ST STP21NM50N, STF21NM50N, STW21NM50N, STB21NM50N, STB21NM50N-1 User Manual

STB21NM50N
STP21NM50N-STF21NM50N-STW21NM50N STB21NM50N - STB21NM50N-1
N-CHANNEL 500V - 0.15Ω - 18A TO-220/FP/D2/I2PAK/TO-247 SECOND GENERATION MDmesh™ MOSFET
Table 1: General Features
TYPE |
VDSS |
RDS(on) |
ID |
|
(@Tjmax) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
STB21NM50N |
550 V |
< 0.19 Ω |
18 A |
STB21NM50N-1 |
550 V |
< 0.19 Ω |
18 A |
STF21NM50N |
550 V |
< 0.19 Ω |
18 A (*) |
STP21NM50N |
550 V |
< 0.19 Ω |
18 A |
STW21NM50N |
550 V |
< 0.19 Ω |
18 A |
|
|
|
|
■100% AVALANCHE TESTED
■LOW INPUT CAPACITANCE AND GATE CHARGE
■LOW GATE INPUT RESISTANCE
DESCRIPTION
The STx21NM50N is realized with the second generation of MDmesh Technology. This revolutionary MOSFET associates a new vertical structure to the Company's strip layout to yield one of the world's lowest on-resistance and gate charge. It is therefore suitable for the most demanding high efficiency converters
APPLICATIONS
The MDmesh™ II family is very suitable for in - creasing power density of high voltage converters allowing system miniaturization and higher efficiencies.
Table 2: Order Codes
Figure 1: Package
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
|
3 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
D2PAK |
TO-220 |
|
TO-220FP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
I2PAK |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
TO-247 |
Figure 2: Internal Schematic Diagram
|
SALES TYPE |
MARKING |
PACKAGE |
PACKAGING |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STB21NM50N |
B21NM50N |
D2PAK |
TAPE & REEL |
|
|
STB21NM50N-1 |
B21NM50N |
I2PAK |
TUBE |
|
|
STF21NM50N |
F21NM50N |
TO-220FP |
TUBE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STP21NM50N |
P21NM50N |
TO-220 |
TUBE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STW21NM50N |
W21NM50N |
TO-247 |
TUBE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rev. 3 |
|
|
October 2005 |
|
|
1/16 |
|

STP21NM50N - STF21NM50N - STB21NM50N - STB21NM50N-1 - STW21NM50N
Table 3: Absolute Maximum ratings
Symbol |
Parameter |
Value |
|
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO-220 / D2PAK / I2PAK |
|
TO-220FP |
|
|
|
/ TO-247 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VDS |
Drain-source Voltage (VGS = 0) |
500 |
|
|
V |
VDGR |
Drain-gate Voltage (RGS = 20 kΩ ) |
500 |
|
|
V |
VGS |
Gatesource Voltage |
±25 |
|
|
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ID |
Drain Current (continuous) at TC = 25°C |
18 |
|
18 (*) |
A |
ID |
Drain Current (continuous) at TC = 100°C |
11 |
|
11 (*) |
A |
IDM ( ) |
Drain Current (pulsed) |
72 |
|
72 (*) |
A |
PTOT |
Total Dissipation at TC = 25°C |
140 |
|
30 |
W |
|
Derating Factor |
1.12 |
|
0.23 |
W/°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
dv/dt(1) |
Peak Diode Recovery voltage slope |
15 |
|
|
V/ns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Viso |
Insulation Winthstand Voltage (DC) |
-- |
|
2500 |
V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tstg |
Storage Temperature |
–55 to 150 |
|
°C |
|
Tj |
Max. Operating Junction Temperature |
150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
( ) Pulse width limited by safe operating area
(*) Limited only by maximum temperature allowed
(1) ISD ≤ 18 A, di/dt ≤ 400 A/µs, VDD =80% V(BR)DSS
Table 4: Thermal Data
|
|
TO-220 / D²PAK / I²PAK |
|
TO-220FP |
|
|
|
/ TO-247 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rthj-case |
Thermal Resistance Junction-case Max |
0.89 |
|
4.21 |
°C/W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rthj-amb |
Thermal Resistance Junction-ambient Max |
62.5 |
|
°C/W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tl |
Maximum Lead Temperature For Soldering |
300 |
|
°C |
|
|
Purpose |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 5: Avalanche Characteristics
Symbol |
Parameter |
Max Value |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
IAS |
Avalanche Current, Repetitive or Not-Repetitive |
9 |
A |
|
(pulse width limited by Tj max) |
|
|
EAS |
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy |
480 |
mJ |
|
(starting Tj = 25 °C, ID = IAR, VDD = 50 V) |
|
|
2/16

STP21NM50N - STF21NM50N - STB21NM50N - STB21NM50N-1 - STW21NM50N
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (TCASE =25°C UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED)
Table 6: On/Off
Symbol |
Parameter |
Test Conditions |
|
Value |
|
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min. |
Typ. |
Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V(BR)DSS |
Drain-source |
ID = 1mA, VGS = 0 |
500 |
|
|
V |
|
Breakdown Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
dv/dt(2) |
Drain Source Voltage |
Vdd=400V, Id=25A, Vgs=10V |
|
44 |
|
V/ns |
|
Slope |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IDSS |
Zero Gate Voltage |
VDS = Max Rating |
|
|
1 |
µA |
|
Drain Current (VGS = 0) |
VDS = Max Rating |
|
|
10 |
µA |
|
|
TC = 125 °C |
|
|
|
|
IGSS |
Gate-body Leakage |
VGS = ± 20V |
|
|
100 |
nA |
|
Current (VDS = 0) |
|
|
|
|
|
VGS(th) |
Gate Threshold Voltage |
VDS = VGS, ID = 250 µA |
2 |
3 |
4 |
V |
RDS(on) |
Static Drain-source On |
VGS = 10V, ID = 9 A |
|
0.150 |
0.190 |
Ω |
|
Resistance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) Characteristic value at turn off on inductive load
Table 7: Dynamic
Symbol |
Parameter |
Test Conditions |
Min. |
Typ. |
Max. |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
gfs (1) |
Forward Transconductance |
VDS = 15 V, ID = 9 A |
|
12 |
|
S |
Ciss |
Input Capacitance |
VDS = 25V, f = 1 MHz, VGS = 0 |
|
1950 |
|
pF |
Coss |
Output Capacitance |
|
|
420 |
|
pF |
Crss |
Reverse Transfer |
|
|
60 |
|
pF |
|
Capacitance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coss eq. (*) |
Equivalent Output |
VGS = 0V, VDS = 0V to 400V |
|
270 |
|
pF |
|
Capacitance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
td(on) |
Turn-on Delay Time |
VDD =250 V, ID = 9 A |
|
22 |
|
ns |
tr |
Rise Time |
RG = 4.7Ω VGS = 10 V |
|
18 |
|
ns |
td(off) |
Off-voltageRise Time |
(see Figure 18) |
|
90 |
|
ns |
tf |
Fall Time |
|
|
30 |
|
ns |
Qg |
Total Gate Charge |
VDD = 400V, ID = 18 A, |
|
65 |
|
nC |
Qgs |
Gate-Source Charge |
VGS = 10V, |
|
10 |
|
nC |
Qgd |
Gate-Drain Charge |
(see Figure 21) |
|
30 |
|
nC |
Rg |
Gate Input Resistance |
f=1MHz Gate DC Bias=0 |
|
1.6 |
|
Ω |
|
|
Test Signal Level=20mV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Open Drain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(*) Coss eq. is defined as a constant equivalent capacitance giving the same charging time as Coss when VDS increases from 0 to 80% VDSS
Table 8: Source Drain Diode
Symbol |
Parameter |
Test Conditions |
Min. |
Typ. |
Max. |
Unit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISD |
Source-drain Current |
|
|
|
18 |
A |
ISDM |
Source-drain Current (pulsed) |
|
|
|
72 |
A |
VSD (1) |
Forward On Voltage |
ISD = 18 A, VGS = 0 |
|
|
1.5 |
V |
trr |
Reverse Recovery Time |
ISD = 18 A, di/dt = 100 A/µs |
|
360 |
|
ns |
Qrr |
Reverse Recovery Charge |
VDD = 100 V, Tj = 25°C |
|
5 |
|
µC |
IRRM |
Reverse Recovery Current |
(see Figure 19) |
|
27 |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
trr |
Reverse Recovery Time |
ISD = 18A, di/dt = 100 A/µs |
|
640 |
|
ns |
Qrr |
Reverse Recovery Charge |
VDD = 100 V, Tj = 150°C |
|
6.5 |
|
µC |
IRRM |
Reverse Recovery Current |
(see Figure 19) |
|
27 |
|
A |
Note: 1. Pulsed: Pulse duration = 300 µs, duty cycle 1.5 %.
3/16

STP21NM50N - STF21NM50N - STB21NM50N - STB21NM50N-1 - STW21NM50N
Figure 3: Safe Operating Area For TO-220 |
Figure 6: Thermal Impedance For TO-220 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 4: Safe Operating Area For TO-220FP |
Figure 7: Thermal Impedance For TO-220FP |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 5: Output Characteristics |
Figure 8: Transfer Characteristics |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4/16
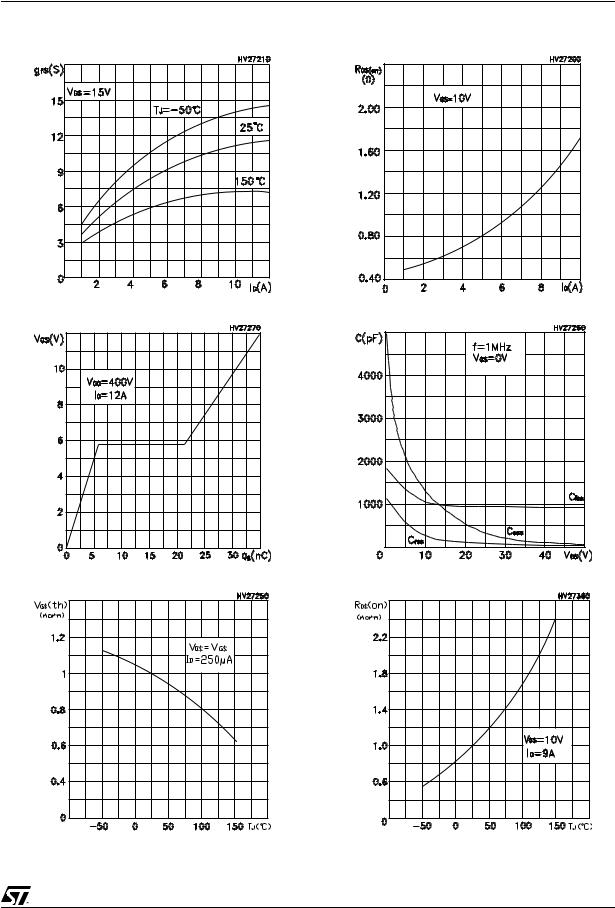
STP21NM50N - STF21NM50N - STB21NM50N - STB21NM50N-1 - STW21NM50N
Figure 9: Transconductance
Figure 10: Gate Charge vs Gate-source Voltage
Figure 11: Normalized Gate Threshold Voltage vs Temperature
Figure 12: Static Drain-source On Resistance
Figure 13: Capacitance Variations
Figure 14: Normalized On Resistance vs Temperature
5/16
 Loading...
Loading...