
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125
PDIP8 (BN)
SO8 (MN)
150 mil width
TSSOP8 (DW)
169 mil width
M93C56-125 M93C46-125
Automotive 16-Kbit, 8-Kbit, 4-Kbit, 2-Kbit and 1-Kbit
(8-bit or 16-bit wide) MICROWIRE serial EEPROM
Datasheet − production data
Features
■ Industry standard MICROWIRE
■ Memory array: 1 Kb, 2Kb, 4Kb, 8 Kb or 16 Kb
■ Dual organization: by word (x16) or byte (x8)
■ Write
– Byte within 5 ms
– Word within 5 ms
■ READY/BUSY signal during programming
■ 2 MHz clock rate
■ Sequential read operation
■ Single supply voltage: 4.5 V to 5.5 V or 2.5 V
to 5.5 V
■ Operating temperature range: -40°c up to
125°C
■ Enhanced ESD protection
■ More than 1 million Write cycles
■ More than 40-year data retention
■ Packages
– SO8, TSSOP8 packages: RoHS-compliant
and Halogen-free (ECOPACK2
– PDIP8 package: RoHS-compliant
(ECOPACK1
®
)
TM
bus
®
)
March 2012 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 1/32
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
1

Contents M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Connecting to the serial bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Operating features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1 Supply voltage (VCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.1 Operating supply voltage (VCC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.2 Power-up conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.3 Power-up and device reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.4 Power-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Memory organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5 Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.1 Read Data from Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2 Write Enable and Write Disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3 Erase Byte or Word . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.4 Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.5 Erase All . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.6 Write All . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6 READY/BUSY status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7 Initial delivery state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
8 Common I/O operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
9 Clock pulse counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
10 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
11 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
12 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Contents
13 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
14 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 3/32

List of tables M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
List of tables
Table 1. Memory size versus organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 2. Signal names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 3. Instruction set for the M93Cx6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 4. Instruction set for the M93C46 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 5. Instruction set for the M93C56 and M93C66 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6. Instruction set for the M93C76 and M93C86 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 7. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. Operating conditions (M93Cx6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Operating conditions (M93Cx6-W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 10. AC measurement conditions (M93Cx6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 11. AC measurement conditions (M93Cx6-W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 12. Capacitance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 13. DC characteristics (M93Cx6, device grade 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 14. DC characteristics (M93Cx6-W, device grade 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 15. AC characteristics (M93Cx6, device grade 3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 16. AC characteristics (M93Cx6-W, device grade 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 17. PDIP8 – 8 lead plastic dual in-line package, 300 mils body width, package
mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 18. SO8 narrow – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package data . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 19. TSSOP8 – 8 lead thin shrink small outline, package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 20. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 21. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2. DIP, SO and TSSOP connections (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 3. Bus master and memory devices on the serial bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 4. READ, WRITE, WEN, WDS sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 5. ERASE, ERAL sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 6. WRAL sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 7. Write sequence with one clock glitch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 8. AC testing input output waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 9. Synchronous timing (start and op-code input) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 10. Synchronous timing (Read or Write). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 11. Synchronous timing (Read or Write). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 12. PDIP8 – 8 lead plastic dual in-line package, 300 mils body width, package
outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 13. SO8 narrow – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package outline . . . . . . . 28
Figure 14. TSSOP8 – 8 lead thin shrink small outline, package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 5/32
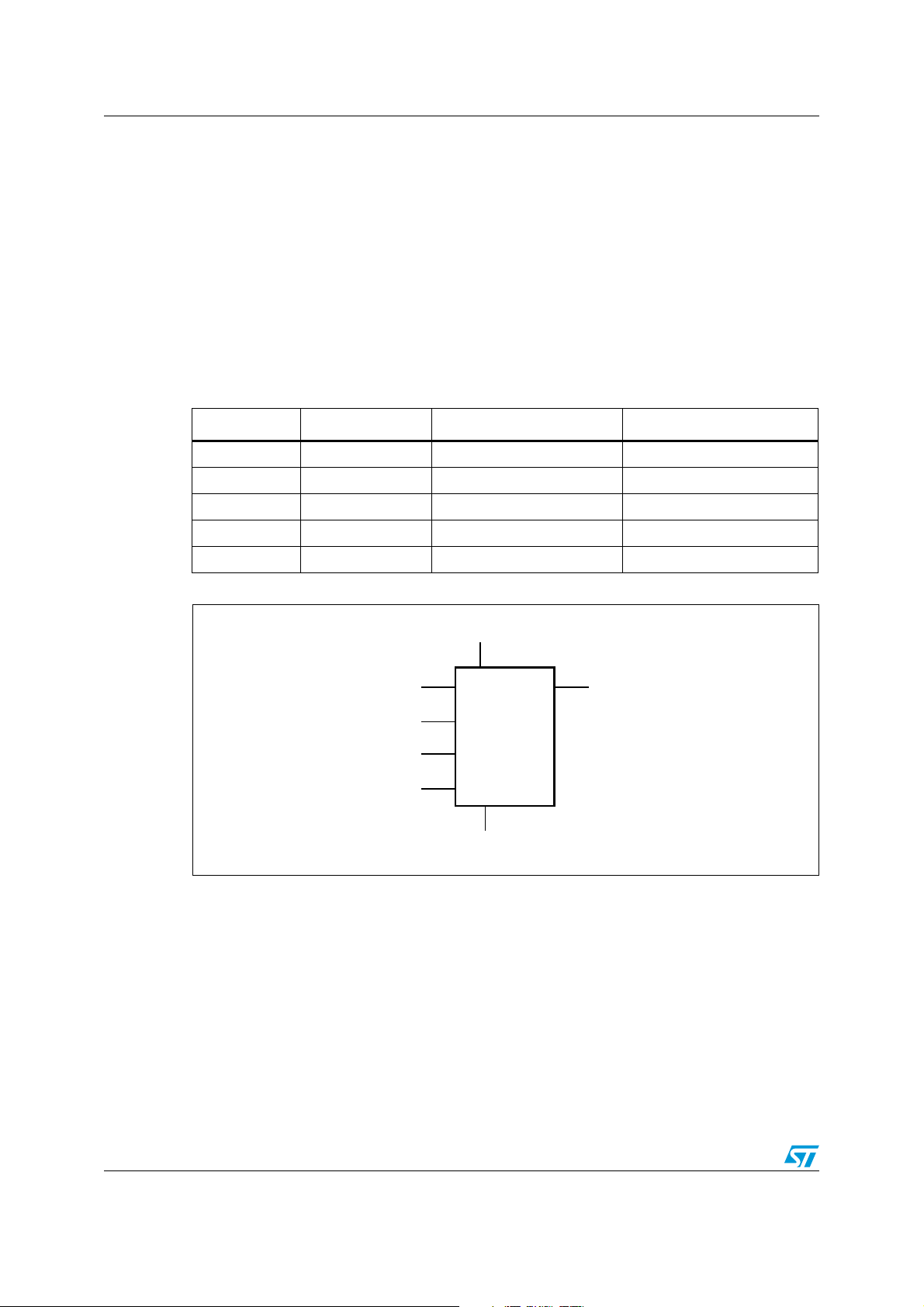
Description M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
AI01928
D
V
CC
M93Cx6
V
SS
C
Q
S
ORG
1 Description
The M93C46 (1 Kbit), M93C56 (2 Kbit), M93C66 (4 Kbit), M93C76 (8 Kbit) and M93C86
(16 Kbit) are Electrically Erasable PROgrammable Memory (EEPROM) devices accessed
through the MICROWIRE bus protocol. The memory array can be configured either in bytes
(x8b) or in words (x16b).
The M93Cx6 devices operate within a voltage supply range from 4.5 V to 5.5 V, and the
M93Cx6-W devices operate within a voltage supply range from 2.5 V to 5.5 V.
The M93Cx6 devices are guaranteed over the -40°C/+125°C temperature range and are
compliant with the Automotive standard AEC-Q100 Grade 1.
Table 1. Memory size versus organization
Device Number of bits Number of 8-bit bytes Number of 16-bit words
M93C86 16384 2048 1024
M93C76 8192 1024 512
M93C66 4096 512 256
M93C56 2048 256 128
M93C46 1024 128 64
Figure 1. Logic diagram
6/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
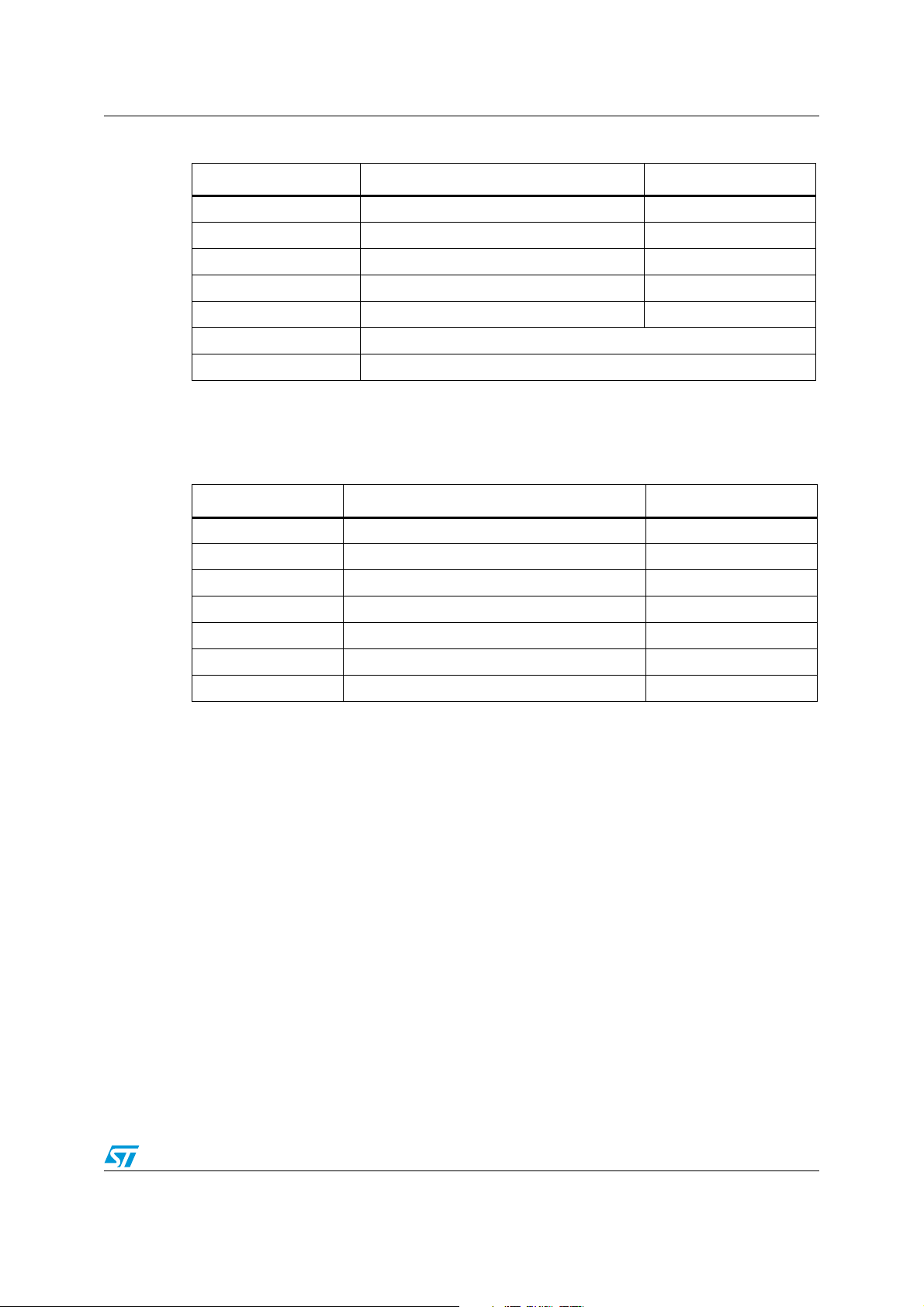
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Description
Table 2. Signal names
Signal name Function Direction
S Chip Select Input
D Serial Data input Input
Q Serial Data output Output
C Serial Clock Input
ORG Organization Select Input
V
CC
V
SS
Supply voltage
Ground
The M93Cx6 is accessed by a set of instructions, as summarized in Ta bl e 3 , and in more
detail in Table 4: Instruction set for the M93C46 to Table 6: Instruction set for the M93C76
and M93C86).
Table 3. Instruction set for the M93Cx6
Instruction Description Data
READ Read Data from Memory Byte or Word
WRITE Write Data to Memory Byte or Word
WEN Write Enable
WDS Write Disable
ERASE Erase Byte or Word Byte or Word
ERAL Erase All Memory
WRAL Write All Memory with same Data
A Read Data from Memory (READ) instruction loads the address of the first byte or word to
be read in an internal address register. The data at this address is then clocked out serially.
The address register is automatically incremented after the data is output and, if Chip Select
Input (S) is held High, the M93Cx6 can output a sequential stream of data bytes or words. In
this way, the memory can be read as a data stream from eight to 16384 bits long (in the
case of the M93C86), or continuously (the address counter automatically rolls over to 00h
when the highest address is reached).
Programming is internally self-timed (the external clock signal on Serial Clock (C) may be
stopped or left running after the start of a Write cycle) and does not require an Erase cycle
prior to the Write instruction. The Write instruction writes 8 or 16 bits at a time into one of the
byte or word locations of the M93Cx6. After the start of the programming cycle, a
Busy/Ready signal is available on Serial Data Output (Q) when Chip Select Input (S) is
driven High.
An internal Power-on Data Protection mechanism in the M93Cx6 inhibits the device when
the supply is too low.
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 7/32
Description M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
V
SS
Q
ORG
DUC
SV
CC
D
AI01929B
M93Cx6
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
Figure 2. DIP, SO and TSSOP connections (top view)
1. See Section 12: Package mechanical data for package dimensions, and how to identify pin-1.
2. DU = Don’t Use. The DU (do not use) pin does not contribute to the normal operation of the device. It is
reserved for use by STMicroelectronics during test sequences. The pin may be left unconnected or may be
connected to V
or VSS.
CC
8/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
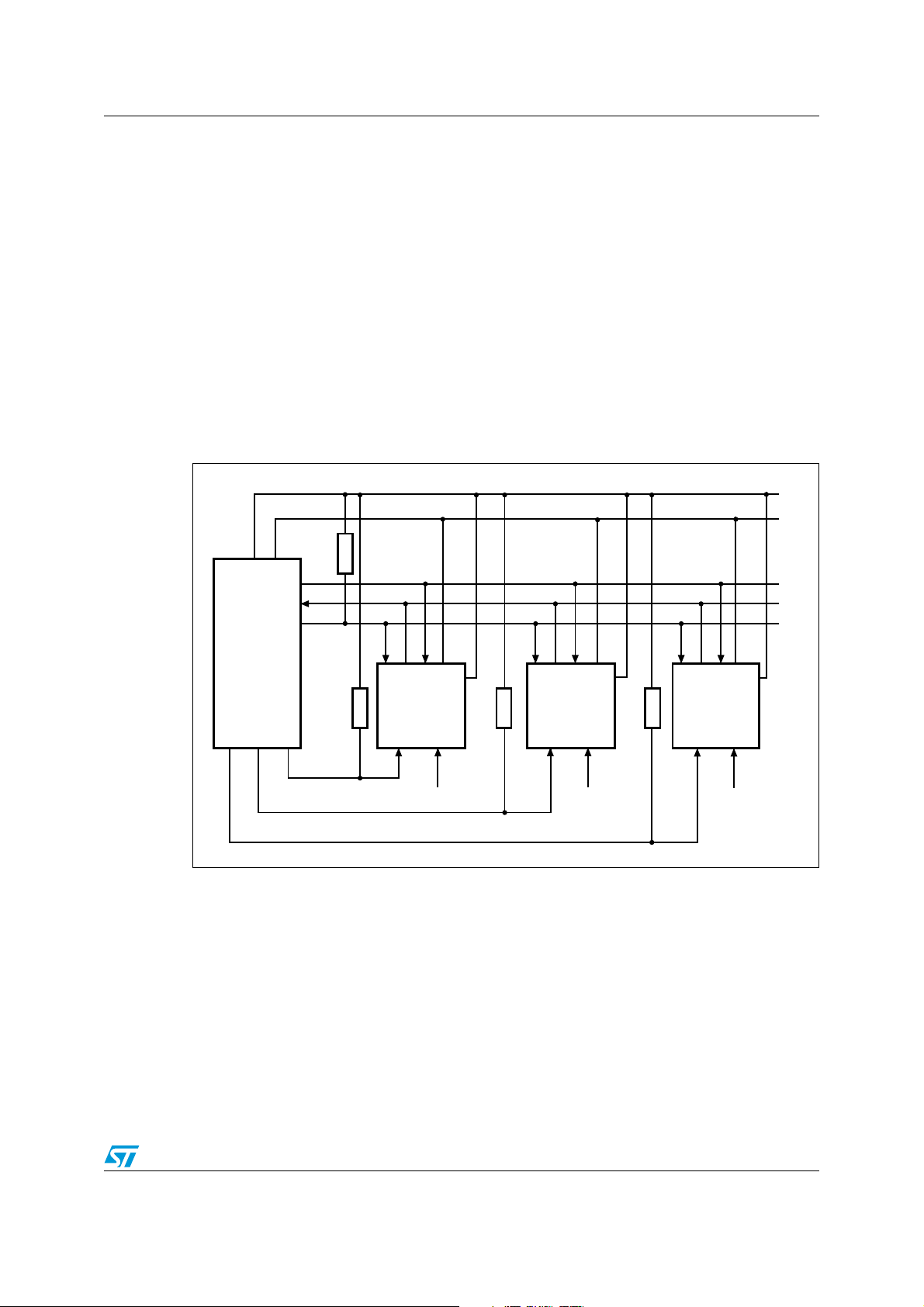
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Connecting to the serial bus
AI14377b
Bus master
M93xxx
memory device
SDO
SDI
SCK
CQD
S
M93xxx
memory device
CQD
S
M93xxx
memory device
CQD
S
CS3 CS2 CS1
ORG
ORG
ORG
RR R
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
R
2 Connecting to the serial bus
Figure 3 shows an example of three memory devices connected to an MCU, on a serial bus.
Only one device is selected at a time, so only one device drives the Serial Data output (Q)
line at a time, the other devices are high impedance.
The pull-down resistor R (represented in Figure 3) ensures that no device is selected if the
bus master leaves the S line in the high impedance state.
In applications where the bus master may be in a state where all inputs/outputs are high
impedance at the same time (for example, if the bus master is reset during the transmission
of an instruction), the clock line (C) must be connected to an external pull-down resistor so
that, if all inputs/outputs become high impedance, the C line is pulled low (while the S line is
pulled low): this ensures that C does not become high at the same time as S goes low, and
so, that the t
Figure 3. Bus master and memory devices on the serial bus
requirement is met. The typical value of R is 100 kΩ.
SLCH
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 9/32

Operating features M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
3 Operating features
3.1 Supply voltage (VCC)
3.1.1 Operating supply voltage (VCC)
Prior to selecting the memory and issuing instructions to it, a valid and stable VCC voltage
within the specified [V
DC supply voltage, it is recommended to decouple the V
(usually of the order of 10 nF to 100 nF) close to the V
This voltage must remain stable and valid until the end of the transmission of the instruction
and, for a Write instruction, until the completion of the internal write cycle (t
3.1.2 Power-up conditions
When the power supply is turned on, VCC rises from VSS to VCC. During this time, the Chip
Select (S) line is not allowed to float and should be driven to V
recommended to connect the S line to V
The V
rise time must not vary faster than 1 V/µs.
CC
(min), VCC(max)] range must be applied. In order to secure a stable
CC
via a suitable pull-down resistor.
SS
line with a suitable capacitor
CC
CC/VSS
package pins.
, it is therefore
SS
).
W
3.1.3 Power-up and device reset
In order to prevent inadvertent Write operations during power-up, a power on reset (POR)
circuit is included. At power-up (continuous rise of V
instruction until V
lower than the minimum V
has reached the power on reset threshold voltage (this threshold is
CC
operating voltage defined in Operating conditions, in
CC
Section 11: DC and AC parameters).
When V
● Standby Power mode
● deselected (assuming that there is a pull-down resistor on the S line)
passes the POR threshold, the device is reset and is in the following state:
CC
3.1.4 Power-down
At power-down (continuous decrease in VCC), as soon as VCC drops from the normal
operating voltage to below the power on reset threshold voltage, the device stops
responding to any instruction sent to it.
During power-down, the device must be deselected and in the Standby Power mode (that is,
there should be no internal Write cycle in progress).
), the device does not respond to any
CC
10/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Memory organization
4 Memory organization
The M93Cx6 memory is organized either as bytes (x8) or as words (x16). If Organization
Select (ORG) is left unconnected (or connected to V
when Organization Select (ORG) is connected to Ground (V
selected. When the M93Cx6 is in Standby mode, Organization Select (ORG) should be set
either to V
or VCC for minimum power consumption. Any voltage between VSS and VCC
SS
applied to Organization Select (ORG) may increase the Standby current.
) the x16 organization is selected;
CC
) the x8 organization is
SS
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 11/32

Instructions M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
5 Instructions
The instruction set of the M93Cx6 devices contains seven instructions, as summarized in
Ta bl e 4 to Ta b le 6 . Each instruction consists of the following parts, as shown in Figure 4:
READ, WRITE, WEN, WDS sequences:
● Each instruction is preceded by a rising edge on Chip Select Input (S) with Serial Clock
(C) being held low.
● A start bit, which is the first ‘1’ read on Serial Data Input (D) during the rising edge of
Serial Clock (C).
● Two op-code bits, read on Serial Data Input (D) during the rising edge of Serial Clock
(C). (Some instructions also use the first two bits of the address to define the op-code).
● The address bits of the byte or word that is to be accessed. For the M93C46, the
address is made up of 6 bits for the x16 organization or 7 bits for the x8 organization
(see Ta bl e 4 ). For the M93C56 and M93C66, the address is made up of 8 bits for the
x16 organization or 9 bits for the x8 organization (see Tab le 5 ). For the M93C76 and
M93C86, the address is made up of 10 bits for the x16 organization or 11 bits for the x8
organization (see Tab le 6 ).
The M93Cx6 devices are fabricated in CMOS technology and are therefore able to run as
slow as 0 Hz (static input signals) or as fast as the maximum ratings specified in “AC
characteristics” tables, in Section 11: DC and AC parameters.
Table 4. Instruction set for the M93C46
Instruction Description
READ
WRITE
WEN Write Enable 1 00
WDS Write Disable 1 00
ERASE
ERAL Erase All Memory 1 00
WRAL
1. X = Don't Care bit.
Read Data from
Memory
Write Data to
Memory
Erase Byte or
Word
Write All Memory
with same Data
Start
bit
code
1 10 A6-A0 Q7-Q0 A5-A0 Q15-Q0
1 01 A6-A0 D7-D0 18 A5-A0 D15-D0 25
1 11 A6-A0 10 A5-A0 9
100
Op-
x8 origination (ORG = 0) x16 origination (ORG = 1)
Address
(1)
11X
XXXX
00X
XXXX
10X
XXXX
01X
XXXX
Required
Data
D7-D0 18 01 XXXX D15-D0 25
clock
cycles
10 11 XXXX 9
10 00 XXXX 9
10 10 XXXX 9
Address
(1)
Data
Required
cycles
clock
12/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Instructions
Table 5. Instruction set for the M93C56 and M93C66
x8 origination (ORG = 0) x16 origination (ORG = 1)
Start
Instruction Description
READ
WRITE
Read Data from
Memory
Write Data to
Memory
WEN Write Enable 1 00
WDS Write Disable 1 00
ERASE
ERAL
WRAL
1. X = Don't Care bit.
2. Address bit A8 is not decoded by the M93C56.
3. Address bit A7 is not decoded by the M93C56.
Table 6. Instruction set for the M93C76 and M93C86
Erase Byte or
Word
Erase All
Memory
Write All Memory
with same Data
Op-
bit
code
Address
(1) (2)
Data
1 10 A8-A0 Q7-Q0 A7-A0 Q15-Q0
1 01 A8-A0 D7-D0 20 A7-A0 D15-D0 27
1 1XXX
XXXX
0 0XXX
XXXX
1 11 A8-A0 12 A7-A0 11
100
100
1 0XXX
XXXX
0 1XXX
XXXX
D7-D0 20
Required
clock cycles
12
12
12
Address
(1) (3)
11XX
XXXX
00XX
XXXX
10XX
XXXX
01XX
XXXX
Data
Required
clock cycles
11
11
11
D15-D0 27
x8 Origination (ORG = 0) x16 Origination (ORG = 1)
Instruction Description
READ
WRITE
Read Data from
Memory
Write Data to
Memory
Start
WEN Write Enable 1 00
WDS Write Disable 1 00
bit
Op-
code
Address
(2)
(1),
Data
Required
clock
cycles
Address
(1) (3)
Data
Required
clock
cycles
1 10 A10-A0 Q7-Q0 A9-A0 Q15-Q0
1 01 A10-A0 D7-D0 22 A9-A0 D15-D0 29
11X XXXX
XXXX
00X XXXX
XXXX
14
14
11 XXXX
XXXX
00 XXXX
XXXX
ERASE Erase Byte or Word 1 11 A10-A0 14 A9-A0 13
ERAL Erase All Memory 1 00
WRAL
1. X = Don't Care bit.
2. Address bit A10 is not decoded by the M93C76.
3. Address bit A9 is not decoded by the M93C76.
Write All Memory
with same Data
100
10X XXXX
XXXX
01X XXXX
XXXX
14
D7-D0 22
10 XXXX
XXXX
01 XXXX
XXXX
D15-D0 29
13
13
13
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 13/32

Instructions M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
5.1 Read Data from Memory
The Read Data from Memory (READ) instruction outputs data on Serial Data Output (Q).
When the instruction is received, the op-code and address are decoded, and the data from
the memory is transferred to an output shift register. A dummy 0 bit is output first, followed
by the 8-bit byte or 16-bit word, with the most significant bit first. Output data changes are
triggered by the rising edge of Serial Clock (C). The M93Cx6 automatically increments the
internal address register and clocks out the next byte (or word) as long as the Chip Select
Input (S) is held High. In this case, the dummy 0 bit is not output between bytes (or words)
and a continuous stream of data can be read.
5.2 Write Enable and Write Disable
The Write Enable (WEN) instruction enables the future execution of erase or write
instructions, and the Write Disable (WDS) instruction disables it. When power is first
applied, the M93Cx6 initializes itself so that erase and write instructions are disabled. After
an Write Enable (WEN) instruction has been executed, erasing and writing remains enabled
until an Write Disable (WDS) instruction is executed, or until V
reset threshold voltage. To protect the memory contents from accidental corruption, it is
advisable to issue the Write Disable (WDS) instruction after every write cycle. The Read
Data from Memory (READ) instruction is not affected by the Write Enable (WEN) or Write
Disable (WDS) instructions.
falls below the power-on
CC
14/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Instructions
AI00878d
1 1 0 An A0
Qn Q0
DATA OUT
D
S
Q
Read
SWrite
ADDR
OP
CODE
1 0An A0
DATA IN
D
Q
OP
CODE
Dn D01
BUSY READY
SWrite
Enable
1 0XnX0D
OP
CODE
101
SWrite
Disable
1 0XnX0D
OP
CODE
0 00
CHECK
STATUS
ADDR
Figure 4. READ, WRITE, WEN, WDS sequences
1. For the meanings of An, Xn, Qn and Dn, see Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6.
5.3 Erase Byte or Word
The Erase Byte or Word (ERASE) instruction sets the bits of the addressed memory byte (or
word) to 1. Once the address has been correctly decoded, the falling edge of the Chip
Select Input (S) starts the self-timed Erase cycle. The completion of the cycle can be
detected by monitoring the READY/BUSY
status.
line, as described in Section 6: READY/BUSY
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 15/32

Instructions M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
AI00879B
SERASE
1 1D
Q
ADDR
OP
CODE
1
BUSY READY
CHECK
STATUS
SERASE
ALL
1 0D
Q
OP
CODE
1
BUSY READY
CHECK
STATUS
0 0
An A0
Xn X0
ADDR
5.4 Write
For the Write Data to Memory (WRITE) instruction, 8 or 16 data bits follow the op-code and
address bits. These form the byte or word that is to be written. As with the other bits, Serial
Data Input (D) is sampled on the rising edge of Serial Clock (C).
After the last data bit has been sampled, the Chip Select Input (S) must be taken low before
the next rising edge of Serial Clock (C). If Chip Select Input (S) is brought low before or after
this specific time frame, the self-timed programming cycle will not be started, and the
addressed location will not be programmed. The completion of the cycle can be detected by
monitoring the READY/BUSY
Once the Write cycle has been started, it is internally self-timed (the external clock signal on
Serial Clock (C) may be stopped or left running after the start of a Write cycle). The cycle is
automatically preceded by an Erase cycle, so it is unnecessary to execute an explicit erase
instruction before a Write Data to Memory (WRITE) instruction.
Figure 5. ERASE, ERAL sequences
line, as described later in this document.
1. For the meanings of An and Xn, please see Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6.
5.5 Erase All
The Erase All Memory (ERAL) instruction erases the whole memory (all memory bits are set
to 1). The format of the instruction requires that a dummy address be provided. The Erase
cycle is conducted in the same way as the Erase instruction (ERASE). The completion of
the cycle can be detected by monitoring the READY/BUSY
READY/BUSY status.
16/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
line, as described in Section 6:

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Instructions
AI00880C
SWRITE
ALL
DATA IN
D
Q
ADDR
OP
CODE
Dn D0
BUSY READY
CHECK
STATUS
1
0
00 1
Xn X0
5.6 Write All
As with the Erase All Memory (ERAL) instruction, the format of the Write All Memory with
same Data (WRAL) instruction requires that a dummy address be provided. As with the
Write Data to Memory (WRITE) instruction, the format of the Write All Memory with same
Data (WRAL) instruction requires that an 8-bit data byte, or 16-bit data word, be provided.
This value is written to all the addresses of the memory device. The completion of the cycle
can be detected by monitoring the READY/BUSY
Figure 6. WRAL sequence
line, as described next.
1. For the meanings of Xn and Dn, please see Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6.
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 17/32

READY/BUSY status M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
6 READY/BUSY status
While the Write or Erase cycle is underway, for a WRITE, ERASE, WRAL or ERAL
instruction, the Busy signal (Q=0) is returned whenever Chip Select input (S) is driven high.
(Please note, though, that there is an initial delay, of t
becomes available). In this state, the M93Cx6 ignores any data on the bus. When the Write
cycle is completed, and Chip Select Input (S) is driven high, the Ready signal (Q=1)
indicates that the M93Cx6 is ready to receive the next instruction. Serial Data Output (Q)
remains set to 1 until the Chip Select Input (S) is brought low or until a new start bit is
decoded.
, before this status information
SLSH
7 Initial delivery state
The device is delivered with all bits in the memory array set to 1 (each byte contains FFh).
8 Common I/O operation
Serial Data Output (Q) and Serial Data Input (D) can be connected together, through a
current limiting resistor, to form a common, single-wire data bus. Some precautions must be
taken when operating the memory in this way, mostly to prevent a short circuit current from
flowing when the last address bit (A0) clashes with the first data bit on Serial Data Output
(Q). Please see the application note AN394 for details.
18/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
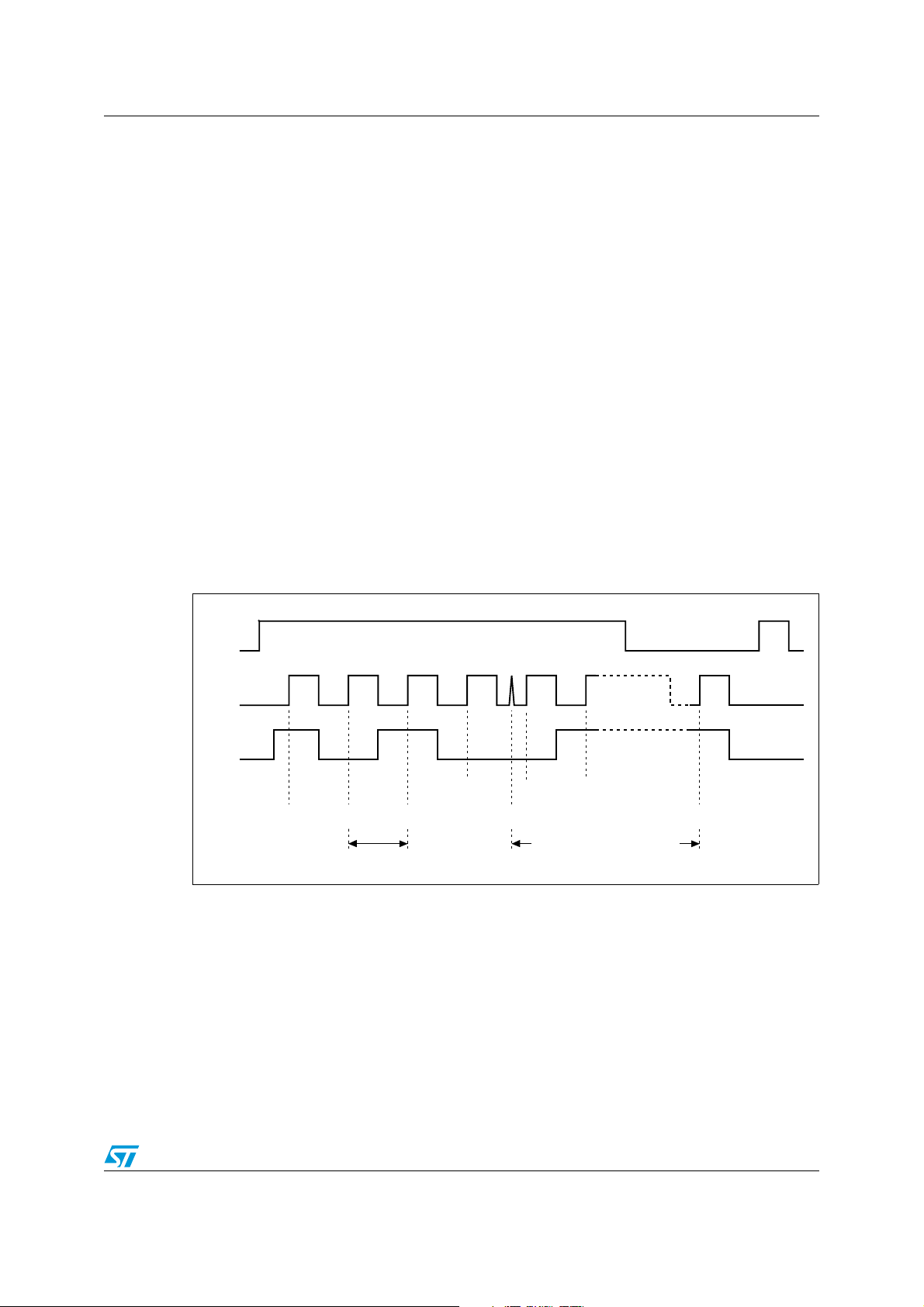
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Clock pulse counter
AI01395
S
An-1
C
D
WRITE
START
D0"1""0"
An
Glitch
An-2
ADDRESS AND DATA
ARE SHIFTED BY ONE BIT
9 Clock pulse counter
In a noisy environment, the number of pulses received on Serial Clock (C) may be greater
than the number delivered by the master (the microcontroller). This can lead to a
misalignment of the instruction of one or more bits (as shown in Figure 7) and may lead to
the writing of erroneous data at an erroneous address.
To avoid this problem, the M93Cx6 has an on-chip counter that counts the clock pulses from
the start bit until the falling edge of the Chip Select Input (S). If the number of clock pulses
received is not the number expected, the WRITE, ERASE, ERAL or WRAL instruction is
aborted, and the contents of the memory are not modified.
The number of clock cycles expected for each instruction, and for each member of the
M93Cx6 family, are summarized in Table 4: Instruction set for the M93C46 to Ta bl e 6 :
Instruction set for the M93C76 and M93C86. For example, a Write Data to Memory (WRITE)
instruction on the M93C56 (or M93C66) expects 20 clock cycles (for the x8 organization)
from the start bit to the falling edge of Chip Select Input (S). That is:
1 Start bit
+ 2 Op-code bits
+ 9 Address bits
+ 8 Data bits
Figure 7. Write sequence with one clock glitch
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 19/32
Maximum rating M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
10 Maximum rating
Stressing the device outside the ratings listed in the Absolute maximum ratings table may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and operation of the
device at these, or any other conditions outside those indicated in the operating sections of
this specification, is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Table 7. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
Ambient operating temperature –40 130 °C
T
T
LEAD
Storage temperature –65 150 °C
STG
PDIP 260
Lead temperature during soldering
other packages See note
(2)
(1)
°C
V
V
V
V
1. T
2. Compliant with JEDEC Std J-STD-020 (for small body, Sn-Pb or Pb assembly), the ST ECOPACK®
7191395 specification, and the European directive on Restrictions on Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
2002/95/EU.
3. Positive and negative pulses applied on pin pairs, according to the AEC-Q100-002 (compliant with JEDEC
Std JESD22-A114, C1 = 100pF, R1 = 1500Ω, R2 = 500Ω).
Output range (Q = VOH or Hi-Z) –0.50 VCC+0.5 V
OUT
Input range –0.50 VCC+1 V
IN
Supply voltage –0.50 6.5 V
CC
Electrostatic discharge voltage (human body model)
ESD
max must not be applied for more than 10 s.
LEAD
(3)
4000 V
20/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 DC and AC parameters
11 DC and AC parameters
This section summarizes the operating and measurement conditions, and the dc and ac
characteristics of the device. The parameters in the dc and ac characteristic tables that
follow are derived from tests performed under the measurement conditions summarized in
the relevant tables. Designers should check that the operating conditions in their circuit
match the measurement conditions when relying on the quoted parameters.
Table 8. Operating conditions (M93Cx6)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
V
CC
T
Table 9. Operating conditions (M93Cx6-W)
Supply voltage 4.5 5.5 V
Ambient operating temperature –40 125 °C
A
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
V
CC
T
Table 10. AC measurement conditions (M93Cx6)
Supply voltage 2.5 5.5 V
Ambient operating temperature –40 125 °C
A
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
C
Load capacitance 100 pF
L
Input rise and fall times 50 ns
Input voltage levels 0.4 V to 2.4 V V
Input timing reference voltages 1.0 V and 2.0 V V
Output timing reference voltages 0.8 V and 2.0 V V
Table 11. AC measurement conditions (M93Cx6-W)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
C
Load capacitance 100 pF
L
Input rise and fall times 50 ns
Input voltage levels 0.2 V
Input timing reference voltages 0.3 V
Output timing reference voltages 0.3 V
to 0.8 V
CC
to 0.7 V
CC
to 0.7 V
CC
CC
CC
CC
V
V
V
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 21/32
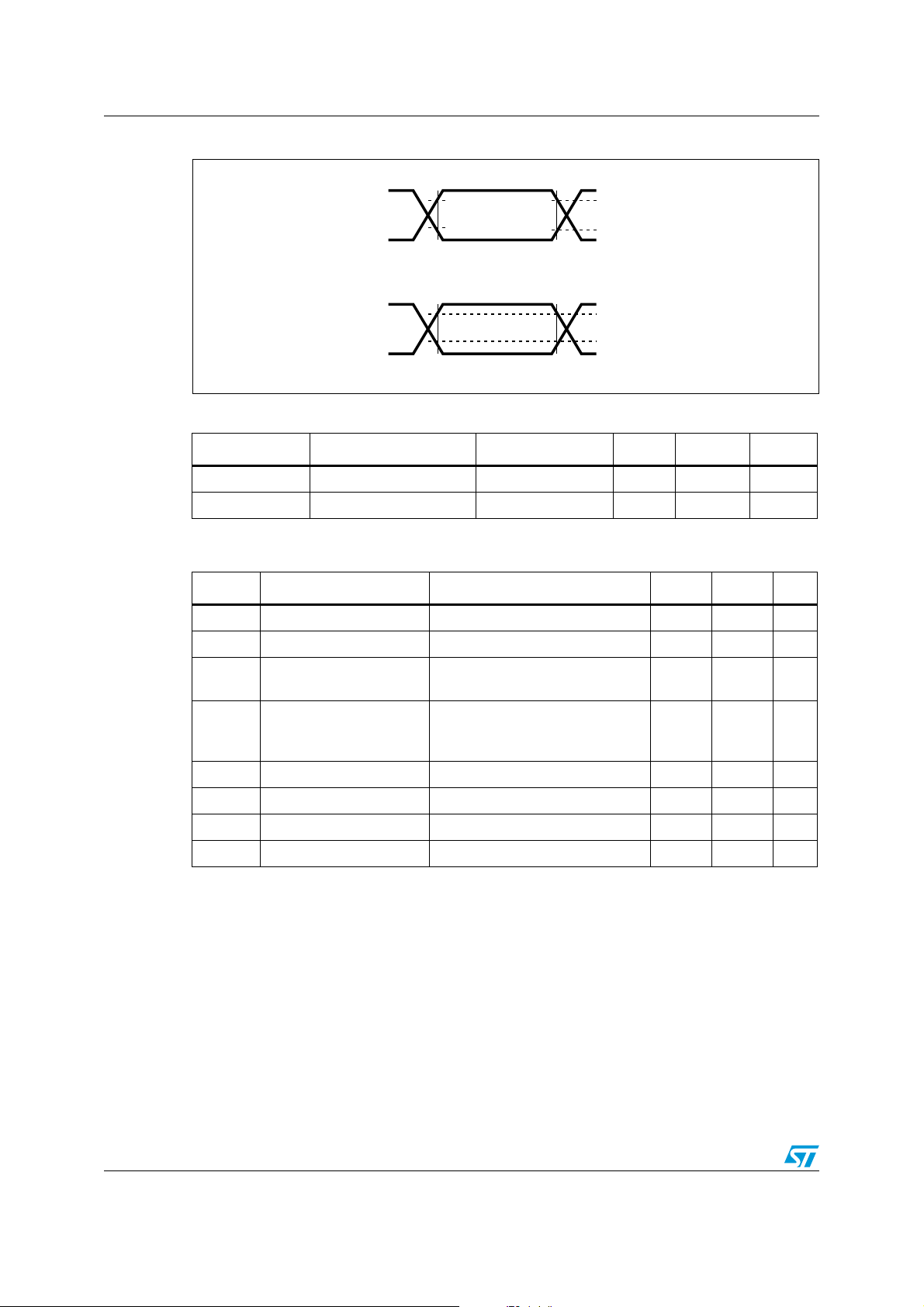
DC and AC parameters M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
-36
2.4V
0.4V
6
0.8V
2V
1V
)NPUT
0.8V
CC
0.2V
CC
0.7V
CC
0.3V
CC
M93CXX
/UTPUT
)NPUTVOLTAGELEVELS
)NPUTANDOUTPUT
TIMINGREFERENCELEVELS
)NPUTVOLTAGELEVELS
-#887
Figure 8. AC testing input output waveforms
Table 12. Capacitance
Symbol Parameter Test condition
(1)
Min Max Unit
C
C
OUT
IN
Output capacitance V
= 0V 5 pF
OUT
Input capacitance VIN = 0V 5 pF
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested, at TA = 25 °C and a frequency of 1 MHz.
Table 13. DC characteristics (M93Cx6, device grade 3)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Max. Unit
I
I
I
Input leakage current 0V ≤ VIN ≤ V
LI
Output leakage current 0V ≤ V
LO
V
CC
Supply current
CC
CC
≤ VCC, Q in Hi-Z ±2.5 µA
OUT
= 5 V, S = VIH, f = 2 MHz,
Q = open
2 mA
±2.5 µA
VCC = 5 V, S = VSS, C = VSS,
I
CC1
V
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
Supply current (Standby)
(1)
Input low voltage VCC = 5 V ± 10% –0.45 0.8 V
IL
(1)
Input high voltage VCC = 5 V ± 10% 2 VCC + 1 V
(1)
Output low voltage VCC = 5 V, IOL = 2.1 mA 0.4 V
(1)
Output high voltage VCC = 5 V, IOH = –400 µA 0.8 V
ORG = VSS or VCC,
pin7 = V
CC
, V
SS
or Hi-Z
1. Please note that the input and output levels defined in this table are compatible with TTL logic levels and
are NOT fully compatible with CMOS levels (as defined in Table 14).
15 µA
CC
V
22/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 DC and AC parameters
Table 14. DC characteristics (M93Cx6-W, device grade 3)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Max. Unit
I
Input leakage current 0V ≤ VIN ≤ V
LI
Output leakage current 0V ≤ V
I
LO
OUT
CC
≤ VCC, Q in Hi-Z ±2.5 µA
VCC = 5 V, S = VIH, f = 2 MHz,
Supply current (CMOS
I
CC
inputs)
V
CC
Q = open
= 2.5 V, S = VIH, f = 2 MHz,
Q = open
VCC = 2.5 V, S = VSS, C = VSS,
I
V
V
Supply current (Standby)
CC1
V
Input low voltage (D, C, S) –0.45 0.2 V
IL
Input high voltage (D, C, S) 0.7 VCCVCC + 1 V
V
IH
Output low voltage (Q)
OL
Output high voltage (Q)
OH
ORG = VSS or VCC,
pin7 = VCC, V
V
= 5 V, IOL = 2.1 mA 0.4 V
CC
V
= 2.5 V, IOL = 100 µA 0.2 V
CC
V
= 5 V, IOH = –400 µA 0.8 V
CC
V
= 2.5 V, IOH = –100 µA VCC–0.2 V
CC
SS
or Hi-Z
±2.5 µA
2 mA
1 mA
5 µA
V
CC
CC
V
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 23/32
DC and AC parameters M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
Table 15. AC characteristics (M93Cx6, device grade 3)
Test conditions specified in Tab l e 8 and Table 10
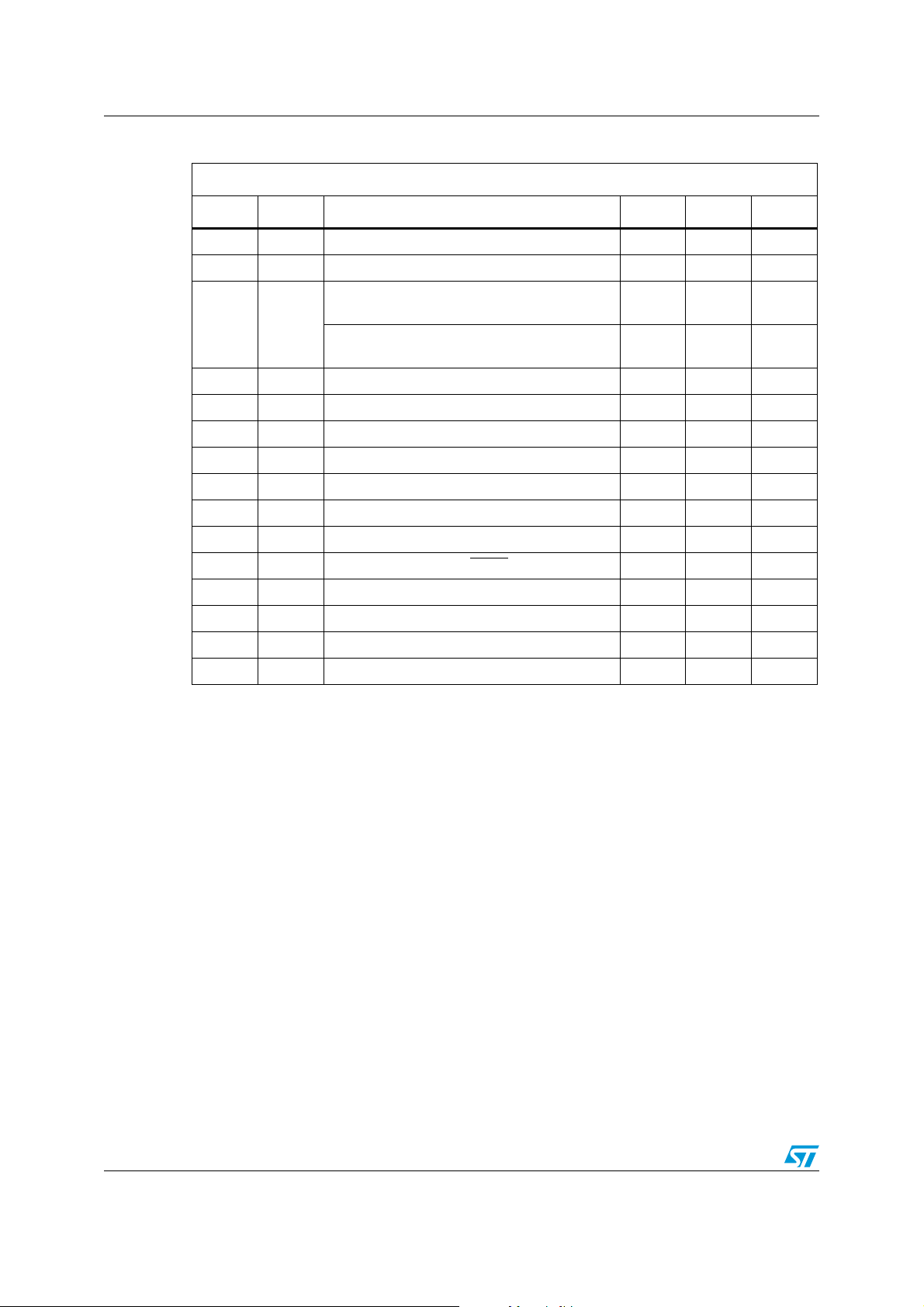
Symbol Alt. Parameter Min. Max. Unit
f
t
SLCH
C
f
Clock frequency D.C. 2 MHz
SK
Chip Select low to Clock high 50 ns
Chip Select setup time
M93C46, M93C56, M93C66
t
SHCH
t
CSS
Chip Select setup time
M93C76, M93C86
(1)
t
SLSH
(2)
t
CHCL
(2)
t
CLCH
t
DVC H
t
CHDX
t
CLSH
t
CLSL
t
SHQV
t
SLQZ
t
CHQL
t
CHQV
t
W
1. Chip Select Input (S) must be brought low for a minimum of t
2. t
CHCL
+ t
CLCH
t
CS
t
SKH
t
SKL
t
DIS
t
DIH
t
SKS
t
CSH
t
SV
t
DF
t
PD0
t
PD1
t
WP
≥ 1 / fC.
Chip Select low to Chip Select high 200 ns
Clock high time 200 ns
Clock low time 200 ns
Data in setup time 50 ns
Data in hold time 50 ns
Clock setup time (relative to S) 50 ns
Chip Select hold time 0 ns
Chip Select to READY/BUSY status 200 ns
Chip Select low to output Hi-Z 100 ns
Delay to output low 200 ns
Delay to output valid 200 ns
Erase or Write cycle time 5 ms
50 ns
50 ns
between consecutive instruction cycles.
SLSH
24/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 DC and AC parameters
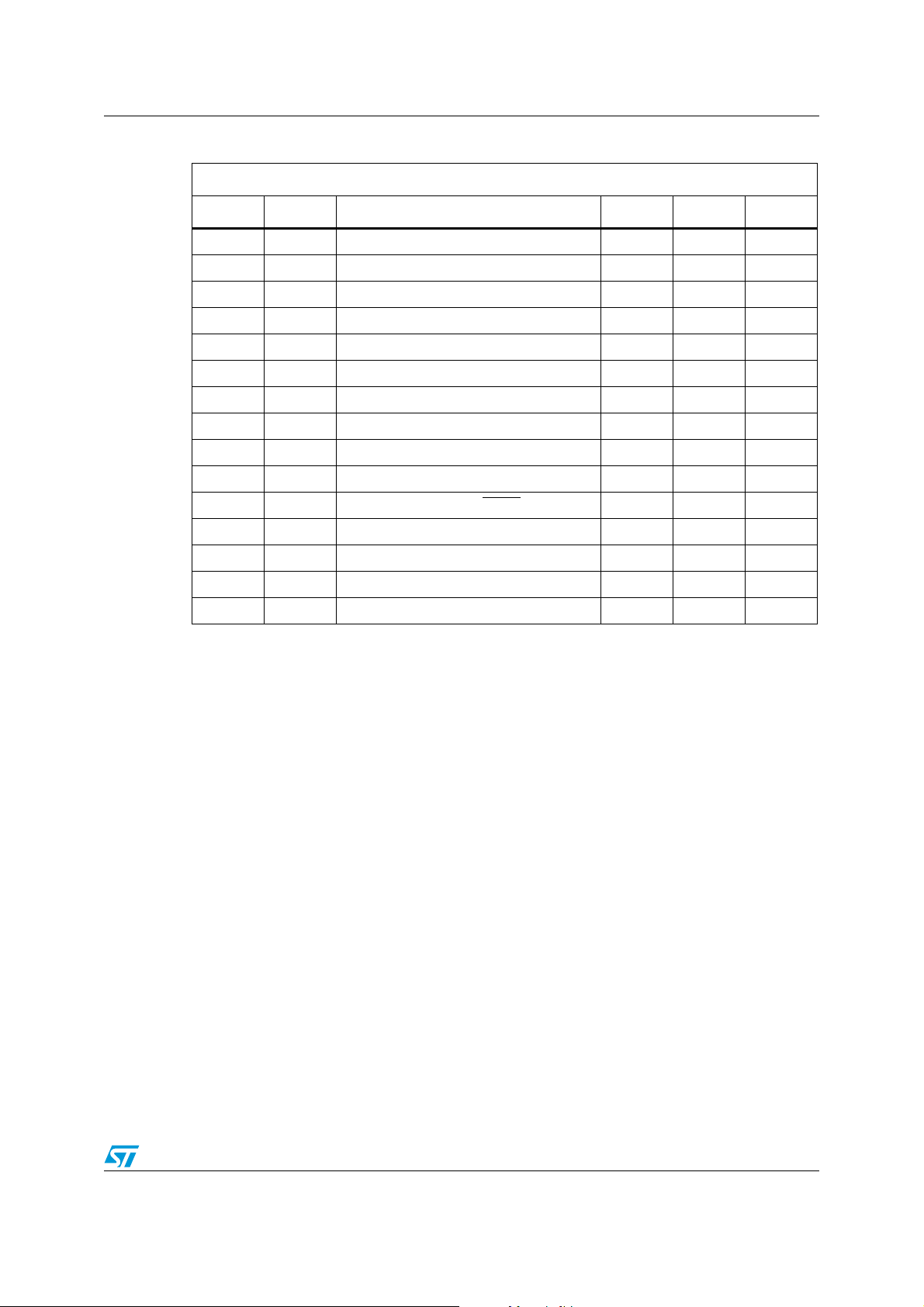
Table 16. AC characteristics (M93Cx6-W, device grade 3)
Test conditions specified in Tabl e 9 and Table 11
Symbol Alt. Parameter Min. Max. Unit
f
C
t
SLCH
t
SHCH
(1)
t
SLSH
(2)
t
CHCL
(2)
t
CLCH
t
DVC H
t
CHDX
t
CLSH
t
CLSL
t
SHQV
t
SLQZ
t
CHQL
t
CHQV
t
W
1. Chip Select Input (S) must be brought low for a minimum of t
2. t
CHCL
+ t
f
Clock frequency D.C. 2 MHz
SK
Chip Select low to Clock high 50 ns
CLCH
t
CSS
t
t
SKH
t
SKL
t
DIS
t
DIH
t
SKS
t
CSH
t
t
t
PD0
t
PD1
t
WP
≥ 1 / fC.
Chip Select set-up time 50 ns
Chip Select low to Chip Select high 200 ns
CS
Clock high time 200 ns
Clock low time 200 ns
Data in set-up time 50 ns
Data in hold time 50 ns
Clock set-up time (relative to S) 50 ns
Chip Select hold time 0 ns
Chip Select to READY/BUSY status 200 ns
SV
Chip Select low to output Hi-Z 100 ns
DF
Delay to output low 200 ns
Delay to output valid 200 ns
Erase or Write cycle time 5 ms
between consecutive instruction cycles.
SLSH
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 25/32

DC and AC parameters M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
AI01428
C
OP CODE OP CODE
START
S
D
OP CODE INPUTSTART
tDVCH
tSHCH
tCLSH tCHCL
tCLCH
tCHDX
AI00820C
C
D
Q
ADDRESS INPUT
Hi-Z
tDVCH
tCLSL
A0
S
DATA OUTPUT
tCHQVtCHDX
tCHQL
An
tSLSH
tSLQZ
Q15/Q7 Q0
AI01429
C
D
Q
ADDRESS/DATA INPUT
Hi-Z
tDVCH
tSLCH
A0/D0
S
WRITE CYCLE
tSLSHtCHDX
An
tCLSL
tSLQZ
BUSY
tSHQV
tW
READY
Figure 9. Synchronous timing (start and op-code input)
Figure 10. Synchronous timing (Read or Write)
Figure 11. Synchronous timing (Read or Write)
26/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Package mechanical data
PDIP-B
A2
A1AL
be
D
E1
8
1
c
eA
b2
eB
E
12 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers the M93Cxx devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a lead-free second level interconnect. The category of
second level interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at www.st.com.
Figure 12. PDIP8 – 8 lead plastic dual in-line package, 300 mils body width, package
outline
1. Drawing is not to scale.
Table 17. PDIP8 – 8 lead plastic dual in-line package, 300 mils body width, package
mechanical data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
A 5.33 0.2098
A1 0.38 0.015
A2 3.3 2.92 4.95 0.1299 0.115 0.1949
b 0.46 0.36 0.56 0.0181 0.0142 0.022
b2 1.52 1.14 1.78 0.0598 0.0449 0.0701
c 0.25 0.2 0.36 0.0098 0.0079 0.0142
D 9.27 9.02 10.16 0.365 0.3551 0.4
E 7.87 7.62 8.26 0.3098 0.3 0.3252
E1 6.35 6.1 7.11 0.25 0.2402 0.2799
e 2.54 - - 0.1 - -
eA 7.62 - - 0.3 - -
eB 10.92 0.4299
1. Values in inches are converted from mm and rounded to 4 decimal digits.
L 3.3 2.92 3.81 0.1299 0.115 0.15
(1)
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 27/32

Package mechanical data M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
SO-A
E1
8
ccc
b
e
A
D
c
1
E
h x 45˚
A2
k
0.25 mm
L
L1
A1
GAUGE PLANE
Figure 13. SO8 narrow – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package
outline
1. Drawing is not to scale.
Table 18. SO8 narrow – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package
data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
(1)
A 1.75 0.0689
A1 0.1 0.25 0.0039 0.0098
A2 1.25 0.0492
b 0.28 0.48 0.011 0.0189
c 0.17 0.23 0.0067 0.0091
ccc 0.1 0.0039
D 4.9 4.8 5 0.1929 0.189 0.1969
E 6 5.8 6.2 0.2362 0.2283 0.2441
E1 3.9 3.8 4 0.1535 0.1496 0.1575
e 1.27 - - 0.05 - -
h 0.25 0.5 0.0098 0.0197
k 0°8° 0°8°
L 0.4 1.27 0.0157 0.05
L1 1.04 0.0409
1. Values in inches are converted from mm and rounded to 4 decimal digits.
28/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Package mechanical data
TSSOP8AM
1
8
CP
c
L
EE1
D
A2A
α
eb
4
5
A1
L1
Figure 14. TSSOP8 – 8 lead thin shrink small outline, package outline
1. Drawing is not to scale.
Table 19. TSSOP8 – 8 lead thin shrink small outline, package mechanical data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Typ. Min. Max. Typ. Min. Max.
(1)
A 1.2 0.0472
A1 0.05 0.15 0.002 0.0059
A2 1 0.8 1.05 0.0394 0.0315 0.0413
b 0.19 0.3 0.0075 0.0118
c 0.09 0.2 0.0035 0.0079
CP 0.1 0.0039
D 3 2.9 3.1 0.1181 0.1142 0.122
e 0.65 - - 0.0256 - -
E 6.4 6.2 6.6 0.252 0.2441 0.2598
E1 4.4 4.3 4.5 0.1732 0.1693 0.1772
L 0.6 0.45 0.75 0.0236 0.0177 0.0295
L1 1 0.0394
α 0° 8° 0° 8°
N (pin number) 8 8
1. Values in inches are converted from mm and rounded to 4 decimal digits.
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 29/32

Part numbering M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
13 Part numbering
Table 20. Ordering information scheme
Example: M93C86 – W MN 3 T P /S
Device type
M93 = MICROWIRE serial EEPROM
Device function
86 = 16 Kbit (2048 x 8)
76 = 8 Kbit (1024 x 8)
66 = 4 Kbit (512 x 8)
56 = 2 Kbit (256 x 8)
46 = 1 Kbit (128 x 8)
Operating voltage
blank = V
W = V
Package
BN = PDIP8
MN = SO8 (150 mils width)
DW = TSSOP8 (169 mils width)
= 4.5 to 5.5 V
CC
= 2.5 to 5.5 V
CC
Device grade
3 = Device tested with high reliability certified flow.
Automotive temperature range (–40 to 125 °C)
Packing
blank = standard packing
T = tape and reel packing
Plating technology
®
P or G = ECOPACK
(RoHS compliant)
Process
/S = Manufacturing technology code
For a list of available options (speed, package, etc.) or for further information on any aspect
of this device, please contact your nearest ST sales office.
30/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125 Revision history
14 Revision history
Table 21. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
14-Mar-2012 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 022572 Rev 1 31/32

M93C86-125 M93C76-125 M93C66-125 M93C56-125 M93C46-125
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
32/32 Doc ID 022572 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...