ST STPS5L60-Y User Manual

Features
■ Negligible switching losses
■ Low forward voltage drop for higher efficiency
■ Low thermal resistance
■ Avalanche capability specified
■ AEC-Q101 qualified
■ ECOPACK
®
2 compliant component
Description
Power Schottky rectifier suited for switch mode
power supplies and high frequency inverters.
This device is intended for use in low voltage
output for small battery chargers and battery
protection in automotive applications.
STPS5L60-Y
Automotive power Schottky rectifier
Datasheet − production data
A
K
SMC
STPS5L60SY
Table 1. Device summary
I
5 A
F(AV)
V
RRM
150 °C
T
j (max)
V
F (max)
60 V
0.53 V
March 2012 Doc ID 022951 Rev 1 1/7
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
7
Characteristics STPS5L60-Y
1 Characteristics
Table 2. Absolute ratings (limiting values)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
P
ARM
T
T
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage (rated V
dPtot
---------------
1. condition to avoid thermal runaway for a diode on its own heatsink
dTj
Table 3. Thermal parameters
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 60 V
Forward rms current 15 A
= 100 °C δ = 0.5
Average forward current
Surge non repetitive forward
current
Repetitive peak avalanche power
Storage temperature range -65 to +175 °C
stg
Operating junction temperature
j
1
--------------------------
<
Rth j a–()
Half wave, single phase
= 10 ms
t
p
= 1 µs Tj = 25 °C
t
p
(1)
T
l
150 A
4000 W
-40 to +150 °C
, Tj = 25 °C) 10000 V/µs
R
5A
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
Junction to leads 15 °C/W
th (j-l)
Table 4. Static electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Tests conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
(1)
IR
V
1. Pulse test: tp = 380 µs, δ < 2%
Reverse leakage current
(1)
Forward voltage drop
F
T
= 25 °C
j
= V
V
R
= 125 °C 40 100
T
j
T
= 25 °C
j
= 5 A
I
F
= 125 °C 0.42 0.48
T
j
RRM
0.47 0.52
0.22
mA Tj = 100 °C 10 25
VTj = 100 °C 0.43 0.49
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation:
P = 0.39 x I
F(AV)
+ 0.028x I
F2(RMS)
2/7 Doc ID 022951 Rev 1
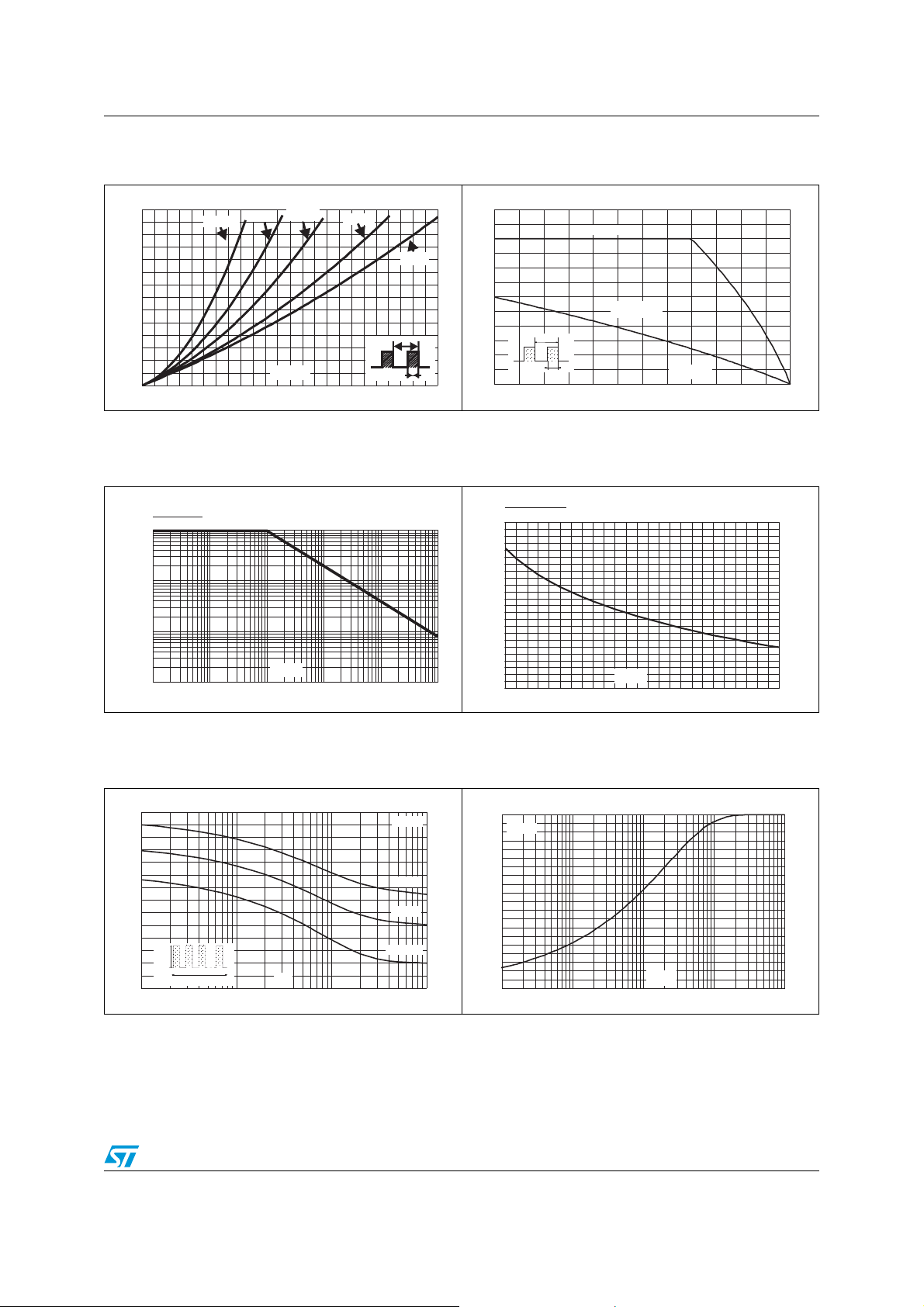
STPS5L60-Y Characteristics
0
Figure 1. Conduction losses versus average
current
PF(av)(W)
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.1
δ = 0.2
IF(av)(A)
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 3. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus pulse duration
P(t)
ARM p
P (1µs)
ARM
1
0.1
Figure 2. Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (
IF(av)(A)
6
5
4
3
2
1
=tp/T
δ
0
0 150
Rth(j-a)=Rth(j-l)
SMC
Rth(j-a)=90°C/W
T
tp
25 50 75 100 125
δ = 0.5)
Tamb(°C)
Figure 4. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus junction
temperature
P(t)
ARM j
P (25°C)
ARM
1
0.01
t (µs)
0.001
0.10.01 1
p
10 100 1000
Figure 5. Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration
(maximum values)
IM(A)
14
12
10
8
6
4
I
M
2
0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
δ=0.5
t
t(s)
SMC
Ta=25°C
Ta=75°C
Ta=125°C
T (°C)
0
j
25 50 75 100 125 150
Figure 6. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient
versus pulse duration
Z/R
th(j-a) th(j-a)
1.0
SMC
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03
t (s)
p
Doc ID 022951 Rev 1 3/7
 Loading...
Loading...