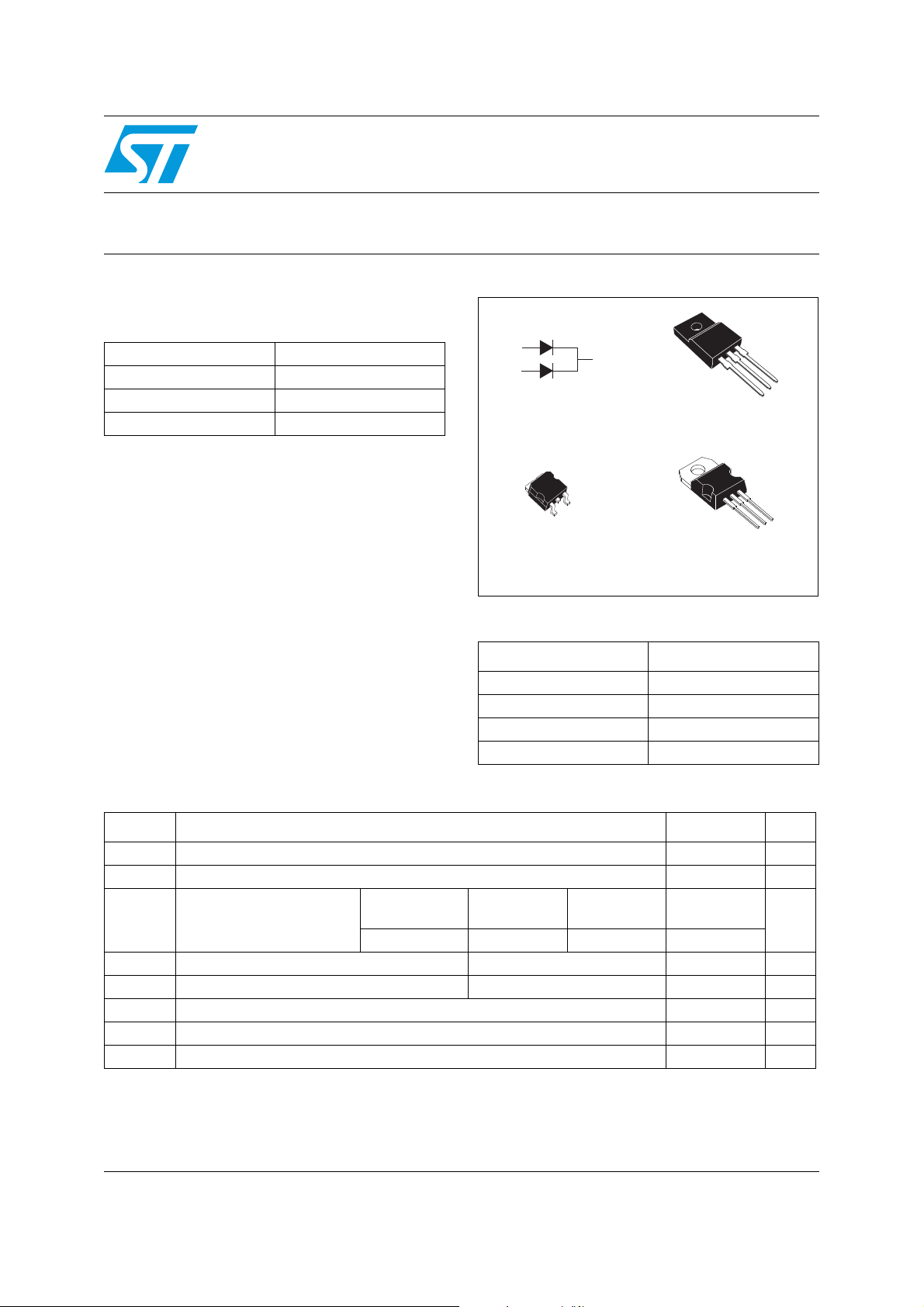
Main product characteristics
STPS10150C
High voltage power Schottky rectifier
I
F(AV)
V
RRM
T
j
(max) 0.75 V
V
F
2 x 5 A
150 V
175° C
Features and benefits
■ HIgh junction temperature capability
■ Good trade off between leakage current and
forward voltage drop
■ Low leakage current
■ Avalanche capability specified
■ Insulated package
– TO-220FPAB
Insulating voltage = 2000 V
Typical package capacitance 12 pF
Description
Dual center tap schottky rectifier designed for
A1
A2
K
TO-220FPAB
STPS10150CFP
K
A2
A1
D2PA K
STPS10150CG
TO-220AB
STPS10150CT
Order Codes
Part Number Marking
STPS10150CT STPS10150CT
STPS10150CG STPS10150CG
STPS10150CG-TR STPS10150CG
STPS10150CFP STPS10150CFP
A1
K
A1
high frequency Switched Mode Power Supplies.
Table 1. Absolute ratings (limiting values)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
RRM
I
F(RMS)
I
F(AV)
I
FSM
P
ARM
T
dV/dt Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage 10000 V/µs
dPtot
---------------
1. condition to avoid thermal runaway for a diode on its own heatsink
T
dTj
stg
j
Repetitive peak reverse voltage 150
RMS forward voltage 10
Average forward current
δ = 0.5
TO-220AB
2
PA K
D
TO-22 0FPAB TC = 145° C Per device 10
= 155° C Per diode 5
T
C
Surge non repetitive forward current tp = 10 ms sinusoidal 120
Repetitive peak avalanche power tp = 1 µs Tj = 25° C 3100
Storage temperature range -65 to + 175 ° C
Maximum operating junction temperature
1
------------------ --------
<
Rth j a–()
(1)
175 ° C
A2
K
A2
V
A
A
A
W
June 2006 Rev 6 1/9
www.st.com
9
Characteristics STPS10150C
1 Characteristics
Table 2. Thermal resistance
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
TO-220AB, D
2
PA K
4
Per diode
TO-220FPAB 7
R
th(j-c)
Junction to case
TO-220AB, D
2
PA K
2.4
To t a l
TO-220FPAB 5.3
2
R
th(c)
Coupling
TO-220AB, D
TO-220FPAB 3.7
PA K 0 . 7
When the diodes 1 and 2 are used simultaneously:
∆T
(diode 1) = P(diode 1) x R
j
Table 3. Static electrical characteristics (per diode)
Symbol Parameter Tests conditions Min. Typ Max. Unit
(1)
I
R
Reverse leakage current
T
T
Tj = 25° C
VF
(2)
Forward voltage drop
T
T
T
1. tp = 5 ms, δ < 2%
= 380 µs, δ < 2%
2. t
p
(Per diode) + P(diode 2) x R
th(j-l)
= 25° C
j
= 125° C 0.40 2.0 mA
j
= V
V
R
RRM
th(c)
2.0 µA
0.92
= 5 A
I
= 125° C 0.69 0.75
j
= 25° C
j
= 125° C 0.79 0.85
j
F
= 10 A
I
F
1
° C/W
V
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation:
P = 0.65 x I
F(AV)
+ 0.02 I
F2(RMS)
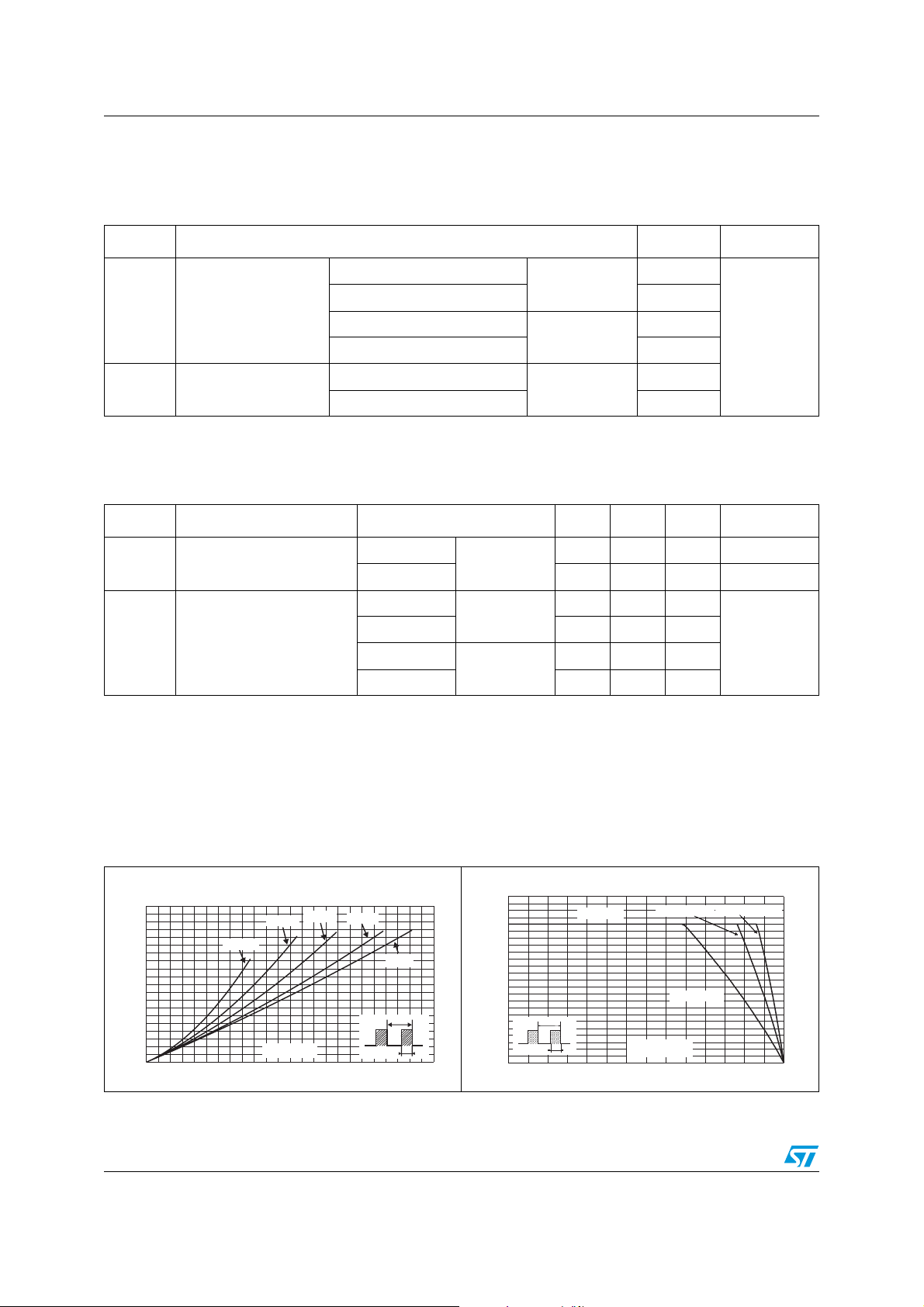
Figure 1. Average forward power
dissipation versus average
forward current (per diode)
P(W)
F(av)
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0
δ = 0.05
2/9
δ = 0.2
δ = 0.1
I(A)
F(av)
δ = 0.5
δ
=tp/T
δ = 1
T
tp
Figure 2. Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (δ = 0.5, per
diode)
I (A)
F(av)
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
=tp/T
d
0.0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175
R
th(j-a)=Rth(j-c)
T
tp
TO-220FPABTO-220FPAB
T (°C)
amb
R
th(j-a)
TO-220AB/D²PAKTO-220AB/D²PAK
=15 °C/W
STPS10150C Characteristics
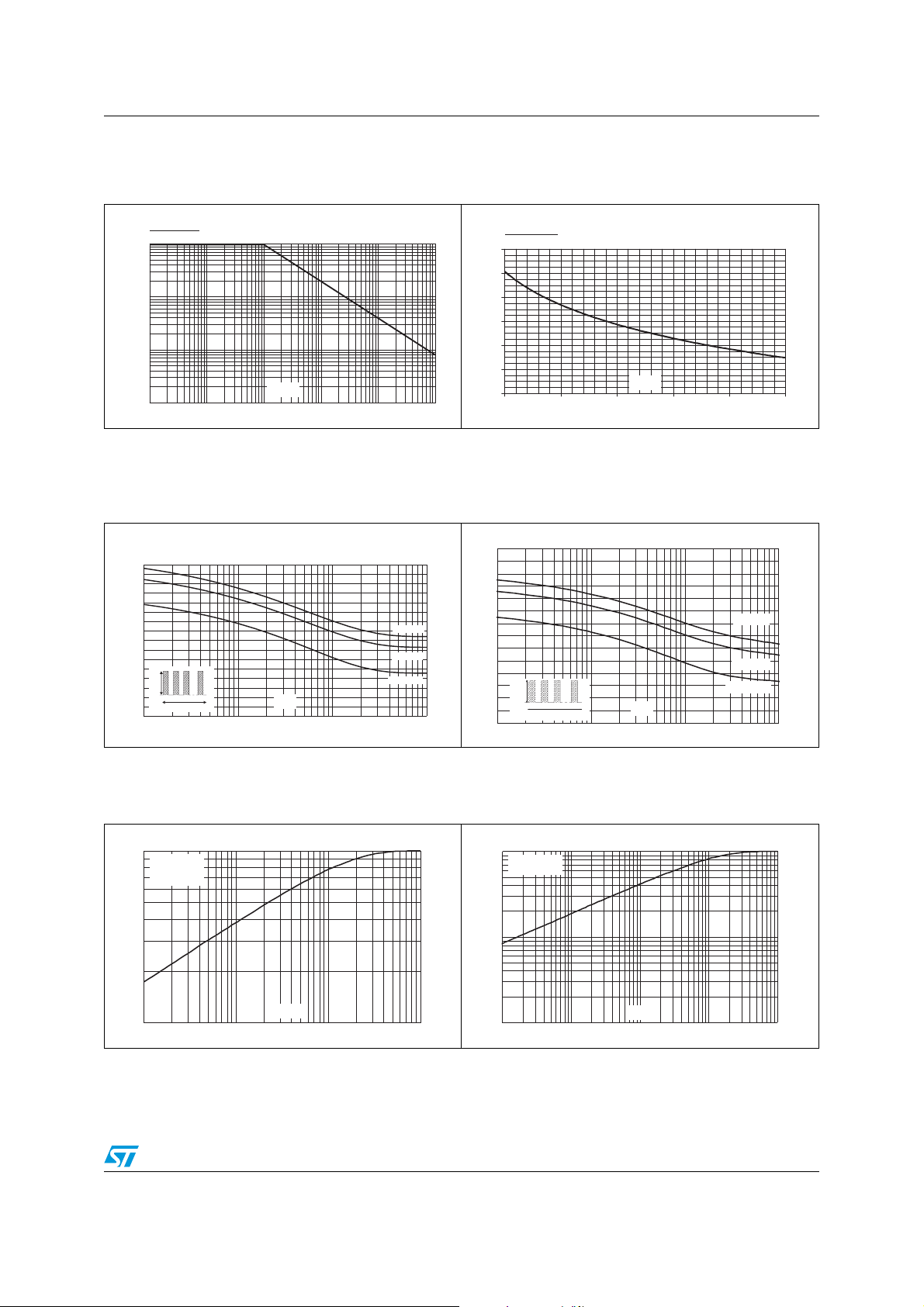
Figure 3. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus pulse duration
P(t)
ARM p
P (1µs)
ARM
1
0.1
0.01
t (µs)
0.001
0.10.01 1
p
10 100 1000
Figure 5. Non repetitive surge peak
forward current versus overload
duration - maximum values, per
diode (TO-220AB, D
I(A)
M
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
IM
10
0
1E-3 1E-2 1E-1 1E+0
δ=0.5
t
t(s)
2
PAK)
Tc=50°C
Tc=75°C
Tc=125°C
Figure 4. Normalized avalanche power
derating versus junction
temperature
P(t)
ARM p
P (25°C)
ARM
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
T (°C)
0
j
25 50 75 100 125 150
Figure 6. Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration
- maximum values, per diode
(TO-220FPAB)
I(A)
M
70
60
50
40
30
20
I
M
10
0
1.E-3 1.E-2 1.E-1 1.E+0
d=0.5
t
t(s)
TC=50 °C
TC=75 °C
TC=125 °C
Figure 7. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to case versus
pulse duration (TO-220AB, D
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
Single pulse
TO-220AB
D²PAK
0.1
1.E-3 1.E-2 1.E-1 1.E+0
tp(s)
2
PAK)
Figure 8. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to case versus
pulse duration (TO-220FPAB)
Zth(j-c)/Rth(j-c)
1.0
Single pulse
TO-220FPAB
0.1
0.0
1.E-3 1.E-2 1.E-1 1.E+0 1.E+1
3/9
tp(s)
 Loading...
Loading...