Page 1
Adaptive 3.4 Gbps 3:1 TMDS/HDMI signal equalizer
Features
■ Digital video signal equalizer with 3:1 HDMI
switch
■ Compatible with the high-definition multimedia
interface (HDMI) v1.3 digital interface
■ 340 MHz maximum clock speed operation
supports all video formats with deep color at
maximum refresh rates
■ 3.4 Gbps data rate per channel
■ Fully automatic adaptive equalizer for cable
lengths up to 25 m
■ Selectable 50 Ω input termination to V
3.135 to 3.465 V
■ Low speed control lines supply to V
5 V (typ)
■ ESD HBM model: > ±5 KV for TMDS I/Os
■ Integrated open-drain I
data channel (DDC)
■ 5.3 V tolerant DDC and HPD I/Os
■ Lock-up free operation of I
■ 0 to 400 kHz clock frequency for I
■ Low capacitance TMDS channels
■ Equalizer for signal regeneration
■ Low output skew and jitter
Applications
■ Advanced TVs supporting the HDMI/DVI
standard
■ Front projectors, LCD TVs and PDPs
■ Monitors and notebooks
■ Set-top box and DVD players
Table 1. Device summary
Order code Operating temperature Package Packaging
2
C buffer for display
2
C bus
2
CC
:
DD
C bus
STDVE103A
TQFP64
:
Description
The STDVE103A integrates a 4-channel 3.4 Gbps
TMDS equalizer and a 3:1 switch to select one of
the three HDMI ports. The high-speed data paths
and flow-through pinout minimize the internal
device jitter and simplify the board layout. The
equalizer overcomes the jitter effects from lossy
cables. The buffer/driver on the output can drive
the TMDS output signals over long distances.
Also, STDVE103A integrates the 50 Ω
termination resistor on all the input channels to
improve performance and reduce board space.
The device can be placed in a low-power mode by
disabling the output current drivers.
The differential signal from the HDMI/DVI ports
can be routed through the STDVE103A to
guarantee good signal quality at the HDMI
receiver.
Designed for very low skew, jitter and low I/O
capacitance, the switch preserves the signal
integrity to pass the stringent HDMI compliance
requirements.
STDVE103ABTR -40°C to 85°C TQFP64 Tape and reel
STDVE103ABTY -40°C to 85°C TQFP64 Tray
June 2009 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 1/44
www.st.com
44
Page 2

Contents STDVE103A
Contents
1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Application diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.1 Adaptive equalizer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.2.1 SEL operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.3 HPD pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.4 DDC channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.5 I2C DDC line repeater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.6 Power-down condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.7 Bias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.8 Timing between HPD and DDC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.1 Recommended operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.2 DC electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.3 DC electrical characteristics (I2C repeater) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.4 Dynamic switching characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.5 Dynamic switching characteristics (I2C repeater) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.1 Power supply sequencing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.2 Power supply requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3 Differential traces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3.1 I2C lines application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 3

STDVE103A Contents
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 3/44
Page 4

List of tables STDVE103A
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 3. Gain frequency response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 4. SEL operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 5. Bias parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 6. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 7. Thermal data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 8. Power supply characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 9. DC specifications for TMDS differential inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 10. DC specifications for TMDS differential outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 11. DC specifications for SEL (S1, S2) inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 12. Input termination resistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 13. External reference resistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 14. DDC I/O pins (switch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 15. Status pins (HPD_SINK). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 16. Status pins (HPD1, HPD2, HPD3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 17. Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 18. Input/output SDA, SCL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 19. Clock and data rate. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 20. Equalizer gain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 21. Differential output timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 22. Skew times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 23. Turn-on and turn-off times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 24. DDC I/O pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 25. Status pins (HPD_SINK, HPD1, HPD2, HPD3, S1, S2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 26. Jitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 27. I2C repeater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 28. ESD performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 29. TQFP64 mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 30. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
4/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 5

STDVE103A List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. STDVE103A block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 2. Equalizer functional diagram (one signal pair) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3. DDC I2C bus repeater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 4. STDVE103A in a digital TV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 5. Pin configuration (TQFP64 package) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 6. STDVE103A gain vs. frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 7. Test circuit for electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 8. TMDS output driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 9. Test circuit for HDMI receiver and driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 10. Test circuit for turn off and turn off times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 11. Test circuit for short circuit output current. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 12. Propagation delays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 13. Turn-on and turn-off times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 14. TSK(O) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 15. TSK(P) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 16. TSK(D) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 17. AC waveform 1 (I2C lines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 18. Test circuit for AC measurements (I2C lines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 19. I2C bus timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 20. Typical application of I2C bus system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 21. TQFP64 package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 22. TQFP64 tape and reel information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 23. TQFP64 tray drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 24. TQPF64 tray drawing dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 5/44
Page 6

General description STDVE103A
1 General description
The STDVE103A is a TMDS/HDMI 3:1 switch with signal equalizer. The device is a HDMI
switch featuring an integrated 4-channel 3.4 Gbps TMDS equalizer and 3:1 switch to select
one of the three HDMI ports (either external ports or internal sources).
The high-speed data paths and flow-through pinout minimize the internal device jitter and
simplify the board layout.
The equalizer provides compensation to overcome the intersymbol interference (ISI) jitter
effects from lossy cables.
The output driver buffers the TMDS output signals over long distances.
Also, the STDVE103A integrates the 50 Ω termination resistor on all the input channels to
improve performance and reduce board space.
The device can operate in a low-power mode by disabling the output current drivers.
The STDVE103A is ideal for advanced TV and STB applications supporting the HDMI/DVI
standard. The differential signal from the HDMI/DVI ports can be routed through the
STDVE103A to guarantee good signal quality at the HDMI receiver. Designed for very low
skew, jitter and low I/O capacitance, the switch preserves the signal integrity to pass the
stringent HDMI compliance requirements.
The STDVE103A provides the ability to boost the incoming TMDS signal and drive it to a
level which allows efficient signal recovery at the HDMI receiver. It is especially useful for
boosting signals for longer distance transmission when the HDMI receiver is physically
distant from the HDMI input port.
6/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 7
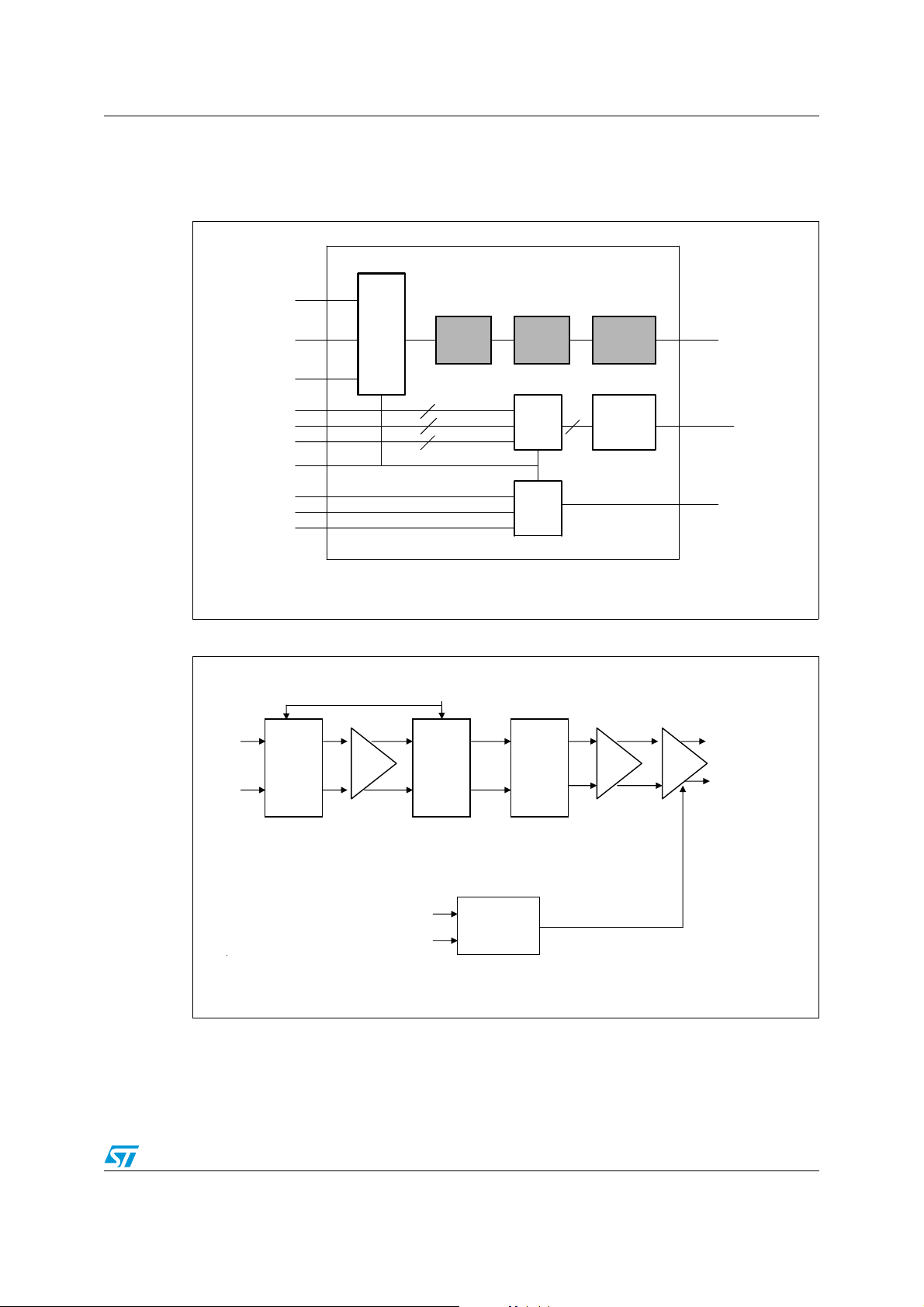
STDVE103A Block diagram
2 Block diagram
Figure 1. STDVE103A block diagram
HDMI input
port A
HDMI input
port B
HDMI input
port C
DDC port A
DDC port B
DDC port C
S1,S2
3:1
HDMI
input
select
switch
Input stage
2
2
2
Equalizer
DDC
switch
2
Output
driver/
transmitter
2
I C
repeater
HDMI output
port Y
DDC
port Y
HPD port A
HPD port B
HPD port C
HPD
analog
switch
Figure 2. Equalizer functional diagram (one signal pair)
S1, S2
Data+
Ω
Data-
50
termination
selectable
Pre-Amp
S1,S2
REXT
Switch
(3:1)
Current
control
Equalizer
HPD
port Y
CS00061A
Data+
driver
Quantizer
Output I
Data-
AM00716V1
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 7/44
Page 8
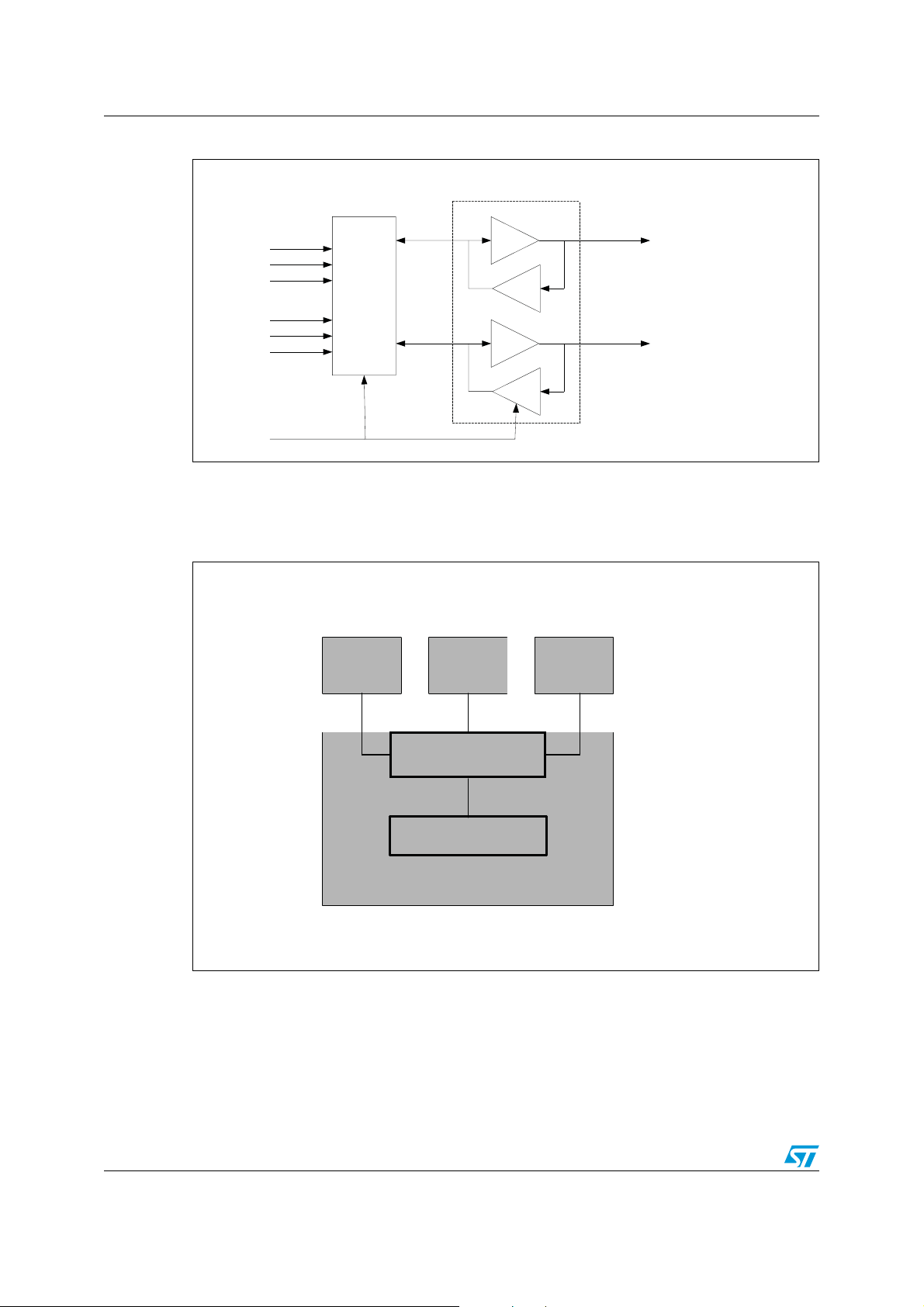
Block diagram STDVE103A
A
Figure 3. DDC I2C bus repeater
2
I
C Bus Repeater
A_DDC_SDA
B_DDC_SDA
C_DDC_SDA
Switch
A_DDC_SCL
B_DDC_SCL
C_DDC_SCL
S1, S2
2.1 Application diagrams
Figure 4. STDVE103A in a digital TV
Game
console
Y_DDC_SD
Y_DDC_SCL
DVD-R STB
Digital TV
STDVE103A
HDMI receiver
8/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
CS00063A
Page 9
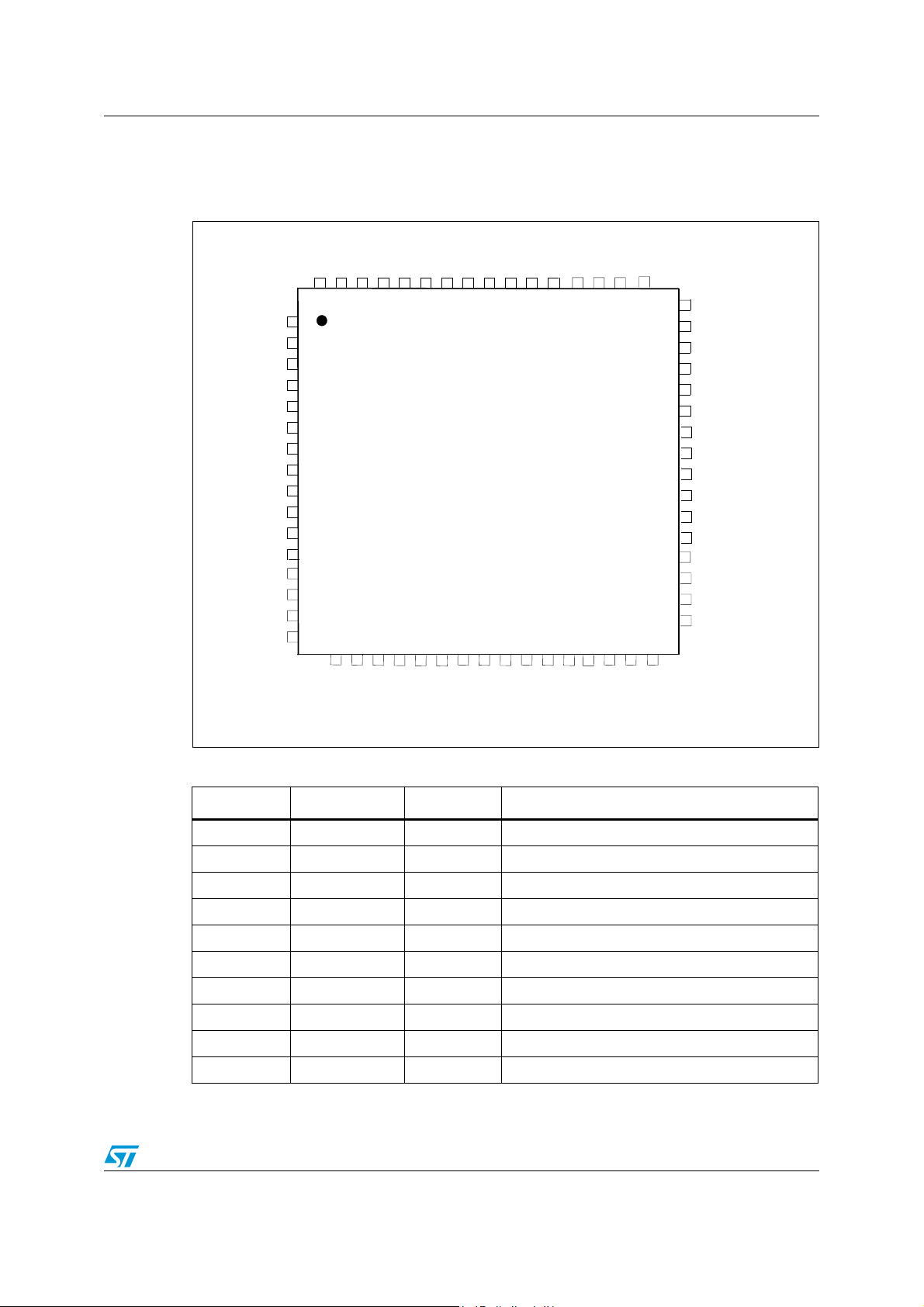
STDVE103A Pin configuration
3 Pin configuration
Figure 5. Pin configuration (TQFP64 package)
SDA3
SCL3
GND
B31
A31
VCC
B32
A32
GND
B33
A33
VCC
B 34
A34
GND
REXT
A24
HPD3
B24
4
62
63
6
VCC
61
A23
60
B23
59
GND
58
B22
A22
57
56
55
A21
B21
SCL2
54
52
53
VCC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
STDVE103A
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
7
1
4
Y
0
8
1
4
Z
1
9
2
1
3
C
Y
C
V
3
2
2
2
2
2
3
D
Y
Z
GN
6
4
2
2
Z
7
9
5
2
C
C
V
8
2
2
2
2
1
1
Y
K
D
Z
N
N
I
G
S
_
L
C
S
SDA2
51
VDD
HPD2
48
50
49
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
2
0
1
3
3
3
1
K
K
S
N
N
I
I
S
S
_
_
A
D
D
P
S
H
A14
B14
VCC
A13
B13
GND
A12
B12
VCC
A11
B11
SCL1
SDA1
HPD1
NC
S2
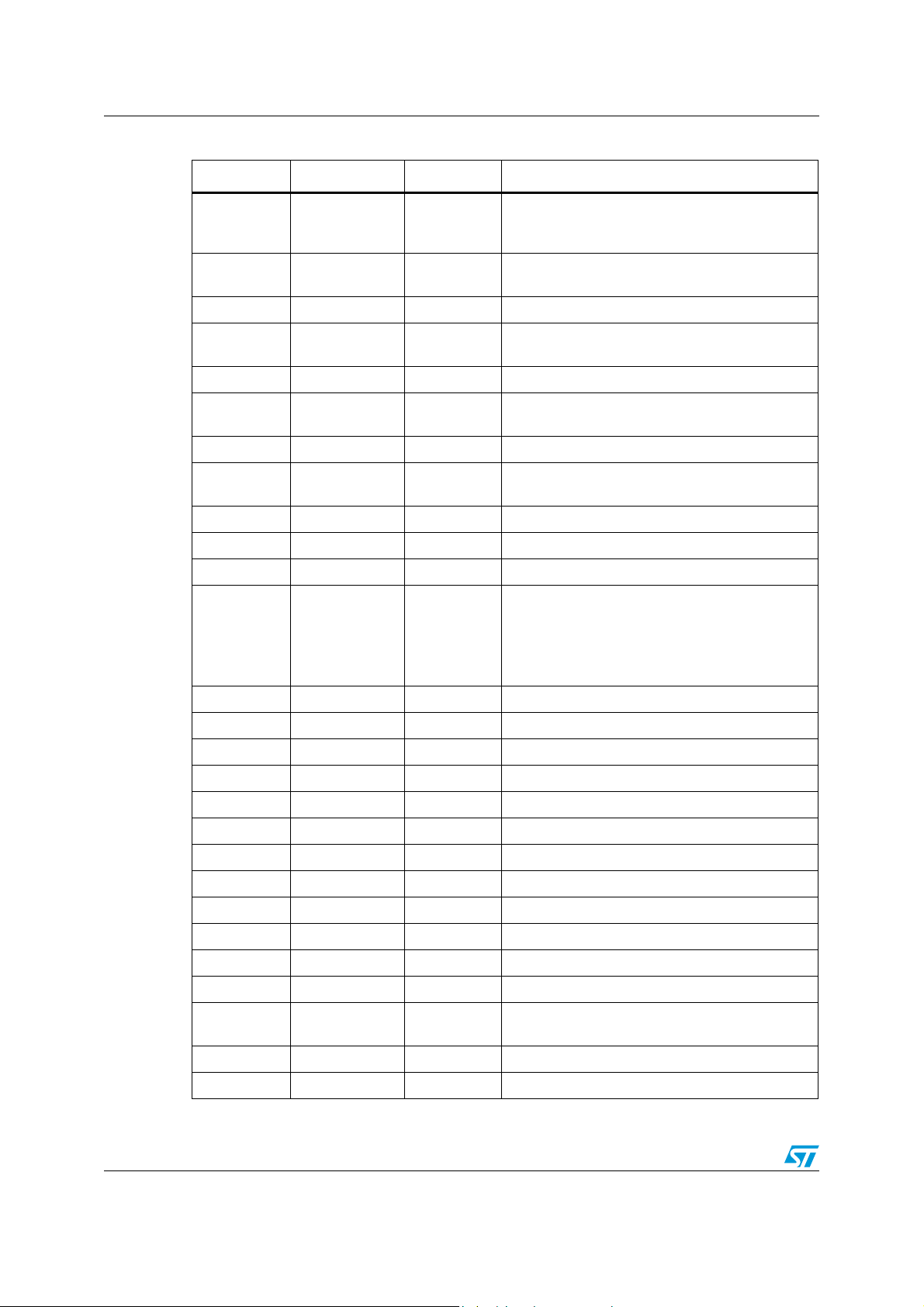
Table 2. Pin description
Pin number Pin name Type Function
1-2 SDA3, SCL3 I/O Port3 DDC bus data and clock lines
3 GND Power Ground
4-5 B31, A31 Input, TMDS Port 3 differential inputs for channel 1
6 V
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
7-8 B32, A32 Input, TMDS Port 3 differential inputs for channel 2
9 GND Power Ground
10-11 B33, A33 Input, TMDS Port 3 differential inputs for channel 3
12 V
13-14 B34, A34 Input, TMDS Port 3 differential inputs for channel 4
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
15 GND Power Ground
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 9/44
Page 10
Pin configuration STDVE103A
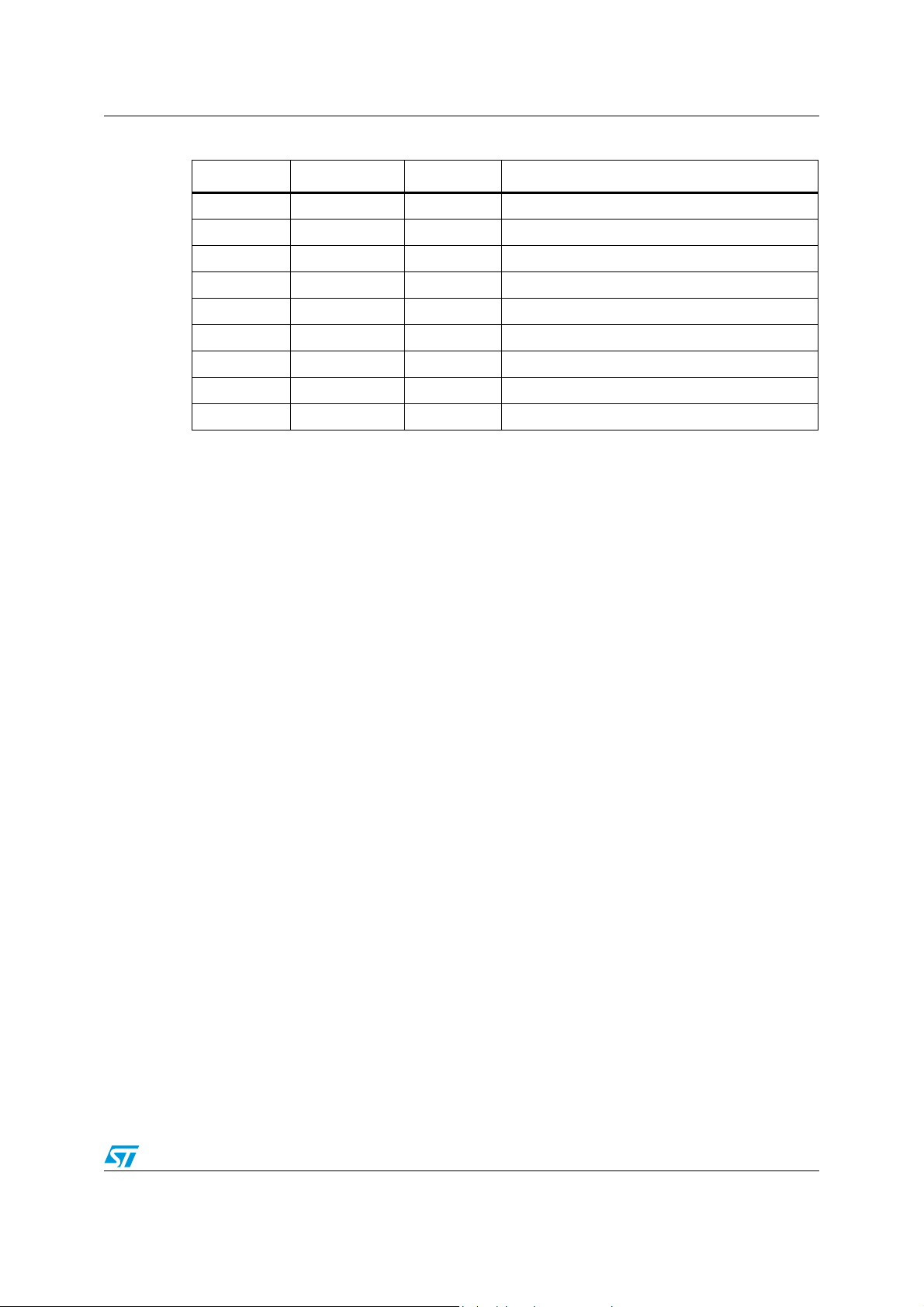
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
Pin number Pin name Type Function
Connect to GND through a 4.7 K ± 1% precision
16 R
17-18 Y4, Z4
19
20-21 Y3, Z3
22 GND Power Ground
23-24 Y2, Z2
25
26-27 Y1, Z1
28 GND Power Ground
29 SCL_SINK I/O Sink side DDC bus clock line
30 SDA_SINK I/O Sink side DDC bus data line
31 HPD_SINK Input
Analog
EXT
Output,
TMDS
V
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
Output,
TMDS
Output,
TMDS
V
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
Output,
TMDS
reference resistor. Sets the output current to
generate the output voltage compliant with TMDS
Channel 4 differential outputs
Channel 3 differential outputs
Channel 2 differential outputs
Channel 1 differential outputs
Sink side hot plug detector input
High: 5 V power signal asserted from source to
sink and EDID is ready
Low: No 5 V power signal is asserted from source
to sink or EDID is not ready
32-33 S1,S2 Input Source select inputs
34 NC No connect
35 HPD1 Output Port 1 hot plug detector output.
36
SDA1 I/O Port 1 DDC bus data line
37 SCL1 I/O Port 1 DDC bus clock line
38-39 B11, A11 Input, TMDS Port 1 differential inputs for channel 1
40
V
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
41-42 B12, A12 Input, TMDS Port 1 differential inputs for channel 2
43 GND Power Ground
44-45 B13, A13 Input, TMDS Port 1 differential inputs for channel 3
46 V
CC
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
47-48 B14, A14 Input, TMDS Port 1 differential inputs for channel 4
49 V
Power
DD
Supply voltage (5.0 V ± 10%) for DDC, HPD and
source selector pins
50 HPD2 Output Port 2 hot plug detector output
51 SDA2 I/O Port 2 DDC bus data line
10/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 11
STDVE103A Pin configuration
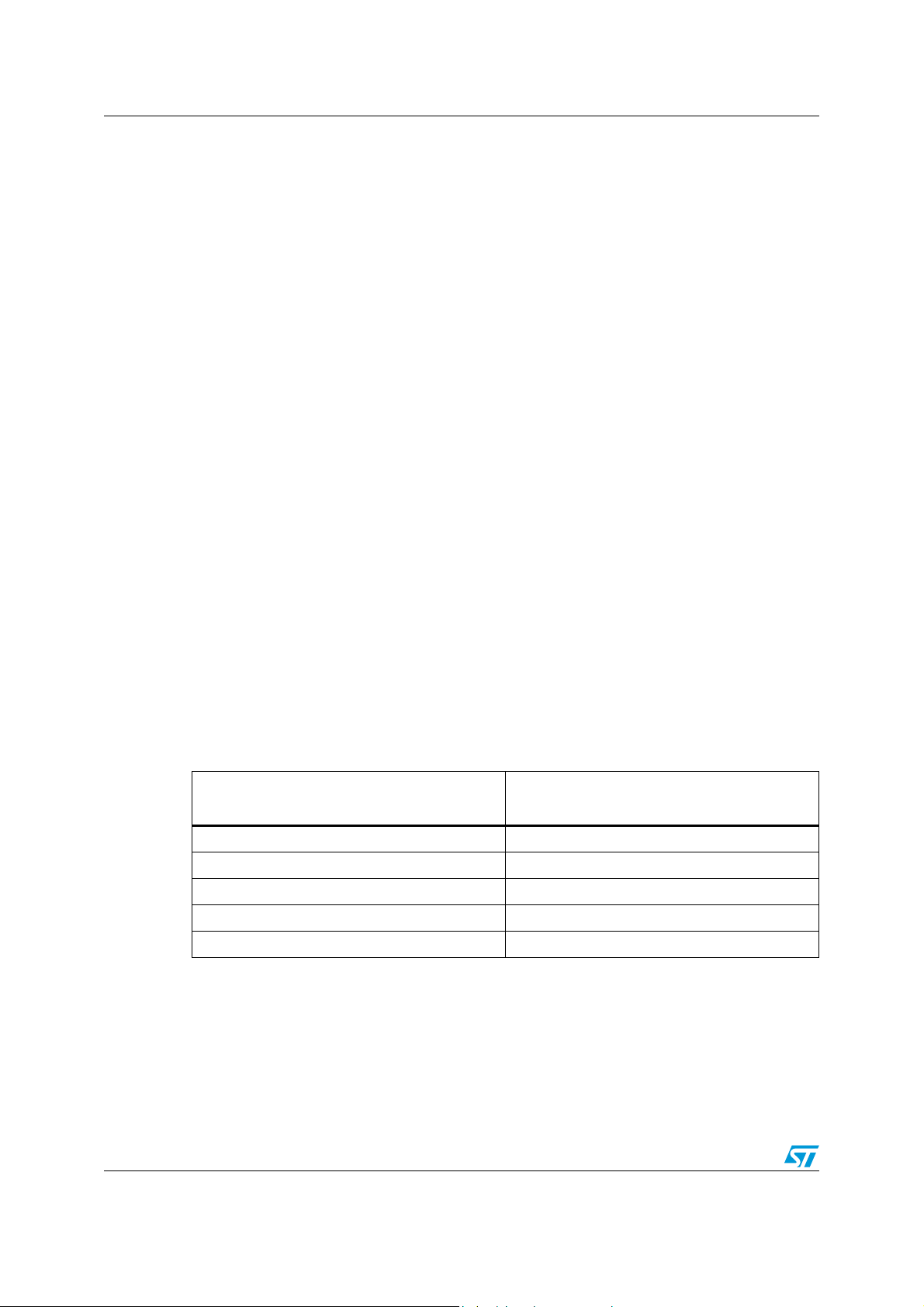
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
Pin number Pin name Type Function
52 SCL2 I/O Port 2 DDC bus clock line
53-54 B21, A21 Input, TMDS Port 2 differential inputs for channel 1
55 VCC Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
56-57 B22, A22 Input, TMDS Port 2 differential inputs for channel 2
58 GND Power Ground
59-60 B23, A23 Input, TMDS Port 2 differential inputs for channel 3
61
V
CC
62-63 B24, A24 Input, TMDS Port 2 differential inputs for channel 4
64 HPD3 Port 3 hot plug detector output.
Power Supply voltage (3.3 V ± 5%)
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 11/44
Page 12
Functional description STDVE103A
4 Functional description
The STDVE103A routes physical layer signals for high bandwidth digital video and is
compatible with low voltage differential signaling standards such as the TMDS. The device
passes the differential inputs from a video source to a common display when it is in the
active mode of operation. The device conforms to the TMDS standard on both inputs and
outputs.
The low on-resistance and low I/O capacitance of the switch in STDVE103A result in a very
small propagation delay. The device integrates SPDT-type switches for 3 differential data
TMDS channels and 1 differential clock channel. Additionally, it integrates the switches for
DDC and HPD line switching with I
2
The I
C interface of the selected input port is linked to the I2C interface of the output port,
and the hot plug detector (HPD) of the selected input port is output to HPD_SINK. For the
unused ports, the I
2
C interfaces are isolated and the HPD pins are driven to L state.
4.1 Adaptive equalizer
The equalizer dramatically reduces the intersymbol interference (ISI) jitter and attenuation
from long or lossy transmission media. The inputs present high impedance when the device
is not active or when V
on input channels are present.
is absent or 0 V. In all other cases, the 50 Ω termination resistors
CC
2
C repeater on the DDC lines.
This circuit helps to improve the signal eye pattern significantly. Shaping is performed by the
gain stage of the equalizer to compensate the signal degradation and then the signals are
driven on to the output ports.
The equalizer is fully adaptive and automatic in function providing smaller gain at low
frequencies and higher gain at high frequencies. The equalizer is optimized internally for an
adaptive operation.
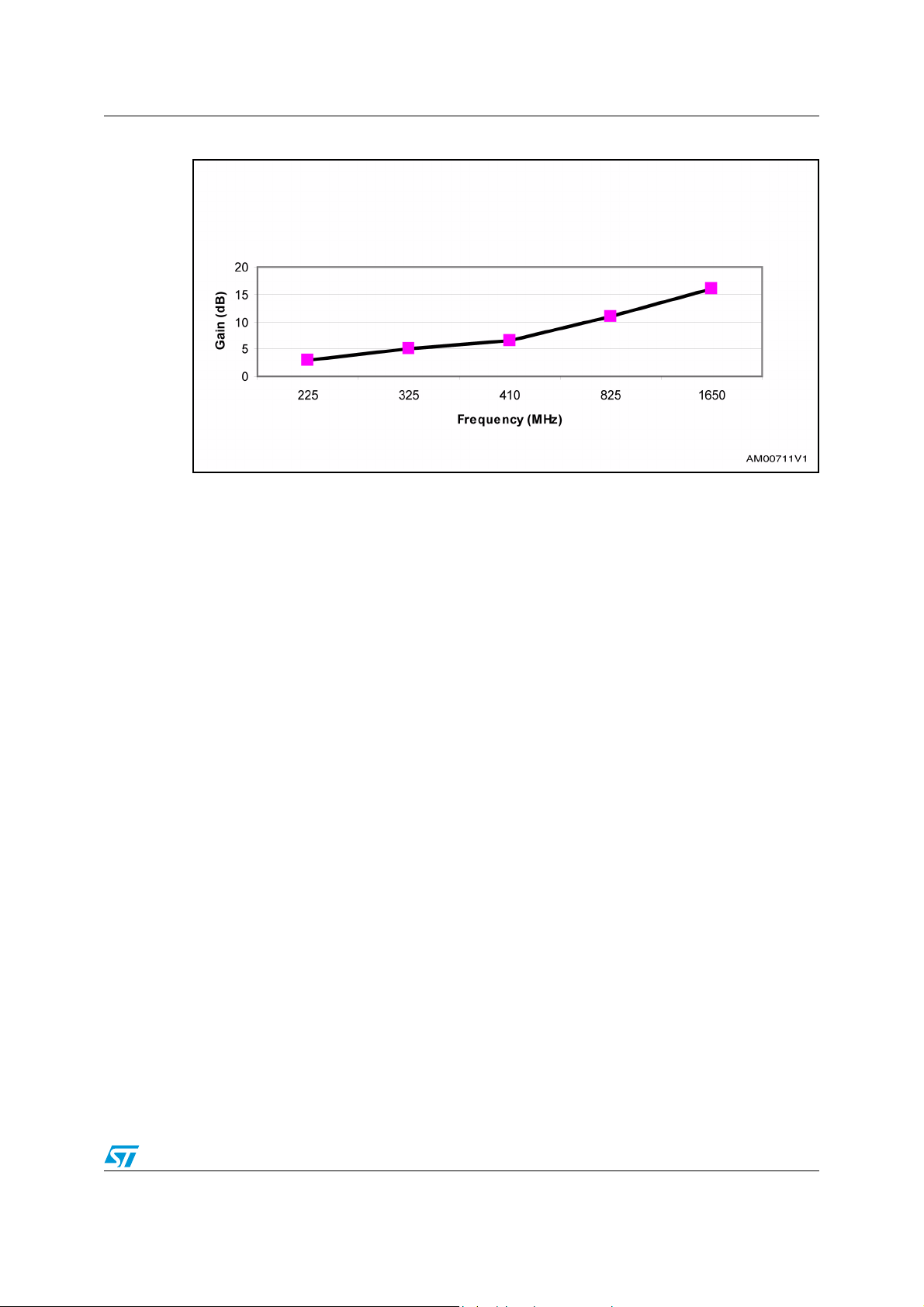
Table 3. Gain frequency response
Frequency
(MHz)
225 3
325 5
410 6.5
825 11
1650 16
Gain in dB
12/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 13
STDVE103A Functional description
Figure 6. STDVE103A gain vs. frequency
The STDVE103A equalizer is fully adaptive and automatic in function. The equalizer’s
performance is optimized for all frequencies over the cable lengths from 1 m to 25 m.
Input termination
The STDVE103A integrates precise 50 Ω ± 5% termination resistors, pulled up to VCC, on all
its differential input channels. External terminations are not required. This gives better
performance and also minimizes the PCB board space. These on-chip termination resistors
should match the differential characteristic impedance of the transmission line. Since the
output driver consists of current steering devices, an output voltage is not generated without
a termination resistor. Output voltage levels are dependent on the value of the total
termination resistance. The STDVE103A produces TMDS output levels for point-to-point
links that are doubly terminated (100
Ω at each end). With the typical 10 mA output current,
the STDVE103A produces an output voltage of 3.3 – 0.5 V = 2.8 V when driving a
termination line terminated at each end. The input terminations are selectable thus saving
power for the unselected ports.
Output buffers
Each differential output of the STDVE103A drives external 50 Ω load (pull-up resistor) and
conforms to the TMDS voltage standard. The output drivers consist of 10 mA differential
current-steering devices.
The driver outputs are short-circuit current limited and are high-impedance to ground when
S1, S2 = HL or the device is not powered. The current steering architecture requires a
resistive load to terminate the signal to complete the transmission loop from V
through the termination resistor. Because the device switches the direction of the current
flow and not voltage levels, the output voltage swing is determined by V
minus the voltage
CC
drop across the termination resistor. The output current drivers are controlled by the S1, S2
pin and are turned off when S1, S2 is a HL. A stable 10 mA current is derived by accurate
internal current mirrors of a stable reference current which is generated by band-gap voltage
across the REXT. The differential output driver provides a typical 10 mA current sink
capability, which provides a typical 500 mV voltage drop across a 50
Ω termination resistor.
to GND
CC
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 13/44
Page 14

Functional description STDVE103A
TMDS voltage levels
The TMDS interface standard is a signaling method intended for point-to-point
communication over a tightly controlled impedance medium. The TMDS standard uses a
lower voltage swing than other common communication standards, achieving higher data
rates with reduced power consumption while reducing EMI emissions and system
susceptibility to noise. The device is capable of detecting differential signals as low as
100 mV within the entire common mode voltage range.
14/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 15

STDVE103A Functional description
4.2 Operating modes
4.2.1 SEL operating modes
The active source is selected by configuring source select inputs, S1 and S2. The selected
TMDS inputs from each port are switched through a 3-to-1 multiplexer. The I
the selected input port is linked to the I
2
C interface of the output port, and the hot plug
2
C interface of
detector (HPD) of the selected input port is output to HPD_SINK.
Table 4. SEL operating modes
Control pins I/O selected Hot-plug detect status
S2 S1 Y/Z
A1/B1 terminations
HH
of A2/B2 and A3/B3
are disconnected
A2/B2 terminations
HL
of A1/B1 and A3/B3
are disconnected
A3/B3 terminations
LL
of A1/B1 and A2/B2
are disconnected
None (Z).
LH
All terminations are
disconnected
SCL_SINK
SDA_SINK
SCL1
SDA1
SCL2
SDA2
SCL3
SDA3
None (Z).
Pulled high by
external
termination
HPD1 HPD2 HPD3
HPD_SINK Z Z
ZHPD_SINKZ
Z Z HPD_SINK
ZZZ
H: logic high; L: logic low; X: don't care; Z: high impedance
4.3 HPD pins
The input pin HPD_SINK is 5 V tolerant, allowing direct connection to 5 V signals. The
switch is able to pass both 0 V and 5 V signal levels. The HPD_SINK is an input pin while
the HPD1, HPD2 and HPD3 are outputs.
4.4 DDC channels
The DDC channels are designed with a bidirectional NMOS gate, providing 5 V signal
tolerance. The 5 V tolerance allows direct connection to a standard I
the need for a level shifter. There should be external pull-up resistors on either side of the
device on both the SCL and SDA lines.
2
C bus, thus eliminating
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 15/44
Page 16

Functional description STDVE103A
4.5 I2C DDC line repeater
The device contains two identical bidirectional open-drain, non-inverting buffer circuits that
enable I
STDVE103A buffers both the serial data (DDC SDA) and serial clock (DDC SCL) on the I
bus, while retaining all the operating modes and features of the I
two buses of 400 pF bus capacitance to be connected in an I
2
C DDC bus lines to be extended without degradation in system performance. The
2
C system. This enables
2
C application. These buffers
2
C
are operational from a supply voltage of 3.0 to 3.6 V.
2
The I
C bus capacitance limit of 400 pF restricts the number of devices and bus length. The
STDVE103A enables the system designer to isolate the two halves of a bus,
accommodating more I
2
C devices or longer trace lengths. It can also be used to run two
buses, one at 5 V and the other at 3.3 V or a 400 kHz and 100 kHz bus, where the 100 kHz
bus is isolated when 400 kHz operation of the other bus is required. The STDVE103A can
be used to run the I
2
C bus at both 5 V and 3.3 V interface levels.
Two or more STDVE103As cannot be connected in series. The STDVE103A design does
not allow this configuration. Since there is no direction pin, slightly different “legal” low
voltage levels are used to avoid lock-up conditions between the input and output. A valid low
applied at the input of STDVE103A is propagated as a buffered low with a slightly higher
value on the enabled outputs.
When this buffered low is applied to another STDVE103A in series, the second STDVE103A
will not recognize it as a valid low and will not propagate it as a buffered low again.
The S1 and S2 (SEL) lines act as control signals for the corresponding A, B or C ports. Note
that the SEL line has an internal pull-down resistor. The SEL line should not change state
during an I
enabling part way through a bus cycle could confuse the I
2
C operation, because disabling during bus operation hangs the bus and
2
C parts being enabled. The SEL
input should change state only when the global bus and the repeater port are in idle state, to
prevent system failures.
The output low levels for each internal buffer are approximately 0.5 V, but the input voltage
of each internal buffer must be 70 mV or more below the output low level, when the output
internally is driven low. This prevents a lock-up condition from occurring when the input low
condition is released.
As with the standard I
levels on the buffered bus. The STDVE103A has standard open collector configuration of
2
the I
C bus. The size of the pull up resistors depends on the system, but each side of the
repeater must have a pull up resistor.
This part is designed to work with standard mode and fast mode I
mode I
in a generic I
2
C devices only specify 3 mA output drive, this limits the termination current to 3 mA
2
C system where standard mode devices and multiple masters are possible.
Under certain conditions, higher termination currents can be used.
4.6 Power-down condition
The HL combination of S1, S2 is used to disable most of the internal circuitry of
STDVE103A that puts the device in a low power mode of operation.
2
C system, pull up resistors are required to provide the logic high
2
C devices. Standard
16/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 17
STDVE103A Functional description
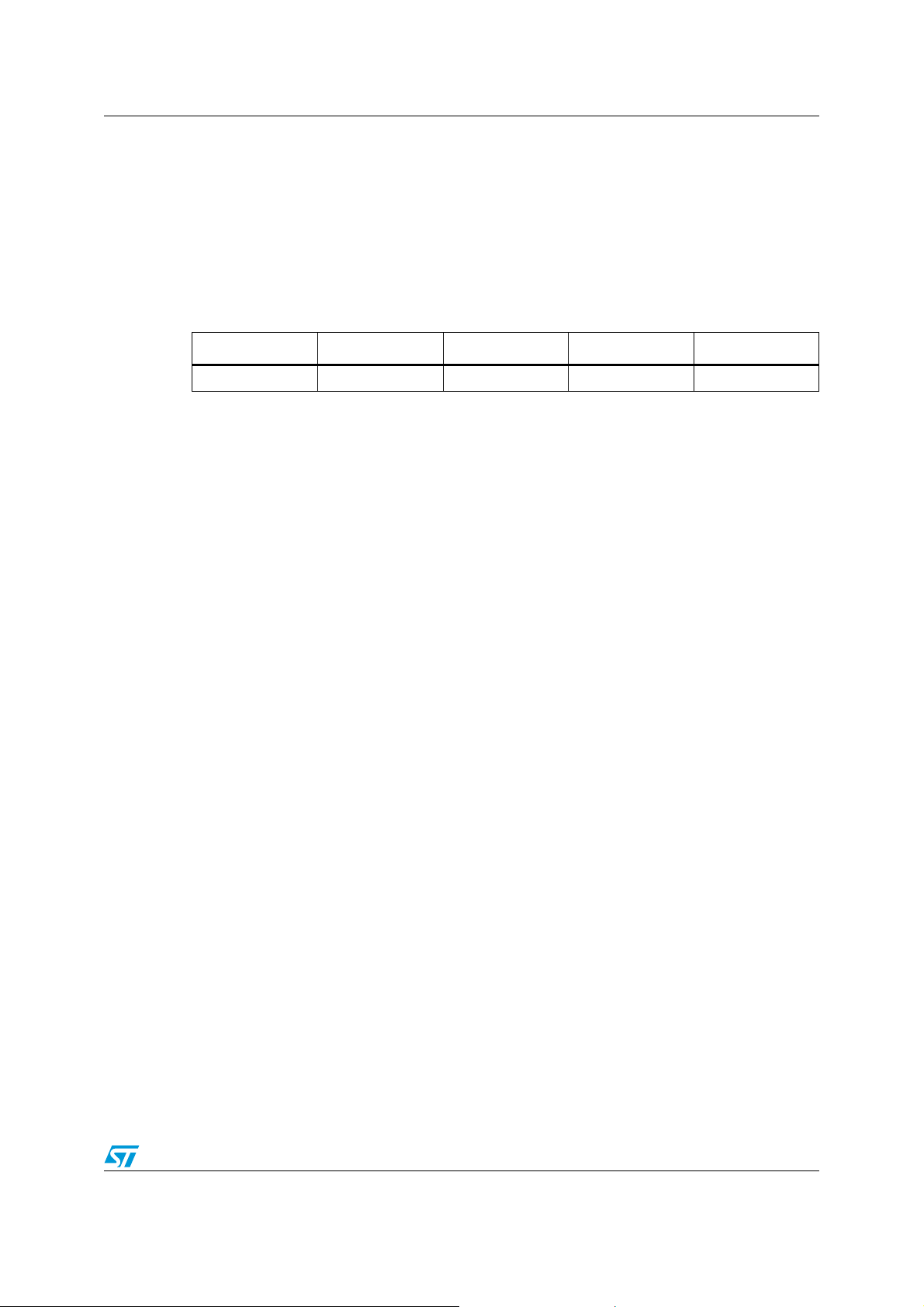
4.7 Bias
The bandgap reference voltage over the external R
reference resistor sets the internal
EXT
bias reference current. This current and its factors (achieved by employing highly accurate
and well matched current mirror circuit topologies) are generated on-chip and used by
several internal modules. The 10 mA current used by the transmitter block is also generated
using this reference current. It is important to ensure that the R
value is within the ±1%
EXT
tolerance range of its typical value.
Table 5. Bias parameter
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Bandgap voltage
The output voltage swing depends on 3 components: supply voltage (V
resistor (R
) and current drive (I
T
termination resistor can vary from 50
- 1.2 - V
, termination
). The supply voltage can vary from 3.3 V ±5%,
drive
Ω ±10%.
supply)
The voltage on the output is given by:
The variation on I
V
supplyIdriveRT
must be controlled to ensure that the voltage on HDMI output is within
drive
×–
the HDMI specification under all conditions.
This is achieved when:
400mV I
with typical value centered at 500 mV.
4.8 Timing between HPD and DDC
It is important to ensure that the I2C DDC interface is ready by the time the HPD detection is
complete.
As soon as the discovery is finished by the HPD detection, the configuration data is
exchanged between a source and sink through the I
DDC interface is ready for communication as soon as the power supply to the chip is
present and stable. When the desired port is enabled and the chip is out of shutdown mode,
2
the I
C DDC lines can be used for communication.
Thus, as soon as the HPD detection sequence is complete, the DDC interface can be
readily used. There is no delay between the HPD detection and I
ready.
× 600m V≤≤
driveRT
2
C DDC interface. The STDVE003’s
2
C DDC interface to be
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 17/44
Page 18
Maximum rating STDVE103A
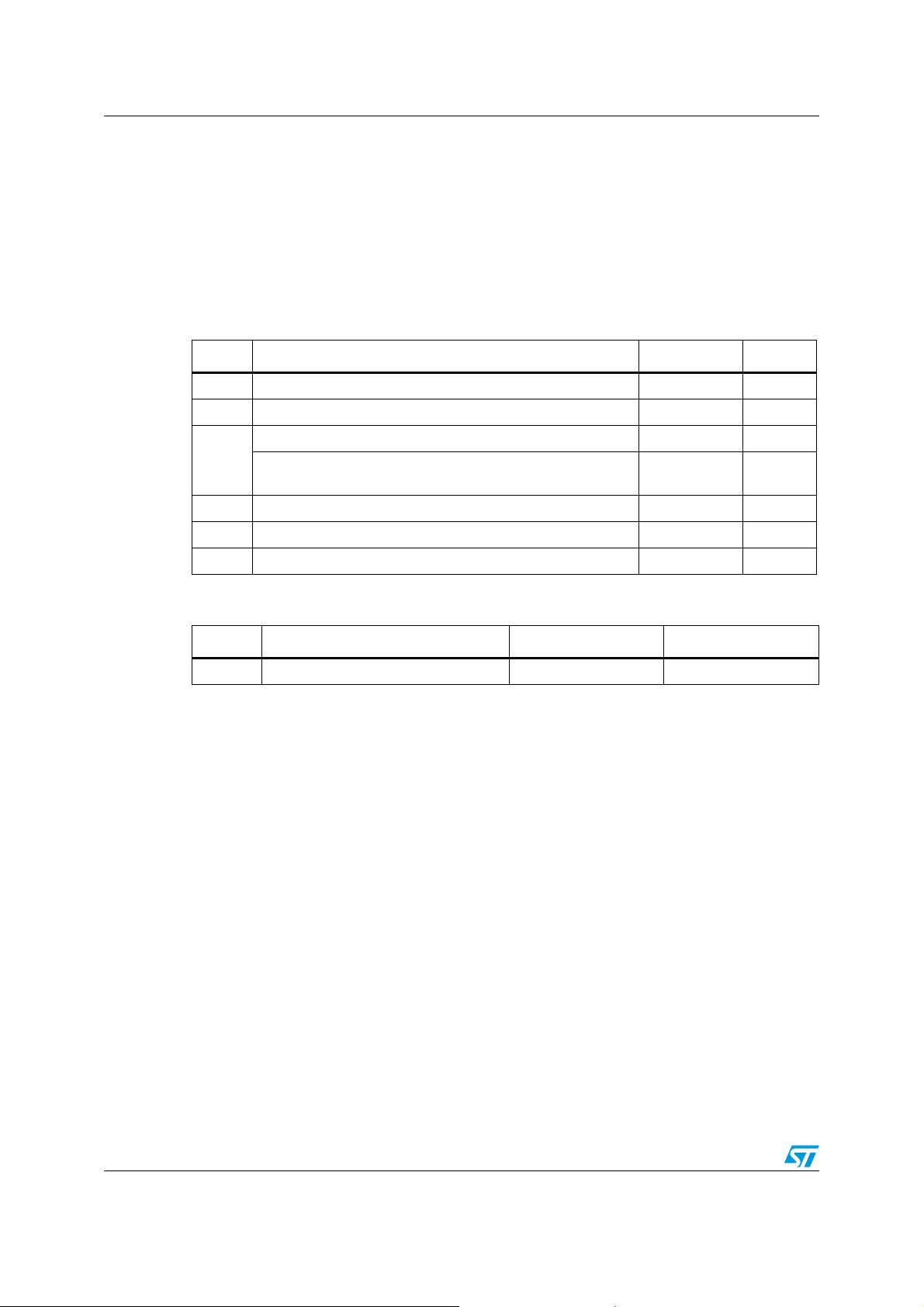
5 Maximum rating
Stressing the device above the rating listed in the “absolute maximum ratings” table may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Table 6. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
V
Supply voltage to ground -0.5 to +4.0 V
CC
Supply voltage to Ground (DDC, HPD, S1, S2) -0.5 to +6.0 V
DD
DC input voltage (TMDS ports) 1.7 to +4.0 V
V
I
T
SDA1, SCL1, SDA2, SCL2, SDA3, SCL3,SDA_SINK,
SCL_SINK, HPD_SINK, HPD1, HPD2, HPD3, S1, S2
I
DC output current 120 mA
O
Storage temperature -65 to +150 °C
STG
T
Lead temperature (10 sec) 300 °C
L
-0.5 to +6.0 V
Table 7. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter TQFP-64 Unit
Θ
Thermal coefficient (junction-ambient) 35 °C/W
JA
18/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 19

STDVE103A Maximum rating
5.1 Recommended operating conditions
5.2 DC electrical characteristics
TA = -40 to +85 °C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 5%
Table 8. Power supply characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition
(a)
Val u e
Unit
Min Typ Max
V
CC
V
DD
Supply voltage 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
All inputs/outputs are
enabled.
I
CC
Supply current
Inputs are terminated
50 Ω to VCC.
with
= 3.465 V
V
CC
Data rate = 3.4 Gbps
I
CC
I
DD
Table 9. DC specifications for TMDS differential inputs
Supply current S1, S2 = HL --20 mA
Supply current
(VDD supply)
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Differential input high
V
TH
threshold
(peak-to-peak)
V
TL
Differential input low
threshold
VCC = 3.465 V
over the entire V
= 3.465 V
V
CC
over the entire V
CMR
-150 0 - mV
CMR
Differential input
V
V
ID
CMR
voltage
(peak-to-peak)
Common mode
voltage range
(1)
VCC = 3.465 V 150 - 1560 mV
V
CC
--300 mA
- 25mA
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
- 0 150 mV
- 0.3 VCC - 0.04 V
C
IN
1. Differential output voltage is defined as | (OUT+ - OUT-) |.
Differential input voltage is defined as | (IN+ - IN-) |.
Input capacitance
a. Typical parameters are measured at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = +25 °C.
IN+ or IN- to GND
F = 1 MHz
- 3.5 - pF
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 19/44
Page 20

Maximum rating STDVE103A
Table 10. DC specifications for TMDS differential outputs
Value
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
Unit
V
V
V
|I
OH
V
OL
swing
OD
I
OL
SC
Single-ended high level
output voltage
Single-ended low level
output voltage
Single ended output
swing voltage
Differential output
voltage
(peak-to-peak)
Differential output low
level current
Output driver short-
|
circuit current
(continuous)
(1)
= 3.3 V
V
CC
R
= 50 Ω
TERM
VCC = 3.3 V
R
= 50 Ω
TERM
OUT± = GND
through a 50 Ω
resistor.
See Figure 11
-10 - VCC+10 mV
V
CC
V
-600 - VCC-400 mV
CC
400 500 600 mV
800 1000 1200 mV
81012mA
--12 mA
OUT+ or OUT-
C
OUT
Output capacitance
to GND when tristate
- 5.5 - pF
F = 1 MHz
1. Differential output voltage is defined as | (OUT+ - OUT-) |. Differential input voltage is defined as | (IN+ - IN-) |
20/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 21
STDVE103A Maximum rating
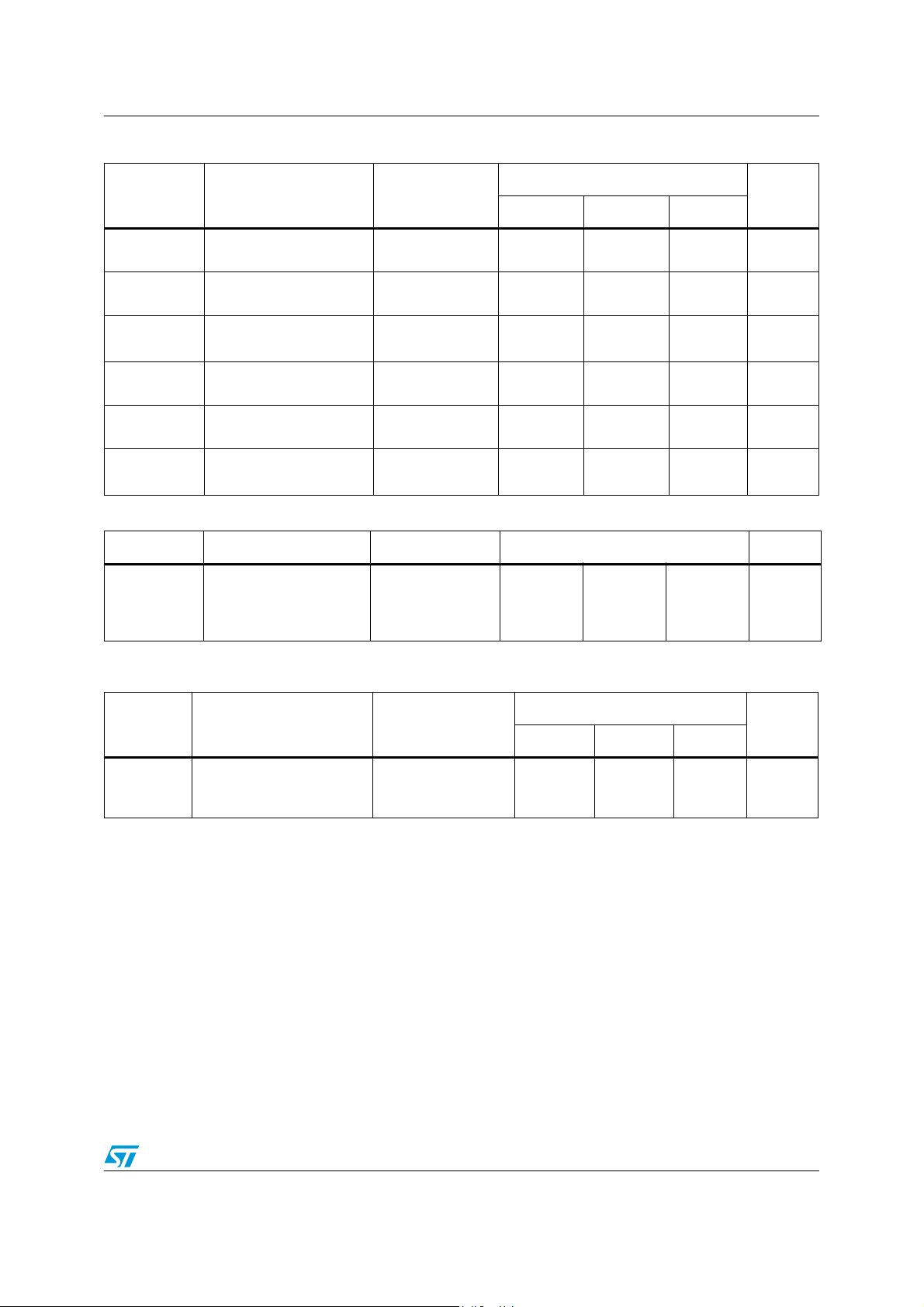
Table 11. DC specifications for SEL (S1, S2) inputs
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
V
IH
V
IL
V
IK
I
IH
I
IL
C
IN
Table 12. Input termination resistor
HIGH level input voltage
LOW level input voltage
Clamp diode voltage
Input high current
Input low current
Input capacitance
High level
guaranteed
Low level
guaranteed
V
= 3.465 V
CC
= -18 mA
I
IN
= 3.465 V
V
CC
V
= V
IN
CC
V
= 3.465 V
CC
V
= GND
IN
Pin to GND
F = 1 MHz
2.0 −−V
-0.5
-1.2 -0.8
− 0.8 V
− V
-5 − +5 µA
-5
− +5 µA
− 3.5 − pF
Symbol Parameter Test condition Value Unit
Differential input
R
TERM
termination resistor on
IN± channels relative to
V
CC
IIN = -10 mA 45 50 55 Ω
Unit
Table 13. External reference resistor
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Resistor for TMDS
R
EXT
compliant voltage swing
range
Tolerance for
R = ±1%
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
− 4.7 − KΩ
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 21/44
Page 22
Maximum rating STDVE103A
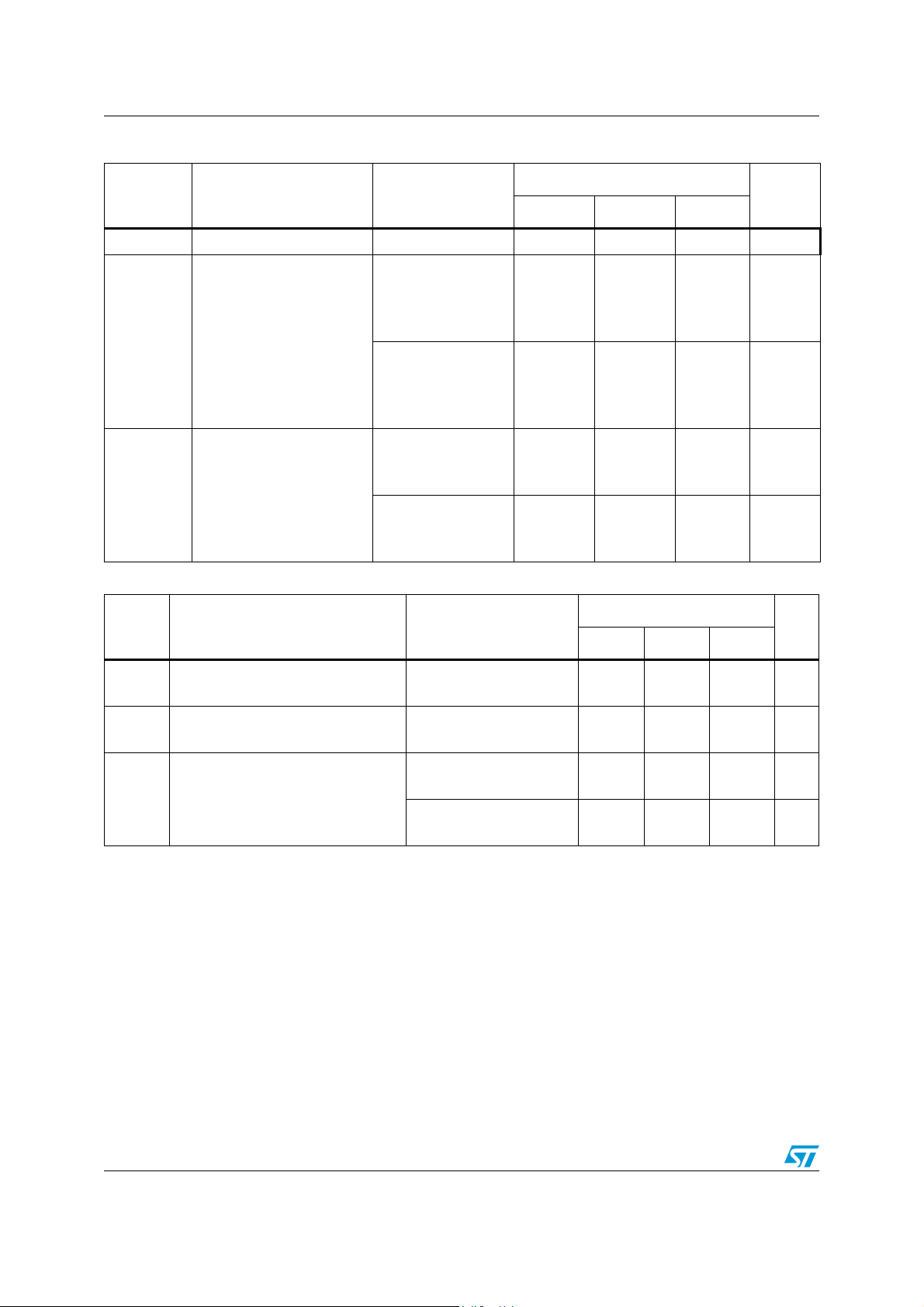
Table 14. DDC I/O pins (switch)
Symbol Parameter Test condition
V
I(DDC)
Input voltage GND − 5.3 V
VCC = 3.465 V
A, B, C ports = 5.3 V
Y port = 0.0 V
Switch is isolated
I
I(leak)
Input leakage current
V
= 3.465 V
CC
A, B, C ports = 3.3 V
Y port = 0.0 V
Switch is isolated
=0 V
V
I
F = 1 MHz
Switch disabled
C
I/O
Input/output capacitance
VI=0 V
F = 1 MHz
Switch enabled
Table 15. Status pins (HPD_SINK)
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
−−6µA
−−2µA
− 5 − pF
− 9 − pF
Symbol Parameter Test condition
V
= 3.3 V
V
V
High level input voltage
IH
Low level input voltage
IL
CC
High level guaranteed
V
= 3.3 V
CC
Low level guaranteed
= 3.465 V
V
CC
Y = 5.3 V
I
I(leak)
Input leakage current
V
CC
= 3.465 V
Y = 3.3 V
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
2.0
GND
− 5.3 V
− 0.8 V
−−4µA
−−2µA
22/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 23

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Table 16. Status pins (HPD1, HPD2, HPD3)
(1)
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
V Voltage GND − 5.3 V
=0V
V
I
F = 1 MHz
− 5 − pF
Switch disabled
C
Input/output capacitance
I/O
V
=0V
I
F = 1 MHz
− 9 − pF
Switch enabled
= 3.3 V
V
Output low voltage
OL
(open drain I/Os)
1. Typical parameters are measured at VCC = 3.3 V, TA = +25 °C.
V
CC
I
OL
=8mA
−−0.4 V
Unit
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 23/44
Page 24

Maximum rating STDVE103A
5.3 DC electrical characteristics (I2C repeater)
(TA = -40 to +85 °C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 5%, GND = 0 V; unless otherwise specified)
Table 17. Supplies
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
V
CC
Table 18. Input/output SDA, SCL
DC supply voltage 3.135 3.3 3.465 V
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
V
IH
V
IL
V
ILc
V
IK
I
IL
I
IH
V
OL
I
OH
C
1. VIL specification is for the first low level seen by the SDA/SCL lines. V
by the SDA/SCL lines.
2. The SCL/SDA C
secured to the repeater but an active bus remains on either set of the SDA/SCL pins.
High level input
voltage
Low level input
(1)
voltage
Low level input voltage
contention
(1)
0.7 V
CC
-0.5 − 0.3 V
-0.5
Input clamp voltage II = -18 mA −−-1.2 V
Input current low
(SDA, SCL)
Input current high
(SDA, SCL)
LOW-level output
voltage
Output high level
leakage current
Input capacitance VI = 3V or 0V − 67
I
is about 200 pF when VCC= 0 V. The STDVE103A should be used in applications where power is
I
Input current low
(SDA, SCL)
= 3.465 V
V
I
(SDA, SCL)
VI = 5.3 V
(SDA, SCL)
= 3 mA 0.4 V
I
OL
= 6 mA 0.65 V
I
OL
= 3.6 V;
V
O
driver disabled
VO = 5.3 V;
driver disabled
−−1µA
−−10 µA
−−10 µA
−−10 µA
−−10 µA
is for the second and subsequent low levels seen
ILc
Val ue
− 5.3 V
CC
− 0.4 V
(2)
Unit
V
pF
24/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 25

STDVE103A Maximum rating
5.4 Dynamic switching characteristics
TA = -40 to +85 °C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 5%, R
Typical values are at T
f
CK
rate
Clock frequency
(1/10th of the
differential data rate)
Signaling rate −−3.4 Gbps
Table 19. Clock and data rate
Symbol Parameter Test condition
D
Table 20. Equalizer gain
Symbol Parameter Test condition
G_EQ Equalizer gain
Table 21. Differential output timings
= +25 °C and VCC = 3.3 V.
A
At 225 MHz − 10 − dB
At 340 MHz
= 50 Ω ± 5%, CL = 5 pF).
TERM
(b)
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
25 − 340 MHz
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
− 15 − dB
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Unit
Min Typ Max
t
r
Differential data and
20% to 80% of V
OD
75 150 240 ps
clock output rise/fall
t
f
t
PLH
t
PHL
times
Differential low to high
propagation delay
Differential high to low
propagation delay
80% to 20% of V
OD
Alternating 1 and 0 pattern
at slow and fast data rates
Measure at 50% V
OD
between input to output
75 150 240 ps
250 − 800 ps
250
− 800 ps
b. The timing values in this section are tested during characterization and are guaranteed by
design and simulation. Not tested in production.
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 25/44
Page 26

Maximum rating STDVE103A
Table 22. Skew times
Symbol Parameter Test condition
t
SK(O)
t
SK(P)
t
SK(D)
Inter-pair channel-tochannel output skew
Pulse skew | t
Intra-pair differential
skew
PLH
- t
PHL
Difference in
propagation
t
SK(CC)
Output channel to
channel skew
delay
(t
PLH
or t
among all output
channels
Table 23. Turn-on and turn-off times
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Time from
t
ON
TMDS output enable
time
OE_N to OUT±
change from tristate to active
Time from
OE_N to OUT±
change from
active to tri-
t
OFF
TMDS output disable
time
state
Val u e
Min Typ Max
−−100 ps
| − 25 80 ps
−−50 ps
PHL
)
− 50 125 ps
Val ue
Min Typ Max
− 12 20 ns
− 610 ns
Unit
Unit
Table 24. DDC I/O pins
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
Refer to Section 5.5
Table 25. Status pins (HPD_SINK, HPD1, HPD2, HPD3, S1, S2)
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
Propagation delay
t
PD(HPD)
(from Y_HPD to the
active port of HPD)
T
ON/OFF
Switch time
(from port select to the
latest valid status of
= 10 pF,
C
L
RPU=1KΩ
= 10 pF − 50 − ns
C
L
HPD)
26/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Val ue
Unit
Val ue
Unit
− 150 − ns
Page 27

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Table 26. Jitter
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
Unit
t
JIT
Total jitter
(1)
PRBS pattern
at 1.6 Gbps
− 35 − ps (p-p)
(800 MHz)
1. Total jitter is measured peak-to-peak with a histogram including 3500 window hits. Stimulus and fixture jitter has been
subtracted. Input differential voltage = V
parameter is not production-tested but guaranteed through characterization on a sample-to-sample basis.
= 500 mV, PRBS random pattern at 1.65 Gbps, tr=tf=50 ps (20% to 80%). Jitter
ID
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 27/44
Page 28
Maximum rating STDVE103A
5.5 Dynamic switching characteristics (I2C repeater)
TA = -40 to +85 °C, VCC = 3.3 V ± 5%.
Typical values are at T
= +25 °C and VCC = 3.3 V.
A
.
Table 27. I
2
C repeater
Symbol Parameter Test condition
f
SCL
t
LOW
t
LOW
I2C clock frequency
Low duration on SCL pin
Low duration on SCL pin
(1)
Standard mode −−100 kHz
Fast mode
100 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 5V
Cmax=400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions.
400 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 5V
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions.
100 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions.
400 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions.
Val ue
Min Typ Max
−−400 kHz
4.7
1.3
4.7
1.3
−−µs
−−µs
−−µs
−−µs
Unit
28/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 29

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Table 27. I2C repeater
Symbol Parameter Test condition
t
HIGH
t
HIGH
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PHL
High duration on SCL pin
High duration on SCL pin
Propagation delay
Propagation delay
Propagation delay
(1)
(continued)
100 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 5V
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions
400 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 5 V
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax=2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions
100 KHz
Refer section 14.12,
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions
400 KHz
See Figure 19
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax=400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Depends on input signal rise time.
Includes the 20% time intervals
on both transitions
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Val ue
Min Typ Max
4.0
0.6
4.0
0.6
−−µs
−−µs
−−µs
−−µs
−−250 µs
−−300 µs
−−250 ns
Unit
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 29/44
Page 30

Maximum rating STDVE103A
Table 27. I2C repeater
(1)
(continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition
400 KHz
t
PLH
Propagation delay
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
t
PHL
Propagation delay
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
t
PLH
Propagation delay
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
t
PHL
Propagation delay
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
t
PLH
Propagation delay
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V,
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
Val ue
Unit
Min Typ Max
−−450 ns
−−250 ns
−−300 ns
−−250 ns
−−450 ns
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V
(2)
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
t
Output fall time
f
400 KHz
Waveform 1
(2)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V
(2)
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
t
Output fall time
f
100 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
(2)
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
30/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 31

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Table 27. I2C repeater
(1)
(continued)
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test condition
Min Typ Max
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 5 V
(2)
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
t
Output rise time
r
400 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
(2)
−−300 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
100 KHz
Waveform 1,
Voltage on line = 5 V
(2)
−−1000 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
t
Output rise time
r
100 KHz
Waveform 1 (Figure 17)
Voltage on line = 3.3 V
(2)
−−1000 ns
Cmax = 400 pF, Rmax = 2 K
1. All the timing values are tested during characterization and are guaranteed by design and simulation. Not tested in
production.
2. The t
transition time is specified with maximum load of 2 kΩ pull-up resistance and 400 pF load capacitance. Different load
r
resistance and capacitance will alter the RC time constant, thereby changing the propagation delay and transition times.
Refer to Figure 9.
Unit
Table 28. ESD performance
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
ESD
(HBM)
TMDS I/Os Human body model
Other I/Os Human body model
− ±5 − kV
− ±2 − kV
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 31/44
Page 32
Maximum rating STDVE103A
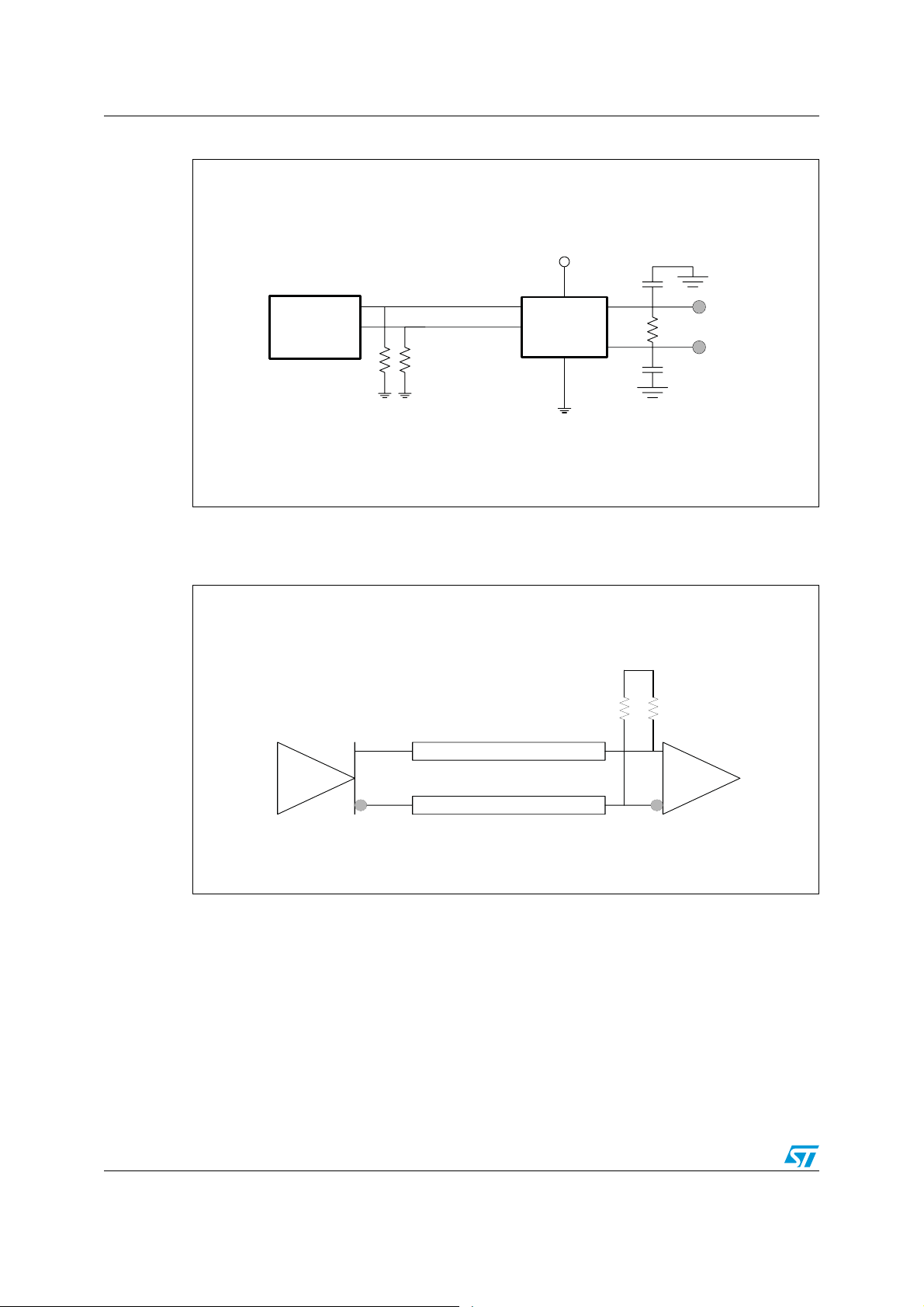
Figure 7. Test circuit for electrical characteristics
V
CC
C
L
V
V
IN+
Pulse
generator
R
T
R
T
V
IN-
1. CL= load capacitance: include jig and probe capacitance.
= termination resistance; should be equal to Z
2. R
T
of the pulse generator.
OUT
STDVE103A
OUT+
100 Ω
V
OUT-
C
L
CS00065A
Figure 8. TMDS output driver
R
ZO = R
T
TMDS
driver
1. ZO = characteristic impedance of the cable.
= termination resistance: should be equal to ZO of the cable. Both are equal to 50W.
2. R
T
ZO = R
T
V
CC
T
R
T
TMDS
receiver
CS00069
32/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 33

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Figure 9. Test circuit for HDMI receiver and driver
VCC
V
A
VB
1. RT = 50 Ω.
RT
A
VID
B
VID = VA - VB
RT
TMDS
receiver
TMDS
driver
VSwing = VY - VZ
Y
CL =
0.5pF
Z
VZ
VY
RT
RT
V
CC
CS00071
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 33/44
Page 34

Maximum rating STDVE103A
Figure 10. Test circuit for turn off and turn off times
0.01
10µF 0.1 µF
µF
1.15 V
VIN+
V
CC
1.0 V
1.15 V
STDVE103A
VIN-
1.0 V
Pulse
generator
50 Ω
4.7 KΩ
SHDN_N
REXT
GND
±1%
1. CL = 5 pF
Figure 11. Test circuit for short circuit output current
50 Ω
CL
50 Ω
1.2 V
50 Ω
CL
CS00072A
TMDS
driver
34/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
50 Ω
0V or 3.465 V
I
SC
Page 35

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Figure 12. Propagation delays
VA
ID
ID(p-p)
V
80%
tr tf
VB
V
Output
VCM V
ID
tpLH
20% 20%
Figure 13. Turn-on and turn-off times
VCC
VCM
VCC – 0.4
0.4V
VID
0V
-0.4V
V
OD(O)
OD(p-p)
V
tpHL
80%
V
OD(U)
100%
0V Differential
0%
SHDN_N
V
OUT+
when VID= +150mV
OUT-
when VID= -150mV
V
1.50 V
OFF
t
50%
1.50 V
t
ON
50%
3.0 V
0 V
OH
V
1.2 V
t
OFF
t
ON
1.2 V
OUT+
when VID= -150mV
V
OUT-
when VID= +150mV
V
50%
50%
OL
V
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 35/44
Page 36

Maximum rating STDVE103A
Figure 14. TSK(O)
3.5V
2.5V
Data In
Data Out at Port 0
Data Out at Port 1
Figure 15. TSK(P)
tpLHX tpHLX
2.5V
tpLHY
tSK(o) = | tpLHy – tpLHx | or | tpHLy – tpHLx |
tpHLY
tSK(o)
1.5V
V
2.5V
V
V
2.5V
V
OH
OL
OH
OL
Figure 16. TSK(D)
36/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 37

STDVE103A Maximum rating
Figure 17. AC waveform 1 (I2C lines)
Figure 18. Test circuit for AC measurements (I
2
Figure 19. I
C bus timing
2
C lines)
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 37/44
Page 38

Application information STDVE103A
6 Application information
6.1 Power supply sequencing
Proper power-supply sequencing is advised for all CMOS devices. It is recommended to
always apply V
6.2 Power supply requirements
before applying any signals to the input/output or control pins.
CC
Bypass each of the V
pins with 0.1 μF and 1 nF capacitors in parallel as close to the
CC
device as possible, with the smaller-valued capacitor as close to the V
possible.
All V
from each V
pins can be tied to a single 3.3 V power source. A 0.01 μF capacitor is connected
CC
pin directly to ground to filter supply noise. The maximum power supply
CC
variation can only be ±5% as per the HDMI specifications.
The maximum tolerable noise ripple on 3.3 V supply must be within a specified limit.
6.3 Differential traces
The high-speed TMDS inputs are the most critical parts for the device. There are several
considerations to minimize discontinuities on these transmission lines between the
connectors and the device.
(a) Maintain 100-Ω differential transmission line impedance into and out of the STDVE103A.
(b) Keep an uninterrupted ground plane below the high-speed I/Os.
(c) Keep the ground-path vias to the device as close as possible to allow the shortest return
current path.
(d) Layout of the TMDS differential inputs should be with the shortest stubs from the
connectors.
Output trace characteristics affect the performance of the STDVE103A. Use controlled
impedance traces to match trace impedance to both the transmission medium impedance
and termination resistor. Run the differential traces close together to minimize the effects of
the noise. Reduce skew by matching the electrical length of the traces. Avoid discontinuities
in the differential trace layout. Avoid 90 degree turns and minimize the number of vias to
further prevent impedance discontinuities.
pin of the device as
CC
38/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 39
STDVE103A Application information
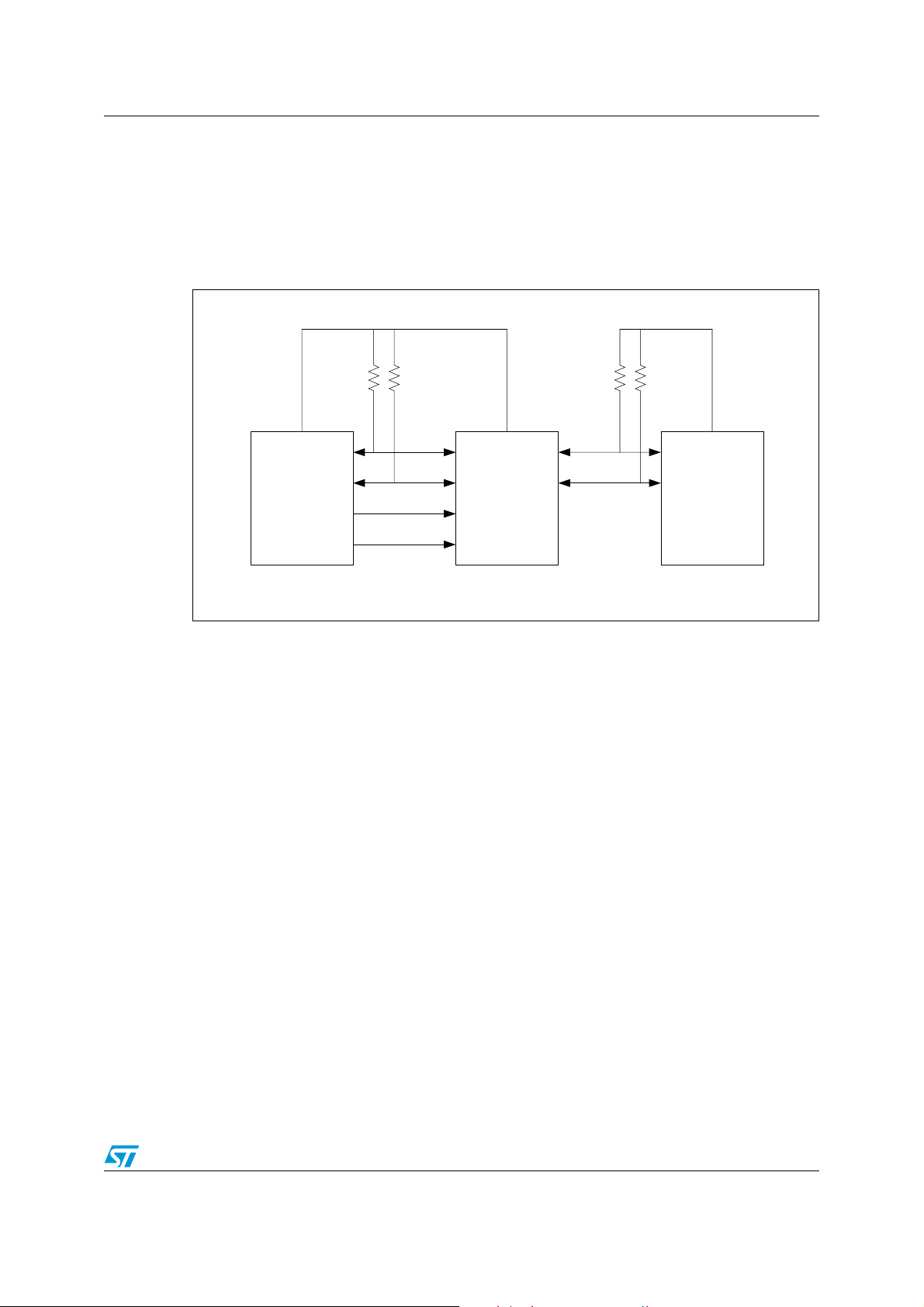
6.3.1 I2C lines application information
A typical application is shown in the figure below. In the example, the system master is
running on a 3.3 V I
2
C-bus while the slave is connected to a 5 V bus. Both buses run at
100 kHz unless the slave bus is isolated and then the master bus can run at 400 kHz.
Master devices can be placed on either bus.
Figure 20. Typical application of I
3.3V 5.0V
SDA
SCL
Bus Master
400 kHz
SHDN_N
2
C bus system
SDA SDA
SCL SCL
STDVE103A
SEL
SDA
SCL
Slave
100 kHz
BUS 0 BUS 1
AM00712V1
The STDVE103A DDC lines are 5 V tolerant; so it does not require any extra circuitry to
translate between the different bus voltages.
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 39/44
Page 40
Package mechanical data STDVE103A
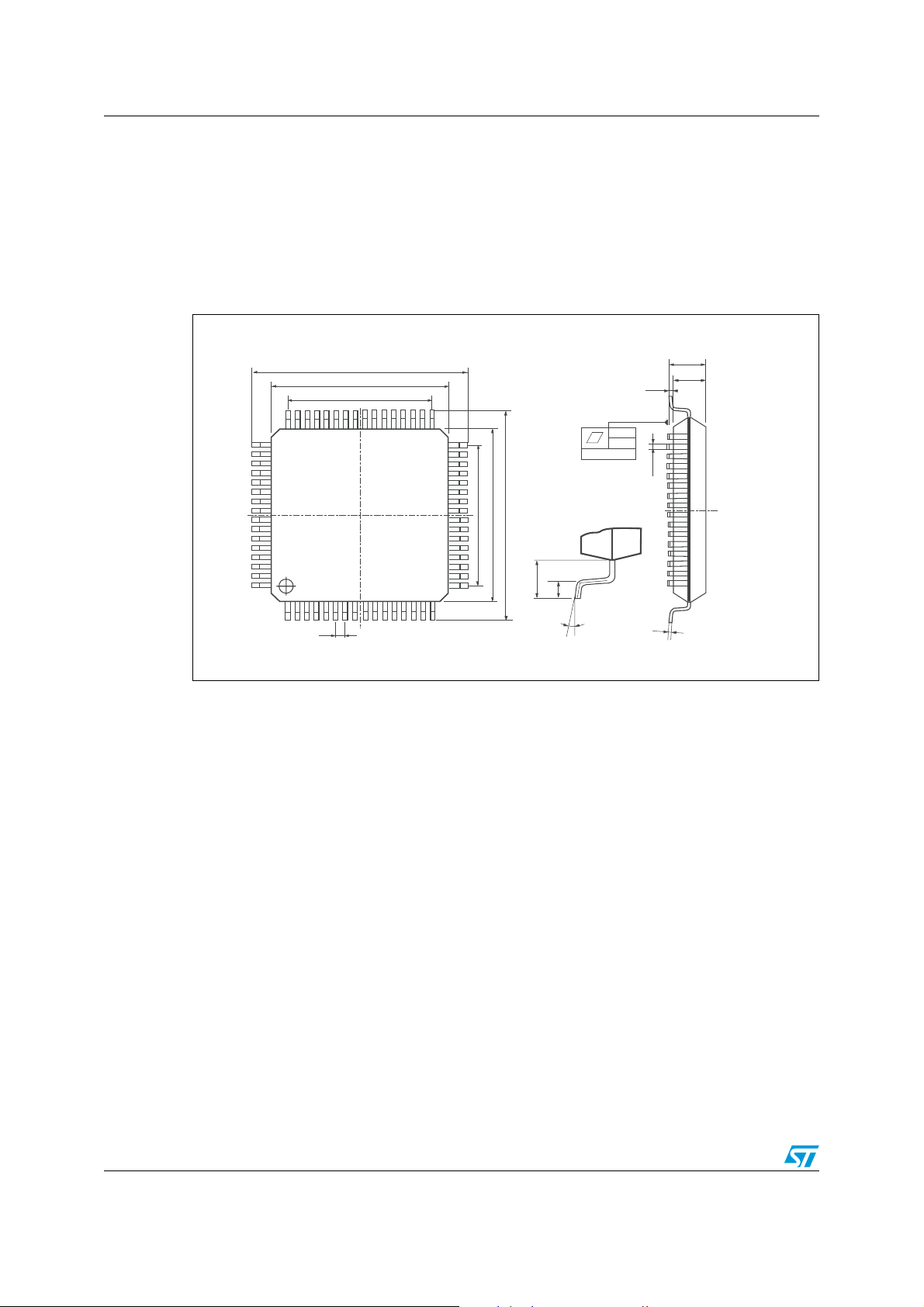
7 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
Figure 21.
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
TQFP64 package outline
D
D1
48
49
64
1
D3
e
33
32
E
E1
E3
L1
17
16
L
Seating Plane
K
0.10mm
.004
A
A2
A1
B
C
0051434/E
40/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 41
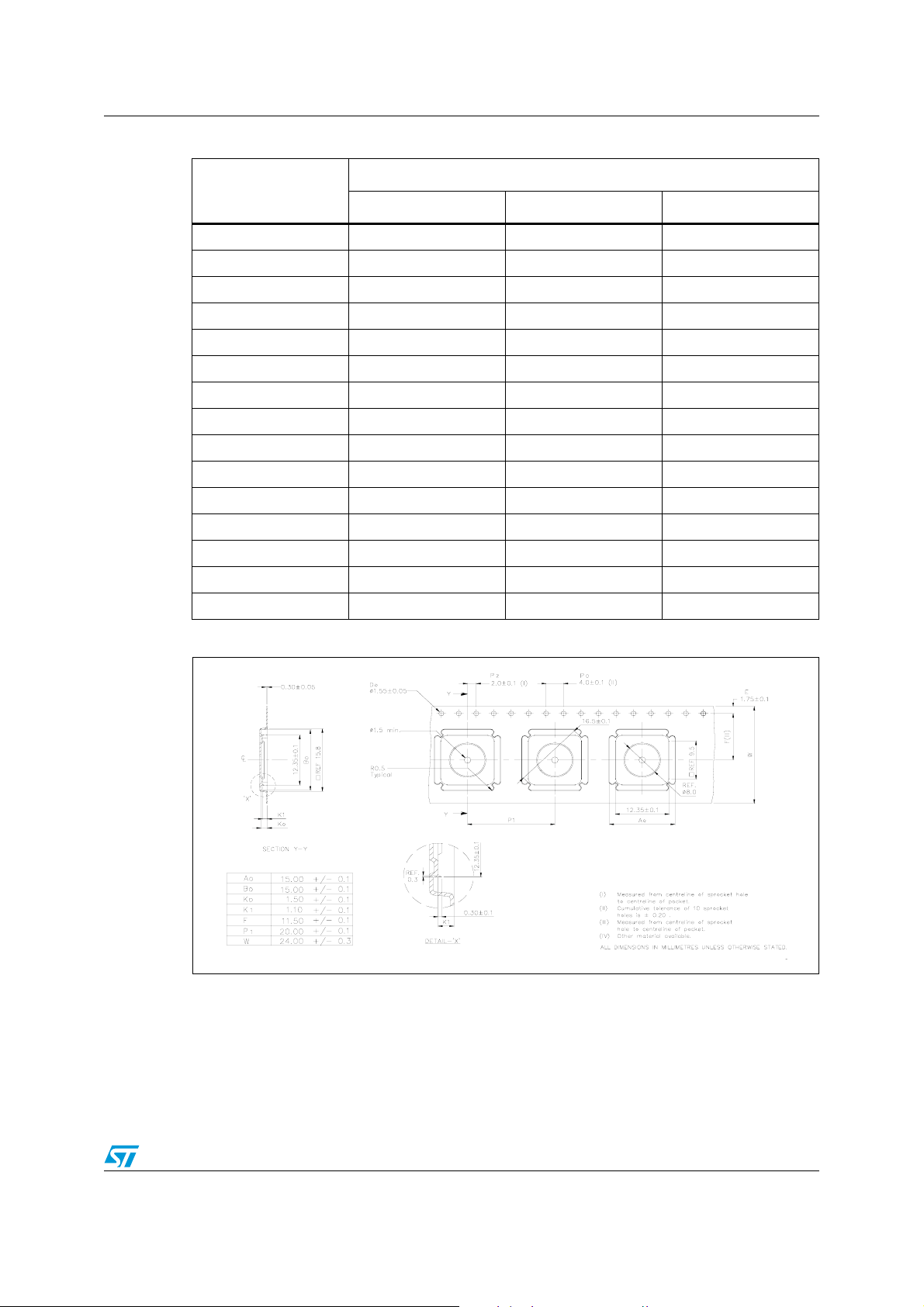
STDVE103A Package mechanical data
Table 29. TQFP64 mechanical data
Millimeters
Symbol
Min Typ Max
A
−−1.20
A1 0.05 0.10 0.15
A2 0.95 1 1.05
b 0.17 0.22 0.27
c 0.09 0.15 0.20
D 11.80 12 12.20
D1 9.80 10 10.20
D3
− 7.50 −
E 11.80 12 12.20
E1 9.80 10 10.20
E3 − 7.50 −
e − 0.50 −
L 0.45 0.60 0.75
L1
−1 −
K0°−7°
Figure 22. TQFP64 tape and reel information
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 41/44
Page 42

Package mechanical data STDVE103A
Figure 23. TQFP64 tray drawing
Figure 24. TQPF64 tray drawing dimensions
42/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
Page 43

STDVE103A Revision history
8 Revision history
Table 30. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
21-Jul-2008 1 Initial release.
Changed Table 1: Device summary on page 1 to add new order
code.
Modified the hot-plug detect status in Table 4: SEL operating modes
on page 15.
09-Sept-2008 2
Updated ESD information in the Features section and Table 28: ESD
performance on page 31
Added TQFP64 tray drawing in Figure 23: TQFP64 tray drawing on
page 42 and Figure 24: TQPF64 tray drawing dimensions on
page 42.
27-Mar-2009 3
Updated: Features section and thermal junction value in Chapter 5:
Maximum rating.
01-Jun-2009 4 Updated: Ta b l e 1 0 .
Doc ID 14911 Rev 4 43/44
Page 44

STDVE103A
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
44/44 Doc ID 14911 Rev 4
 Loading...
Loading...