
®
120-MHz On-Screen Display for Monitors including
PictureBooST
Main Features
■ Horizontal frequency up to 150 kHz
■ I²C interface for microcontrollers with slave
address BA(h) in Read and Write modes
TM
and 4 True Independent Window Displays
STV9937
DATASHEET
PictureBoost
■ Pixel clock (F
ä
PIXEL1
) for the PictureBooSTä
(PB) from 30 to 60 MHz synchronised either
on Hsync or on Hfly: CLK1
■ Window position programmable by RGB or
2
I
C interface
■ Video Analog inputs with comparator on
three channels
■ Three 8 bit registers for other data,
programmable by RGB
OSD
■ On-chip Pixel Clock Generat or (F
PIXEL2
7.68 MHz to 120 MHz, CLK2
■ OSD clock synchronized on Hsync or Hfly
■ Programmable horizontal resolutions from
384 to 1524 dots per scan line
■ 4 independent windows all with character
display
■ Overlapping windows with automatic control
of display priorities and scrolling menu
effects
■ Independent and programmable displays,
positions and sizes for each window
■ Transparent or 8 programmable background
colors for each window
■ Window size up to 16 rows of 32 characters
■ Each window has its own bordering or
shadowing effects with programmable color,
height and width
) from
PDIP 24 (Plastic Dual In line Shrink Package)
ORDER CODE: STV9937P/AA
■ 496 standard and 16 multi-color characters or
graphic fonts in ROM. Character fonts can be
customized using a mask-programmable
ROM
■ Characters
● Common character height and ro w spa ce.
Character height from 18 to 127 lines and
space lines from 0 to 62 spli t abo v e and bel o w
character rows
● 12 x 18 dot matrix per character
● Display of up to 640 characters
● Programmable shadow effects for characters
in each separate window
● 32 programmable background, foreground,
blinking character colors for character s (8
possibilities per window)
● 8 selectable colors for standard characters
● Transparent and 8 selectable colors for
background
■ On-Screen Effects
● Fade-in/Fade-out effects
● Possibility of full-screen display with a
selectable color
■ Each window can be separately erased
■ Programmable common positioning to easily
control centered display
February 2004 1/49

STV9937
Chapter 1 General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.1 Pin Descript io n ................................................................................. .. .. ..............................7
Chapter 2 Register Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
2.1 I²C Protocol ......................................................... .. .. ........................... .. .. ............. ... .. ............9
2.1.1 Data to Write .........................................................................................................................................................9
2.1.2 Transmission Formats ...................................... ....................................... ..............................................................9
2.1.3 Format, Window and Row Address (FWR) .........................................................................................................10
2.1.4 Format, Attribute and Column Address (FAC) ....................................................................................................10
2.1.5 Control Data, Color Codes or Character Codes .................................................................................................11
2.1.6 Configuration of Transmission Formats .............................................................................................................11
2.2 Format Chang ing ................. .......................... ... .. ............. .. .. ........................... .. .. ...............11
To change from Format A to Format B ...............................................................................................................11
To change from Format A to Format C ...............................................................................................................11
To change from Format B to Format A ...............................................................................................................11
To change from Format B to Format C ...............................................................................................................12
2.3 Read Mode ....................... ............................. .. ............................. .. ....................................12
2.4 Addressing Ma p . .. ..............................................................................................................12
Chapter 3 Window Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.1 Enable Display ...................................................................................................................14
3.2 Origin Positions for the 4 Wind ows .......... .. ........................................................................14
3.2.1 General Horizontal Delay (HD) ...........................................................................................................................14
3.2.2 General Vertical Delay (VD) ................................................................................................................................14
3.3 Window Positions in the Frame ................................... .. .......................... ...........................15
3.3.1 Window Horizontal Delay ....................................................................................................................................15
3.3.2 Window Vertical Delay ........................................................................................................................................15
3.4 Window Size: Number of Characte r Rows and Character Columns ............................. .. ...16
3.4.1 Window Horizontal Size ......................................................................................................................................16
3.4.2 Window Vertical Size ..........................................................................................................................................16
3.5 Window Background Color ......... ................................................................................. .......17
3.6 Window Bordering and Shadowing Effects ........................... ....................... .. ....................17
3.6.1 Enable Bordering or Shadowing Effects .............................................................................................................17
3.6.2 Bordering or Shadowing Selection .....................................................................................................................17
3.6.3 Border or Shadow Color .....................................................................................................................................18
3.6.4 Bordering or Shadowing Size .............................................................................................................................18
3.7 Window Display Priority Management .............................. ...................... ...................... .. ...19
Chapter 4 Character Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
4.1 General Description ....................................................................... ....................... .............20
4.2 Horizontal R e so l u tio n ......................... ... .. ..........................................................................20
4.3 Character Height ...............................................................................................................20
2/49

STV9937
4.4 Space Lines .......................................................................................................................21
4.5 Character Colors ................................................................................................................22
4.5.1 Character Background Color ..............................................................................................................................22
4.5.2 Character Color ...................................................................................................................................................23
4.5.3 Character Blinking Effect ....................................................................................................................................24
4.6 Character Shadowing .................................................... .. ............................................ .. .....24
4.7 Character Font ...................................................................................................................25
Chapter 5 RAM Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
5.1 Character Coding ...............................................................................................................26
5.2 Window Memory Allocation ............................................................. .. ............................ .. ...26
5.3 Memory Size Allocation ......................................................................................................26
5.4 Window Reset ............................................... .. ............................... ....................................28
Chapter 6 Pixel Clock Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Chapter 7 Picture BooSTTM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
7.1 Video RGB Input Stage ......................................................................................................30
7.2 PictureBooSTTM RGB Decoder ........................................................................................31
7.2.1 Data Sent Using I²C ............................................................................................................................................31
7.2.2 Data Sent Using the RGB Channel ....................................................................................................................31
7.3 Control Reg is te r s D e s cr ip tion ................ .. ............. .. .. .............. .. .. ........................... .. .. ........33
7.4 Line and Pixel O ff s ets .......... .. ........................................ .. .. ........................... .. .. .................34
7.5 PLL Synchronised ..............................................................................................................34
Chapter 8 General OSD Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
8.1 Enable OSD .......................................................................................................................35
8.2 Fade-in and Fade-out Effect ....................... ........................ ...............................................35
8.3 Full Screen Display ..................................... .................. .................. ................... ................35
8.4 Signal Polarity and Triggering ...........................................................................................36
Vertical Sync Triggering (VS input) .....................................................................................................................36
Horizontal Sync Triggering (HSYNC input) .........................................................................................................36
RGB Output Polarity (ROUT, GOUT and BOUT outputs) ...................................................................................36
Fast Blanking Output Polarity (FBLK output) ......................................................................................................37
8.5 Reset ..... ............... ................ ............. ................ ............... ................ ............. .....................37
Power On Reset .................................................................................................................................................37
Soft Reset ...........................................................................................................................................................37
PLL Register Reset .............................................................................................................................................37
Chapter 9 Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
3/49

STV9937
9.1 Register Specification ........................................................................................................38
Chapter 10 Application Hints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
10.1 Software Hints .............................................................. .. .. ..................................................42
10.1.1 Programming Recommendations .......................................................................................................................42
10.1.2 Examples of Programming ..................................................................................................................................42
Hard reset at power-up (following a power-up) ...................................................................................................42
Change of position & size of 1 window (ex. window 3) without disable of window .............................................42
Re-allocation, reset, and writing new characters in windows ..............................................................................43
10.2 Hardware Hints ..................................................................................................................43
Chapter 11 Application Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Chapter 12 Electrical and Timing Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
12.1 Absolute Max im u m Ratings ............ .. ..................................................... .. ... .......................45
12.2 Operating Co nd itions ............. .. ..................................................... ... .. .......................... .. ....45
12.3 Electrical and Timing Characteristics ........................................................ .........................45
12.4 I²C Bus Characteristics .................................. ... .. .......................... ... .. .......................... .. ....46
Chapter 13 Package Mechanical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Chapter 14 Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
4/49

STV9937 General Description
1 General Description
The STV9937 is an Advanced On Screen Dis pla y gener ator for CR T monit ors . It in cludes a speci fic
architecture allowing mul tiple menu displays, a built in 512 charact e r ROM and the Picture
BooST
The patented Picture BooST
screen area or even over the entir e screen.
TM
system.
TM
feature allows images to be boosted either within a window, a
Using traditional architecture (OSD + Preamp STV9212) and without any additional devices on the
TM
CRT board, Picture BooST
boosts the brightness and sharpness of the video on CRT displays
giving a TV like effect.
TM
The STV9937 can drive Picture BooST
either through the VGA cable (using RGB or DDC),
through the USB channel via the MCU or through the OSD menu (the registers can be accessed b y
the MCU via I²C).
TM
The STV9937 embeds the RGB data decoder, the Pic tur e BooST
Picture BooST
Along with the Picture BooST
TM
signal generator.
TM
and traditional OSD features, the STV9937 allows a simultaneous
Control Registers and the
display of up to four menus anywhere on the screen. Each of the four independent windows, all
displaying characters, can be overlapped and display priorities are automatically controlled.
● Window sizes and posit i ons are i ndependentl y prog r ammable as well as scrol ling men u ef fects.
● Programming of the general OSD and of the 4 windo ws is controll ed b y an I²C bus in Re ad and
Write modes, to suit the various CRT displays.
● Associated with an easily programmable character height, the internal PLL generates the
programmable pixel clock, without using a crystal oscillator, that defines the character width
making the device suitable for multi-sync applications.
● A maximum of 640 charac ters, defi ned in the mask-pr ogrammab le R OM, are distrib uted among
the 4 windows and displayed simultaneously.
Figure 1: Multi-window Concept with Character Display
5/49
General Description STV9937
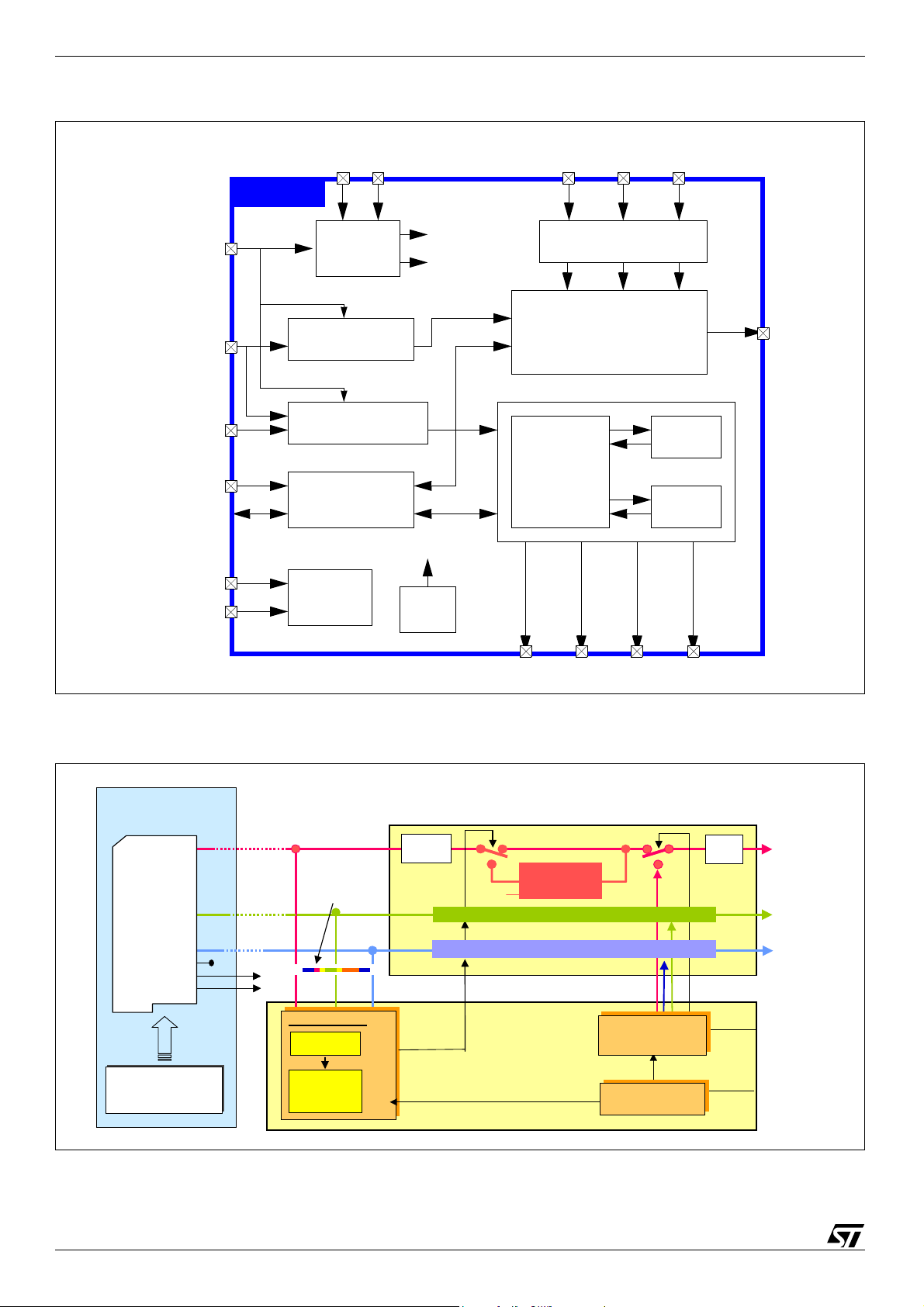
Figure 2: STV9937 Block Diagram
STV9937
HSYNC
TEST1
TEST2
VS
HFLY
SCL
SDA
STV9937
PB Sequencer
OSD Sequencer
I2C Interface
And Registers
Test
RPVCO
PLL
Reset Signals
OSD Pixel Clock
PB Pixel Clock
Reset
RIN GIN
RGB Input Buffer
Picture BooST
Decoder and Generator
4 Windows
OSD
Generator
BIN
TM
PB
RAM
ROM
ROUT
ContrastContrast
TM
System Block Diagram
I2C
PreAmplifier: STV9212
OSD: STV9937
Figure 3: PictureBooST
Computer main Unit Monitor CRT board
4
2
P
I
D
S
PictureBooST™
Video Card
DDC
H Sync
V Sync
Picture booST ™
Picture booST ™
Window ™ Software
Window ™ Software
I
D
Color code
R G B Boost OSD FBlk
4
2
P
PictureBooST ™
Decoder
Window
Coordinate
register
GOUT BOUT FBLK
Boost gain
& Sharpness
OSD
OSD
generator
generator
Line PLLLine PLL
Video Amplifier AC or DC
DriveDrive
H Fly
H Sync
6/49

STV9937 General Description
1.1 Pin Description
Figure 4: Pin Connections
AVSS
RP
VCO
AVDD
TEST1
TEST2
HFLY
VS
HSYNC
SDA
SCL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
IVSS
BIN
GIN
RIN
IVDD
DVDD
DVSS
PB
BOUT
GOUT
ROUT
FBLK
Table 1: Pin Descriptions
N° Pin Name Direction Digital/Analog Function
1 AVSS - Supply Analog Ground
2 RP I/O Analog for VCO
3 VCO I/O Analog for VCO
4 AVDD - Supply Analog Power Supply
5 TEST1 Input Digital Remains at 0 (for test purposes only)
6 TEST2 Input Digital Remains at 0 (for test purposes only)
7 HFLY Input Digital Horizontal Flyback Input
8 VS Input Digital Vertical Synchronization Input
9 HSYNC Input Digital Hor i zontal Synchronization Input
10 SDA I/O Digital Serial Data of I²C bus
11 SCL Input Digital Serial Clock of I²C bus
11 DVDD - Supply Digital Power Supply
12 N/C - - 13 FBLK Output Digit al Fast Blanking Output
14 ROUT Output Digital OSD Red Color Output
15 GOUT Output Digital OSD Green Color Output
16 BOUT Output Digital OSD Blue Color Output
17 PB Output Digital
18 DVSS - Supply Digital Ground
PictureBooST
7/49
TM
Output

General Description STV9937
Table 1: Pin Descriptions (Continued)
N° Pin Name Direction Digital/Analog Function
19 DVDD - Supply Digital Power Supply
20 IVDD - Supply Power Supply for Video Input
21 RIN Input Analog VGA Signal Input, Red Channel
22 GIN Input Analog VGA Signal Input, Green Channel
23 BIN Input Analog VGA Signal Input, Blue Channel
24 IVSS - Supply Ground for Video Input
8/49

STV9937 Register Addressing
2 Register Addressing
All OSD control registers are located in Wi ndow 0, Row 0. PictureBooSTTM control registers are
located in Window 0, Row 1. All color-boxes data are located in Window 0, Row 2.
Three formats are available: A, B and C, as described in the I²C protocol (see Section 2.1: I²C
Protocol).
All addresses (FAC and FWR bytes) are based on Formats A or B, and are written in hexadecimal
format.
2.1 I²C Protocol
The serial interface with t he microcontroller is an I²C bus with 2 wires: SCL and SD A. The OSD is a
slav e circuit with 2 modes: Write and Read. The sla v e address of the OSD is BAh in write mode and
BBh in read mode.
2.1.1 Data to Write
In the OSD, the I²C bus is used to write - read:
● the contro l data
● the character codes and their respective color codes
● the color-boxes (8 color-boxes per window).
A color-box contains the character color, character background color and blink data. There are 8
color-boxes for each OSD window which are used to define the colors available for all the
characters of the given OSD window. 3 bits are required to code the 8 color-boxes. These bits are
the color code.
For more information, refer to Section 4.5: Character Colors on page 22.
Each character code is related to its own window, row and column. Consequently, the protocol of
the I²C transmission inclu des this information (window, ro w and column) to define the position of t he
character on the screen. These 3 piec es of information about the position are tr ansmitted in 2 b ytes .
As each character on the screen has its own color code, the same protocol is used to write all the
color codes and character codes. Only the attribute bit called ‘A’ allows the character codes to be
distinguished from the color co des corresponding to one position on the screen.
The control data is also written with the same protocol using windows, rows and columns. Window
0 is reserved for control data and color codes.
2.1.2 Transmission Formats
There are 3 transmission formats to suit the amount of data to update. The transmission format is
coded in the “window/row/column” bytes.
Format A is suitab le for updating small amounts of data whi ch are allocated to different windo w, row
and column addresses.
Format B is recommended for updating data for the same window and the same row address, but
with a different column address and when changing the Character/Color-box attribute (bit A), or
when writing to a different I²C control register.
Format C is appropriate for updating large amounts of data from a full window or full screen. The
window, row and column addresses are incremented automatically when this format is applied.
Data is written to fill all the allocation memory of the windows .
9/49

Register Addressing STV9937
The transmission formats are as follows:
1. Format A: S-FWR-FAC-D
® FWR-FAC-D ® FWR-FAC-D ® FWR-FAC-D...Stop
2. Format B: S-FWR-FAC-D
3. Format C: S-FWR-FAC-D
® FAC-D ® FAC-D ® FAC-D...Stop
® D ® D ®D...Stop
Where:
S = Slave address = BAh
FWR = Format, Window and Row address
FAC = Format, Attribute and Column address
D = CTRL Control data (8 bits), CB Color codes (3 bits) or RC Character codes (9 bits).
In Format C, t he order of automati c incrementat ion for data D i s first t he column v alue , then t he ro w
value, and then the window value.
Table 2: Various Bytes coded in the I²C Transmission
Byte Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
FWR
FAC
D: Control Data (in window 0 only) CTRL[7:0]
D: Color Code and Character Code MSB 0 0 0 RC[8] 0 CB[2:0]
D: Character Code LSBs RC[7:0]
1
0
W[2:0] R[3:0]
F A C[4:0]
2.1.3 Format, Window and Row Address (FWR)
Bit 7 indicates the ‘Window & Row’ byte when set to 1.
W[2:0]: Window Number
000: Control Data and Color Codes
001: Window 1
010: Window 2
011: Window 3
100: Window 4
R[3:0]: Row Numbers from 0 to 15. Each window has a maximum number of 16 rows.
2.1.4 Format, Attribute and Column Address (FAC)
Bit 7 indicates the ‘Attrib ute & Column’ byte when set to 0.
F: Format
0: Format A or B
1: Format C
A: Transmission of character code or color code
0: Character Code
1: Color Code and Character Code MSB
When reading or writing control data and/or character codes, bit A must be set to 0. For color code
and character code MSB, bit A must be set to 1.
10/49

STV9937 Register Addressing
C[4:0]: Column Number
There are 32 possible columns .
00000: 1 column
11111: 32 columns
2.1.5 Control Data, Color Codes or Character Codes
Color codes are stored on 3 bits. Control data is stored on 8 bits and Charact er codes are stored on
9 bits.
2.1.6 Configuration of Transmission Formats
Table 3: Configuration of Transmission Formats
Byte Format Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Address bytes
for Characters
Codes
Address bytes
for Color Codes
Windows & Rows
Column (A and B)
Column (C)
Windows & Rows
Column (A and B)
Column (C)
All formats must start with the S, FWR and FAC bytes.
2.2 Format Changing
To change from Format A to Format B
S-FWR[0]- FAC[0] -D[0] ® FWR[1]- FAC[1]- D[1] ® FWR[2]- FAC[2]- D[2] ® FAC[3]- D[3] ® FAC[4]D[4]
® FAC[5]- D[5]...
The F bit from the FAC byte is alwa ys 0 in this case.
FWR
FAC
FAC
FWR
FAC
FAC
A, B or C 1 W[2:0] R[3:0]
A or B 0 0 0 C[4:0]
C 0 1 0 C[4:0]
A, B or C 1 W[2:0] R[3:0]
A or B 0 0 1 C[4:0]
C 0 1 1 C[4:0]
To change from Format A to Format C
S - FWR[0]- FAC[0]- D[0] ® FWR[1]- FAC[1]- D[1] ® FWR[2]- FAC[2]- D[2] ® D[3] ® D[4] ® D[5]...
The “F” bit from the FAC byte is as follo w s:
F[0] = F[1] = “0”
F[2] = “1”
To change from Format B to Format A
S - FWR[0]- FAC[0]-D[0]® FAC[1]- D[1] ® FAC[2]-D[2] ® FWR[3]- FAC[3]- D[3] ® FWR[4]- FAC[4]D[4]...
The F bit from the FAC byte is alwa ys 0 in this case.
11/49

Register Addressing STV9937
To change from Format B to Format C
S - FWR[0]- FAC[0]- D[0] ® FAC[1]- D[1] ® FAC[2]- D[2] ® D[3] ® D[4]...
The “F” bit from the FAC byte is as follows: F[0] = F[1] = “0” and F[2] = “1”
It is not possible to change from Format C back to Format A or B.
Figure 5: Format Changing Sequences
Start
start
2.3 Read Mode
The transmission format is shown as below:
Start - S(w) - FWR- FAC - Stop - Start - S(r) - D
Where:
S(w) = Slave address in write mode = BAh = 10111010,
S(r) = Slave address in read mode = BBh = 10111011.
Registers and data in RAM are readable.
This mode is useful when developing OSD applications.
2.4 Addressing Map
Format A
Format C
Format B
® D ® D ® D...Stop
Table 4: Window Addressing Map
Window Row Column Data
Window 0 Row 0 Columns 0 to 31 Control Data (8 bits)
Window 0 Row 1 Columns 0 to 31
Window 0 Row 2 Columns 0 to 31 Color-boxes (8 bits)
Windows 1, 2, 3 and 4 Rows 0 to n (n = 15 max.) Columns 0 to m (m = 31 max.) Characters Coding (12 bits)
12/49
PictureBooST
TM
Data

STV9937 Window Specifications
3 Window Specifications
Four different independent windows with separate character displays can be simultaneously
display ed on screen . It is pos sib le to ha v e o v erlapping windo ws with an automat ic control of display
priorities: downscale priorities from Window 4 to Window 1.
Window 1 is well-ad apted for the OSD general menu.
The 4 windows, each with its own character display, can be positioned anywhere on the screen.
The following characteristics are defined for each window:
● Enable Display
● Position
● Size, adjustable with memory allocation
● Background Color
● Bordering or Shadowing effects with programmable color, height and width.
Figure 6: Example of Window Displays
Axis
Origin
Screen
HD
Window 2
VD
Window 1
Window 3
Window 4
13/49

Window Specifications STV9937
3.1 Enable Display
The Enable Display command for each window is selected by bits ENW1, ENW2, ENW3 and
ENW4. If the ENWi bit is set to 1, the corresponding window is displayed.
Table 5: Enable Display
FWR FAC Default Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
80h 07h 0h ENW4 ENW3 ENW2 ENW1
3.2 Origin Positions for the 4 Windows
The 4 windows are arranged in a fr ame whose origin coordinates are t he horizontal dela y ( HD) and
the vertical delay (VD) loc ated at the upper left-hand corner of the monitor screen. When the HD
and VD values are changed, the 4 windows within the frame position are automatically shifted by
the same value. The origin (HD, VD) can be programmed anywhere on the screen. Adjusting the
origin position is used to globally reposition the OSD windows.
The advantages of this system are easi er programming, the possibility to adapt the position of all
windows at a single time without changing the relative position of each window and the possibility
for the user to program all 4 window positions.
3.2.1 General Horizontal Delay (HD)
Table 6: Origin of Windows on Horizontal Axis: Horizontal Delay
FWR FAC Default Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
80h 04h 0h HD[6:0]
The general horizontal delay defines the horizontal position of the origin coordinate f or all four OSD
windows. The horizontal delay is selected by bits HD[6:0].
General Horizontal Offset = 50 pixels
General Horizontal Delay = HD[6:0] x 6 pixels + General Offset (i n pixels)
The default value of the horiz ontal delay is 0h (left-hand side of the moni tor screen).
3.2.2 Gen eral Vertical Delay (VD)
Table 7: Origin of Windows on Vertical Axis: Vertical Delay
FWR FAC Default Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
80h 05h 0h VD[7:0]
The general vertical delay defines the vertical position of the origin coordinate for all four OSD
windows. The v ertical delay is selected by bits VD[7:0] . A general vertical offset of 2 scan lines is
also applied.
The range of the vertical delay is from 2 to 1022 scan lines, in steps of 4 scan lines each.
General Ver tical Delay = VD[7:0] x 4 + 2 (in scan lines)
The default value of the vertical delay is 0h (top of screen).
14/49

STV9937 Window Specifications
3.3 Window Positions in the Frame
All values are referenced to the origin coordinates (HD, VD). For more information, refer to
Figure 6 on page 13.
3.3.1 Window Horizontal Delay
The window horizontal delay defines the horizontal start position for each separate OSD window.
This value is selected by bits HDW1[6:0] , HDW2[6:0], HDW3[6:0] and HDW4[6:0], respectively.
Table 8: Window Horizontal Delay
FWR FAC Default Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
80h
0Ch, 11h,
16h, 1Bh
0h, 20h,
0h, 10h
HDWi[6:0]
The range of the window horizontal delay is from 0 to 1524 pixels, in steps of 12 pixels each.
Window Horizontal Delay = HDWi[6:0] x 12 pixels
The total horizontal delay of a window is:
General Horizontal Delay + HDWi[6:0] x 12 pixels; or,
HD[6:0] x 6 pixels + HDWi[6:0] x 12 pixels + (50 pixels).
The default values for the window horizontal delay for each of the four OSD windows is given in
Table 8.
3.3.2 Window Vertical Delay
The window vertical delay defines the vertical start position for each separate OSD window. This
value is selected by bits VDW1[5:0], VDW2[ 5:0], VDW3[5: 0] and VDW4[5:0], respectively.
Table 9: Window Vertical Delay
FWR FAC Default Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
80h
0Dh, 12h,
17h, 1Ch
0h, 0h,
Ch, Ch
VDWi[5:0]
The range of the window v ertical delay i s from 0 to 63 rows of c haracters, in steps of 1 charact er row
each. It is important to note that the height of each character row is defined by the row height
parameter. For more information, refer to Section 4.4: Space Lines on page 21.
Window Vertical Delay = VDWi[5: 0] x Row_Height
The total vertical delay of a windo w is:
General Ver tical Delay + VDWi[5:0] x Row_Height (in scan lines); or,
(VD[7:0] x 4 + 2) + VDWi[5:0] x Row_Height (in scan lines).
The default values for the window vertical delay for each of the four OSD windows is given in
Table 9.
15/49
 Loading...
Loading...