ST STPS41H100C-Y User Manual

STPS41H100C-Y
Automotive low drop power Schottky rectifier
Features
■ Negligible switching losses
■ Low leakage current
■ Good trade off between leakage current and
foward voltage drop
■ Low thermal resistance
■ Avalanche capability specified
■ AEC-Q101 qualified
Description
Dual center tab Schottky rectifier suited for switch
mode power supply and high frequency DC to DC
converters.
Packaged in D
use in high frequency inverters for automotive
application.
2
PAK, this device is intended for
A1
K
A2
K
A2
A1
D2PAK
STPS41H100CG-Y
j
Table 1. Device summary
Symbol Value
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
(max) 175 °C
T
j
(max) 0.67 V
V
F
2 x 20 A
100 V
October 2011 Doc ID 018564 Rev 1 1/7
www.st.com
7
Characteristics STPS41H100C-Y
1 Characteristics
Table 2. Absolute ratings (limiting values, per diode)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
I
P
T
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 100 V
RRM
Forward rms current 30 A
T
= 50 °C
Average forward current
Surge non repetitive forward current tp = 10 ms sinusoidal 220 A
FSM
Repetitive peak reverse current tp = 2 µs square F = 1 kHz 1 A
RRM
Repetitive peak avalanche power tp = 1 µs Tj = 25 °C 18100 W
ARM
Storage temperature range -65 to + 175 °C
stg
T
Maximum operating junction temperature range
j
c
δ = 0.5
(1)
Per diode
Per device
-40 to + 175 °C
20
40
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage 10000 V/µs
<
Rth(j-a)
1
dPtot
1. condition to avoid thermal runaway for a diode on its own heatsink
dTj
Table 3. Thermal resistance
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Per diode 1.5
R
R
Junction to case
th(j-c)
Coupling 0.1
th(c)
°C/WTo ta l 0 .8
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously:
A
ΔTj(diode 1) = P(diode1) x R
Table 4. Static electrical characteristics (per diode)
(Per diode) + P(diode 2) x R
th(j-c)
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
= 25 °C
T
Reverse leakage
(1)
I
R
current
(1)
V
1. Pulse test: tp = 380 µs, δ < 2%
Forward voltage drop
F
j
= 125 °C 3 10 mA
T
j
= 25 °C IF = 20 A 0.80
T
j
T
= 125 °C IF = 20 A 0.62 0.67
j
= 25 °C IF = 40 A 0.90
T
j
T
= 125 °C IF = 40 A 0.70 0.76
j
V
R
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation:
P = 0.58 x I
2/7 Doc ID 018564 Rev 1
F(AV)
+ 0.0045 I
F2(RMS)
= V
th(c)
10 μA
RRM
V
STPS41H100C-Y Characteristics
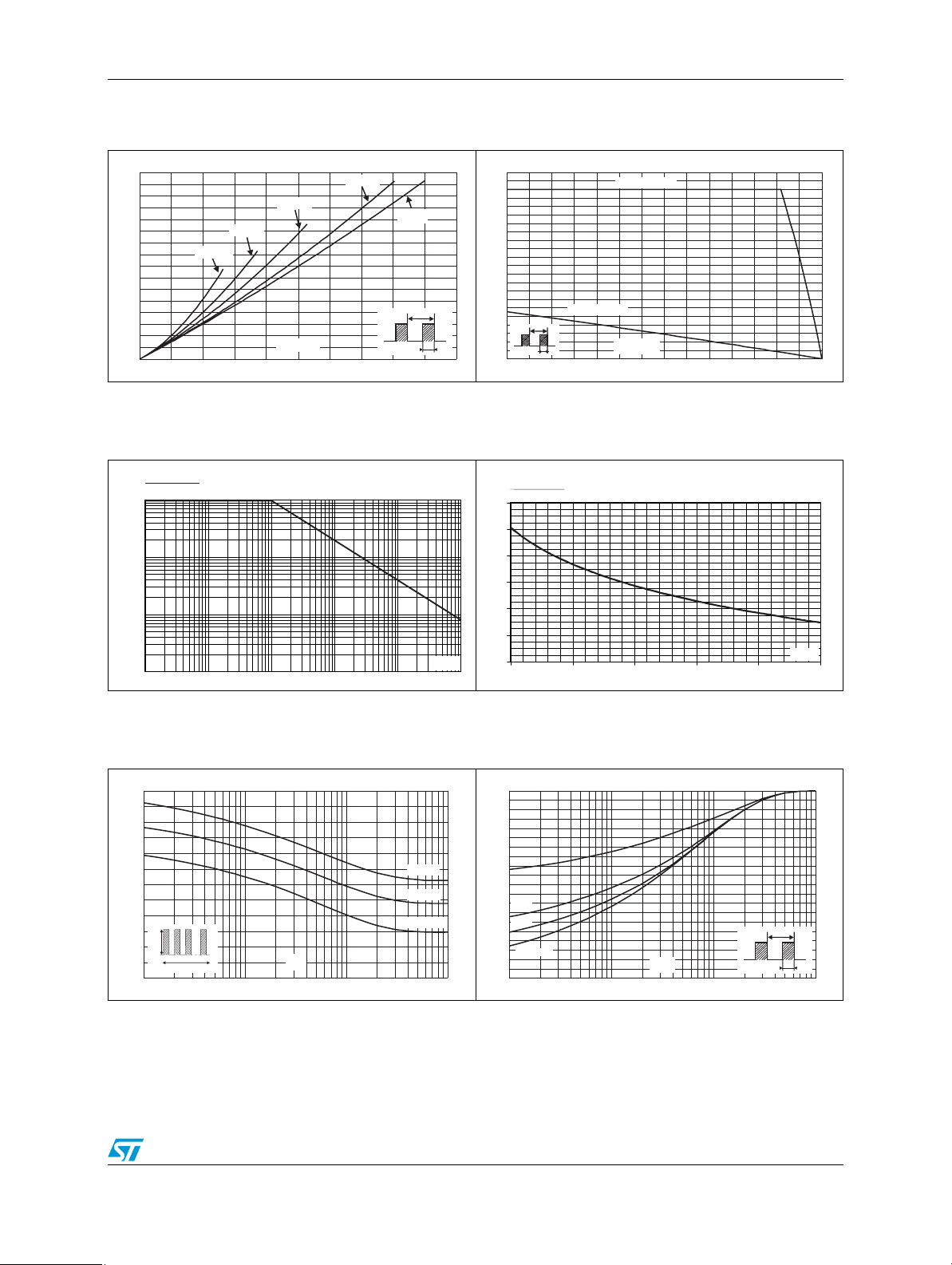
Figure 1. Conduction losses versus average
current
PF(av)(W)
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
δ = 0.05
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
IF(av)(A)
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 3. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus pulse duration
P(tp)
ARM
P (1µs)
ARM
1
0.1
0.01
t (µs)
0.001
0.10.01 1
10 100
p
1000
Figure 5. Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration
(maximum values)
IM(A)
300
250
200
150
100
IM
50
0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
δ=0.5
t
t(s)
Tc=25°C
Tc=75°C
Tc=125°C
Figure 2. Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (δ = 0.5)
IF(av)(A)
22
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
=tp/T
δ
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
Rth(j-a)=50°C/W
T
tp
Rth(j-a)=Rth(j-c)
Tamb(°C)
Figure 4. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus junction
temperature
P(T)
ARM j
P (25 °C)
ARM
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
T (°C)
0
25 50 75 100 125
j
Figure 6. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to case versus
pulse duration
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
δ = 0.5
0.6
0.5
0.4
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
0.3
0.2
Single pulse
0.1
0.0
1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00
tp(s)
δ
=tp/T
T
tp
150
Doc ID 018564 Rev 1 3/7
 Loading...
Loading...