Page 1

Bluetooth™ V2.1 + EDR ("Lisbon") for automotive applications
Features
■ Based on Ericsson technology licensing
baseband core (EBC)
■ Bluetooth™ specification compliance:
V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon”)
– Point-to-point, point-to-multipoint (up to 7
slaves) and scatternet capability
– Support ACL and SCO links
– Extended SCO (eSCO) links
– Faster connection
■ HW support for packet types
– ACL: DM1, DM3, DM5, DH1, DH3, DH5, 2-
DH1, 2-DH3, 2-DH5, 3-DH1, 3-DH3, 3-DH5
– SCO: HV1, HV3 and DV
– eSCO: EV3, EV4, EV5, 2-EV3, 2-EV5, 3-
EV3, 3-EV5
■ Adaptive frequency hopping (AFH)
■ Channel quality driven data rate (CQDDR)
■ “Lisbon” features
– Encryption pause/resume (EPR)
– Extended inquiry response (EIR)
– Link supervision time out (LSTO)
– Secure simple pairing
– Sniff subrating
– Quality of service (QoS)
Packet boundary flag
Erroneous data delivery
■ Transmit power
– Power class 2 and power class 1.5 (above
4 dBm)
– Programmable output power
– Power class 1 compatible
■ HCI
– HCI H4 and enhanced H4 transport layer
– HCI proprietary commands (e.g.
peripherals control)
– Single HCI command for patch/upgrade
download
– eSCO over HCI supported
■
Supports pitch-period error concealment (PPEC)
■ Efficient and flexible support for WLAN
coexistence scenarios
STA2500D
LFBGA48 (6x6x1.4mm; 0.8mm Pitch)
■ Low power consumption
– Ultra low power architecture with 3 different
low-power levels
– Deep sleep modes, including host-power
saving feature
– Dual wake-up mechanism: initiated by the
host or by the Bluetooth device
■ Communication interfaces
– Fast UART up to 4 MHz
– Flexible SPI interface up to 13 MHz
– PCM interface
– Up to 10 additional flexibly programmable
GPIOs
– External interrupts possible through the
GPIOs
–Fast I
■ Clock support
– System clock input (digital or sine wave) at
– Low power clock input at 3.2 kHz, 32 kHz
■ ARM7TDMI CPU
■ Memory organization
– On chip RAM, including provision for
– On chip ROM, preloaded with SW up to
■ Ciphering support up to 128-bit key
■ Single power supply with internal regulators for
core voltage generation
■ Supports 1.65 V to 2.85 V I/O systems
■ Auto calibration (VCO, filters)
2
C interface as master
9.6, 10, 13, 16, 16.8, 19.2, 26, 33.6 or 38.4 MHz
and 32.768 kHz
patches
HCI
January 2010 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 1/58
www.st.com
1
Page 2

Contents STA2500D
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Quick reference data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Operating ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3 I/O specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.4 Clock specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.5 Current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Block diagram and electrical schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4 Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1 Pin description and assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.2 HW configuration of the STA2500D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.3 I/O Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.1 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.2 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.3 PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.4 Bluetooth controller V1.2 and V2.0 + EDR features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.5 Bluetooth controller V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.6 Processor and memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.7 TX output power control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6 General specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.1 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.2 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.3 Class 1 operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.4 Power-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.5 System clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.6 Low power clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.7 Clock detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 3

STA2500D Contents
6.8 Clock request signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.9 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.10 Low power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.10.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.10.2 Some examples for the usage of the low power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.10.3 Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.11 Patch RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.12 Download of SW parameter file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.13 Bluetooth - WLAN coexistence in collocated scenario . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.13.1 Algorithm 1: PTA (packet traffic arbitration) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.13.2 Algorithm 2: WLAN master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.13.3 Algorithm 3: Bluetooth master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.13.4 Algorithm 4: two-wire mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.13.5 Algorithm 5: Alternating wireless medium access (AWMA) . . . . . . . . . . 40
7 Digital interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.1 The UART interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.2 The SPI interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7.3 The PCM interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.4 The JTAG interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.5 Alternate I/O functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.6 The I
2
C interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8 HCI transport layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.1 H4 UART transport layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.2 Enhanced H4 SPI transport layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.3 H4 SPI transport layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.4 eSCO over HCI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
9 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
10 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11 Acronyms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
12 Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
13 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 3/58
Page 4

List of tables STA2500D
List of tables
Table 1. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. Operating ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 3. DC input specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 4. DC output specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 5. System clock supported frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 6. System clock overall specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 7. System clock, sine wave specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 8. System clock, digital clock DC specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 9. System clock, digital clock AC specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 10. Low power clock specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 11. Current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 12. The STA2500D pin list (functional and supply) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 13. Configuration programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 14. I/O supply split diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 15. Mbps receiver parameters - GFSK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 16. Mbps receiver parameters - π/4-DQPSK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 17. Mbps receiver parameters - 8-DPSK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 18. Transmitter parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 19. Output power: class 1 control signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 20. Output power: class 1 device pin configuration (depending on SW parameter download). 26
Table 21. Output power: class 1 device pin configuration (depending on SW parameter download). 26
Table 22. Use of the BT_CLK_REQ_IN and BT_CLK_REQ_OUT signals in different modes. . . . . . 28
Table 23. Low power modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 24. WLAN HW signal assignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 25. SPI timing parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 26. PCM interface parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 27. PCM interface timing (at PCM_CLK = 2048 kHz) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 28. Examples of BT_GPIO pin programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 29. Package markings legend . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 30. References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 31. Acronyms and abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 32. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 33. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 5

STA2500D List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Block diagram and electrical schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 2. Pinout (bottom view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 3. Active high clock request input and output combined with UART or SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 4. Active low clock request input and output combined with UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 5. Active low clock request input and output combined with SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 6. Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 7. Entering deep sleep mode through enhanced H4 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 8. Wake-up by the host through enhanced H4 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 9. Wake-up by the Bluetooth controller with data transmission to the host, through enhanced H4
SPI 34
Figure 10. Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 11. Entering deep sleep mode, pending data on UART interface, through UART with handshake
36
Figure 12. Wakeup by host through UART with handshake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 13. PTA diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 14. WLAN master . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 15. Bluetooth master. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 16. SPI interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 17. SPI data transfer timing for data length of 8 bits and lsb first, full duplex . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 18. SPI setup and hold timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 19. PCM (A-law, µ-law) standard mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 20. Linear mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 21. Multislot operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 22. PCM interface timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 23. UART transport layer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 24. LFBGA48 (6x6x1.4mm) mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 25. Package markings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 5/58
Page 6

Description STA2500D
1 Description
The STA2500D is a single chip Bluetooth solution that is fully optimized for automotive
applications such as telematics, navigation and portable navigation. Power consumption
levels are targeted at battery powered devices and single chip solution brings cost
advantages. Manufacturers can easily and quickly integrate the STA2500D on their product
to enable a rapid time to market.
STA2500D supports the Bluetooth specification V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon“) and is optimized in
terms of RF performance and cost.
The STA2500D is a ROM-based solution targeted at applications requiring integration up to
HCI level. Patch RAM is available, enabling multiple patches/upgrades and fast time to
volume. The STA2500D’s main interfaces are UART or SPI for HCI transport, PCM for voice
and GPIOs for control purposes.
The radio has been designed specifically for single chip requirements, for low power
consumption and minimum BOM count.
6/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 7

STA2500D Quick reference data
2 Quick reference data
BT_VIO_x means BT_VIO_A, BT_VIO_B.
BT_HVx means BT_HVA, BT_HVD.
(See also Ta bl e 1 2.)
2.1 Absolute maximum ratings
The absolute maximum rating (AMR) corresponds to the maximum value that can be
applied without leading to instantaneous or very short-term unrecoverable hard failure
(destructive breakdown).
Table 1. Absolute maximum ratings
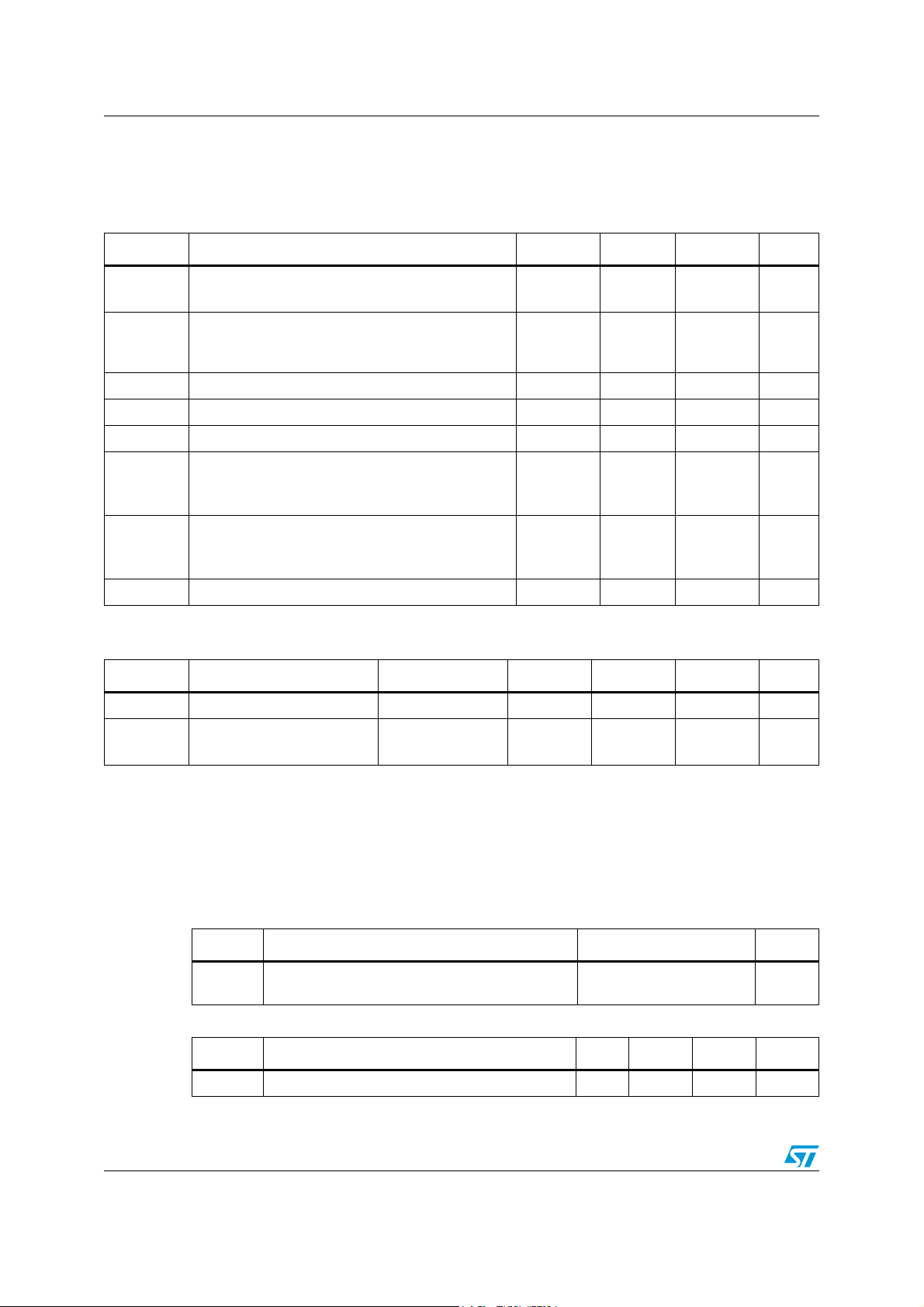
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
BT_HVx Core supply voltages -0.3 4.0 V
BT_VIO_A Supply voltage I/O -0.3 4.0 V
BT_VIO_B Supply voltage I/O (for the low power clock) -0.3 4.0 V
BT_V
V
ssdiff
T
stg
Input voltage of any digital pin -0.3 4.0 V
in
Maximum voltage difference between different types of
V
pins.
ss
Storage temperature - 65 + 150 °C
2.2 Operating ranges
Operating ranges define the limits for functional operation and parametric characteristics of
the device. Functionality outside these limits is not implied.
Table 2. Operating ranges
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
BT_T
BT_HVx Core supply voltages 2.65 2.75 2.85 V
BT_VIO_A I/O supply voltage 1.65 - 2.85 V
BT_VIO_B I/O supply voltage (for the low power clock) 1.17 - 2.85 V
Operating ambient temperature -40 25 +85
amb
-0.3 0.3 V
°
C
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 7/58
Page 8
Quick reference data STA2500D
2.3 I/O specifications
The I/Os comply with the EIA/JEDEC standard JESD8-B.
Table 3. DC input specification
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
V
C
IL_BT
IH_BT
in_BT
R
pu
R
pd
Low level input voltage -0.2 -
High level input voltage
Input capacitance
(1)
Pull-up equivalent resistance (with V
Pull-down equiv. resistance (with V
= 0 V) 31 47 73 kΩ
in
= BT_VIO_x) 29 50 100 kΩ
in
0.65 *
BT_VIO_x
1-2.5pF
-
0.35 *
BT_VIO_x
(BT_VIO_x
+ 0.2) and
(≤ 2.85)
Schmitt trigger hysteresis (at BT_VIO_A = 1.8 V)
V
hyst
except for BT_CONFIG1-3, BT_RESETN,
0.4 0.5 0.6 V
BT_WAKEUP
Schmitt trigger hysteresis (at BT_VIO_x = 1.8 V)
V
hyst
for BT_CONFIG1-3, BT_RESETN, BT_WAKEUP,
0.223 - 0.314 V
BT_LP_CLK
V
hyst
1. Except for the system clock.
Table 4. DC output specification
Schmitt trigger hysteresis (at BT_VIO_B = 1.3 V) 0.2 - 0.3 V
Symbol Parameter Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
OL_BT
V
OH_BT
1. X is the source/sink current under worst-case conditions according to the drive capabilities (see Section 3)
Low level output voltage Id = X
High level output voltage Id = X
(1)
(1)
mA
mA
--0.15V
BT_VIO_x
- 0.25
--V
V
V
2.4 Clock specifications
The STA2500D supports, on the BT_REF_CLK_IN pin, the system clock both as a sine
wave clock and as a digital clock. For configuration, see Tab le 1 2 : pin BT_VDD_CLD (E6).
Table 5. System clock supported frequencies
Symbol Parameter Values Unit
F
Table 6. System clock overall specifications
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
F
INTOL
8/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Clock input frequency list
IN
Tolerance on input frequency -20 - 20 ppm
9.6, 10, 13, 16, 16.8, 19.2,
26, 33.6, 38.4
MHz
Page 9

STA2500D Quick reference data
Table 7. System clock, sine wave specifications
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
PP
N
Z
INRe
Z
INIm
Z
IDRe
Z
IDim
1. Equivalent to max 10 ps time jitter (rms).
Table 8. System clock, digital clock DC specifications
Peak to peak voltage range 0.27 0.5 1.8 V
Total harmonic content of input signal - - -25 dBc
H
Real part of parallel input impedance at pin 30 60 90 kΩ
Imaginary part of parallel input impedance at pin - 5 8 pF
Real impedance discrepancy between active and nonactive mode of clock input
Imaginary impedance discrepancy between active and
non-active mode of clock input
Phase noise @ 10 kHz
(1)
-- 7kΩ
--500fF
---126dBc/Hz
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
IL
V
IH
C
IN
Table 9. System clock, digital clock AC specifications
Low level input voltage -0.2 -
High level input voltage
BT_VDD_CLD
Input capacitance - 5 8 pF
0.65 *
-
0.35 *
BT_VDD_CLD
(BT_VDD_CLD
+ 0.2) and
(≤ 2.85)
V
V
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
RISE
T
FAL L
D
CYCLE
- Phase noise @ 10 kHz
1. Equivalent to max 15 ps time jitter (rms).
Table 10. Low power clock specifications
10% - 90% rise time - 1.5 6 ns
90% - 10% fall time - 1.5 6 ns
Duty cycle 45 50 55 %
(1)
- - -121 dBc/Hz
The low power clock pin is powered by connecting BT_VIO_B to the wanted supply.
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
F
IN
- Duty cycle 30 - 70 %
- Tolerance on input frequency −250 - 250 ppm
V
IL
V
IH
V
hyst
Clock input frequencies 3.2, 32, 32.768 kHz
Low level input voltage - -
High level input voltage
0.65 *
BT_VIO_B
--V
0.35 *
BT_VIO_B
Schmitt trigger hysteresis (BT_VIO_B = 1.8 V) 0.4 0.5 0.6 V
V
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 9/58
Page 10

Quick reference data STA2500D
Table 10. Low power clock specifications (continued)
The low power clock pin is powered by connecting BT_VIO_B to the wanted supply.
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
hyst
C
IN
T
RISE
T
FAL L
- Total jitter
1. The rise and fall time are not the most important parameters for the low power clock input due to the Schmitt trigger logic. It
is more important that the noise on the Low power clock line remains substantially below the hysteresis in amplitude.
2. The total jitter is defined as the error that can appear on the actual frequency between two clock edges compared to the
perfect frequency. Due to this, the total jitter value must contain the jitter itself and the error due to the accuracy on the
clock frequency. The lower the accuracy, the smaller the jitter is allowed to be.
Schmitt trigger hysteresis (BT_VIO_B = 1.3 V) 0.2 0.3 0.4 V
Input capacitance 1 - 2.5 pF
(1)
(1)
--1μs
--1μs
- - 250 ppm
10% - 90% rise time
90% - 10% fall time
(2)
2.5 Current consumption
T
= 25°C, 13 MHz digital clock, 7 dBm output power for BR packets, 3 dBm output power
amb
for EDR packets.
Table 11. Current consumption
Complete Power Down 1 μA
Deep Sleep mode 20 μA
Functional Sleep mode
(2)
Sniff mode (1.28 s, 2 attempts, 0 timeouts), combined with H4 UART Deep Sleep
mode
(see section 6.10.3)
Master mode
Slave mode
(1)
State Typ. Unit
1.2 mA
55
83
μA
μA
Inquiry scan (1.28 seconds period), combined with H4 UART Deep Sleep mode
(see section 6.10.3) 318 μA
HW Page scan (1.28 seconds period), combined with H4 UART Deep Sleep mode
(see section 6.10.3) 312 μA
HW Inquiry and Page scan (1.28 seconds period), combined with H4 UART Deep
Sleep mode
(see section 6.10.3)
Idle ACL connection (Master) 3.6 mA
Idle ACL connection (Slave) 8.2 mA
Active: audio (HV3) Master (not sniffed) 11.7 mA
Active: audio (HV3) Slave (Sniff 1.28 s, 2 attempts, 0 timeouts) 10.6 mA
Active: data (DH1) Master or Slave
(172.8 kbps asymmetrical in TX mode)
(172.8 kbps symmetrical)
10/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
591 μA
23
28.5
mA
Page 11

STA2500D Quick reference data
Table 11. Current consumption
(1)
(continued)
State Typ. Unit
Active: data (DH5) Master or Slave
(723.2 kbps asymmetrical in TX mode)
(433.9 kbps symmetrical)
35.4
35.4
Active: data (2-DH5) Master or Slave (869.7 kbps symmetrical) 35.4 mA
Active: data (3-DH5) Master or Slave (1306.9 kbps symmetrical) 35.4 mA
Active: audio eSCO (EV3), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Master mode
Slave mode
Active: audio eSCO (2-EV3), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Master mode
Slave mode
Active: audio eSCO (3-EV3), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Master mode
Slave mode
Active: audio eSCO (EV5), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Active: audio eSCO (EV5), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Active: audio eSCO (2-EV5), (64 kbps symmetrical T
Active: audio eSCO (3-EV5), (64 kbps symmetrical T
1. The power consumption (except for power safe modes i.e. complete power down and deep sleep mode)
will rise (with approx. 200 µA) if an analog system clock is used instead of a digital clock.
2. In functional sleep mode, the baseband clock is still running.
= 6)
eSCO
12
15
= 12)
eSCO
7.8
11.7
= 18)
eSCO
6.5
10.5
= 36), Master mode 8 mA
eSCO
= 36), Slave mode 11.9 mA
eSCO
= 36), Master mode 6.3 mA
eSCO
= 36), Master mode 5.75 mA
eSCO
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 11/58
Page 12

Block diagram and electrical schematic STA2500D
/
3 Block diagram and electrical schematic
Figure 1. Block diagram and electrical schematic
BT_RFP
Filter
BT_RFN
BT_REF_CLK_IN
BT_VDD[4:0]
INTERNAL SUPPLY MANAGEMENT
RECEIVER
RF PLL
Fracti onal N
TRANSMI TTER
AUTOCALIBRATION
BT_TEST[1:0] BT_VDD_CLD
BT_HV[1:0] BT_VIO_A BT_VIO_B
DEMO-
DULATOR
CONTROL
AND
REGISTER
BASEBAND
CORE
MODULATOR
PLL
EBC
AMBA
PERIPH.
BUS
BT_AF_PRG BT_VSS[5:0]
ARM7TDMI
CPU Wrapper
RAM
ROM
INTERRUPT
UART/
SPI
TIMER
PCM
WLAN
I2C
JTAG
BT_GPIO_0
BT_GPIO/JTAG
[4: 0]
BT_LP_CLK
BT_HOST_WAKEUP
BT_SPI_INT
BT_WAKEUP
BT_RESETN
BT_UART/BT_SPI
[3: 0]
BT_PCM
[3: 0]
BT_CONFIG
[2: 0]
BT_CLK_REQ_IN
[1: 0]
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT
[1:0]
12/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 13

STA2500D Pinout
4 Pinout
Figure 2. Pinout (bottom view)
7654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
BT_VDD_DSM
BT_VDD_N
BT_VDD_CL
BT_VDD_CLD
BT_HOST_WAKEUP
/BT_SPI_I NT
GPIO_ 3
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2
BT_TEST2
BT_VSSANA
BT_CLK_REQ_IN _1
BT_UART_T XD
/ BT_SPI_DO
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2
BT_VSSRF
BT_WAKEUP
BT_GPIO_0
GPIO_ 0
BT_UART_RXD
/ BT_SPI_D I
BT_VSSANABT_VSSANA BT_TEST1
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1
BT_UART_R TS
/ BT_SPI_C S
BT_UART_C TS
/ BT_SPI_C LK
BT_RFPBT_RFNBT_HVA
BT_GPIO_16
BT_GPIO_8
JTAG_T CK
BT_RESETNBT_REF_CLK_ IN
BT_VSSDIGBT_VSSDIGBT_AF_PRG
BT_VIO_B
BT_LP_CL K
BT_VSSRF
BT_GPIO_11
BT_PCM_SYNC
BT_CONFIG_1
BT_CONFIG_3
BT_VDD_RF
BT_GPIO_9
BT_GPIO_10
BT_PCM_CLKBT_PCM_A
BT_PCM_B
BT_CONFIG_2
BT_HVDBT_VDD_DBT_VIO_A
4.1 Pin description and assignment
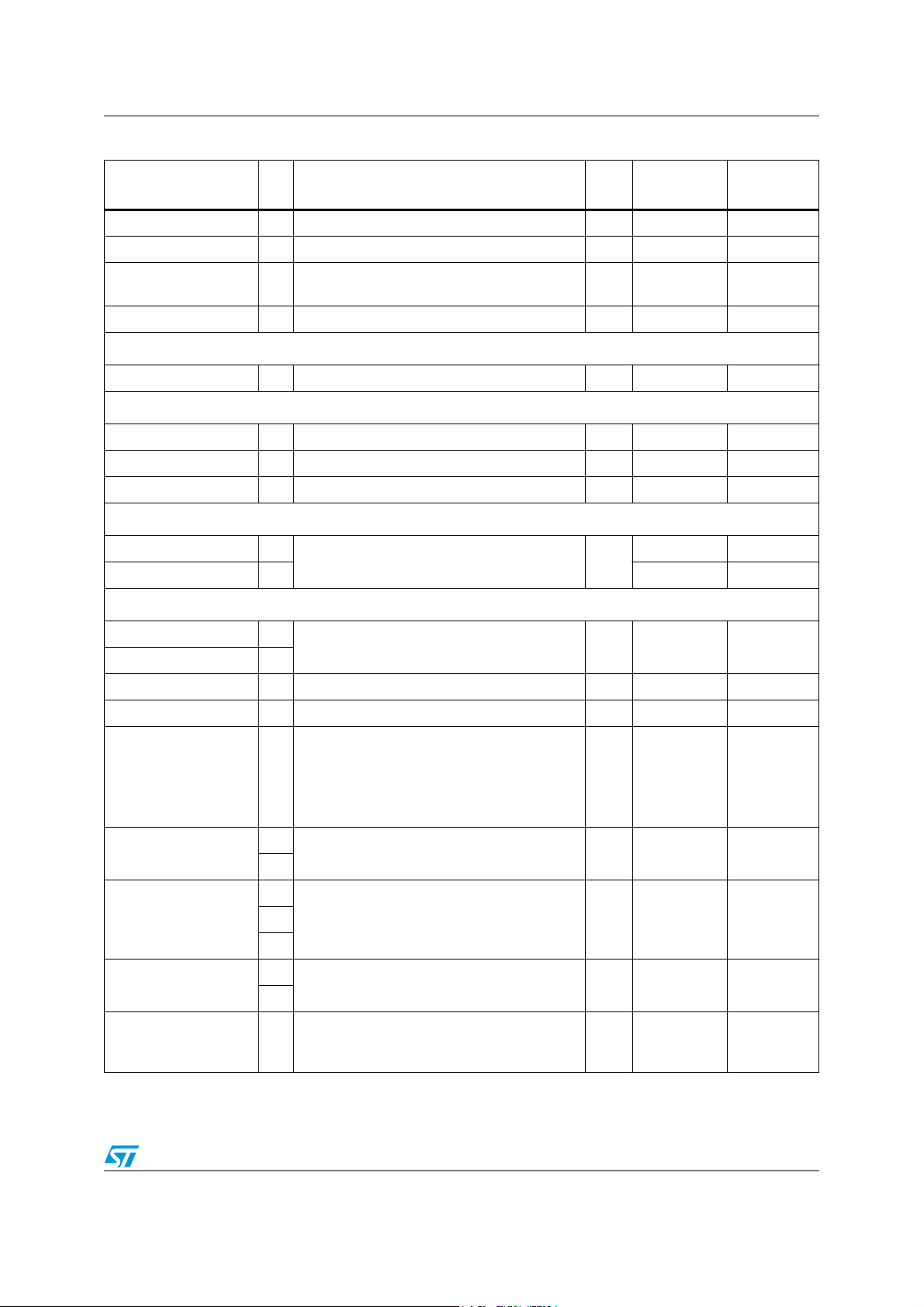
Ta bl e 1 2 shows the pin list of the STA2500D.
In columns “Reset” and “Default after reset”, the “PD/PU” shows the pads implementing an
internal pull-down/up.
The column “Reset” shows the state of the pins during hardware reset; the column “Default
after reset” shows the state of the pins after the hardware reset state is left, but before any
software parameter download.
The column “Type” describes the pin directions:
– I for Input (All inputs have a Schmitt trigger function.)
– O for Output
– I/O for Input/Output
– O/t for tri-state output
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 13/58
Page 14

Pinout STA2500D
For the output pin the default drive capability is 2 mA, except for pin K3 (BT_GPIO_11) and
pin L3 (BT_GPIO_8) where it is 8 mA such that when used for Class 1, these 2 pins can be
used for a switch control in a cheaper way.
Name
Pin
#
Description Type Reset
(3)
I Input Input
(1)
Default
after reset
(2)
Table 12. The STA2500D pin list (functional and supply)
Clock and reset pins
BT_RESETN D3 Global reset - active low - -
BT_REF_CLK_IN D6 Reference clock input
BT_LP_CLK G3 Low power clock input - -
SW initiated low power mode
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 C4
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2 G7
Wake-up signal to Host (Active high or Active
low, depending on configuration pins)
Wake-up signal to Host. Active low
(SPI mode only)
I/O
(4)
Input PD/PU,
depends on
config
Input PU
Output
depends on
config
I/O depends
on config
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 E6 Clock request input (Active high) Input PD Input PD
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 G6 Clock request input (Active low) Input PU Input PU
BT_HOST_WAKEUP/
BT_SPI_INT
BT_WAKEUP C5 Wake-up signal to Bluetooth (Active high) I/O Input
F7 Wake-up signal to Host or SPI interrupt Input PD Output
(5)
Input
UART interface
BT_UART_RXD/
BT_SPI_DI
UART receive data
F5
SPI data in Input PD
Input PD
Input PD
BT_UART_TXD/
BT_SPI_DO
BT_UART_CTS/
BT_SPI_CLK
UART transmit data Output high
F6
SPI data out Input PD
I/O
(4)
UART clear to send
G4
SPI clock Input PD
Input PU
Input PU
BT_UART_RTS/
BT_SPI_CSN
UART request to send Output low
F4
SPI chip select Input PU
PCM interface
BT_PCM_SYNC C2 PCM frame signal
BT_PCM_CLK D1 PCM clock signal
I/O
BT_PCM_A D2 PCM data
BT_PCM_B E1 PCM data
JTAG interface
BT_GPIO_9 B1 JTAG_TDI or GPIO - Input PU
14/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
(4)
Input PD Input PD
(6)
Input PU
(6)
Page 15
STA2500D Pinout
Table 12. The STA2500D pin list (functional and supply) (continued)
(6)
(6)
(6)
(6)
(2)
Name
Pin
#
Description Type Reset
BT_GPIO_11 B2 JTAG_TDO or GPIO - Input PD
BT_GPIO_10 C1 JTAG_TMS or GPIO I/O
BT_GPIO_16 B3
JTAG_NTRST (Active low) or Alternate
function.
(4)
Input PD
- Input PD
BT_GPIO_8 C3 JTAG_TCK or GPIO - Input PD
(1)
(6)
(6)
(6)
(6)
General purpose input/output pins
(4)
BT_GPIO_0 D5 General purpose I/O I/O
Input PD Input PD
Configuration pins
BT_CONFIG_1 E2 - - -
BT_CONFIG_2 F1 Configuration signal I Input Input
BT_CONFIG_3 F2 - - -
RF signals
Default
after reset
Input PD
Input PD
Input PD
Input PD
BT_RFP A3
Differential RF port I/O
BT_RFN A4 - -
Power supply
BT_HVA A7
Power supply (Connect to 2.75 V) - - -
BT_HVD G1
BT_VIO_A G5 1.65 V to 2.85 V I/Os supply
BT_VIO_B F3 1.17 V to 2.85 V I/Os supply
(7)
(7)
-- -
-- -
System clock supply
1.65 V to 2.85 V
BT_VDD_CLD E7
(Connect to BT_VIO_A in case of a digital
-- -
reference clock input, to BT_VSSANA in case
of an analog reference clock input.)
E3
BT_VSSDIG
Digital ground - - -
E4
B4
BT_VSSANA
Analog ground - - -B6
C6
A2
BT_VSSRF
RF ground - - -
A5
--
BT_VDD_CL D7
Internal supply decoupling/Regulator output.
Need 220nF decoupling capacitor to
BT_VSSANA.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 15/58
-- -
Page 16

Pinout STA2500D
Table 12. The STA2500D pin list (functional and supply) (continued)
Name
BT_VDD_D G2
BT_VDD_DSM B7
BT_VDD_N C7
BT_VDD_RF A1
Other pins
Pin
#
Description Type Reset
Internal supply decoupling/Regulator output.
Need 220nF decoupling capacitor to
BT_VSSDIG.
Internal supply decoupling/Regulator output.
Need 220nF decoupling capacitor to
BT_VSSANA.
Internal supply decoupling/Regulator output.
Need 220nF decoupling capacitor to
BT_VSSANA.
Internal supply decoupling/Regulator output.
Need 220nF decoupling capacitor to
BT_VSSRF.
(1)
Default
after reset
-- -
-- -
-- -
-- -
(2)
BT_TEST1 B5
Test pin I/O Input
(8)
Input
(8)
BT_TEST2 A6
BT_AF_PRG E5 Test pin (Leave unconnected)
1. Pin behaviour during HW reset (BT_RESETN low).
2. Pin behaviour immediately after HW reset and internal chip initialization, but before SW parameter download.
3. See also pin BT_VDD_CLD in Table 12.
4. Reconfigurable I/O pin.The functionality of these I/Os can be configured through software parameter download (see
Section 7.5).
5. Should be strapped to BT_VSSDIG if not used.
6. JTAG mode.
7. Described in Section 4.3.
8. To be strapped to BT_VSSANA.
9. Pin is ST - reserved for test function and it must be soldered to an isolated pad (not connected to anything, just floating).
(9)
I/O Open Open
4.2 HW configuration of the STA2500D
By means of the three configuration pins, one can select the Host interface (UART or SPI)
and clock request signal polarity to be used at startup.
The available combinations of Host interface and protocol are illustrated in Tab l e 1 3 (where
‘1’ = BT_VIO_A and ‘0’ = BT_VSSDIG). Additionally, the polarity of the BT_CLK_REQ
signals can be programmed through the same pins. The polarity of the BT_CLK_REQ_IN
and BT_CLK_REQ_OUT signals is further described in Section 6.8.
16/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 17

STA2500D Pinout
Table 13. Configuration programming
BT_CONFIG_1 BT_CONFIG_2 BT_CONFIG_3
Communication
Protocol
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2
0 1 0 H4 UART Active high
0 1 1 H4 UART Active low
Depending on SW
config
Depending on SW
config
1 1 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 1 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved
1 0 1 Enhanced H4 SPI
(1)
Active high Active low
0 0 1 Reserved Reserved Reserved
0 0 0 Reserved Reserved Reserved
1. In order to get other SPI modes, the Host must send a specific configuration at start-up in addition of these configuration
pins.
4.3 I/O Supply
The device STA2500D has two different I/O supplies: BT_VIO_A and BT_VIO_B.
The two different pins may be potentially connected to separate dedicated voltage supplies
in order to harmonize the digital levels to the platform.
They are linked to different interfaces as described in Ta bl e 1 4 .
Table 14. I/O supply split diagram
I/O supply
name
BT_VIO_A 1.65 - 2.85
Vol tag e
range [V]
Function Associated pins
Configuration BT_CONFIG_1, BT_CONFIG_2, BT_CONFIG_3
Control
GPIO (JTAG)
PCM BT_PCM_A, BT_PCM_B, BT_PCM_SYNC, BT_PCM_CLK
Control BT_REG_CTRL
UART (SPI)
Control (GPIO) BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 (GPIO_1), BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 (GPIO_2)
GPIO BT_GPIO_0
BT_WAKEUP
BT_RESETN
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1, BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2
BT_GPIO_8 (JTAG_TCK), BT_GPIO_9 (JTAG_TDI),
BT_GPIO_10 (JTAG_TMS), BT_GPIO_11 (JTAG_TDO),
BT_GPIO_16 (JTAG_NTRST)
BT_UART_RXD (SPI_DI), BT_UART_TXD (SPI_DO),
BT_UART_RTS (SPI_CSN), BT_UART_CTS (SPI_CLK),
BT_HOST_WAKEUP (SPI_INT)
BT_VIO_B 1.17 - 2.85 Low - power clock BT_LP_CLK
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 17/58
Page 18

Functional description STA2500D
5 Functional description
5.1 Transmitter
The transmitter uses the serial transmit data from the Bluetooth Controller. The transmitter
modulator converts this data into GFSK, π/4-DQPSK or 8-DPSK modulated I and Q digital
signals for respectively 1, 2 and 3 Mbps transmission speed. These signals are then
converted to analog signals that are low pass filtered before up-conversion. The carrier
frequency drift is limited by a closed loop PLL.
5.2 Receiver
The STA2500D implements a low-IF receiver for Bluetooth modulated input signals. The
radio signal is taken from a balanced RF input and amplified by an LNA. The mixers are
driven by two quadrature LO signals, which are locally generated from a VCO signal running
at twice the frequency. The I and Q mixer output signals are band pass filtered by a polyphase filter for channel filtering and image rejection. The output of the band pass filter is
amplified by a VGA to the optimal input range for the A/D converter. Further channel filtering
is done in the digital part. The digital part demodulates the GFSK,
coded bit stream by evaluating the phase information. RSSI data is extracted. Overall
automatic gain amplification in the receive path is controlled digitally. The RC time constants
for the analog filters are automatically calibrated on chip.
π/4-DQPSK or 8-DPSK
5.3 PLL
The on chip VCO is part of a PLL. The tank resonator circuitry for the VCO is completely
integrated without need of external components. Variations in the VCO centre frequency are
calibrated out automatically.
18/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 19

STA2500D Functional description
5.4 Bluetooth controller V1.2 and V2.0 + EDR features
The Bluetooth controller is backward compatible with the Bluetooth specification V1.2 [] and
V2.0 + EDR []. Here below is a list with the main features of those specifications:
● Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH): hopping kernel, channel assessment as Master
and as Slave
● Fast Connection: Interlaced scan for Page and Inquiry scan, answer FHS at first
reception, RSSI used to limit range
● Extended SCO (eSCO) links: supports EV3, EV4 and EV5 packets
● Channel Quality Driven Data Rate change (CQDDR)
● QoS Flush
● Synchronization: BT clocks are available at HCI level for synchronization of parallel
applications on different Slaves
● L2CAP Flow & Error control
● LMP SCO handling
● 2 Mbps packet types
– ACL: 2-DH1, 2-DH3, 2-DH5
– eSCO: 2-EV3, 2-EV5
● 3 Mbps packet types
– ACL: 3-DH1, 3-DH3, 3-DH5
– eSCO: 3-EV3, 3-EV5
5.5 Bluetooth controller V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon”)
● Encryption Pause/Resume (EPR)
● Extended Inquiry Response (EIR)
● Link Supervision Time Out (LSTO)
● Secure Simple Pairing
● Sniff Subrating
● Quality of Service (Qos)
– Packet Boundary Flag
– Erroneous Data Delivery
5.6 Processor and memory
● ARM7TDMI
● On chip RAM, including provision for patches
● On chip ROM, preloaded with SW up to HCI
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 19/58
Page 20

Functional description STA2500D
5.7 TX output power control
The STA2500D supports output power control with advanced features:
● Basic feature:
– With the standard TX power control algorithm enabled, the STA2500D will adapt
its output power when a remote BT device supports the RSSI feature; this allows
the remote device to measure the link strength and to request the STA2500D to
decrease/increase its output power. In case the remote device does not support
the RSSI feature, the STA2500D will use its ‘default’ output power level.
● Advanced features, available via specific HCI commands:
– Enhanced power control feature: allows the STA2500D to decrease autonomously
its output power until the remote BT device, supporting the RSSI feature, requests
to increase the output power.
20/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 21

STA2500D General specification
6 General specification
All the values are provided according to the Bluetooth specification V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon”)
unless otherwise specified. The below values are preliminary and will be updated in the next
version of this datasheet.
6.1 Receiver
All specifications below are given at device pin level and with the conditions as specified.
Parameters are given for each of the 3 modulation types supported.
Typical is defined at T
= 25 °C, BT_HV = 2.75 V. Minimum and Maximum are worst cases
amb
over corner lots and temperature. Parameters are given at device pin, except for receiver
interferers measured at antenna with a filter having a typical attenuation of 2.3 dB.
Table 15. Mbps receiver parameters - GFSK
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
RFin Input frequency range - 2402 - 2480 MHz
RXsensC
RXsensD
RXmax
Receiver blocking performance @ BER 0.1% on Channel 58 (without Filter)
Receiver sensitivity
(Clean transmitter)
Receiver sensitivity
(Dirty transmitter)
Maximum useable input signal
level
-
-
-
signal in GSM band 900 MHz
(824 MHz to 960 MHz)
signal in GSM band 1800 MHz
(1805 MHz to 1990 MHz)
signal in WCDMA band
(2010 MHz to 2170 MHz)
@ BER 0.1% - -88 -86 dBm
@ BER 0.1% - -87 -84 dBm
@ BER 0.1% - 10 15 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
--15-dBm
- -2.5 - dBm
--1.5-
dBm
Receiver interferer performance @ BER 0.1%
C/I
co-channel
C/I
C/I
C/I
C/I
1MHz
+2MHz
-2MHz
+3MHz
Co-channel interference
Adjacent (±1 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (-2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+3 MHz) interference
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 21/58
-9.511dB
--90dB
--40-30dB
--26-9dB
- -46.5 -40 dB
Page 22

General specification STA2500D
Table 15. Mbps receiver parameters - GFSK (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
C/I
C/I
-3MHz
≥
4MHz
Adjacent (-3 MHz) interference
Adjacent (≥ ±4 MHz)
interference
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
--43-20dB
--48-40dB
Receiver inter-modulation
IMD Inter-modulation
Typical is defined at T
= 25 °C, BT_HV = 2.75 V. Minimum and Maximum are worst cases
amb
Measured as defined in BT
test specification [].
-39 -32 = dBm
over corner lots and temperature. Parameters are given at device pin, except for receiver
interferers measured at antenna with a filter having a typical attenuation of 2.3 dB.
Table 16. Mbps receiver parameters - π/4-DQPSK
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
RFin Input frequency range = 2402 2480 MHz
RXsensC
RXsensD
RXmax
Receiver sensitivity
(Clean transmitter)
Receiver sensitivity
(Dirty transmitter)
Maximum useable input signal
level
@ BER 0.01% - -87 -85 dBm
@ BER 0.01% - -86.5 -84.5 dBm
@ BER 0.1% -15 -9 - dBm
Receiver blocking performance @ BER 0.1% on channel 58 (without Filter)
-
-
-
signal in GSM band 900 MHz
(824 MHz to 960 MHz)
signal in GSM band 1800 MHz
(1805 MHz to 1990 MHz)
signal in WCDMA band
(2010 MHz to 2170 MHz)
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
Receiver interferer performance @ BER 0.1%
C/I
co-channel
C/I
C/I
C/I
C/I
1MHz
+2MHz
-2MHz
+3MHz
Co-channel interference
Adjacent (±1 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (-2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+3 MHz) interference
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
- -15.5 - dBm
- -3.5 - dBm
- -2.5 - dBm
-1113dB
- -11.5 0 dB
-
-40
-30 dB
--20-7dB
- -48.5 -40 dB
22/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 23

STA2500D General specification
Table 16. Mbps receiver parameters - π/4-DQPSK (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
C/I
C/I
-3MHz
≥
4MHz
Adjacent (-3 MHz) interference
Adjacent (≥ ±4 MHz)
interference
Typical is defined at T
= 25 °C, BT_HV = 2.75 V. Minimum and Maximum are worst cases
amb
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
--47-20dB
--48-40dB
over corner lots and temperature. Parameters are given at device pin, except for receiver
interferers measured at antenna with a filter having a typical attenuation of 2.3 dB.
Table 17. Mbps receiver parameters - 8-DPSK
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
RFin Input frequency range - 2402 - 2480 MHz
RXsensC
RXsensD
RXmax
Receiver blocking performance @ BER 0.1% on channel 58 (without Filter)
Receiver sensitivity
(Clean transmitter)
Receiver sensitivity
(Dirty transmitter)
Maximum useable input signal
level
-
Signal in GSM band 900 MHz
(824 MHz to 960 MHz)
@ BER 0.01% - -79.5 -77.5 dBm
@ BER 0.01% - -77 -74.5 dBm
@ BER 0.1% -20 -15 - dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
--20-dBm
-
-
Signal in GSM band 1800 MHz
(1805 MHz to 1990 MHz)
Signal in WCDMA band
(2010 MHz to 2170 MHz)
Receiver interferer performance @ BER 0.1%
C/I
co-channel
C/I
C/I
C/I
C/I
C/I
C/I
1MHz
+2MHz
-2MHz
+3MHz
-3MHz
≥
4MHz
Co-channel interference
Adjacent (±1 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (-2 MHz) interference
Adjacent (+3 MHz) interference
Adjacent (-3 MHz) interference
Adjacent (≥ ±4 MHz)
interference
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -60 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
@ Input signal
strength = -67 dBm
- -14.5 - dBm
--14-dBm
-1921dB
--45dB
--37-25dB
--120dB
--46-33dB
--40-13dB
--43-33dB
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 23/58
Page 24

General specification STA2500D
6.2 Transmitter
Unless otherwise stated, typical is defined at T
= 25 °C, BT_HV = 2.75 V. Minimum and
amb
Maximum are worst cases over corner lots and temperature. Parameters are given at device
pin, except for in-band spurious measured at antenna.
Table 18. Transmitter parameters
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
RFout Output frequency range - 2402 - 2480 MHz
RF Transmit Power
TXpout
(GFSK)
TXpout
(GFSK)
TXpout
(GFSK)
TXpout
(π/4-DQPSK)
TXpout
(π/4-DQPSK)
TXpoutrel
(π/4-DQPSK)
TXpout
(8-DPSK)
TXpout
(8-DPSK)
TXpoutrel
(8-DPSK)
In-band spurious emission
Maximum output power
(1)
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz
@ 25 °C
6 8 10 dBm
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz
Maximum output power
(1)
@ worst cases over
corner lots and
4.5 8 10.5 dBm
temperature
Minimum output power @ 2402 - 2480 MHz -52.5 -47.5 -42.5 dBm
Maximum output power
Minimum output power
Relative transmit power
Maximum output power
Minimum output power
Relative transmit power
(4)
(1) (2)
(2)
(3)
(1) (2)
(2)
(3)
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz
@ 25 °C
3.5 6 8 dBm
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz -43.5 -38.5 -33.5 dBm
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz - -0.2 - dB
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz
@ 25 °C
3.5 6 8 dBm
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz -43.5 -38.5 -33.5 dBm
@ 2402 - 2480 MHz - -0.2 - dB
FCC FCC’s 20 dB BW - 900 930 950 kHz
ACP_2 Channel offset = ±2 MHz - - -43.5 -20 dBm
ACP_3 Channel offset = ±-3 MHz - - -52.5 -40 dBm
ACP_4 Channel offset ≥ ±4 MHz - - -54.5 -40 dBm
EDR_IBS_1
EDR_IBS_2
EDR_IBS_3
EDR_IBS_4
Channel offset = ±1 MHz (2 and
3 Mbps)
Channel offset = ±2 MHz (2 and
3 Mbps)
Channel offset = ±3 MHz (2 and
3 Mbps)
Channel offset = ±4 MHz (2 and
3 Mbps)
- - -33.5 -26
---31.5-20
---45-40
---50-40
24/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
dB
dBm
dBm
dBm
Page 25

STA2500D General specification
Table 18. Transmitter parameters (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Initial carrier frequency tolerance (for an exact reference)
ΔF |f_TX-f0| - - 0 - kHz
Carrier frequency stability
(6)
|Δf_s| Carrier frequency stability - - 3.2 10 kHz
Carrier frequency drift
(7)
|Δf_p1| One slot packet - - 12 25 kHz
|Δf_p3| Three slots packet - - 14 40 kHz
|Δf_p5| Five slots packet - - 14 40 kHz
Carrier frequency drift rate
(7)
|Δf/50us| Frequency drift rate - - 8/50 20/50 kHz/µs
(6) (7)
Modulation accuracy
(8)
Δf1avg Maximum modulation - 140 163 175 kHz
Δf2max Minimum modulation - 115 135 - kHz
Δ
f1avg/Δf2avg
-0.80.9-
- 2-DH5 RMS DEVM - - 8 20 %
- 2-DH5 99% DEVM - - - 30 %
- 2-DH5 Peak DEVM - - 21 35 %
- 3-DH5 RMS DEVM - - 8 13 %
- 3-DH5 99% DEVM - - - 20 %
- 3-DH5 Peak DEVM - - 21 25 %
(5)
TX out of band emission
E850 Emission in GSM band 850 MHz BW = 200 kHz
E900 Emission in GSM band 900 MHz BW = 200 kHz
E1500 Emission in GPS band BW = 200 kHz
E1800
E1900
Emission in GSM band 1800 MHz
Emission in GSM band 1900 MHz
BW = 200 kHz
BW = 200 kHz
Ewcdma Emission in WCDMA band BW = 3.8 MHz
1. Lower transmit power (i.e. Class 2) can be obtained by programming the radio init power table via software parameter
download or an HCI command.
2. Power of GFSK part.
3. Relative power of EDR part compared to the GFSK part.
4. At antenna with maximum output power, filter attenuation of 2.3 dB.
5. Phase noise will add maximum [-10 kHz;10 kHz] for worst case clock 270 mVpp at 13 MHz.
6. Worst case clock 270 mVpp at 13 MHz. Measurement according to EDR RF test spec V2.0.E.3 [].
7. With maximum output power (BR or EDR).
8. Measured on reference design STLC2555_rev1.1 following eBOM and layout recommendations.
9. Measurement bandwidth.
10. Transmitting DH5 packets.
(7) (9) (10)
(7) (9) (10)
(7) (9) (10)
(7) (9) (10)
(7) (9) (10)
(7) (9) (10)
--79-76dBm
--79-76dBm
--85-84dBm
--87-84dBm
--87-84dBm
--78-75dBm
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 25/58
Page 26

General specification STA2500D
6.3 Class 1 operation
The STA2500D supports operation at Class 1 output power levels with the use of an
external PA. The operation of the external PA and antenna switch are controlled by the
following signals:
Table 19. Output power: class 1 control signals
Control signal name Function
PAEN PA enable (active during TX slot)
PA_VAL0 Bit 0 of the power level delivered by the PA
PA_VAL1 Bit 1 of the power level delivered by the PA
RXEN LNA enable (if present)
AntSw Control of the antenna switch
edr_mode Indication to PA whether TX is EDR or BR
If Class 1 functionality is enabled through SW parameter download, then these 6 control
signals are available on the pins as indicated in Ta bl e 2 0 and Tab le 2 1 .
Table 20. Output power: class 1 device pin configuration (depending on SW
parameter download)
Function SW configuration 1 SW configuration 2
PA_VAL0 BT_GPIO_0 BT_GPIO_10
PA_VAL1 BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 BT_GPIO_9
RXEN BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 BT_GPIO_8
AntSw (BT_GPIO_11) BT_GPIO_11
Table 21. Output power: class 1 device pin configuration (depending on SW
Function SW configuration a SW configuration b SW configuration c
edr_mode BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2 not available on a pin
Configuration 2 allows to deploy the STA2500D in Class 1 mode, still maintaining the
necessary control signals to coexist and cooperate with a WLAN transceiver. The
handshake between the STA2500D and a WLAN device happens in this case through other
BT_GPIO pins.
6.4 Power-up
The BT_RESETN pin should be active while powering up BT_VDD_HV and should stay
active at least two cycles of the low power clock (BT_LP_CLK) after power-up is completed.
PAEN BT_HOST_WAKEUP BT_GPIO_16
parameter download)
The time between the STA2500D making BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x active and the platform
providing a stable clock should maximally be 15 ms.
26/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 27

STA2500D General specification
6.5 System clock
The STA2500D works with a sine wave or digital clock provided on the BT_REF_CLK_IN
pin. Detailed specifications are found in Section 2.4.
6.6 Low power clock
The low power clock is used by the Bluetooth Controller as reference clock during the low
power modes. It requires an accuracy of +
to be provided on the BT_LP_CLK pin, with frequencies of 3.2 kHz, 32 kHz and 32.768 kHz.
After power-up, the low power clock must be available before the reset is released. It must
remain active all the time until the STA2500D is powered off.
250 ppm. The STA2500D requires a digital clock
6.7 Clock detection
An integrated automatic detection algorithm detects the system and low power clock
frequencies after a hardware reset. The steps in the clock detection routine are:
● Identification of the system clock frequency (9.6 MHz, 10 MHz, 13 MHz, 16 MHz,
16.8MHz, 19.2 MHz, 26 MHz, 33.6 MHz or 38.4 MHz)
● Identification of the low power clock (3.2 kHz, 32.768 kHz or 32 kHz).
6.8 Clock request signals
To allow minimum power consumption, a clock request feature is available so that the
system clock (BT_REF_CLK_IN) can be stopped when not needed by the Bluetooth
system. The clock request signal can be active high or active low, and the STA2500D
supports internal propagation of clock request signal coming from another device in the
system.
Different configurations as described below are supported immediately after reset and in all
Bluetooth operation modes, provided that BT_VIO_A is available.
The clock request functionality is based on four different signals: BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1,
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2, BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1, BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2, with the following
function:
● BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1: active low or high clock request, depending on HW
configuration pins (Table ). Support for either push-pull or open drain output.
● BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2: active low clock request, only used in combination with SPI
mode. Support for either push-pull or open drain output.
● BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1: active high clock request input from an other device, depending
on HW configuration pin.
● BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2: active low clock request input from an other device.
The following modes are supported:
● Active high clock request input and output combined with UART or SPI:
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 27/58
Page 28

General specification STA2500D
Figure 3. Active high clock request input and output combined with UART or SPI
Internal BT CLK Request
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2
(*) BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 and BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 are used UNLESS one or both are re-programmed as alternate function(s) via Parameter File
NOT
(*)
OR
(*)
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1
● Active low clock request input and output combined with UART:
Figure 4. Active low clock request input and output combined with UART
Internal BT CLK Request
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2
(*) BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 and BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 are used UNLESS one or both are re-programmed as alternate function(s) via Parameter File
NOT
(*)
AND
(*)
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1
● Active low clock request input and output combined with SPI:
Figure 5. Active low clock request input and output combined with SPI
Internal BT CLK Request
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2
(*) BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 and BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 are used UNLESS one or both are re-programmed as alternate function(s) via Parameter File
Table 22. Use of the BT_CLK_REQ_IN and BT_CLK_REQ_OUT signals in different modes
NOT
BT_CONFIG_1 BT_CONFIG_2 BT_CONFIG_3 Protocol
010H4 UART
011H4 UART
101
1. BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 and BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 are used in the configuration logic, UNLESS one or both I/Os reprogrammed as alternate function(s) via the Parameter File.
Enhanced
H4 SPI
(*)
AND
(*)
BT_CLK_
REQ_IN_1
Active
(1)
high
Active
(1)
low
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2
BT_CLK_
REQ_IN_2
Active
(1)
low
Active
(1)
low
BT_CLK_R
EQ_OUT_1
BT_CLK_R
EQ_OUT_2
Active high not used
Active low not used
Active high Active low Active high Active low
The pins which are “not used” are available for alternate functions as described in
Section 7.5.
28/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 29

STA2500D General specification
6.9 Interrupts
The user can program the BT_GPIOs as external interrupt sources.
6.10 Low power modes
6.10.1 Overview
To save power, three low power modes are supported as described in Ta b le 2 3.
Depending of the Bluetooth and of the Host's activity, the STA2500D decides to use Sleep
mode or Deep Sleep mode. Note however that the Deep Sleep mode must first be activated
via SW parameter download or an HCI command prior to any possibility to use it as the
default configuration is only Sleep mode. Complete Power Down is entered only after an
explicit command from the Host.
Table 23. Low power modes
Low power mode Description
Deep Sleep mode
Sleep mode
The STA2500D:
– Accepts HCI commands from the Host.
– Supports all types of Bluetooth links.
– Can transfer data over Bluetooth links.
– Dynamically switches between sleep and active mode when needed.
– The system clock is still active in part of the design.
– Parts of the chip are dynamically powered off depending on the Bluetooth activity.
The STA2500D:
– Does not accept HCI commands from the Host.
– Supports Page and Inquiry scans.
– Supports Bluetooth links that are in Sniff or Sniff Subrating.
– Dynamically switches between Deep Sleep and active mode during Bluetooth
activity. The Deep Sleep mode entry is initiated by the Host, the STA2500D
acknowledges or not. The wake-up mechanism must be enabled by a SW
parameter download before it can be used. More details in section 6.10.3.
– The system clock is not active in any part of the design.
– Parts of the chip are dynamically powered off depending on the Bluetooth activity.
Complete Power Down
The STA2500D is effectively powered down:
– No Bluetooth activity is supported.
– The HCI interface is shut down.
– The system clock is not active in any part of the design.
– Most parts of the chip are completely powered off.
– RAM content is not maintained (initialisation is required at wake-up).
– Some pins (UART/SPI I/Os and the 4 clock request signals and BT_GPIO_16)
keep their previous configuration (input or output, pull behaviour) during
Completed Power Down.
– The Complete Power Down entry is initiated by an HCI command followed by a
Deep Sleep command, this in order to ensure a smooth transition from active to
Complete Power Down state. In order to go out of this mode, either a HW reset or
BT_WAKEUP = ‘1’ is needed.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 29/58
Page 30

General specification STA2500D
6.10.2 Some examples for the usage of the low power modes
Sniff or sniff subrating
The STA2500D is in active mode with a Bluetooth connection. Once the transmission is
concluded, Sniff or Sniff Subrating is programmed. When one of these two states is entered,
the STA2500D goes into Sleep mode. After that, the Host may decide to place the
STA2500D in Deep Sleep mode as described in Section 6.10.3. The Deep Sleep mode
allows for lower power consumption. When the STA2500D needs to send or receive a
packet (e.g. at T
enters active mode for the needed transmission/reception. Immediately afterwards, the
STA2500D will go back to Deep Sleep mode. If some HCI transmission is needed, the
UART/SPI link will be reactivated, using one of the four ways explained in Section 6.10.3
and the STA2500D will move from Deep Sleep mode to Sleep mode.
Inquiry/page scan
When only Inquiry scan or Page scan is enabled, the STA2500D will go in Sleep mode or
Deep Sleep mode outside the receiver activity. The selection between Sleep mode and
Deep Sleep mode depends on the UART/SPI activity as in Sniff or Sniff Subrating.
No connection
or at the beacon instant), the STA2500D requests the system clock and
sniff
If the Host allows Deep Sleep mode (as described in Section 6.10.3) and there is no activity,
then the STA2500D puts itself in Deep Sleep mode. It is possible to exit the Deep Sleep
mode by using one of the four methods explained in Section 6.10.3. In this Deep Sleep
mode (no connection), the Host can also decide to put the STA2500D in Complete Power
Down to further reduce the power consumption. In this case some part of the STA2500D will
be completely powered off. The request to quit the Complete Power Down is done either by
putting the BT_WAKEUP signal to ‘1’ or with an HW reset.
Active link
When there is an active link ((e)SCO or ACL), the Bluetooth Controller will not go in Deep
Sleep mode and not in Complete Power Down. But the Bluetooth Controller is made in such
a way that whenever it is possible, depending on the scheduled activity (number of link, type
of link, amount of data exchanged), it goes in Sleep mode.
6.10.3 Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up
During periods of no activity on the Bluetooth and on the Host side, the chip can be placed
in Deep Sleep mode. Four ways to initiate Deep Sleep mode and to wake up are supported
(selection is done through software parameter download): they are respectively based on a
UART interface in the first case, an SPI interface in the second case and third case, while
either UART or SPI interfaces can be used in the fourth case that is based on an handshake
mechanism.
Deep sleep mode entry and wake up through H4 UART
It requires BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1, BT_UART_RXD and BT_UART_RTS. The
BT_UART_RXD is used as wake-up signal from the Host, the BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1
requires the clock from the Host and the BT_UART_RTS indicates when the STA2500D is
30/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 31

STA2500D General specification
available. In this mode, the break function (BT_UART_RXD is low for more than 1 word) is
used to distinguish between normal operation and low power mode usage.
● Deep sleep mode entry
The Host tells the STA2500D that it can go in Deep Sleep mode power by forcing the
BT_UART_RXD of the STA2500D to '0' for more than 1 word. The STA2500D decides
to go in Deep Sleep mode, or not, depending on its scheduled activity and on the
number of events or data packets to be sent to the Host. In case it decides to go in
Deep Sleep mode, it signals it by forcing BT_UART_RTS high; then it asserts
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 low to tell the Host that it does not need the clock anymore. The
STA2500D cannot go in Deep Sleep mode by itself. This is a logical consequence of
the fact that the system clock is needed to receive characters on the UART.
Note that when the system is in Deep Sleep mode, the UART is closed.
● Deep sleep mode wake-up
The wake-up procedure can be initiated by the Host or by the STA2500D. In the latter
case, it can be with or without communication, depending if there are data to be
transmitted to the Host.
1. Wake-up initiated by the Host
The Host sets the BT_UART_RXD pin of the STA2500D to '1'. Then the STA2500D
asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to '1'. When
the clock is available, the STA2500D confirms it is awake by releasing BT_UART_RTS
to '0'.
2. Autonomous wake-up with UART communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D first asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to '1'.
When the clock is available, the STA2500D sets BT_UART_RTS low, and then the Host
can give confirmation by releasing the BT_UART_RXD of the STA2500D.
Another possibility is that the STA2500D sets BT_HOST_WAKEUP to ‘1’ to request the
Host attention. Then the Host can give confirmation by releasing the BT_UART_RXD of
the STA2500D and the STA2500D sets BT_UART_RTS low.
The choice between the two possibilities is selected by a software parameter.
3. Autonomous wake-up without UART communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to '1'.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 31/58
Page 32

General specification STA2500D
Figure 6. Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 UART
UART on
UART on
Active
Active
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 1’ or ‘ 0’
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 1’ or ‘ 0’
Hos t: UART _RXD=‘ 1’
Hos t: BT _UA RT_R XD =‘ 1’
BT Co nt ro l ler :
BT Co nt ro l ler :
BB
BB
Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode
UART_ RTS=‘0’
BT_ UA RT_RT S =‘0’
Or
Or
HOST_WAKEUP=‘1’
BT_H OST_WA KEUP =‘1’
Hos t: UART _RXD=‘ 0’
Hos t: BT _UA RT_ RXD =‘ 0’
BT Co nt ro l ler :
BT Co nt ro l ler :
Hos t: UART _RXD=‘ 1’
Hos t: BT _UA RT_ RXD =‘ 1’
AND
AND
BT Co nt ro l ler :
BT Controller: BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ A’
UART_ RTS=‘1’
BT_ UART _RT S=‘ 1’
CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ A’
and
and
UART_ RTS=‘0’
BT_ UART _RT S=‘ 0 ’
UART off
UART off
Active
Active
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 0’
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 0’
BB
BB
Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode
=‘ A’
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1
BT Co n trol le r :CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ A’
BT Co n trol le r :
Deep Sleep
BT Co n trol le r :CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ P’
BT Co n trol le r : BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘P’
UART off
UART off
Mode
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 =
‘A’: Active
‘P’ : Passive
high/low
low/high
Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through enhanced H4 SPI
In this case no additional signals are needed to control the Deep Sleep mode and the wakeup mechanism except for BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x (BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 for active high
polarity and BT_ CLK_REQ_OUT_2 for active low polarity).
The enhanced H4 protocol makes use of three messages: SLEEP, WAKEUP and WOKEN.
More details on the enhanced H4 protocol can be found in Section 8.2.
● Deep sleep mode entry
Entering Deep Sleep mode can only be initiated by the Host sending a SLEEP
message to the Bluetooth Controller.
If that one accepts it, the device enters Deep Sleep mode: consequently the Bluetooth
Controller de-asserts BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x and internally gates the system clock.
This is illustrated in Figure 7.
If there is still pending activity at the Bluetooth side on the air, the Bluetooth Controller
does not immediately enter Deep Sleep mode and therefore BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x
stays 'active' during this period: however the Bluetooth Controller will go in Deep Sleep
mode at the end of the air activity.
If there is pending data to be transferred to the Host, the Bluetooth Controller will
request a data transfer: however the Bluetooth Controller will go in Deep Sleep mode at
the end of the data transfer.
● Deep sleep mode wake-up
Wake-up can be requested by the Host or autonomously by the Bluetooth Controller. In
the latter case, it can be with or without communication on the interface (i.e. during
Page scan, there is no data to transfer to the Host).
1. Wake-up initiated by the Host
In the case of a wake-up by the Host, it sends a WAKEUP command and waits for a
WOKEN response before starting the data exchange. Of course the Bluetooth
Controller must first request the system clock through BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x.
It should be noted that the WAKEUP message is decoded in the Bluetooth Controller's
32/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 33

STA2500D General specification
SPI HW block even before the system clock is available. This block will generate an
interrupt, allowing the Bluetooth Controller to reply with a WOKEN message. This is
illustrated in Figure 8.
2. Autonomous wake-up with communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
In the case of an autonomous wake-up with data transmission, the Bluetooth Controller
sets BT_SPI_INT high to request the SPI interface and waits for BT_SPI_CSN going
low, indicating the SPI transaction starts. Of course the Bluetooth Controller must first
request the system clock through BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x before being able to start the
process. This is illustrated in Figure 9. Note that the Bluetooth Controller goes back to
Deep Sleep mode at the end of the data transfer.
3. Autonomous wake-up without communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
For autonomous wake-up without SPI communication, the STA2500D only asserts
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x to get the system clock.
Figure 7. Entering deep sleep mode through enhanced H4 SPI
SPI_CSN
SPI_CLK
1
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
SPI_INT
CLK _REQ _OUT _1
REF_CLK _IN
2
SLEEP
3
Figure 8. Wake-up by the host through enhanced H4 SPI
SPI_CSN
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
SPI_INT
CLK _REQ _OUT _1
REF_CLK _IN
1
2
WAKEUP
3
WOKEN
5
4
4
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 33/58
Page 34

General specification STA2500D
Figure 9. Wake-up by the Bluetooth controller with data transmission to the host,
through enhanced H4 SPI
SPI_CSN
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
SPI_INT
CLK _REQ_OUT_1
4
3
5
DATA
2
1
REF_CLK _IN
Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 SPI
It requires BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x (BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 for active high polarity and
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2 for active low polarity), BT_WAKEUP and BT_SPI_INT. The
BT_WAKEUP is used as wake-up signal from the Host, the BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x requires
the clock from the Host and BT_SPI_INT is used as a wake-up signal from the Bluetooth
Controller.
● Deep sleep mode entry
The Host tells the STA2500D that it can go in Deep Sleep mode by forcing the
BT_WAKEUP of the STA2500D to ‘0’. The STA2500D decides to go in Deep Sleep
mode, or not, depending on its scheduled activity and on the number of events or data
packets to be sent to the Host. In case it decides to go in Deep Sleep mode, it asserts
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x ‘inactive’ to tell the Host that it does not need the clock
anymore. The STA2500D cannot go in Deep Sleep mode by itself. Note that the Host
cannot force BT_WAKEUP to ‘0’ before the end of a write operation from the Host, this
in order to allow correct decoding of the message by the Bluetooth Controller.
● Deep sleep mode wake-up
The wake-up procedure can be initiated by the Host or by the STA2500D. In the latter
case, it can be with or without communication, depending if there are data to be
transmitted to the Host.
1. Wake-up initiated by the Host
The Host sets the BT_WAKEUP pin of the STA2500D to ‘1’. Then the STA2500D asks
the Host to restart the system clock by setting BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x to ‘active’. When
the clock is available and stable, the Host can use BT_SPI_CSN to start an SPI
transaction if needed (there is a programmable minimum delay between the assertion
of BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x and the moment the Host can assert BT_SPI_CSN).
2. Autonomous wake-up with SPI communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D first asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x to ‘active’.
When the clock is available, the STA2500D sets BT_SPI_INT high to request the SPI
interface to the Host and waits for BT_SPI_CSN going low, indicating the SPI
transaction starts.
3. Autonomous wake-up without SPI communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_x to ‘active’.
34/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 35

STA2500D General specification
Figure 10. Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 SPI
SPI on
SPI on
Active
Active
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 1’ o r ‘ 0’
HOST_WAKEUP =‘1’ or ‘0’
Hos t: BT_WAKEUP=‘1’
Hos t: BT_WAKEUP=‘1’
OR
OR
BT Co nt ro ll er :
BT Co nt ro ll er :
BB
BB
Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode
SPI_INT=‘ 1’
BT_SPI_INT =‘1 ’
Hos t: BT_WAKEUP=‘0’
Host: BT_WAKEUP=‘0’
Hos t: BT_WAKEUP=‘ 1’
Host: BT_WAKEUP=‘1’
AND
AND
BT Co nt ro ll er :
BT Co nt ro ll er :
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ A’
SPI off
SPI off
Active
Active
CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ A ’
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 0’
HOST_WAKEUP=‘ 0’
BB
BB
Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode
BT Co nt ro l ler :CLK_ REQ_O UT_1=‘A ’
BT Co nt ro l ler :BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 =‘A’
Mode
Deep Sleep
BT Co nt ro l ler :CLK_REQ_OUT_1=‘ P’
BT Co nt ro l ler :BT _C LK _ R EQ_ O UT_ 1=‘ P’
SPI off
SPI off
Mode
CLK_REQ_OUT_1 = ‘ A’ : Active high/low
CLK_REQ_OUT_1 = ‘ A’ : Active high/low
‘P’:
‘P’:
Passive
Passive
low/high
low/high
Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 UART or H4 SPI with
handshake
This method is supported by both H4 UART and H4 SPI. The description below is for H4
UART.
It requires BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1, BT_WAKEUP and BT_HOST_WAKEUP. The
BT_WAKEUP is used as wake-up signal from the Host, the BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 requires
the clock from the Host and BT_HOST_WAKEUP is used as a wake-up signal from the
Bluetooth Controller.
● Deep sleep mode entry
The Host tells the STA2500D that it can go in Deep Sleep mode by forcing the
BT_WAKEUP of the STA2500D to ‘0’. The STA2500D decides to go in Deep Sleep
mode, or not, depending on its scheduled activity and on the number of events or data
packets to be sent to the Host. In case it decides to go in Deep Sleep mode, it asserts
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 low to tell the Host that it does not need the clock anymore. On
the contrary, if it still wants the interface active for up-transmission, it keeps
BT_HOST_WAKEUP to ‘1’ as long as needed before de-asserting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1. This is illustrated in Figure 11.
● Deep sleep mode wake-up
The wake-up procedure can be initiated by the Host or by the STA2500D. In the latter
case, it can be with or without communication, depending if there are data to be
transmitted to the Host.
1. Wake-up initiated by the Host
The Host sets the BT_WAKEUP pin of the STA2500D to ‘1’. Then the STA2500D asks
the Host to restart the system clock by setting BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to ‘1’. When the
clock is available and stable, the STA2500D puts BT_UART_RTS low to allow
communication. In case the STA2500D wants to send events to the Host, it then puts
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 35/58
Page 36

General specification STA2500D
BT_HOST_WAKEUP to ‘1’ in order to warm the Host and traffic starts when the Host
puts BT_UART_CTS to low. This is illustrated in Figure 12.
2. Autonomous wake-up with communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D first asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to ‘1’.
When the clock is available, the STA2500D requests traffic by asserting
HOST_WAKEUP high. Then either it puts BT_UART_RTS low to start traffic exchange
directly or it waits for the Host to first assert BT_WAKEUP high. The selection in
between the two behaviours is done by a SW parameter in the Parameter File.
3. An autonomous wake-up without communication (i.e. initiated by the STA2500D)
The STA2500D asks the Host to restart the system clock by setting
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to ‘1’. The UART signals are not changing.
Figure 11. Entering deep sleep mode, pending data on UART interface, through
UART with handshake
BT_WAKEUP
BT_WAKEUP
UART_RTS
UART_RTS
UART_RTS
UART_RTS
12
12
3
HOST_WAKEUP
HOST_WAKEUP
CLK_REQ_OUT_1
CLK_REQ_OUT_1
REF_CLK_IN
REF_CLK_IN
3
4
4
1. Host puts BT_WAKEUP low. BT Controller notices it. But as there is pending traffic to
be send to Host, it keeps HOST_WAKEUP high as long as needed for up-transmission
and then de-asserts HOST_WAKEUP, telling the Host there is nothing more to
transmit.
2. BT Controller puts UART_RTS high to set “flow off”. This is done in fixed number of
instructions.
3. Then BT Controller puts CLK_REQ_OUT_1 to ‘0’, telling the Host it can cut the clock.
This is done in fixed number of instructions.
4. There is no clock, BT is in Deep Sleep mode.
36/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 37

STA2500D General specification
Figure 12. Wakeup by host through UART with handshake
BT_WAKEUP
UART_RTS
UART_RTS
UART_RTS
UART_CTS
HOST_WAKEUP
CLK_REQ_OUT_1
REF_CLK_IN
5. Host pulls BT_WAKEUP high to wake-up BT Controller. HW starts driving
CLK_REQ_OUT_1 high (after 2*LP_CLK).
6. Host starts 13 MHz clock and distribute it when stable. Delay between
CLQ_REQ_OUT_1 and usage of stable clock is programmable in between 3 and 39
ms.
7. When BT Controller starts with clock, it sets “flow on” by putting UART_RTS low. There
is a fixed SW latency. Host can send commands.
8. BT Controller sets HOST_WAKEUP high telling to the Host it has events to send to the
Host.
9. When the Host is ready for data transmission, it asserts UART_CTS low.
6.11 Patch RAM
8
5
7
9
6
The STA2500D includes a HW block that allows patching of the ROM code.
Additionally, a SW patch mechanism allows replacing complete SW functions without
changing the ROM image.
A part of the RAM memory is used for HW and SW patches.
6.12 Download of SW parameter file
To change the device configuration a set of customizable parameters have been defined
and put together in one file, the parameter file. This Parameter File is downloaded at startup into the STA2500D.
Examples of parameters are: radio configuration, PCM settings etc.
The same HCI command is used to download the file containing the patches (both those for
the SW and HW mechanism).
A more detailed description of the SW parameter file is available upon request.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 37/58
Page 38

General specification STA2500D
6.13 Bluetooth - WLAN coexistence in collocated scenario
The coexistence interface uses up to 4 WLAN control signal pins, which can be mapped via
software parameter download on different pins of the STA2500D (see Section 7.5).
The functionality of the 4 WLAN control signal pins depends on the selected algorithm, as
explained
below and summarized in Ta bl e 2 4.
Bluetooth and WLAN 802.11 b/g [] [] technologies occupy the same 2.4 GHz ISM band. The
STA2500D implements a set of mechanisms to avoid interference in a collocated scenario.
The STA2500D supports 5 different algorithms in order to provide efficient and flexible
simultaneous functionality between the two technologies in collocated scenarios:
● Algorithm 1: PTA (Packet Traffic Arbitration) based coexistence algorithm defined in
accordance with the IEEE 802.15.2 recommended practice [].
● Algorithm 2: the WLAN is the Master and it indicates to the STA2500D when not to
operate in case of simultaneous use of the air interface.
● Algorithm 3: the STA2500D is the Master and it indicates to the WLAN chip when not
to operate in case of simultaneous use of the air interface.
● Algorithm 4: Two-wire mechanism
● Algorithm 5: Alternating Wireless Medium Access (AWMA), defined in accordance
with the WLAN 802.11 b/g [] [] technologies.
The algorithm is selected via an HCI command. The default algorithm is algorithm 1.
6.13.1 Algorithm 1: PTA (packet traffic arbitration)
The algorithm is based on a bus connection between the STA2500D and the WLAN chip:
Figure 13. PTA diagram
RF_REQUEST
STATUS
STLC2500 D
By using this coexistence interface it is possible to dynamically allocate bandwidth to the two
devices when simultaneous operations are required while the full bandwidth can be
allocated to one of them in case the other one does not require activity.
The algorithm involves
● a priority mechanism, which allows preserving the quality of certain types of link.
● a mechanism to indicate that a periodic communication is ongoing.
A typical application would be to guarantee optimal quality to the Bluetooth voice
communication while an intensive WLAN communication is ongoing.
FREQ
RF_CONFIRM
WLAN
Several algorithms have been implemented in order to provide a maximum of flexibility and
efficiency for the priority handling. ST specific HCI commands are implemented to select the
algorithm and to tune the priority handling.
38/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 39

STA2500D General specification
The combination of time division multiplexing and the priority mechanism avoids the
interference due to packet collision. It also allows the maximization of the 2.4 GHz ISM
bandwidth usage for both devices while preserving the quality of some critical types of link.
6.13.2 Algorithm 2: WLAN master
In case the STA2500D has to cooperate, in a collocated scenario, with a WLAN chip not
supporting a PTA based algorithm, it is possible to put in place a simpler mechanism.
The interface is reduced to 1 line:
Figure 14. WLAN master
STLC2500 D
BT_RF_NOT_ALLOWED
When the WLAN has to operate, it alerts high the BT_RF_NOT_ALLOWED signal and the
STA2500D will not operate while this signal stays high.
This mechanism permits to avoid packet collision in order to make an efficient use of the
bandwidth but cannot provide guaranteed quality over the Bluetooth links.
6.13.3 Algorithm 3: Bluetooth master
This algorithm represents the symmetrical case of algorithm 2. Also in this case the
interface is reduced to 1 line:
Figure 15. Bluetooth master
STLC2500 D WLAN
WLAN_RF_NOT_ALLOWED
WLAN
When the STA2500D has to operate it alerts high the WLAN_RF_NOT_ALLOWED signal
and the WLAN will not operate while this signal stays high.
This mechanism permits to avoid packet collision in order to make an efficient use of the
bandwidth, it provides high quality for all Bluetooth links but cannot provide guaranteed
quality over the WLAN links.
6.13.4 Algorithm 4: two-wire mechanism
Based on algorithm 2 and 3, the Host decides, on a case-by-case basis, whether WLAN or
Bluetooth is master.The Master role can be checked and changed at run-time by the Host
via an HCI command.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 39/58
Page 40

General specification STA2500D
6.13.5 Algorithm 5: Alternating wireless medium access (AWMA)
AWMA utilizes a portion of the WLAN beacon interval for Bluetooth operations. From a
timing perspective, the medium assignment alternates between usage following WLAN
procedures and usage following Bluetooth procedures.
The timing synchronization between the WLAN and the STA2500D is done by the HW signal
MEDIUM_FREE.
Table 24. WLAN HW signal assignment
WLAN control
signal
(see also
Tabl e 2 8)
Scenario 1:
PTA
Scenario 2:
WLAN master
Scenario 3:
BT master
Scenario 4:2-wire
Scenario 5:
AWM A
WLAN 1 RF_CONFIRM
WLAN 2 RF_REQUEST Not used
WLAN 3 STATUS Not used Not used Not used Not used
WLAN 4
FREQ
(optional)
BT_RF_NOT_
ALLOWED
Not used Not used Not used Not used
Not used
WLAN_RF_NOT_
ALLOWED
BT_RF_NOT_
ALLOWED
WLAN_RF_NOT_
ALLOWED
MEDIUM_F
REE
Not used
40/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 41

STA2500D Digital interfaces
7 Digital interfaces
7.1 The UART interface
The STA2500D contains a 4-pin (BT_UART_RXD, BT_UART_TXD, BT_UART_RTS, and
BT_UART_CTS) UART compatible with 16450, 16550 and 16750 standards. It is running up
to 4000 kbps (+1.5% / -1%).
The configuration is 8 data bits, 1 start bit, 1 stop bit, and no parity bit. The transmit and
receive paths contain a DMA function for low CPU load and high throughput. Auto RTS/CTS
is implemented in HW, controllable by SW.
The UART accepts all HCI commands as described in the Bluetooth specification, it
supports H4 proprietary commands and the Deep Sleep mode entry and wake-up through
H4 UART (see Section : Deep sleep mode entry and wake up through H4 UART). The
complete list of supported proprietary HCI commands is available upon request.
At startup, the UART baud rate is fixed at 115200 bps independently of the
BT_REF_CLK_IN frequency. A specific HCI command is provided to change the UART
baud rate when necessary within the range 9600 bps to 4000 kbps. All standard baud rates
and many other ones are supported.
7.2 The SPI interface
The physical SPI interface is made up of 5 signals: clock, chip select, data in, data out and
interrupt. When the SPI mode is selected, these signals are available through the
BT_UART/BT_SPI and BT_HOST_WAKEUP pins.
Figure 16. SPI interface
Host
SPI_CLK
SPI_CSN
SPI_MISO
SPI_MOSI
SPI_INT
● SPI_CSN (on pin BT_UART_RTS/BT_SPI_CSN): chip select allows the use of multiple
Slaves (1 chip select per Slave). This signal is active low. This signal is mandatory,
even with only 1 Slave, because the Host must drive this signal to indicate SPI frames.
● SPI_CLK (on pin BT_UART_CTS/BT_SPI_CLK): clock signal, active for a multiple of
data length cycles during an SPI transfer (SPI_CSN active). The clock is allowed to be
active when SPI_CSN is not active, in order to serve other Slaves.
● SPI_DO (on pin BT_UART_TXD/BT_SPI_DO): data transfer from Slave to Master.
Data is generated on the negative edge of SPI_CLK by the Slave and sampled on the
BT Controller
SPI_CLK
SPI_CSN
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
SPI_INT
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 41/58
Page 42

Digital interfaces STA2500D
positive edge of SPI_CLK. When SPI_CSN is inactive, this BT Controller output is in
tristate mode.
● SPI_DI (on pin BT_UART_RXD/BT_SPI_DI): data transfer from Master to Slave. Data
is generated on the negative edge of SPI_CLK by the Master and sampled on the
positive edge of SPI_CLK.
● SPI_INT (on pin BT_HOST_WAKEUP/BT_SPI_INT): interrupt from the Slave, used to
request an SPI transfer by the Slave to the Master. The signal is active high (Host input
must be level sensitive).
The SPI interface is Master at the Host side, and Slave at Bluetooth Controller side. It is
designed to work with the H4 and enhanced H4 protocol. Also synchronous data packet
transfer (eSCO) over HCI is supported.
The SPI data length and endianness are configurable.
The SPI interface can only operate in half duplex mode.
Also the use of flow control is configurable. The flow control consists of an indication from
the Bluetooth Controller whether its receive buffers are ready to receive data. This indication
is available in three ways:
● On the SPI_DO during T
(time between SPI_CSN becoming active and SPI_CLK
SCS
becoming high), see FC in Figure 17 and Tscs in Figure 18
● In a register that can be read by the Host
● Optionally on one of the programmable GPIOs: GPIO_16. This is enabled by a SW
parameter download, see Section 7.5
The default SPI configuration is:
● Half duplex mode
● 16 bit data length
● Most significant byte first
● Most significant bit first
● Flow control on SPI_DO and in a register
More detailed information on the SPI interface is available upon request.
Figure 17. SPI data transfer timing for data length of 8 bits and lsb first, full duplex
SPI_CSN
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI
SPI_INT
Z FCb0b1b2b3b4b5b6b7 Z
b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7
42/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 43

STA2500D Digital interfaces
Figure 18. SPI setup and hold timing
SPI_CSN
SPI_CLK
SPI_DI
T
CSL
P
CL
T
SCS
T
CLL
T
CLH
T
T
SDC
HCD
T
CSH
T
SCL
SPI_DO
T
SCLD
Table 25. SPI timing parameters
Symbol Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
T
P
SCLD
SPI_CLK full period 70 0 0 ns
CL
High period of SPI_CLK 16.6 ns
CLH
Low period of SPI_CLK 26.4 ns
CLL
High period of SPI_CSN 1 * P
CSH
Low period of SPI_CSN 9 * P
CSL
Setup time, SPI_CSN Low to SPI_CLK high 1 * P
SCS
Setup time, SPI_CLK Low to SPI_CSN high1/2 * P
SCL
Setup time, SPI_MOSI valid to SPI_CLK high 9.7 5 ns
SDC
Hold time, SPI_MOSI valid after SPI_CLK
HCD
high
CL
CL
CL
CL
0ns
Setup time, SPI_CLK Low to SPI_MISO valid 26.5 ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
7.3 The PCM interface
The chip contains a 4-pin direct voice interface to connect to standard CODEC.
The interface supports multiport PCM operations for voice transfer. It can be programmed to
act as a Master or a Slave via a SW parameter download or via specific HCI commands.
The four signals of the multiport PCM interface are:
● PCM_CLK : PCM clock
● PCM_SYNC : PCM 8 kHz sync (every 125 μs)
● PCM_A : PCM data (TX or RX)
● PCM_B : PCM data (RX or TX)
As a Master the interface by default generates a PCM clock rate of 2048 kHz, but it can be
configured to rates from 8 kHz up to 2048 kHz. As a Slave, it can automatically handle
external PCM clock rates from 128 kHz up to 4000 kHz. The default PCM_SYNC rate is 8
kHz.
The following external PCM data format are supported: linear (13 - 16 bit), µ−law (8 bit) or Alaw (8 bit).
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 43/58
Page 44

Digital interfaces STA2500D
In Slave mode, all possible PCM_SYNC lengths are supported (including “short frame” (= 1
PCM_CLK period) and “long frame” (> 1 PCM_CLK period)). In Master mode, the length is
configurable (1 (“short frame”), 8 or 16 (“long frame”) PCM_CLK periods).
The start of the PCM data is configurable. One possible configuration is e.g. for a short
frame, the falling edge of the PCM_SYNC indicating the start of the PCM word. Another
possible configuration is e.g. for a long frame, the rising edge of the PCM_SYNC indicating
the start of the PCM word.
TX data are by default generated on the positive edge of PCM_CLK and expected to be
latched by the external device on the negative edge while RX data are latched on the
negative edge of PCM_CLK. But the inverted clock mode is also supported, whereby the
generation of TX data is on the negative edge and the latching of TX and RX data is on the
positive edge.
One additional PCM_SYNC signal can be provided via the GPIOs. See section 7.5 for more
details.
Figure 19. PCM (A-law, µ-law) standard mode
PCM_CLK
PCM_SYNC
PCM_A B B
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
PCM_B
B
Figure 20. Linear mode
PCM_CLK
PCM_SYNC
PCM_A
PCM_B
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Figure 21. Multislot operation
125µs
125μs
B
D02TL558
D02TL559
The PCM implementation supports from 1 up to 3 slots per frame with the following
parameters:
44/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 45

STA2500D Digital interfaces
Table 26. PCM interface parameters
Symbol Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
PCM Interface
F
PCM_CLK
F
PCM_SYNC
P
sync_delay
S
s
Frequency of PCM_CLK (Slave) 128
(1)
2048 4000
Frequency of PCM_SYNC - 8 - kHz
Delay of the starting of the first slot 0 - 255 cycles
Slot start (programmable for every slot) 0 - 255 cycles
(2)
D Data size 8 - 16 bits
N Number of slots per frame 1 - 3 -
1. Note that it is not possible to use 16 bits in Slave case if pcm_clk is 128kHz. This is the only exception.
2. In Master case, the maximum of PCM_CLK is 2048 kHz.
Table 27. PCM interface timing (at PCM_CLK = 2048 kHz)
Symbol Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
t
WCH
t
WCL
t
WSH
t
SSC
t
SDC
t
HCD
t
DCD
High period of PCM_CLK 200 - - ns
Low period of PCM_CLK 200 - - ns
High period of PCM_SYNC 200 - - ns
Setup time, PCM_SYNC high to PCM_CLK low 100 - - ns
Setup time, PCM_A/B input valid to PCM_CLK low 100 - - ns
Hold time, PCM_CLK low to PCM_A/B input valid 100 - - ns
Delay time, PCM_CLK high to PCM_A/B output valid - - 150 ns
kHz
Figure 22. PCM interface timing
PCM_CLK
t
WCH
PCM_SYNC
t
WSH
PCM_A/B in
PCM_B/A out
t
WCL
t
SSC
t
SDC
MSB MSB-1 MSB-2 MSB-3 MSB-4
t
DCD
MSB MSB-1 MSB-2 MSB-3 MSB-4
t
HCD
D02TL557
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 45/58
Page 46

Digital interfaces STA2500D
7.4 The JTAG interface
The JTAG interface is compliant with the JTAG IEEE Standard 1149.1. It allows both the
boundary scan of the digital pins and the debug of the ARM7TDMI application when
connected with the standard ARM7 developments tools. It is also used for the industrial test
of the device. The JTAG interface is available through the following 5 pins: BT_GPIO_8,
BT_GPIO_9, BT_GPIO_10, BT_GPIO_11 and BT_GPIO_16.
7.5 Alternate I/O functions
The STA2500D has 10 additional general purpose pins on top of the 4 PCM pins, the 4
UART pins and BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 that can also be reconfigured. They are fully
programmable via specific HCI commands. They can be configured as input, output,
interrupt with asynchronous or synchronous edge or level detection and/or wake-up.
The alternative functions are:
● Wake-up by the Host in Deep Sleep mode through UART or SPI with handshake (see
Section : Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through H4 UART or H4 SPI with
handshake)
● WLAN coexistence control
● I2C interface
● PCM synchronization
● GPIOs
● UART / SPI interface
● external driver/LNA control for Class 1 operation.
19 pins can be redefined by SW to perform other functions. Pin BT_HOST_WAKEUP e.g.
can be redefined to perform up to 7 functions, depending on SW settings.
4 exemplary combinations of pin programmings are given in Tab l e 28 . The available
functions are
● ex. 1: UART + I2C + Class 1 control
● ex. 2: UART + WLAN + Class 1 control
● ex. 3: SPI + WLAN + Class 1 control
● ex. 4: SPI + WLAN + I
2
C + Class 1 control
(The complete list of alternate functions is available upon request).
Table 28. Examples of BT_GPIO pin programming
STA2500D Pin Name ex. 1 ex. 2 ex. 3 ex. 4
BT_UART_RXD/BT_SPI_DI UART_RXD UART_RXD SPI_DI SPI_DI
BT_UART_TXD/BT_SPI_DO UART_TXD UART_TXD SPI_DO SPI_DO
BT_UART_CTS/BT_SPI_CLK UART_CTS UART_CTS SPI_CLK SPI_CLK
BT_UART_RTS/BT_SPI_CSN UART_RTS UART_RTS SPI_CS SPI_CS
BT_PCM_CLK PCM_CLK PCM_CLK PCM_CLK PCM_CLK
BT_PCM_SYNC PCM_SYNC PCM_SYNC PCM_SYNC PCM_SYNC
BT_PCM_A PCM_A PCM_A PCM_A PCM_A
46/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 47

STA2500D Digital interfaces
Table 28. Examples of BT_GPIO pin programming (continued)
STA2500D Pin Name ex. 1 ex. 2 ex. 3 ex. 4
BT_PCM_B PCM_B PCM_B PCM_B PCM_B
BT_GPIO_0 I2C_CLK WLAN1 WLAN1 WLAN1
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_1 I2C_DAT WLAN2 WLAN2 I2C_DAT
BT_CLK_REQ_IN_2 GPIO_2 WLAN3 WLAN3 WLAN3
BT_HOST_WAKEUP/BT_SPI
_INT
BT_GPIO_11 ANT_SWITCH ANT_SWITCH ANT_SWITCH WLAN2
BT_GPIO_9 PA_LEVEL2 PA_LEVEL2 PA_LEVEL2 PA_LEVEL2
BT_GPIO_10 PA_LEVEL1 PA_LEVEL1 PA_LEVEL1 PA_LEVEL1
BT_GPIO_8 RX_ENABLE RX_ENABLE RX_ENABLE RX_ENABLE
BT_GPIO_16 PA_ENABLE PA_ENABLE PA_ENABLE PA_ENABLE
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_1 CLK_REQ_OUT_1 CLK_REQ_OUT_1 CLK_REQ_OUT_1 CLK_REQ_OUT_1
BT_CLK_REQ_OUT_2 NA NA WLAN4 IC2_CLK
HOST_WAKEUP WLAN4 SPI_INT SPI_INT
7.6 The I2C interface
The I2C interface is used to access I2C peripherals.
The interface is a fast Master I
functionality is not supported.
2
C; it has full control of the interface at all times. I2C Slave
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 47/58
Page 48

HCI transport layer STA2500D
8 HCI transport layer
The STA2500D supports the HCI transport layer as defined by the SIG: H4 []. It is supported
in combination with UART and SPI mode. The STA2500D also supports an enhanced
version of the H4 protocol in combination with SPI mode.
8.1 H4 UART transport layer
The objective of HCI UART transport layer is to make it possible to use Bluetooth HCI over a
serial interface between two UARTs on the same PCB. The HCI UART transport layer
assumes that the UART communication is free from line errors.
UART settings
The HCI UART transport layer uses the following settings for RS232:
● Baud rate :configurable (default baud rate 115200 bps)
● Number of data bits :8
● Parity bit :no parity
● Stop bit :1 stop bit
● Flow control :RTS/CTS
● Flow-off response time :500 µs
The flow-off response time defines the maximum time that the STA2500D can still receive
data after setting RTS high.
RTS/CTS flow control is used to prevent temporary UART buffer overrun between the
Bluetooth Controller and the Host.
The RS232 signals should be connected in a null-modem fashion, i.e. the Bluetooth
Controller TXD output should be connected to the Host RXD input and the Bluetooth
Controller RTS output should be connected to the Host CTS input and vice versa.
If the Bluetooth Controller RTS output (connected to the Host CTS input) is low, then the
Host is allowed to send.
If the Bluetooth Controller RTS output (connected to the Host CTS input) is high, then the
Host is not allowed to send.
If the Bluetooth Controller CTS input (connected to the Host RTS output) is low, then the
Bluetooth Controller is allowed to send.
If the Bluetooth Controller CTS input (connected to the Host RTS output) is high, then the
Bluetooth Controller is not allowed to send.
Figure 23. UART transport layer
BLUETOOTH
HOST
BLUETOOTH HCI
BLUETOOTH
HOST
CONTROLLER
HCI UART TRANSPORT LAYER
48/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 49

STA2500D HCI transport layer
8.2 Enhanced H4 SPI transport layer
This is the default SPI mode.
The enhanced H4 protocol is based on the H4 protocol as defined by the SIG []. In addition
a messaging protocol is defined for controlling the Deep Sleep mode entry and wake-up,
see Section : Deep sleep mode entry and wake-up through enhanced H4 SPI.
Three messages are defined: SLEEP, WAKEUP and WOKEN. More details on the
messages are available upon request.
At SPI level, the default configuration is used:
● The SPI interface works in half duplex mode
● The data are exchanged in multiple of 16 bits
● The most significant byte first
● The most significant bit first
● There is a read and write command from the Host to access the Bluetooth device
● The Bluetooth device requests a transfer by the activation of the interrupt line
● Flow control on SPI_DO and in a register
8.3 H4 SPI transport layer
As stated in the previous section, the SPI interface is configurable. One possible
configuration is the following, implementing a simple H4 SPI transport layer.
● The SPI interface works in half duplex mode
● The data are exchanged in multiples of 8 bits
● The least significant bit first
● There is a read and write command from the Host to access the Bluetooth device
● The Bluetooth device requests a transfer by the activation of the interrupt line
● Flow control on BT_SPI_DO and in a register
8.4 eSCO over HCI
The STA2500D supports synchronous data packet transfer (eSCO) over HCI.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 49/58
Page 50

Package information STA2500D
9 Package information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK
®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
is an ST trademark.
Figure 24. LFBGA48 (6x6x1.4mm) mechanical data and package dimensions
DIM.
A 1.250 0.0492
A1 0.210 0.0083
A2 0.890 0.0350
A3 0.300 0.0118
A4 0.600 0.0236
b 0.350 0.400 0.450 0.0138 0.0157 0.0177
D 5.850 6.000 6.150 0.2303 0.2362 0.2421
D1 4.800 0.1890
E 5.850 6.000 6.150 0.2303 0.2362 0.2421
E1 4.800 0.1890
e 0.800 0.0315
F 0.600 0.0236
ddd 0.100 0.0039
eee 0.150 0.0059
fff 0.080 0.0031
mm inch
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
Body: 6 x 6 x 1.4mm
LFBGA48
Low profile Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array
50/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
8092328 B
Page 51

STA2500D Package information
Figure 25. Package markings
A
B D
G
H
Table 29. Package markings legend
C
E
F
Item Description Format Value
A Type + version XXXXXX 2500D7
B Assembly Plant P -
C BE sequence (LL) LL -
D Assembly Year (Y) Y -
E Assembly Week (WW) WW -
F Second_lvl_intct - -
G Standard ST Logo - -
HDot (pin A1) - -
Note: The ECO level is reflected in the “Order code” (see Ta b le 3 2)
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 51/58
Page 52

References STA2500D
10 References
Short
name
Name Date Owner
Specification of the Bluetooth System - Host Controller
Interface [Transport Layer] Volume 04 Revision 1.2 or later,
2006, part A: UART v1.1
Radio Frequency Test Suite Structure (TSS) and Test
Purposes (TP) System Specification 1.2/2.0/2.0 + EDR,
document number RF.TS/2.0.E.3
IEEE 802.15.2, IEEE Recommended Practice for
Telecommunications and Information exchange between
systems – Local and metropolitan area networks Specific
Requirements - Part 15.2: Coexistence of Wireless Personal
Area Networks with Other Wireless Devices Operating in
Unlicensed Frequency Band
IEEE 802.11, IEEE Standards for Information Technology -Telecommunications and Information Exchange between
Systems -- Local and Metropolitan Area Network -- Specific
Requirements -- Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access
Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications
Table 30. References
ID
[1] - Specification of the Bluetooth System V2.1 + EDR (“Lisbon”)
[2] - Specification of the Bluetooth System V2.0 + EDR
[3] - Specification of the Bluetooth System V1.2
[4] -
[5] -
[6] -
[7] WLAN
Not yet
released
November
2004
November
2003
January
2006
March
2005
August
2003
1999 IEEE
Bluetooth SIG
Bluetooth SIG
Bluetooth SIG
Bluetooth SIG
Bluetooth SIG
IEEE
IEEE 802.11b, Supplement to 802.11-1999, Wireless LAN
[8] 802.11b
[9] 802.11g
[10] -
52/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
MAC and PHY specifications: Higher speed Physical Layer
(PHY) extension in the 2.4 GHz band
IEEE 802.11g, IEEE Standard for Information technology—
Telecommunications and information exchange between
systems—Local and metropolitan area networks—Specific
requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access
Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications—
Amendment 4: Further Higher-Speed Physical Layer
Extension in the 2.4 GHz Band
STLC2500C_DS_Rev2.0.pdf, Datasheet of Bluetooth
2.0&EDR compliant single chip, Rev2.0 or later
1999 IEEE
2003 IEEE
--
Page 53

STA2500D Acronyms and abbreviations
11 Acronyms and abbreviations
Table 31. Acronyms and abbreviations
Acronyms/
abbreviation
Description
2-DH12-
DH32-DH5
2-EV3
2-EV5
3-DH1
3-DH3
3-DH5
3-EV3
3-EV5
8-DPSK 8 phase Differential Phase Shift Keying
A/D Analog to Digital
AC Alternating Current
ACL Asynchronous Connection Oriented
AHB Advanced High-performance Bus
A-law Audio encoding standard
AMBA Advanced Micro-controller Bus Architecture
AMR Absolute Maximum Rating
APB Advanced Peripheral Bus
ARM7 Micro-processor
ARM7TDMI Micro-processor
AWMA Alternating Wireless Medium Access
BB Base Band
BER Bit Error Rate
BOM Bill Of Materials
BR Basic Rate
BT Bluetooth
BW Band Width
C/I Carrier-to-co-channel Interference
CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
CODEC COder DEcoder
CPU Central Processing Unit
CQDDR Channel Quality Driven Data Rate change
CVSD Continuous Variable Slope Delta modulation
DC Direct Current
Bluetooth 2 Mbps ACL packet types
Bluetooth 2 Mbps synchronous packet types
Bluetooth 3 Mbps ACL packet types
Bluetooth 3 Mbps synchronous packet types
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 53/58
Page 54

Acronyms and abbreviations STA2500D
Table 31. Acronyms and abbreviations (continued)
Acronyms/
abbreviation
DEVM Differential Error Vector Amplitude
DH1
DH3
DH5
DM1
DM3
DM5
DMA Direct Memory Access
DV Bluetooth 1 Mbps synchronous packet type
EBC Ericsson technology licensing Baseband Core
EDR Enhanced Data Rate
EIR Extended Inquiry Response
EPR Encryption Pause/Resume
eSCO extended SCO
EV3
EV4
EV5
FHS Frequency Hopping Synchronization
GFSK Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying
GPIO General Purpose I/O pin
GSM Global System for Mobile communications
H4 UART based HCI transport
HCI Host Controller Interface
HV1
HV3
HW HardWare
I/O Input/Output
I2C Inter-Integrated Circuit
IF Intermediate Frequency
ISM Industrial, Scientific and Medical
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
L2CAP Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol
LMP Link Manager Protocol
LNA Low Noise Amplifier
LO Local Oscillator
LSTO Link Supervision Time Out
μ-law Audio encoding standard
Bluetooth 1 Mbps ACL packet types
Bluetooth 1 Mbps ACL packet types
Bluetooth 1 Mbps synchronous packet types
Bluetooth 1 Mbps synchronous packet types
Description
54/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 55

STA2500D Acronyms and abbreviations
Table 31. Acronyms and abbreviations (continued)
Acronyms/
abbreviation
π/4-DQPSK π/4 rotated Differential Quaternary Phase Shift Keying
PA Power Amplifier
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PD Pull-Down
PLL Phase Locked Loop
PPEC Pitch-Period Error Concealment
PTA Packet Traffic Arbitration
PU Pull-Up
QoS Quality of Service
RAM Random Access Memory
RC Resistance-Capacitance
RF Radio Frequency
rms root mean squared
ROM Read Only Memory
RS232
ANSI/EIA/TIA-232-F, September 1997, Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment
and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange
RSSI Receive Signal Strength Indication
RX Receive
SCO Synchronous Connection Oriented
SIG Bluetooth Special Interest Group
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
ST STMicroelectronics
SW SoftWare
TBD To Be Defined
T
eSCO
T
T
SCO
sniff
eSCO interval
SCO interval
Sniff interval
TX Transmit
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
VGA Variable Gain Amplifier
WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
WFBGA Very Very Thin Profile Fine Pitch Ball Grid Array
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network
WLCSP Wafer-Level Chip Scale Package
Description
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 55/58
Page 56

Order codes STA2500D
12 Order codes
Table 32. Ordering information
Order code Package Packing Production
STA2500DC LFBGA48 Tray Simplified production flow
STA2500DCTR LFBGA48 Tape and reel Simplified production flow
STA2500D LFBGA48 Tray Automotive version
STA2500DTR LFBGA48 Tape and reel Automotive version
56/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
Page 57

STA2500D Revision history
13 Revision history
Table 33. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
24-Jul-2009 1 Initial release.
18-Jan-2010 2
Removed device summary table in cover page.
Added Section 12: Order codes on page 56.
Doc ID 16067 Rev 2 57/58
Page 58

STA2500D
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2010 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
58/58 Doc ID 16067 Rev 2
 Loading...
Loading...