
Features
■ Counters for seconds, minutes, hours, day,
date, month, years, and century
■ 32 KHz crystal oscillator integrating load
capacitance and high crystal series resistance
operation
■ Oscillator stop detection monitors clock
operation
■ Serial interface supports I
■ 350 nA timekeeping current at 3 V
■ Low operating current of 35 µA (at 400 kHz)
■ Timekeeping down to 1.0 V
■ 1.3 V to 4.4 V I
■ Software clock calibration to compensate
2
C bus operating voltage
deviation of crystal due to temperature
■ Software programmable output (OUT)
■ Operating temperature of –40 to 85 °C
■ Automatic leap year compensation
■ Lead-free 16-pin QFN package
■ Li-ion rechargeable operation
2
C bus (400 kHz)
M41T60
Serial access real-time clock
QFN16 (Q)
3 mm x 3 mm
VSOJ20 (47.6mm2)
1
2
3
4
(21.5mm2)
XI
XO
ST QFN16
GND Plane
CRYSTAL
Guard Ring
SMT
Footprint comparison of ST’s QFN16 with
SMT crystal vs. competing VSOJ20 package
April 2010 Doc ID 10396 Rev 13 1/27
www.st.com
1

Contents M41T60
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 2-wire bus characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.1 Bus not busy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.2 Start data transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.3 Stop data transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.4 Data valid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1.5 Acknowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 READ mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 WRITE mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3 Clock operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1 Calibrating the clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.2 Century bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.3 Output driver pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.4 Oscillator stop detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.5 Initial power-on defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2/27 Doc ID 10396 Rev 13

M41T60 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Signal names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 2. Register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 3. Century bits examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Table 4. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 5. Operating and AC measurement conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 6. Capacitance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 7. DC characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 8. Crystal electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 9. Crystals suitable for use with M41T6x series RTCs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 10. Oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 11. AC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 12. QFN16 – 16-lead, quad, flat package, no lead, 3 x 3 mm body size, mechanical data . . . 23
Table 13. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 14. Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Doc ID 10396 Rev 13 3/27

List of figures M41T60
List of figures
Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. 16-pin QFN connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. Hardware hookup for SuperCap™ backup operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 5. Serial bus data transfer sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6. Acknowledgement sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 7. Slave address location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 8. READ mode sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 9. Alternate READ mode sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 10. WRITE mode sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 11. Crystal accuracy across temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 12. Calibration waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 13. AC testing I/O waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 14. Crystal isolation example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 15. Bus timing requirements sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 16. QFN16 – 16-lead, quad, flat package, no lead, 3 x 3 mm body size, outline . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 17. QFN16, quad, flat package, no lead, 3 x 3 mm, recommended footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 18. 32 KHz crystal + QFN16 vs. VSOJ20 mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4/27 Doc ID 10396 Rev 13
M41T60 Description
1 Description
The M41T60 is a low power serial RTC with a built-in 32.768 kHz oscillator (external crystal
controlled). Eight registers are used for the clock/calendar function and are configured in
binary coded decimal (BCD) format. Addresses and data are transferred serially via a twoline bi-directional bus. The built-in address register is increased automatically after each
WRITE or READ data byte.
The eight clock address locations contain the century, year, month, date, day, hour, minute,
and second in 24-hour BCD format. Corrections for 28-, 29- (leap year), 30-, and 31-day
months are made automatically.
The M41T60 is supplied in 16-lead QFN package.
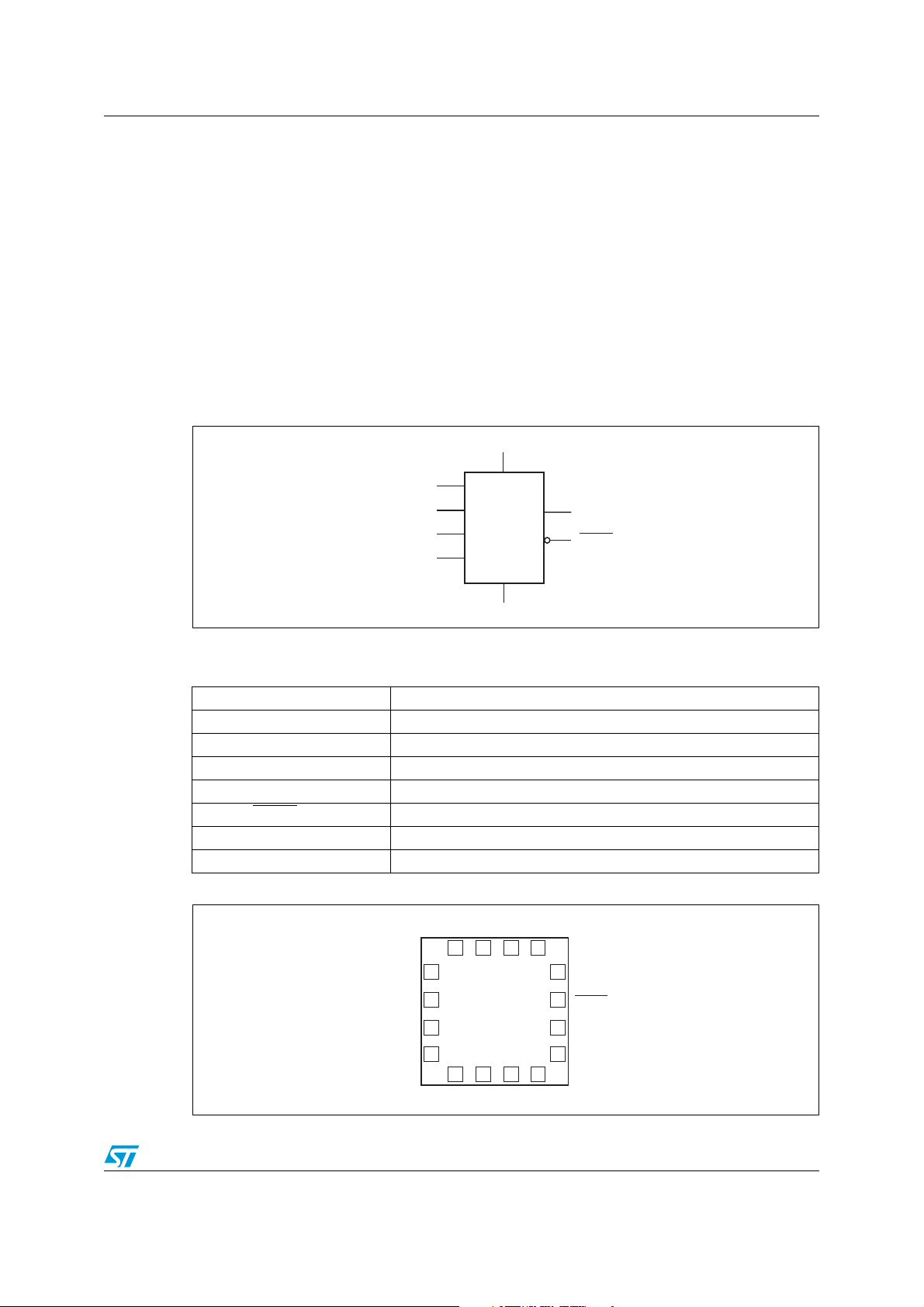
Figure 1. Logic diagram
V
CC
XI
XO
SCL
SDA
M41T60
(1)
FT
OFIRQ/OUT
(1)
1. Open drain
Table 1. Signal names
XI Oscillator input
XO Oscillator output
FT Frequency test output (open drain)
SDA Serial data address input/output
SCL Serial clock
/OUT Oscillator fail interrupt/out output (open drain)
OFIRQ
V
CC
V
SS
Supply voltage
Ground
Figure 2. 16-pin QFN connections
XI
1
XO
2
V
3
SS
(1)
4
FT
V
SS
CC
NC
16
5
SS
V
V
NC
15
6
NC
NC
14
13
NC
12
11
OFIRQ/OUT
SCL
10
9
SDA
8
7
NC
NC
(1)
AI08869
AI08870
Doc ID 10396 Rev 13 5/27
Description M41T60
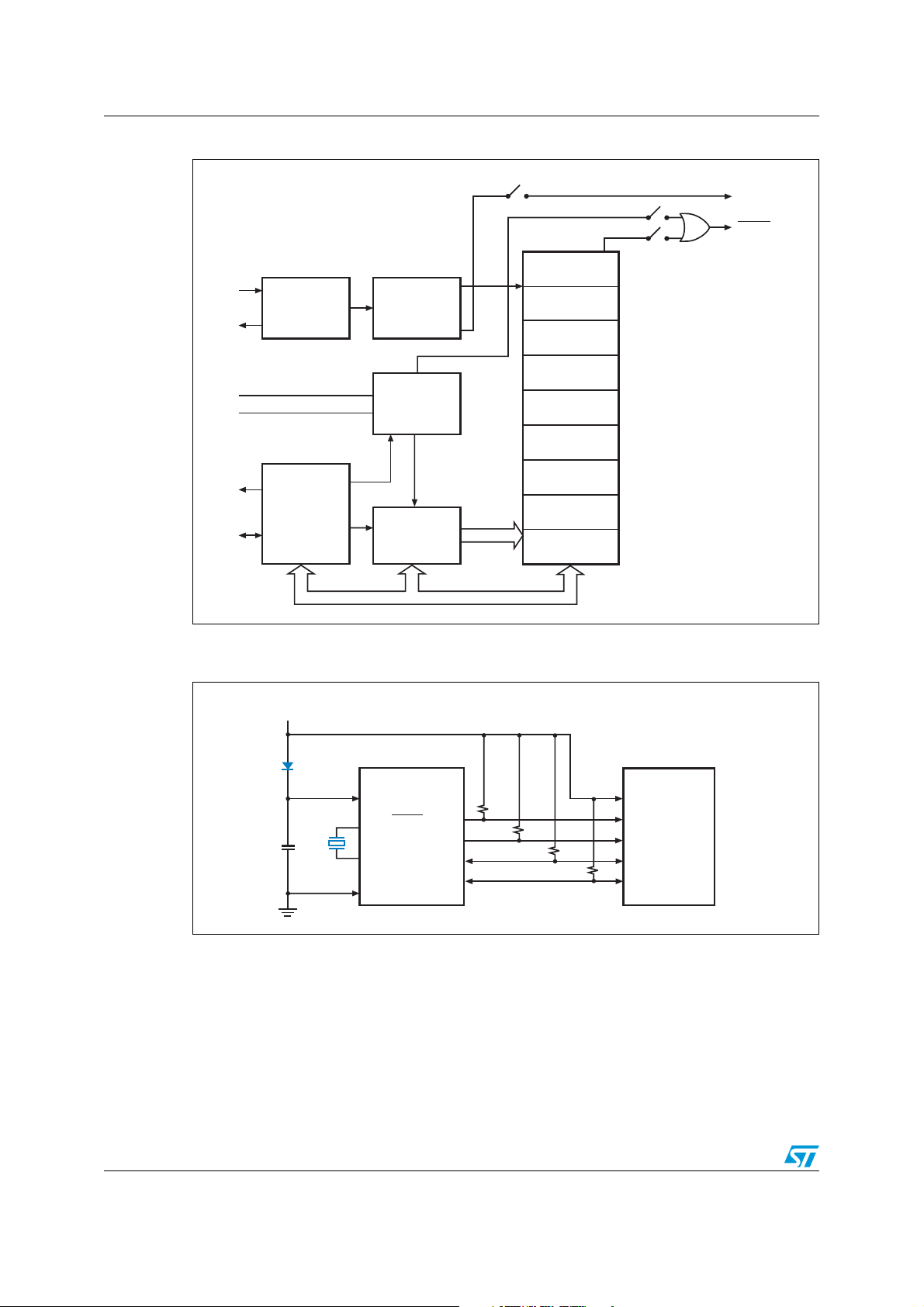
Figure 3. Block diagram
(1)
FT
OFIRQ/OUT
(1)
XO
V
CC
V
SS
SCL
SDA
FT
OSCILLATOR
XI
OSCILLATOR
32.768 kHz
SERIAL
BUS
INTERFACE
DIVIDER
CONTROL
LOGIC
ADDRESS
REGISTER
1 Hz
FAIL DETECT
SECONDS
MINUTES
HOURS
DAY
DATE
CENTURY/
MONTH
YEAR
CALIBRATION
OUT
OFIE
1. Open drain output.
Figure 4. Hardware hookup for SuperCap™ backup operation
V
CC
M41T60
1. Open drain output.
V
XI
XO
V
CC
SS
OFIRQ/OUT
FT
(1)
(1)
SCL
SDA
V
CC
Por t
Por t
Serial Clock Line
Serial Data Line
AI08871
MCU
AI10476b
6/27 Doc ID 10396 Rev 13

M41T60 Operation
2 Operation
The M41T60 clock operates as a slave device on the serial bus. Access is obtained by
implementing a start condition followed by the correct slave address (D0h). The 8 bytes
contained in the device can then be accessed sequentially in the following order:
1. Seconds register
2. Minutes register
3. Hours register
4. Day register
5. Date register
6. Century/month register
7. Years register
8. Calibration register
2.1 2-wire bus characteristics
This bus is intended for communication between different ICs. It consists of two lines: one
bi-directional for data signals (SDA) and one for clock signals (SCL). Both the SDA and the
SCL lines must be connected to a positive supply voltage via a pull-up resistor.
The following protocol has been defined:
● Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not busy.
● During data transfer, the data line must remain stable whenever the clock line is high.
Changes in the data line while the clock line is high will be interpreted as control
signals.
Accordingly, the following bus conditions have been defined:
2.1.1 Bus not busy
Both data and clock lines remain high.
2.1.2 Start data transfer
A change in the state of the data line, from high to low, while the clock is high, defines the
START condition.
2.1.3 Stop data transfer
A change in the state of the data line, from low to high, while the clock is high, defines the
STOP condition.
2.1.4 Data valid
The state of the data line represents valid data when after a start condition, the data line is
stable for the duration of the high period of the clock signal. The data on the line may be
changed during the low period of the clock signal. There is one clock pulse per bit of data.
Doc ID 10396 Rev 13 7/27
Operation M41T60
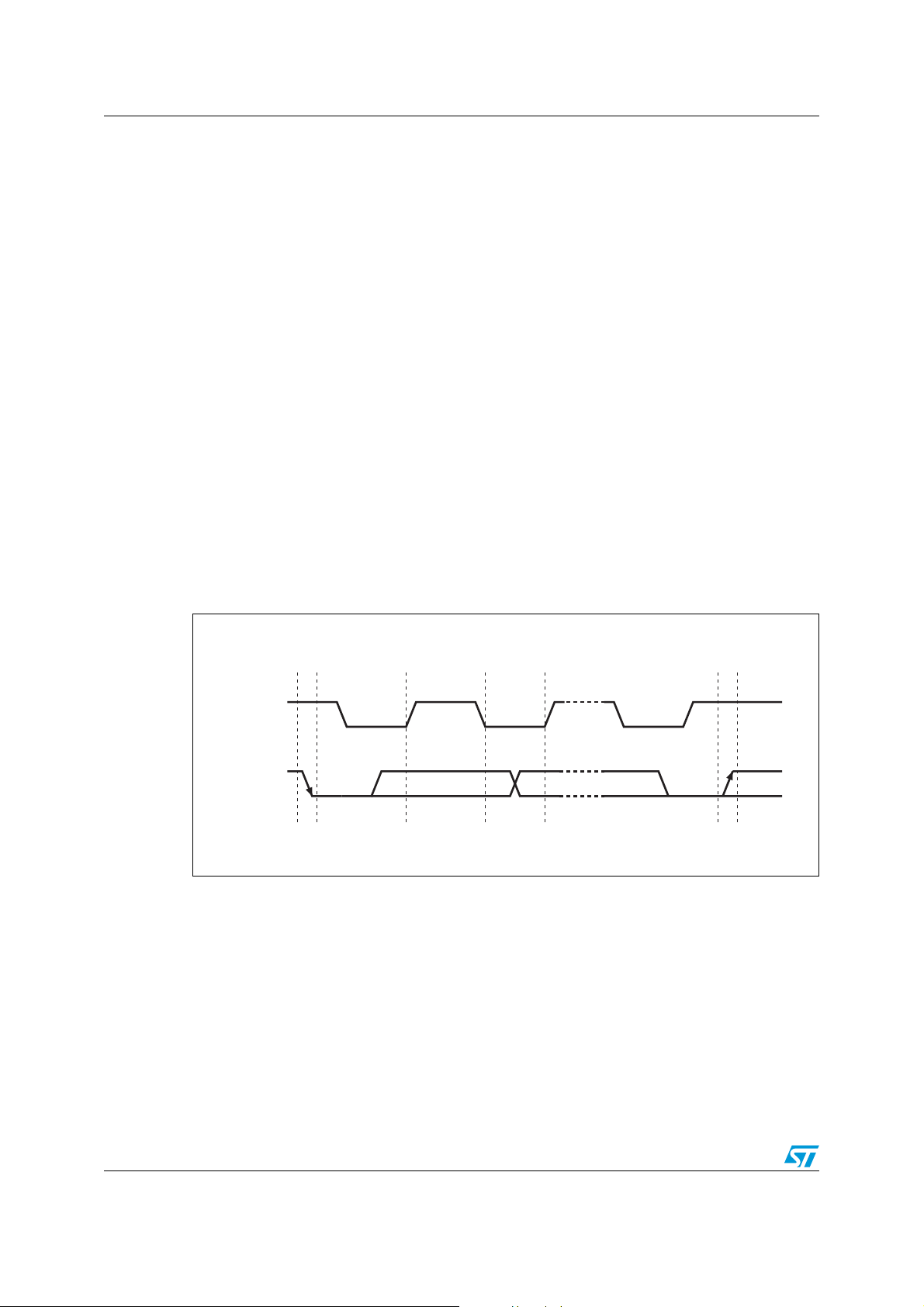
Each data transfer is initiated with a start condition and terminated with a stop condition.
The number of data bytes transferred between the start and stop conditions is not limited.
The information is transmitted byte-wide and each receiver acknowledges with a ninth bit.
By definition, a device that gives out a message is called “transmitter”, the receiving device
that gets the message is called “receiver”. The device that controls the message is called
“master”. The devices that are controlled by the master are called “slaves”.
2.1.5 Acknowledge
Each byte of eight bits is followed by one acknowledge bit. This acknowledge bit is a low
level put on the bus by the receiver, whereas the master generates an extra acknowledge
related clock pulse.
A slave receiver which is addressed is obliged to generate an acknowledge after the
reception of each byte. Also, a master receiver must generate an acknowledge after the
reception of each byte that has been clocked out of the slave transmitter.
The device that acknowledges has to pull down the SDA line during the acknowledge clock
pulse in such a way that the SDA line is a stable low during the high period of the
acknowledge related clock pulse. Of course, setup and hold times must be taken into
account. A master receiver must signal an end-of-data to the slave transmitter by not
generating an acknowledge on the last byte that has been clocked out of the slave. In this
case, the transmitter must leave the data line high to enable the master to generate the
STOP condition.
Figure 5. Serial bus data transfer sequence
DATA LINE
STABLE
DATA VALID
CLOCK
DATA
STA RT
CONDITION
CHANGE OF
DATA ALLOWED
STOP
CONDITION
AI00587
8/27 Doc ID 10396 Rev 13
M41T60 Operation
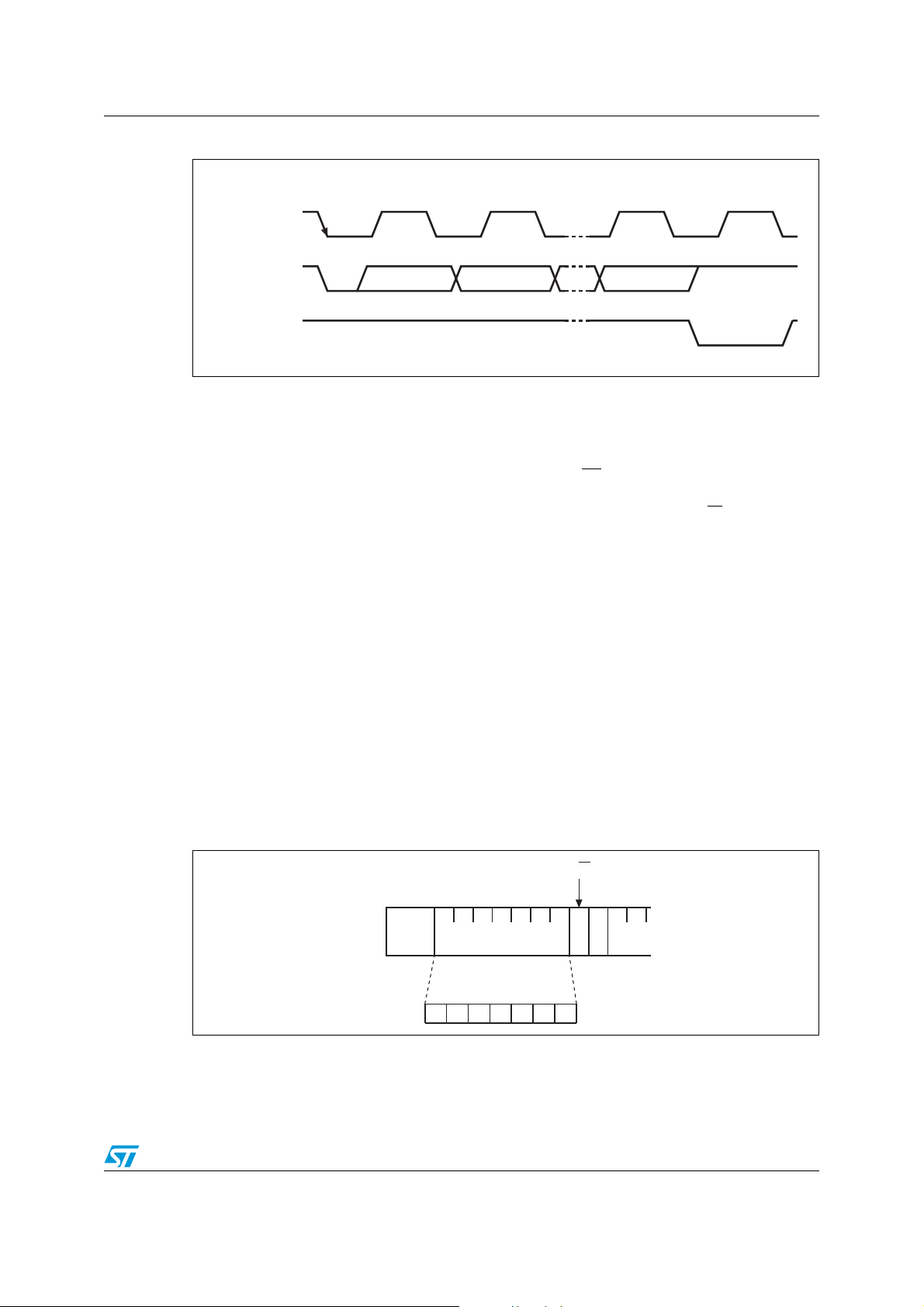
Figure 6. Acknowledgement sequence
CLOCK PULSE FOR
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
SCL FROM
MASTER
STA RT
12 8 9
DATA OUTPUT
BY TRANSMITTER
DATA OUTPUT
BY RECEIVER
2.2 READ mode
In this mode, the master reads the M41T60 slave after setting the slave address
(see Figure 7). Following the WRITE mode control bit (R/W
the word address An is written to the on-chip address pointer. Next the START condition
and slave address are repeated, followed by the READ mode control bit (R/W
point, the master transmitter becomes the master receiver. The data byte which was
addressed will be transmitted and the master receiver will send an acknowledge bit to the
slave transmitter. The address pointer is only increased on reception of an acknowledge bit.
The M41T60 slave transmitter will now place the data byte at address A
master receiver reads and acknowledges the new byte and the address pointer is increased
to A
This cycle of reading consecutive addresses will continue until the master receiver sends a
STOP condition to the slave transmitter.
The system-to-user transfer of clock data will be halted whenever the address being read is
a clock address (0h to 6h). The update will resume due to a stop condition or when the
pointer increments to any non-clock address (7h).
n+2
.
MSBLSB
= 0) and the acknowledge bit,
= 1). At this
on the bus. The
n+1
AI00601
An alternate READ mode may also be implemented, whereby the master reads the M41T60
slave without first writing to the (volatile) address pointer. The first address that is read is the
last one stored in the pointer (see Figure 9 on page 10).
Figure 7. Slave address location
R/W
STA RT A
Doc ID 10396 Rev 13 9/27
SLAVE ADDRESS
MSB
0100 011
LSB
AI00602
 Loading...
Loading...