Page 1

STM6315
Open drain microprocessor reset
Features
■ Low supply current of 1.5µA (typ)
■ ±1.8% reset threshold accuracy (25°C)
■ Guaranteed RST assertion down to
V
= 1.0V
CC
■ Open drain RST output can exceed V
■
Power supply transient immunity
■ Operating temperature: –40 to +125°C
■ Available in SOT143-4 package.
CC
SOT143-4 (W1)
March 2007 Rev 5 1/21
www.st.com
1
Page 2

Contents STM6315
Contents
1 Summary description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Reset output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Manual reset input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3 Negative-going V
2.4 Valid RST
output down to VCC = 0V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
transients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
CC
3 Typical operating characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2/21
Page 3

STM6315 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Signal names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 3. Operating and AC measurement conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 4. DC and AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 5. SOT143-4 – 4-lead small outline transistor package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 6. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 7. Marking description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 8. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3/21
Page 4

List of figures STM6315
List of figures
Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. SOT143-4 connections (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. Hardware hookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 5. Reset timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6. Manual reset timing diagram, switch bounce/debounce. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 7. Supply current vs. supply voltage, V
Figure 8. Supply current vs. temperature (no load), V
Figure 9. RST
Figure 10. Normalized reset time-out period vs. temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 11. Normalized reset threshold vs. temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 12. Max. transient duration not causing reset pulse vs. reset threshold Overdrive . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 13. AC testing input/output waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 14. SOT143-4 – 4-lead small outline transistor package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
output voltage vs. output current, VCC = 4.25V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
= 2.63V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
RST
= 2.63V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
RST
4/21
Page 5

STM6315 Summary description
1 Summary description
The STM6315 Microprocessor Reset Circuit is a low power supervisory device used to
monitor power supplies. It performs a single function: asserting a reset signal whenever the
V
supply voltage drops below a preset value and keeping it asserted until VCC has risen
CC
above the preset threshold for a minimum period of time (t
reset input (MR
). The open drain RST output can be pulled up to a voltage higher than VCC,
but less than 6V.
The STM6315 comes with standard factory-trimmed reset thresholds of 2.63V, 2.93V,
3.08V, 4.38V, and 4.63V. The STM6315 is available in the SOT143-4 package.
Figure 1. Logic diagram
V
CC
). It also provides a manual
rec
STM6315
V
SS
Table 1. Signal names
Symbol Description
V
CC
MR
RST
V
SS
Supply voltage
Manual reset input
Active-low open drain reset output
Ground
MR
Figure 2. SOT143-4 connections (top view)
V
SS
1
RST
AI11162
V
4
CC
RST
2
5/21
3
MR
AI11163
Page 6

Summary description STM6315
Figure 3. Block diagram
V
V
CC
RST
COMPARE
t
rec
Generator
RST
MR
Figure 4. Hardware hookup
V
CC
Manual
Reset
DEBOUNCE
V
CC
10k
STM6315 MCU
MR
(1)
RST
V
SS
RESET
Input
AI11164
V
CC
V
SS
1. Open drain RST output requires external pull-up resistor.
6/21
AI11165
Page 7

STM6315 Operation
2 Operation
2.1 Reset output
The STM6315 Microprocessor Reset Circuit has an active-low, open drain reset output. This
output structure will sink current when RST
to any supply voltage up to 6V (see Figure 4 on page 6). Select a resistor value large
enough to register a logic low, and small enough to register a logic high while supplying all
input current and leakage paths connected to the reset output line. A 10k pull-up is sufficient
in most applications.
is asserted. Connect a pull-up resistor from RST
The STM6315 asserts a reset signal to the MCU whenever V
threshold (V
Figure 6 on page 8). RST
During power-up, (once V
for the reset time-out period, t
If V
drops below the reset threshold, RST goes low. Each time RST is asserted, it stays
CC
), or when the manual reset input (MR) is taken low (see Figure 5 and
RST
is guaranteed valid down to VCC = 1.0V.
exceeds the reset threshold) an internal timer keeps RST low
CC
. After this interval, RST returns high.
rec
low for at least the reset time-out period. Any time V
internal timer clears. The reset timer starts when V
2.2 Manual reset input
A logic low on MR asserts RST. RST remains asserted while MR is low, and for t
returns high. The MR
input has an internal pull-up resistor 63kΩ (typ), allowing it to be left
open if not used.
This input can be driven with TTL/CMOS-logic levels or with open drain/collector outputs.
Connect a standard open push-button switch from MR
function (see Figure 4 on page 6); external debounce circuitry is not required. If the device is
used in a noisy environment, connect a 0.1µF capacitor from MR
additional noise immunity.
2.3 Negative-going VCC transients
goes below the reset
CC
goes below the reset threshold, the
CC
returns above the reset threshold.
CC
rec
to VSS to create a manual reset
to VSS to provide
after it
The STM6315 is relatively immune to negative-going VCC transients (glitches). Figure 12 on
page 11 shows typical transient duration versus reset comparator overdrive (for which the
STM6315 will NOT generate a reset pulse). The graph was generated using a negative
pulse applied to V
, starting at 0.5V above the actual reset threshold and ending below it
CC
by the magnitude indicated (Reset Threshold Overdrive). The graph indicates the maximum
pulse width a negative V
transient can have without causing a reset pulse. As the
CC
magnitude of the transient increases (further below the threshold), the maximum allowable
pulse width decreases. Any combination of duration and overdrive which lies under the
curve will NOT generate a reset signal (see Figure 12). A 0.1µF bypass capacitor mounted
as close as possible to the V
pin provides additional transient immunity.
CC
7/21
Page 8

Operation STM6315
2.4 Valid RST output down to VCC = 0V
When VCC falls below 1V, the RST output no longer sinks current, but becomes an open
circuit. In most systems this is not a problem, as most MCUs do not operate below 1V.
However, in applications where RST
may be added to hold the RST
the RST
output, and still be small enough to pull the output to Ground. A 100KΩ resistor is
recommended.
Figure 5. Reset timing diagram
V
CC
RST
V
CC
(min)
V
RST
Figure 6. Manual reset timing diagram, switch bounce/debounce
output must be valid down to 0V, a pull-down resistor
output low. This resistor must be large enough to not load
t
rec
AI11166
MR
RST
MR Glitch Rejection
MR-to-RST Delay
MR Input Pulse Width
trec
AI11167b
8/21
Page 9

STM6315 Typical operating characteristics
3 Typical operating characteristics
Note: Typical values are at TA = 25°C.
Figure 7. Supply current vs. supply voltage, V
3.00
2.75
2.50
2.25
(µA)
2.00
CC
1.75
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
Supply Current, I
0.50
0.25
0.00
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
Supply Voltage, VCC (V)
RST
= 2.63V
AI11871c
Figure 8. Supply current vs. temperature (no load), V
2.25
2.00
1.75
(µA)
1.50
CC
1.25
1.00
0.75
0.50
Supply Current, I
0.25
0.00
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature, TA (°C)
RST
= 2.63V
VCC = 2V
VCC = 3V
VCC = 4V
VCC = 5V
AI11872c
9/21
Page 10
Typical operating characteristics STM6315
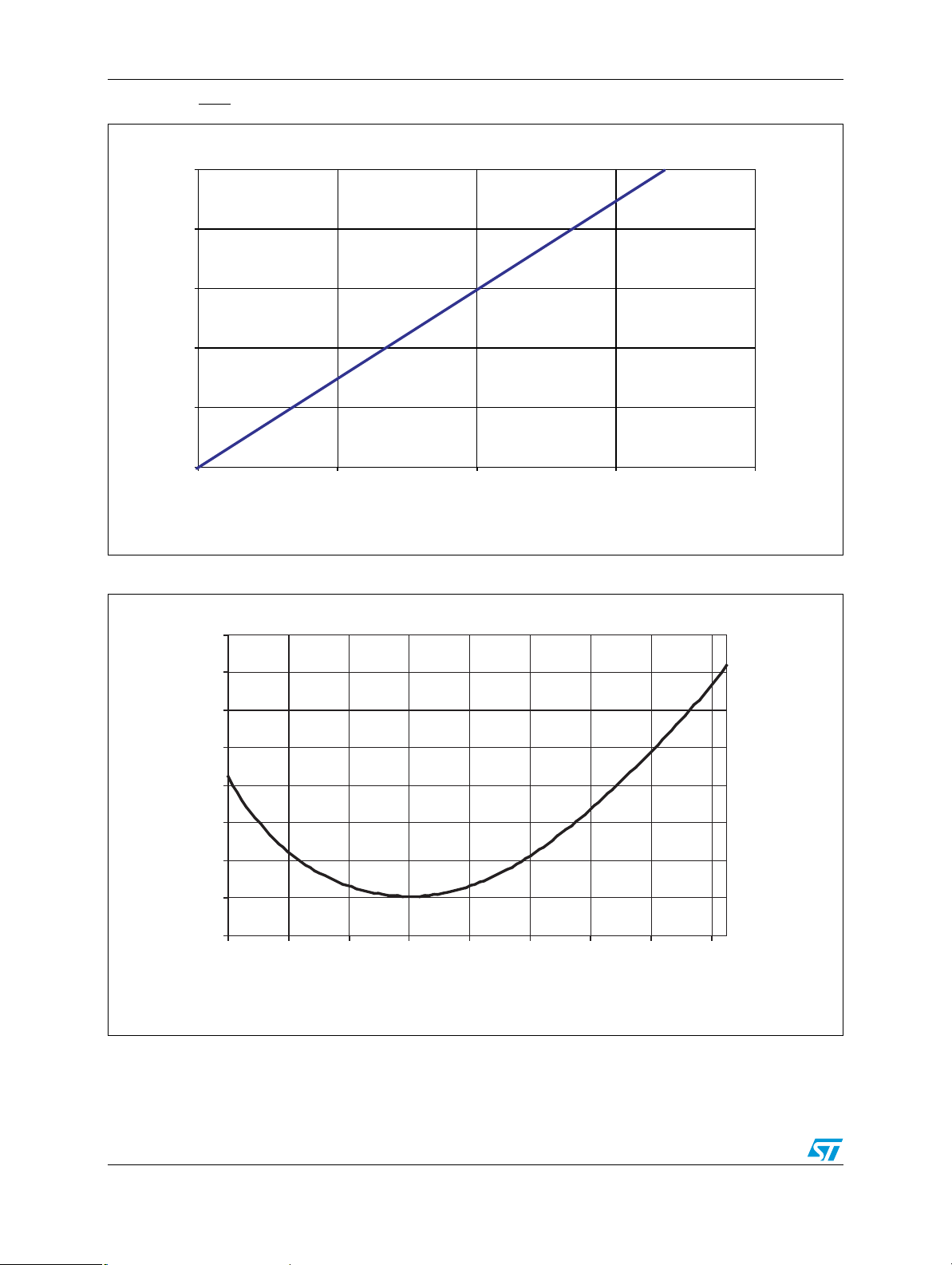
Figure 9. RST output voltage vs. output current, VCC = 4.25V
0.20
0.16
0.12
0.08
Output Voltage (V)
0.04
0
0369
Output Current (mA)
12
AI11873c
Figure 10. Normalized reset time-out period vs. temperature
1.14
1.12
1.10
(–)
1.08
1.06
rec (typ)
/t
1.04
rec
t
1.02
Normalized Reset Time-out Period,
1.00
0.98
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature, TA (°C)
AI11875b
10/21
Page 11

STM6315 Typical operating characteristics
Figure 11. Normalized reset threshold vs. temperature
(–)
1.01
RST-typ
/V
1.005
RST
1
0.995
0.99
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Normalized Reset Threshold, V
Temperature, TA (°C)
AI11876c
Figure 12. Max. transient duration not causing reset pulse vs. reset threshold Overdrive
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Transient Duration (µs)
20
10
0
1 10 100 1000
Reset Threshold Overdrive (mV)
AI11877
Note: Reset occurs above the curve.
11/21
Page 12

Maximum rating STM6315
4 Maximum rating
Stressing the device above the rating listed in the Table 2: Absolute maximum ratings may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE
Program and other relevant quality documents.
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
STG
T
SLD
V
IO
V
CC
I
O
P
1. Reflow at peak temperature of 260°C (total thermal budget not to exceed 245°C for greater than 30
seconds).
Storage temperature (VCC Off) –55 to 150 °C
(1)
Lead solder temperature for 10 seconds 260 °C
Input or output voltage –0.3 to VCC + 0.3 V
Supply voltage –0.3 to 7.0 V
Output current 20 mA
Power dissipation 320 mW
D
12/21
Page 13

STM6315 DC and AC parameters
5 DC and AC parameters
This section summarizes the operating measurement conditions, and the DC and AC
characteristics of the device. The parameters in the DC and AC characteristics Tables that
follow are derived from tests performed under the measurement conditions summarized in
Table 3: Operating and AC measurement conditions. Designers should check that the
operating conditions in their circuit match the operating conditions when relying on the
quoted parameters.
Table 3. Operating and AC measurement conditions
Parameter STM6315 Unit
V
Supply Voltage 1.0 to 5.5 V
CC
Ambient Operating Temperature (T
Input Rise and Fall Times ~5 ns
) –40 to +125 °C
A
Input Pulse Voltages 0.2 to 0.8V
Input and Output Timing Reference Voltages 0.3 to 0.7V
Figure 13. AC testing input/output waveforms
0.8V
0.2V
CC
CC
0.7V
0.3V
AI02568
CC
CC
CC
CC
V
V
13/21
Page 14

DC and AC parameters STM6315
Table 4. DC and AC characteristics
Sym Description Test Condition
Operating voltage 1.0 5.5 V
V
CC
VCC = 5.5V, no load
= –40 to +85°C
T
A
V
= 5.5V, no load
CC
= –40 to +125°C
T
I
CCVCC
V
OL
supply current
RST output voltage
RST
Leakage Current
output open drain
A
V
= 3.6V, no load
CC
= –40 to +85°C
T
A
V
= 3.6V, no load
CC
= –40 to +125°C
T
A
V
> 4.25V, I
CC
> 2.5V, I
V
CC
> 1.0V, I
V
CC
VCC > V
SINK
SINK
SINK
, RST not
RST
asserted
Reset Thresholds
V
falling; TA = 25°C V
Reset threshold
(see Table 6 on page 18
V
RST
for detailed listing)
(2)
CC
falling; TA = –40 to 85°C V
V
CC
falling; TA = –40 to 125°C V
V
CC
VCC falling from
t
RDVCC
t
rec
-to-RST delay
RST pulse
(2)
width
STM6315xAxxxx
STM6315xBxxxx
STM6315xDxxxx
STM6315xGxxxx
(V
+ 100mV) to
RST
– 200mV) at 1mV/µs
(V
RST
T
= –40 to +85°C 1
A
T
= –40 to +125°C 0.8 2.4 ms
A
T
= –40 to +85°C 20
A
= –40 to +125°C 16 48 ms
T
A
T
= –40 to +85°C 140
A
= –40 to +125°C 112 336 ms
T
A
T
= –40 to +85°C 1120
A
= –40 to +125°C 896 2688 ms
T
A
Reset threshold temperature
coefficient
(1)
Min Typ Max Unit
2.0 12 µA
15 µA
1.5 10 µA
12 µA
= 3.2mA0.4V
= 1.2mA0.3V
= 80µA0.3V
1µA
– 1.8%
RST
– 2.5% V
RST
– 3.5% V
RST
V
RST
V
+ 1.8% V
RST
+ 2.5% V
RST
+ 3.5% V
RST
35 µs
2ms
1.5
40 ms
30
280 ms
210
2240 ms
1680
60 ppm/°C
14/21
Page 15

STM6315 DC and AC parameters
Table 4. DC and AC characteristics (continued)
Sym Description Test Condition
Manual Reset Input
V
> 4.0V 0.8 V
V
MR low input threshold
IL
V
MR low input threshold
IH
MR
input pulse width 1 µs
glitch rejection 100 ns
MR
-to-RST delay 500 ns
MR
MR
pull-up resistance 32 63 100 kΩ
1. Valid for ambient operating temperature: TA = –40 to 125°C; VCC = 2.5 to 5.5V (except where noted).
2. Other V
availability.
thresholds and t
RST
timings are offered. Minimum order quantities may apply. Contact local sales office for
rec
RST
V
< 4.0V 0.3V
RST
V
> 4.0V 2.4 V
RST
< 4.0V 0.7V
V
RST
(1)
Min Typ Max Unit
CC
CC
V
V
15/21
Page 16

Package mechanical data STM6315
6 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect. The category of
second Level Interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com.
16/21
Page 17

STM6315 Package mechanical data
Figure 14. SOT143-4 – 4-lead small outline transistor package outline
E
E1
B
0.15
M
CAB
A1
1
e1
M
0.20
3X b
C
SOT143-4
Note: Drawing is not to scale.
Table 5. SOT143-4 – 4-lead small outline transistor package mechanical data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A – 0.89 1.12 – 0.035 0.044
CAB
L
e/2
M
0.15
e
D
CAB
b2
4X
A
0.10C
C
θ
L1
C
mm inches
A2
A
A1 – 0.01 0.10 – 0.001 0.004
A2 – 0.88 1.02 – 0.035 0.042
b – 0.37 0.51 – 0.015 0.020
b2 – 0.76 0.94 – 0.030 0.037
C – 0.09 0.18 – 0.004 0.007
D – 2.80 3.04 – 0.110 0.120
E – 2.10 2.64 – 0.083 0.104
E1 – 1.20 1.40 – 0.047 0.055
e1.92– –0.076– –
e1 0.20 – – 0.008 – –
L0.55– –0.022– –
L1 – 0.40 0.60 – 0.016 0.024
Θ 0° 10° 0° 10°
N4 4
17/21
Page 18

Part numbering STM6315
7 Part numbering
Table 6. Ordering information scheme
Example: STM6315 R D W1 3 F
Device Type
STM6315
Reset Threshold Voltage
L = V
M = V
S = V
R = V
RST
A = t
B = t
D = t
G = t
= 4.63V
RST
= 4.38V
RST
= 2.93V
RST
= 2.63V
RST
Pulse Width
= 1.5ms
rec
= 30ms
rec
= 210ms
rec
= 1680ms
rec
(1)
Package
W1 = SOT143-4
Temperature Range
3 = –40 to 125°C
(1)
Shipping Method
F = ECOPACK Package, Tape & Reel
1. Other V
sales office for availability.
thresholds and t
RST
timings are offered. Minimum order quantities may apply. Contact local
rec
Note: For other options, or for more information on any aspect of this device, please contact the
ST Sales Office nearest you.
18/21
Page 19

STM6315 Part numbering
Table 7. Marking description
Part Number
Reset Threshold
(V)
(1)
RST Pulse Width
(ms)
STM6315LB 4.63 30 Open drain RST 9LBx
STM6315MD 4.38 210 Open drain RST
STM6315SD 2.93 210 Open drain RST
(1)
Output
Topside
Marking
(2)
9MDx
9SDx
STM6315RA 2.63 1.5 Open drain RST
STM6315RB 2.63 30 Open drain RST
STM6315RD 2.63 210 Open drain RST
STM6315RG 2.63 1680 Open drain RST
1. Other V
sales office for availability.
2. Where "x" = Assembly Work Week (A to Z), such that "A" = WW01-02, "B" = WW03-04, and so forth.
thresholds and t
RST
timings are offered. Minimum order quantities may apply. Contact local
rec
9RAx
9RBx
9RDx
9RGx
19/21
Page 20

Revision history STM6315
8 Revision history
Table 8. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
14-Nov-2005 1.0 First edition.
08-Feb-2006 2.0
12-Apr-2006 3 Updated characteristics (Figure 7, 8, and 11; Table 4, 6, and 7).
27-Jul-2006 4 Updated Ta bl e 3 , 5 and 6.
21-Mar-2007 5 Updated Ta bl e 2 , 6, and 7.
Update template, characteristics, marking (Figure 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11;
Ta bl e 4, 6, and 7).
20/21
Page 21

STM6315
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2007 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
21/21
 Loading...
Loading...