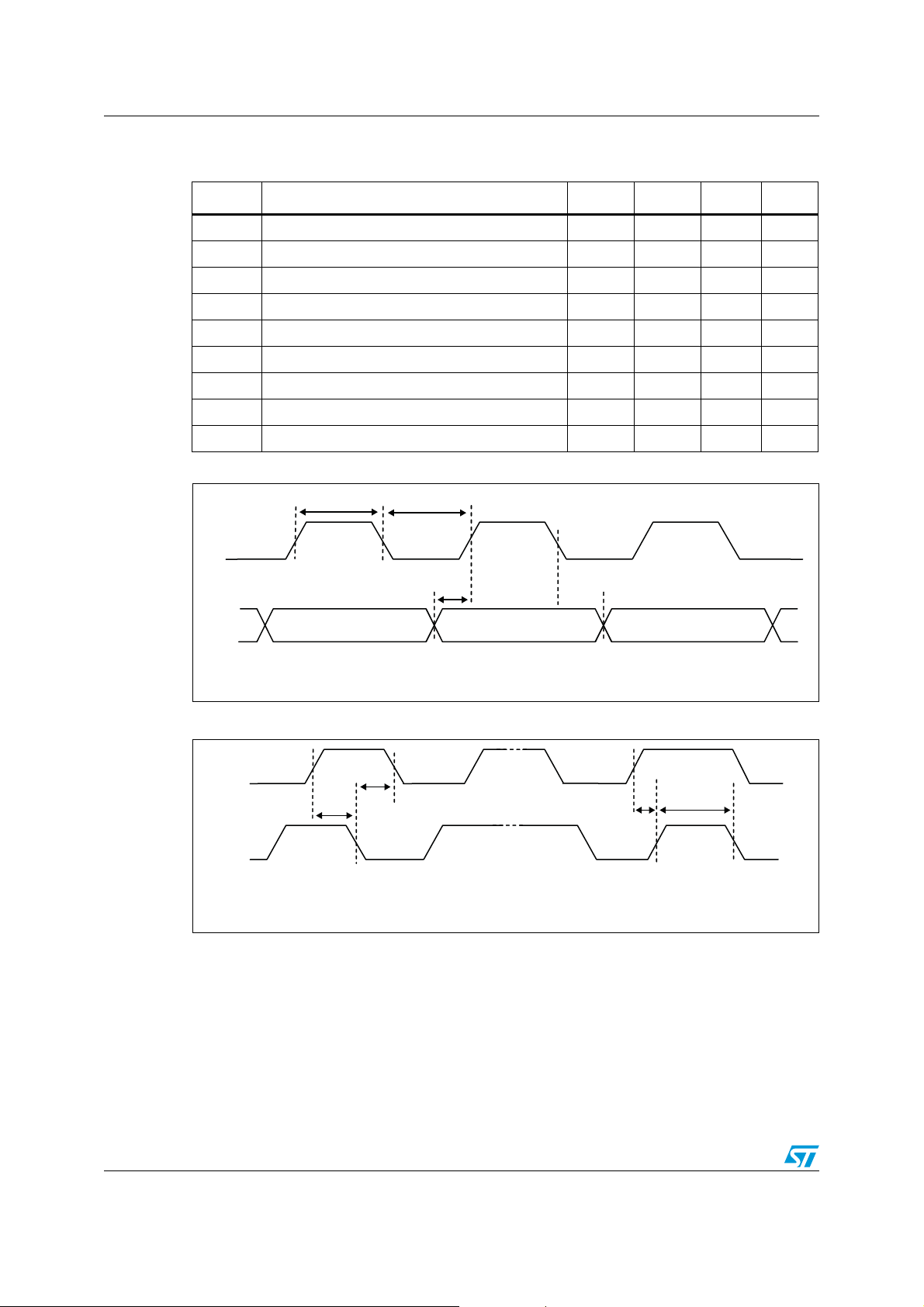
Figure 2. SCL and SDA timing diagram
t
d(H)
t
SCL
SDA
d(L)
t
st1
t
h1
Figure 3. Start and stop condition timing diagram
SCL
t
t
st2
h2
SDA
Start condition Stop condition
AM06113
t
f
t
st3
AM06114
12/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
TS4621B Electrical characteristics
No load; No input Signal
SDA=SCL = 0V
Ta = 25°C
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7
0
20
40
60
80
THD+N=10% (180°)
THD+N=10% (0°)
THD+N=1% (0°)
RL = 32Ω, F = 1kHz
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
THD+N=1% (180°)
Output power (mW)
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
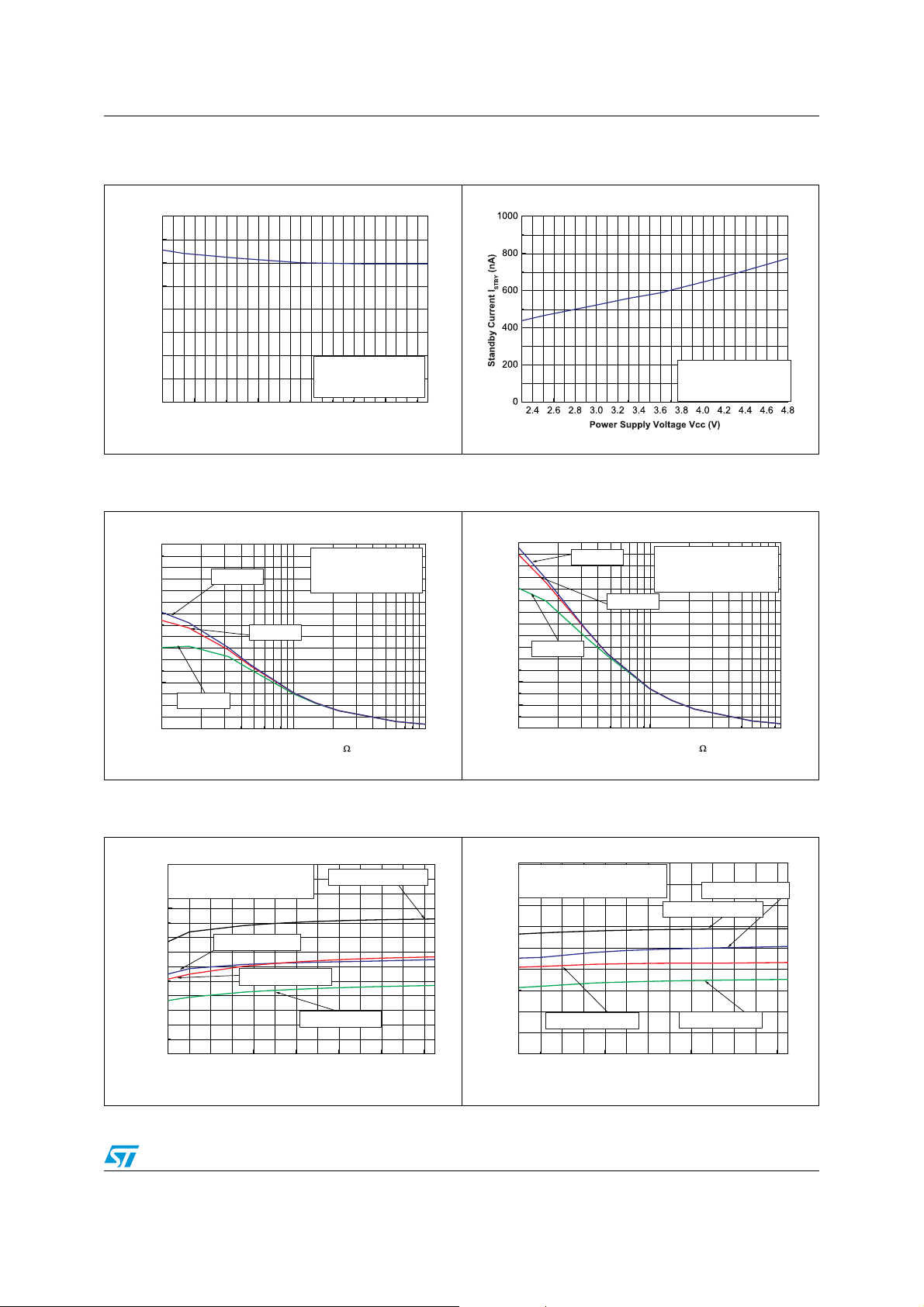
Figure 4. Current consumption vs. power
supply voltage
1.6
1.4
(mA)
1.2
CC
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
Quiscent Supply Current I
0.2
0.0
2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
No load; No input Signal
Both channels enabled
Ta = 25°C
Figure 6. Maximum output power vs. load
in-phase
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
Output power (mW)
10
0
10 100 1k
VCC=4.8V
VCC=3.6V
VCC=2.3V
RL Load resistance ( )
Inputs = 0°, F = 1kHz
THD+N = 1%
Tamb = 25°C
Figure 5. Standby current consumption vs.
power supply voltage
Figure 7. Maximum output power vs. load
out-of-phase
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
Output power (mW)
10
0
10 100 1k
VCC=4.8V
VCC=3.6V
VCC=2.3V
RL Load resistance ( )
Inputs = 180°, F = 1kHz
THD+N = 1%
Tamb = 25°C
Figure 8. Maximum output power vs. power
supply voltage, RL = 16 Ω
RL = 16Ω, F = 1kHz
120
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
100
80
60
40
Output power (mW)
20
0
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7
THD+N=10% (0°)
THD+N=1% (180°)
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
Figure 9. Maximum output power vs. power
supply voltage, RL = 32 Ω
THD+N=10% (180°)
THD+N=1% (0°)
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 13/48
Electrical characteristics TS4621B
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
1300
1400
1500
1600
10 K
Ω
600
Ω
60
Ω
47
Ω
16
Ω
F = 1kHz
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Inputs = 0°, THD+N = 1%
32
Ω
Output Voltage (mVrms)
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
0.1 1 10
1
10
100
Vcc=4.8V
Vcc=3.6V
Vcc=2.3V
Both channels enabled
RL = 16Ω, F = 1KHz
Ta = 25°C
Crest Factor = 3dB
Supply Current I
S
(mA)
Total Output Power (mW)
0.1 1 10
1
10
100
Vcc=4.8V
Vcc=3.6V
Vcc=2.3V
Both channels enabled
RL = 47Ω, F = 1 KHz
Ta = 25°C
Crest Factor = 3dB
Supply Current I
S
(mA)
Total Output Power (mW)
Figure 10. Maximum output power vs. power
supply voltage, RL = 47 Ω
RL = 47Ω, F = 1kHz
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
60
THD+N=10% (0°)
THD+N=10% (180°)
40
20
Output power (mW)
THD+N=1% (180°)
0
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
THD+N=1% (0°)
Figure 12. Maximum output voltage vs. power
supply voltage, out-of-phase
1600
1500
1400
1300
1200
1100
1000
Output Voltage (mVrms)
F = 1kHz
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Inputs = 180°, THD+N=1%
47
16
Ω
Ω
32
Ω
900
800
700
2.3 2.7 3.1 3.5 3.9 4.3 4.7
Power Supply Voltage Vcc (V)
60
600
Ω
Ω
10 K
Ω
Figure 11. Maximum output voltage vs. power
supply voltage, in-phase
Figure 13. Current consumption vs. total
output power, RL = 16 Ω
Figure 14. Current consumption vs. total
output power, RL = 32 Ω
100
Both channels enabled
RL = 32Ω, F = 1KHz
Ta = 25°C
Crest Factor = 3dB
(mA)
S
10
Supply Current I
14/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
1
0.1 1 10
Vcc=3.6V
Total Output Power (mW)
Figure 15. Current consumption vs. total
output power, RL = 47 Ω
Vcc=2.3V
Vcc=4.8V
TS4621B Electrical characteristics
-60 -55 -50 -45 -40 -35 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0
30
40
50
60
70
80
Vcc=2.3V to 4.8V
Ta = 25°C
Differential Input Impedance (K )
Gain (dB)
Figure 16. Current consumption vs. total
output power
100
Both channels enabled
RL = 47Ω, F = 1KHz
Ta = 25°C, Vcc = 3.6V
(mA)
S
10
Crest Factor=3dB
Supply Current I
Crest Factor=10dB
1
0.1 1
Total Output Power (mW)
Figure 18. Output impedance vs. frequency in
HiZ mode
Input Floating
Input grounded
Figure 17. Power dissipation vs. total output
power
100
R = 16
Ω
R = 32
Ω
10
R = 47
Ω
Power Dissipation (mW)
1
0.1 1 10
Total Output Power (mW)
Both channels enabled
F = 1KHz,
Ta = 25°C
Crest Factor = 3dB
Figure 19. Differential input impedance vs.
gain
Vcc=2.3V to 4.8V
HIz; Right & Left
Osc level=0.5V
Ta = 25°C
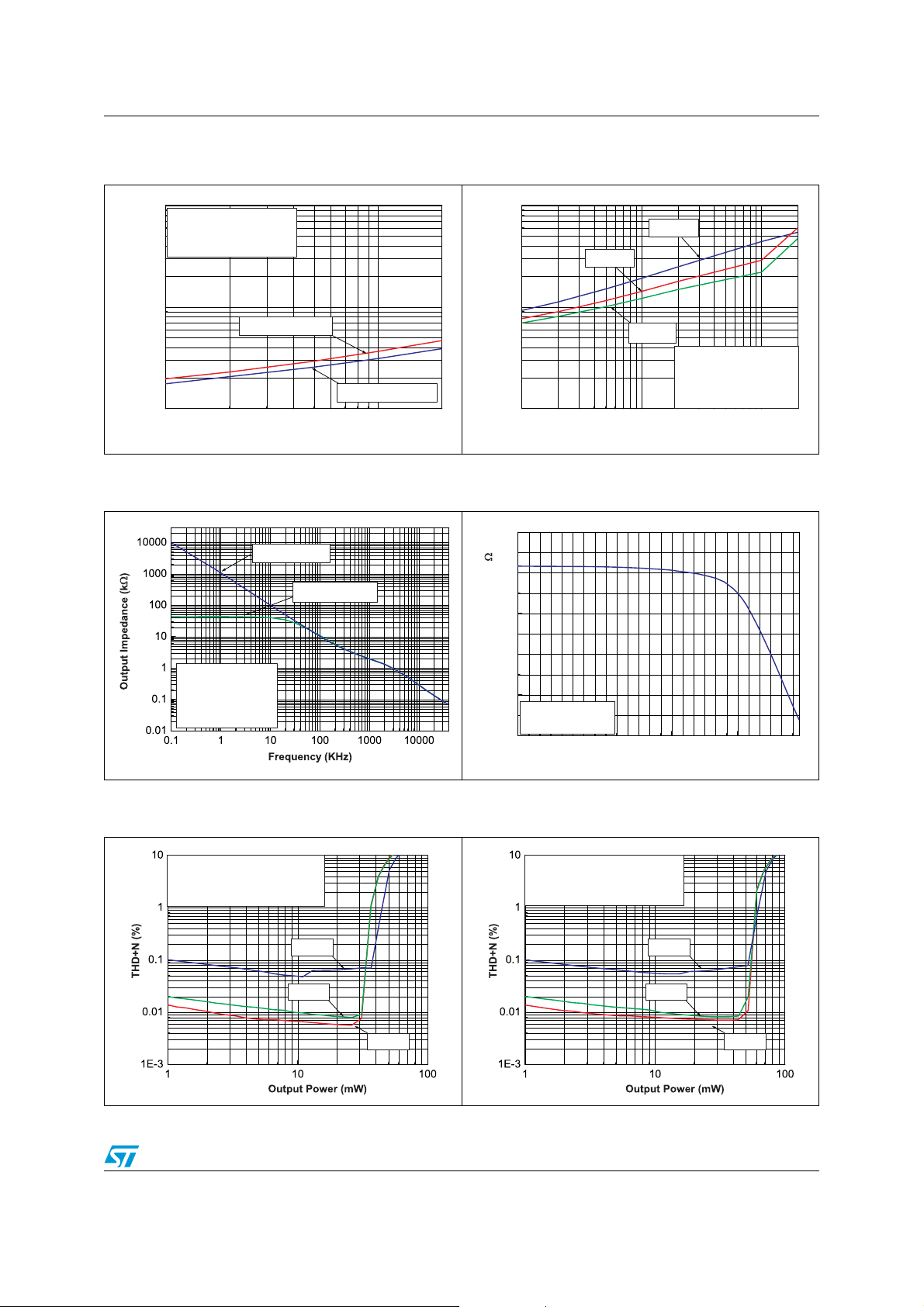
Figure 20. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
RMS
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
F=80Hz
= 2.5 V
Figure 21. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
F=80Hz
= 2.5 V
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 15/48

Electrical characteristics TS4621B
Figure 22. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
Figure 24. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
= 3.6 V
F=80Hz
= 4.8 V
Figure 23. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 25. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 16
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
F=80Hz
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
F=8kHz
F=80Hz, 1kHz
Figure 26. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
= 2.5 V
F=80Hz
F=8kHz
F=80Hz, 1kHz
Figure 27. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
= 2.5 V
CC
F=80Hz
16/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Electrical characteristics
Figure 28. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
F=80Hz
Figure 30. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
Figure 29. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
F=80Hz
Figure 31. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 32
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 32. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
F=80Hz
= 2.5 V
F=80Hz
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 33. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 2.5V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
F=80Hz
CC
F=80Hz
= 2.5 V
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 17/48

Electrical characteristics TS4621B
Po=1mW
Po=15mW
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Figure 34. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
CC
Figure 36. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 0
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
= 3.6 V
F=80Hz
= 4.8 V
Figure 35. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 3.6V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 37. THD+N vs. output power
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
Vcc = 4.8V, RL = 47
G = 4dB, Inputs = 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
CC
F=80Hz
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 38. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Po=15mW
F=80Hz
CC
= 2.5 V
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
Figure 39. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
F=80Hz
CC
= 2.5 V
18/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
20k20

TS4621B Electrical characteristics
Po=1mW
Po=15mW
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Po=1mW
Po=15mW
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Figure 40. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Figure 42. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 16Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
CC
Po=15mW
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
Figure 41. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
20k20
Figure 43. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω, out-of-phase, V
CC
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
Figure 44. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Po=15mW
CC
Po=10mW
20k20
Figure 45. THD+N vs. frequency
= 2.5 V
20k20
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 19/48
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
CC
= 2.5 V

Electrical characteristics TS4621B
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Figure 46. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Figure 48. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 32Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
= 3.6 V
CC
Po=10mW
= 4.8 V
CC
Figure 47. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
20k20
Figure 49. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω, out-of-phase, V
CC
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
Figure 50. THD+N vs. frequency
20/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
Po=1mW
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 2.5V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
= 2.5 V
CC
Po=10mW
20k20
Figure 51. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
20k20
CC
= 2.5 V

TS4621B Electrical characteristics
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 180°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Vo=1Vrms
Vo=100mVrms
RL = RC network + 600Ω
Vcc = 2.3V to 4.8V
G = 0dB, Inputs = 0° & 180°
Bw < 20kHz, Tamb = 25°C
20k20
Figure 52. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 3.6V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
Po=1mW
Figure 54. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω, in-phase, V
RL = 47Ω
Vcc = 4.8V
G = 0dB
Inputs = 0°
Bw < 20kHz
Tamb = 25°C
= 3.6 V
CC
Po=10mW
= 4.8 V
CC
Figure 53. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
20k20
Figure 55. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω, out-of-phase, V
CC
CC
= 3.6 V
= 4.8 V
Figure 56. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 10 kΩ
RL = RC network + 10kΩ
Vcc = 2.3V to 4.8V
G = 0dB, Inputs = 0° & 180°
Bw < 20kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Vo=100mVrms
Vo=1Vrms
Po=1mW
Po=10mW
20k20
Figure 57. THD+N vs. frequency
RL = 600 Ω
20k20
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 21/48

Electrical characteristics TS4621B
F=80Hz
F=1kHz
F=8kHz
RL = RC network + 600
Ω
Vcc = 2.3V to 4.8V, G = 4dB
Inputs = 0° & 180
°
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
100 1000 10000
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
20k
20
Δ
≥ Ω
°
100 1000 10000
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
G=-6dB
G=0dB
G=4dB
20k
20
≥ Ω
°
Figure 58. THD+N vs. output voltage
RL = 10 kΩ
RL = RC network + 10k
Vcc = 2.3V to 4.8V, G = 4dB
Inputs = 0° & 180
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
°
F=8kHz
F=1kHz
F=80Hz
Figure 60. THD+N vs. input voltage, HiZ left
and right
HiZ Left & Right
Vcc = 2.3V to 4.8V
Zout generator = 1k
BW < 30kHz, Tamb = 25°C
Ω
Line In F=8kHz
Line In F=1kHz
Line In F=80Hz
Figure 59. THD+N vs. output voltage
RL = 600 Ω
Figure 61. CMRR vs. frequency
Figure 62. PSRR vs. frequency
22/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
Reference F=80Hz, 1kHz, 8kHz
Figure 63. PSRR vs. frequency
V
= 2.5 V
CC
0
-10
-20
-30
≥ Ω
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
20
°
G=0dB
100 1000 10000
G=4dB
G=-6dB
20k
VCC = 3.6 V

TS4621B Electrical characteristics
Ω
°
100 1000 10000
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
20k
20
Ω
°
100 1000 10000
-130
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
-60
-50
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
20k
20
Ω
°
Figure 64. PSRR vs. frequency
V
= 4.8 V
CC
0
-10
-20
-30
≥ Ω
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
-130
20
°
G=4dB
G=0dB
100 1000 10000
Figure 66. Crosstalk vs. frequency
RL = 16 Ω
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
20
Ω
°
100 1000 10000
Figure 65. Output signal spectrum
G=-6dB
20k
Figure 67. Crosstalk vs. frequency
RL = 32 Ω
20k
Figure 68. Crosstalk vs. frequency
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
-100
-110
-120
Figure 69. Crosstalk vs. frequency
RL = 47 Ω
0
Ω
°
20
100 1000 10000
20k
RL = 10 kΩ
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 23/48

Electrical characteristics TS4621B
Figure 70. Wake-up time Figure 71. Shutdown time
I²C ACK after
SDA
2 ms/div
1V/div
VOUT
2ms/div
20mv/div
Shutdown command
VOUT
10µs/div
100mv/div
24/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
4 Application information
4.1 I2C bus interface
In compliance with the I²C protocol, the TS4621B uses a serial bus to control the chip’s
functions with the clock (SCL) and data (SDA) wires. These two lines are bi-directional
(open collector) and require an external pull-up resistor (typically 10 kΩ). The maximum
clock frequency in fast mode specified by the I²C standard is 400 kHz, which the TS4621B
supports. In this application, the TS4621B is always the slave device and the controlling
microcontroller MCU is the master device.
The slave address of the TS4621B is 1100 000x (C0h).
Ta bl e 8 summarizes the pin descriptions for the I²C bus interface.
Table 8. Pin description of the I²C bus interface
Pin Functional description
SDA Serial data pin
SCL Clock input pin
4.1.1 I²C bus operation
The host MCU can write to the TS4621B control register to control the TS4621B, and read
from the control register to obtain a configuration from the TS4621B. The TS4621B is
addressed by the byte consisting of the 7-bit slave address and the R/W
Table 9. First byte after the START message for addressing the device
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 R/W
1100000X
There are four control registers (Tab le 1 0) named CR1 to CR4. In read mode, all the control
registers can be accessed. In write mode, only CR1, CR2 and CR3 can be addressed.
Table 10. Summary of control registers
Description
CR1 1 HP_EN_L HP_EN_R 0 0 SC_L SC_R T_SH SWS
CR2
volume control
CR3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 HiZ_L HiZ_R
CR4
identification
Register
address
2
4
bit.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Mute_L Mute_R Volume control 0
01000000
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 25/48

Application information TS4621B
Table 11. Control registers at power-up
Description
Register
address
CR1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
CR2 2 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
CR3 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CR4 4 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Writing to the control registers
To write data to the TS4621B, after the "start" message the MCU must:
● send the I²C 7-bit slave address and a low level for the R/W bit.
● send the register address to write to.
● send the data bytes (control register settings).
All bytes are sent MSB first. The transfer of written data ends with a "stop" message. When
transmitting several data bytes, the data can be written without having to repeat the "start"
message or send the byte with the slave address. If several bytes are transmitted, they will
be written repeatedly to CR1, CR2 and CR3.
Figure 72. I²C write operations
SLAVE DEVICE ADDRESS
SDA
S
1100
Start
condition
00 A7
0
0
R/W
Acknowledge
from slave
ACK
Reading from the control registers
To read data from the TS4621B, after the "start" message the MCU must:
● send the I²C 7-bit slave address and a low level for the R/W bit.
● send the register address to read.
● send the I²C 7-bit slave address and a high level for the R/W bit.
● receive the data (control register value).
REGISTER ADDRESS
A6
A1
A0
ACK
D7
D6
CR X
DATA BYTES
D1 D0
ACK
D7 D6
CRX+1
D1 D0
Acknowledge
from slave
ACK P
Stop
condition
AM06115
All bytes are read MSB first. The transfer of read data ends with a "stop" message. When
transmitting several data bytes, the data can be read without having to repeat the "start"
message or send the byte with the slave address. If several bytes are transmitted, they are
read repeatedly from CR1, CR2, CR3 and CR4.
26/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
Figure 73. I²C read operations1
DATA BYTES
CRX CRX+1
SDA
DEVICE ADDRESS
REGISTER ADDRESS
DEVICE ADDRESS
110
S
Start condition
00
000
ACK
R/W
Acknowledge
fom slave
A7 A0
ACK
S
Repeat
start condition
110
4.1.2 Control register CR1 - address 1
Amplifier output short-circuit detection: bits SC_L and SC_R
The amplifier’s outputs are protected from short-circuits that might accidentally occur during
manipulation of the device. In a typical application, if a short-circuit arises on the jack plug,
there will be no detection because of the serial resistor present on the amplifier output, thus
the output current threshold will not be reached.
To be active, the detection has to occur directly on the amplifier’s output with a signal
modulation on the inputs of the TS4621B. This detection is depicted in Figure 74.
Figure 74. Flowchart for short-circuit detection
00100
ACK ACK
D7
R/W
D0
D7
P
AA
D0
Stop
condition
Not
Acknowledge
AM06116
Shortcut detection
Counter < 3
Shortcut detection
Counter = counter + 1
Wait 40 ms
TS4621B power ON
Timeout = 40 ms
Counter = 0
TS4621B power ON
Shortcut detection
TS4621B power OFF
Set flag SC_L or SC_R to 1
Set flag HiZ_L or HiZ_R to 1
Shortcut detection & timeout = 0
Reset
Counter = 3
AM06117
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 27/48

Application information TS4621B
If a short-circuit is detected three consecutive times on one channel, a flag is raised in the
I²C read register CR1.
● SC_L: equals 0 during normal operation, equals 1 when a short-circuit is detected on
the left channel.
● SC_R: equals 0 during normal operation, equals 1 when a short-circuit is detected on
the right channel.
The corresponding channel’s output stage is then set to high impedance mode. An I²C read
command allows the reading of the SC_L and SC_R flags but does not reset them. An I²C
write command has to be sent to CR1 to reset the flags to 0 and restore normal operation.
Thermal shutdown protection: bit T_SH
A thermal shutdown protection is implemented to protect the device from overheating. If the
temperature rises above the thermal junction of 150°C, the device is put into standby mode
and a flag is raised in the read register CR1.
● T_SH: equals 0 during normal operation, equals 1 when a thermal shutdown is
detected.
When the temperature decreases to safe levels, the circuit switches back to normal
operation and the corresponding flag is cleared.
Software shutdown: bit SWS
When SWS equals 1, the device is set to I²C software shutdown. When SWS equals 0, the
negative supply and buck converters are activated.
Channel activation: bits HP_EN_L and HP_EN_R
When HP_EN_L or HP_EN_R equals 1, the corresponding amplifier channel is enabled.
28/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
4.1.3 Control register CR2 - address 2
Table 12. Volume control register CR2 - address 2
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
00000 -60 dB 10000 -11 dB
00001 -54 dB 10001 -10 dB
00010-50.5 dB 10010 -9 dB
00011 -47 dB 10011 -8 dB
00100 -43 dB 10100 -7 dB
00101 -39 dB 10101 -6 dB
00110 -35 dB 10110 -5 dB
00111 -31 dB 10111 -4 dB
01000 -27 dB 11000 -3 dB
01001 -25 dB 11001 -2 dB
01010 -23 dB 11010 -1 dB
01011 -21 dB 11011 0 dB
01100 -19 dB 11100 +1 dB
Volume control range: -60 dB to +4 dB
Gain
(in dB)
D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
Gain
(in dB)
01101 -17 dB 11101 +2 dB
01110 -15 dB 11110 +3 dB
01111 -13 dB 11111 +4 dB
Mute function: bits MUTE_L and MUTE_R
In the volume register, MUTE_L and MUTE_R are dedicated to enabling the mute function,
independently of the channel. When MUTE_L and MUTE_R are set to 1, the mute function
is enabled on the corresponding channel and the gain is set to -80 dB. When MUTE_L and
MUTE_R are set to 0, the I²C gain level is applied to the channel.
4.1.4 Control register CR3 - address 3
High output impedance mode: bits HiZ_L and HiZ_R
The TS4621B features a high-output impedance mode used, for example, to share the
headphone jack with the audio and composite video signal.
To set this mode, you must set the HIZ bit to 1 for the targeted output in the CR3 register.
At this time, the considered output is in high-impedance mode with the following
characteristics:
● Maximum input voltage = -1.8 to +1.8 V
● Output impedance = input impedance detected by the video driver. For an example,
refer to Chapter 3: Electrical characteristics on page 10 or Figure 18.
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 29/48

Application information TS4621B
4.1.5 Summary of output impedance
Table 13. Summary table for output impedance vs. output mode
SWS HiZ HP_EN Output impedance
1 0 0 20 to 40 Ω Less than ± 100 mV
1 0 1 20 to 40 Ω Less than ± 100 mV
1 1 0 about 10 kΩ -0.3 V to AVdd
1 1 1 about 10 kΩ -0.3 V to AVdd
0 0 0 20 to 40 Ω Less than ± 100 mV
0 0 1 Less than 1 Ω Not applicable
0 1 0 See Figure 18 -1.8 to +1.8 V
0 1 1 See Figure 18 -1.8 to +1.8 V
4.2 Wake-up and standby time definition
The wake-up time of the TS4621B is guaranteed at 12 ms typical (refer to Chapter 3:
Electrical characteristics). However, since the TS4621B is activated with an I
wake-up start procedure is as follows.
1. The master sends a start bit.
2. The master sends the device address.
3. The slave (TS4621B) answers by an acknowledge bit.
4. The master sends the register address.
5. The slave (TS4621B) answers by an acknowledge bit.
6. The master sends the output mode configuration (CR1).
7. If the TS4621B was previously in standby mode, the wake-up starts on the falling edge
of the eighth clock signal (SCL) corresponding to the CR1 byte.
8. After 12 ms (de-pop sequence time), the TS4621B outputs are operational.
Maximum voltage allowed
on output pin
2
C bus, the
The standby time is guaranteed as 100 µs typical (refer to Chapter 3). However, since the
TS4621B is de-activated with an I
2
C bus, the standby time operates as follows.
1. The master sends a start bit.
2. The master sends the device address.
3. The slave (TS4621B) answers by an acknowledge bit.
4. The master sends the register address.
5. The slave (TS4621B) answers by an acknowledge bit.
6. The master sends the output mode configuration (CR1), which corresponds, in this
case, to standby mode.
7. The standby time starts on the falling edge of the eighth clock signal (SCL)
corresponding to the CR1 byte.
8. After 100 µs, the TS4621B is in standby mode.
30/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
4.3 Overview of the class-G, 2-level headphone amplifier
The TS4621B uses what is referred to as class-G operating mode. This mode is a
combination of the class-AB biasing technique and an adaptive power supply. For this
device, the power supply uses two levels: ±1.2 V and ±1.9 V.
To create the ±1.2 V and ±1.9 V levels, the device uses an internal high-efficiency stepdown converter linked with a fully capacitive inverter from AVdd. Thanks to these internallygenerated symmetrical power supply voltages, the output of the amplifier can be biased at
0 V, thus eliminating the classical bulky DC blocking output capacitors (typically more than
100 μF).
Figure 75. TS4621B architecture
Vbat
Cs
2.2 uF
DC/DC
control
C12
2.2 uF
L1
3.3 uH
Full capacitive
inverter
Css
2.2 uF
Ct
10 uF
In+
In-
1.2 V to 1.9 V
HPVdd
PVss
-1.2 V to -1.9 V
Vout
Level
detector
+Vout
0 V
-Vout
AM06150
When an audio signal is playing with the TS4621B, the class-G feature adjusts in real time
the internal power supply voltage in order to achieve the best efficiency possible. In addition,
thanks to the fast transient response of the internal DC/DC converters, the switching
between ±1.2 V and ±1.9 V can be achieved without audio clipping. Moreover, the out-ofaudio band DC/DC switching frequency keeps the audio quality at a high level (distortion,
noise, etc…).
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 31/48

Application information TS4621B
Figure 76. Efficiency comparison
100
Both channels enabled
RL = 32Ω, F = 1KHz
Vcc = 3.6V, Ta = 25 C
Crest Factor = 3dB
10
Efficiency (%)
1
0.1
0.1 1 10
Total Output Power (mW)
TS4621B
Class G
TS4601
Class AB
Most audio signals have a crest factor higher than 6 dB (10 dB on average), which means
that most of the time the music level is low. In this case, the setting of the internal DC/DC
converters is low (1.2 V) and in this way, helps to minimize the power dissipation.
When the audio signal amplitude increases due to a peak or louder music, the setting of the
internal DC/DC converters increases to 1.9 V, automatically increasing the output dynamic
range. This 1.9 V value remains until the end of the decay time.
Figure 77 shows a music sample played at high levels.
Figure 77. Class-G operating with a music sample
HPVDD
High 1.9V
HPVDD
Low 1.2V
Music
Sample
PVSS
Low -1.2V
PVSS
High -1.9V
Note: HPVDD/PVSS voltages are created internally by DC/DC converters. To avoid destruction of
the TS4621B power amplifier, do not connect any external power supply on these pins.
32/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
4.4 External component selection
The TS4621B requires few external passive components to operate correctly. Each
component is described in the following sections.
4.4.1 Step-down inductor selection (L1)
The TS4621B needs one inductor for the internal step-down DC/DC converter. This inductor
must fit the following constraints:
● Typical value: 2.2 µH to 3.3 µH (3.3 µH is recommended).
● Maximum current in operating mode: 400 mA
● Minimum inductor value at maximum current: 1.5 µH
● Maximum inductor value at zero current: 4.3 µH
● DC resistance: from 50 mΩ up to 450 mΩ
Ta bl e 1 4 shows the part number that should be used according to the inductor value.
Table 14. Recommended inductor
Manufacturer Part number Value
LQM21PN3R3NGRD 3.3 µH
Murata
FDK
LQM2MPN3R3G0L 3.3 µH
LQM2MPN2R2G0L 2.2 µH
MIPSZ2012D3R3 3.3 µH
MIPSZ2012D2R2 2.2 µH
4.4.2 Step-down output capacitor selection (Ct)
For the internal DC/DC step-down converter, the TS4621B needs one output capacitor.
The three criteria for selecting the output capacitor are the range value of the capacitor
including self tolerance, DC variation and the minimum ESR value, which is mandatory to
avoid oscillation of the converter. Therefore the following constraints must be observed.
● Typical capacitor value: 10 µF at DC = 0 V
● Maximum capacitor value: 12 µF at DC = 0 V
● Minimum capacitor value: 4.8 µF at DC = 2 V
● Voltage range across this capacitor: from 1.1 V to 2 V
● Minimum DC ESR value: 5 mΩ
A ceramic capacitor in a 0603-type package is also recommended because of its close
placement to the TS4621B, which makes it easier to minimize parasitic inductance and
resistance that have a negative impact on the audio performance.
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 33/48

Application information TS4621B
Table 15. Recommended capacitor
Manufacturer Part number Value
GRM188R60J106ME47 10 µF, 6.3 V, X5R
Murata
GRM188R60J106ME84 10 µF, 6.3 V, X5R
GRM188R61E106ME73 10 µF, 25 V, X5R
4.4.3 Full capacitive inverter capacitors selection (C12 and Css)
Two capacitors (C12 and Css) are needed for this internal DC/DC inverter.
The three criteria for selecting theses capacitors are the range value of the capacitor
including self tolerance, DC variation and the minimum ESR to minimize power losses.
● Typical capacitor value: 2.2 µF +/-20 %
● Voltage across these capacitors: from 1.1 V to 2 V
● Minimum capacitor value: 1 µF
Again, a ceramic capacitor in a 0603 or 0402-type package is also recommended because
of their close placement to the TS4621B, which makes it easier to minimize parasitic
inductance and resistance that have a negative impact on the audio performance.
4.4.4 Power supply decoupling capacitor selection (Cs)
A 2.2 µF decoupling capacitor with low ESR is recommended for positive power supply
decoupling. Packages such as the 0402 or 0603 are also recommended because of their
close placement to the TS4621B, which makes it easier to minimize parasitic inductance. It
is advised to choose a X5R dielectric for capacitor tolerance, and a 10 V DC rating voltage
for 4.8 V operations (or a 6.3 V DC rating voltage for 3.6 V operations), to take into
consideration the ΔC/ΔV variation of this type of ceramic capacitor.
An important parameter is the rated voltage of the capacitor. A 2.2
at 4.8 V DC typically loses about 40 % of its value. In fact, with a 4.8 V power supply voltage,
the decoupling value is about 1.3
µF instead of 2.2 µF. Because the decoupling capacitor
influences the THD+N in the medium-to-high frequency region, this capacitor variation
becomes decisive. In addition, less decoupling means higher overshoots, which can be
problematic if they reach the power supply’s AMR value (5.5 V). This is why, for a 2.2
value, we recommend a 2.2
µF/10 V, a 4.7 µF/6.3 V or a ceramic capacitor with a low DC
bias variation rated at 6.3 V.
4.4.5 Input coupling capacitor selection (Cin)
Cin input coupling capacitors are mandatory for the TS4621B’s operation. They block any
DC component coming from the audio signal source.
Cin with Rin form a first-order high-pass filter and the -3 dB cutoff frequency is:
FC 3dB–()
--------------------------------------------=
2 π Rin Cin×××
1
µF/6.3 V capacitor used
µF
Rin is the single-ended input impedance that can be approximated at about Rindiff/2.
Rin also depends on the gain setting. Figure 19 provides the differential input impedance vs.
gain. One can also see that Rindiff is minimum for the maximum gain setting (that is, 4 dB).
34/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
Therefore, in most cases, Rin should be set to 4 dB to calculate the minimum input capacitor
Cin.
Example:
At maximum gain G = 4 dB, Rindiff/2 = kΩ/2 = 17 kΩ. However, to take into consideration
the worst case, one has to use Rindiff/2 = 25 kΩ/2 = 12.5 kΩ.
In this case and for a -3 dB cutoff frequency of 20 Hz, Cin = 0.64
value is 0.68
µF but a 1 µF capacitor is more suitable to take into consideration the capacitor
µF. The closest normalized
tolerance +/-20 %.
If the aim is to have the 20 Hz at -1 dB, the capacitor has to be multiplied by 1.96. As such,
Cin = 0.64 x 1.96 = 1.25
µF. The closest normalized value would be 1.5 µF or 2.2 µF.
4.4.6 Low-pass output filter (Rout and Cout) and IEC 61000-4-2 ESD protection
The TS4621B is designed to operate with a passive first-order low-pass filter (as shown in
Figure 1.). This low-pass filter is mandatory to ensure correct operation of the TS4621B over
the volume range and output capacitance range vs. load.
Rout must have a value of 12 Ω minimum and Cout a value of 0.8 nF minimum up to 100 nF
maximum. Values of 12 Ω and 1 nF are a good starting point for a design to be able to drive
a classic headphone (16 Ω, 32 Ω, 60 Ω) and the line-in of any Hi-fi system or sound card.
The cutoff frequency of this filter (12 Ω and 1 nF) is approximately 13 MHz and clearly
above the audio band.
However, this output RC filter is also a part of the IEC 61000-4-2 ESD protection. In most
cases, this RC filter is designed with transient absorbers and the final solution can be a
discrete solution or an integrated solution. ST Microelectronics’ portfolio has many
integrated solutions for ESD, but one dedicated to headphone amplifiers in particular:
(a)
IPAD
To fit the IEC 61000-4-2 standard, this audio line IPAD can be added to the output of the
TS4621B as shown in Figure 78.
reference EMIF02-AV01F3.
a. Copyright STMicroelectronics.
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 35/48

Application information TS4621B
Figure 78. Typical application schematic with IEC 61000-4-2 ESD protection
Negative left input
Positive left input
Positive right input
Negative right input
By adding this ESD protection, the TS4621B complies with the IEC 61000-4-2 level 4
standard on jack pins. Our demonstration board has been tested using the same conditions
as those outlined in the IEC 61000-4-2 standard. Results may differ depending on the layout
of the PCB.
● 15 kV (air discharge)
● 8 kV (contact discharge)
I²C Bus
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
InL-
InL+
InR+
InR-
SDA
SCL
I2C
Cs
2.2 µF
PVss
Css
2.2 µF
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
Vbat
AVdd
Positive
Supply
detector
detector
C1 C2
C12
2.2 µF
Level
Level
Sw
L1
3.3 µH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGnd
A1
Ct
10 µF
IPad
A2
B2
Gnd
J1
3
2
1
2C1C
AM06151
This IPAD has an internal series resistor Rout = 15 Ω +/-20 % and an output capacitor
Cout = 3.2 nF +/-25 %.
4.4.7 Integrated input low-pass filter
The TS4621B has an integrated internal first-order low-pass filter with a -3 dB cutoff
frequency set at 65 kHz and independent of the volume position. This integrated filter is
present on each input and filters any out-of-band audio noise coming from the audio source.
4.5 Single-ended input configuration
The TS4621B can be used in a single-ended input configuration. InR- and InL- or InR+ and
InL+ can be shorted to ground through input capacitors. All Cin capacitors must have the
same value to keep the same PSRR performance as in a differential input configuration.
Figure 79 and Figure 80 show how to connect the TS4621B. Note the ground connection of
each input. To avoid PSRR issues resulting from any ground noise, this connection must be
done on the ground of the audio source and not on the ground of the TS4621B itself.
36/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
Figure 79. Single-ended input configuration1
Audio driver
Cin
InL-
1 µF
Left output
Right output
Audio driver ground
I²C bus
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
InL+
InR+
InR-
SDA
SCL
I2C
Figure 80. Single-ended input configuration 2
Cs
2.2 µF
PVss
Css
2.2 µF
AVdd
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
C1 C2
Vbat
Positive
supply
Level
detector
Level
detector
C12
2.2 µF
Sw
L1
3.3 µH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGnd
Ct
10 µF
Rout
12 ohms min.
Rout
12 ohms min.
Cout
0.8 nF min.
3
J1
2
1
Cout
0.8 nF min.
AM06152
Audio driver
Left output
Right output
Audio driver ground
I²C bus
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
InL-
InL+
InR+
InR-
SDA
SCL
I2C
Cs
2.2 µF
PVss
Css
2.2 µF
AVdd
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
C1 C2
Vbat
Positive
supply
Level
detector
Level
detector
C12
2.2 µF
Sw
L1
3.3 µH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGnd
Ct
10 µF
Rout
12 ohms min.
Rout
12 ohms min.
Cout
0.8 nF min.
J1
3
2
1
Cout
0.8 nF min.
AM06153
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 37/48

Application information TS4621B
The gain range in these configurations remains unchanged and is given by:
VoutLR VinLR Gain×=
With reference to Figure 80., note that the absolute phase in the audio band is 180°.
4.5.1 Layout recommendations for single-ended operation
The connection location of each input that has to be set to ground is extremely important.
Incorrect connection location
Figure 81. Incorrect ground connection for single-ended option
Audio driver
Left output
VaudioL
Right output
VaudioR
Vmc
If these inputs are connected to AGnd (the ground of the TS4621B class-G), the output
voltage can be expressed by the following simplified equation from an AC point of view.
I²C bus
Vgndnoise
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
InL-
InL+
InR+
InR-
SDA
SCL
I2C
Cs
2.2 µF
PVss
Css
2.2 µF
AVdd
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
Vbat
Positive
supply
Level
detector
Level
detector
C12
2.2 µF
Sw
L1
3.3 µH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGndC1 C2
Ct
10 µF
Rout
12 ohms min.
Rout
12 ohms min.
Cout
0.8 nF min.
3
J1
2
1
Cout
0.8 nF min.
AM06154
Vout = Av x (Vaudio + Vmc + Vgndnoise) + Vbatnoise x PSRR (1)
As shown in Equation (1), any ground noise and any parasitic AC voltage on Vmc is directly
multiplied by the gain of the amplifier. If Vmc can be totally controlled by the design of the
audio source device (no parasitic AC voltage), it is not necessarily the case for Vgndnoise.
This noise can be significantly reduced by an adequate low impedance ground plane, but
not totally eliminated. In practice, only ten millivolts in the right frequency range are enough
to produce an audible parasitic sound in the headphone with a volume level as low as
-20 dB.
38/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
Correct connection location
As shown in Figure 82, the best option is to route the single-ended signal in parallel with the
AC ground line of the other input. The AC grounded terminal must be routed in parallel to
the audio signal and grounded with the ground of the audio source.
Figure 82. Correct ground connection for single-ended option
Audio driver
Left output
VaudioL
Right output
VaudioR
Vmc
In this configuration, the AC output voltage is:
I²C bus
Vgndnoise
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
Cin
1 µF
InL-
InL+
InR+
InR-
SDA
SCL
I2C
Cs
2.2 µF
PVss
Css
2.2 µF
AVdd
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
Vbat
Positive
supply
Level
detector
Level
detector
C12
2.2 µF
Sw
L1
3.3 µH
HpVdd
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
AGndC1 C2
Ct
10 µF
Rout
12 ohms min.
Rout
12 ohms min.
Cout
0.8 nF min.
J1
3
2
1
Cout
0.8 nF min.
AM06155
Vout = Av x (Vaudio + Vmc) + Vgndnoise x CMRR + Vbatnoise x PSRR (2)
In equation (2), the ground noise is attenuated by the performance of the CMRR. In practice,
50 dB of CMRR and ten millivolts for ground noise gives an output of approximately 30 µV,
which is normally too low to be perceptible in the headphone. If Vmc is also totally controlled
by the design of the audio source, equation (2) becomes:
Vout = Av x Vaudio + Vbatnoise x PSRR (3)
Like in differential mode, the main contributor for audio signal degradation is the AC noise
voltage on Vbat. Thanks to the TS4621B’s very high PSRR that can attenuate GSM burst
noise, equation (3) becomes:
Vout = Av x Vaudio (4)
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 39/48

Application information TS4621B
4.6 Startup phase
The TS4621B uses different techniques to reduce the DC current consumption and offer a
pop-and-click performance close to none.
4.6.1 Auto zero technology
During the start-up phase, the differential output voltage is sensed and adjusted to 0 V
(+/-500 μV) to avoid any pop noise when the amplifier becomes operational. This also helps
to minimize extra current consumption due to the load (Icc-extra = VoutDC / Rload).
4.6.2 Input impedance
The TS4621B requires input coupling capacitors. The usual lowest frequency used for the
headphone is close to 20 Hz. This frequency means a constant time for a first-order highpass filter of approximately 1 / (2 x Pi x 20) = 8 ms.
To achieve 95 % of the capacitor’s charge, it is necessary to wait 3 x 8 ms = 24 ms, which is
out of range for a device with a fast start-up time.
Because of the mismatching of all input capacitors and input resistors, if it is decided to start
the TS4621B at a time of 8 ms, a voltage difference at the inputs (multiplied by the gain) can
create a voltage step on the output and consequently a pop noise.
To avoid this issue during the starting phase, the TS4621B accelerates the charging of the
input capacitors by reducing the input impedance to 2 kΩ.
In such a case, for a 1 μF capacitor the 95 % charge is reached in 6 ms. As the start-up time
of TS4621B is 12 ms, there remains sufficient time to fully charge the input capacitors and
as such eliminate any pop noise.
4.7 Layout recommendations
Particular attention must be given to the correct layout of the PCB traces and wires between
the amplifier, load and power supply (in most cases, the battery of the cellular phone).
The power and ground traces are critical since they must provide adequate energy and
grounding for all circuits. Good practice is to use short and wide PCB traces to minimize
voltage drops and parasitic inductance.
A track with a width of at least 200 μm for a copper thickness of 18 μm is recommended for
bringing energy to the amplifier from the battery.
Proper grounding guidelines help improve audio performances, minimize crosstalk between
channels, and prevent switching noise from coupling into the audio signal. It is also
recommended to use a large-area and multi-via ground plane to minimize parasitic
impedance.
A multi-layer PCB board allows double or multiple ground planes to be implemented. Most of
the time, the top and bottom layers are used as ground planes and provide shielding for
tracks routed on the intermediate layers. In addition, to minimize parasitic impedance over
the entire surface, a multi-via technique that connects the bottom and top layer ground
planes together in many locations is often used.
The copper traces that connect the output pins to the load and supply pins should be as
wide as possible to minimize the trace resistances.
40/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
4.7.1 Common mode sense layout
The TS4621B implements a common-mode sense pin to correct any voltage differences
that might occur between the return of the headphone jack and the AGND of the device that
can create parasitic noise in the headphone and/or line out.
The solution to strongly reduce and practically eliminate this noise consists in connecting
the headphone jack ground to the CMS pin. This pin senses the difference of potential
(voltage noise) between the TS4621B ground and the headphone ground. Thanks to the
frequency response and the attenuation of the common-mode sense pin, this noise is
removed from the TS4621B outputs.
Figure 83. Common mode sense layout example
Common mode
sense pin
Output jack
connector
Ground plane
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 41/48

Application information TS4621B
4.8 Demonstration board
A demonstration board is available at www.st.com with the order code STEVAL-CCA025V1.
The following figures show the demonstration board schematics and associated PCB
layouts.
Figure 84. Demonstration board schematic
-
+
+
-
Negative
supply
Vcc
A2 A1
AVdd
C3
2.2
Gnd
Level
detector
Level
detector
µF
C1
2.2
Positive
supply
µF
AGndC1 C2
Gnd
HPVdd
L1
3.3 uH
Sw
HpVdd
B1
VoutL
CMS
VoutR
B3
C8
µF
10
Gnd
A3
C3
D3
Gnd
C9
2.2 nF
R1
12
Gnd
R2
12
Gnd
C10
2.2 nF
Gnd
Cn4
Left output
J1
3
2
1
Cn5
Right output
Gnd
TS4621B main application
Cn1
Power
Cn2
Cn9
VccI2C
Gnd
Gnd
Left Input
Gnd
Right input
Cn3
C4
2.2
C5
2.2
C6
2.2
C7
2.2
SDA
SCL
U1
TS4621B
µF
µF
µF
µF
InL-
A4
InL+
B4
InR+
C4
InR-
D4
SDA
D1
I2C
SCL
D2
PVss
C2 B2 C1
C2
µF
2.2
Gnd
J2
DB9
5
9
4
8
3
7
2
6
1
GND
DTR
TXD
RTS
DSR
Cn6
VccI2C
Cn8
VccI2C
R4
180
U2A
16
15
KP1040
R3
1K
R8
2k2
R9
1K
D1
1N4148
D2
1N4148
1
2
GndGND2
GndQ1Gnd
3
4
GND2
5
6
GND2
U2B
KP1040
U2C
KP1040
SCL
Q3
Q2
Gnd
Cn7
SCL SDA
SDA
R5
100
14
13
Gnd
12
11
Gnd
Vcc
R6
R7
10K
10K
RS-232 to I2C converter
AM06156
42/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Application information
Figure 85. Copper layers
Top layer Mid layer 1
Figure 86. Copper layer and overlay layers
Bottom layer Top overlay
Mid layer 2
Bottom overlay
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 43/48

Package information TS4621B
k
5 Package information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
Figure 87. TS4621B footprint recommendation
PCB pad size: Φ = 260 µm maximum
Solder mask opening: Φ = 300 μm min
(for 260 µm diameter pad)
Φ = 220 µm recommended
Not soldered
mask opening
400 μm
400 μm
400 μm
400 μm
75 µm min.
100 μm max.
Trac
150 μm min.
Figure 88. Pinout
TOP VIEW (balls are underneath)
INR -
INR+
INL+
INL -
4 3 21
VOUTR
CMS
HPVDD
VOUTL
SCL
PVSS
C1
AVDD
Pad in Cu 18 μm with Flash NiAu (2-6 μm, 0.2 μm max.)
BOTTOM VIEW
SDA
C2
AGND
SW
D
D
C
B
A
SDA
C2
C
AGND
B
SW
A
123 4
SCL
PVSS
C1
AVDD
VOUTR
CMS
HPVDD
VOUTL
INR -
INR+
INL+
INL -
44/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Package information
Figure 89. Marking (top view)
■ Logo: ST
■ Symbol for lead-free: E
■ Part number: 21
■ X digit: Assembly code
■ Date code: YWW
■ The dot marks pin A1
Figure 90. Flip-chip - 16 bumps
1650 μm
400 μm
400 μm
1650 μm
E
E
21X
21X
YWW
YWW
■ Die size: 1.65 mm x 1.65 mm ± 30 µm
■ Die height (including bumps): 600 µm
±55 µm
■ Bump diameter: 250 µm ±40 µm
■ Bump height: 205 µm ±35 µm
■ Die height: 395 µm ±20 µm
■ Pitch: 400 µm ±40 µm
■ Coplanarity: 50 µm max
600 μm
Figure 91. Device orientation in tape pocket
4
1
A
8
Die size Y + 70 µm
Die size X + 70 µm
4
All dimensions are in mm
User direction of feed
1.5
1
A
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 45/48

Ordering information TS4621B
6 Ordering information
Table 16. Order codes
Order code Temperature range Package Packing Marking
TS4621BEIJT -40°C to +85°C Flip-chip Tape & reel 21
46/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2

TS4621B Revision history
7 Revision history
Table 17. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
06-Sep-2011 1 Initial release.
12-Sep-2011 2
Updated Table 10: Summary of control registers on page 25
Updated Section 4.1.2: Control register CR1 - address 1 on page 27
Doc ID 022194 Rev 2 47/48

TS4621B
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2011 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
48/48 Doc ID 022194 Rev 2
 Loading...
Loading...