Page 1

16-bit MCU with 512 Kbyte Flash memory and 36 Kbyte RAM
Features
■ High performance 16-bit CPU with DSP
functions
– 50ns instruction cycle time at 40 MHz max
CPU clock
– Multiply/accumulate unit (MAC) 16 x 16-bit
multiplication, 40-bit accumulator
– Enhanced boolean bit manipulations
– Single-cycle context switching support
■ Memory organization
– 512 Kbyte on-chip Flash memory single
voltage with erase/program controller (full
performance, 32-bit fetch)
– 100K erasing/programming cycles.
– Up to 16 Mbyte linear address space for
code and data (5 Mbytes with CAN or I
– 2 Kbyte on-chip internal RAM (IRAM)
– 34 Kbyte on-chip extension RAM (XRAM)
– Programmable external bus configuration
and characteristics for different address
ranges
– 5 programmable chip-select signals
– Hold-acknowledge bus arbitration support
■ Interrupt
– 8-channel peripheral event controller for
single cycle interrupt driven data transfer
– 16-priority-level interrupt system with 56
sources, sampling rate down to 25ns
■ Timers
– 2 multifunctional general purpose timer
units with 5 timers
■ Two 16-channel capture / compare units
■ 4-channel PWM unit + 4-channel XPWM
ST10F273M
PQFP144 (28 x 28 x 3.4mm)
(Plastic Quad Flat Package)
■ 24-channel A/D converter
– 16-channel 10-bit, accuracy +/-2 LSB
– 8-channel 10-bit, accuracy +/-5 LSB
– 4.85µs Minimum conversion time
■ Serial channels
– 2 synch. / asynch. serial channels
– 2 high-speed synchronous channels
2
–I
C standard interface
2
C)
■ 2 CAN 2.0B interfaces operating on 1 or 2 CAN
buses (64 or 2x32 messages, C-CAN version)
■ Fail-safe protection
– Programmable watchdog timer
– Oscillator watchdog
■ On-chip bootstrap loader
■ Clock generation
– On-chip PLL and 4 to 12 MHz oscillator
– Direct or prescaled clock input
■ Real time clock and 32 kHz on-chip oscillator
■ Up to 111 general purpose I/O lines
– Individually programmable as input, output
or special function
– Programmable threshold (hysteresis)
■ Idle, power down and standby modes
■ Single voltage supply: 5 V ±10% (embedded
regulator for 1.8V core supply)
■ Temperature range: -40 / +125 °C
LQFP144 (20 x 20 x 1.4mm)
(Low Profile Quad Flat Package)
July 2007 Rev 2 1/182
www.st.com
1
Page 2

Contents ST10F273M
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.2 Special characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.2.1 X-Peripheral clock gating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.2.2 Improved supply ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2 Pin data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4 Memory organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5 Internal Flash memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.2 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.2.1 Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.2.2 Module structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.2.3 Low power mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.3 Write operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.4 Flash control registers description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.4.1 Flash control register 0 low (FCR0L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.4.2 Flash control register 0 high (FCR0H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
5.4.3 Flash control register 1 low (FCR1L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.4.4 Flash control register 1 high (FCR1H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5.4.5 Flash data register 0 low (FDR0L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.4.6 Flash data register 0 high (FDR0H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5.4.7 Flash data register 1 low (FDR1L) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.4.8 Flash data register 1 high (FDR1H) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.4.9 Flash address register low (FARL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
5.4.10 Flash address register high (FARH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
5.4.11 Flash error register (FER) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
5.4.12 XFlash interface control dummy register (XFICR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.5 Protection strategy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.5.1 Protection registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
2/182
Page 3

ST10F273M Contents
5.5.2 Flash non-volatile write protection I register low (FNVWPIRL) . . . . . . . 40
5.5.3 Flash non-volatile write protection I register high (FNVWPIRH) . . . . . . 41
5.5.4 Flash non-volatile write protection I register low Mirror (FNVWPIRL-m) 41
5.5.5 Flash non-volatile write protection I register high Mirror (FVWPIRH-m) 41
5.5.6 Flash non-volatile access protection register 0 (FNVAPR0) . . . . . . . . . 42
5.5.7 Flash non-volatile access protection register 1 low (FNVAPR1L) . . . . . 42
5.5.8 Flash non-volatile access protection register 1 high (FNVAPR1H) . . . . 43
5.5.9 Access protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.5.10 Write protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.5.11 Temporary unprotection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.6 Write operation examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.7 Write operation summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
6 Bootstrap loader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
6.1 Selection among user-code, standard or selective bootstrap . . . . . . . . . . 48
6.2 Standard bootstrap loader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
6.3 Alternate and selective boot mode (ABM and SBM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
6.3.1 Activation of the ABM and SBM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
6.3.2 User mode signature integrity check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
6.3.3 Selective boot mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7 Central processing unit (CPU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7.1 Multiplier-accumulator unit (MAC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
7.2 Instruction set summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.3 MAC co-processor specific instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
8 External bus controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9 Interrupt system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
9.1 X-Peripheral interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
9.2 Exception and error traps list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
10 Capture / compare (CAPCOM) units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
11 General purpose timer unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
11.1 GPT1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3/182
Page 4

Contents ST10F273M
11.2 GPT2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
12 PWM modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
13 Parallel ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13.2 I/O’s special features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13.2.1 Open drain mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13.2.2 Input threshold control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
13.3 Alternate port functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
14 A/D converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
15 Serial channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
15.1 Asynchronous / synchronous serial interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
15.2 ASCx in asynchronous mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
15.3 ASCx in synchronous mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
15.4 High speed synchronous serial interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
16 I2C interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
17 CAN modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
17.1 Configuration support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
17.2 CAN bus configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
17.2.1 Single CAN bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
17.2.2 Multiple CAN bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
17.2.3 Parallel mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
18 Real time clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
19 Watchdog timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
20 System reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
20.1 Input filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
20.2 Asynchronous reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
20.3 Synchronous reset (warm reset) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
4/182
Page 5

ST10F273M Contents
20.4 Software reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
20.5 Watchdog timer reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
20.6 Bidirectional reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
20.7 Reset circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
20.8 Reset application examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
20.9 Reset summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
21 Power reduction modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
21.1 Idle mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
21.2 Power-down mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
21.2.1 Protected power-down mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
21.2.2 Interruptible power-down mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
21.3 Standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
21.3.1 Entering standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
21.3.2 Exiting standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
21.3.3 Real time clock and standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
21.3.4 Power reduction modes summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
22 Programmable output clock divider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
23 Register set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
23.1 Special function registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
23.2 X-registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
23.3 Flash registers ordered by name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
23.4 Identification registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
24 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
24.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
24.2 Recommended operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
24.3 Power considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
24.4 Parameter interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
24.5 DC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
24.6 Flash characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
24.7 A/D converter characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
24.7.1 Conversion timing control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
5/182
Page 6

Contents ST10F273M
24.7.2 A/D conversion accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
24.7.3 Total unadjusted error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
24.7.4 Analog reference pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
24.8 AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
24.8.1 Test waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
24.8.2 Definition of internal timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
24.8.3 Clock generation modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
24.8.4 Prescaler operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
24.8.5 Direct drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
24.8.6 Oscillator watchdog (OWD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
24.8.7 Phase locked loop (PLL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
24.8.8 Voltage controlled oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
24.8.9 PLL jitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
24.8.10 PLL lock / unlock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
24.8.11 Main oscillator specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
24.8.12 32 kHz oscillator specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
24.8.13 External clock drive XTAL1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
24.8.14 Memory cycle variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
24.8.15 External memory bus timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
24.8.16 Multiplexed bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
24.8.17 Demultiplexed bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
24.8.18 CLKOUT and READY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
24.8.19 External bus arbitration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
24.8.20 High-speed synchronous serial interface (SSC) timing . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
25 Package information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
25.1 ECOPACK® . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
25.2 Mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
26 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
27 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
6/182
Page 7

ST10F273M List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 2. Summary of IFlash address range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 3. Flash module address space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 4. Flash module sectorization (read operations). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 5. Flash module sectorization (write operations, or ROMS1 = ‘1’) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 6. Flash control registers summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 7. FCR0L register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 8. FCR0H register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 9. FCR1L register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 10. FCR1H register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 11. Bank (BxS) and sectors (BxFy) status bits meaning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 12. FDR0L register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 13. FDR0H register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 14. FDR1L register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 15. FDR1H register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 16. FARL register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 17. FARH register description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 18. FER register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 19. XFlash interface control register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 20. FNVWPIRL register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 21. FNVWPRIH register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 22. FNVAPR0 register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 23. FNVAPR1L register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 24. FNVAPR1H register bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 25. Summary of access protection level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 26. Flash write operations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 27. ST10F273M boot mode selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 28. Standard instruction set summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 29. MAC instruction set summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 30. Interrupt sources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 31. X-Interrupt detailed mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 32. Trap priorities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 33. Compare modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 34. CAPCOM timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 35. GPT1 timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 36. GPT2 timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 37. PWM unit frequencies and resolutions at 40 MHz CPU clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 38. ASC asynchronous baudrates by reload value and deviation errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Table 39. ASC synchronous baudrates by reload value and deviation errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Table 40. SSC synchronous baudrate and reload values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table 41. WDTREL reload value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 42. Reset event definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Table 43. Reset event. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Table 44. PORT0 latched configuration for the different reset events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Table 45. Power reduction modes summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Table 46. List of special function registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Table 47. List of XBus registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Table 48. List of Flash control registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
7/182
Page 8

List of tables ST10F273M
Table 49. IDMANUF register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 50. IDCHIP register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 51. IDMEM register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Table 52. IDPROG register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Table 53. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Table 54. Recommended operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Table 55. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 56. Package characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 57. DC characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Table 58. Flash characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Table 59. Flash data retention characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Table 60. A/D converter characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Table 61. A/D converter programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Table 62. On-chip clock generator selections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Table 63. Internal PLL divider mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Table 64. PLL characteristics (V
= 5V ± 10%, VSS=0V, TA = -40°C to +125°C) . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
DD
Table 65. Main oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Table 66. Main oscillator negative resistance (module) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Table 67. 32 kHz oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 68. Minimum values of negative resistance (module) for 32 kHz oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Table 69. External clock drive XTAL1 timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Table 70. Memory cycle variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Table 71. Multiplexed bus timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Table 72. Demultiplexed bus timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Table 73. CLKOUT and READY
timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Table 74. External bus arbitration timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Table 75. SSC master mode timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Table 76. SSC slave mode timings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Table 77. Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Table 78. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
8/182
Page 9

ST10F273M List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. ST10F273M Logic symbol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 2. Pin configuration (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 3. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 4. ST10F273M memory mapping (XADRS3 = 800Bh - reset value) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 5. ST10F273M memory mapping (XADRS3 = E009h - user programmed value) . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 6. Flash structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 7. Write operation control flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 8. CPU block diagram (MAC unit not included) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 9. MAC unit architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 10. X-Interrupt basic structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 11. Block diagram of GPT1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 12. Block diagram of GPT2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 13. Block diagram of PWM module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 14. Connection to single CAN bus via separate CAN transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Figure 15. Connection to single CAN bus via common CAN transceivers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Figure 16. Connection to two different CAN buses (for example for gateway application) . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 17. Connection to one CAN bus with internal parallel mode enabled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 18. Asynchronous power-on RESET (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Figure 19. Asynchronous power-on RESET (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 20. Asynchronous hardware RESET (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 21. Asynchronous hardware RESET (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 22. Synchronous short / long hardware RESET (EA = 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 23. Synchronous short / long hardware RESET (EA = 0). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 24. Synchronous long hardware RESET (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 25. Synchronous long hardware RESET (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Figure 26. SW / WDT unidirectional RESET (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Figure 27. SW / WDT unidirectional RESET (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Figure 28. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Figure 29. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Figure 30. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA = 0) followed by a HW RESET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 31. Minimum external reset circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Figure 32. System reset circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 33. Internal (simplified) reset circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 34. Example of software or watchdog bidirectional reset (EA = 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 35. Example of software or watchdog bidirectional reset (EA = 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 36. PORT0 bits latched into the different registers after reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 37. External RC circuitry on RPD pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Figure 38. Port2 test mode structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Figure 39. Supply current versus the operating frequency (RUN and IDLE modes) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Figure 40. A/D conversion characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Figure 41. A/D converter input pins scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Figure 42. Charge-sharing timing diagram during sampling phase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Figure 43. Anti-aliasing filter and conversion rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Figure 44. Input/output waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Figure 45. Float waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Figure 46. Generation mechanisms for the CPU clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Figure 47. ST10F273M PLL jitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Figure 48. Crystal oscillator and resonator connection diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
9/182
Page 10

List of figures ST10F273M
Figure 49. 32 kHz crystal oscillator connection diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Figure 50. External clock drive XTAL1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Figure 51. External memory cycle: Multiplexed bus, with/without read/write delay, normal ALE. . . . 160
Figure 52. External memory cycle: Multiplexed bus, with/without read/write delay, extended ALE. . 161
Figure 53. External memory cycle: Multiplexed bus, with/without r/w delay, normal ALE, r/w CS . . . 162
Figure 54. External memory cycle: Multiplexed bus, with/without r/w delay, extended ALE, r/w CS. 163
Figure 55. External memory cycle: Demultiplexed bus, with/without r/w delay, normal ALE . . . . . . . 166
Figure 56. External memory cycle: Demultiplexed bus, with/without r/w delay, extended ALE . . . . . 167
Figure 57. External memory cycle: Demultipl. bus, with/without r/w delay, normal ALE, r/w CS. . . . 168
Figure 58. External memory cycle: Demultiplexed bus, without r/w delay, extended ALE, r/w CS . . 169
Figure 59. CLKOUT and READY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Figure 60. External bus arbitration (releasing the bus) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Figure 61. External bus arbitration (regaining the bus) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Figure 62. SSC master timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Figure 63. SSC slave timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Figure 64. PQFP144 mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Figure 65. LQFP144 mechanical data and package dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
10/182
Page 11

ST10F273M Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Description
The ST10F273M device is a new derivative of the STMicroelectronics ST10 family of 16-bit
single-chip CMOS microcontrollers.
The ST10F273M combines high CPU performance (up to 20 million instructions per second)
with high peripheral functionality and enhanced I/O capabilities. It also provides on-chip
high-speed single voltage Flash memory, on-chip high-speed RAM, and clock generation
via PLL.
The ST10F273M is processed in 0.18mm CMOS technology. The MCU core and the logic is
supplied with a 5V to 1.8V on-chip voltage regulator. The part is supplied with a single 5V
supply and I/Os work at 5V.
The ST10F273M is an optimized version of the ST10F273E, upward compatible with the
following set of differences:
● Maximum CPU frequency is 40 MHz
● A single bank of IFlash has been implemented but the programming interface has been
kept compatible with the ST10F273E
● Identification registers: the IDMEM register reflects the Flash type difference and allows
to differentiate the two devices by software
● Improved EMC behavior thanks to the introduction of an internal RC filter on the 5V for
the ballast transistors
● The clock to the X-Peripherals is gated: X-Peripheral not used will not get the clock in
order to reduce the power consumption.
1.2 Special characteristics
1.2.1 X-Peripheral clock gating
This new feature have been implemented on the ST10F273M: Once the EINIT instruction
has been executed, only the X-Peripherals enabled in the XPERCON register will be
clocked.
The new feature allows to reduce the power consumption and also should improve the
emissions as it avoids to propagate useless clock signals across the device.
1.2.2 Improved supply ring
An RC filter has been introduced in the 5V power supply ring of the ballast transistor. In
addition, the supply rings for the internal voltage regulators and the IOs have been split.
These two modifications should improve the behavior of the device regarding conducted
emissions.
11/182
Page 12
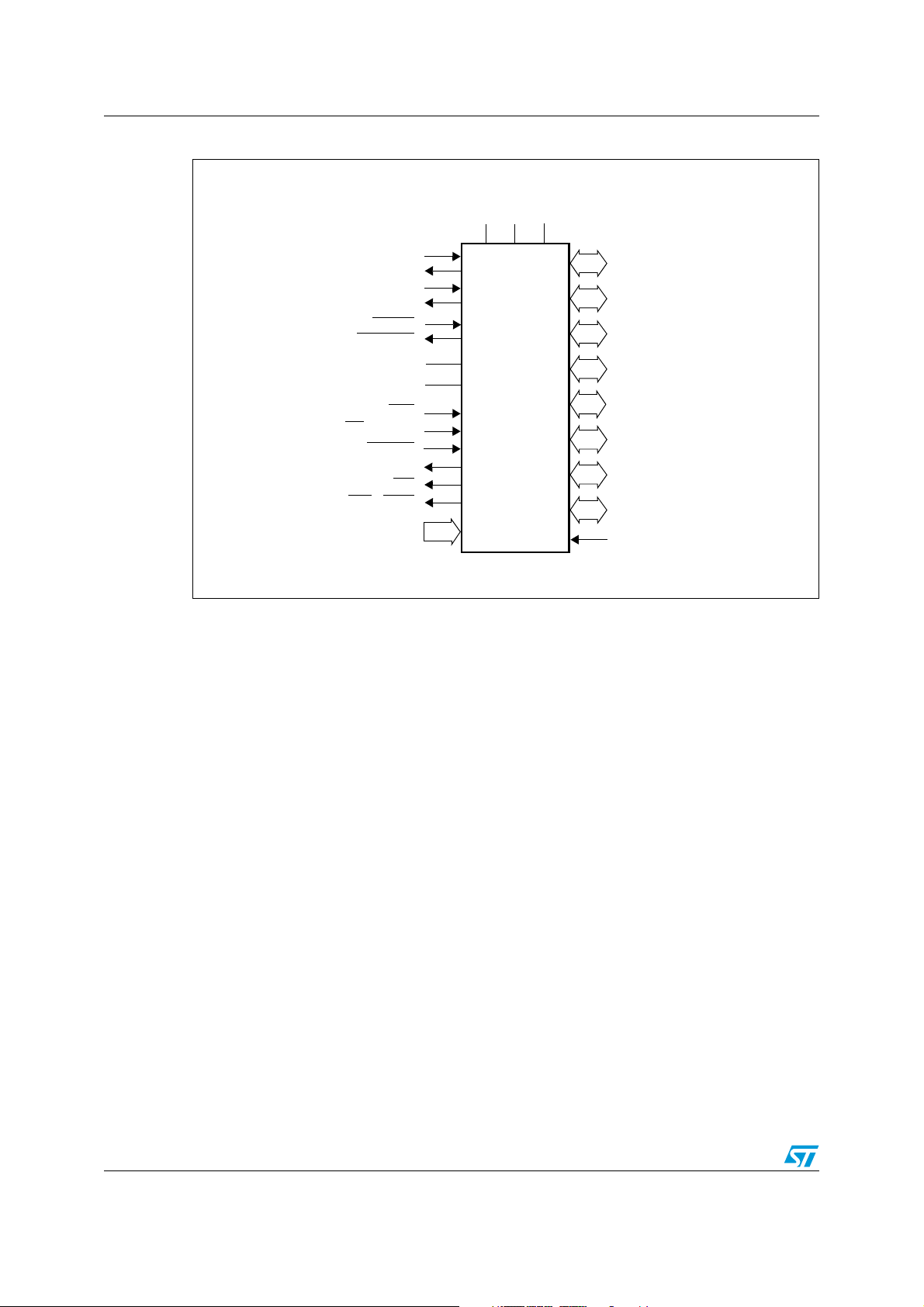
Introduction ST10F273M
Figure 1. ST10F273M Logic symbol
V
V
DDVSS
18
XTAL1
XTAL2
XTAL3
XTAL4
RSTIN
RSTOUT
V
AREF
V
AGND
NMI
EA / V
STBY
READY
ALE
RD
WR / WRL
Por t 5
16-bit
ST10F273M
Por t 0
16-bit
Por t 1
16-bit
Por t 2
16-bit
Por t 3
15-bit
Por t 4
8-bit
Por t 6
8-bit
Por t 7
8-bit
Por t 8
8-bit
RPD
12/182
Page 13
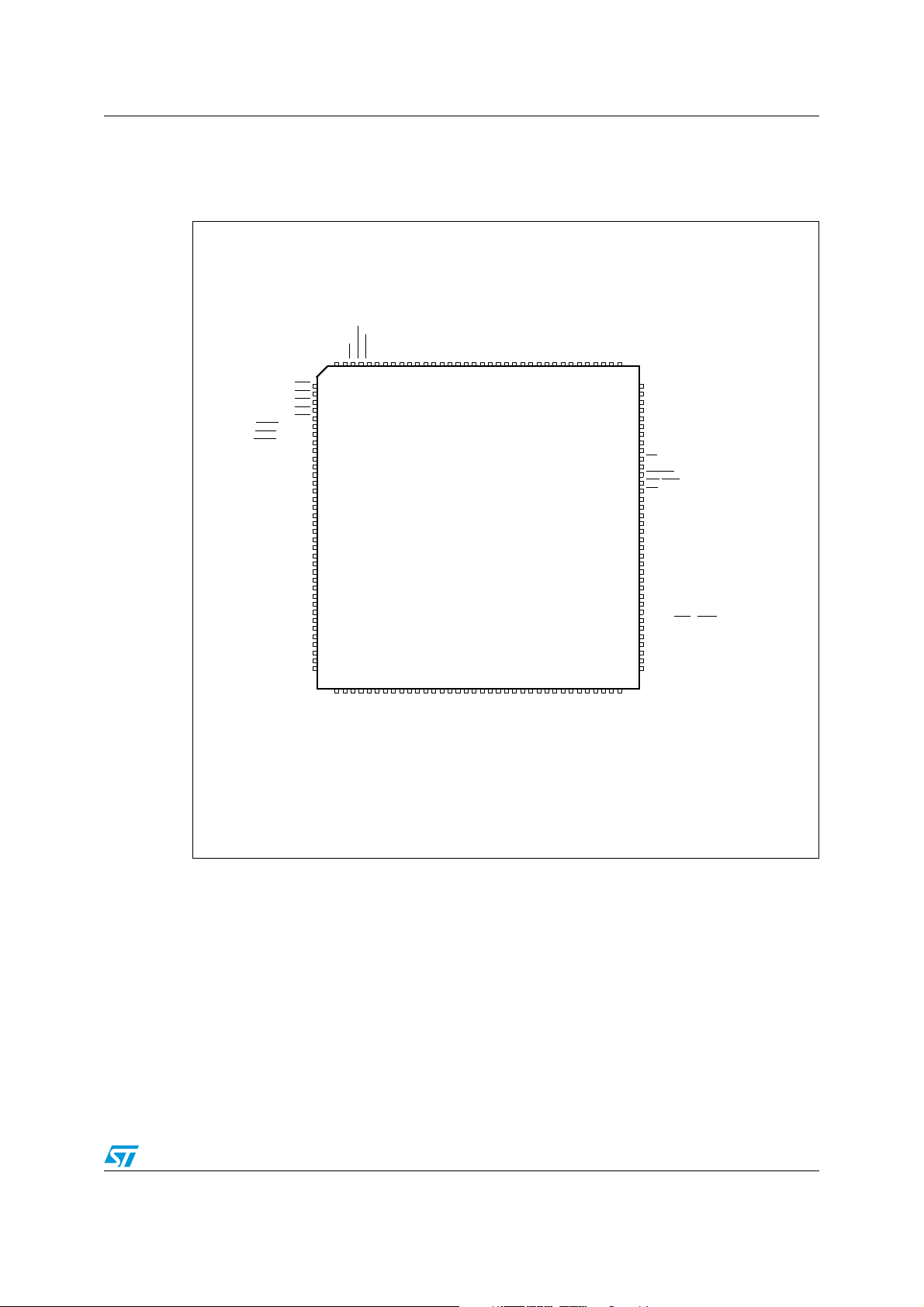
ST10F273M Pin data
2 Pin data
Figure 2. Pin configuration (top view)
XTAL4
XTAL3
NMI
RSTOUT
RSTIN
VSS
XTAL1
XTAL2
VDD
P1H.7 / A15 / CC27I
P1H.6 / A14 / CC26I
P1H.5 / A13 / CC25I
P1H.4 / A12 / CC24I
P1H.3 / A11
P1H.2 / A10
P1H.1 / A9
P1H.0 / A8
VSS
VDD
P1L.7 / A7 / AN23
P1L.6 / A6 / AN22
P1L.5 / A5 / AN21
P1L.4 / A4 / AN20
P1L.3 / A3 / AN19
P1L.2 / A2 / AN18
P1L.1 / A1 / AN17
P1L.0 / A0 / AN16
P0H.7 / AD15
P0H.6 / AD14
P0H.5 / AD13
P0H.4 / AD12
P0H.3 / AD11
P0H.2 / AD10
P0H.1 / AD9
VSS
VDD
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
P6.0 / CS0
P6.1 / CS1
P6.2 / CS2
P6.3 / CS3
P6.4 / CS4
P6.5 / HOLD / SCLK1
P6.6 / HLDA
/ MTSR1
P6.7 / BREQ / MRST1
P8.0 / XPOUT0 / CC16IO
P8.1 / XPOUT1 / CC17IO
P8.2 / XPOUT2 / CC18IO
P8.3 / XPOUT3 / CC19IO
P8.4 / CC20IO
P8.5 / CC21IO
P8.6 / RxD1 / CC22IO
P8.7 / TxD1 / CC23IO
VDD
VSS
P7.0 / POUT0
P7.1 / POUT1
P7.2 / POUT2
P7.3 / POUT3
P7.4 / CC28IO
P7.5 / CC29IO
P7.6 / CC30IO
P7.7 / CC31IO
P5.0 / AN0
P5.1 / AN1
P5.2 / AN2
P5.3 / AN3
P5.4 / AN4
P5.5 / AN5
P5.6 / AN6
P5.7 / AN7
P5.8 / AN8
P5.9 / AN9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
3738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071
P5.12 / AN12 / T6IN
P5.11 / AN11 / T5EUD
P5.13 / AN13 / T5IN
P5.14 / AN14 / T4EUD
P5.15 / AN15 / T2EUD
VSS
VAREF
VAGND
P5.10 / AN10 / T6EUD
VDD
P2.0 / CC0IO
P2.1 / CC1IO
P2.2 / CC2IO
ST10F273M
V18
VSS
P2.3 / CC3IO
P2.4 / CC4IO
P2.5 / CC5IO
P2.6 / CC6IO
P2.7 / CC7IO
P2.8 / CC8IO / EX0IN
P2.9 / CC9IO / EX1IN
P2.10 / CC10IO / EX2IN
P2.11 / CC11IO / EX3IN
P2.12 / CC12IO / EX4IN
P2.13 / CC13IO / EX5IN
P2.14 / CC14IO / EX6IN
P2.15 / CC15IO / EX7IN / T7IN
P3.0 / T0IN
P3.1 / T6OUT
P3.2 / CAPIN
P3.3 / T3OUT
P3.4 / T3EUD
P0H.0 / AD8
107
P0L.7 / AD7
106
P0L.6 / AD6
105
P0L.5 / AD5
104
P0L.4 / AD4
103
P0L.3 / AD3
102
P0L.2 / AD2
101
P0L.1 / AD1
100
P0L.0 / AD0
99
EA
/ VSTBY
98
ALE
97
READY
96
WR/WRL
95
RD
94
VSS
93
VDD
92
P4.7 / A23 / CAN2_TxD / SDA
91
P4.6 / A22 / CAN1_TxD / CAN2_TxD
90
P4.5 / A21 / CAN1_RxD / CAN2_RxD
89
P4.4 / A20 / CAN2_RxD / SCL
88
P4.3 / A19
87
P4.2 / A18
86
P4.1 / A17
85
P4.0 / A16
84
RPD
83
VSS
82
VDD
81
P3.15 / CLKOUT
80
P3.13 / SCLK0
79
P3.12 / BHE
78
P3.11 / RxD0
77
P3.10 / TxD0
76
P3.9 / MTSR0
75
P3.8 / MRST0
74
P3.7 / T2IN
73
P3.6 / T3IN
72
VSS
VDD
P3.5 / T4IN
/ WRH
13/182
Page 14
Pin data ST10F273M
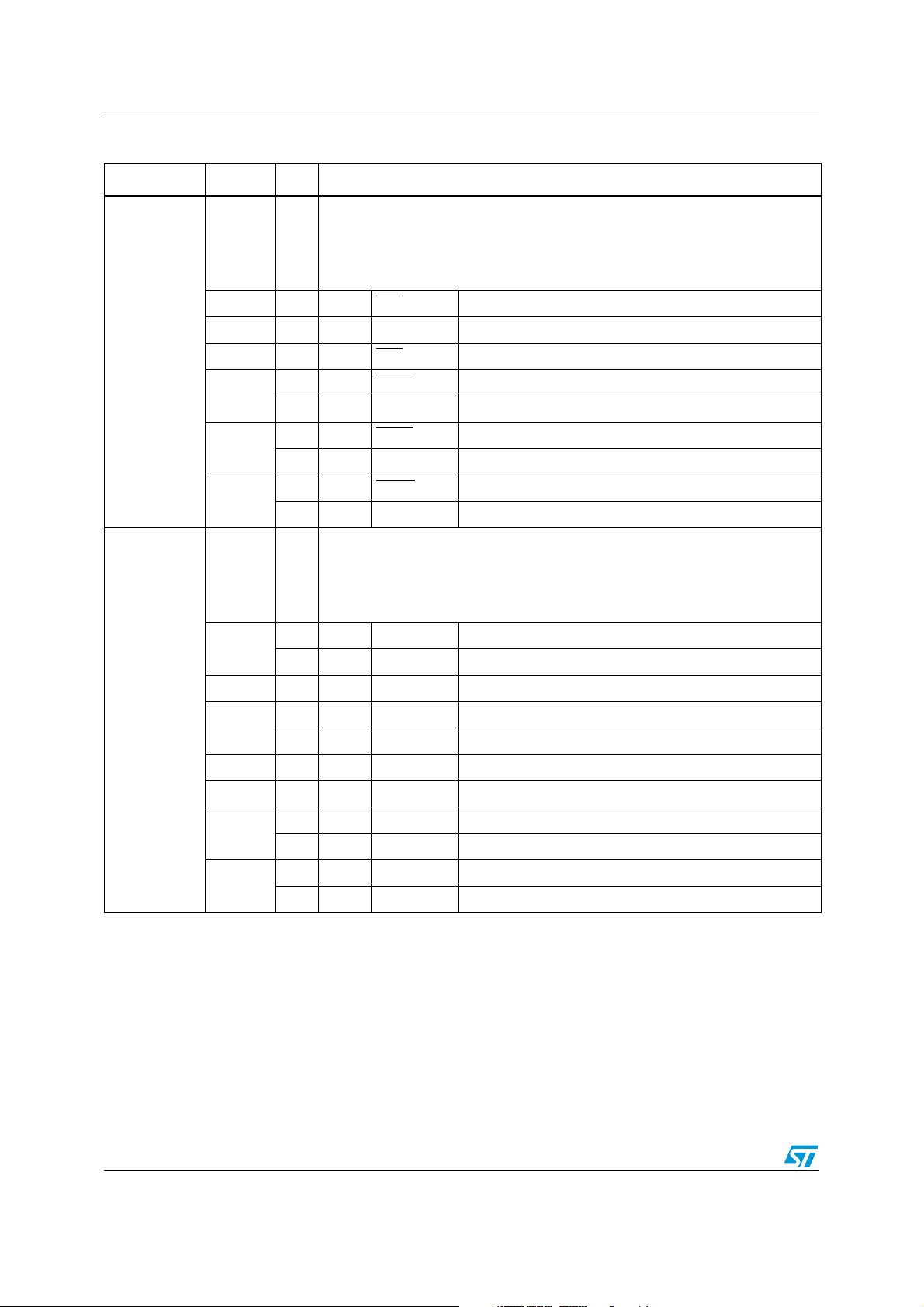
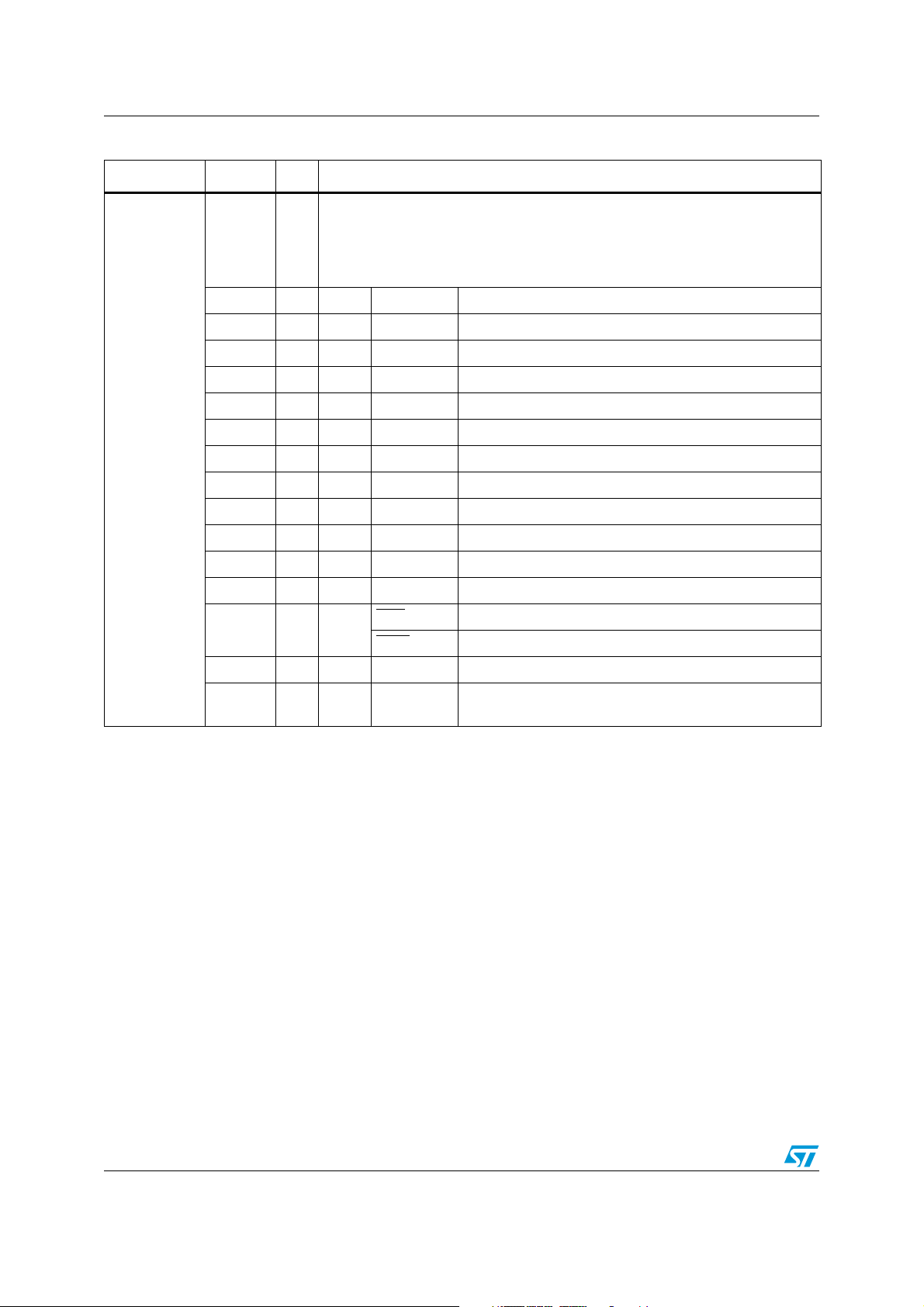
Table 1. Pin description
Symbol Pin Type Function
8-bit bidirectional I/O port, bit-wise programmable for input or output via direction
bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the corresponding output driver to
1 - 8 I/O
high impedance state. Port 6 outputs can be configured as push-pull or open
drain drivers. The input threshold of Port 6 is selectable (TTL or CMOS). The
following Port 6 pins have alternate functions:
1OP6.0CS0
Chip select 0 output
... ... ... ... ...
P6.0 - P6.7
5OP6.4CS4 Chip select 4 output
IP6.5HOLD
External master hold request input
6
I/O SCLK1 SSC1: master clock output / slave clock input
O P6.6 HLDA
Hold acknowledge output
7
I/O MTSR1 SSC1: master-transmitter / slave-receiver O/I
OP6.7 BREQ Bus request output
8
I/O MRST1 SSC1: master-receiver / slave-transmitter I/O
8-bit bidirectional I/O port, bit-wise programmable for input or output via direction
bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the corresponding output driver to
9-16 I/O
high impedance state. Port 8 outputs can be configured as push-pull or open
drain drivers. The input threshold of Port 8 is selectable (TTL or CMOS).
The following Port 8 pins have alternate functions:
I/O P8.0 CC16IO CAPCOM2: CC16 capture input / compare output
9
O XPWM0 PWM1: channel 0 output
... ... ... ... ...
P8.0 - P8.7
12
I/O P8.3 CC19IO CAPCOM2: CC19 capture input / compare output
O XPWM0 PWM1: channel 3 output
13 I/O P8.4 CC20IO CAPCOM2: CC20 capture input / compare output
14 I/O P8.5 CC21IO CAPCOM2: CC21 capture input / compare output
15
I/O P8.6 CC22IO CAPCOM2: CC22 capture input / compare output
I/O RxD1 ASC1: Data input (Asynchronous) or I/O (Synchronous)
I/O P8.7 CC23IO CAPCOM2: CC23 capture input / compare output
16
O TxD1 ASC1: Clock / Data output (Asynchronous/Synchronous)
14/182
Page 15
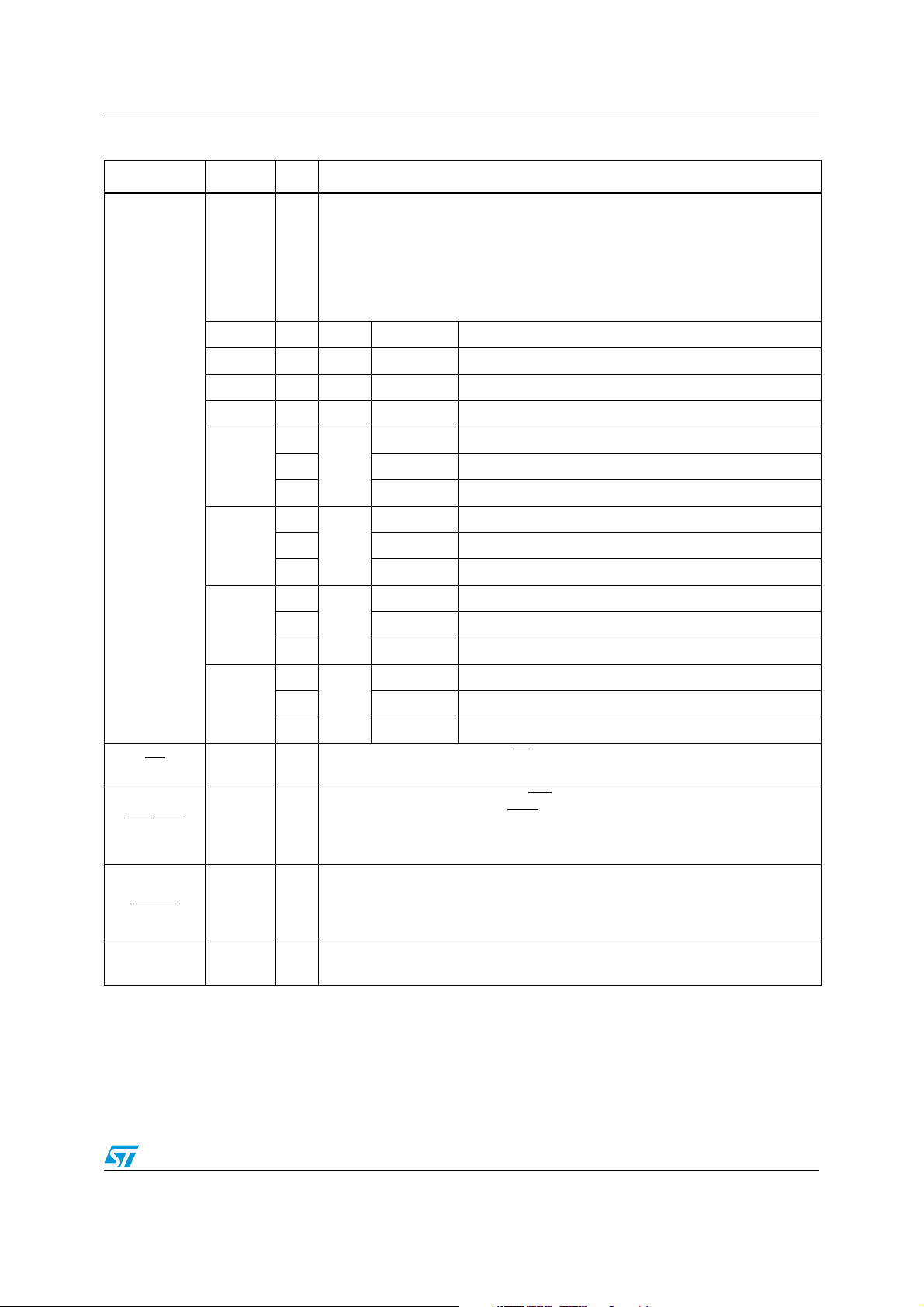
ST10F273M Pin data
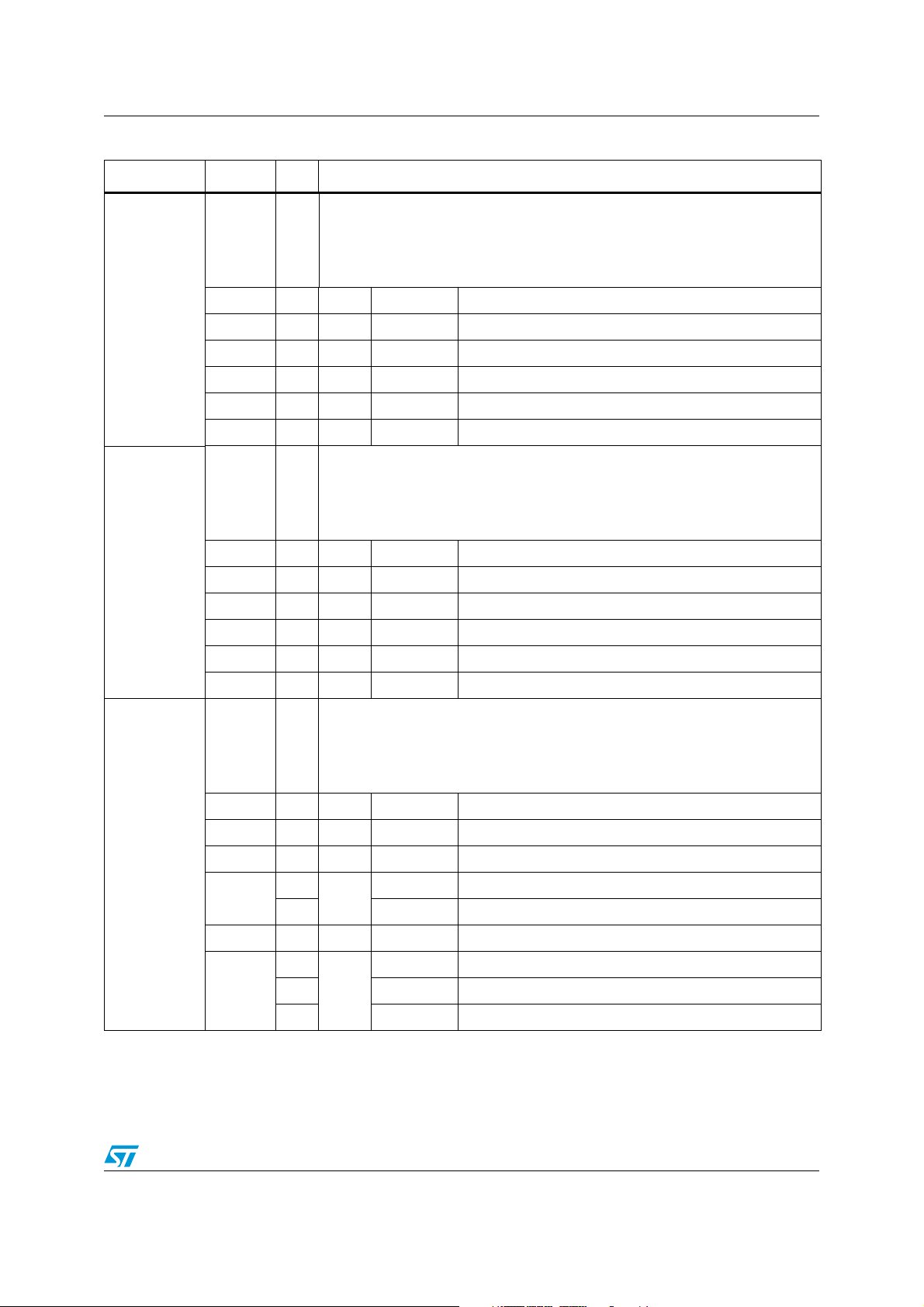
Table 1. Pin description (continued)
Symbol Pin Type Function
8-bit bidirectional I/O port, bit-wise programmable for input or output via direction
bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the corresponding output driver to
P7.0 - P7.7
P5.0 - P5.9
P5.10 - P5.15
19-26 I/O
19 O P7.0 POUT0 PWM0: channel 0 output
... ... ... ... ...
22 O P7.3 POUT3 PWM0: channel 3 output
23 I/O P7.4 CC28IO CAPCOM2: CC28 capture input / compare output
... ... ... ... ...
26 I/O P7.7 CC31IO CAPCOM2: CC31 capture input / compare output
27-36
39-44
39 I P5.10 T6EUD GPT2: timer T6 external up/down control input
40 I P5.11 T5EUD GPT2: timer T5 external up/down control input
41 I P5.12 T6IN GPT2: timer T6 count input
42 I P5.13 T5IN GPT2: timer T5 count input
43 I P5.14 T4EUD GPT1: timer T4 external up/down control input
high impedance state. Port 7 outputs can be configured as push-pull or open
drain drivers. The input threshold of Port 7 is selectable (TTL or CMOS).
The following Port 7 pins have alternate functions:
16-bit input-only port with Schmitt-Trigger characteristics. The pins of Port 5 can
be the analog input channels (up to 16) for the A/D converter, where P5.x equals
I
ANx (Analog input channel x), or they are timer inputs. The input threshold of
I
Port 5 is selectable (TTL or CMOS). The following Port 5 pins have alternate
functions:
P2.0 - P2.7
P2.8 - P2.15
44 I P5.15 T2EUD GPT1: timer T2 external up/down control input
16-bit bidirectional I/O port, bit-wise programmable for input or output via
47-54
57-64
47 I/O P2.0 CC0IO CAPCOM: CC0 capture input/compare output
... ... ... ... ...
54 I/O P2.7 CC7IO CAPCOM: CC7 capture input/compare output
57
... ... ... ... ...
64
direction bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the corresponding output
I/O
driver to high impedance state. Port 2 outputs can be configured as push-pull or
open drain drivers. The input threshold of Port 2 is selectable (TTL or CMOS).
The following Port 2 pins have alternate functions:
I/O
P2.8
I EX0IN Fast external interrupt 0 input
I/O
P2.15
I EX7IN Fast external interrupt 7 input
I T7IN CAPCOM2: timer T7 count input
CC8IO CAPCOM: CC8 capture input/compare output
CC15IO CAPCOM: CC15 capture input/compare output
15/182
Page 16
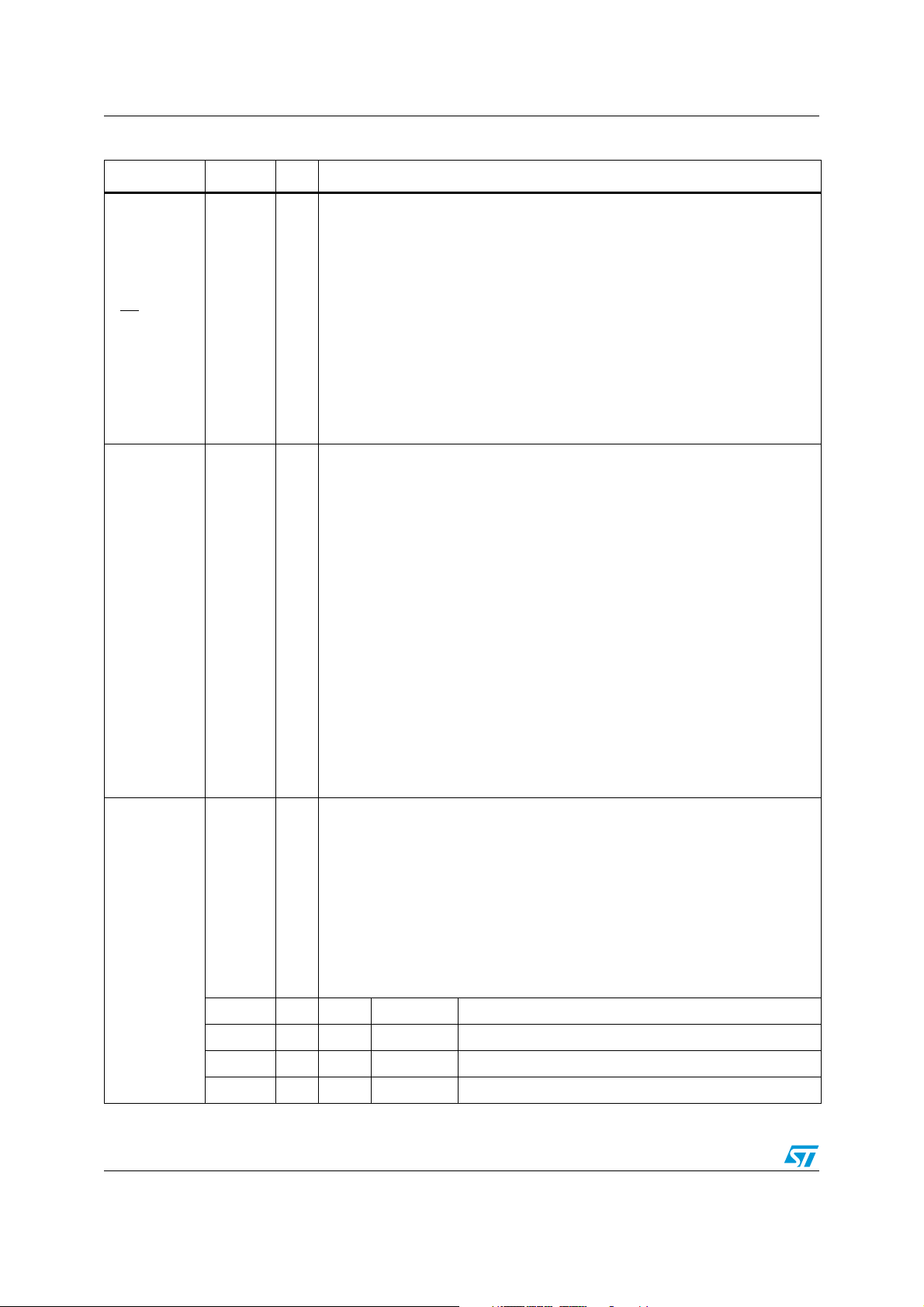
Pin data ST10F273M
Table 1. Pin description (continued)
Symbol Pin Type Function
15-bit (P3.14 is missing) bidirectional I/O port, bit-wise programmable for input or
65-70,
73-80,
81
65 I P3.0 T0IN CAPCOM1: timer T0 count input
66 O P3.1 T6OUT GPT2: timer T6 toggle latch output
67 I P3.2 CAPIN GPT2: register CAPREL capture input
68 O P3.3 T3OUT GPT1: timer T3 toggle latch output
69 I P3.4 T3EUD GPT1: timer T3 external up/down control input
I/O
output via direction bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the
I/O
corresponding output driver to high impedance state. Port 3 outputs can be
I/O
configured as push-pull or open drain drivers. The input threshold of Port 3 is
selectable (TTL or CMOS). The following Port 3 pins have alternate functions:
P3.0 - P3.5
P3.6 - P3.13,
P3.15
70 I P3.5 T4IN GPT1; timer T4 input for count/gate/reload/capture
73 I P3.6 T3IN GPT1: timer T3 count/gate input
74 I P3.7 T2IN GPT1: timer T2 input for count/gate/reload / capture
75 I/O P3.8 MRST0 SSC0: master-receiver/slave-transmitter I/O
76 I/O P3.9 MTSR0 SSC0: master-transmitter/slave-receiver O/I
77 O P3.10 TxD0 ASC0: clock / data output (asynchronous/synchronous)
78 I/O P3.11 RxD0 ASC0: data input (asynchronous) or I/O (synchronous)
79 O P3.12
BHE
WRH
80 I/O P3.13 SCLK0 SSC0: master clock output / slave clock input
81 O P3.15 CLKOUT
External memory high byte enable signal
External memory high byte write strobe
System clock output (programmable divider on CPU
clock)
16/182
Page 17
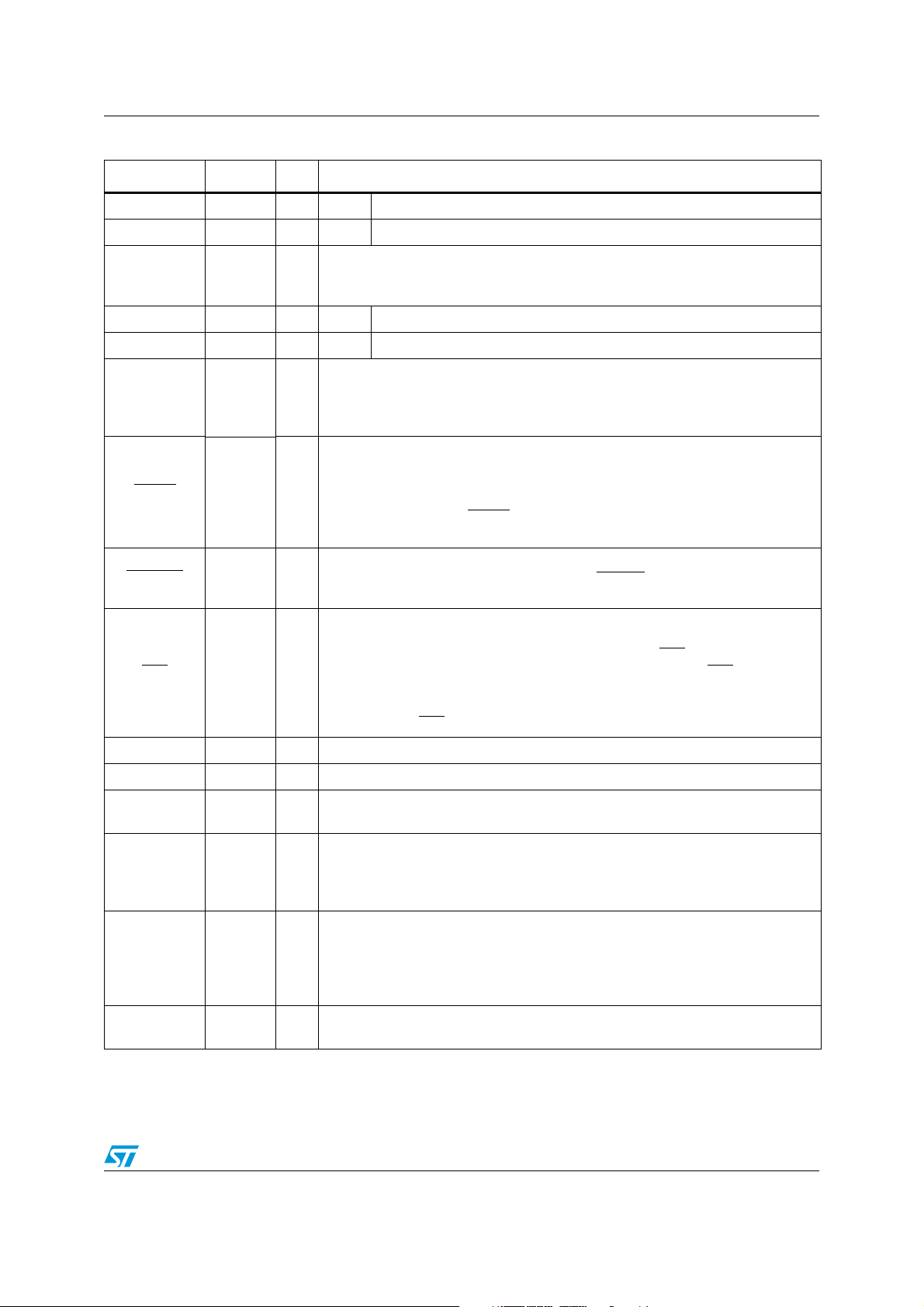
ST10F273M Pin data
Table 1. Pin description (continued)
Symbol Pin Type Function
Port 4 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port. It is bit-wise programmable for input or
output via direction bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the
corresponding output driver to high impedance state. The input threshold is
P4.0 –P4.7
85-92 I/O
85 O P4.0 A16 Segment address line
86 O P4.1 A17 Segment address line
87 O P4.2 A18 Segment address line
88 O P4.3 A19 Segment address line
89
selectable (TTL or CMOS). Port 4.4, 4.5, 4.6 and 4.7 outputs can be configured
as push-pull or open drain drivers.
In case of an external bus configuration, Port 4 can be used to output the
segment address lines:
O
P4.4
I CAN2_RxD CAN2: receive data input
I/O SCL
O
A20 Segment address line
I2C Interface: serial clock
A21 Segment address line
90
91
92
RD 95 O
/WRL 96 O
WR
READY/
READY
97 I
ALE 98 O
P4.5
I CAN1_RxD CAN1: receive data input
I CAN2_RxD CAN2: receive data input
O
P4.6
O CAN1_TxD CAN1: transmit data output
A22 Segment address line
O CAN2_TxD CAN2: transmit data output
O
P4.7
O CAN2_TxD CAN2: transmit data output
I/O SDA
External memory read strobe. RD
A23 Most significant segment address line
I2C Interface: serial data
is activated for every external instruction or
data read access.
External memory write strobe. In WR
external data write access. In WRL
-mode this pin is activated for every
mode this pin is activated for low byte data
write accesses on a 16-bit bus, and for every data write access on an 8-bit bus.
See WRCFG in the SYSCON register for mode selection.
Ready input. The active level is programmable. When the ready function is
enabled, the selected inactive level at this pin, during an external memory
access, will force the insertion of waitstate cycles until the pin returns to the
selected active level.
Address latch enable output. In case of use of external addressing or of
multiplexed mode, this signal is the latch command of the address lines.
17/182
Page 18
Pin data ST10F273M
Table 1. Pin description (continued)
Symbol Pin Type Function
External access enable pin.
A low level applied to this pin during and after Reset forces the ST10F273M to
start the program from the external memory space. A high level forces
ST10F273M to start in the internal memory space. This pin is also used (when
DD
DD
turned
EA / V
STBY
P0L.0 -P0L.7,
P0H.0
P0H.1 - P0H.7
99 I
100-107,
108,
111-117
Standby mode is entered, that is ST10F273M under reset and main V
off) to bias the 32 kHz oscillator amplifier circuit and to provide a reference
voltage for the low-power embedded voltage regulator which generates the
internal 1.8V supply for the RTC module (when not disabled) and to retain data
inside the Standby portion of the XRAM (16 Kbyte).
It can range from 4.5 to 5.5V (6V for a reduced amount of time during the device
life, 4.0V when RTC and 32 kHz on-chip oscillator amplifier are turned off). In
running mode, this pin can be tied low during reset without affecting 32 kHz
oscillator, RTC and XRAM activities, since the presence of a stable V
guarantees the proper biasing of all those modules.
Two 8-bit bidirectional I/O ports P0L and P0H, bit-wise programmable for input or
output via direction bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the
corresponding output driver to high impedance state. The input threshold of
Port 0 is selectable (TTL or CMOS).
In case of an external bus configuration, PORT0 serves as the address (A) and
as the address / data (AD) bus in multiplexed bus modes and as the data (D) bus
in demultiplexed bus modes.
Demultiplexed bus modes
Data path width 8-bit 16-bit
I/O
P0L.0 – P0L.7: D0 – D7 D0 - D7
P0H.0 – P0H.7: I/O D8 - D15
P1L.0 - P1L.7
P1H.0 - P1H.7
Multiplexed bus modes
Data path width 8-bit 16-bit
P0L.0 – P0L.7: AD0 – AD7 AD0 - AD7
P0H.0 – P0H.7: A8 – A15 AD8 - AD15
Two 8-bit bidirectional I/O ports P1L and P1H, bit-wise programmable for input or
output via direction bit. Programming an I/O pin as input forces the
corresponding output driver to high impedance state. PORT1 is used as the 16bit address bus (A) in demultiplexed bus modes: if at least BUSCONx is
118-125
128-135
configured such the demultiplexed mode is selected, the pis of PORT1 are not
available for general purpose I/O function. The input threshold of Port 1 is
I/O
selectable (TTL or CMOS).
The pins of P1L also serve as the additional (up to 8) analog input channels for
the A/D converter, where P1L.x equals ANy (Analog input channel y, where y = x
+ 16). This additional function have higher priority on demultiplexed bus function.
The following PORT1 pins have alternate functions:
132 I P1H.4 CC24IO CAPCOM2: CC24 capture input
133 I P1H.5 CC25IO CAPCOM2: CC25 capture input
134 I P1H.6 CC26IO CAPCOM2: CC26 capture input
135 I P1H.7 CC27IO CAPCOM2: CC27 capture input
18/182
Page 19
ST10F273M Pin data
Table 1. Pin description (continued)
Symbol Pin Type Function
XTAL1 138 I XTAL1 Main oscillator amplifier circuit and/or external clock input.
XTAL2 137 O XTAL2 Main oscillator amplifier circuit output.
To clock the device from an external source, drive XTAL1 while leaving XTAL2
unconnected. Minimum and maximum high / low and rise / fall times specified in
the AC Characteristics must be observed.
XTAL3 143 I XTAL3 32 kHz oscillator amplifier circuit input
XTAL4 144 O XTAL4 32 kHz oscillator amplifier circuit output
When 32 kHz oscillator amplifier is not used, to avoid spurious consumption,
XTAL3 shall be tied to ground while XTAL4 shall be left open. Besides, bit OFF32
in RTCCON register shall be set. 32 kHz oscillator can only be driven by an
external crystal, and not by a different clock source.
Reset Input with CMOS Schmitt-Trigger characteristics. A low level at this pin for
a specified duration while the oscillator is running resets the ST10F273M. An
RSTIN
RSTOUT
NMI
140 I
141 O
142 I
internal pull-up resistor permits power-on reset using only a capacitor connected
. In bidirectional reset mode (enabled by setting bit BDRSTEN in
to V
SS
SYSCON register), the RSTIN
line is pulled low for the duration of the internal
reset sequence.
Internal Reset Indication Output. This pin is driven to a low level during
hardware, software or watchdog timer reset.
RSTOUT
remains low until the EINIT
(end of initialization) instruction is executed.
Non-Maskable Interrupt Input. A high to low transition at this pin causes the CPU
to vector to the NMI trap routine. If bit PWDCFG = ‘0’ in SYSCON register, when
the PWRDN (power down) instruction is executed, the NMI pin must be low in
order to force the ST10F273M to go into power down mode. If NMI is high and
PWDCFG = ‘0’, when PWRDN is executed, the part will continue to run in
normal mode.
If not used, pin NMI
should be pulled high externally.
V
AREF
V
AGND
37 - A/D converter reference voltage and analog supply
38 - A/D converter reference and analog ground
RPD 84 -
17, 46,
V
DD
72,82,93,
109, 126,
136
18,45,
55,71,
V
SS
83,94,
110, 127,
139
V
18
56 -
Timing pin for the return from interruptible power down mode and synchronous /
asynchronous reset selection.
Digital supply voltage = + 5V during normal operation, idle and power down
-
modes.
It can be turned off when Standby RAM mode is selected.
- Digital ground
1.8V decoupling pin: a decoupling capacitor (typical value of 10nF, max 100nF)
must be connected between this pin and nearest V
SS
pin.
19/182
Page 20
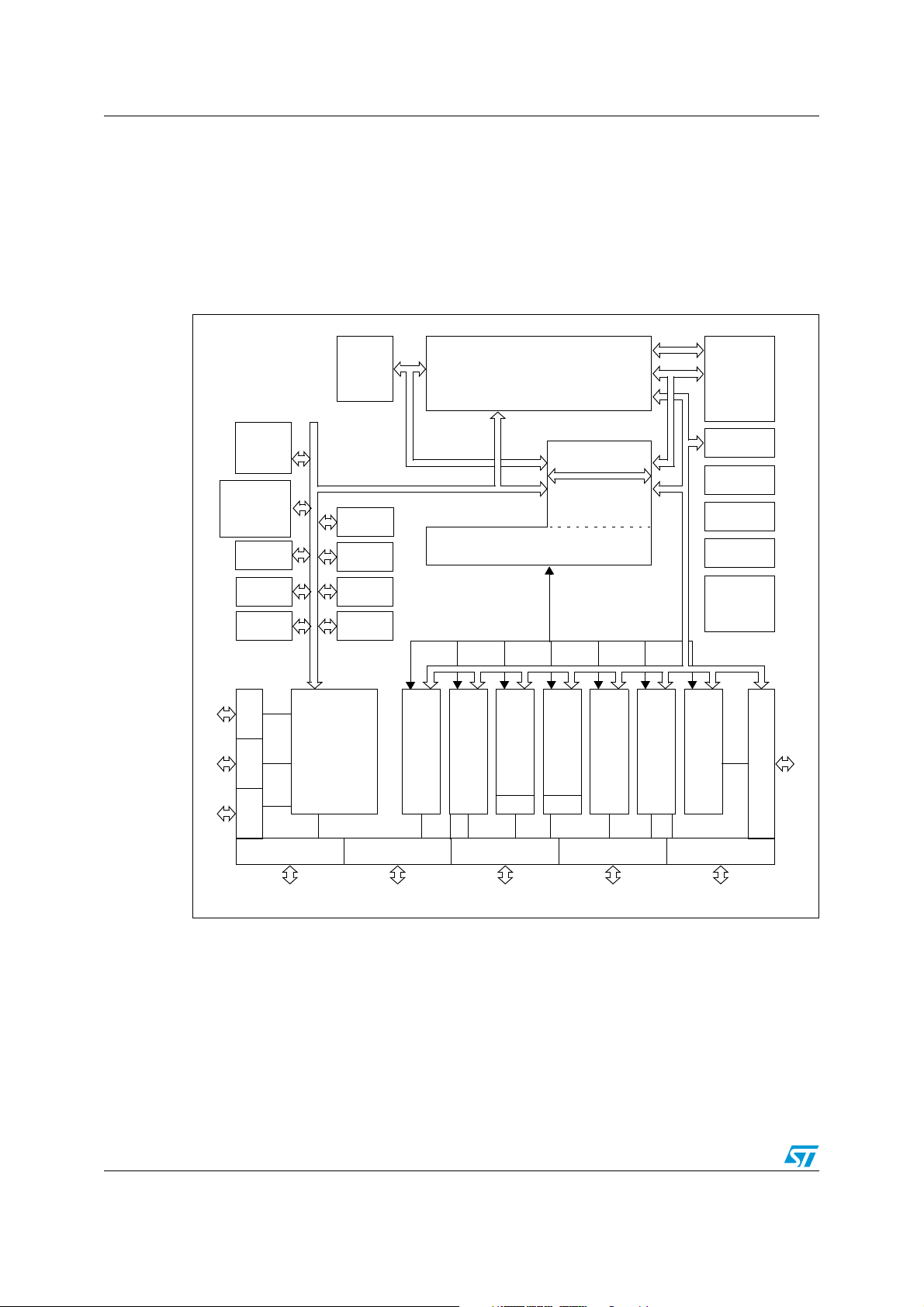
Functional description ST10F273M
3 Functional description
The architecture of the ST10F273M combines advantages of both RISC and CISC
processors and an advanced peripheral subsystem. The block diagram gives an overview of
the different on-chip components and the high bandwidth internal bus structure of the
ST10F273M.
Figure 3. Block diagram
16
IFlash
512K
32
CPU-core and MAC unit
16
IRAM
2K
XRAM1
2K
(PEC)
XRAM2
32K
(16K STBY)
XRTC
XI2C
XCAN1
16
Por t 0
16
Por t 1Por t 4
8
Por t 6
81615 8 8
16
16
16
16 16
16 16
16
16
XPWM
XASC
XSSC
XCAN2
controller
External bus
16
16
Por t 5
10-bit ADC
PEC
Interrupt controller
ASC0
SSC0
GPT1 / GPT2
BRG BRG
Port 3 Port 7 Por t 8
PWM
CAPCOM2
Watchdog
Oscillator
32 kHz
oscillator
PLL
5V-1.8V
voltage
regulator
CAPCOM1
16
Por t 2
20/182
Page 21
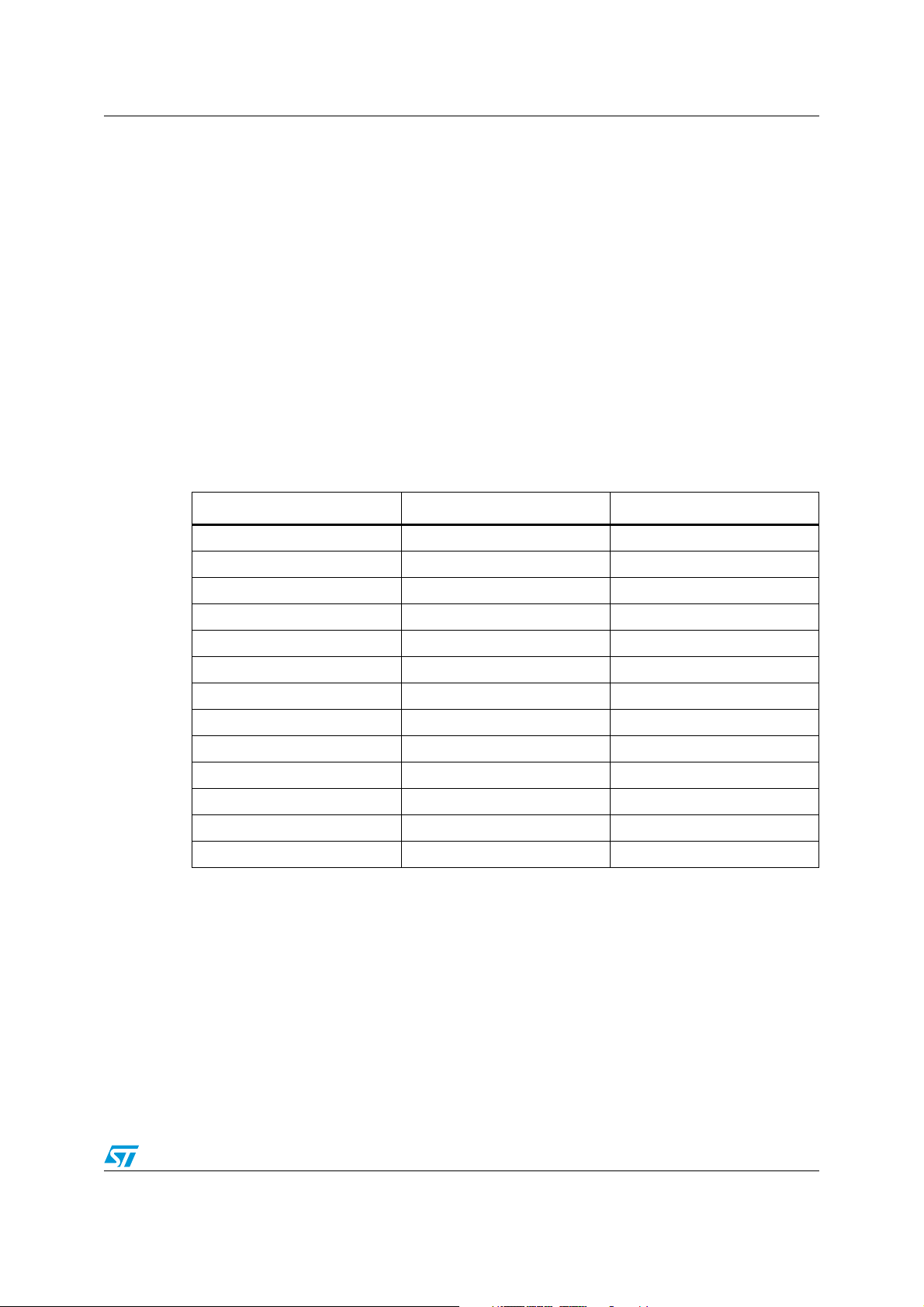
ST10F273M Memory organization
4 Memory organization
The memory space of the ST10F273M is configured in a unified memory architecture. Code
memory, data memory, registers and I/O ports are organized within the same linear address
space of 16 Mbytes. The entire memory space can be accessed Bytewise or Wordwise.
Particular portions of the on-chip memory have additionally been made directly bit
addressable.
IFlash: 512 Kbytes of on-chip Flash memory implemented as a unique Bank (Bank0).
Bank0 is divided in 12 blocks (B0F0...B0F11).
Note: Read-while-write operations are not allowed: Write commands must be executed from a non
IFlash memory area (on-chip RAM or external memory).
When Bootstrap mode is selected, the Test-Flash Block B0TF (4 Kbytes) appears at
address 00’0000h: Refer to the device User Manual for more details on the memory
mapping in Bootstrap mode. The summary of address range for IFlash is the following:
Table 2. Summary of IFlash address range
Blocks User mode Size (bytes)
B0TF Not visible 4 K
B0F0 00’0000h - 00’1FFFh 8 K
B0F1 00’2000h - 00’3FFFh 8 K
B0F2 00’4000h - 00’5FFFh 8 K
B0F3 00’6000h - 00’7FFFh 8 K
B0F4 01’8000h - 01’FFFFh 32 K
B0F5 02’0000h - 02’FFFFh 64 K
B0F6 03’0000h - 03’FFFFh 64 K
B0F7 04’0000h - 04’FFFFh 64 K
B0F8 05’0000h - 05’FFFFh 64 K
B0F9 06’0000h - 06’FFFFh 64 K
B1F0 / B0F10
B1F1 / B0F11
(1)
(1)
07’0000h - 07’FFFFh 64 K
08’0000h - 08’FFFFh 64 K
Note: A single Flash bank is implemented on the ST10F273M compared to the ST10F273E. The
last two sectors (B0F10 and B0F11) can be seen as the Bank1 of the ST10F273E in order
to maintain the compatibility with the existing Flash programming drivers. For this, the
control and status bit of the blocks B0F10 and B0F11 have been duplicated to be usable as
blocks B1F0 and B1F1 of the ST10F273E.
XFLASH / Flash Control Registers: Address range 0E’0000h-0E’FFFFh is reserved for
the Flash Control Register and other internal service memory space used by the Flash
Program/Erase Controller. XFLASHEN bit in XPERCON register must be set to access the
Flash Control Register. Note that when Flash Control Registers are not accessible, no
program/erase operations are possible. The Flash Control Registers are accessed in 16-bit
demultiplexed bus-mode without read/write delay. Byte and word accesses are allowed.
21/182
Page 22

Memory organization ST10F273M
IRAM: 2 Kbytes of on-chip internal RAM (dual-port) is provided as a storage for data,
system stack, general purpose register banks and code. A register bank is 16 Wordwide (R0
to R15) and / or Bytewide (RL0, RH0, …, RL7, RH7) general purpose registers group.
XRAM: 34 Kbytes of on-chip extension RAM (single port XRAM) is provided as a storage for
data, user stack and code.
The XRAM is divided into two areas, the first 2 Kbytes named XRAM1 and the second
32 Kbytes named XRAM2, connected to the internal XBUS and are accessed like an
external memory in 16-bit demultiplexed bus-mode without wait state or read/write delay
(50ns access at 40 MHz CPU clock). Byte and Word accesses are allowed.
The XRAM1 address range is 00’E000h - 00’E7FFh if XPEN (bit 2 of SYSCON register),
and XRAM1EN (bit 2 of XPERCON register) are set.
If XRAM1EN or XPEN is cleared, then any access in the address range 00’E000h -
00’E7FFh will be directed to external memory interface, using the BUSCONx register
corresponding to address matching ADDRSELx register.
The XRAM2 address range is F’0000h - F’7FFFFh if XPEN (bit 2 of SYSCON register), and
XRAM2EN (bit 3 of XPERCON register) are set.
If bit XPEN is cleared, then any access in the address range programmed for XRAM2 will be
directed to external memory interface, using the BUSCONx register corresponding to
address matching ADDRSELx register.
The 16 kbytes lower portion of the XRAM2 (address range F’0000h - F’3FFFFh) represents
also the Standby RAM, which can be maintained biased through EA
main supply V
is turned off.
DD
/V
pin when the
STBY
As the XRAM appears like external memory, it cannot be used as system stack or as
register banks. The XRAM is not provided for single bit storage and therefore is not bit
addressable.
SFR/ESFR: 1024 bytes (2 x 512 bytes) of address space is reserved for the special function
register (SFR) areas. SFRs are Wordwide registers which are used to control and to monitor
the function of the different on-chip units.
CAN1: Address range 00’EF00h - 00’EFFFh is reserved for the CAN1 Module access. The
CAN1 is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and by setting CAN1EN bit
0 of the XPERCON register. Accesses to the CAN Module use demultiplexed addresses
and a 16-bit data bus (only word accesses are possible). Two wait states give an access
time of 100ns at 40 MHz CPU clock. No tri-state wait states are used.
CAN2: Address range 00’EE00h - 00’EEFFh is reserved for the CAN2 Module access. The
CAN2 is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and by setting CAN2EN bit
1 of the new XPERCON register. Accesses to the CAN Module use demultiplexed
addresses and a 16-bit data bus (only word accesses are possible). Two wait states give an
access time of 100ns at 40 MHz CPU clock. No tri-state wait states are used.
Note: If one or the two CAN modules are used, Port 4 cannot be programmed to output all eight
segment address lines. Thus, only four segment address lines can be used, reducing the
external memory space to 5 Mbytes (1 Mbyte per CS line).
RTC: Address range 00’ED00h - 00’EDFFh is reserved for the RTC Module access. The
RTC is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and bit 4 of the XPERCON
register. Accesses to the RTC Module use demultiplexed addresses and a 16-bit data bus
(only word accesses are possible). Two waitstates give an access time of 100ns at 40 MHz
CPU clock. No tristate waitstate is used.
22/182
Page 23

ST10F273M Memory organization
PWM1: Address range 00’EC00h - 00’ECFFh is reserved for the PWM1 Module access.
The PWM1 is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and bit 6 of the
XPERCON register. Accesses to the PWM1 Module use demultiplexed addresses and a 16bit data bus (only word accesses are possible). Two waitstates give an access time of 100ns
at 40 MHz CPU clock. No tristate waitstate is used. Only word access is allowed.
ASC1: Address range 00’E900h - 00’E9FFh is reserved for the ASC1 Module access. The
ASC1 is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and bit 7 of the XPERCON
register. Accesses to the ASC1 Module use demultiplexed addresses and a 16-bit data bus
(only word accesses are possible). Two waitstates give an access time of 100ns at 40 MHz
CPU clock. No tristate waitstate is used.
SSC1: Address range 00’E800h - 00’E8FFh is reserved for the SSC1 Module access. The
SSC1 is enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and bit 8 of the XPERCON
register. Accesses to the SSC1 Module use demultiplexed addresses and a 16-bit data bus
(only word accesses are possible). Two waitstates give an access time of 100ns at 40 MHz
CPU clock. No tristate waitstate is used.
I2C: Address range 00’EA00h - 00’EAFFh is reserved for the I2C Module access. The I2C is
enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON register and bit 9 of the XPERCON register.
Accesses to the I2C Module use demultiplexed addresses and a 16-bit data bus (only word
accesses are possible). Two waitstates give an access time of 100ns at 40 MHz CPU clock.
No tristate waitstate is used.
X-Miscellaneous: Address range 00’EB00h - 00’EBFFh is reserved for the access to a set
of XBUS additional features. They are enabled by setting XPEN bit 2 of the SYSCON
register and bit 10 of the XPERCON register. Accesses to this additional features use
demultiplexed addresses and a 16-bit data bus (only word accesses are possible). Two
waitstates give an access time of 100ns at 40 MHz CPU clock. No tristate waitstate is used.
The following set of features are provided:
● CLKOUT programmable divider
● XBUS interrupt management registers
● ADC multiplexing on P1L register
● Port1L digital disable register for extra ADC channels
● CAN2 multiplexing on P4.5/P4.6
● CAN1-2 main clock prescaler
● Main Voltage Regulator disable for power-down mode
● TTL / CMOS threshold selection for Port0, Port1 and Port5
In order to meet the needs of designs where more memory is required than is provided on
chip, up to 16 Mbytes of external memory can be connected to the microcontroller.
Visibility of XBUS peripherals
In order to keep the ST10F273M compatible with the ST10F168 / ST10F269, the XBUS
peripherals can be selected to be visible on the external address / data bus. Different bits for
X-Peripheral enabling in XPERCON register must be set. If these bits are cleared before the
global enabling with XPEN bit in SYSCON register, the corresponding address space, port
pins and interrupts are not occupied by the peripherals, thus the peripheral is not visible and
not available. Refer to Chapter 23: Register set on page 114.
23/182
Page 24

Memory organization ST10F273M
XPERCON and X-Peripheral clock gating
As already mentioned, the XPERCON register must be programmed to enable the single
XBus modules separately. The XPERCON is a read/write ESFR register.
The new feature of Clock Gating has been implemented by means of this register: Once the
EINIT instruction has been executed, all the peripherals (except RAMs and XMISC) not
enabled in the XPERCON register are not be clocked. The clock gating can reduce power
consumption and improve EMI when the user does not use all X-Peripherals.
Note: When the clock has been gated in the disabled peripherals, no Reset will be raised once the
EINIT instruction has been executed.
24/182
Page 25
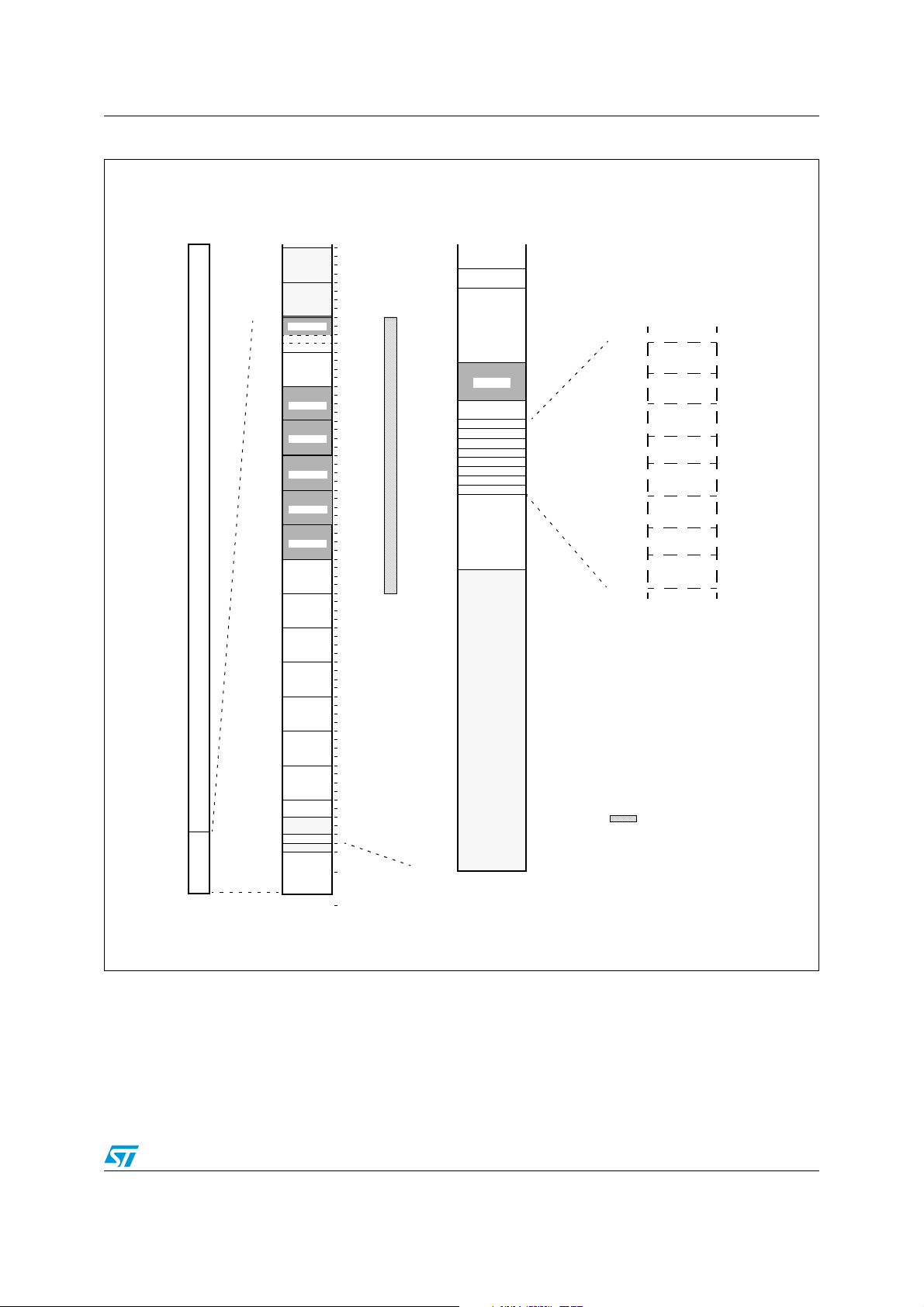
ST10F273M Memory organization
Figure 4. ST10F273M memory mapping (XADRS3 = 800Bh - reset value)
Code
Segment
FF FFFF
255
0
00 0000
16 MB
Data
Page
1023
0
XRAM2
(StandBy)
Flash
Control
B3F1
(XFLASH)
B3F0
(XFLASH)
B2F2
(XFLASH)
B2F1
(XFLASH)
B2F0
(XFLASH)
B0F11
(B1F1)
B0F10
(B1F0)
B0F9
B0F8
B0F7
B0F6
B0F5
B0F4
Data
Page
67
66
65
64
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Segment
11 FFFF
17
11 0000
10 FFFF
16
10 0000
0F FFFF
15
0F 0000
0E FFFF
14
0E 0000
0D FFFF
13
0D 0000
0C FFFF
12
0C 0000
0B FFFF
11
0B 0000
0A FFFF
10
0A 0000
09 FFFF
9
09 0000
08 FFFF
8
08 0000
07 FFFF
7
07 0000
06 FFFF
6
06 0000
05 FFFF
5
05 0000
04 FFFF
4
04 0000
03 FFFF
3
03 0000
02 FFFF
2
02 0000
01 FFFF
1
01 0000
00 FFFF
0
00 0000
Code
Reserved
Registers
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Ext. Mem
Ext. Mem
B0F3
B0F2
B0F1
B0F0
Flash + XRAM - 1Mbyte
32K
64K
00 FFFF
00 FE00
00 FDFF
00 F600
00 F5FF
00 F200
00 F1FF
00 F000
00 EFFF
00 E800
00 E7FF
XADRS3 = 800Bh (512K - Default)
00 E000
00 DFFF
SFR
I-RAM
Reserved
ESFR
XCAN1
XCAN2
XRTC
XPWM
XMiscellaneous
XI2C
XASC
XSSC
XRAM1
Ext. Memory
512
2K
1K
512
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
2K
8K
00 C000
Data Page 3 (Segment 0) - 16Kbyte
X-Peripherals (2Kbyte)
00 F000
00 EFFF
00 EF00
00 EEFF
00 EE00
00 EDFF
00 ED00
00 ECFF
00 EC00
00 EBFF
00 EB00
00 EAFF
00 EA00
00 E9FF
00 E900
00 E8FF
00 E800
00 E7FF
XCAN1
XCAN2
XRTC
XPWM
XMiscellaneous
XI2C
XASC
XSSC
Address Area defined by
XADRS3 by default after reset
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
25/182
Page 26
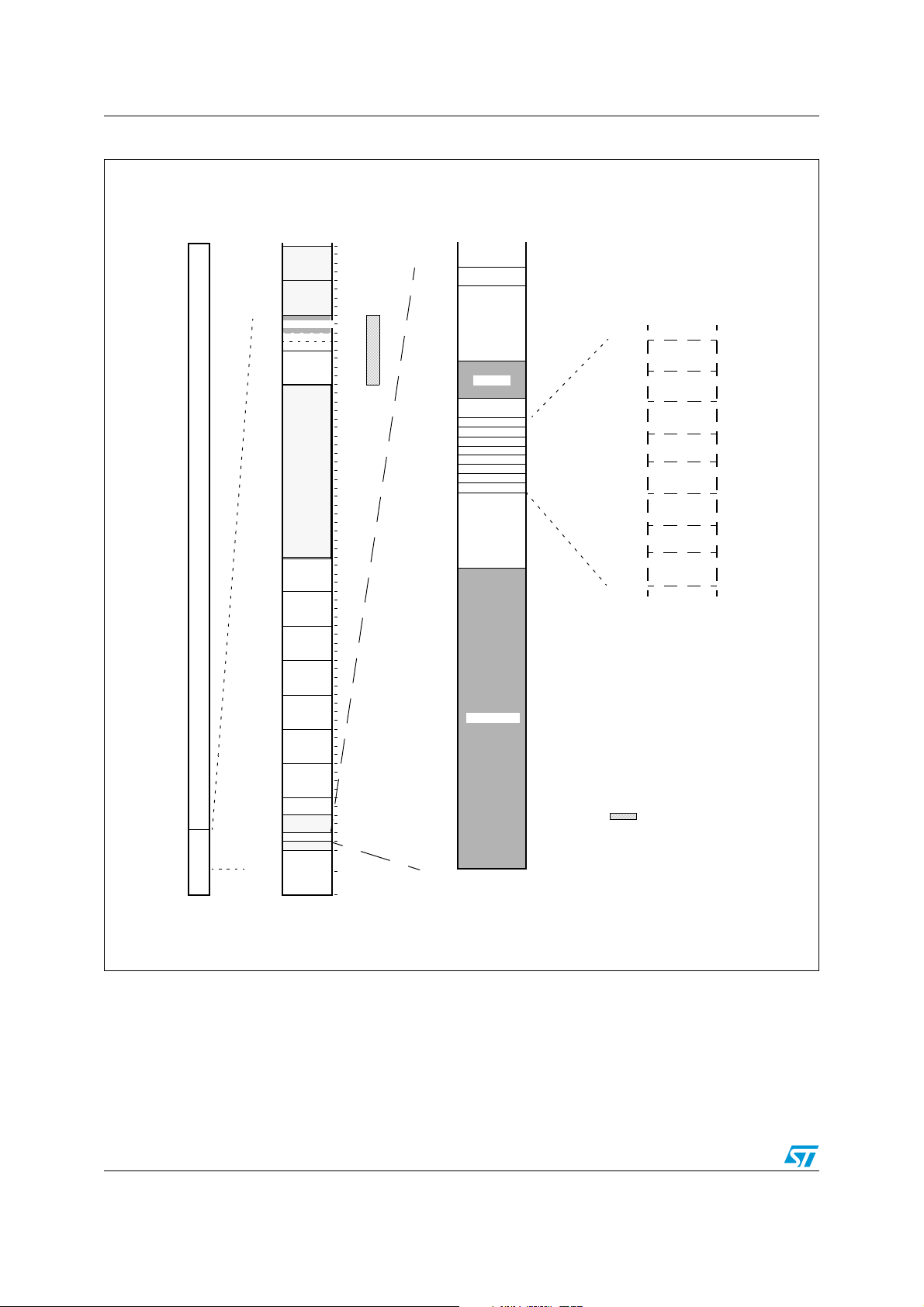
Memory organization ST10F273M
Figure 5. ST10F273M memory mapping (XADRS3 =
Code
Segment
FF FFFF
255
00 0000
0
16 MB
Data
Page
1023
0
XRAM2
(StandBy)
Flash
Control
Ext
B0F11
(B1F1)
B0F10
(B1F0)
B0F9
B0F8
B0F7
B0F6
B0F5
B0F4
B0F3
B0F2
B0F1
B0F0
Data
Page
67
66
65
64
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Segment
11 FFFF
17
11 0000
10 FFFF
16
10 0000
0F FFFF
15
0F 0000
0E FFFF
14
0E 0000
0D FFFF
13
0D 0000
0C FFFF
12
0C 0000
0B FFFF
11
0B 0000
0A FFFF
10
0A 0000
09 FFFF
9
09 0000
08 FFFF
8
08 0000
07 FFFF
7
07 0000
06 FFFF
6
06 0000
05 FFFF
5
05 0000
04 FFFF
4
04 0000
03 FFFF
3
03 0000
02 FFFF
2
02 0000
01 FFFF
1
01 0000
00 FFFF
0
00 0000
Code
Reserved
Registers
Memory
Ext Mem
Ext Mem
Flash + XRAM - 1Mbyte
32K
32K
64K
00 FFFF
00 FE00
00 FDFF
SFR
I-RAM
00 F600
00 F5FF
XADRS3 = E009h
00 F200
00 F1FF
00 F000
00 EFFF
00 E800
00 E7FF
Reserved
ESFR
XCAN1
XCAN2
XRTC
XPWM
XMiscellaneous
XI2C
XASC
XSSC
XRAM1
00 E000
00 DFFF
Ext. Memory
00 C000
Data Page 3 (Segment 0) - 16Kbyte
E009h - user programmed value
512
2K
1K
512
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
2K
8K
X-Peripherals (2Kbyte)
00 F000
00 EFFF
00 EF00
00 EEFF
00 EE00
00 EDFF
00 ED00
00 ECFF
00 EC00
00 EBFF
00 EB00
00 EAFF
00 EA00
00 E9FF
00 E900
00 E8FF
00 E800
00 E7FF
XCAN1
XCAN2
XRTC
XPWM
XMiscellaneous
XI2C
XASC
XSSC
Address Area defined by
XADRS3 after reprogramming
Note: E009h defines a 128K wide
window starting from 0E’0000h
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
)
26/182
Page 27
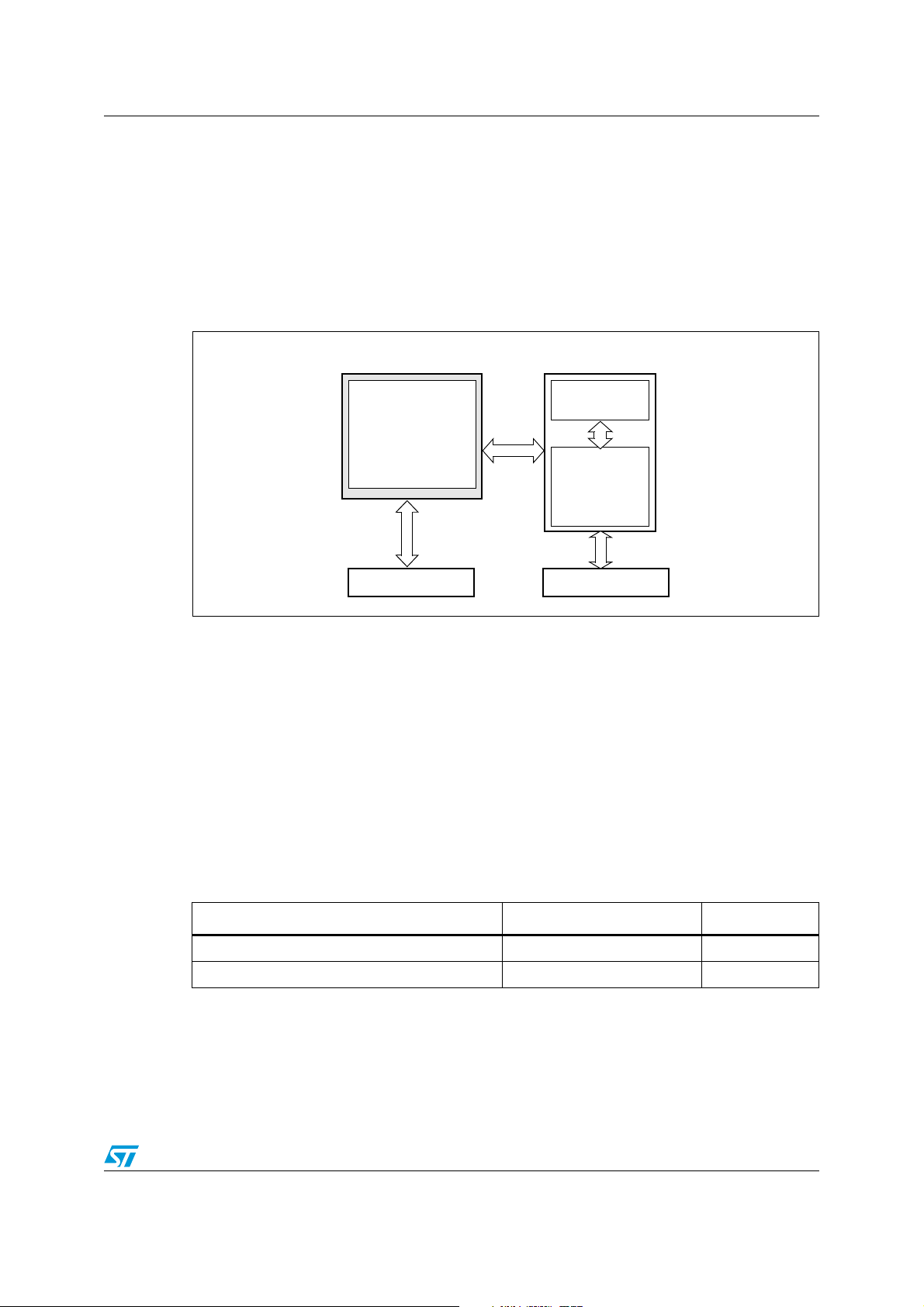
ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
5 Internal Flash memory
5.1 Overview
The on-chip Flash is composed of one matrix module of one bank of 512 Kbytes, named
Bank0, that can be read and modified. This module is called IFlash because it is on the
ST10 Internal bus.
Figure 6. Flash structure
IFlash
Bank 0: 512 Kbyte
program memory
4 Kbyte Test-Flash
+
I-BUS interface
The programming operations of the Flash are managed by an embedded Flash
Program/Erase Controller (FPEC). The high voltages needed for Program/Erase operations
are generated internally.
The Data bus is 32-bit wide for fetch accesses to IFlash. Read/write accesses to IFlash
Control Registers area are 16-bit wide.
5.2 Functional description
Control Section
HV and Ref.
generator
Program/erase
controller
+
Flash control
registers
X-BUS interface
5.2.1 Structure
Ta bl e 3 below shows the address space reserved for the Flash module.
Table 3. Flash module address space
Description Addresses Size
IFlash sectors 0x00 0000 to 0x08 FFFF 512 Kbytes
Registers and Flash internal reserved area 0x0E 0000 to 0x0E FFFF 64 Kbytes
5.2.2 Module structure
The IFlash module is composed of a bank (Bank 0) of 512 Kbytes of program memory
divided in 12 sectors (B0F0...B0F11). Bank 0 also contains a reserved sector named TestFlash.
27/182
Page 28
Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
The Addresses from 0x0E 0000 to 0x0E FFFF are reserved for the Control Register
Interface and other internal service memory space used by the Flash Program/Erase
controller.
The following tables show the memory mapping of the Flash when it is accessed in read
mode (Table 4: Flash module sectorization (read operations)), and when accessed in write
or erase mode (Table 5: Flash module sectorization (write operations, or ROMS1 = ‘1’)).
Note: With this second mapping, the first four sectors are remapped into code segment 1 (same
as obtained setting bit ROMS1 in SYSCON register).
Table 4. Flash module sectorization (read operations)
Bank Description Addresses Size (bytes)
Bank 0 Flash 0 (B0F0) 0x00 0000 - 0x00 1FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 1 (B0F1) 0x00 2000 - 0x00 3FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 2 (B0F2) 0x00 4000 - 0x00 5FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 3 (B0F3) 0x00 6000 - 0x00 7FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 4 (B0F4) 0x01 8000 - 0x01 FFFF 32 K
B0
Bank 0 Flash 5 (B0F5) 0x02 0000 - 0x02 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 6 (B0F6) 0x03 0000 - 0x03 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 7 (B0F7) 0x04 0000 - 0x04 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 8 (B0F8) 0x05 0000 - 0x05 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 9 (B0F9) 0x06 0000 - 0x06 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 10 (B0F10 / B1F0)
Bank 0 Flash 11 (B0F11 / B1F1)
1. A single bank is implemented but the last two sectors can be seen as a Bank 1 in order to maintain
compatibility with the Flash Programming routines developed for the ST10F273E (based on ST10F276E).
This means that the Control and Status flags for the blocks B0F10 and B0F11 are duplicated to also be
accessible as blocks B1F0 and B1F1.
(1)
(1)
0x07 0000 - 0x07 FFFF 64 K
0x08 0000 - 0x08 FFFF 64 K
28/182
Page 29
ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
Table 5. Flash module sectorization (write operations, or ROMS1 = ‘1’)
Bank Description Addresses Size (bytes)
Bank 0 Test-Flash (B0TF) 0x00 0000 - 0x00 0FFF 4 K
Bank 0 Flash 0 (B0F0) 0x01 0000 - 0x01 1FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 1 (B0F1) 0x01 2000 - 0x01 3FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 2 (B0F2) 0x01 4000 - 0x01 5FFF 8 K
Bank 0 Flash 3 (B0F3) 0x01 6000 - 0x01 7FFF 32 K
Bank 0 Flash 4 (B0F4) 0x01 8000 - 0x01 FFFF 64 K
B0
Bank 0 Flash 5 (B0F5) 0x02 0000 - 0x02 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 6 (B0F6) 0x03 0000 - 0x03 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 7 (B0F7) 0x04 0000 - 0x04 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 8 (B0F8) 0x05 0000 - 0x05 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 9 (B0F9) 0x06 0000 - 0x06 FFFF 64 K
Bank 0 Flash 10 (B0F10 / B1F0)
Bank 0 Flash 11 (B0F11 / B1F1)
1. A single bank is implemented but the last two sectors can be seen as a Bank 1 in order to maintain
compatibility with the Flash Programming routines developed for the ST10F273E (based on ST10F276E).
This means that the Control and Status flags for the blocks B0F10 and B0F11 are duplicated to also be
accessible as blocks B1F0 and B1F1.
(1)
(1)
0x07 0000 - 0x07 FFFF 64 K
0x08 0000 - 0x08 FFFF 8 K
Ta bl e 5 above refers to the configuration when bit ROMS1 of SYSCON register is set.
When Bootstrap mode is entered:
● Test-Flash is seen and available for code fetches (address 0x00 0000)
● User IFlash is only available for read and write accesses
● Write accesses must be made with addresses starting in segment 1 from 0x01 0000,
whatever ROMS1 bit in SYSCON value
● Read accesses are made in segment 0 or in segment 1 depending of ROMS1 value.
In Bootstrap mode, by default ROMS1 = 0, so the first 32 Kbytes of IFlash are mapped in
segment 0.
Example:
In default configuration, to program address 0, the user must put the value 0x01 0000 in the
FARL and FARH registers but to verify the content of the address 0, a read to 0x00 0000
must be performed.
The next Tabl e 6 shows the Control Register interface composition: This set of registers can
be addressed by the CPU .
29/182
Page 30
Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
Table 6. Flash control registers summary
Name Description Addresses Size Bus size
FCR1 - 0
FDR1 - 0
FAR Flash address registers 0x0E 0010 - 0x0E 0013 4 byte
FER Flash error register 0x0E 0014 - 0x0E 0015 2 byte
FVWPIR-mirror
FVWPIR Flash volatile protection I registers 0x0E DFB4 - 0x0E DFB7 4 byte
FVAPR0
FVAPR1
XFICR
Flash control registers 1 - 0 High &
Low
Flash data registers 1 - 0 High &
Low
Flash non-volatile protection I
registers mirrored
Flash volatile access protection
register 0
Flash non-volatile access
protection register 1
XFlash Interface Control register
(dummy register)
0x0E 0000 - 0x0E 0007 8 byte
0x0E 0008 - 0x0E 000F 8 byte
0x0E DFB0 - 0x0E DFB3 4 byte
0x0E DFB8 - 0x0E DFB9 2 byte
0x0E DFBC - 0x0E DFBF 4 byte
0x0E E000 - 0x0E E001 2 byte
Note: FVWPIR-mirror is a mirror of the FVWPIR to maintain software compatibility with the
ST10F273E in the handling of the last two blocks B0F10/B1F0 and B0F11/B1F1.
XFICR is a dummy register that can be read and written (for compatibility with the
ST10F273E) but its content has no effect on the XBus timings.
16-bit
(XBus)
5.2.3 Low power mode
The Flash module is automatically switched off executing PWRDN instruction. The
consumption is drastically reduced, but exiting this state can require a long time (t
PD
).
Recovery time from Power-down mode for the Flash modules is anyway shorter than the
main oscillator start-up time. To avoid any problem in restarting to fetch code from the Flash,
it is important to size properly the external circuit on RPD pin.
Note: PWRDN instruction must not be executed while a Flash program/erase operation is in
progress.
5.3 Write operation
The Flash module has a single register interface mapped in the XBus memory space
0x0E 0000 - 0x0E 0015. All the operations are enabled through four 16-bit control registers:
Flash Control Register 1-0 High/Low (FCR1H/L-FCR0H/L). Eight other 16-bit registers are
used to store Flash Address and Data for Program operations (FARH/L and FDR1H/LFDR0H/L) and Write Operation Error flags (FER). All registers are accessible with 8- and
16-bit instructions (since they are mapped on the XBus).
Note: To have access to the Flash Control Registers used for program/erasing operations,
bit 5 (XFLASHEN) in XPERCON register must be set.
Caution: During a Flash write operation any attempt to read the IFlash will output the invalid data
009Bh (corresponding, for code fetch, to the software trap 009Bh). This means that the
30/182
Page 31

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
IFlash is not fetchable when a programming operation is active: The write operation
commands must be executed from another memory (one of the on-chip RAMs or some
external memory).
Warning: During a Write operation, when bit LOCK of FCR0 is set, it is
forbidden to write into the Flash Control Registers.
Power supply drop
If during a write operation the internal low voltage supply drops below a certain internal
voltage threshold, any write operation running is suddenly interrupted and the module is
reset to Read mode. At following Power-on, the interrupted Flash write operation must be
repeated.
5.4 Flash control registers description
5.4.1 Flash control register 0 low (FCR0L)
The Flash Control Register 0 Low (FCR0L), together with the Flash Control Register 0 High
(FCR0H), is used to enable and to monitor all the write operations on the IFlash. The user
has no access in write mode to the Test-Flash (B0TF). Moreover, the Test-Flash block is
seen by the user in Bootstrap mode only.
FCR0L (0x0E 0000) FCR Reset value: 0000h
1514131211109876543210
Reserved
DBSY1BSY
0
LOCK Reserved
- RORORO - RO -
Table 7. FCR0L register description
Bit Name Function
15:7 - Reserved. These bits must be left to their reset value (0).
Dummy Bank1 Busy
It is a replication of the BSY0 bit: it is set whenever a write operation is on-going.
6 DBSY1
This bit is emulating the BSY1 bit of the ST10F273E device. When write
operations are on going on B0F10 and/or B0F11 blocks of the ST10F273M, this
bit will be set in order to indicate that their equivalent B1F0 or B1F1 in the
ST10F273E are busy.
Bank0 Busy
This bits indicate that a write operation is running in the Bank0. It is automatically
set when bit WMS is set. When this bit is set every read access to the Bank0 will
5 BSY0
output invalid data (software trap 009Bh), while every write access will be ignored.
At the end of the write operation or during a Program or Erase Suspend this bit is
automatically reset and Flash Bank returns to read mode. After a Program or
Erase Resume this bit is automatically set again.
BSY
NVR
Res
31/182
Page 32

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
Table 7. FCR0L register description (continued)
Bit Name Function
Flash registers access locked
When this bit is set, it means that the access to the Flash Control Registers
FCR0H/-FCR1H/L, FDR0H/L-FDR1H/L, FARH/L and FER is locked by the FPEC:
any read access to the registers will output invalid data (software trap 009Bh) and
any write access will be ineffective. LOCK bit is automatically set when the Flash
4LOCK
3:2 - Reserved. These bits must be left to their reset value (0).
1BSYNVR
bit WMS is set.
This is the only bit the user can always access to detect the status of the Flash:
once it is found low, the rest of FCR0L and all the other Flash registers are
accessible by the user as well.
Note that FER content can be read when LOCK is low, but its content is updated
only when also BSYx bits are reset.
Busy of Non-Volatile Registers
This bit indicate that a write operation is running in the corresponding on “Nonvolatile registers”. They are automatically set when bit WMS is set. When this bit
is set every read access to the IFlash will output the value 009Bh (software trap),
while every write access to the IFlash will be ignored. At the end of the write
operation or during a Program Suspend this bit is automatically reset and the
IFlash returns to read mode. After a Program this bit is automatically set again.
0 - Reserved. This bit must be left to its reset value (0).
5.4.2 Flash control register 0 high (FCR0H)
The Flash Control Register 0 High (FCR0H) together with the Flash Control Register 0 Low
(FCR0L) is used to enable and to monitor all the write operations on the IFlash. The user
has no access in write mode to the Test-Flash (B0TF). Moreover, the Test-Flash block is
seen by the user in Bootstrap mode only.
FCR0H (0x0E 0002) FCR Reset value: 0000h
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
WMS SUSP WPG DWPG SER Reserved SPR
RS RW RW RW RW - RW RW -
Table 8. FCR0H register description
Bit Name Function
Write mode start
This bit must be set to start every write operation in the Flash module. At the end
of the write operation or during a Suspend, this bit is automatically reset. To
resume a suspended operation, this bit must be set again.
15 WMS
It is forbidden to set this bit if bit ERR of FER is high (the operation is not
accepted).
It is also forbidden to start a new write (program or erase) operation (by setting
WMS high) when bit SUSP of FCR0 is high. Resetting this bit by software has no
effect.
DS
MOD
Reserved
32/182
Page 33

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
Table 8. FCR0H register description (continued)
Bit Name Function
Suspend
This bit must be set to suspend the current Program (Word or Double Word) or
Sector Erase operation in order to read data in another part of the Flash. The
14 SUSP
13 WPG
12 DWPG
Suspend operation resets the Bank0 to normal read mode (automatically resetting
bits BSYx). When in Program Suspend, the Flash module accepts only the
following operations: Read and Program Resume. When in Erase Suspend the
module accepts only the following operations: Read, Erase Resume. To resume a
suspended operation, the WMS bit must be set again, together with the selection
bit corresponding to the operation to resume (WPG, DWPG, SER).
(1)
Word program
This bit must be set to select the Word (32 bits) Program operation in the Flash
module. The Word Program operation allows to program 0s in place of 1s. The
Flash Address to be programmed must be written in the FARH/L registers, while
the Flash Data to be programmed must be written in the FDR0H/L registers before
starting the execution by setting bit WMS. WPG bit is automatically reset at the
end of the Word Program operation.
Double word program
This bit must be set to select the Double Word (64 bits) Program operation in the
Flash module. The Double Word Program operation allows to program 0s in place
of 1s. The Flash Address in which to program (aligned with even words) must be
written in the FARH/L registers, while the two Flash Data words to be programmed
must be written in the FDR0H/L registers (even word) and FDR1H/L registers (odd
word) before starting the execution by setting bit WMS. DWPG bit is automatically
reset at the end of the Double Word Program operation.
Sector erase
This bit must be set to select the Sector Erase operation. The Sector Erase
operation allows to erase all the Flash locations to value 0xFFFF. From 1 to all of
11 SER
Bank0’s sectors (excluding Test-Flash) can be selected to be erased through bits
BxFy of FCR1H/L registers before starting the execution by setting bit WMS. It is
not necessary to preprogram the sectors to 0, because this is done automatically.
SER bit is automatically reset at the end of the Sector Erase operation.
10:9 - Reserved. This bit must be left to their reset value (0).
Set protection
This bit must be set to select the Set Protection operation. The Set Protection
operation allows to program 0s in place of 1s in the Flash Non-Volatile Protection
Registers. The Flash Address in which to program must be written in the FARH/L
8 SPR
registers, while the Flash Data to be programmed must be written in the FDR0H/L
before starting the execution by setting bit WMS. A sequence error is flagged by bit
SEQER of FER if the address written in FARH/L is not in the range 0x0E DFB00x0E DFBF.
SPR bit is automatically reset at the end of the Set Protection operation.
Dummy Select Module
7DSMOD
This is a dummy SMOD bit that is maintaining software compatibility with the
ST10F273E where it must be set before every Write Operation to the IFlash.
It has no effect in the ST10F273M.
6:0 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their reset value (0).
1. It is forbidden to start a new Write operation with bit SUSP already set.
33/182
Page 34

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
5.4.3 Flash control register 1 low (FCR1L)
The Flash Control Register 1 Low (FCR1L), together with Flash Control Register 1 High
(FCR1H), is used to select the sectors to erase or during any write operation, to monitor the
status of each sector and bank.
FCR1L (0x0E 0004) FCR Reset value: 0000h
1514131211109876543210
Reserved
B0F11B0F10B0F9B0F8B0F7B0F6B0F5B0F4B0F3B0F2B0F1B0F
- RSRSRSRSRSRSRSRSRSRSRSRS
Table 9. FCR1L register description
Bit Name Function
15:12 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
Bank0 IFlash sector 11:10 status
These bits are a copy of bits B0F10 and B0F11 in FCR1H.
11:10
B0F11
B0F10
It is possible use these bits as well as the bits B0F10/B1F0 and B0F11/B1F1 in
FCR1H.
To preserve compatibility with the ST10F273E, these bits must be left at their
default value ‘0’ and the FCR1H register must be used.
Bank 0 IFlash sector 9:0 status
These bits must be set during a Sector Erase operation to select the sectors to
9:0
B0F9
...
B0F0
erase in Bank 0. Besides, during any erase operation, these bits are
automatically set and give the status of the first 10 sectors of Bank 0 (B0F9B0F0). The meaning of B0Fy bit for Sector y of Bank 0 is given by Tab l e 1 1 :
Bank (BxS) and sectors (BxFy) status bits meaning. These bits are
automatically reset at the end of a Write operation if no errors are detected.
5.4.4 Flash control register 1 high (FCR1H)
0
The Flash Control Register 1 High (FCR1H), together with Flash Control Register 1 Low
(FCR1L), is used to select the sectors to erase or during any write operation, to monitor the
status of each sector and bank.
FCR1H (0x0E 0006) FCR Reset value: 0000h
151413121110 9 8 765432 1 0
Reserved DB1S B0S Reserved
- RS RS - RS RS
34/182
B0F11
/B1F1
B0F10
/B1F0
Page 35

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
Table 10. FCR1H register description
Bit Name Function
15:10 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
Dummy Bank1 status
9DB1S
8B0S
7:2 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
B0F10/B1F0
1:0
B0F11/B1F1
Table 11. Bank (BxS) and sectors (BxFy) status bits meaning
This is a replication of B0S bit.
In order to maintain compatibility with the ST10F273E where operations on
the last 2 sectors were flagged in this position.
Bank0 status
During any erase operation, this bit is automatically modified and gives the
status of the Bank 0. The meaning of B0S bit is given in the next Table 11:
Bank (BxS) and sectors (BxFy) status bits meaning. This bit is automatically
reset at the end of a erase operation if no errors are detected.
Bank0 IFlash sector 11:10 status / Bank1 IFlash sector 1:0 status
These bits must be set during a Sector Erase operation to select the last 2
sectors of Bank0. Besides, during any erase operation, these bits are
automatically set and give the status of the last two sectors of Bank0
(B0F11-B0F10). The meaning of B0Fy bit for Sector y of Bank 0 is given by
the next Table 11: Bank (BxS) and sectors (BxFy) status bits meaning.
These bits are automatically reset at the end of a Write operation if no errors
are detected.
Note: These bits can also be seen as selecting the two sectors of Bank1 for
compatibility with the ST10F273E.
Operation
BxS = 1 meaning BxFy = 1 meaning
Erase Suspend
1 - Erase error Erase error in sector y
0 1 Erase suspended in bank x Erase suspended in sector y of bank x
0 0 Don’t care Don’t care
5.4.5 Flash data register 0 low (FDR0L)
During program operations, the Flash Address Registers (FARH/L) are used to store the
Flash address in which to program and the Flash Data Registers (FDR1H/L-FDR0H/L) are
used to store the Flash data to program.
FDR0L (0x0E 0008) FCR Reset value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
DIN15DIN14DIN13DIN12DIN11DIN10DIN9DIN8DIN7DIN6DIN5DIN4DIN3DIN2DIN1DIN
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
0
35/182
Page 36

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
Table 12. FDR0L register description
Bit Name Function
Data input 15:0
15:0 DIN[15:0]
These bits must be written with the Data to program in Flash during the following
operations: Word Program (32-bit), Double Word Program (64-bit) and Set
Protection.
5.4.6 Flash data register 0 high (FDR0H)
FDR0H (0x0E 000A) FCR Reset value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
DIN31DIN30DIN29DIN28DIN27DIN26DIN25DIN24DIN23DIN22DIN21DIN20DIN19DIN18DIN17DIN
16
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 13. FDR0H register description
Bit Name Function
Data input 31:16
15:0 DIN[31:16]
These bits must be written with the Data to program in Flash during the following
operations: Word Program (32-bit), Double Word Program (64-bit) and Set
Protection.
36/182
Page 37

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
5.4.7 Flash data register 1 low (FDR1L)
FDR1L (0x0E 000C) FCR Reset value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
DIN15 DIN14 DIN13 DIN12 DIN11 DIN10
DIN9 DIN8 DIN7 DIN6 DIN5 DIN4 DIN3 DIN2 DIN1 DIN0
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 14. FDR1L register description
Bit Name Function
Data input 15:0
15:0 DIN[15:0]
These bits must be written with the Data to program in Flash during the following
operations: Double Word Program (64-bit) and Set Protection.
5.4.8 Flash data register 1 high (FDR1H)
FDR1H (0x0E 000E) FCR Reset value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
DIN31 DIN30 DIN29 DIN28 DIN27 DIN26 DIN25 DIN24 DIN23 DIN22 DIN21 DIN20 DIN19 DIN18 DIN17 DIN16
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 15. FDR1H register description
Bit Name Function
Data input 31:16
15:0 DIN[31:16]
These bits must be written with the Data to program in Flash during the following
operations: Double Word Program (64-bit) and Set Protection.
5.4.9 Flash address register low (FARL)
FARL (0x0E 0010) FCR Reset value: 0000h
1514131211109876543210
ADD15ADD14ADD13 ADD12 ADD11 ADD10
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW -
Table 16. FARL register description
Bit Name Function
Address 15:2
These bits must be written with the Address of the Flash location to program
15:2 ADD[15:2]
during the following operations: Word Program (32-bit) and Double Word
Program (64-bit).
In Double Word Program bit ADD2 must be written to ‘0’.
1:0 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
ADD9 ADD8 ADD7 ADD6 ADD5 ADD4 ADD3 ADD2
37/182
Reserved
Page 38

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
5.4.10 Flash address register high (FARH)
FARH (0x0E 0012) FCR Reset value: 0000h
1514131211109876543210
Reserved
- RWRWRWRWRW
Table 17. FARH register description
Bit Name Function
Address 20:16
These bits must be written with the Address of the Flash location to program
during the following operations: Word Program and Double Word Program.
4:0
ADD20
...
ADD6
15:5 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
5.4.11 Flash error register (FER)
The Flash error register, as well as all the other Flash registers, can be read only once the
LOCK bit of register FCR0L is low. Nevertheless, the FER content is updated after
completion of the Flash operation, that is, when BSYx bits are reset. Therefore, the FER
content can only be read once the LOCK and BSYx bits are cleared.
FER (0xE 0014h) FCR Reset value: 0000h
1514131211109876543210
Reserved WPF RESER SEQER Reserved 10ER PGER ERER ERR
ADD20ADD19ADD18ADD17ADD
16
- RC RC RC - RC RC RC RC
Table 18. FER register bits
Bit Name Function
15:9 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
Write protection flag
This bit is automatically set when trying to program or erase in a sector write
8WPF
protected. In case of multiple Sector Erase, the not protected sectors are
erased, while the protected sectors are not erased and bit WPF is set. This
bit must be cleared by software.
Resume error
7 RESER
This bit is automatically set when a suspended Program or Erase operation is
not resumed correctly due to a protocol error. In this case the suspended
operation is aborted. This bit must be cleared by software.
Sequence error
This bit is automatically set when the control registers (FCR1H/L-FCR0H/L,
6 SEQER
FARH/L, FDR1H/L-FDR0H/L) are not correctly filled to execute a valid Write
Operation. In this case no Write Operation is executed. This bit must be
cleared by software.
5:4 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
38/182
Page 39

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
Table 18. FER register bits (continued)
Bit Name Function
1 over 0 error
This bit is automatically set when trying to program at 1 bits previously set at
310ER
2PGER
1ERER
0ERR
0 (this does not happen when programming the Protection bits). This error is
not due to a failure of the Flash cell, but only flags that the desired data has
not been written. This bit must be cleared by software.
Program error
This bit is automatically set when a Program error occurs during a Flash write
operation. This error is due to a real failure of a Flash cell, that can no more
be programmed. The word where this error occurred must be discarded. This
bit must be cleared by software.
Erase error
This bit is automatically set when an Erase error occurs during a Flash write
operation. This error is due to a real failure of a Flash cell, that can no more
be erased. This kind of error is fatal and the sector where it occurred must be
discarded. This bit must be cleared by software.
Write error
This bit is automatically set when an error occurs during a Flash write
operation or when a bad write operation setup is done. Once the error has
been discovered and understood, ERR bit must be cleared by software.
5.4.12 XFlash interface control dummy register (XFICR)
XFICR (0x0E E0000) FCR Reset value: 0007h
1514131211109876543210
Reserved WS3 WS2 WS1 WS0
- RWRWRWRW
Table 19. XFlash interface control register
Bit Name Function
Dummy Wait States 3:0
In the ST10F273E, these bits were used to configure the number of wait-
3:0 WS3...WS0
states to access the XFlash. As there is no XFlash on the ST10F273M, these
bits have no effect.
This register is implemented for software compatibility with the ST10F273E.
15:4 - Reserved. These bits must be kept to their default value (0).
5.5 Protection strategy
The protection bits are stored in Non-Volatile Flash cells that are read once at reset and
stored in five Volatile registers. Before they are read from the Non-Volatile cells, all the
available protections are forced active during reset.
39/182
Page 40

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
Note: The protection bits in the Non-Volatile registers are programmable one time and this
programing is permanent. Temporary unprotection will be handled with their Volatile
equivalent.
The protections can be programmed using the Set Protection operation (see Section 5.4:
Flash control registers description) that must be executed from the on-chip RAMs or from
external memories.
Two kind of protections are available:
● write protections to avoid unwanted writings
● access protections to avoid piracy
The next sections show the different level of protections and highlight the architecture
limitations.
5.5.1 Protection registers
The five Non-Volatile Protection Registers are one-time programmable for the user.
Two registers, FVWPIRL and FVWPIRH, are used to store the Write Protection fuses for
each sector IFlash module. The other three registers (FNVAPR0 and FNVAPR1L/H) are
used to store the Access Protection fuses.
Note: On-going protection operations are flagged with BSYNVR, bit 1 of FCR0L register.
5.5.2 Flash non-volatile write protection I register low (FNVWPIRL)
FNVWPIRL (0x0E DFB4) NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
Reserved
- RO RO RWRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
Table 20. FNVWPIRL register bits
Bit Name Function
15:12 -
11:10
9:0
W0P11
W0P10
W0P9
...
W0P0
W0P11W0P10W0P9W0P8W0P7W0P6W0P5W0P4W0P3W0P2W0P1W0P
Reserved. These bits must be left to their default value ‘1’ when programming
PVWPIRL.
Read-Only for Write protection Bank0 sectors 11 and 10
These bits must be left to their default value ‘1’ when programming FVWPIRL
(they can not be used to set write protection on sectors B0F11 and B0F10).
After a protection command, these bits will reflect the value of bit 0 and 1 of
FVWPIRH register (W0P11 and W0P10).
Write protection bank 0 / sectors 9-0
These bits, if programmed at 0, disable any write access to the sectors of
Bank 0 (IFlash).
0
40/182
Page 41

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
5.5.3 Flash non-volatile write protection I register high (FNVWPIRH)
FNVWPIRH (0x0E DFB6) NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
15141312111098765432 1 0
W0P11-
Reserved
W1P1
W0P10-
W1P0
-RWRW
Table 21. FNVWPRIH register bits
Bit Name Function
15:2 - Reserved. These bits must be left to their default value ‘1’.
W0P11/W1P1
1:0
W0P10/W1P0
Write protection Bank0 - sectors 11:10 / Write protection Bank1 - sectors 1:0
These bits, if programmed at 0, disable any write access to the selected
sectors.
5.5.4 Flash non-volatile write protection I register low Mirror (FNVWPIRL-m)
FNVWPIRL-m (0x0E DFB0) NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
Reserved
W0P11W0P10W0P9W0P8W0P7W0P6W0P5W0P4W0P3W0P2W0P1W0P
- RO RO RWRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRWRW
This register is mirroring the register at FVWPIRL (address 0x0E DFB4). It is intended to
maintain software compatibility with the ST10F273E.
In applications ported from a ST10F273E, FVWPIRL-m register (address 0x0E DFB0) must
be used to maintain the existing Flash drivers.
In applications ported from a ST10F272x, FVWPIRL register (address 0x0E DFB4) must be
used to maintain existing drivers.
5.5.5 Flash non-volatile write protection I register high Mirror (FVWPIRH-m)
FVWPIRH-m (0x0E DFB2 NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
W0P11-
Reserved
-RWRW
This register is mirroring the register at FVWPIRH (address 0x0E DFB6). It is intended to
maintain software compatibility with the ST10F273E.
W1P1
W0P10-
W1P0
0
In applications ported from a ST10F273E, FVWPIRH-m register (address 0x0E DFB2) must
be used to maintain the existing Flash drivers.
In applications ported from a ST10F272x, FVWPIRH register (address 0x0E DFB6) must be
used to maintain existing drivers.
41/182
Page 42

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
5.5.6 Flash non-volatile access protection register 0 (FNVAPR0)
FNVAPR0 (0x0E DFB8) NVR Delivery value: ACFFh
1514131211109876543210
Reserved DBGP ACCP
-RWRW
Table 22. FNVAPR0 register bits
Bit Name Description
15:2 - Reserved. These bits must be left to their default value.
Debug protection
This bit, if erased at 1, allows to bypass all the protections using the Debug
features through the Test Interface. If programmed at 0, on the contrary, all
1DBGP
0 ACCP
the debug features, the Test Interface and all the Flash Test modes are
disabled.
Even STMicroelectronics will not be able to access the device to run any
eventual failure analysis.
Access protection
This bit, if programmed at 0, disables any access (read/write) to data mapped
inside IFlash Module address space, unless the current instruction is fetched
from IFlash.
5.5.7 Flash non-volatile access protection register 1 low (FNVAPR1L)
FNVAPR1L (0x0E DFBC) NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
PDS15PDS14PDS13PDS12PDS11PDS10PDS9PDS8PDS7PDS6PDS5PDS4PDS3PDS2PDS1PDS
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 23. FNVAPR1L register bits
Bit Name Function
Protections disable15-0
15:0
PDS15
...
PDS0
If bit PDSx is programmed at 0 and bit PENx is erased at 1, the action of bit
ACCP is disabled. Bit PDS0 can be programmed at 0 only if both bits DBGP and
ACCP have already been programmed at 0. Bit PDSx can be programmed at 0
only if bit PENx-1 has already been programmed at 0.
0
42/182
Page 43

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
5.5.8 Flash
non-
volatile access
FNVAPR1H (0x0E DFBE) NVR Delivery value: FFFFh
1514131211109876543210
PEN15PEN14PEN13PEN12PEN11PEN10PEN9PEN8PEN7PEN6PEN5PEN4PEN3PEN2PEN1PEN
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW
Table 24. FNVAPR1H register bits
Bit Name Function
PEN15
15:0
PEN0
Protections enable 15-0
...
If bit PENx is programmed at 0 and bit PDSx+1 is erased at 1, the action of bit
ACCP is enabled again. Bit PENx can be programmed at 0 only if bit PDSx has
already been programmed at 0.
5.5.9 Access protection
The IFlash module has one level of access protection (access to data both in Reading and
Writing): If bit ACCP of FNVAPR0 is programmed at 0, the IFlash module becomes access
protected, meaning data in the IFlash module can be read only if the current execution is
from the IFlash module itself.
Protection can be permanently disabled by programming bit PDS0 of FNVAPR1H (user
operation before returning parts to STMicroelectronics for analysis). Protection can be
permanently enabled again by programming bit PEN0 of FNVAPR1L. The action to disable
and enable again Access Protections in a permanent way can be executed a maximum of
16 times.
protection register 1 high (FNVAPR1H
)
0
Trying to write into the access protected Flash from internal RAM or external memories will
be unsuccessful. Trying to read into the access protected Flash from internal RAM or
external memories will output a dummy data (software trap 009Bh).
When the Flash module is protected in access, data access through PEC of a peripheral is
also forbidden. To read/write data in PEC mode from/to a protected Bank, it is necessary to
first temporarily unprotect the Flash module.
The following table summarizes all possible Access Protection levels: In particular, it shows
what is possible and not possible to do when fetching from a memory (see fetch location
column) supposing all possible access protections are enabled.
Table 25. Summary of access protection level
Read XRAM or
Fetch location
Fetching from IFlash Yes / Yes Yes / Yes Yes Yes
Fetching from IRAM No / Yes Yes / Yes Yes No
Read IFlash /
Jump to IFlash
external memory /
Jump to XRAM or
external memory
Read Flash
registers
Write Flash
registers
43/182
Page 44

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
Table 25. Summary of access protection level (continued)
Read XRAM or
Fetch location
Fetching from XRAM No / Yes Yes / Yes Yes No
Read IFlash /
Jump to IFlash
external memory /
Jump to XRAM or
external memory
Read Flash
registers
Write Flash
registers
Fetching from external
memory
N o / Ye s Ye s / Ye s Ye s N o
5.5.10 Write protection
The Flash modules have one level of Write Protections: Each sector can be Software Write
Protected by programming at 0 the related bit WyPx in FNVWPIRL/H register.
5.5.11 Temporary unprotection
Bits WyPx of FNVWPIRL/H can be temporarily unprotected by executing the Set Protection
operation and writing 1 into these bits.
Bit ACCP can be temporarily unprotected by executing the Set Protection operation and
writing are executed from IFlash.
To restore the write access protection bits it is necessary to reset the microcontroller or to
execute a Set Protection operation and write 0 into the desired bits.
In reality, when a temporary unprotection operation is executed, the corresponding volatile
register is written to 1, while the non-volatile registers bits previously written to 0 (for a
protection set operation), will continue to maintain the 0. For this reason, the user software
must be in charge to track the current protection status (for instance using a specific RAM
area), it is not possible to deduce it by reading the non-volatile register content (a temporary
unprotection cannot be detected).
5.6 Write operation examples
In the following, examples for each kind of Flash write operation are presented.
The examples are showing the sequence of instructions needed to start an operation. Write
operations should be followed by a status check (FER register).
Note: After a write operation has started, the Flash control registers are not accessible for a short
time. The LOCK bit, bit 4 of FCR0L register, must be polled in order to know when the Flash
control registers can be accessed again (LOCK = ‘1’: no access to Flash control registers).
Write operation on IBus registers is 16 bits wide.
Word program
Example: 32-bit Word Program of data 0xAAAAAAAA at address 0x025554
FCR0H|= 0x2000; /*Set WPG in FCR0H*/
FARL = 0x5554; /*Load Add in FARL*/
FARH = 0x0002; /*Load Add in FARH*/
FDR0L = 0xAAAA; /*Load Data in FDR0L*/
FDR0H = 0xAAAA; /*Load Data in FDR0H*/
44/182
Page 45

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
FCR0H|= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Double word program
Example: Double Word Program (64-bit) of data 0x55AA55AA at address 0x035558 and
data 0xAA55AA55 at address 0x03555C.
FCR0H |= 0x1000; /*Set DWPG in FCR0H*/
FARL = 0x5558; /*Load Add in FARL*/
FARH = 0x0003; /*Load Add in FARH*/
FDR0L = 0x55AA; /*Load Data in FDR0L*/
FDR0H = 0x55AA; /*Load Data in FDR0H*/
FDR1L = 0xAA55; /*Load Data in FDR1L*/
FDR1H = 0xAA55; /*Load Data in FDR1H*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Double Word Program is always performed on the Double Word aligned on an even Word:
bit ADD2 of FARL is ignored.
Sector erase
Example: Sector Erase of sectors B0F1 and B0F0 of Bank 0.
FCR0H |= 0x0800; /*Set SER in FCR0H*/
FCR1L |= 0x0003; /*Set B0F1, B0F0*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Suspend and resume
Word Program, Double Word Program, and Sector Erase operations can be suspended in
the following way:
FCR0H |= 0x4000; /*Set SUSP in FCR0H*/
Then the operation can be resumed in the following way:
FCR0H |= 0x0800; /*Set SER in FCR0H*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation resume*/
Before resuming a suspended Erase, FCR1H/FCR1L must be read to check if the Erase is
already completed (FCR1H = FCR1L = 0x0000 if Erase is complete). Original setup of
Select Operation bits in FCR0H/L must be restored before the operation resume, otherwise
the operation is aborted and bit RESER of FER is set.
Set protection
Example 1: Enable Write Protection of sectors B0F3-0 of Bank 0.
FCR0H |= 0x0100; /*Set SPR in FCR0H*/
FARL = 0xDFB4; /*Load Add of register FNVWPIR in FARL*/
FARH = 0x000E; /*Load Add of register FNVWPIR in FARH*/
FDR0L = 0xFFF0; /*Load Data in FDR0L*/
FDR0H = 0xFFFF; /*Load Data in FDR0H*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Example 2: Enable Access and Debug Protection.
FCR0H |= 0x0100; /*Set SPR in FCR0H*/
45/182
Page 46

Internal Flash memory ST10F273M
FARL = 0xDFB8; /*Load Add of register FNVAPR0 in FARL*/
FARH = 0x000E; /*Load Add of register FNVAPR0 in FARH*/
FDR0L = 0xFFFC; /*Load Data in FDR0L*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Example 3: Disable in a permanent way Access and Debug Protection.
FCR0H |= 0x0100; /*Set SPR in FCR0H*/
FCR0H |= 0x0100; /*Set SPR in FCR0H*/
FARL = 0xDFBC; /*Load Add of register FNVAPR1L in FARL*/
FARH = 0x000E; /*Load Add of register FNVAPR1L in FARH*/
FDR0L = 0xFFFE; /*Load Data in FDR0L for clearing PDS0*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Example 4: Enable again in a permanent way Access and Debug Protection, after having
disabled them.
FCR0H|= 0x0100; /*Set SPR in FCR0H*/
FARL = 0xDFBC; /*Load Add register FNVAPR1H in FARL*/
FARH = 0x000E; /*Load Add register FNVAPR1H in FARH*/
FDR0H = 0xFFFE; /*Load Data in FDR0H to clear PEN0*/
FCR0H |= 0x8000; /*Operation start*/
Disable and re-enable of Access and Debug Protection in a permanent way (as shown by
examples 3 and 4) can be done for a maximum of 16 times.
46/182
Page 47

ST10F273M Internal Flash memory
5.7 Write operation summary
In general, each write operation is started through a sequence of three steps:
1. The first instruction is used to select the desired operation by setting its corresponding
selection bit in the Flash Control Register 0.
2. The second step is the definition of the Address and Data for programming or the
sectors to erase.
3. The last instruction is used to start the write operation, by setting the start bit WMS in
the FCR0. This last instruction must not be executed from Flash.
Once selected, but not yet started, one operation can be canceled by resetting the operation
selection bit.
Available Flash Module Write Operations are summarized in the following Ta bl e 2 6 .
Table 26. Flash write operations
Operation Select bit Address and data Start bit
Word Program (32-bit) WPG
FAR L/FARH
FDR0L/FDR0H
FAR L/FARH
Double Word Program (64-bit) DWPG
FDR0L/FDR0H
FDR1L/FDR1H
WMS
Sector Erase SER FCR1L/FCR1H
Set Protection SPR FDR0L/FDR0H
Program/Erase Suspend SUSP None None
Figure 7 shows the complete flow needed for a Write operation.
Figure 7. Write operation control flow
Start Write Operation
FCR0L.LOCK == 0?
Ye s
Write Operation finished?
(Check related busy bit)
Ye s
No
No
Check Error Status
No error:
Proceed with application
47/182
Error:
Error handler, ...
Re-start operation
Page 48

Bootstrap loader ST10F273M
6 Bootstrap loader
The ST10F273M implements Boot capabilities in order to:
● Support bootstrap via UART or bootstrap via CAN for the standard bootstrap
● Support a Selective Bootstrap Loader, to manage the bootstrap sequence in a different
way
6.1 Selection among user-code, standard or selective bootstrap
The boot modes are triggered with a special combination set on Port0L[5...4]. Those
signals, as other configuration signals, are latched on the rising edge of RSTIN
● Decoding of reset configuration (P0L.5 = 1, P0L.4 = 1) selects the normal mode (also
called User mode) and selects the user Flash to be mapped from address 00’0000h.
● Decoding of reset configuration (P0L.5 = 1, P0L.4 = 0) selects ST10 standard bootstrap
mode (Test-Flash is active and overlaps user Flash for code fetches from address
00'0000h; user Flash is active and available for read accesses).
● Decoding of reset configuration (P0L.5 = 0, P0L.4 = 1) activates additional verifications
to select which bootstrap software to execute:
– if the User mode signature in the User Flash is programmed correctly, then a
software reset sequence is selected and the User code is executed;
– if the User mode signature is not programmed correctly in the user Flash, then the
User key location is read again. Its value determines which communication
channel will be enabled for bootstrapping.
.
Table 27. ST10F273M boot mode selection
pin.
P0.5 P0.4 ST10 decoding
11User mode: User Flash mapped at 00’0000h
10
01
00Reserved
Standard Bootstrap Loader: User Flash mapped from 00’0000h, code fetches
redirected to Test-Flash at 00’0000h
Selective Boot mode: User Flash mapped from 00’0000h, code fetches
redirected to Test-Flash at 00’0000h (different sequence execution compared to
Standard Bootstrap Loader)
6.2 Standard bootstrap loader
After entering the standard BSL mode and the respective initialization, the ST10F273M
scans the RxD0 line and the CAN1_RxD line to receive either a valid dominant bit from the
CAN interface or a start condition from the UART line.
Start condition on UART RxD: ST10F273M starts standard bootstrap loader. This
bootstrap loader is identical to that of other ST10 devices (example: ST10F269, ST10F168).
Valid dominant bit on CAN1 RxD: ST10F273M start bootstrapping via CAN1.
Caution: As both UART_RxD and CAN1_RxD lines are polled to detect a start of communication,
ensure a stable level on the unused channel by adding a pull-up resistor.
48/182
Page 49

ST10F273M Bootstrap loader
6.3 Alternate and selective boot mode (ABM and SBM)
6.3.1 Activation of the ABM and SBM
Alternate boot is activated with the combination ‘01’ on Port0L[5..4] at the rising edge of
RSTIN
6.3.2 User mode signature integrity check
The behavior of the Selective Boot mode is based on the computing of a signature between
the content of two memory locations and a comparison with a reference signature. This
requires that users who use Selective Boot have reserved and programmed the Flash
memory locations.
6.3.3 Selective boot mode
When the user signature is not correct, instead of executing the Standard Bootstrap Loader
(triggered by P0L.4 low at reset), additional check is made.
Depending on the value at the User key location, the following behavior occurs:
● A jump is performed to the Standard Bootstrap Loader
● Only UART is enabled for bootstrapping
● Only CAN1 is enabled for bootstrapping
● The device enters an infinite loop
.
49/182
Page 50

Central processing unit (CPU) ST10F273M
7 Central processing unit (CPU)
The CPU includes a 4-stage instruction pipeline, a 16-bit arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) and
dedicated SFRs. Additional hardware has been added for a separate multiply and divide
unit, a bit-mask generator and a barrel shifter.
Most of the ST10F273M’s instructions can be executed in one instruction cycle which
requires 50ns at 40 MHz CPU clock. For example, shift and rotate instructions are
processed in one instruction cycle independent of the number of bits to be shifted.
Multiple-cycle instructions have been optimized: branches are carried out in 2 cycles,
16 x 16-bit multiplication in 5 cycles and a 32-/16-bit division in 10 cycles.
The jump cache reduces the execution time of repeatedly performed jumps in a loop, from
2 cycles to 1 cycle.
The CPU uses a bank of 16 word registers to run the current context. This bank of General
Purpose Registers (GPR) is physically stored within the on-chip Internal RAM (IRAM) area.
A Context Pointer (CP) register determines the base address of the active register bank to
be accessed by the CPU.
The number of register banks is only restricted by the available Internal RAM space. For
easy parameter passing, a register bank may overlap others.
A system stack of up to 2048 bytes is provided as a storage for temporary data. The system
stack is allocated in the on-chip RAM area, and it is accessed by the CPU via the stack
pointer (SP) register.
Two separate SFRs, STKOV and STKUN, are implicitly compared against the stack pointer
value upon each stack access for the detection of a stack overflow or underflow.
Figure 8. CPU block diagram (MAC unit not included)
16
512 Kbyte
Flash
memory
32
SP
STKOV
STKUN
Exec. Unit
Instr. Ptr
4-Stage
Pipeline
PSW
SYSCON
BUSCON 0
BUSCON 1
BUSCON 2
BUSCON 3
BUSCON 4
Data Pg. Ptrs
CPU
MDH
MDL
Mul./Div.-HW
Bit-Mask Gen.
ALU
16-Bit
Barrel-Shift
CP
ADDRSEL 1
ADDRSEL 2
ADDRSEL 3
ADDRSEL 4
Code Seg. Ptr.
R15
General
Purpose
Registers
R0
16
2Kbyte
Internal
RAM
Bank
n
Bank
i
Bank
0
50/182
Page 51

ST10F273M Central processing unit (CPU)
7.1 Multiplier-accumulator unit (MAC)
The MAC co-processor is a specialized co-processor added to the ST10 CPU Core in order
to improve the performances of the ST10 Family in signal processing algorithms.
The standard ST10 CPU has been modified to include new addressing capabilities which
enable the CPU to supply the new co-processor with up to 2 operands per instruction cycle.
This new co-processor (so-called MAC) contains a fast multiply-accumulate unit and a
repeat unit.
The co-processor instructions extend the ST10 CPU instruction set with multiply, multiplyaccumulate, 32-bit signed arithmetic operations.
Figure 9. MAC unit architecture
Operand 2Operand 1
16
GPR Pointers
IDX0 pointer
IDX1 pointer
QR0 GPR offset register
QR1 GPR offset register
QX0 IDX offset register
QX1 IDX offset register
(1)
Concatenation
16
16 x 16
signed/unsigned
multiplier
Interrupt
controller
ST10 CPU
1. Shared with standard ALU
MRW
Repeat unit
MCW
Control Unit
32 32
Mux
Sign Extend
Scaler
0h 0h08000h
40 40
MSW
Flags MAE
40
40
Mux
40
AB
40-bit signed arithmetic unit
40
MAH MAL
40
8-bit left/right
40
Mux
40
shifter
51/182
Page 52

Central processing unit (CPU) ST10F273M
7.2 Instruction set summary
Ta bl e 2 8 lists the instructions of the ST10F273M. The detailed description of each
instruction can be found in the ST10 Family Programming Manual.
Table 28. Standard instruction set summary
Mnemonic Description Bytes
ADD(B) Add word (byte) operands 2 / 4
ADDC(B) Add word (byte) operands with Carry 2 / 4
SUB(B) Subtract word (byte) operands 2 / 4
SUBC(B) Subtract word (byte) operands with Carry 2 / 4
MUL(U) (Un)Signed multiply direct GPR by direct GPR (16-/16-bit) 2
DIV(U) (Un)Signed divide register MDL by direct GPR (16-/16-bit) 2
DIVL(U) (Un)Signed long divide reg. MD by direct GPR (32-/16-bit) 2
CPL(B) Complement direct word (byte) GPR 2
NEG(B) Negate direct word (byte) GPR 2
AND(B) Bitwise AND, (word/byte operands) 2 / 4
OR(B) Bitwise OR, (word/byte operands) 2 / 4
XOR(B) Bitwise XOR, (word/byte operands) 2 / 4
BCLR Clear direct bit 2
BSET Set direct bit 2
BMOV(N) Move (negated) direct bit to direct bit 4
BAND, BOR, BXOR AND/OR/XOR direct bit with direct bit 4
BCMP Compare direct bit to direct bit 4
BFLDH/L
CMP(B) Compare word (byte) operands 2 / 4
CMPD1/2 Compare word data to GPR and decrement GPR by 1/2 2 / 4
CMPI1/2 Compare word data to GPR and increment GPR by 1/2 2 / 4
PRIOR
SHL / SHR Shift left/right direct word GPR 2
ROL / ROR Rotate left/right direct word GPR 2
ASHR Arithmetic (sign bit) shift right direct word GPR 2
MOV(B) Move word (byte) data 2 / 4
MOVBS Move byte operand to word operand with sign extension 2 / 4
Bitwise modify masked high/low byte of bit-addressable direct word
memory with immediate data
Determine number of shift cycles to normalize direct word GPR and
store result in direct word GPR
4
2
MOVBZ Move byte operand to word operand with zero extension 2 / 4
JMPA, JMPI, JMPR Jump absolute/indirect/relative if condition is met 4
JMPS Jump absolute to a code segment 4
52/182
Page 53

ST10F273M Central processing unit (CPU)
Table 28. Standard instruction set summary (continued)
Mnemonic Description Bytes
J(N)B Jump relative if direct bit is (not) set 4
JBC Jump relative and clear bit if direct bit is set 4
JNBS Jump relative and set bit if direct bit is not set 4
CALLA, CALLI,
CALLR
CALLS Call absolute subroutine in any code segment 4
PCALL
TRAP Call interrupt service routine via immediate trap number 2
PUSH, POP Push/pop direct word register onto/from system stack 2
Call absolute/indirect/relative subroutine if condition is met 4
Push direct word register onto system stack and call absolute
subroutine
4
SCXT
RET Return from intra-segment subroutine 2
RETS Return from inter-segment subroutine 2
RETP
RETI Return from interrupt service subroutine 2
SRST Software Reset 4
IDLE Enter Idle mode 4
PWRDN Enter Power-down mode (supposes NMI
SRVWDT Service Watchdog Timer 4
DISWDT Disable Watchdog Timer 4
EINIT Signify End-of-Initialization on RSTOUT-pin 4
ATOMIC Begin ATOMIC sequence 2
EXTR Begin EXTended Register sequence 2
EXTP(R) Begin EXTended Page (and Register) sequence 2 / 4
EXTS(R) Begin EXTended Segment (and Register) sequence 2 / 4
NOP Null operation 2
Push direct word register onto system stack and update register
with word operand
Return from intra-segment subroutine and pop direct word register
from system stack
-pin being low) 4
4
2
53/182
Page 54

Central processing unit (CPU) ST10F273M
7.3 MAC co-processor specific instructions
Ta bl e 2 9 lists the MAC instructions of the ST10F273M. The detailed description of each
instruction can be found in the ST10 Family Programming Manual. Note that all MAC
instructions are encoded on 4 bytes.
Table 29. MAC instruction set summary
Mnemonic Description
CoABS Absolute value of the accumulator
CoADD(2) Addition
CoASHR(rnd) Accumulator arithmetic shift right & optional round
CoCMP Compare accumulator with operands
CoLOAD(-,2) Load accumulator with operands
CoMAC(R,u,s,-,rnd) (Un)signed/(Un)Signed Multiply-Accumulate & Optional Round
CoMACM(R)(u,s,-,rnd)
CoMAX / CoMIN maximum / minimum of operands and accumulator
CoMOV Memory to memory move
CoMUL(u,s,-,rnd) (Un)signed/(Un)signed multiply & optional round
CoNEG(rnd) Negate accumulator & optional round
CoNOP No-operation
CoRND Round accumulator
CoSHL / CoSHR Accumulator logical shift left / right
CoSTORE Store a MAC unit register
CoSUB(2,R) Subtraction
(Un)Signed/(Un)signed multiply-accumulate with parallel data move
& optional round
54/182
Page 55

ST10F273M External bus controller
8 External bus controller
All of the external memory accesses are performed by the on-chip external bus controller.
The EBC can be programmed to single chip mode when no external memory is required, or
to one of four different external memory access modes:
● 16- / 18- / 20- / 24-bit addresses and 16-bit data, demultiplexed
● 16- / 18- / 20- / 24-bit addresses and 16-bit data, multiplexed
● 16- / 18- / 20- / 24-bit addresses and 8-bit data, multiplexed
● 16- / 18- / 20- / 24-bit addresses and 8-bit data, demultiplexed
In demultiplexed bus modes addresses are output on PORT1 and data is input / output on
PORT0 or P0L, respectively. In the multiplexed bus modes both addresses and data use
PORT0 for input / output.
Timing characteristics of the external bus interface (memory cycle time, memory tri-state
time, length of ALE and read / write delay) are programmable giving the choice of a wide
range of memories and external peripherals.
Up to four independent address windows may be defined (using register pairs ADDRSELx /
BUSCONx) to access different resources and bus characteristics.
These address windows are arranged hierarchically where BUSCON4 overrides BUSCON3
and BUSCON2 overrides BUSCON1.
All accesses to locations not covered by these four address windows are controlled by
BUSCON0. Up to five external CS
signals (four windows plus default) can be generated in
order to save external glue logic. Access to very slow memories is supported by a ‘Ready’
function.
A HOLD
/ HLDA protocol is available for bus arbitration which shares external resources
with other bus masters.
The bus arbitration is enabled by setting bit HLDEN in register PSW. After setting HLDEN
once, pins P6.7...P6.5 (BREQ
master mode (default after reset) the HLDA
slave mode is selected where pin HLDA
, HLDA, HOLD) are automatically controlled by the EBC. In
pin is an output. By setting bit DP6.7 to ‘1’ the
is switched to input. This directly connects the slave
controller to another master controller without glue logic.
For applications which require less external memory space, the address space can be
restricted to 1 Mbyte, 256 Kbytes or to 64 Kbytes. Port 4 outputs all eight address lines if an
address space of 16 Mbytes is used, otherwise four, two or no address lines.
Chip select timing can be made programmable. By default (after reset), the CSx
lines
change half a CPU clock cycle after the rising edge of ALE. With the CSCFG bit set in the
SYSCON register the CSx
lines change with the rising edge of ALE.
The active level of the READY pin can be set by bit RDYPOL in the BUSCONx registers.
When the READY function is enabled for a specific address window, each bus cycle within
the window must be terminated with the active level defined by bit RDYPOL in the
associated BUSCON register.
55/182
Page 56

Interrupt system ST10F273M
9 Interrupt system
The interrupt response time for internal program execution is from 125ns to 300ns at
40 MHz CPU clock.
The ST10F273M architecture supports several mechanisms for fast and flexible response to
service requests that can be generated from various sources (internal or external) to the
microcontroller. Any of these interrupt requests can be serviced by the Interrupt Controller or
by the Peripheral Event Controller (PEC).
In contrast to a standard interrupt service where the current program execution is
suspended and a branch to the interrupt vector table is performed, just one cycle is ‘stolen’
from the current CPU activity to perform a PEC service. A PEC service implies a single Byte
or Word data transfer between any two memory locations with an additional increment of
either the PEC source or destination pointer. An individual PEC transfer counter is implicitly
decremented for each PEC service except when performing in the continuous transfer
mode. When this counter reaches zero, a standard interrupt is performed to the
corresponding source related vector location. PEC services are very well suited to perform
the transmission or the reception of blocks of data. The ST10F273M has eight PEC
channels, each of them offers such fast interrupt-driven data transfer capabilities.
An interrupt control register which contains an interrupt request flag, an interrupt enable flag
and an interrupt priority bit-field is dedicated to each existing interrupt source. Thanks to its
related register, each source can be programmed to one of sixteen interrupt priority levels.
Once starting to be processed by the CPU, an interrupt service can only be interrupted by a
higher prioritized service request. For the standard interrupt processing, each of the
possible interrupt sources has a dedicated vector location.
Software interrupts are supported by means of the ‘TRAP’ instruction in combination with an
individual trap (interrupt) number.
Fast external interrupt inputs are provided to service external interrupts with high precision
requirements. These fast interrupt inputs feature programmable edge detection (rising edge,
falling edge or both edges).
Fast external interrupts may also have interrupt sources selected from other peripherals; for
example the CANx controller receive signals (CANx_RxD) and I
2
C serial clock signal can be
used to interrupt the system.
Ta bl e 3 0 shows all the available ST10F273M interrupt sources and the corresponding
hardware-related interrupt flags, vectors, vector locations and trap (interrupt) numbers.
Table 30. Interrupt sources
Source of interrupt or
PEC service request
CAPCOM Register 0 CC0IR CC0IE CC0INT 00’0040h 10h
CAPCOM Register 1 CC1IR CC1IE CC1INT 00’0044h 11h
CAPCOM Register 2 CC2IR CC2IE CC2INT 00’0048h 12h
CAPCOM Register 3 CC3IR CC3IE CC3INT 00’004Ch 13h
CAPCOM Register 4 CC4IR CC4IE CC4INT 00’0050h 14h
CAPCOM Register 5 CC5IR CC5IE CC5INT 00’0054h 15h
Request
flag
Enable
flag
Interrupt
vector
Vector
location
Trap
number
56/182
Page 57

ST10F273M Interrupt system
Table 30. Interrupt sources (continued)
Source of interrupt or
PEC service request
CAPCOM Register 6 CC6IR CC6IE CC6INT 00’0058h 16h
CAPCOM Register 7 CC7IR CC7IE CC7INT 00’005Ch 17h
CAPCOM Register 8 CC8IR CC8IE CC8INT 00’0060h 18h
CAPCOM Register 9 CC9IR CC9IE CC9INT 00’0064h 19h
CAPCOM Register 10 CC10IR CC10IE CC10INT 00’0068h 1Ah
CAPCOM Register 11 CC11IR CC11IE CC11INT 00’006Ch 1Bh
CAPCOM Register 12 CC12IR CC12IE CC12INT 00’0070h 1Ch
CAPCOM Register 13 CC13IR CC13IE CC13INT 00’0074h 1Dh
CAPCOM Register 14 CC14IR CC14IE CC14INT 00’0078h 1Eh
CAPCOM Register 15 CC15IR CC15IE CC15INT 00’007Ch 1Fh
CAPCOM Register 16 CC16IR CC16IE CC16INT 00’00C0h 30h
CAPCOM Register 17 CC17IR CC17IE CC17INT 00’00C4h 31h
CAPCOM Register 18 CC18IR CC18IE CC18INT 00’00C8h 32h
CAPCOM Register 19 CC19IR CC19IE CC19INT 00’00CCh 33h
CAPCOM Register 20 CC20IR CC20IE CC20INT 00’00D0h 34h
CAPCOM Register 21 CC21IR CC21IE CC21INT 00’00D4h 35h
CAPCOM Register 22 CC22IR CC22IE CC22INT 00’00D8h 36h
Request
flag
Enable
flag
Interrupt
vector
Vector
location
Trap
number
CAPCOM Register 23 CC23IR CC23IE CC23INT 00’00DCh 37h
CAPCOM Register 24 CC24IR CC24IE CC24INT 00’00E0h 38h
CAPCOM Register 25 CC25IR CC25IE CC25INT 00’00E4h 39h
CAPCOM Register 26 CC26IR CC26IE CC26INT 00’00E8h 3Ah
CAPCOM Register 27 CC27IR CC27IE CC27INT 00’00ECh 3Bh
CAPCOM Register 28 CC28IR CC28IE CC28INT 00’00F0h 3Ch
CAPCOM Register 29 CC29IR CC29IE CC29INT 00’0110h 44h
CAPCOM Register 30 CC30IR CC30IE CC30INT 00’0114h 45h
CAPCOM Register 31 CC31IR CC31IE CC31INT 00’0118h 46h
CAPCOM Timer 0 T0IR T0IE T0INT 00’0080h 20h
CAPCOM Timer 1 T1IR T1IE T1INT 00’0084h 21h
CAPCOM Timer 7 T7IR T7IE T7INT 00’00F4h 3Dh
CAPCOM Timer 8 T8IR T8IE T8INT 00’00F8h 3Eh
GPT1Timer 2 T2IR T2IE T2INT 00’0088h 22h
GPT1 Timer 3 T3IR T3IE T3INT 00’008Ch 23h
GPT1 Timer 4 T4IR T4IE T4INT 00’0090h 24h
GPT2Timer 5 T5IR T5IE T5INT 00’0094h 25h
57/182
Page 58
Interrupt system ST10F273M
Table 30. Interrupt sources (continued)
Source of interrupt or
PEC service request
GPT2 Timer 6 T6IR T6IE T6INT 00’0098h 26h
GPT2 CAPREL Register CRIR CRIE CRINT 00’009Ch 27h
A/D Conversion Complete ADCIR ADCIE ADCINT 00’00A0h 28h
A/D Overrun Error ADEIR ADEIE ADEINT 00’00A4h 29h
ASC0 Transmit S0TIR S0TIE S0TINT 00’00A8h 2Ah
ASC0 Transmit Buffer S0TBIR S0TBIE S0TBINT 00’011Ch 47h
ASC0 Receive S0RIR S0RIE S0RINT 00’00ACh 2Bh
ASC0 Error S0EIR S0EIE S0EINT 00’00B0h 2Ch
SSC Transmit SCTIR SCTIE SCTINT 00’00B4h 2Dh
SSC Receive SCRIR SCRIE SCRINT 00’00B8h 2Eh
SSC Error SCEIR SCEIE SCEINT 00’00BCh 2Fh
PWM Channel 0...3 PWMIR PWMIE PWMINT 00’00FCh 3Fh
See Section 9.1 XP0IR XP0IE XP0INT 00’0100h 40h
See Section 9.1 XP1IR XP1IE XP1INT 00’0104h 41h
See Section 9.1 XP2IR XP2IE XP2INT 00’0108h 42h
See Section 9.1 XP3IR XP3IE XP3INT 00’010Ch 43h
Request
flag
Enable
flag
Interrupt
vector
Vector
location
Trap
number
Hardware traps are exceptions or error conditions that arise during run-time. They cause
immediate non-maskable system reaction similar to a standard interrupt service (branching
to a dedicated vector table location).
The occurrence of a hardware trap is additionally signified by an individual bit in the trap flag
register (TFR). A hardware trap will interrupt any other program execution except when
another higher prioritized trap service is in progress. Hardware trap services cannot not be
interrupted by a standard interrupt or by PEC interrupts.
9.1 X-Peripheral interrupt
The limited number of X-Bus interrupt lines of the present ST10 architecture, imposes some
constraints on the implementation of the new functionality. In particular, the additional XPeripherals SSC1, ASC1, I
and PEC transfer capabilities. For this reason, a multiplexed structure for the interrupt
management is proposed. In the next Figure 10, the principle is explained through a simple
diagram, which shows the basic structure replicated for each of the four X-interrupt available
vectors (XP0INT, XP1INT, XP2INT and XP3INT).
It is based on a set of 16-bit registers XIRxSEL (x = 0,1,2,3), divided in two portions each:
● Byte High XIRxSEL[15:8] Interrupt Enable bits
● Byte Low XIRxSEL[7:0] Interrupt Flag bits
When different sources submit an interrupt request, the enable bits (Byte High of XIRxSEL
register) define a mask which controls which sources will be associated with the unique
2
C, PWM1 and RTC need some resources to implement interrupt
58/182
Page 59

ST10F273M Interrupt system
available vector. If more than one source is enabled to issue the request, the service routine
will have to take care to identify the real event to be serviced. This can easily be done by
checking the flag bits (Byte Low of XIRxSEL register). Note that the flag bits can also
provide information about events which are not currently serviced by the interrupt controller
(since masked through the enable bits), allowing an effective software management also in
absence of the possibility to serve the related interrupt request: a periodic polling of the flag
bits may be implemented inside the user application.
Figure 10. X-Interrupt basic structure
7
Flag[7:0]
IT Source 7
IT Source 6
IT Source 5
IT Source 4
IT Source 3
IT Source 2
IT Source 1
IT Source 0
0
XIRxSEL[7:0] (x = 0, 1, 2, 3)
XPxIC.XPxIR (x = 0, 1, 2, 3)
Enable[7:0]
15 8
XIRxSEL[15:8] (x = 0, 1, 2, 3)
Ta bl e 3 1 summarizes the mapping of the different interrupt sources which shares the four X-
interrupt vectors.
Table 31. X-Interrupt detailed mapping
Interrupt source XP0INT XP1INT XP2INT XP3INT
CAN1 Interrupt x x
CAN2 Interrupt x x
I2C Receive x x x
I2C Transmit x x x
I2C Error x
SSC1 Receive x x x
SSC1 Transmit x x x
SSC1 Error x
ASC1 Receive x x x
ASC1 Transmit x x x
ASC1 Transmit Buffer x x x
ASC1 Error x
PLL Unlock / OWD
PWM1 Channel 3...0
xx
x
59/182
Page 60

Interrupt system ST10F273M
9.2 Exception and error traps list
Ta bl e 3 2 shows all of the possible exceptions or error conditions that can arise during run-
time.
Table 32. Trap priorities
Exception condition
Trap
flag
Trap
vector
Vector
location
Trap
number
Trap
priority
Reset Functions:
Hardware Reset
Software Reset
Watchdog Timer Overflow
RESET
RESET
RESET
00’0000h
00’0000h
00’0000h
00h
00h
00h
III
III
III
Class A Hardware Traps:
Non-Maskable Interrupt
Stack Overflow
Stack Underflow
NMI
STKOF
STKUF
NMITRAP
STOTRAP
STUTRAP
00’0008h
00’0010h
00’0018h
02h
04h
06h
II
II
II
Class B Hardware Traps:
Undefined Opcode
MAC Interruption
Protected Instruction Fault
Illegal word Operand Access
Illegal Instruction Access
Illegal External Bus Access
UNDOPC
MACTRP
PRTFLT
ILLOPA
ILLINA
ILLBUS
BTRAP
BTRAP
BTRAP
BTRAP
BTRAP
BTRAP
00’0028h
00’0028h
00’0028h
00’0028h
00’0028h
00’0028h
0Ah
0Ah
0Ah
0Ah
0Ah
0Ah
I
I
I
I
I
I
Reserved [002Ch - 003Ch] [0Bh - 0Fh]
Software Traps
TRAP Instruction
1. - All the class B traps have the same trap number (and vector) and the same lower priority compared to the
class A traps and to the resets.
- Each class A trap has a dedicated trap number (and vector). They are prioritized in the second priority
level.
- The resets have the highest priority level and the same trap number.
- The PSW.ILVL CPU priority is forced to the highest level (15) when these exceptions are serviced.
Any
0000h – 01FCh
in steps of 4h
Any
[00h - 7Fh]
Current
CPU
Priority
(1)
60/182
Page 61

ST10F273M Capture / compare (CAPCOM) units
10 Capture / compare (CAPCOM) units
The ST10F273M has two 16-channel CAPCOM units which support generation and control
of timing sequences on up to 32 channels with a maximum resolution of 200ns at 40 MHz
CPU clock.
The CAPCOM units are typically used to handle high speed I/O tasks such as pulse and
waveform generation, pulse width modulation (PMW), digital to analog (D/A) conversion,
software timing, or time recording relative to external events.
Four 16-bit timers (T0/T1, T7/T8) with reload registers provide two independent time bases
for the capture/compare register array.
The input clock for the timers is programmable to several prescaled values of the internal
system clock, or may be derived from an overflow/underflow of timer T6 in module GPT2.
This provides a wide range of variation for the timer period and resolution and allows precise
adjustments to application specific requirements. In addition, external count inputs for
CAPCOM timers T0 and T7 allow event scheduling for the capture/compare registers
relative to external events.
Each of the two capture/compare register arrays contain 16 dual purpose capture/compare
registers, each of which may be individually allocated to either CAPCOM timer T0 or T1 (T7
or T8, respectively), and programmed for capture or compare functions. Each of the 32
registers has one associated port pin which serves as an input pin for triggering the capture
function, or as an output pin to indicate the occurrence of a compare event.
When a capture/compare register has been selected for capture mode, the current contents
of the allocated timer will be latched (captured) into the capture/compare register in
response to an external event at the port pin which is associated with this register. In
addition, a specific interrupt request for this capture/compare register is generated.
Either a positive, a negative, or both a positive and a negative external signal transition at
the pin can be selected as the triggering event. The contents of all registers which have
been selected for one of the five compare modes are continuously compared with the
contents of the allocated timers.
When a match occurs between the timer value and the value in a capture / compare
register, specific actions will be taken based on the selected compare mode.
The input frequencies f
, for the timer input selector Tx, are determined as a function of the
Tx
CPU clocks. The timer input frequencies, resolution and periods which result from the
selected prescaler option in TxI when using a 40 MHz CPU clock are listed in Tab le 3 4.
The numbers for the timer periods are based on a reload value of 0000h. Note that some
numbers may be rounded off to three significant figures.
Table 33. Compare modes
Compare modes Function
Mode 0 Interrupt-only compare mode; several compare interrupts per timer period are possible
Mode 1 Pin toggles on each compare match; several compare events per timer period are possible
Mode 2 Interrupt-only compare mode; only one compare interrupt per timer period is generated
61/182
Page 62

Capture / compare (CAPCOM) units ST10F273M
Table 33. Compare modes (continued)
Compare modes Function
Mode 3
Double Register mode
Table 34. CAPCOM timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz
Pin set ‘1’ on match; pin reset ‘0’ on compare time overflow; only one compare event per
timer period is generated
Two registers operate on one pin; pin toggles on each compare match; several compare
events per timer period are possible.
Timer input selection TxI
f
= 40 MHz
CPU
000b 001b 010b 011b 100b 101b 110b 111b
Prescaler for
f
CPU
8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024
Input frequency 5 MHz 2.5 MHz 1.25 MHz 625 kHz 312.5 kHz 156.25 kHz 78.125 kHz 39.1 kHz
Resolution 200ns 400ns 0.8µs 1.6µs 3.2µs 6.4µs 12.8µs 25.6µs
Period 13.1ms 26.2ms 52.4ms 104.8ms 209.7ms 419.4ms 838.9ms 1.678s
62/182
Page 63

ST10F273M General purpose timer unit
11 General purpose timer unit
The GPT unit is a flexible multifunctional timer/counter structure which is used for time
related tasks such as event timing and counting, pulse width and duty cycle measurements,
pulse generation, or pulse multiplication. The GPT unit contains five 16-bit timers organized
into two separate modules GPT1 and GPT2. Each timer in each module may operate
independently in several different modes, or may be concatenated with another timer of the
same module.
11.1 GPT1
Each of the three timers T2, T3, T4 of the GPT1 module can be configured individually for
one of four basic modes of operation: timer, gated timer, counter mode and incremental
interface mode.
In timer mode, the input clock for a timer is derived from the CPU clock, divided by a
programmable prescaler.
In counter mode, the timer is clocked in reference to external events.
Pulse width or duty cycle measurement is supported in gated timer mode where the
operation of a timer is controlled by the ‘gate’ level on an external input pin. For these
purposes, each timer has one associated port pin (TxIN) which serves as gate or clock
input.
Ta bl e 3 5 lists the timer input frequencies, resolution and periods for each prescaler option at
40 MHz CPU clock.
In Incremental Interface mode, the GPT1 timers (T2, T3, T4) can be directly connected to
the incremental position sensor signals A and B by their respective inputs TxIN and TxEUD.
Direction and count signals are internally derived from these two input signals so that the
contents of the respective timer Tx corresponds to the sensor position. The third position
sensor signal TOP0 can be connected to an interrupt input.
Timer T3 has output toggle latches (TxOTL) which changes state on each timer over flow /
underflow. The state of this latch may be output on port pins (TxOUT) for time out monitoring
of external hardware components, or may be used internally to clock timers T2 and T4 for
high resolution of long duration measurements.
In addition to their basic operating modes, timers T2 and T4 may be configured as reload or
capture registers for timer T3.
Table 35. GPT1 timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz
f
CPU
Prescaler factor 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024
Input frequency 5 MHz 2.5 MHz 1.25 MHz 625 kHz 312.5 kHz 156.25 kHz 78.125 kHz 39.1 kHz
Resolution 200ns 400ns 0.8µs 1.6µs 3.2µs 6.4µs 12.8µs 25.6µs
Timer input selection T2I / T3I / T4I
= 40 MHz
000b 001b 010b 011b 100b 101b 110b 111b
Period maximum 13.1ms 26.2ms 52.4ms 104.8ms 209.7ms 419.4ms 838.9ms 1.678s
63/182
Page 64

General purpose timer unit ST10F273M
Figure 11. Block diagram of GPT1
T2EUD
CPU clock
T2IN
CPU clock
T3IN
T3EUD
T4IN
CPU clock
T4EUD
2n n=3...10
n
n=3...10
2
n
2
n=3...10
T2
mode
control
T3
mode
control
T4
mode
control
Reload
Capture
Capture
Reload
U/D
GPT1 timer T2
GPT1 timer T3
U/D
GPT1 timer T4
U/D
T3OTL
Interrupt
request
T3OUT
Interrupt
request
Interrupt
request
64/182
Page 65

ST10F273M General purpose timer unit
11.2 GPT2
The GPT2 module provides precise event control and time measurement. It includes two
timers (T5, T6) and a capture/reload register (CAPREL). Both timers can be clocked with an
input clock which is derived from the CPU clock via a programmable prescaler or with
external signals. The count direction (up/down) for each timer is programmable by software
or may additionally be altered dynamically by an external signal on a port pin (TxEUD).
Concatenation of the timers is supported via the output toggle latch (T6OTL) of timer T6
which changes its state on each timer overflow/underflow.
The state of this latch may be used to clock timer T5, or it may be output on a port pin
(T6OUT). The overflow / underflow of timer T6 can additionally be used to clock the
CAPCOM timers T0 or T1, and to cause a reload from the CAPREL register. The CAPREL
register may capture the contents of timer T5 based on an external signal transition on the
corresponding port pin (CAPIN), and timer T5 may optionally be cleared after the capture
procedure. This allows absolute time differences to be measured or pulse multiplication to
be performed without software overhead.
The capture trigger (timer T5 to CAPREL) may also be generated upon transitions of GPT1
timer T3 inputs T3IN and/or T3EUD. This is advantageous when T3 operates in Incremental
Interface mode.
Ta bl e 3 6 lists the timer input frequencies, resolution and periods for each prescaler option at
40 MHz CPU clock.
Table 36. GPT2 timer input frequencies, resolutions and periods at 40 MHz
Timer Input Selection T5I / T6I
f
= 40 MHz
CPU
Prescaler factor 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512
Input frequency 10 MHz 5 MHz 2.5 MHz 1.25 MHz 625 kHz 312.5 kHz 156.25 kHz 78.125 kHz
Resolution 100ns 200ns 400ns 0.8µs 1.6µs 3.2µs 6.4µs 12.8µs
Period maximum 6.55ms 13.1ms 26.2ms 52.4ms 104.8ms 209.7ms 419.4ms 838.9ms
000b 001b 010b 011b 100b 101b 110b 111b
65/182
Page 66

General purpose timer unit ST10F273M
Figure 12. Block diagram of GPT2
T5EUD
CPU clock
T5IN
CAPIN
T6IN
CPU clock
T6EUD
2n n=2...9
n
2
n=2...9
T5
mode
control
T6
mode
control
Clear
Capture
U/D
GPT2 timer T5
GPT2 CAPREL
GPT2 timer T6
U/D
Reload
Toggle FF
T60TL
Interrupt
request
Interrupt
request
Interrupt
request
T6OUT
to CAPCOM
timers
66/182
Page 67

ST10F273M PWM modules
12 PWM modules
Two pulse width modulation modules are available on ST10F273M: standard PWM0 and
XBUS PWM1. They can generate up to four PWM output signals each, using edge-aligned
or center-aligned PWM. In addition, the PWM modules can generate PWM burst signals and
single shot outputs. Tab l e 3 7 shows the PWM frequencies for different resolutions. The level
of the output signals is selectable and the PWM modules can generate interrupt requests.
Figure 13. Block diagram of PWM module
PPx period register *
*
Match
Match
Output control
Up/down/
clear control
Write control
Enable
POUTx
Comparator
Clock 1
Clock 2
* User readable / writeable register
Table 37. PWM unit frequencies and resolutions at 40 MHz CPU clock
Input
control
Run
PWx pulse width register *
PTx
16-bit up/down counter
Comparator
Shadow register
Mode 0 Resolution 8-bit 10-bit12-bit14-bit16-bit
CPU Clock/1 25ns 156.25 kHz 39.1 kHz 9.77 kHz 2.44 Hz 610 Hz
CPU Clock/64 1.6µs 2.44 kHz 610 Hz 152.6 Hz 38.15 Hz 9.54 Hz
Mode 1 Resolution 8-bit 10-bit12-bit14-bit16-bit
CPU Clock/1 25ns 78.12 kHz 19.53 kHz 4.88 kHz 1.22 kHz 305.2 Hz
CPU Clock/64 1.6µs 1.22 kHz 305.17Hz 76.29 Hz 19.07 Hz 4.77 Hz
67/182
Page 68

Parallel ports ST10F273M
13 Parallel ports
13.1 Introduction
The ST10F273M MCU provides up to 111 I/O lines with programmable features. These
capabilities permit this MCU to be adapted to a wide range of applications.
The ST10F273M I/O lines are organized in nine groups:
● Port 0 is a two time 8-bit port named P0L (low as less significant byte) and P0H (high
as most significant byte)
● Port 1 is a two time 8-bit port named P1L and P1H
● Port 2 is a 16-bit port
● Port 3 is a 15-bit port (P3.14 line is not implemented)
● Port 4 is an 8-bit port
● Port 5 is a 16-bit port input only
● Port 6, Port 7 and Port 8 are 8-bit ports
These ports may be used as general purpose bidirectional input or output, software
controlled with dedicated registers.
For example, the output drivers of six of the ports (2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8) can be configured
(bitwise) for push-pull or open drain operation using ODPx registers.
The input threshold levels are programmable (TTL/CMOS) for all the ports. The logic level of
a pin is clocked into the input latch once per state time, regardless whether the port is
configured for input or output. The threshold is selected with PICON and XPICON registers
control bits.
A write operation to a port pin configured as an input causes the value to be written into the
port output latch, while a read operation returns the latched state of the pin itself. A readmodify-write operation reads the value of the pin, modifies it, and writes it back to the output
latch.
Writing to a pin configured as an output (DPx.y = ‘1’) causes the output latch and the pin to
have the written value, since the output buffer is enabled. Reading this pin returns the value
of the output latch. A read-modify-write operation reads the value of the output latch,
modifies it, and writes it back to the output latch, thus also modifying the level at the pin.
I/O lines support an alternate function which is detailed in the following description of each
port.
13.2 I/O’s special features
13.2.1 Open drain mode
Some of the I/O ports of ST10F273M support the open drain capability. This programmable
feature may be used with an external pull-up resistor, in order to get an AND wired logical
function.
This feature is implemented for ports P2, P3, P4, P6, P7 and P8 (see respective sections)
and is controlled through the respective Open Drain Control Registers ODPx.
68/182
Page 69

ST10F273M Parallel ports
13.2.2 Input threshold control
The standard inputs of the ST10F273M determine the status of input signals according to
TTL levels. In order to accept and recognize noisy signals, CMOS input thresholds can be
selected instead of the standard TTL thresholds for all the pins. These CMOS thresholds
are defined above the TTL thresholds and feature a higher hysteresis to prevent the inputs
from toggling while the respective input signal level is near the thresholds.
The Port Input Control registers PICON and XPICON are used to select these thresholds for
each byte of the indicated ports, this means the 8-bit ports P0L, P0H, P1L, P1H, P4, P7 and
P8 are controlled by one bit each while ports P2, P3 and P5 are controlled by two bits each.
All options for individual direction and output mode control are available for each pin,
independent of the selected input threshold.
13.3 Alternate port functions
Each port line has one associated programmable alternate input or output function.
● PORT0 and PORT1 may be used as address and data lines when accessing external
memory. Additionally, PORT1 provides:
– Input capture lines
– 8 additional analog input channels to the A/D converter
● Port 2, Port 7 and Port 8 are associated with the capture inputs or compare outputs of
the CAPCOM units and/or with the outputs of the PWM0 module, of the PWM1 module
and of the ASC1.
Port 2 is also used for fast external interrupt inputs and for timer 7 input.
● Port 3 includes the alternate functions of timers, serial interfaces, the optional bus
control signal BHE
● Port 4 outputs the additional segment address bit A23...A16 in systems where more
than 64 Kbytes of memory are to be access directly. In addition, CAN1, CAN2 and I
lines are provided.
● Port 5 is used as analog input channels of the A/D converter or as timer control signals.
● Port 6 provides optional bus arbitration signals (BREQ, HLDA, HOLD) and chip select
signals and the SSC1 lines.
and the system clock output (CLKOUT).
2
C
If the alternate output function of a pin is to be used, the direction of this pin must be
programmed for output (DPx.y = ‘1’), except for some signals that are used directly after
reset and are configured automatically. Otherwise the pin remains in the high-impedance
state and is not effected by the alternate output function. The respective port latch should
hold a ‘1’, because its output is ANDed with the alternate output data (except for PWM
output signals).
If the alternate input function of a pin is used, the direction of the pin must be programmed
for input (DPx.y = ‘0’) if an external device is driving the pin. The input direction is the default
after reset. If no external device is connected to the pin, however, the direction for this pin
can also be set to output. In this case, the pin reflects the state of the port output latch.
Thus, the alternate input function reads the value stored in the port output latch. This can be
used for testing purposes to allow a software trigger of an alternate input function by writing
to the port output latch.
On most of the port lines, the user software is responsible for setting the proper direction
when using an alternate input or output function of a pin.
69/182
Page 70

Parallel ports ST10F273M
This is done by setting or clearing the direction control bit DPx.y of the pin before enabling
the alternate function.
There are port lines, however, where the direction of the port line is switched automatically.
For instance, in the multiplexed external bus modes of PORT0, the direction must be
switched several times for an instruction fetch in order to output the addresses and to input
the data.
Obviously, this cannot be done through instructions. In these cases, the direction of the port
line is switched automatically by hardware if the alternate function of such a pin is enabled.
To determine the appropriate level of the port output latches, check how the alternate data
output is combined with the respective port latch output.
There is one basic structure for all port lines with only an alternate input function. Port lines
with only an alternate output function, however, have different structures due to the way the
direction of the pin is switched and depending on whether the pin is accessible by the user
software or not in the alternate function mode.
All port lines that are not used for these alternate functions may be used as general purpose
I/O lines.
70/182
Page 71

ST10F273M A/D converter
14 A/D converter
A 10-bit A/D converter with 24 multiplexed input channels and a sample and hold circuit is
integrated on-chip. An automatic self-calibration adjusts the A/D converter module to
process parameter variations at each reset event. The sample time (for loading the
capacitors) and the conversion time is programmable and can be adjusted to the external
circuitry.
The ST10F273M has 16 + 8 multiplexed input channels on Port 5 and Port 1 respectively.
The selection between Port 5 and Port 1 is made via a bit in an XBus register. Refer to the
User Manual for a detailed description.
A different accuracy is guaranteed (Total Unadjusted Error) on Port 5 and Port 1 analog
channels (with higher restrictions when overload conditions occur); in particular, Port 5
channels are more accurate than the Port 1 channels. Refer to Section 24: Electrical
characteristics for details.
The A/D converter input bandwidth is limited by the achievable accuracy: Supposing a
maximum error of 0.5LSB (2mV) impacting the global TUE (TUE depends also on other
causes), in worst case of temperature and process, the maximum frequency for a sine wave
analog signal is around 7.5 kHz. Of course, to reduce the effect of the input signal variation
on the accuracy down to 0.05LSB, the maximum input frequency of the sine wave must be
reduced to 800 Hz.
If a static signal is applied during the sampling phase, a series resistance shall not be
greater than 20kΩ (this taking into account eventual input leakage). It is suggested to not
connect any capacitance on analog input pins, in order to reduce the effect of charge
partitioning (and consequent voltage drop error) between the external and the internal
capacitance: In case an RC filter is necessary, the external capacitance must be greater
than 10nF to minimize the accuracy impact.
Overrun error detection / protection is controlled by the ADDAT register. Either an interrupt
request is generated when the result of a previous conversion has not been read from the
result register at the time the next conversion is complete, or the next conversion is
suspended until the previous result has been read. For applications which require less than
16+8 analog input channels, the rning channel inputs can be used as digital input port pins.
The A/D converter of the ST10F273M supports different conversion modes:
● Single channel single conversion: The analog level of the selected channel is
sampled once and converted. The result of the conversion is stored in the ADDAT
register.
● Single channel continuous conversion: The analog level of the selected channel is
repeatedly sampled and converted. The result of the conversion is stored in the ADDAT
register.
● Auto scan single conversion: The analog level of the selected channels are sampled
once and converted. After each conversion the result is stored in the ADDAT register.
The data can be transferred to the RAM by interrupt software management or using the
powerful Peripheral Event Controller (PEC) data transfer.
● Auto scan continuous conversion: The analog level of the selected channels are
repeatedly sampled and converted. The result of the conversion is stored in the ADDAT
71/182
Page 72

A/D converter ST10F273M
register. The data can be transferred to the RAM by interrupt software management or
using the PEC data transfer.
● Wait for ADDAT read mode: When using continuous modes, in order to avoid to
overwrite the result of the current conversion by the next one, the ADWR bit of ADCON
control register must be activated. Then, until the ADDAT register is read, the new
result is stored in a temporary buffer and the conversion is on hold.
● Channel injection mode: When using continuous modes, a selected channel can be
converted in between without changing the current operating mode. The 10-bit data of
the conversion are stored in ADRES field of ADDAT2. The current continuous mode
remains active after the single conversion is completed.
A full calibration sequence is performed after a reset. This full calibration lasts up to 40630
CPU clock cycles. During this time, the busy flag ADBSY is set to indicate the operation. It
compensates the capacitance mismatch, so the calibration procedure does not need any
update during normal operation.
No conversion can be performed during this time: The bit ADBSY shall be polled to verify
when the calibration is over, and the module is able to start a conversion.
72/182
Page 73

ST10F273M Serial channels
15 Serial channels
Serial communication with other microcontrollers, microprocessors, terminals or external
peripheral components is provided by up to four serial interfaces: two asynchronous /
synchronous serial channels (ASC0 and ASC1) and two high-speed synchronous serial
channel (SSC0 and SSC1). Dedicated baudrate generators set up all standard baudrates
without the requirement of oscillator tuning. For transmission, reception and erroneous
reception, separate interrupt vectors are provided for ASC0 and SSC0 serial channel. A
more complex mechanism of interrupt sources multiplexing is implemented for ASC1 and
SSC1 (XBUS mapped).
15.1 Asynchronous / synchronous serial interfaces
The asynchronous / synchronous serial interfaces (ASC0 and ASC1) provides serial
communication between the ST10F273M and other microcontrollers, microprocessors or
external peripherals.
15.2 ASCx in asynchronous mode
In asynchronous mode, 8- or 9-bit data transfer, parity generation and the number of stop
bits can be selected. Parity framing and overrun error detection is provided to increase the
reliability of data transfers. Transmission and reception of data is double-buffered. Fullduplex communication up to 1.25 Mbaud (at 40 MHz of f
Table 38. ASC asynchronous baudrates by reload value and deviation errors
Baudrate (baud) Deviation error
1 250 000 0.0% / 0.0% 0000 / 0000 833 333 0.0% / 0.0% 0000 / 0000
112 000 +1.5% / -7.0% 000A / 000B 112 000 +6.3% / -7.0% 0006 / 0007
S0BRS = ‘0’, f
56 000 +1.5% / -3.0% 0015 / 0016 56 000 +6.3% / -0.8% 000D / 000E
38 400 +1.7% / -1.4% 001F / 0020 38 400 +3.3% / -1.4% 0014 / 0015
19 200 +0.2% / -1.4% 0040 / 0041 19 200 +0.9% / -1.4% 002A / 002B
9 600 +0.2% / -0.6% 0081 / 0082 9 600 +0.9% / -0.2% 0055 / 0056
4 800 +0.2% / -0.2% 0103 / 0104 4 800 +0.4% / -0.2% 00AC / 00AD
2 400 +0.2% / 0.0% 0207 / 0208 2 400 +0.1% / -0.2% 015A / 015B
1 200 0.1% / 0.0% 0410 / 0411 1 200 +0.1% / -0.1% 02B5 / 02B6
600 0.0% / 0.0% 0822 / 0823 600 +0.1% / 0.0% 056B / 056C
= 40 MHz S0BRS = ‘1’, f
CPU
Reload value
(hex)
Baudrate (baud) Deviation error
) is supported in this mode.
CPU
= 40 MHz
CPU
Reload value
(hex)
300 0.0% / 0.0% 1045 / 1046 300 0.0% / 0.0% 0AD8 / 0AD9
153 0.0% / 0.0% 1FE8 / 1FE9 102 0.0% / 0.0% 1FE8 / 1FE9
Note: The deviation errors given in the Ta bl e 3 8 are rounded off. To avoid deviation errors use a
baudrate crystal (providing a multiple of the ASC0 sampling frequency).
73/182
Page 74

Serial channels ST10F273M
15.3 ASCx in synchronous mode
In synchronous mode, data is transmitted or received synchronously to a shift clock which is
generated by the ST10F273M. Half-duplex communication up to 5 Mbaud (at 40 MHz of
f
) is possible in this mode.
CPU
Table 39. ASC synchronous baudrates by reload value and deviation errors
S0BRS = ‘0’, f
Baudrate (baud) Deviation error
5 000 000 0.0% / 0.0% 0000 / 0000 3 333 333 0.0% / 0.0% 0000 / 0000
112 000 +1.5% / -0.8% 002B / 002C 112 000 +2.6% / -0.8% 001C / 001D
56 000 +0.3% / -0.8% 0058 / 0059 56 000 +0.9% / -0.8% 003A / 003B
38 400 +0.2% / -0.6% 0081 / 0082 38 400 +0.9% / -0.2% 0055 / 0056
19 200 +0.2% / -0.2% 0103 / 0104 19 200 +0.4% / -0.2% 00AC / 00AD
9 600 +0.2% / 0.0% 0207 / 0208 9 600 +0.1% / -0.2% 015A / 015B
4 800 +0.1% / 0.0% 0410 / 0411 4 800 +0.1% / -0.1% 02B5 / 02B6
2 400 0.0% / 0.0% 0822 / 0823 2 400 +0.1% / 0.0% 056B / 056C
1 200 0.0% / 0.0% 1045 / 1046 1 200 0.0% / 0.0% 0AD8 / 0AD9
900 0.0% / 0.0% 15B2 / 15B3 600 0.0% / 0.0% 15B2 / 15B3
612 0.0% / 0.0% 1FE8 / 1FE9 407 0.0% / 0.0% 1FFD / 1FFE
= 40 MHz S0BRS = ‘1’, f
CPU
Reload value
(hex)
Baudrate (baud) Deviation error
= 40 MHz
CPU
Reload value
(hex)
Note: The deviation errors given in the are rounded off. To avoid deviation errors use a baudrate
crystal (providing a multiple of the ASC0 sampling frequency).
15.4 High speed synchronous serial interfaces
The High-Speed Synchronous Serial Interfaces (SSC0 and SSC1) provides flexible highspeed serial communication between the ST10F273M and other microcontrollers,
microprocessors or external peripherals.
The SSCx supports full-duplex and half-duplex synchronous communication. The serial
clock signal can be generated by the SSCx itself (master mode) or be received from an
external master (slave mode). Data width, shift direction, clock polarity and phase are
programmable.
This allows communication with SPI-compatible devices. Transmission and reception of data
is double-buffered. A 16-bit baudrate generator provides the SSCx with a separate serial
clock signal. The serial channel SSCx has its own dedicated 16-bit baudrate generator with
16-bit reload capability, allowing baudrate generation independent from the timers.
Ta bl e 4 0 lists some possible baudrates against the required reload values and the resulting
bit times for the 40 MHz CPU clock. The maximum is limited to 8 Mbaud.
74/182
Page 75

ST10F273M Serial channels
Table 40. SSC synchronous baudrate and reload values
Baudrate for f
= 40 MHz Bit time Reload value
CPU
Reserved - 0000h
Can be used only with f
= 32 MHz (or lower) - 0001h
CPU
6.6 Mbaud 150ns 0002h
5 Mbaud 200ns 0003h
2.5 Mbaud 400ns 0007h
1 Mbaud 1µs 0013h
100 Kbaud 10µs 00C7h
10 Kbaud 100µs 07CFh
1 Kbaud 1ms 4E1Fh
306 baud 3.26ms FF4Eh
75/182
Page 76

I2C interface ST10F273M
16 I2C interface
The integrated I2C Bus Module handles the transmission and reception of frames over the
two-line SDA/SCL in accordance with the I
2
C Bus specification. The I2C Module can
operate in slave mode, in master mode or in multi-master mode. It can receive and transmit
data using 7-bit or 10-bit addressing. Data can be transferred at speeds up to 400 Kbit/s
(both Standard and Fast I
2
C bus modes are supported).
The module can generate three different types of interrupt:
● requests related to bus events, such as start or stop events, or arbitration lost
● requests related to data transmission
● requests related to data reception
These requests are issued to the interrupt controller by three different lines, and identified as
Error, Transmit, and Receive interrupt lines.
When the I
2
C module is enabled by setting bit XI2CEN in XPERCON register, pins P4.4 and
P4.7 (where SCL and SDA are respectively mapped as alternate functions) are
automatically configured as bidirectional open-drain: the value of the external pull-up
resistor depends on the application. P4, DP4 and ODP4 cannot influence the pin
configuration.
When the I
2
C cell is disabled (clearing bit XI2CEN), P4.4 and P4.7 pins are standard I/ O
controlled by P4, DP4 and ODP4.
The speed of the I
2
Fast I
C mode (100 to 400 kHz).
2
C interface can be selected between Standard mode (0 to 100 kHz) and
76/182
Page 77

ST10F273M CAN modules
17 CAN modules
The two integrated CAN modules (CAN1 and CAN2) are identical and handle the
completely autonomous transmission and reception of CAN frames according to the CAN
specification V2.0 part B (active). It is based on the C-CAN specification.
Each on-chip CAN module can receive and transmit standard frames with 11-bit identifiers
as well as extended frames with 29-bit identifiers.
Because of duplication of the CAN controllers, the following adjustments are to be
considered:
● Same internal register addresses of both CAN controllers, but with base addresses
differing in address bit A8; separate chip select for each CAN module. Refer to
Section 4: Memory organization on page 21.
● The CAN1 transmit line (CAN1_TxD) is the alternate function of the Port P4.6 pin and
the receive line (CAN1_RxD) is the alternate function of the Port P4.5 pin.
● The CAN2 transmit line (CAN2_TxD) is the alternate function of the Port P4.7 pin and
the receive line (CAN2_RxD) is the alternate function of the Port P4.4 pin.
● Interrupt request lines of the CAN1 and CAN2 modules are connected to the XBUS
interrupt lines together with other X-Peripherals sharing the four vectors.
● The CAN modules must be selected with corresponding CANxEN bit of XPERCON
register before the bit XPEN of SYSCON register is set.
● The reset default configuration is: CAN1 enabled, CAN2 disabled.
Note: If one or both CAN modules is used, Port 4 cannot be programmed to output all eight
segment address lines. Thus, only four segment address lines can be used, reducing the
external memory space to 5 Mbytes (1 Mbyte per CS
line).
17.1 Configuration support
It is possible that both CAN controllers are working on the same CAN bus, supporting
together up to 64 message objects. In this configuration, both receive signals and both
transmit signals are linked together when using the same CAN transceiver. This
configuration is especially supported by providing open drain outputs for the CAN1_Txd and
CAN2_TxD signals. The open drain function is controlled with the ODP4 register for port P4:
in this way it is possible to connect together P4.4 with P4.5 (receive lines) and P4.6 with
P4.7 (transmit lines configured to be configured as Open-Drain).
The user may also map internally both CAN modules on the same pins P4.5 and P4.6. In
this way, P4.4 and P4.7 can be used either as general purpose I/O lines, or used for I
interface. This is possible by setting bit CANPAR of the XMISC register. To access this
register it is necessary to set bit XMISCEN of the XPERCON register and bit XPEN of the
SYSCON register.
17.2 CAN bus configurations
Depending on the application, CAN bus configuration may be one single bus with a single or
multiple interfaces or a multiple bus with a single or multiple interfaces. The ST10F273M can
support both configurations.
2
C
77/182
Page 78

CAN modules ST10F273M
17.2.1 Single CAN bus
The single CAN bus multiple interfaces configuration may be implemented using two CAN
transceivers as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14. Connection to single CAN bus via separate CAN transceivers
XMISC.CANPAR = 0
CAN_H
CAN_L
CAN1
RX TX
CAN CAN
CAN bus
CAN2
RX TX
P4.4 P4.7P4.5 P4.6
transceivertransceiver
The ST10F273M also supports single CAN bus multiple (dual) interfaces using the open
drain option of the CANx_TxD output as shown in Figure 15. Thanks to the OR-Wired
Connection, only one transceiver is required. In this case the design of the application must
take in account the wire length and the noise environment.
Figure 15. Connection to single CAN bus via common CAN transceivers
XMISC.CANPAR = 0
2.7kW
CAN1
RX TX
+5V
OD
CAN2
RX TX
P4.4 P4.7P4.5 P4.6
OD
CAN
transceiver
CAN_H
CAN_L
78/182
CAN bus
OD = Open Drain Output
Page 79

ST10F273M CAN modules
17.2.2 Multiple CAN bus
The ST10F273M provides two CAN interfaces to support such kind of bus configuration as
shown in Figure 16.
Figure 16. Connection to two different CAN buses (for example for gateway
application)
XMISC.CANPAR = 0
CAN1
RX TX
CAN CAN
CAN2
RX TX
P4.4 P4.7P4.5 P4.6
transceivertransceiver
CAN_H
17.2.3 Parallel mode
In addition to previous configurations, a parallel mode is supported. This is shown in
Figure 17.
Figure 17. Connection to one CAN bus with internal parallel mode enabled
CAN_L
RX TX
P4.5 P4.6
CAN bus 1
CAN1
CAN
transceiver
CAN bus 2
CAN2
RX TX
(1)
P4.4
P4.7
CAN_H
CAN_L
XMISC.CANPAR = 1
(Both CAN enabled)
(1)
CAN_H
CAN_L
1. P4.4 and P4.7 when not used as CAN functions can be used as general purpose I/O while they cannot be
used as external bus address lines.
CAN bus
79/182
Page 80

Real time clock ST10F273M
18 Real time clock
The Real Time Clock is an independent timer, in which the clock is derived directly from the
clock oscillator on XTAL1 (main oscillator) input or XTAL3 input (32 kHz low-power oscillator)
so that it can continue running even in Idle or Power-down modes (if so enabled). Registers
access is implemented onto the XBUS. This module is designed with the following
characteristics:
● generation of the current time and date for the system
● cyclic time based interrupt, on Port2 external interrupts every “RTC basic clock tick”
and after n ’RTC basic clock ticks’ (n is programmable) if enabled
● 58-bit timer for long term measurement
● capability to exit the ST10 chip from Power-down mode (if PWDCFG of SYSCON set)
after a programmed delay
The real time clock is based on two main blocks of counters. The first block is a prescaler
which generates a basic reference clock (for example, a 1 second period). This basic
reference clock is provided by the 20-bit DIVIDER. This 20-bit counter is driven by an input
clock derived from the on-chip CPU clock, predivided by a 1/64 fixed counter. This 20-bit
counter is loaded at each basic reference clock period with the value of the 20-bit
PRESCALER register. The value of the 20-bit RTCP register determines the period of the
basic reference clock.
A timed interrupt request (RTCSI) may be sent on each basic reference clock period. The
second block of the RTC is a 32-bit counter that may be initialized with the current system
time. This counter is driven with the basic reference clock signal. In order to provide an
alarm function the contents of the counter is compared with a 32-bit alarm register. The
alarm register may be loaded with a reference date. An alarm interrupt request (RTCAI),
may be generated when the value of the counter matches the alarm register.
The timed RTCSI and the alarm RTCAI interrupt requests can trigger a fast external
interrupt via the EXISEL register of port 2 and wake up the ST10 chip when running powerdown mode. Using the RTCOFF bit of the RTCCON register, the user may switch off the
clock oscillator when entering the power-down mode.
The last function implemented in the RTC is to switch off the main on-chip oscillator and the
32 kHz on chip oscillator if the ST10 enters the Power-down mode, so that the chip can be
fully switched off (if RTC is disabled).
At power-on, and after Reset phase, if the presence of a 32 kHz oscillation on XTAL3 /
XTAL4 pins is detected, then the RTC counter is driven by this low frequency reference
clock: when Power-down mode is entered, the RTC can either be stopped or left running,
and in both the cases the main oscillator is turned off, reducing the power consumption of
the device to the minimum required to keep on running the RTC counter and relative
reference oscillator. This is also valid if Standby mode is entered (switching off the main
supply V
V
STBY
), since both the RTC and the low power oscillator (32 kHz) are biased by the
DD
. Vice versa, when at power on and after Reset, the 32 kHz is not present, the main
oscillator drives the RTC counter, and since it is powered by the main power supply, it
cannot be maintained running in Standby mode, while in Power-down mode the main
oscillator is maintained running to provide the reference to the RTC module (if not disabled).
80/182
Page 81

ST10F273M Watchdog timer
19 Watchdog timer
The Watchdog Timer is a fail-safe mechanism which prevents the microcontroller from
malfunctioning for long periods of time.
The Watchdog Timer is always enabled after a reset of the chip and can only be disabled in
the time interval until the EINIT (end of initialization) instruction has been executed.
Therefore, the chip start-up procedure is always monitored. The software must be designed
to service the watchdog timer before it overflows. If, due to hardware or software related
failures, the software fails to do so, the watchdog timer overflows and generates an internal
hardware reset. It pulls the RSTOUT
to be reset.
Each of the different reset sources is indicated in the WDTCON register:
● Watchdog Timer Reset in case of an overflow
● Software Reset in case of execution of the SRST instruction
● Short,Long and Power-On Reset in case of hardware reset (and depending of reset
pulse duration and RPD pin configuration)
The indicated bits are cleared with the EINIT instruction. The source of the reset can be
identified during the initialization phase.
pin low in order to allow external hardware components
The Watchdog Timer is 16-bit, clocked with the system clock divided by 2 or 128. The high
byte of the watchdog timer register can be set to a prespecified reload value (stored in
WDTREL).
Each time it is serviced by the application software, the high byte of the watchdog timer is
reloaded. For security, rewrite WDTCON each time before the watchdog timer is serviced
Ta bl e 4 1 shows the watchdog time range for 40 MHz CPU clock.
Table 41. WDTREL reload value
Prescaler for f
Reload value in WDTREL
2 (WDTIN = ‘0’) 128 (WDTIN = ‘1’)
FFh 12.8µs 819.2µs
00h 3.277ms 209.7ms
= 40 MHz
CPU
81/182
Page 82

System reset ST10F273M
20 System reset
System reset initializes the MCU in a predefined state. There are six ways to activate a reset
state. The system start-up configuration is different for each case as shown in Tab le 4 2 .
Table 42. Reset event definition
Reset source Flag
Power-on reset PONR Low Power-on
Asynchronous hardware reset
Synchronous long hardware
reset
Synchronous short hardware
reset
Watchdog timer reset WDTR
Software reset SWR
1. RSTIN pulse should be longer than 500ns (Filter) and than settling time for configuration of Port0.
2. See next Section 20.1 for more details on minimum reset pulse duration
3. The RPD status has no influence unless Bidirectional Reset is activated (bit BDRSTEN in SYSCON): RPD
low inhibits the Bidirectional reset on SW and WDT reset events, that is RSTIN is not activated (refer to
Sections 20.4, 20.5 and 20.6).
LHWR
SHWR High
RPD
status
Low t
High t
(2)
(3)
Conditions
(1)
>
RSTIN
> (1032 + 12)TCL + max(4 TCL, 500ns)
RSTIN
t
> max(4 TCL, 500ns)
RSTIN
t
≤ (1032 + 12)TCL + max(4 TCL, 500ns)
RSTIN
WDT overflow
SRST instruction execution
The figures in the upcoming sections 20.2, 20.3, 20.5 and 20.6 use the following
terminology:
● transparent = level of the pin affects the internal reset logic
● not transparent = level of the pin does not affect internal logic
20.1 Input filter
On the RSTIN input pin an on-chip RC filter is implemented. It is sized to filter all spikes
shorter than 50ns. On the other hand, a valid pulse longer than 500ns is required for the
ST10 to recognize a reset command. In between 50ns and 500ns a pulse can either be
filtered or recognized as valid, depending on the operating conditions and process
variations.
For this reason all minimum durations mentioned in this chapter for the different kinds of
reset events must be carefully evaluated, taking into account the above requirements.
In particular, for Short Hardware Reset, where only 4 TCL is specified as minimum input
reset pulse duration, the operating frequency is a key factor.
Examples:
● For a CPU clock of 40 MHz, 4 TCL is 50ns, so it would be filtered. In this case the
minimum becomes the one imposed by the filter (that is 500ns).
● For a CPU clock of 4 MHz, 4 TCL is 500ns. In this case the minimum from the formula
is coherent with the limit imposed by the filter.
82/182
Page 83

ST10F273M System reset
20.2 Asynchronous reset
An asynchronous reset is triggered when RSTIN pin is pulled low while RPD pin is at low
level. Then the ST10F273M is immediately (after the input filter delay) forced in reset default
state. It pulls low RSTOUT
internal/external bus cycles, it switches buses (data, address and control signals) and I/O
pin drivers to high-impedance, it pulls high Port0 pins.
Note: If an asynchronous reset occurs during a read or write phase in internal memories, the
content of the memory itself could be corrupted: To avoid this, synchronous reset usage is
strongly recommended.
Power-on reset
The asynchronous reset must be used during the power-on of the device. Depending
on crystal or resonator frequency, the on-chip oscillator needs about 1ms to 10ms to
stabilize (refer to Section 24: Electrical characteristics), with an already stable V
logic of the ST10F273M does not need a stabilized clock signal to detect an asynchronous
reset, so it is suitable for power-on conditions. To ensure a proper reset sequence, the
RSTIN
stabilized and the system configuration value on Port0 is settled.
At power-on it is important to respect some additional constraints introduced by the start-up
phase of the different embedded modules.
pin and the RPD pin must be held at low level until the device clock signal is
pin, it cancels pending internal hold states if any, it aborts all
. The
DD
In particular the on-chip voltage regulator needs at least 1ms to stabilize the internal 1.8V
for the core logic: this time is computed from when the external reference (V
stable (inside specification range, that is at least 4.5V). This is a constraint for the
application hardware (external voltage regulator): the RSTIN
to guarantee the voltage regulator stabilization.
A second constraint is imposed by the embedded Flash. When booting from internal
memory, starting from RSTIN
releasing, it needs a maximum of 1ms for its initialization:
before that, the internal reset (RST signal) is not released, so the CPU does not start code
execution in internal memory.
Note: This is not true if external memory is used (pin EA
once RSTIN
pin is released, and after few CPU clock (Filter delay plus 3...8 TCL), the
internal reset signal RST is released as well, so the code execution can start immediately
after. Obviously, an eventual access to the data in internal Flash is forbidden before its
initialization phase is completed: an eventual access during starting phase will return FFFFh
(just at the beginning), while later 009Bh (an illegal opcode trap can be generated).
At power-on, the RSTIN
up time of the main oscillator (t
synchronization time (t
RSTIN
pin could be released before the main oscillator and PLL are stable to recover some
pin shall be tied low for a minimum time that includes also the start-
= 1ms for resonator, 10ms for crystal) and PLL
STUP
= 200µs): this means that if the internal Flash is used, the
PSUP
time in the start-up phase (Flash initialization only needs stable V
stable system clock since an internal dedicated oscillator is used).
) becomes
DD
pin assertion shall be extended
held low during reset phase). In this case,
, but does not need
18
Warning: It is recommended to provide the external hardware with a
current limitation circuitry. This is necessary to avoid
permanent damage of the device during the power-on
transient, when the capacitance on V
pin is charged. For
18
the on-chip voltage regulator functionality 10nF is sufficient:
83/182
Page 84

System reset ST10F273M
In any case, a maximum of 100nF on V18 pin should not
generate problems of over-current (higher value is allowed if
current is limited by the external hardware). External current
limitation is nevertheless also recommended to avoid risks of
damage in case of a temporary short between V
18
and
ground: The internal 1.8V drivers are sized to drive currents
of several tens of amps, so the current must be limited by the
external hardware.
The limit of current is imposed by power dissipation
considerations (refer to Section 24: Electrical
characteristics).
In Figures 18 and 19 Asynchronous Power-on timing diagrams are shown, respectively with
boot from internal or external memory, highlighting the reset phase extension introduced by
the embedded IFlash module when selected.
Caution: Never power the device without keeping the RSTIN pin grounded: The device could enter
into unpredictable states, risking also permanent damage.
84/182
Page 85

ST10F273M System reset
Figure 18. Asynchronous power-on RESET (EA = 1)
≤ 1.2 ms (for resonator oscillation + PLL stabilization)
≤ 10.2 ms (for crystal oscillation + PLL stabilization)
≥ 1 ms (for on-chip VREG stabilization)
V
DD
V
18
≤
2 TCL
XTAL1
...
RPD
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13]
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0] not t.
transparent
transparent
not transparent
3..4 TCL
not t.
not t.
not t.
7 TCL
IBUS-CS
(Internal)
≤ 1 ms
FLARST
RST
Latching point of Port0 for
system start-up configuration
85/182
Page 86

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 19. Asynchronous power-on RESET (EA = 0)
≥ 1.2 ms (for resonator oscillation + PLL stabilization)
≥ 10.2 ms (for crystal oscillation + PLL stabilization)
≥ 1 ms (for on-chip VREG stabilization)
V
DD
V
18
3..8 TCL
(1)
XTAL1
...
RPD
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13]
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0] not t.
transparent
transparent
not transparent
3..4 TCL
not t.
not t.
8 TCL
ALE
RST
Latching point of Port0 for
system start-up configuration
1. 3 to 8 TCL depending on clock source selection
Hardware reset
The asynchronous reset must be used to recover from catastrophic situations of the
application. It may be triggered by the hardware of the application. Internal hardware logic
and application circuitry are described in Reset circuitry chapter and Figures 31, 32 and 33.
It occurs when RSTIN
86/182
is low and RPD is detected (or becomes) low as well.
Page 87

ST10F273M System reset
Figure 20. Asynchronous hardware RESET (EA = 1)
1)
≤ 2 TCL
RPD
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTIN
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13]
P0[12:2]
not transparent
not transparent
P0[1:0] not t.
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
3..4 TCL
transparent
transparent
not transparent
not t.
not t.
not t.
7 TCL
IBUS-CS
(internal)
≤ 1 ms
FLARST
RST
Latching point of Port0 for
system start-up configuration
1. Longer than Port0 settling time + PLL synchronization (if needed, that is P0(15:13) changed).
Longer than 500ns to take into account of Input Filter on RSTIN pin.
87/182
Page 88

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 21. Asynchronous hardware RESET (EA = 0)
(1)
RPD
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTIN
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13]
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0] not t.
ALE
RST
not transparent
not transparent
transparent
transparent
not transparent
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
Latching point of Port0 for
system start-up configuration
3..8 TCL
3..4 TCL
(2)
not t.
not t.
8 TCL
1. Longer than Port0 settling time + PLL synchronization (if needed, that is P0(15:13) changed).
Longer than 500ns to take into account of Input Filter on RSTIN pin.
2. 3 to 8 TCL depending on clock source selection.
Exit from asynchronous reset state
When the
Flash is used, the restarting occurs after the embedded Flash initialization routine is
completed. The system configuration is latched from Port0: ALE, RD
driven to their inactive level. The ST10F273M starts program execution from memory
location 00'0000h in code segment 0. This starting location will typically point to the general
initialization routine. The timings of asynchronous Hardware Reset sequence are
summarized in Figure 20 and Figure 21.
RSTIN
pin is pulled high, the device restarts: As already mentioned, if internal
20.3 Synchronous reset (warm reset)
A synchronous reset is triggered when RSTIN pin is pulled low while RPD pin is at high
level. In order to properly activate the internal reset logic of the device, the RSTIN
be held low, at least, during 4 TCL (two periods of CPU clock): refer also to Section 20.1 for
details on minimum reset pulse duration. The I/O pins are set to high impedance and
RSTOUT
12 TCL (six periods of CPU clock) elapses, during which pending internal hold states are
cancelled and the current internal access cycle if any is completed. External bus cycle is
aborted. The internal pull-down of RSTIN
pin is driven low. After RSTIN level is detected, a short duration of a maximum of
pin is activated if bit BDRSTEN of SYSCON
and WR/WRL pins are
pin must
88/182
Page 89

ST10F273M System reset
register was previously set by software. Note that this bit is always cleared on power-on or
after a reset sequence.
Short and long synchronous reset
Once the first maximum 16 TCL are elapsed (4+12TCL), the internal reset sequence starts.
It is 1024 TCL cycles long: at the end of it, and after other 8TCL the level of RSTIN
sampled (after the filter, see RSTF
in the drawings): if it is already at high level, only Short
Reset is flagged (refer to Chapter 19 for details on reset flags); if it is recognized still low, the
Long reset is flagged as well. The major difference between Long and Short reset is that
during the Long reset, also P0(15:13) become transparent, so it is possible to change the
clock options.
Warning: In case of a short pulse on RSTIN pin, and when Bidirectional
reset is enabled, the RSTIN
pin is held low by the internal
circuitry. At the end of the 1024 TCL cycles, the RTSIN
released, but due to the presence of the input analog filter the
internal input reset signal (RSTF
in the drawings) is released
later (from 50 to 500ns). This delay is in parallel with the
additional 8 TCL, at the end of which the internal input reset
line (RSTF
) is sampled, to decide if the reset event is Short or
Long. In particular:
is
pin is
● If 8 TCL > 500ns (f
● If 8 TCL < 500ns (f
< 8 MHz), the reset event is always recognized as Short
CPU
> 8 MHz), the reset event could be recognized either as Short or
CPU
Long, depending on the real filter delay (between 50 and 500ns) and the CPU
frequency (RSTF
sampled High means Short reset, RSTF sampled Low means Long
reset). Note that in case a Long Reset is recognized, once the 8 TCL are elapsed, the
P0(15:13) pins becomes transparent, so the system clock can be reconfigured. The
port returns not transparent 3-4TCL after the internal RSTF
signal becomes high.
The same behavior just described, occurs also when unidirectional reset is selected and
RSTIN
pin is held low till the end of the internal sequence (exactly 1024TCL + max 16 TCL)
and released exactly at that time.
Note: When running with CPU frequency lower than 40 MHz, the minimum valid reset pulse to be
recognized by the CPU (4 TCL) could be longer than the minimum analog filter delay (50ns);
so it might happen that a short reset pulse is not filtered by the analog input filter, but on the
other hand it is not long enough to trigger a CPU reset (shorter than 4 TCL): this would
generate a Flash reset but not a system reset. In this condition, the Flash answers always
with FFFFh, which leads to an illegal opcode and consequently a trap event is generated.
Exit from synchronous reset state
The reset sequence is extended until RSTIN level becomes high. Besides, it is internally
prolonged by the Flash initialization when EA
code execution restarts. The system configuration is latched from Port0, and ALE, RD
WR
/WRL pins are driven to their inactive level. The ST10F273M starts program execution
from memory location 00'0000h in code segment 0. This starting location will typically point
to the general initialization routine. Timing of synchronous reset sequence are summarized
in Figures 22 and 23 where a Short Reset event is shown, with particular emphasis on the
fact that it can degenerate into Long Reset: The two figures show the behavior when booting
= 1 (internal memory selected). Then, the
and
89/182
Page 90

System reset ST10F273M
from internal or external memory respectively. Figures 24 and 25 report the timing of a
typical synchronous Long Reset, again when booting from internal or external memory.
Synchronous reset and RPD pin
Whenever the RSTIN pin is pulled low (by external hardware or as a consequence of a
Bidirectional reset), the RPD internal weak pull-down is activated. The external capacitance
(if any) on RPD pin is slowly discharged through the internal weak pull-down. If the voltage
level on RPD pin reaches the input low threshold (around 2.5V), the reset event becomes
immediately asynchronous. In case of hardware reset (short or long) the situation goes
immediately to the one illustrated in Figure 20. There is no effect if RPD comes again above
the input threshold: the asynchronous reset is completed coherently. To grant the normal
completion of a synchronous reset, the value of the capacitance shall be big enough to
maintain the voltage on RPD pin sufficient high along the duration of the internal reset
sequence.
For a Software or Watchdog reset events, an active synchronous reset is completed
regardless of the RPD status.
It is important to highlight that the signal that makes RPD status transparent under reset is
the internal RSTF
(after the noise filter).
90/182
Page 91

ST10F273M System reset
Figure 22. Synchronous short / long hardware RESET (EA = 1)
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
4)
1)
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
< 1032 TCL≤4 TCL3)≤12 TCL
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0]
not t.
transparent
not transparent
IBUS-CS
(Internal)
FLARST
1024 TCL
RST
≤ 2 TCL
not t.
not t.
7 TCL
≤ 1 ms
8 TCL
At this time RSTF is sampled HIGH or LOW
RSTOUT
so it is SHORT or LONG reset
RPD
2)
V
> 2.5V Asynchronous Reset not entered
200µA Discharge
1. RSTIN assertion can be released there. Refer also to Section 21.1 for details on minimum pulse duration.
2. If during the reset condition (RSTIN low), RPD voltage drops below the threshold voltage (about 2.5V for
5V operation), the asynchronous reset is then immediately entered.
3. RSTIN pin is pulled low if bit BDRSTEN (bit 3 of SYSCON register) was previously set by software. Bit
BDRSTEN is cleared after reset.
4. Minimum RSTIN low pulse duration shall also be longer than 500ns to guarantee the pulse is not masked
by the internal filter (refer to Section 21.1).
RPD
91/182
Page 92

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 23. Synchronous short / long hardware RESET (EA = 0)
< 1032 TCL≤4 TCL4)≤12 TCL
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
1)
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0]
not t.
transparent
not transparent
ALE
1024 TCL
RST
RSTOUT
RPD
not t.
not t.
3..8 TCL3)
8 TCL
At this time RSTF is sampled HIGH or LOW
so it is SHORT or LONG reset
8 TCL
200µA Discharge
1. RSTIN assertion can be released there. Refer also to Section 21.1 for details on minimum pulse duration.
2. If during the reset condition (RSTIN low), RPD voltage drops below the threshold voltage (about 2.5V for
5V operation), the asynchronous reset is then immediately entered.
3. 3 to 8 TCL depending on clock source selection.
4. RSTIN pin is pulled low if bit BDRSTEN (bit 3 of SYSCON register) was previously set by software. Bit
BDRSTEN is cleared after reset.
5. Minimum RSTIN low pulse duration shall also be longer than 500ns to guarantee the pulse is not masked
by the internal filter (refer to Section 21.1).
2) VRPD > 2.5V Asynchronous Reset not entered
92/182
Page 93

ST10F273M System reset
Figure 24. Synchronous long hardware RESET (EA = 1)
1024+8 TCL≤4 TCL2)≤12 TCL
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
≤
2 TCL
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:2]
not t.
P0[1:0]
IBUS-CS
(Internal)
FLARST
1024+8 TCL
RST
RSTOUT
RPD
200µA Discharge
transparent
transparent
not transparent
At this time RSTF is sampled LOW
so it is definitely LONG reset
3..4 TCL
≤ 1 ms
1)
V
RPD
not entered
not t.
not t.
not t.
7 TCL
> 2.5V Asynchronous reset
1. If during the reset condition (RSTIN low), RPD voltage drops below the threshold voltage (about 2.5V for
5V operation), the asynchronous reset is then immediately entered. Even if RPD returns above the
threshold, the reset is definitely taken as asynchronous.
2. Minimum RSTIN
by the internal filter (refer to Section 21.1).
low pulse duration shall also be longer than 500ns to guarantee the pulse is not masked
93/182
Page 94

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 25. Synchronous long hardware RESET (EA = 0)
1024+8 TCL4 TCL2)12 TCL
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
3..4 TCL
RSTF
(After Filter)
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:2]
P0[1:0]
transparent
transparent
not transparent
3..8 TCL
not t.
not t.
not t.
3)
8 TCL
ALE
1024+8 TCL
RST
At this time RSTF is sampled LOW
RSTOUT
so it is LONG reset
RPD
1)
V
200µA Discharge
1. If during the reset condition (RSTIN low), RPD voltage drops below the threshold voltage (about 2.5V for
5V operation), the asynchronous reset is then immediately entered.
2. Minimum RSTIN
by the internal filter (refer to Section 21.1).
3. 3 to 8 TCL depending on clock source selection.
low pulse duration shall also be longer than 500ns to guarantee the pulse is not masked
> 2.5V Asynchronous reset not entered
RPD
20.4 Software reset
A software reset sequence can be triggered at any time by the protected SRST (software
reset) instruction. This instruction can be deliberately executed within a program, for
example, to leave bootstrap loader mode, or on a hardware trap that reveals system failure.
On execution of the SRST instruction, the internal reset sequence is started. The
microcontroller behavior is the same as for a synchronous short reset, except that only bits
P0.12...P0.8 are latched at the end of the reset sequence, while previously latched, bits
P0.7...P0.2 are cleared (that is written at ‘1’).
A Software reset is always taken as synchronous: there is no influence on Software Reset
behavior with RPD status. In case Bidirectional Reset is selected, a Software Reset event
pulls RSTIN
low even though Bidirectional Reset is selected.
94/182
pin low: this occurs only if RPD is high; if RPD is low, RSTIN pin is not pulled
Page 95

ST10F273M System reset
Refer to the next Figures 26 and 27 for unidirectional SW reset timing, and to Figures 28, 29
and 30 for bidirectional.
20.5 Watchdog timer reset
When the watchdog timer is not disabled during the initialization, or serviced regularly
during program execution, it will overflow and trigger the reset sequence.
Unlike hardware and software resets, the watchdog reset completes a running external bus
cycle if this bus cycle either does not use READY
the programmed wait states.
, or if READY is sampled active (low) after
When READY
is sampled inactive (high) after the programmed wait states the running
external bus cycle is aborted. Then the internal reset sequence is started.
Bit P0.12...P0.8 are latched at the end of the reset sequence and bit P0.7...P0.2 are cleared
(that is written at ‘1’).
A Watchdog reset is always taken as synchronous: there is no influence on Watchdog Reset
behavior with RPD status. In case Bidirectional Reset is selected, a Watchdog Reset event
pulls RSTIN
pin low: this occurs only if RPD is high; if RPD is low, RSTIN pin is not pulled
low even though Bidirectional Reset is selected.
Refer to the next Figures 26 and 27 for unidirectional SW reset timing, and to Figures 28, 29
and 30 for bidirectional.
Figure 26. SW / WDT unidirectional RESET (EA
RSTIN
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:8]
P0[7:2] not transparent
transparent
= 1)
≤ 2 TCL
not t.
P0[1:0]
IBUS-CS
(Internal)
FLARST
RST
RSTOUT
not transparent
≤ 1 ms
1024 TCL
95/182
not t.
7 TCL
Page 96

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 27. SW / WDT unidirectional RESET (EA = 0)
RSTIN
P0[15:13] not transparent
P0[12:8]
P0[7:2]
P0[1:0]
ALE
RST
RSTOUT
20.6 Bidirectional reset
As shown in the previous sections, the RSTOUT pin is driven active (low level) at the
beginning of any reset sequence (synchronous/asynchronous hardware, software and
watchdog timer resets). RSTOUT
routine, until the protected EINIT instruction (End of Initialization) is completed.
transparent
not transparent
not transparent
1024 TCL
not t.
not t.
8 TCL
pin stays active low beyond the end of the initialization
The Bidirectional Reset function is useful when external devices require a reset signal but
cannot be connected to RSTOUT
pin, because RSTOUT signal lasts during initialization. It
is, for instance, the case of external memory running initialization routine before the
execution of EINIT instruction.
Bidirectional reset function is enabled by setting bit 3 (BDRSTEN) in SYSCON register. It
only can be enabled during the initialization routine, before EINIT instruction is completed.
When enabled, the open drain of the RSTIN
for the duration of the internal reset sequence (synchronous/asynchronous hardware,
synchronous software and synchronous watchdog timer resets). At the end of the internal
reset sequence the pull down is released and:
● After a Short Synchronous Bidirectional Hardware Reset, if RSTF is sampled low eight
TCL periods after the internal reset sequence completion (refer to Figure 22 and
Figure 23), the Short Reset becomes a Long Reset. On the contrary, if RSTF
sampled high the device simply exits reset state.
● After a Software or Watchdog Bidirectional Reset, the device exits from reset. If RSTF
remains still low for at least four TCL periods (minimum time to recognize a Short
Hardware reset) after the reset exiting (refer to Figure 28 and Figure 29), the Software
96/182
pin is activated, pulling down the reset signal,
is
Page 97

ST10F273M System reset
or Watchdog Reset become a Short Hardware Reset. On the contrary, if RSTF remains
low for less than 4 TCL, the device simply exits reset state.
The Bidirectional reset is not effective in case RPD is held low, when a Software or
Watchdog reset event occurs. On the contrary, if a Software or Watchdog Bidirectional reset
event is active and RPD becomes low, the RSTIN
internal reset sequence is completed regardless of RPD status change (1024 TCL).
Note: The bidirectional reset function is disabled by any reset sequence (bit BDRSTEN of
SYSCON is cleared). To be activated again it must be enabled during the initialization
routine.
pin is immediately released, while the
WDTCON flags
Similarly to what already highlighted in the previous section when discussing about Short
reset and the degeneration into Long reset, similar situations may occur when Bidirectional
reset is enabled. The presence of the internal filter on RSTIN
RSTIN
so it remains still active (low) for a while. It means that depending on the internal clock
speed, a short reset may be recognized as a long reset: the WDTCON flags are set
accordingly.
Besides, when either Software or Watchdog bidirectional reset events occur, again when the
RSTIN
(after the filter) remains low for a while, and depending on the clock frequency it is
recognized high or low: 8TCL after the completion of the internal sequence, the level of
RSTF
WDTCON will flag this last event, masking the previous one (Software or Watchdog reset).
Typically, a Short Hardware reset is recognized, unless the RSTIN
internal signal RSTF
Hardware reset. After this occurrence, the initialization routine is not able to recognize a
Software or Watchdog bidirectional reset event, since a different source is flagged inside
WDTCON register. This phenomenon does not occur when internal Flash is selected during
reset (EA
well beyond the filter delay.
is released, the internal signal after the filter (see RSTF in the drawings) is delayed,
pin is released (at the end of the internal reset sequence), the RSTF internal signal
signal is sampled, and if recognized still low a Hardware reset sequence starts, and
) is sufficiently held low by the external hardware to inject a Long
= 1), since the initialization of the Flash itself extend the internal reset duration
pin introduces a delay: when
pin (and consequently
The next Figures 28, 29 and 30 summarize the timing for Software and Watchdog Timer
Bidirectional reset events: In particular Figure 30 shows the degeneration into Hardware
reset.
97/182
Page 98

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 28. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA =1)
RSTIN
≥
RSTF
(After Filter)
50 ns
≤
500 ns
≥
50 ns
≤
500 ns
P0[15:13]
P0[12:8]
P0[7:2]
P0[1:0]
IBUS-CS
(Internal)
FLARST
RST
RSTOUT
1024 TCL
not transparent
transparent
not transparent
not transparent
≤
1 ms
≤
2 TCL
not t.
not t.
7 TCL
98/182
Page 99

ST10F273M System reset
Figure 29. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA = 0)
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13] not transparent
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
P0[12:8]
P0[7:2]
P0[1:0]
ALE
RST
RSTOUT
transparent
not transparent
not transparent
1024 TCL
not t.
not t.
8 TCL
At this time RSTF is sampled HIGH
so SW or WDT Reset is flagged in WDTCON
99/182
Page 100

System reset ST10F273M
Figure 30. SW / WDT bidirectional RESET (EA = 0) followed by a HW RESET
RSTIN
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
RSTF
(After Filter)
P0[15:13] not transparent
≥ 50 ns
≤ 500 ns
P0[12:8]
P0[7:2] not transparent
P0[1:0]
ALE
RST
RSTOUT
20.7 Reset circuitry
Internal reset circuitry is described in Figure 33. The
resistor of 50kΩ to 250kΩ (The minimum reset time must be calculated using the lowest
value).
It also provides a programmable (BDRSTEN bit of SYSCON register) pull-down to output
internal reset state signal (synchronous reset, watchdog timer reset or software reset).
transparent
not transparent
1024 TCL
not t.
not t.
8 TCL
At this time RSTF is sampled LOW
so HW Reset is entered
RSTIN
pin provides an internal pull-up
This bidirectional reset function is useful in applications where external devices require a
reset signal but cannot be connected to
This is the case of an external memory running codes before EINIT (end of initialization)
instruction is executed.
RSTOUT
pin is pulled high only when EINIT is executed.
The RPD pin provides an internal weak pull-down resistor which discharges external
capacitor at a typical rate of 200µA. If bit PWDCFG of SYSCON register is set, an internal
pull-up resistor is activated at the end of the reset sequence. This pull-up will charge any
capacitor connected on RPD pin.
The simplest way to reset the ST10F273M is to insert a capacitor C1 between
and V
RPD pin and V
, and a capacitor between RPD pin and VSS (C0) with a pull-up resistor R0 between
SS
. The input
DD
RSTIN
provides an internal pull-up device equalling a resistor of
50kΩ to 250kΩ (the minimum reset time must be determined by the lowest value). Select C1
that produce a sufficient discharge time to permit the internal or external oscillator and / or
internal PLL and the on-chip voltage regulator to stabilize.
100/182
RSTOUT
pin.
RSTIN
pin
 Loading...
Loading...