
STTH16003
High frequency secondary rectifier
Features
■ Combines highest recovery and reverse
voltage performance
■ Ultra-fast, soft and noise-free recovery
■ Insulated package: ISOTOP
– insulated voltage: 2500 V rms
– capacitance: < 45 pF
■ Low inductance and low capacitance allow
simplified layout
Description
Dual rectifiers suited for switch mode power
supply and high frequency DC to DC converters.
Packaged in ISOTOP, this device is intended for
use in low voltage, high frequency inverters, free
wheeling operation, welding equipment and
telecom power supplies.
A1
A2
K1
K2
A2
ISOTOP™
STTH16003TV1
Table 1. Device summary
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
T
j
(typ) 0.95 V
V
F
(typ) 80 ns
t
rr
K1
K2
A1
2 x 60 A
300 V
150 °C
TM: ISOTOP is a registered trademark of
STMicroelectronics
June 2008 Rev 5 1/7
www.st.com
7
Characteristics STTH16003
1 Characteristics
Table 2. Absolute ratings (limiting values, per diode, T
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
= 25 °C unless otherwise stated)
amb
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
I
RSM
T
Table 3. Thermal parameters
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 300 V
RMS forward current 180 A
Average forward current Tc = 85°C δ = 0.5
Per diode
Per device
Surge non repetitive forward current tp = 10 ms Sinusoidal 800 A
Non repetitive peak reverse current tp = 100 µs square 5 A
Storage temperature range -55 to + 150 °C
stg
Maximum operating junction temperature 150 °C
T
j
60
160
Symbol Parameter Maximum Unit
Per diode 0.7
R
R
th(j-c)
th(c)
Junction to case
Coupling 0.1
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously:
Δ T
j (diode1)
Table 4. Static electrical characteristics (per diode)
= P
(diode1)
x R
th(j-c) (per diode)
+ P
(diode2)
x R
th(c)
A
°C/WTotal 0.4
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ Max. Unit
(1)
I
R
V
1. Pulse test: tp = 5 ms, δ < 2 %
2. Pulse test: tp = 380 µs, δ < 2 %
Reverse leakage current
(2)
Forward voltage drop
F
1. to evaluate the maximum conduction losses use the following equation:
P = 0.75 x I
F(AV)
+ 0.0025 I
F2(RMS)
T
= 25 °C
j
= 125 °C 0.2 2
T
j
T
= 25 °C
j
= 125 °C 0.8 0.95
T
j
= 300 V
V
R
= 80 A
I
F
200 µA
1.2
2/7
mA
V
STTH16003 Characteristics
Table 5. Recovery characteristics
Symbol Parameter
t
Reverse recovery time Tj = 25 °C
rr
Forward recovery time
t
fr
V
I
S
Forward recovery voltage 5 V
FP
Reverse recovery current
RM
factor
T
Tj = 125 °C
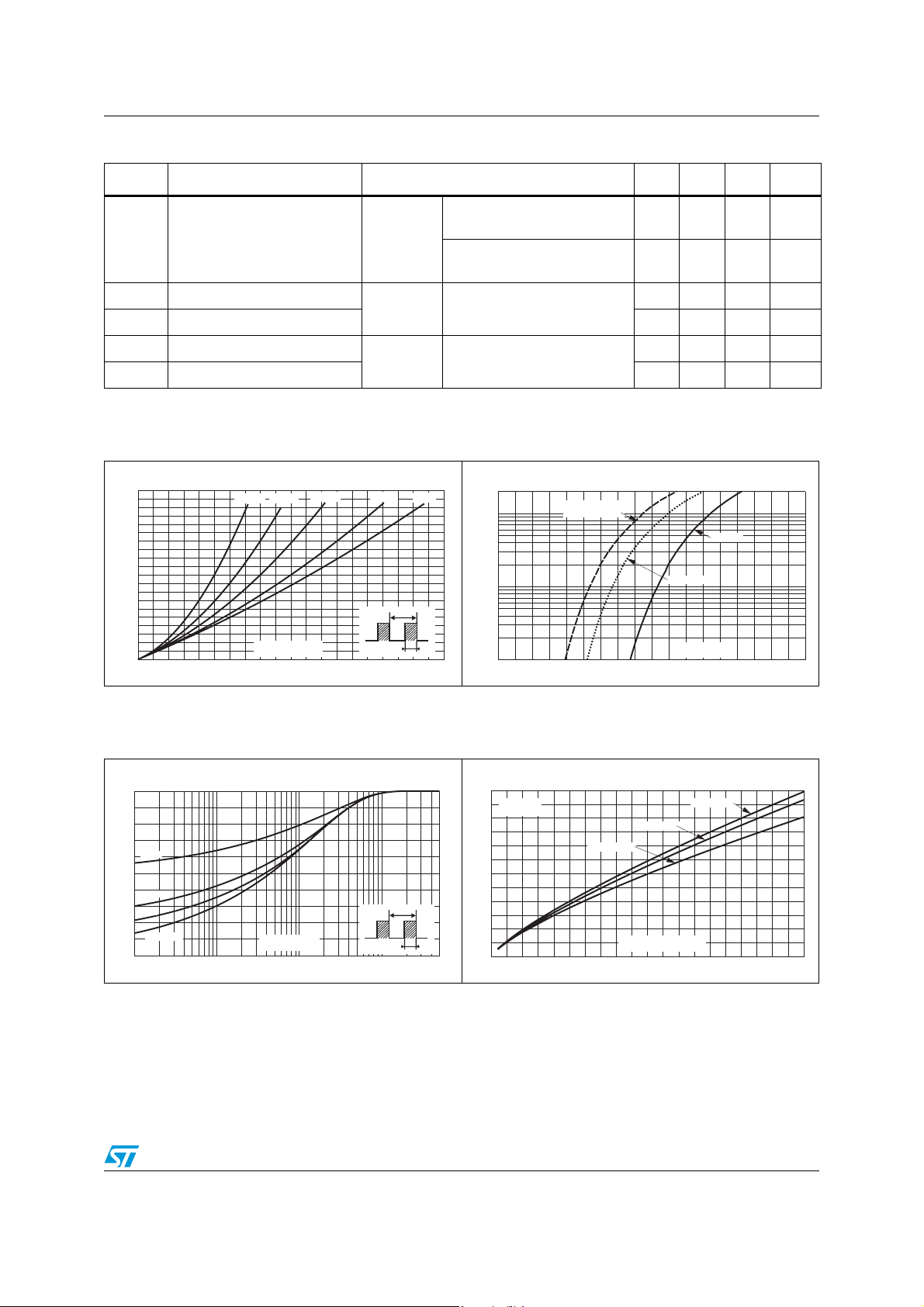
Figure 1. Conduction losses versus
average current (per diode)
= 25 °C
j
Test conditions
I
= 0.5 A, Irr = 0.25 A
F
Min. Typ Max. Unit
IR = 1 A
= 1 A, dIF/dt = 50 A/µs,
I
F
= 30 V
V
R
= 80 A dIF/dt = 200 A/µs
I
F
VFR = 1.1 x V
I
= 60 A, dIF/dt = 200 A/µs,
F
Vcc = 200 V
Fmax
0.3 -
Figure 2. Forward voltage drop versus
forward current (maximum values,
60 ns
80 ns
1000 ns
16 A
per diode)
P1(W)
100
90
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.5
80
70
60
50
40
30
T
20
10
0
0 102030405060708090100
IF(av) (A)
δ
=tp/T
Figure 3. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to case versus
pulse duration
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
0.8
δ = 0.5
0.6
0.4
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
0.2
Single pulse
0.0
1E-3 1E-2 1E-1 1E+0 5E+0
tp(s)
δ
T
=tp/T
δ = 1
IFM(A)
200
100
10
tp
1
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
Tj=125°C
(Typical values)
Tj=125°C
Figure 4. Peak reverse recovery current
versus dI
/dt (90% confidence, per
F
diode)
IRM(A)
30
VR=200V
Tj=125°C
25
20
IF=0.5xIF(av)
15
10
5
tp
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
IF=IF(av)
dIF/dt(A/µs)
Tj=25°C
VFM(V)
IF=2xIF(av)
3/7
 Loading...
Loading...